Page 1

Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
First Published: July 26, 2013
Last Modified: March 28, 2014
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-30226-03
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH
THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY,
CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB's public domain version
of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright©1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS.
CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network
topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional
and coincidental.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://
www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
©
2014 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway 1
Finding Feature Information 1
Prerequisites for the iWAG 2
Restrictions for the iWAG 2
Information About the iWAG 2
Benefits of the iWAG 3
AAA Attributes 3
Supported Hardware and Software Compatibility Matrix for the iWAG 7
How to Configure the iWAG 8
Configuring the iWAG for Simple IP Users 8
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users 8
Configuring Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting for the iWAG 8
Configuring DHCP when the iWAG Acts as a DHCP Proxy 10
Configuring the Cisco ISG Class Map and Policy Map for the iWAG 12
Configuring a Session Initiator for the iWAG 15
Configuring a Tunnel Interface for the iWAG 16
Enabling Mobile Client Service Abstraction 17
Configuring the GTP of the iWAG 18
Configuring the iWAG for 4G Mobile IP Users 21
Configuring PMIPv6 for the iWAG 21
Enabling Mobile Client Service Abstraction 21
Additional References 22
Feature Information for the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway 23
24
CHAPTER 2
IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel 25
Finding Feature Information 25
Restrictions for IPoGEC 25
OL-30226-03 iii
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 4
Contents
Information About IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel 26
Supported Features for IPoGEC 26
Configuring IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel 26
Configuring Member Links for IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel 28
Configuration Examples for IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel 29
Additional References 29
Feature Information for IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel 30
31
CHAPTER 3
CHAPTER 4
Multiple-Flow Tunnel 33
Finding Feature Information 33
Information About Multiple-Flow Tunnel 33
Additional References 34
Feature Information for Multiple-Flow Tunnel 35
35
Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE 37
Finding Feature Information 37
Information About Ethernet Over GRE 38
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE 38
Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE 39
Information About Configuring Ethernet Over GRE 39
EoGRE Deployment with PMIPv6 Integrated for Mobility Service 42
EoGRE Deployment with GTP Integrated for Mobility Service 43
EoGRE Deployment with ISG Integrated for Simple IP Service 43
Supported Features 44
How to Configure the EoGRE Feature 45
Example: Configuring the EoGRE Feature 46
Additional References 48
Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE 49
CHAPTER 5
GTPv2 Support in the iWAG 51
Finding Feature Information 51
Restrictions for GTPv2 of the iWAG 51
Information About GTPv2 in the iWAG 52
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
iv OL-30226-03
Page 5

Contents
GTPv2 Configuration 52
RADIUS Configuration 53
Intra-iWAG Roaming 53
Configuration for the GTPv1 and GTPv2 Roaming Scenario 53
Additional References 54
Feature Information for GTPv2 Support in the iWAG 55
55
CHAPTER 6
CHAPTER 7
iWAG SSO Support for GTP 57
Finding Feature Information 57
Information About iWAG SSO Support for GTP 57
Enabling SSO Support for the GTP 58
Additional References 59
Feature Information for iWAG SSO Support for GTP 60
60
Configuring ISG Policy Templates 61
Finding Feature Information 61
Restrictions for Configuring ISG Policy Templates 61
Information About Configuring ISG Policy Templates 61
How to Configure ISG Policy Templates 62
Additional References 62
Feature Information for Configuring ISG Policy Templates 63
63
CHAPTER 8
Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions 65
Finding Feature Information 65
Information About Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions 65
Additional References 66
Feature Information for Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions 67
67
CHAPTER 9
Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP 69
Finding Feature Information 69
Information About Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6 69
OL-30226-03 v
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 6

Contents
Features Supported for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 Sessions 70
Information About Dual-Stack Support for GTP 70
Restrictions for Dual-Stack GTP 70
AAA Attributes for Dual Stack 70
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 71
Example: Configuring an Access List Traffic Classmap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 71
Example: Configuring a Classmap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 71
Example: Configuring a Policymap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 72
Example: Configuring a Control Policy for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 72
Example: Configuring an Access Interface for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 73
Example: Configuring the Local Mobility Anchor for Cisco ASR 5000 Routers 73
Example: Configuring Mobile Access Gateways for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 74
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack GTP 75
CHAPTER 10
Example: Configuring Dual-Stack Sessions for GTP 75
Example: Configuring an Interface to PGW or GGSN 75
Example: Configuring a Control Policy for Dual-Stack GTP 75
Example: Configuring an Access Interface for Dual-Stack GTP 75
Enabling IPv6 Routing 76
Additional References 76
Feature Information for Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP 77
77
Flow-Based Redirect 79
Finding Feature Information 79
Flow-Based Redirect for Adult Content Filtering 80
Flow-Based Redirect for Selective IP Traffic Offload 81
Activating and Deactivating the Flow-Based Redirect Feature Through Vendor-Specific
Attributes 82
Configuring Flow-Based Redirect for a Traffic Class Service 82
Examples 85
Best Practices for Configuring the NAT on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers 87
NAT Overloading and Port Parity 88
NAT Interface Overloading with VRF 88
Additional References 89
Feature Information for Flow-Based Redirect 89
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
vi OL-30226-03
Page 7

Contents
90
CHAPTER 11
CHAPTER 12
Call Flows for Simple IP Users 91
Finding Feature Information 91
Simple IP Unclassified MAC Authentication (MAC TAL and Web Login) Call Flows 91
Simple IP Unclassified MAC with MAC TAL Authentication Call Flow 93
Simple IP Unclassified MAC with Web Login Authentication Call Flow 95
Simple IP Unclassified MAC Authentication Call Flow Configuration 96
Additional References 98
Feature Information for Call Flows for Simple IP Users 99
99
Call Flows for 3G and 4G Mobile IP Users 101
Finding Feature Information 101
3G DHCP Discover Call Flow 101
3G DHCP Discover Call Flow Configuration 104
4G DHCP Discover Call Flow 108
4G DHCP Discover Call Flow Configuration 110
CHAPTER 13
4G Roaming Call Flow 111
4G Roaming Call Flow Configuration 114
Additional References 115
Feature Information for Call Flows for 3G and 4G Mobile IP Users 116
116
Call Flows for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 and GTP 117
Finding Feature Information 117
Dual-Stack Mobile IPoE Session with DHCPv4 as FSOL for PMIPv6 Call Flow 118
Dual-Stack Mobile IPoE Session with IPv6 ND as FSOL for PMIPv6 Call Flow 121
Dual-Stack Mobile IPoE Session with DHCPv4 as FSOL for GTP Call Flow 124
Dual-Stack Mobile IPoE Session with IPv6 ND as FSOL for GTP Call Flow 126
Additional References 128
Feature Information for Call Flows for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 and GTP 129
130
CHAPTER 14
OL-30226-03 vii
iWAG Scalability and Performance 131
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 8

Contents
iWAG Scaling 131
Restrictions for iWAG Scalability 132
Layer 4 Redirect Scaling 133
Configuring Call Admission Control 133
Walk-by User Support for PWLAN in iWAG 133
Additional References 134
Feature Information for iWAG Scalability and Performance 135
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
viii OL-30226-03
Page 9

CHAPTER 1
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access
Gateway
Service providers use a combination of WiFi and mobility offerings to offload their mobility networks in
the area of high-concentration service usage. This led to the evolution of the Intelligent Wireless Access
Gateway (iWAG).
The iWAG provides a WiFi offload option to 4G and 3G service providers by enabling a single-box solution
that provides the combined functionality of Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6) and GPRS Tunneling Protocol
(GTP) on the Cisco Intelligent Services Gateway (Cisco ISG) framework. This document provides information
about the iWAG and how to configure it, and contains the following sections:
Finding Feature Information, page 1
•
Prerequisites for the iWAG, page 2
•
Restrictions for the iWAG, page 2
•
Information About the iWAG, page 2
•
How to Configure the iWAG, page 8
•
Additional References, page 22
•
Feature Information for the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway, page 23
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
OL-30226-03 1
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 10

Prerequisites for the iWAG
Prerequisites for the iWAG
Enable mobile client service abstraction (MCSA).
•
Enable the ipv6 unicast-routing command.
•
Restrictions for the iWAG
Roaming from a 3G mobility network to a WLAN is not supported for the GTP and Cisco ISG sessions.
•
IP subscriber-routed (L3) sessions are not supported.
•
IPv6 and quality of service (QoS) are not supported in a 3G mobility network.
•
Only newly established calls are offloaded to the WLAN Third-Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)
•
IP access.
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
The iWAG solution for WLAN offload is currently available only for the 3G Universal Mobile
•
Telecommunications System (UMTS).
Information About the iWAG
The iWAG deployment includes a combination of simple IP users (traditional ISG and WiFi) and mobile IP
users (PMIPv6 or GTP tunneling). The term mobility service is used to refer to either the GTP service or the
PMIPv6 service applied to user traffic. The iWAG provides mobility services to mobile IP users, and as a
result, a mobile client can seamlessly access a 3G or 4G mobility network. However, the iWAG does not
provide mobility services to simple IP users. Therefore, simple IP users can access the Public Wireless LAN
(PWLAN) network through the Cisco ISG. Clients are devices that access WiFi Internet (public wireless),
where possible. However, if WiFi is not available, the same clients can
connect to the Internet service using a 3G or 4G mobility network.
The iWAG has a transport or switching element with Cisco ISG subscriber awareness. The iWAG also has
RADIUS-based authentication and accounting, and policy-based subscriber routing for the WiFi wholesale
model.
For more information about the iWAG, see the Overview of iWAG video.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
2 OL-30226-03
Page 11

Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
The following figure shows a deployment model of the iWAG on a Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation
Services Router.
Figure 1: iWAG Deployment on a Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router
Benefits of the iWAG
Benefits of the iWAG
The iWAG offers the following benefits for mobile operators:
Reduces network congestion by reducing OpEx and increasing network efficiency by offloading 3G
•
and 4G traffic.
Provides access to 3G and 4G core inspite of a lack of or weak cell signal, leading to subscriber retention.
•
Lowers CapEx on per user basis or bandwidth basis in dense metro environments.
•
The iWAG offers the following benefits for wireline and WiFi operators:
Provides WiFi security and subscriber control. Delivers scalable, manageable, and secure wireless
•
connectivity.
Enables new revenue-sharing business models, such as Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNO)
•
and others.
Delivers a WiFi platform that offers new location-based services.
•
The iWAG offers the following benefits for subscribers:
Provides enhanced quality of experience to subscribers on WiFi networks.
•
Provides unified billing across access networks.
•
• Provides mobility across radio access technologies—3G or 4G to WiFi and WiFi to WiFi.
Provides multiple options within the WiFi platform, thereby enabling location-based services.
•
AAA Attributes
The following table lists the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) attributes required for the
iWAG configuration:
OL-30226-03 3
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 12
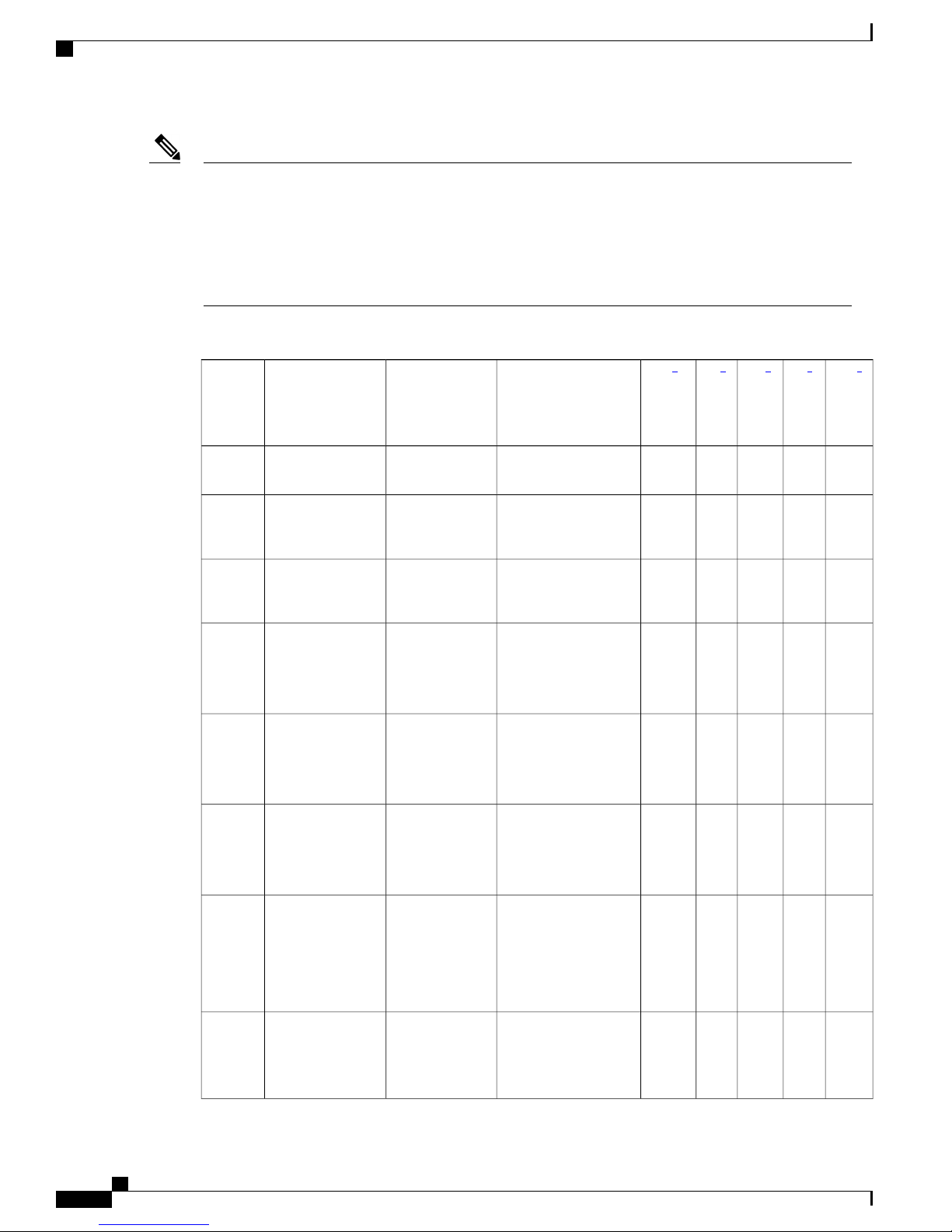
AAA Attributes
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Note
The following indicate the availability of the attributes:
C: Conditional
M: Mandatory
O: Optional
N: Not present
Table 1: iWAG AAA Attributes
Attrib
ute
/Subattri
bute
Name
DescriptionValueAttri
bute
StringUser Name1
Identifier
4
-Address
31
Station-ID
StringNAS-IP
MAG
StringCalling-
mobile node
ARq
CoA
5
AA
2
ARj
AS
1
4
3
COMMMNetwork Access
OMNNMIP address of the
MMMMMMAC address of the
26/
10415/
1
26/
10415
/13
26
/9
/1
26
/9
/1
26
/9/1
IMSI
-Charging
-Characteristics
-Selection
-Mobile
-Node
-Identifier
-WLAN
-SSID
ONNON3GPP IMSIString3GPP-
String3GPP
OONONRules for producing
charging information
StringCisco-Service
CNNCNService Identifier
(APN)
StringCisco
CMNMNMobile Node
Identifier
StringCisco
NCNNCSSID of the Access
Point
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
4 OL-30226-03
Page 13
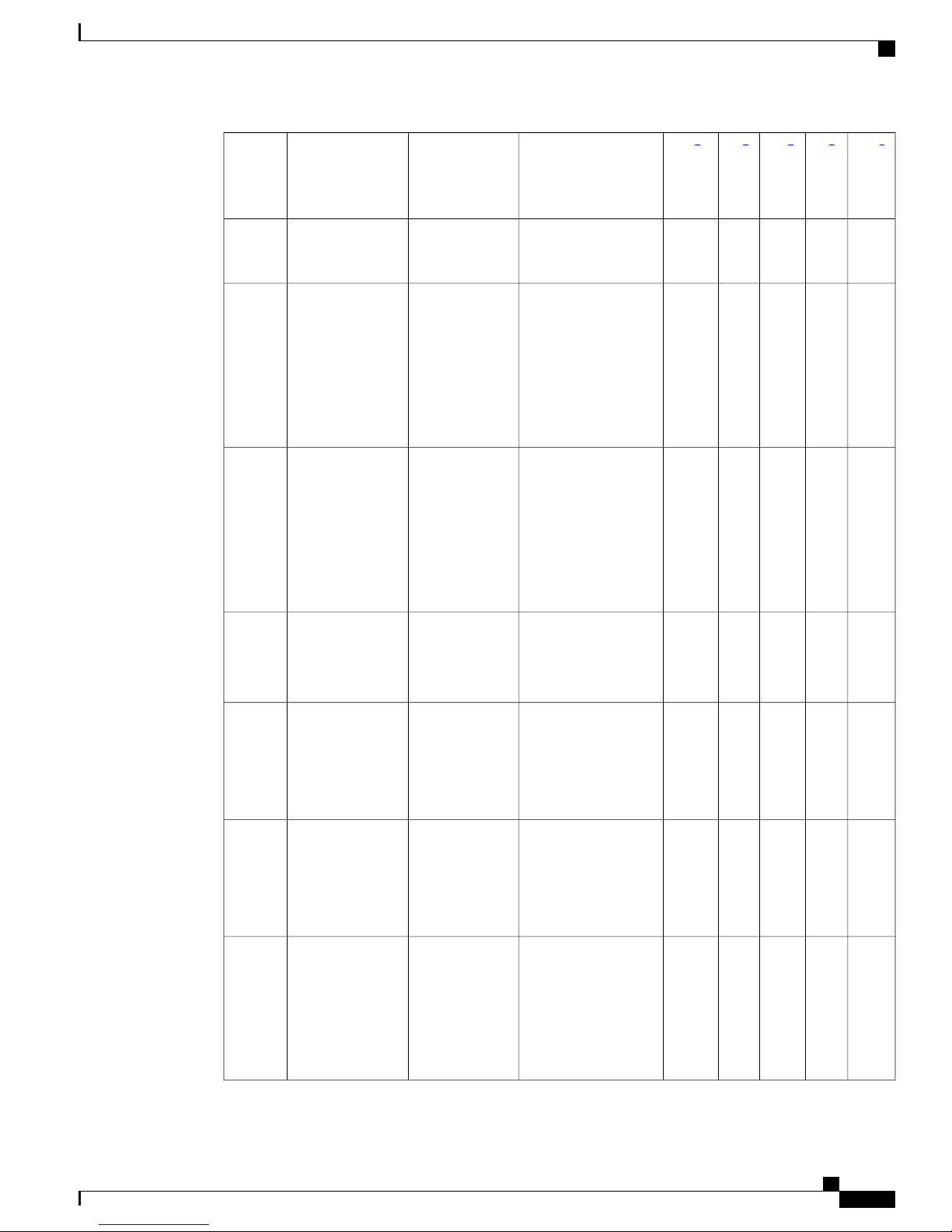
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
AAA Attributes
Attrib
ute
/Subattri
bute
26/9/1
26/9/1
26/9/1
bute
Name
-MSISDN
Cisco-MN
-Service
Cisco-MPC
-Protocol
-Interface
StringCisco
ENUM
•
•
•
•
ENUM
•
•
•
•
none
ipv4
ipv6
dual
none
pmipv6
gtpv1
pmipv4
DescriptionValueAttri
ISDN number
type
be used for
interfacing with MPC
ARq
CoA
5
AA
2
ARj
AS
1
4
3
CCNCNMobile Subscriber
OMNMNMobile Node Service
OONMNProtocol Interface to
26/9/1
26/9/1
26/9/1
26/9/1
-Multihoming
-Support
-Uplink
-GRE
-Key
-Downlink
-GRE
-Key
-Home
-LMA
-IPv6
-Address
BinaryCisco
ONNONTrue/False:
Multihoming support
for mobile node
IntegerCisco
ONNON32-bit GRE Key to be
used on the uplink
path (4-octet hex
encoding)
IntegerCisco
ONNON32-bit GRE Key to be
used on the downlink
path (4-octet hex
encoding)
StringCisco
ONNCNMobile node's Home
LMA IPv6 address
OL-30226-03 5
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 14

AAA Attributes
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Attrib
ute
/Subattri
bute
26/9/1
26/9/1
26/9/1
bute
Name
-Visited
-LMA
-IPv6
-Address
-Home
-LMA
-IPv4
-Address
-Visited
-LMA
-IPv4
-Address
CoA
ONNCNMobile node's Visited
5
AA
2
ARj
AS
1
DescriptionValueAttri
ARq
4
3
StringCisco
LMA IPv6 address
IPv4 AddressCisco
ONNCNMobile node's Home
LMA IPv4 address
IPv4 AddressCisco
ONNCNMobile node's Visited
LMA IPv4 address
26/9/1
26/9/1
26
/10415
/5
-Home
-IPv4
-Home
-Address
-Visited
-IPv4
-Home
-Address
_GPRS
_QOS
_PROFILE
IPv4 AddressCisco
CNNONMobile node's Visited
LMA IPv4 address
IPv4 AddressCisco
CNNONMobile node's Visited
IPv4 address
NNNONGRPS QoS ProfileStringTHREEGENPP
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
6 OL-30226-03
Page 15

Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Supported Hardware and Software Compatibility Matrix for the iWAG
1
Access Request
2
Access Accept
3
Access Reject
4
Accounting Start
5
Change of Authorization
Attrib
ute
/Subattri
bute
26
/10415
/7
26/9/1
26/9/1
bute
Name
_GGSN
_ADDRESS
-Access
-Vrf
-Id
-Apn
-Vrf
-Id
CoA
5
AA
2
ARj
AS
1
DescriptionValueAttri
ARq
4
3
NNNONGGSN's AddressIPv4 AddressTHREEGENPP
NNNONAccess-side VRF IDStringCisco
NNNONGGSN's IPv4 addressIPv4 AddressCisco
Supported Hardware and Software Compatibility Matrix for the iWAG
ESPRP MemoryChassis
IntegratedIntegrated RP with 16 GBCisco ASR 1001 Router
IntegratedIntegrated RP with 16 GBCisco ASR 1002-X Router
ESP-40GRP2 16 GBCisco ASR 1004 Router
ESP-40GRP2 16 GBCisco ASR 1006 Router and Cisco
ASR 1013 Router offering duplex
RP or ESP setup
ESP-100GRP2 16 GBCisco ASR 1006 Router and Cisco
ASR 1013 Router offering duplex
RP or ESP setup
OL-30226-03 7
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 16

How to Configure the iWAG
For information about the field-replaceable units (FRUs) of the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services
Routers supported by each ROMmon release, see the "ROMmon Release Requirements" section in the Cisco
ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers Release Notes.
How to Configure the iWAG
Configuring the iWAG for Simple IP Users
You must configure the Cisco Intelligent Services Gateway (ISG) for the iWAG to enable simple IP users to
access Internet services.
The tasks listed below enable IP sessions and indicate how these sessions are identified. For detailed steps,
see the "Creating ISG Sessions for IP Subscribers" section in the Intelligent Services Gateway Configuration
Guide.
Creating ISG IP interface sessions
•
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Creating ISG Static Sessions
•
Creating ISG IP Subnet Sessions
•
Configuring IP Session Recovery for DHCP-Initiated IP Sessions
•
Verifying ISG IP Subscriber Sessions
•
Clearing ISG IP Subscriber Sessions
•
Troubleshooting ISG IP Subscriber Sessions
•
You must configure DHCP support in your network before performing the tasks listed below. For detailed
steps on assigning IP addresses using DHCP, see the "Assigning ISG Subscriber IP Addresses by Using
DHCP" section in the Intelligent Services Gateway Configuration Guide.
Configuring an ISG Interface for Dynamic DHCP Class Association
•
Configuring DHCP Server User Authentication
•
Configuring a DHCP Class in a Service Policy Map
•
Configuring a DHCP Class in a Service Profile or User Profile on the AAA Server
•
Configuring a DHCP Server IP Address
•
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
You must configure GTP for the iWAG to allow access to 3G mobile IP users. The various tasks described
in the following sections are mandatory for configuring the iWAG for 3G mobile IP users.
Configuring Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting for the iWAG
This section describes how to configure authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) for the iWAG
on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
8 OL-30226-03
Page 17

Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
aaa new-model
3.
aaa group server radius group-name
4.
server-private ip-address [auth-port port-number | acct-port port-number ] [non-standard] [timeout
5.
seconds ] [retransmit retries ] [ key string]
aaa authentication login {default | list-name} { [passwd-expiry] method1 [method2...]}
6.
aaa authorization network authorization-name group server-group name
7.
aaa authorization subscriber-service {default {cache | group | local} | list-name} method1 [method2...]
8.
aaa accounting{auth-proxy| system | network | exec | connection | commands level | dot1x} { {default
9.
| list-name } [vrf vrf-name] {start-stop | stop-only | none} [broadcast] group group-name
action-type {none | start-stop | stop-only}
10.
group {tacacs+ server-group}
11.
aaa accounting {auth-proxy | system | network | exec | connection | commands level | dot1x } {default
12.
|list-name } [vrf vrf-name ] {start-stop | stop-only | none} [broadcast] group group-name
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
Example:
Router(config)# aaa new-model
Step 4
Step 5
aaa group server radius group-name
Example:
Router(config)# aaa group server radius AAA_SERVER_CAR
server-private ip-address [auth-port port-number | acct-port
port-number ] [non-standard] [timeout seconds ] [retransmit retries
] [ key string]
PurposeCommand or Action
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enables the AAA access control model.aaa new-model
Groups different RADIUS server hosts into distinct
lists and methods.
Configures the IP address of the private RADIUS
server for the group server.
Example:
Router(config-sg-radius)# server-private 5.3.1.76
auth-port 2145 acct-port 2146 key cisco
OL-30226-03 9
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 18
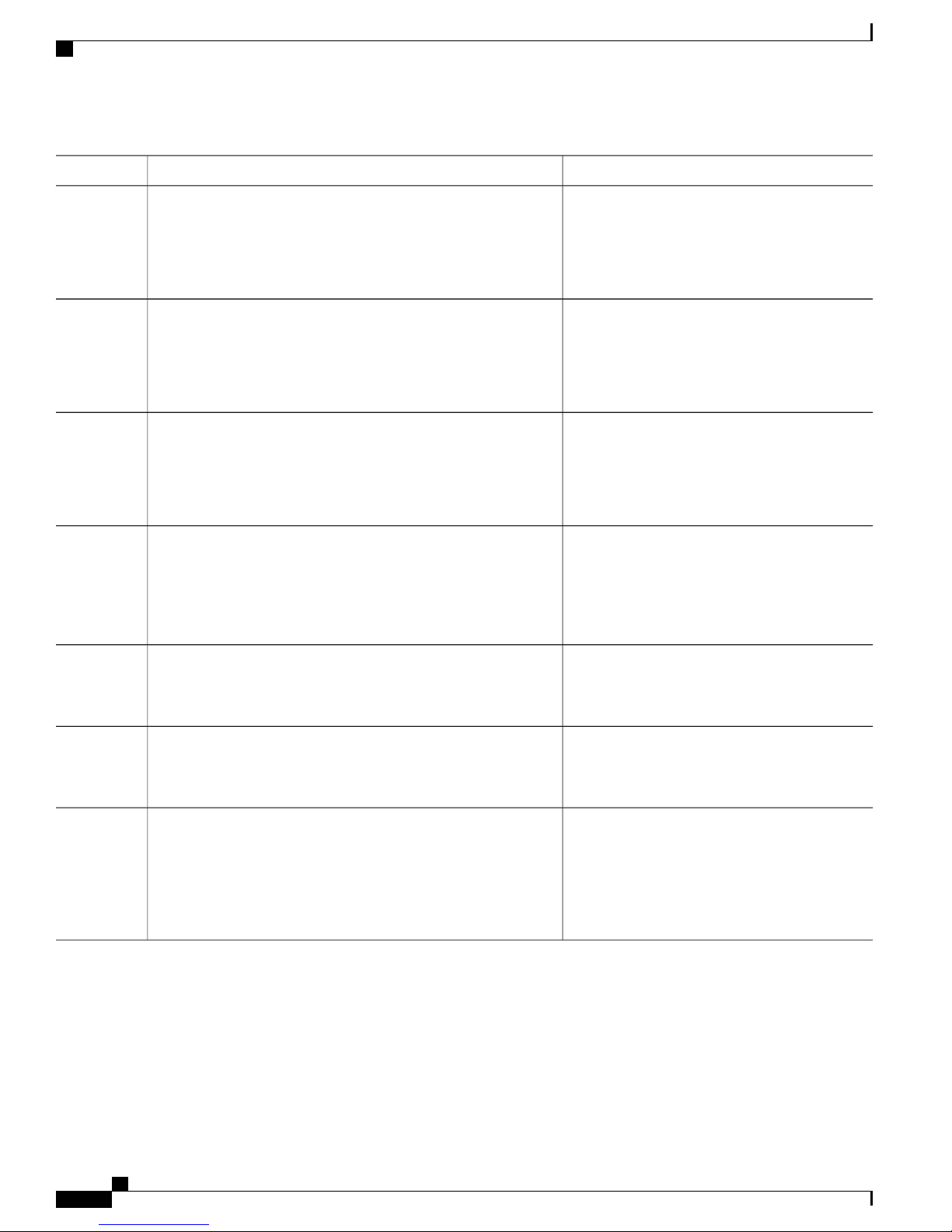
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
aaa authentication login {default | list-name} { [passwd-expiry]
method1 [method2...]}
Example:
Router(config-sg-radius)# aaa authentication login
default none
aaa authorization network authorization-name group
server-group name
Example:
Router(config)# aaa authorization network ISG_PROXY_LIST
group AAA_SERVER_CAR
aaa authorization subscriber-service {default {cache | group |
local} | list-name} method1 [method2...]
Example:
Router(config)# aaa authorization subscriber-service
default local group AAA_SERVER_CAR
aaa accounting{auth-proxy| system | network | exec | connection
| commands level | dot1x} { {default | list-name } [vrf vrf-name]
{start-stop | stop-only | none} [broadcast] group group-name
Example:
Router(config)# aaa accounting network PROXY_TO_CAR
action-type {none | start-stop | stop-only}
Example:
Router(cfg-acct-mlist)# action-type start-stop
group {tacacs+ server-group}
Example:
Router(cfg-preauth)# group AAA_SERVER_CAR
aaa accounting {auth-proxy | system | network | exec | connection
| commands level | dot1x } {default |list-name } [vrf vrf-name ]
{start-stop | stop-only | none} [broadcast] group group-name
Example:
Router(config)# aaa accounting network ISG_PROXY_LIST
start-stop group AAA_SERVER_CAR
Sets AAA authentication at login.
Runs authorization for all network-related service
requests.
Specifies one or more AAA authorization methods
for the Cisco ISG to provide subscriber service.
Enables AAA accounting of requested services
for billing and security purposes when either the
RADIUS server or the TACACS+ server is used.
Enables the type of actions to be performed on
accounting records.
Specifies the AAA TACACS+ server group to use
for preauthentication.
Enables AAA accounting of requested services
for billing and security purposes when you use
either the RADIUS server or the TACACS+
server.
Configuring DHCP when the iWAG Acts as a DHCP Proxy
This section describes how to configure the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for the iWAG
solution when the iWAG acts as a DHCP proxy.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
10 OL-30226-03
Page 19

Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
ip dhcp excluded-address [vrf vrf-name] ip-address
3.
ip dhcp pool pool-name
4.
network network-number [ mask [secondary] | /prefix-length [secondary]
5.
default-router ip-address [last-ip-address]
6.
domain-name domain
7.
lease {days [hours [ minutes ]] | infinite}
8.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Router> enable
Example:
Router# configure terminal
ip dhcp excluded-address [vrf vrf-name] ip-address
Example:
Router(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address
192.168.10.1
ip dhcp pool pool-name
Example:
Router(config)# ip dhcp pool test
network network-number [ mask [secondary] |
/prefix-length [secondary]
Example:
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Specifies the IP address that a DHCP server should not assign
to DHCP clients.
Configures a DHCP address pool on a DHCP server and enters
the DHCP pool configuration mode.
Configures the network number and mask for a DHCP address
pool primary subnet or DHCP address pool secondary subnet on
a Cisco IOS DHCP server.
Router(dhcp-config)# network 192.168.0.0
255.255.0.0
Step 6
OL-30226-03 11
default-router ip-address [last-ip-address]
Example:
Router(dhcp-config)# default-router
192.168.10.1
Specifies the default router list for a DHCP client.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 20
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 7
Step 8
domain-name domain
Example:
Router(dhcp-config)# domain-name example.com
lease {days [hours [ minutes ]] | infinite}
Specifies the domain name for a DHCP client.
Configures the duration of the lease for an IP address that is
assigned from a Cisco IOS DHCP server to a DHCP client.
Example:
Note
The DHCP pool lease time is applicable only to simple
sessions. For mobile GTP sessions, lease time from the
Router(dhcp-config)# lease 1 2 2
GTP configuration will be used. Under the GTP
configuration, lease duration should be configured the
same way as the address hold timer in the GGSN or
PGW.
Configuring the Cisco ISG Class Map and Policy Map for the iWAG
This section describes how to configure the Cisco ISG class map and policy map for the iWAG.
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
class-map type traffic match-any class-map-name
3.
match access-group output {access-group | name access-group-name}
4.
match access-group input {access-group | name access-group-name}
5.
policy-map type service policy-map-name
6.
[ priority ] class type traffic {class-map-name | default {in-out | input | output } }
7.
accounting aaa list aaa-method-list
8.
[ priority ] class type traffic { class-map-name | default {in-out | input | output}}
9.
drop
10.
policy-map type control policy-map-name
11.
class type control control-class-name | always} [event{access-reject | account-logoff | account-logon |
12.
acct-notification | credit-exhausted | dummy-event | quota-depleted | radius-timeout | service-failed |
service-start | service-stop | session-default-service | session-restart | session-service-found | session-start
| timed-policy-expiry}]
action-number service-policy type service [unapply] [aaa list list-name ] { name service-name |
13.
identifier {authenticated-domain | authenticated-username | dnis | nas-port | tunnel-name |
unauthenticated-domain | unauthenticated-username }}
action-number authorize[aaa{list-name | list { list-name | default}} [password password]] [upon
14.
network-service-found {continue | stop}] [use method authorization-type] identifier identifier-type
[plus identifier-type]
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
12 OL-30226-03
Page 21
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Router> enable
Example:
Router# configure terminal
class-map type traffic match-any class-map-name
Example:
Router(config)# class-map type traffic match-any
TC_OPENGARDEN
match access-group output {access-group | name
access-group-name}
Example:
Router(config-traffic-classmap)# match access-group
output name ACL_OUT_OPENGARDEN
match access-group input {access-group | name
access-group-name}
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Creates or modifies a traffic class map that is used
for matching packets to a specified Cisco ISG
traffic class.
Configures the match criteria for a Cisco ISG
traffic class map on the basis of the specified
access control list (ACL).
Configures the match criteria for a Cisco ISG
traffic class map on the basis of the specified ACL.
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Example:
Router(config-traffic-classmap)# match access-group input
name ACL_IN_OPENGARDEN
policy-map type service policy-map-name
Example:
Router(config)# policy-map type service
OPENGARDEN_SERVICE
[ priority ] class type traffic {class-map-name | default {in-out |
input | output } }
Example:
Router(config-service-policymap)# 20 class type traffic
TC_OPENGARDEN
accounting aaa list aaa-method-list
Example:
Router(config-service-policymap)# accounting aaa list
PROXY_TO_CAR
Creates or modifies a service policy map that is
used to define a Cisco ISG subscriber service.
Creates or modifies a traffic class map that is used
for matching packets to a specified Cisco ISG
traffic class.
Enables Cisco ISG accounting and specifies an
AAA method list to which accounting updates are
forwarded.
OL-30226-03 13
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 22
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
[ priority ] class type traffic { class-map-name | default {in-out |
input | output}}
Example:
Router(config-service-policymap)# class type traffic
default in-out
drop
Example:
Router(config-service-policymap)# drop
policy-map type control policy-map-name
Example:
Router(config)# policy-map type control BB_PROFILE
class type control control-class-name | always}
[event{access-reject | account-logoff | account-logon |
acct-notification | credit-exhausted | dummy-event | quota-depleted
| radius-timeout | service-failed | service-start | service-stop |
session-default-service | session-restart | session-service-found |
session-start | timed-policy-expiry}]
Creates or modifies a traffic class map that is used
for matching packets to a specified Cisco ISG
traffic class.
Configures a Cisco ISG to discard packets
belonging to the default traffic class.
Creates or modifies a control policy map that
defines a Cisco ISG control policy.
Specifies a control class for which actions can be
configured in a Cisco ISG control policy.
Step 13
Step 14
Example:
Router (config-control-policymap)# class type control
always event session-start
action-number service-policy type service [unapply] [aaa list
list-name ] { name service-name | identifier
{authenticated-domain | authenticated-username | dnis | nas-port
| tunnel-name | unauthenticated-domain |
unauthenticated-username }}
Example:
Router(config-control-policymap-class-control)# 10
service-policy type service name OPENGARDEN_SERVICE
action-number authorize[aaa{list-name | list { list-name |
default}} [password password]] [upon network-service-found
{continue | stop}] [use method authorization-type] identifier
identifier-type [plus identifier-type]
Example:
Router(config-control-policymap-class-control)# 20
authorize aaa list ISG_PROXY_LIST password cisco
identifier mac-address
Activates a Cisco ISG service.
Initiates a request for authorization based on a
specified identifier in a Cisco ISG control policy.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
14 OL-30226-03
Page 23
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Configuring a Session Initiator for the iWAG
This section describes how to configure a session initiator for the iWAG solution. A session can be created
using different triggers, such as an unknown MAC address, an unclassified MAC address, a RADIUS message
with the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router acting as RADIUS proxy or a DHCP DISCOVER
message with the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router acting as DHCP proxy.
To enable roaming, one initiator is required for DHCP sessions and another for the unclassified MAC.Note
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
interface GigabitEthernet slot/subslot/port
3.
description string
4.
ip address ip-address mask [secondary [vrf vrf-name]]
5.
negotiation auto
6.
service-policy type control policy-map-name
7.
ip subscriber {l2-connected}
8.
initiator {dhcp | radius-proxy | static ip subscriber list listname | unclassified ip | unclassified
9.
mac-address}
initiator {dhcp | radius-proxy | static ip subscriber list listname | unclassified ip | unclassified
10.
mac-address}
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Example:
Router> enable
Example:
Router# configure terminal
interface GigabitEthernet slot/subslot/port
Example:
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1/3/3
PurposeCommand or Action
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the interface configuration mode for Gigabit
Ethernet.
OL-30226-03 15
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 24
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
description string
Example:
Router(config-if)# description access interface
connected to subscriber
ip address ip-address mask [secondary [vrf vrf-name]]
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.171.10.1
255.255.0.0
Example:
Router(config-if)# negotiation auto
service-policy type control policy-map-name
Example:
Router(config-if)# service-policy type control
BB_Profile
ip subscriber {l2-connected}
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip subscriber l2-connected
Adds a description to an interface configuration.
Sets a primary IP address or secondary IP address for
an interface.
Enables auto negotiation on a Gigabit Ethernet interface.negotiation auto
Applies a control policy to a context.
Enables Cisco ISG IP subscriber support on an interface
and specifies the access method that IP subscribers use
for connecting to the Cisco ISG on an interface.
Note
The iWAG does not support the routed access
method.
Step 9
initiator {dhcp | radius-proxy | static ip subscriber list
listname | unclassified ip | unclassified mac-address}
Example:
Router(config-subscriber)# initiator unclassified
mac-address
Step 10
initiator {dhcp | radius-proxy | static ip subscriber list
listname | unclassified ip | unclassified mac-address}
Example:
Router(config-subscriber)# initiator dhcp
Configuring a Tunnel Interface for the iWAG
This section describes how to configure a tunnel interface between the iWAG solution and the GGSN.
Enables the Cisco ISG to create an IP subscriber session
upon receipt of a specified type of packet.
Enables the Cisco ISG to create an IP subscriber session
upon receipt of a specified type of packet.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
16 OL-30226-03
Page 25
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
interface GigabitEthernet slot/subslot/port
3.
description string
4.
ip address ip-address mask [secondary [vrf vrf-name ]]
5.
negotiation auto
6.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Example:
Router> enable
Example:
Router# configure terminal
interface GigabitEthernet slot/subslot/port
Example:
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1/3/5
description string
Example:
Router(config-if)#description interface connected
to GGSN
ip address ip-address mask [secondary [vrf vrf-name ]]
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.170.10.1
255.255.0.0
negotiation auto
Example:
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the interface configuration mode for Gigabit
Ethernet interface.
Adds a description to an interface configuration.
Sets a primary IP address or secondary IP address for
an interface.
Enables auto negotiation on a Gigabit Ethernet
interface.
Router(config-if)# negotiation auto
Enabling Mobile Client Service Abstraction
This section describes how to enable Mobile Client Service Abstraction (MCSA) for PMIPv6.
OL-30226-03 17
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 26

Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Note
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Enabling MCSA is mandatory before you enable the Mobility feature in the Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
mcsa
3.
enable sessionmgr
4.
PurposeCommand or Action
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Example:
Router> enable
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
mcsa
Example:
Router(config)# mcsa
Step 4
Example:
Router(config-mcsa)# enable sessionmgr
Configuring the GTP of the iWAG
This section describes how to configure GTPv1 for the iWAG solution.
Before You Begin
Enable mobile client service abstraction (MCSA).
Enables MCSA on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation
Services Router.
Enables MCSA to receive notifications from the Cisco ISG.enable sessionmgr
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
18 OL-30226-03
Page 27
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
gtp
3.
n3-request number of requests
4.
interval t3-response number of seconds
5.
interval echo-request request-number
6.
interface local GigabitEthernet slot/subslot/port
7.
apn apn-name
8.
ip address ggsn ip-address
9.
default-gw address prefix-len value
10.
dns-server ip-address
11.
dhcp-server ip-address
12.
dhcp-lease seconds
13.
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Router> enable
Step 2
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
gtp
Example:
Router(config)# gtp
n3-request number of requests
Example:
Router(config-gtp)# n3-request 3
interval t3-response number of seconds
Example:
PurposeCommand or Action
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Configures the GTP for the iWAG solution on the Cisco ASR 1000
Series Aggregation Services Router.
Specifies the number of times a control message must be retried
before a failure message is sent. The default value is 5.
Specifies the time interval, in seconds, for which the SGSN of the
iWAG waits for a response for the control message sent. The default
value is 1.
Router(config-gtp)# interval t3-response
10
OL-30226-03 19
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 28
Configuring the iWAG for 3G Mobile IP Users
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
interval echo-request request-number
Example:
Router(config-gtp)# interval echo-request
60
interface local GigabitEthernet slot/subslot/port
Example:
Router(config-gtp)# interface local
GigabitEthernet 0/0/3
apn apn-name
Example:
Router(config-gtp)# apn example.com
ip address ggsn ip-address
Example:
Router(config-gtp-apn)# ip address ggsn
192.170.10.2
default-gw address prefix-len value
Example:
Router(config-gtp-apn)# default-gw
192.171.10.1 prefix-len 16
dns-server ip-address
Example:
Specifies the time interval, in seconds, for which the SGSN of the
iWAG waits for before sending an echo request message. The range
is from 60 to 65535. The default value is 60. The value of 0 disables
the Echo Request feature.
Configures the transport interface to communicate with the GGSN.
Configures an ASCII regular expression string to be matched against
the Access Point Name (APN) for GPRS load balancing.
Sets the IP address for the GGSN.
Specifies the default gateway address of the subscriber.
Note
This is the default gateway address of the IP provided by
the GGSN using GTP, and not the default gateway address
on the physical local interface that the subscriber is
connected to. They can be the same, but we recommend
that they be two different subnets.
Specifies the Domain Name System (DNS) IP servers that are
available for a DHCP client.
Router(config-gtp-apn)# dns-server
192.165.1.1
Step 12
dhcp-server ip-address
Example:
Router(config-gtp-apn)# dhcp-server
192.168.10.1
Step 13
dhcp-lease seconds
Example:
Router(config-gtp-apn)# dhcp-lease 3000
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
20 OL-30226-03
Specifies the primary and backup DHCP servers that are used to
allocate IP addresses to mobile station users entering a particular
public data network (PDN) access point.
Configures the duration (in seconds) of the lease for an IP address
that is assigned from a Cisco IOS DHCP Server to a DHCP client.
Page 29

Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Configuring the iWAG for 4G Mobile IP Users
Configuring PMIPv6 for the iWAG
You must configure PMIPv6 for the iWAG to allow access to mobile IP users.
The tasks listed below describe the procedures involved in configuring the Mobile Access Gateway. For
detailed steps, see the "How to Configure Proxy Mobile IPv6 Support for MAG Functionality" section in the
IP Mobility: PMIPv6 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S .
Configuring a Proxy Mobile IPv6 Domain by Using the Configuration from the AAA Server
•
Configuring the Minimum Configuration for a MAG to Function
•
Configuring a Detailed Configuration for a MAG when an AAA Server is not Available
•
Configuring a Minimum Configuration for a MAG
•
Configuring a Detailed Configuration for a MAG
•
Configuring the iWAG for 4G Mobile IP Users
The tasks listed below describe the procedures involved in configuring Local Mobility Anchor. For detailed
steps, see the "How to Configure Proxy Mobile IPv6 Support for LMA Functionality" section in the IP
Mobility: PMIPv6 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S .
Configuring a Proxy Mobile IPv6 Domain by Using the Configuration from the AAA Server
•
Configuring a Minimum Configuration for a Domain When an AAA Server Is Not Available
•
Configuring a Detailed Configuration for a Domain When the AAA Server Is Not Available
•
Configuring a Minimum Configuration for an LMA
•
Configuring a Detailed Configuration for an LMA
•
Enabling Mobile Client Service Abstraction
This section describes how to enable Mobile Client Service Abstraction (MCSA) for PMIPv6.
Note
SUMMARY STEPS
Enabling MCSA is mandatory before you enable the Mobility feature in the Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
mcsa
3.
enable sessionmgr
4.
OL-30226-03 21
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 30

Additional References
DETAILED STEPS
Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Example:
Router> enable
Step 2
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
mcsa
Example:
Router(config)# mcsa
Step 4
Example:
Router(config-mcsa)# enable sessionmgr
Additional References
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enables MCSA on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation
Services Router.
Enables MCSA to receive notifications from the Cisco ISG.enable sessionmgr
Related Documents
Cisco IOS commands
ISG concepts, configuration tasks, and examples
ISG commands
iWAG commands
Mobile IP configuration concepts, tasks, and examples
IP Mobility commands
GGSN configuration concepts, tasks, and examples
Document TitleRelated Topic
Cisco IOS Master Command List, All
Releases
ISG Configuration Guide
Cisco IOS Intelligent Services Gateway
Command Reference
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access
Gateway Command Reference
IP Mobility: PMIPv6 Configuration Guide
Cisco IOS IP Mobility Command Reference
Mobile Wireless GGSN Configuration Guide
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
22 OL-30226-03
Page 31

Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Standards and RFCs
Feature Information for the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
TitleStandard/RFC
Mobility Support in IPv6RFC 3775
Proxy Mobile IPv6RFC 5213
RFC 5844
RFC 5845
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support and Documentation website
provides online resources to download documentation,
software, and tools. Use these resources to install and
configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve
technical issues with Cisco products and technologies.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and
Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID
and password.
IPv4 Support for Proxy Mobile
IPv6
Generic Routing Encapsulation
(GRE) Key Option for Proxy
Mobile IPv6
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
LinkDescription
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Feature Information for the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
OL-30226-03 23
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 32

Overview of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Table 2: Feature Information for the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Gateway
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.8SIntelligent Wireless Access
The iWAG solution offers the
following tunneling
technologies to integrate WiFi
access with the Evolved
Packet Core (EPC):
GPRS Tunnel Protocol
•
version 1 (GTPv1)
allows integration of a
3G environment, where
iWAG behaves in a way
that is similar to a
Serving GPRS Support
Node (SGSN)
connecting to a Gateway
GPRS Support Node
(GGSN).
Proxy Mobile IPv6
•
(PMIPv6) allows the
integration of a 4G
environment where
iWAG behaves as a
PMIPv6 Mobile Access
Gateway (MAG)
connecting to an Local
Mobility Anchor (LMA)
that is co-located with a
Packet Gateway (PGW),
which acts as PMIPv6
LMA.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks.
Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
24 OL-30226-03
In Cisco IOS XE Release
3.8S, this feature was
implemented on the Cisco
ASR 1000 Series Aggregation
Services Routers.
Page 33

CHAPTER 2
IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
The IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel (IPoGEC) feature enables you to add the Link Aggregation
Control Protocol (LACP) functionality for IP sessions. The LACP defines a virtual interface for a port channel
or a port bundle, and adds physical member links to the port channel. This section provides information
about the IPoGEC and how to configure it.
Finding Feature Information, page 25
•
Restrictions for IPoGEC, page 25
•
Information About IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel, page 26
•
Configuring IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel, page 26
•
Configuring Member Links for IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel, page 28
•
Configuration Examples for IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel, page 29
•
Additional References, page 29
•
Feature Information for IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel, page 30
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for IPoGEC
IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel (IPoGEC) currently supports the 1:1 model, where only one member
link is active while the second member link is passive and does not carry traffic.
OL-30226-03 25
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 34

IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
Information About IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel
Information About IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel
The IP sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel (IPoGEC) feature ensures consistency between systems by adding
redundancy and allows dynamic link management during local and remote system failures. LACP fast
switchover enables the standby member link to take over instantly (in milliseconds) when the active member
link goes down. As a result, the port channel remains up. The carrier-delay {delay-seconds | msec
milliseconds} command used in the configuration of the IPoGEC ensures fast switchover, with the delay in
switchover being in milliseconds rather than seconds.
Supported Features for IPoGEC
IPoGEC supports both simple IP sessions and mobile IP sessions.
•
IPoGEC is supported over virtual local area network (VLAN) and subinterfaces.
•
IPoGEC is supported on all Ethernet SPAs, including 10-Gigabit Ethernet ports and 1-Gigabit Ethernet
•
ports.
Configuring IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
interface port-channel channel-number
2.
description string
3.
ip address ip-address mask [secondary [vrf vrf-name] ]
4.
load-interval seconds
5.
lacp fast-switchover
6.
lacp max-bundle max-bundle-number
7.
service-policy type control policy-map-name
8.
ip subscriber {l2-connected}
9.
initiator {dhcp | radius-proxy | static ip subscriber list listname | unclassified ip | unclassified
10.
mac-address}
initiator {dhcp | radius-proxy | static ip subscriber list listname | unclassified ip | unclassified
11.
mac-address}
DETAILED STEPS
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
26 OL-30226-03
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Page 35

IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
Configuring IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
interface port-channel channel-number
Example:
Router(config)#interface port-channel 1
description string
Example:
Router(config-if)#description GEC:1 interface
towards switch
ip address ip-address mask [secondary [vrf vrf-name] ]
Example:
Router(config-if)#ip address 21.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
load-interval seconds
Example:
Router(config-if)#load-interval 30
Example:
Router(config-if)#lacp fast-switchover
lacp max-bundle max-bundle-number
Example:
Router(config-if)#lacp max-bundle 1
service-policy type control policy-map-name
Creates a port-channel virtual interface.
Adds a description to an interface configuration.
Removes an IP address from an interface.
Changes the length of time for which data is used to
compute load statistics.
Enables the LACP 1:1 link redundancy.lacp fast-switchover
Defines the maximum number of active, bundled LACP
ports allowed in a port channel.
Applies a control policy to a context.
Example:
Router(config-if)#service-policy type control
BB_PMAP
Step 9
ip subscriber {l2-connected}
Example:
Router(config-if)#ip subscriber l2-connected
Step 10
initiator {dhcp | radius-proxy | static ip subscriber list
listname | unclassified ip | unclassified mac-address}
Example:
Router(config-subscriber)# initiator unclassified
mac-address
OL-30226-03 27
Enables Cisco Intelligent Services Gateway (ISG) IP
subscriber support on an interface, and specifies the
access method that IP subscribers use for connecting
to the Cisco ISG on an interface.
Note
The iWAG does not support the routed access
method.
Enables the Cisco ISG to create an IP subscriber session
upon receipt of a specified type of packet.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 36

Configuring Member Links for IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel
IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 11
initiator {dhcp | radius-proxy | static ip subscriber list
listname | unclassified ip | unclassified mac-address}
Example:
Router(config-subscriber)# initiator dhcp
Enables the Cisco ISG to create an IP subscriber session
upon receipt of a specified type of packet.
Configuring Member Links for IP Sessions over Gigabit
EtherChannel
SUMMARY STEPS
interface GigabitEthernet slot/subslot/port
1.
no ip address ip-address mask [secondary [vrf vrf-name] ]
2.
carrier-delay {delay-seconds | msec milliseconds}
3.
lacp port-priority priority
4.
channel-group channel-group-number mode {active | passive}
5.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
interface GigabitEthernet slot/subslot/port
Example:
Router(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
no ip address ip-address mask [secondary [vrf
vrf-name] ]
Example:
Router(config-if)#no ip address
carrier-delay {delay-seconds | msec milliseconds}
Example:
Router(config-if)# carrier-delay msec 50
lacp port-priority priority
Example:
Router(config-if)#lacp port-priority 4000
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters the interface configuration mode for Gigabit Ethernet
interface.
Removes an IP address from an interface.
Sets the carrier delay on a serial interface. To achieve faster
switchover from active to standby member link, the carrier delay
value can be set to 0 ms.
Sets the LACP priority for a physical interface. IPoGEC currently
supports 1:1 model, that is one active member link and one
standby member link, which only requires choosing two different
values for priority field to make sure one interface is active while
the other is standby. The value set for the priority field shall
match the value configured on the switch.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
28 OL-30226-03
Page 37

IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
Configuration Examples for IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 5
channel-group channel-group-number mode {active
| passive}
Example:
Router(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode active
Configures the interface in a channel group and sets the LACP
mode.
Configuration Examples for IP Sessions Over Gigabit
EtherChannel
Example: Configuring IPoGEC
interface Port-channel1
description GEC:1 interface towards switch
ip address 21.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
load-interval 30
lacp fast-switchover
lacp max-bundle 1
service-policy type control BB_PMAP
ip subscriber l2-connected
initiator unclassified mac-address ipv4
initiator dhcp
Example: Configuring Member Links for IPoGEC
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
no ip address
carrier-delay msec 50
lacp port-priority 4000
channel-group 1 mode active
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
no ip address
carrier-delay msec 50
lacp port-priority 3000
channel-group 1 mode active
Additional References
Related Documents
iWAG commands
Document TitleRelated Topic
Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All ReleasesCisco IOS commands
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Command Reference
OL-30226-03 29
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 38

Feature Information for IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel
MIBs
IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
MIBs LinkMIB
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
LinkDescription
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Feature Information for IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
30 OL-30226-03
Page 39

IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
Table 3: Feature Information for IP Sessions over Gigabit EtherChannel
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.9IP Sessions over Gigabit
EtherChannel
The IP sessions over Gigabit
EtherChannel (IPoGEC) feature
enables you to add the Link
Aggregation Control Protocol
(LACP) functionality for IP
sessions.
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.9S, this
feature was implemented on the
Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks.
Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
OL-30226-03 31
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 40

IP Sessions Over Gigabit EtherChannel
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
32 OL-30226-03
Page 41

Multiple-Flow Tunnel
A tunnel facilitates bidirectional transport or acts as a conduit for forwarding subscriber traffic. In PMIPv6,
subscriber traffic is transported between the MAG and the Local Mobility Anchor (LMA) through the Generic
Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnel. In the GTP, subscriber traffic is transported between the iWAG and
the GGSN through the GTP tunnel. The tunnel information structure is associated with each tunnel and
specifies common tunnel attributes, such as source address, destination address, protocol, port, key, tunnel
transport VRF, and tunnel mode.
Finding Feature Information, page 33
•
Information About Multiple-Flow Tunnel, page 33
•
Additional References, page 34
•
Feature Information for Multiple-Flow Tunnel, page 35
•
Finding Feature Information
CHAPTER 3
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About Multiple-Flow Tunnel
Both the GTP and PMIPv6 support multiple flows per tunnel. A multiple-flow tunnel mechanism configures
and manages multiple flows of traffic within the same tunnel. Each flow is identified by a flow key. A flow
identifier or flow key is a 32-bit integer. The key is globally unique per system for the GTP. However, the
key can be unique per tunnel for PMIPv6. The flow key for the GTP is the Tunnel Endpoint Identifier (TEID),
and for PMIPv6, it is the GRE key. Each flow has parameters to describe the per-flow attributes.
PMIPv6 uses a multipoint GRE tunnel per LMA, and creates one adjacency per flow. An LMA can support
scaling numbers up to 128,000 MAG. From the LMA perspective, only one multipoint GRE tunnel interface
is created and 128,000 tunnel endpoints are populated. This scaling level supports the MAG functionality that
OL-30226-03 33
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 42

Additional References
is implemented on access points or hotspots, from which only one or few PMIPv6 subscribers can be attached.
Cisco high-end routing platforms, such as the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Route Processor 2, the Cisco ASR 1000
Series 40-Gbps ESP, and the Cisco ASR 1000 Series 100-Gbps ESP support 128,000 scaling for the LMA.
To support 128,000 scaling, configure the following on the LMA:
ipv6 mobile pmipv6-lma LMA1 domain D1
bce maximum 128000
Additional References
Related Documents
Multiple-Flow Tunnel
Document TitleRelated Topic
Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All ReleasesCisco IOS commands
iWAG commands
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Command Reference
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
LinkDescription
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
34 OL-30226-03
Page 43

Multiple-Flow Tunnel
Feature Information for Multiple-Flow Tunnel
Feature Information for Multiple-Flow Tunnel
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Table 4: Feature Information for Multiple-Flow Tunnel
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.9SMultiple-Flow Tunnel
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks.
Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.9S, this
feature was implemented on the
Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
OL-30226-03 35
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 44

Multiple-Flow Tunnel
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
36 OL-30226-03
Page 45

