Page 1
CHAPTER
9
Service/Subscriber Provisioning
The Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager (SCM) allows you to make and manage network
connections through a set of menu options available by right clicking on an appropriate
Cisco 6400 Chassis, NSP, NRP, NLC, orport object in MapViewer window.These menu options allow
you to create and configure services and subscribers, and to manage the subsequent connection of the
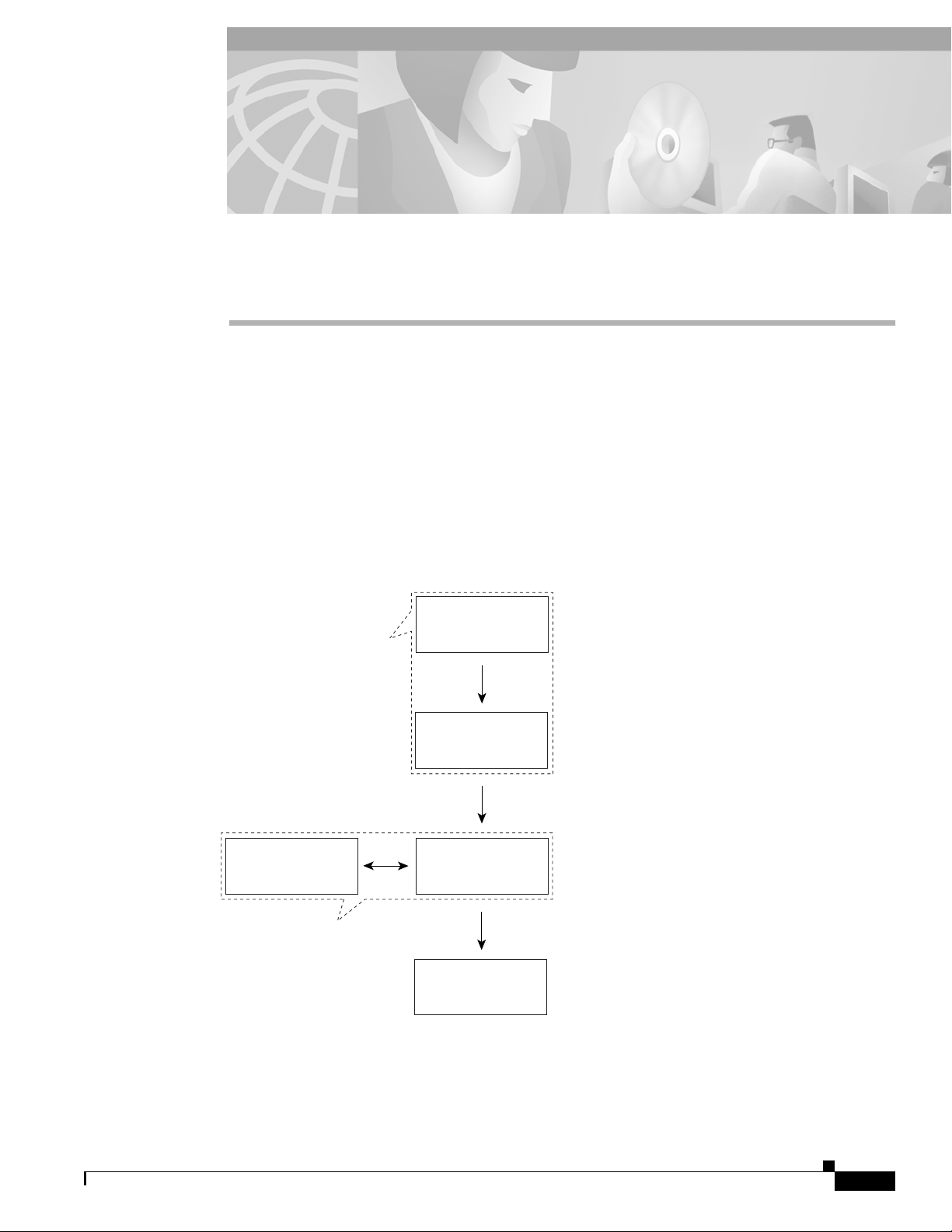
subscribers to the services. Figure 9-1 describes the basic workflow for service and subscriber
provisioning.
This chapter details the tasks you need to use during day to day service connection management and the
name we use to describe combined service and subscriber provisioning.
Figure 9-1 Service/Subscriber Provisioning Workflow
Defining Policies for
Service and Subscriber
Provisioning
Apply an existing
Service Profile to a
Service Instance
Service
Provisioning
Create
Service Profiles
Create/Configure
Connection
Templates
Create/Configure
and Commission
Service Instances
Subscriber
Provisioning
Service profiles allow you to configure and save
some or all of the configuration information for a
service instance. You can then later apply the profile
to many service instances.
Connection templates allow you to set the Quality of
Service (QoS) parameters for the connection
between the Cisco 6400 UAC and the subscriber.
Apply a profile (optional) and then configure the
remaining parameters manually or configure all of the
parameters manually. Some manual configuration is
always required (for example, uplink VPI/VCI). Click
the Commission Service button to "roll" the selected
service configuration onto the 6400 UAC hardware.
Create a subscriber to connect to a service
instance (created earlier). Configure the subscribers
information. Connect the subscriber to one or more
service instances using a connection template.
41809
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-1
Page 2
Note Each of the windows that appear in this chapter are described in greater detail in
Chapter 10, “Service/Subscriber Provisioning Windows: Detailed Description”.
See the “SCM Tasks” section on page 9-2 for details of the SCM tasks that you can execute and the
objects that you select to begin the task.
SCM Tasks
Table 9-1 This section describes the tasks that you execute from each object type using the
Cisco 6400 SCM Manager (c6400Manager) view. For example, you would select a Site, Shelf or
Chassis object when you wish to deploy a service instance object or select a Shelf or Chassis object
when you wish to deploy a connection template.
Table 9-1 Launch Points for Service Connection Management Tasks
Objects (that can be selected) to Open the Window
Node
ATM
Port
Node
Line
Card
LineCard
ATM Port
Cisco 6400 Task
Create Service
Profiles
Deploy
Connection
Template
Connection
Template
Configuration
Deploy Service
Instance
Configure and
Commission a
Service Instance
Deploy
Subscriber
Configure
Subscriber
Connect
Subscriber
Disconnect
Subscriber
Site Shelf Chassis NSP NRP NRP
Yes Yes Yes No No No No No Yes No Cisco 6400 UAC, Profile,
No Yes Yes No No No No No No No Cisco 6400 UAC,
No Yes Yes No No No No No No No Cisco 6400 UAC,
Yes Yes Yes No No No No No Yes No Cisco 6400 UAC, Service,
Yes Yes Yes No No No No No Yes No Cisco 6400 UAC, Service,
Yes Yes Yes No No Yes No Yes No No Cisco 6400 UAC,
Yes Yes Yes No No Yes No Yes No Yes Cisco 6400 UAC,
Yes Yes Yes No No Yes No Yes Yes Yes Cisco 6400 UAC,
Yes Yes Yes No No Yes No Yes Yes Yes Cisco 6400 UAC,
Service
Instance
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Subscriber
Menu Options to Select to
Open Window
Configure, service type
Connection Template,
Deploy
Connection Template,
Configure Connection
Template
Deploy, service type
Configure service type
Subscriber, Deploy
Subscriber, Configure
Subscriber, Connect
Subscriber, Disconnect
9-2
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 3
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Many service providers and telecommunications carriers now offer tiered service levels to their
customers and/or subscribers. These service levels are generally defined by the marketing policy of the
carrier or service provider. Configuration of the Cisco 6400 SCM service and subscriber provisioning
involves the definition of a large number of parameters that are common across these policies.
The Cisco 6400 SCM uses the concept of a configuration profile to simplify the definition of service
parameters.
A configuration profile is a set of configurationparameters (or attributes)that you can set up in advance
before the actual configuration operation. These profiles are saved in the Cisco EMF database. The
Cisco 6400 SCM profiles speed up both subscriber provisioning and service provisioning.
Withoutprofiles,you would haveto enter a repetitivedefinitionof the same (or similar) information for
service or subscriber provisioning operations. For example, you may wish to define “bronze” (low data
rate, inexpensive), “silver” and “gold” (high data rate, expensive) profiles for subscriber QoS using a
connection template. Connection templates therefore provide a simple method of applying information
for use during subscriber provisioning and saves retyping all of the QoS parameters individually for
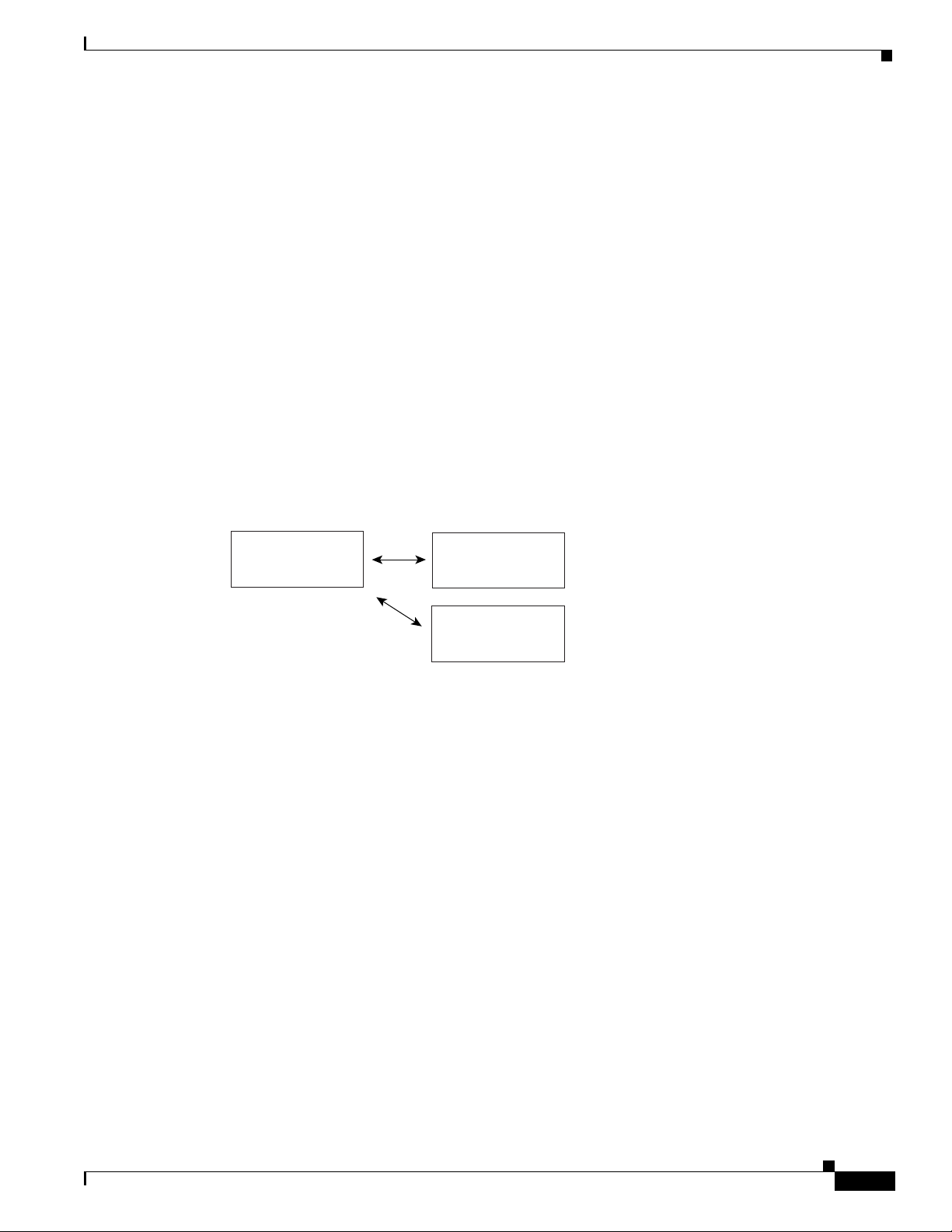
each new subscriber. A typical work flow is provided (see Figure 9-2) to help you.
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Figure 9-2 Defining Profiles For Service Provisioning
Create
Service Profiles
Editing Existing
Service Profiles
Deleting Existing
Service Profiles
41491
This section describes how to access and configure the Cisco 6400 SCM Service Profile Configuration
windows. The values that you select for each service depends on your network topology and market
service offerings.
See the Chapter 10, “Service/Subscriber Provisioning Windows: Detailed Description” for further
information on the meaning of each service topology and service parameter.
Creating Service Profiles for a PPPoA-SD Service
Service profiles define configuration parameters for the uplink from the Cisco 6400 UAC to the service
provider.
You can set up profiles and apply them or, alternatively, you can set up and apply a profile with some
of the parameters set and then configure the remaining parameters manually. The services available on
the Cisco 6400 UAC have a number of parameters to configure. It is worth setting up a number of
different service profiles with at least some of the values complete (that can be applied later) to save
time.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-3
Page 4
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
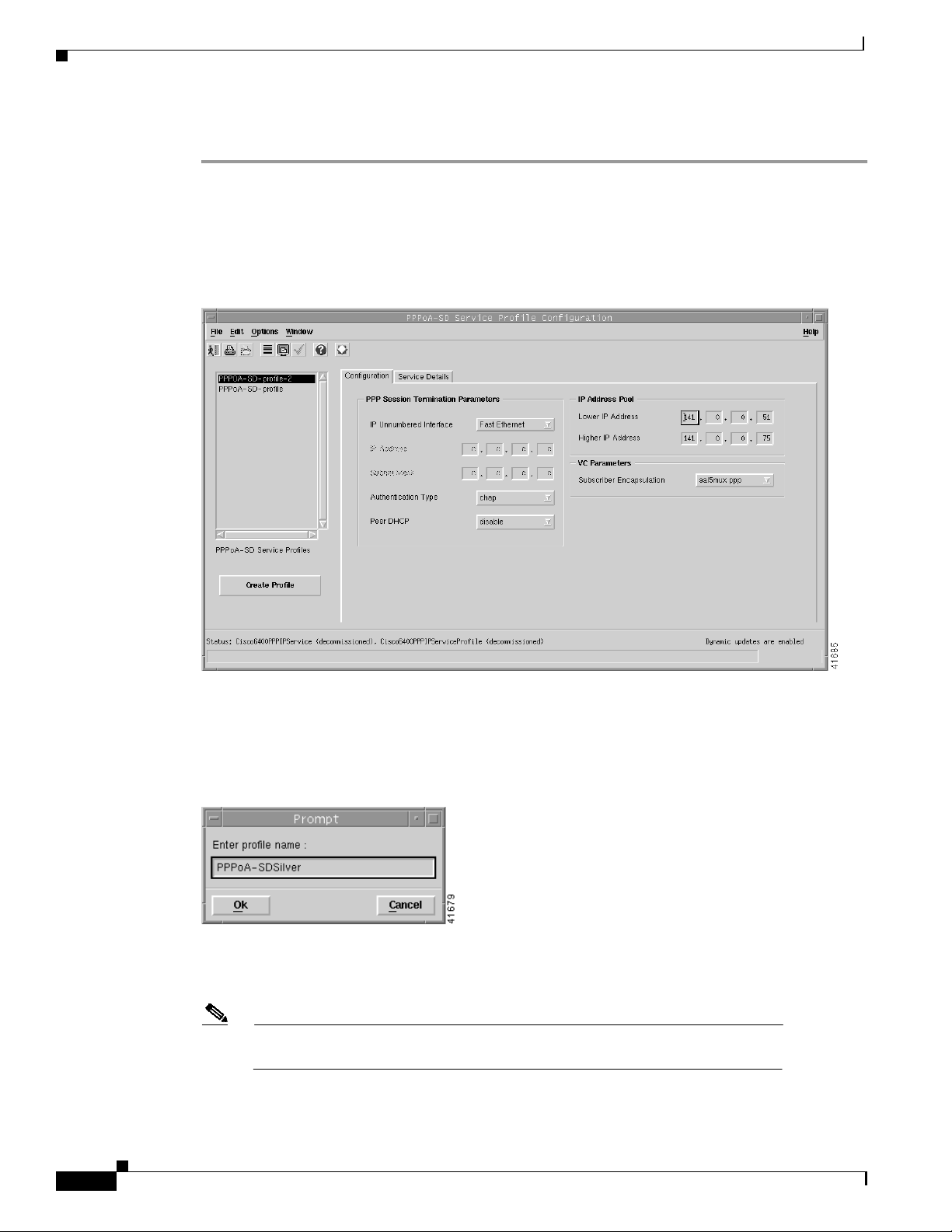
To create a PPPoA-SD service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC,Profiles, ConfigurePPPoA-SD Service Profilesoption from a Site, Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window. Profiles are “globally” available within
the Cisco 6400 SCM.
The PPPoA-SD Service Profile Configuration window appears with the Configuration tab displayed.
Figure 9-3 PPPoA-SD Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-4
Step 2 Select Create Profile.
A Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-4) for you to enter a name for you new profile.
Figure 9-4 Prompt Window
Step 3 Enter a name for the profile in the Enter profile name data entry box. PPPoA-SDSilver was entered in
the example shown in Figure 9-4.
Note Each service profile must have a unique name. Do not insert spaces into a service
profile name.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 5
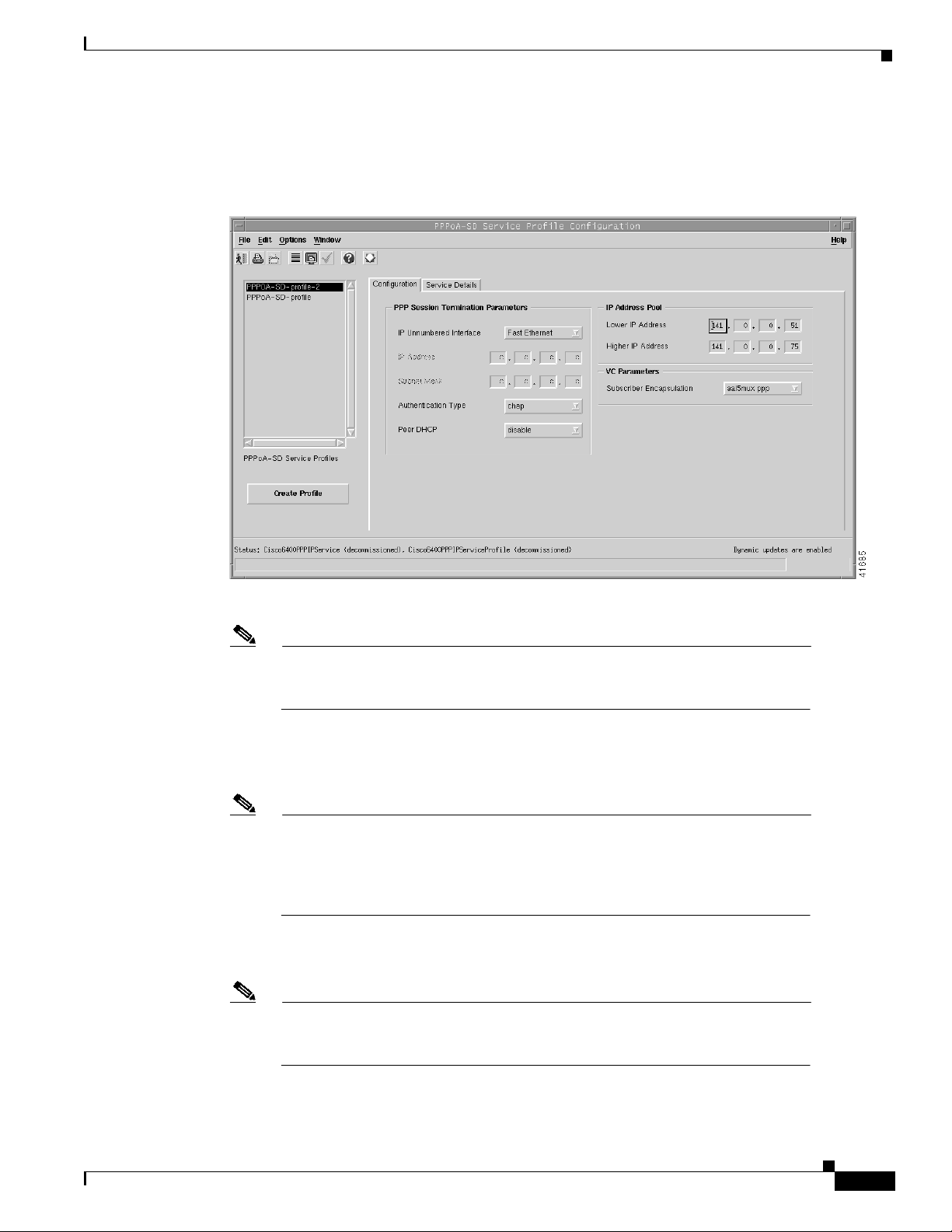
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
The PPPoA-SD Service Profile Configuration window reappears with the new profile name displayed
in the PPPoA-SD Service Profiles list at left side of the window (see Figure 9-5).
Figure 9-5 PPPoA-SD Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Note Select the Copy and Copy Page Configuration options in the Edit menu to cut
and paste between different profiles. This is useful when you wish to copy profile
information from one to the next.
Step 4 Configure the parameters in the PPP Session Termination Parameters panel, as required. The PPP
Session Termination Parameters describe the PPP characteristics used to terminate the incoming PPP
traffic. You should set the parameters appropriate to your network topology and services offered.
Note You can apply an existing profile to a new profile to save time when configuring
new profiles. Select the Apply Profile option from the Edit menu and then select
the existing profile you wish to apply from the profiles listed. The configuration
settings are copiedfrom the existingprofileto the new profile. The settings copied
appear in blue.
Step 5 Enter values for the Lower and Higher IP Addresses into the IP Address Pool panel, as required. The
IP Address Pool set the range of IP addresses available to a subscriber.
Note If you select to enable the Peer DHCP option, it appears that you are using an
external DHCP Server for IP address allocation, and values entered into the IP
Address Pool panel are grayed out and ignored.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-5
Page 6
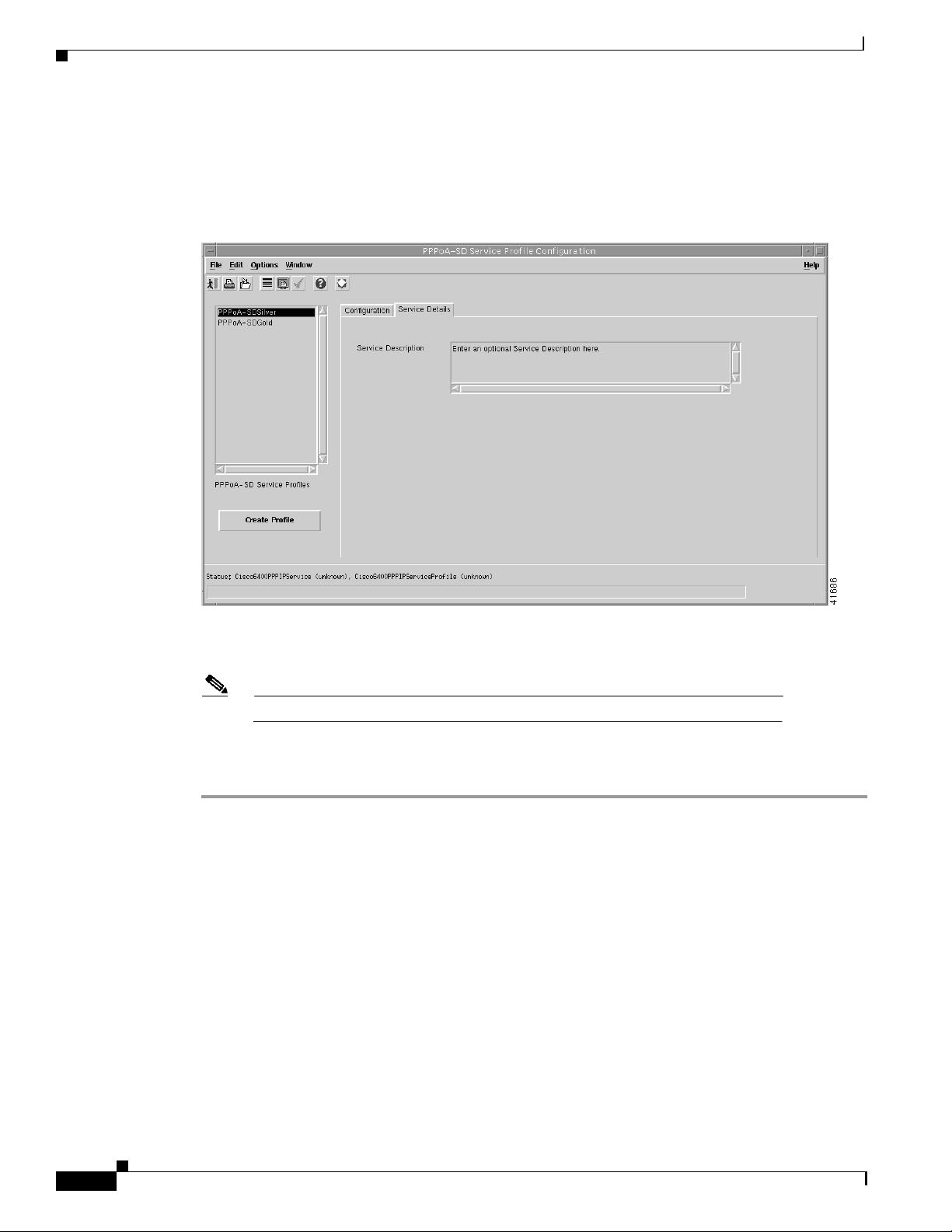
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Step 6 Select a Subscriber Encapsulation type in the VC Parameters panel. The VC Parameters define the
characteristics of the incoming ATM traffic.
Step 7 Select the Service Details tab (see Figure 9-6).
Figure 9-6 PPPoA-SD Service Profile Configuration Window (Service Details Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 8 Enter a description into the Service Description data entry box in the Service Details panel, if required.
Note Entering a Service Description is optional.
Step 9 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters you have selected for your service profile.
Step 10 Select Close from the File menu to close the window.
9-6
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 7
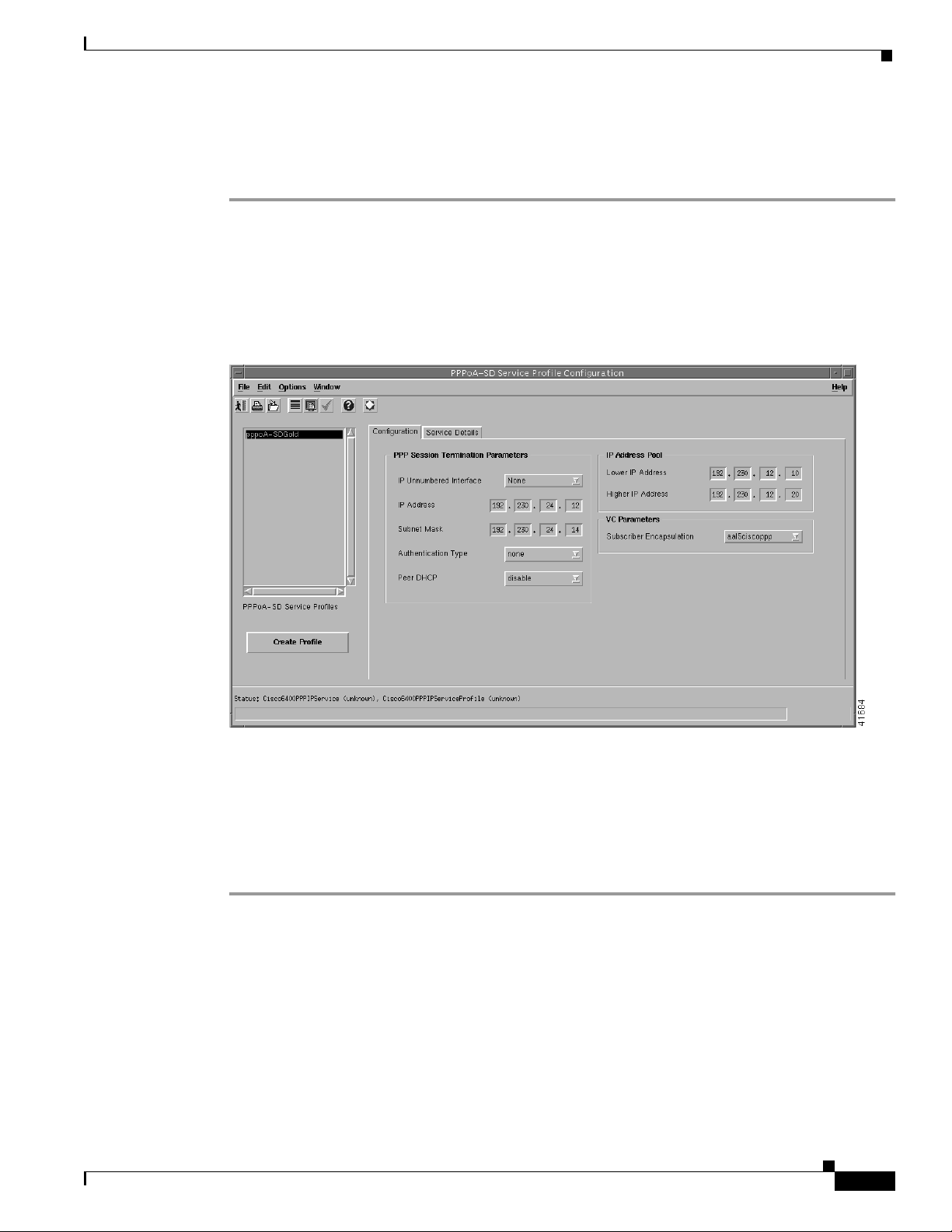
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Editing an Existing PPPoA-SD Service Profile
To edit an existing PPPoA-SD service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC,Profiles, ConfigurePPPoA-SD Service Profilesoption from a Site, Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window.
The PPPoA-SD Service Profile Configuration window appears with the PPPoA-SD Configuration tab
displayed. Existing service profiles are displayed in the PPPoA-SD Service Profiles list at the left side
of the window.
Figure 9-7 PPPoA-SD Service Profile Configuration Window (PPPoA-SD Configuration Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
Step 2 Select the profile you wish to edit from the list of profiles displayed in the PPPoA-SD Service Profiles
list.
Step 3 Edit the parameters displayed in the Configuration and Service Details tabs, as required.
Step 4 Select Save from the File menu to save the changes made to the service profile.
Step 5 Select Close from the File menu to close the window.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-7
Page 8
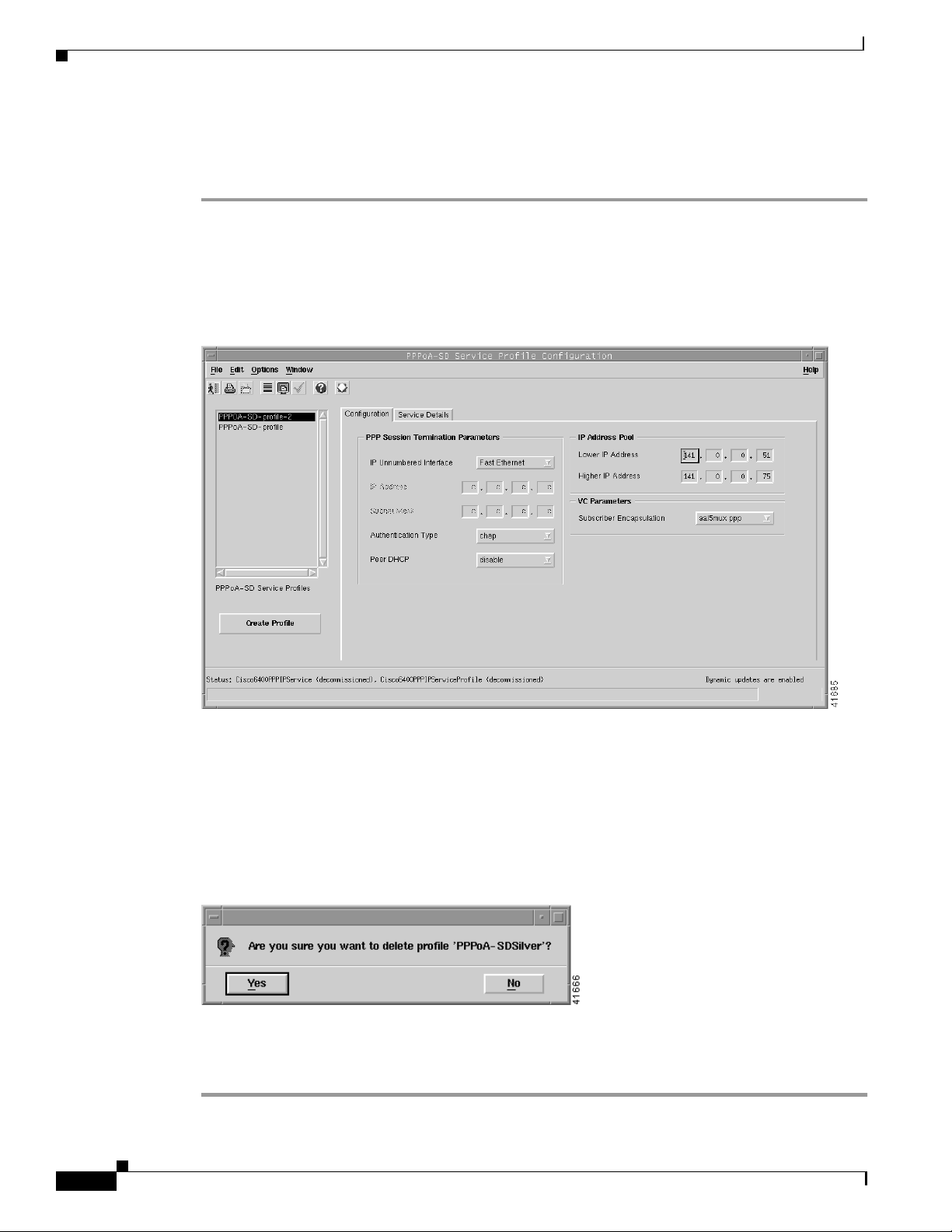
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Deleting an Existing PPPoA-SD Service Profile
To delete an existing PPPoA service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC,Profiles, ConfigurePPPoA-SD Service Profilesoption from a Site, Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window.
The PPPoA-SD Service Profile Configuration window appears. Existing service profiles are displayed
in the PPPoA-SD Service Profiles list on the left side of the window.
Figure 9-8 PPPoA-SD Service Profile Configuration Window (PPPoA-SD Configuration Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-8
Step 2 Select the existing service profile (displayed in the PPPoA-SD Service Profiles list) that you wish to
delete.
Step 3 Select the Delete Profile option from the Edit menu. Select the profile you wish to delete from the list
displayed.
A Deletion Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-9) for you to confirm that you wish to delete the
selected profile.
Figure 9-9 Deletion Prompt Window
Step 4 Click Yes to delete the selected profile or click No to close the window without deleting the profile.
When a profile is deleted it disappears from the list of PPPoA Service Profilesin the PPPoA-SDService
Profile Configuration window.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 9
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Creating Service Profiles for an L2TP Service
L2TP service profiles define the configuration parameters for the uplink from the Cisco 6400 UAC to
the service provider. You can set up profiles and apply them to the relevant NRP or, alternatively, you
can set up and apply a profile with some of the parameters set and then configure the remaining
parameters manually. The services available on the Cisco 6400 UAC have a number of parameters to
configure. It is worth setting up a number of different service profiles with at least some of the values
complete (that can be applied later) to save time.
To create an L2TP service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure L2TP Service Profiles option from a Site, Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window. Profiles are “globally” available within
the Cisco 6400 SCM.
The L2TP Service Profile Configuration window appears with the Configuration tab displayed.
Figure 9-10 L2TP Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
41559
Step 2 Select Create Profile.
A Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-11) for you to enter a name for your new profile.
Figure 9-11 Prompt Window
Step 3 Enter a name for the profile in the Enter profile name data entry box. L2TP Bronze was entered in the
example shown in Figure 9-11.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-9
Page 10

Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Note Each service profile must have a unique name. Do not insert spaces into a service
profile name.
The L2TP Service Profile Configuration window reappears with the name of the new profile displayed
in the L2TP Service Profiles list at left side of the window. See the “L2TP Service Profile Configuration
Window” section on page 10-4 for details of the parameters displayed.
Figure 9-12 L2TP Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Note Select the Copy and Copy Page Configuration options in the Edit menu to cut
and paste between different profiles. This is useful when you wish to copy profile
information from one to the next.
Step 4 Configure the parameters displayed in the L2TP Configuration tab as required.
Note You can apply an existing profile to a new profile to save time when configuring
new profiles. Select the Apply Profile option from the Edit menu and then select
the existing profile you wish to apply from the profiles listed. The configuration
settings are copiedfrom the existingprofileto the new profile. The settings copied
appear in blue.
41558
9-10
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 11
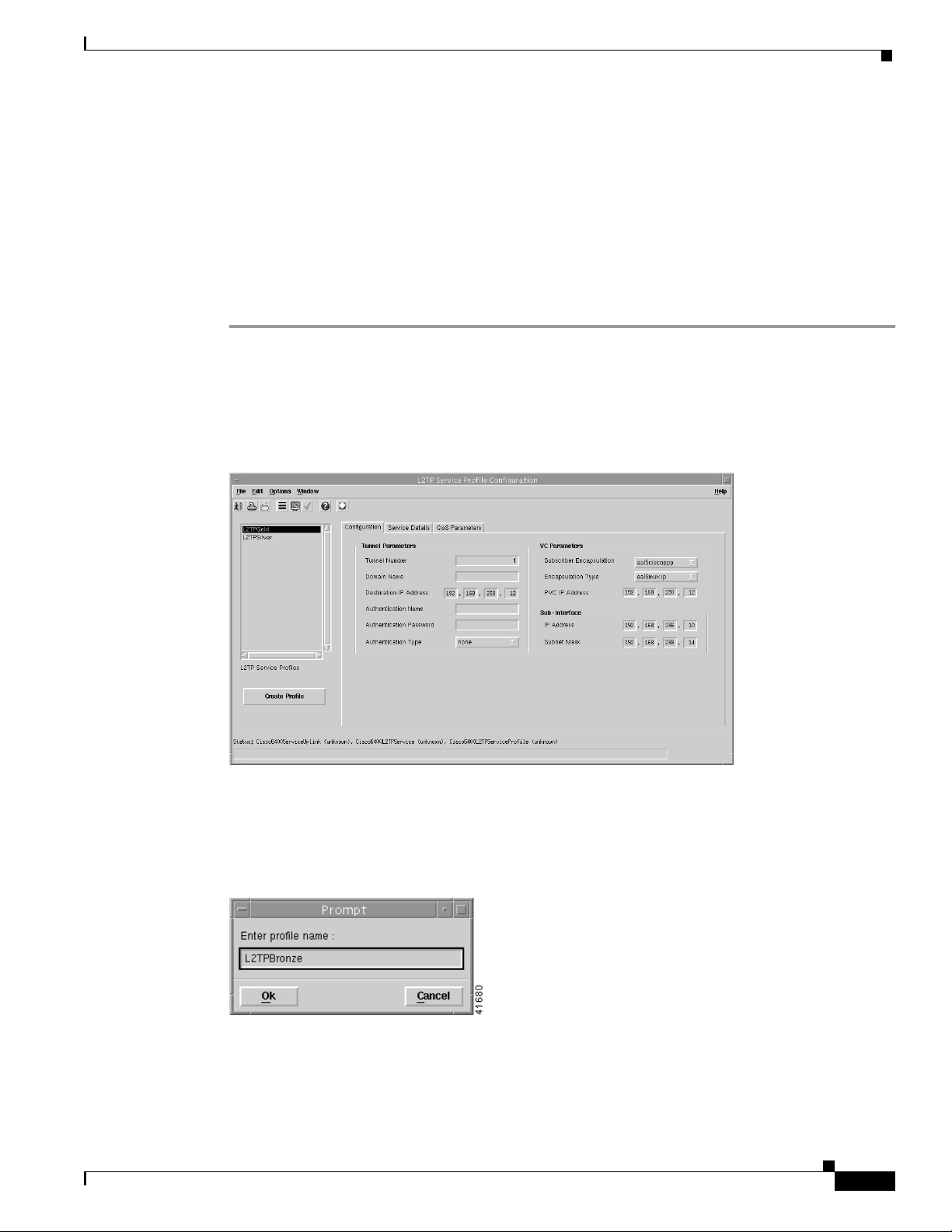
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 5 Select the Service Details tab.
Figure 9-13 L2TP Service Profile Configuration Window (Service Details Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
41560
Step 6 Enter a description into the Service Description data entry box in the Service Details panel, when
required. Entering a Service Description is optional.
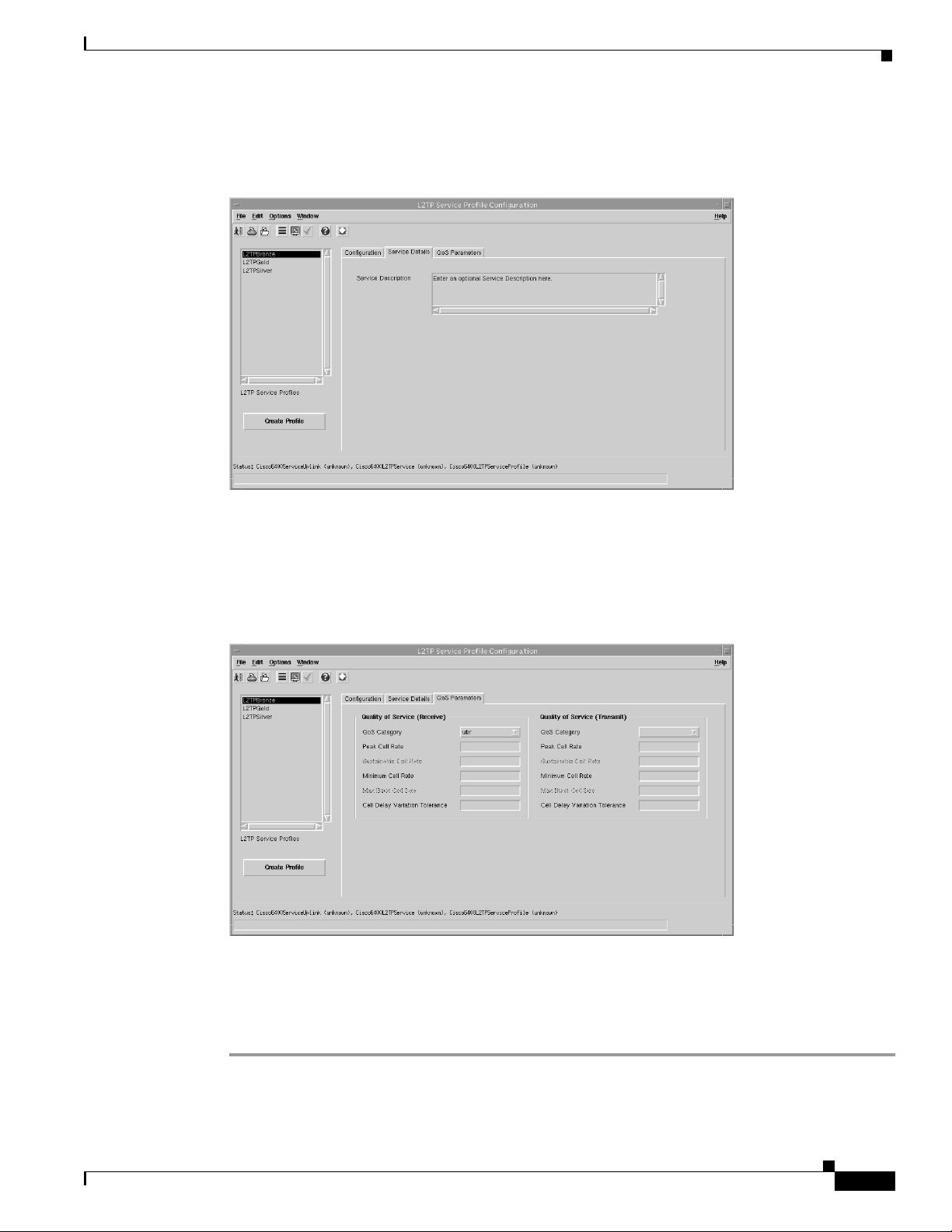
Step 7 Select the QoS Parameters tab.
Figure 9-14 L2TP Service Profile Configuration Window (QoS Parameters Tab)
41561
Step 8 Configure the parameters displayed on the QoS Parameters tab, as required.
Step 9 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters you have selected for your service profile.
Step 10 Select Close from the File menu to close the window.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-11
Page 12

Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Editing an Existing L2TP Service Profile
To edit an existing L2TP service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure L2TP Service Profiles option from a Site, Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window.
The L2TP Service Profile Configuration window appears with the L2TP Configuration tab displayed.
Existing service profiles are displayed in the L2TP Service Profiles list at the left side of the window.
Figure 9-15 L2TP Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
41558
Step 2 Select the profile you wish to edit from the list of profiles displayed in the PPPoA-SD Service Profiles
list.
Step 3 Edit the parameters displayed in the Configuration, Service Details and QoS Parameters tabs as
required.
Step 4 Select Save from the File menu to save the changes made to the service profile.
Step 5 Select Close from the File menu to close the window.
9-12
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 13
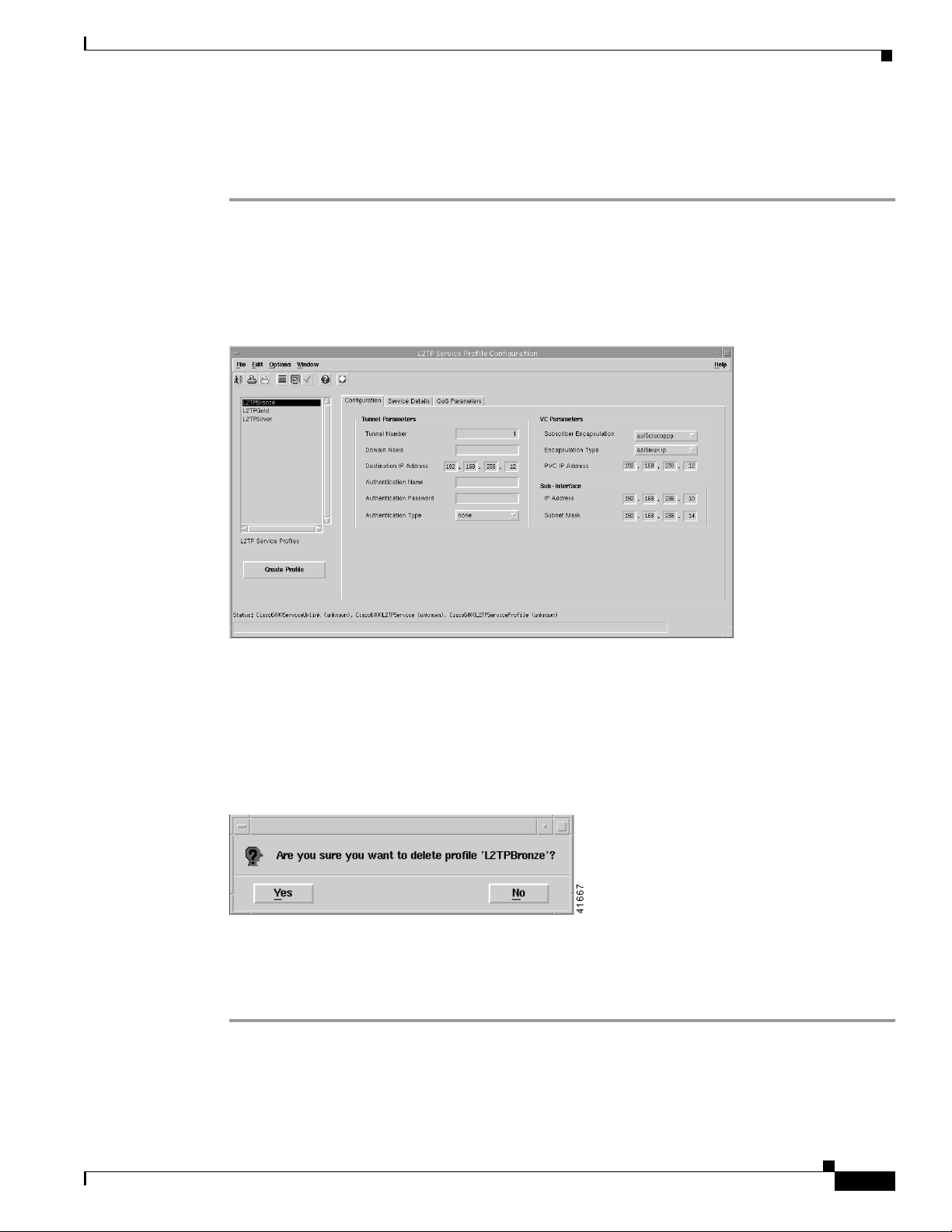
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Deleting an Existing L2TP Service Profile
To delete an existing L2TP service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure L2TP Service Profiles option from a Site, Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window.
The L2TP Service ProfileConfiguration window appears. Existing service profiles are displayed in the
L2TP Service Profiles list on the left side of the window.
Figure 9-16 L2TP Service Profile Configuration Window (L2TP Configuration Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
41558
Step 2 Select the Delete Profile option from the Edit menu. Select the profile you wish to delete from the list
displayed.
A Deletion Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-9) for you to confirm that you wish to delete the
selected profile.
Figure 9-17 Deletion Prompt Window
Step 3 Click Yes to delete the selected profile or click No to close the window without deleting the profile.
Step 4 When a profile is deleted it disappears from the list of L2TPService Profilesin the L2TP Service Profile
Configuration window.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-13
Page 14
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Creating Service Profiles for an RFC1483 Bridging Service
Service profiles define configuration parameters for the uplink from the Cisco 6400 UAC to the service
provider.
You can set up profiles and apply them or, alternatively, you can set up and apply a profile with some
of the parameters set and then configure the remaining parameters manually. The services available on
the Cisco 6400 UAC have a number of parameters to configure. It is worth setting up a number of
different service profiles with at least some of the values complete (that can be applied later) to save
time.
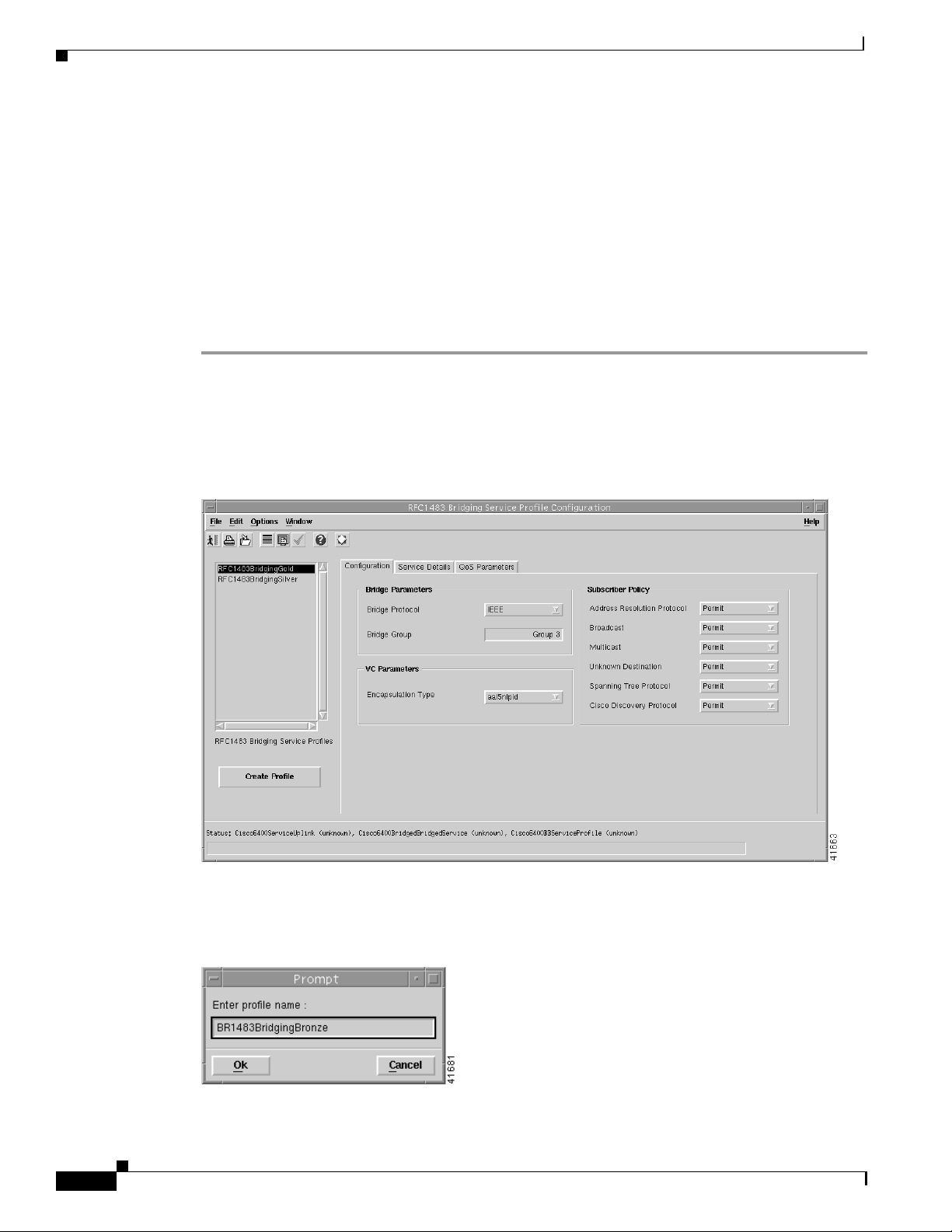
To create an RFC1483 Bridging service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure RFC1483 Bridging Service Profiles option from a
Site, Shelf, Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window. Profiles are “globally”
available within the Cisco 6400 SCM.
The RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration window appears:
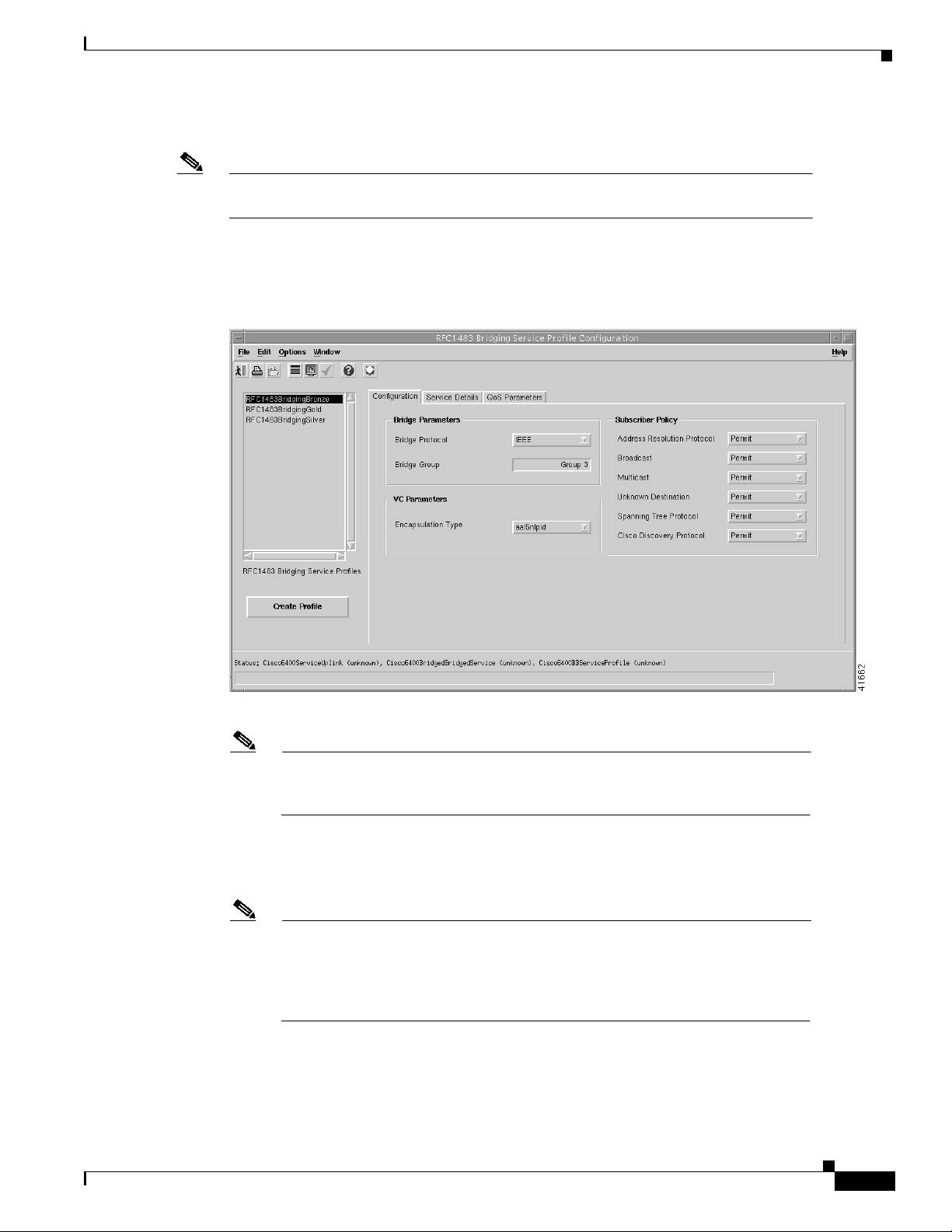
Figure 9-18 RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
9-14
Step 2 Select Create Profile. A Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-19).
Figure 9-19 Prompt Window
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 15
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 3 Enter a name for the profile in the Enter profile name data entry box.
Note Each service profile must have a unique name. Do not insert spaces into a service profile
name.
Step 4 BR1483 Bridging Bronze was entered in the example shown in Figure 9-19. The new profile name
appears in the BB Service Profiles list at left side of the window (see Figure 9-20).
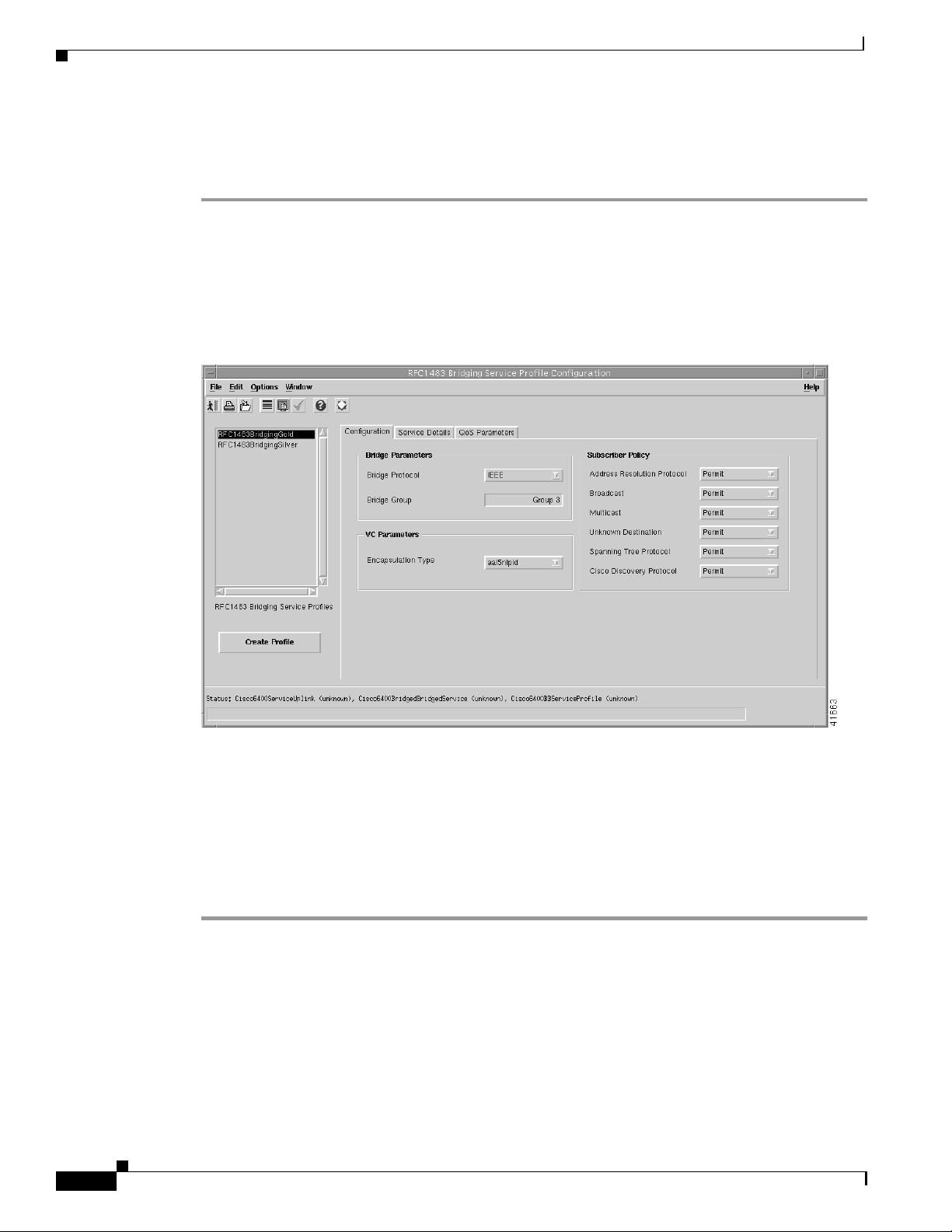
Figure 9-20 RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
Note Select the Copy and Copy Page Configuration options in the Edit menu to cut
and paste between different profiles. This is useful when you wish to copy profile
information from one to the next.
Step 5 Configure the parameters displayed in the Configuration tab, as required. See the “RFC1483 Bridging
Service Profile Configuration Window” section on page 10-7 for details of the parameters displayed on
each of the tabs.
Note You can apply an existing profile to a new profile to save time when configuring
new profiles. Select the Apply Profile option from the Edit menu and then select
the existing profile you wish to apply from the profiles listed. The configuration
settings are copiedfrom the existingprofileto the new profile. The settings copied
appear in blue.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-15
Page 16
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
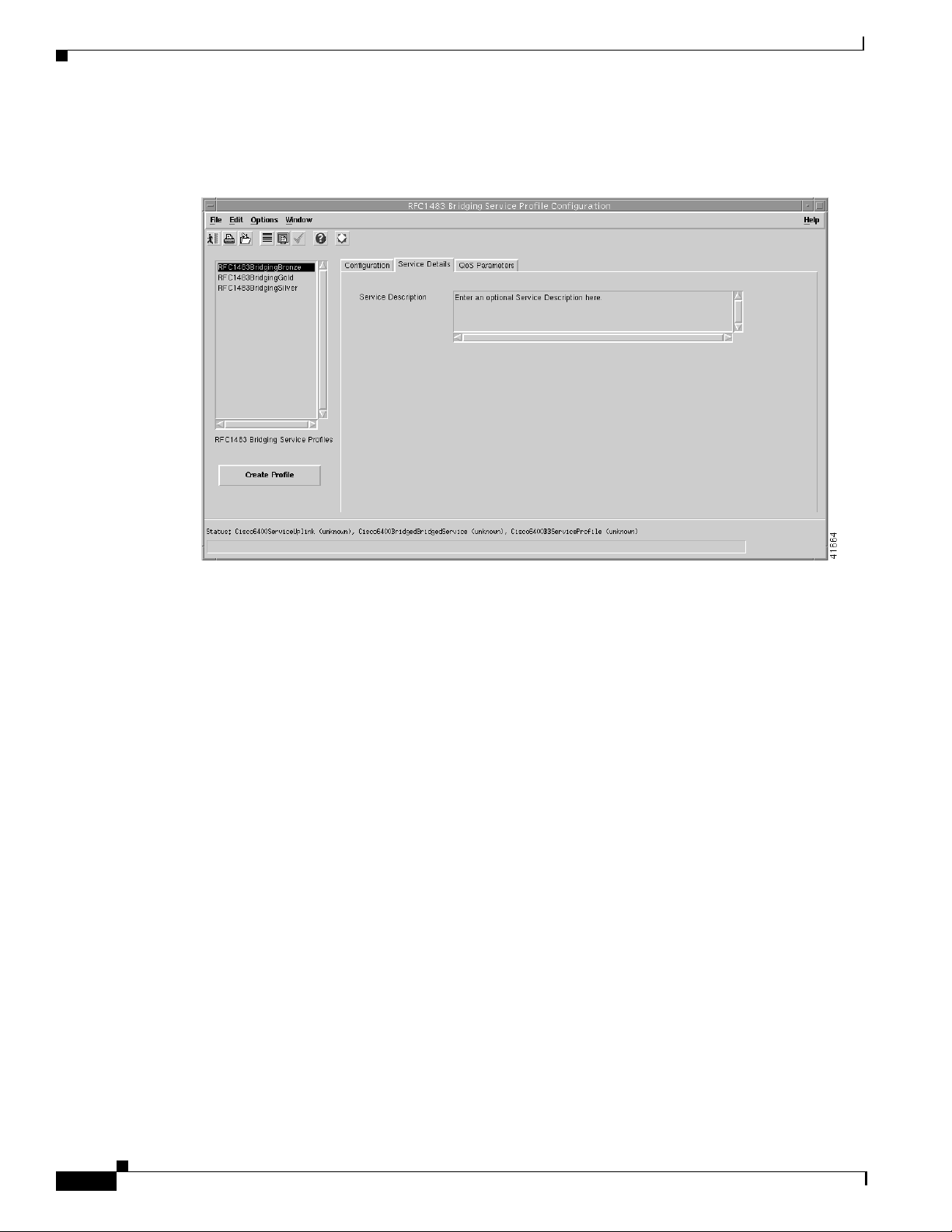
Step 6 Select the Service Details tab (see Figure Figure 9-21).
Figure 9-21 RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration Window (Service Details Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 7 Enter a description into the Service Description data entry box in the Service details panel, if required.
Entering a Service Description is optional.
9-16
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 17
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
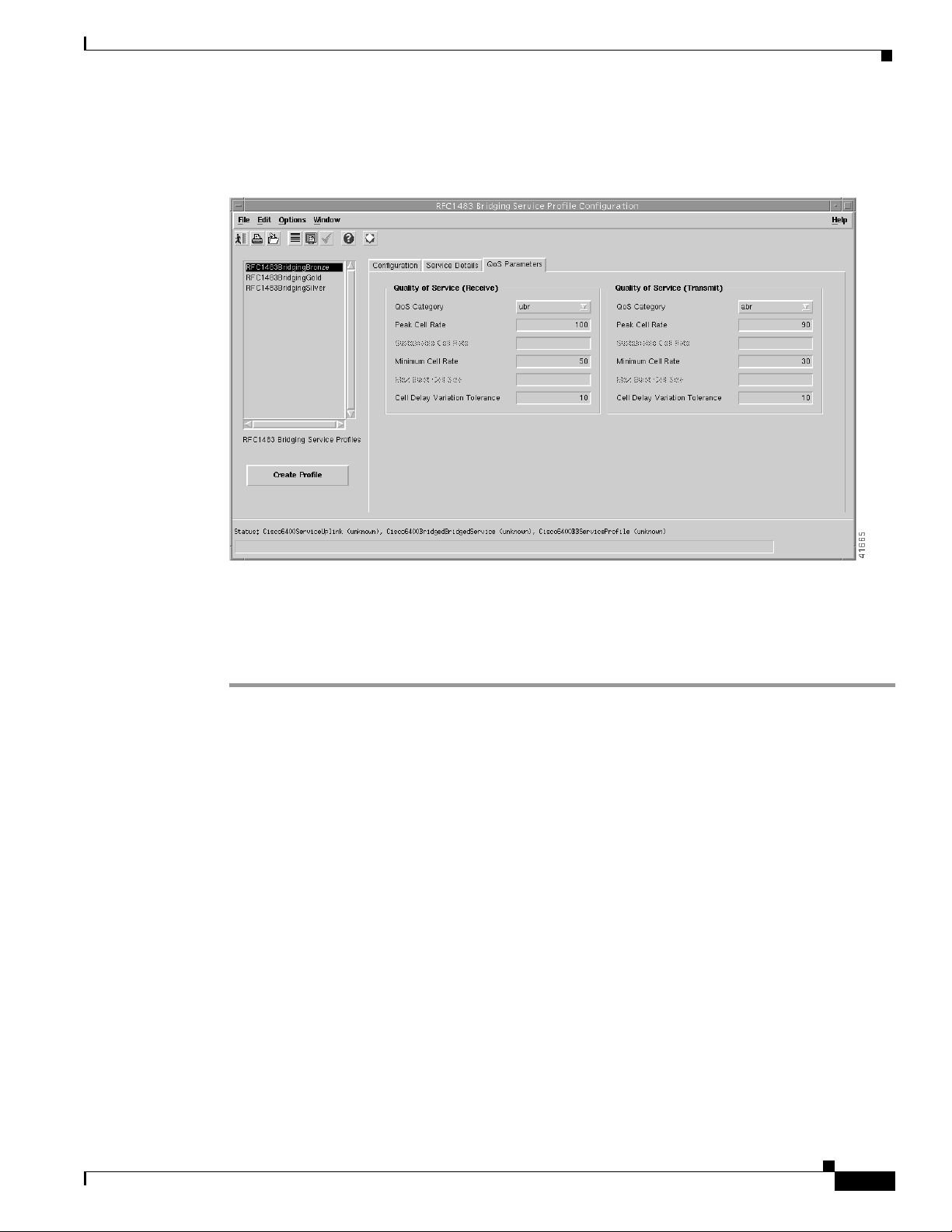
Step 8 Select the QoS Parameters tab (see Figure 9-22).
Figure 9-22 RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration Window (QoS Parameters Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Step 9 Configure the parameters displayed in the QoS Parameters tab, as required.
Step 10 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters you have selected for your service profile.
Step 11 Select Close from the File menu to close the window.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-17
Page 18
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Editing an Existing RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile
To edit an existing RFC1483 Bridging service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure RFC1483 Bridging Service Profiles option from a
Site, Shelf, Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window.
The RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration window appears with the Service Details tab
displayed. Existing service profiles are displayed in the BB Service Profiles list at the left side of the
window.
Figure 9-23 RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration Window (BB Configuration Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-18
Step 2 Select the profile you wish to edit from the list of profiles displayed in the RFC1483 Bridging Service
Profiles list.
Step 3 Edit the parameters displayed in the Configuration, Service Details, and QoS Parameters tabs, as
required.
Step 4 Select Save from the File menu to save the changes made to the service profile.
Step 5 Select Close from the File menu to close the window.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 19
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Deleting an Existing RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile
To delete an existing RFC1483 Bridging service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure RFC1483 Bridging Service Profiles option from a
Site, Shelf, Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window.
The RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration window appears. Existing service profiles are
displayed in the BB Service Profiles list on the left side of the window.
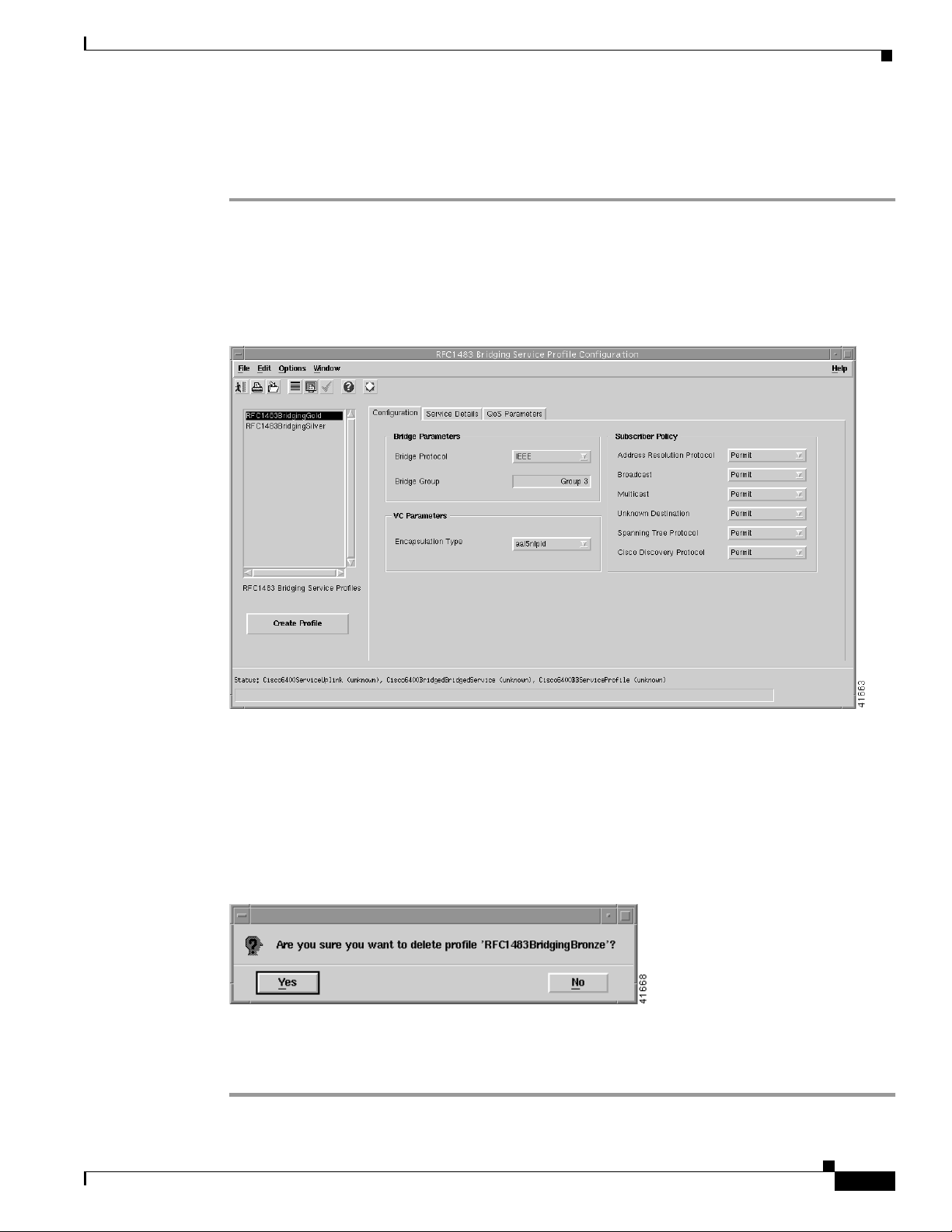
Figure 9-24 RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
Step 2 Select the existing service profile (displayed in the RFC1483 Bridging Service Profiles list) that you
wish to delete.
Step 3 Select the Delete Profile option from the Edit menu. Select the profile you wish to delete from the list
displayed.
A Deletion Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-25) for you to confirm that you wish to delete the
selected profile.
Figure 9-25 Deletion Prompt Window
Step 4 Click Yes to delete the selected profile or click No to close the window without deleting the profile.
When a profile is deleted it disappears from the list of RFC1483 Bridging Service Profiles in the
RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration window.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-19
Page 20
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Creating Service Profiles for an RFC1483 IRB Service
Service profiles define configuration parameters for the uplink from the Cisco 6400 UAC to the service
provider.
You can set up profiles and apply them or, alternatively, you can set up and apply a profile with some
of the parameters set and then configure the remaining parameters manually. The services available on
the Cisco 6400 UAC have a number of parameters to configure. It is worth setting up a number of
different service profiles with at least some of the values complete (that can be applied later) to save
time.
To create an RFC1483 IRB service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure RFC1483 IRB Service Profiles option from a Site,
Shelf, Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window. Profiles are “globally” available
within the Cisco 6400 SCM.The RFC1483 IRBService Profile Configurationwindowappears with the
Configuration tab displayed:
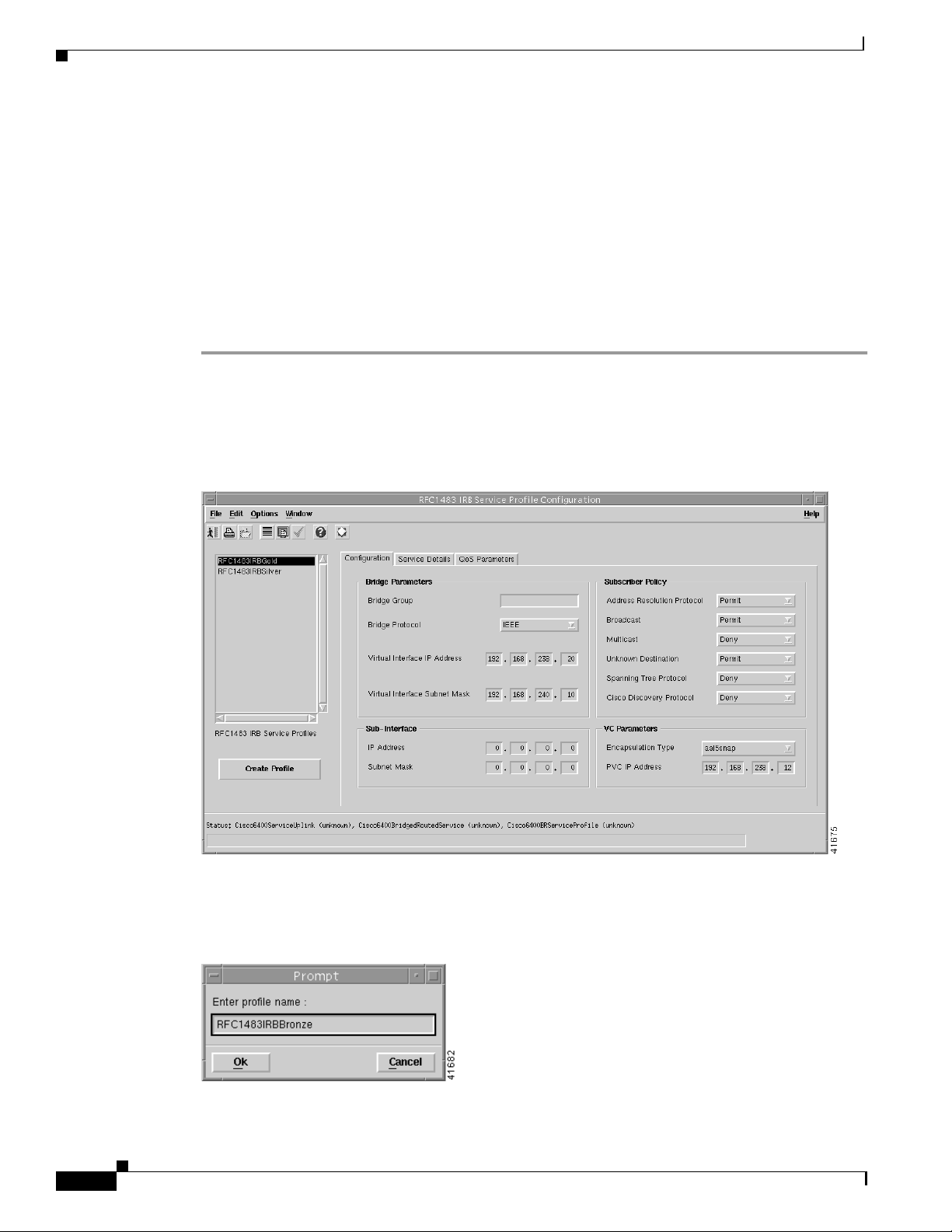
Figure 9-26 RFC1483 IRB Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-20
Step 2 Select Create Profile. A Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-27).
Figure 9-27 Prompt Window
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 21

