Page 1

Cisco IW3702 Access Point Getting Started Guide
Cisco IW3702 Access Point Getting Started Guide 2
Organization 2
Conventions 2
Overview 3
Installation 13
Antennas and RF Accessories 23
Configuration 41
Technical Specifications 65
Ports and Connectors 75
Related Documentation 78
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request 78
Page 2
Revised: January 22, 2020
Cisco IW3702 Access Point Getting Started Guide
This guide documents the hardware features of the Cisco IW3702 access point. It describes the physical and performance characteristics
of each access point, and explains how to install and configure an access point.
This publication is for the network technicians who install and configure access points. You must be familiar with network structures,
terms, and concepts.
The Cisco IW3702 access point is referred to as access point in this document.
Organization
This guide includes the following sections:
DescriptionSection
Describes text conventions used in this document.Conventions, on page 2
Describes the major components and features of the access point.Overview, on page 3
Installation, on page 13
Antennas and RF Accessories, on page 23
Provides warnings, safety information, and installation information you need to install
your access point.
Provides information about the antennas used by the access point and the antenna
configurations deployed.
Describes the steps to configure the access point.Configuration, on page 41
Lists technical specifications for the access point.Technical Specifications, on page 65
Describes the port and connector pinouts for the access point.Ports and Connectors, on page 75
Conventions
This document uses the following conventions.
IndicationConvention
Commands and keywords and user-entered text appear in bold font.bold font
Document titles, new or emphasized terms, and arguments for which you supply values are in italic font.italic font
Elements in square brackets are optional.[ ]
Required alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars.{x | y | z }
string
2
Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by vertical bars.[ x | y | z ]
A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string or the string will include the quotation
marks.
Page 3

IndicationConvention
Terminal sessions and information the system displays appear in courier font.courier font
Nonprinting characters such as passwords are in angle brackets.< >
Default responses to system prompts are in square brackets.[ ]
An exclamation point (!) or a pound sign (#) at the beginning of a line of code indicates a comment line.!, #
Note
Means reader take note . Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the manual.
Caution
Danger
Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might perform an action that could result in equipment damage or loss
of data.
IMPORTANTSAFETY INSTRUCTIONSMeans danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury.Before
you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involvedwith electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard
practicesforpreventingaccidents. Use the statementnumber provided at the endof each warningtolocate its translation
in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device.SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Overview
This document describes the Cisco IW3702 access point. The access point is an IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac compliant, dual-band WiFi
access point with external antennas.
The access point is IP67 rated, ruggedized, and certified for on-board rail and outdoor use-cases such as train and trackside, mining,
intelligent transportation systems, and smart city applications. You can mount the access point on a DIN rail in an industrial enclosure.
Its components are designed to withstand extremes in temperature, vibration, and shock common in industrial environments.
The access point features:
• IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n compliant operation
• IEEE 802.11ac Wave 1 support
• Dual-radio design for 2.4 GHz and/or 5 GHz bands
• 4x4 multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology with three spatial streams
• Cisco CleanAir support for 20, 40, and 80 MHz channels
• DC input port (M12 connector)
• 2 Power over Ethernet (PoE) ports with M12 X-code connectors:
• 1 x PoE-IN Gigabit Ethernet port compliant with IEEE 802.3at POE+ PD
• 1 x PoE-OUT Gigabit Ethernet port compliant with IEEE 802.3af POE PSE
3
Page 4

• RS232 console port with cover (RJ-45 connector)
• 4 antenna ports (N connector-female)
• Rugged IP67 rated housing and -40 to 167°F (-40 to 75°C) operating temperature range (ambient—without solar loading or
wind cooling)
• Compact size for space constrained environments
Access Point Models
There are two access point models, based on antenna configuration. The following table lists the available IW3702 models.
Table 1: Access Point Models
DescriptionModel
Cisco IW3700 Series Access Points with Regulatory Domain Code
IW3702-2E-x-K9
Access point with four antenna connectors: 2 on the top and 2 on the bottom.
1
Access point with four antenna connectors on top side.IW3702-4E-x-K9
Cisco IW3700 Series Universal Access Points
IW3702-2E-UXK9
Access point with four antenna connectors: 2 on the top and 2 on the bottom.
Access point with four antenna connectors on top side.IW3702-4E-UXK9
1
Regulatory Domains: (x=regulatory domains)Domain codes available for the IW3700 Series are x=A, B, D, E, F, M, R, Q, S,
and Z. Other regulatory domains are supported by the universal access points. Customers are responsible for verifying approval
for use in their individual countries. To verify approval and to identify the regulatory domain that corresponds to a particular
country, visit https://www.cisco.com/go/aironet/compliance.
4
Page 5
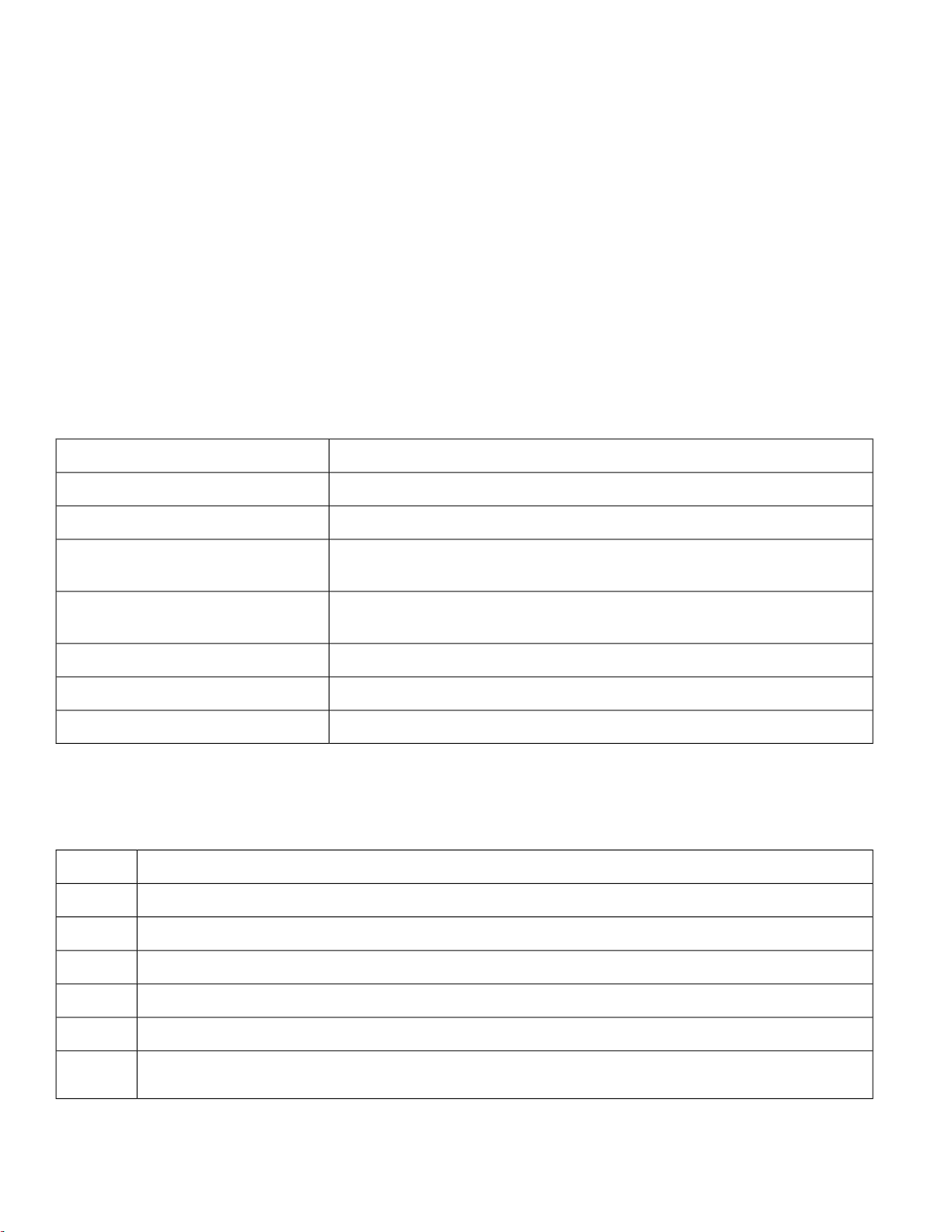
Bottom and Top Panel Views
Figure 1: Cisco IW3702-2E-UXK9/IW3702-2E-x-K9 Bottom Panel View
Protective vent port / Reset button (covered)5
Note
Power (PWR) connector6Status LED1
Console (CON) port7Antenna port B2
Antenna port A8PoE OUT port3
Ground connection9PoE IN port4
There are four antenna ports on the Cisco IW3702-2E-UXK9/IW3702-2E-x-K9 model: two on the top and two on the bottom.
5
Page 6
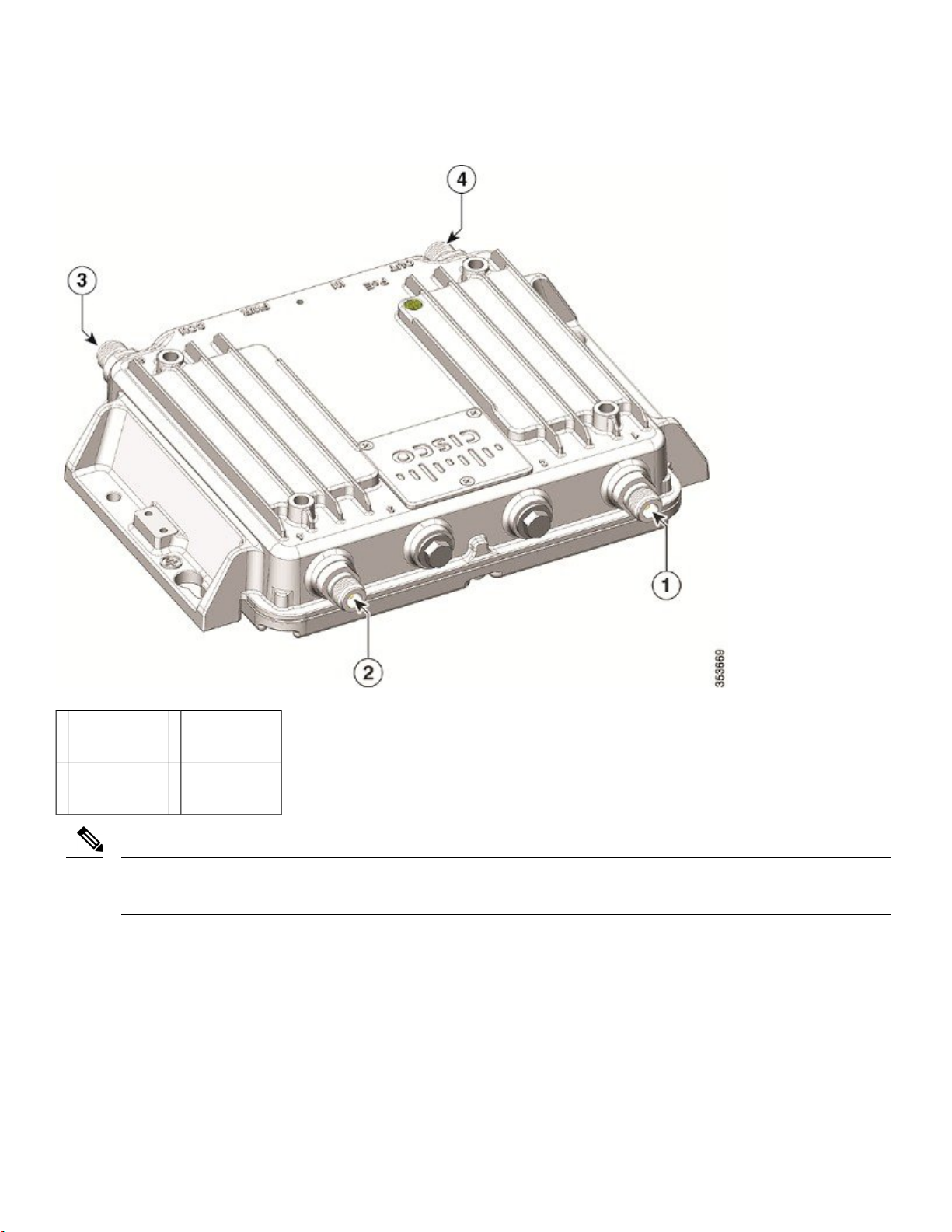
Figure 2: Cisco IW3702-2E-UXK9/IW3702-2E-x-K9 Top Panel View
1
2
C
D
Note
Antenna port
3Antenna port
A
Antenna port
4Antenna port
B
There are four antenna ports on the Cisco IW3702-4E-UXK9/IW3702-4E-x-K9 model: all four connectors are on the top
side.
6
Page 7
Figure 3: Cisco IW3702-4E-UXK9/IW3702-4E-x-K9 Bottom Panel View
Power (PWR) connector5Status LED1
Console (CON) port6PoE OUT port2
Ground connection7PoE IN port3
Protective vent port / Reset button (covered)4
7
Page 8
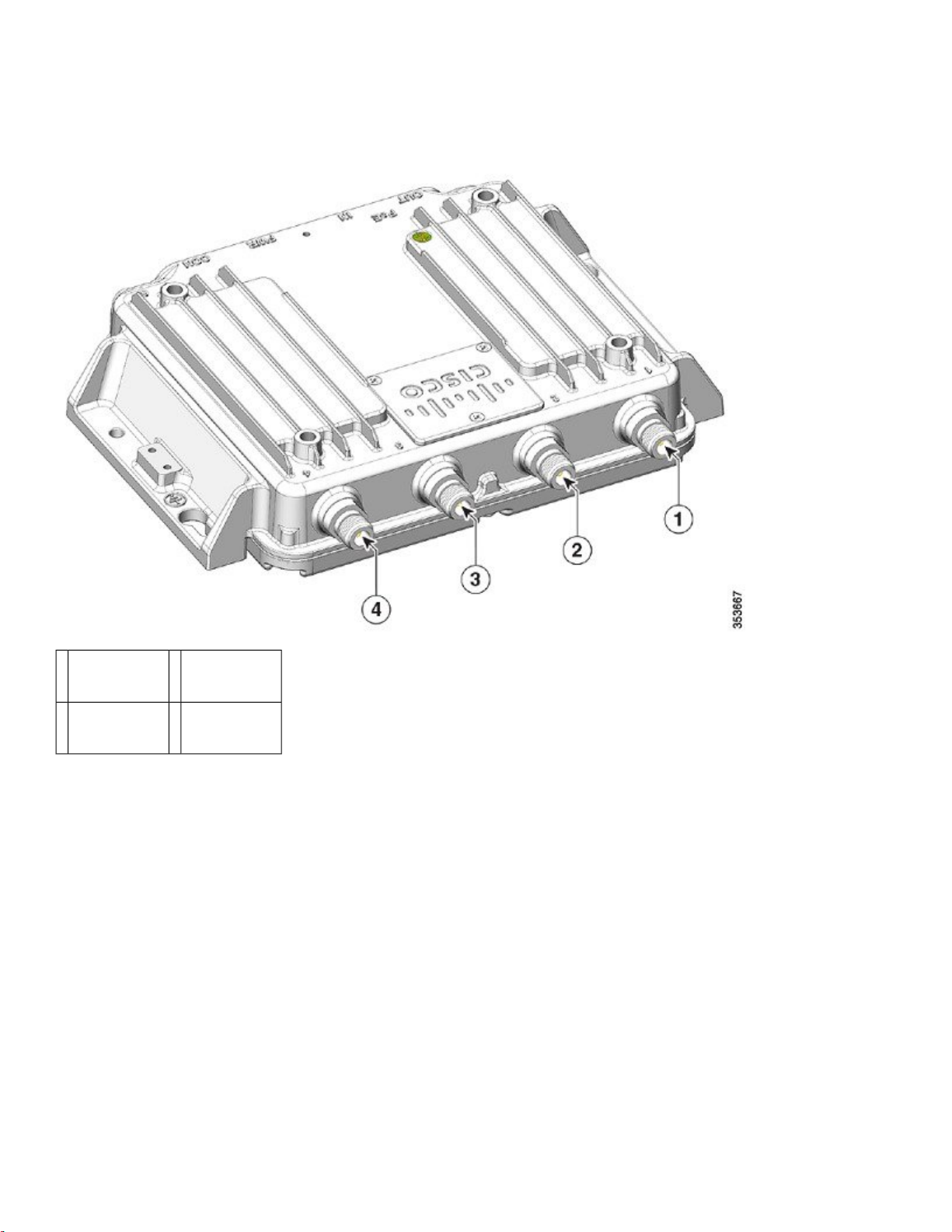
Figure 4: Cisco IW3702-4E-UXK9/IW3702-4E-x-K9 Top Panel View
Antenna port
1
C
2
A
3Antenna port
B
Antenna port
4Antenna port
D
Bottom Panel Components
This section describes the bottom panel components.
Status LED
The Status LEDs provide information on access point status, activity, and performance. The following table describes status LED
states.
8
Page 9
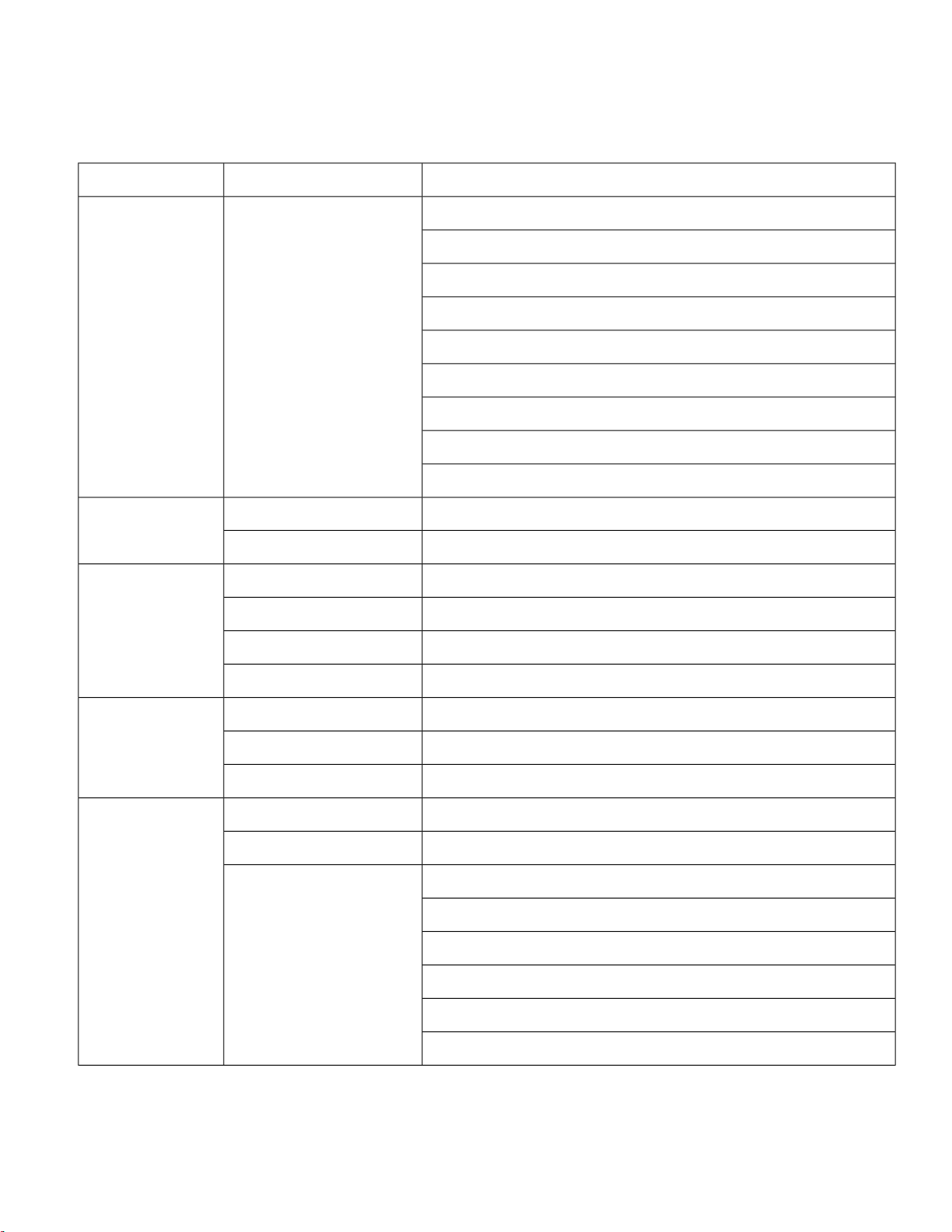
Table 2: Status LED
System StateLED ColorMessage Type
DRAM memory test in progress.Blinking pinkBoot loader status
DRAM memory test OK.
Board initialization in progress.
Initializing flash file system.
Flash memory test OK.
Initializing Ethernet.
Ethernet OK.
Starting Cisco IOS.
Initialization successful.
Client association
status
Normal operating condition but no wireless client association.Green
Normal operating condition with at least one wireless client association.Blue
Blinking blueOperational status
Software upgrade in progress.
Discovery/join process in progress.Cycling green-red-off
Access point location command invoked.Rapidly cycling blue-green-red
Ethernet link not operational.Blinking red
Blinking blueBoot loader warnings
Configuration recovery in progress (RESET button pushed for 30 seconds).
Ethernet failure or image recovery (RESET button pushed for 50 seconds).Red
Image recovery in progress (MODE button released).Blinking pink
RedBoot loader errors
DRAM memory test failure.
FLASH file system failure.Blinking red-blue
Environment variable failure.Blinking red-off
Bad MAC address.
Ethernet failure during image recovery.
Boot environment failure.
No Cisco image file.
Boot failure.
9
Page 10
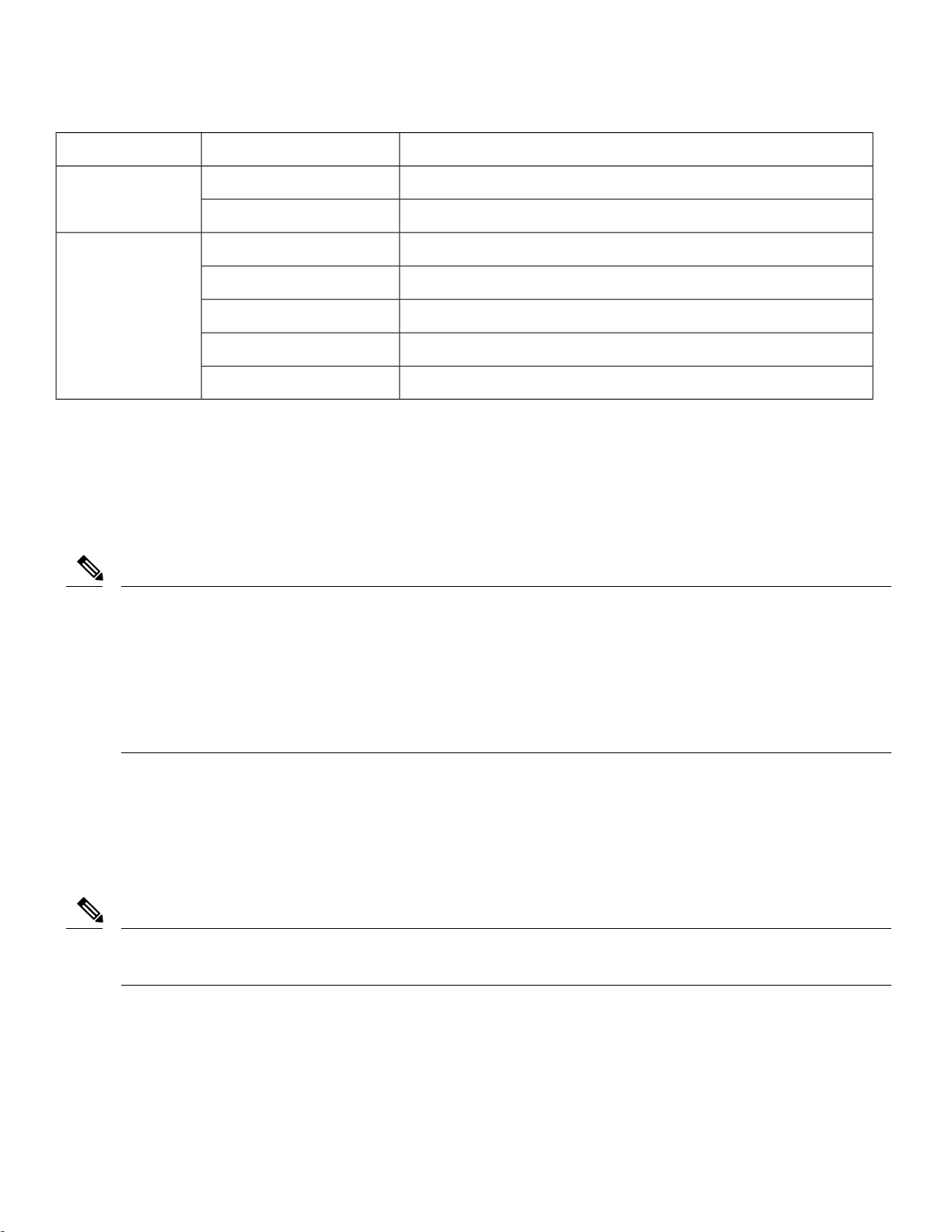
System StateLED ColorMessage Type
Cisco IOS errors
Cycling red-green-offAP status when
provisioned by Cisco
AirProvision
PWR Connectors
There are two options for powering the access point:
• DC input over the PWR connector.
• PoE inline power over the PoE IN port.
Note
When powering the access point:
Software failure. Disconnect and reconnect unit power.Red
General warning. Insufficient inline power.Cycling blue-green-red-off
AP waiting to be primed.
AP priming via Cisco NDP in progress.Blinking white
AP upon successful connection to Cisco AirProvision.Blinking teal (for 15 seconds)
AP priming via Cisco AirProvision in progress.Blinking blue
AP primed to wrong regulatory domain.Chirping red
1. Power can be supplied via DC input (PWR connector) or PoE inline (PoE IN port), but not both.
2. We recommend that you not use two power options concurrently, but no harm results if both are present.
3. If using both power inputs, DC input (PWR connector) power takes precedence and PoE inline power is not used.
4. Power supply redundancy is not supported.
The access point requires a DC power supply. To power the access point with a DC power supply, you connect the DC power to the
PWR connector on the bottom panel. The DC input voltage range is +12 to +48 VDC (-20%, +25%).
The PWR connector is an M12 A-code, 4-pin (male) connector. See Power Port, on page 75 and DC Input and PoE IN Specifications,
on page 67.
PoE OUT Port
Note
The PoE OUT port is only supported when the access point is powered over the PWR port. When powered over the PoE IN
port, PoE OUT functionality is not supported.
The PoE OUT port is a 10/100/1000 BASE-T port with an M12 X-code connector. The PoE OUT port supplies PoE inline DC power
to power external devices. The PoE OUT port pin-out conforms to Alternative A-MDIX mode.
10
Page 11

