Page 1

WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
First Published: June 30, 2014
Last Modified: 0,
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-32353-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH
THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY,
CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB's public domain version
of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright©1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWAREOF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS.
CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network
topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional
and coincidental.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://
www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
©
2014 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface
CHAPTER 1
Preface vii
Document Conventions vii
Related Documentation ix
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request ix
Using the Command-Line Interface 1
Information About Using the Command-Line Interface 1
Command Modes 1
Using the Help System 3
Understanding Abbreviated Commands 4
No and Default Forms of Commands 5
CLI Error Messages 5
Configuration Logging 5
How to Use the CLI to Configure Features 6
Configuring the Command History 6
Changing the Command History Buffer Size 6
Recalling Commands 6
Disabling the Command History Feature 7
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features 7
Editing Commands Through Keystrokes 8
Editing Command Lines That Wrap 9
Searching and Filtering Output of show and more Commands 10
Accessing the CLI on a Switch Stack 11
Accessing the CLI Through a Console Connection or Through Telnet 11
CHAPTER 2
Using the Web Graphical User Interface 13
Prerequisites for Using the Web GUI 13
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 iii
Page 4

Contents
Information About Using The Web GUI 13
Web GUI Features 13
Connecting the Console Port of the Switch 15
Logging On to the Web GUI 15
Enabling Web and Secure Web Modes 15
Configuring the Switch Web GUI 16
CHAPTER 3
Configuring WLANs 21
Finding Feature Information 21
Prerequisites for WLANs 21
Restrictions for WLANs 22
Information About WLANs 23
Band Selection 24
Off-Channel Scanning Defer 24
DTIM Period 25
Session Timeouts 25
Cisco Client Extensions 25
Peer-to-Peer Blocking 26
Diagnostic Channel 26
Per-WLAN Radius Source Support 26
How to Configure WLANs 27
Creating WLANs (CLI) 27
Creating WLANs (GUI) 28
Deleting WLANs 29
Deleting WLANs (GUI) 29
Searching WLANs 30
Searching WLANs (GUI) 30
Enabling WLANs (CLI) 31
Disabling WLANs (CLI) 32
Configuring General WLAN Properties (CLI) 32
Configuring General WLAN Properties (GUI) 35
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI) 36
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI) 39
Applying a QoS Policy on a WLAN (GUI) 43
Monitoring WLAN Properties (CLI) 44
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
iv OL-32353-01
Page 5

Contents
Viewing WLAN Properties (GUI) 45
Where to Go Next 45
Additional References 45
Feature Information for WLANs 46
CHAPTER 4
Configuring DHCP for WLANs 47
Finding Feature Information 47
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs 48
Information About the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol 48
Internal DHCP Servers 49
External DHCP Servers 49
DHCP Assignments 50
Information About DHCP Option 82 51
Configuring DHCP Scopes 51
Information About DHCP Scopes 52
How to Configure DHCP for WLANs 52
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI) 52
Configuring DHCP Scopes (CLI) 55
Additional References 56
Feature Information for DHCP for WLANs 57
CHAPTER 5
Configuring WLAN Security 59
Finding Feature Information 59
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security 59
Information About AAA Override 60
How to Configure WLAN Security 61
Configuring Static WEP + 802.1X Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI) 61
Configuring Static WEP Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI) 62
Configuring WPA + WPA2 Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI) 63
Configuring 802.1X Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI) 64
Configuring Layer 2 Parameters (GUI) 66
Additional References 69
Feature Information about WLAN Layer 2 Security 70
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 v
Page 6

Contents
CHAPTER 6
CHAPTER 7
Configuring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy 71
Finding Feature Information 71
Restrictions for the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy 71
Information About the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy 71
How to Configure Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy 72
Configuring the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI) 72
Disabling Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI) 73
Monitoring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI) 74
Additional References for Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy 74
Feature Information about Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy 75
Configuring Access Point Groups 77
Finding Feature Information 77
Prerequisites for Configuring AP Groups 77
Restrictions for Configuring Access Point Groups 78
Information About Access Point Groups 78
How to Configure Access Point Groups 79
Creating Access Point Groups 79
Assigning an Access Point to an AP Group 80
Viewing Access Point Group 80
Additional References 81
Feature History and Information for Access Point Groups 82
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
vi OL-32353-01
Page 7

Preface
Document Conventions, page vii
•
Related Documentation, page ix
•
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, page ix
•
Document Conventions
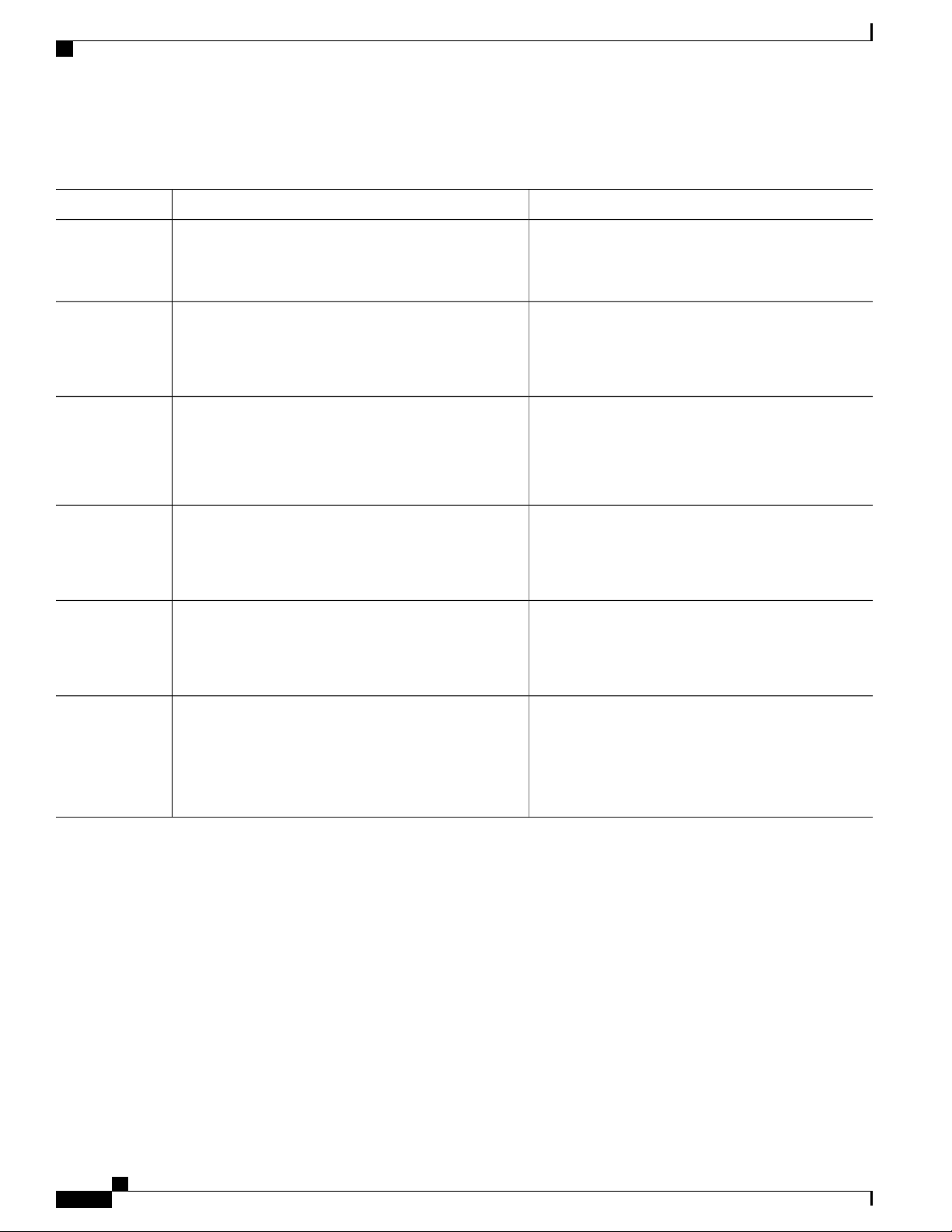
This document uses the following conventions:
DescriptionConvention
^ or Ctrl
Italic font
...
|
[x | y]
Both the ^ symbol and Ctrl represent the Control (Ctrl) key on a keyboard. For
example, the key combination ^D or Ctrl-D means that you hold down the Control
key while you press the D key. (Keys are indicated in capital letters but are not
case sensitive.)
Commands and keywords and user-entered text appear in bold font.bold font
Document titles, new or emphasized terms, and arguments for which you supply
values are in italic font.
Terminal sessions and information the system displays appear in courier font.Courier font
Bold Courier font indicates text that the user must enter.Bold Courier font
Elements in square brackets are optional.[x]
An ellipsis (three consecutive nonbolded periods without spaces) after a syntax
element indicates that the element can be repeated.
A vertical line, called a pipe, indicates a choice within a set of keywords or
arguments.
Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by vertical
bars.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 vii
Page 8

Document Conventions
Preface
DescriptionConvention
Note
{x | y}
Required alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by vertical
bars.
[x {y | z}]
Nested set of square brackets or braces indicate optional or required choices
within optional or required elements. Braces and a vertical bar within square
brackets indicate a required choice within an optional element.
string
A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string or
the string will include the quotation marks.
Nonprinting characters such as passwords are in angle brackets.< >
Default responses to system prompts are in square brackets.[ ]
!, #
An exclamation point (!) or a pound sign (#) at the beginning of a line of code
indicates a comment line.
Reader Alert Conventions
This document may use the following conventions for reader alerts:
Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
manual.
Tip
Caution
Timesaver
Warning
Means the following information will help you solve a problem.
Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage
or loss of data.
Means the described action saves time. You can save time by performing the action described in the
paragraph.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you
work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with
standard practices for preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each warning
to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device. Statement 1071
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
viii OL-32353-01
Page 9

Preface
Related Documentation
Before installing or upgrading the switch, refer to the switch release notes.Note
Cisco Catalyst 3650 Switch documentation, located at:
•
http://www.cisco.com/go/cat3650_docs
Cisco SFP and SFP+ modules documentation, including compatibility matrixes, located at:
•
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/modules/ps5455/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Error Message Decoder, located at:
•
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/index.cgi
Related Documentation
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information,
see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco
technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 ix
Page 10

Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Preface
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
x OL-32353-01
Page 11

CHAPTER 1
Using the Command-Line Interface
Information About Using the Command-Line Interface, page 1
•
How to Use the CLI to Configure Features, page 6
•
Information About Using the Command-Line Interface
Command Modes
The Cisco IOS user interface is divided into many different modes. The commands available to you depend
on which mode you are currently in. Enter a question mark (?) at the system prompt to obtain a list of commands
available for each command mode.
You can start a CLI session through a console connection, through Telnet, a SSH, or by using the browser.
When you start a session, you begin in user mode, often called user EXEC mode. Only a limited subset of
the commands are available in user EXEC mode. For example, most of the user EXEC commands are one-time
commands, such as show commands, which show the current configuration status, and clear commands,
which clear counters or interfaces. The user EXEC commands are not saved when the switch reboots.
To have access to all commands, you must enter privileged EXEC mode. Normally, you must enter a password
to enter privileged EXEC mode. From this mode, you can enter any privileged EXEC command or enter
global configuration mode.
Using the configuration modes (global, interface, and line), you can make changes to the running configuration.
If you save the configuration, these commands are stored and used when the switch reboots. To access the
various configuration modes, you must start at global configuration mode. From global configuration mode,
you can enter interface configuration mode and line configuration mode.
This table describes the main command modes, how to access each one, the prompt you see in that mode, and
how to exit the mode.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 1
Page 12

Command Modes
Using the Command-Line Interface
Table 1: Command Mode Summary
About This ModeExit MethodPromptAccess MethodMode
User EXEC
Privileged EXEC
Global
configuration
Begin a session
using Telnet, SSH,
or console.
While in user
EXEC mode, enter
the enable
command.
While in privileged
EXEC mode, enter
the configure
command.
Switch>
Switch#
Switch(config)#
Enter logout or
quit.
Enter disable
to exit.
To exit to
privileged
EXEC mode,
enter exit or
end, or press
Ctrl-Z.
Use this mode to
Change
•
terminal
settings.
Perform basic
•
tests.
Display system
•
information.
Use this mode to
verify commands
that you have
entered. Use a
password to protect
access to this mode.
Use this mode to
configure parameters
that apply to the
entire switch.
VLAN
configuration
Interface
configuration
While in global
configuration
mode, enter the
vlan vlan-id
command.
While in global
configuration
mode, enter the
interface command
(with a specific
interface).
Switch(config-vlan)#
Switch(config-if)#
To exit to
global
configuration
mode, enter the
exit command.
To return to
privileged
EXEC mode,
press Ctrl-Z or
enter end.
Use this mode to
configure VLAN
parameters. When
VTP mode is
transparent, you can
create
extended-range
VLANs (VLAN IDs
greater than 1005)
and save
configurations in the
switch startup
configuration file.
Use this mode to
configure parameters
for the Ethernet
ports.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
2 OL-32353-01
Page 13

