Page 1

Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release
3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
First Published: October 10, 2013
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-28697-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH
THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY,
CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB's public domain version
of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright©1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWAREOF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS.
CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network
topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional
and coincidental.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://
www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
©
2013 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface
CHAPTER 1
Preface ix
Document Conventions ix
Related Documentation xi
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request xi
Using the Command-Line Interface 1
Information About Using the Command-Line Interface 1
Command Modes 1
Using the Help System 3
Understanding Abbreviated Commands 4
No and Default Forms of Commands 4
CLI Error Messages 4
Configuration Logging 5
How to Use the CLI to Configure Features 5
Configuring the Command History 5
Changing the Command History Buffer Size 6
Recalling Commands 6
Disabling the Command History Feature 7
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features 7
Editing Commands Through Keystrokes 8
Editing Command Lines That Wrap 9
Searching and Filtering Output of show and more Commands 10
Accessing the CLI Through a Console Connection or Through Telnet 11
CHAPTER 2
Using the Web Graphical User Interface 13
Prerequisites for Using the Web GUI 13
Information About Using The Web GUI 13
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 iii
Page 4

Contents
Web GUI Features 13
Connecting the Console Port of the Switch 15
Logging On to the Web GUI 15
Enabling Web and Secure Web Modes 15
Configuring the Switch Web GUI 16
CHAPTER 3
Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery 19
Finding Feature Information 19
Prerequisites for Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery 19
Restrictions for Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery 20
Information About Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery 20
Access Point Communication Protocols 20
Viewing Access Point Join Information 21
Troubleshooting the Access Point Join Process 21
How to Configure Access Point Discovery 22
Configuring the Syslog Server for Access Points (CLI) 22
Monitoring Access Point Join Information (CLI) 23
Searching for Access Point Radios (GUI) 24
Monitoring the Interface Details (GUI) 24
Configuration Examples for Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery 25
Displaying the MAC Addresses of all Access Points: Example 25
DHCP Option 43 for Lightweight Cisco Aironet Access Points Configuration Example 26
CHAPTER 4
Configuring Data Encryption 27
Finding Feature Information 27
Prerequisites for Configuring Data Encryption 27
Restrictions for Configuring Data Encryption 27
Information About Data Encryption 28
How to Configure Data Encryption 28
Configuring Data Encryption (CLI) 28
Configuring Data Encryption (GUI) 29
Configuration Examples for Configuring Data Encryption 29
Displaying Data Encryption States for all Access Points: Examples 29
CHAPTER 5
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
iv OL-28697-01
Configuring Retransmission Interval and Retry Count 31
Page 5

Contents
Finding Feature Information 31
Prerequisites for Configuring the Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count 31
Information About Retransmission Interval and Retry Count 31
How to Configure Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count 32
Configuring the Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count (CLI) 32
Configuring the Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count (GUI) 33
Viewing CAPWAP Maximum Transmission Unit Information (CLI) 34
Viewing CAPWAP Maximum Transmission Unit Information (GUI) 34
Configuration Examples for Configuring Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry
Count 35
Viewing the CAPWAP Retransmission Details: Example 35
Viewing Maximum Transmission Unit Information: Example 35
CHAPTER 6
CHAPTER 7
Configuring Adaptive Wireless Intrusion Prevention System 37
Finding Feature Information 37
Prerequisites for Configuring wIPS 37
How to Configure wIPS on Access Points 38
Configuring wIPS on an Access Point (CLI) 38
Configuring wIPS on an Access Point (GUI) 39
Monitoring wIPS Information 40
Configuration Examples for Configuring wIPS on Access Points 41
Displaying the Monitor Configuration Channel Set: Example 41
Displaying wIPS Information: Examples 41
Configuring Authentication for Access Points 43
Finding Feature Information 43
Prerequisites for Configuring Authentication for Access Points 43
Restrictions for Configuring Authentication for Access Points 44
Information about Configuring Authentication for Access Points 44
How to Configure Authentication for Access Points 44
Configuring Global Credentials for Access Points (CLI) 44
Configuring Global Credentials for Access Points (GUI) 46
Configuring Authentication for Access Points (CLI) 47
Configuring Authentication for Access Points (GUI) 49
Configuring the Switch for Authentication (CLI) 50
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 v
Page 6

Contents
Configuration Examples for Configuring Authentication for Access Points 51
Displaying the Authentication Settings for Access Points: Examples 51
CHAPTER 8
Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode 53
Finding Feature Information 53
Prerequisites for Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode 53
Information About Autonomous Access Points Converted to Lightweight Mode 54
Reverting from Lightweight Mode to Autonomous Mode 54
Using DHCP Option 43 and DHCP Option 60 54
How Converted Access Points Send Crash Information to the Switch 55
Uploading Memory Core Dumps from Converted Access Points 55
Displaying MAC Addresses for Converted Access Points 55
Configuring a Static IP Address for a Lightweight Access Point 55
How to Convert a Lightweight Access Point Back to an Autonomous Access Point 56
Converting a Lightweight Access Point Back to an Autonomous Access Point (CLI) 56
Converting a Lightweight Access Point Back to an Autonomous Access Point (Using the
Mode Button and a TFTP Server) 56
Authorizing Access Points (CLI) 57
Authorizing Access Points (GUI) 58
CHAPTER 9
Disabling the Reset Button on Converted Access Points (CLI) 59
Monitoring the AP Crash Log Information 60
How to Configure a Static IP Address on an Access Point 61
Configuring a Static IP Address on an Access Point (CLI) 61
Configuring a Static IP Address on an Access Point (GUI) 62
Recovering the Access Point Using the TFTP Recovery Procedure 63
Configuration Examples for Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode 63
Displaying the IP Address Configuration for Access Points: Example 63
Displaying Access Point Crash File Information: Example 64
Using Cisco Workgroup Bridges 65
Finding Feature Information 65
Information About Cisco Workgroup Bridges and non-Cisco Workgroup bridges 65
Monitoring the Status of Workgroup Bridges 66
Debugging WGB Issues (CLI) 66
Configuration Examples for Configuring Workgroup Bridges 68
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
vi OL-28697-01
Page 7

Contents
WGB Configuration: Example 68
CHAPTER 10
CHAPTER 11
CHAPTER 12
Configuring Probe Request Forwarding 69
Finding Feature Information 69
Information About Configuring Probe Request Forwarding 69
How to Configure Probe Request Forwarding (CLI) 69
Optimizing RFID Tracking 71
Finding Feature Information 71
Optimizing RFID Tracking on Access Points 71
How to Optimize RFID Tracking on Access Points 71
Optimizing RFID Tracking on Access Points (CLI) 71
Configuration Examples for Optimizing RFID Tracking 72
Displaying all the Access Points in Monitor Mode: Example 72
Configuring Country Codes 75
Finding Feature Information 75
Prerequisites for Configuring Country Codes 75
CHAPTER 13
Information About Configuring Country Codes 76
How to Configure Country Codes (CLI) 76
Configuration Examples for Configuring Country Codes 79
Displaying Channel List for Country Codes: Example 79
Configuring Link Latency 81
Finding Feature Information 81
Prerequisites for Configuring Link Latency 81
Restrictions for Configuring Link Latency 81
Information About Configuring Link Latency 82
TCP MSS 82
Link Tests 82
How to Configure Link Latency 83
Configuring Link Latency (CLI) 83
Configuring Link Latency (GUI) 85
How to Configure TCP MSS 86
Configuring TCP MSS (CLI) 86
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 vii
Page 8

Contents
Configuring TCP MSS (GUI) 86
Performing a Link Test (CLI) 87
Configuration Examples for Configuring Link Latency 88
Running a Link Test: Example 88
Displaying Link Latency Information: Example 88
Displaying TCP MSS Settings: Example 89
CHAPTER 14
Configuring Power over Ethernet 91
Finding Feature Information 91
Information About Configuring Power over Ethernet 91
How to Configure Power over Ethernet 91
Configuring Power over Ethernet (CLI) 91
Configuring Power over Ethernet (GUI) 92
Configuration Examples for Configuring Power over Ethernet 93
Displaying Power over Ethernet Information: Example 93
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
viii OL-28697-01
Page 9

Preface
Document Conventions, page ix
•
Related Documentation, page xi
•
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, page xi
•
Document Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
DescriptionConvention
^ or Ctrl
Italic font
...
|
[x | y]
Both the ^ symbol and Ctrl represent the Control (Ctrl) key on a keyboard. For
example, the key combination ^D or Ctrl-D means that you hold down the Control
key while you press the D key. (Keys are indicated in capital letters but are not
case sensitive.)
Commands and keywords and user-entered text appear in bold font.bold font
Document titles, new or emphasized terms, and arguments for which you supply
values are in italic font.
Terminal sessions and information the system displays appear in courier font.Courier font
Bold Courier font indicates text that the user must enter.Bold Courier font
Elements in square brackets are optional.[x]
An ellipsis (three consecutive nonbolded periods without spaces) after a syntax
element indicates that the element can be repeated.
A vertical line, called a pipe, indicates a choice within a set of keywords or
arguments.
Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by vertical
bars.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 ix
Page 10

Document Conventions
Preface
DescriptionConvention
Note
{x | y}
Required alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by vertical
bars.
[x {y | z}]
Nested set of square brackets or braces indicate optional or required choices
within optional or required elements. Braces and a vertical bar within square
brackets indicate a required choice within an optional element.
string
A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string or
the string will include the quotation marks.
Nonprinting characters such as passwords are in angle brackets.< >
Default responses to system prompts are in square brackets.[ ]
!, #
An exclamation point (!) or a pound sign (#) at the beginning of a line of code
indicates a comment line.
Reader Alert Conventions
This document may use the following conventions for reader alerts:
Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
manual.
Tip
Caution
Timesaver
Warning
Means the following information will help you solve a problem.
Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage
or loss of data.
Means the described action saves time. You can save time by performing the action described in the
paragraph.
Means reader be warned. In this situation, you might perform an action that could result in bodily
injury.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
x OL-28697-01
Page 11

Preface
Related Documentation
Related Documentation
Before installing or upgrading the switch, refer to the switch release notes.Note
Error Message Decoder, located at:
•
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/index.cgi
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information,
see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco
technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 xi
Page 12

Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Preface
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
xii OL-28697-01
Page 13

CHAPTER 1
Using the Command-Line Interface
Information About Using the Command-Line Interface, page 1
•
How to Use the CLI to Configure Features, page 5
•
Information About Using the Command-Line Interface
Command Modes
The Cisco IOS user interface is divided into many different modes. The commands available to you depend
on which mode you are currently in. Enter a question mark (?) at the system prompt to obtain a list of commands
available for each command mode.
You can start a CLI session through a console connection, through Telnet, a SSH, or by using the browser.
When you start a session, you begin in user mode, often called user EXEC mode. Only a limited subset of
the commands are available in user EXEC mode. For example, most of the user EXEC commands are one-time
commands, such as show commands, which show the current configuration status, and clear commands,
which clear counters or interfaces. The user EXEC commands are not saved when the switch reboots.
To have access to all commands, you must enter privileged EXEC mode. Normally, you must enter a password
to enter privileged EXEC mode. From this mode, you can enter any privileged EXEC command or enter
global configuration mode.
Using the configuration modes (global, interface, and line), you can make changes to the running configuration.
If you save the configuration, these commands are stored and used when the switch reboots. To access the
various configuration modes, you must start at global configuration mode. From global configuration mode,
you can enter interface configuration mode and line configuration mode.
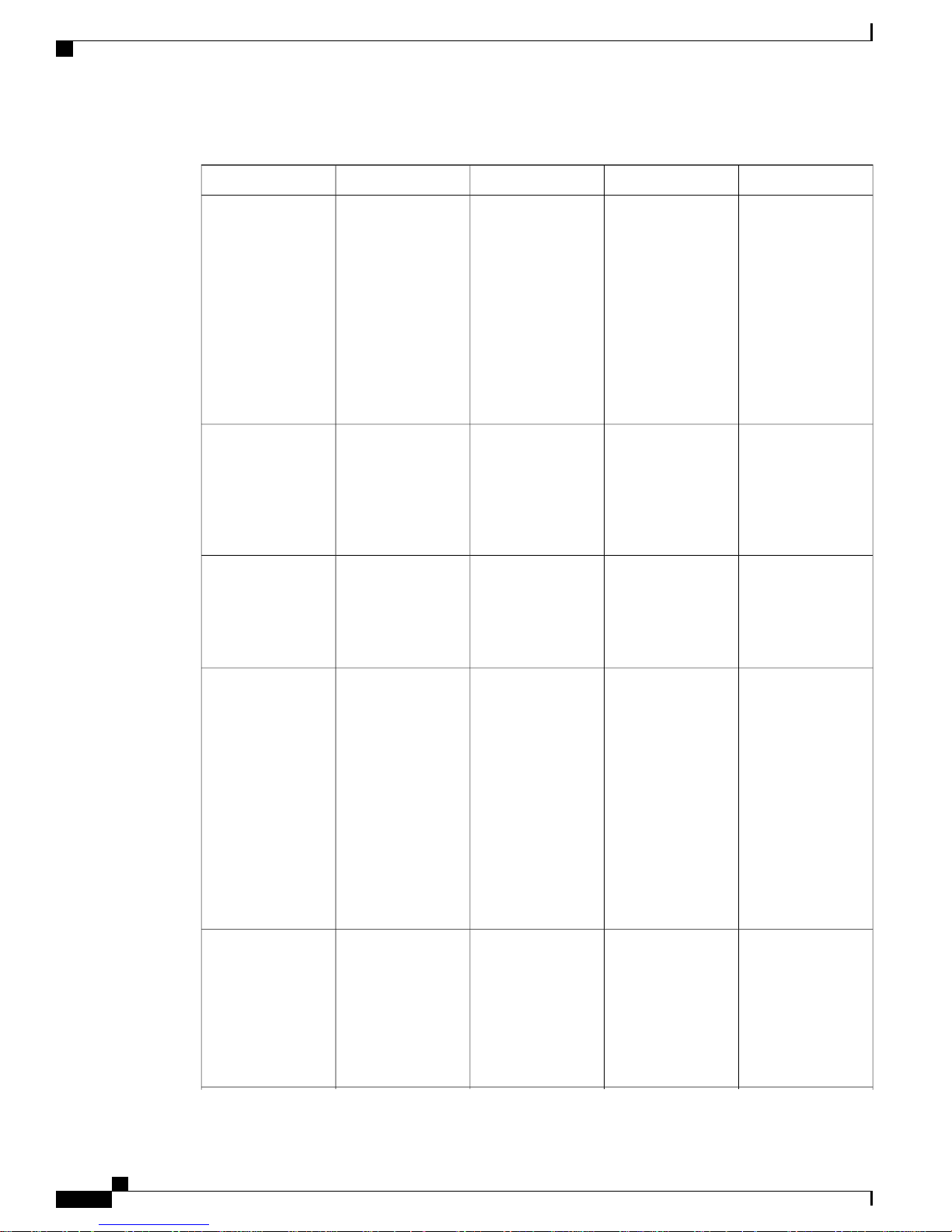
This table describes the main command modes, how to access each one, the prompt you see in that mode, and
how to exit the mode.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 1
Page 14
Command Modes
Using the Command-Line Interface
Table 1: Command Mode Summary
About This ModeExit MethodPromptAccess MethodMode
User EXEC
Privileged EXEC
Global
configuration
Begin a session
using Telnet, SSH,
or console.
While in user EXEC
mode, enter the
enable command.
While in privileged
EXEC mode, enter
the configure
command.
Switch>
Switch#
Switch(config)#
Enter logout or
quit.
Enter disable to
exit.
To exit to privileged
EXEC mode, enter
exit or end, or press
Ctrl-Z.
Use this mode to
Change
•
terminal
settings.
Perform basic
•
tests.
Display
•
system
information.
Use this mode to
verify commands
that you have
entered. Use a
password to protect
access to this mode.
Use this mode to
configure
parameters that
apply to the entire
switch.
VLAN
configuration
Interface
configuration
While in global
configuration mode,
enter the vlan
vlan-id command.
While in global
configuration mode,
enter the interface
command (with a
specific interface).
Switch(config-vlan)#
Switch(config-if)#
To exit to global
configuration mode,
enter the exit
command.
To return to
privileged EXEC
mode, press Ctrl-Z
or enter end.
To exit to global
configuration mode,
enter exit.
To return to
privileged EXEC
mode, press Ctrl-Z
or enter end.
Use this mode to
configure VLAN
parameters. When
VTP mode is
transparent, you can
create
extended-range
VLANs (VLAN IDs
greater than 1005)
and save
configurations in the
switch startup
configuration file.
Use this mode to
configure
parameters for the
Ethernet ports.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
2 OL-28697-01
Page 15