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 3 Enter a name for the profile in the Enter profile name data entry box. Premium Profile was entered in
the example shown in Figure 9-27.
Note Each service profile must have a unique name. Do not insert spaces into a service
profile name.
The new profile name displays in the BR Service Profiles list at left side of the window (see
Figure 9-28).
Figure 9-28 RFC1483 IRB Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
Note Select the Copy and Copy Page Configuration options in the Edit menu to cut
and paste between different profiles. This is useful when you wish to copy profile
information from one to the next.
Step 4 Configure the parameters displayed in the Configuration tab as required. See the “RFC1483 IRB
Service Profile Configuration Window” section on page 10-11 for details of the parameters displayed
on each of the tabs.
Note You can apply an existing profile to a new profile to save time when configuring
new profiles. Select the Apply Profile option from the Edit menu and then select
the existing profile you wish to apply from the profiles listed. The configuration
settings are copiedfrom the existingprofileto the new profile. The settings copied
appear in blue.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-21
Page 22
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
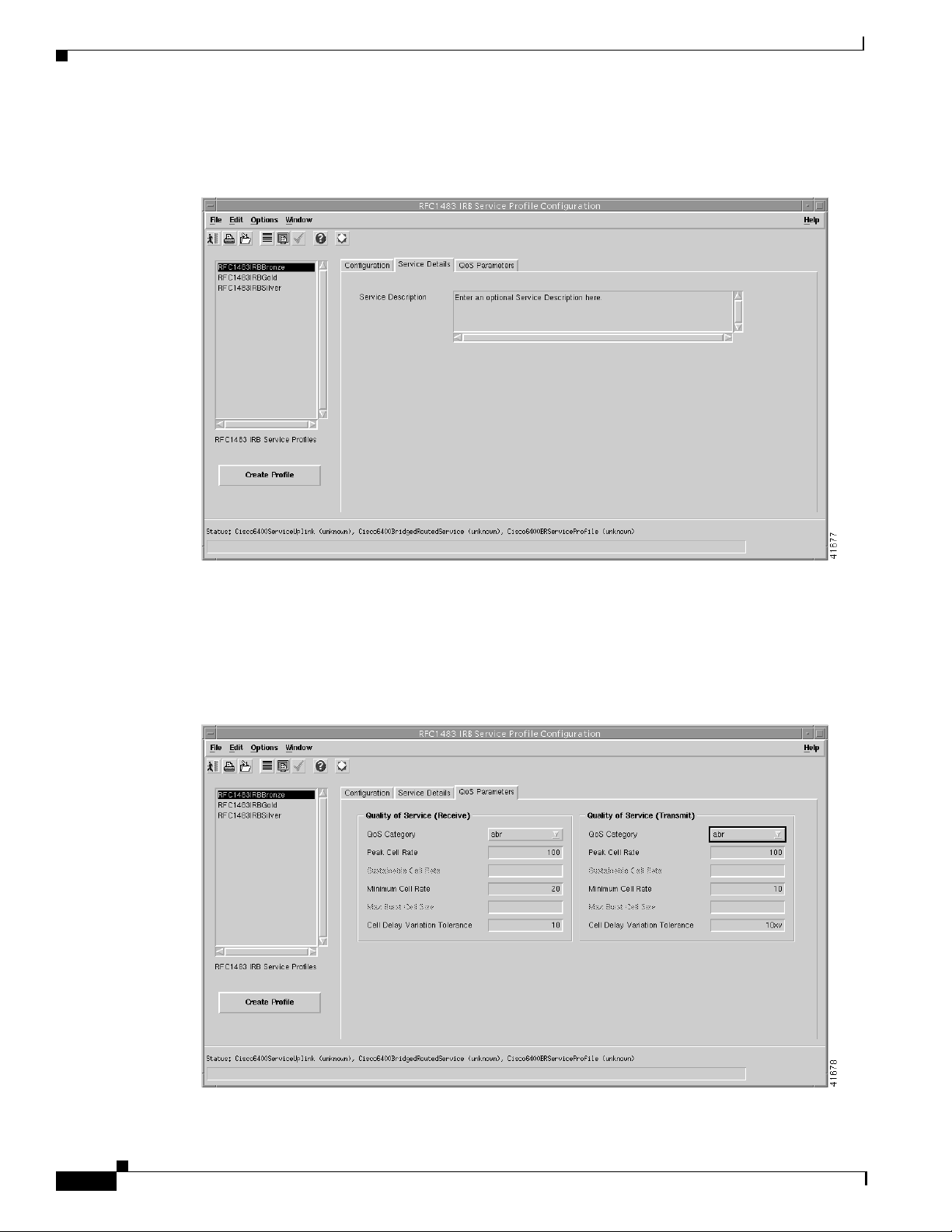
Step 5 Select the Service Details tab (see Figure 9-29).
Figure 9-29 RFC1483 IRB Service Profile Configuration Window (Service Details Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 6 Enter a description into the Service Description data entry box in the Service Details panel, as required.
Entering a Service description is optional.
Step 7 Select the QoS Parameters tab.
Figure 9-30 RFC1483 IRB Service Profile Configuration Window (QoS Parameters Tab)
9-22
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 23