Note
PoE inline power supports IEEE 802.3af compliant devices and delivers up to 15.4 W of PoE.
For more information about the PoE OUT, PoE IN, and DC input, see DC Input and PoE IN Specifications, on page 67.
PoE IN Port
The PoE IN port is a 10/100/1000 BASE-T port with an M12 X-code connector. The port has auto-sensing and auto-MDIX capabilities.
Note
The PoE IN port is an alternate power input to DC input over the PWR port.
• Power the access point over the PWR port to enable the PoE OUT port.
• When powered over the PoE IN port, PoE OUT functionality is not supported.
For more information, see DC Input and PoE IN Specifications, on page 67.
Protective Vent Port
The protective vent port relieves pressure inside the access point chassis possibly caused by changing temperatures in the installation
environment. The vent prevents pressure from building up and damaging enclosure seals and potentially exposing sensitive components
to water. The vent also protects the access point interior from dust, dirt, water, and other environmental elements.
Note
If the vent is removed or damaged, the access point is subject to moisture damage.
Reset Button
You use the reset button for configuration or image recovery. The reset button is under the protective vent port. To access the reset
button:
1. Use a 5/8" socket to remove the protective vent.
2. Disconnect power (the power jack for external power or the Ethernet cable for in-line power) from the access point.
3. Press and hold the RESET button while you reconnect power to the access point.
4. Press the reset button.
• Hold the RESET button until the Status LED turns blinking blue (usually, pushed for 30 seconds) to reset the access point
to its factory settings.
• Hold the RESET button until the Status LED turns solid Red (usually, pushed for 50 seconds) to do image recovery.
5. Replace the protective vent using 5/8" socket.
6. Torque the protective vent to 5-7 inch-lbs.
11
Page 12

Console Port
You can connect the access point to a PC or laptop through the RJ45 CON port. The RJ45 CON port uses the Cisco console port
RJ45-to-DB9 cable (Cisco PN 72-3383-01).
A cable port seal covers the CON port. This liquid-tight plug protects the access point from environmental elements. Ensure that the
plug is installed during normal operation or when unit is unattended. You can remove and install the port plug with a 1/2" (13 mm)
socket. Torque it to 6-7 ft-lbs
For more information, see Console Port, on page 77.
Ground Stud
The ground stud is the access point ground. You use screws to attach the wired grounding lug to the ground stud. Connect the other
end of the ground wire to an earth ground such as a grounding rod or appropriate ground point on a grounded pole.
Top Panel Components
This section describes the top panel components.
Antenna Port
The antenna connector is a type N female coaxial connector.
Hard Points
The hard points are alternate mounting or attachment points for additional equipment such as directional antennas or covers.
Note
Do not attach third-party radios using these hard points.
12
Page 13
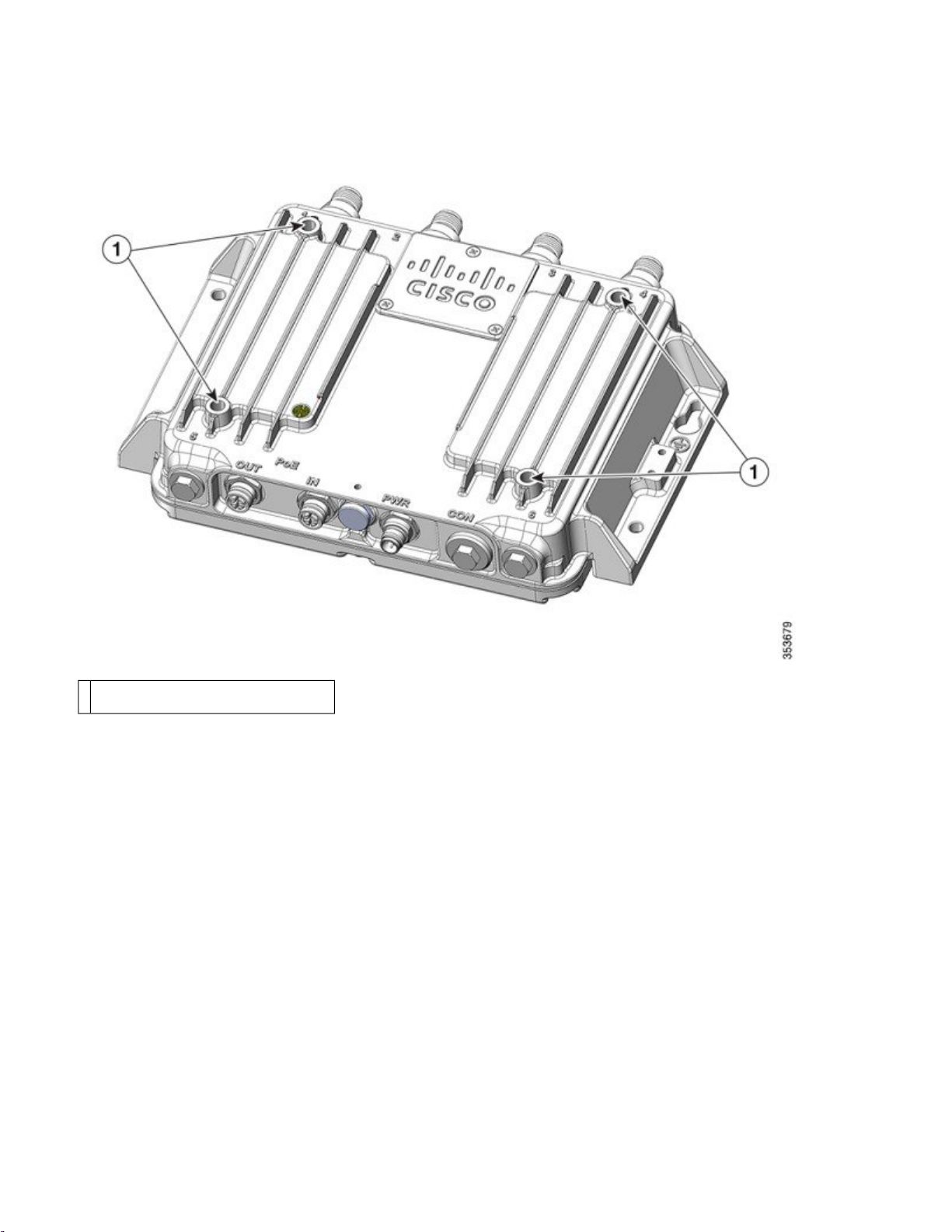
Figure 5: Cisco IW3702 Series Access Point Hard Points
Hard points 1/4-20UNC-2B, .45" deep1
Management Options
You can manage the access point using the following options:
• Web browser Interface—Contains management pages to change the wireless device settings, upgrade firmware, and monitor
and configure other wireless devices on the network.
• Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI)—Configures the access point. You can access the CLI by directly connecting a PC to
the console port, or you can access the CLI using a Telnet session from a remote management station.
Installation
You can install the access point on a wall, ceiling or pole, in a cabinet or rack, under a seat, or in a plenum airspace. You can direct
mount, DIN rail mount, or attach the access point on a pole mounting bracket.
Perform the installation procedures in this order:
1. Preparing for Installation, on page 14
2. Unpacking the Components, on page 17
13
Page 14

3. Mounting the Access Point, on page 19
4. Connecting the Protective Ground and Power, on page 19
5. Connecting the Antennas, on page 22
6. Connecting to Access Point Ports, on page 22
Preparing for Installation
The following topics prepare you for installing the unit:
Warnings
These warnings are translated into several languages in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco IW3702
Access Point on Cisco.com.
Danger
Danger
Danger
Danger
Danger
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
In order to comply with FCC radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, antennas for this product should be located a
minimum of 7.9 in. (20 cm) or more from the body of all persons. Statement 332
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source. Statement 1004
This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area can be accessed only through
the use of a special tool, lock and key,or other means of security. Statement 1017
This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the absence of a
suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you
are uncertain that suitable grounding is available. Statement 1024
Danger
Danger
14
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. Statement 1040
Topreventthesystem from overheating, do not operate it inan area that exceeds the maximum recommendedambient
temperature of: 70°C Statement 1047
Page 15