Using the Command-Line Interface
Using the Help System
About This ModeExit MethodPromptAccess MethodMode
Line configuration Use this mode to
Using the Help System
You can enter a question mark (?) at the system prompt to display a list of commands available for each
command mode. You can also obtain a list of associated keywords and arguments for any command.
SUMMARY STEPS
help
1.
abbreviated-command-entry ?
2.
abbreviated-command-entry <Tab>
3.
?
4.
command ?
5.
command keyword ?
6.
While in global
configuration mode,
specify a line with
the line vty or line
console command.
Switch(config-line)#
To exit to global
configuration mode,
enter exit.
To return to
privileged EXEC
mode, press Ctrl-Z
or enter end.
configure
parameters for the
terminal line.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
help
Example:
Switch# help
abbreviated-command-entry ?
Example:
Switch# di?
dir disable disconnect
abbreviated-command-entry <Tab>
Example:
Switch# sh conf<tab>
Switch# show configuration
PurposeCommand or Action
Obtains a brief description of the help system in any
command mode.
Obtains a list of commands that begin with a particular
character string.
Completes a partial command name.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 3
Page 16

Understanding Abbreviated Commands
Using the Command-Line Interface
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
?
Example:
Switch> ?
command ?
Example:
Switch> show ?
command keyword ?
Example:
Switch(config)# cdp holdtime ?
<10-255> Length of time (in sec) that receiver
must keep this packet
Understanding Abbreviated Commands
You need to enter only enough characters for the switch to recognize the command as unique.
This example shows how to enter the show configuration privileged EXEC command in an abbreviated form:
Lists all commands available for a particular command
mode.
Lists the associated keywords for a command.
Lists the associated arguments for a keyword.
Switch# show conf
No and Default Forms of Commands
Almost every configuration command also has a no form. In general, use the no form to disable a feature or
function or reverse the action of a command. For example, the no shutdown interface configuration command
reverses the shutdown of an interface. Use the command without the keyword no to reenable a disabled feature
or to enable a feature that is disabled by default.
Configuration commands can also have a default form. The default form of a command returns the command
setting to its default. Most commands are disabled by default, so the default form is the same as the no form.
However, some commands are enabled by default and have variables set to certain default values. In these
cases, the default command enables the command and sets variables to their default values.
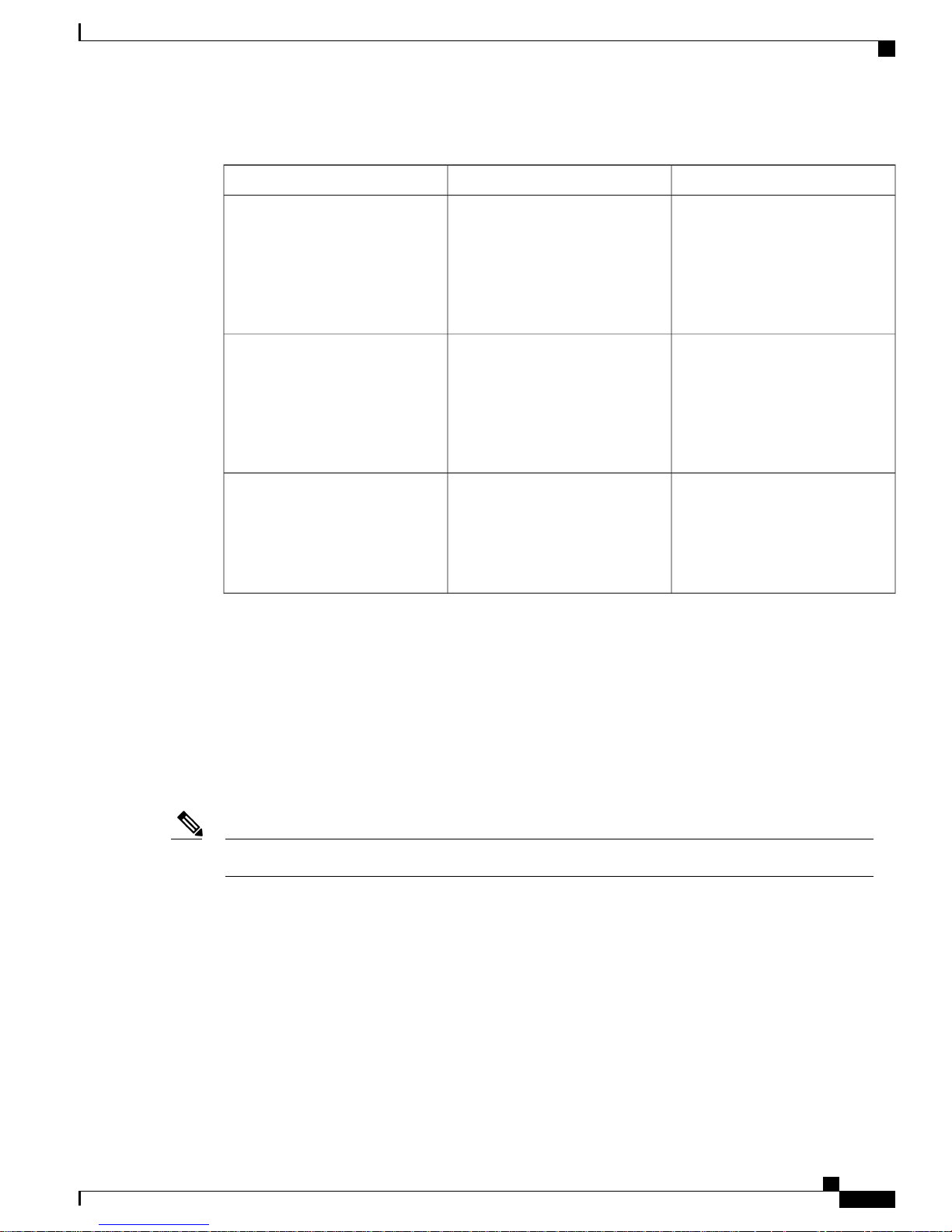
CLI Error Messages
This table lists some error messages that you might encounter while using the CLI to configure your switch.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
4 OL-28697-01
Page 17
Using the Command-Line Interface
Table 2: Common CLI Error Messages
% Ambiguous command: "show
con"
You did not enter enough
characters for your switch to
recognize the command.
Configuration Logging
How to Get HelpMeaningError Message
Reenter the command followed by
a question mark (?) without any
space between the command and
the question mark.
The possible keywords that you can
enter with the command appear.
% Incomplete command.
% Invalid input detected at
‘^’ marker.
Configuration Logging
You can log and view changes to the switch configuration. You can use the Configuration Change Logging
and Notification feature to track changes on a per-session and per-user basis. The logger tracks each
configuration command that is applied, the user who entered the command, the time that the command was
entered, and the parser return code for the command. This feature includes a mechanism for asynchronous
notification to registered applications whenever the configuration changes. You can choose to have the
notifications sent to the syslog.
You did not enter all of the
keywords or values required by this
command.
You entered the command
incorrectly. The caret (^) marks the
point of the error.
Reenter the command followed by
a question mark (?) with a space
between the command and the
question mark.
The possible keywords that you can
enter with the command appear.
Enter a question mark (?) to display
all of the commands that are
available in this command mode.
The possible keywords that you can
enter with the command appear.
Only CLI or HTTP changes are logged.Note
How to Use the CLI to Configure Features
Configuring the Command History
The software provides a history or record of commands that you have entered. The command history feature
is particularly useful for recalling long or complex commands or entries, including access lists. You can
customize this feature to suit your needs.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 5
Page 18
Configuring the Command History
Changing the Command History Buffer Size
By default, the switch records ten command lines in its history buffer. You can alter this number for a current
terminal session or for all sessions on a particular line. This procedure is optional.
SUMMARY STEPS
terminal history [size number-of-lines]
1.
DETAILED STEPS
Using the Command-Line Interface
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
terminal history [size number-of-lines]
Example:
Switch# terminal history size 200
Recalling Commands
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Changes the number of command lines that the switch records during
the current terminal session in privileged EXEC mode. You can
configure the size from 0 to 256.
To recall commands from the history buffer, perform one of the actions listed in this table. These actions are
optional.
The arrow keys function only on ANSI-compatible terminals such as VT100s.Note
Ctrl-P or use the up arrow key
1.
Ctrl-N or use the down arrow key
2.
show history
3.
Step 1
Step 2
6 OL-28697-01
Ctrl-P or use the up arrow key
Ctrl-N or use the down arrow key
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
PurposeCommand or Action
Recalls commands in the history buffer, beginning with the most recent command.
Repeat the key sequence to recall successively older commands.
Returns to more recent commands in the history buffer after recalling commands
with Ctrl-P or the up arrow key. Repeat the key sequence to recall successively
more recent commands.
Page 19
Using the Command-Line Interface
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 3
show history
Example:
Switch# show history
Disabling the Command History Feature
The command history feature is automatically enabled. You can disable it for the current terminal session or
for the command line. This procedure is optional.
SUMMARY STEPS
terminal no history
1.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
terminal no history
Example:
Switch# terminal no history
Lists the last several commands that you just entered in privileged EXEC mode.
The number of commands that appear is controlled by the setting of the terminal
history global configuration command and the history line configuration
command.
PurposeCommand or Action
Disables the feature during the current terminal session in
privileged EXEC mode.
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
Although enhanced editing mode is automatically enabled, you can disable it and reenable it.
SUMMARY STEPS
terminal editing
1.
terminal no editing
2.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
OL-28697-01 7
terminal editing
Example:
Switch# terminal editing
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
PurposeCommand or Action
Reenables the enhanced editing mode for the current terminal
session in privileged EXEC mode.
Page 20
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
Using the Command-Line Interface
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 2
terminal no editing
Example:
Switch# terminal no editing
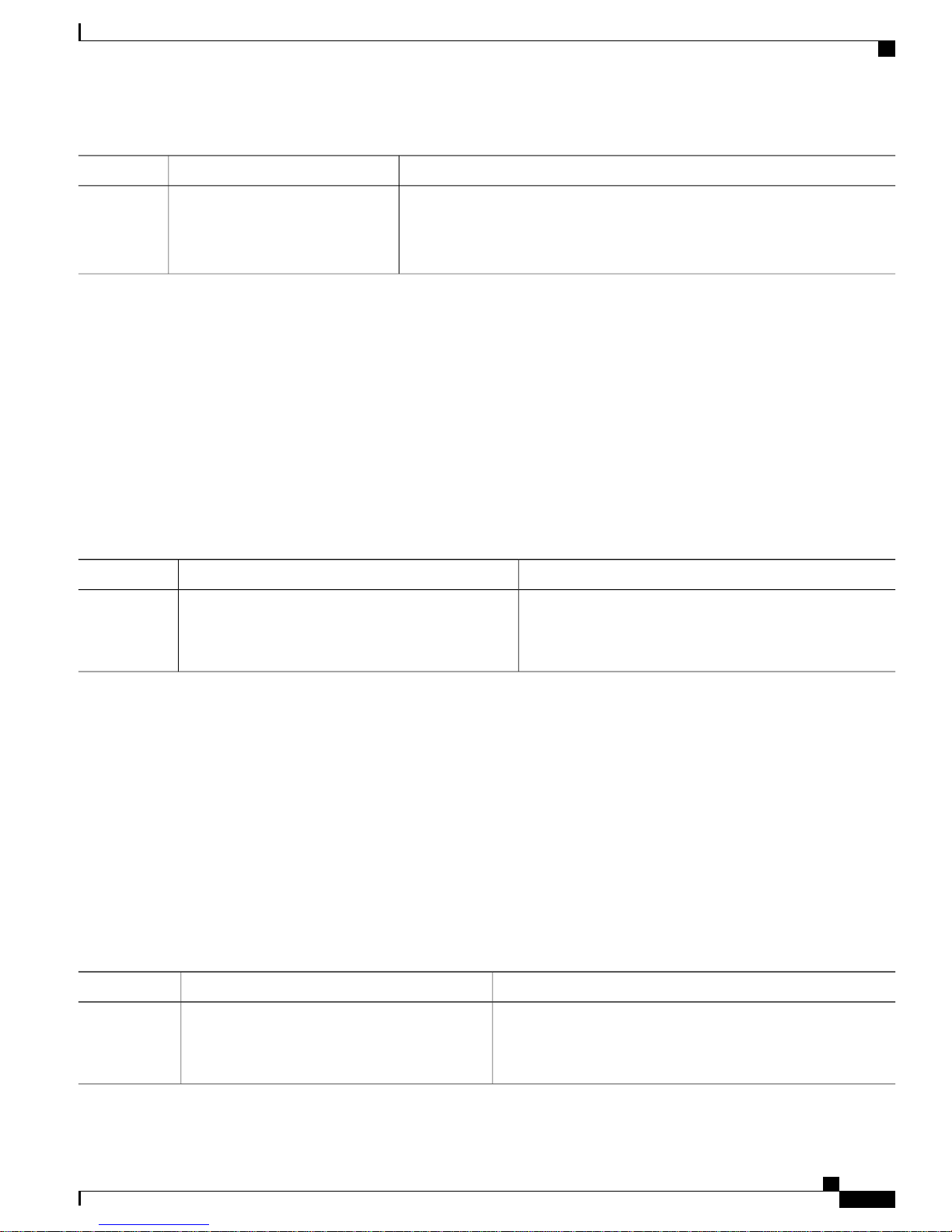
Editing Commands Through Keystrokes
The keystrokes help you to edit the command lines. These keystrokes are optional.
The arrow keys function only on ANSI-compatible terminals such as VT100s.Note
Table 3: Editing Commands
Ctrl-A
Disables the enhanced editing mode for the current terminal
session in privileged EXEC mode.
DescriptionEditing Commands
Moves the cursor back one character.Ctrl-B or use the left arrow key
Moves the cursor forward one character.Ctrl-F or use the right arrow key
Moves the cursor to the beginning of the command
line.
Ctrl-T
Ctrl-K
Ctrl-U or Ctrl-X
Moves the cursor to the end of the command line.Ctrl-E
Moves the cursor back one word.Esc B
Moves the cursor forward one word.Esc F
Transposes the character to the left of the cursor with
the character located at the cursor.
Erases the character to the left of the cursor.Delete or Backspace key
Deletes the character at the cursor.Ctrl-D
Deletes all characters from the cursor to the end of
the command line.
Deletes all characters from the cursor to the beginning
of the command line.
Deletes the word to the left of the cursor.Ctrl-W
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
8 OL-28697-01
Page 21