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 8 Configure the parameters displayed in the QoS Parameters tab as required.
Step 9 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters you have selected for your service profile.
Step 10 Select Close from the File menu to close the window.
Editing an Existing RFC1483 IRB Service Profile
To edit an existing RFC1483 IRB service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure RFC1483 IRB Service Profiles option from a Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window.
The RFC1483 IRB Service Profile Configuration window appears with the BR Configuration tab
displayed. Existing service profiles are displayed in the BR Service Profiles list at the left side of the
window.
Figure 9-31 RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
Step 2 Select the profile you wish to edit from the list of profiles displayed in the RFC1483 IRB Service
Profiles list.
Step 3 Edit the parameters displayed in the Configuration, Service Details, and QoS Parameters tabs, as
required.
Step 4 Select Save from the File menu to save the changes made to the service profile.
Step 5 Select Close from the File menu to close the window.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-23
Page 24
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Deleting an Existing RFC1483 IRB Service Profile
To delete an existing IRB service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure RFC1483 IRB Service Profiles option from a Site,
Shelf, Chassis, or service instance object in the MapViewer window.
The RFC1483 IRB Service Profile Configuration window appears. Existing service profiles are
displayed in the BR Service Profiles list on the left side of the window.
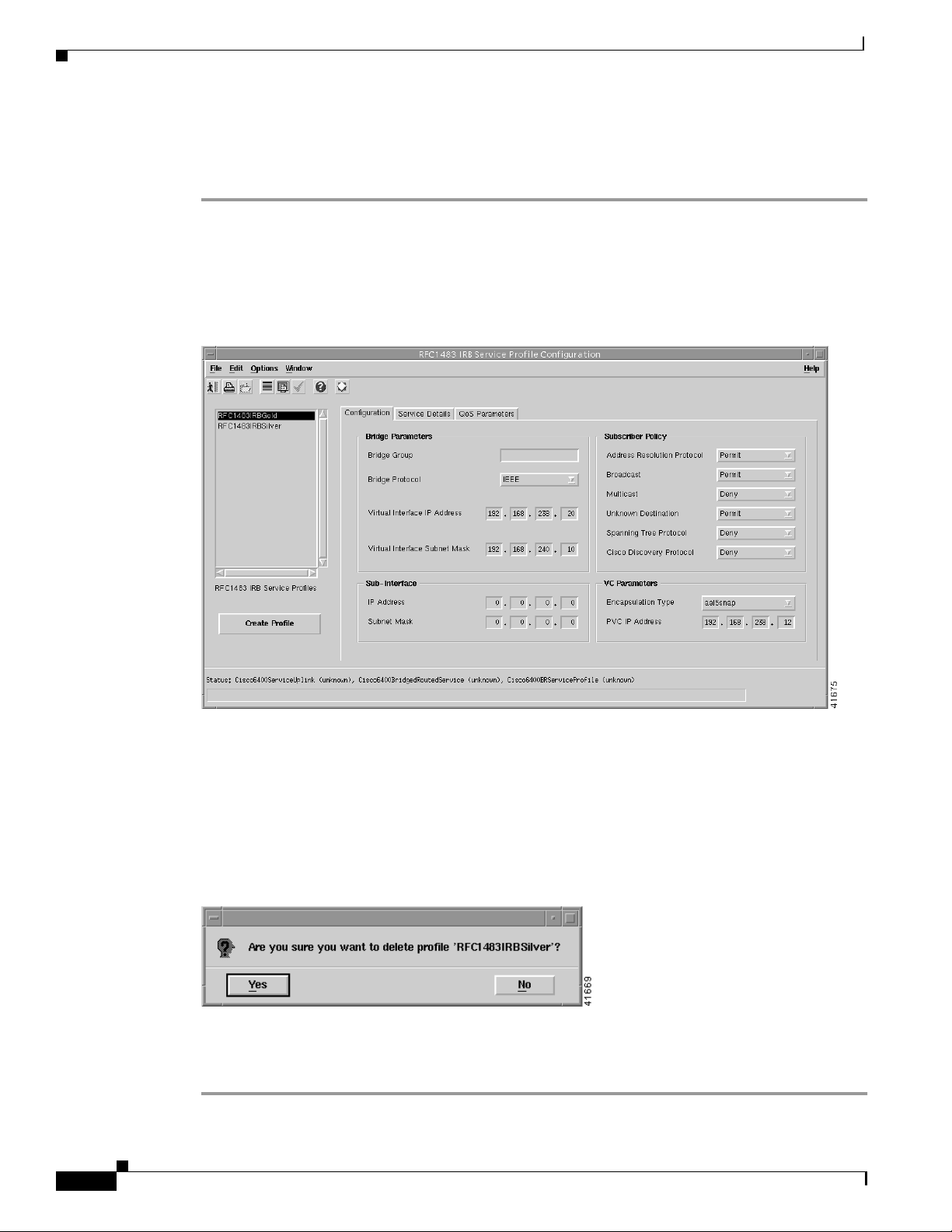
Figure 9-32 RFC1483 IRB Service Profile Configuration Window (BR Configuration Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-24
Step 2 Select the existing service profile (displayed in the RFC1483 IRB Service Profiles list) that you wish to
delete.
Step 3 Select the Delete Profile option from the Edit menu. Select the profile you wish to delete from the list
displayed.
A Deletion Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-33) for you to confirm that you wish to delete the
selected profile.
Figure 9-33 Deletion Prompt Window
Step 4 Click Yes to delete the selected profile or click No to close the window without deleting the profile.
Step 5 When a profile is deleted it disappears from the list of RFC1483 IRB Profiles in the RFC1483 IRB
Service Profile Configuration window.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 25