Using the Command-Line Interface
Using the Help System
About This ModeExit MethodPromptAccess MethodMode
To exit to
global
configuration
mode, enter
exit.
To return to
privileged
EXEC mode,
press Ctrl-Z or
enter end.
Line configuration
Using the Help System
You can enter a question mark (?) at the system prompt to display a list of commands available for each
command mode. You can also obtain a list of associated keywords and arguments for any command.
SUMMARY STEPS
help
1.
abbreviated-command-entry ?
2.
abbreviated-command-entry <Tab>
3.
?
4.
command ?
5.
command keyword ?
6.
While in global
configuration
mode, specify a line
with the line vty or
line console
command.
Switch(config-line)#
To exit to
global
configuration
mode, enter
exit.
To return to
privileged
EXEC mode,
press Ctrl-Z or
enter end.
Use this mode to
configure parameters
for the terminal line.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 3
Page 14
Understanding Abbreviated Commands
DETAILED STEPS
Using the Command-Line Interface
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
help
Example:
Switch# help
abbreviated-command-entry ?
Example:
Switch# di?
dir disable disconnect
abbreviated-command-entry <Tab>
Example:
Switch# sh conf<tab>
Switch# show configuration
?
Example:
Switch> ?
command ?
Example:
Switch> show ?
Obtains a brief description of the help system in any
command mode.
Obtains a list of commands that begin with a particular
character string.
Completes a partial command name.
Lists all commands available for a particular command
mode.
Lists the associated keywords for a command.
Step 6
command keyword ?
Example:
Switch(config)# cdp holdtime ?
<10-255> Length of time (in sec) that receiver
must keep this packet
Understanding Abbreviated Commands
You need to enter only enough characters for the switch to recognize the command as unique.
This example shows how to enter the show configuration privileged EXEC command in an abbreviated form:
Switch# show conf
Lists the associated arguments for a keyword.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
4 OL-32353-01
Page 15

Using the Command-Line Interface
No and Default Forms of Commands
Almost every configuration command also has a no form. In general, use the no form to disable a feature or
function or reverse the action of a command. For example, the no shutdown interface configuration command
reverses the shutdown of an interface. Use the command without the keyword no to reenable a disabled feature
or to enable a feature that is disabled by default.
Configuration commands can also have a default form. The default form of a command returns the command
setting to its default. Most commands are disabled by default, so the default form is the same as the no form.
However, some commands are enabled by default and have variables set to certain default values. In these
cases, the default command enables the command and sets variables to their default values.
CLI Error Messages
This table lists some error messages that you might encounter while using the CLI to configure your switch.
Table 2: Common CLI Error Messages
No and Default Forms of Commands
% Ambiguous command: "show
con"
% Incomplete command.
% Invalid input detected at
‘^’ marker.
You did not enter enough
characters for your switch to
recognize the command.
You did not enter all of the
keywords or values required by this
command.
You entered the command
incorrectly. The caret (^) marks the
point of the error.
How to Get HelpMeaningError Message
Reenter the command followed by
a question mark (?) without any
space between the command and
the question mark.
The possible keywords that you can
enter with the command appear.
Reenter the command followed by
a question mark (?) with a space
between the command and the
question mark.
The possible keywords that you can
enter with the command appear.
Enter a question mark (?) to display
all of the commands that are
available in this command mode.
The possible keywords that you can
enter with the command appear.
Configuration Logging
You can log and view changes to the switch configuration. You can use the Configuration Change Logging
and Notification feature to track changes on a per-session and per-user basis. The logger tracks each
configuration command that is applied, the user who entered the command, the time that the command was
entered, and the parser return code for the command. This feature includes a mechanism for asynchronous
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 5
Page 16

How to Use the CLI to Configure Features
notification to registered applications whenever the configuration changes. You can choose to have the
notifications sent to the syslog.
Only CLI or HTTP changes are logged.Note
How to Use the CLI to Configure Features
Configuring the Command History
The software provides a history or record of commands that you have entered. The command history feature
is particularly useful for recalling long or complex commands or entries, including access lists. You can
customize this feature to suit your needs.
Using the Command-Line Interface
Changing the Command History Buffer Size
By default, the switch records ten command lines in its history buffer. You can alter this number for a current
terminal session or for all sessions on a particular line. This procedure is optional.
SUMMARY STEPS
terminal history [size number-of-lines]
1.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
terminal history [size number-of-lines]
Example:
Switch# terminal history size 200
Recalling Commands
To recall commands from the history buffer, perform one of the actions listed in this table. These actions are
optional.
PurposeCommand or Action
Changes the number of command lines that the switch records during
the current terminal session in privileged EXEC mode. You can
configure the size from 0 to 256.
The arrow keys function only on ANSI-compatible terminals such as VT100s.Note
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
6 OL-32353-01
Page 17

Using the Command-Line Interface
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Ctrl-P or use the up arrow key
1.
Ctrl-N or use the down arrow key
2.
show history
3.
PurposeCommand or Action
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Ctrl-P or use the up arrow key
Ctrl-N or use the down arrow key
show history
Example:
Switch# show history
Disabling the Command History Feature
The command history feature is automatically enabled. You can disable it for the current terminal session or
for the command line. This procedure is optional.
SUMMARY STEPS
terminal no history
1.
DETAILED STEPS
Recalls commands in the history buffer, beginning with the most recent command.
Repeat the key sequence to recall successively older commands.
Returns to more recent commands in the history buffer after recalling commands
with Ctrl-P or the up arrow key. Repeat the key sequence to recall successively
more recent commands.
Lists the last several commands that you just entered in privileged EXEC mode.
The number of commands that appear is controlled by the setting of the terminal
history global configuration command and the history line configuration
command.
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
terminal no history
Disables the feature during the current terminal session in
privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Switch# terminal no history
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
Although enhanced editing mode is automatically enabled, you can disable it and reenable it.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 7
Page 18

Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
terminal editing
1.
terminal no editing
2.
Using the Command-Line Interface
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
terminal editing
Example:
Switch# terminal editing
terminal no editing
Example:
Switch# terminal no editing
Editing Commands Through Keystrokes
The keystrokes help you to edit the command lines. These keystrokes are optional.
The arrow keys function only on ANSI-compatible terminals such as VT100s.Note
Table 3: Editing Commands
Reenables the enhanced editing mode for the current terminal
session in privileged EXEC mode.
Disables the enhanced editing mode for the current terminal
session in privileged EXEC mode.
DescriptionEditing Commands
Moves the cursor back one character.Ctrl-B or use the left arrow key
Moves the cursor forward one character.Ctrl-F or use the right arrow key
Ctrl-A
Moves the cursor to the beginning of the command
line.
Moves the cursor to the end of the command line.Ctrl-E
Moves the cursor back one word.Esc B
Moves the cursor forward one word.Esc F
Ctrl-T
Transposes the character to the left of the cursor with
the character located at the cursor.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
8 OL-32353-01
Page 19

Using the Command-Line Interface
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
Erases the character to the left of the cursor.Delete or Backspace key
Deletes the character at the cursor.Ctrl-D
Ctrl-K
Ctrl-U or Ctrl-X
Esc U
Ctrl-V or Esc Q
Return key
Deletes all characters from the cursor to the end of
the command line.
Deletes all characters from the cursor to the beginning
of the command line.
Deletes the word to the left of the cursor.Ctrl-W
Deletes from the cursor to the end of the word.Esc D
Capitalizes at the cursor.Esc C
Changes the word at the cursor to lowercase.Esc L
Capitalizes letters from the cursor to the end of the
word.
Designates a particular keystroke as an executable
command, perhaps as a shortcut.
Scrolls down a line or screen on displays that are
longer than the terminal screen can display.
Note
The More prompt is used for any output that
has more lines than can be displayed on the
terminal screen, including show command
output. You can use the Return and Space
bar keystrokes whenever you see the More
prompt.
Scrolls down one screen.Space bar
Ctrl-L or Ctrl-R
Redisplays the current command line if the switch
suddenly sends a message to your screen.
Editing Command Lines That Wrap
You can use a wraparound feature for commands that extend beyond a single line on the screen. When the
cursor reaches the right margin, the command line shifts ten spaces to the left. You cannot see the first ten
characters of the line, but you can scroll back and check the syntax at the beginning of the command. The
keystroke actions are optional.
To scroll back to the beginning of the command entry, press Ctrl-B or the left arrow key repeatedly. You can
also press Ctrl-A to immediately move to the beginning of the line.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 9
Page 20

Searching and Filtering Output of show and more Commands
The arrow keys function only on ANSI-compatible terminals such as VT100s.Note
The following example shows how to wrap a command line that extends beyond a single line on the screen.
SUMMARY STEPS
access-list
1.
Ctrl-A
2.
Return key
3.
DETAILED STEPS
Using the Command-Line Interface
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
access-list
Example:
Switch(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp
10.15.22.25 255.255.255.0 10.15.22.35
Switch(config)# $ 101 permit tcp
10.15.22.25 255.255.255.0 10.15.22.35
255.25
Switch(config)# $t tcp 10.15.22.25
255.255.255.0 131.108.1.20 255.255.255.0
eq
Switch(config)# $15.22.25 255.255.255.0
10.15.22.35 255.255.255.0 eq 45
Example:
Switch(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp
10.15.22.25 255.255.255.0 10.15.2$
Displays the global configuration command entry that extends beyond
one line.
When the cursor first reaches the end of the line, the line is shifted ten
spaces to the left and redisplayed. The dollar sign ($) shows that the
line has been scrolled to the left. Each time the cursor reaches the end
of the line, the line is again shifted ten spaces to the left.
Checks the complete syntax.Ctrl-A
The dollar sign ($) appears at the end of the line to show that the line
has been scrolled to the right.
Execute the commands.Return key
The software assumes that you have a terminal screen that is 80 columns
wide. If you have a different width, use the terminal width privileged
EXEC command to set the width of your terminal.
Use line wrapping with the command history feature to recall and
modify previous complex command entries.
Searching and Filtering Output of show and more Commands
You can search and filter the output for show and more commands. This is useful when you need to sort
through large amounts of output or if you want to exclude output that you do not need to see. Using these
commands is optional.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
10 OL-32353-01
Page 21

Using the Command-Line Interface
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
{show | more} command | {begin | include | exclude} regular-expression
1.
PurposeCommand or Action
Accessing the CLI on a Switch Stack
Step 1
{show | more} command | {begin | include | exclude}
regular-expression
Example:
Switch# show interfaces | include protocol
Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up
Vlan10 is up, line protocol is down
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is up, line protocol is down
GigabitEthernet1/0/2 is up, line protocol is up
Accessing the CLI on a Switch Stack
You can access the CLI through a console connection, through Telnet, a SSH, or by using the browser.
You manage the switch stack and the stack member interfaces through the . You cannot manage stack members
on an individual switch basis. You can connect to the through the console port or the Ethernet management
port of one or more stack members. Be careful with using multiple CLI sessions on the . Commands that you
enter in one session are not displayed in the other sessions. Therefore, it is possible to lose track of the session
from which you entered commands.
We recommend using one CLI session when managing the switch stack.Note
Searches and filters the output.
Expressions are case sensitive. For example, if you enter
| exclude output, the lines that contain output are not
displayed, but the lines that contain output appear.
If you want to configure a specific stack member port, you must include the stack member number in the CLI
command interface notation.
Accessing the CLI Through a Console Connection or Through Telnet
Before you can access the CLI, you must connect a terminal or a PC to the switch console or connect a PC to
the Ethernet management port and then power on the switch, as described in the hardware installation guide
that shipped with your switch.
If your switch is already configured, you can access the CLI through a local console connection or through a
remote Telnet session, but your switch must first be configured for this type of access.
You can use one of these methods to establish a connection with the switch:
Connect the switch console port to a management station or dial-up modem, or connect the Ethernet
•
management port to a PC. For information about connecting to the console or Ethernet management
port, see the switch hardware installation guide.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 11
Page 22

Accessing the CLI Through a Console Connection or Through Telnet
Use any Telnet TCP/IP or encrypted Secure Shell (SSH) package from a remote management station.
•
The switch must have network connectivity with the Telnet or SSH client, and the switch must have an
enable secret password configured.
The switch supports up to 16 simultaneous Telnet sessions. Changes made by one Telnet user are
•
reflected in all other Telnet sessions.
The switch supports up to five simultaneous secure SSH sessions.
•
After you connect through the console port, through the Ethernet management port, through a Telnet
session or through an SSH session, the user EXEC prompt appears on the management station.
Using the Command-Line Interface
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
12 OL-32353-01
Page 23

Using the Web Graphical User Interface
Prerequisites for Using the Web GUI, page 13
•
Information About Using The Web GUI, page 13
•
Connecting the Console Port of the Switch , page 15
•
Logging On to the Web GUI, page 15
•
Enabling Web and Secure Web Modes , page 15
•
Configuring the Switch Web GUI, page 16
•
Prerequisites for Using the Web GUI
The GUI must be used on a PC running Windows 7, Windows XP SP1 (or later releases), or Windows
•
2000 SP4 (or later releases).
CHAPTER 2
The switch GUI is compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer version 10.x, Mozilla Firefox 20.x, or
•
Google Chrome 26.x.
Information About Using The Web GUI
A web browser, or graphical user interface (GUI), is built into each switch.
You can use either the service port interface or the management interface to access the GUI. We recommend
that you use the service-port interface. Click Help at the top of any page in the GUI to display online help.
You might need to disable your browser’s pop-up blocker to view the online help.
Web GUI Features
The switch web GUI supports the following:
The Configuration Wizard—After initial configuration of the IP address and the local username/password or
auth via the authentication server (privilege 15 needed), the wizard provides a method to complete the initial
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 13
Page 24

