Page 1

Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release
8.6(4)
First Published: June 21, 2012
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-27022-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH
THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY,
CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB's public domain version
of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright©1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS.
CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: http://
www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown
for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
©
2012 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface
PART I
CHAPTER 1
Preface xvii
Purpose xvii
Audience xvii
Organization xvii
Conventions xviii
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request xix
Cisco Product Security Overview xix
Introduction to Cisco Business Edition 3000 1
Overview of Cisco Business Edition 3000 3
Benefits of Deploying Cisco Business Edition 3000 3
Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System 3
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 Server 4
USB Support 5
Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File 7
Phones 8
Attendant Console 9
Video Support 9
Voicemail 10
Auto Attendant 13
Gateway 15
SPA8800 Gateway 18
OL-27022-01 iii
Overview 19
Configure the Related Connections on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 GUI 19
Add SPA8800 connections from the PSTN Connections page 19
Edit SPA8800 connections from the PSTN Connections page 20
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 4

Contents
Delete SPA8800 connections from the PSTN Connections page 20
Configure the SPA8800 Analog Phones on the Cisco Business Edition 3000
GUI 21
Add a SPA8800 analog phone from the Phones page 21
Edit a SPA8800 analog phone from the Phones page 21
Delete a SPA8800 analog phone from the Phones page 22
Edit SPA8800 devices from the Devices page 22
Delete SPA8800 devices from the Devices page 22
DID and ELIN configuration 22
PSTN Connection Settings 23
Perform the Initial Setup on the SPA8800 for IP Addresses using SPA Interactive
Voice Response 23
Configure settings for TFTP on the SPA8800 GUI 24
SPA8800 Feature Codes 25
SPA8800 Limitations 25
SIP Trunking 26
Limitations of SIP Trunking 27
E1 R2 Connections 28
Connection Pack 28
Installing the Connection Pack File 29
Carrier Selection Profiles for Brazil 30
Connection Groups 31
Best Practices for Using DHCP for Acquiring IP Addresses 32
IP Addressing 32
DNS and Hostname Resolution 33
SFTP Server 33
Support for Computer Telephony Integration 34
Support for Voicemail with Email Integration 34
Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000 35
Network Settings 35
Dial Plans 36
Sites 39
Remote Management of Cisco Business Edition 3000 using Cisco OnPlus 42
Usage Profiles 44
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
iv OL-27022-01
Signing on to Cisco Business Edition 3000 using Cisco Onplus 43
Page 5
Contents
Users, Departments, Phones, and Lines 46
Significant Behavior of SIP Trunk 48
Incoming 302 Moved Temporarily 48
Incoming OOD REFER Message Handling 49
Calling Party Transformation 49
Connected Party Transformation 50
Attendant Group 50
Hunt Lists 51
Call Pickup Groups 51
Example of Typical Deployment Model 53
CHAPTER 2
CHAPTER 3
Frequently Asked Questions 55
Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard 67
Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface 67
Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface 68
Accessing the Icons on the Page 68
Accessing the Buttons On the Page 69
Finding Your Configuration 69
Deleting Your Configuration 70
Adding Your Configuration 71
Editing Your Configuration 71
Copying (Duplicating) Configuration 72
MCS 7890-C1 will not power up. Why not? 72
Connecting a USB DVD Drive 73
Disconnecting a USB DVD Drive 73
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File 75
When You Can Use the Cisco-provided .xls Data Configuration File 75
Considerations for Using the Cisco-provided .xls Data Configuration File 76
For Both the Initial Deployment and Bulk Insertion of Users and Phones After Initial
For the Initial Deployment Only 77
For Bulk Insertion of Users and Phones After Initial Deployment 78
Network Tab Settings 78
Date and Time Tab Settings 80
OL-27022-01 v
Deployment 77
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 6

Contents
PSTN Gateway Tab Settings 80
Dial Plan Tab Settings 81
Block Rules Tab Settings 83
Abbreviated Dialing Tab Settings 83
Sites Tab Settings 84
Usage Profiles Tab Settings 86
Phones Tab Settings 89
Users Tab Settings 91
CHAPTER 4
Cisco User Connect Licensing 95
Checklist for Licensing Before You Add a Phone to the System 95
Understanding How Licensing Works 96
Understanding The License Types 97
Understanding How Borrowing and Loaning of Licenses Works 99
Interactions and Restrictions 101
Working with Licenses 101
Obtaining Licenses 101
Installing a License File 102
Viewing Contents of the License File 103
Viewing Status for Licensing 103
Viewing the Number of Licenses That Are Used and Available 103
Backing Up and Restoring License Files 104
Deleting License Files 104
Understanding the Error Messages for Licensing 104
CHAPTER 5
Phone Features 107
Ad hoc Conference 108
Barge 108
Call Back 109
Call Divert 110
Call Forward All 112
Call Forward Busy 112
Call Forward No Answer 112
Call Hold and Resume 113
Call History 113
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
vi OL-27022-01
Page 7

Contents
Call Park 113
Call Pickup 114
Call Transfer (Direct and Consultative) 114
Call Waiting 114
Caller ID 115
Cisco Extension Mobility 115
Cisco Web Dialer 116
Click to Call 116
Distinctive Ringing 116
Do Not Disturb 116
Meet-Me Conference 117
Music On Hold 118
PART II
CHAPTER 6
Mute/Volume Control 119
Phone Applications 119
Reach Me Anywhere 119
Rollover Lines 120
Shared Lines 120
Speed Dials 121
Busy Lamp Feature (BLF) 121
Voicemail 122
Checklists for Common Configuration Tasks 123
Checklists To Review Before Deployment 125
Gathering Customer Data Before a Deployment 125
Setting Up the Customer Network and Central Site 126
Using a Cable to Set Up Server Access to the Network 127
Using the Cisco Network Configuration USB Flash Drive 128
Questions to Ask Your Customer 129
CHAPTER 7
Checklists for Configuring the Gateway 133
Installing the Gateway 133
Configuring the Gateway for the First Time 133
Editing the Gateway Configuration 135
Deleting the Gateway 137
OL-27022-01 vii
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 8

Contents
CHAPTER 8
Checklists for Users, Departments, Lines, and Phones 139
Adding a User to the System 140
Adding a Phone for a User 141
Adding a Department and a Public-Space Phone 143
Setting Up the Cisco VG224 Analog Phone Gateway for Fax 143
Setting Up Ad hoc Conferences 144
Setting Up Barge 144
Setting Up Call Divert 144
Setting Up Call Forward All 145
Setting Up Call Forward Busy 145
Setting Up Call Forward No Answer 145
Setting Up Call Park 146
Setting Up Call Pickup 146
Setting Up Cisco Extension Mobility 146
Setting Up Do Not Disturb 147
Setting Up Meet-Me Conferences 147
Setting Up Music On Hold 147
Setting Up Phone Applications 148
Setting Up Rollover Lines 149
Setting Up Reach Me Anywhere 149
Setting Up Shared Lines 150
Setting Up Speed Dials 150
Setting Up Voicemail 150
Setting Up Attendant Group 151
Setting Up Auto Attendant 151
Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Operator 152
Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Auto Attendant 152
Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Auto Attendant if the Operator is
Not Available 153
Configuring Dial by Name on Auto Attendant 153
Configuring Cisco Mobile Client Support for Users 154
Checklist for Configuring Cisco Mobile Client Support for Users 155
CHAPTER 9
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
viii OL-27022-01
Checklists for Backups, Upgrades, and Configuration Export 157
Page 9

Contents
Backing Up Your Data 157
Upgrading Cisco Business Edition 3000 158
Reverting to a Previous Version of Cisco Business Edition 3000 160
Exporting Your Data and Importing to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business
Edition 5000 160
PART III
CHAPTER 10
CHAPTER 11
CHAPTER 12
CHAPTER 13
CHAPTER 14
CHAPTER 15
Field Descriptions for the Graphical User Interfaces 163
Add or Edit Call Pickup Group Settings 165
Administrator Settings 169
Attendant Group Settings 173
Auto Attendant Settings 175
Auto Attendant with One Menu for All Hours 175
Auto Attendant with Different Menus for Open and Closed Hours 177
Backup Settings 181
Call Detail Reports 185
Date Range and Time Zone 186
Summary Tab 186
Call Details Tab 187
Call Details Report Offloading 189
Remote Server Parameter Settings 190
Customize Call Classification Settings 191
CHAPTER 16
CHAPTER 17
CHAPTER 18
CHAPTER 19
OL-27022-01 ix
Carrier Selection Profiles Settings 193
Country/Locale Settings 197
Cisco Extension Mobility Report 199
Configuration Export Settings 201
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 10

Contents
CHAPTER 20
CHAPTER 21
CHAPTER 22
CHAPTER 23
CHAPTER 24
Connection Groups 205
Date and Time Settings 209
Department Settings 211
Devices Settings 215
Diagnostics Settings 217
Collect Logs 217
USB Flash Drive 218
Packet Capture 219
Ping 220
Gateway Loopback 220
PCM Capture 221
CHAPTER 25
CHAPTER 26
CHAPTER 27
CHAPTER 28
CHAPTER 29
CHAPTER 30
Dial Plan Settings 223
Dial Plan Settings 223
Translation Rules Settings 226
Block Rules Settings 228
Abbreviated Dialing Settings 230
Application Dial Rules Tab Settings 232
Hunt List Settings 235
Health Summary 239
License Settings 241
Music On Hold Settings 243
Network Settings 245
CHAPTER 31
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
x OL-27022-01
Phones Settings 249
Page 11

Contents
CHAPTER 32
CHAPTER 33
CHAPTER 34
Phone Applications Settings 251
Post-Setup Wizard 253
PSTN Connection Settings 257
PSTN Connection Settings 258
Connection Type 259
Device 259
Adding/Editing a Device 261
Provider 262
Connection Settings 262
Connection Type: E1 PRI 263
Connection Type: T1 PRI 271
Connection Type: T1 CAS 280
Connection Type: SIP Trunk 283
Connection Type: FXO 294
CHAPTER 35
CHAPTER 36
CHAPTER 37
CHAPTER 38
CHAPTER 39
CHAPTER 40
Connection Type: E1 R2 300
Digit Discard Instructions Settings 308
Calling Party Transformations Settings 310
Reach Me Anywhere Settings 311
Restart/Shutdown Settings 317
Restore Settings 319
Search Settings 323
Setup Mode Settings 327
Sites Settings 329
Configuring Central Site 331
Configure Remote Site 339
Configure Remote User Site 347
OL-27022-01 xi
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 12

Contents
Configuring Logical Partitioning 354
Dial Plan Pattern Settings 355
SPA Dial Plan Patterns 358
CHAPTER 41
CHAPTER 42
CHAPTER 43
CHAPTER 44
CHAPTER 45
CHAPTER 46
System Notifications Settings 361
Summary Settings 363
Upgrade Settings 365
Installed Software Settings 371
Usage Profiles Settings 373
General Tab 373
Phone Button Template Tab 378
Phone Features Tab 379
Phone Application Tab 383
User Settings 385
CHAPTER 47
CHAPTER 48
CHAPTER 49
PART IV
CHAPTER 50
CHAPTER 51
User Preferences Settings 393
Voice Feature Settings 403
Voicemail Notification Settings 407
Troubleshooting in Cisco Business Edition 3000 409
Troubleshooting Overview 411
Troubleshooting Tools 411
Troubleshooting Tips 411
Related Topics 412
How to Diagnose a Problem 413
Troubleshooting Using MCS 7890-C1 LEDs 414
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
xii OL-27022-01
Page 13