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Creating Service Profiles for an IP Uplink (for PTA-MD and RBE Subscribers) Service
Service profiles define configuration parameters for the uplink from the Cisco 6400 UAC to the service
provider.
You can set up profiles and apply them or, alternatively, you can set up and apply a profile with some
of the parameters set and then configure the remaining parameters manually. The services available on
the Cisco 6400 UAC have a number of parameters to configure. It is worth setting up a number of
different service profiles with at least some of the values complete (that can be applied later) to save
time.
To create an IP Uplink service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure IP Uplink Profilesoption from a Site, Shelf, Chassis,
or service instance object using the MapViewer application.
The IP Uplink Service Profile Configuration window appears (see Figure 9-34) with the Configuration
tab displayed.
Figure 9-34 IP Uplink Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-25
Page 26

Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Step 2 Select Create Profile. A Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-35).
Figure 9-35 Prompt Window
Step 3 Enter a name for the profile in the Enter profile name data entry box. IP Uplink Bronze was entered
in the example shown in Figure 9-35.
Note Each service profile must have a unique name. Do not insert spaces into a service
profile name.
The new profilename appears in the IP Uplink Service Profileslist on the left side of the window (see
Figure 9-36).
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-36 IP Uplink Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Step 4 Configure the parameters displayed in the Configuration tab (shown in Figure 9-34), as required. The
Configure option (in the Local Service Profile panel on the Configuration tab) must be set to Yes to
allow you to configure the parameters displayed in the Local Service Profile tab.
9-26
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 27

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Note You can apply an existing profile to a new profile to save time when configuring
new profiles. Select the Apply Profile option from the Edit menu and then select
the existing profile you wish to apply from the profiles listed. The configuration
settings are copiedfrom the existingprofileto the new profile. The settings copied
appear in blue.
Note Select the Copy and Copy Page Configuration options in the Edit menu to cut
and paste between different profiles. This is useful when you wish to copy profile
information from one to the next.
Step 5 Select the Local Service Profile tab (when applicable).
Note The Configure option (in the Local Service Profilepanel on the Configurationtab)
must be set to Yes to allow you to configure the parameters displayed in the Local
Service Profile tab.
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Figure 9-37 IP Uplink Service Profile Configuration Window (Local Service Profile Tab)
See the “Local Service Profile Tab” section on page 10-18 for details of the parameters displayed.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-27
Page 28

Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Step 6 Configure the General, DNS Redirection / Fault Tolerance, and the Remote RADIUS Configuration
parameters.
Step 7 Select the QoS Parameters tab.
Figure 9-38 IP Uplink Service Profile Configuration Window (QoS Parameters Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 8 Configure the Quality of Service (Receive) and Quality of Service (Transmit) parameters, as required.
Step 9 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters you have selected for your service profile.
Step 10 Select Close from the File menu to close the window.
9-28
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 29

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Editing an Existing IP Uplink Service Profile
To edit an existing IP Uplink service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure IP Uplink Profilesoption from a Site, Shelf, Chassis,
or service instance object in the Map Viewer window.
The IP Uplink Service Profile Configuration window appears with the Configuration tab displayed (see
Figure 9-39).
Figure 9-39 IP Uplink Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
Step 2 Select the profile you wish to edit from the list of profiles displayed in the IP Uplink Service Profiles
list on the left side of the window.
Step 3 Configure the parameters displayed in the Configuration, Local Service Profile, and QoS Parameters
tabs as required.
Step 4 Select Save from the File menu to save the configuration.
Step 5 Select Close from the File menu to close the window and save the changes made.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-29
Page 30

Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Deleting an Existing IP Uplink Service Profile
To delete an existing IP Uplink service profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Profiles, Configure IP Uplink Profilesoption from a Site, Shelf, Chassis,
or service instance object in the Map Viewer window. The IP Uplink Service Configuration Profile
window appears.
Figure 9-40 IP Uplink Service Profile Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-30
Step 2 Select the existing service profile (displayed in the IP Uplink Service Profiles list) that you wish to
delete.
Step 3 Select the Delete Profile option from the Edit menu. Select the profile you wish to delete from the list
displayed.
A Deletion Prompt window appears (see Figure 9-41) for you to confirm that you wish to delete the
selected profile.
Figure 9-41 Deletion Prompt Window
Step 4 Click Yes to delete the selected profile or click No to close the window without deleting the profile.
Step 5 When a profile is deleted it disappears from the list of IP Uplink Service Profiles in the IP Uplink
Service Profiles Configuration window.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 31

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Connection Templates
Connection Templates are very similar to VC Classes in Cisco IOS. The main difference is that, where
a VC class is local to a specific NRP, Connection Templates are available for each Cisco 6400 UAC
managed by the Cisco 6400 SCM application. When aparameter in aconnection template is altered and
applied, this change applies to all connections that use the template. A connection template is basically
a “wrapper” that represents several VC classes, one for each NRP.
Connection templates allow you to set the QoS parameters for the connection between the subscriber
PVC and the selected NRP. The connection templates are applied later when connecting the subscriber
to a service instance. See the “Connecting a Subscriber to a Service Instance” section on page 9-72 for
further details on connecting subscribers to a service instance.
Figure 9-42 shown an example workflow for creating and configuring connection templates.
Figure 9-42 Subscriber Provisioning Work Flow
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
You cannot delete a
connection template
until all subscribers
using the connection
template have been
disconnected.
Deploying Connection Templates
To deploy a Connection Template, follow these steps:
Step 1 Place the cursor over a relevant object in the a network map, a relevant object in the map view, or by
using an object pick list on an open Element Manager window. See Table 9-1 on page 9-2 for
information on the objects you can deploy from.
Step 2 Click and hold down the right mouse button.
Step 3 Select the Deployment, Cisco 6400 UAC, Connection Template, Deploy Connection Template
option. The Deployment Wizard - Object Parameters window (see Figure 9-43) appears.
Delete an Existing
Connection
Template
Deploy
Connection
Templates
Configure
Connection
Template
Deploy (create) connection
template objects and
name them.
Configure the Quality of
Service (Receive) and
Quality of Service
(Transmit) parameters.
35360
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-31
Page 32

Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Figure 9-43 Deployment Wizard - Object Parameters Window
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Enter the number of
Connection T emplate
objects to create
Step 4 Enter the Number of Connection Template objects you wish to deploy.
Step 5 Click Forward.
Step 6 Enter a name for the new Connection Template in the Object Parameters panel.
Figure 9-44 Deployment Wizard - Object Parameters Window
Enter a name for the new
Connection T emplate object
41501
9-32
41502
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 33

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 7 Click Forward.
Step 8 Repeat steps 6 and 7 for the Number of Connection Template objects entered in step 4.
Step 9 The Deployment Summary details appear in the Deployment Wizard - Summary window (see
Figure 9-45).
Figure 9-45 Deployment Wizard - Summary Window
Check the
Deployment
Summary
information
is correct
Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Step 10 Check the summary information displayed is correct.
Step 11 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct) to complete the deployment.
After deploying a connection template, you should then configure them. Proceed to the “Configuring
Connection Templates” section on page 9-33 for further details.
Configuring Connection Templates
To configure connection templates, follow these steps:
Step 1 Place the cursor over a relevant object in the a network map, a relevant object in the map view, or use
an object pick list on an open Element Manager window. See the Table 9-1 on page 9-2 for information
on the objects you can deploy from.
Step 2 Click and hold down the right mouse button.
41503
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-33
Page 34

Defining Policies For Service Provisioning
Step 3 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Connection, Connection Template Configuration option. The
Connection Template Configuration window (see Figure 9-46) appears.
Figure 9-46 Connection Template Configuration Window (QoS Parameters Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 4 Select a connection template from the Connection Template list displayed.
Step 5 Configure the Quality of Service (Receive) and Quality of Service (Transmit) parameters, as required.
See the“Service/Subscriber Connection Window” section on page 10-60 for further details on the
parameters displayed.
Step 6 Click Apply to apply the settings to the selected connection template.
Note Connection templates allow you to reconfigure the Quality of Service (Receive)
and Quality of Service (Transmit) parameters set for a subscriber without
disruption to the service (thatis, without having to disconnect asubscriber,change
parameters and then reconnect the subscriber).
Step 7 Select the Close option from the File menu to close the Connection Template Configuration window.
35329
9-34
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 35

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Deleting Connection Templates
Note Before deleting a connection template you must disconnect any subscribers connected to
a service instance using that connection template.
To delete connection templates, follow these steps:
Step 1 Place the cursor over a relevant object in the a network map, a relevant object in the map view, or an
object pick list on an open Element Manager window.See Table 9-1 on page 9-2 for information on the
objects you can deploy from.
Step 2 Click and hold down the right mouse button.
Step 3 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Connection, Connection Template Configuration option. The
Connection Template Configuration window (see Figure 9-46) appears.
Step 4 Select a connection template from the Connection Template list displayed.
Step 5 Click Delete to delete the selected connection template.
Step 6 Select Close from the File menu to close the Connection Template Configuration window.
Service Provisioning
Service Provisioning
One of the most important aspect of the Cisco 6400 SCM application is Service Connection
Management. The Cisco 6400 UAC contains multiple network elements, an ATM switch, multiple
router cards (NRPs), and multiple line cards. Services are deployed across these network elements, a
multistage process involvingbothSNMPand Cisco IOS management commands. TheCisco 6400 SCM
application enables point-and-clickconnection of endsubscribers to 6400-basedservices with allof the
underlying Cisco IOS and SNMP operation hidden.
The Cisco 6400 SCM software is designed to help simplify Cisco 6400 UAC service configuration. A
typical work flow is described in Figure 9-47.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-35
Page 36

Service Provisioning
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-47 Setting Up Services on the Cisco 6400 UAC
All three steps are
accomplished within the
Service Configuration
window appropriate for
the selected service
Create (Deploy) a
Service Instance
Apply an existing
Service Profile to a
Service Instance
Configure an
Appropriate
Service Instance
Commission the
Service Instance
A Service Instance holds all of the
information related to that service.
Apply an existing profile (if required)
and then configure
the remaining
parameters
manually
or configure all of
the parameters manually.
Some manual configuration
is always required (for example,
uplink VPI/VCI)
Click Commission Service to
"roll" the selected service configuration
onto the 6400 UAC hardware.
41807
Note The“Configuringand Commissioning a Service Instance” section on page 9-40 is the only
section that involves direct configuration of the Cisco 6400 UAC hardware.
Creating a Service Instance
A service instance is an object that holds all the information related to that service. A service instance
object must be created (deployed) before the service instance can be configured.
This section includes an example that describes how to create a service instance for an ATM Service.
The procedure for creating a service instance for any other service types is very similar to that for the
ATM Service.
To create a service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Service, Deploy, Appropriate Service option from a selected chassis.
Note Where the Appropriate Service is the type of service instance you wish to create
(that is, ATM, PPPoA-SD, L2TP, RFC1483 Bridging, RFC1483 IRB, IP Uplink,
or RFC1483 Routing).
9-36
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 37

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
The Deployment Wizard Object Parameters (1 of 2) window appears (see Figure 9-48).
Figure 9-48 Deployment Wizard - Object Parameters (1 of 2) Window
Service Provisioning
Enter the number of
service objects you
wish to create
41524
Step 2 Enter the Number of Service objects to create. A single ATM Service object was entered in the
example shown in Figure 9-48.
Step 3 Select Forward. The Deployment Wizard Object Parameters (2 of 2) window appears (see
Figure 9-49).
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-37
Page 38

Service Provisioning
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-49 Deployment Wizard - Object Parameters (2 of 2)
Enter the name for
the service instance
41525
Step 4 Enter a Service Instance Name. ATM Service- One was entered in the example shown in Figure 9-49.
Step 5 Select Forward.
Note Repeat steps 4 and 5 for the Number of Service Instancesentered in step 2, when
required.
9-38
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 39

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 6 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard Summary window appears (see Figure 9-50).
Figure 9-50 Deployment Wizard - Summary
The Summary panel
displays information
about the deployment
Service Provisioning
Summary information displays in the Summary panel.
Step 7 Check the Summary information is correct.
Step 8 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct) to create the new Service
Instance objects.
Step 9 Proceed to the “Configuring and Commissioning a Service Instance” section on page 9-40.
The new service instances created now displays in the Cisco 6400 Service View at the left side of the
Map Viewer window. You will have to refresh the view. Figure 9-51 shows an example of the ATM
Service-ATM Service Instance One service instance created in the previous example.
Figure 9-51 Service Instances Displayed in the Cisco 6400 Service View
Service instances are displayed in
the Cisco 6400 Service View. ATM
Service-One is the service instance
created in the example.
41526
OL-0569-01
41527
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-39
Page 40

Service Provisioning
Configuring and Commissioning a Service Instance
After you create the service instance object, you should configure and then commission the service
instance from the appropriate Service Configuration window. The service instance object can be
configured in two ways:
• By applying an appropriate service profile and then manually configuring each of the remaining
parameter in that service instance.
• By manually configuring each parameter in the service instance.
This section describes how launch the appropriate Service Configuration window, apply a service
profile (if required), configure the remaining parameters, and then commission the service instance for
each of the available Cisco 6400 SCM services. Figure 9-52displays a typical workflowfor configuring
and then commissioning a service instance.
Figure 9-52 Configuring and Commissioning a Service Instance
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Launch the
appropriate Service
Configuration Window
For example, launch the
ATM Service Configuration
window to configure a
Pure ATM service.
Apply an existing
Service Profile to a
Service Instance
Apply an existing
profile (if required).
It is not possible to create
and apply a profile to
a Pure ATM service.
Configure an
Appropriate
Service Instance
Configure the remaining
parameters manually
or configure all of the
parameters manually
(if you did not apply a
service profile).
Click the
Commission Service
button
Click the Commission
Service button to save the
configuration and "roll"
the service onto the 6400
UAC hardware.
41808
9-40
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 41

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Configuring and Commissioning a Pure ATM Service Instance
To configure and commission a Pure ATM switching service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Service, Configure ATM Service option from the egress ATM line card
object in MapViewer.
Note You cannot apply a profile to the pure ATM switching service.
The ATM Service Configuration window appears (see Figure 9-53). See the “ATM Service
Configuration Window” section on page 10-24 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Figure 9-53 ATM Service Configuration Window (Service Details Tab)
Select a
chassis
Service Provisioning
Select an ATM
service instance
(only ATM service
instances are
displayed here)
Step 2 Select the appropriate Cisco 6400 chassis and ATM Service instance from the lists displayed at the left
side of the window.
Only the ATM service instance objects (for the selected chassis) are displayed in the ATM Services list.
Service instances for other service types are listed in their appropriate Service Configuration windows.
For example, L2TP service instance objects are displayedin the L2TPConfigurationwindow. The ATM
Services list is empty when no ATM Service instances have been created. See the “Creating a Service
Instance” section on page 9-36 for details on how to create a service instance.
Configuring the ATM Service Parameters
Step 3 Enter a Service Description (when required).
Step 4 Select a connection from the ATM Connection list.
Step 5 Enter Subscriber VPI, Subscriber VCI and Subscriber Name in the Subscriber Connections panel, as
required.
35298
OL-0569-01
Step 6 Select the Service Uplink tab.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-41
Page 42