Using the Command-Line Interface
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
Deletes from the cursor to the end of the word.Esc D
Capitalizes at the cursor.Esc C
Changes the word at the cursor to lowercase.Esc L
Esc U
Ctrl-V or Esc Q
Return key
Ctrl-L or Ctrl-R
Editing Command Lines That Wrap
Capitalizes letters from the cursor to the end of the
word.
Designates a particular keystroke as an executable
command, perhaps as a shortcut.
Scrolls down a line or screen on displays that are
longer than the terminal screen can display.
Note
The More prompt is used for any output that
has more lines than can be displayed on the
terminal screen, including show command
output. You can use the Return and Space
bar keystrokes whenever you see the More
prompt.
Scrolls down one screen.Space bar
Redisplays the current command line if the switch
suddenly sends a message to your screen.
SUMMARY STEPS
You can use a wraparound feature for commands that extend beyond a single line on the screen. When the
cursor reaches the right margin, the command line shifts ten spaces to the left. You cannot see the first ten
characters of the line, but you can scroll back and check the syntax at the beginning of the command. The
keystroke actions are optional.
To scroll back to the beginning of the command entry, press Ctrl-B or the left arrow key repeatedly. You can
also press Ctrl-A to immediately move to the beginning of the line.
The arrow keys function only on ANSI-compatible terminals such as VT100s.Note
The following example shows how to wrap a command line that extends beyond a single line on the screen.
access-list
1.
Ctrl-A
2.
Return key
3.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 9
Page 22
Searching and Filtering Output of show and more Commands
DETAILED STEPS
Using the Command-Line Interface
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
access-list
Example:
Switch(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp
10.15.22.25 255.255.255.0 10.15.22.35
Switch(config)# $ 101 permit tcp
10.15.22.25 255.255.255.0 10.15.22.35
255.25
Switch(config)# $t tcp 10.15.22.25
255.255.255.0 131.108.1.20 255.255.255.0
eq
Switch(config)# $15.22.25 255.255.255.0
10.15.22.35 255.255.255.0 eq 45
Example:
Switch(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp
10.15.22.25 255.255.255.0 10.15.2$
Displays the global configuration command entry that extends beyond
one line.
When the cursor first reaches the end of the line, the line is shifted ten
spaces to the left and redisplayed. The dollar sign ($) shows that the
line has been scrolled to the left. Each time the cursor reaches the end
of the line, the line is again shifted ten spaces to the left.
Checks the complete syntax.Ctrl-A
The dollar sign ($) appears at the end of the line to show that the line
has been scrolled to the right.
Execute the commands.Return key
The software assumes that you have a terminal screen that is 80 columns
wide. If you have a different width, use the terminal width privileged
EXEC command to set the width of your terminal.
Use line wrapping with the command history feature to recall and
modify previous complex command entries.
Searching and Filtering Output of show and more Commands
You can search and filter the output for show and more commands. This is useful when you need to sort
through large amounts of output or if you want to exclude output that you do not need to see. Using these
commands is optional.
SUMMARY STEPS
{show | more} command | {begin | include | exclude} regular-expression
1.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
{show | more} command | {begin | include | exclude}
regular-expression
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
10 OL-28697-01
PurposeCommand or Action
Searches and filters the output.
Page 23

Using the Command-Line Interface
Accessing the CLI Through a Console Connection or Through Telnet
PurposeCommand or Action
Expressions are case sensitive. For example, if you enter
Example:
Switch# show interfaces | include protocol
Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up
Vlan10 is up, line protocol is down
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is up, line protocol is down
GigabitEthernet1/0/2 is up, line protocol is up
| exclude output, the lines that contain output are not
displayed, but the lines that contain output appear.
Accessing the CLI Through a Console Connection or Through Telnet
Before you can access the CLI, you must connect a terminal or a PC to the switch console or connect a PC to
the Ethernet management port and then power on the switch, as described in the hardware installation guide
that shipped with your switch.
If your switch is already configured, you can access the CLI through a local console connection or through a
remote Telnet session, but your switch must first be configured for this type of access.
You can use one of these methods to establish a connection with the switch:
Connect the switch console port to a management station or dial-up modem, or connect the Ethernet
•
management port to a PC. For information about connecting to the console or Ethernet management
port, see the switch hardware installation guide.
Use any Telnet TCP/IP or encrypted Secure Shell (SSH) package from a remote management station.
•
The switch must have network connectivity with the Telnet or SSH client, and the switch must have an
enable secret password configured.
The switch supports up to 16 simultaneous Telnet sessions. Changes made by one Telnet user are
•
reflected in all other Telnet sessions.
The switch supports up to five simultaneous secure SSH sessions.
•
After you connect through the console port, through the Ethernet management port, through a Telnet
session or through an SSH session, the user EXEC prompt appears on the management station.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 11
Page 24

Accessing the CLI Through a Console Connection or Through Telnet
Using the Command-Line Interface
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
12 OL-28697-01
Page 25

Using the Web Graphical User Interface
Prerequisites for Using the Web GUI, page 13
•
Information About Using The Web GUI, page 13
•
Connecting the Console Port of the Switch , page 15
•
Logging On to the Web GUI, page 15
•
Enabling Web and Secure Web Modes , page 15
•
Configuring the Switch Web GUI, page 16
•
Prerequisites for Using the Web GUI
The GUI must be used on a PC running Windows 7, Windows XP SP1 (or later releases), or Windows
•
2000 SP4 (or later releases).
CHAPTER 2
The switch GUI is compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer version 10.x, Mozilla Firefox 20.x, or
•
Google Chrome 26.x.
Information About Using The Web GUI
A web browser, or graphical user interface (GUI), is built into each switch.
You can use either the service port interface or the management interface to access the GUI. We recommend
that you use the service-port interface. Click Help at the top of any page in the GUI to display online help.
You might need to disable your browser’s pop-up blocker to view the online help.
Web GUI Features
The switch web GUI supports the following:
The Configuration Wizard—After initial configuration of the IP address and the local username/password or
auth via the authentication server (privilege 15 needed), the wizard provides a method to complete the initial
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 13
Page 26

Web GUI Features
Using the Web Graphical User Interface
wireless configuration. Start the wizard through Configuration -> Wizard and follow the nine-step process to
configure the following:
Admin Users
•
SNMP System Summary
•
Management Port
•
Wireless Management
•
RF Mobility and Country code
•
Mobility configuration
•
WLANs
•
802.11 Configuration
•
Set Time
•
The Monitor tab:
Displays summary details of switch, clients, and access points.
•
Displays all radio and AP join statistics.
•
Displays air quality on access points.
•
Displays list of all Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) neighbors on all interfaces and the CDP traffic
•
information.
Displays all rogue access points based on their classification-friendly, malicious, ad hoc, classified, and
•
unclassified.
The Configuration tab:
Enables you to configure the switch for all initial operation using the web Configuration Wizard. The
•
wizard allows you to configure user details, management interface, and so on.
Enables you to configure the system, internal DHCP server, management, and mobility management
•
parameters.
Enables you to configure the switch, WLAN, and radios.
•
Enables you to configure and set security policies on your switch.
•
Enables you to access the switch operating system software management commands.
•
The Administration tab enables you to configure system logs.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
14 OL-28697-01
Page 27

Using the Web Graphical User Interface
Connecting the Console Port of the Switch
Before You Begin
Before you can configure the switch for basic operations, you need to connect it to a PC that uses a VT-100
terminal emulation program (such as HyperTerminal, ProComm, Minicom, or Tip).
Connecting the Console Port of the Switch
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Connect one end of a null-modem serial cable to the switch's RJ-45 console port and the other end to your PC's serial
port.
Plug the AC power cord into the switch and a grounded 100 to 240 VAC, 50/60-Hz electrical outlet. Turn on the power
supply. The bootup script displays operating system software initialization (code download and power-on self-test
verification) and basic configuration. If the switch passes the power-on self-test, the bootup script runs the configuration
wizard, which prompts you for basic configuration input.
Enter yes. Proceed with basic initial setup configuration parameters in the CLI setup wizard. Specify the IP address for
the service port which is the gigabitethernet 0/0 interface.
After entering the configuration parameters in the configuration wizard, you can access the Web GUI. Now, the switch
is configured with the IP address for service port.
Logging On to the Web GUI
Step 1
Step 2
Enter the switch IP address in your browser’s address line. For a secure connection, enter https://ip-address. For a less
secure connection, enter http://ip-address.
Enabling Web and Secure Web Modes
Step 1
Step 2
OL-28697-01 15
Choose Configuration > Management > Protocol Management > HTTP-HTTPS.
The HTTP-HTTPS Configuration page appears.
To enable web mode, which allows users to access the switch GUI using “http://ip-address,” choose Enabled from the
HTTP Access drop-down list. Otherwise, choose Disabled. Web mode (HTTP) is not a secure connection.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Page 28

Configuring the Switch Web GUI
Using the Web Graphical User Interface
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
To enable secure web mode, which allows users to access the switch GUI using “https://ip-address,” choose Enabled
from the HTTPS Access drop-down list. Otherwise, choose Disabled. Secure web mode (HTTPS) is a secure connection.
Choose to track the device in the IP Device Tracking check box.
Choose to enable the trust point in the Enable check box.
Choose the trustpoints from the Trustpoints drop-down list.
Enter the amount of time, in seconds, before the web session times out due to inactivity in the HTTP Timeout-policy (1
to 600 sec) text box.
The valid range is from 1 to 600 seconds.
Enter the server life time in the Server Life Time (1 to 86400 sec) text box.
The valid range is from1 to 86400 seconds.
Enter the maximum number of connection requests that the server can accept in the Maximum number of Requests (1
to 86400) text box.
The valid range is from 1 to 86400 connections.
Click Apply.
Click Save Configuration.
Configuring the Switch Web GUI
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
The configuration wizard enables you to configure basic settings on the switch. You can run the wizard after
you receive the switch from the factory or after the switch has been reset to factory defaults. The configuration
wizard is available in both GUI and CLI formats.
Connect your PC to the service port and configure an IPv4 address to use the same subnet as the switch. The switch is
loaded with IOS XE image and the service port interface is configured as gigabitethernet 0/0.
Start Internet Explorer 10 (or later), Firefox 2.0.0.11 (or later), or Google Chrome on your PC and enter the management
interface IP address on the browser window. The management interface IP address is same as the gigabitethernet 0/0
(also known as service port interface). When you log in for the first time, you need to enter HTTP username and password.
By default, the username is admin and the password is cisco.
You can use both HTTP and HTTPS when using the service port interface. HTTPS is enabled by default and HTTP can
also be enabled.
When you log in for the first time, the <Model Number> <Hostname> page appears.
On the page, click the Wireless Web GUI link to access switch web GUI Home page.
Choose Configuration > Wizard to perform all steps that you need to configure the switch initially.
The Admin Users page appears.
On the Admin Users page, enter the administrative username to be assigned to this switch in the User Name text box
and the administrative password to be assigned to this switch in the Password and Confirm Password text boxes. Click
Next.
The default username is admin and the default password is cisco. You can also create a new administrator user for the
switch. You can enter up to 24 ASCII characters for username and password.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
16 OL-28697-01
Page 29

Using the Web Graphical User Interface
The SNMP System Summary page appears.
Configuring the Switch Web GUI
Step 6
Step 7
On the SNMP System Summary page, enter the following SNMP system parameters for the switch, and click Next:
Customer-definable switch location in the Location text box.
•
Customer-definable contact details such as phone number with names in the Contact text box.
•
Choose enabled to send SNMP notifications for various SNMP traps or disabled not to send SNMP notifications
•
for various SNMP traps from the SNMP Global Trap drop-down list.
Choose enabled to send system log messages or disabled not to send system log messages from the SNMP Logging
•
drop-down list.
Note
The SNMP trap server, must be reachable through the distribution ports (and not through the gigabitethernet0/0
service or management interface).
The Management Port page appears.
In the Management Port page, enter the following parameters for the management port interface (gigabitethernet 0/0)
and click Next.
Interface IP address that you assigned for the service port in the IP Address text box.
•
Network mask address of the management port interface in the Netmask text box.
•
The IPv4 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) address for the selected port in the IPv4 DHCP Server
•
text box.
The Wireless Management page appears.
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
In the Wireless Management page, enter the following wireless interface management details, and click Next.
• Choose the interface—VLAN, or Ten Gigabit Ethernet from the Select Interface drop-down list.
VLAN tag identifier, or 0 for no VLAN tag in the VLAN id text box.
•
IP address of wireless management interface where access points are connected in the IP Address text box.
•
Network mask address of the wireless management interface in the Netmask text box.
•
DHCP IPv4 IP address in the IPv4 DHCP Server text box.
•
When selecting VLAN as interface, you can specify the ports as –Trunk or Access ports from the selected list displayed
in the Switch Port Configuration text box.
The RF Mobility and Country Code page appears.
In the RF Mobility and Country Code page, enter the RF mobility domain name in the RF Mobility text box, choose
current country code from the Country Code drop-down list, and click Next. From the GUI, you can select only one
country code.
Note
Before configuring RF grouping parameters and mobility configuration, ensure that you refer to the relevant
conceptual content and then proceed with the configuration.
The Mobility Configuration page with mobility global configuration settings appears.
In the WLANs page, enter the following WLAN configuration parameters, and click Next.
WLAN identifier in the WLAN ID text box.
•
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 17
Page 30

Configuring the Switch Web GUI
SSID of the WLAN that the client is associated with in the SSID text box.
•
Name of the WLAN used by the client in the Profile Name text box.
•
The 802.11 Configuration page appears.
Using the Web Graphical User Interface
Step 11
Step 12
Step 13
In the 802.11 Configuration page, check either one or both 802.11a/n/ac and 802.11b/g/n check boxes to enable the
802.11 radios, and click Next.
The Set Time page appears.
In the Set Time page, you can configure the time and date on the switch based on the following parameters, and click
Next.
Displays current timestamp on the switch in the Current Time text box.
•
Choose either Manual or NTP from the Mode drop-down list.
•
On using the NTP server, all access points connected to the switch, synchronizes its time based on the NTP server
settings available.
Choose date on the switch from the Year, Month, and Day drop-down list.
•
Choose time from the Hours, Minutes, and Seconds drop-down list.
•
Enter the time zone in the Zone text box and select the off setting required when compared to the current time
•
configured on the switch from the Offset drop-down list.
The Save Wizard page appears.
In the Save Wizard page, you can review the configuration settings performed on the switch using these steps, and if
you wish to change any configuration value, click Previous and navigate to that page.
You can save the switch configuration created using the wizard only if a success message is displayed for all the wizards.
If the Save Wizard page displays errors, you must recreate the wizard for initial configuration of the switch.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
18 OL-28697-01
Page 31

Configuring the Switch for Access Point
Discovery
Finding Feature Information, page 19
•
Prerequisites for Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery, page 19
•
Restrictions for Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery, page 20
•
Information About Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery, page 20
•
How to Configure Access Point Discovery, page 22
•
Configuration Examples for Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery, page 25
•
Finding Feature Information
CHAPTER 3
Prerequisites for Configuring the Switch for Access Point
Discovery
Ensure that the Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) UDP ports 5246 and
•
5247 (similar to the Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) UDP ports 12222 and 12223) are
enabled and are not blocked by an intermediate device that could prevent an access point from joining
the switch.
If access control lists (ACLs) are in the control path between the switch and its access points, you must
•
open new protocol ports to prevent access points from being stranded.
If an access point is in the UP state and its IP address changes, the access point tears down the existing
•
CAPWAP tunnel and rejoins the switch.
Access points must be discovered by a switch before they can become an active part of the network.
•
The lightweight access points support the following switch discovery processes:
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 19
Page 32

Restrictions for Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery
◦ Layer 3 CAPWAP discovery—You can enable this feature on different subnets from the access
point. This feature uses IP addresses and UDP packets rather the MAC addresses used by Layer
2 discovery.
◦ Locally stored switch IP address discovery—If the access point was previously associated to a
switch, the IP addresses of the primary, secondary, and tertiary switchs are stored in the access
point’s nonvolatile memory. This process of storing switch IP addresses on an access point for
later deployment is called priming the access point.
◦ DHCP server discovery—This feature uses DHCP option 43 to provide switch IP addresses to the
access points. Cisco switches support a DHCP server option that is typically used for this capability.
◦ DNS discovery—The access point can discover switchs through your domain name server (DNS).
You must configure your DNS to return switch IP addresses in response to
CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.localdomain, where localdomain is the access point domain
name. When an access point receives an IP address and DNS information from a DHCP server, it
contacts the DNS to resolve CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.localdomain. When the DNS
sends a list of switch IP addresses, the access point sends discovery requests to the switchs.
Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery
Restrictions for Configuring the Switch for Access Point
Discovery
Ensure that the switchs are configured with the correct date and time. If the date and time configured
•
on the switch precedes the creation and installation date of certificates on the access points, the access
point fails to join the switch.
During the discovery process, access points that are supported by the Cisco switch, such as the 1140,
•
1260, 3500, 1040,1600, 2600, or 3600 query only for Cisco switchs.
Information About Configuring the Switch for Access Point
Discovery
In a CAPWAP environment, a lightweight access point discovers a switch by using CAPWAP discovery
mechanisms and then sends a CAPWAP join request to the switch. The switch sends a CAPWAP join response
to the access point that allows the access point to join the switch. When the access point joins the switch, the
switch manages its configuration, firmware, control transactions, and data transactions.
Access Point Communication Protocols
Cisco lightweight access points use the IETF standard CAPWAP to communicate with the switch and other
lightweight access points on the network.
CAPWAP, which is based on LWAPP, is a standard, interoperable protocol that enables a switch to manage
a collection of wireless access points. CAPWAP is implemented in switch for these reasons:
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
20 OL-28697-01
Page 33

Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery
To provide an upgrade path from Cisco products that use LWAPP to next-generation Cisco products
•
that use CAPWAP
To manage RFID readers and similar devices
•
To enable switchs to interoperate with third-party access points in the future
•
Viewing Access Point Join Information
Join statistics for an access point that sends a CAPWAP discovery request to the switch at least once are
maintained on the switch even if the access point is rebooted or disconnected. These statistics are removed
only when the switch is rebooted or when you choose to clear the statistics.
Troubleshooting the Access Point Join Process
Access points can fail to join a switch for many reasons such as a RADIUS authorization is pending, self-signed
certificates are not enabled on the switch, the access point and switch’s regulatory domains do not match, and
so on.
You can configure the access points to send all CAPWAP-related errors to a syslog server. You do not need
to enable any debug commands on the switch because all of the CAPWAP error messages can be viewed
from the syslog server itself.
The state of the access point is not maintained on the switch until it receives a CAPWAP join request from
the access point, so it can be difficult to determine why the CAPWAP discovery request from a certain access
point was rejected. In order to troubleshoot such joining issues without enabling CAPWAP debug commands
on the switch, the switch collects information for all access points that send a discovery message to this switch
and maintains information for any access points that have successfully joined this switch.
The switch collects all join-related information for each access point that sends a CAPWAP discovery request
to the switch. Collection begins when the first discovery message is received from the access point and ends
when the last configuration payload is sent from the switch to the access point.
When the switch is maintaining join-related information for the maximum number of access points, it does
not collect information for any more access points.
You can also configure a DHCP server to return a syslog server IP address to the access point using option 7
on the server. The access point then starts sending all syslog messages to this IP address.
You can configure the syslog server IP address through the access point CLI, if the access point is not connected
to the switch by entering the capwap ap log-server syslog_server_IP_address command.
Viewing Access Point Join Information
When the access point joins a switch for the first time, the switch pushes the global syslog server IP address
(the default is 255.255.255.255) to the access point. After that, the access point sends all syslog messages to
this IP address, until it is overridden by one of the following scenarios:
The access point is still connected to the same switch, and you changed the global syslog server IP
•
address configuration on the switch by using the ap syslog host Syslog_Server_IP_Address command.
In this case, the switch pushes the new global syslog server IP address to the access point.
The access point is still connected to the same switch, and you configured a specific syslog server IP
•
address for the access point on the switch by using the ap name Cisco_AP syslog host
Syslog_Host_IP_Address command. In this case, the switch pushes the new specific syslog server IP
address to the access point.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 21
Page 34

Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery
How to Configure Access Point Discovery
The access point gets disconnected from the switch, and you configured the syslog server IP address
•
from the access point CLI by using the capwap ap log-server syslog_server_IP_address command.
This command works only if the access point is not connected to any switch.
The access point gets disconnected from the switch and joins another switch. In this case, the new switch
•
pushes its global syslog server IP address to the access point.
Whenever a new syslog server IP address overrides the existing syslog server IP address, the old address is
erased from persistent storage, and the new address is stored in its place. The access point also starts sending
all syslog messages to the new IP address, if the access point can reach the syslog server IP address.
How to Configure Access Point Discovery
Configuring the Syslog Server for Access Points (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# enable
Step 2
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Step 3
ap syslog host host_ip_address
Example:
Switch(config)# ap syslog host
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
10.9.9.16
enable
configure terminal
ap syslog host host_ip_address
end
show ap config global
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Configures the global syslog server for all access points that join this
switch.
Note
By default, the global syslog server IP address for all access
points is 255.255.255.255. Make sure that the access points
can reach the subnet on which the syslog server resides
before configuring the syslog server on the switch. If the
access points cannot reach this subnet, the access points are
unable to send out syslog messages.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
22 OL-28697-01
Page 35

Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery
Monitoring Access Point Join Information (CLI)
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 4
end
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press
Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Step 5
show ap config global
Displays the global syslog server settings for all access points that
join the switch.
Example:
Switch# show ap config global
Step 6
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
Example:
Switch# show ap name AP03 config general
Displays the syslog server settings for a specific access point.
Monitoring Access Point Join Information (CLI)
The procedure to perform this task using the switch GUI is not currently available.Note
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
enable
1.
show ap join stats summary
2.
show ap mac-address mac_address join stats summary
3.
show ap mac-address mac_address join stats detailed
4.
clear ap join statistics
5.
Example:
Switch# enable
show ap join stats summary
Example:
Switch# show ap join stats summary
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Displays the MAC addresses of all the access points that are
joined to the switch or that have tried to join.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 23
Page 36

Searching for Access Point Radios (GUI)
Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 3
show ap mac-address mac_address join stats
summary
Example:
Switch# show ap mac-address
000.2000.0400 join stats summary
Step 4
Step 5
show ap mac-address mac_address join stats detailed
Example:
Switch# show ap mac-address
000.2000.0400 join stats detailed
clear ap join statistics
Example:
Switch# clear ap join statistics
Searching for Access Point Radios (GUI)
Displays all the statistics for the AP including the last join
error detail.
Displays all join-related statistics collected for a specific
access point.
Clears the join statistics for all access points.
Note
To clear the join statistics that correspond to specific
access points, enter the clear ap mac-address
mac_address join statistics command.
Step 1
Choose Monitor > Wireless > Access Points and click 802.11a/n/ac Statistics or 802.11b/g/n Statistics.
The 802.11 Radio pages are displayed. These pages show all of the 802.11a/n/ac or 802.11b/g/n access point radios that
are associated with the switch and their current settings.
Note
In a Cisco converged access environment, the 802.11a/n/ac and 802.11b/g/n radios should not be differentiated
based on their Base Radio MAC addresses, because they might have the same addresses. Instead, the radios
should be differentiated based on their physical addresses.
Step 2
From the Show drop-down list, choose Quick Filter.
The filter options (text boxes) appear in each of the column header in the table.
Step 3
Enter a keyword in the corresponding text boxes to specify the filter criteria based on which you want to search, and
click the Filter icon.
Monitoring the Interface Details (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > All APs.
The All APs page is displayed showing a list of access points that are associated with the switch.
Click the access point name.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
24 OL-28697-01
Page 37

Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery
The AP > Edit page is displayed.
Configuration Examples for Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery
Step 3
Click the Interface tab.
The interface details are displayed.
Configuration Examples for Configuring the Switch for Access
Point Discovery
Displaying the MAC Addresses of all Access Points: Example
This example shows how to display MAC addresses of all the access points that are joined to the switch:
Switch# show ap join stats summary
Number of APs.......................................... 4
Base Mac EthernetMac AP Name IP Address Status
----------------- ----------------- ------- ------------- ---------00:0b:85:57:bc:c0 00:0b:85:57:bc:c0 AP1130 10.10.163.217 Joined
00:1c:0f:81:db:80 00:1c:63:23:ac:a0 AP1140 10.10.163.216 Not joined
00:1c:0f:81:fc:20 00:1b:d5:9f:7d:b2 AP1 10.10.163.215 Joined
00:21:1b:ea:36:60 00:0c:d4:8a:6b:c1 AP2 10.10.163.214 Not joined
This example shows how to display the last join error details for a specific access point:
Switch# show ap mac-address 000.2000.0400 join stats summary
Is the AP currently connected to controller................ Yes
Time at which the AP joined this
controller last time................................. Aug 21 12:50:36.061
Type of error
that occurred last.................. AP got or has been disconnected
Reason for error
that occurred last........... The AP has been reset by the controller
Time at which the last join error occurred......... Aug 21 12:50:34.374
This example shows how to display all join-related statistics collected for a specific access point:
Switch# show ap mac-address 000.2000.0400 join stats detailed
Discovery phase statistics
- Discovery requests received........................ 2
- Successful discovery responses sent................ 2
- Unsuccessful discovery request processing.......... 0
- Reason for last unsuccessful discovery attempt..... Not applicable
- Time at last successful discovery attempt.......... Aug 21 12:50:23.335
- Time at last unsuccessful discovery attempt........ Not applicable
Join phase statistics
- Join requests received............................. 1
- Successful join responses sent..................... 1
- Unsuccessful join request processing............... 1
- Reason for last unsuccessful join attempt..... RADIUS authorization
- Time at last successful join attempt............... Aug 21 12:50:34.481
- Time at last unsuccessful join attempt............. Aug 21 12:50:34.374
Configuration phase statistics
- Configuration requests received..................... 1
- Successful configuration responses sent............. 1
- Unsuccessful configuration request processing....... 0
is pending
for the AP
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 25
Page 38

Configuring the Switch for Access Point Discovery
DHCP Option 43 for Lightweight Cisco Aironet Access Points Configuration Example
- Reason for last unsuccessful configuration attempt.. Not applicable
- Time at last successful configuration attempt....... Aug 21 12:50:34.374
- Time at last unsuccessful configuration attempt..... Not applicable
Last AP message decryption failure details
- Reason for last message decryption failure.......... Not applicable
Last AP disconnect details
- Reason for last AP connection failure............... The AP has been reset by
Last join error summary
- Type of error that occurred last.................... AP got or has been
- Reason for error that occurred last................. The AP has been reset
- Time at which the last join error occurred.......... Aug 21 12:50:34.374
the controller
disconnected
by the controller
DHCP Option 43 for Lightweight Cisco Aironet Access Points Configuration
Example
For more information about the AP join process, see DHCP OPTION 43 for Lightweight Cisco Aironet Access
Points Configuration Example at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk722/tk809/technologies_configuration_
example09186a00808714fe.shtml.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
26 OL-28697-01
Page 39

CHAPTER 4
Configuring Data Encryption
Finding Feature Information, page 27
•
Prerequisites for Configuring Data Encryption, page 27
•
Restrictions for Configuring Data Encryption, page 27
•
Information About Data Encryption, page 28
•
How to Configure Data Encryption, page 28
•
Configuration Examples for Configuring Data Encryption, page 29
•
Finding Feature Information
Prerequisites for Configuring Data Encryption
Cisco 1260, 3500, 3600, 801, 1140, 1310, and 1520 series access points support Datagram Transport
•
Layer Security (DTLS) data encryption.
You can use the switch to enable or disable DTLS data encryption for a specific access point or for all
•
access points.
Non-Russian customers who use the Cisco switch do not need a data DTLS license.
•
Restrictions for Configuring Data Encryption
Encryption limits throughput at both the switch and the access point, and maximum throughput is desired
•
for most enterprise networks.
If your switch does not have a data DTLS license and if the access point associated with the switch has
•
DTLS enabled, the data path will be unencrypted.
In images that do not have a DTLS license, the DTLS commands are not available.
•
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 27
Page 40

Information About Data Encryption
Information About Data Encryption
The switch enables you to encrypt Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) control
packets (and optionally, CAPWAP data packets) that are sent between the access point and the switch using
DTLS. DTLS is a standards-track Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) protocol based on TLS. CAPWAP
control packets are management packets exchanged between a switch and an access point while CAPWAP
data packets encapsulate forwarded wireless frames. CAPWAP control and data packets are sent over separate
UDP ports: 5246 (control) and 5247 (data). If an access point does not support DTLS data encryption, DTLS
is enabled only for the control plane, and a DTLS session for the data plane is not established.
How to Configure Data Encryption
Configuring Data Encryption (CLI)
Configuring Data Encryption
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
ap link-encryption
Example:
Switch(config)# ap link-encryption
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
show ap link-encryption
Example:
Switch# show ap link-encryption
configure terminal
1.
ap link-encryption
2.
end
3.
show ap link-encryption
4.
show wireless dtls connections
5.
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enables data encryption for all access points or a specific access point by
entering this command. The default value is disabled.
Changing the data encryption mode requires the access points to rejoin the
switch.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z
to exit global configuration mode.
Displays the encryption state of all access points or a specific access point.
This command also shows authentication errors, which track the number
of integrity check failures and replay errors. Relay errors help in tracking
the number of times the access point receives the same packet.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
28 OL-28697-01
Page 41

Configuring Data Encryption
Configuring Data Encryption (GUI)
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 5
Example:
Switch# show wireless dtls
connections
Configuring Data Encryption (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > All APs.
The All APs page is displayed.
Click the name of the access point for which you want to enable data encryption.
The AP > Edit page is displayed.
Click the Advanced tab.
Select or unselect the Data Encryption check box.
Note
Changing the data encryption mode requires the access points to reassociate with the
switch.
Click Apply.
Click Save Configuration.
Displays a summary of all active DTLS connections.show wireless dtls connections
Note
If you experience any problems with DTLS data encryption, enter
the debug dtls ap {all | event | trace} command to debug all
DTLS messages, events, or traces.
Configuration Examples for Configuring Data Encryption
Displaying Data Encryption States for all Access Points: Examples
This example shows how to display the encryption state of all access points or a specific access point. This
command also shows authentication errors, which track the number of integrity check failures and replay
errors. Relay errors help in tracking the number of times the access point receives the same packet:
Switch# show ap link-encryption
AP Name State Count Count Update
------------------ ---------- -------- -------- -----3602a Enabled 0 0 Never
This example shows how to display a summary of all active DTLS connections:
Switch# show wireless dtls connections
AP Name Local Port Peer IP Peer Port Ciphersuite
--------------- ------------ ------------- ---------- -------------------3602a Capwap_Ctrl 10.10.21.213 46075 TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
3602a Capwap_Data 10.10.21.213 46075 TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 29
Encryption Dnstream Upstream Last
Page 42

Displaying Data Encryption States for all Access Points: Examples
Configuring Data Encryption
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
30 OL-28697-01
Page 43

CHAPTER 5
Configuring Retransmission Interval and Retry
Count
Finding Feature Information, page 31
•
Prerequisites for Configuring the Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count, page 31
•
Information About Retransmission Interval and Retry Count, page 31
•
How to Configure Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count, page 32
•
Viewing CAPWAP Maximum Transmission Unit Information (CLI), page 34
•
Viewing CAPWAP Maximum Transmission Unit Information (GUI), page 34
•
Configuration Examples for Configuring Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count, page
•
35
Finding Feature Information
Prerequisites for Configuring the Access Point Retransmission
Interval and Retry Count
You can configure the retransmission intervals and retry count both at a global and a specific access
•
point level. A global configuration applies these configuration parameters to all the access points.
Alternatively, when you configure the retransmission level and retry count at a specific access point
level, the values are applied to that particular access point. The access point specific configuration has
a higher precedence than the global configuration.
Information About Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
The switch and the access points exchange packets using the Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access
Points (CAPWAP) reliable transport protocol. For each request, a response is defined. This response is used
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 31
Page 44

Configuring Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
How to Configure Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
to acknowledge the receipt of the request message. Response messages are not explicitly acknowledged;
therefore, if a response message is not received, the original request message is retransmitted after the retransmit
interval. If the request is not acknowledged after a maximum number of retransmissions, the session is closed
and the access points reassociate with another switch.
How to Configure Access Point Retransmission Interval and
Retry Count
Configuring the Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
ap capwap retransmit interval interval_time
3.
ap capwap retransmit count count_value
4.
end
5.
ap name Cisco_AP capwap retransmit interval interval_time
6.
ap name Cisco_AP capwap retransmit count count_value
7.
show ap capwap retransmit
8.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Example:
Switch# enable
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
ap capwap retransmit interval interval_time
Example:
Switch(config)# ap capwap retransmit interval
2
ap capwap retransmit count count_value
Example:
Switch(config)# ap capwap retransmit count
3
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Configures the control packet retransmit interval for all access
points globally.
Note
Configures the control packet retry count for all access points
globally.
Note
The range for the interval parameter is from 2
to 5.
The range for the count is from 3
to 8.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
32 OL-28697-01
Page 45

