Page 1

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage
Configuration Guide
First Published: April 2017
X8.9.2
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
Page 2
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Preface
Change History
Table 1 Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide Change History
Date Change Reason
July
Correction Outbound SIPsignaling removed from MRAdiagram and table.
2017
April
2017
New
document
Related Documents
For Installation, See:
■ Cisco Expressway Virtual Machine Installation Guide on the Expressway installation guides page.
■ Cisco Expressway CE1100 Appliance Installation Guide on the Expressway installation guides page.
For Administration and Maintenance:
■ See Expressway Administrator Guide
■ See the Cisco Expressway Serviceability Guide on the Expressway Maintain and Operate Guides page.
■ See Cisco Expressway External Policy Deployment Guide at the Cisco Expressway Series Configuration
Guides page.
For Clustering and Certificates (All Deployments):
■ See Cisco Expressway Certificate Creation and Use Deployment Guide on the Expressway configuration
guides page.
■ See the Cisco Expressway Cluster Creation and Maintenance Deployment Guide, for your version, on the
Cisco Expressway Series configuration guides page.
New format for information previously held in Expressway IP Port Usage for Firewall
Traversal.
For Basic Call Control Deployment:
See Cisco Expressway Registrar Deployment Guide on the Expressway configuration guides page.
For Mobile and Remote Access to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Services:
See Mobile and Remote Access Through Cisco Expressway on the Expressway configuration guides page.
For Remote Configuration of MRA:
See Cisco Expressway RESTAPIReference Guide on the Expressway installation guides page.
For Microsoft Interoperability:
■ See Cisco Expressway with Microsoft Infrastructure Deployment Guide on the Expressway configuration
guides page.
■ See Cisco Jabber and Microsoft Skype for Business Infrastructure Configuration Cheatsheet on the
Expressway configuration guides page.
For Cisco Meeting Server:
■ See the Cisco Meeting Server installation guides page.
■ See deployment guides on the Cisco Meeting Server configuration guides page.
2
Page 3

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
■ See the Cisco Expressway with Cisco Meeting Server Deployment Guide on the Expressway configuration
guides page.
Contents
Preface 2
Change History 2
Related Documents 2
How to Use This Document 5
Default Port Ranges 5
Basic Networking Connections 7
Basic Networking:Expressway 7
Networking Port Reference:Expressway 7
Basic Networking:Traversal Pair 9
Networking Port Reference:Expressway Traversal Pair 10
Clustering Connections 12
Cluster Connections Before X8.8 12
Cluster Port Reference Before X8.8 12
Cluster Connections X8.8 Onwards 13
Cluster Port Reference X8.8 Onwards 13
Provisioning, Registrations, Authentication, and Calls 14
SIP Calls 15
SIP Calls Port Reference 16
H.323 Calls 18
H.323 Calls Port Reference 20
TMS Connections 22
TMS Port Reference 22
LDAP Connections 24
LDAP Port Reference 24
Mobile and Remote Access 26
MRA Connections 26
MRA Port Reference 27
Jabber Guest Services 29
Jabber Guest:Dual NICDeployment 30
Jabber Guest:Dual NICDeployment Ports 31
3
Page 4