Contents
Troubleshooting from the Health Summary Page 416
Troubleshooting From the Diagnostics Page 418
Troubleshooting When You Cannot Access the Graphical User Interfaces 419
Troubleshooting by Using Cisco Diagnostics USB 419
Troubleshooting with the Network USB Flash Drive When You Cannot Access the
Administrative Interface 422
Troubleshooting Using the System LED 424
CHAPTER 52
Troubleshooting Issues 427
A critical internal software component is down and the system must be restarted 429
The conference bridge is experiencing an issue 429
The system has reached maximum capacity for multiparty conferencing 429
A large number of devices (phones) are unable to register with the system possibly indicating
a problem with the internal network or network services 430
The gateway is experiencing an issue 430
One or more gateway ports are unable to communicate with the telephone network 431
The system is unable to communicate with the telephone network through the SIP trunk 431
Problems have been detected with the gateways connecting the system to the telephone
network 432
The system is unable to offload call detail records 432
The maximum storage capacity for call detail records has been exceeded 433
The DNS service is incorrectly configured or unreachable 433
A required service failed 433
A problem has been detected with the system hardware 434
A firmware update is required for MCS 7890 434
An MCS 7890 is experiencing hardware issues 434
An MCS 7890 requires a BIOS recovery 434
Windows 7 435
The system is experiencing sustained high CPU usage 437
The system is nearing maximum memory capacity 437
The system is nearing maximum processing capacity 437
The system has reached maximum capacity for calls going through the telephone network 438
OL-27022-01 xiii
Linux 435
Automatic Mode 436
Manual Mode 436
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 14

Contents
The system is nearing maximum call capacity 438
The system has experienced an internal software error and must be restarted 438
A phone failed to register 439
PSTN calls are not established due to the value of the Called Party type number 439
Product licensing is out of compliance 440
The system has overheated and must be powered off and then restarted 440
The system fan is not operating properly and the system must be powered off and then
restarted 440
The system CPU voltage is too high and the system must be powered off and then
restarted 440
The system has experienced an error with voicemail and auto attendant services and must
be restarted 440
The system has experienced an error with voicemail and auto attendant services and must
be restarted 441
The system has reached capacity for voicemail and auto attendant calls. Voicemail and auto
attendant services are unreachable 441
Voicemail and auto attendant capacity is reduced due to an unresponsive connection 442
The system has experienced an error with voicemail and auto attendant services and must
be restarted 442
Due to an internal problem the system is running very low on hard disk space 442
A VM/AA service is utilizing a large amount of CPU resources 442
The system has experienced an error with voicemail and auto attendant services and must
be restarted 443
How do I Enable or disable T1/E1 and ECAN Statistics Logging? 443
The phone is registered but automatically resets 444
The phone has one-way audio 444
A phone call cannot be established 444
Operator Assisted and Transit Network Dialing does not always work 445
A gateway is not listed in the Site Gateway Usage list 445
When you choose Local Gateways a remote gateway is listed in the Local Gateway list 445
Local gateway is not listed in the Local Gateway list 445
Gateways from a deleted site are no longer used 446
Problems reported with the SPA8800 446
Order of the PSTN Gateways used to route calls changes 447
Upgrade of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 software failed 447
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
xiv OL-27022-01
Page 15
Contents
Text displays in English not in my chosen locale 448
The restore of data failed 448
Cannot delete SPA8800 phone/connection 448
Unable to make calls to local mobile phone numbers 449
Outgoing PSTN calls take a long time to get established 449
Upgrade of Connection Pack fails during installation 450
Cisco OnPlus is unable to discover Cisco Business Edition 3000 450
The system is unable to connect to the outgoing email server used for sending System
Notifications email 450
The system is unable to authenticate with the outgoing email server used for sending System
Notifications 451
The system experiences an issue on generating a System Notifications email 451
CHAPTER 53
CHAPTER 54
CHAPTER 55
Reimaging or Replacing the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Server 453
Reimaging an MCS 7890-C1 453
Using a Network Cable to Set Up Server Access to the Network 456
Using the Cisco Network Configuration USB Flash Drive 457
Performing Upgrade Using an USB Flash Drive 458
Performing COP file Installation Using an USB Flash Drive 460
Performing a Server Recovery 461
Replacing the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Server 461
Cisco Business Edition 3000 TCP and UDP Port Usage 463
Port Descriptions 463
Glossary 465
References 466
IETF TCP/UDP Port Assignment List 466
Opening a Case with Cisco Technical Assistance Center 467
Information You Will Need 468
Required Preliminary Information 468
Online Cases 469
OL-27022-01 xv
Network Layout 468
Problem Description 469
General Information 469
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 16

Contents
Related Topics 469
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
xvi OL-27022-01
Page 17

Purpose
Preface
This preface describes the purpose, audience, organization, and conventions of this guide and provides
information on how to obtain related documentation.
• Purpose, page xvii
• Audience, page xvii
• Organization, page xvii
• Conventions, page xviii
• Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, page xix
• Cisco Product Security Overview, page xix
The Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000 provides conceptual information about Cisco
Business Edition 3000 and its components as well as tips for setting up features by using the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard and the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
Audience
The Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000 provides information for network administrators
who are responsible for managing the Cisco Business Edition 3000 system. This guide requires knowledge
of telephony and IP networking technology.
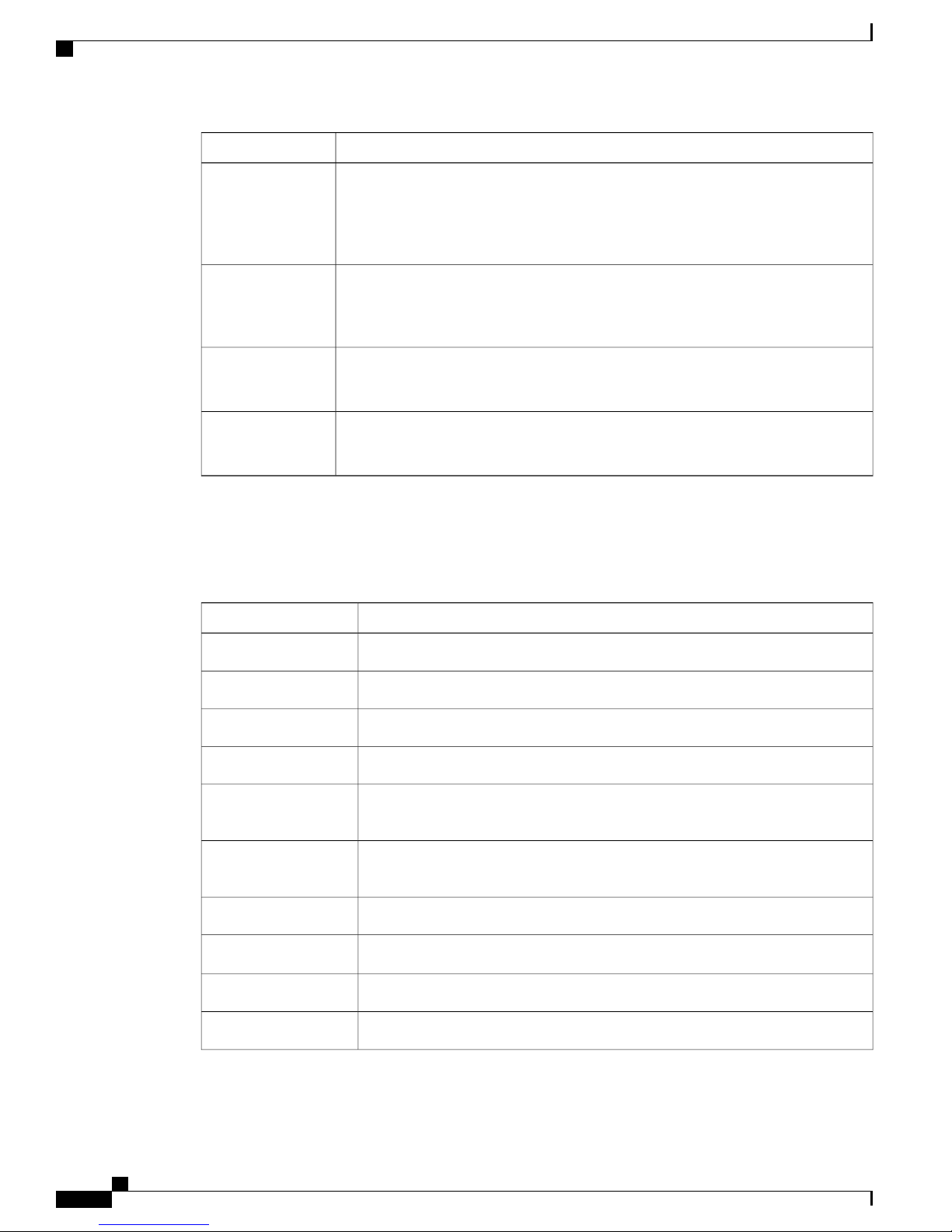
Organization
The following table shows the organization of this guide:
OL-27022-01 xvii
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 18
Conventions
Preface
DescriptionPart
Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
Part 1
Part 2
Part 3
Part 4
Introduction to Cisco Business Edition 3000
Provides an overview of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 system, including the
components that you need to use the system; provides an overview of working in the
GUIs; provides information on licensing
Configuration Checklists for Cisco Business Edition 3000
Provides information on how to perform common tasks, such as setting up music on
hold or configuring shared lines
Field Descriptions for the Graphical User Interfaces
Provides the descriptions for the fields that display in the various GUIs
Troubleshooting in Cisco Business Edition 3000
Provides information on how to troubleshoot your Cisco Business Edition 3000 system
DescriptionConvention
[ x | y | z ]
string
Commands and keywords are in boldface.boldface font
Arguments for which you supply values are in italics.italic font
Elements in square brackets are optional.[ ]
Alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars.{ x | y | z }
Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by vertical
bars.
A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string or
the string will include the quotation marks.
Terminal sessions and information the system displays are in screen font.screen font
Information you must enter is in boldface screen font.boldface screen font
Arguments for which you supply values are in italic screen font.italic screen font
This pointer highlights an important line of text in an example.——>
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
xviii OL-27022-01
Page 19

Preface
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
DescriptionConvention
Note
Caution
^
Notes use the following conventions:
Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
publication.
Tips use the following conventions:
Means the information contains useful tips.Tip
Cautions use the following conventions:
Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage
or loss of data.
The symbol ^ represents the key labeled Control - for example, the key combination
^D in a screen display means hold down the Control key while you press the D
key.
Nonprinting characters, such as passwords, are in angle brackets.< >
Warnings use the following conventions:
Warning
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you
work on any equipment, you must be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and familiar
with standard practices for preventing accidents.
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information,
see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised
Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
Cisco Product Security Overview
This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United States and local country laws governing
import, export, transfer and use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply third-party authority
OL-27022-01 xix
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 20

Cisco Product Security Overview
to import, export, distribute or use encryption. Importers, exporters, distributors and users are responsible for
compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product you agree to comply with applicable laws
and regulations. If you are unable to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately.
Further information regarding U.S. export regulations may be found at http://www.access.gpo.gov/bis/ear/
ear_data.html.
Preface
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
xx OL-27022-01
Page 21

PART I
Introduction to Cisco Business Edition 3000
• Overview of Cisco Business Edition 3000, page 3
• Frequently Asked Questions, page 55
• Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 75
• Cisco User Connect Licensing, page 95
• Phone Features, page 107
Page 22