Web GUI Features
Using the Web Graphical User Interface
wireless configuration. Start the wizard through Configuration -> Wizard and follow the nine-step process to
configure the following:
Admin Users
•
SNMP System Summary
•
Management Port
•
Wireless Management
•
RF Mobility and Country code
•
Mobility configuration
•
WLANs
•
802.11 Configuration
•
Set Time
•
The Monitor tab:
Displays summary details of switch, clients, and access points.
•
Displays all radio and AP join statistics.
•
Displays air quality on access points.
•
Displays list of all Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) neighbors on all interfaces and the CDP traffic
•
information.
Displays all rogue access points based on their classification-friendly, malicious, ad hoc, classified, and
•
unclassified.
The Configuration tab:
Enables you to configure the switch for all initial operation using the web Configuration Wizard. The
•
wizard allows you to configure user details, management interface, and so on.
Enables you to configure the system, internal DHCP server, management, and mobility management
•
parameters.
Enables you to configure the switch, WLAN, and radios.
•
Enables you to configure and set security policies on your switch.
•
Enables you to access the switch operating system software management commands.
•
The Administration tab enables you to configure system logs.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
14 OL-32353-01
Page 25

Using the Web Graphical User Interface
Connecting the Console Port of the Switch
Before You Begin
Before you can configure the switch for basic operations, you need to connect it to a PC that uses a VT-100
terminal emulation program (such as HyperTerminal, ProComm, Minicom, or Tip).
Connecting the Console Port of the Switch
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Connect one end of a null-modem serial cable to the switch's RJ-45 console port and the other end to your PC's serial
port.
Plug the AC power cord into the switch and a grounded 100 to 240 VAC, 50/60-Hz electrical outlet. Turn on the power
supply. The bootup script displays operating system software initialization (code download and power-on self-test
verification) and basic configuration. If the switch passes the power-on self-test, the bootup script runs the configuration
wizard, which prompts you for basic configuration input.
Enter yes. Proceed with basic initial setup configuration parameters in the CLI setup wizard. Specify the IP address for
the service port which is the gigabitethernet 0/0 interface.
After entering the configuration parameters in the configuration wizard, you can access the Web GUI. Now, the switch
is configured with the IP address for service port.
Logging On to the Web GUI
Enter the switch IP address in your browser’s address bar. For a secure connection, enter https://ip-address. For a less
secure connection, enter http://ip-address.
Enabling Web and Secure Web Modes
Step 1
Step 2
OL-32353-01 15
Choose Configuration > Switch > Management > Protocol Management > HTTP-HTTPS.
The HTTP-HTTPS Configuration page appears.
To enable web mode, which allows users to access the switch GUI using “http://ip-address,” choose Enabled from the
HTTP Access drop-down list. Otherwise, choose Disabled. Web mode (HTTP) is not a secure connection.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Page 26

Configuring the Switch Web GUI
Using the Web Graphical User Interface
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
To enable secure web mode, which allows users to access the switch GUI using “https://ip-address,” choose Enabled
from the HTTPS Access drop-down list. Otherwise, choose Disabled. Secure web mode (HTTPS) is a secure connection.
Choose to track the device in the IP Device Tracking check box.
Choose to enable the trust point in the Enable check box.
Choose the trustpoints from the Trustpoints drop-down list.
Enter the amount of time, in seconds, before the web session times out due to inactivity in the HTTP Timeout-policy (1
to 600 sec) text box.
The valid range is from 1 to 600 seconds.
Enter the server life time in the Server Life Time (1 to 86400 sec) text box.
The valid range is from1 to 86400 seconds.
Enter the maximum number of connection requests that the server can accept in the Maximum number of Requests (1
to 86400) text box.
The valid range is from 1 to 86400 connections.
Click Apply.
Click Save Configuration.
Configuring the Switch Web GUI
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
The configuration wizard enables you to configure basic settings on the switch. You can run the wizard after
you receive the switch from the factory or after the switch has been reset to factory defaults. The configuration
wizard is available in both GUI and CLI formats.
Connect your PC to the service port and configure an IPv4 address to use the same subnet as the switch. The switch is
loaded with IOS XE image and the service port interface is configured as gigabitethernet 0/0.
Start Internet Explorer 10 (or later), Firefox 2.0.0.11 (or later), or Google Chrome on your PC and enter the management
interface IP address on the browser window. The management interface IP address is same as the gigabitethernet 0/0
(also known as service port interface). When you log in for the first time, you need to enter HTTP username and password.
By default, the username is admin and the password is cisco.
You can use both HTTP and HTTPS when using the service port interface. HTTPS is enabled by default and HTTP can
also be enabled.
When you log in for the first time, the Accessing Cisco Switch <Model Number> <Hostname> page appears.
On the Accessing Cisco Switch page, click the Wireless Web GUI link to access switch web GUI Home page.
Choose Configuration > Wizard to perform all steps that you need to configure the switch initially.
The Admin Users page appears.
On the Admin Users page, enter the administrative username to be assigned to this switch in the User Name text box
and the administrative password to be assigned to this switch in the Password and Confirm Password text boxes. Click
Next.
The default username is admin and the default password is cisco. You can also create a new administrator user for the
switch. You can enter up to 24 ASCII characters for username and password.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
16 OL-32353-01
Page 27

Using the Web Graphical User Interface
The SNMP System Summary page appears.
Configuring the Switch Web GUI
Step 6
Step 7
On the SNMP System Summary page, enter the following SNMP system parameters for the switch, and click Next:
Customer-definable switch location in the Location text box.
•
Customer-definable contact details such as phone number with names in the Contact text box.
•
Choose enabled to send SNMP notifications for various SNMP traps or disabled not to send SNMP notifications
•
for various SNMP traps from the SNMP Global Trap drop-down list.
Choose enabled to send system log messages or disabled not to send system log messages from the SNMP Logging
•
drop-down list.
Note
The SNMP trap server, must be reachable through the distribution ports (and not through the gigabitethernet0/0
service or management interface).
The Management Port page appears.
In the Management Port page, enter the following parameters for the management port interface (gigabitethernet 0/0)
and click Next.
Interface IP address that you assigned for the service port in the IP Address text box.
•
Network mask address of the management port interface in the Netmask text box.
•
The IPv4 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) address for the selected port in the IPv4 DHCP Server
•
text box.
The Wireless Management page appears.
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
In the Wireless Management page, enter the following wireless interface management details, and click Next.
• Choose the interface—VLAN, or Ten Gigabit Ethernet from the Select Interface drop-down list.
VLAN tag identifier, or 0 for no VLAN tag in the VLAN id text box.
•
IP address of wireless management interface where access points are connected in the IP Address text box.
•
Network mask address of the wireless management interface in the Netmask text box.
•
DHCP IPv4 IP address in the IPv4 DHCP Server text box.
•
When selecting VLAN as interface, you can specify the ports as –Trunk or Access ports from the selected list displayed
in the Switch Port Configuration text box.
The RF Mobility and Country Code page appears.
In the RF Mobility and Country Code page, enter the RF mobility domain name in the RF Mobility text box, choose
current country code from the Country Code drop-down list, and click Next. From the GUI, you can select only one
country code.
Note
Before configuring RF grouping parameters and mobility configuration, ensure that you refer to the relevant
conceptual content and then proceed with the configuration.
The Mobility Configuration page with mobility global configuration settings appears.
In the Mobility Configuration page, view and enter the following mobility global configuration settings, and click Next.
Choose Mobility Controller or Mobility Agent from the Mobility Role drop-down list:
•
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 17
Page 28

Configuring the Switch Web GUI
If Mobility Agent is chosen, enter the mobility controller IP address in the Mobility Controller IP Address
•
text box and mobility controller IP address in the Mobility Controller Public IP Address text box.
If Mobility Controller is chosen, then the mobility controller IP address and mobility controller public IP
•
address are displayed in the respective text boxes.
Displays mobility protocol port number in the Mobility Protocol Port text box.
•
Displays the mobility switch peer group name in the Mobility Switch Peer Group Name text box.
•
Displays whether DTLS is enabled in the DTLS Mode text box.
•
DTLS is a standards-track Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) protocol based on TLS.
Displays mobility domain identifier for 802.11 radios in the Mobility Domain ID for 802.11 radios text box.
•
The amount of time (in seconds) between each ping request sent to an peer switch in the Mobility Keepalive Interval
•
(1-30)sec text box.
Valid range is from 1 to 30 seconds, and the default value is 10 seconds.
Using the Web Graphical User Interface
Step 11
Step 12
Number of times a ping request is sent to an peer switch before the peer is considered to be unreachable in the
•
Mobility Keepalive Count (3-20) text box.
The valid range is from 3 to 20, and the default value is 3.
The DSCP value that you can set for the mobility switch in the Mobility Control Message DSCP Value (0-63) text
•
box.
The valid range is 0 to 63, and the default value is 0.
Displays the number of mobility switch peer group member configured in the Switch Peer Group Members
•
Configured text box.
The WLANs page appears.
In the WLANs page, enter the following WLAN configuration parameters, and click Next.
WLAN identifier in the WLAN ID text box.
•
SSID of the WLAN that the client is associated with in the SSID text box.
•
Name of the WLAN used by the client in the Profile Name text box.
•
The 802.11 Configuration page appears.
In the 802.11 Configuration page, check either one or both 802.11a/n/ac and 802.11b/g/n check boxes to enable the
802.11 radios, and click Next.
The Set Time page appears.
Step 13
In the Set Time page, you can configure the time and date on the switch based on the following parameters, and click
Next.
Displays current timestamp on the switch in the Current Time text box.
•
Choose either Manual or NTP from the Mode drop-down list.
•
On using the NTP server, all access points connected to the switch, synchronizes its time based on the NTP server
settings available.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
18 OL-32353-01
Page 29

Using the Web Graphical User Interface
Choose date on the switch from the Year, Month, and Day drop-down list.
•
Choose time from the Hours, Minutes, and Seconds drop-down list.
•
Enter the time zone in the Zone text box and select the off setting required when compared to the current time
•
configured on the switch from the Offset drop-down list.
The Save Wizard page appears.
Configuring the Switch Web GUI
Step 14
In the Save Wizard page, you can review the configuration settings performed on the switch using these steps, and if
you wish to change any configuration value, click Previous and navigate to that page.
You can save the switch configuration created using the wizard only if a success message is displayed for all the wizards.
If the Save Wizard page displays errors, you must recreate the wizard for initial configuration of the switch.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 19
Page 30

Configuring the Switch Web GUI
Using the Web Graphical User Interface
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
20 OL-32353-01
Page 31

Configuring WLANs
Finding Feature Information, page 21
•
Prerequisites for WLANs, page 21
•
Restrictions for WLANs, page 22
•
Information About WLANs, page 23
•
How to Configure WLANs, page 27
•
Monitoring WLAN Properties (CLI), page 44
•
Viewing WLAN Properties (GUI), page 45
•
Where to Go Next, page 45
•
Additional References, page 45
•
Feature Information for WLANs, page 46
•
CHAPTER 3
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature
information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information
about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported,
see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not
required.
Prerequisites for WLANs
You can associate up to 16 WLANs with each access point group and assign specific access points to
•
each group. Each access point advertises only the enabled WLANs that belong to its access point group.
The access point (AP) does not advertise disabled WLANs in its access point group or WLANs that
belong to another group.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 21
Page 32

Restrictions for WLANs
Configuring WLANs
We recommend that you assign one set of VLANs for WLANs and a different set of VLANs for
•
management interfaces to ensure that switches properly route VLAN traffic.
The switch uses different attributes to differentiate between WLANs with the same Service Set Identifier
•
(SSID).
WLANs with the same SSID and same Layer 2 policy cannot be created if the WLAN ID is lower
•
than 17.
Two WLANs with IDs that are greater than 17 and that have the same SSID and same Layer 2
•
policy is allowed if WLANs are added in different AP groups.
Note
Related Topics
Creating WLANs (CLI), on page 27
Creating WLANs (GUI), on page 28
Configuring General WLAN Properties (CLI), on page 32
Configuring General WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 35
Deleting WLANs, on page 29
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI), on page 36
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Band Selection, on page 24
Off-Channel Scanning Defer
DTIM Period
Session Timeout
Cisco Client Extensions, on page 25
Peer-to-Peer Blocking, on page 26
Diagnostic Channel
Client Count Per WLAN
Enabling WLANs (CLI), on page 31
Disabling WLANs (CLI), on page 32
This requirement ensures that clients never detect the SSID present on the same access
point radio.
Restrictions for WLANs
Peer-to-peer blocking does not apply to multicast traffic.
•
You can configure a maximum of up to 1000 clients.
•
The WLAN name and SSID can have up to 32 characters. Spaces are not allowed in the WLAN profile
•
name and SSID.
You cannot map a WLAN to VLAN0, and you cannot map VLANs 1002 to 1006.
•
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
22 OL-32353-01
Page 33