Service Provisioning
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-54 ATM Service Configuration Window (Service Uplink Tab)
Step 7 Enter details into the parameters displayed in the Service Uplink PVC panel, as required. See the
“Service Uplink Tab” section on page 10-25 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Commissioning the Pure ATM Service Instance
Note This is the first stage at which you actually “roll” the selected service configuration onto
the Cisco 6400 UAC hardware.
Step 8 Click Commission Service to save the configurationinformation you have entered and roll the service
onto the Cisco 6400 UAC. A pop up window appears for you to confirm that you wish to commission
the selected service.
Figure 9-55 About to Change Service State Confirmation Window
Step 9 Select Yes to commission the service (or No to return to the ATM Service Instance Configuration
window without commissioning the ATM service). An Action Report window appears. The Action
Report window details the Cisco IOS commands executed when the service is commissioned. Invalid
Cisco IOS commands result in a failure to commission the service.
9-42
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 43

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 10 Check the details in the Action Report window to ensure that the service was commissioned
successfully.
Step 11 Select Save to save the Action Report, if required.
Step 12 Select Close to close the Action Report window and return to the Service Instance Configuration
window.
Step 13 Select Close from the File menu to close the Service Instance Configuration window.
Configuring and Commissioning a PPPoA-SD Service Instance
To configure and commission a PPPoA-SD service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC,Service,ConfigurePPPoA-SDServiceoption from a Site, Shelf, Chassis,
or service instance object. The PPPoA-SD Service Configuration window appears (see Figure 9-56).
Figure 9-56 PPPoA-SD Service Configuration Window (PPPoA-SD Configuration Tab)
Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
Step 2 Select the appropriate Cisco 6400 and PPPoA-SD Service instance from the lists displayed on the left
side of the window.
Only the PPPoA-SD service instance objects (for the selected chassis) are displayed in the PPPoA-SD
Services list. Service instances for other service types are listed in their appropriate Service
Configuration windows. For example, L2TP service instance objects are displayed in the L2TP
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-43
Page 44

Service Provisioning
Configuration window. The PPPoA-SD Services list is empty when no PPPoA-SD instances have been
created. See the “Creating a Service Instance” section on page 9-36 for details on how to create a
service instance.
Note Proceed to the “Configuring the PPPoA-SD Service Parameters” section on
page 9-44 if you are not applying a service profile.
Applying a PPPoA-SD Service Profile
Step 3 Select Apply Profile from the Edit menu.
Step 4 Select the appropriate profile from the list of profiles displayed. The profile parameters are copied to
the appropriate service instance parametersin the PPPoA-SD Service Configuration windowandappear
in blue.
Configuring the PPPoA-SD Service Parameters
See the “PPPoA-SD Service Configuration Window” section on page 10-26 for further details on the
parameters displayed.
Step 5 Configure the parameters displayed in the Virtual Template Parameters, IP Address Pool, and VC
Parameters panels, as required.
Step 6 Select the Service Details tab.
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-57 PPPoA-SD Service Configuration Window (Service Details Tab)
9-44
See the “PPPoA-SD Service Configuration Window” section on page 10-26 for further details on the
parameters displayed.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 45

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 7 Enter a Service Description, if required.
Step 8 Select a connection from the Current Connection list and configure the values in the Subscriber
Connections panel, as required.
Commissioning the PPPoA-SD Service
Step 9 Click Commission Service to roll the service onto the selected Cisco 6400 UAC. A pop up window
appears for you to confirm that you wish to commission the selected service.
Figure 9-58 About to Change Service State Confirmation Window
Step 10 Select Yes to commission the service (or No to return to the Service Instance Configuration window).
The Action Report window appears.
Service Provisioning
Figure 9-59 Action Report Window
The Action Report window details the Cisco IOS commands executed when the service is
commissioned. Invalid Cisco IOS commands result in a failure to commission the service.
Step 11 Check the details in the Action Report window to ensure that the service was commissioned
successfully.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-45
Page 46

Service Provisioning
Caution The Cisco 6400 SCM will roll-back configuration changes applied if an error is detected
Step 12 Select Save to save the Action Report, if required.
Step 13 Select Close to close the Action Report window and return to the Service Instance Configuration
Step 14 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters configured.
Step 15 Select Close from the File menu to close the PPPoA-SD Service Configuration window.
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
in the execution of the Cisco IOS command sequence with your selected parameters. This
insures that the Cisco 6400 UAC remains in a consistent state, even when errors are made
entering parameters.
window.
Note The PPPoA-SD Service requires additional configuration. Proceed to the
“Additional IOS Configuration For the PPPoA-SD Service” section on page 9-46
for further details.
Additional IOS Configuration For the PPPoA-SD Service
For the PPPoA-SD service to pass traffic to a designated trunk port, Cisco IOS must be used (to route
traffic via layer 3 to a destination network). One way of doing this is to create a PVC on the NRP to
support the routing of traffic to the trunk port and then create the required entries in the IP Routing
Table.
Execute (on the selected NRP) the following Cisco IOS commands to configure a PPPoA-SD service to
pass traffic to a designated trunk port:
NRP(config)#interface atm0/0/0.<Sub-Interface Number> point-to-point
NRP(config-if)#ip address <IP Address> <Subnet Mask>
NRP(config-if)#pvc <NRP-Interface-vpi>/<NRP-Interface-vci>
NRP(config-if-vc)#class <vc-class-name>
NRP(config-if-vc)#protocol ip <Dest IP Address> no broadcast
where,
<Sub-Interface Number> is a number for the sub-interface
<IP Address> is the IP Address of the sub-interface
<Subnet Mask> is the Subnet Mask of the sub-interface
<NRP-Interface-vpi> is the same VPI value as used when a PVC is created on the NSP
<NRP-Interface-vci> is the same VPI value as used when a PVC is created on the NSP
<Dest IP Address> is the destination IP Address mapped to the PVC
<vc-class-name> is the name of the vc-class created previously
9-46
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 47

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Now create the required entries in the IP Routing Table:
NRP(config)#ip route <Dest IP Address> 255.255.255.255 atm0/0/0.<Sub-Interface Number>
where,
<Dest IP Address> is as configured previously
<Sub-Interface Number> is as configured previously.
Configuring and Commissioning an L2TP Service Instance
To configure and commission an L2TP service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Service, Configure L2TP Service option from a Site, Shelf, Chassis, or
service instance object. The L2TP Service Configuration window appears (see Figure 9-60).
Figure 9-60 L2TP Service Configuration Window (PPPoA-SD L2TP Configuration Tab)
Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
41555
See the “Configuration Tab” section on page 10-29 for details on the parameters displayed.
Step 2 Select the appropriate Cisco 6400 and L2TP Service from the lists displayed on the left side of the
window.
Only the L2TP service instance objects (for the selected chassis) are displayed in the L2TP Services
list. Service instances for other service types are listed in their appropriate Service Configuration
windows. For example,IP Uplink service instance objects are displayed in the IP Uplink Configuration
window. The L2TP Services list is empty when no L2TP service instances have been created. See the
“Creating a Service Instance” section on page 9-36 for details on how to create a service instance.
Note Proceed to the “Configuring the L2TP Service Parameters” section on page 9-48
when you are not applying a service profile.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-47
Page 48

Service Provisioning
Applying an L2TP Service Profile
Step 3 Select Apply Profile from the Edit menu.
Step 4 Select the appropriate profile from the list of profiles displayed. The profile parameters are copied to
the appropriate service instance parameters in the L2TP Service Configuration window and appear in
blue.
Configuring the L2TP Service Parameters
Step 5 Configure the parameters displayed on the Configuration tab, as required.
Step 6 Select the Service Details tab.
Figure 9-61 L2TP Service Configuration Window (Service Details Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-48
See the “Service Details Tab” section on page 10-31 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Step 7 Enter a Service Description in the Service Details panel, if required.
Step 8 Select Allow or Prevent over-subscription.
Over-subscriptionis set to Allowby default and an unlimited number of subscribers can be connected
to the service. Selecting to Prevent Oversubscription ensures that the SCM limits the number of
subscribers connected such that the sum of the subscriber’s peak cell rates never exceeds the peak cell
rate reserved for the service on the uplink. Over-subscription functionality is not applicable to the
PPPoA-SD and ATM services.
Step 9 Select a connection from the Current Connection list and configure the values in the Subscriber
Connections panel, as required.
Step 10 Select the Service Uplink tab.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 49

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-62 L2TP Service Configuration Window (Service Uplink Tab)
Service Provisioning
41557
See the “Service Uplink Tab” section on page 10-32 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Step 11 Configure the parameters displayed in the Service Uplink PCV, Quality of Service (Receive), Internal
NSP, NRP PVC and Quality of Service (Transmit), as required.
Commissioning the L2TP Service
Step 12 Click Commission Service to roll the service onto the Cisco 6400 UAC.
A pop up window appears for you to confirm that you wish to commission the selected service.
Figure 9-63 About to Change Service State Confirmation Window
Step 13 Select Yes to commission the service (or No to return to the L2TP Service Configuration window). The
Action Report window appears.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-49
Page 50

Service Provisioning
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-64 Action Report Window
The Action Report window details the Cisco IOS commands executed when the service is
commissioned. Invalid Cisco IOS commands result in a failure to commission the service.
Step 14 Check the details in the Action Report window to ensure that the service was commissioned
successfully.
Caution The Cisco 6400 SCM will roll-back configuration changes applied if an error is detected
in the execution of the Cisco IOS command sequence with your selected parameters. This
insures that the Cisco 6400 UAC remains in a consistent state, even when errors are made
entering parameters.
Step 15 Select Save to save the Action Report, if required.
Step 16 Select Close to close the Action Report window and return to the Service Instance Configuration
window.
Step 17 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters configured.
Step 18 Select Close from the File menu to close the L2TP Service Configuration window.
9-50
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 51

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Configuring and Commissioning an RFC1483 Bridging Service Instance
To configure and commission an RFC1483 Bridging service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Service,ConfigureRFC1483 Bridging Serviceoption from a Site, Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object. The RFC1483 Bridging Service Configuration window appears:
Figure 9-65 RFC1483 Bridging Service Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
See the “Configuration Tab” section on page 10-34 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Step 2 Select the appropriate Cisco 6400 and RFC1483 Bridging Service from the lists displayed on the left
side of the window.
Only the RFC1483 Bridging service instance objects (for the selected chassis) are displayed in the
RFC1483 Bridging Services list. Service instances for other service types are listed in their appropriate
Service Configuration windows. For example, L2TP service instance objects are displayed in the L2TP
Configuration window. The RFC1483 Bridging Services list is empty when no RFC1483 Bridging
Service instances have been created. See the “Creating a Service Instance” section on page 9-36 for
details on how to create a service instance.
Note Proceed to the “Configuring the RFC1483 Bridging Service Parameters” section
on page 9-52 when you are not applying a service profile.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-51
Page 52

Service Provisioning
Applying a RFC1483 Bridging Service Profile
Step 3 Select Apply Profile from the Edit menu.
Step 4 Select the appropriate profile from the list of profiles displayed. The profile parameters are copied to
the appropriate service instance parameters in the RFC1483 Bridging Service Configuration window
and appear in blue.
Configuring the RFC1483 Bridging Service Parameters
Step 5 Configure the parameters displayed in the Bridge Parameters, VC Parameters, and Subscriber Policy
panels, as required.
Step 6 Select the Service Details tab.
Figure 9-66 RFC1483 Bridging Service Configuration Window (BR Configuration Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-52
See the “Service Details Tab” section on page 10-35 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Step 7 Enter a Service Description in the Service Details panel, if required.
Step 8 Select Allow or Prevent oversubscription.
Oversubscription is set to Allow by default and an unlimited number of subscribers can be connected
to the service. Select Prevent Oversubscription to ensure the SCM limits the number of subscribers
connected such that the sum of the subscriber’s peak cell rates never exceeds the peak cell rate reserved
for the service on the uplink. Oversubscription functionality is not applicable to the PPPoA-SD and
ATM services.
Step 9 Select a connection from the Connection list and configure the values in the Subscriber Connections
panel, as required.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 53

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 10 Configure the parameters displayed in the Subscriber Connections panel.
Step 11 Select the Service Uplink tab.
Figure 9-67 RFC1483 Bridging Service Configuration Window (Service Uplink Tab)
Service Provisioning
See the “Service Uplink Tab” section on page 10-37 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Step 12 Configure the parameters displayed in the Service Uplink PCV, Quality of Service (Receive), Internal
NSP, NRP PVC, and Quality of Service (Transmit) panels, as required.
Commissioning the RFC1483 Bridging Service
Step 13 Click Commission Service to roll the service onto the Cisco 6400 UAC.
A pop up window appears for you to confirm that you wish to commission the selected service.
Figure 9-68 About to Change Service State Confirmation Window
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-53
Page 54

Service Provisioning
Step 14 Select Yes to commission the service (or No to return to the RFC1483 Bridging Service Configuration
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
window). The Action Report window appears.
Figure 9-69 Action Report Window
The Action Report window details the Cisco IOS commands executed when the service is
commissioned. Invalid Cisco IOS commands result in a failure to commission the service.
Step 15 Check the details in the Action Report window to ensure that the service was commissioned
successfully.
Caution The Cisco 6400 SCM will roll-back configuration changes applied if an error is detected
in the execution of the Cisco IOS command sequence with your selected parameters. This
insures that the Cisco 6400 UAC remains in a consistent state, even when errors are made
entering parameters.
Step 16 Select Save to save the Action Report, if required.
Step 17 Select Close to close the Action Report window and return to the Service Instance Configuration
window.
Step 18 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters configured.
Select Close from the File menu to close the RFC1483 Bridging Service Configuration window.
9-54
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 55

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Configuring and Commissioning a RFC1483 IRB Service Instance
To configure and commission an RFC1483 IRB service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Service, Configure RFC1483 IRB Service option from a Site, Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object.
The RFC1483 IRB Service Configuration window appears.
Figure 9-70 RFC1483 IRB Service Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
See the “Configuration Tab” section on page 10-39 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Step 2 Select the appropriate Cisco 6400 and RFC1483 IRB Service Instance from the lists displayed on the
left side of the window.
Only the RFC1483 IRB service instance objects (forthe selected chassis) are displayed in the RFC1483
IRB Services list. Service instances for other service types are listed in their appropriate Service
Configuration windows. For example, L2TP service instance objects are displayed in the L2TP
Configuration window. The RFC1483 IRB Services list is empty when no RFC1483 IRB Service
instances have been created. See the “Creating a Service Instance” section on page 9-36 for details on
how to create a service instance.
Note Proceed to the “Configuring the RFC1483 IRB Service Parameters” section on
page 9-56 when you are not applying a service profile.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-55
Page 56

Service Provisioning
Applying a RFC1483 IRB Service Profile
Step 3 Select Apply Profile from the Edit menu.
Step 4 Select the appropriate profile from the list of profiles displayed. The profile parameters are copied to
the appropriate service instance parameters in the RFC1483 IRB Service Configuration window and
appear in blue.
Configuring the RFC1483 IRB Service Parameters
Step 5 Configure the parameters displayed on the Configuration tab, as required.
Step 6 Select the Service Details tab.
Figure 9-71 RFC1483 IRB Service Configuration Window (Service Details Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-56
See the “Service Details Tab” section on page 10-41 for details on the parameters displayed.
Step 7 Enter a Service Description in the Service Details panel, if required.
Step 8 Select whether to Allow or Prevent oversubscription.
Oversubscription is set to Allow by default and an unlimited number of subscribers can be connected
to the service. Selecting to Prevent Oversubscription ensures that the SCM limits the number of
subscribers connected such that the sum of the subscriber’s peak cell rates never exceeds the peak cell
rate reserved for the service on the uplink. Oversubscription functionality is not applicable to the
PPPoA-SD and ATM services.
Step 9 Select a connection from the Connection list and configure the values in the Subscriber Connections
panel, as required.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 57

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 10 Select the Service Uplink tab.
Figure 9-72 RFC1483 IRB Service Configuration Window (Service Uplink Tab)
Service Provisioning
See the “Service Uplink Tab” section on page 10-43 for details on the parameters displayed on the
Service Uplink tab.
Step 11 Configure the parameters displayed on the Service Uplink tab, as required.
Commissioning the RFC1483 IRB Service
Step 12 Click Commission Service to roll the service onto the Cisco 6400 UAC.
A pop up window appears for you to confirm that you wish to commission the selected service.
Figure 9-73 About to Change Service State Confirmation Window
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-57
Page 58

Service Provisioning
Step 13 Select Yes to commission the service (or No to return to the RFC1483 IRB Service Configuration
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
window). The Action Report window appears.
Figure 9-74 Action Report Window
The Action Report window details the Cisco IOS commands executed when the service is
commissioned. Invalid Cisco IOS commands result in a failure to commission the service.
Step 14 Check the details in the Action Report window to ensure that the service was commissioned
successfully.
Caution The Cisco 6400 SCM will roll-back configuration changes applied if an error is detected
in the execution of the Cisco IOS command sequence with your selected parameters. This
insures that the Cisco 6400 UAC remains in a consistent state, even when errors are made
entering parameters.
Step 15 Select Save to save the Action Report, if required.
Step 16 Select Close to close the Action Report window and return to the Service Instance Configuration
window.
Step 17 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters configured.
Select Close from the File menu to close the RFC1483 IRB Service Configuration window.
9-58
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 59