Configuring Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
Configuring the Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count (GUI)
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
ap name Cisco_AP capwap retransmit interval
interval_time
Example:
Switch# ap name AP02 capwap retransmit
interval 2
ap name Cisco_AP capwap retransmit count
count_value
Example:
Switch# ap name AP02 capwap retransmit
count 3
Example:
Switch# show ap capwap retransmit
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also
press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Configures the control packet retransmit interval for the
individual access point that you specify.
Note
The range for the interval is from 2
to 5.
Note
You must be in privileged EXEC mode to use the ap
name commands.
Configures the control packet retry count for the individual
access point that you specify.
Note
The range for the retry count is from 3
to 8.
Displays the CAPWAP retransmit details.show ap capwap retransmit
Configuring the Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count (GUI)
Global configuration applicable to all APs:
•
a) Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > Global AP Configuration.
The Global Configuration page is displayed.
b) In the AP Retransmit Config Parameters area, enter the values for the following parameters:
• AP Retransmit Count—Number of times you want the access point to retransmit the request
to the switch. The valid range is between 3 and 8.
• AP Retransmit Interval—Duration between the retransmission of requests. The valid range
is between 2 and 5.
c) Click Apply.
d) Click Save Configuration.
Configuration that is applicable to a specific AP:
•
a) Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > All APs.
The All APs page is displayed with a list of access points.
b) Click the access point name.
The AP > Edit page is displayed.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 33
Page 46

Configuring Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
Viewing CAPWAP Maximum Transmission Unit Information (CLI)
c) Click the Advanced tab.
d) In the AP Retransmit Config Parameters area, enter the values for the following AP Retransmit
Count and AP Retransmit Interval parameters:
• AP Retransmit Count—Number of times you want the access point to retransmit the request
to the switch. The valid range is between 3 and 8.
• AP Retransmit Interval—Duration between the retransmission of requests. The valid range
is between 2 and 5.
e) Click Apply.
f) Click Save Configuration.
Viewing CAPWAP Maximum Transmission Unit Information
(CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
2.
DETAILED STEPS
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Example:
Switch# enable
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
Example:
Switch# show ap name Maria-1250 config
general | include MTU
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Displays the maximum transmission unit (MTU) for the
CAPWAP path on the switch. The MTU specifies the maximum
size of any packet (in bytes) in a transmission.
Viewing CAPWAP Maximum Transmission Unit Information
(GUI)
Step 1
34 OL-28697-01
Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > All APs.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Page 47

Configuring Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
The All APs page is displayed.
Configuration Examples for Configuring Access Point Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
Step 2
Step 3
Click the AP name.
The AP > Edit page is displayed.
Click the Advanced tab.
The CAPWAP MTU field shows the CAPWAP maximum retransmission unit information.
Configuration Examples for Configuring Access Point
Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
Viewing the CAPWAP Retransmission Details: Example
Enter the following command:
Switch# show ap capwap retransmit
Global control packet retransmit interval : 3
Global control packet retransmit count : 5
AP Name Retransmit Interval Retransmit Count
--------------------------------- -------------------------------
-------------------------------3602a 5 3
Viewing Maximum Transmission Unit Information: Example
This example shows how to view the maximum transmission unit (MTU) for the CAPWAP path on the switch.
The MTU specifies the maximum size of any packet (in bytes) in a transmission:
Switch# show ap name cisco-ap-name config general | include MTU
CAPWAP Path MTU.................................. 1500
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 35
Page 48

Viewing Maximum Transmission Unit Information: Example
Configuring Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
36 OL-28697-01
Page 49

Configuring Adaptive Wireless Intrusion
Prevention System
Finding Feature Information, page 37
•
Prerequisites for Configuring wIPS, page 37
•
How to Configure wIPS on Access Points, page 38
•
Monitoring wIPS Information, page 40
•
Configuration Examples for Configuring wIPS on Access Points, page 41
•
Finding Feature Information
CHAPTER 6
Prerequisites for Configuring wIPS
The regular local mode access point has been extended with a subset of Wireless Intrusion Prevention
•
System (wIPS) capabilities. This feature enables you to deploy your access points to provide protection
without needing a separate overlay network.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 37
Page 50

Configuring Adaptive Wireless Intrusion Prevention System
How to Configure wIPS on Access Points
How to Configure wIPS on Access Points
Configuring wIPS on an Access Point (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
ap name Cisco_AP mode local
1.
ap name Cisco_AP dot11 5ghz shutdown
2.
ap name Cisco_AP dot11 24ghz shutdown
3.
ap name Cisco_AP mode monitor submode wips
4.
ap name Cisco_AP monitor-mode wips-optimized
5.
show ap dot11 24ghz monitor
6.
ap name Cisco_AP no dot11 5ghz shutdown
7.
ap name Cisco_AP no dot11 24ghz shutdown
8.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
ap name Cisco_AP mode local
Example:
Switch# ap name AP01 mode local
ap name Cisco_AP dot11 5ghz shutdown
Example:
Switch# ap name AP01 dot11 5ghz shutdown
ap name Cisco_AP dot11 24ghz shutdown
Example:
Switch# ap name AP02 dot11 24ghz shutdown
ap name Cisco_AP mode monitor submode
wips
Example:
Switch# ap name AP01 mode monitor
submode wips
Step 5
ap name Cisco_AP monitor-mode
wips-optimized
PurposeCommand or Action
Configures an access point for monitor mode.
A message appears that indicates that changing the AP's mode causes
the access point to reboot. This message also displays a prompt that
enables you to specify whether or not you want to continue with
changing the AP mode. Enter y at the prompt to continue.
Disables the 802.11a radio on the access point.
Disables the 802.11b radio on the access point.
Configures the wIPS submode on the access point.
Note
To disable wIPS on the access point, enter the ap name
Cisco_AP modemonitor submode none command.
Enables wIPS optimized channel scanning for the access point.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
38 OL-28697-01
Page 51

Configuring Adaptive Wireless Intrusion Prevention System
Example:
Switch# ap name AP01 monitor-mode
wips-optimized
Configuring wIPS on an Access Point (GUI)
PurposeCommand or Action
The access point scans each channel for 250 milliseconds. It derives
the list of channels to be scanned from the monitor configuration.
You can choose the following options:
• All—All channels supported by the access point’s radio.
• Country—Only the channels supported by the access point’s
country of operation.
• DCA—Only the channel set used by the dynamic channel
assignment (DCA) algorithm, which by default includes all of
the nonoverlapping channels allowed in the access point’s
country of operation.
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Example:
Switch# show ap dot11 24ghz monitor
ap name Cisco_AP no dot11 5ghz shutdown
Example:
Switch# ap name AP01 no dot11
5ghz shutdown
ap name Cisco_AP no dot11 24ghz shutdown
Example:
Switch# ap name AP01 no dot11
24ghz shutdown
Displays the monitor configuration channel set.show ap dot11 24ghz monitor
Note
The 802.11b Monitor Channels value in the output of the
command indicates the monitor configuration channel set.
Enables the 802.11a radio on the access point.
Enables the 802.11b radio on the access point.
Configuring wIPS on an Access Point (GUI)
Step 1
Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > All APs
The All APs page is displayed.
Step 2
Click the access point name.
The AP > Edit page is displayed.
Step 3
OL-28697-01 39
From the AP Mode drop-down list, choose one of the following options to configure the AP mode parameters:
Local
•
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Page 52

Monitoring wIPS Information
Monitor
•
Configuring Adaptive Wireless Intrusion Prevention System
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
From the AP Sub Mode drop-down list, choose WIPS.
Click Apply.
Click Save Configuration.
Monitoring wIPS Information
The procedure to perform this task using the switch GUI is not currently available.Note
SUMMARY STEPS
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
1.
show ap monitor-mode summary
2.
show wireless wps wips summary
3.
show wireless wps wips statistics
4.
clear wireless wips statistics
5.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
Example:
Switch# show ap name AP01 config general
show ap monitor-mode summary
Example:
Switch# show ap monitor-mode summary
show wireless wps wips summary
Example:
Switch# show wireless wps wips summary
show wireless wps wips statistics
Example:
Switch# show wireless wps wips statistics
PurposeCommand or Action
Displays information on the wIPS submode on the
access point.
Displays the wIPS optimized channel scanning
configuration on the access point.
Displays the wIPS configuration forwarded by NCS
or Prime to the switch.
Displays the current state of wIPS operation on the
switch.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
40 OL-28697-01
Page 53

Configuring Adaptive Wireless Intrusion Prevention System
Configuration Examples for Configuring wIPS on Access Points
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 5
Clears the wIPS statistics on the switch.clear wireless wips statistics
Example:
Switch# clear wireless wips statistics
Configuration Examples for Configuring wIPS on Access Points
Displaying the Monitor Configuration Channel Set: Example
This example shows how to display the monitor configuration channel set:
Switch# show ap dot11 24ghz monitor
Default 802.11b AP monitoring
802.11b Monitor Mode........................... enable
802.11b Monitor Channels....................... Country channels
802.11b AP Coverage Interval................... 180 seconds
802.11b AP Load Interval....................... 60 seconds
802.11b AP Noise Interval...................... 180 seconds
802.11b AP Signal Strength Interval............ 60 seconds
Displaying wIPS Information: Examples
This example shows how to display information on the wIPS submode on the access point:
Switch# show ap name AP01 config general
Cisco AP Identifier.............. 3
Cisco AP Name.................... AP1131:46f2.98ac
...
AP Mode ......................... Monitor
Public Safety ................... Disabled Disabled
AP SubMode ...................... WIPS
This example shows how to display the wIPS optimized channel scanning configuration on the access point:
Switch# show ap monitor-mode summary
AP Name Ethernet MAC Status Scanning
------------- -------------- -------- --------AP1131:4f2.9a 00:16:4:f2:9:a WIPS 1,6,NA,NA
Channel
List
This example shows how to display the wIPS configuration forwarded by WCS to the switch:
Switch# show wireless wps wips summary
Policy Name.............. Default
Policy Version........... 3
This example shows how to display the current state of wIPS operation on the switch:
Switch# show wireless wps wips statistics
Policy Assignment Requests............ 1
Policy Assignment Responses........... 1
Policy Update Requests................ 0
Policy Update Responses............... 0
Policy Delete Requests................ 0
Policy Delete Responses............... 0
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 41
Page 54

Displaying wIPS Information: Examples
Alarm Updates......................... 13572
Device Updates........................ 8376
Device Update Requests................ 0
Device Update Responses............... 0
Forensic Updates...................... 1001
Invalid WIPS Payloads................. 0
Invalid Messages Received............. 0
CAPWAP Enqueue Failed................. 0
NMSP Enqueue Failed................... 0
NMSP Transmitted Packets.............. 22950
NMSP Transmit Packets Dropped......... 0
NMSP Largest Packet................... 1377
Configuring Adaptive Wireless Intrusion Prevention System
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
42 OL-28697-01
Page 55

CHAPTER 7
Configuring Authentication for Access Points
Finding Feature Information, page 43
•
Prerequisites for Configuring Authentication for Access Points, page 43
•
Restrictions for Configuring Authentication for Access Points, page 44
•
Information about Configuring Authentication for Access Points, page 44
•
How to Configure Authentication for Access Points, page 44
•
Configuration Examples for Configuring Authentication for Access Points, page 51
•
Finding Feature Information
Prerequisites for Configuring Authentication for Access Points
You can set a global username, password, and enable password for all access points that are currently
•
joined to the switch and any that join in the future inherit as they join the switch. If desired, you can
override the global credentials and assign a unique username, password, and enable password for a
specific access point.
After an access point joins the switch, the access point enables console port security, and you are prompted
•
for your username and password whenever you log into the access point’s console port. When you log
in, you are in nonprivileged mode, and you must enter the enable password in order to use the privileged
mode.
The global credentials that you configure on the switch are retained across switch and access point
•
reboots. They are overwritten only if the access point joins a new switch that is configured with a global
username and password. If the new switch is not configured with global credentials, the access point
retains the global username and password configured for the first switch.
You must track the credentials used by the access points. Otherwise, you might not be able to log into
•
an access point’s console port. If you need to return the access points to the default Cisco/Cisco username
and password, you must clear the switch’s configuration and the access point’s configuration to return
them to factory-default settings. To reset the default access point configuration, enter the ap name
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 43
Page 56

Configuring Authentication for Access Points
Restrictions for Configuring Authentication for Access Points
Cisco_AP mgmtuser username Cisco password Cisco command. Entering the command does not clear
the static IP address of the access point. Once the access point rejoins a switch, it adopts the default
Cisco/Cisco username and password.
You can configure global authentication settings for all access points that are currently joined to the
•
switch and any that join in the future. If desired, you can override the global authentication settings and
assign unique authentication settings for a specific access point.
This feature is supported on the following hardware:
•
All Cisco switches that support authentication.
◦
Cisco Aironet 1140, 1260, 1310, 1520, 1600, 2600, 3500, and 3600 access points
◦
Restrictions for Configuring Authentication for Access Points
The switch name in the AP configuration is case sensitive. Therefore, make sure to configure the exact
•
system name on the AP configuration. Failure to do this results in the AP fallback not working.
Information about Configuring Authentication for Access Points
Cisco IOS access points are shipped from the factory with Cisco as the default enable password. This password
allows users to log into the nonprivileged mode and enter the show and debug commands that pose a security
threat to your network. You must change the default enable password to prevent unauthorized access and to
enable users to enter configuration commands from the access point’s console port.
You can configure 802.1X authentication between a lightweight access point and a Cisco switch. The access
point acts as an 802.1X supplicant and is authenticated by the switch where it uses EAP-FAST with anonymous
PAC provisioning.
How to Configure Authentication for Access Points
Configuring Global Credentials for Access Points (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
ap mgmtuser username user_name password 0 passsword secret 0 secret_value
3.
end
4.
ap name Cisco_AP mgmtuser username user_name password password secret secret
5.
show ap summary
6.
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
7.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
44 OL-28697-01
Page 57

Configuring Authentication for Access Points
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Global Credentials for Access Points (CLI)
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Switch# enable
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
ap mgmtuser username user_name
password 0 passsword secret 0 secret_value
Example:
Switch(config)# ap mgmtuser apusr1
password appass 0 secret 0 appass1
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
ap name Cisco_AP mgmtuser username
user_name password password secret secret
Example:
Switch(config)# ap name TSIM_AP-2
mgmtuser apusr1 password appass secret
secret
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Configures the global username and password and enables the password
for all access points that are currently joined to the switch and any access
points that join the switch in the future. In the command, the parameter
0 specifies that an unencrypted password will follow and 8 specifies that
an AES encrypted password will follow.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press
Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Overrides the global credentials for a specific access point and assigns
a unique username and password and enables password to this access
point.
The credentials that you enter in this command are retained across switch
and access point reboots and if the access point joins a new switch.
Note
If you want to force this access point to use the switch’s global
credentials, enter the ap name Cisco_AP no mgmtuser
command. The following message appears after you execute
this command: “AP reverted to global username configuration.”
Step 6
Example:
Switch# show ap summary
Step 7
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
Example:
Switch# show ap name AP02 config
general
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 45
Displays a summary of all connected Cisco APs.show ap summary
Displays the global credentials configuration for a specific access point.
Note
If this access point is configured for global credentials, the AP
User Mode text boxes shows “Automatic.” If the global
credentials have been overwritten for this access point, the AP
User Mode text box shows “Customized.”
Page 58

Configuring Authentication for Access Points
Configuring Global Credentials for Access Points (GUI)
Configuring Global Credentials for Access Points (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > Global AP Configuration.
The Global Configuration page is displayed.
In the Login Credentials area, enter the following parameters:
User Name
•
Password
•
Confirm Password
•
Secret Password
•
Confirm Secret Password
•
The password should contain characters from at least three of the following classes: lowercase letters, uppercase letters,
digits, and special characters. No character in the password can be repeated more than three times consecutively. The
password should not contain the management username or the reverse of the username. The password should not contain
words like Cisco, oscic, admin, nimda or any variant obtained by changing the capitalization of letters by substituting
1, |, or ! or substituting 0 for o or substituting $ for s.
Click Apply.
The global username and password are applied to all the access points that are associated with the switches
Click Save Configuration.
(Optional) You can override the global credentials for a specific access point and assign a unique username and password
by following these steps:
a) Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > All APs.
The All APs page is displayed.
b) Click the name of an access point.
The AP > Edit page is displayed.
c) Click the Credentials tab.
d) In the Login Credentials area, select the Over-ride Global Credentials check box.
e) Enter the values for the following parameters:
Username
•
Password
•
Enable Password
•
f) Click Apply.
g) Click Save Configuration.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
46 OL-28697-01
Page 59