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Jabber Guest:Single NICDeployment 32
Jabber Guest:Single NICDeployment Ports 33
Microsoft Interoperability Using Gateway Expressway 34
On-Premises Microsoft Clients 34
Off-Premises Microsoft Clients 35
Expressway with Microsoft Infrastructure Port Reference 36
Cisco Meeting Server 38
Web Proxy for Cisco Meeting Server WebRTC Connections 38
Web Proxy for Cisco Meeting Server Port Reference 39
SIP Edge for Meeting Server Connections 40
SIP Edge for Cisco Meeting Server Port Reference 41
XMPP Federation 43
XMPP Federation Connections 43
XMPP Port Reference 44
Serviceability 45
Serviceability:Expressway-C 45
Serviceability:Traversal Pair 46
Serviceability Ports:Traversal Pair 46
Cisco Legal Information 47
Cisco Trademark 47
4
Page 5
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
How to Use This Document
The purpose of this document is to help you configure and troubleshoot connections between infrastructure
components related to Expressway deployments.
There is a section for each of the popular Expressway deployments. Each has a diagram showing the major
infrastructure components and the connections between them, and also lists the connections in a table format.
The deployments build on each other where necessary. For example, if you wish to implement Mobile and Remote
Access, you should first configure a traversal pair. These relationships are described in the relevant deployment
guides.
Default Port Ranges
The following defaults are used throughout this document. Default port ranges may occasionally change (if
unavoidable) as new features are developed. Our documents list the current default ports for the given version
number.
Note:In some cases throughout this document we list port ranges used by third party infrastructure. These are default
values and we cannot guarantee that these are correct for your environment. We recommend you follow the
supplier's documentation to configure those connections.
Table 2 Default Port Ranges on Expressway
Protocol Purpose Current
Range
TCP Ephemeral ports 1024-65535 Outbound HTTP/S, LDAP
UDP Ephemeral ports 1024-65535 DNS, outbound TURNrequests
TCP Ephemeral ports 30000-
35999
UDP Ephemeral ports 30000-
35999
TCP Outbound SIP 25000-
29999
UDP&TCP Inbound TURN
requests on
Small/Medium
Expressway-E
UDP&TCP Inbound TURN
requests on
Large
Expressway-E
3478 On Expressway-E only. Configurable to a port >= 1024
3478-3483 On Large Expressway-E only. Configurable to a six port range with
Details
first port >=1024.
UDP TURN relays 24000-
On Expressway-E only.
29999
5
Page 6
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Table 2 Default Port Ranges on Expressway (continued)
Protocol Purpose Current
Range
UDP RTP/RTCPmedia 36000-
59999
UDP Multiplexed
media on
Small/Medium
2776/2777
OR
36000/36001
Expressway-E
systems
UDP Multiplexed
media on Large
36000-
36011
Expressway-E
systems
Details
The range is configurable.
On S/MExpressway, the first two ports can be used for multiplexed
media if you do not use default/custom ports.
On LExpressway, the first twelve ports of the range are used for
multiplexed media. You cannot customize that subrange.
2776/2777 is older pair but kept as default by the ability to
customize when the new default range was introduced with
S/Msystem options. Custom pair is defined on Configuration
>Traversal >Ports.
On Expressway-E only.
Note:In the connection maps and port references we do not show
all the port options for the sake of clarity. For example, if the
diagram shows 2776/2776, but you have chosen to use
36000/36001 instead, then you don't need to also open 2776/2777.
New range introduced with Largesystem option. This range is
always the first twelve ports of the RTP/RTCPmedia range, so it
will be different if you configure a different media range.
On Expressway-E Large OVAs or large scale appliances only.
Note:In the connection maps and port references we do not show
all the port options for the sake of clarity. For example, if the
diagram shows 2776/2776, but you have a large Expressway, then
you should open the first twelve ports of the media range instead of
2776/2777.
TCP SIPtraversal 7001 Configurable. SIPlistening port on the first Expressway-E traversal
server zone. Subsequent traversal server zones will use incremental
port numbers, eg. 7002, by default.
UDP H.323 traversal 6001 Configurable. H.323 listening port on the first Expressway-E
traversal server zone. Subsequent traversal server zones will use
incremental port numbers, eg. 6002, by default.
6
Page 7
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
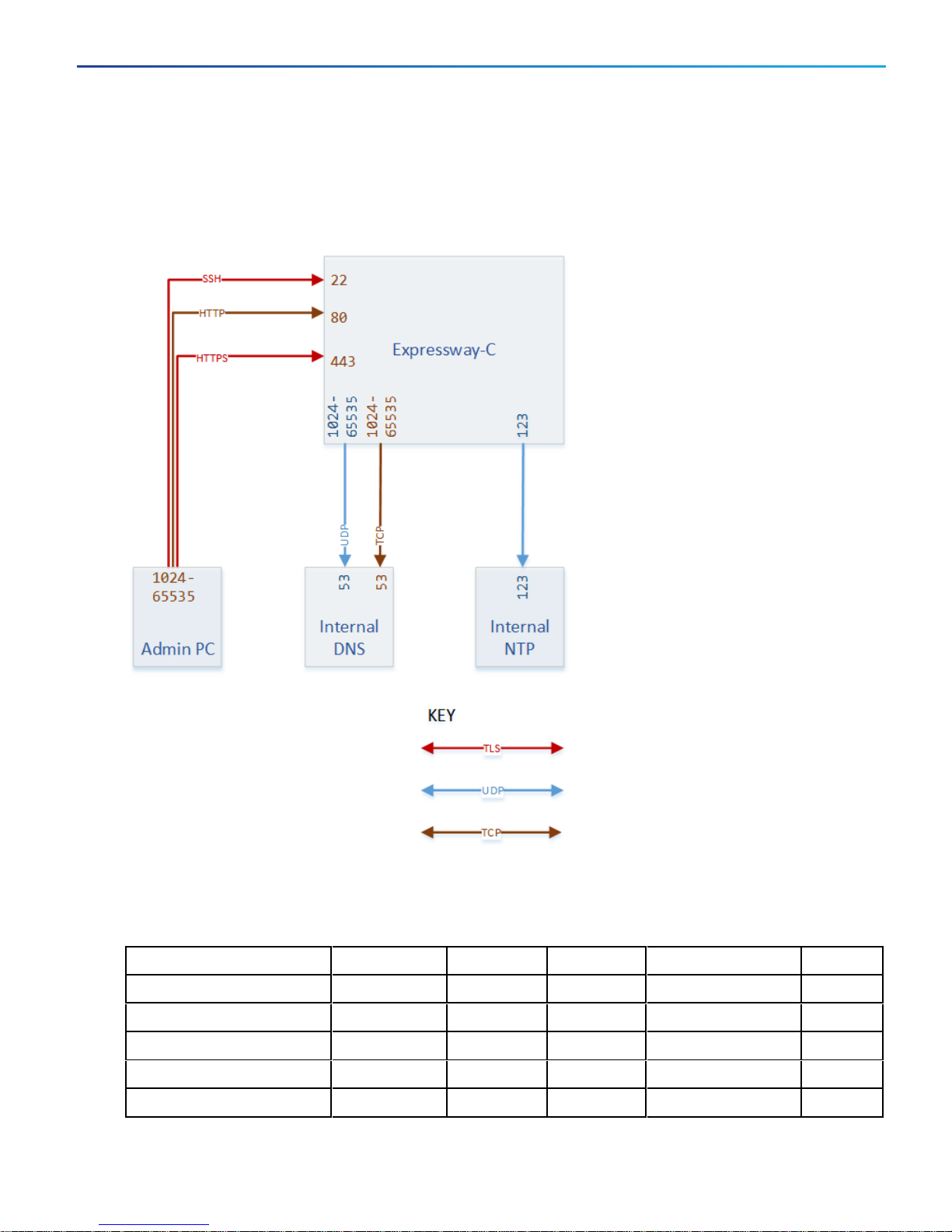
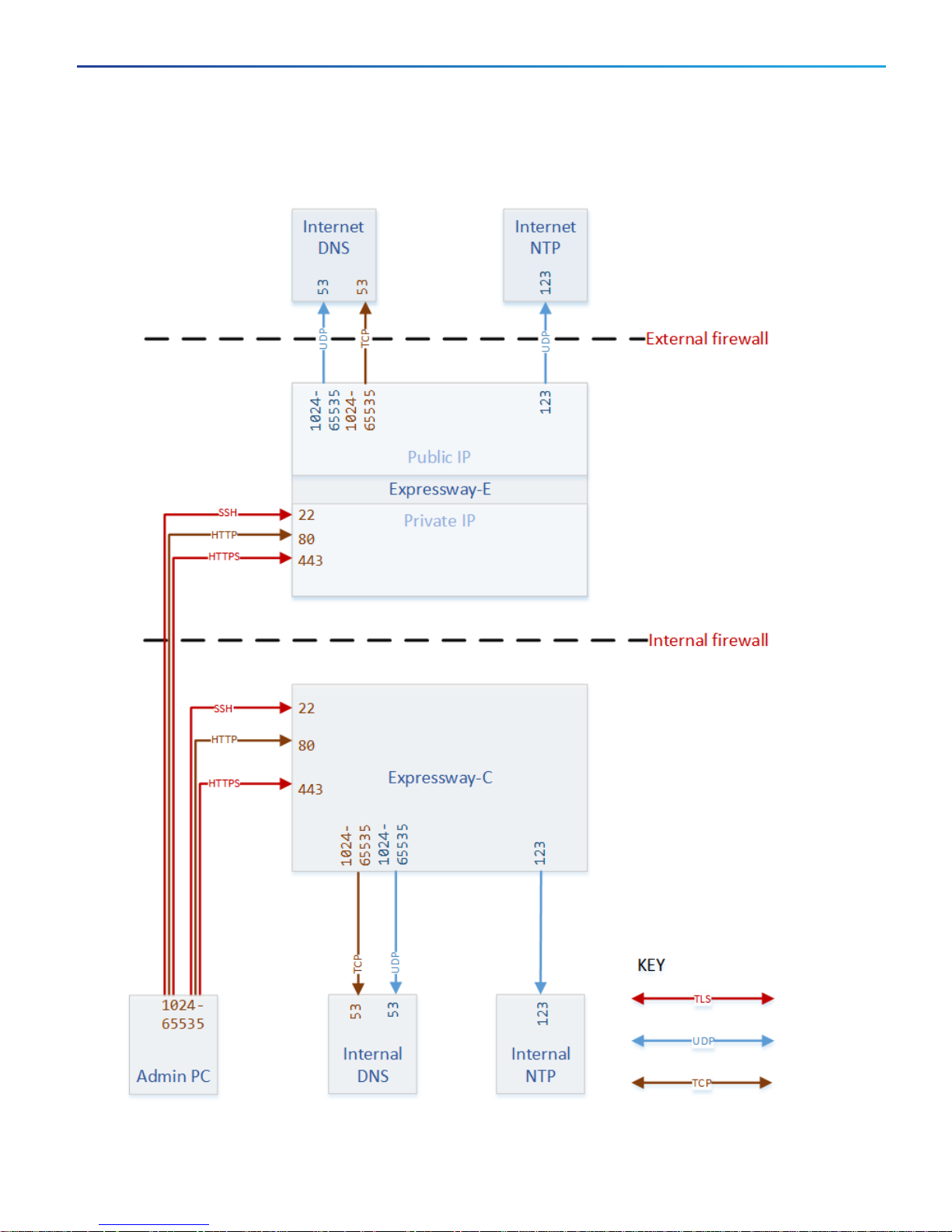
Basic Networking Connections
Basic Networking:Expressway
Networking Port Reference:Expressway
Table 3 Basic Networking Ports for Expressway-C
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
Administrator SSH Admin PCs 1024-65535 TCP Expressway-C 22
Administrator HTTP
Administrator HTTPS Admin PCs 1024-65535 TCP Expressway-C 443
Name resolution (DNS) Expressway-C 1024-65535 UDP & TCP†Internal name server 53
Time synchronization (NTP) Expressway-C 123 UDP Internal time server 123
*
Admin PCs 1024-65535 TCP Expressway-C 80
7
Page 8