Danger
Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes. Statement 1074
Danger
Danger
Caution
Note
Note
This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that the protective
device is rated not greater than: 15 A. Statement 1005
Do not operate your wireless network device near unshielded blasting caps or in an explosive environmentunless the
device has been modified to be especially qualified for such use. Statement 245B
The fasteners you use to mount an access point on a ceiling must be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 20
lbs (9 kg) and must use all 4 indented holes on the mounting bracket.
The access point is suitable for use in environmental air space in accordance with section 300.22.C of the National Electrical
Code and sections 2-128, 12-010(3), and 12-100 of the Canadian Electrical Code, Part 1, C22.1. You should not install the
power supply or power injector in air handling spaces.
Use only with listed ITE equipment.
EMC Environmental Conditions for Products Installed in the European Union
This section applies to products installed in the European Union. The equipment is intended to operate under the following environmental
conditions with respect to EMC:
• A separate defined location under the user’s control.
• Earthing and bonding meets the requirements of ETSI EN 300 253 or ITU-T K.27.
• AC-power distribution shall be one of the following types, where applicable: TN-S and TN-C as defined in IEC 60364-3.
In addition, if equipment is operated in a domestic environment, interference could occur.
National Restrictions within the European Union
Within the European Union as well as within the majority of the other European Countries, the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands are available
for use by wireless LANs.
The following table provides an overview of the regulatory requirements that are generally applicable for 2.4 and 5 GHz bands.
The requirements for any country might evolve. We recommend that you check with your local authorities for the current status of
regulations for 2.4 and 5 GHz wireless LANs within your country.
15
Page 16
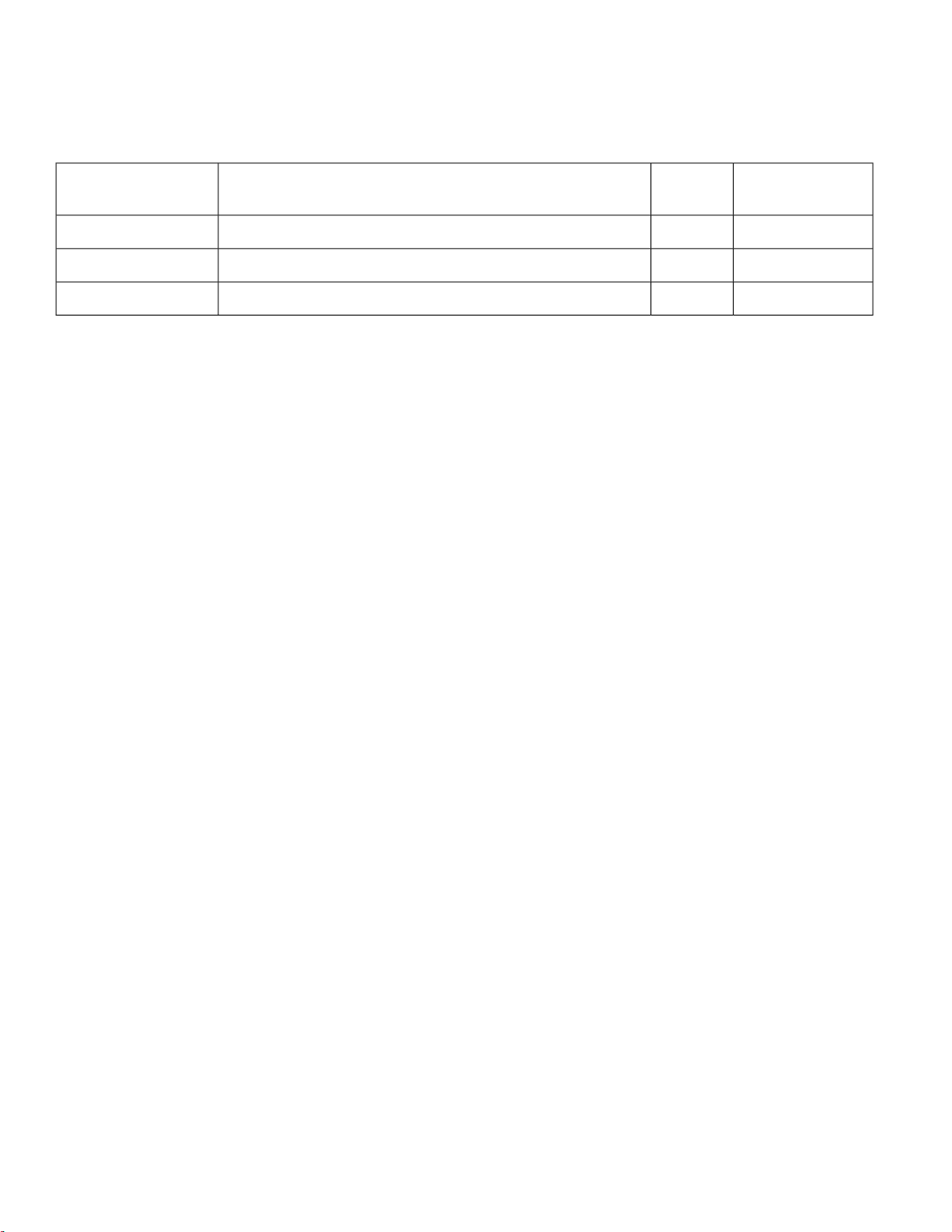
Table 3: Overview of Regulatory Requirements for Wireless LANs
FrequencyBand(MHz)
MaximumPowerLevelEffectiveIsotropicRadiatedPower(EIRP)
mW
Tools and Hardware Required
These tools and hardware are required for access point installation:
• Crimping tool (such as Thomas & Bett part number WT2000, ERG-2001, or equivalent)
• 6-gauge copper ground wire
• Wire-stripping tools for stripping 6-gauge wire
• Number 2 Phillips screwdriver
• 1/2" (13 mm) socket for port plug
• 5/8" (16 mm) socket for protective vent
• 5/32" (4 mm) hex key for mounting screws
• Torque wrench (both inch-lbs and ft-lbs)
IndoorandOutdoorIndoor
only
x—1002400-2483.5
—x2005150-5350
x—10005470-5725
Installation Guidelines
Because the access point is a radio device, it is susceptible to common causes of interference that can reduce throughput and range.
Follow these guidelines to ensure the best possible performance:
• For information on planning and initially configuring your Cisco Mesh network, refer to the Cisco Wireless Mesh Access Points,
Design and Deployment Guide.
• Review the FCC Guidelines for Installation and Operation of Outdoor Wireless LAN Devices (U-NII devices) Operating in the
5470-5725 MHz Band Data Sheet at:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/routers/3200-series-rugged-integrated-services-routers-isr/data_sheet_c78-647116.html
The above document provides guidelines to mitigate interference to Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Terminal Doppler
Weather Radar (TDWR) as well as details on registering your access point with the Wireless Internet Service Providers Association
(WISPA).
• Perform a site survey before beginning the installation.
• Install the access point in an area where structures, trees, or hills do not obstruct radio signals to and from the devices.
• For information on priming a Cisco universal access point, see the Cisco Aironet Universal AP Priming and Cisco AirProvision
User Guide at: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/access_point/ux-ap/guide/uxap-mobapp-g.html
16
Page 17

Site Surveys
Every network application is a unique installation. Before installing an access point, perform a site survey to determine the optimum
use of networking components and maximize range, coverage, and network performance.
Consider the following operating and environmental conditions when performing a site survey:
• Data rates—Sensitivity and range are inversely proportional to data bit rates. The maximum radio range is achieved at the lowest
workable data rate. A decrease in receiver sensitivity occurs as the radio data increases.
• Antenna type and placement—Proper antenna configuration is a critical factor in maximizing radio range. As a general rule,
range increases in proportion to antenna height. However, do not place the antenna higher than necessary, because extra height
increases potential interference from other unlicensed radio systems and decreases the wireless coverage from the ground.
• Physical environment—Clear or open areas provide better radio range than closed or filled areas.
• Obstructions—Physical obstructions such as buildings, trees, or hills can hinder performance of wireless devices. Avoid locating
the devices in a location where an obstruction exists between the sending and receiving antennas.
Unpacking the Components
The typical access point package contains the following items:
• Access point
• Cisco product documentation and translated safety warnings
• Ground lug (Panduit PLCD6-10A-L), screws, and oxide inhibitor (contained in a tube)
• Console cable
• CoaxSeal—Coaxial cable/connector seal tape for N connectors
• Two M12 Ethernet connector caps (installed on the PoE OUT and PoE IN ports)
• One M12 power connector cap (installed on the PWR port)
Note
The M12 connector caps are installed on the ports for protection when the AP is shipped. Remove the caps before using the
ports. See the following figure for the locations of each port with M12 cap.
17
Page 18
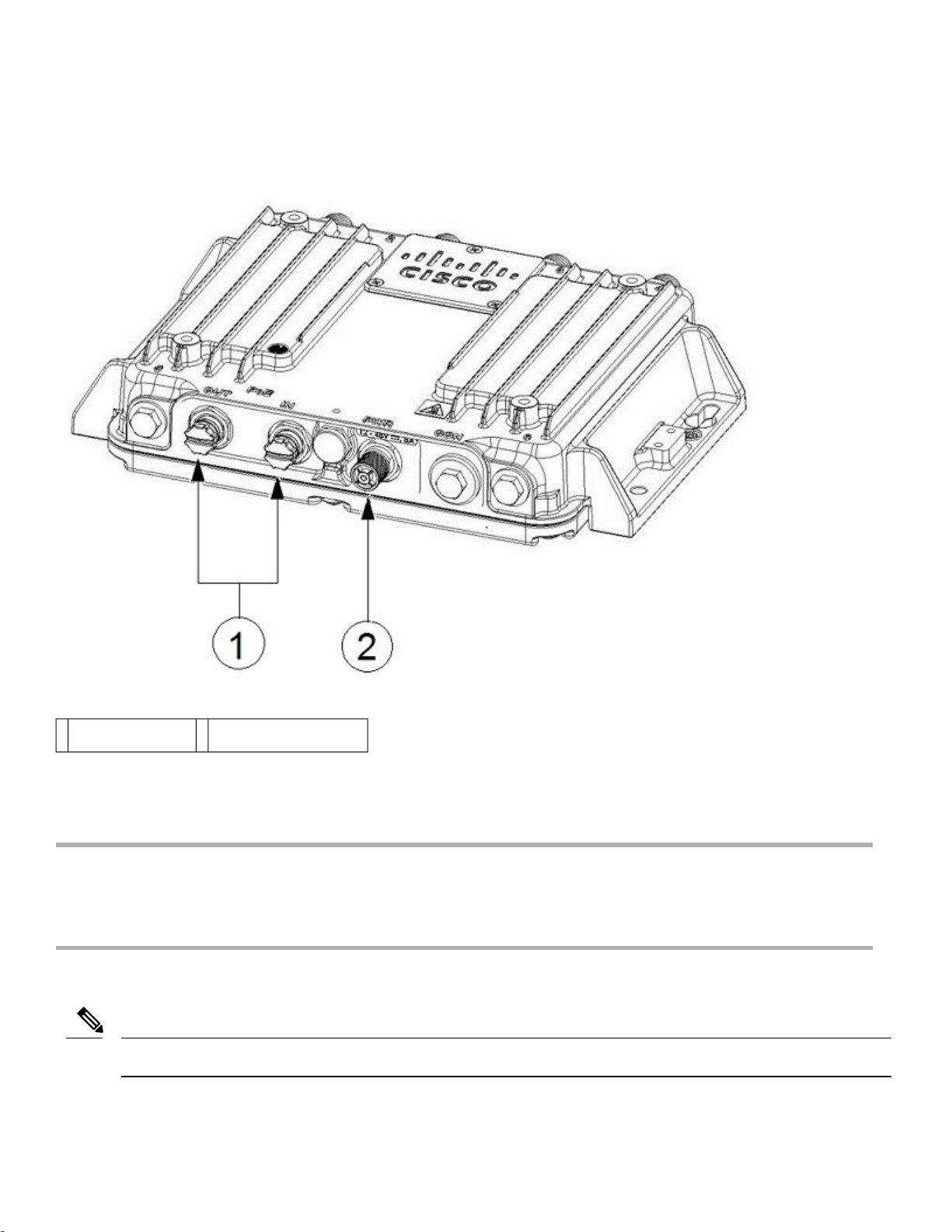
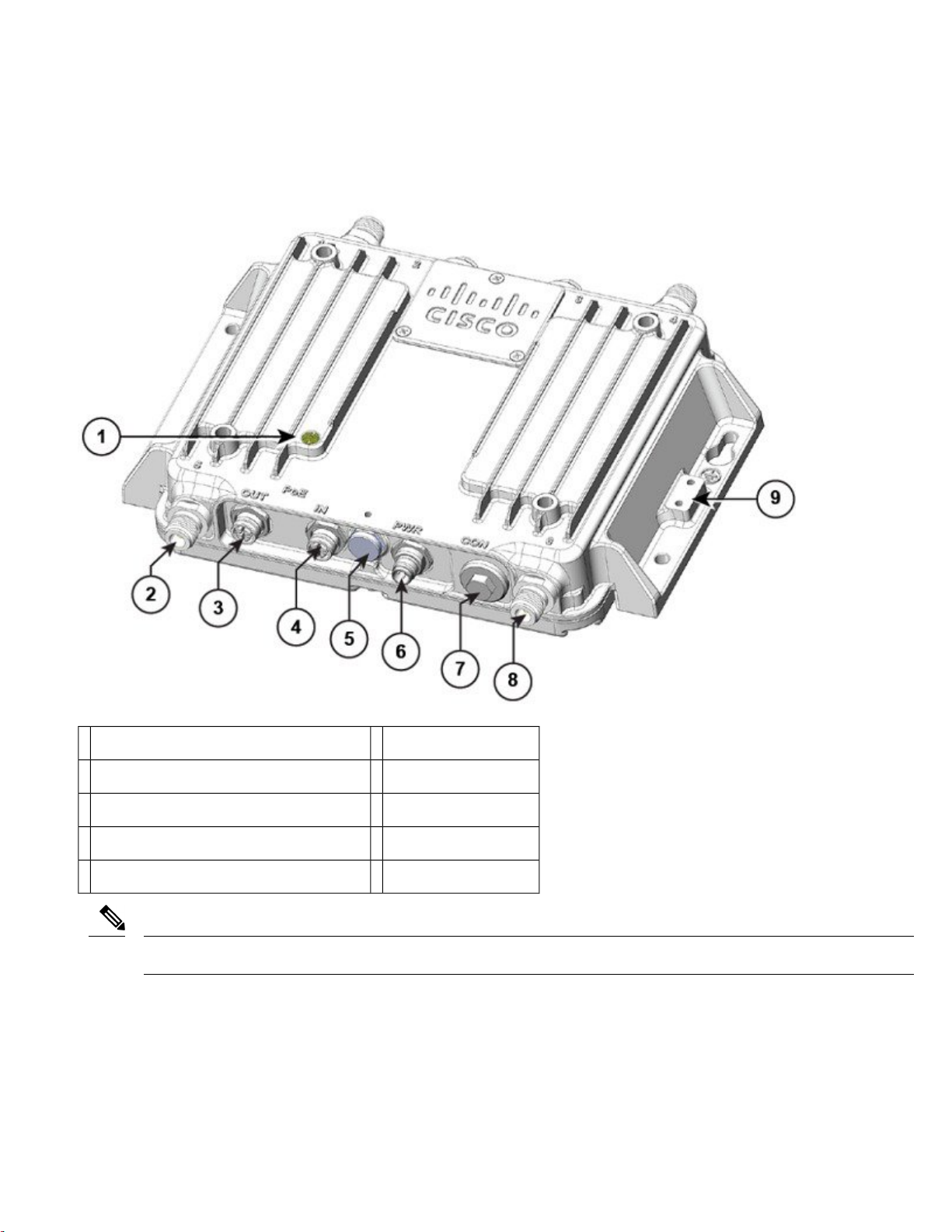
Figure 6: PoE and PWR Connectors With Caps
PWR connector with cap2PoE ports with caps1
To unpack the access point:
Procedure
Step 1 Open the shipping container and carefully remove the contents.
Step 2 Return all packing materials to the shipping container, and save it.
Step 3 Ensure that all the access point package items are included in the shipment.
What to do next
Note
If any item is damaged or missing, notify your sales representative.
18
Page 19
Mounting the Access Point
For instructions about mounting the access point, see the Cisco IW3702 Access Point Mounting Guide
Connecting the Protective Ground and Power
Perform the following steps in order when connecting the access point to power and ground.
1. Grounding the Access Point, on page 19
2. Wiring the Access Point DC Power, on page 21
Grounding the Access Point
In all installations, after mounting the access point, you must properly ground the unit before connecting power cables.
Danger
Danger
The access point is shipped with a grounding kit.
Figure 7: Access Point Grounding Kit Contents
Grounding lug1
Screws x 2, M4 x 6mm2
This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the absence of a
suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you
are uncertain that suitable grounding is available. Statement 1024
Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes. Statement 1074
Note
The grounding kit also includes the oxide inhibitor, which is contained in a tube.
To ground the access point:
Procedure
19
Page 20

Step 1 Use a crimping tool to crimp a 6-AWG ground wire (not included in the grounding kit) to the ground lug.
Step 2 Connect the supplied ground lug to the access point ground connection point using the supplied screws. Apply supplied
oxide inhibitor between the ground lug and the access point ground connection.
Step 3 Tighten the screws to 20-25 inch-lbs of torque.
20
Ground connection1
Page 21