CHAPTER 4
Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated
Ethernet Over GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a tunneling protocol that encapsulates a wide variety of network
layer protocols inside virtual point-to-point links over a Layer 3 IPv4 or Layer 3 IPv6 access network.
Finding Feature Information, page 37
•
Information About Ethernet Over GRE, page 38
•
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE, page 38
•
Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE, page 39
•
Information About Configuring Ethernet Over GRE, page 39
•
Supported Features, page 44
•
How to Configure the EoGRE Feature, page 45
•
Example: Configuring the EoGRE Feature, page 46
•
Additional References, page 48
•
Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE, page 49
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
OL-30226-03 37
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 46

Information About Ethernet Over GRE
Information About Ethernet Over GRE
Ethernet over GRE (EoGRE) is a new aggregation solution for aggregating WiFi traffic from hotspots. This
solution enables customer premises equipment (CPE) devices to bridge the Ethernet traffic coming from an
end host, and encapsulate the traffic in Ethernet packets over an IP GRE tunnel. When the IP GRE tunnels
are terminated on a service provider broadband network gateway, the end host’s traffic is terminated and
subscriber sessions are initiated for the end host.
The following figure shows the structure of the Ethernet over GRE.
Figure 2: Ethernet Over GRE Structure
Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
The following features are not supported on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers:
IPsec tunnel between the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers and the CPE devices
•
Native multicast coexistence for subscribers
•
Per-CPE QoS
•
IPv6 subscriber
•
The Cisco Intelligent Services Gateway (ISG) RADIUS proxy initiator
•
QinQ tag for the inner L2 frame
•
High Availability is not supported
•
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
38 OL-30226-03
Page 47

Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
Before you configure the Ethernet over GRE feature on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services
Routers, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
A physical interface or dot1Q interface should be configured.
•
The ISG policy should not be applied to the physical interface.
•
Information About Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
The Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers serve as a service provider broadband network
gateway that:
Terminates IPv4 or IPv6 GRE tunnels.
•
Manages the subscriber session for end-host clients.
•
The EoGRE feature works with legacy residential gateways and CPE devices to terminate the Ethernet L2
traffic in the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers. When configured as an intelligent Wireless
Access Gateway (iWAG) with EoGRE access tunneling support, the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation
Services Routers can extend mobility and the ISG services in support of these legacy devices.
OL-30226-03 39
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 48

Information About Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
The following figure shows the structure of the EoGRE feature with PMIP/GTP integrated for mobility service.
Figure 3: Structure of the EoGRE Feature with PMIP/GTP Integrated for Mobility Service
Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
40 OL-30226-03
Page 49

Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
The following figure shows the structure of the EoGRE feature for simple IP service.
Figure 4: Structure of the EoGRE Feature for Simple IP Service
Information About Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
The EoGRE feature supports the following deployments:
EoGRE Deployment with PMIPv6 Integrated for Mobility Service
•
EoGRE Deployment with GTP Integrated for Mobility Service
•
EoGRE Deployment with ISG Integrated for Simple IP Service
•
OL-30226-03 41
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 50

Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
EoGRE Deployment with PMIPv6 Integrated for Mobility Service
EoGRE Deployment with PMIPv6 Integrated for Mobility Service
Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6) provides mobility service to the mobile nodes that are connected to the Mobile
Access Gateway (MAG) via an EoGRE tunnel. The following figure shows the structure of the EoGRE
deployment with PMIPv6 integrated for mobility service.
Figure 5: Structure of the EoGRE Deployment with PMIPv6 Integrated for Mobility Service
Note
Mobile nodes access the mobile internet service over Wi-Fi access points. The access points are either
autonomous access points or are connected to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). These access points
and WLCs are used as residential gateways or CPE devices. CPEs are preconfigured with a point-to-multipoint
GRE IP tunnel to the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers as the MAG. The tunnel from
the CPE device can be configured with a static GRE key. The CPEs are provisioned to forward the Ethernet
traffic from both public and private customers to the GRE tunnel, and to add a VLAN tag on the Ethernet
frame before forwarding the traffic.
As with regular PMIPv6 deployments, the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers can create
IP sessions on EoGRE access tunnels similar to the regular IP sessions on the physical Ethernet interfaces,
and allocate IP addresses for mobile nodes, either locally or in the proxy mode. Mobility service is provided
to the mobile nodes and the tunneled Ethernet traffic is forwarded via IP tunnels to the Local Mobility Anchor
(LMA).
When you ping a mobile node from the MAG with a packet size that is larger than that of the path maximum
transmission unit (PMTU) that is configured with the DF bit set, the packet will be dropped. However,
you will not get the return type as M.M.M (could not fragment). This is reflected in the log messages or
error messages.
For more information about PMIPv6 and the ISG configurations for the iWAG, see the Intelligent Wireless
Gateway Configuration Guide.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
42 OL-30226-03
Page 51

Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
EoGRE Deployment with GTP Integrated for Mobility Service
EoGRE Deployment with GTP Integrated for Mobility Service
GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) provides mobility service to the mobile nodes that are connected to the
iWAG via an EoGRE tunnel, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 6: Structure of the EoGRE Deployment with GTP Integrated for Mobility Service
For more information about the GTP and ISG configurations for the iWAG, see the Intelligent Wireless
Gateway Configuration Guide.
EoGRE Deployment with ISG Integrated for Simple IP Service
The ISG provides simple IP service to mobile nodes that are connected to ISG via the EoGRE tunnel, as
shown in the following figure. The Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers use the ISG
OL-30226-03 43
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 52

Supported Features
Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
framework to allocate IP sessions for authenticated subscribers. Simple IP subscribers are provided ISG
services, including Internet access, but are not provided access to mobility services via GTP or PMIPv6.
Figure 7: Structure of the EoGRE Deployment with ISG Integrated for Simple IP Service
Supported Features
The following features are supported as part of the EoGRE feature on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation
Services Routers:
Ethernet over GRE traffic termination on the routers
•
Frames can have up to one dot1Q VLAN tag
•
L2-connected IPv4 mobile nodes
•
GRE tunnel for IPv4 or IPv6
•
ISG and PMIPv6 or GTP integrated with the EoGRE tunnel
•
ISG initiator-unclassified MAC, DHCP, DNAv4
•
Subscriber roaming
•
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
44 OL-30226-03
Page 53

Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
How to Configure the EoGRE Feature
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
interface interface-name
3.
ip unnumbered loopback interface-name or ip address ip-address
4.
tunnel source interface-type interface-number
5.
(For simple IP mode) mac-address H.H.H
6.
tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv4 or tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv6
7.
(Optional) tunnel vlan vlan-id
8.
end
9.
How to Configure the EoGRE Feature
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Router> enable
Step 2
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
Step 4
interface interface-name
Example:
Router(config)# interface Tunnel 0
ip unnumbered loopback interface-name or ip
address ip-address
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered loopback 0
or
Router(config-if)# ip address 20.1.1.2
255.255.255.0
PurposeCommand or Action
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Specifies the logical interface for the EoGRE tunnel.
For PMIPv6 and GTP scenarios, an unnumbered address or
a specified IP address can be configured on the tunnel
interface.
For a simple IP scenario, only a specified IP address can be
configured on the tunnel interface. This IP address can be used
as a default gateway IP address.
OL-30226-03 45
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 54

Example: Configuring the EoGRE Feature
Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
tunnel source interface-type interface-number
Example:
Router(config-if)# tunnel source Loopback 0
(For simple IP mode) mac-address H.H.H
Example:
Router(config-if)# mac-address 0000.5e00.5213
tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv4 or tunnel mode
ethernet gre ipv6
Example:
Router(config-if)# tunnel mode ethernet gre
ipv4
or
Router(config-if)# tunnel mode ethernet gre
ipv6
(Optional) tunnel vlan vlan-id
Example:
Router(config-if)# tunnel vlan 1000
Sets the source interface for the EoGRE tunnel interface.
Sets the source MAC address for the EoGRE tunnel interface.
The MAC address is mandatory for simple IP deployment.
For PMIPv6/GTP, the default MAC address associated with
EoGRE Tunnel is 0000.5e00.5213.
Sets the EoGRE encapsulation mode for the tunnel interface
for IPv4.
or
Sets the EoGRE encapsulation mode for the tunnel interface
for IPv6.
(Optional) Sets the VLAN ID of the EoGRE tunnel.
Ends the current configuration session.end
Example:
Router(config-if)# end
Example: Configuring the EoGRE Feature
aaa new-model
!
aaa group server radius AAA_SERVER_CAR
server-private 5.3.1.76 auth-port 2145 acct-port 2146 key cisco
!
aaa authentication login default none
aaa authentication login ISG_PROXY_LIST group AAA_SERVER_CAR
aaa authorization network ISG_PROXY_LIST group AAA_SERVER_CAR
aaa authorization subscriber-service default local group AAA_SERVER_CAR
aaa accounting network PROXY_TO_CAR
action-type start-stop
group AAA_SERVER_CAR
!
aaa accounting network ISG_PROXY_LIST start-stop group AAA_SERVER_CAR
!
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
46 OL-30226-03
Page 55

Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
aaa server radius dynamic-author
client 5.3.1.76 server-key cisco
auth-type any
ignore server-key
!
!
ip dhcp excluded-address 172.16.254.254
!
ip dhcp pool ISG_SIMPLE_IP
network 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0
default-router 172.16.254.254
domain-name cisco.com
!
policy-map type control EOGRE_L2_ISG
class type control always event session-start
2 authorize aaa list ISG_PROXY_LIST password cisco identifier mac-address
4 set-timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMER 5
!
class type control always event service-start
1 service-policy type service identifier service-name
2 collect identifier nas-port
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 9.9.9.9 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/0
ip address 192.168.0.9 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/0.778
description "to ASR5K GGSN"
encapsulation dot1Q 778
ip address 172.16.199.9 255.255.255.0
!
interface Tunnel10
description "EoGRE Tunnel for Simple IP subscribers"
mac-address 0000.5e00.5213
ip address 172.16.254.254 255.255.0.0
no ip redirects
tunnel source 172.16.199.9
tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv4
service-policy type control EOGRE_L2_ISG
ip subscriber l2-connected
initiator unclassified mac-address
initiator dhcp
interface Tunnel100
description "IPv4 EoGRE Tunnel for PMIP/GTP subscribers"
ip unnumbered Loopback0
tunnel source GigabitEthernet1/0/0
tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv4
tunnel vlan 100
service-policy type control EOGRE_L2_ISG
ip subscriber l2-connected
initiator unclassified mac-address
initiator dhcp
!
interface Tunnel200
description "IPv6 EoGRE Tunnel for PMIP/GTP subscribers"
ip unnumbered Loopback0
tunnel source 2001:161::9
tunnel mode ethernet gre ipv6
tunnel vlan 200
service-policy type control EOGRE_L2_ISG
ip subscriber l2-connected
initiator unclassified mac-address
initiator dhcp
!
mcsa
enable sessionmgr
!
ipv6 mobile pmipv6-domain D1
replay-protection timestamp window 255
lma LMA_5K
Example: Configuring the EoGRE Feature
OL-30226-03 47
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 56

Additional References
Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
ipv4-address 192.168.199.1
!
ipv6 mobile pmipv6-mag M1 domain D1
sessionmgr
role 3GPP
address ipv4 9.9.9.9
interface Tunnel100
interface Tunnel200
lma LMA_5K D1
ipv4-address 192.168.199.1
encap gre-ipv4
!
ntp master
!
gtp
information-element rat-type wlan
interface local GigabitEthernet1/0/0.778
apn 1
apn-name gtp.com
ip address ggsn 172.16.199.1
fixed link-layer address 00ab.00cd.00ef
default-gw 20.100.254.254 prefix-len 16
dns-server 20.100.254.254
dhcp-server 20.100.254.254
!
end
You can use the following commands to check and show subscriber session information:
show ip dhcp sip statistics
show subscriber statistics
show subscriber session
show ipv6 mobile pmipv6 mag binding
show gtp pdp-context all
show interface tunnel-name
Additional References
Related Documents
iWAG commands
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Document TitleRelated Topic
Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All ReleasesCisco IOS commands
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Command Reference
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
48 OL-30226-03
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
Page 57

Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
LinkDescription
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
OL-30226-03 49
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 58

Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet Over GRE
Table 5: Feature Information for Configuring the Ethernet Over GRE Feature
Service Provider WiFi: Support for Integrated Ethernet Over GRE
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Integrated Ethernet Over
GRE
3.9.1SService Provider WiFi:
This feature enables the
Ethernet over Generic
Routing Encapsulation
(EoGRE) tunnel to be
used as a service provider
WiFi access interface
from CPE devices. A
Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services
Router is used as an L2
aggregator to terminate
L2 traffic at the GRE
tunnel interface and
provide L3 services.
In Cisco IOS XE Release
3.9.1S, this feature is
implemented on the Cisco
ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services
Routers.
The following sections
provide information about
this feature:
Information About
•
Configuring
Ethernet Over
GRE, on page 39
How to Configure
•
the EoGRE
Feature, on page
45
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
50 OL-30226-03
Page 59

CHAPTER 5
GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
Effective from Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S, the support for GPRS Tunneling Protocol Version 2 (GTPv2)
is offered on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers as an enhancement to the GTPv1
offering in the iWAG solution that was introduced in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.8S. GTPv2 provides support
for both the 4G and 3G mobile users, whereas GTPv1 provides support only for 3G mobile users.
Finding Feature Information, page 51
•
Restrictions for GTPv2 of the iWAG, page 51
•
Information About GTPv2 in the iWAG, page 52
•
GTPv2 Configuration, page 52
•
Intra-iWAG Roaming, page 53
•
Additional References, page 54
•
Feature Information for GTPv2 Support in the iWAG, page 55
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for GTPv2 of the iWAG
The same domain name cannot be configured in different APNs, for example:
•
gtp
n3-request 7
interval t3-response 1
interval echo-request 64
information-element rat-type wlan
OL-30226-03 51
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 60

Information About GTPv2 in the iWAG
interface local GigabitEthernet1/3/0
apn 1
different
apn 2356
apn-name example.com #Same domain name as apn1, not supported, should be different
!
The same pool cannot be associated with different APNs. The PGW or GGSN must have different IPs
•
for pools configured on different domains, for example:
gtp
n3-request 7
interval t3-response 1
interval echo-request 64
information-element rat-type wlan
interface local GigabitEthernet1/3/0
apn 1
apn-name example.com
ip address ggsn 98.0.7.13
default-gw 192.168.0.1 prefix-len 16 #different domain name but same pool ip; this
is not supported
dns-server 192.168.255.253
dhcp-lease 3000
apn 2356
apn-name example.com #Same domain name as apn1, not supported, should be different
this is not supported
!
GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
apn-name example.com #Same donamin name as apn2356, not supported, should be
ip address ggsn 98.0.7.13
default-gw 192.168.0.1 prefix-len 16
dns-server 192.168.255.253
dhcp-lease 3000
ip address ggsn 98.0.7.14
default-gw 10.254.0.1 prefix-len 16
dns-server 10.254.255.253
dhcp-lease 3000
ip address ggsn 98.0.7.14
default-gw 192.168.0.1 prefix-len 16 #different domain name but same pool ip;
dns-server 10.254.255.253
dhcp-lease 3000
Information About GTPv2 in the iWAG
A GTP session with GTPv2 support uses more memory than a GTP session with GTPv1 support. GTPv2
support does not require any new AAA attributes. However, the new gtpv2 enum value for the
Cisco-MPC-Protocol-Interface attribute is necessary to specify the use of GTPv2. The AAA server identifies
a subscriber depending upon whether the subscriber profile is sent over GTPv1 tunnel or GTPv2 tunnel from
the iWAG back to the Evolved Packet Core (EPC). The GTPv1 and GTPv2 sessions can exist simultaneously
on the iWAG.
GTPv2 Configuration
All the configurations required for GTPv1 support are also needed for GTPv2 support.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
52 OL-30226-03
Page 61

GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
RADIUS Configuration
The following configurations are required on the RADIUS server to differentiate between a GTPv1 subscriber
and a GTPv2 subscriber:
subscriber-profile profile1 { # this is a GTPv2 profile
access-accept {
reply-msg "Default profile"
cisco-avpair { "cisco-mn-service=ipv4" }
cisco-avpair { "cisco-mpc-protocol-interface=gtpv2" }
cisco-avpair { "cisco-service-selection=example.com" }
cisco-avpair { "cisco-msisdn=4910000000" }
3gpp {
imsi 406091000000000
}
}
}
subscriber-profile profile2 { # this is a GTPv1 profile
access-accept {
reply-msg "Default profile"
cisco-avpair { "cisco-mn-service=ipv4" }
cisco-avpair { "cisco-mpc-protocol-interface=gtpv1" }
cisco-avpair { "cisco-service-selection=example.com" }
cisco-avpair { "cisco-msisdn=4900000000" }
3gpp {
imsi 406090000000000
}
}
}
sub-grp-mgr sub-grp1 {
control-by round-robin
group-profiles {
subscriber-profile profile1 profile-priority 99
subscriber-profile profile2 profile-priority 98
}
}
RADIUS Configuration
Intra-iWAG Roaming
Effective from Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S, both GTPv1 and GTPv2 support connected subscriber roaming
across different access interfaces of the iWAG. GTPv1 and GTPv2 preserve and update their existing sessions
to allow their data traffic to flow through the new ingress interfaces from the access network.
Configuration for the GTPv1 and GTPv2 Roaming Scenario
The initiator unclassified mac-address command must be configured on every iWAG access interface to
support subscriber roaming between these interfaces. As shown in the following configuration, all the access
interfaces must be specified under the GTP configuration before bringing up the IP subscriber sessions. If the
access interface is not specified under the GTP, a subscriber’s roaming option is not enabled for that interface.
Also, adding interfaces under the GTP after the sessions bring up fails subscriber roaming.
The following example shows the configuration for GTPv1 and GTPv2 roaming scenario:
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
description To client facing interface
ip address 192.1.1.1 255.255.0.0
negotiation auto
service-policy type control ISG_GTP_CONTROL
ip subscriber l2-connected
OL-30226-03 53
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 62

Additional References
GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
initiator unclassified mac-address # must for roaming config
initiator dhcp
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3
description To client facing interface
ip address 192.2.1.1 255.255.0.0
negotiation auto
service-policy type control ISG_GTP_CONTROL
ip subscriber l2-connected
initiator unclassified mac-address # must for roaming config
initiator dhcp
!
gtp
n3-request 3
interval t3-response 10
interval echo-request 64
information-element rat-type wlan
interface local GigabitEthernet1/3/0
apn 1200
apn-name example.com
ip address ggsn 98.0.7.13
default-gw 192.168.0.1 prefix-len 16
dns-server 192.168.255.253
dhcp-lease 3000
interface access GigabitEthernet0/0/2
interface access GigabitEthernet0/0/3
Additional References
Related Documents
iWAG commands
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Document TitleRelated Topic
Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All ReleasesCisco IOS commands
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Command Reference
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
54 OL-30226-03
Page 63

GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
LinkDescription
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Feature Information for GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Table 6: Feature Information for GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks.
Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S,
this feature was implemented on
the Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
OL-30226-03 55
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 64

GTPv2 Support in the iWAG
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
56 OL-30226-03
Page 65

CHAPTER 6
iWAG SSO Support for GTP
Effective from Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S, the per-session Stateful Switchover (SSO)/In Service Software
Upgrade (ISSU) feature supports iWAG mobility sessions that are tunneled to MNO using GTP. The SSO
feature takes advantage of Route Processor (RP) redundancy by establishing one of the RPs as the active
processor, while the other RP is designated as the standby processor, and then synchronizing the critical
state information between them. When a failover occurs, the standby device seamlessly takes over, starts
performing traffic-forwarding services, and maintains a dynamic routing table.
Finding Feature Information, page 57
•
Information About iWAG SSO Support for GTP, page 57
•
Enabling SSO Support for the GTP, page 58
•
Additional References, page 59
•
Feature Information for iWAG SSO Support for GTP, page 60
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About iWAG SSO Support for GTP
The SSO/ISSU feature supports only the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers intrachassis
(RP-to-RP) SSO, but not the interchassis (Cisco ASR1K-to-Cisco ASR1K) SSO. The First Sign Of Life
(FSOL) triggers that are supported on SSO include DHCP proxy (where the iWAG acts as the DHCP proxy
server) and DHCP proxy plus unclassified MAC.
For more information about ISSU, see the “Overview of ISSU on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers” section
of the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers Software Configuration Guide.
OL-30226-03 57
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 66

Enabling SSO Support for the GTP
The process as part of iWAG SSO handling GTP checkpoints to the standby RP the information that is
necessary to create a copy of the session on the standby RP. Such an inactive copy of the session becomes
active when the standby RP becomes active.
When an iWAG mobility session with GTP tunneling is enabled using the SSO/ISSU feature, the Cluster
Control Manager on the active RP needs to wait for a few more components, including the GTP, to become
ready before checkpoint data collection, and polls these additional components for checkpoint data during
data collection. A very similar operation is performed on the standby RP as well. Although such additional
CPU consumption is per session, it is not expected to be too heavy since processing in each of these components
should include the time spent on a few data structure lookups and memory-copying operations.
During ISSU SIP and SPA upgrade, there is traffic interruption. To avoid session disconnect because of
dropped echo messages during such traffic interruption, a user has the following options:
Option 1 (preferred):
•
1
Disable the echo messages on the iWAG and GGSN for the duration of the ISSU.
2
Re-enable the echo messages after ISSU is completed on the iWAG and GGSN.
Option 2: Extend the t3 and n3 configurations to exceed the expected traffic interruption. The traffic
•
interruption characterized in the Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S is 127 seconds. Hence, we recommend
the following t3 and n3 settings (t3_response: 1 and n3_request: 7, resulting in 127 seconds on both the
iWAG and GGSN) but the duration of the traffic interruption may depend on the types of SIPs and SPAs
and how loaded the router is. If traffic interruption exceeds the configured t3 and n3 limits, the session
is disconnected.
iWAG SSO Support for GTP
Enabling SSO Support for the GTP
This section describes how to enable SSO support for the GTP on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation
Services Routers.
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
redundancy
3.
mode SSO
4.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Router> enable
PurposeCommand or Action
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enter your password, if prompted.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
58 OL-30226-03
Page 67

iWAG SSO Support for GTP
Additional References
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 2
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
Example:
Router(config)# redundancy
Step 4
Example:
Router(config-redundan)# mode SSO
Additional References
Related Documents
Enters the global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the redundancy configuration mode.redundancy
Configures the SSO redundancy mode of operation.mode SSO
Document TitleRelated Topic
iWAG commands
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All ReleasesCisco IOS commands
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Command Reference
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
OL-30226-03 59
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 68

Feature Information for iWAG SSO Support for GTP
Technical Assistance
iWAG SSO Support for GTP
LinkDescription
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Feature Information for iWAG SSO Support for GTP
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Table 7: Feature Information for iWAG SSO Support for GTP
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10iWAG SSO Support for GTP
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks.
Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S,
this feature was implemented on
the Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
60 OL-30226-03
Page 69

Configuring ISG Policy Templates
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S, the Configuring Intelligent Services Gateway (ISG) Policy Templates
feature optimizes the provisioning of ISG policies on IPv4 and IPv6 subscriber sessions. It enables support
of up to 128,000 IP subscriber sessions with more complex ISG policies at a higher churn rate on the Cisco
ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers.
Finding Feature Information, page 61
•
Restrictions for Configuring ISG Policy Templates, page 61
•
Information About Configuring ISG Policy Templates, page 61
•
Additional References, page 62
•
Feature Information for Configuring ISG Policy Templates, page 63
•
Finding Feature Information
CHAPTER 7
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for Configuring ISG Policy Templates
Enabling policy templates in the ISG is not supported for any type of PPP sessions and IP interface sessions.
Information About Configuring ISG Policy Templates
A typical ISG configuration has very few distinct policies and many sessions that use these policies. ISG
policy templates take advantage of this to optimize resource consumption and enable support for higher scale.
Instead of provisioning an ISG policy with all its individual services and features on each target IP subscriber
OL-30226-03 61
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 70

How to Configure ISG Policy Templates
session, it provisions a template of the policy through the system only once and references the template after
that to apply the policy on each target session. Enabling policy templates in the ISG does not impact session
SSO.
How to Configure ISG Policy Templates
By default, the ISG policy templates are disabled. The platform subscriber template command enables the
ISG policy templates.
Configuring ISG Policy Templates
Note
The platform subscriber template command does not take effect until the router is reloaded. For example,
if this command is entered at the configuration prompt, policy templating remains disabled until the router
is reloaded. Similarly, if templating is enabled, the router has to be reloaded after the no subscriber template
command is entered to disable ISG policy templating.
Additional References
Related Documents
iWAG commands
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Document TitleRelated Topic
Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All ReleasesCisco IOS commands
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Command Reference
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
62 OL-30226-03
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
Page 71

Configuring ISG Policy Templates
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for Configuring ISG Policy Templates
LinkDescription
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Feature Information for Configuring ISG Policy Templates
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Table 8: Feature Information for Configuring ISG Policy Templates
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10Configuring ISG Policy Templates
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks.
Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S,
this feature was implemented on
the Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
OL-30226-03 63
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 72

Configuring ISG Policy Templates
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
64 OL-30226-03
Page 73

CHAPTER 8
Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions
The ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions feature improves the accuracy of reported statistics for the
LNS sessions and traffic classes in the Stop Accounting messages. Because of the distributed nature of the
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers, subscriber statistics are collected periodically every
10 seconds to balance the impact to statistics accuracy, and call setup and teardown rates. Statistics reports
that are generated using this collection are therefore up to 10 seconds old. When the Accounting Accuracy
feature is enabled, the most recent statistics are retrieved for particular subscribers in specific conditions,
such as when a session is torn down or stopped.
Finding Feature Information, page 65
•
Information About Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions, page 65
•
Additional References, page 66
•
Feature Information for Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions, page 67
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS
Sessions
You can enable or disable the ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions feature using the subscriber
accounting accuracy timeout value command.
When the ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions feature is enabled, the LNS sessions that are getting
disconnected are held off until the timeout value configured in the subscriber accounting accuracy timeout
value command is reached. The sessions are torn down when their most recent statistics have been collected,
OL-30226-03 65
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 74

Additional References
or when the timeout period expires, whichever is sooner. The minimum timeout that can be configured is 1
second, and the maximum timeout that can be configured is 10 seconds.
Additional References
Related Documents
Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions
Document TitleRelated Topic
Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All ReleasesCisco IOS commands
iWAG commands
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Command Reference
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
LinkDescription
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
66 OL-30226-03
Page 75

Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions
Feature Information for Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions
Feature Information for Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS
Sessions
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Table 9: Feature Information for Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy
for LNS Sessions
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks.
Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
The ISG Accounting Accuracy for
Sessions feature improves the
accuracy of reported statistics for
L2TP Network Server (LNS)
sessions and traffic classes in the
Stop Accounting messages.
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S,
this feature was implemented on
the Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
OL-30226-03 67
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 76

Cisco ISG Accounting Accuracy for LNS Sessions
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
68 OL-30226-03
Page 77

CHAPTER 9
Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Effective from Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S, the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway (iWAG) supports
dual-stack session for Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6) and GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) sessions.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Finding Feature Information, page 69
•
Information About Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6, page 69
•
Information About Dual-Stack Support for GTP, page 70
•
AAA Attributes for Dual Stack, page 70
•
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack PMIPv6, page 71
•
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack GTP, page 75
•
Additional References, page 76
•
Feature Information for Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP, page 77
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6
The Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 feature allows both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic streams to flow through a single
PMIPv6 session. The IPv4 and IPv6 traffic streams from a subscriber are identified using the Subscriber MAC
address. The iWAG supports following functionalities:
IPv6 L2-connected subscriber sessions
•
OL-30226-03 69
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 78

Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Features Supported for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 Sessions
Dual-stack L2-connected Internet Protocol Over Ethernet (IPoE) subscriber sessions
•
Features Supported for Dual-Stack PMIPv6 Sessions
IPv4 address allocation method using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
•
IPv6 address allocation method using Stateless Address Auto Configuration (SLAAC)
•
Idle timeout for per-user accounting and per-flow accounting
•
Absolute timeout for per-user accounting and per-flow accounting
•
Postpaid for per-user accounting and per-flow accounting
•
QoS policy for per-user accounting and per-flow accounting
•
Information About Dual-Stack Support for GTP
The Dual Stack Support for GTP feature allows both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic streams to flow through a single
GTP session. The IPv4 and IPv6 traffic streams from a subscriber are identified using the Subscriber MAC
address. This feature enables the assignment of both an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address to a client. Therefore,
the overall number of supported subscribers on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers are
not affected by a mix of IPv4 and IPv6 traffic.
Prior to the introduction of the Dual-Stack feature, GTP supported only IPv4 sessions.Note
Dual-Stack GTP sessions support the following session initiators:
Unclassified MAC
•
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
•
DHCPv4
•
Restrictions for Dual-Stack GTP
The connection between the iWAG and GGSN or PGW can only be IPv4 even though the sessions can
•
be IPv4, IPv6, or dual stack.
The DNS server (under the gtp or apn configuration submode) can be configured only for IPv4.
•
AAA Attributes for Dual Stack
After the AAA server authenticates a subscriber, an AAA attribute is returned in the Access Accept message
sent to the iWAG to indicate the session type.
The AAA attribute for the Dual Stack configuration can have the following values:
"cisco-AVPair=mn-service=dual"
•
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
70 OL-30226-03
Page 79

Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
(The iWAG retrieves both the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, but will assign the IPv4 or IPv6 address to the
subscriber based on the FSOL. )
"cisco-AVPair=mn-service=ipv4"
•
(The iWAG retrieves only the IPv4 address for the subscriber. )
"cisco-AVPair=mn-service=ipv6"
•
(The iWAG retrieves only the IPv6 address for the subscriber. )
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
Example: Configuring an Access List Traffic Classmap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
ip access-list extended ACL_OUT_INTERNET
permit ip any any
ip access-list extended ACL_OUT_INTERNET2
permit ip any any
ip access-list extended ACL_OUT_OPENGARDEN
permit ip any any
permit udp any any
ip access-list extended ACL_IN_INTERNET
permit ip any any
ip access-list extended ACL_IN_INTERNET2
permit ip any any
ip access-list extended ACL_IN_OPENGARDEN
permit ip any any
permit udp any any
ipv6 access-list IPV6_ACL_INTERNET
permit ipv6 any any
ipv6 access-list IPV6_ACL_INTERNET2
permit ipv6 any any
ipv6 access-list IPV6_ACL_OPENGARDEN
permit ipv6 any any
Example: Configuring a Classmap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
class-map type traffic match-any TC_OPENGARDEN #defines the traffic rule used in the service
using ACL.
match access-group output name ACL_OUT_OPENGARDEN
match access-group input name ACL_IN_OPENGARDEN
!
class-map type traffic match-any TC_INTERNET2
match access-group output name ACL_OUT_INTERNET2
match access-group input name ACL_IN_INTERNET2
!
class-map type traffic match-any TC_INTERNET
match access-group output name ACL_OUT_INTERNET
match access-group input name ACL_IN_INTERNET
class-map type traffic match-any TC_INTERNET_IPV6
match access-group output name IPV6_ACL_INTERNET
match access-group input name IPV6_ACL_INTERNET
class-map type traffic match-any TC_INTERNET_IPV6_2
match access-group output name IPV6_ACL_INTERNET2
OL-30226-03 71
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 80

Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Example: Configuring a Policymap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
match access-group input name IPV6_ACL_INTERNET2
class-map type traffic match-any TC_OPENGARDEN_IPV6
match access-group output name IPV6_ACL_OPENGARDEN
match access-group input name IPV6_ACL_OPENGARDEN
Example: Configuring a Policymap for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
policy-map type service DRL_V4 #provides service definition for services applied
during session start and restart
20 class type traffic TC_INTERNET
police input 512000 512000 10000
police output 1280000 560000 20000
!
policy-map type service ACC_V4
20 class type traffic TC_INTERNET2
accounting aaa list default
!
policy-map type service TO_V4
20 class type traffic TC_OPENGARDEN
timeout idle 60
!
policy-map type service DRL_V6
20 class type traffic TC_INTERNET_IPV6
police input 512000 512000 10000
police output 1280000 560000 20000
!
policy-map type service ACC_V6
20 class type traffic TC_INTERNET_IPV6_2
accounting aaa list default
!
policy-map type service TO_V6
20 class type traffic TC_OPENGARDEN_IPV6
timeout idle 60
!
Example: Configuring a Control Policy for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
policy-map type control PMIP_DUAL_STACK
class type control always event session-start
10 service-policy type service name DRL_V4 #applying services during dual stack
11 service-policy type service name DRL_V6 #applying services during dual stack
15 service-policy type service name ACC_V4 #applying services during dual stack
16 service-policy type service name ACC_V6 #applying services during dual stack
20 service-policy type service name TO_V4 #applying services during dual stack
21 service-policy type service name TO_V6 #applying services during dual stack
25 service-policy type service name SESSION_TIMEOUT_SERVICE #applying services during
dual stack
30 authorize aaa list default identifier mac-address #performs MAC TAL authorization
class type control always event session-restart
10 service-policy type service name DRL_V4 #applying services during dual
stack
11 service-policy type service name DRL_V6 #applying services during dual
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
72 OL-30226-03
Page 81

Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Example: Configuring an Access Interface for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
stack
15 service-policy type service name ACC_V4 #applying services during dual
stack
16 service-policy type service name ACC_V6 #applying services during dual
stack
20 service-policy type service name TO_V4 #applying services during dual
stack
21 service-policy type service name TO_V6 #applying services during dual
stack
25 service-policy type service name SESSION_TIMEOUT_SERVICE #applying services during
dual stack
30 authorize aaa list default identifier mac-address #performs MAC TAL authorization
Example: Configuring an Access Interface for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
description manthiya connected to MN1
ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
ipv6 address FE80::200:5EFF:FE00:5213 link-local
service-policy type control PMIP_DUAL_STACK #subscriber services are applied based on
ip subscriber l2-connected #invokes iWAG functionality
initiator unclassified mac-address #unclassified MAC address with IPv4 and IPv6
packets,
are treated as FSOL to create a session
initiator dhcp #DHCP control packets are used as FSOL
to create DHCPv4 only session
end
the control policy definition
Example: Configuring the Local Mobility Anchor for Cisco ASR 5000 Routers
context pgw
ip pool PMIP_POOL 70.70.0.1 255.255.0.0 public 0 subscriber-gw-address 70.70.70.1
ip pool v4_staticpool 9.9.9.1 255.255.0.0 static
ipv6 pool v6_pool prefix eeee::1/48 public 0 policy allow-static-allocation
router rip
network ip 70.70.0.0/16
network name lma2
redistribute connected
version 2
exit
interface lma2
ipv6 address aaaa:bbbb::2/64
ip address 60.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 secondary
exit
subscriber default
exit
apn cisco.com
pdp-type ipv4 ipv6 #enables dual-stack address assignment under ASR 5K LMA
selection-mode sent-by-ms
accounting-mode none
ip context-name pgw
exit
aaa group default
exit
gtpp group default
exit
lma-service lma2
no aaa accounting
reg-lifetime 40000
timestamp-replay-protection tolerance 0
mobility-option-type-value standard
revocation enable
OL-30226-03 73
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 82

Example: Configuring Mobile Access Gateways for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
bind address aaaa:bbbb::2
exit
pgw-service pgw1
plmn id mcc 100 mnc 200
associate lma-service lma2
exit
ipv6 route 2002::/64 next-hop aaaa:bbbb::1 interface lma2
ip igmp profile default
exit
exit
port ethernet 17/1
boxertap eth4
no shutdown
bind interface lma2 pgw
exit
port ethernet 17/3
vlan 200
no shutdown
exit
exit
port ethernet 17/4
no shutdown
exit
end
Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Example: Configuring Mobile Access Gateways for Dual-Stack PMIPv6
ipv6 mobile pmipv6-domain D1 #domain with name D1 configuration
replay-protection timestamp window 255
mn-profile-load-aaa #subscriber service profile downloaded from AAA
server
lma lma1 #associating LMA with name lma1 to domain D1
ipv6-address 2003::4
ipv4-address 16.1.1.2
mag M1 #associating MAG with name M1 to domain D1
ipv6-address 2002::4
ipv4-address 15.1.1.1
nai MN1@example.com #local subscriber NAI definition for authotrization,
where service for this particular NAI is defined
apn example.com
lma lma1
service dual #dual stack is enabled for MN1@example.com client
int att ETHERNET l2-addr 0000.1111.2222
!
ipv6 mobile pmipv6-mag M1 domain D1
no discover-mn-detach
sessionmgr
apn example.com
address ipv6 2002::4
address ipv4 15.1.1.2
binding maximum 40000
replay-protection timestamp window 255
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
enable pmipv6 default MN1@example.com
lma lma1 D1
ipv6-address 2003::4
ipv4-address 16.1.1.2
encap gre-ipv4
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
74 OL-30226-03
Page 83

Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack GTP
Configuration Examples for Dual-Stack GTP
Example: Configuring Dual-Stack Sessions for GTP
gtp
information-element rat-type wlan
interface local GigabitEthernet0/1/3
apn 1
apn-name example1.com
ip address ggsn 10.201.31.2
default-gw 30.1.0.1 prefix-len 16
dns-server 192.165.1.1
dhcp-lease 1801
apn 2
apn-name example2.com
ip address ggsn 10.201.31.4
default-gw 30.2.0.1 prefix-len 16
dns-server 192.165.1.1
dhcp-lease 1801
Example: Configuring an Interface to PGW or GGSN
interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3
description SGSN to GGSN port
ip address 10.201.31.1 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
ipv6 address 2007::2/64
end
Example: Configuring a Control Policy for Dual-Stack GTP
policy-map type control BB_PMAP
class type control always event session-start
10 authorize aaa list BB_1 password cisco identifier mac-address
Example: Configuring an Access Interface for Dual-Stack GTP
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3
ip address 21.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
ipv6 address 8001::1/16
ipv6 enable
ipv6 nd ra interval 600
service-policy type control BB_PMAP
ip subscriber l2-connected
initiator unclassified mac-address
initiator dhcp
end
OL-30226-03 75
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 84

Enabling IPv6 Routing
Enabling IPv6 Routing
ipv6 unicast-routing
Additional References
Related Documents
Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Document TitleRelated Topic
Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All ReleasesCisco IOS commands
iWAG commands
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Command Reference
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
LinkDescription
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
76 OL-30226-03
Page 85

Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Feature Information for Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Feature Information for Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Table 10: Feature Information for Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11Dual-Stack Support for PMIPv6
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11Dual-Stack Support for GTP
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks.
Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
The Dual-Stack Support for
PMIPv6 feature allows both IPv4
and IPv6 traffic streams to flow
through a single PMIPv6 session.
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S,
this feature was implemented on
the Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
The Dual-Stack Support for GTP
feature allows both IPv4 and IPv6
traffic streams to flow through a
single GTP session.
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S,
this feature was implemented on
the Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers.
OL-30226-03 77
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 86

Dual Stack Support for PMIPv6 and GTP
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
78 OL-30226-03
Page 87

CHAPTER 10
Flow-Based Redirect
The traffic from an IP session is redirected based on the destination address (for a simple IP session), and
to a tunnel (for a mobile IP session). However, in some application scenarios, some of the traffic is routed
to a specific system or a specific interface for additional service or processing. Through the Adult Content
Filtering (ACF) capability, web traffic of some sessions can be routed to an ACF appliance that filters the
traffic based on the URL or content. The Flow-Based Redirect (FBR) feature enables applications such as
the ACF to route matching traffic to a specified next hop device.
The FBR feature is Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF)-aware. You can map an interface to a VRF or
transfer a VRF as long as the session and the interface connecting the next hop device are within the same
VRF network.
Finding Feature Information, page 79
•
Flow-Based Redirect for Adult Content Filtering, page 80
•
Flow-Based Redirect for Selective IP Traffic Offload, page 81
•
Activating and Deactivating the Flow-Based Redirect Feature Through Vendor-Specific Attributes,
•
page 82
Configuring Flow-Based Redirect for a Traffic Class Service, page 82
•
Examples, page 85
•
Best Practices for Configuring the NAT on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers, page 87
•
NAT Overloading and Port Parity, page 88
•
NAT Interface Overloading with VRF, page 88
•
Additional References, page 89
•
Feature Information for Flow-Based Redirect, page 89
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
OL-30226-03 79
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 88

Flow-Based Redirect for Adult Content Filtering
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Flow-Based Redirect for Adult Content Filtering
In a typical WiFi hotspot deployment, all subscriber traffic goes through Cisco ISG (Intelligent Service
Gateway) after successful authentication. For unauthenticated traffic, L4R feature offers a logic to redirect
traffic based on a pre-defined access-list (ACL). This L4R feature acts as a way to redirect some traffic to a
web portal or opengarden environment using a translation logic. In order to implement a similar redirection
logic after successful authentication without the need for translating the traffic, the flow based redirect has
been implemented in ISG to allow traffic to be redirected/rerouted. A typical use case is Adult Content Filtering
(ACF) where web traffic needs to be redirected to a Web Filtering Appliance.
You can apply the ACF policy to subscriber traffic in the following ways:
If the Wi-Fi hotspot provider allows individual subscribers to opt out of the ACF, the ACF policy is not
•
applied on their personal profile. For those subscribers who do not opt out of the ACF, the ACF policy
is applied on their personal profile through the RADIUS vendor-specific attribute (VSA) when they log
in to their account. For more information about RADIUS VSA attributes, see Activating and Deactivating
the Flow-Based Redirect Feature Through Vendor-Specific Attributes .
Flow-Based Redirect
If the Wi-Fi hotspot provider enforces ACF on all the subscribers accessing the internet from their site,
•
the ACF policy is configured in the local policy of the Cisco ISG.
The following figure shows a typical scenario where ACF is applied on Wi-Fi hotspots.
Figure 8: Adult Content Filtering on Wi-Fi Hotspots
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
80 OL-30226-03
Page 89

Flow-Based Redirect
Flow-Based Redirect for Selective IP Traffic Offload
Flow-Based Redirect for Selective IP Traffic Offload
Mobile IP sessions are provisioned with a traffic class service in the Cisco Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
(iWAG) for routing web traffic to a next hop device, depending on the local policies or the policies that are
downloaded from the Cisco IOS authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) network security services.
The traffic class service can be configured for routing traffic to the next hop along with the other supported
features such as policing and Dynamic Rate Limit (DRL) accounting. You can configure multiple TC services
with different next hop addresses with the Flow-Based Redirect feature. However, only 16 traffic class services
can be applied to a session.
Network Address Translation (NAT) with Selective IP Traffic Offload (SIPTO) is required only for IPv4 and
Dual Stack IPv4 traffic sessions. NAT is enabled at the outgoing interface level so NAT does not need to be
IPoE session aware when used with Flow Based Redirect for Selective IP Traffic Offload.
Note
In existing deployment, a NAT or Carrier Grade Network Address Translation (CGN) device may exist
upstream of the Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway (iWAG) device. In such a scenario, it is possible to
keep the architecture in place without enabling NAT on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services
Router acting as iWAG, if and only if, there is a simple way for the return traffic to go from the NAT or
CGN device back to the iWAG. This needs to be verified prior to deployment to guarantee return paths.
The following figure shows a typical deployment scenario where internet traffic is offloaded from the access
network, and is routed directly through the nearest IP gateway.
Figure 9: Flow-Based Redirect for Selective IP Traffic Offload
OL-30226-03 81
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 90