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
* Expressway redirects HTTPto HTTPSby default. You don't need to open the HTTP port, but you can allow HTTPfor
convenience and redirect to HTTPS.
† Expressway will attempt DNSresolution over TCPif the response is too large.
8
Page 9
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
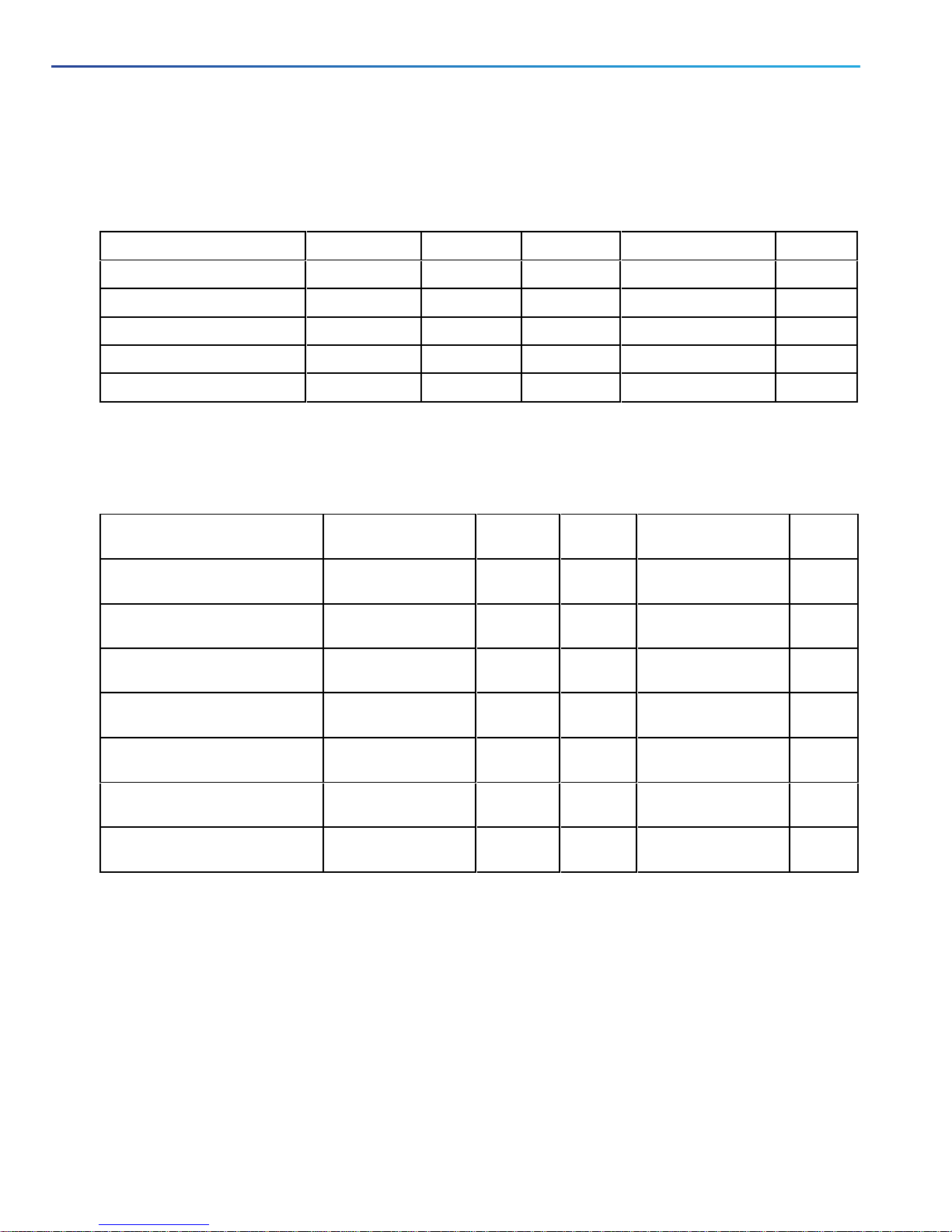
Basic Networking:Traversal Pair
9
Page 10
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Networking Port Reference:Expressway Traversal Pair
Table 4 Basic Networking Ports for Expressway-C
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
Administrator SSH Admin PCs 1024-65535 TCP Expressway-C 22
Administrator HTTP
Administrator HTTPS Admin PCs 1024-65535 TCP Expressway-C 443
Name resolution (DNS) Expressway-C 1024-65535 UDP & TCP†Internal name server 53
Time synchronization (NTP) Expressway-C 123 UDP Internal time server 123
* Expressway redirects HTTPto HTTPSby default. You don't need to open the HTTP port, but you can allow HTTPfor
convenience and redirect to HTTPS.
† Expressway will attempt DNSresolution over TCPif the response is too large.
*
Admin PCs 1024-65535 TCP Expressway-C 80
Table 5 Basic Networking Ports for Expressway-E
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst.
Administrator SSH Admin PCs 1024-
65535
Administrator HTTP Admin PCs 1024-
65535
Administrator HTTPS Admin PCs 1024-
65535
Internal name resolution (DNS)* Expressway-E privateIP1024-
65535
External name resolution (DNS) Expressway-E publicIP1024-
65535
Internal time synchronization
(NTP)*
External time synchronization
(NTP)
* You may prefer to connect Expressway-E to external DNSand NTP. You do not need both.
Expressway-E privateIP123 UDP Internal time server 123
Expressway-E publicIP123 UDP External time server 123
TCP Expressway-E privateIP22
TCP Expressway-E privateIP80
TLS Expressway-E privateIP443
UDP
&TCP
UDP
&TCP
Internal name server 53
External name server 53
Ports
10
Page 11