Step 4 If necessary, strip the other end of the ground wire and connect it to a reliable earth ground such as a grounding rod or
appropriate ground point on a grounded pole. Length of the ground cable should not exceed 1 meter, and 0.5 meter is
preferred. Use supplied oxide inhibitor on the grounded interface.
Wiring the Access Point DC Power
To wire the access point to a DC power source:
Procedure
Step 1 Verify that the access point is grounded (see Grounding the Access Point, on page 19).
Step 2 Connect the power lead to the PWR connector by turning the cable clockwise, as shown in the following figure.
Power cable and PWR connector1
21
Page 22

Step 3 Connect the other end of the power cable to the DC power source using the power source wiring instructions. The PWR
connector pinout descriptions are in Power Port, on page 75.
Connecting the Antennas
Connect each antenna based on:
• Antenna arrangement, cabling, lightning arrestor, and adapter information in Examples of Access Point and Antenna Deployment
Configurations, on page 26.
• Installation information in Antenna Types and Models, on page 24.
Connecting to Access Point Ports
This section describes connecting the access point to PoE.
Danger
For connections outside the building where the equipment is installed, the following ports must be connected through
an approved network termination unit with integral circuit protection.10/100/1000 Ethernet Statement 1044
Connecting to the PoE IN or PoE OUT Port
Procedure
Step 1 Use shielded cables with a M12 X-Code plug to connect to the PoE IN or PoE OUT ports.
Note
Step 2 Connect the PoE IN cable to the PoE IN port, or the PoE OUT cable to the PoE OUT port by turning the cable clockwise,
as shown in the following figure.
Ethernet cables must have an internal shield around the signal wires. There must be a contiguous ground between
the connector shell that interfaces with the IW3702 and the connector shell on the far end of the cable. Maximum
cable length should not exceed 100 meters.
22
Page 23
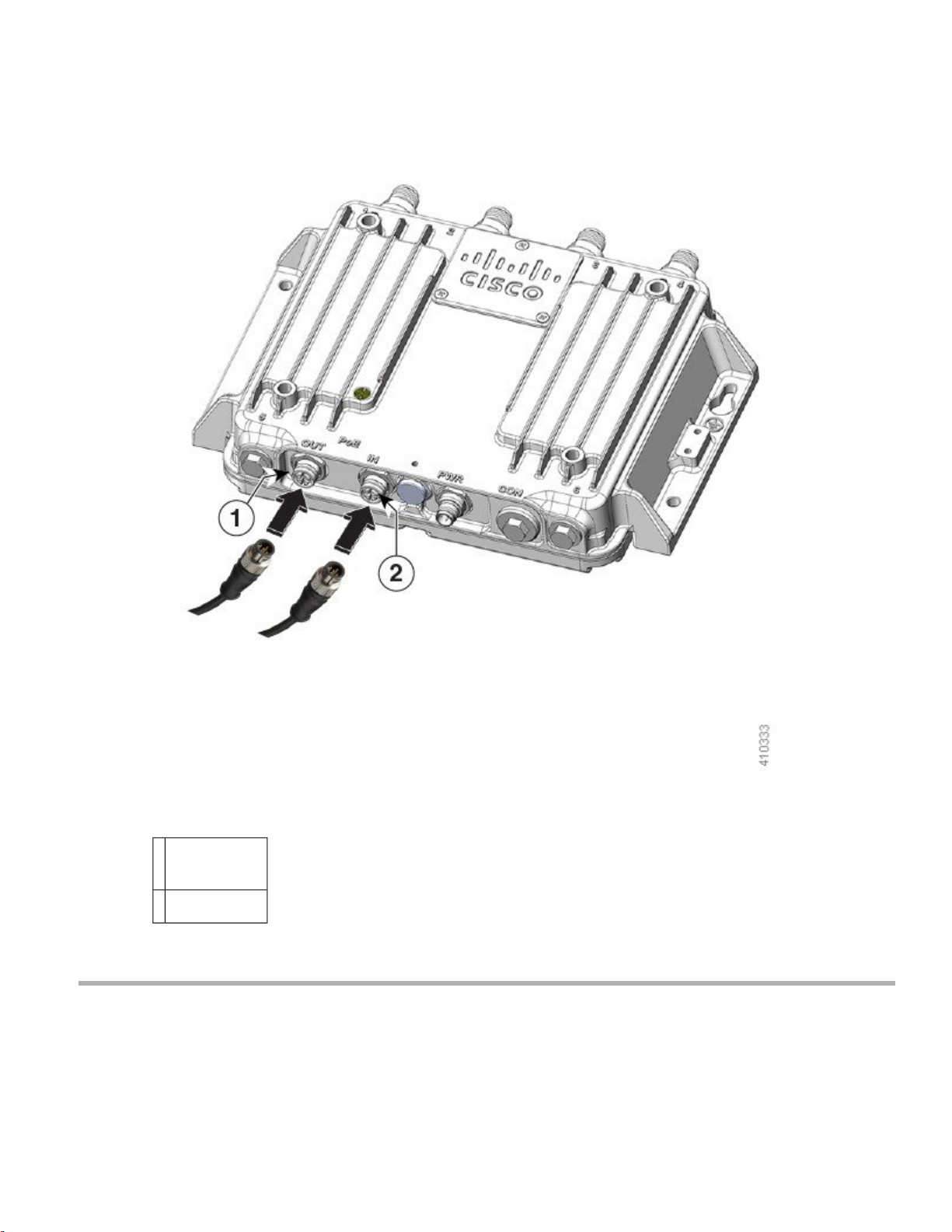
Figure 8: Connecting to the PoE IN or PoE OUT Ports
PoE OUT
1
cable
PoE IN cable2
Note
When powered over the PoE IN port, PoE OUT functionality is not supported.
Antennas and RF Accessories
This section describes antennas, RF Accessories, and their configuration for the access point.
23
Page 24
Cisco recommends using a coax seal (such as CoaxSeal) for outdoor connections, to prevent moisture and other weathering elements
from affecting performance. For more information on using coax seal on the N connector to cable or antenna interface, see the
instructions on your antenna documents.
Antenna Types and Models
The antennas used in these configurations are:
• Cisco Aironet Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antenna (White model—Cisco PID AIR-ANT2547V-N)
Cisco Aironet Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antenna (Cisco PID AIR-ANT2547VG-N)
These are the related models:
• White model (Cisco PID AIR-ANT2547V-N=)
• Grey Model (Cisco PID AIR-ANT2547VG-N=)
• Cisco Aironet Four-Port Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Array Antenna (Cisco PID AIR-ANT2513P4M-N)
• Cisco Aironet Four-Element, MIMO, Dual-Band Ceiling Mount Omnidirectional Antenna (Cisco PID AIR-ANT2524V4C-R)
• Cisco Aironet Dual-Band MIMO Wall-Mounted Omnidirectional Antenna (Cisco PID AIR-ANT2544V4M-R)
• Cisco Aironet 2.4 GHz/5 GHz MIMO 4-Element Patch Antenna (Cisco PID AIR-ANT2566P4W-R)
• Cisco Aironet Dual-band Dipole Antenna (Cisco PID AIR-ANT2524DB-R, AIR-ANT2524DG-R, and AIR-ANT2524DW-R)
• Cisco Aironet 2.4-GHz 13-dBi Directional Antenna (Cisco PID AIR-ANT2413P2M-N)
• Cisco Aironet 5-GHz 13-dBi Directional Antenna (Cisco PID AIR-ANT5114P2M-N)
• Cisco Aironet 2.4 GHz/5 GHz Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Directional Array Antenna (AIR-ANT2566D4M-R)
RF Accessories
This section contains the IW3702 RF accessories: cables, adapters, and lightning arrestors.
The following table defines the cables available for interconnecting the antennas and the access point.
Table 4: RF Cables
Cisco PID
N(m) to N(m) RF cables:
AIR-CAB002L240-N
CAB-L400-5-N-N
Description
Type: Indoor Interconnect.
Not DB, CMR or CMP
Type: outdoor DB (direct burial)
2
Loss at 2.4
GHz
Loss at 5.8
GHz
0.8 dB0.5 dBN(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-240 , 2ft RF cable
0.8 dB0.5 dBN(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5ft RF cable
24
Page 25

Cisco PID
Description
2
Loss at 2.4
GHz
Loss at 5.8
GHz
CAB-L400-5-N-NS
Type: outdoor DB (direct burial)
AIR-CAB010LL-N
Type: outdoor DB (direct burial)
CAB-L400-20-N-N
Type: outdoor DB (direct burial)
CAB-L600-30-N-N
Type: outdoor DB (direct burial)
AIR-CAB025HZ-N
to offer petrochemical resistance and oils resistance
Type: outdoor DB (direct burial) with additional resistance to petrochemicals
and oils
N(m) to RP-TNC(jack) RF cables:
CAB-L240-10-N-R
Type: outdoor DB (direct burial)
CAB-L400-20-N-R
0.8 dB0.5 dBN(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5ft RF cable
1.5 dB0.9 dBN(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 10ft RF cable
2.5 dB1.6 dBN(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 20ft RF cable
2.5 dB1.6 dBN(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-600-DB, 30ft RF cable
3.5 dB2.0 dBN(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400, 25ft RF cable with ruggedised jacket
2.5 dB1.5 dBN(m)-R/A to RP-TNC(jack), LMR-240-DB, 10 ft RF cable
2.5 dB1.6 dBN(m)-R/A to RP-TNC(jack), LMR-400-DB, 20 ft RF cable
Type: outdoor DB (direct burial)
2
N(m)-R/A = N(male) right angle connector
N(m)-STR = N(male) straight connector
RP-TNC connectors used on cables specified in the table are straight.
The following table shows the RF coaxial adapters.
Table 5: RF Coaxial Adapters
DescriptionCisco PID
AIR-ACC370-NF-NF
N(f) to N(f) RF adapter DC-11 GHz
Typical use is adapting between two N(m) cables.
N(m) to RP-TNC (jack) RF adapter DC-6 GHzAIR-ACC370-NM-RF
The following table shows the lightning arrestors.
25
Page 26

Table 6: Lightning Arrestors
DescriptionCisco PID
CGR-LA-NF-NF
CGR-LA-NM-NF
N(f)-N(f) lightning arrestor, GDT type, DC-6GHz.
Supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz operation and has two N(f) connectors.
Provides lightning and related energy surges at the antenna from reaching the radio circuitry. A ground ring is included.
N(m)-N(f) lightning arrestor, GDT type, DC-6GHz
Supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz operation and has N(m) and N(f) connectors.
Provides lightning and related energy surges at the antenna from reaching the radio circuitry. A ground ring is included.
For more information, see
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/connectedgrid/lightning_arrestor/Lightning_Arrestor_for_the_Cisco_1240_Connected_Grid_Router.html
Examples of Access Point and Antenna Deployment Configurations
The section provides examples of antenna installation configurations, including applicable accessories such as cables, lighting arrestors,
and adapters.
Indoor or Outdoor Cisco Aironet Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point
Table 7: Indoor or Outdoor Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
4 x Cisco Aironet dual-band AIR-ANT2547V-N or AIR-ANT2547VG-N omnidirectional antennas
directly connected to access point antenna connectors.
Access Point
Arrestor
IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-2E-x-K9
Note
N/AIndoor Cable
N/AAdapter and/or Lightning
N/AOutdoor Cable
Do not use this configuration with the IW3702-4E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-x-K9 model.
For the -4E models, all four antenna ports are on one side, and would be too close to
each other for optimal MIMO IEEE 802.11ac operation if attached antennas directly
to all 4 ports.
26
Page 27

DescriptionItem
Antenna
Select from:
• White model, Cisco PID3AIR-ANT2547V-N
• Grey Model, Cisco PID AIR-ANT2547VG-N
4 x Cisco Aironet dual-band omnidirectional antennas are required.
The antenna specifications are:
• 2400–2484MHz, 5150–5875MHz, dual-band, WiFi, operating frequency range
• 4 dBi (2.4 GHz), 7 dBi (5 GHz) gain
• 11 in. (27.94 cm) stick antennas for indoor or outdoor use with a type N(m) connector
• IP67 rated, -40 to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C) operating temperature range
3
PID = Product identifier code.
Outdoor Cisco Aironet Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point for Remote and Indoor Use Scenario
Table 8: Outdoor Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point for Remote and Indoor Use Scenario
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
4 x Cisco Aironet dual-band AIR-ANT2547V-N or AIR-ANT2547VG-N omnidirectional antennas mounted
remotely outdoors, with the access point located remotely, indoors, or enclosed.
Adapter and/or
Lightning Arrestor
Indoor Cable
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9, IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
You need:
• 4 x DC pass, N(f)-N(f) lightning arrestors. Cisco PID CGR-LA-NF-NF.
Note
Lightning arrestors must be appropriately grounded to infrastructure system ground designed
to conduct lightning currents to Earth ground.
This configuration assumes that the lightning arrestor is mounted on a building or enclosure
penetration panel, and that it is interfaced on both sides with N(m) cables.
• 4 x N(f) to N(f) RF adapters. Cisco PID AIR-ACC370-NF-NF.
This configuration assumes that there is an N(m) to N(m) cable connected between the lightning arrestor
and the Access Point.
For indoor cable routing, the deployment must balance the requirements of Fire Code, Electrical Code,
and any other applicable regulations, versus RF cable type, cost, RF cable length, and RF cable insertion
loss.
27
Page 28

DescriptionItem
Outdoor Cable
Antenna
Select from:
• 4x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-NS
• 4x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 10’ RF cable, Cisco PID: AIR-CAB010LL-N
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 20 ft. cables. Cisco PID CAB-L400-20-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-600-DB, 30 ft. cables. Cisco PID CAB-L600-30-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 25’ RF cable with petrochemical and oils resistance,
Cisco PID AIR-CAB025HZ-N
Select from:
• White model, Cisco PID AIR-ANT2547V-N=
• Grey Model, Cisco PID AIR-ANT2547VG-N=
4 x Cisco Aironet dual-band omnidirectional antennas are required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2400-2484MHz, 5150-5875MHz, dual-band, WiFi, operating frequency range
• 4 dBi (2.4 GHz), 7 dBi (5 GHz) gain
• 11 in. (27.94 cm) stick antennas for indoor or outdoor use with a type N(m) connector
• IP67 rated, -40 to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C) operating temperature range
Note
To mast-mount the antenna, you must purchase a mast-mount U-bolt bracket from a third party.
Indoor Cisco Aironet Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antenna Directly and Cable Connected to Access Point
Table 9: Indoor Dual-Band Omnidirectional Antenna Directly and Cable Connected to Access Point
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
4 x indoor Cisco Aironet dual-band AIR-ANT2547V-N or AIR-ANT2547VG-N omnidirectional antennas
connected to the IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-2E-x-K9 model:
• 2 x antennas directly mounted on top panel side.
• 2 x antennas connected via cables on the bottom side.
IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-2E-x-K9Access Point
28
Page 29

DescriptionItem
Adapter and/or Lightning
Arrestor
Indoor Cable
Outdoor Cable
You need:
• 2 x N(f) to N(f) RF adapters. Cisco PID AIR-ACC370-NF-NF.
• 2 x DC pass, N(m)-N(f) lightning arrestors. Cisco PID CGR-LA-NM-NF.
Installed on the router ports with cables.
Note
Lightning arrestors must be appropriately grounded to infrastructure system ground designed
to conduct lightning currents to Earth ground.
For indoor cable routing, the deployment must balance the requirements of Fire Code, Electrical Code,
and any other applicable regulations, versus RF cable type, cost, RF cable length, and RF cable insertion
loss.
Select from:
• 2 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-N
• 2x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-NS
• 2x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 10’ RF cable, Cisco PID: AIR-CAB010LL-N
• 2 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 20’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-20-N-N
• 2 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-600-DB, 30’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L600-30-N-N
• 2 x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 25’ RF cable with petrochemical and oils resistance,
Cisco PID AIR-CAB025HZ-N
Antenna
Select from:
• White model, Cisco PID AIR-ANT2547V-N
• Grey Model, Cisco PID AIR-ANT2547VG-N
4 x Cisco Aironet dual-band omnidirectional antennas are required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2400-2484MHz, 5150-5875MHz, dual-band, WiFi, operating frequency range
• 4 dBi (2.4 GHz), 7 dBi (5 GHz) gain
• 11 in. (27.94 cm) stick antennas for indoor or outdoor use with a type N(m) connector
• IP67 rated, -40 to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C) operating temperature range
29
Page 30

Indoor Only Dual-Band Omnidirectional Articulating Joint Antenna and Access Point
Table 10: Indoor only Dual-Band Omnidirectional Articulating Joint Antenna and Access Point
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
Access Point
Adapter and/or Lightning
Arrestor
Antenna
4 x Cisco Aironet dual-band AIR-ANT2524DW-R omnidirectional articulating joint indoor antennas
connected to access point with adapters in between. This configuration is for indoor applications
where swivel mount is desirable to control dipole antenna tilt/polarization.
IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-2E-x-K9
Note
Do not use this configuration with the IW3702-4E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-x-K9 model.
For the -4E models, all four antenna ports are on one side, and would be too close to each
other for optimal MIMO IEEE 802.11ac operation with all antennas directly connected.
N/AIndoor Cable
You need:
• 4 x N(m) to RP-TNC (jack), RF coax adapters. Cisco PID AIR-ACC370-NM-RF.
Note
No lightning arrestors are required.
N/AOutdoor Cable
4 x Cisco Aironet dual-band AIR-ANT2524DW-R indoor articulating joint omnidirectional antennas
are required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2400–2500MHz, 5150–5850MHz, dual-band, WiFi, operating frequency range
• 2 dBi (2.4 GHz), 4 dBi (5 GHz) gain
• Articulating joint.
• 6.63 in. (16.95 cm) dipole antennas for indoor only use.
• RP-TNC (plug) connector.
• -4 to 140°F (-20°C to 60°C) operating temperature range.
• White color model, Cisco PID AIR-ANT2524DW-R.
Outdoor Cisco Aironet Four-Port Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Array Antenna and Access Point
Table 11: Outdoor Four-Port Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Array Antenna and Access Point
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2513P4M-N four-port dual-band polarization-diverse array antenna
located outdoors, connected by external cable to the access point antenna connector.
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9, or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
30
Page 31