Page 23

CHAPTER 1
Overview of Cisco Business Edition 3000
This chapter contains information on the following topics:
• Benefits of Deploying Cisco Business Edition 3000, page 3
• Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System, page 3
• Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000, page 35
• Example of Typical Deployment Model, page 53
Benefits of Deploying Cisco Business Edition 3000
Cisco Business Edition 3000, a system under the Cisco Unified Communications family of products, provides
an IP telephony solution that enables:
• Easy setup of deployments
• Easy provisioning of users, phones, lines, and phone features
• Easy monitoring and troubleshooting
• Easy maintenance of your system (simplified backups and simplified restores)
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 software is preinstalled on the server so that you do not have to perform a
software installation to get your server up and running. Deployment of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server,
phones, and the gateway across an IP network provides a distributed, virtual telephony network. Quality of
service is maintained across constricted WAN links, Internet, or VPN connections.
Your Cisco Business Edition 3000 system is designed to support up to 300 users and 400 phones. Supplementary
and enhanced services such as hold, transfer, forward, conference, multiple-line appearances, speed dials,
last-number redial, and other features extend to the phones.
Web-browser interfaces allow configuration of the system. These interfaces also provide access to online
help.
Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Your Cisco Business Edition 3000 system consists of the following components:
OL-27022-01 3
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 24
Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
• The Cisco Business Edition 3000 Server, on page 4
• USB Support, on page 5
• Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 7
• Phones, on page 8
• Attendant Console, on page 9
• Video Support, on page 9
• Voicemail, on page 10
• Auto Attendant, on page 13
• Gateway, on page 15
• SPA8800 Gateway, on page 18
• SIP Trunking, on page 26
• E1 R2 Connections, on page 28
• Connection Pack, on page 28
• Connection Groups, on page 31
• Best Practices for Using DHCP for Acquiring IP Addresses, on page 32
• DNS and Hostname Resolution, on page 33
• SFTP Server, on page 33
• Support for Computer Telephony Integration, on page 34
• Support for Voicemail with Email Integration, on page 34
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 Server
Cisco Business Edition 3000 is installed for you on a standalone Cisco MCS 7890-C1. When you plug in the
server, the Cisco Business Edition 3000 software is installed and ready for use. Cisco Unified Communications
Manager, an internal component of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 software that provides call processing
for your system, resides on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server. Cisco Unity Connection, an internal
component of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 software that provides voicemail support for your system, also
resides on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server. The Cisco Business Edition 3000 server also contains the
database where your configuration records are stored. Internal services that are part of the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 software allow you to troubleshoot, monitor, and perform maintenance tasks, such as backups
and upgrades.
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 server must use a static IP address.Tip
Because you use web-browsable graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for configuration, monitoring, and
troubleshooting, you need not connect a keyboard and mouse to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server. The
following graphical user interfaces (GUIs) exist on the server so that you can perform tasks to support your
system:
Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
4 OL-27022-01
Page 25
Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard guides you through the deployment steps that are
necessary to complete an initial configuration. From this wizard, an administrator can select the automatic
option that requires data to be uploaded through a Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file. Also, an
administrator can manually configure settings by moving throughout the wizard. The Cisco Business Edition
3000 First Time Setup Wizard supports forward and back capability through Back and Next buttons that
display on every page of the wizard.
If you click Next throughout the wizard without updating any of the settings, your system uses the default
Tip
settings.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
After you complete the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, the next time that you log in
to the server, you can access the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. The Cisco Business
Edition 3000 Administrative Interface allows you to perform the tasks that are described in this chapter. For
example, in this GUI, you can monitor and troubleshoot the system, add, edit, delete configuration data, such
as phones, users, sites, and so on, and perform maintenance tasks, such as backups, restorations, upgrades,
add and view licenses.
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface uses a three-section layout, which consists of a
top-level header, navigation menus that display on the left of the page that expand and collapse to display
individual menu options, and a content section that displays on the right of the page where you can view, add,
update, and delete data.
When you click an arrow next to a navigation menu, the navigation section displays the items that belongs to
the navigation menu. To display the contents of an item in the navigation menu, click the item. The contents
of that item display on the right side of the GUI.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface
USB Support
When users that exist in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface log in to the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface, a web page displays where the user can manage user preferences
for phone features; for example, the user can update Reach Me Anywhere, call forwarding, speed dials, the
phone PIN for Cisco Extension Mobility, and the password for the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User
Preferences Interface. In addition, the user can use Cisco Web Dialer to place a call to an extension in the
corporate directory.
Users can manage their user preferences settings for phone features by selecting check boxes and entering
the appropriate information in the provided fields. Each user accesses his own Cisco Business Edition 3000
User Preferences Interface page, and this page is not shared by users.
Most settings that display in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface are dynamic; the
settings display only if the user is allowed to use the feature (as configured by you, the system administrator).
For example, if you do not enable Reach Me Anywhere in the usage profile that is assigned to the user, the
user cannot see the Reach Me Anywhere setting in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 gives you the option of using USB flash drive or a USB hard disk for the following
functionality:
• Updating the network parameters—You can copy the configure.xml file to a USB flash drive to update
the network parameters. The temporary network address allows you to log in to the First Time Setup
Wizard through a browser. The purpose of the .xls data configuration file is to create temporary network
OL-27022-01 5
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 26

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
parameters so that they do not have to connect a laptop to the server using a cable, and access the GUIs
using default addresses.
Note
After you run the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, designate a
single USB DVD drive key for this function.
• Uploading a Cisco-provided country pack—You copy the Cisco-provided country pack to the USB flash
drive and then install the country pack through the Country/Locale page in the Cisco Business Edition
3000 First Time Setup Wizard.
• Uploading the Cisco-provided.xls data configuration file—You can copy the Cisco-provided .xls data
configuration file to the USB flash drive and then upload the spreadsheet to the system through the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard.
• Backing Up and Restoring Your Data—You may store your backup tar file to a USB hard disk, and if
you must restore you data for any reason, you can access the backup tar file on the USB hard disk to
restore the data through the Restore page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
• Uploading an audio source file for Music On Hold—You can copy the .wav file that you want to use
for music on hold to the USB flash drive; after you insert the USB flash drive in the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 server, you can upload the file through the Music On Hold page in the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
• Uploading Cisco User Connect licenses—Cisco User Connect license allow you to track the users and
phones that are in your system. You may use a USB flash drive to upload licenses.
Note
Some operating systems do not allow you to copy an entire file that is larger than 4 GB
to the USB flash drive. The system silently copies only 4 GB of the file to the USB flash
drive. Hence, Cisco recommends that you use USB flash drives that are formatted as
FAT32 in the Cisco Business Edition 3000.
Linux platform supports USB flash drives formatted with FAT32.Note
• Exporting your configured data—By using the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface,
you can export all of your configured data to a storage device that is connected to a USB port or to a
SFTP server. You may store the exported configuration to a USB flash drive or USB hard disk.
• Using the Cisco Diagnostic Tool—The Cisco Diagnostic Tool allows you to diagnose your system if
you cannot access the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. You copy the diagnose.xml
file that is used with the Cisco Diagnostic Tool to a USB flash drive.
Note
Make sure that you designate a USB flash drive just for this purpose. Do not use the
USB flash drive for other functions.
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 75
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
6 OL-27022-01
Page 27
Using the Cisco Network Configuration USB Flash Drive, on page 128
Troubleshooting When You Cannot Access the Graphical User Interfaces, on page 419
Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File
The data configuration file, which is a Cisco-provided .xls spreadsheet template where you can enter the
majority of your configuration data, provides the following support:
• Allows you to plan your configuration before you begin your first day of deployment.
• Allows you to insert users and phones in bulk through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface after your initial deployment.
To quickly import (add) your configuration data to Cisco Business Edition 3000 after you plug in your Cisco
Business Edition 3000 server, you can enter your data and then upload the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration
file to the server from a USB flash drive or your desktop when you run the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First
Time Setup Wizard. If you upload the file, you bypass the configuration pages in the Cisco Business Edition
3000 First Time Setup Wizard, and the wizard immediately takes you to the Summary page where you can
confirm your data.
After the server restarts at the end of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, you can log
into the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface and verify that you data got added to Cisco
Business Edition 3000. If you include user and phone data in the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file,
the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface allows you to import the users and phones and then
informs you of import errors for users and phones.
Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Tip
Note
If you do not want to upload the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file when you run the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, consider entering your data in the file and using it as a
guide when you manually enter the information in the GUIs.
For example, during your initial deployment, you inserted 25 users and phones; now, you must insert 25 more
users and phones. To accomplish this task, you can modify the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file
that you used for automatic set up during the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard or you
can obtain a new Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file and add your new users and phones to that new
spreadsheet.
Make sure that you have installed the appropriate country-pack .cop files during the automatic setup of the
Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard. From Release 8.6(3) onwards, you can localized
spreadsheets provided your local browser matches the locale of the spreadsheet being uploaded. The localized
spreadsheet contains texts and drop-down fields in the locale that you have chosen from the language drop-down
list box.
Be aware that when you download the localized spreadsheet on the Cisco Business Edition 3000, the
options in the Advanced Options drop-down menu for various functionalities may remain in English. Only
the non-technical texts and the non-reserved strings will be translated to the chosen locale. For example,
PRI 4ESS, PRI 5E8, SFTP, CentralSite, and Remote Site remains in English.
OL-27022-01 7
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 28

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Caution
Phones
Note
Cisco recommends that all users set their supported browsers to the desired locale version that is available
in the installed country pack version, so that the text displays as expected.
Do not use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file to modify your configuration data. Cisco Business
Edition 3000 only supports the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file for the initial deployment and
for bulk insertion (adding) of users and phones after the initial deployment. For example, if you attempt
to update existing user and phone information through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, the
updates fail.
For More Information
• Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 75
Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports a variety of phones that are available through Cisco. If the phone model
can support either SIP or SCCP, Cisco Business Edition 3000 uses SIP with the phone. For example, Cisco
Unified IP Phone 7937 supports SCCP.
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 server sends a phone-specific configuration file to each phone in your system.
(This file is not the same as the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file that is described in the
Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 7.) This configuration file contains data that your
phone requires to work; for example, the configuration file specifies whether the phone can use barge, whether
phones can use phone applications, and what the locale is for the system.
You can configure the phone for Cisco Business Edition 3000 by using the following methods:
• Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time
Setup Wizard (after initial deployment and when server comes up after the reboot)
• Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface (after initial deployment)
• Under Users/Phones > Phones in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial
deployment)
Your phone requires an IP address and other network settings to work. For information on how your phone
obtains its IP address and other network settings, refer to your phone administration documentation.
For your phone to work, you must install licenses. You cannot add a phone to the system if the appropriate
license is not installed and available for use.
All features that are available with Cisco Business Edition 3000 are not supported on all phone models. Before
you configure your Cisco Business Edition 3000, determine which features are supported on your phone by
obtaining the phone administration documentation that is available with your phone and this version of Cisco
Business Edition 3000.
For More Information
• Sites, on page 39 (for information on how phones get associated with a site)
• Best Practices for Using DHCP for Acquiring IP Addresses, on page 32
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
8 OL-27022-01
Page 29

• Users, Departments, Phones, and Lines, on page 46
• Cisco User Connect Licensing, on page 95
• Checklists for Users, Departments, Lines, and Phones, on page 139
Attendant Console
Using Cisco Unified IP Phone 8961 as an Attendant Console
Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports the Cisco Unified IP Phone 8961 which, can be used as an attendant
console when a Cisco Unified IP Color Key Expansion Module (KEM) is attached to the phone. For information
on connecting a KEM, see Cisco Unified IP Phone 8961, 9951, and 9971 Administration Guide for Cisco
Unified Communications Manager 8.5 (SIP).
The addition of the KEM expands the number of buttons that are available to the Cisco Unified IP Phone
8961 to 41 buttons for use as an attendant console. This provides the user with up to 40 buttons that can be
used as speed dials, line buttons, or other features as required.
Using Cisco Unified IP Phone 7962, 7965, and 7975 as an Attendant Console
Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7962, 7965, and 7975 which, can be used
as an attendant console when a Cisco Unified IP Phone Expansion Module 7915 or Cisco Unified IP Phone
Expansion Module 7916 is attached to the phone. For information on connecting a Key Expansion Module
(KEM), see Cisco Unified IP Phone Expansion Module 7915 and Cisco Unified IP Phone Expansion Module
7916 .
The addition of the KEM expands the number of buttons that are available to the Cisco Unified IP Phone
7962, 7965, and 7975 by 48 buttons when two Key Expansion Modules are added for use as an attendant
console. This provides the user with extra buttons that can be used as speed dials, line buttons, or other features
as required.
Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Configuring the Key Expansion Module
The system administrator uses the Usage Profile of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
to set up a usage profile for an attendant console. Using the Phone Button Template, the administrator can
configure the buttons that are available when one or two KEMs are attached to the phone.
Button number 1 is automatically designated as a line by the system because button number 1 is used to
correlate the phone and user when the user extension is assigned to line 1 on the phone. You cannot update
Line Button 1.
The Phone Button Template is automatically provisioned with speed dials for the buttons that are available.
The system administrator can use the Phone Button Template to change the function of the buttons that are
available.
During migration all speed-dial details are saved and migrated to the new system.
For more information about configuring the Usage Profile, see Usage Profiles Settings, on page 373 .
Video Support
Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports point-to-point video calls between two video-capable, nonteleworker
phones (for example, Cisco Unified IP Phones 8941 and 8945) within the same site or when calling between
OL-27022-01 9
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 30