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
11
Page 12
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
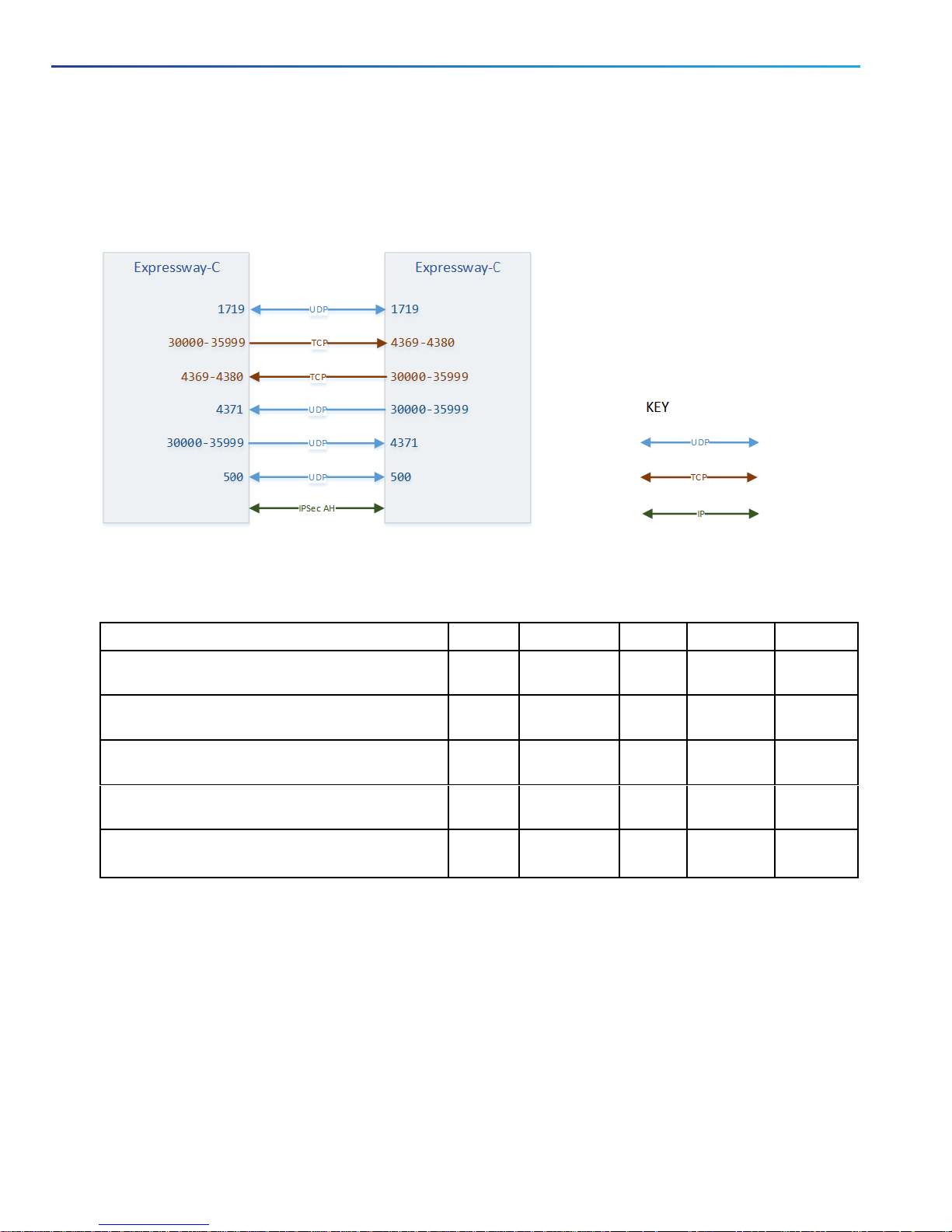
Clustering Connections
Cluster Connections Before X8.8
Cluster Port Reference Before X8.8
Table 6 Cluster Synchronization and Communications
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
Cluster database synchronization (IPSec AH) This
Key exchange between peers (ISAKMP) This
Cluster recovery This
Cluster communication This
Bandwidth management (Expressway-C cluster
only)
peer
peer
peer
peer
This
peer
N/A 51 Other
peers
500 UDP Other
peers
3000035999
3000035999
1719 UDP Other
UDP Other
peers
TCP Other
peers
peers
N/A
500
4371
43694380
1719
12
Page 13
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
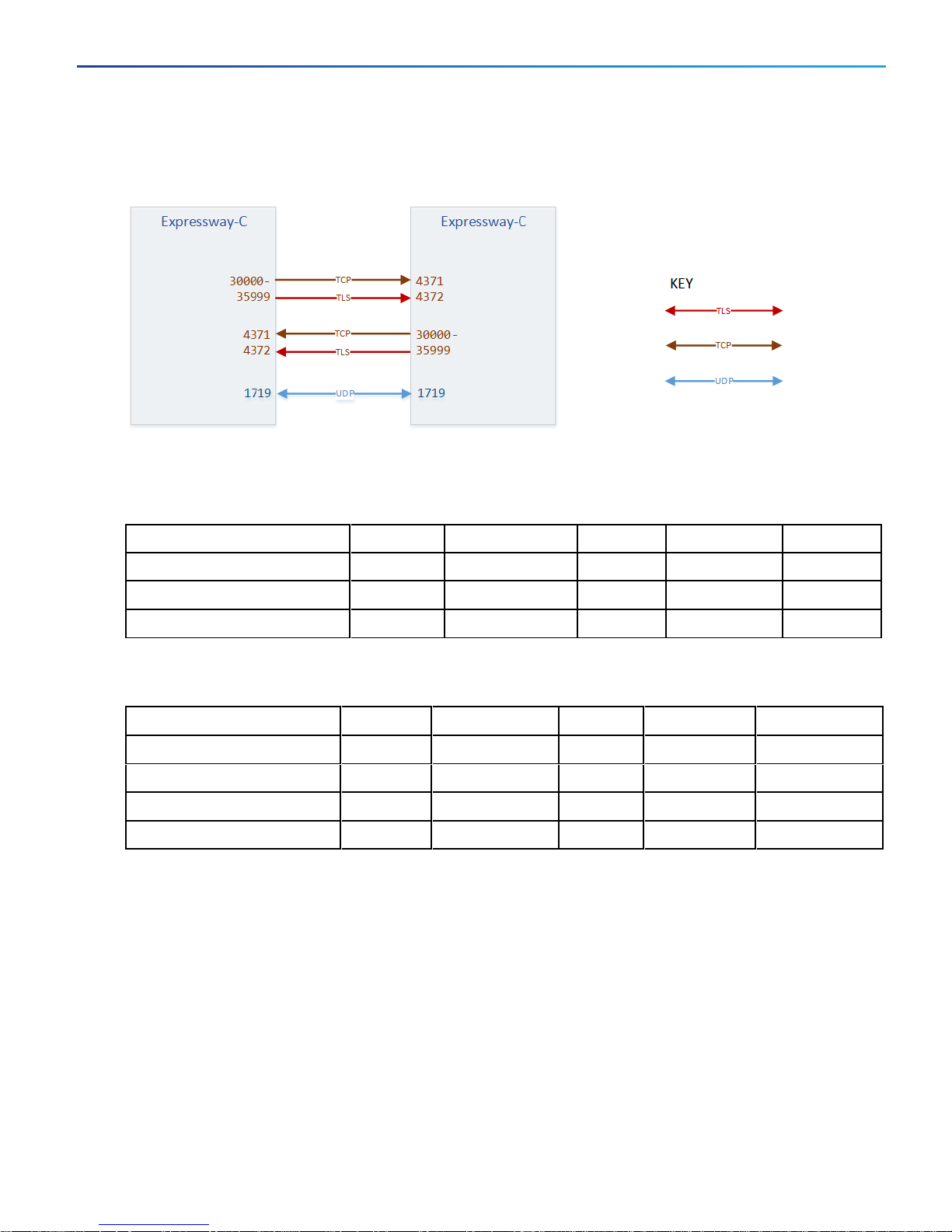
Cluster Connections X8.8 Onwards
Cluster Port Reference X8.8 Onwards
Table 7 Expressway-C Cluster Database Synchronization and Communications
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
Cluster recovery This peer 30000-35999 TCP Other peers 4371
Cluster communication This peer 30000-35999 TLS Other peers 4372
Bandwidth management This peer 1719 UDP Other peers 1719
Table 8 SIPCalls Routed Between Peers (not shown on diagram)
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
SIPTCPSignaling This peer 25000-29999 TCP Other peers 5061
SIPTLSSignaling This peer 25000-29999 TLS Other peers 5061
RTP/RTCP This peer 36000-59999 UDP Other peers 36000-59999
Bandwidth management This peer 1719 UDP Other peers 1719
13
Page 14