DescriptionItem
Adapter and/or Lightning
Arrestor
Outdoor Cable
Antenna
4 x DC pass, N(m)-N(f) lightning arrestors. Cisco PID CGR-LA-NM-NF.
Note
Lightning arrestors must be appropriately grounded to infrastructure system ground designed
to conduct lightning currents to Earth ground.
N/AIndoor Cable
Select from:
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, RF cable, CAB-L400-5-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-NS
• 4x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 10’ RF cable, Cisco PID: AIR-CAB010LL-N
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 20’, CAB-L400-20-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-600-DB, 30’, CAB-L600-30-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 25’ RF cable with petrochemical and oils resistance,
Cisco PID AIR-CAB025HZ-N
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2513P4M-N four-port dual-band polarization-diverse array antenna is
required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2.4-2.5 GHz, 5.15-5.925 GHz dual-band WiFi operating frequency ranges
• 13 dBi peak gain
• Type N(f) connector
• IP67 rated, -40 to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C) operating temperature range
• Cisco PID AIR-ANT2513P4M-N
Outdoor Cisco Aironet Four-Port Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Array Antenna and Access Point for Remote or Indoor Use Scenario
Table 12: Outdoor Four-Port Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Array Antenna and Access Point for Remote or Indoor Use Scenario
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
Adapter and/or Lightning
Arrestor
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2513P4M-N four-port dual-band polarization-diverse array antenna mounted
remotely outdoors, with access point indoors or enclosed.
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
4 x DC pass, N(f)-N(f) lightning arrestors. Cisco PID CGR-LA-NF-NF.
Note
Lightning arrestors must be appropriately grounded to infrastructure system ground designed
to conduct lightning currents to Earth ground.
This configuration assumes that the lightning arrestor is mounted on a building or enclosure
penetration panel, and that it is interfaced on both sides with N(m) cables.
31
Page 32

DescriptionItem
Indoor Cable
Outdoor Cable
Antenna
This configuration assumes that there is an N(m) to N(m) cable connected between the lightning arrestor
and the Access Point.
For indoor cable routing, the deployment must balance the requirements of Fire Code, Electrical Code,
and any other applicable regulations, versus RF cable type, cost, RF cable length, and RF cable insertion
loss.
Select from:
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-NS
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 10’ RF cable, Cisco PID: AIR-CAB010LL-N
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 20 ft. cable, Cisco PID CAB-L400-20-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-600-DB, 30 ft. cable, Cisco PID CAB-L600-30-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 25’ RF cable with petrochemical and oils resistance,
Cisco PID AIR-CAB025HZ-N
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2513P4M-N four-port dual-band polarization-diverse array antenna is required.
The antenna specifications are:
• 2.4-2.5 GHz, 5.15-5.925 GHz dual-band WiFi operating frequency ranges
• 13 dBi peak gain
• Type N(f) connector
• IP67 rated, -40 to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C) operating temperature range
• Cisco PID AIR-ANT2513P4M-N
Indoor Cisco Aironet Four-Element MIMO Dual-Band Ceiling Mount Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point
Table 13: Indoor Four-Element MIMO Dual-Band Ceiling Mount Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
Adapter and/or Lightning
Arrestor
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2524V4C-R indoor four-element MIMO dual-band ceiling mount
omnidirectional antenna directly connected to the access point. Antennas are indoor only.
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9, or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
You need:
• 4 x N(m) to RP-TNC (jack), RF coax adapters. Cisco PID AIR-ACC370-NM-RF.
Note
No lightning arrestors are required.
32
Page 33

DescriptionItem
Indoor Cable
For indoor cable routing, the deployment must balance the requirements of Fire Code, Electrical
Code, and any other applicable regulations, versus RF cable type, cost, RF cable length, and RF
cable insertion loss.
N/AOutdoor Cable
Antenna
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2524V4C-R indoor four-element, MIMO, dual-band ceiling mount
omnidirectional antennas are required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2400-2500 MHz, 5150-5850 MHz dual-band WiFi operating frequency range
• MIMO operation
• 2 dBi (2.4 GHz), 4 dBi (5.8 GHz) gain
• 4 x integrated cables with RP-TNC (plug) connector
• Indoor operation, 32 to 133°F (0 to 56°C) operating temperature range
• Cisco PID AIR-ANT2524V4C-R=
Indoor or Outdoor Cisco Aironet Dual-Band MIMO Wall-Mounted Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point
Table 14: Indoor or Outdoor Dual-Band MIMO Wall-Mounted Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
Adapter and/or Lightning Arrestor
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2544V4M-R dual-band MIMO wall-mounted omnidirectional antenna
directly connected to the access point antenna connector.
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
You need:
• 4 x N(m) to RP-TNC (jack), RF coax adapters. Cisco PID AIR-ACC370-NM-RF
Note
No lightning arrestors are required.
N/AIndoor Cable
N/AOutdoor Cable
33
Page 34

DescriptionItem
Antenna
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2544V4M-R dual-band MIMO wall-mounted omnidirectional
antennas are required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2400-2484 MHz, 5150-5850MHz dual-band WiFi operating frequency range
• Bands 5150-5350MHz are not supported for outdoor installations within Regulatory
Domain E
• MIMO, omnidirectional operation
• 4 dBi (2.4 GHz), 4 dBi (5.8 GHz) gain
• Indoor or outdoor operation, -40 to 158°F (-40 to +70°C) operating temperature range
• 4 x integrated cables with RP-TNC (plug) connector
• Cisco PID AIR-ANT2544V4M-R
Outdoor Cisco Aironet Dual-Band MIMO Wall-Mounted Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point for Indoor Use Scenario
Table 15: Outdoor Dual-Band MIMO Wall-Mounted Omnidirectional Antenna and Access Point for Indoor Use Scenario
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2544V4M-R dual-band MIMO wall-mounted omnidirectional antenna
mounted remotely outdoors.
Adapter and/or Lightning
Arrestor
Indoor Cable
Outdoor Cable
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
4 x DC pass, N(f)-N(f) lightning arrestors, Cisco PID CGR-LA-NF-NF.
Note
Lightning arrestors must be appropriately grounded to infrastructure system ground designed
to conduct lightning currents to Earth ground.
This configuration assumes that the lightning arrestor is mounted on a building or enclosure
penetration panel, and that it is interfaced on both sides with N(m) cables.
This configuration assumes that there is an N(m) to N(m) cable connected between the lightning arrestor
and the Access Point.
For indoor cable routing, the deployment must balance the requirements of Fire Code, Electrical Code,
and any other applicable regulations, versus RF cable type, cost, RF cable length, and RF cable insertion
loss.
Select from:
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to RP-TNC (jack), LMR-240-DB, 10 ft. cable. Cisco PID CAB-L240-10-N-R
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to RP-TNC (jack), LMR-400-DB, 20 ft. cable. Cisco PID CAB-L400-20-N-R
34
Page 35

DescriptionItem
Antenna
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2544V4M-R dual-band MIMO wall-mounted omnidirectional antenna is
required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2400-2484 MHz, 5150-5850MHz dual-band WiFi operating frequency range
• MIMO, omnidirectional operation
• 4 dBi (2.4 GHz), 4 dBi (5.8 GHz) gain
• Indoor or outdoor operation, -40 to 158°F (-40 to +70°C) operating temperature range
• 4 x integrated cables with RP-TNC (plug) connector
• Cisco PID AIR-ANT2544V4M-R
Indoor or Outdoor Cisco Aironet Dual-Band MIMO 4-Element Patch Antenna and Access Point
Table 16: Indoor or Outdoor Dual-Band MIMO 4-Element Patch Antenna and Access Point
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2566P4W-R dual-band WiFi MIMO 4-element patch antenna directly
connected to the access point.
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
Adapter and/or Lightning Arrestor
Antenna
You need:
• 4 x N(m) to RP-TNC (jack), RF coax adapters. Cisco PID AIR-ACC370-NM-RF.
Note
No lightning arrestors are required.
N/AIndoor Cable
N/AOutdoor Cable
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2566P4W-R dual-band WiFi MIMO 4-element patch antenna is
required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2400-2484 MHz, 5150-5850 MHz operating frequency range
• WiFi, MIMO operation
• Single polarization
• 6dBi (2.4 GHz), 6 dBi (5.8 GHz) gain
• IP54 rated, indoor or outdoor operation, -40 to 158°F (-40 to +70°C) operating temperature
range
• 4 x integrated cables with RP-TNC (plug) connector
• Cisco PID AIR-ANT2566P4W-R
35
Page 36

Outdoor Cisco Aironet Dual-Band MIMO 4-Element Patch Antenna and Access Point for Indoor or Enclosed Use Scenario
Table 17: Outdoor Dual-Band MIMO 4-Element Patch Antenna and Access Point for Indoor or Enclosed Use Scenario
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
Adapter and/or Lightning
Arrestor
Indoor Cable
Outdoor Cable
Antenna
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2566P4W-R dual-band WiFi MIMO 4-element patch antenna mounted
remotely outdoors, access point is indoors.
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
4 x DC pass, N(f)-N(f), lightning arrestors. Cisco PID CGR-LA-NF-NF.
Note
Lightning arrestors must be appropriately grounded to infrastructure system ground designed
to conduct lightning currents to Earth ground.
This configuration assumes that the lightning arrestor is mounted on a building or enclosure
penetration panel, and that it is interfaced on both sides with N(m) cables.
This configuration assumes that there is an N(m) to N(m) cable connected between the lightning arrestor
and the Access Point.
For indoor cable routing, the deployment must balance the requirements of Fire Code, Electrical Code,
and any other applicable regulations, versus RF cable type, cost, RF cable length, and RF cable insertion
loss.
Select from:
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to RP-TNC (jack), LMR-240-DB, 10 ft. cables. Cisco PID CAB-L240-10-N-R
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to RP-TNC (jack), LMR-400-DB, 20 ft. cables. Cisco PID CAB-L400-20-N-R
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2566P4W-R dual-band WiFi MIMO 4-element patch antenna is required.
The antenna specifications are:
• 2400-2484 MHz, 5150-5850 MHz operating frequency range
• WiFi, MIMO operation
• Single polarization
• 6dBi (2.4 GHz), 6 dBi (5.8 GHz) gain
• IP54 rated, indoor or outdoor operation, -40 to 158°F (-40 to +70°C) operating temperature range
• 4 x integrated cables with RP-TNC (plug) connector
• Cisco PID AIR-ANT2566P4W-R
36
Page 37

Indoor or Outdoor Cisco Aironet Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Directional Array Antenna and Access Point
Table 18: Indoor or Outdoor Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Directional Array Antenna and Access Point
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
Adapter and/or Lightning Arrestor
Antenna
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2566D4M-R Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Directional Array
antennas directly connected to the access point.
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
You need:
• 4 x N(m) to RP-TNC (jack), RF coax adapters. Cisco PID AIR-ACC370-NM-RF.
Note
No lightning arrestors are required.
N/AIndoor Cable
N/AOutdoor Cable
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2566D4M-R Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Directional Array
antenna is required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2400-2484 MHz, 5150-5850 MHz operating frequency range
• WiFi, MIMO operation
• Dual polarization
• 6dBi (2.4 GHz), 6 dBi (5.8 GHz) gain
• IP67 rated, indoor or outdoor operation, -40 to 158°F (-40 to +70°C) operating temperature
range
• 4 x integrated cables with RP-TNC (plug) connector
• Cisco PID AIR-ANT2566D4M-R
OutdoorCiscoAironetDual-Band Polarization-Diverse Directional Array Antenna and Access Point for Indoor or Enclosed AP Use Scenario
Table 19: Outdoor Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Directional Array Antenna and Access Point for Indoor or Enclosed AP Use Scenario
DescriptionItem
Antenna Arrangement
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2566D4M-R Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Directional Array antenna
mounted remotely outdoors, access point is indoors.
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
37
Page 38

DescriptionItem
Adapter and/or Lightning
Arrestor
Indoor Cable
Outdoor Cable
Antenna
4 x DC pass, N(f)-N(f), lightning arrestors. Cisco PID CGR-LA-NF-NF.
Note
Lightning arrestors must be appropriately grounded to infrastructure system ground designed
to conduct lightning currents to Earth ground.
This configuration assumes that the lightning arrestor is mounted on a building or enclosure
penetration panel, and that it is interfaced on both sides with N(m) cables.
This configuration assumes that there is an N(m) to N(m) cable connected between the lightning arrestor
and the Access Point.
For indoor cable routing, the deployment must balance the requirements of Fire Code, Electrical Code,
and any other applicable regulations, versus RF cable type, cost, RF cable length, and RF cable insertion
loss.
Select from:
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to RP-TNC, LMR-240-DB, 10 ft. cables. Cisco PID CAB-L240-10-N-R
• 4 x N(m)-R/A to RP-TNC, LMR-400-DB, 20 ft. cables. Cisco PID CAB-L400-20-N-R
1 x Cisco Aironet AIR-ANT2566D4M-R Dual-Band Polarization-Diverse Directional Array antenna
is required. The antenna specifications are:
• 2400-2484 MHz, 5150-5850 MHz operating frequency range
• WiFi, MIMO operation
• Dual polarization
• 6dBi (2.4 GHz), 6 dBi (5.8 GHz) gain
• IP67 rated, indoor or outdoor operation, -40 to 158°F (-40 to +70°C) operating temperature range
• 4 x integrated cables with RP-TNC (plug) connector
• Cisco PID AIR-ANT2566D4M-R
Outdoor Single Band Antennas in Flexible Antenna Port (Flex Port) Configuration and Access Point
Table 20: Outdoor Single band antennas in Flexible Antenna Port (Flex Port) configuration and Access Point
DescriptionItem
Antenna
Arrangement
1 x Cisco Aironet 2.4 GHz 13-dBi Directional Antenna AIR-ANT2413P2M-N dual port antenna connected to
IW3702 ports “A” and “B” together with
1 x Cisco Aironet 5 GHz 13-dBi Directional Antenna AIR-ANT5114P2M-N dual port antenna connected to
IW3702 ports “C” and “D”.
Access point can be located outdoors, indoors, or located in an enclosure.
Extension cables may be needed depending on distance between antennas and the access point.
38
Page 39

DescriptionItem
IW3702-2E-x-K9, IW3702-4E-x-K9, IW3702-2E-UXK9 or IW3702-4E-UXK9Access Point
Adapter and/or
Lightning
Arrestor
4 x DC pass, N(m)-N(f) lightning arrestors. Cisco PID CGR-LA-NM-NF.
Adapters:
2 x AIR-ACC370-NF-NF per antenna, if using extension cables.
Description:
In addition to lightning arrestors, select from these cables and adapters:
1. No cables or adapters requried if 30” integrated antenna cables are of sufficient length for your intended
deployment. Each of the AIR-ANT2413P2M-N and AIR-ANT5114P2M-N antennas have 2 x 30” integrated
cables with N(m) connectors, which can be connected directly to the IW3702 antenna port N(f) connectors.
2. If longer cable lengths are needed for deployment, choose an appropriate number of AIR-ACC370-NF-NF
adapters and cables below.
Note
N(f) to N(f) adapter is needed to connect the N(m) port of the antenna with the N(m) port of the
extension cables.
For example, if AIR-ANT2413P2M-N needs to be extended by 5ft, and AIR-ANT5114P2M-N needs to be
extended by 20ft, then choose:
2 x AIR-ACC370-NF-NF adapters, plus 2 x CAB-L400-5-N-N for the AIR-ANT2413P2M-N dual port antenna,
2 x AIR-ACC370-NF-NF adapters, plus 2 x CAB-L400-20-N-N for the AIR-ANT5114P2M-N dual port antenna.
Selection:
Indoor Cable
• N(f) to N(f) RF adapter: Cisco PID, AIR-ACC370-NF-NF
• N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-N,
• N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-NS
• N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 10’ RF-cable, Cisco PID: AIR-CAB010LL-N
• N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 20’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-20-N-N
• N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-600-DB, 30’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L600-30-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 25’ RF cable with petrochemical and oils resistance, Cisco
PID AIR-CAB025HZ-N
For indoor cable routing, the deployment must balance the requirements of Fire Code, Electrical Code, and any
other applicable regulations, versus RF cable type, cost, RF cable length, and RF cable insertion loss.
39
Page 40

DescriptionItem
Outdoor Cable
Antenna
Select from the following list, and choose appropriate quantity according to the descriptions above.
• N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-N
• N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 5’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-5-N-NS
• N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB , 10’ RF cable, Cisco PID: AIR-CAB010LL-N
• N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 20’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L400-20-N-N
• N(m)-R/A to N(m)-STR, LMR-600-DB, 30’ RF cable, Cisco PID: CAB-L600-30-N-N
• 4 x N(m)-STR to N(m)-STR, LMR-400-DB, 25’ RF cable with petrochemical and oils resistance, Cisco
PID AIR-CAB025HZ-N
1 x Cisco Aironet 2.4 GHz 13-dBi Directional Antenna AIR-ANT2413P2M-N dual port antenna connected to
IW3702 ports “A” and “B”, together with:
1 x Cisco Aironet 5 GHz 13-dBi Directional Antenna AIR-ANT5114P2M-N dual port antenna connected to
IW3702 ports “C” and “D”.
AIR-ANT2413P2M-N antenna specifications:
2.4 GHz 13-dBi Directional Antenna, dual port, dual polarization.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/connectedgrid/antennas/installing-combined/
industrial-routers-and-industrial-wireless-antenna-guide/AIR-ANT2413P2M-N.html
AIR-ANT5114P2M-N antenna specifications:
5-GHz 13-dBi Directional Antenna, dual port, dual polarization.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/connectedgrid/antennas/installing-combined/
industrial-routers-and-industrial-wireless-antenna-guide/AIR-ANT5114P2M-N.html
Note
AIR-ANT5114P2M-N should be specified as 13dBi in the CLI, when specifying 5GHz antenna gain
selection of IW3702.
IW3702 Flexible Antenna Port
• Supports either dual-band or single band antennas on the same platform.
• Configurable via a software command.
• In single band mode, 2.4GHz radio uses antenna ports A and B, and 5GHz radio uses antenna ports C and D.
40
Page 41