Configuring Authentication for Access Points
Configuring Authentication for Access Points (CLI)
Configuring Authentication for Access Points (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
ap dot1x username user_name_value password 0 password_value
3.
end
4.
ap name Cisco_AP dot1x-user username username_value password password_value
5.
configure terminal
6.
no ap dot1x username user_name_value password 0 password_value
7.
end
8.
show ap summary
9.
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
10.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# enable
Step 2
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Step 3
ap dot1x username user_name_value
password 0 password_value
Example:
Switch(config)# ap dot1x username
AP3 password 0
password
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Configures the global authentication username and password for all access
points that are currently joined to the switch and any access points that join
the switch in the future. This command contains the following keywords and
arguments:
• username—Specifies an 802.1X username for all access points.
• user-id—Username.
• password—Specifies an 802.1X password for all access points.
• 0—Specifies an unencrypted password.
• 8—Specifies an AES encrypted password.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 47
• passwd—Password.
Note
You must enter a strong password for the password parameter. Strong
passwords are at least eight characters long, contain a combination
of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and are
not a word in any language.
Page 60

Configuring Authentication for Access Points (CLI)
Configuring Authentication for Access Points
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
ap name Cisco_AP dot1x-user
username username_value password
password_value
Example:
Switch# ap name AP03 dot1x-user
username apuser1 password appass
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z
to exit global configuration mode.
Overrides the global authentication settings and assigns a unique username
and password to a specific access point. This command contains the following
keywords and arguments:
• username—Specifies to add a username.
• user-id—Username.
• password—Specifies to add a password.
• 0—Specifies an unencrypted password.
• 8—Specifies an AES encrypted password.
• passwd—Password.
Note
You must enter a strong password for the password parameter. See
the note in Step 2 for the characteristics of strong passwords.
The authentication settings that you enter in this command are retained across
switch and access point reboots and whenever the access point joins a new
switch.
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
no ap dot1x username user_name_value
password 0 password_value
Example:
Switch(config)# no ap dot1x
username
dot1xusr password 0 dot1xpass
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Example:
Switch# show ap summary
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
Disables 802.1X authentication for all access points or for a specific access
point.
The following message appears after you execute this command: “AP reverted
to global username configuration.”
Note
You can disable 802.1X authentication for a specific access point only
if global 802.1X authentication is not enabled. If global 802.1X
authentication is enabled, you can disable 802.1X for all access points
only.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z
to exit global configuration mode.
Displays the authentication settings for all access points that join the switch.show ap summary
Note
If global authentication settings are not configured, the Global AP
Dot1x User Name text box shows “Not Configured.”
Displays the authentication settings for a specific access point.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
48 OL-28697-01
Page 61

Configuring Authentication for Access Points
Configuring Authentication for Access Points (GUI)
PurposeCommand or Action
Note
Example:
Switch# show ap name AP02 config
general
If this access point is configured for global authentication, the AP
Dot1x User Mode text boxes shows “Automatic.” If the global
authentication settings have been overwritten for this access point,
the AP Dot1x User Mode text box shows “Customized.”
Configuring Authentication for Access Points (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > Global AP Configuration.
The Global Configuration page is displayed.
In the 802.1x Supplicant Credentials area, select the Credentials Required check box.
Enter the username and password details.
You must enter a strong password in these text boxes. Strong passwords have the following characteristics:Note
They are at least eight characters long
•
They contain a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols
•
They are not a word in any language
•
Click Apply.
Click Save Configuration.
(Optional) You can override the global configuration and assign a unique username and password to a specific access
point by following these steps:
a) Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > All APs.
The All APs page is displayed.
Click the name of an access point.
The AP > Edit is displayed.
Click the Credentials tab.
In the 802.1x Supplicant Credentials area, select the Over-ride Global Credentials check box.
Enter the username and password details.
Click Apply.
Click Save Configuration.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 49
Page 62

Configuring the Switch for Authentication (CLI)
Configuring the Switch for Authentication (CLI)
The procedure to perform this task using the switch GUI is not currently available.Note
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
dot1x system-auth-control
3.
aaa new-model
4.
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
5.
radius-server host host_ip_adress acct-port port_number auth-port port_number key 0
6.
unencryptied_server_key
interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/1
7.
switch mode access
8.
dot1x pae authenticator
9.
end
10.
Configuring Authentication for Access Points
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Switch# enable
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Example:
Switch(config)# dot1x system-auth-control
Example:
Switch(config)# aaa new-model
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
Example:
Switch(config)# aaa authentication
dot1x default group radius
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enables system authentication control.dot1x system-auth-control
Enables new access control commands and functions.aaa new-model
Sets the default authentications lists for IEEE 802.1X
by using all the radius hosts in a server group.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
50 OL-28697-01
Page 63

Configuring Authentication for Access Points
Configuration Examples for Configuring Authentication for Access Points
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
radius-server host host_ip_adress acct-port port_number
auth-port port_number key 0 unencryptied_server_key
Example:
Switch(config)# radius-server host
10.1.1.1 acct-port 1813 auth-port 6225 key 0
encryptkey
Example:
Switch(config)# interface
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/1
switch mode access
Example:
Switch(config-if)# switch mode access
Example:
Switch(config-if)# dot1x pae
authenticator
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Sets a clear text encryption key for the RADIUS
authentication server.
Sets the 10-Gigbit Ethernet interface.interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/1
The command prompt changes from Controller(config)#
to Controller(config-if)#.
Sets the unconditional truncking mode access to the
interface.
Sets the 802.1X interface PAE type as the authenticator.dot1x pae authenticator
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you
can also press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Configuration Examples for Configuring Authentication for
Access Points
Displaying the Authentication Settings for Access Points: Examples
This example shows how to display the authentication settings for all access points that join the switch:
Switch# show ap summary
Number of APs.................................... 1
Global AP User Name.............................. globalap
Global AP Dot1x User Name........................ globalDot1x
This example shows how to display the authentication settings for a specific access point:
Switch# show ap name AP02 config dot11 24ghz general
Cisco AP Identifier.............................. 0
Cisco AP Name.................................... TSIM_AP2
...
AP Dot1x User Mode............................... AUTOMATIC
AP Dot1x User Name............................... globalDot1x
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 51
Page 64

Displaying the Authentication Settings for Access Points: Examples
Configuring Authentication for Access Points
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
52 OL-28697-01
Page 65

CHAPTER 8
Converting Autonomous Access Points to
Lightweight Mode
Finding Feature Information, page 53
•
Prerequisites for Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode, page 53
•
Information About Autonomous Access Points Converted to Lightweight Mode, page 54
•
How to Convert a Lightweight Access Point Back to an Autonomous Access Point, page 56
•
Authorizing Access Points (CLI), page 57
•
Authorizing Access Points (GUI), page 58
•
Disabling the Reset Button on Converted Access Points (CLI), page 59
•
Monitoring the AP Crash Log Information, page 60
•
How to Configure a Static IP Address on an Access Point, page 61
•
Recovering the Access Point Using the TFTP Recovery Procedure, page 63
•
Configuration Examples for Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode, page 63
•
Finding Feature Information
Prerequisites for Converting Autonomous Access Points to
Lightweight Mode
Access points that are converted to lightweight mode do not support Wireless Domain Services (WDS).
•
Converted access points communicate only with Cisco wireless LAN switchs and cannot communicate
with WDS devices. However, the switch provides functionality that is equivalent to WDS when the
access point associates to it.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 53
Page 66

Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
Information About Autonomous Access Points Converted to Lightweight Mode
All Cisco lightweight access points support 16 Basic Service Set Identifiers (BSSIDs) per radio and a
•
total of 16 wireless LANs per access point. When a converted access point associates to a switch, only
wireless LANs with IDs 1 through 16 are pushed to the access point unless the access point is a member
of an access point group.
Access points that are converted to lightweight mode must get an IP address and discover the switch
•
using DHCP, DNS, or IP subnet broadcast.
Information About Autonomous Access Points Converted to
Lightweight Mode
You can convert autonomous Cisco Aironet access points to lightweight mode. When you upgrade the access
points to lightweight mode, the access point communicates with the switch and receives a configuration and
software image from the switch.
See the Upgrading Autonomous Cisco Aironet Access Points to Lightweight Mode document for instructions
to upgrade an autonomous access point to lightweight mode:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/access_point/conversion/lwapp/upgrade/guide/lwapnote.html
Reverting from Lightweight Mode to Autonomous Mode
After you convert an autonomous access point to lightweight mode, you can convert the access point from a
lightweight unit back to an autonomous unit by loading a Cisco IOS release that supports autonomous mode
(Cisco IOS Release 12.3(7)JA or earlier releases). If the access point is associated with a switch, you can use
the switch to load the Cisco IOS release. If the access point is not associated to a switch, you can load the
Cisco IOS release using TFTP. In either method, the access point must be able to access a TFTP server that
contains the Cisco IOS release to be loaded.
Using DHCP Option 43 and DHCP Option 60
Cisco Aironet access points use the type-length-value (TLV) format for DHCP option 43. You must program
the DHCP servers to return the option based on the access point’s DHCP Vendor Class Identifier (VCI) string
(DHCP option 60).
For more information about DHCP VCI strings of access points, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk722/
tk809/technologies_configuration_example09186a00808714fe.shtml.
See the product documentation for your DHCP server for instructions on configuring DHCP option 43. The
Upgrading Autonomous Cisco Aironet Access Points to Lightweight Mode document contains example steps
for configuring option 43 on a DHCP server.
If the access point is ordered with the Service Provider Option - AIR-OPT60-DHCP selected, the VCI string
for that access point will be different than those strings listed in the previous table. The VCI string has the
following suffix: ServiceProvider. For example, a 1260 with this option returns this VCI string: Cisco AP
c1260-ServiceProvider.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
54 OL-28697-01
Page 67

Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
How Converted Access Points Send Crash Information to the Switch
Note
The switch IP address that you obtain from the DHCP server should be a unicast IP address. Do not
configure the switch IP address as a multicast address when configuring DHCP option 43.
How Converted Access Points Send Crash Information to the Switch
When a converted access point unexpectedly reboots, the access point stores a crash file on its local flash
memory at the time of the crash. After the unit reboots, it sends the reason for the reboot to the switch. If the
unit rebooted because of a crash, the switch pulls up the crash file using existing CAPWAP messages and
stores it in the switch flash memory. The crash information copy is removed from the access point flash
memory when the switch pulls it from the access point.
Uploading Memory Core Dumps from Converted Access Points
By default, access points converted to lightweight mode do not send memory core dumps to the switch. This
section provides instructions to upload access point core dumps using the switch GUI or CLI.
Displaying MAC Addresses for Converted Access Points
There are some differences in the way that controllers display the MAC addresses of converted access points
on information pages in the controller GUI:
On the AP Summary page, the controller lists the Ethernet MAC addresses of converted access points.
•
On the AP Detail page, the controller lists the BSS MAC addresses and Ethernet MAC addresses of
•
converted access points.
On the Radio Summary page, the switch lists converted access points by the radio MAC address.
•
Configuring a Static IP Address for a Lightweight Access Point
If you want to specify an IP address for an access point rather than having one assigned automatically by a
DHCP server, you can use the controller GUI or CLI to configure a static IP address for the access point.
Static IP addresses are generally used only for deployments with a limited number of users.
An access point cannot discover the switch using domain name system (DNS) resolution if a static IP address
is configured for the access point, unless you specify a DNS server and the domain to which the access point
belongs. You can configure these parameters using either the switch CLI or the GUI.
Note
If you configure an access point to use a static IP address that is not on the same subnet on which the
access point’s previous DHCP address was, the access point falls back to a DHCP address after the access
point reboots. If the access point falls back to a DHCP address, enter the show ap config general Cisco_AP
CLI command to show that the access point is using a fallback IP address. However, the GUI shows both
the static IP address and the DHCP address, but it does not identify the DHCP address as a fallback address.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 55
Page 68

Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
How to Convert a Lightweight Access Point Back to an Autonomous Access Point
How to Convert a Lightweight Access Point Back to an
Autonomous Access Point
Converting a Lightweight Access Point Back to an Autonomous Access Point
(CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
ap name Cisco_AP tftp-downgrade tftp_server_ip_address tftp_server_image_filename
2.
DETAILED STEPS
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Example:
Switch# enable
ap name Cisco_AP tftp-downgrade
tftp_server_ip_address tftp_server_image_filename
Example:
Switch# ap name AP02 tftp-downgrade
10.0.0.1 tsrvname
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Converts the lightweight access point back to autonomous
mode.
Note
After entering this command, you must wait until the
access point reboots and then reconfigure the access
point using the CLI or GUI.
Converting a Lightweight Access Point Back to an Autonomous Access Point
(Using the Mode Button and a TFTP Server)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Configure the PC on which your TFTP server software runs with a static IP address in the range of 10.0.0.2 to 10.0.0.30.
Make sure that the PC contains the access point image file (such as c1140-k9w7-tar.123-7.JA.tar for a 1140 series access
point) in the TFTP server folder and that the TFTP server is activated.
Rename the access point image file in the TFTP server folder to c1140-k9w7-tar.default for a 1140 series access point.
Connect the PC to the access point using a Category 5 (CAT5) Ethernet cable.
Disconnect power from the access point.
Press and hold the MODE button while you reconnect power to the access point.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
56 OL-28697-01
Page 69

Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
Authorizing Access Points (CLI)
Note
The MODE button on the access point must be
enabled.
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Hold the MODE button until the status LED turns red (approximately 20 to 30 seconds), and release the MODE button.
Wait until the access point reboots as indicated by all LEDs turning green followed by the Status LED blinking green.
After the access point reboots, reconfigure the access point using the GUI or the CLI.
Authorizing Access Points (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
ap auth-list ap-policy authorize-ap
3.
username user_name mac aaa attribute list list_name
4.
aaa new-model
5.
aaa authorization credential-download auth_list local
6.
aaa attribute list list
7.
aaa session-id common
8.
aaa local authentication default authorization default
9.
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
10.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Example:
Switch# enable
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Configures an access point authorization policy.ap auth-list ap-policy authorize-ap
Example:
Switch(config)# ap auth-list ap-policy
authorize-ap
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 57
Page 70

Authorizing Access Points (GUI)
Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
username user_name mac aaa attribute list list_name
Example:
Switch(config)# username aaa.bbb.ccc mac aaa attribute
list attrlist
aaa new-model
Example:
Switch(config)# aaa new-model
aaa authorization credential-download auth_list local
Example:
Switch(config)# aaa authorization credential-download
auth_download local
aaa attribute list list
Example:
Switch(config)# aaa attribute list alist
Example:
Switch(config)# aaa session-id common
Configures the MAC address of an access point
locally.
Enables new access control commands and
functions.
Downloads EAP credentials from the local server.
Configures AAA attribute list definitions.
Configures the AAA common session ID.aaa session-id common
Configures the local authentication method list.aaa local authentication default authorization default
Example:
Switch(config)# aaa local authentication default
authorization default
Step 10
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
Example:
Switch(config)# show ap name AP01 config general
Authorizing Access Points (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Choose Configuration > Security > AAA > AP Policy.
The AP Policy page is displayed.
In the Policy Configuration area, enable or disable the following parameters:
Authorize LSC APs against Auth-List
•
AP with Self-Signed Certificate
•
Displays the configuration information that
corresponds to a specific access point.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
58 OL-28697-01
Page 71

Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
Authorize MIC APs against AAA
•
AP with Manufacturing Installed Certificate
•
Disabling the Reset Button on Converted Access Points (CLI)
Step 3
Step 4
Click Apply.
Click Save Configuration.
Disabling the Reset Button on Converted Access Points (CLI)
You can enable or disable the Reset button on access points that are converted to lightweight mode. The Reset
button is labeled MODE on the outside of the access point.
The procedure to perform this task using the controller GUI is not currently available.Note
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
no ap reset-button
3.
end
4.
ap name Cisco_AP reset-button
5.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Example:
Switch# enable
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
no ap reset-button
Example:
Switch(config)# no ap reset-button
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Disables the Reset buttons on all converted access points that are
associated to the switch.
Note
To enable the Reset buttons on all converted access points
that are associated to the switch, enter the ap reset-button
command.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 59
Page 72

Monitoring the AP Crash Log Information
Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 4
end
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also
press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Step 5
ap name Cisco_AP reset-button
Enables the Reset button on the converted access point that you
specify.
Example:
Switch# ap name AP02 reset-button
Monitoring the AP Crash Log Information
The procedure to perform this task using the switch GUI is not currently available.Note
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
show ap crash-file
2.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Example:
Switch# enable
show ap crash-file
Example:
Switch# show ap crash-file
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Verifies whether the crash file is downloaded to the
switch.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
60 OL-28697-01
Page 73

Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
How to Configure a Static IP Address on an Access Point
How to Configure a Static IP Address on an Access Point
Configuring a Static IP Address on an Access Point (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
ap name Cisco_AP static-ip ip-address static_ap_address netmask static_ip_netmask gateway
2.
static_ip_gateway
enable
3.
configure terminal
4.
ap static-ip name-server nameserver_ip_address
5.
ap static-ip domain static_ip_domain
6.
end
7.
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
8.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# enable
Step 2
ap name Cisco_AP static-ip ip-address
static_ap_address netmask static_ip_netmask
gateway static_ip_gateway
Example:
Switch# ap name AP03 static-ip
ip-address
9.9.9.16 netmask 255.255.0.0 gateway
9.9.9.2
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Configures a static IP address on the access point. This command
contains the following keywords and arguments:
• ip-address— Specifies the Cisco access point static IP address.
• ip-address— Cisco access point static IP address.
• netmask—Specifies the Cisco access point static IP netmask.
• netmask— Cisco access point static IP netmask.
• gateway—Specifies the Cisco access point gateway.
• gateway— IP address of the Cisco access point gateway.
The access point reboots and rejoins the switch, and the static IP address
that you specify is pushed to the access point. After the static IP address
has been sent to the access point, you can configure the DNS server IP
address and domain name. You must perform Steps 3 and 4 after the
access points reboot.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 61
Page 74

Configuring a Static IP Address on an Access Point (GUI)
Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Example:
Switch# enable
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
ap static-ip name-server
nameserver_ip_address
Example:
Switch(config)# ap static-ip
name-server
10.10.10.205
ap static-ip domain static_ip_domain
Example:
Switch(config)# ap static-ip domain
domain1
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Configures a DNS server so that a specific access point or all access
points can discover the switch using DNS resolution.
Note
To undo the DNS server configuration, enter the no ap static-ip
name-server nameserver_ip_address command.
Configures the domain to which a specific access point or all access
points belong.
Note
To undo the domain name configuration, enter the no ap
static-ip domain static_ip_domain command.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press
Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Displays the IP address configuration for the access point.
Example:
Switch# show ap name AP03 config
general
Configuring a Static IP Address on an Access Point (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > All APs.
The All APs page is displayed.
Click the name of the access point.
The AP > Edit page is displayed.
In the General tab, in the IP Config area, select the Static IP check box if you want to assign a static IP address to the
access point.
Enter the following details:
Static IP
•
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
62 OL-28697-01
Page 75

Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
Netmask
•
Gateway
•
Recovering the Access Point Using the TFTP Recovery Procedure
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Click Apply.
The access point reboots and rejoins the switch, and the static IP address that you specified is sent to the access point.
After the static IP address has been sent to the access point, configure the DNS IP Address and Domain Name.
Click Apply.
Click Save Configuration.
Recovering the Access Point Using the TFTP Recovery
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Download the required recovery image from Cisco.com (ap3g2-k9w8-tar.152-2.JA.tar) and install it in the root directory
of your TFTP server.
Connect the TFTP server to the same subnet as the target access point and power-cycle the access point. The access point
boots from the TFTP image and then joins the switch to download the oversized access point image and complete the
upgrade procedure.
After the access point has been recovered, you can remove the TFTP server.
Configuration Examples for Converting Autonomous Access
Points to Lightweight Mode
Displaying the IP Address Configuration for Access Points: Example
This example shows how to display the IP address configuration for the access point:
Switch# show ap name AP03 dot11 24ghz config general
Cisco AP Identifier.............. 4
Cisco AP Name............................. AP6
IP Address Configuration.................. Static IP assigned
IP Address................................ 10.10.10.118
IP NetMask................................ 255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Addr........................... 10.10.10.1
Domain.................................... Domain1
Name Server............................... 10.10.10.205
...
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 63
Page 76

Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
Displaying Access Point Crash File Information: Example
Displaying Access Point Crash File Information: Example
This example shows how to display access point crash file information. Using this command, you can verify
whether the file is downloaded to the switch:
Switch# show ap crash-file
Local Core Files:
lrad_AP1130.rdump0 (156)
The number in parentheses indicates the size of the file. The size should
be greater than zero if a core dump file is available.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
64 OL-28697-01
Page 77

CHAPTER 9
Using Cisco Workgroup Bridges
Finding Feature Information, page 65
•
Information About Cisco Workgroup Bridges and non-Cisco Workgroup bridges, page 65
•
Monitoring the Status of Workgroup Bridges, page 66
•
Debugging WGB Issues (CLI), page 66
•
Configuration Examples for Configuring Workgroup Bridges, page 68
•
Finding Feature Information
Information About Cisco Workgroup Bridges and non-Cisco
Workgroup bridges
A WGB is a mode that can be configured on an autonomous Cisco IOS access point to provide wireless
connectivity to a lightweight access point on behalf of clients that are connected by Ethernet to the WGB
access point. A WGB connects a wired network over a single wireless segment by learning the MAC addresses
of its wired clients on the Ethernet interface and reporting them to the lightweight access point using Internet
Access Point Protocol (IAPP) messaging. The WGB provides wireless access connectivity to wired clients
by establishing a single wireless connection to the lightweight access point.
When a Cisco WGB is used, the WGB informs the access points of all the clients that it is associated with.
The switch is aware of the clients that are associated with the access point. When non-Cisco WGBs are used,
the switch has no information about the IP address of the clients on the wired segment behind the WGB.
Without this information, the switch drops the following types of messages:
ARP REQ from the distribution system for the WGB client.
•
ARP RPLY from the WGB client.
•
DHCP REQ from the WGB client.
•
DHCP RPLY for the WGB client.
•
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 65
Page 78

Monitoring the Status of Workgroup Bridges
Monitoring the Status of Workgroup Bridges
The procedure to perform this task using the switch GUI is not currently available.Note
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
show wireless wgb summary
2.
show wireless wgb mac-address wgb_mac_address detail
3.
DETAILED STEPS
PurposeCommand or Action
Using Cisco Workgroup Bridges
Step 1
Example:
Switch# enable
Step 2
Example:
Switch# show wireless wgb summary
Step 3
show wireless wgb mac-address wgb_mac_address detail
Example:
Switch# show wireless wgb mac-address
00:0d:ed:dd:25:82 detail
Debugging WGB Issues (CLI)
The procedure to perform this task using the switch GUI is not currently available.Note
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Displays the WGBs on your network.show wireless wgb summary
Displays the details of any wired clients that are
connected to a particular WGB.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
66 OL-28697-01
Page 79

Using Cisco Workgroup Bridges
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
enable
1.
debug iapp all
2.
debug iapp error
3.
debug iapp packet
4.
debug mobility handoff [switch switch_number]
5.
debug dhcp
6.
debug dot11 mobile
7.
debug dot11 state
8.
Debugging WGB Issues (CLI)
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Example:
Switch# enable
Example:
Switch# debug iapp all
Example:
Switch# debug iapp error
Example:
Switch# debug iapp packet
debug mobility handoff [switch switch_number]
Example:
Switch# debug mobility handoff
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enables debugging for IAPP messages.debug iapp all
Enables debugging for IAPP error events.debug iapp error
Enables debugging for IAPP packets.debug iapp packet
Enables debugging for any roaming issues.
Debug an IP assignment issue when DHCP is used.debug dhcp
Example:
Switch# debug dhcp
Step 7
OL-28697-01 67
debug dot11 mobile
Example:
Switch# debug dot11 mobile
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Enables dot11/mobile debugging. Debug an IP
assignment issue when static IP is used.
Page 80

Configuration Examples for Configuring Workgroup Bridges
Using Cisco Workgroup Bridges
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 8
debug dot11 state
Enables dot11/state debugging. Debug an IP assignment
issue when static IP is used.
Example:
Switch# debug dot11 state
Configuration Examples for Configuring Workgroup Bridges
WGB Configuration: Example
This example shows how to configure a WGB access point using static WEP with a 40-bit WEP key:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# dot11 ssid WGB_with_static_WEP
Switch(config-ssid)# authentication open
Switch(config-ssid)# guest-mode
Switch(config-ssid)# exit
Switch(config)# interface dot11Radio 0
Switch(config)# station-role workgroup-bridge
Switch(config-if)# encry mode wep 40
Switch(config-if)# encry key 1 size 40 0 1234567890
Switch(config-if)# ssid WGB_with_static_WEP
Switch(config-if)# end
Verify that the WGB is associated to an access point by entering this command on the WGB:
show dot11 association
Information similar to the following appears:
Switch# show dot11 associations
802.11 Client Stations on Dot11Radio0:
SSID [FCVTESTING] :
MAC Address IP address Device Name Parent State
000b.8581.6aee 10.11.12.1 WGB-client map1 - Assoc
ap#
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
68 OL-28697-01
Page 81

CHAPTER 10
Configuring Probe Request Forwarding
Finding Feature Information, page 69
•
Information About Configuring Probe Request Forwarding, page 69
•
How to Configure Probe Request Forwarding (CLI), page 69
•
Finding Feature Information
Information About Configuring Probe Request Forwarding
Probe requests are 802.11 management frames that are sent by clients to request information about the
capabilities of Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs). By default, access points forward acknowledged probe requests
to the switch for processing. Acknowledged probe requests are probe requests for SSIDs that are supported
by the access point. If desired, you can configure access points to forward both acknowledged and
unacknowledged probe requests to the switch. The switch can use the information from unacknowledged
probe requests to improve the location accuracy.
How to Configure Probe Request Forwarding (CLI)
The procedure to perform this task using the switch GUI is not currently available.Note
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
wireless probe filter
2.
wireless probe filter num_probes interval
3.
end
4.
show wireless probe
5.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 69
Page 82

How to Configure Probe Request Forwarding (CLI)
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Probe Request Forwarding
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
wireless probe filter
Example:
Switch(config)# wireless probe
filter
wireless probe filter num_probes interval
Example:
Switch(config)# wireless probe
filter 5 5
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enables or disables the filtering of probe requests forwarded from an access
point to the switch.
Note
If you enable probe filtering, the default filter setting, the access
point forwards only acknowledged probe requests to the switch. If
you disable probe filtering, the access point forwards both
acknowledged and unacknowledged probe requests to the switch.
Limits the number of probe requests sent to the switch per client per access
point radio in a given interval. You must specify the following arguments
with this command:
• num_probes—Number of probe requests forwarded to the switch per
client per access point radio in a given interval. The range is from 1
to 100.
• interval—Probe limit interval in milliseconds. The range is from 100
to 10000.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z
to exit global configuration mode.
Displays the advanced probe request configuration.show wireless probe
Example:
Switch# show wireless probe
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
70 OL-28697-01
Page 83

CHAPTER 11
Optimizing RFID Tracking
Finding Feature Information, page 71
•
Optimizing RFID Tracking on Access Points, page 71
•
How to Optimize RFID Tracking on Access Points, page 71
•
Configuration Examples for Optimizing RFID Tracking, page 72
•
Finding Feature Information
Optimizing RFID Tracking on Access Points
To optimize the monitoring and location calculation of RFID tags, you can enable tracking optimization on
up to four channels within the 2.4-GHz band of an 802.11b/g access point radio. This feature allows you to
scan only the channels on which tags are usually programmed to operate (such as channels 1, 6, and 11).
How to Optimize RFID Tracking on Access Points
Optimizing RFID Tracking on Access Points (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
ap name Cisco_AP mode monitor submode none
1.
ap name Cisco_AP dot11 24ghz shutdown
2.
ap name Cisco_AP monitor-mode tracking-opt
3.
ap name Cisco_AP monitor-mode dot11b {fast-channel [first_channel second_channel third_channel
4.
fourth_channel]}
ap name Cisco_AP no dot11 24ghz shutdown
5.
show ap monitor-mode summary
6.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 71
Page 84

Configuration Examples for Optimizing RFID Tracking
DETAILED STEPS
Optimizing RFID Tracking
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
ap name Cisco_AP mode monitor submode none
Example:
Switch# ap name 3602a mode monitor
submode none
ap name Cisco_AP dot11 24ghz shutdown
Example:
Switch# ap name AP01 dot11 24ghz shutdown
ap name Cisco_AP monitor-mode tracking-opt
Example:
Switch# ap name TSIM_AP1 monitor-mode
tracking-opt
ap name Cisco_AP monitor-mode dot11b
{fast-channel [first_channel second_channel
third_channel fourth_channel]}
Example:
Switch# ap name AP01 monitor-mode dot11b
fast-channel 1 2 3 4
ap name Cisco_AP no dot11 24ghz shutdown
Specifies the monitor submode for the access point as none.
Note
A warning message indicates that changing the access
point's mode will cause the access point to reboot and
prompts you to specify whether you want to continue
by entering Y.
After you enter Y, the access point reboots.
Disables the access point radio.
Configures the access point to scan only the Dynamic Channel
Assignment (DCA) channels supported by its country of
operation.
Note
To disable tracking optimization for an access point,
enter the ap name Cisco_AP monitor-mode
tracking-opt no-optimization command.
Chooses up to four specific 802.11b channels to be scanned by
the access point.
Note
In the United States, you can assign any value from 1
to 11 (inclusive) to the channel variable. Other countries
support additional channels. You must assign at least
one channel.
Enables the access point radio.
Example:
Switch# ap name AP01 no dot11 24ghz shutdown
Step 6
Example:
Switch# show ap monitor-mode summary
Configuration Examples for Optimizing RFID Tracking
Displaying all the Access Points in Monitor Mode: Example
This example shows how to display all the access points in monitor mode:
Switch# show ap monitor-mode summary
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
72 OL-28697-01
Displays all the access points in monitor mode.show ap monitor-mode summary
Page 85

Optimizing RFID Tracking
Displaying all the Access Points in Monitor Mode: Example
AP Name Ethernet MAC Status Scanning
------------- -------------- -------- --------AP1131:4f2.9a 00:16:4:f2:9:a Tracking 1,6,NA,NA
Channel
List
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 73
Page 86

Displaying all the Access Points in Monitor Mode: Example
Optimizing RFID Tracking
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
74 OL-28697-01
Page 87

CHAPTER 12
Configuring Country Codes
Finding Feature Information, page 75
•
Prerequisites for Configuring Country Codes, page 75
•
Information About Configuring Country Codes, page 76
•
How to Configure Country Codes (CLI), page 76
•
Configuration Examples for Configuring Country Codes, page 79
•
Finding Feature Information
Prerequisites for Configuring Country Codes
Generally, you configure one country code per switch; you configure one code that matches the physical
•
location of the switch and its access points. You can configure up to 20 country codes per switch. This
multiple-country support enables you to manage access points in various countries from a single switch.
When the multiple-country feature is used, all switchs that are going to join the same RF group must be
•
configured with the same set of countries, configured in the same order.
Access points are capable of using all the available legal frequencies. However, access points are assigned
•
to the frequencies that are supported in their relevant domains.
The country list configured on the RF group leader determines which channels the members would
•
operate on. This list is independent of which countries have been configured on the RF group members.
For switchs in the Japan regulatory domain, you must have had one or more Japan country codes (JP,
•
J2, or J3) configured on your switch at the time you last booted your switch.
For switchs in the Japan regulatory domain, you must have at least one access point with a -J regulatory
•
domain joined to your switch.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 75
Page 88

Information About Configuring Country Codes
Information About Configuring Country Codes
Controllers and access points are designed for use in many countries with varying regulatory requirements.
The radios within the access points are assigned to a specific regulatory domain at the factory (such as -E for
Europe), but the country code enables you to specify a particular country of operation (such as FR for France
or ES for Spain). Configuring a country code ensures that each radio’s broadcast frequency bands, interfaces,
channels, and transmit power levels are compliant with country-specific regulations.
Information About Japanese Country Codes
Country codes define the channels that can be used legally in each country. These country codes are available
for Japan:
• JP—Allows only -J radios to join the controller
• J2—Allows only -P radios to join the controller
• J3—Uses the -U frequencies but allows -U, -P and -Q (other than 1550/1600/2600/3600) radios to join
the controller
Configuring Country Codes
• J4—Allows 2.4G JPQU and 5G PQU to join the controller.
The 1550, 1600, 2600, and 3600 APs require J4.Note
See the Channels and Maximum Power Settings for Cisco Aironet Lightweight Access Points document for
the list of channels and power levels supported by access points in the Japanese regulatory domains.
How to Configure Country Codes (CLI)
The procedure to perform this task using the switch GUI is not currently available.Note
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
76 OL-28697-01
Page 89