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Provisioning, Registrations, Authentication, and Calls
SIP Calls 15
SIP Calls Port Reference 16
H.323 Calls 18
H.323 Calls Port Reference 20
TMS Connections 22
TMS Port Reference 22
LDAP Connections 24
LDAP Port Reference 24
14
Page 15
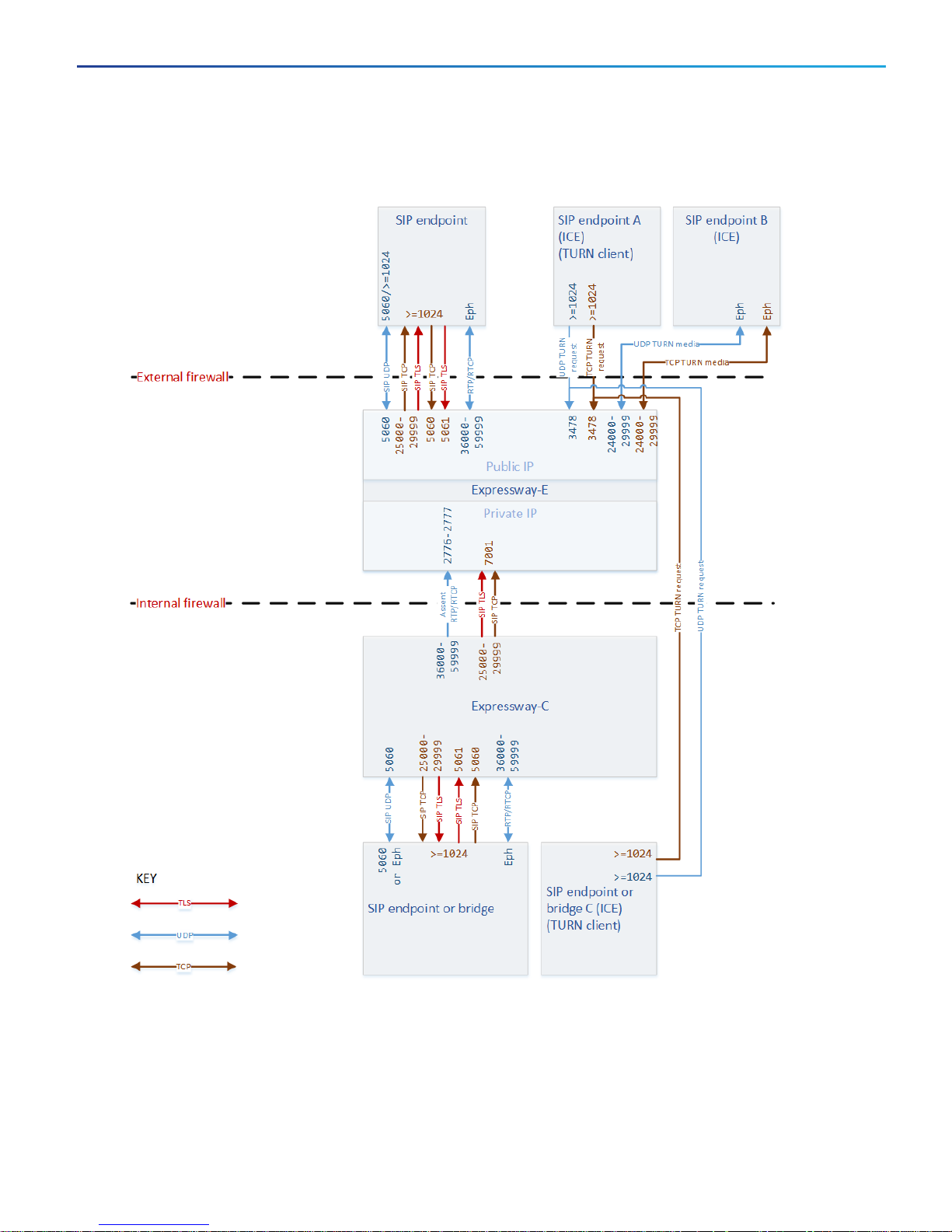
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
SIP Calls
15
Page 16

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
SIP Calls Port Reference
Table 9 SIPCalls Port Reference
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
SIPsignaling Expressway-C25000-29999 TCP or
TLS
SIPsignaling Expressway-C5060 UDP SIPendpoint
SIPsignaling Expressway-C25000-29999 TCPor
TLS
SIPsignaling SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
SIPsignaling SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
SIPsignaling SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
>=1024 UDP Expressway-
>=1024 TCP Expressway-
>=1024 TLS Expressway-E5061
Expressway-E7001 (for first traversal zone;
SIPendpoint
E
E
7002 for second etc.)
5060 (often, but could be
different, >=1024)
Port number defined by
registration (if registered) or by
DNSlookup
>=1024
Port number defined by
registration (if registered) or by
DNSlookup
5060
SIPUDPdisabled by default.
Not recommended for internet
facing connections.
5060
SIPTCPdisabled by default
(X8.9.2 and later).
SIPsignaling SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
Assent RTP
(traversed
media)
Assent RTCP
(traversed
media)
Assent RTP
(traversed
media)
Expressway-C36000-59999 UDP Expressway-
Expressway-C36000-59999 UDP Expressway-
SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
>=1024 MTLS Expressway-E5062
2776 or 36000 (Small/Medium)
>=1024
Could be the firewall
port where the media
egressed, rather than an
endpoint port
E
E
UDP Expressway-E36000-59999
36000 - 36010 (even ports)
(Large)
2777 or 36001 (Small/Medium)
36001 - 36011 (odd ports)
(Large)
16
Page 17

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Table 9 SIPCalls Port Reference (continued)
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
Assent RTCP
(traversed
media)
SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
>=1024
Could be translated by
the firewall to port where
the media egressed,
rather than an endpoint
port
UDP Expressway-E36000-59999
Assent RTP
(traversed
media)
Expressway-E36000-59999 UDP SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
>=1024
Expressway waits until it
receives media, then sends
media to that source port
(which could be the port where
the media egressed the firewall,
not an endpoint port)
TURNcontrol Any
IPaddress
TURNmedia
Expressway-E24000-29999 UDP
TURNmedia Any
IPaddress
>=1024 (signaling port
†
from endpoint or the
firewall)
>=1024
‡
Port of relevant
UDP
&TCP
&TCP
UDP
&TCP
ExpresswayE
Any
IPaddress
Expressway-E24000-29999
3478 (Small/Medium)
3478-3483 (Large)
>=1024
ICEcandidate:host
IPport, server reflexive
port (outside firewall
port), or TURNserver
port
† The request could be from any IPaddress, unknown to the TURNserver. Assume for example, that endpoint A and
endpoint C (TURNclients) in the diagram can use the Expressway-E TURNserver. The actual IPaddress from which
the TURNserver receives the request could be the endpoint's firewall egress address (NATed).
‡ The media could go to any of the candidate addresses. For example, before ICEnegotiation the TURNserver does
not know which of endpoint B's candidate addresses will be the highest priority.
Note:The endpoints A, B, and C in the diagram only show media connections to avoid unnecessary lines. They would
use the same signaling connections as shown for the other endpoints / bridges.
17
Page 18

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
H.323 Calls
Note:This diagram and following table apply specifically to Cisco VCSdeployments. You can use this information to
prepare an Expressway-based H.323 deployment, but remember that Expressway-Edoes not accept H.323
registrations.
18
Page 19