• Configuring Antenna Band Mode for autonomous mode:
ap(config)# dot11 ant-band-mode {dual|single}
• Configuring Antenna Band Mode from the WLC CLI:
(Cisco Controller)> config ap antenna-band-mode <single|dual> <ap_name>
Configuration
This section contains the following topics:
• Management Options, on page 13
• Configuring the Access Point, on page 42
Management Options
You can manage the access point using the following options:
• Using the Command Line Interface, on page 41
• Using the Web Browser Interface, on page 42
Using the Command Line Interface
Use either of the following methods to access the CLI:
• Telnet—This protocol allows TCP/IP connections to a host. Telnet allows a user at one site to establish a TCP connection to a
login server at another site, and then pass the keystrokes from one device to the other. Telnet can accept either an IP address or
domain name as the remote device address.
41
Page 42

• Secure Shell (SSH)—This protocol provides a secure, remote connection to networking devices. The SSH software package
provides secure login sessions by encrypting the entire session. SSH features strong cryptographic authentication, strong
encryption, and integrity protection.
For more information about using the CLI, see the “Using the Command-Line Interface” chapter of the Cisco IOS Configuration
Guide for Autonomous Aironet Access Points.
Using the Web Browser Interface
The web browser interface contains management pages you can use to change the wireless device settings, upgrade firmware, and
monitor and configure other wireless devices on the network.
You use the wireless device IP address of the access point to access the web browser interface. Prior to using the web browser interface
for the first time, you must assign an IP address to the access point (see Configuring the Access Point, on page 42).
To use the web browser interface:
Procedure
Step 1 Open your browser and enter the IP address of the access point in the address field.
The login screen appears.
Step 2 Enter the user name Cisco and password Cisco.
The username and password are case-sensitive.
Note
Step 3 Use the system management pages to define the access point configuration settings.
What to do next
For more information about using the web browser interface, see the “Using the Web Browser Interface” chapter of the Cisco IOS
Configuration Guide for Autonomous Aironet Access Points.
We recommend that you change your user name and password after first-time log in.
Configuring the Access Point
Note
Refer to Installation Guidelines, on page 16 for details on registering your access point with the Wireless Internet Service
Providers Association (WISPA) database.
Obtaining an IP Address
Your access point requires an IP address to operate. The access point is not shipped with a default IP address. It obtains an IP address
from the DHCP server in your network when you make the connection. If your network does not have a DHCP server, the access
point continues to request an IP address until you assign it one. You must configure the IP address by opening the CLI from a terminal
session established through the console port on the access point.
42
Page 43

You must know the IP address assigned to the access before you can use the browser-based management GUI. If your access point
obtained its IP address the network DHCP server, you or your network administrator can obtain it by querying the DHCP server using
the MAC address of the access point.
For more information, see the “Obtaining and Assigning an IP Address” section of the “Configuring the Access Point for the First
Time” chapter of the Cisco IOS Configuration Guide for Autonomous Aironet Access Points.
Connecting to the Access Point Console Port
You can connect to the console port and open the CLI from a terminal session to begin configuring the device.
To connect to the access point:
Procedure
Step 1 Use a 0.5 in. (13 mm) socket wrench to remove the console (CON) port cover by turning it counterclockwise.
Console port cover1
43
Page 44

Step 2 Connect the RJ-45-to-DB-9 adapter cable to the 9-pin serial port on the PC.
Step 3 Connect the other end of the cable to the access point console port.
Console port1
RJ-45-to-DB-9 adapter cable2
USB-to-DB-9 adapter cable3
Step 4 Set up a terminal emulator (for example, puTTy or SSH) on your PC to communicate with the access point, using the
following connection settings:
44
Page 45

• 9600 baud
• 8 data bits
• No parity
• 1 stop bit
• No flow control
Step 5 When connected, press enter or type en to access the command prompt.
Entering en prompts you for a password, and then enters privileged exec mode. The default password is Cisco and is
case-sensitive.
When you finish configuring the access point:
Step 6 Use a small flat-blade screwdriver to depress the tab on the RJ45 connector and disconnect the cable from the CON port.
Step 7 Replace the CON port cover.
Step 8 Use a 0.5 in. (13 mm) socket wrench to torque the CON port cover to 6-7 ft-lbs (8.13-9.49 N-m).
45
Page 46

Console port cover1
Setting Access Point Settings
Use the system management pages in the web browser interface to set the access point settings. For information on how to access
the web browser interface, see Configuring the Access Point for Autonomous Operation, on page 46.
Use the system management pages to define configuration settings. A navigation bar appears on the left side of the page; the
configuration action buttons appear at the bottom. Use the navigation bar to access the various management pages. Use the configuration
action buttons to save or cancel setting changes.
Configuring the Access Point for Autonomous Operation
For information about configuring the access point for autonomous operations, see the Cisco IOS Configuration Guide for Autonomous
Aironet Access Points.
Connecting the Access Point to a Wireless LAN Controller
This section describes how to connect the access point to a wireless LAN controller. Because the configuration process occurs on
the controller, see the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide for additional information.
The Controller Discovery Process
The access point uses standard Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points Protocol (CAPWAP) to communicate between
the controller and other wireless access points on the network. CAPWAP is a standard, interoperable protocol that allows an access
controller to manage a collection of wireless termination points. The discovery process using CAPWAP is identical to the Lightweight
Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) used with Cisco IW3702 access points. LWAPP-enabled access points are compatible with CAPWAP,
and conversion to a CAPWAP controller is seamless. Deployments can combine CAPWAP and LWAPP software on the controllers.
The functionality provided by the controller does not change, except for customers who have Layer 2 deployments, which CAPWAP
does not support.
In a CAPWAP environment, the wireless access point discovers a controller by using CAPWAP discovery mechanisms and then
sends it a CAPWAP join request. The controller sends the access point a CAPWAP join response to allow the access point to join
the controller. When the access point joins the controller, the controller manages its configuration, firmware, control transactions,
and data transactions.
For additional information about the discovery process and CAPWAP, see the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Software Configuration
Guide .
Note
Refer to the Release Notes for the minimum required Cisco Wireless LAN Controller software release for the Cisco IW3702
access points.
• You cannot edit or query any access point using the controller CLI if the name of the access point contains a space.
• Ensure that the controller is set to the current time. If the controller is set to a time that has already occurred, the access point
might not join the controller because its certificate may not yet be valid.
Access points must be discovered by a controller before they can become active in the network. The access point supports these
controller discovery processes:
46
Page 47

• Layer 3 CAPWAP discovery—Can occur on different subnets than the access point and uses IP addresses and UDP packets
rather than MAC addresses used by Layer 2 discovery.
• Locally stored controller IP address discovery—If the access point was previously joined to a controller, the IP addresses of the
primary, secondary, and tertiary controllers are stored in the access point’s non-volatile memory. This process of storing controller
IP addresses on an access point for later deployment is called priming the access point . See Performing a Pre-Installation
Configuration, on page 47.
• DHCP server discovery—This feature uses DHCP option 43 to provide controller IP addresses to access points. Cisco switches
support a DHCP server option that is typically used for this capability. See Configuring DHCP Option 43 and DHCP Option
60, on page 49.
• DNS discovery—The access point can discover controllers through your domain name server (DNS). To use this discovery
method, you must configure the DNS to return controller IP addresses in response to
CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.localdomain, where localdomain is the access point domain name. Configuring the
CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER provides backward compatibility in an existing deployment. When an access point receives
the IP address and DNS information from a DHCP server, it contacts the DNS to resolve
CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.localdomain. When the DNS sends a list of controller IP addresses, the access point sends
discovery requests to the controllers.
Performing a Pre-Installation Configuration
The following procedures ensure a successful access point installation and initial operational setup. Pre-installation configuration –
priming the access point – is optional.
Note
If your network controller already properly configured, you can skip priming and simply install your access point in its final
location and connect it to the network. See Deploying in a Wireless Network, on page 51.
The following figure shows the pre-installation configuration setup.
Figure 9: Pre-Installation Configuration Setup
To prime the access point:
47
Page 48

Procedure
Step 1 Ensure that the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Management DS Port is connected to the network. Use the CLI,
browser-based interface, or Cisco WCS procedures described in the appropriate Cisco Wireless LAN Controller guide
to perform the following:
a) Ensure that the access points have Layer 3 connectivity to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Management and
AP-Manager Interface.
b) Configure the switch to which your access point is to attach. See the appropriate Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
guide.
c) Set the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller as the master so that new access points always join with it.
d) Ensure that DHCP is enabled on the network.
Note
The access point must receive its IP address through DHCP.
e) Ensure that no CAPWAP UDP ports are blocked in the network.
f) Use a DHCP, DNS, or IP subnet broadcast to ensure that the access point finds the IP address of the controller.
This guide describes the DHCP method to convey the controller IP address. For other methods, refer to product
documentation. See also Using DHCP Option 43, on page 49.
Step 2 Apply power to the access point:
The access point is IEEE 802.3at (30 W) compliant and can be powered by a third-party DC power supply that you
provide. The Cisco power injector option is AIR-PWRINJ1500-2=.
Note
• The access point downgrades to 3x3 when connected to a 15.4W power supply. For maximum operating
efficiency, use an IEEE 802.3at compliant PoE switch or AIR-PWRINJ1500-2= power injector.
• To prevent Ethernet port bottlenecks due to wireless traffic speeds exceeding 10/100 Ethernet port transmit
speeds, the Cisco IW3702 access point requires a Gigabit Ethernet link.
As the access point attempts to connect to the controller, the LEDs cycle through a green-red-amber sequence, which can
take up to 5 minutes.
Note
• If this connection takes longer than five minutes, the access point cannot find the master Cisco Wireless
LAN Controller. Check the connection, and ensure that both are on the same subnet.
• To prevent Ethernet port bottlenecks due to wireless traffic speeds exceeding 10/100 Ethernet port transmit
speeds, the Cisco IW3702 access point requires a Gigabit Ethernet link.
• If the access point shuts down, check the power source.
After a successful connection, the access point compares operating system code versions with the Cisco Wireless LAN
Controller. If versions differ, it downloads the newest version. The Status LED blinks dark blue during this process. On
a successful download, the access point reboots.
Step 3 (Optional) Configure the access point.
Use the controller CLI, controller GUI, or Cisco Prime Infrastructure to customize access-point-specific IEEE 802.11ac
network settings.
On successful access point priming, the Status LED is green indicating normal operation.
Step 4 Disconnect the access point and mount it in location.
48
Page 49

Notes:
• If the access point LEDs do not indicate normal operation, turn it off and repeat the access point priming
procedure (see Performing a Pre-Installation Configuration, on page 47).
• When installing a Layer 3 access point on a different subnet than the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, ensure
that:
• a DHCP server is reachable from the subnet on which you are installing the access point and that
subnet has a return route to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller.
• the return route to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller has destination UDP ports 5246 and 5247 open
for CAPWAP communications.
• the return route to the primary, secondary, and tertiary Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers allows IP
packet fragments.
• if using address translation, the access point and the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller have a static
1-to-1 NAT to an outside address. (Port address translation is not supported.)
Using DHCP Option 43
You can use DHCP Option 43 to provide a list of controller IP addresses to the access points, enabling them to find and join a
controller. For additional information, refer to Configuring DHCP Option 43 and DHCP Option 60, on page 49.
Configuring DHCP Option 43 and DHCP Option 60
This section contains a DHCP Option 43 configuration example on a Windows 2003 Enterprise DHCP server for use with Cisco
wireless access points. For other DHCP server implementations, consult the product documentation for configuring DHCP Option
43.
With DHCP Option 43, use the IP address of the controller management interface.
Notes:
• DHCP Option 43 is limited to one access point type per DHCP pool. You must configure a separate DHCP pool for
each access point type.
• DHCP servers must be programmed to return the option based on the DHCP Vendor Class Identifier (VCI) string of
the access point (DHCP Option 60). The VCI string for the access point is:
Cisco AP iw3702
If you ordered an access point with the Service Provider Option (AIR-OPT60-DHCP) selected in the ordering tool, the VCI
string for the access point contains -ServiceProvider. For example, an access point with this option returns this VCI string:
Cisco AP iw3702-ServiceProvider
The Cisco IW3702 access point uses the type-length-value (TLV) format for DHCP Option 43. The TLV block format is:
• Type: 0xf1 (decimal 241)
• Length: Number of controller IP addresses * 4
• Value: List of Cisco Wireless LAN Controller management interfaces
To configure DHCP Option 43 in the embedded Cisco IOS DHCP server:
49
Page 50

Procedure
Step 1 Enter configuration mode at the Cisco IOS CLI.
Step 2 Create the DHCP pool, including the necessary parameters such as default router and name server.
Example DHCP scope commands:
Example:
ip dhcp pool pool_name
network IP_network netmask
default-router default_router
dns-server DNS_Server
where,
• pool_name is the name of the DHCP pool (for example, AP3702).
• IP_network is the network IP address where the controller resides (for example, 10.0.15.1).
• netmask is the subnet mask (for example, 255.255.255.0).
• default_router is the IP address of the default router (for example,10.0.0.1).
• DNS_Server is the IP address of the DNS server (for example, 10.0.10.2).
Step 3 Add the option 60 line using the following syntax:
Example:
option 60 ascii VCI_string
where,
• VCI_string = “Cisco AP iw3702”
Note
You must include the quotation marks.
Step 4 Add the option 43 line using the following syntax:
Example:
option 43 hex <hex_string>
The hex string is assembled by concatenating the TLV values: Type + Length + Value
where,
• Type is always f1(hex).
• Length is the number of controller management IP addresses times 4 in hex.
• Value is the IP address of the controller listed sequentially in hex.
TLV Example
For two controllers with management interface IP addresses 10.126.126.2 and 10.127.127.2
50
• Type is f1(hex)
Page 51

• Length is 2 * 4 = 8 = 08 (hex)
The resultant IP addresses translate to 0a7e7e02 and 0a7f7f02. Assembling the string yields f1080a7e7e020a7f7f02.
The resulting Cisco IOS command added to the DHCP scope is option 43 hex f1080a7e7e020a7f7f02.
Deploying in a Wireless Network
To deploy the access point in a wireless network:
Procedure
Step 1 Connect and power up the access point.
Step 2 Observe the Status LED (see Status LED, on page 8).
On successful power-up, the discovery and join process begins. During this process, the Status LED blinks green-red-off.
On a successful join, the Status LED is green when no clients are associated, or blue when one or more clients are
associated.
Note
• If the Status LED is not on, the access point may not have power.
• If the Status LED blinks green-red-off longer than 5 minutes, it cannot find its primary, secondary, and
tertiary Cisco Wireless LAN Controller. Check the connection, and ensure that both are on the same subnet
or that the access point has a return route to its primary, secondary, and tertiary Cisco Wireless LAN
Controller.
• If the access point is not on the same subnet as the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, ensure that there is a
properly configured DHCP server on the same subnet. See Configuring DHCP Option 43 and DHCP
Option 60, on page 49.
Step 3 Reconfigure the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller so that it is not the master .
Configuring PoE Out Function
You can configure the PoE-Out port power function in autonomous mode for by using the following CLIs:
• To disable the PSE function, use the power out-never command.
• To turn on the PoE out function, use the no power out-never command.
ap(config)# power [inline | out-never]
inline Inline power configuration
out-never Never apply PoE out power
Note
This command will not be effective if the AP is powered only by PoE/PoE+.
51
Page 52

Connecting Ethernet Daisy Chain
The Ethernet daisy chain feature is available on IW3702 autonomous mode.
IW3702 has two Ethernet ports: POE-IN (Gig0) and POE-OUT (Gig1). You can connect several IW3702 access points in daisy chain
via Ethernet cables directly.
Note
Make sure that you use 4-pair cables which support 1000 Mbps. This feature cannot work properly with 2-pair cables which
support 100 Mbps.
For the speed and duplex settings on the Ethernet port of the access point, it is recommended that you configure auto for both,
which is the default setting.
In daisy chain topology, each IW3702 can be powered either by DC input (through PWR connector) or POE inline (through POE IN
port), but not both. To avoid inadvertently powering by dual sources, when connecting IW3702 to a device capable of PoE power
sourcing (PSE, including another IW3702), see the following requirements:
• Connection between two IW3702 access points:
• POE-IN to POE-IN connection
• POE-OUT to POE-OUT connection
• Connection between other PSE (POE source) and IW3702:
• Connect PSE to the POE-OUT port of IW3702
• Connect non-PSE device to the POE-IN port of IW3702
Daisy Chain Connection Topologies
You can use the following connections for daisy chain topology:
• Both IW3702-1 and IW3702-2 are powered by DC power source, with POE-IN to POE-IN connection between IW3702s.
• Both IW3702-1 and IW3702-2 are powered by DC power source, with POE-OUT to POE-OUT connection between IW3702s.
52
Page 53