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
sites that are configured with network interfaces of at least T1 capacity or larger and with video services
between sites enabled.
Note
Caution
Voicemail
Point-to-point video is not supported within the teleworker site or between the teleworker site and any
other site that is connected to the teleworker site.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 does not support video conferencing.Note
The number of video calls is expected to be small. Because, bandwidth is usually limited between sites,
the system does not reserve video bandwidth for infrequent video calls so that this bandwidth can be used
for the audio-only calls. Thus, if a large number of video calls are made (relative to the number of video
calls between sites as shown on the sites page), audio and video quality can suffer between the sites. If
you encounter poor quality due to a large number of video calls, you may find it necessary to disable video
to and from that particular site.
The system administrator accesses System Settings > Sites on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface to configure the system for point-to-point video.
For more information, see Sites, on page 39 .
Cisco Unity Connection, an internal component of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 software that provides
voicemail support for your system, resides on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server. With Cisco Business
Edition 3000, users can perform the following tasks:
• Call into the voice messaging system
• Send voice messages by using the phone keypad
• Check voice messages by using the phone keypad
• Reply to voice messages by using the phone keypad
• Forward voice messages by using the phone keypad
• Manage receipts by using the phone keypad— Receipts indicate when a voice message was played by
an intended recipient, when it was received by the intended recipient, and if it was received by the
intended recipient.
• Divert an incoming call to voicemail
• Notify new voicemail through email
Voicemail support requires the use of voicemail licenses. You must install one Voicemail license for each
Tip
user that requires voicemail.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 shares a single pilot extension for both Voicemail and Auto Attendant features.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
10 OL-27022-01
Page 31

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
• If the Voicemail is enabled and the user dials the Voicemail or the Auto Attendant extension, the call
will be connected to the Voicemail. Press the pound (#) key to switch to Auto Attendant.
• If the Voicemail is disabled and the user dials the Voicemail or the Auto Attendant extension, the call
will be connected to the Auto Attendant. Press the star (*) key to switch to Voicemail.
The external callers will always be connected to the Auto Attendant.Note
You can enable or disable the Voicemail on Users/Phones > Usage Profiles page using the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. Check the usage profile associated with the user to confirm is the
Voicemail is enabled or disabled for the user.
Creating and configuring an IMAP account to access Cisco Business Edition 3000 Voicemail in Microsoft
Outlook
To use Outlook to access the voicemail for Cisco Business Edition 3000 , create and configure a new Outlook
account for the user. You need the following information:
• Business Edition 3000 server username (alias).
• Password (This is the web application password that is set on the User pages in Cisco Business Edition
3000 Administrative Interface).
• The IP address, or if DNS is configured, the fully qualified domain name of the Business Edition 3000
server.
To create and configure a new account in outlook:
1
Start Outlook.
2
On the Outlook Tools menu, select E-Mail Accounts.
3
In the E-Mail Accounts wizard, select Add a New E-Mail Account.
4
Select Next.
5
On the Server Type page, select IMAP.
6
Select Next.
7
Enter values in the User Information section:
1
In the Your Name field, enter a display name for the account. The value that you enter here is visible
only in Outlook.
2
In the E-Mail Address field, enter one of the following:
• The SMTP Address of the user and the name of the Business Edition 3000 server. You can find
this information in the SMTP Address field on the User Basics page in Cisco Business Edition
3000 Administrative Interface. The E-Mail Address typically follows this format:
<User ID>@<domain name of the Business Edition 3000 server>
• The proxy address for the user.
8
Enter values in the Server Information Section:
OL-27022-01 11
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 32

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
a
In the Incoming Server field, enter the IP address or the fully qualified domain name of the Business
Edition 3000 server.
Caution
Caution
Do not use the fully qualified domain name of the Business Edition 3000 server unless DNS is configured
for the network.
b
In the Outgoing Server field, select the IP address or the fully qualified domain name of the Business
Edition 3000 server.
9
Enter values in the Logon Information section:
1
In the User Name field, enter the username.
2
In the Password field, enter the password of the user.
3
Verify that the Remember Password check box is not checked. If this option is checked, and the
password of the user expires, changes, or is locked, Microsoft Outlook does not prompt the user to
enter the password. The result is that users do not receive voice messages from Business Edition 3000
server.
10
If you do not want to encrypt voice messages and other data that are sent over the network between Outlook
and Business Edition 3000 server, skip to step 14.
If you want to encrypt voice messages and other data that are sent between Outlook and Business Edition
3000 server, continue with step 11.
11
Select More Settings
12
In the Internet E-Mail Settings dialog box, select the Advanced tab.
13
Select OK to close the Internet E-Mail Settings dialog box.
14
If the SMTP server is configured to allow connections from untrusted IP addresses, skip to step 20.
If the SMTP server is configured to require authentication from untrusted IP addresses, continue with step
15.
15
Select More Settings.
16
In the Internet E-mail Settings dialog box, select the Outgoing Server tab.
17
Verify that the My outgoing server (STMP) requires authentication check box is checked.
18
Verify that Use same settings as my incoming mail server is selected.
19
Select OK to close the Internet E-Mail settings dialog box.
20
Select Next.
21
Select Finish.
22
In the left pane of Outlook, select the Inbox folder for the new account.
23
On the Outlook Tools menu, select Send/Receive > This Folder.
24
If prompted, enter the Business Edition 3000 server username and password.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
12 OL-27022-01
Page 33

For more information, see the following topics:
Auto Attendant
In Cisco Business Edition 3000, the auto attendant serves as the virtual receptionist; that is, the caller receives
an automated greeting and series of prompts in order to successfully transfer the call to a user without the
assistance of an operator. The following options describe the auto attendant support.
Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
• Support for Voicemail with Email Integration, on page 34
• Setting Up Voicemail, on page 150
• Cisco User Connect Licensing, on page 95
Note
Auto attendant uses the same internal components as voicemail. Auto attendant is turned on by default,
and you cannot turn it off. The system can handle up to 12 simultaneous calls to voicemail and auto
attendant.
• The auto attendant uses a single menu for both business and closed hours (default); the auto attendant
plays the same greeting and set of prompts during both business and nonbusiness hours. Cisco Business
Edition 3000 automatically comes with a sample menu that provides the following functionality. If you
do not want to use the sample menu, you can upload another menu that can be used by the system.
Note
Cisco recommends that you install QuickTime Player plugin in your respective browser
so that the audio greeting playback controls works as expected. Cisco Business Edition
3000 supports QuickTime Player with a minimum version of 6.
◦ The auto attendant plays a greeting announcing that the corporate directory has been reached.
◦ The auto attendant requests that the caller enter the extension on the phone to transfer the call.
◦ If the caller does not enter the extension quickly, the auto attendant requests that the caller enter
the extension again.
◦ The auto attendant transfers the call to the user of the extension.
◦ The auto attendant requests that the caller reenter the extension of the user when the system cannot
find the extension.
◦ The auto attendant plays a farewell prompt.
The auto attendant does not support a different menu for holidays.Tip
To use the auto attendant, you must first configure the Voicemail and Auto Attendant Extension setting in
the dial plan. You can configure this setting
• Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time
Setup Wizard (for initial deployment)
OL-27022-01 13
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 34

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
• On the Dial Plan page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (during initial
deployment if you do not use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file)
• Under System Settings > Dial Plan in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after
initial deployment)
After you configure the Voicemail and Auto Attendant Extension setting in the dial plan, configure the Auto
Attendant page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (select System Settings > Auto
Attendant). After you set it up, remember to test your auto attendant functionality.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 shares a single pilot extension for both Voicemail and Auto Attendant features.
• If the Voicemail is enabled and the user dials the Voicemail or the Auto Attendant extension, the call
will be connected to the Voicemail. Press the pound (#) key to switch to Auto Attendant.
• If the Voicemail is disabled and the user dials the Voicemail or the Auto Attendant extension, the call
will be connected to the Auto Attendant. Press the star (*) key to switch to Voicemail.
The external callers will always be connected to the Auto Attendant.Note
Note
Auto attendant uses an internal user called operator. You cannot edit or delete this user, and it does not
display in the Search User page. In addition, you cannot add a user with the user ID of operator. (User
IDs should indicate who the user is, not the functions or tasks that the user perform.)
Do not assign the Voicemail and Auto Attendant Extension that you configure in the dial plan to the user
that is your operator.
Example
Assume Main Number = 4011000, Voicemail is enabled, and Auto Attendant extension = 1999. When you
call 4011999 from PSTN, call will directly go to Auto Attendant System and will enable the PSTN users to
call any extension they want to speak. If the users want to switch to Voicemail System, they can press the *
(star) key in the Auto Attendant menu.
Example
Assume new user = 1001, Voicemail is not enabled, and Auto Attendant extension = 1999. Add a new user
(1001) and associate a usage profile with Voicemail not enabled. When you call 1999 from 1001, the call will
reach the Auto Attendant System and will enable the users to dial any number they want to speak. If the users
want to switch to Voicemail System, they can press the * (star) key in the Auto Attendant menu.
Example
Assume new user = 1002, Voicemail is enabled, and Auto Attendant extension = 1999. Add a new user (1002)
and associate a usage profile with Voicemail enabled. When you call 1999 from 1002, the call will reach the
Voice Mail System. If the users want to switch to Auto Attendant System, they can press the # (pound) key
in the Voicemail menu.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
14 OL-27022-01
Page 35

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Example
On the phone set Call Forward All to Auto Attendant number. When you try to make a call to DN, call will
be forwarded to Auto Attendant number.
Example
In the usage profile, you can set Forward Busy Calls To / Forward No Answer Calls To to the Voicemail
/ Auto Attendant number.
Note
Gateway
The Voicemail and Auto Attendant Systems share the same pilot extension. The Voicemail capability of
the user who makes the call determines where the call should be delivered to. If the user has Voicemail
enabled, dialing the Voicemail / Auto Attendant pilot extension will transfer the call to the Voicemail
system. If the user does not have Voicemail enabled, dialing the Voicemail / Auto Attendant pilot extension
will transfer the call to the Auto Attendant System. External or outside callers will always reach the Auto
Attendant System.
For more information, see the following topics:
• Auto Attendant Settings, on page 175
• Setting Up Auto Attendant, on page 151
• Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Operator, on page 152
• Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Auto Attendant, on page 152
• Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Auto Attendant if the Operator is Not Available,
on page 153
For all calls that go through the PSTN, the Cisco Business Edition 3000 uses the following gateways:
• Gateway built in to Cisco Media Convergence Server 7890C1 (MCS 7890-C1)
• Cisco 2901 Integrated Services Router (ISR2901)
• SPA8800
• SIP Trunk
Table 1: Supported PSTN connections, on page 16 shows the supported PSTN connections for Cisco Business
Edition 3000.
OL-27022-01 15
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 36

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Table 1: Supported PSTN connections
UsageMax number of portsConnection typeGateway typeSI No.
MCS 7890-C11
• MGCP T1 PRI
2
• MGCP T1 CAS
• MGCP E1 R2
Central Site Only
Note
With Cisco
Business
Edition 3000,
only the media
• MGCP E1 PRI
resource on
MCS 7890-C1
box can be
configured as a
media resource.
Cisco ISR29012
• MGCP T1 PRI
Unlimited for
Provisioning
Central Site and/or
Remote Site
• MGCP T1 CAS
4FXOSPA88003
Central Site and/or
Remote Site
SIP trunkSIP Trunk4
Unlimited for
Provisioning
Central Site and/or
Remote Site
The gateways serve as your connection to the PSTN; that is, the gateway allows all of your users to place and
receive calls that go through the PSTN.
Note
For Cisco ISR2901, ensure that you connect the T1/E1 PSTN connections to slot 0 only.Note
The Cisco ISR2901 that you use with Cisco Business Edition 3000 cannot be used for any IP routing functions
other than those that are supported with Cisco Business Edition 3000.
The Cisco Unified Communications (UC) Technology Package License must be purchased with the order of
Cisco ISR2901.
Install the Cisco Unified Communications Technology Package License before you configure any Voice
features on the Cisco Business Edition 3000.
When you order a new router, it is shipped preinstalled with the software image and the corresponding
permanent licenses for the packages and features that you specified. You do not need to activate or register
the software before use. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/
sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html#wp1057952.
To verify if the Cisco Unified Communications Technology Package License is installed and activated, see
License Settings, on page 241.
The Cisco MCS7890-C1 supports approximately 300 users and 400 devices.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
16 OL-27022-01
Page 37