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
19
Page 20

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
H.323 Calls Port Reference
Table 10 H.323 Ports Reference
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
Initial
RASconnection
Initial
RASconnection
Q.931 / H.225
signaling
Q.931 / H.225
signaling
Q.931 / H.225
signaling
Q.931 / H.225
signaling
H.245 Expressway-C 15000-
H.245 Expressway-C 15000-
H.245 Any (endpoint in the
External address of
firewall protecting offpremises endpoint
Expressway-C 1719 UDP Expressway-
Any (endpoint in the
Internet)
Expressway-E (public) 15000-
Expressway-C 15000-
Expressway-C 15000-
Internet)
>=1024 UDP Expressway-
1720 TCP Expressway-
19999
19999
19999
19999
19999
>=1024 TCP Expressway-
E (public)
E (private)
E (public)
TCP Any
(endpoint in
the Internet)
TCP Expressway-
E (private)
TCP Expressway-
E (private)
TCP Expressway-
E (private)
TCP Expressway-
E (private)
E (public)
1719
6001 (for first traversal zone,
6002 for second etc.)
1720
1720 (endpoint signaling port,
specified during registration.
Could be another port
>=1024)
2776 (Assent calls)
1720 (H.460.18 calls)
2776 (Assent calls)
2777 (H.460.18 calls)
Expressway-E (public)
H.245 Expressway-E (public) 15000-
19999
H.245 External address of
firewall protecting offpremises Assent endpoint
H.245 External address of
firewall protecting offpremises H.460.18/19
endpoint
RTP
(multiplexed
traversal media)
RTCP
(multiplexed
traversal media)
Expressway-C 36000-
Expressway-C
>=1024 TCP Expressway-
>=1024 TCP Expressway-
59998
(even
ports)
3600159999
(odd ports)
TCP Any
(endpoint in
the Internet)
E (public)
E (public)
UDP Expressway-
E (private)
UDP Expressway-
E (private)
>=1024 (endpoint H.245
signaling port)
2776
2777
2776 (Small/Medium)
or 36000-36010 (even ports)
(Large)
2777 (Small/Medium)
or 36001-36011 (odd ports)
(Large)
20
Page 21

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Table 10 H.323 Ports Reference (continued)
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
RTP (nonmultiplexed
traversal media)
RTCP(nonmultiplexed
traversal media)
RTP (nonmultiplexed)
RTCP(nonmultiplexed)
RTP (nonmultiplexed)
RTCP(nonmultiplexed)
Expressway-C 36000-
59998
(even
ports)
Expressway-C
3600159999
(odd ports)
Expressway-E (public) 36000-
59998
(even
ports)
Expressway-E (public)
3600159999
(odd ports)
Any (endpoint in the
Internet)
>=1024
(endpoint
media
range)
Any (endpoint in the
Internet)
>=1024
(endpoint
media
range)
UDP Expressway-
E (private)
UDP Expressway-
E (private)
UDP Any
(endpoint in
the Internet)
UDP Any
(endpoint in
the Internet)
UDP Expressway-
E (public)
UDP Expressway-
E (public)
36000-59998 (even ports)
36001-59999 (odd ports)
>=1024 (endpoint media
range)
>=1024 (endpoint media
range)
36000-59998 (even ports)
36001-59999 (odd ports)
21
Page 22

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
TMS Connections
TMS Port Reference
Cisco TMS can have two IPaddresses; for managing public systems, or managing systems on the LAN. On Cisco
TMS, go to Administrative Tools > Configuration > Network Settings >Advanced Network Settings. You should use
the TMSpublic address with the Expressway-E, and the default LANaddress with the Expressway-C.
22
Page 23

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Table 11 TMSPort Reference
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst.
Ports
SNMPfor discovery of
Expressway-E
SNMPfor discovery of
Expressway-C
HTTPManagement of
Expressway-E
HTTPManagement of
Expressway-C
HTTPSManagement of
Expressway-E
HTTPSManagement of
Expressway-C
Feedback events (HTTP) Expressway-E
Cisco TMS ExternalIP1024-
65535
Cisco TMS 1024-
65535
Cisco TMS ExternalIP1024-
65535
Cisco TMS 1024-
65535
Cisco TMS ExternalIP1024-
65535
Cisco TMS 1024-
65535
1024-
private
65535
Feedback events (HTTP) Expressway-C 1024-
65535
Feedback events (HTTPS) Expressway-E
private
102465535
Feedback events (HTTPS) Expressway-C 1024-
65535
UDP Expressway-E private 161
UDP Expressway-C 161
TCP Expressway-E privateIP80
TCP Expressway-E privateIP80
TCP Expressway-E private 443
TCP Expressway-C 443
TCP Cisco TMS ExternalIP80
TCP Cisco TMS 80
TCP Cisco TMS ExternalIP443
TCP Cisco TMS 443
23
Page 24

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
LDAP Connections
LDAP Port Reference
You can choose to use an LDAPserver to authenticate and authorize administrator or user logins. You would only
need to allow the LDAPports inbound from the Expressway-E in the rare case where you want a user to log in from
outside the network and you also do not allow credentials to be stored on the Expressway.
24
Page 25

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Table 12 LDAPPort Reference
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst.
Ports
Authentication requests from the Expressway-C Expressway-C 1024-
65535
Authentication requests from the Expressway-E Expressway-E
private
Encrypted authentication requests from the
Expressway-C 1024-
Expressway-C
Encrypted authentication requests from the
Expressway-E
Expressway-E
private
102465535
65535
102465535
TCP Directory
Server
TCP Directory
Server
TLS Directory
Server
TLS Directory
Server
389
389
636
636
25
Page 26

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Mobile and Remote Access
MRA Connections
26
Page 27

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
MRA Port Reference
Table 13 Connections Between Off-premises Endpoints and the Expressway-E
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
UDS(phonebook and
provisioning)
SIP signaling Off-premises
RTP/RTCP media Off-premises
RTP/RTCP media Expressway-E
XMPP(IMand Presence) Off-premises
Table 14 Connections Between Expressway-C and Expressway-E
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
SSHtunnels Expressway-C30000-
SIPsignaling Expressway-C25000-
SIPmedia Expressway-C36000-
XMPP (IM and
Presence)
Off-premises
endpoint
endpoint
endpoint
Public IP
endpoint
35999
29999
59999
Expressway-C30000-
35999
102465535
102465535
102465535
3600059999
102465535
TLS Expressway-E PrivateIP2222
TLS Expressway-E PrivateIP7001
UDP Expressway-E PrivateIP2776/7 or 36000-
TCP Expressway-E PrivateIP7400
TLS Expressway-E
Public IP
TLS Expressway-E
Public IP
UDP Expressway-E
Public IP
UDP Off-premises
endpoint
TCP Expressway-E
Public IP
11
8443
5061
3600059999
102465535
5222
Table 15 Connections Between Expressway-C and On-premises Infrastructure
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
SIPsignaling (TCP) Expressway-C25000-
29999
SIPsignaling (TCP) Unified CM 5060/5061 TCP Expressway-C25000-29999
SIPsignaling (TLS) Expressway-C25000-
29999
SIPsignaling (TLS) Unified CM 5061 TLS Expressway-C25000-29999
HTTPConfiguration file download
(TFTP)
(Pre 11.x Jabber and pre 11.x
Unified CM)
Expressway-C30000-
35999
TCP Unified CM 5060/5061
TLS Unified CM 5061
TCP Unified CM
Node
6970
27
Page 28