• IW3702-1 is powered by DC power source, and IW3702-2 has no DC input. IW3702-2 can be powered on only when the
POE-OUT port of IW3702-1 connects to the POE-IN port of IW3702.
RAP Ethernet Daisy Chain on IW3702
The RAP Ethernet Daisy Chain feature is supported on Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Release 8.10.105.0.
In the daisy chain topology shown in the following figure, if the link between RAP1 and RAP2 is broken, or RAP1 loses CAPWAP
connectivity to the controller or switch, RAP2 will change its backhaul to wireless link. The Ethernet interfaces of RAP2 will be
blocked and no child mesh AP will be allowed. Then, RAP3 and RAP4 will lose connection if they are far away from RAP1.
For the access point joining over wireless backhaul, it stays on wireless backhaul for 15 minutes and comes back to scan state every
15 minutes, until it finds a wired backhaul and joins the controller.
If the link between RAP1 and RAP2 is recovered, it takes up to 15 minutes for RAP2 to detect it and change back to Ethernet backhaul.
Similarly, RAP3 and RAP4 will take additional time (maximum of 15 minutes at each hop) if they have joined over wireless backhaul.
Figure 10: Ethernet Daisy Chain Topology
The RAP Ethernet Daisy Chain feature enhances the existing Ethernet bridging functionality by introducing a new command to
configure strict wired uplink on each access point. It forces the bridge AP to stick to the Ethernet link, and block the selecting of
wireless link for uplink backhaul. Even the Ethernet link failure happens, the access point will never select a parent over wireless
backhaul.
53
Page 54

Note
To support this Ethernet daisy chain topology, you MUST use power injector as the power supply for the access point.
Supported power injectors are: AIR-PWRINJ1500-2=, AIR-PWRINJ-60RGD1=, and AIR-PWRINJ-60RGD2=.
If there is a CAPWAP loss on the first access point (RAP1) connected to switch, the entire chain will lose uplink. It takes about 15
seconds for each access point to recovery the CAPWAP connection after the upstream RAP1 is recovered. The last RAP in N hop
chain takes maximum 15xN seconds to recover the connection.
You can configure strict wired uplink only if the AP is configured as Bridge or Flex Bridge mode, Root AP role, and connected to
WLC using wired connection. If it connects to WLC using radio link, the configuration is not allowed.
Note
After the configuration, the AP may be in MAP role. It is required to prime all AP to RAP role before connecting all of them
with the wired connection. Otherwise there may be loop issues if MAP uses wireless backhaul to connect to the other AP.
WLC Configuration for RAP Ethernet Daisy Chain
Procedure
Step 1 Configure the AP in bridge/flex bridge mode.
CLI: config ap mode [bridge|flex+bridge]{submode none} <Cisco_AP>
GUI: wireless -> All APs -> Details (General) page -> AP mode
54
Note
Before changing the mode to the bridge/flex bridge, make sure that the AP’s MAC is added in MAC filter list
of WLC. Otherwise the bridge mode AP will not be able to join the WLC.
For more details, refer to:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/technotes/8-7/b_mesh_87/b_mesh_87_chapter_0110.html#ID4755
Page 55

Step 2 Change the AP role to Root.
CLI: config ap role {rootAP|meshAP} <Cisco_AP>
GUI: Wireless -> All APs -> Details (Mesh) page -> AP role
Step 3 Enable Ethernet interface 1 for all the APs from the controller.
CLI:config ap lan port-id 1 enable <Cisco_AP>
Step 4 Configure Ethernet bridging.
Ethernet bridging must be enabled on all APs in the Bridge mode.
CLI:config ap bridging enable <Cisco_AP>
GUI: Wireless > Access Point > (AP_NAME) > Mesh, and then check the Ethernet bridging check box
For more details, refer to the Connecting the Cisco 1500 Series Mesh Access Points to the Network chapter of the Cisco
Wireless Mesh Access Points, Design and Deployment Guide.
55
Page 56

Step 5 Configure Strict Wired Uplink
Use the following command to enabled or disable strict wired uplink on a specific AP:
CLI:
config ap strict-wired-uplink {enable|disable} <Cisco_AP>
Step 6 (Optional) For Multiple VLAN deployment, follow step 6 to 8.
Disable VLAN transparency from the controller.
CLI: config mesh ethernet-bridging vlan-transparent {enable|disable}
GUI: Wireless--> Mesh ---> Ethernet Bridging
Step 7 If Multiple VLANs are used with one native VLAN and other as allowed VLAN, verify VLAN support is enabled in
each RAP.
CLI:
• config ap vlan-trunking enable <ap-name>
• config ap vlan-trunking native <native vlan-id> <ap-name>
GUI:
• Wireless --> AP --> Mesh --> VLAN support
• Wireless --> AP --> Mesh --> Native VLAN ID
56
Page 57

Step 8 Configure the Ethernet interface of each RAP with native VLAN and add the other allowed VLAN.
CLI:
• config ap ethernet <intf-num> mode trunk enable <ap-name> native-vlan <vlan-Id>
• config ap ethernet <intf-num> mode trunk {add|delete} <ap-name> <vlan-Id>
GUI:
• Wireless --> AP --> Mesh --> Ethernet Interface 0/1
• Add/Delete Allowed VLAN
57
Page 58

Verifying the Configuration
Use the following command to display the feature state for AP:
(Cisco Controller) >show ap config general <Cisco_AP>
AP Mode ......................................... Bridge
AP Role ......................................... RootAP
Ethernet Bridging ............................... Enabled
Strict Wired Uplink ............................. Enabled
Use the following command to ensure whether the admin status and line protocol of the Ethernet interfaces 0/1 are up.
AP#show interfaces gigabitEthernet 0
GigabitEthernet0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is PowerPC Ethernet, address is 2cd0.2de8.ab80 (bia 2cd0.2de8.ab80)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation 802.1Q Virtual LAN, Vlan ID 1., loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full Duplex, 1Gbps, media type is T
output flow-control is unsupported, input flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Input queue: 2/42878/649/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
WLC GUI: Wireless --> AP --> Mesh --> Ethernet link Status
58
Page 59

Use the following command to display the feature status for all bridge RAP:
(Cisco Controller) >show mesh strict-wired-uplink summary
AP Name AP Model BVI MAC Role Bridge Group Name Strict Wired Uplink
-------- ------------------- ----------------- ---- ----------------- -------------------IW1 IW3702-2E-A-K9 00:a2:ee:59:4b:c0 RAP Qia_37 Enable
IW37-3 IW3702-4E-A-K9 2c:d0:2d:e8:ab:80 RAP Qia_37 Enable
Number of Mesh RAP Strict Wired Uplink Set....... 2
Use the following command to display strict wired uplink status on the access point:
Daisychain-AP#show mesh status
show MESH Status
RootAP in state Maint
Uplink Backbone: GigabitEthernet0, hw GigabitEthernet0
Configured BGN: DSAP3702, Extended mode 0
Children: Accept child
No.of Children: 0
Strict Wired Uplink: Enable
Configuration Guidelines
Note
To make sure this feature works properly, the power injector MUST be used as power supply for the AP.
• Ethernet bridging on all RAPs in the chain should be enabled and secondary Ethernet interfaces needs to be configured according
to the mesh deployment guidelines.
• Strict wired uplink configuration needs to be done on each AP in order to enable this feature.
• Strict wired uplink configuration is supported only on IOS-based IW3702 Access Points and applicable only when the AP is
operating in Bridge or Flex Bridge mode in Root AP role.
• For Flex bridge mode, if it is local switching WLAN, WGB multiple VLAN is not supported.
• If this feature is enabled, the AP will keep scanning until at least one Ethernet adjacency is found. The Ethernet link will not be
added to blacklist and continue being used as backhaul.
59
Page 60

• All the traffic will go through the RAP1 which is a bottleneck and the total network throughput is limited. There should be
around 10% bandwidth reserved for CAPWAP management traffic in high traffic load case.
• Make sure that you use 4-pair cables which support 1000 Mbps. This feature cannot work properly with 2-pair cables which
support 100 Mbps.
• Follow the Ethernet chaining guideline in the Connecting Ethernet Daisy Chain, on page 52 section to establish cable connections.
• Connecting one IW3702’s G0 interface to another IW3702’s G1 interface directly may cause issues in the AP’s POE function
and may damage the AP. To support this feature, the power injector MUST be used as power supply for the AP.
Deployment Option 1
Procedure
Step 1 Connect the mesh AP to WLC through wired connection.
Step 2 Prime all APs to RAP role on the daisy chain topology.
Step 3 Configure config ap bridging enable <Cisco_AP> to enable Ethernet bridging. This command allows the next AP to
connect on its Secondary Ethernet interface.
Step 4 Configure configap strict-wired-uplink enable <Cisco_AP> to enable the feature. At this time, the AP can only connect
to WLC through a wired connection.
Step 5 Connect all APs using wired daisy chain topology.
Deployment Option 2
Procedure
Step 1 Connect all the APs using wired daisy chain topology. Make sure all APs are powered off.
Step 2 Power on the first AP which is closest to the switch or WLC. Make sure it can connect to WLC through a wired connection.
Step 3 Set the AP role to RAP.
Step 4 Configure config ap bridging enable <Cisco_AP> to enable Ethernet bridging. This command allows the next AP to
connect on its Secondary Ethernet interface.
Step 5 Configure configap strict-wired-uplink enable <Cisco_AP> to enable the feature. At this time, the AP can only connect
to WLC through a wired connection.
Step 6 Power on the AP which is next to the previous AP.
Step 7 Repeat Step3 to Step 5.
Troubleshoot Guidelines
Debug to be enabled on AP:
1. debug capwap client event
2. debug capwap client payload—To ensure that strict-wired-uplink config payload from WLC to AP
60
Page 61

3. debug mesh ethernet bridging—Debugs Ethernet bridging
Show commands on AP:
#show interfaces gigabitEthernet 0
GigabitEthernet0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is PowerPC Ethernet, address is 2cd0.2de8.ab80 (bia 2cd0.2de8.ab80)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit/sec, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation 802.1Q Virtual LAN, Vlan ID 1., loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full Duplex, 1Gbps, media type is T
output flow-control is unsupported, input flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Input queue: 2/42878/649/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 1000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 7000 bits/sec, 3 packets/sec
3382115 packets input, 390507998 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 1812139 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 0 multicast, 0 pause input
4807536 packets output, 1258122159 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 4 interface resets
0 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
#show capwap client rcb
AdminState : ADMIN_ENABLED
Primary SwVer : 8.10.118.37
Backup SwVer : 0.0.0.0
NumFilledSlots : 2
Name : AP00ee.abe3.6240
Location : default location
MwarName : Cisco-cc70.ed03.d3b2
MwarApMgrIp : 10.100.60.150
MwarHwVer : 0.0.0.0
ApMode : Bridge
ApSubMode : Not Configured
OperationState : UP
CAPWAP Path MTU : 1485
Link-Encryption (AP) : Disabled
Link-Encryption (MWAR) : Enabled
Prefer-mode : IPv4
LinkAuditing : disabled
ApRole : RootAP
ApBackhaul : 802.11a
ApBackhaulChannel : 0
ApBackhaulSlot : 3
ApBackhaul11gEnabled : 0
ApBackhaulTxRate : 0
Ethernet Bridging State : 1
Daisy Chaining State : Enabled
Public Safety State : disabled
AP Rogue Detection Mode : Enabled
AP Tcp MSS Adjust : Enabled
AP Tcp MSS size : 1250
61
Page 62

Predownload Status : None
Auto Immune Status : Disabled
RA Guard Status : Enabled
Efficient Upgrade State : Disabled
Efficient Upgrade Role : None
Antenna Band Mode : Dual Band
Universal AP Priming mode : Unprimed
802.11bg(0) Radio
ADMIN State = DISABLE [2]
OPER State = DOWN [1]
CONFIG State = DOWN [1]
HW State = DOWN [6]
Radio Mode : Bridge
GPR Period : 10
Beacon Period : 100
DTIM Period : 0
World Mode : 1
VoceraFix : 0
Dfs peakdetect : 0
Fragmentation Threshold : 2346
Current Tx Power Level : 1
Current Channel : 1
Current Bandwidth : 20
802.11a(1) Radio
ADMIN State = ENABLE [1]
OPER State = UP [2]
CONFIG State = UP [2]
HW State = UP [4]
Radio Mode : Bridge
GPR Period : 10
Beacon Period : 100
DTIM Period : 0
World Mode : 1
VoceraFix : 0
Dfs peakdetect : 1
Fragmentation Threshold : 2346
Current Tx Power Level : 1
Current Channel : 36
Current Bandwidth : 20
Nexthop MAC Address : cc70.ed03.d3b8
HYPERLOCATION ADMIN STATE : 0
WLC GATEWAY MAC : 00:00:00:00:00:00
WLC HYPERLOCATION SRC PORT : 0
Remote Machine's IP : 0.0.0.0
#show mesh status
RootAP in state Scan
No active links
Configured BGN: , Extended mode 0
Children: Not accept child
No.of Children: 0
Preferred Parent 0000.0000.0000
Block Child Status: Disable
Strict Wired Uplink: Disable
rxNeighReq 0 rxNeighRsp 0 txNeighReq 0 txNeighRsp 0
rxNeighRsp 211 txNeighUpd 0
nextchan 0 nextant 0 downAnt 0 downChan 0 curAnts 0
nextNeigh 0, malformedNeighPackets 0,poorNeighSnr 0
excludedPackets 0,insufficientMemory 0, authenticationFailures 0
Parent Changes 0, Neighbor Timeouts 0
Auto Parent Switch 0
Authentication Failure statistics
Child MAC No.Of PSK Failures
62
Page 63

show mesh module adjacency
show mesh ethernet vlan config running
#show mesh module mesh-control
mesh lwapp module
skip cleanup: Not set
join timer: Set
boot timer: Set
capwap dhcp: Set
standalone: Not set
was standalone: Not set
abort standalone: Not set
joined once: Set
Mesh Capwap State: JOINED-UP
Lwapp link 00ee.abe3.6241
#show mesh forwarding interfaces
GigabitEthernet0: GigabitEthernet0(state is OPEN)
GigabitEthernet1: GigabitEthernet1(state is OPEN)
Node 00ee.abe3.6241
GigabitEthernet2: GigabitEthernet2(state is OPEN)
GigabitEthernet3: GigabitEthernet3(state is OPEN)
GigabitEthernet4: GigabitEthernet4(state is OPEN)
#show mesh ethernet vlan config running
Running Ethernet VLAN Configuration
Ethernet Interface: 0 mode: TRUNK Native Vlan: 1
Vlans: 4095
Ethernet Interface: 1 mode: TRUNK Native Vlan: 1
Vlans: 4095
Ethernet Interface: 2 mode: TRUNK Native Vlan: 1
Vlans: 4095
Ethernet Interface: 3 mode: TRUNK Native Vlan: 1
Vlans: 4095
Ethernet Interface: 4 mode: TRUNK Native Vlan: 1
Vlans: 4095
VLAN - root hwidb:GigabitEthernet1 global BVI:NULL
VlanID BrgGrp Type Routed Active
---------------------------------------------
GigabitEthernet0 enabled: 1, active: 0, etherbridge 1, line-p: 0, state-up: 1
GigabitEthernet1 enabled: 1, active: 0, etherbridge 1, line-p: 1, state-up: 1
GigabitEthernet2 enabled: 1, active: 0, etherbridge 1, line-p: 0, state-up: 1
GigabitEthernet3 enabled: 1, active: 0, etherbridge 1, line-p: 0, state-up: 1
GigabitEthernet4 enabled: 1, active: 0, etherbridge 1, line-p: 0, state-up: 1
For more details on troubleshoot, refer to:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-3/config-guide/b_cg83/troubleshooting_mesh_access_points.html#ID9205
Configuring Indoor Support for Q Domain Models
Both indoor and outdoor use are supported for IW3702 Q domain models, for unified mode and autonomous mode. By default,
outdoor mode is enable, and channel 36-64 are disabled. After enabling indoor support on the access point, channel 36-64 will be
open for indoor use.
63
Page 64

Note
After factory reset, the indoor mode will be changed back to default outdoor mode.
Enabling Indoor Support for Unified Mode AP
In WLC, use the following command to configure IW3702 in unified mode for indoor support:
(Cisco Controller)> config ap indoor {enable|disable} <AP-Name>
Example:
(Cisco Controller)> config ap indoor enable AP3
Changing the AP's indoor mode will cause the AP to reboot.
Are you sure you want to continue? (y/n) y
Use the following command to check the current mode of AP:
show ap env <AP-Name>
Example:
show ap env AP3
AP Name.......................................... AP3
AP Model......................................... IW3702-4E-Q-K9
AP Role.......................................... Normal
Temperature...................................... N/A
Backhaul......................................... N/A
Indoor Mode...................................... True
GigabitEthernet0 Status.......................... UP
Duplex....................................... FULL
Speed........................................ 1000
Rx Unicast Packets........................... 13148
Rx Non-Unicast Packets....................... 72406
Tx Unicast Packets........................... 18423
Tx Non-Unicast Packets....................... 4420
GigabitEthernet1 Status.......................... DOWN
Battery.......................................... N/A
Enabling Indoor Support for Autonomous Mode AP
Use the following command to configure indoor support for autonomous AP:
ap(config)# dot11 indoor {enable|disable}
Example:
ap(config)# dot11 indoor enable
Enable AP indoor support in the "Q" Regulatory Domain.
WARNING: The configed AP will reboot.
Begin to enable AP indoor support. Do you want to Continue ? (yes/[no]): yes
Use the following command to display the current status of indoor support:
show dot11 indoor
64
Page 65