Configuring WLANs
Information About WLANs
Dual stack clients with a static-IPv4 address is not supported.
•
When creating a WLAN with the same SSID, you must create a unique profile name for each WLAN.
•
When multiple WLANs with the same SSID get assigned to the same AP radio, you must have a unique
•
Layer 2 security policy so that clients can safely select between them.
Caution
Some clients might not be able to connect to WLANs properly if they detect the same SSID with multiple
security policies. Use this feature with care.
Related Topics
Creating WLANs (CLI), on page 27
Creating WLANs (GUI), on page 28
Configuring General WLAN Properties (CLI), on page 32
Configuring General WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 35
Deleting WLANs, on page 29
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI), on page 36
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Band Selection, on page 24
Off-Channel Scanning Defer
DTIM Period
Session Timeout
Cisco Client Extensions, on page 25
Peer-to-Peer Blocking, on page 26
Diagnostic Channel
Client Count Per WLAN
Enabling WLANs (CLI), on page 31
Disabling WLANs (CLI), on page 32
Information About WLANs
This feature enables you to control up to 64 WLANs for lightweight access points. Each WLAN has a separate
WLAN ID, a separate profile name, and a WLAN SSID. All switches publish up to 16 WLANs to each
connected access point, but you can create up to the maximum number of WLANs supported and then
selectively publish these WLANs (using access point groups) to different access points to better manage your
wireless network.
You can configure WLANs with different SSIDs or with the same SSID. An SSID identifies the specific
wireless network that you want the switch to access.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 23
Page 34

Band Selection
Band Selection
Band selection enables client radios that are capable of dual-band (2.4- and 5-GHz) operation to move to a
less congested 5-GHz access point. The 2.4-GHz band is often congested. Clients on this band typically
experience interference from Bluetooth devices, microwave ovens, and cordless phones as well as co-channel
interference from other access points because of the 802.11b/g limit of three nonoverlapping channels. To
prevent these sources of interference and improve overall network performance, you can configure band
selection on the switch.
Band selection works by regulating probe responses to clients. It makes 5-GHz channels more attractive to
clients by delaying probe responses to clients on 2.4-GHz channels.
Related Topics
Configuring WLANs
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI), on page 36
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Off-Channel Scanning Defer
In deployments with certain power-save clients, you sometimes need to defer the Radio Resource Management's
(RRM) normal off-channel scanning to avoid missing critical information from low-volume clients (for
example, medical devices that use power-save mode and periodically send telemetry information). This feature
improves the way that Quality of Service (QoS) interacts with the RRM scan defer feature.
You can use a client's Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) UP marking to configure the access point to defer off-channel
scanning for a configurable period of time if it receives a packet marked UP.
Off-Channel Scanning Defer is essential to the operation of RRM, which gathers information about alternate
channel choices such as noise and interference. Additionally, Off-Channel Scanning Defer is responsible for
rogue detection. Devices that need to defer Off-Channel Scanning Defer should use the same WLAN as often
as possible. If there are many of these devices (and the possibility exists that Off-Channel Defer scanning
could be completely disabled by the use of this feature), you should implement an alternative to local AP
Off-Channel Scanning Defer, such as monitoring access points, or other access points in the same location
that do not have this WLAN assigned.
You can assign a QoS policy (bronze, silver, gold, and platinum) to a WLAN to affect how packets are marked
on the downlink connection from the access point regardless of how they were received on the uplink from
the client. UP=1,2 is the lowest priority, and UP=0,3 is the next higher priority. The marking results of each
QoS policy are as follows:
Bronze marks all downlink traffic to UP= 1.
•
Silver marks all downlink traffic to UP= 0.
•
Gold marks all downlink traffic to UP=4.
•
Platinum marks all downlink traffic to UP=6.
•
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
24 OL-32353-01
Page 35

Configuring WLANs
DTIM Period
DTIM Period
In the 802.11 networks, lightweight access points broadcast a beacon at regular intervals, which coincides
with the Delivery Traffic Indication Map (DTIM). After the access point broadcasts the beacon, it transmits
any buffered broadcast and multicast frames based on the value set for the DTIM period. This feature allows
power-saving clients to wake up at the appropriate time if they are expecting broadcast or multicast data.
Typically, the DTIM value is set to 1 (to transmit broadcast and multicast frames after every beacon) or 2 (to
transmit after every other beacon). For instance, if the beacon period of the 802.11 network is 100 ms and the
DTIM value is set to 1, the access point transmits buffered broadcast and multicast frames 10 times per second.
If the beacon period is 100 ms and the DTIM value is set to 2, the access point transmits buffered broadcast
and multicast frames 5 times per second. Either of these settings are suitable for applications, including Voice
Over IP (VoIP), that expect frequent broadcast and multicast frames.
However, the DTIM value can be set as high as 255 (to transmit broadcast and multicast frames after every
255th beacon) if all 802.11 clients have power save enabled. Because the clients have to listen only when the
DTIM period is reached, they can be set to listen for broadcasts and multicasts less frequently which results
in a longer battery life. For example, if the beacon period is 100 ms and you set the DTIM value to 100, the
access point transmits buffered broadcast and multicast frames once every 10 seconds. This rate allows the
power-saving clients to sleep longer before they have to wake up and listen for broadcasts and multicasts,
which results in a longer battery life.
Note
A beacon period, which is specified in milliseconds on the switch, is converted internally by the software
to 802.11 Time Units (TUs), where 1 TU = 1.024 milliseconds. On Cisco’s 802.11n access points, this
value is rounded to the nearest multiple of 17 TUs. For example, a configured beacon period of 100 ms
results in an actual beacon period of 104 ms.
Many applications cannot tolerate a long time between broadcast and multicast messages, which results in
poor protocol and application performance. We recommend that you set a low DTIM value for 802.11 networks
that support such clients.
Session Timeouts
You can configure a WLAN with a session timeout. The session timeout is the maximum time for a client
session to remain active before requiring reauthorization.
Cisco Client Extensions
The Cisco Client Extensions (CCX) software is licensed to manufacturers and vendors of third-party client
devices. The CCX code resident on these clients enables them to communicate wirelessly with Cisco access
points and to support Cisco features that other client devices do not, including those features that are related
to increased security, enhanced performance, fast roaming, and power management.
The software supports CCX versions 1 through 5, which enables switches and their access points to
•
communicate wirelessly with third-party client devices that support CCX. CCX support is enabled
automatically for every WLAN on the switch and cannot be disabled. However, you can configure
Aironet information elements (IEs).
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 25
Page 36

Peer-to-Peer Blocking
If Aironet IE support is enabled, the access point sends an Aironet IE 0x85 (which contains the access
•
point name, load, number of associated clients, and so on) in the beacon and probe responses of this
WLAN, and the switch sends Aironet IEs 0x85 and 0x95 (which contains the management IP address
of the switch and the IP address of the access point) in the reassociation response if it receives Aironet
IE 0x85 in the reassociation request.
Related Topics
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI), on page 36
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Peer-to-Peer Blocking
Peer-to-peer blocking is applied to individual WLANs, and each client inherits the peer-to-peer blocking
setting of the WLAN to which it is associated. Peer-to-Peer enables you to have more control over how traffic
is directed. For example, you can choose to have traffic bridged locally within the switch, dropped by the
switch, or forwarded to the upstream VLAN.
Peer-to-peer blocking is supported for clients that are associated with the local switching WLAN.
Configuring WLANs
Related Topics
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI), on page 36
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Diagnostic Channel
You can choose a diagnostic channel to troubleshoot why the client is having communication problems with
a WLAN. You can test the client and access points to identify the difficulties that the client is experiencing
and allow corrective measures to be taken to make the client operational on the network. You can use the
switch GUI or CLI to enable the diagnostic channel, and you can use the switch CLI to run the diagnostic
tests.
Note
We recommend that you enable the diagnostic channel feature only for nonanchored SSIDs that use the
management interface. CCX Diagnostic feature has been tested only with clients having Cisco ADU card
Per-WLAN Radius Source Support
By default, the switch sources all RADIUS traffic from the IP address on its management interface, which
means that even if a WLAN has specific RADIUS servers configured instead of the global list, the identity
used is the management interface IP address.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
26 OL-32353-01
Page 37

Configuring WLANs
If you want to filter WLANs, you can use the callStationID that is set by RFC 3580 to be in the APMAC:SSID
format. You can also extend the filtering on the authentication server to be on a per-WLAN source interface
by using the NAS-IP-Address attribute.
When you enable the per-WLAN RADIUS source support, the switch sources all RADIUS traffic for a
particular WLAN by using the dynamic interface that is configured. Also, RADIUS attributes are modified
accordingly to match the identity. This feature virtualizes the switch on the per-WLAN RADIUS traffic, where
each WLAN can have a separate layer 3 identity. This feature is useful in deployments that integrate with
ACS Network Access Restrictions and Network Access Profiles.
You can combine per-WLAN RADIUS source support with the normal RADIUS traffic source and some
WLANs that use the management interface and others using the per-WLAN dynamic interface as the address
source.
How to Configure WLANs
Creating WLANs (CLI)
How to Configure WLANs
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Step 2
wlan profile-name wlan-id [ssid]
Example:
Switch(config)# wlan mywlan 34
mywlan-ssid
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name wlan-id [ssid]
2.
end
3.
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Specifies the WLAN name and ID:
For the profile-name, enter the profile name. The range is from 1 to
•
32 alphanumeric characters.
For the wlan-id, enter the WLAN ID. The range is from 1 to 512.
•
For the ssid, enter the Service Set Identifier (SSID) for this WLAN.
•
If the SSID is not specified, the WLAN profile name is set as the
SSID.
Note
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 27
By default, the WLAN is
disabled.
Page 38

Creating WLANs (GUI)
Configuring WLANs
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 3
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Related Topics
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Creating WLANs (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Click Configuration > Wireless.
The WLANs page is displayed.
Click New to create a WLAN.
The WLANs > Create New page is displayed.
Enter the following parameters:
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z
to exit global configuration mode.
DescriptionParameter
Step 4
WLAN identifier. The value ranges from 1 to 512.WLAN ID
Broadcast name of the WLAN.SSID
WLAN profile name.Profile
Click Apply.
Related Topics
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
28 OL-32353-01
Page 39

Configuring WLANs
Deleting WLANs
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
2.
3.
DETAILED STEPS
Deleting WLANs
configure terminal
no wlan wlan-name wlan-id ssid
end
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
no wlan wlan-name wlan-id ssid
Example:
Switch(config)# no wlan test2
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Related Topics
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Deletes the WLAN. The arguments are as follows:
The wlan-name is the WLAN profile name.
•
The wlan-id is the WLAN ID.
•
The ssid is the WLAN SSID name configured for the WLAN.
•
Note
If you delete a WLAN that is part of an AP group, the WLAN
is removed from the AP group and from the AP's radio.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press
Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Deleting WLANs (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
OL-32353-01 29
Click Configuration > Wireless.
The WLANs page is displayed.
Select the checkbox corresponding to the WLAN you want to delete.
Note
If you delete a WLAN that is part of an AP group, the WLAN is removed from the AP group and from the AP's
radio.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Page 40

Searching WLANs
Configuring WLANs
Step 3
Click Remove.
Searching WLANs
SUMMARY STEPS
show wlan summary
1.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
show wlan summary
Example:
Switch# show wlan summary
Switch# show wlan summary
Number of WLANs: 4
WLAN Profile Name SSID VLAN Status
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 test1 test1-ssid 137 UP
3 test2 test2-ssid 136 UP
2 test3 test3-ssid 1 UP
45 test4 test4-ssid 1 DOWN
You can also use wild cards to search WLANs. For example show wlan summary include | variable. Where
variable is any search string in the output.
Switch# show wlan summary | include test-wlan-ssid
1 test-wlan test-wlan-ssid 137 UP
PurposeCommand or Action
Displays the list of all WLANs configured on the device. You
can search for the WLAN in the output.
Searching WLANs (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
30 OL-32353-01
Click Configuration > Wireless.
The WLANs page is displayed.
Type the first few characters in the text box above the column you are searching. Fo For example, to search the WLAN
based on the Profile, type the first few characters of the profile name.
You can search a WLAN based on the following criteria:
Profile
•
ID
•
SSID
•
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Page 41

Configuring WLANs
VLAN
•
Status
•
If a WLAN exists, it would appear based on the accuracy of the match.
Enabling WLANs (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
no shutdown
3.
end
4.
Enabling WLANs (CLI)
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# no shutdown
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name
is the profile name of the configured WLAN.
Enables the WLAN.no shutdown
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also
press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Related Topics
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 31
Page 42