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Table 15 Connections Between Expressway-C and On-premises Infrastructure (continued)
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
HTTPSConfiguration file
Expressway-C30000-
download (TFTP)
(11.x or later Jabber and 11.x or
later Unified CM)
35999
TLS Unified CM
Node
6972
HTTPfor UDS (User Data Services)
and AXL (Administrative
Expressway-C30000-
35999
XMLLayer)
XMPP (IMand Presence) Expressway-C30000-
35999
HTTPSSOAP (IMand Presence) Expressway-C30000-
35999
File transfer (IMand Presence) Expressway-C30000-
35999
HTTPSto visual voicemail Expressway-C30000-
35999
MWI (Message Waiting Indicator) Expressway-C30000-
35999
MWI (Message Waiting Indicator) Expressway-C30000-
35999
Audio Video Media (RTP/RTCP) Expressway-C36000-
59999
TLS Unified CM
Node
TLS IMand
Presence
Service Node
TLS IMand
Presence
Service Node
TLS IMand
Presence
Service Node
TLS Cisco Unity
Connection
TCP Cisco Unity
Connection
TLS Cisco Unity
Connection
UDP On-prem
media
destination
443 or 8443
7400
8443
7336
443 or 8443
7080
7443
Destination's media
range, eg. 1638432767 (DXSeries)
28
Page 29

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Jabber Guest Services
Jabber Guest:Dual NICDeployment 30
Jabber Guest:Dual NICDeployment Ports 31
Jabber Guest:Single NICDeployment 32
Jabber Guest:Single NICDeployment Ports 33
29
Page 30

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Jabber Guest:Dual NICDeployment
30
Page 31

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Jabber Guest:Dual NICDeployment Ports
Table 16 Port Reference for Jabber Guest Dual NICDeployment
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
Jabber Guest Client Signaling
(HTTP always redirected to
HTTPS)
Jabber Guest Client Secure
Signaling (HTTPS)
To avoid port conflicts, traffic to Expressway-E public:80 must
NAT&PATto private:9980. HTTPis always redirected to HTTPS.
To avoid port conflicts, traffic to Expressway-Epublic:443 must
NAT&PATto private:9443
Jabber Guest Client Media
(TURN)
SIPTCP signaling Expressway-E
SIPTLSsignaling Expressway-E
Any (web browser) 1024-65535 TCP Expressway-
Any (web browser) 1024-65535 TLS Expressway-
Any (web browser) 1024-65535 UDP Expressway-
30000-35999 TCP Jabber
private IP
30000-35999 TLS Jabber
private IP
TLS
TLS
E Public IP
E Public IP
ExpresswayEPrivate IP
(Outward
NIC)
ExpresswayEPrivate IP
(Outward
NIC)
E Public IP
Guest Server
Guest Server
80
443
‡
9980
‡
9443
3478
(S/Msystems)
3478-3483 (L
systems)*
5060
5061
SIPTCP signaling Jabber Guest
Server
SIPTLSsignaling Jabber Guest
Server
*On Large systems you can configure a range of TURN request listening ports. The default range is 3478 – 3483.
‡ Port translation required
Eph TCP Expressway-
E private IP
Eph TLS Expressway-
E private IP
5060
5061
31
Page 32

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Jabber Guest:Single NICDeployment
32
Page 33

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Jabber Guest:Single NICDeployment Ports
Table 17 Port Reference for Jabber Guest Single NICDeployment
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
Jabber Guest Client Media
(TURN)
Any 1024-65535 UDP Expressway-
E Public IP
3478
(S/Msystems)
3478-3483 (L
systems)*
Jabber Guest Client Signaling
(HTTP always redirected to
HTTPS)
Jabber Guest Client Secure
Signaling (HTTPS)
To avoid port conflicts, traffic to Expressway-E public:80 must
NAT&PATto private:9980. HTTPis always redirected to HTTPS.
To avoid port conflicts, traffic to Expressway-Epublic:443 must
NAT&PATto private:9443
SSHTunnels from
Expressway-C to ExpresswayE
SIPSignaling Expressway-C 25000-25999 TLS Expressway-
TURNmedia relays Expressway-C 36000-59999 UDP Expressway-
TURNmedia relays
SIPTCP signaling Expressway-C 30000-35999 TCP Jabber
SIPTLSsignaling Expressway-C 30000-35999 TLS Jabber
†
Any 1024-65535 TCP Expressway-
E Public IP
Any 1024-65535 TLS Expressway-
E Public IP
TLS Expressway-
EPrivate IP
TLS Expressway-
EPrivate IP
Expressway-C 35000-35999 TCP Expressway-
E Public IP
E Public IP
E Public IP
Expressway-E
Public IP
24000-29999 UDP Expressway-C36000-59999
Guest Server
Guest Server
80
443
‡
9980
‡
9443
2222
7001
24000-29999
5060
5061
SIPTCP signaling Jabber Guest
SIPTLSsignaling Jabber Guest
*On Large systems you can configure a range of TURN request listening ports. The default range is 3478 – 3483.
‡ Port translation in external firewall
† Inbound media ports only required for unidirectional media initiated from Jabber Guest client, eg. BFCP. Otherwise
it is enough to allow the outbound media range from Expressway-C to Expressway-E (previous row).
Eph TCP Expressway-C5060
Server
Eph TLS Expressway-C5061
Server
33
Page 34

Microsoft Interoperability Using Gateway Expressway
On-Premises Microsoft Clients
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
34
Page 35

Off-Premises Microsoft Clients
Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
35
Page 36

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Expressway with Microsoft Infrastructure Port Reference
Notes about the deployment connections and ports
■ Trunk connections between Microsoft infrastructure elements not shown.
■ Media/signaling connections required for Microsoft client to client calls not shown.
■ Microsoft port ranges may vary from those shown here; check the Microsoft documentation to determine the
port ranges defined for your infrastructure.
■ Cisco Unified Communications Manager and collaboration endpoint connections not shown (for clarity). You
can see an example of those on MRA Connections, page 26.
■ Multiple media paths are possible because there are two TURNservers in the DMZ. "Any" source IPaddress is
listed because ICEnegotiation could mean the media path uses a relay address provided by one of the
TURNservers, or a reflexive address from the egress side of a firewall/NAT.
■ The Microsoft Interoperability service on the gateway Expressway has a shared pool of media ports (default
56000-57000). The service can use any port in the range for media connection on either TCPor
UDPtransport.
■ The drawing shows two IPaddresses on the Expressway-E because you may have one or two NICs enabled
on the Expressway-E. The address you enter for the TURNserver (on the Microsoft interoperability
configuration of the gateway Expressway) is the one that should listen on 3478 (TCPand UDP).
Table 18 SIPSignaling Port Reference
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst.
SIPsignaling to Lync
environment
SIPsignaling from Lync
environment
SIP signaling Microsoft
Gateway
Expressway
Lync
FEServer
25000-29999 TLS Lync FEServer 5061
Ephemeral ports
(1024-65535)
TLS Gateway Expressway:
MSinterop B2BUA
5061 MTLS Microsoft Edge 5061
client
SIP signaling Microsoft
5061 MTLS Microsoft client 5061
Edge
SIP/TLS & TCPTURN Microsoft
443 TLS Microsoft Edge 443
client
SIP/TLS &TCPTURN Microsoft
443 TLS Microsoft client 443
Edge
STUN Microsoft
3478 UDP Microsoft Edge 3478
client
STUN Microsoft
3478 UDP Microsoft client 3478
Edge
Ports
65072
36
Page 37