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Service Provisioning
Configuring and Commissioning an IP Uplink (for PTA-MD and RBE Subscribers) Service Instance
To configure and commission an IP Uplink service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC,Service, Configure IP Uplink Service option from a Site, Shelf, Chassis,
or service instance object. The IP Uplink Service Configuration window appears (see Figure 9-75).
Figure 9-75 IP Uplink Service Configuration Window (IP Uplink Configuration Tab)
OL-0569-01
See the “Service Uplink Tab” section on page 10-50 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Step 2 Select the appropriate Cisco 6400 and IP Uplink service instance from the lists displayed on the left
side of the window.
Only the IP Uplink service instance objects (for the selected chassis) are displayed in the IP Uplink
Services list. Service instances for other service types are listed in their appropriate Service
Configuration windows. For example, L2TP service instance objects are displayed in the L2TP
Configuration window. The IP Uplink Services list is empty when no IP Uplink Service instances have
been created. See the “Creating a Service Instance” section on page 9-36 for details on how to create a
service instance.
Note Proceed to the “Configuring the IP Uplink (for PTA-MD and RBE Subscribers)
Service Parameters” section on page 9-60 when you are not applying a IP Uplink
service profile.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-59
Page 60

Service Provisioning
Applying a IP Uplink (for PTA-MD and RBE Subscribers) Service Profile
Step 3 Select Apply Profile from the Edit menu.
Step 4 Select the appropriate profile from the list of profiles displayed. The profile parameters are copied to
the appropriate service instance parameters in the IP Uplink Service Configuration window and appear
in blue.
Configuring the IP Uplink (for PTA-MD and RBE Subscribers) Service Parameters
Step 5 Configure the parameters displayed on the IP Uplink Configuration tab, as required.
Step 6 Select the Local Service Profile tab.
Figure 9-76 IP Uplink Service Configuration Window (Local Service Profile Tab)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
9-60
See the “Local Service Profile Tab” section on page 10-48 for further details on the parameters
displayed.
Step 7 Configure the parameters displayed on the Local Service Profile tab, as required.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 61

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 8 Select the Service Uplink tab.
Figure 9-77 IP Uplink Service Configuration Window (Service Uplink Tab)
Service Provisioning
See the “Service Uplink Tab” section on page 10-50 for further details on the parameters displayed.
Step 9 Configure the parameters displayed on the Service Uplink tab, as required.
Commissioning the IP Uplink (for PTA-MD and RBE Subscribers) Service
Step 10 Click Commission Service to roll the service onto the Cisco 6400 UAC. A pop up window appears for
you to confirm that you wish to commission the selected service.
Figure 9-78 About to Change Service State Confirmation Window
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-61
Page 62

Service Provisioning
Step 11 Select Yes to commission the service (or No to return to the IP Uplink Service Configuration window).
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
The Action Report window appears.
Figure 9-79 Action Report Window
The Action Report window details the Cisco IOS commands executed when the service is
commissioned. Invalid Cisco IOS commands result in a failure to commission the service.
Step 12 Check the details in the Action Report window to ensure that the service was commissioned
successfully.
Caution The Cisco 6400 SCM will roll-back configuration changes applied if an error is detected
in the execution of the Cisco IOS command sequence with your selected parameters. This
insures that the Cisco 6400 UAC remains in a consistent state, even when errors are made
entering parameters.
Step 13 Select Save to save the Action Report, if required.
Step 14 Select Close to close the Action Report window and return to the Service Instance Configuration
window.
Step 15 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters configured.
Select Close from the File menu to close the IP Uplink Service Configuration window.
9-62
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 63

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Configuring and Commissioning an RFC1483 Routing Service Instance
To configure and commission an RFC1483 routing service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC,Service,ConfigureRFC1483 Routing Servicesoption from a Site, Shelf,
Chassis, or service instance object. The RFC1483 Routing Service Configuration window appears (see
Figure 9-80).
Figure 9-80 RFC1483 Routing Service Configuration Window (Configuration Tab)
Service Provisioning
OL-0569-01
See the “RFC1483 IRB Service Profile Configuration Window” section on page 10-11 for further
details on the parameters displayed.
Step 2 Select the appropriate Cisco 6400 and RFC1483 Routing Service instance from the lists displayed on
the left side of the window.
Note RFC1483 Routing service profiles cannot be created for the RFC1483 Routing
service and therefore cannot be applied.
Step 3 Configure the parameters displayed on the Configuration tab, as required.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-63
Page 64

Service Provisioning
Step 4 Select the Service Details tab.
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-81 RFC1483 Routing Service Configuration Window (Service Details Tab)
Step 5 Enter a Service Description in the Service Details panel, when required.
Step 6 Select a connection from the Current Connection list and configure the parameters in the Subscriber
Connections panel, as required.
Step 7 Select the Service Uplink tab.
9-64
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 65

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-82 RFC1483 Routing Service Configuration Window (Service Uplink Tab)
Service Provisioning
See the “RFC1483 Routing Service Configuration Window” section on page 10-52 for further details
on the parameters displayed.
Step 8 Configure the parameters displayed on the Service Uplink tab, as required.
Step 9 Click Add to add a new service uplink. The RFC1483 services can have multiple service uplinks.
Commissioning the RFC1483 Routing Service
Step 10 Click Commission Service to roll the service onto the Cisco 6400 UAC. A pop up window appears for
you to confirm that you wish to commission the selected service.
Figure 9-83 About to Change Service State Confirmation Window
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-65
Page 66

Service Provisioning
Step 11 Select Yes to commission the service (or No to return to the RFC1483 Routing Service Configuration
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
window). The Action Report window appears.
Figure 9-84 Action Report Window
The Action Report window details the Cisco IOS commands executed when the service is
commissioned. Invalid Cisco IOS commands result in a failure to commission the service.
Step 12 Check the details in the Action Report window to ensure that the service was commissioned
successfully.
Caution The Cisco 6400 SCM will roll-back configuration changes applied if an error is detected
in the execution of the Cisco IOS command sequence with your selected parameters. This
insures that the Cisco 6400 UAC remains in a consistent state, even when errors are made
entering parameters.
Step 13 Select Save to save the Action Report, if required.
Step 14 Select Close to close the Action Report window and return to the Service Instance Configuration
window.
Step 15 Select Save from the File menu to save the parameters configured.
Select Close from the File menu to close the RFC1483 Routing Service Configuration window.
9-66
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 67

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-85 displays a typicalwork flowthat describeshowto create, configure and connect subscribers
(that is, provision end customers).
Figure 9-85 Subscriber Provisioning Work Flow
Create Subscriber
Subscriber Provisioning
Create a subscriber to
connect to a service
instance (created earlier)
Configure subscribers
information (for example,
connection information or
name and address details)
Connect subscribers
to one or more
service instances
Configure an
Existing Subscriber
Connect a
Subscriber to a
Service Instance
The first step is to create (deploy) one or more subscriber objects. Each subscriber object can then be
configured with their own particular details (for example, connection or contact details).
Each subscriber can then be connected to one or more service instances. Service instances were created
earlier. See the “Creating a Service Instance” section on page 9-36 for further details.
Creating a Subscriber
Subscriber objects hold information related to the end subscriber. Subscribers are created by deploying
them onto a selected Line Card.
To create subscribers, follow these steps:
Delete a Subscriber
Disconnect a
Subscriber from a
Service Instance
Delete a subscriber object
when they are no longer
required (for example, when a
subscriber cancels their service
agreement)
Disconnect a subscriber
(for example, when a
subscriber changes from
one category of service to
another)
41811
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-67
Page 68

Subscriber Provisioning
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Subscriber, Deploy option from a Line Card. The Deployment Wizard -
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Object Parameters window (1 of 2) appears. (see Figure 9-86)
Figure 9-86 Deployment Wizard - Object Parameters (1 of 2)
Enter the number of
Subscriber objects to create
41529
Step 2 Enter the Number of Subscriber objects you wish to create. A single Subscriber object was entered in
the example. (see Figure 9-86)
9-68
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 69

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 3 Select Forward. The Deployment Wizard - Object Parameters (2 of 2) window appears. (see
Figure 9-87)
Figure 9-87 Deployment Wizard - Object Parameters (2 of 2)
Subscriber Provisioning
Enter the Subscriber's ID
41530
Step 4 Enter a Subscriber ID. John Smith was entered in the example. (see Figure 9-87)
Step 5 Click Forward.
Note Repeat steps 4 and 5 for the Number of Subscribers entered in step 2.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-69
Page 70

Subscriber Provisioning
Step 6 Click Forward. The Deployment Wizard Summary window appears (see Figure 9-88).
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-88 Deployment Wizard - Summary
The Summary panel
displays information
about the deployment
Summary information displays in the Summary panel.
Step 7 Check the Summary information is correct.
Step 8 Click Finish (when the Deployment Summary information is correct) to create the new Subscriber
objects.
Step 9 Proceed to the “Configuring a Subscriber” section on page 9-71.
Deleting a Subscriber
To delete a subscriber object, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Subscriber, Configure Subscriber option at an appropriate Line Card.
Step 2 Select the Subscriber from the list at the left side of the window and right click.
Step 3 Select Delete Objects.
Step 4 Check the Deletion Summary details.
Step 5 Click Finish.
41531
9-70
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 71

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Configuring a Subscriber
To configure a subscriber’s details, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Subscriber, Configure Subscriber option at an appropriate Line Card.
The Subscriber Configuration window appears (see Figure 9-89).
Figure 9-89 Subscriber Configuration Window (Connections Tab)
Subscriber Provisioning
OL-0569-01
See the “Subscriber Configuration Window” section on page 10-57 for details on the parameters that
appear on the Subscriber Configuration window.
Step 2 Select a Cisco 6400 and Subscriber from the appropriate lists at the left side of the window.
Step 3 Select a Current Connection from the list displayed in the Connection Details panel.
Step 4 Configure the parameters displayed in the Connection Details panel.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-71
Page 72

Subscriber Provisioning
Step 5 Select the Subscriber Details (Optional) tab.
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-90 Subscriber Configuration Window (Subscriber Details (Optional) Tab)
Note Entering information into the SubscriberDetails(Optional)tab is voluntary.You
can enter any information you like into the Subscriber Details tab. For example,
you may decide to enter a subscriber identification in the Subscriber Name box
and an e-mail address in the Subscriber Address box.
Step 6 Enter a Contact ID / Name and Contact Address into the Contact Name & Address panel, as required.
Step 7 Enter a Subscriber ID / Name and Subscriber Details into the Subscriber Name & Address panel, as
required.
Step 8 Select the Save option from the File menu to save the subscriber information.
Step 9 Select the Close option from the File menu to close the Subscriber Configuration window.
Connecting a Subscriber to a Service Instance
Subscribers are connected to service instances within the Service/Subscriber Connection window. The
Service/Subscriber Connection window displays three tabs: Connection details, Connect to Single
Domain, and Connect to Multi-Domain. Configuration information is required into one or more tabs
when connecting a subscriber to a service instance. Certain parameters are grayed out, depending upon
what type of service you are trying to connect to.
9-72
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 73

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Table 9-2 displays the Cisco 6400 SCM service types and the tabs in the Service/Subscriber Connection
window that should be configured for each service type.
Table 9-2 Connecting a Subscriber to a Service Instance
Subscriber Provisioning
Cisco 6400
Service Type Connection Details Tab
Pure ATM
Switching
Service
PPPoA Single
Domain
Configure the parameters
displayed in the Connection
Parameters and Internal
NSP, NRP PVC panels for
all service types, as
required.
Connect To Single Domain
Tab
Configure the parameters
displayed, as required forall
servicetypes. Click Connect
when required.
Connect to
Multi-Domain Tab
Not required
Not required
L2TP Not required
RFC1483
Not required
Routing
RFC1483
Not required
Bridging
RFC1483 IRB Not required
IP Uplink Configure the
parameters displayed,
as required. Click
Connect when
required.
To connect a subscriber to a service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Subscriber, Connect option from an NSP card.
The Service/Subscriber Connection window (shown in Figure 9-91) appears. See the
“Service/Subscriber Connection Window” section on page 10-60 for further details on the parameters
displayed.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-73
Page 74

Subscriber Provisioning
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-91 Service/Subscriber Connection Window (Connection Details Tab)
Step 2 Select a Cisco 6400 chassis from the Cisco 6400 list displayed on the left side of the window.
Step 3 Select a Subscriber from the Subscriber list displayed on the left side of the window.
Step 4 Select a Connection Template from the Connection Template list displayed on the left side of the
window.
Step 5 Configure the parameters in the Connection Parameters, and Internal NPS, NRP PVC frames, as
required.
9-74
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 75

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 6 Select the Connect to Single Domain tab.
Note When you select an IP Uplink service (Service Typeof PTA-MD) and this service
instance does not have a Local Service Profile (LSP) configured, the Connect
button is grayed out. When you do connect to an IP Uplink service using the
Connect to Single Domain tab, this is equivalent to the PTA-MD static case used
in Release 1.3 of the Cisco 6400 SCM software.
Figure 9-92 Service/Subscriber Connection Window (Connect to Single Domain Tab)
Subscriber Provisioning
OL-0569-01
Step 7 Select a Service Instance from the list displayed in the Service Instance panel.
A Service Instance is a service object, that is, a single service deployed on the Cisco 6400 UAC. It
contains all of the configuration information required for the service to run.
Note Inappropriate parameters are grayed out in each of the frames displayed on the
Connection Details, Connect to Single Domain, and Connect to Multi-Domain
tabs when a Service Instance is selected.
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-75
Page 76

Subscriber Provisioning
Step 8 Configure the parameters displayed in the Connect to Single Domain tab, as required.
Step 9 Select the Connect to Multi-Domain tab.
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Figure 9-93 Service/Subscriber Connection Window (Connect to Multi-Domain Tab)
Step 10 Select an NRP from the Node Route Processor list.
Step 11 Configure the parameters displayed in the Connect to Multi-Domain tab, as required.
Step 12 Click Connect. A pop up window appears (see Figure 9-94) asking you to confirm that you wish to
connect the selected subscriber.
Figure 9-94 Connect Subscriber to NRP Window
Step 13 Click Yes to proceed. An Action report window appears displaying the Cisco IOS transaction log as
connection occurs.
9-76
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 77

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Note A Subscriber connection object is automatically created and placed below the
appropriate service instance in the Cisco6400ServiceView and also in the
Cisco6400SubscriberView below the appropriate subscriber object. Performance
logging can be Activated or Deactivated for each subscriber connection object.
See Table 8-1 on page 8-2 for further details.
Note The Connect button is grayed out when the Service Instance is in a
Commissioned state.
If the Connect operation fails the service instance remains in the Decommissioned state (that is, no
configuration is applied to the Cisco 6400 UAC). The Action Report window may identify why the
connection failed. Failure diagnostics information can also be located by examining the Cisco IOS log.
Common failure causes can include:
• Specifying duplicate (already used) Ingress PVC details.
• Forgetting to configure the QoS Parameters in the connection template.
• Specifying invalid Ingress PVC details.
• Selecting the Manual option for Internal PVC Parameters allocation and selecting a PVC that is
already allocated.
Subscriber Provisioning
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-77
Page 78

Subscriber Provisioning
Disconnecting a Subscriber from a Service Instance
To disconnect a subscriber from a service instance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Cisco 6400 UAC, Subscriber, Disconnect s option from an NSP card. The
Service/Subscriber Disconnection window appears.
Figure 9-95 Service/Subscriber Disconnection Window (Disconnect)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
41536
See the “Service/Subscriber Disconnection Window” section on page 10-64 for further details on the
parameters contained in the Service/Subscriber Disconnection window.
Step 2 Select the Cisco 6400 chassis and ATM Port from the lists displayed on the left side of the window.
Step 3 Select a Subscriber and Current Connections from the from the lists displayed in the Connection
Details panel.
Step 4 Click Disconnect. A pop up window appears to inform you that the selected subscriber is about to be
disconnected.
Figure 9-96 About to Disconnect Subscriber
41534
9-78
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
Page 79

Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
Step 5 Click Yes to disconnect the subscriber. The Action Report window appears confirming that the
subscriber was disconnected.
Figure 9-97 Action Report Window
Subscriber Provisioning
Step 6 Click Close to close the Action Report window or click Save to save the Action Report. The Action
Report can be saved and used for diagnostic purposes. The “*** No errors encountered *** ” message
appears to show that disconnection was successful.
OL-0569-01
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
9-79
Page 80

Administration
Administration
Editing a Currently Connected Subscriber’s Details
This operation can be performed without disconnecting the subscriber.
To edit a currently connected subscriber’s details, follow these steps:
Step 1 Select the Configure Subscribers option from a line card.
Step 2 Select the NSP, DSLAM and Subscriber to display the subscribers details.
Step 3 Enter the Contact and Subscriber Details and then save your changes.
Moving Subscribers between Services (or NRPs)
Chapter 9 Service/Subscriber Provisioning
To move subscribers between services (or NRPs), follow these steps:
Step 1 From a line card select disconnect subscribers.
Step 2 Select the subscriber to disconnected.
Step 3 Press the Disconnect button.
Step 4 Select a new service.
Step 5 Connect the subscriber to a new service instance (and NRP, if appropriate).
9-80
Cisco 6400 Service Connection Manager User Guide
OL-0569-01
 Loading...
Loading...