Configuring Heaters
There are two heaters for each IW3702 access point. By default, they are enabled and will start to work when the environment
tempreature is under -20°C. If you determine that the environment tempreature where the IW3702 is deployed will never be under
-20°C, you can turn off the heaters, which allows the IW3702 to request less power from the switch when the IW3702 is powered
by PoE+.
Note
You must be cautious to turn off the heaters. If the temperature is under -20°C while the heaters are turned off, IW3702 will
not work properly, which might cause damage to the AP.
Note
Two heaters will be disabled or enabled together.
Use the following command to enable or disable the heaters:
(config)#heater {disable|enable}
disable Disable AP heater
enable Enable AP heater
Note
By default, the heaters are enabled. The execution of the heater enable or disable command will trigger the AP reload.
• If the heaters are disabled, AP requests maximum power of 21w. The heaters will never start to work even the environment
tempreature is under -20°C.
• If the heaters are enabled, AP requests maximum power of 30w. The heaters will be turned on automatically when the environment
tempreature is under -20°C.
Use the following command to display the current status of the heaters:
#show heater_status
MCU Firmware Version = 7
Heater1 - OFF, Heater2 – OFF
Heaters admin disabled
Technical Specifications
This section provides the following technical specifications for the access point:
Environmental and Operational Specifications
Table 21: Environmental and Operating Specifications for the Access Point
SpecificationDescription
–40 to 158°F (–40 to +70°C) with solar load and still airOperating temperature
65
Page 66

SpecificationDescription
15,000 ft. (4.5 m)Altitude
5 to 95% (non-condensing)Humidity
Extended operating temperature (DC power)
Power Specifications
Power Requirements
Table 22: Power Requirements for the Access Point
Power Input Type
Condition/Heaters
PoE 802.3af
No heaters active
–58 to 167°F (–50 to +75°C) without solar loading, still air, and cold start limited to
–40°C
185°F (85°C) for 16 hoursOperating type test
–40 to 185°F (–40 to +85°C)Storage temperature
Per IEEE 1613, IEC 61850, EN50155, and AREMAVibration
Per IEEE 1613, IEC 61850, EN50155, and AREMAShock
Per IEC 61850-3 Class 2Seismic
Power Budget (Watts)PoE OutWi-Fi Radio ModeEnvironment
15.4N/A3x3:3 on 2.4/5 GHz> -20°C
PoE+ 802.3at
PoE+ 802.3at
DC In
DC In
DC In
21N/A4x4:3 on 2.4/5 GHz> -20°C
No heaters active
30N/A4x4:3 on 2.4/5 GHz-50°C to -20°C
Still air
1 heater active
20No4x4:3 on 2.4/5 GHz> -20°C
No heaters active
37No4x4:3 on 2.4/5 GHz-50°C to -20°C
Still air
1 heater active
53No4x4:3 on 2.4/5 GHz-50°C to -20°C
Wind cooling
2 heaters active
66
Page 67

Power Input Type
Power Budget (Watts)PoE OutWi-Fi Radio ModeEnvironment
Condition/Heaters
DC In
No heaters active
DC In
Still air
1 heater active
DC In
Wind cooling
2 heaters active
DC Input and PoE IN Specifications
The access point supports two power options:
• DC input from the PWR connector.
• PoE inline power from the PoE IN port.
Note
The PoE OUT port is enabled only when the access point is powered over the PWR port. When powered over the PoE IN
port, PoE OUT functionality is not supported.
38Yes4x4:3 on 2.4/5 GHz> -20°C
55Yes4x4:3 on 2.4/5 GHz-50°C to -20°C
71Yes4x4:3 on 2.4/5 GHz-50°C to -20°C
In relation to powering the access point:
• Power can be supplied by the DC input (PWR port connection) or the PoE inline power (PoE IN port), but not both.
• We recommend not using the two power options at the same time, but no harm results if both are present.
• If both power inputs are present, the DC input (PWR port connection) takes precedence and PoE IN becomes idle and unused.
• Power supply redundancy is not supported.
Supported Power Adapters
The following table shows the power adapters supported for the Cisco IW3702 access point.
DescriptionPID
AC to DC power adapter, with North American plugAIR-PWRADPT3700NA=
AC to DC power adapter, international version without AC plugAIR-PWRADPT3700IN=
Supported PoE Power Injectors
The following power injectors are supported for the Cisco IW3702 access point:
• AIR-PWRINJ1500-2=: PoE+ power injector, for indoor environments
67
Page 68

Note
The power injector AIR-PWRINJ1500-2= is not IP rated for outdoors. Use it in an indoor environment only or put
it in an NEMA enclosure. For more information, see Cisco Aironet Series Power Injector AIR-PWRINJ1500-2=
Installation Instructions.
• AIR-PWRINJ-60RGD1=: PoE+ power injector, for outdoor environments, with North American plug
• AIR-PWRINJ-60RGD2=: PoE+ power injector, for outdoor environments, international version without AC plug
Note
The power injectors AIR-PWRINJ-60RGD1= and AIR-PWRINJ-60RGD2= are IP66 rated. It does not meet all
industrial specifications as supported by the IW3702. For more information, see Cisco Aironet Series Power Injectors
AIR-PWRINJ-60RGD1= and AIR-PWRINJ-60RGD2= Installation Instructions.
The following table lists specifications for the available power inputs.
Table 23: Power Connections Specifications
Power INPUT
WiFi
4 x 4
MIMO
GE-POE-OUT
(POE PSE)
GE-POE-OUT
(10/100/1000)
Operating
Temperature
4
Range
Wire Thickness, Min
Rating
YesYes, 802.3afYesDC Input at +12V
75°C)
YesYes, 802.3afYesDC Input at +24V
75°C)
YesYes, 802.3afYesDC Input at +48V
75°C)
YesNoYesPOE-IN, 802.3at
(POE+, 25W)
POE-IN, 802.3af
(POE, 13W)
4
Refer to Table 14 on page 40 for the restrictions on the temperature limits.
5
When you use a thicker cable, the maximum length can be increased. When the unit is installed in the environment where the
only)
-40 to 167°F (-40 to
75°C)
-4 to 167°F (-20 to 75°C)NoNoNo(3x3
A, shielded
A, shielded
temperature is always higher than -20°C, the maximum length can be double of the value in the table for DC inputs. Furthermore,
if the GE-POE-OUT port is not used as POE-PSE (power source), the maximum length can be increased by 10 feet.
Length
(Max)
20'/6.1m16 AWG, 8 A-58 to 167°F (-50 to
30'/9.1m20 AWG, 4 A-58 to 167°F (-50 to
60'/18.3m20 AWG, 2 A-58 to 167°F (-50 to
100mCAT5e(24AWG), 0.6
100mCAT5e(24AWG), 0.6
5
68
Page 69

Mechanical Specifications
Table 24: Mechanical Specifications for the Access Point
SpecificationDescription
IP67 Type 4XEnclosure type
Dimensions (h x w x d)
• IW3702-2E-UXK9: 2.34 x 11.30 x 8.00 in. (5.94 x 28.7 x 20.32
cm)
• IW3702-4E-UXK9: 2.34 x 11.30 x 8.00 in. (5.94 x 28.7 x 20.32
cm)
6.7 lbs. (3.0 kg)Weight
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
For information about the international regulatory compliance and safety information for the Cisco IW3702 access point, see the
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco IW3702 Access Point on Cisco.com.
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure
This section contains information on compliance with guidelines related to RF exposure.
Generic Discussion on RF Exposure
The Cisco products are designed to comply with the following national and international standards on human exposure to radio
frequencies:
• US 47 Code of Federal Regulations Part 2 Subpart J
• American National Standards Institute (ANSI) / Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers / IEEE C 95.1 (99)
• International Commission on Non Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) 98
• Ministry of Health (Canada) Safety Code 6. Limits on Human exposure to radio frequency fields in the range from 3kHz to 300
GHz
• Australia Radiation Protection Standard
To ensure compliance with various national and international Electromagnetic Field (EMF) standards, the system should only be
operated with Cisco approved antennas and accessories.
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure (ANSI)
United States
This system has been evaluated for RF exposure for humans in reference to ANSI C 95.1 (American National Standards Institute)
limits. The evaluation was based on ANSI C 95.1 and FCC OET Bulletin 65C rev 01.01. The minimum separation distance from the
antenna to general bystanders is 9 inches (23 cm) to maintain compliance.
69
Page 70

Canada
This system has been evaluated for RF exposure for humans in reference to ANSI C 95.1 (American National Standards Institute)
limits. The evaluation was based on RSS-102 Rev 2. The minimum separation distance from the antenna to general bystanders is 9
inches (23cm) to maintain compliance.
This Device Meets International Guidelines for Exposure to Radio Waves (ICNIRP)
The Cisco IW3702 access point includes a radio transmitter and receiver. It is designed not to exceed the limits for exposure to radio
waves (radio frequency electromagnetic fields) recommended by international guidelines. The guidelines were developed by an
independent scientific organization (ICNIRP) and include a substantial safety margin designed to ensure the safety of all persons,
regardless of age and health. As such, the systems are designed to be operated to avoid contact with the antennas by the end user.
It is recommended to place the system in a location where the antennas can remain the minimum distance from the user specified in
the regulatory guidelines, which are designed to reduce the overall exposure of the user or operator.
SeparationDistance
LimitDistanceMPE
0.63 mW/cm2
The World Health Organization has stated that present scientific information does not indicate the need for any special precautions
for the use of wireless devices. They recommend that if you are interested in further reducing your exposure, you can easily orient
antennas away from users or place the antennas at a greater separation distance than recommended.
7.87 in. (20
cm)
1.00
mW/cm2
This Device Meets FCC Guidelines for Exposure to Radio Waves
The Cisco IW3702 access point includes a radio transmitter and receiver. It is designed not to exceed the limits for exposure to radio
waves (radio frequency electromagnetic fields) as referenced in FCC Part 1.1310. The guidelines are based on IEEE ANSI C 95.1
(92) and include a substantial safety margin designed to ensure the safety of all persons, regardless of age and health. As such, the
systems are designed to be operated to avoid contact with the antennas by the end user. We recommend that you place the system in
a location where antennas remain a minimum distance from the user in accordance to the regulatory guidelines, which are designed
to reduce the overall exposure of the user or operator.
The device has been tested and found compliant with the applicable regulations as part of the radio certification process.
SeparationDistance
LimitDistanceMPE
20 cm (7.87 inches)0.63 mW/cm2
The US Food and Drug Administration has stated that present scientific information does not indicate the need for any special
precautions for the use of wireless devices. The FCC recommends that if you are interested in further reducing your exposure, you
can easily orient antennas away from the user or place the antennas at a greater separation distance than recommended, or lower the
transmitter power output.
1.00
mW/cm2
This Device Meets the Industry Canada Guidelines for Exposure to Radio Waves
The Cisco IW3702 access point includes a radio transmitter and receiver. It is designed not to exceed the limits for exposure to radio
waves (radio frequency electromagnetic fields) as referenced in Health Canada Safety Code 6. The guidelines include a substantial
safety margin designed into the limit to ensure the safety of all persons, regardless of age and health. As such, the systems are designed
70
Page 71

to be operated to avoid contact with the antennas by the end user. We recommend that you place the system in a location where
antennas remain a minimum distance from the user in accordance to the regulatory guidelines, which are designed to reduce the
overall exposure of the user or operator.
SeparationDistance
LimitDistanceMPE
20 cm (7.87 inches)0.63 mW/cm2
Health Canada states that present scientific information does not indicate the need for any special precautions for the use of wireless
devices. They recommend that if you are interested in further reducing your exposure, you can easily orient antennas away from the
user or place the antennas at a greater separation distance than recommended, or lower the transmitter power output.
1.00
mW/cm2
Additional Information on RF Exposure
You can find additional information on the subject at the following links:
• Cisco Systems Spread Spectrum Radios and RF Safety white paper
• FCC Bulletin 56: Questions and Answers about Biological Effects and Potential Hazards of Radio Frequency Electromagnetic
Fields
• FCC Bulletin 65: Evaluating Compliance with the FCC guidelines for Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic
Fields
• FCC Bulletin 65C (01-01): Evaluating Compliance with the FCC guidelines for Human Exposure to Radio Frequency
Electromagnetic Fields: Additional Information for Evaluating Compliance for Mobile and Portable Devices with FCC limits
for Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Emission
You can obtain additional information from the following organizations:
• World Health Organization Internal Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection at this URL: www.who.int/emf
• United Kingdom, National Radiological Protection Board at this URL: www.nrpb.org.uk
• Cellular Telecommunications Association at this URL: www.wow-com.com
• The Mobile Manufacturers Forum at this URL: www.mmfai.org
Guidelines for Operating Cisco IW3702 Access Points in Japan
This section provides guidelines for avoiding interference when operating Cisco IW3702 access points in Japan. These guidelines
are provided in both Japanese and English.
71
Page 72

Japanese
English
This equipment operates in the same frequency bandwidth as industrial, scientific, and medical devices such as microwave ovens
and mobile object identification (RF-ID) systems (licensed premises radio stations and unlicensed specified low-power radio stations)
used in factory production lines.
1. Before using this equipment, ensure that no premises radio stations or specified low-power radio stations of RF-ID are in the
vicinity.
2. If this equipment causes RF interference to a premises radio station of RF-ID, promptly change the frequency or stop using the
device; call the number below and ask for recommendations on avoiding radio interference such as setting partitions.
3. If this equipment causes RF interference to a specified low-power radio station of RF-ID, call the number below. Contact Number:
03-6434-6500
Administrative Rules for Cisco IW3702 Access Points in Taiwan
This section provides administrative rules for operating Cisco IW3702 access points in Taiwan. The rules for all access points are
provided in both Chinese and English.
72
Page 73

Chinese Translation Part 1
English Translation Part 1
Administrative Rules for Low-power Radio-Frequency Devices
Article 12: For those low-power radio-frequency devices that have already received a type-approval, companies, business units or
users should not change its frequencies, increase its power or change its original features and functions.
Article 14: The operation of the low-power radio-frequency devices is subject to the conditions that no harmful interference is caused
to aviation safety and authorized radio station; and if interference is caused, the user must stop operating the device immediately and
can't re-operate it until the harmful interference is clear.
The authorized radio station means a radio-communication service operating in accordance with the Communication Act.
The operation of the low-power radio-frequency devices is subject to the interference caused by the operation of an authorized radio
station, by another intentional or unintentional radiator, by industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) equipment, or by an incidental
radiator.
73
Page 74

Chinese Translation Part 2
English Translation Part 2
Low-power Radio-frequency Devices Technical Specifications:
Unlicensed National Information Infrastructure4.7
Within the 5.25-5.35 GHz band, U-NII devices will be restricted to indoor operations to reduce any potential for harmful
4.7.5
interference to co-channel MSS operations.
The U-NII devices shall accept any interference from legal communications and shall not interfere the legal communications.
4.7.6
If interference is caused, the user must stop operating the device immediately and can't re-operate it until the harmful interference
is clear.
Manufacturers of U-NII devices are responsible for ensuring frequency stability such that an emission is maintained within
4.7.7
the band of operation under all conditions of normal operation as specified in the user manual.
Operation of Cisco IW3702 Access Points in Brazil
This section contains information for operating Cisco IW3702 access points in Brazil.
Regulatory Information
Portuguese Translation
Este equipamento opera em caráter secundário, isto é, não tem direito a proteção contra interferência prejudicial, mesmo de estações
do mesmo tipo, e não pode causar interferência a sistemas operando em caráter primário.
English Translation
This equipment operates on a secondary basis and consequently must accept harmful interference, including interference from stations
of the same kind. This equipment may not cause harmful interference to systems operating on a primary basis.
Declaration of Conformity Statements
All the Declaration of Conformity statements related to this product can be found at the following location:
74
Page 75

http://www.ciscofax.com
Ports and Connectors
The port pinouts and connector details are described in this section.
Power Port
The power port is a 4-pin M12 A-code male connector.
Figure 11: Power Port Connector Pinouts
PoE OUT Port
The PoE OUT port is an 8-pin M12 X-code female connector.
Negative DC power connection3Positive DC power connection1
Negative DC power connection4Positive DC power connection2
75
Page 76

Figure 12: PoE OUT Port Pinouts
3_P50_P signal1
3_N60_N signal2
PoE IN Port
The PoE IN port is a 8-pin M12 X-code female connector.
2_N71_P signal3
2_P81_N signal4
76
Page 77

Figure 13: PoE IN Port Pinouts
3_P50_P signal1
3_N60_N signal2
Console Port
The console port is an RJ-45 connector.
Table 25: Console Port Pinouts
SignalPin
RTS output1
DTR input2
TxD output3
GND4
GND5
RxD input6
DSR output7
2_N71_P signal3
2_P81_N signal4
CTS input8
77
Page 78

Related Documentation
The following are other documents in the IW3700 Industrial Wireless Access Point Series:
• Cisco IW3702 Access Point Mounting Guide
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Software Release Notes
• Cisco Industrial Wireless 3700 Series Access Points Ordering Guide
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a service request, and gathering
additional information, see What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation .
To receive new and revised Cisco technical content directly to your desktop, you can subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product
Documentation RSS feed . The RSS feeds are a free service.
78
Page 79

©
2015-2020 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 80

Europe HeadquartersAsia Pacific HeadquartersAmericas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide. Addresses, phone numbers, and fax numbers are listed on the
Cisco Website at www.cisco.com/go/offices.
CiscoSystems(USA)Pte.Ltd.
Singapore
CiscoSystemsInternationalBV
Amsterdam,TheNetherlands
 Loading...
Loading...