Disabling WLANs (CLI)
Disabling WLANs (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
shutdown
3.
end
4.
show wlan summary
5.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring WLANs
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# shutdown
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
show wlan summary
Example:
Switch# show wlan summary
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name is
the profile name of the configured WLAN.
Disables the WLAN.shutdown
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also
press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Displays the list of all WLANs configured on the device. You
can search for the WLAN in the output.
Related Topics
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Configuring General WLAN Properties (CLI)
You can configure the following properties:
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
32 OL-32353-01
Page 43

Configuring WLANs
SUMMARY STEPS
Media stream
•
Broadcast SSID
•
Call Snooping
•
Radio
•
Interface
•
Status
•
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
shutdown
3.
broadcast-ssid
4.
radio {all | dot11a | dot11ag | dot11bg | dot11g}
5.
client vlan vlan-identifier
6.
ip multicast vlan vlan-name
7.
media-stream multicast-direct
8.
call-snoop
9.
no shutdown
10.
end
11.
Configuring General WLAN Properties (CLI)
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
Example:
Switch# shutdown
broadcast-ssid
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# broadcast-ssid
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name is the
profile name of the configured WLAN.
Disables the WLAN before configuring the parameters.shutdown
Broadcasts the SSID for this WLAN. This field is enabled by
default.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 33
Page 44

Configuring General WLAN Properties (CLI)
Configuring WLANs
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
dot11g}
Example:
Switch# radio all
client vlan vlan-identifier
Example:
Switch# client vlan test-vlan
ip multicast vlan vlan-name
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# ip multicast vlan
test
Enables radios on the WLAN. The keywords are as follows:radio {all | dot11a | dot11ag | dot11bg |
• all—Configures the WLAN on all radio bands.
• dot1a—Configures the WLAN on only 802.11a radio bands.
• dot11g—Configures the WLAN on 802.11ag radio bands.
• dot11bg—Configures the WLAN on only 802.11b/g radio
bands (only 802.11b if 802.11g is disabled).
• dot11ag— Configures the wireless LAN on 802.11g radio
bands only.
Enables an interface group on the WLAN.
vlan-identifier—Specifies the VLAN identifier. This can be the
VLAN name, VLAN ID, or VLAN group name.
Enables IP multicast on a WLAN. The keywords are as follows:
• vlan—Specifies the VLAN ID.
• vlan-name—Specifies the VLAN name.
Enables multicast VLANs on this WLAN.media-stream multicast-direct
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# media-stream
multicast-direct
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# call-snoop
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# no shutdown
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Related Topics
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Enables call-snooping support.call-snoop
Enables the WLAN.no shutdown
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also
press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
34 OL-32353-01
Page 45

Configuring WLANs
Configuring General WLAN Properties (GUI)
Use this procedure to perform the following actions on a WLAN:
Set WLAN Status
•
Configure Radio Policies
•
Assign Interface/Interface Groups
•
Enable or Disable Multicast VLAN Feature
•
Enable or Disable Broadcast SSID Feature
•
Before You Begin
Configuring General WLAN Properties (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Click Configuration > Wireless.
The WLANs page is displayed.
Locate the WLAN you want to configure by using the search mechanisms on the page.
Click on the WLAN Profile of the WLAN.
The WLAN > Edit page is displayed.
Click the General tab. This tab is displayed by default.
Configure the General parameters.
DescriptionParameter
Displays the configured profile name of the WLAN.Profile Name
Displays the configured LAN type.Type
Displays the configured SSID of the WLAN.SSID
Check box to enable the WLAN. The default value is enabled.Status
WLAN security policies set using the Security tab.Security Policies
Radio Policy
WLAN radio policy to enable radios on the WLAN. Values are the following:
All
•
802.11a only
•
802.11g only
•
802.11a/g only
•
802.11b/g only
•
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 35
Page 46

Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI)
DescriptionParameter
Configuring WLANs
Step 6
Interface/Interface
Group
Multicast VLAN
Feature
Click Apply.
What to Do Next
Proceed to configure the Security, QoS, and Advanced Properties.
Related Topics
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Interface or interface group that you want this WLAN to be mapped. Displays the non-service
port and non-virtual interface names configured on the Interfaces page.
Note
This field displays a drop down box only when the VLAN for a WLAN is mapped
using a existing VLAN name on the switch.
Check box to broadcast this SSID. The default is enabled.Broadcast SSID
Check box to enable the multicast VLAN. The default is disabled.
Note
The Multicast Interface field appears only after you enable the Multicast VLAN feature
text box.
Note
You have to configure the multicast VLAN feature only once if you want to use the
multicast feature.
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI)
You can configure the following advanced properties:
AAA Override
•
Coverage Hole Detection
•
Session Timeout
•
Cisco Client Extensions
•
Diagnostic Channels
•
Interface Override ACLs
•
P2P Blocking
•
Client Exclusion
•
Maximum Clients Per WLAN
•
Off Channel Scan Defer
•
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
36 OL-32353-01
Page 47

Configuring WLANs
SUMMARY STEPS
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI)
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
aaa-override
3.
chd
4.
session-timeout time-in-seconds
5.
ccx aironet-iesupport
6.
diag-channel
7.
ip access-group [web] acl-name
8.
peer-blocking [drop | forward-upstream]
9.
exclusionlist time-in-seconds
10.
client association limit max-number-of-clients
11.
channel-scan defer-priority {defer-priority {0-7} | defer-time {0 - 6000}}
12.
end
13.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Step 2
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
Step 3
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# aaa-override
Step 4
Step 5
chd
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# chd
session-timeout time-in-seconds
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# session-timeout
450
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name is the
profile name of the configured WLAN.
Enables AAA override.aaa-override
Enables coverage hole detection for this WLAN. This field is enabled
by default.
Sets the session timeout in seconds. The range and default values vary
according to the security configuration. If the WLAN security is
configured to dot1x, the range is 300 to 86400 seconds and the default
value is 1800 seconds. For all other WLAN security configurations,
the range is 1 to 65535 seconds and the default value is 0 seconds. A
value of 0 indicates no session timeout.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 37
Page 48

Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI)
Configuring WLANs
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
ccx aironet-iesupport
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# ccx
aironet-iesupport
diag-channel
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# diag-channel
ip access-group [web] acl-name
Example:
Switch(config)# ip access-group
test-acl-name
peer-blocking [drop | forward-upstream]
Example:
Switch(config)# peer-blocking drop
exclusionlist time-in-seconds
Example:
Switch(config)# exclusionlist 10
client association limit max-number-of-clients
Example:
Switch(config)# client association limit
200
channel-scan defer-priority {defer-priority
{0-7} | defer-time {0 - 6000}}
Enables support for Aironet IEs for this WLAN. This field is enabled
by default.
Enables diagnostic channel support to troubleshoot client
communication issues on a WLAN.
Configures the WLAN ACL group. The variable acl-name specifies
the user-defined IPv4 ACL name. The keyword web specifies the
IPv4 web ACL.
Configures peer to peer blocking parameters. The keywords are as
follows:
• drop—Enables peer-to-peer blocking on the drop action.
• forward-upstream—Enables peer-to-peer blocking on the
forward upstream action.
Specifies the timeout in seconds. The valid range is from 0 to
2147483647. Enter 0 for no timeout. A zero (0) timeout indicates that
the client is permanently added to the exclusion list.
Sets the maximum number of clients that can be configured on a
WLAN.
Sets the channel scan defer priority and defer time. The arguments
are as follows:
Example:
Switch(config)# channel-scan
defer-priority 6
• defer-priority—Specifies the priority markings for packets that
can defer off-channel scanning. The range is from 0 to 7. The
default is 3.
• defer-time—Deferral time in milliseconds. The range is from
0 to 6000. The default is 100.
Step 13
end
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press
Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Example:
Switch(config)# end
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
38 OL-32353-01
Page 49

Configuring WLANs
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI)
Related Topics
Band Selection, on page 24
Off-Channel Scanning Defer
DTIM Period
Session Timeout
Cisco Client Extensions, on page 25
Peer-to-Peer Blocking, on page 26
Diagnostic Channel
Client Count Per WLAN
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Information About AAA Override, on page 60
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI)
Before You Begin
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Click Configuration > Wireless.
The WLANs page is displayed.
Locate the WLAN you want to configure by using the search mechanisms on the page.
Click on the WLAN Profile of the WLAN.
The WLAN > Edit page is displayed.
Click on the Advanced Properties tab.
Configure the Advanced properties.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 39
Page 50

Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI)
DescriptionParameter
Configuring WLANs
Allow AAA Override
Coverage Hole
Detection
AAA override for global WLAN parameters that you can enable or disable.
When AAA Override is enabled, and a client has conflicting AAA and switches WLAN
authentication parameters, client authentication is performed by the AAA server. As part of
this authentication, the operating system moves clients from the default Cisco WLAN Solution
WLAN VLAN to a VLAN returned by the AAA server and predefined in the switches interface
configuration. In all cases, the operating system also uses QoS, DSCP, 802.1p priority tag
values, and ACLs provided by the AAA server, if they are predefined in the switches interface
configuration. (This VLAN switching by AAA Override is also referred to as Identity
Networking.)
If the Corporate WLAN primarily uses a Management Interface assigned to VLAN 2, and if
AAA Override returns a redirect to VLAN 100, the operating system redirects all client
transmissions to VLAN 100, regardless of the physical port to which VLAN 100 is assigned.
When AAA Override is disabled, all client authentication defaults to the switches authentication
parameter settings, and authentication is performed only by the AAA server if the switches
WLAN does not contain any client-specific authentication parameters.
The AAA override values might come from a RADIUS server, for example.
Coverage hole detection (CHD) on this WLAN that you can enable or disable.
By default, CHD is enabled on all WLANs on the switches. You can disable CHD on a WLAN.
When you disable CHD on a WLAN, a coverage hole alert is still sent to the Switch, but no
other processing is done to mitigate the coverage hole. This feature is useful for guest WLANs
where guests are connected to your network for short periods of time and are likely to be highly
mobile.
Session Timeout
P2P Blocking Action
Configure a WLAN with a session timeout in seconds. The session timeout is the maximum
time for a client session to remain active before requiring reauthorization. The minimum session
timeout allowed is 1 second and the maximum timeout allowed is 65535 seconds.
Note
Entering zero denotes the session will never
expire.
Support of Aironet IEs per WLAN that you can enable or disable. The default is disabled.Aironet IE
Diagnostic channel support on the WLAN that you can enable or disable. The default is disabled.Diagnostic Channel
Peer-to-peer blocking settings that you can choose from the following:
• Disabled—(Default) Disables peer-to-peer blocking and bridges traffic locally within the
switch whenever possible.
• Drop—Causes the switches to discard the packets.
• Forward-UpStream—Causes the packets to be forwarded on the upstream VLAN. The
device above the switches decides what action to take regarding the packets.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
40 OL-32353-01
Page 51

Configuring WLANs
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI)
DescriptionParameter
Client Exclusion
Timeout Value (secs)
Max Allowed Client
DHCP
DHCP Server IP
Address
DHCP Address
Assignment Required
Timeout in seconds for disabled client machines that you can enable or disable. Client machines
are disabled by their MAC address and their status can be observed on the Clients > Details
page. A timeout setting of 0 indicates that the client is disabled permanently. Administrative
control is required to reenable the client. The default is enabled and the timeout setting is
configured as 60 seconds.
The minimum timeout value allowed is 0 seconds and the maximum timeout value allowed is
2147483647 seconds.
Maximum clients allowed per Switch.
You can set a limit to the number of clients that can connect to a WLAN. This feature is useful
in scenarios where you have a limited number of clients that can connect to a Switch. You can
set a limit on the number of guest clients that can access a given WLAN. The number of clients
that you can configure per WLAN depends on the platform that you are using. A maximum of
up to 12000 clients are supported.
Note
The maximum number of clients per WLAN feature is supported only for access points
that are in connected mode.
Enter the DHCP server on the WLAN that overrides the DHCP server address on the interface
assigned to the WLAN.
Enables the DHCP address assignment and makes it mandatory for clients to get their IP address
from the DHCP server.
Enables the DHCP82 payload on the WLAN.DHCP Option 82
DHCP option 82
Format
Specifies the DHCP option 82 format. Values are as follows:
• add-ssid— Set RemoteID format that is the AP radio MAC address and SSID.
• ap-ethmac—Set RemoteID format that is the AP Ethernet MAC address.
Note
DHCP Option ASCII
Mode
Configures ASCII for DHCP Option 82. If this is not configured, the option 82 format is set
to ASCII format.
Adds the Cisco 2 Byte RID for DHCP option 82.DHCP Option 82 RID
Mode
NAC
Enables the NAC on the WLAN.NAC State
Off Channel Scanning Defer
If the format option is not configured, only the AP radio MAC address is
used.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 41
Page 52

Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI)
DescriptionParameter
Configuring WLANs
Scan Differ Priority
Defer priority for the channel scan that you can assign by clicking on the priority argument.
The valid range for the priority is 0 to 7. The priority is 0 to 7 (this value should be set to 6 on
the client and on the WLAN).
Multiple values can be set. The default values are 4, 5 and 6.
Scan Differ Time
Channel scan defer time in milliseconds that you can assign. The valid range is 100 (default)
to 60000 (60 seconds). This setting should match the requirements of the equipment on your
wireless LAN.
Override Interface ACL
IPv4 ACL
IPv6 ACL
The WLANs IPv4 ACL group. Values are as follows:
The WLANs IPv6 ACL group. Values are as follows:
Un-configured
•
Pre-auth_ipv4_acl
•
Un-configured
•
Pre-auth_ipv6_acl
•
Step 6
Click Apply.
Related Topics
Band Selection, on page 24
Off-Channel Scanning Defer
DTIM Period
Session Timeout
Cisco Client Extensions, on page 25
Peer-to-Peer Blocking, on page 26
Diagnostic Channel
Client Count Per WLAN
Prerequisites for WLANs, on page 21
Restrictions for WLANs, on page 22
Information About the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, on page 48
Internal DHCP Servers, on page 49
External DHCP Servers, on page 49
DHCP Assignments, on page 50
Information About DHCP Option 82, on page 51
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
42 OL-32353-01
Page 53

Configuring WLANs
Configuring DHCP Scopes, on page 51
Information About DHCP Scopes, on page 52
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 48
Applying a QoS Policy on a WLAN (GUI)
Applying a QoS Policy on a WLAN (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Choose Configuration > Wireless.
Expand the WLAN node by clicking on the left pane and choose WLANs.
The WLANs page is displayed.
Select the WLAN for which you want to configure the QoS policies by clicking on the WLAN Profile.
Click the QoS tab to configure the QoS policies on the WLAN.
You can also configure precious metal policies for the WLAN.
The following options are available:
DescriptionParameter
QoS SSID Policy
Egress Policy
QoS downstream policy configuration.
The Existing Policy column displays the current applied policy. To change the existing policy,
select the policy from the drop-down list in the Assign Policy column.
If a policy is not selected, NONE is displayed.
Ingress Policy
QoS upstream policy configuration.
The Existing Policy column displays the current applied policy. To change the existing policy,
select the policy from the drop-down list in the Assign Policy column.
If a policy is not selected, NONE is displayed.
QoS Client Policy
Egress Policy
QoS downstream policy configuration.
The Existing Policy column displays the current applied policy. To change the existing policy,
select the policy from the drop-down list in the Assign Policy column.
If a policy is not selected, NONE is displayed.
Ingress Policy
QoS upstream policy configuration.
The Existing Policy column displays the current applied policy. To change the existing policy,
select the policy from the drop-down list in the Assign Policy column.
If a policy is not selected, NONE is displayed.
WMM
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 43
Page 54

Monitoring WLAN Properties (CLI)
Configuring WLANs
DescriptionParameter
WMM Policy. This parameter has the following values:
• Disabled—Disables this WMM policy.
• Allowed—Allows the clients to communicate with the WLAN.
• Require—Ensures that it is mandatory for the clients to have WMM features enabled on
them to communicate with the WLAN.
Step 5
WMM Policy
Click Apply.
Monitoring WLAN Properties (CLI)
show wlan id wlan-id
show wlan name wlan-name
DescriptionCommand
Displays WLAN properties based on the WLAN ID.
Displays WLAN properties based on the WLAN
name.
show wlan summary
show running-config wlan wlan-name
show running-config wlan
Displays WLAN properties of all configured WLANs.show wlan all
Displays a summary of all WLANs. The summary
details includes the following information:
WLAN ID
•
Profile name
•
SSID
•
VLAN
•
Status
•
Displays the running configuration of a WLAN based
on the WLAN name.
Displays the running configuration of all WLANs.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
44 OL-32353-01
Page 55

Configuring WLANs
Viewing WLAN Properties (GUI)
Before You Begin
You must have administrator privileges.
•
Viewing WLAN Properties (GUI)
Step 1
Step 2
Select Configuration > WLAN
The WLANs page is displayed.
Click the WLAN Profile link.
The WLANs > Edit page is displayed. The WLANs page contains the following tabs:
General : Displays the WLAN general properties.
•
Security: Displays the security properties. The properties include Layer 2, Layer 3, and AAA properties.
•
QoS: Displays the QoS configuration properties.
•
Advanced: Displays the advanced properties.
•
Where to Go Next
Proceed to configure DHCP for WLANs.
Additional References
Related Documents
Document TitleRelated Topic
WLAN command reference
Mobility Anchor configuration
WebAuth Configuration
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 45
WLAN Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release
3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Mobility Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release
3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Security Configuration Guide (Catalyst 3650
Switches)
Page 56

Feature Information for WLANs
Error Message Decoder
Configuring WLANs
LinkDescription
To help you research and resolve system error
messages in this release, use the Error Message
Decoder tool.
MIBs
All supported MIBs for this release.
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/
index.cgi
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB
Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
LinkDescription
http://www.cisco.com/support
Feature Information for WLANs
This table lists the features in this module and provides links to specific configuration information:
ModificationReleaseFeature
Cisco IOS XE 3.3SEWLAN Functionality
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
46 OL-32353-01
This feature was
introduced.
Page 57

Configuring DHCP for WLANs
Finding Feature Information, page 47
•
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, page 47
•
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, page 48
•
Information About the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, page 48
•
How to Configure DHCP for WLANs, page 52
•
Additional References, page 56
•
Feature Information for DHCP for WLANs, page 57
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature
information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information
about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported,
see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not
required.
CHAPTER 4
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs
To be able to use the DHCP option 82, you must configure DHCP on Cisco IOS software. By default,
•
DHCP option 82 is enabled for all clients. You can control the wireless client behavior using the WLAN
suboptions.
It is recommended to enable dhcp snooping on the Switches irrespective of the DHCP address requirement
•
being checked or unchecked on the WLAN. This avoids any client connectivity issues when DHCP
snopping is not turned on.
This example shows how to enable DHCP snooping on the Switches:
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping 136, 139
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 47
Page 58

Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping trust
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping trust
Related Topics
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI), on page 52
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Information About the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, on page 48
Internal DHCP Servers, on page 49
External DHCP Servers, on page 49
DHCP Assignments, on page 50
Information About DHCP Option 82, on page 51
Configuring DHCP Scopes, on page 51
Information About DHCP Scopes, on page 52
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs
Configuring DHCP for WLANs
If you override the DHCP server in a WLAN, you must ensure that you configure the underlying Cisco
•
IOS configuration to make sure that the DHCP server is reachable.
WLAN DHCP override works only if DHCP service is enabled on the switch.
•
You can configure DHCP service in the following ways:
Configuring the DHCP pool on the switch.
◦
Configuring a DHCP relay agent on the SVI. Note: the VLAN of the SVI must be mapped to the
◦
WLAN where DHCP override is configured.
Related Topics
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI), on page 52
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Information About the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, on page 48
Internal DHCP Servers, on page 49
External DHCP Servers, on page 49
DHCP Assignments, on page 50
Information About DHCP Option 82, on page 51
Configuring DHCP Scopes, on page 51
Information About DHCP Scopes, on page 52
Information About the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
You can configure WLANs to use the same or different Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers
or no DHCP server. Two types of DHCP servers are available: internal and external.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
48 OL-32353-01
Page 59

Configuring DHCP for WLANs
Related Topics
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI), on page 52
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 48
Internal DHCP Servers
The switches contain an internal DHCP server. This server is typically used in branch offices that do not
already have a DHCP server. The wireless network generally contains a maximum of 10 access points or
fewer, with the access points on the same IP subnet as the switch. The internal server provides DHCP addresses
to wireless clients, direct-connect access points, and DHCP requests that are relayed from access points. Only
lightweight access points are supported. When you want to use the internal DHCP server, you must set the
management interface IP address of the switch as the DHCP server IP address.
DHCP option 43 is not supported on the internal server. Therefore, the access point must use an alternative
method to locate the management interface IP address of the switch, such as local subnet broadcast, Domain
Name System (DNS), or priming.
An internal DHCP server pool only serves the wireless clients of that switch, not clients of other switches.
Also, an internal DHCP server can serve only wireless clients, not wired clients.
When clients use the internal DHCP server of the switch, IP addresses are not preserved across reboots. As
a result, multiple clients can be assigned with the same IP address. To resolve any IP address conflicts, clients
must release their existing IP address and request a new one. Wired guest clients are always on a Layer 2
network connected to a local or foreign switch.
Internal DHCP Servers
DHCPv6 is not supported in the internal DHCP servers.Note
Related Topics
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI), on page 52
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 48
External DHCP Servers
The operating system is designed to appear as a DHCP Relay to the network and as a DHCP server to clients
with industry-standard external DHCP servers that support DHCP Relay, which means that each switch appears
as a DHCP Relay agent to the DHCP server and as a DHCP server at the virtual IP address to wireless clients.
Because the switch captures the client IP address that is obtained from a DHCP server, it maintains the same
IP address for that client during intra switch, inter switch, and inter-subnet client roaming.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 49
Page 60

DHCP Assignments
External DHCP servers can support DHCPv6.Note
Related Topics
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI), on page 52
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 48
DHCP Assignments
You can configure DHCP on a per-interface or per-WLAN basis. We recommend that you use the primary
DHCP server address that is assigned to a particular interface.
You can assign DHCP servers for individual interfaces. You can configure the management interface,
AP-manager interface, and dynamic interface for a primary and secondary DHCP server, and you can configure
the service-port interface to enable or disable DHCP servers. You can also define a DHCP server on a WLAN.
In this case, the server overrides the DHCP server address on the interface assigned to the WLAN.
Configuring DHCP for WLANs
Note
Security Considerations
For enhanced security, we recommend that you require all clients to obtain their IP addresses from a DHCP
server. To enforce this requirement, you can configure all WLANs with a DHCP Addr. Assignment Required
setting, which disallows client static IP addresses. If DHCP Addr. Assignment Required is selected, clients
must obtain an IP address via DHCP. Any client with a static IP address is not allowed on the network. The
switch monitors DHCP traffic because it acts as a DHCP proxy for the clients.
WLANs that support management over wireless must allow management (device-servicing) clients to
obtain an IP address from a DHCP server.
If slightly less security is tolerable, you can create WLANs with DHCP Addr. Assignment Required disabled.
Clients then have the option of using a static IP address or obtaining an IP address from a designated DHCP
server.
DHCP Addr. Assignment Required is not supported for wired guest LANs.Note
You can create separate WLANs with DHCP Addr. Assignment Required configured as disabled. This is
applicable only if DHCP proxy is enabled for the switch. You must not define the primary/secondary
configuration DHCP server you should disable the DHCP proxy. These WLANs drop all DHCP requests and
force clients to use a static IP address. These WLANs do not support management over wireless connections.
Related Topics
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI), on page 52
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
50 OL-32353-01
Page 61

Configuring DHCP for WLANs
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 48
Information About DHCP Option 82
DHCP option 82 provides additional security when DHCP is used to allocate network addresses. It enables
the switch to act as a DHCP relay agent to prevent DHCP client requests from untrusted sources. You can
configure the switch to add option 82 information to DHCP requests from clients before forwarding the
requests to the DHCP server.
Figure 1: DHCP Option 82
Information About DHCP Option 82
The access point forwards all DHCP requests from a client to the switch. The switch adds the DHCP option
82 payload and forwards the request to the DHCP server. The payload can contain the MAC address or the
MAC address and SSID of the access point, depending on how you configure this option.
Any DHCP packets that already include a relay agent option are dropped at the switch.Note
For DHCP option 82 to operate correctly, DHCP proxy must be enabled.
Related Topics
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI), on page 52
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 48
Configuring DHCP Scopes
Related Topics
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI), on page 52
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 51
Page 62

How to Configure DHCP for WLANs
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 48
Information About DHCP Scopes
Switches have built-in DHCP relay agents. However, when you desire network segments that do not have a
separate DHCP server, the switches can have built-in DHCP scopes that assign IP addresses and subnet masks
to wireless clients. Typically, one switch can have one or more DHCP scopes that each provide a range of IP
addresses.
DHCP scopes are needed for internal DHCP to work. Once DHCP is defined on the switch, you can then
point the primary DHCP server IP address on the management, AP-manager, and dynamic interfaces to the
switch’s management interface.
Related Topics
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI), on page 52
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (GUI), on page 39
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 48
Configuring DHCP Scopes (CLI), on page 55
Configuring DHCP for WLANs
How to Configure DHCP for WLANs
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI)
Use this procedure to configure the following DHCP parameters on a WLAN:
DHCP Option 82 Payload
•
DHCP Required
•
DHCP Override
•
Before You Begin
You must have admin privileges for configuring the WLAN.
•
To configure the DHCP override, you must have the IP address of the DHCP server.
•
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
52 OL-32353-01
Page 63

Configuring DHCP for WLANs
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
configure terminal
1.
shutdown
2.
wlan profile-name
3.
ip dhcp opt82 {ascii | format {add-ssid | ap-ethmac} | rid}
4.
ip dhcp required
5.
ip dhcp server ip-address
6.
no shutdown
7.
end
8.
show wlan wlan-name
9.
PurposeCommand or Action
Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI)
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Example:
Switch(config)# shutdown
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
ip dhcp opt82 {ascii | format {add-ssid |
ap-ethmac} | rid}
Example:
Switch(config)# ip dhcp opt82 format
add-ssid
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Shut down the WLAN.shutdown
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name is the
profile name of the configured WLAN.
Specifies the DHCP82 payload on the WLAN. The keyword and
arguments are as follows:
• ascii—Configures ASCII for DHCP Option 82. If this is not
configured, the option 82 format is set to ASCII format.
• format—Specifies the DHCP option 82 format. The following
options are available:
• add-ssid—Set RemoteID format that is the AP radio MAC
address and SSID.
• ap-ethmac—Set RemoteID format that is the AP Ethernet
MAC address.
Note
If the format option is not configured, only the AP
radio MAC address is used.
• rid—Adds the Cisco 2 byte RID for DHCP option 82.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 53
Page 64