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
For MCS78901-C1, you can create an internal gateway during the First Time Setup using the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard.
For the Cisco MCS7890-C1 gateway, you can configure the general settings, such as the Media Resource IP
address and the hostname. The settings that you configure for the gateway allows the gateway, the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 server, and the phones to interact with each other for calls that go through the PSTN
connection.
Note
Note
Ensure that you retain minimum of one T1/E1 PSTN connection configured with the internal gateway.
The media transcoding and conferencing will not work properly if all the internal gateway connections
are deleted.
Ensure that you assign a static IP address for the Cisco MCS7890-C1 internal gateway. However, there is no
such restriction of a static IP address for ISR2901 gateways. If you plan to use DHCP, see the Best Practices
for Using DHCP for Acquiring IP Addresses, on page 32.
With Release 8.6.4 and later, you can associate each gateway with a site. However, the internal gateway, by
default, is always associated with the central site of the system and cannot be modified. You can change the
associated site for the gateway by editing the settings on the Connections > Device page using the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
You can associate the gateways with sites for the following PSTN connections:
• E1 PRI
• T1 PRI
• T1 CAS
• SIP Trunk
• SPA8800 (FXO)
The external gateways do not support E1 R2 connection type. Therefore, the E1 R2 connections are always
associated with the internal gateway.
You can configure the gateway for Cisco Business Edition 3000 by using one of the following methods:
• Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time
Setup Wizard (for initial deployment).
• On the Gateway page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (during initial
deployment if you do not use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file).
• Under Connections > PSTN Connections > Add PSTN Connection > Connection Type > Device >
Device > Add Device in Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial deployment).
After you add the Cisco ISR2901 gateway configuration to Cisco Business Edition 3000, you must update
Tip
the gateway with the appropriate CLI commands. See Devices Settings, on page 215.
OL-27022-01 17
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 38

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Inbound and Outbound Called Party and Calling Party Transformations
Administrators can add or edit transformation patterns through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface. Administrators can set digit discard instructions from the Outbound Call Routing section that appears
under Advanced Settings in order to transform called party numbers for each PSTN connection. Digit discard
instructions allow you to manipulate dialed digits or called party number for outgoing calls by appending or
removing prefix digits. The default digit discard instructions at the egress connection down-size the called
party number to contain the subscriber digits only. For outbound call routing to function properly, the called
party number is up-sized based on the calling party location and routed based on class of service. The called
party number is down-sized at the gateway egress.
Different service providers may use a different number of digits for the called number. For example, a service
provider in North America may expect 11 digits for a local call and 8 digits for an international call. To support
advanced routing cases, Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to customize called party transformation
patterns for each connection.
To route inbound calls to your internal extensions, you must remove the significant digits at the ingress gateway
and append prefix digits to match the resulting number to an extension. By default, the significant digits that
are retained in the calling party number is set to be equal to extension length and no prefix digits are added.
To customize inbound call routing, Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to alter the significant digits and
prefix digits for each connection.
You can edit the called party transformation and the calling party transformation patterns while configuring
or editing the PSTN connection using the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
Related links:
• SPA8800 Gateway, on page 18
• SIP Trunking, on page 26
• Connection Groups, on page 205
• Best Practices for Using DHCP for Acquiring IP Addresses, on page 32
• IP Addressing, on page 32
• DNS and Hostname Resolution, on page 33
• Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 75
• Checklists for Configuring the Gateway, on page 133
SPA8800 Gateway
SPA8800 is a small business analog gateway that supports the following functionality:
• Analog trunking (FXO) to the PSTN
• Devices such as analog phones and fax machines
Cisco Business Edition 3000 is not responsible for upgrading SPA8800 firmware. Therefore, users must
upgrade SPA8800 to the latest firmware (version 6.1.7 or later) prior to setting up analog trunks and lines on
the Cisco Business Edition 3000. Firmware can be downloaded from http://wwwin.cisco.com/voice/products/
callcontrol/cmbe/3000/index.shtml.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
18 OL-27022-01
Page 39

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Note
The user interface for SPA8800 gateway interface is supported in English only. When the user interface
on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 is changed to another language, the options in the Advanced Options
drop-down menu for the device or gateway remain in English.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports connection to SPA8800 using static IP addresses only.
Overview
To correctly configure the SPA8800, perform the following procedures in sequence:
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Configure the Related Connections on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 GUI, on page 19
Configure the SPA8800 Analog Phones on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 GUI, on page 21
Perform the Initial Setup on the SPA8800 for IP Addresses using SPA Interactive Voice Response, on page
23
Step 4
Configure settings for TFTP on the SPA8800 GUI, on page 24
Configure the Related Connections on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 GUI
You must configure the SPA8800 device in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 first, and then add Phone 1 or
Line 1 for the SPA8800 device.
Use the following procedures to add, edit, or delete SPA8800 connections on the Cisco Business Edition 3000
GUI.
Add SPA8800 connections from the PSTN Connections page
Perform the following procedure to add SPA8800 connections from the PSTN Connections page:
Procedure
Step 1
From the PSTN Connections page, click the Add PSTN Connection... button.
The Add PSTN Connection window appears.
Step 2
Choose the connection type FXO, and then click Next.
The Device options appear.
Step 3
Select SPA8800 from the Device Type drop-down menu, and choose Add Device from the Device drop-down
menu.
Step 4
Enter the MAC address, IP address, and description. The name is derived from the MAC address. Click OK.
The new device is now listed as an option under Device in the Add PSTN Connection window.
Step 5
Step 6
Select the new device from the drop-down list and click Next.
From the drop-down menu, select a service provider. Click Next.
The Connection Settings appear.
Step 7
Enter the appropriate connection settings and advanced settings.
Refer to Connection Type: FXO, on page 294 for information on each of these settings.
Step 8
Click Finish to complete the addition of the device.
OL-27022-01 19
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 40

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Note
Any changes that you make on the SPA8800 connection and phone causes the SPA8800 to reboot.
Reboots for configuration changes can take several minutes to take effect.
Edit SPA8800 connections from the PSTN Connections page
Procedure
Step 1
To edit a connection, choose Edit for that connection, as shown in the following illustration.
Figure 1: Edit PSTN connections
The Edit window appears.
Step 2
From this window, you can edit the Description, Direct Inward Dial (DID) Number, Line Usage fields, and
Advanced Settings.
Refer to Connection Type: FXO, on page 294 for information on each of these settings.
Step 3
Choose Save in the Edit window to save your edits.
Note
Any changes that you make on the SPA8800 connection and phone causes the SPA8800 to reboot.
Reboots for configuration changes can take several minutes to take effect.
The device reset dialog appears to notify the user that the SPA8800 device is being reset and that all calls for
the associated phones and PSTN connections will be disconnected.
Delete SPA8800 connections from the PSTN Connections page
Procedure
Step 1
To delete a connection, choose Delete for that connection from the PSTN Connection table.
Note
A warning appears for connections that are configured for Emergency Calls Only, indicating that the
DID used for the connection can no longer be used as an ELIN.
Step 2
The deletion will not occur for Line 1 if Phone 1 is not configured, and the user will get a message saying
that the port is a master port and it can be deleted only as part of the SPA8800 device deletion. In all other
cases the device reset dialog will appear notifying the user that the SPA8800 device will be reset and all calls
of the associated phones and PSTN connections will be disconnected.
Step 3
The connection is removed from the PSTN Connections list.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
20 OL-27022-01
Page 41

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Note
An associated device is not deleted as a result of removing the connection. A device can be deleted
only from the Devices page.
Any change made on the SPA8800 connection and phone results in a reboot of the SPA8800. Reboots
for configuration changes can take several minutes to take effect.
Configure the SPA8800 Analog Phones on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 GUI
Use the following procedures to add, edit, or delete SPA8800 analog phones and other devices from the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 GUI.
Add a SPA8800 analog phone from the Phones page
Procedure
Step 1
From the Phones page, click the Add Phone button.
The Add Phone window appears.
Step 2
Step 3
Choose Analog Phone (SPA8800) from the drop-down menu.
Choose Add Device from the Device Name drop-down menu to add a new SPA8800 and proceed to Step 4.
To select an existing SPA8800, proceed to Step 5.
The Add Device window appears.
Step 4
Enter the MAC address and the IP address (the name is derived from the MAC address) of the new SPA8800.
Click OK. Devices are added through modal dialog box, with a value returned to Add Phone dialog box.
The Device Name now appears in the Add Phone window, along with the Device Port. Proceed to Step 6.
Step 5
To add an existing SPA8800, select a device name from the drop-down list. Only available ports are listed in
the Device Port field. If certain ports are unavailable, the Device Port field defaults to the next available port.
The Phone Name is filled out automatically based on the SPA8800 MAC address and port number.
Step 6
Choose an extension from the drop-down menu.
All configured extensions are listed in the drop-down menu.
Step 7
Click OK to add the phone and return to Phones table.
Note
Any change made on the SPA8800 connection and phone results in a reboot of the SPA8800. Reboots
for configuration changes can take several minutes to take effect.
Edit a SPA8800 analog phone from the Phones page
Procedure
Step 1
To edit an analog phone, click the Edit button for that phone in the Phones table.
The Edit window appears.
Step 2
Step 3
Edit the description and extensions.
Click Save in the Edit window to return to the Phones table.
Note
Any change made on the SPA8800 connection and phone will cause the SPA8800 to reboot. Reboots
for configuration changes can take several minutes to take effect.
The device reset dialog box will appear notifying the user that the SPA8800 device will be reset and all calls
of the associated phones and PSTN connections will be disconnected.
OL-27022-01 21
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 42

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Delete a SPA8800 analog phone from the Phones page
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
To delete a phone, click the Delete button for that phone in the Phones table.
The delete will not occur for Phone 1 if Line 1 is not configured and the user the user will get a message
telling them that the port is a master port and it can only be deleted as part of the SPA8800 device deletion.
In all other cases the device reset dialog box will appear notifying the user that the SPA8800 device will be
reset and all calls of the associated phones and PSTN connections will be disconnected.
Step 3
The phone is removed from the Phones page.
Note
Any change that you make on the SPA8800 connection and phone causes the SPA8800 to reboot.
Reboots for configuration changes can take several minutes to take effect.
Edit SPA8800 devices from the Devices page
Procedure
Step 1
In the Devices page, locate the SPA8800 you wish to edit and click the Edit button under the Actions column.
The Edit window appears.
Step 2
Step 3
From this window, you can edit the MAC address, IP address, description, and advanced settings.
Click Save in the Edit window to return to the Devices page.
Any change made on the SPA8800 connection and phone will cause the SPA8800 to reboot. Reboots for
configuration changes can take several minutes to take effect.
Delete SPA8800 devices from the Devices page
Procedure
Step 1
To delete an SPA8800, locate the SPA8800 you wish to delete and click the Delete button in the Actions
column.
The Confirm Delete window appears. Listed in this window are all phones and PSTN connections associated
with this SPA8800.
Step 2
Click Delete to confirm deletion of the SPA8800.
Note
If the SPA8800 you wish to delete has one or more FXO connections that are configured for emergency
calling, any associated ELINs will be removed.
Any change made on the SPA8800 connection and phone will cause the SPA8800 to reboot. Reboots
for configuration changes can take several minutes to take effect.
DID and ELIN configuration
DIDs for the trunk is configured on the same page as translation patterns, attendant numbers, directory numbers,
or hunt lists in order to route incoming calls. Simply placing a DID on a trunk does not allow it to associate
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
22 OL-27022-01
Page 43