Flow-Based Redirect
Activating and Deactivating the Flow-Based Redirect Feature Through Vendor-Specific Attributes
Activating and Deactivating the Flow-Based Redirect Feature
Through Vendor-Specific Attributes
You can provision or activate a traffic class service with the Flow-Based Redirect feature by adding the
following vendor-specific attribute (VSA) in the user profile of the RADIUS server:
vsa cisco 250 ACF_SERVICE
You can activate a traffic class service with the Flow-Based Redirect feature for an established session through
the RADIUS Change of Authorization (CoA) feature, using the following VSAs:
vsa cisco 250 S<sessionID>
vsa cisco generic 1 string "subscriber:command=activate-service"
vsa cisco generic 1 string "subscriber:service-name=ACF_SERVICE”
You can deactivate a traffic class service with the Flow-Based Redirect feature for an established session
through the RADIUS CoA feature, using the following VSAs:
vsa cisco 250 S<sessionID>
vsa cisco generic 1 string "subscriber:command=deactivate-service"
vsa cisco generic 1 string "subscriber:service-name=ACF_SERVICE”
Configuring Flow-Based Redirect for a Traffic Class Service
The following steps show how to configure the Flow-Based Redirect feature for a traffic class service.
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
ip access-list extended traffic class
3.
permit tcp source_IP destination_IP eq port
4.
class-map type traffic match-any traffic class map
5.
match access-group input name traffic class
6.
policy-map type service policy-map name
7.
class type traffic traffic class map
8.
reroute to next-hop ip IP address
9.
policy-map type control policy-map name
10.
class type control always event account-logon
11.
20 service-policy type service name service-policy name
12.
class type control always event service-stop
13.
1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-name
14.
class type control always event service-start
15.
10 service-policy type service identifier service-name
16.
class type control always event account-logoff
17.
10 service disconnect delay 5
18.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
82 OL-30226-03
Page 91

Flow-Based Redirect
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Flow-Based Redirect for a Traffic Class Service
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
enable
Example:
Router> enable
Example:
Router# configure terminal
ip access-list extended traffic class
Example:
Router (config)# ip access-list extended WEB_ACL_IN
permit tcp source_IP destination_IP eq port
Example:
Router (config-ext-nacl)# permit tcp any any eq www
class-map type traffic match-any traffic class map
Example:
Router (config)# class-map type traffic match-any
ACF_ACL
match access-group input name traffic class
Example:
Router (config-traffic-classmap)# match access-group
input name WEB_ACL_IN
policy-map type service policy-map name
Example:
Router (config)# policy-map type service ACF_SERVICE
class type traffic traffic class map
Example:
Router (config-service-policymap)# class type traffic
ACF_ACL
reroute to next-hop ip IP address
Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your
password if prompted.
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Defines the traffic class WEB_ACL_IN
Permits TCP traffic with destination port values
that match WWW (port 80).
Creates the traffic class map ACF_ACL.
Configures the match criteria for the ACF_ACL
traffic class map on the basis of the specified host
traffic class.
Creates the ACF_SERVICE policy map, which
is used to define an ISG service.
Associates the ACF_ACL traffic class map with
the service policy map.
Redirects traffic to the specified IP address.
Example:
Router (config-service-policymap-class-traffic)# reroute
to next-hop ip 44.0.0.22
OL-30226-03 83
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 92

Configuring Flow-Based Redirect for a Traffic Class Service
Flow-Based Redirect
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
Step 13
Step 14
Step 15
Step 16
Step 17
Step 18
policy-map type control policy-map name
Example:
Router (config)# policy-map type control
INTERNET_SERVICE_RULE
class type control always event account-logon
Example:
Router (config-control-policymap)# class type control
always event account-logon
20 service-policy type service name service-policy name
Example:
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# 20
service-policy type service name ACF_SERVICE
Example:
Router (config-control-policymap)# class type control
always event service-stop
1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-name
Example:
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# 1
service-policy type service unapply identifier
service-name
class type control always event service-start
Example:
Router (config-control-policymap)# class type control
always event service-start
10 service-policy type service identifier service-name
Example:
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# 10
service-policy type service identifier service-name
class type control always event account-logoff
Example:
Router (config-control-policymap)# class type control
always event account-logoff
10 service disconnect delay 5
Example:
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# 10
service disconnect delay 5
Creates the INTERNET_SERVICE_RULE
policy map, which is used to define a control
policy.
Specifies a control class for an account-logon
event.
Applies the ACF_SERVICE policy.
Specifies a control class for a service-stop event.class type control always event service-stop
Specifies the service name that is currently
associated with the user.
Specifies a control class for the service-start
event.
Applies the defined service upon a service-start
event.
Specifies a control class for an account-logoff
event.
Disconnects upon an account-logoff event, after
a 5 second delay.
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
84 OL-30226-03
Page 93

Flow-Based Redirect
Examples
Examples
Configuring Flow-Based Redirect for a Traffic Class Service
The following sample output shows how a traffic class service with the Flow-Based Redirect feature is
configured to redirect all HTTP traffic to a different next hop device upon logging in to the account:
Router# configure terminal
Router (config)# ip access-list extended WEB_ACL_IN
Router (config-ext-nacl)# permit tcp any any eq www
Router (config-ext-nacl)# permit tcp any any eq www
Router (config-ext-nacl)# class-map type traffic match-any ACF_ACL
Router (config-traffic-classmap)# match access-group input name WEB_ACL_IN
Router (config-traffic-classmap)# policy-map type service ACF_SERVICE
Router (config-service-policymap)# class type traffic ACF_ACL
Router (config-service-policymap-class-traffic)# reroute to next-hop ip 44.0.0.22
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# policy-map type control INTERNET_SERVICE_RULE
Router (config-control-policymap)# class type control always event account-logon
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# 20 service-policy type service name
ACF_SERVICE
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# class type control always event service-stop
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# 1 service-policy type service unapply
identifier service-name
Router (config-control-policymap)# class type control always event service-start
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# 10 service-policy type service identifier
service-name
Router (config-control-policymap)# class type control always event account-logoff
Router (config-control-policymap-class-control)# 10 service disconnect delay 5
Viewing the FBR Policy that is Attached to a Session
To view the FBR policy that is attached to a session at session start, use the show subscriber session uid uid
command:
Router# show subscriber session uid 249
Type: IPv4, UID: 249, State: authen, Identity: 33.0.0.4
IPv4 Address: 33.0.0.4
Session Up-time: 00:01:43, Last Changed: 00:01:43
Switch-ID: 16972
Policy information:
Authentication status: authen
Active services associated with session:
name "ACF_SERVICE", applied before account logon
Rules, actions and conditions executed:
subscriber rule-map INTERNET_SERVICE_RULE
condition always event session-start
80 authorize identifier source-ip-address
subscriber rule-map default-internal-rule
condition always event service-start
1 service-policy type service identifier service-name
Classifiers:
Class-id Dir Packets Bytes Pri. Definition
0 In 499 31936 0 Match Any
1 Out 0 0 0 Match Any
56 In 499 31936 0 Match ACL WEB_ACL_IN
57 Out 0 0 0 Match ACL WEB_ACL_OUT
Template Id : 1
Features:
Absolute Timeout:
Class-id Timeout Value Time Remaining Source
0 3000 00:48:16 Peruser
OL-30226-03 85
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 94

Examples
Flow-Based Redirect
Forced Flow Routing:
Class-id FFR Tunnel Details Source
56
Next-hop IP: 44.0.0.2
ACF_SERVICE
Configuration Sources:
Type Active Time AAA Service ID Name
SVC 00:01:43 - ACF_SERVICE
USR 00:01:43 - Peruser
INT 00:01:43 - GigabitEthernet0/0/4
Verifying the Packet Count Status
To verify whether the packet count on the interface that is connected to the next hop device is increasing, use
the show interface interface connected to the next hop device command:
Router(config)# show interface GigabitEthernet0/0/5
GigabitEthernet0/0/5 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is SPA-8X1GE-V2, address is 0021.d81a.d305 (bia 0021.d81a.d305)
Description: IXIA_Client_Facing
Internet address is 44.0.0.1/24
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive not supported
Full Duplex, 1000Mbps, link type is auto, media type is SX
output flow-control is on, input flow-control is on
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:05:03, output 00:05:03, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:06:48
Input queue: 0/375/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 12000 bits/sec, 20 packets/sec
7 packets input, 690 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 2 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 0 multicast, 0 pause input
4897 packets output, 382284 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Viewing Statistics of Dropped Packets
To display the statistics of all the dropped packets on the Embedded Services Processor (ESP), use the show
platform hardware qfp active statistics drop command.
Note
As per FBR behavior, the ISG drops packets if next hop is unreachable. The show platform hardware
qfp active statistics drop command output shows counters for the dropped packets.
Router# Show platform hardware qfp active statistics drop
------------------------------------------------------------------------Global Drop Stats Packets Octets
------------------------------------------------------------------------Disabled 13 1166
essipsubfsoldrop 2327 216495
UnconfiguredIpv6Fia 90 9492
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
86 OL-30226-03
Page 95

Flow-Based Redirect
Best Practices for Configuring the NAT on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers
Configuring NAT Access Interface for Ingress Traffic
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/4
ip address 36.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
negotiation auto
ipv6 address FE80::200:5EFF:FE00:5213 link-local
service-policy type control PREMS
ip subscriber l2-connected
initiator unclassified mac-address
initiator dhcp
!
Configuring NAT Network Interface for Egress Traffic
interface GigabitEthernet1/2/4
description IXIA_port_for_offload
ip address 44.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat outside
load-interval 30
negotiation auto
ipv6 address 44::1/60
!
Enabling Carrier Grade NAT
ip nat settings mode cgn
no ip nat settings support mapping outside
ip nat pool natpool 55.0.0.3 55.0.255.250 netmask 255.255.0.0
ip nat inside source list 100 pool natpool overload
Best Practices for Configuring the NAT on the Cisco ASR 1000
Series Routers
The following are the recommended best practices to configure the NAT on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series
Aggregation Services Routers:
Restriction on the total QFP DRAM usage
•
At 97 percent DRAM utilization, depletion messages are displayed in the syslog as a warning message
to make the operator aware of low QFP DRAM availability. We recommend that you configure QFP
DRAM CAC in the system to avoid any unexpected behavior. The Call Admission Control (CAC)
functionality ensures that new subscriber sessions cannot be established when QFP DRAM utilization
exceeds the configured threshold.
The configuration example below demonstrates configuration of a QFP DRAM threshold set to 95
percent:
platform subscriber cac mem qfp 95.
Set the maximum limit for total number of NAT translations:
•
ESP40: ip nat translation max-entries 1000000
◦
ESP100: ip nat translation max-entries 4000000
◦
OL-30226-03 87
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 96

NAT Overloading and Port Parity
The ip nat translation max-entries all-host command can be used in scenarios where the Cisco ASR
•
1000 Series Router acting as ISG, performs NAT on all or most of the subscriber traffic. This helps the
operator to prevent a single host from occupying the entire translation table, while allowing a reasonable
upper limit to each host.
The maximum number of translations per host can be configured using either of these ways:
•
Ensure that you keep the translations timeout low, around 2 minutes for TCP, and 1 minute for UDP
•
translations:
Flow-Based Redirect
Configuring the same number of maximum translation entries for all the subscribers using the
◦
following command:
ip nat translation max-entries all-host maximum number of NAT entries for each host
Configuring the maximum translation entries for a given subscriber using the following command:
◦
ip nat translation max-entries host ip-address [per-host NAT entry limit]
ip nat translation timeout 120
◦
ip nat translation tcp-timeout 120
◦
ip nat translation udp-timeout 60
◦
NAT Overloading and Port Parity
You can preserve the addresses in the global address pool by allowing a device to use one global address for
many local addresses. This type of NAT configuration is called overloading.
When an Interface IP is overloaded for the translations and a single IP address is used for all the expected
translations, a maximum of 60,000 translations can be achieved with this configuration depending on the
traffic ports and the port parity involved. You can use the NAT Pool Overload configuration to achieve
maximum translations.
There is a concept of port parity (even/odd) in NAT and NAT64. If a source port is in the port range of 0 to
1023, it is translated between ports 512 to 1023. If a source port range is more than 1023, it takes ports from
1024 onwards.
NAT Interface Overloading with VRF
The NAT Interface Overloading with VRF scenario assumes that the service provider is only interested in
performing application-specific NAT, for example, the service provider perform NAT only on the DNS
requests from clients and the rest of the traffic will proceed as it is. Therefore, we can use Interface Overloading
instead of a pool. With this, we can have a maximum of 60000 translations per interface, which is deemed
good for the application-specific NAT. Also, the IP sessions and NAT are in a VRF (named
PROVIDER_WIFI_01, in the example below).
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
88 OL-30226-03
Page 97

Flow-Based Redirect
Additional References
Related Documents
Additional References
Document TitleRelated Topic
Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All ReleasesCisco IOS commands
iWAG commands
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this
feature.
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
Cisco IOS Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway
Command Reference
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco
MIB Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
LinkDescription
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Feature Information for Flow-Based Redirect
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This
table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release
train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
OL-30226-03 89
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 98

Flow-Based Redirect
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Table 11: Feature Information for Flow-Based Redirect
Feature InformationReleasesFeature Name
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11Flow-Based Redirect
Flow-Based Redirect (FBR) feature
enables Adult Content Filtering
(ACF) to route matching traffic to
a specified next hop device.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.12Flow-Based Redirect for Selective
IP Traffic Offload
Flow-Based Redirect (FBR) feature
enables Selective IP Traffic
Offload (SIPTO) to route matching
traffic to a specified next hop
device.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and
other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks.
Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
90 OL-30226-03
Page 99

Call Flows for Simple IP Users
This chapter provides various call flows for simple IP users.
Finding Feature Information, page 91
•
Simple IP Unclassified MAC Authentication (MAC TAL and Web Login) Call Flows, page 91
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and
feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To
find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each
feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
CHAPTER 11
Simple IP Unclassified MAC Authentication (MAC TAL and Web
Login) Call Flows
The MAC Transparent Auto Login (TAL) authentication method is associated with the web authentication
method and is prevalent in public access control as used in public wireless LAN (PWLAN) applications or
in limited usage as in broadband residential access. Here, many sessions are aggregated on a single VLAN
or interface at the broadband remote access server (BRAS), and individual sessions are identified based on
the source MAC address for the Layer 2 access subscriber.
MAC TAL enables the iWAG to authorize a subscriber on the basis of the subscriber’s source MAC address.
After authentication, the iWAG applies the auto-login services on the session and the subscriber will be able
to access the service. If the initial authorization based on the MAC address fails, then the iWAG subscriber
is redirected to the ISP’s web portal, where the subscriber enters the ISP-assigned credentials (username and
password) to complete the authentication in order to avail the ISP’s services. The iWAG then applies the
services that the subscriber selected from the portal, and provides the subscriber full access to those services.
This use case covers the following:
iWAG session creation
•
OL-30226-03 91
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
Page 100

Simple IP Unclassified MAC Authentication (MAC TAL and Web Login) Call Flows
User authorization based on MAC address
•
Default service activation (Internet)
•
Auto-login service activation and access
•
User redirection to the portal (on user authorization failure only)
•
User authentication at the RADIUS server
•
Profile download and auto-login service activation
•
Access to features such as change of authorization (CoA), account logout, account stop, account ping
•
Call Flows for Simple IP Users
Intelligent Wireless Access Gateway Configuration Guide
92 OL-30226-03
 Loading...
Loading...