Configuring DHCP for WLANs (CLI)
Configuring DHCP for WLANs
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
ip dhcp required
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# ip dhcp required
ip dhcp server ip-address
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# ip dhcp server
200.1.1.2
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# no shutdown
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
show wlan wlan-name
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# show wlan test-wlan
Makes it mandatory for clients to get their IP address from the DHCP
server. Static clients are not allowed.
Defines a DHCP server on the WLAN that overrides the DHCP server
address on the interface assigned to the WLAN.
Restarts the WLAN.no shutdown
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press
Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Verifies the DHCP configuration.
Related Topics
Information About the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, on page 48
Internal DHCP Servers, on page 49
External DHCP Servers, on page 49
DHCP Assignments, on page 50
Information About DHCP Option 82, on page 51
Configuring DHCP Scopes, on page 51
Information About DHCP Scopes, on page 52
Prerequisites for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 47
Restrictions for Configuring DHCP for WLANs, on page 48
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
54 OL-32353-01
Page 65

Configuring DHCP for WLANs
Configuring DHCP Scopes (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
ip dhcp pool pool-name
2.
network network-name mask-address
3.
dns-server hostname
4.
end
5.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring DHCP Scopes (CLI)
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
ip dhcp pool pool-name
Example:
Switch(config)#ip dhcp pool test-pool
network network-name mask-address
Example:
Switch(dhcp-config)#network 209.165.200.224
255.255.255.0
dns-server hostname
Example:
Switch(dhcp-config)#dns-server example.com
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Configures the DHCP pool address.
Specifies the network number in dotted-decimal notation
and the mask address.
Specifies the DNS name server. You can specify an IP
address or a hostname.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can
also press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Related Topics
Information About DHCP Scopes, on page 52
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 55
Page 66

Additional References
Additional References
Related Documents
Configuring DHCP for WLANs
Document TitleRelated Topic
System Management
Error Message Decoder
To help you research and resolve system error
messages in this release, use the Error Message
Decoder tool.
MIBs
All supported MIBs for this release.
System Management Configuration Guide (Catalyst
3650 Switches)
LinkDescription
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/
index.cgi
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB
Locator found at the following URL:
http://cisco.com/go/mibs
Technical Assistance
LinkDescription
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
56 OL-32353-01
http://www.cisco.com/support
Page 67

Configuring DHCP for WLANs
Feature Information for DHCP for WLANs
Feature Information for DHCP for WLANs
Feature InformationReleaseFeature Name
This feature was introduced.Cisco IOS XE 3.3SEDHCP functionality for WLAN
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 57
Page 68

Feature Information for DHCP for WLANs
Configuring DHCP for WLANs
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
58 OL-32353-01
Page 69

Configuring WLAN Security
Finding Feature Information, page 59
•
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, page 59
•
Information About AAA Override, page 60
•
How to Configure WLAN Security, page 61
•
Additional References, page 69
•
Feature Information about WLAN Layer 2 Security, page 70
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature
information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information
about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported,
see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not
required.
CHAPTER 5
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security
WLANs with the same SSID must have unique Layer 2 security policies so that clients can make a WLAN
selection based on information advertised in beacon and probe responses. The available Layer 2 security
policies are as follows:
None (open WLAN)
•
Static WEP or 802.1X
•
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 59
Page 70

Information About AAA Override
Configuring WLAN Security
Note
WPA/WPA2
•
Note
Related Topics
Configuring Static WEP + 802.1X Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI), on page 61
Configuring Layer 2 Parameters (GUI), on page 66
Configuring Static WEP Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI), on page 62
Configuring Layer 2 Parameters (GUI), on page 66
Configuring WPA + WPA2 Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI), on page 63
Configuring Layer 2 Parameters (GUI), on page 66
Configuring 802.1X Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI), on page 64
Configuring Layer 2 Parameters (GUI), on page 66
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI), on page 36
Information About AAA Override, on page 60
Because static WEP and 802.1X are both advertised by the same bit in beacon and probe
responses, they cannot be differentiated by clients. Therefore, they cannot both be used
by multiple WLANs with the same SSID.
Although WPA and WPA2 cannot be used by multiple WLANs with the same SSID,
you can configure two WLANs with the same SSID with WPA/TKIP with PSK and
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA )/Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) with 802.1X,
or with WPA/TKIP with 802.1X or WPA/AES with 802.1X.
Information About AAA Override
The AAA Override option of a WLAN enables you to configure the WLAN for identity networking. It enables
you to apply VLAN tagging, Quality of Service (QoS), and Access Control Lists (ACLs) to individual clients
based on the returned RADIUS attributes from the AAA server.
Related Topics
Configuring Advanced WLAN Properties (CLI), on page 36
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
60 OL-32353-01
Page 71

Configuring WLAN Security
How to Configure WLAN Security
How to Configure WLAN Security
Configuring Static WEP + 802.1X Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI)
Before You Begin
You must have administrator privileges.
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
security static-wep-key {authentication {open | sharedkey} | encryption {104 | 40} [ascii | hex] {0|8}}
3.
wep-key wep-key-index1-4
end
4.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Step 2
Step 3
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
security static-wep-key {authentication
{open | sharedkey} | encryption {104 | 40}
[ascii | hex] {0|8}} wep-key wep-key-index1-4
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# security
static-wep-key encryption 40 hex 0 test
2
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name is the profile
name of the configured WLAN.
Configures static WEP security on a WLAN. The keywords and
arguments are as follows:
• authentication—Configures 802.11 authentication.
• encryption—Sets the static WEP keys and indices.
• open—Configures open system authentication.
• sharedkey—Configures shared key authentication.
• 104, 40—Specifies the WEP key size.
• hex, ascii—Specifies the input format of the key.
• wep-key-index , wep-key-index1-4—Type of password that follows.
A value of 0 indicates that an unencrypted password follows. A
value of 8 indicates that an AES encrypted follows.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 61
Page 72

Configuring Static WEP Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI)
Configuring WLAN Security
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 4
end
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press
Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Related Topics
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
Configuring Static WEP Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI)
Before You Begin
You must have administrator privileges.
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
security static-wep-key [authentication {open | shared} | encryption {104 | 40} {ascii | hex} [0 | 8]]
3.
end
4.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Step 2
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
Step 3
{open | shared} | encryption {104 | 40}
{ascii | hex} [0 | 8]]
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# security
static-wep-key authentication open
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name is the profile
name of the configured WLAN.
The keywords are as follows:security static-wep-key [authentication
• static-wep-key—Configures Static WEP Key authentication.
• authentication—Specifies the authentication type you can set. The
values are open and shared.
• encryption—Specifies the encryption type that you can set. The
valid values are 104 and 40. 40-bit keys must contain 5 ASCII text
characters or 10 hexadecimal characters. 104-bit keys must contain
13 ASCII text characters or 26 hexadecimal characters
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
62 OL-32353-01
Page 73

Configuring WLAN Security
Configuring WPA + WPA2 Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI)
PurposeCommand or Action
• ascii—Specifies the key format as ASCII.
• hex—Specifies the key format as HEX.
Step 4
end
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press
Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Related Topics
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
Configuring WPA + WPA2 Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI)
The default security policy is WPA2.Note
Before You Begin
You must have administrator privileges.
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
security wpa
3.
security wpa wpa1
4.
security wpa wpa1 ciphers [aes | tkip]
5.
security wpa wpa2
6.
security wpa wpa2 ciphers [aes | tkip]
7.
end
8.
DETAILED STEPS
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 63
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Page 74

Configuring 802.1X Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI)
Configuring WLAN Security
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# security wpa
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# security wpa wpa1
security wpa wpa1 ciphers [aes | tkip]
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# security wpa wpa1 ciphers
aes
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# security wpa
security wpa wpa2 ciphers [aes | tkip]
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# security wpa wpa2 ciphers
tkip
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name
is the profile name of the configured WLAN.
Enables WPA.security wpa
Enables WPA1.security wpa wpa1
Specifies the WPA1 cipher. Choose one of the following
encryption types:
• aes—Specifies WPA/AES support.
• tkip—Specifies WPA/TKIP support.
Enables WPA 2.security wpa wpa2
Configure WPA2 cipher. Choose one of the following
encryption types:
• aes—Specifies WPA/AES support.
• tkip—Specifies WPA/TKIP support.
Step 8
end
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can
also press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Related Topics
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
Configuring 802.1X Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI)
Before You Begin
You must have administrator privileges.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
64 OL-32353-01
Page 75

Configuring WLAN Security
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring 802.1X Layer 2 Security Parameters (CLI)
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
security dot1x
3.
security [authentication-list auth-list-name | encryption {0 | 104 | 40}
4.
end
5.
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# security dot1x
security [authentication-list auth-list-name |
encryption {0 | 104 | 40}
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# security encryption
104
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name is the
profile name of the configured WLAN.
Specifies 802.1X security.security dot1x
The keywords and arguments are as follows:
• authentication-list—Specifies the authentication list for IEEE
802.1X.
• encryption—Specifies the length of the CKIP encryption key.
The valid values are 0, 40, and 104. Zero (0) signifies no
encryption. This is the default.
Note
All keys within a WLAN must be of the same
size.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press
Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
Related Topics
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 65
Page 76

Configuring Layer 2 Parameters (GUI)
Configuring Layer 2 Parameters (GUI)
Before You Begin
You must have administrator privileges.
•
Configuring WLAN Security
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Click Configuration > WLAN > .
The WLANs page appears.
Click the WLANs profile of the WLAN you want to configure.
The WLANs > Edit > page appears.
Click the Security > Layer 2 > tab.
DescriptionParameter
Layer2 Security
Layer 2 security for the selected WLAN. Values are the following:
• None—No Layer 2 security selected.
• WPA+WPA2—Wi-Fi Protected Access.
• 802.1X—WEP 802.1X data encryption type. For information on these settings, see the
Layer 2 802.1X Parameters topic.
• Static WEP—Static WEP encryption parameters.
• Static WEP + 802.1x—Both Static WEP and 802.1X parameters.
MAC Filtering
MAC address filtering. You can locally configure clients by their MAC addresses in the MAC
Filters > New page . You can add a maximum of 12000 local net users. Otherwise, configure
the clients on a RADIUS server.
MAC Filtering is also known as MAC Authentication By Pass (MAB).Note
Check box to enable or disable a fast transition between access points.Fast Transition
Check box to enable or disable a fast transition over a distributed system.Over the DS
Time in seconds after which a fast transition reassociation times out.Reassociation Timeout
To configure the WPA + WPA2 parameters, provide the following details:
DescriptionParameter
Check box to enable or disable WPA policy.WPA Policy
WPA2 encryption type: TKIP or AES. Available only if the WPA policy is enabled.WPA Encryption
Check box to enable or disable WPA2 policy.WPA2 Policy.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
66 OL-32353-01
Page 77

Configuring WLAN Security
Configuring Layer 2 Parameters (GUI)
DescriptionParameter
WPA2 encryption type: TKIP or AES. Available only if the WPA2 policy is enabled.WPA2 Encryption
Authentication Key
Management
PSK Format
The rekeying mechanism parameter.. Values are the following:
802.1X
•
CCKM
•
PSK
•
802.1x + CCKM
•
Enabled when you select the PSK value for Authentication Key Management. Choose ASCII
or the HEX format and enter the preshared key.
To configure 802.1x parameters, provide the following details:
DescriptionParameter
WEP 802.11 data encryption type.802.11 data encryption
Security type.Type
Key size
Key size. Values are the following:
None
•
40 bits
•
104 bits
•
The third-party AP WLAN (17) can only be configured with 802.1X encryption. Drop-down
configurable 802.1X parameters are not available for this WLAN.
To specify Static WEP, configure the following parameters:
DescriptionParameter
Static WEP encryption type.802.11 Data
Encryption
Displays the current selected key details.Current Key
Security type.Type
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 67
Page 78

Configuring Layer 2 Parameters (GUI)
Configuring WLAN Security
DescriptionParameter
Key size
Key Index
Key size. Values are the following:
Not set
•
40 bits
•
104 bits
•
Key index from 1 to 4.
One unique WEP key index can be applied to each WLAN. Because there are only four WEP
key indexes, only four WLANs can be configured for static WEP Layer 2 encryption.
Because there are only four WEP key indexes, only four WLANs can be configured for static
WEP Layer 2 encryption.
Encryption key.Encryption Key
Encryption key format in ASCII or HEX.Key Format
Key authentication that you can enable or disable.Allow Shared Key
Authentication
To configure Static WEP + 802.1X Parameters
Static WEP Parameters
Encryption
Key size
Key Index
DescriptionParameter
Static WEP encryption type.802.11 Data
Displays the current selected key details.Current Key
Security type.Type
Key size. Values are the following:
Not set
•
40 bits
•
104 bits
•
Key index from 1 to 4.
The key index is unique per WLAN. You can only have one "key 1" on a given WLAN. You
can define up to 4 keys per WLAN, and the switch will announce the key index, to allow clients
configured the same way to know what key to use. This is per WLAN.
You can configure all your WLANs (up to 512) as WEP if you want, each with up to 4 keys.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
68 OL-32353-01
Page 79