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
with a particular station within the system. In the case of the All Call Types option, customers are responsible
for determining how calls on a trunk are routed (for example: attendant number or directory number).
In the case of Emergency Calls Only, a call-back pattern is set up that ensures that incoming calls are routed
to the last number that called out on that particular gateway.
If an ELIN is associated with an analog trunk, Cisco recommends that it be configured on that analog trunk.
If the ELIN is using a digital gateway (example: T1 or PRI connection), Cisco recommends that it be configured
on the site.
To confirm that the configuration for emergency calling is successful, after the SPA8800 is configured, go to
the site page and confirm that the DID for that trunk is listed as an ELIN. If it is not listed as an ELIN, check
the other sites to see if it appears on one of them, it may have been set up on the wrong site. If this happens,
check the IP address and subnet settings in Cisco Business Edition 3000 to ensure that the gateway is registering
at the correct site.
Note
The manner in which a particular SPA8800 is associated with a site is based on the IP address and the
subnets that have been set up for that site.
PSTN Connection Settings
For information about how to edit the SPA8800 connections, see Connection Type: FXO, on page 294.
Perform the Initial Setup on the SPA8800 for IP Addresses using SPA Interactive Voice Response
The SPA8800 requires setup through the SPA Interactive Voice Response (IVR) menu to locate the Cisco
Business Edition 3000.
Use the following procedure to perform this setup.
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Connect an analog phone to port 1.
Go off hook and enter the configuration menu by pressing the * (star) key four times.
Enter 101 followed by the # (pound) key to set the Internet connection type, followed by 1# to set it to static
IP addressing.
Step 4
Enter 111# to set the static IP address.
Note
DHCP must be set to Disabled; otherwise you
hear
Invalid option
if you try to set this value. A password is
required.
Step 5
Enter IP address using numbers on the telephone key pad. Use the * (star) key to enter a decimal point, followed
by the # (pound) key. Press 1 to save the configuration change.
If, while entering a value (for example, an IP address), you decide to exit without saving any changes, you
must press the * (star) key twice within a half-second window of time. Otherwise, the entry of the * (star) key
will be treated as a dot (decimal point).
To enter IP address, use numbers 0 - 9 on the telephone key pad and use the * (star) key to enter a
Tip
decimal point.
OL-27022-01 23
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 44

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Check the subnet mask by entering 120#.
If necessary, change the subnet mask by entering 121#.
Set the default gateway IP address by entering 131#, and then check the gateway IP address by entering 130#.
Hang up the phone for the values to take effect.
Configure settings for TFTP on the SPA8800 GUI
Procedure
Step 1
Enter the web interface using the following URL: http://IP_Address_Of_SPA/admin/advanced
If you have problems accessing the SPA8800 device using the web interface, the issue may be a problem with
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP).
By connecting your laptop directly to the SPA8800 using an Ethernet cable, you can access the SPA8800
administrative interface to enable/disable CDP by choosing Network > Wan Status > VLAN Settings >
Enable CDP.
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Set the default password.
Set the TFTP address for syncing the SPA8800 configuration from the Cisco Business Edition 3000.
Click the Voice button on the upper left corner and then click the Provision tab, as shown in the following
illustration.
Step 5
Figure 2: Provision tab
In the Profile Rule field, specify the TFTP protocol and the IP address of the Cisco Business Edition 3000.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
24 OL-27022-01
Page 45

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
In the example in the previous illustration, tftp://192.168.2.251/spa$MA.cnf.xml is the TFTP
protocol where 192.168.2.251 is the IP address of the Cisco Business Edition 3000.
Note
Note
Step 6
Step 7
Click the Submit All Changes button.
Reboot the SPA8800 now.
This can be done by unplugging the power cord for the SPA8800 and plugging it back in.
SPA8800 Feature Codes
The following table lists the feature codes that are supported for SPA8800.
Table 2: Supported feature codes
SPA8800 treats $MA as a placeholder for its own MAC address. $MA must be entered in capital
letters. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/csbpvga/ata/
provisioning/guide/Cisco_Small_Business_IP_Telephony_Provisioning_Guide.pdf.
Only TFTP is supported in the current
release.
Code numberFeature
*07Call Redial
*66Call Back
*86Call Back Deactivate Code
SPA8800 Limitations
1
2
3
4
*56Call Waiting
*57Call Waiting Deactivate Code
*71Call Waiting Per Call Act Code
*70Call Waiting Per Call Deact Code
*69Call Return
*84Attn-Transfer
*85Conference
The Do Not Disturb (DND) setting cannot be configured for SPA8800 analog phones.
Music On Hold (MOH) is not supported on the SPA8800 analog phones.
Blind Transfer is not supported on the SPA8800 analog phones.
Call Forwarding must be set from the Cisco Business Edition 3000 and not from the SPA8800.
OL-27022-01 25
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 46

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
5
In a clear call scenario, such as the updating of phones or PSTN connections on the SPA8800 gateway,
Cisco IP Phones with active PSTN calls receive a fast busy tone when a corresponding active FXO line
is cleared.
SIP Trunking
In the Cisco Business Edition 3000, the SIP trunk serves as a connection to the SIP service provider network
for PSTN connectivity. To interact with the SIP trunk connection, the Cisco Business Edition 3000 requires
SBE (Session Border Elements) to provide security, topology hiding, and ALG (Application Level Gateway)
functionalities.
To achieve SIP trunking, use the following operations:
• Provision Cisco Business Edition 3000 to interact with the SBE. You can achieve this by the installation
of Connection Packs, and by adding the SIP trunk connection through Cisco Business Edition 3000
Administrative Interface.
For information on connection packs, see Connection Pack, on page 28.
• Provision SBE to interact with Cisco Business Edition 3000. You can achieve this using the configurations
provided by the service provider.
• Provision SBE to interact with the service provider. You can manage this using the service provider.
The following list describes the different types of SIP trunk connections that are used with Cisco Business
Edition 3000:
• Standard Cisco SIP trunk connection - SIP trunk is connected to the service provider through the Cisco
Unified Border Element (CUBE) on Cisco ISR8xx Series (Integrated Services Router). The parameters
on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 for the SIP trunk connection are preconfigured to support general
SIP trunk functionalities.
Note
Cisco TAC provides support for Cisco Unified Border Element (CUBE) only. For other
sessions, contact your service providers.
• Service Provider SIP trunk connection - SIP trunk is connected to the service provider through other
SBEs. The parameters of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 SIP trunk connection is preconfigured based
on the inter-operational tests with specific service provider. The service provider for provisioning is
available after the installation of the SIP trunk connection pack that is customized for the service provider.
If the Cisco Business Edition 3000 deployment requires SIP trunk connection in your site, deploy an SBE in
the site to route PSTN calls. This SIP trunk connection can also be used to route the PSTN calls from other
sites.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 also supports multiple SIP trunks to the service provider through a single or
multiple session border elements.
Note
If a remote site needs to deploy a SIP trunk connection to its local SIP service provider, deploy a session
border element on the remote site, rather than using the SIP trunk on the central site. The SIP trunk
configured on the central site can also be used.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
26 OL-27022-01
Page 47

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
To add, edit, or delete SIP trunk connections, sign in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface (Connections > PSTN Connections).
Additionally, you must bind a SIP trunk/SBE with a site using the service provider IP address specified on
the SIP trunk connection and provision the subnet on the site (Connections > Sites > General tab).
Figure 3: Provisioning scope for SIP trunk with Cisco Business Edition 3000
SIP Trunk is another PSTN connection type along with T1/E1 PRI, T1 CAS, and FXO connections.Note
Based on the requirement of PSTN connections for Cisco Business Edition 3000, provisioning is performed
for routing of PSTN calls using the gateway on Connections > Sites > Add Site > PSTN Access.
Limitations of SIP Trunking
Cisco Business Edition 3000 does not support the following features on SIP trunk to service providers:
• Digest authentication
• QSIG
• TLS
• IME
• MLPP
• IPV6
• MTP
OL-27022-01 27
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 48

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
• Raw DTMF
• RSVP
Cisco Business Edition 3000 does not support the following functionalities on SIP trunk:
• pTime - This media-based parameter cannot be configured on Cisco Business Edition 3000. However,
a fixed value will be used.
• DTMF - The PSTN calls with SIP trunk connection encountering DTMF incompatibility requires an
MTP to normalize the DTMF. As Cisco Business Edition 3000 does not support MTP, the call fails.
• Early media on 180 - For SIP trunk connections, Cisco Business Edition 3000 signals calling phone to
play local ringback as it does not receive SDP in the 180 response. However, the system receives as
SDP in the 183 response.
E1 R2 Connections
R2 signaling is a Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) system developed in the 1960s that is still in use today
in Europe, Latin America, Australia, and Asia. R2 signaling exists in several country versions or variants in
an international version called Consultative Committee for International Telegraph and Telephone (CCITT-R2).
The E1 R2 signaling is an international signaling standard that is common to channelized E1 networks.
In the Cisco Business Edition 3000, R2 signaling serves as a connection to the E1 interface for PSTN
connectivity. This connection is achieved by the installation of the country packs, and adding the E1 R2
connection through Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
You can set up the E1 R2 connection only if you have installed the Brazil, Mexico, or Saudi Arabia country
pack. The parameters of the E1 R2 interface may vary from one country to another and may also vary from
one service provider to another. You must install the country pack during First Time Setup (FTS) or at a later
stage import the COP file before you choose the provider for an E1 R2 PSTN connection.
To add, edit, or delete E1 R2 connections, sign in to Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
(Connections > PSTN Connections).
Connection Pack
The provisioning of SIP trunks to SBE from Cisco Business Edition 3000 is supported through the installation
of connection packs. The connection pack is a Cisco Options Package (COP) file signed by Cisco. The main
advantage of using the connection pack is that it allows quick and easy configuration of the SIP Trunk with
minimal or no errors.
The connection pack is bundled with the Provider XML file, and Logical Unit Application (LUA) scripts
necessary for the operation of SIP Trunks.
• Provider XML - A configuration file detailing the connection definition for a particular SIP trunk on
the Cisco Business Edition 3000.
The provider XML file controls the default values and the display of Administrative Interface elements
for PSTN Connection configurations for provisioning the SIP trunk.
• LUA script - (Optional) A mechanism supports transparency and normalization of SIP messages for
interacting with the service provider.
For the service provider SIP trunk connection, the provider XML is defined and bundled with the connection
pack. The connection pack must be installed before provisioning the service provider SIP trunk.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
28 OL-27022-01
Page 49

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
The mechanism to upgrade the connection pack is through the Maintenance > Upgrade page on the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. For more information, see Installing the Connection Pack
File, on page 29.
The connection pack is used to upgrade the following SIP trunk connections:
• Cisco Standard SIP Connection - The connection pack bundles the provider XML for configuring the
SIP trunks using CUBE on Cisco ISR8xx as the service provider.
You can edit the parameters through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
• Service Provider SIP Connection - The connection pack bundles the provider XML for configuring the
SIP trunks using other service providers. This ensures that the Cisco Business Edition 3000 SIP trunk
interworks with the service provider through SBEs (including third-party session border elements). The
new parameter definitions are effective for the SIP trunks using service provider SIP Connection.
After the installation of a connection pack for a service provider, create SIP trunk using the service provider.
The SIP parameters of the SIP trunk connection are preconfigured with the values in the connection pack
automatically. When a SIP trunk connection is created, a minimal set of parameters, as designed by the service
provider, is editable through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (PSTN Connections
> Add PSTN Connection > Connection Settings > Configure Connection Settings).
Note
The parameters in the SIP trunk connection pack are preconfigured based on the inter-operability tests
between the Cisco Business Edition 3000 SIP trunk and the service provider. Therefore, the SIP trunk
that is created with the service provider connection type will be configured correctly to inter-operate with
the service provider.
When you edit a SIP trunk connection, a minimal set of parameters, as designed by the service provider, is
editable through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (PSTN Connections > Add PSTN
Connection > Connection Settings > Configure Connection Settings). For more information, see Connection
Type: SIP Trunk, on page 283.
Versioning of the Connection Pack file
The naming convention of the connection pack is based on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 version and the
service provider version.
cm-conp-<Cisco Business Edition
3000-version>-<serviceprovidername>-<version>.cop.sgn
For example:cm-conp-CP-8.6.2-foo-1.cop.sgn
cm-conp-CP-8.6.2-foo-2.cop.sgn
Installing the Connection Pack File
You can upgrade the connection pack through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. For
instructions on how to import the connection pack file, see Upgrade Settings, on page 365
1
Download—Download the SIP trunk connection pack (.cop.sgn) file. You can burn the file to a DVD or
save it on SFTP location for uploading. You can click Cancel to terminate the upgrade process on the
progress bar.
You can get the connection pack (.cop.sgn) file from your Service Provider or from www.cisco.com.Note
OL-27022-01 29
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 50