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Table 19 Media Path Port Reference
Purpose Src. IP Src.
ports
AVmedia to on-prem Lync clients Gateway
Expressway
Screen sharing from on-prem Lync
Lync client
5600057000
443
clients
Media from Microsoft interoperability
B2BUA towards on-premises Cisco
Gateway
Expressway
5600057000
collaboration recipients
ICEnegotiation and TURNrequests
from Gateway Expressway to
Gateway
Expressway
5600057000
Expressway-E TURNserver
UDPTURNmedia relays Expressway-
E
2400029999
TURNserver
TCPTURNmedia relays Expressway-
E
2400029999
TURNserver
Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
UDP Lync clients Lync client
media ports
TCP Gateway
56000-57000
Expressway
UDP Deployment
dependent; bridge,
Endpoint media
ports
endpoint, or a
SIPproxy
UDP or
TCP
Expressway-E
TURNserver
UDP3478
TCP3478
(3478-3483 on
large systems)
UDP Any (reflexive or
relay) from
MSclient or Edge
50000-59999
(Edge range) or
client media
ports
TCP Any (reflexive or
relay) from
MSclient or Edge
50000-59999
(Edge range) or
client media
ports
VCS Only
Presence to Lync FEServer
VCS Only
B2BUAcommunication with an
external transcoder (eg. Cisco AMGW)
Gateway
Expressway
Gateway
Expressway
10011 TLS Lync FEServer 5061
65080 TLS External transcoder 5061
37
Page 38

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Cisco Meeting Server
Web Proxy for Cisco Meeting Server WebRTC Connections
38
Page 39

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Web Proxy for Cisco Meeting Server Port Reference
Table 20 Web Proxy for Meeting Server
Purpose Src. IP Src.
ports
WebRTC client
access
Web interface
access
SSHtunnels for
firewall traversal
SIPsignaling Expressway-C25000-
TURNclient
requests
TURNclient
requests
TURNrelays
† You must change the administration port because WebRTCclients use 443. If the WebRTCbrowser tries to access
port 80, the Expressway-E redirects the connection to 443.
*Options for alternative management ports are shown on the web interface. You can use the CLIto change it to a
different port, eg. 7443, so that you can lock it down. We strongly advise against opening an external management
port on the public IPaddress. If the browser tries to access port 80, the Expressway-E redirects the connection to
your chosen port.
‡
Guest PCs 1024-
65535
Administrator
PCs
Expressway-C30000-
Any IP UDP and
Meeting
Server
Expressway-E
public IP
102465535
35999
29999
3478 UDP and
2400029999
Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
TLS Expressway-E publicIP443
TLS Expressway-E IP NOT443
TCP Expressway-E privateIP2222
TCP or
TLS
TCP
TCP
UDPand
TCP
Expressway-E 7001 (for first traversal zone;
Expressway-E
TURNserver public IP
Expressway-E
TURNserver private IP
Expressway-E publicIP24000-29999
†
7002 for second etc.)
3478
3478
*
‡ You must configure your external firewall to allow NATreflection for the Expressway-Epublic IPaddress. (Firewalls
typically mistrust packets that have the same source and destination IPaddress)
39
Page 40

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
SIP Edge for Meeting Server Connections
40
Page 41

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
SIP Edge for Cisco Meeting Server Port Reference
Table 21 SIPEdge for Meeting Server Port Reference
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
SIPsignaling Expressway-C25000-29999 TCP or
TLS
SIPsignaling Expressway-C5060 UDP Meeting
SIPsignaling Expressway-C25000-29999 TCPor
TLS
SIPsignaling SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
SIPsignaling SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
Assent RTP
(traversed media)
Assent RTCP
(traversed media)
Expressway-C36000-59999 UDP Expressway-
Expressway-C36000-59999 UDP Expressway-
>=1024 TCP Expressway-E5060
>=1024 TLS Expressway-E5061
Expressway-E7001 (for first traversal
Server
Meeting
Server
E
E
zone; 7002 for second
etc.)
5060
5061
2776 or 36000
(Small/Medium)
36000 - 36010 (even
ports) (Large)
2777 or 36001
(Small/Medium)
36001 - 36011 (odd ports)
(Large)
Assent RTP
(traversed media)
Assent RTCP
(traversed media)
Assent RTP
(traversed media)
SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
SIPendpoint
(or its
firewall)
Expressway-E36000-59999 UDP SIPendpoint
>=1024
Could be the firewall
port where the media
egressed, rather than
an endpoint port
>=1024
Could be the firewall
port where the media
egressed, rather than
an endpoint port
UDP Expressway-E36000-59999
UDP Expressway-E36000-59999
(or its
firewall)
41
>=1024
Expressway waits until it
receives media, then
sends media to that
source port (which could
be the port where the
media egressed the
firewall, not an endpoint
port)
Page 42

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Table 21 SIPEdge for Meeting Server Port Reference (continued)
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
TURNcontrol Any
IPaddress
>=1024 (signaling port
from endpoint or the
firewall)
UDP Expressway-
E
3478 (Small/Medium)
3478-3483 (Large)
TURNmedia
Expressway-E24000-29999 UDP
TURNmedia Any
>=1024
Port of relevant
ICEcandidate:host
IPport, server reflexive
port (outside firewall
port), or TURNserver
port
Any
>=1024
IPaddress
UDP Expressway-E24000-29999
42
Page 43

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
XMPP Federation
XMPP Federation Connections
43
Page 44

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
XMPP Port Reference
Table 22 XMPPFederation Port Reference
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst.
Ports
Internal XMPPconnections Expressway-C Ephemeral
(30000-
35999)
Outbound XMPPtraversal Expressway-C Ephemeral
(30000-
35999)
Inbound XMPPconnections
from federated domain
Outbound XMPPconnections
to federated domain
Any (An
XMPPserver)
Expressway-E Ephemeral
Ephemeral TCP or TLS Expressway-E 5269
(30000-
35999)
TCP IMand Presence
Service
TCP Expressway-E 7400
TCP or TLS Any (An
XMPPserver)
7400
5269
44
Page 45

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Serviceability
Serviceability:Expressway-C
45
Page 46

Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage Configuration Guide
Serviceability:Traversal Pair
Serviceability Ports:Traversal Pair
Table 23 Serviceability Ports for Expressway-E and Expressway-C
Purpose Src. IP Src. ports Protocol Dest. IP Dst. Ports
Network management (SNMP) SNMPManager 1024-65535 UDP Expressway-C 161
System metrics Expressway 25826 UDP Analytics server(s) 25826
Remote logging (syslog) Expressway 30000-35999 UDP Syslog server(s) 514
Remote logging (syslog) Expressway 30000-35999 TCP Syslog server(s) 514
Remote logging (syslog) Expressway 30000-35999 TLS Syslog server(s) 6514
46
Page 47

Cisco Legal Information
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE
WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED
TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST
TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE
INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS
REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR
CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of
California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE
SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL
WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING,
USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA
ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual
addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other
figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone
numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
All printed copies and duplicate soft copies are considered un-Controlled copies and the original on-line version
should be referred to for latest version.
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide. Addresses, phone numbers, and fax numbers are listed on the Cisco
website at www.cisco.com/go/offices.
© 2017 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Trademark
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other
countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks
mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
47
 Loading...
Loading...