Configuring WLAN Security
Authentication
802.1x Parameters
Encryption
Additional References
DescriptionParameter
Encryption key.Encryption Key
Encryption key format in ASCII or HEX.Key Format
Key authentication that you can enable or disable.Allow Shared Key
Static WEP encryption type.802.11 Data
Security type.Type
Key size. Values are the following:
Not set
•
40 bits
•
104 bits
•
Step 4
Key size
Click Apply.
Related Topics
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Security, on page 59
Additional References
Related Documents
Document TitleRelated Topic
WLAN command reference
Security configuration guide
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 69
WLAN Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release
3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Security Configuration Guide (Catalyst 3650
Switches)
Page 80

Feature Information about WLAN Layer 2 Security
Error Message Decoder
Configuring WLAN Security
LinkDescription
To help you research and resolve system error
messages in this release, use the Error Message
Decoder tool.
MIBs
All supported MIBs for this release.
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/
index.cgi
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB
Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
LinkDescription
http://www.cisco.com/support
Feature Information about WLAN Layer 2 Security
This table lists the features in this module and provides links to specific configuration information.
Feature InformationReleaseFeature Name
This feature was introduced.Cisco IOS XE 3.3SEWLAN Security functionality
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
70 OL-32353-01
Page 81

Configuring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Finding Feature Information, page 71
•
Restrictions for the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy, page 71
•
Information About the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy, page 71
•
How to Configure Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy, page 72
•
Additional References for Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy, page 74
•
Feature Information about Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy, page 75
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature
information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information
about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported,
see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not
required.
CHAPTER 6
Restrictions for the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy is applicable to WLANs that have APs in local mode only.
Information About the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Devices that are Wi-Fi Direct capable can connect directly to each other quickly and conveniently to do tasks
such as printing, synchronization, and sharing of data. Wi-Fi Direct devices may associate with multiple
peer-to-peer (P2P) devices and with infrastructure wireless LANs (WLANs) concurrently. You can use the
switch to configure the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy, on a per WLAN basis, where you can allow or disallow
association of Wi-Fi devices with infrastructure WLANs, or disable Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy altogether for
WLANs.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 71
Page 82

How to Configure Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Related Topics
Configuring the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI), on page 72
Disabling Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI), on page 73
Monitoring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI), on page 74
How to Configure Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Configuring the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
wifidirect policy {permit | deny }
3.
end
4.
Configuring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
Step 2
Step 3
wlan profile-name
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)#
wifidirect policy permit
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name is the profile name of
the configured WLAN.
Configures the Wi-Fi Direct client policy on the WLAN using one of the following:wifidirect policy {permit | deny }
• permit—Enables Wi-Fi Direct clients to associate with the WLAN.
• deny—When the Wi-Fi Direct policy is configured as "deny," the switch
permits or denies Wi-Fi Direct devices based on the device capabilities. A
Wi-Fi Direct device reports these capabilities in its association request to the
switch and these are based on the Wi-Fi capabilities of the device. These
include:
Concurrent operation
•
Cross connection
•
Note
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
72 OL-32353-01
The command no wifidirect policy ignores the client's Wi-Fi direct
status. Additionally, the access point also does not advertise any
beacons and probes. Effectively, the no form of the command disables
the Wi-Fi direct feature on the WLAN.
Page 83

Configuring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Disabling Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI)
PurposeCommand or Action
If the Wi-Fi device supports either concurrent operations or cross connections
or both, the client association is denied. The client can associate if the device
does not support concurrent operations and cross connections.
Step 4
end
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-z to exit
global configuration mode.
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# end
Related Topics
Information About the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy, on page 71
Monitoring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI), on page 74
Disabling Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI)
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
wlan profile-name
2.
no wifidirect policy
3.
end
4.
DETAILED STEPS
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
Step 2
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
wlan profile-name
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Enters the WLAN configuration submode. The profile-name is
the profile name of the configured WLAN.
Example:
Switch# wlan test4
Step 3
no wifidirect policy
Ignores the Wi-Fi Direct status of clients thereby allowing Wi-Fi
Direct clients to associate.
Example:
Switch(config)# no wifidirect policy
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 73
Page 84

Monitoring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI)
Configuring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 4
end
Example:
Switch(config-wlan)# end
Related Topics
Information About the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy, on page 71
Monitoring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI), on page 74
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also
press Ctrl-z to exit global configuration mode.
Monitoring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI)
The following commands can be used to monitor Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy:
DescriptionCommand
show wireless client wifidirect stats
Displays the total number of clients associated and the number
of association requests rejected if the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
is enabled.
Displays status of the Wi-Fi Direct on the WLAN.show wlan summary
Displays the detail information of a client.show wireless cli mac-address
mac-address
Related Topics
Configuring the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI), on page 72
Disabling Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy (CLI), on page 73
Information About the Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy, on page 71
Additional References for Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Related Documents
Document TitleRelated Topic
WLAN Command reference
WLAN Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release
3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
74 OL-32353-01
Page 85

Configuring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Error Message Decoder
Feature Information about Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
LinkDescription
To help you research and resolve system error
messages in this release, use the Error Message
Decoder tool.
MIBs
All Supported MIBs for this release.
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/
index.cgi
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB
Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
LinkDescription
http://www.cisco.com/support
Feature Information about Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Feature InformationReleaseFeature Name
This feature was introduced.Cisco IOS XE 3.3SEWi-Fi Direct Feature
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 75
Page 86

Feature Information about Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
Configuring Wi-Fi Direct Client Policy
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
76 OL-32353-01
Page 87

Configuring Access Point Groups
Finding Feature Information, page 77
•
Prerequisites for Configuring AP Groups, page 77
•
Restrictions for Configuring Access Point Groups, page 78
•
Information About Access Point Groups, page 78
•
How to Configure Access Point Groups, page 79
•
Additional References, page 81
•
Feature History and Information for Access Point Groups, page 82
•
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature
information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information
about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported,
see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not
required.
CHAPTER 7
Prerequisites for Configuring AP Groups
The following are the prerequisites for creating access point groups on a switch:
The required access control list (ACL) must be defined on the router that serves the VLAN or subnet.
•
Multicast traffic is supported with access point group VLANs. However, if the client roams from one
•
access point to another, the client might stop receiving multicast traffic, unless IGMP snooping is enabled.
Related Topics
Information About Access Point Groups, on page 78
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 77
Page 88

Configuring Access Point Groups
Restrictions for Configuring Access Point Groups
Restrictions for Configuring Access Point Groups, on page 78
Restrictions for Configuring Access Point Groups
Suppose that the interface mapping for a WLAN in the AP group table is the same as the WLAN interface.
•
If the WLAN interface is changed, the interface mapping for the WLAN in the AP group table also
changes to the new WLAN interface.
Suppose that the interface mapping for a WLAN in the AP group table is different from the one defined
for the WLAN. If the WLAN interface is changed, then the interface mapping for the WLAN in the AP
group table does not change to the new WLAN interface.
If you clear the configuration on the switch, all of the access point groups disappear except for the default
•
access point group “default-group,” which is created automatically.
The default access point group can have up to 16 WLANs associated with it. The WLAN IDs for the
•
default access point group must be less than or equal to 16. If a WLAN with an ID greater than 16 is
created in the default access point group, the WLAN SSID will not be broadcasted. All WLAN IDs in
the default access point group must have an ID that is less than or equal to 16. WLANs with IDs greater
than 16 can be assigned to custom access point groups.
Related Topics
Information About Access Point Groups, on page 78
Prerequisites for Configuring AP Groups, on page 77
Information About Access Point Groups
After you create up to 512 WLANs on the switch, you can selectively publish them (using access point groups)
to different access points to better manage your wireless network. In a typical deployment, all users on a
WLAN are mapped to a single interface on the switch. Therefore, all users that are associated with that WLAN
are on the same subnet or VLAN. However, you can choose to distribute the load among several interfaces
or to a group of users based on specific criteria such as individual departments (such as Marketing) by creating
access point groups. Additionally, these access point groups can be configured in separate VLANs to simplify
network administration.
Related Topics
Creating Access Point Groups, on page 79
Viewing Access Point Group, on page 80
Assigning an Access Point to an AP Group, on page 80
Prerequisites for Configuring AP Groups, on page 77
Restrictions for Configuring Access Point Groups, on page 78
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
78 OL-32353-01
Page 89

Configuring Access Point Groups
How to Configure Access Point Groups
Creating Access Point Groups
Before You Begin
You must have administrator privileges to perform this operation.
SUMMARY STEPS
configure terminal
1.
ap group ap-group-name
2.
wlan wlan-name
3.
(Optional) vlan vlan-name
4.
end
5.
How to Configure Access Point Groups
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Switch# configure terminal
ap group ap-group-name
Example:
Switch(config)# ap group my-ap-group
wlan wlan-name
Example:
Switch(config-apgroup)# wlan wlan-name
vlan vlan-name
Example:
Switch(config-apgroup)# vlan test-vlan
end
Example:
Switch(config)# end
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.configure terminal
Creates an access point group.
Associates the AP group to a WLAN.
(Optional)
Assigns the access point group to a VLAN.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you
can also press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode.
This example shows how to create an AP group:
Switch# configure terminal
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 79
Page 90

Assigning an Access Point to an AP Group
Switch(config-apgroup)# ap group test-ap-group-16
Switch(config-wlan-apgroup)# wlan test-ap-group-16
Switch(config-wlan-apgroup)# vlan VLAN1300
Related Topics
Information About Access Point Groups, on page 78
Assigning an Access Point to an AP Group
Before You Begin
You must have administrator privileges to perform this operation.
SUMMARY STEPS
ap name ap-name ap-group-name ap-group
1.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Access Point Groups
Step 1
ap name ap-name ap-group-name
ap-group
Example:
Switch# ap name 1240-101
ap-groupname apgroup_16
Related Topics
Information About Access Point Groups, on page 78
Viewing Access Point Group
Before You Begin
PurposeCommand or Action
Assigns the access point to the access point group. The keywords and arguments
are as follows:
• name—Specifies that the argument following this keyword is the name of
an AP that is associated to the switch.
• ap-name—AP that you want to associate to the AP group.
• ap-group-name—Specifies that the argument following this keyword is the
name of the AP group that is configured on the switch.
• ap-group—Name of the access point group that is configured on the switch.
You must have administrator privileges to perform this operation.
SUMMARY STEPS
show ap groups [extended ]
1.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
80 OL-32353-01
Page 91

Configuring Access Point Groups
DETAILED STEPS
Additional References
PurposeCommand or Action
Step 1
show ap groups [extended ]
Example:
Switch# show ap groups
Related Topics
Information About Access Point Groups, on page 78
Additional References
Related Documents
WLAN commands
Lightweight Access Point configuration
Lightweight Access Point commands
Displays the AP groups configured on the switch. The extended
keyword displays all AP Groups information defined in the system
in detail.
Document TitleRelated Topic
WLAN Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release
3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Lightweight Access Point Configuration Guide, Cisco
IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Lightweight Access Point Command Reference, Cisco
IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
Error Message Decoder
LinkDescription
To help you research and resolve system error
messages in this release, use the Error Message
Decoder tool.
MIBs
All supported MIBs for this release.
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 81
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/
index.cgi
MIBs LinkMIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms,
Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB
Locator found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs
Page 92

Feature History and Information for Access Point Groups
Technical Assistance
Configuring Access Point Groups
LinkDescription
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online
resources, including documentation and tools for
troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies.
To receive security and technical information about
your products, you can subscribe to various services,
such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field
Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter,
and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
http://www.cisco.com/support
Feature History and Information for Access Point Groups
This table lists the features in this modules and provides links to specific configuration information.
Feature InformationReleaseFeature Name
This feature was introduced.Cisco IOS XE 3.3SEAP Groups
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
82 OL-32353-01
Page 93

INDEX
C
CCX 25
described 25
D
default-group access point group 78
DHCP option 82 51
described 51
example 51
DHCP servers 49
internal 49
diagnostic channel 26
described 26
DTIM 25
P
peer-to-peer blocking 26
described 26
Precious Metal Policies 43
configuring using GUI 43
Q
QoS Policy, WLAN 43
configuring using GUI 43
S
SSID 23
described 23
W
WLAN broadcast ssid, Configure 33
WLAN call snoop, Configure 33
WLAN interface VLAN, Configure 33
WLAN media stream multicast, Configure 33
WLAN radio, Configure 33
WLAN, enable, disable 33
WLANs 25
session timeout 25
described 25
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-32353-01 IN-1
Page 94

Index
WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
IN-2 OL-32353-01
 Loading...
Loading...