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
2
Validation—The Cisco Business Edition 3000 validates the connection pack and the version based on the
checksum before upgrade.
3
Installation—The connection pack is installed on the Cisco Business Edition 3000. A progress bar depicts
the status of the upgrade. You cannot cancel the upgrade process after the installation process is initiated.
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface notifies the status of installation as a progress bar.
If there are PSTN connections using the connection pack that is upgraded, the Administrative Interface notifies
that the connection will be reset and all the calls associated with SIP trunk using that connection pack are
dropped. The Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface will request confirmation. If you choose
to cancel, the installation process will be terminated and there will be no impact on the current connection
and service provider. If you confirm to upgrade, the upgrade process begins.
After you upgrade the connection pack successfully, a confirmation message appears indicating that the
connection pack was successfully installed. The connection pack upgrade process takes 2 to 7 minutes if you
confirm to upgrade, and 2 to 4 minutes if you choose to cancel the upgrade.
The advance settings of the SIP trunk connections will be updated with the new set of parameters through the
connection pack file. After the connection pack upgrade is complete, the SIP trunk connection will be reset
and active calls will be dropped.
Upgrade failure handling
If the upgrade fails during validation (for example, if you have a corrupt .cop.sgn file) or installation (for
example, if you have an invalid provider XML file), the upgrading process stops and the Administrative
Interface displays a message to reboot the system. It is mandatory to reboot the system if this error is
encountered. For more information, see Troubleshooting Issues, on page 427.
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to revert to the previous version of the connection pack. You
can achieve this by upgrading the system using the connection pack of the desired version.
Impact during Cisco Business Edition 3000 Upgrade
The SIP trunk connection will be reset while the Cisco Business Edition 3000 is upgrading. All the active
calls will be dropped.
The upgrading of the new Cisco Business Edition 3000 may result in change of various parameters on the
Administrative Interface. Some parameters can be removed and new parameters may be introduced. The
user-configured SIP trunk parameter settings will be saved after upgrade also.
Carrier Selection Profiles for Brazil
This section is applicable if you have installed a Brazil country pack using the Cisco Business Edition 3000
First Time Setup Wizard.
In Brazil, the user has to specify a carrier selection code to place a long distance or an international PSTN
call. Carrier Selection Profiles allow subscribers to choose a service provider and configure a carrier selection
code for national or international calls. You can configure the Carrier Selection Profiles for long distance,
international and mobile calls through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
Note
You can configure Carrier Selection Profiles on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
only if you have installed the Brazil country pack through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time
Setup Wizard during the initial setup.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
30 OL-27022-01
Page 51

Users are can route national and international PSTN calls through the service provider by dialing the appropriate
carrier selection code. You can configure the Carrier Selection Profiles under Connections > Carrier Selection
Profiles in Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
For More Information
• Table 33: Settings on the Carrier Selection Profiles Page, on page 193 (for the Carrier Selection Profiles
page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface)
Connection Groups
Prior to Release 8.6.4, Cisco Business Edition 3000 supported the configuration of single connection group
for each site consisting of local connections only or all connections in the system or a custom selection of the
available connections.
With Release 8.6.4, the administrator can configure different connection groups for each site. A connection
group is a group of PSTN connections that is used to route a particular group of calls. The criteria for
configuring the connection groups include the class of call and the outside dial code. Each connection group
is a group of PSTN connections with a route list and a route group with selected connections.
You can configure only the internal gateway during the First Time Setup. Therefore, the calls are routed
through the internal gateways after the First Time Setup. A default system-generated “All Connections” group
is created which includes all the gateways configured on the Cisco Business Edition 3000. The PSTN
connections are listed in the order of SIP connections, MGCP connections, PRI connections, CAS connections
and SPA analog gateways. The connections are further ordered based on the description. Every site is configured
to use All Connections group to route PSTN calls.
Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
Note
If you have upgraded the Cisco Business Edition 3000 from an earlier version to Release 8.6.4, a
system-generated connection group is formed which includes all the gateways in that site before the
upgrade. The naming convention for this connection group is <<SiteName>> Connections. Each site will
be associated to its respective connection group. By default, the sites will use their connection groups.
When a new site is created, the system creates the All Connections connection group and uses it as the
default connection group.
New configuration groups can be created using the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
corresponding to the gateway usage of each site. All the calls from this site will be routed through the
corresponding connection group. You can configure the connection groups using the Cisco Business Edition
3000 Administrative Interface on the Connections > Connection Groups page. For more information about
the parameters to configure a connection group using the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface,
see Table 37: Settings on the Connection Groups Page, on page 205. An error message appears if there are
no PSTN connections in the connection group.
All calls from the site will be configured to use the corresponding connection group. The configuration of
PSTN call routing allows you to:
• Route all calls through a single connection group
• Route calls through different connection groups based on outside dial code
• Route calls through different connection groups based on a combination of outside dial code and class
of call
OL-27022-01 31
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 52

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
The connection group for redial and click-to-call depends on the outside dial code used during translation of
E.164 number to a national number. The administrator configures the outside dial code for redial and
click-to-call calls for each site.
Best Practices for Using DHCP for Acquiring IP Addresses
This document does not provide detailed information on DHCP; you should have a thorough understanding
of DHCP before you use it with your Cisco Business Edition 3000 system. Typically, the IT support staff for
the company or the Internet service provider handles your DHCP setup. DHCP may be run on a computer or
on a router. Before you implement DHCP with Cisco Business Edition 3000, consider the following best
practices:
• Use custom option 150 or option 66.
• You can use a DHCP server to issue IP addresses to the phones.
If DHCP is enabled on a phone, which is the default for the phone, DHCP automatically assigns an IP
address to the phone after you connect it to the network. The DHCP server directs the phone to the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 server, which serves a phone-specific configuration file to the phone.
If DHCP is not enabled on a phone, you must manually assign an IP address to the phone and configure
the IP address or the hostname of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server locally on the phone (configure
it under the TFTP server option on the phone).
IP Addressing
• The Cisco Business Edition 3000 server must use a static IP address that you assign to it. If you use a
DHCP server to issue IP addresses to computers and other network devices, make sure that the IP address
for the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server is not in the active range of IP addresses on the DHCP server.
Make sure that you configure your DHCP server so that it does not hand out the IP address for the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 server to a different network device.
• Cisco strongly recommends that you assign a static IP address to the gateway. If you use a DHCP server
to issue IP addresses to computers and other network devices, make sure that the IP address for the
gateway is not in the active range of IP addresses on the DHCP server. Make sure that you configure
your DHCP server so that it does not hand out the IP address for the gateway to a different network
device.
If DHCP is enabled on a gateway, DHCP automatically assigns an IP address to the gateway after you
connect it to the network.
• Before you configure your sites and DHCP, Cisco strongly recommends that you determine the number
of sites that you need and determine how many phones will be located at each site. Configure your
DHCP server so that it correctly distributes the IP addresses to the phones at the various sites.
For more information, see the following:
• Phone administration documentation that supports your phone model
• Sites, on page 39 (for subnet and subnet mask information for sites)
The Cisco MCS7890-C1 uses two external IP addresses. The main IP address is the published IP address on
the MCS7890-C1 device. This is the system IP address of the Cisco Business Edition 3000. This IP address
is set by your administrator during the First Time Setup of Cisco Business Edition 3000. You can configure
this IP address using DHCP or static. The second IP address is the IP address of the media resource used for
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
32 OL-27022-01
Page 53

transcoding and conferencing. Cisco recommends that the media resource IP address be static and unique for
MCS7890-C1.
For Cisco ISR2901 gateway, the media resource IP address is the same as the ISR2901 gateway IP address.Note
DNS and Hostname Resolution
This document does not provide detailed information on DNS. You should have a thorough understanding of
DNS before you use it with your Cisco Business Edition 3000 system. DNS is optional; you do not have to
use a DNS server unless you plan to resolve hostnames for your Cisco Business Edition 3000 server or gateway.
If you include a hostname for the server or gateway on the Network or Gateway page and you must use DNS,
make sure that you map the hostname(s) to the IP address(es) on the DNS server for both forward and reverse
DNS resolution. Cisco recommends that you perform this task before you add or edit the hostname in the
Cisco Business Edition 3000 GUIs.
The current version of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 does not require a DNS server; however, it is configured
for future requirements such as SIP trunks.
Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
SFTP Server
Caution
Cisco recommends that you do not configure Cisco Business Edition 3000 to use DNS.Note
Cisco allows you to use any SFTP server product but recommends SFTP products that are certified with Cisco
through the Cisco Technology Developer Partner program (CTDP). CTDP partners, such as GlobalSCAPE,
certify their products with a specified release of your software.
For information on using GlobalSCAPE with supported Cisco Unified Communications versions, refer to the
following URL:
http://www.globalscape.com/gsftps/cisco.aspx
Cisco uses the following servers for internal testing. Be aware that you may use the servers, but you must first
contact the appropriate vendor for support at the following URLs:
• Open SSH (refer to http://sshwindows.sourceforge.net/)
• Cygwin (refer to http://www.cygwin.com/)
• Titan (refer to http://www.titanftp.com/)
Cisco does not support using the SFTP product, freeFTPd, because of the file size limit on this SFTP
product. For issues with third-party products that have not been certified through the CTDP process,
contact the third-party vendor for support.
You can use a SFTP server to complete the following tasks:
• Upload the upgrade file from the SFTP server to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server before you
perform an upgrade
OL-27022-01 33
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 54

Components of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 System
• Store your backup file to a SFTP server, and if you must restore your data, restore the data from the
SFTP server
• Export your configuration data to a SFTP server
Support for Computer Telephony Integration
Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) allows you to use computer-processing functions while making,
receiving, and managing telephone calls. CTI can allow you to perform such tasks as retrieving customer
information from a database on the basis of information that caller ID provides.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 provides user support for CTI applications. Cisco Business Edition 3000
automatically gives all users the ability to run CTI applications, including Cisco Jabber clients. Cisco Jabber
clients must be configured as phones in the Phone Configuration window. During the configuration process,
the Cisco Jabber client must be given a unique name or identifier and the client must then be associated with
a user.
During the Cisco Jabber client registration process, the Cisco Business Edition 3000 TFTP service sends the
following three XML files from Cisco Business Edition 3000 to the Cisco Jabber client. These files contain
the registration details, application dial rules, and directory lookup dial rules:
• Identifier.cnf.xml (file is named according to naming of Identifier field during configuration)
• AppDialRules.xml
• DirLookupDialRules.xml
Cisco Business Edition 3000 listens on port 2748 for requests from CTI applications. All telephone calls that
are placed through the CTI application must use the E.164 number format. The dial rules that are sent during
registration convert the following phone number formats to an E.164 format of +{country code}{area
code}{local number}, thereby allowing the CTI application to support the Click to Call phone feature.
• {area code}{local number} for example, 972 813 0000
• {country code}{area code}{local number} for example, 1 972 813 0000
• {national access code}{area code}{local number} for example, 1 972 813 0000
• {out of country code}{country code}{area code}{local number} for example, 011 8621 972 813 0000
Support for Voicemail with Email Integration
Voicemail with Email integration allows you to configure a voicemail alert where the entire voicemail is
forwarded as a .WAV attachment to an SMTP or IMAP compliant email application (Microsoft Outlook,
Exchange, Lotus Notes, etc.). You can hear the message by double-clicking the .WAV attachment. Forwarding
allows emails and voicemail messages to be integrated and collected from a single source. The voicemail alert
option forwards only the called party number in the subject of the email.
Forwarding voicemail to email is particularly useful for group voicemail boxes as it allows a single voicemail
message to be copied to the email of every member in that group.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
34 OL-27022-01
Page 55