Configuring Country Codes
SUMMARY STEPS
enable
1.
show wireless country supported
2.
configure terminal
3.
ap dot11 24ghz shutdown
4.
ap dot11 5ghz shutdown
5.
ap country country_code
6.
end
7.
show wireless country channels
8.
configure terminal
9.
no ap dot11 5ghz shutdown
10.
no ap dot11 24ghz shutdown
11.
end
12.
ap name Cisco_AP shutdown
13.
configure terminal
14.
ap country country_code
15.
end
16.
ap name Cisco_AP no shutdown
17.
How to Configure Country Codes (CLI)
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Example:
Switch# enable
Displays a list of all available country codes.show wireless country supported
Example:
Switch# show wireless country supported
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Disables the 802.11a network.ap dot11 24ghz shutdown
Example:
Switch(config)# ap dot11 5ghz shutdown
Disables the 802.11b/g network.ap dot11 5ghz shutdown
Example:
Switch(config)# ap dot11 24ghz shutdown
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 77
Page 90

How to Configure Country Codes (CLI)
Configuring Country Codes
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
ap country country_code
Example:
Switch(config)# ap country IN
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
show wireless country channels
Example:
Switch# show wireless country channels
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Example:
Switch(config)# no ap dot11 5ghz shutdown
Assigns access points to a specific country.
Note
Make sure that the country code you choose is
compatible with the regulatory domain of at least one
of the access point’s radios.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also
press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Displays the list of available channels for the country codes
configured on your switch.
Note
Perform Steps 9 through 17 only if you have configured
multiple country codes in Step 6.
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enables the 802.11a network.no ap dot11 5ghz shutdown
Enables the 802.11b/g network.no ap dot11 24ghz shutdown
Step 12
Step 13
Step 14
Example:
Switch(config)# no ap dot11 24ghz shutdown
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
ap name Cisco_AP shutdown
Example:
Switch# ap name AP02 shutdown
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also
press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Disables the access point.
Note
Ensure that you disable only the access point for which
you are configuring country codes.
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
78 OL-28697-01
Page 91

Configuring Country Codes
Configuration Examples for Configuring Country Codes
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 15
ap country country_code
Example:
Switch# ap country IN
Assigns an access point to a specific country.
Note
Ensure that the country code that you choose is
compatible with the regulatory domain of at least one
of the access point’s radios.
Note
If you enabled the networks and disabled some access
points and then enter the ap country country_code
command, the specified country code is configured on
only the disabled access points. All other access points
are ignored.
Step 16
end
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also
press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Step 17
ap name Cisco_AP no shutdown
Enables the access point.
Example:
Switch# ap name AP02 no shutdown
Configuration Examples for Configuring Country Codes
Displaying Channel List for Country Codes: Example
This example shows how to display the list of available channels for the country codes configured on your
switch:
Switch# show wireless country channels
Configured Country........................: US - United States
KEY: * = Channel is legal in this country and may be configured manually.
A = Channel is the Auto-RF default in this country.
. = Channel is not legal in this country.
C = Channel has been configured for use by Auto-RF.
x = Channel is available to be configured for use by Auto-RF.
(-,-) = (indoor, outdoor) regulatory domain allowed by this country.
-----------------:+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-
802.11bg :
Channels : 1 1 1 1 1
: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4
-----------------:+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+(-A ,-AB ) US : A * * * * A * * * * A . . .
Auto-RF : . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-----------------:+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-
802.11a : 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Channels : 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 0 0 0 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6
: 4 6 8 0 2 4 6 8 2 6 0 4 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 9 3 7 1 5
-----------------:+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+(-A ,-AB ) US : . A . A . A . A A A A A * * * * * . . . * * * A A A A
*
Auto-RF : . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-----------------:+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 79
Page 92

Displaying Channel List for Country Codes: Example
4.9GHz 802.11a :
Channels : 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
-----------------:+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+US (-A ,-AB ): * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * A * * * * * A
Auto-RF : . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-----------------:+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-
Configuring Country Codes
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
80 OL-28697-01
Page 93

Configuring Link Latency
Finding Feature Information, page 81
•
Prerequisites for Configuring Link Latency, page 81
•
Restrictions for Configuring Link Latency, page 81
•
Information About Configuring Link Latency, page 82
•
How to Configure Link Latency, page 83
•
How to Configure TCP MSS, page 86
•
Performing a Link Test (CLI), page 87
•
Configuration Examples for Configuring Link Latency, page 88
•
Finding Feature Information
CHAPTER 13
Prerequisites for Configuring Link Latency
The switch displays the current round-trip time as well as a running minimum and maximum round-trip
•
time. The minimum and maximum times continue to run as long as the switch is up or can be cleared
and allowed to restart.
You can configure link latency for a specific access point using the switch GUI or CLI or for all access
•
points joined to the switch using the CLI.
Restrictions for Configuring Link Latency
Link latency calculates the Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) response
•
time between the access point and the switch. It does not measure network latency or ping responses.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 81
Page 94

Information About Configuring Link Latency
Information About Configuring Link Latency
You can configure link latency on the switch to measure the link between an access point and the switch. You
can use this feature with all access points that are joined to the switch where the link can be a slow or unreliable
WAN connection.
TCP MSS
If the client’s maximum segment size (MSS) in a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) three-way handshake
is greater than the maximum transmission unit can handle, the client might experience reduced throughput
and the fragmentation of packets. To avoid this problem, you can specify the MSS for all access points that
are joined to the switch or for a specific access point.
When you enable this feature, the access point selects the MSS for TCP packets to and from wireless clients
in its data path. If the MSS of these packets is greater than the value that you configured or greater than the
default value for the CAPWAP tunnel, the access point changes the MSS to the new configured value.
Configuring Link Latency
Link Tests
A link test is used to determine the quality of the radio link between two devices. Two types of link-test
packets are transmitted during a link test: request and response. Any radio receiving a link-test request packet
fills in the appropriate text boxes and echoes the packet back to the sender with the response type set.
The radio link quality in the client-to-access point direction can differ from that in the access point-to-client
direction due to the asymmetrical distribution of the transmit power and receive sensitivity on both sides. Two
types of link tests can be performed: a ping test and a CCX link test.
With the ping link test, the controller can test link quality only in the client-to-access point direction. The RF
parameters of the ping reply packets received by the access point are polled by the controller to determine the
client-to-access point link quality.
With the CCX link test, the switch can also test the link quality in the access point-to-client direction. The
switch issues link-test requests to the client, and the client records the RF parameters (received signal strength
indicator [RSSI], signal-to-noise ratio [SNR], and so on) of the received request packet in the response packet.
Both the link-test requestor and responder roles are implemented on the access point and switch. Not only
can the access point or switch initiate a link test to a CCX v4 or v5 client, but a CCX v4 or v5 client can
initiate a link test to the access point or switch.
The switch shows the link-quality metrics for CCX link tests in both directions (out— the access point to the
client; in— the client to the access point):
Signal strength in the form of RSSI (minimum, maximum, and average)
•
Signal quality in the form of SNR (minimum, maximum, and average)
•
Total number of packets that are retried
•
Maximum retry count for a single packet
•
Number of lost packets
•
Data rate of a successfully transmitted packet
•
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
82 OL-28697-01
Page 95

Configuring Link Latency
The controller shows this metric regardless of direction:
Link test request/reply round-trip time (minimum, maximum, and average)
•
The controller software supports CCX versions 1 through 5. CCX support is enabled automatically for every
WLAN on the controller and cannot be disabled. The controller stores the CCX version of the client in its
client database and uses it to limit the features for this client. If a client does not support CCXv4 or v5, the
controller performs a ping link test on the client. If a client supports CCXv4 or v5, the controller performs a
CCX link test on the client. If a client times out during a CCX link test, the controller switches to the ping
link test automatically.
How to Configure Link Latency
Configuring Link Latency (CLI)
How to Configure Link Latency
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# enable
Step 2
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Step 3
ap link-latency
Example:
Switch(config)# ap link-latency
enable
1.
configure terminal
2.
ap link-latency
3.
ap tcp-adjust-mss size size
4.
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
5.
ap name Cisco_AP link-latency [reset]
6.
show ap name Cisco_AP config general
7.
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters privileged EXEC mode.enable
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enables link latency for all access points that are currently associated with the
switch.
Note
Note
To disable link latency for all the access points that are associated with
the switch, use the no ap link-latency command.
These commands enable or disable link latency only for access points
that are currently joined to the switch. You have to enable or disable
link latency for the access points that join in the future.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 83
Page 96

Configuring Link Latency (CLI)
PurposeCommand or Action
Note
Configuring Link Latency
To enable or disable link latency for specific access points that are
associated with the switch, enter the following commands in Priveleged
EXEC mode:
• ap name Cisco_AP link-latency—Enables link latency.
• ap name Cisco_AP no link-latency—Disables link latency.
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
ap tcp-adjust-mss size size
Example:
Switch(config)# ap tcp-adjust-mss
size 537
show ap name Cisco_AP config
general
Example:
Switch(config)# show ap name AP02
config general
ap name Cisco_AP link-latency [reset]
Example:
Switch(config)# ap name AP02
link-latency
reset
show ap name Cisco_AP config
general
Configures TCP MSS adjust size for all access points. The range is from 536
to 1363.
Displays the general configuration details of the access point. These
configuration details contain the link latency results that correspond to the
access point that you specify in the command.
The output of this command contains the following link latency results:
• Current Delay—The current round-trip time (in milliseconds) of CAPWAP
heartbeat packets from the access point to the switch and back.
• Maximum Delay—Since the time that link latency has been enabled or
reset, the maximum round-trip time (in milliseconds) of CAPWAP
heartbeat packets from the access point to the switch and back.
• Minimum Delay—Since the time that link latency has been enabled or
reset, the minimum round-trip time (in milliseconds) of CAPWAP
heartbeat packets from the access point to the switch and back.
Clears the current, minimum, and maximum link latency statistics on the switch
for a specific access point.
Displays the general configuration details of the access point. Use this command
to see the result of the reset operation.
Example:
Switch(config)# show ap name AP02
config general
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
84 OL-28697-01
Page 97

Configuring Link Latency
Configuring Link Latency (GUI)
Configuring Link Latency (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > All APs.
The All APs page appears with a list of access points.
Click the name of the access point.
The AP > Edit page appears.
Click the Advanced tab.
In the Link Latency area, select or unselect the Enable Link Latency check box.
Note
You can select the Enable Link Latency check box to enable link latency for this access point or unselect it to
prevent the access point from sending the round-trip time to the switch after every echo response is received.
The default state is unselected.
Click Apply.
When a message box appears that indicates that AP Parameters are modified successfully, click OK.
When the All APs page is displayed, click the access point that you have modified earlier.
The AP > Edit page appears.
Click the Advanced tab.
In the Link Latency area, the following link latency and data latency results are displayed:
• Current(mSec)—The current round-trip time (in milliseconds) of CAPWAP heartbeat packets or data packets
from the access point to the switch and back.
• Minimum(mSec)—Since the time that link latency has been enabled or reset, the minimum round-trip time (in
milliseconds) of CAPWAP heartbeat packets or data packets from the access point to the switch and back.
• Maximum(mSec)—Since the time that link latency has been enabled or reset, the maximum round-trip time (in
milliseconds) of CAPWAP heartbeat packets or data packets from the access point to the switch and back.
Step 9
Click Reset Link Latency to clear the current, minimum, and maximum link latency and data latency statistics on the
switch for this access point.
Note
After the page refreshes and the All APs page is displayed again, click the Advanced tab. The updated statistics
appear in the Minimum and Maximum text boxes.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 85
Page 98

How to Configure TCP MSS
How to Configure TCP MSS
Configuring TCP MSS (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
ap tcp-adjust-mss size size_value
2.
reload
3.
show ap tcp-adjust-mss
4.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Link Latency
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
ap tcp-adjust-mss size size_value
Example:
Switch(config)# ap tcp-adjust-mss
size 537
Example:
Switch# reload
show ap tcp-adjust-mss
Example:
Switch# show ap tcp-adjust-mss
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enables the TCP MSS on the particular access point that you specify.
Note
Reboots the switch in order for your change to take effect.reload
Displays the current TCP MSS setting for all the access points that are
associated with the switch.
Note
To enable TCP MSS on all the access points that are associated
with the switch, enter the ap tcp-adjust-mss size size_value
command, where the size parameter is from 536 to 1363 bytes.
The default value varies for different clients.
To display the TCP MSS settings that correspond to a specific
access point, enter the show ap name Cisco_AP tcp-adjust-mss
command.
Configuring TCP MSS (GUI)
Step 1
86 OL-28697-01
Choose Configuration > Wireless > Access Points > Global AP Configuration.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Page 99

Configuring Link Latency
The Global Configuration page is displayed.
Performing a Link Test (CLI)
Step 2
In the TCP MSS area, select the Global TCP Adjust MSS check box and set the MSS for all access points that are
associated with the switch. The valid range is from 536 to 1363 bytes.
Step 3
Step 4
Click Apply.
Click Save Configuration.
Performing a Link Test (CLI)
The procedure to perform this task using the switch GUI is not currently available.Note
SUMMARY STEPS
test wireless linktest mac_address
1.
configure terminal
2.
wireless linktest frame-size frame_size
3.
wireless linktest number-of-frames number_of_frames
4.
end
5.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
test wireless linktest mac_address
Example:
Switch# test wireless linktest
00:0d:88:c5:8a:d1
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
wireless linktest frame-size frame_size
Example:
Switch(config)# wireless linktest
frame-size 41
wireless linktest number-of-frames number_of_frames
Example:
Switch(config)# wireless linktest
number-of-frames 50
PurposeCommand or Action
Runs a link test.
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Configures the link test frame size for each packet.
Configures the number of frames to send for the link
test.
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-28697-01 87
Page 100

Configuration Examples for Configuring Link Latency
Configuring Link Latency
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 5
end
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively,
you can also press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration
Example:
Switch(config)# end
mode.
Configuration Examples for Configuring Link Latency
Running a Link Test: Example
This example shows how to run a link test:
Switch# test wireless linktest 00:0d:88:c5:8a:d1
When CCX v4 or later releases is enabled on both the controller and the client being tested,
information similar to the following appears:
CCX Link Test to 00:0d:88:c5:8a:d1.
Link Test Packets Sent...................................... 20
Link Test Packets Received.................................. 10
Link Test Packets Lost (Total/AP to Client/Client to AP).... 10/5/5
Link Test Packets round trip time (min/max/average)......... 5ms/20ms/15ms
RSSI at AP (min/max/average)................................ -60dBm/-50dBm/-55dBm
RSSI at Client (min/max/average)............................ -50dBm/-40dBm/-45dBm
SNR at AP (min/max/average)................................. 40dB/30dB/35dB
SNR at Client (min/max/average)............................. 40dB/30dB/35dB
Transmit Retries at AP (Total/Maximum)...................... 5/3
Transmit Retries at Client (Total/Maximum).................. 4/2
Transmit rate: 1M 2M 5.5M 6M 9M 11M 12M 18M 24M 36M 48M 54M 108M
Packet Count: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 18 0
Transmit rate: 1M 2M 5.5M 6M 9M 11M 12M 18M 24M 36M 48M 54M 108M
Packet Count: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 8 0
When CCX v4 or later releases is not enabled on either the controller or the client being
tested, fewer details appear:
Ping Link Test to 00:0d:88:c5:8a:d1.
Link Test Packets Sent.......................... 20
Link Test Packets Received...................... 20
Local Signal Strength........................... -49dBm
Local Signal to Noise Ratio..................... 39dB
Displaying Link Latency Information: Example
This example shows how to display general configuration details of the access point. These configuration
details contain the link latency results that correspond to the access point that you specify in the command.
Switch# show ap name AP01 config general
Cisco AP Name : AP01
Cisco AP Identifier : 55
Country Code : US - United States
Regulatory Domain Allowed by Country : 802.11bg:-A 802.11a:-A
AP Country Code : US - United States
AP Regulatory Domain : Unconfigured
Switch Port Number : Te1/0/1
MAC Address : 0000.2000.03f0
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
88 OL-28697-01
 Loading...
Loading...