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
This section describes common configuration concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000. In addition, this
section describes considerations that you should review before you configure the items:
• Network Settings, on page 35
• Dial Plans, on page 36
• Sites, on page 39
• Remote Management of Cisco Business Edition 3000 using Cisco OnPlus, on page 42
• Usage Profiles, on page 44
• Users, Departments, Phones, and Lines, on page 46
• Significant Behavior of SIP Trunk, on page 48
• Attendant Group, on page 50
• Hunt Lists, on page 51
• Call Pickup Groups, on page 51
• Example of Typical Deployment Model, on page 53
Network Settings
Your network settings include the IPv4 address or hostname of the server, the subnet mask and default gateway
for the server, the primary and secondary DNS server (if you use DNS), the link speed for the Network
Interface Controller (NIC) on the server, and the Message Transmission Units (Maximum Transmission Units,
MTU) for the network.
The network settings can be configured using one of the following methods:
• Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time
• On the Network page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (if you are not using
• Under System Settings > Network in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after
• Through the configure.xml file (used primarily for troubleshooting when you cannot access the GUIs)
• Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 75
Setup Wizard (for initial deployment)
the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file during initial deployment)
initial deployment)
For more information, see the following sections:
• Network Settings, on page 245 (for the Network page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time
Setup Wizard and Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface)
• Using the Cisco Network Configuration USB Flash Drive, on page 457
OL-27022-01 35
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 56

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
Dial Plans
Your Cisco Business Edition 3000 Dial Plan allows you to allocate phone numbers and translation rules for
your system. You can choose the country where you are installing the Cisco Business Edition 3000. The Cisco
Business Edition 3000 installs a Dial Plan based on the regulations in your country.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports a local gateway in every site and multiple gateways in any site; therefore
the installation of Dial Plan is required.
For load balancing and backup purposes, the routing is set up such that if a local gateway is not available, the
calls can be routed to the gateway on the other site.
Prior to Release 8.6.3, dial plans were configured during First Time Setup by selecting the appropriate country
pack. For other countries, the dial plans were configured through an upgrade using the country pack during
the First Time Setup. The dial plan configured for a particular country is dependent on the classes of services
available for that country. There was no scope to change or enhance the dial plan. The patterns were noneditable,
and administrators had to contact the Cisco TAC for assistance. To change the dial plan, the dial plan in the
Cisco Business Edition 3000 had to be upgraded using an updated country pack that replaced the old dial plan
with the new dial plan.
With Release 8.6.4, Cisco Business Edition 3000 automatically assigns the default dial plan based on the
country that you choose during First Time Setup. The default dial plan supports various classes of services
based on the country pack you have installed on the system. You can switch to another default dial plan by
installing another country pack. Cisco Business Edition 3000 uses an enhanced IDP file to generate dial plan
patterns.
In addition, Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface provisions the configuration of customized
dial plan patterns. Administrators can add, edit, and delete dial plan patterns depending on their requirements.
Dial plan patterns are organized based on the class of service offered by Cisco Business Edition 3000.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 is provisioned with explicit dial plan patterns, which comprise the configuration
of:
• translation patterns
• call routing patterns
• called party transformation patterns
• calling party transformation patterns
• application dial rules
• SPA dial rules
• CDR rules
From Release 8.6.4, Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports multiple outside dial codes for different sites. You
can enter a maximum of 5 outside dial codes separated with a comma. Connection groups allow you to route
different PSTN calls based on the class of service and the outside dial code. To extend this routing capability,
Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to configure multiple outside dial codes for your dial plan. You can
configure multiple outside dial code and connection groups using the Cisco Business Edition 3000
Administrative Interface.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
36 OL-27022-01
Page 57

Table 3: Classes of Service Supported Based on the Country Pack
Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
of
Service
Country
Pack
Kingdom
LocalServiceEmergencyClass
Local
Mobile
Local
Collect
Local
Mobile
collect
Long
Distance
Collect
Toll
Free
Long
Distance
Distance
Mobile
InternationalPremiumLong
×××××××××Australia
××××××××××××Brazil
××××××××China
××××××France
×××××××United
×××××××××India
××××××Indonesia
×××××××Italy
××××××××Malaysia
××××××××Mexico
××××××Russia
States
of
America
×××××××Spain
×××××××United
You can configure the highest level of calls allowed for each usage profile using the Cisco Business Edition
3000 Administrative Interface on the Users\Phones > Usage Profiles > General tab. The list of options that
appear in the Highest Level of Calls Allowed drop-down list is based on the country pack you have installed
on the Cisco Business Edition 3000. The list is ordered from lowest to highest privilege with International
Calls being the highest level of calls that a user can place. This setting works in conjunction with the Highest
Privilege Allowed setting that is on the Sites page (System Settings > Sites). The Highest Privilege Allowed
setting applies to the entire site. The Highest Level of Calls Allowed in the usage profile applies to users. If
the values do not match for the usage profile and the site, the value that is the lowest level takes precedence
and applies to the user.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to specify an outside dial code for redial and click-to-call features
for each site. You can configure the outside dial code for these options on the Connection > Sites > Call
Settings > PSTN Access area using the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. You can also
edit the existing dial plan settings from the PSTN Access page. For information on editing the dial plan, see
Dial Plan Pattern Settings, on page 355.
Information about Dial Plans is available in the following files:
• Numbering Plan file—Specifies information about Dial Plan tags.
OL-27022-01 37
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 58

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
• Cisco-provided .xml file—Specifies the metadata information to set up a Dial Plan for your country. It
includes XML elements for Route Filters, Route Filter Members, Translation Patterns, Route Patterns,
and Called and Calling Party Transformation Patterns.
• Route Filters .xsd—Specifies XML definition.
For the default countries, the United States, India, and Canada, the dial plans are available with the installation
file. To install dial plans for all other countries, use the country pack for the applicable country.
For more information, see Country/Locale Settings, on page 197.
Phone Numbers
For your dial plan, you specify the main business number, the area codes, the length of the extension, the
extension ranges, and dialing prefixes for the outside dialing code (access code), operator dialing code, and
the feature codes, which a user presses on the phone for certain features, including Meet-Me Conferences,
call pickup, and so on.
After you set up your default extension range, you cannot change it. You can change other settings for your
dial plan in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
The extension length and range that you set in the dial plan impact the extensions that you can assign to your
users, departments, and pilot extensions for your hunt lists and voicemail and auto attendant. You cannot add
an extension to a user or department that does not belong in the extension range. (Pilot extensions for hunt
lists must also be in the extension range, but pilot extensions do not get assigned to users or departments.)
Your system can support various call types. The call types supported depends on the country pack installed
on your system. You can set the level of access for a site on the Sites page; you can set the level of access
authorized for the user in the Usage Profile. When a user places a call from a phone in a particular site, the
call gets connected if the phone at that site is allowed to make that level of call and if the user that owns the
line is also authorized to make that level of call.
Translation Rules
Translation rules allow Cisco Business Edition 3000 to manipulate an incoming phone number that is part of
your system and transform it to an extension before routing the call. The following list provides examples of
when you would configure translation rules:
• To translate the Meet-Me conference number to an extension
• To translate a toll-free number, such as an 800 number, to an extension
• To translate an extension to a pilot extension in a hunt list
Block Rules
Block rules allow you to configure a system-wide pattern to block unwanted calls in the Cisco Business Edition
3000. The Block rules are applied on the called party number based on the number pattern. Called party
numbers matching the patterns specified in the Blocking Rules will be blocked by the system. The outgoing
calls are routed or blocked based on the most specific matching patterns defined in the system. If the call you
intend to block is still being routed through the system, make the blocking rule more specific by specifying
more Beginning Digits. The letter 'd' displayed in the patterns represents any digit dialed by the user.
Prior to Release 8.6.4, when you modify an outside dial code, the block rules patterns are updated automatically
to use the new outside dial code. With Release 8.6.4, a modification in outside dial code will not update the
block rules. You must update the block rules manually.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
38 OL-27022-01
Page 59

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
If the user dials a blocked number, the system plays a recorded message stating that the route does not exist.
You can configure the Block Rules under System Settings > Dial Plan > Blocking Rules tab in Cisco
Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. You can also import the block rules from the Cisco-provided
.xls data configuration file.
Abbreviated Dialing
Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to configure an abbreviated number to place PSTN calls. You can
configure system-wide abbreviated dialing rules through which users can reach external numbers without
dialing the complete number of the recipient.
Prior to Release 8.6.4, when you modify an outside dial code, the abbreviated dial rules patterns are updated
automatically to use the new outside dial code. With Release 8.6.4, a modification in outside dial code will
not update the abbreviated dial rules. You must update the abbreviated dialing rules manually.
You can configure Abbreviated Dialing under System Settings > Dial Plan > Abbreviated Dialing tab in
Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. You can also import the block rules from the
Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file.
Application Dial Rules
Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to create customized application dial rules that you can apply when
applications place calls through Cisco Business Edition 3000. Cisco Business Edition 3000 applies the
translation pattern against the called number before forwarding the call.
You can configure application dial rules under the System Settings > Dial Plan > Application Dial Rules
tab in Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
For more information, see the following sections:
Sites
• Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 75
• Dial Plan Settings, on page 223 (for the Dial Plan page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time
Setup Wizard and Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface)
• Checklists for Users, Departments, Lines, and Phones, on page 139
Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports PSTN calls from every site through a local Gateway or a gateway
located in other sites.
Your Cisco Business Edition 3000 system may contain multiple sites, which are geographical locations that
define where the users are working.
• Central Site—The central site contains the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server and the gateway that
allows access to the PSTN. In most cases, the central site is the location where the majority of users
work; in most cases, the company headquarters is the central site. You can have only one central site,
and you cannot delete the central site.
• Remote Sites—Remote sites are branch offices that work with the central site; a dedicated WAN link
or Internet connection must exist between the remote and central sites. You can have up to nine remote
sites.
• Teleworker Site—The teleworker site is for workers who do not work only at the central site or branch
offices; these employees (users) use VPN connections to connect to the central site. A router is not
OL-27022-01 39
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 60

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
required to contact the central site because their Internet connection provides access to the central site.
You can have only one teleworker site.
When you configure a site, you must specify the maximum bandwidth that is required between sites, the
maximum bandwidth that is required for internal calls that take place within the site, calling privileges for the
site as a whole. You can configure the bandwidth between the remote site and the central site.
You can configure a site by using any of the following methods:
• Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time
Setup Wizard (for initial deployment)
• On the Sites page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (if you are not using the
Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file during initial deployment)
• Under Connections > Sites in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial
deployment)
A phone gets associated with a site through the subnet and subnet masks that are configured on the Sites page.
If you are using DHCP to assign IP addresses to the phones, the values that you enter for the subnet and subnet
mask depend on your DHCP configuration. In this case, the subnet and subnet mask translate to a range of
IP addresses that get distributed to the phones that are associated with the site.
Considerations for Configuring Sites
Before you configure your sites and DHCP, Cisco strongly recommends that you determine the number of
sites that you need and how many phones will be located at each site. Configure your DHCP server so that it
correctly distributes the IP addresses to the phones at the various sites.
If you do not configure the subnet and subnet masks for any site, the phones automatically get assigned to the
central site. By default, subnet address 192.168.1.0 with a subnet mask of 24 are displayed on the central site
page. You may update this information if it does not apply to your setup. You cannot enter the same subnet
and subnet mask for multiple sites. In addition, Cisco recommends that your subnet and subnet masks do not
overlap. If you configure multiple subnet and subnet masks on the Sites page, Cisco Business Edition 3000
selects the subnet and subnet mask that is most clearly defined and associates the phone with that site. To
associate phones with the remote sites, you must configure the subnet and subnet masks on the Sites pages
for the remote sites.
If no teleworker site exists and Cisco Business Edition 3000 cannot determine where the phone is located,
Cisco Business Edition 3000 automatically places the phone in the central site. If you have a teleworker site,
you must configure the subnet and subnet masks for the central site and all remote sites. For the teleworker
site, you cannot specify the subnet and subnet masks. It is not uncommon to disallow emergency calls for the
teleworker site. If you disallow emergency calls for the teleworker site, make sure that the users understand
that they cannot place emergency calls from their work phone that is outside of the office.
If you enable Reach Me Anywhere in the usage profile, the call privileges for the Reach Me Anywhere call
are always based on the highest calling privileges that are selected for the central site.
Device Mobility
When you do not configure any remote site in the Cisco Business Edition 3000, the endpoints will register
with the central site even when the endpoint is situated in a different subnet.
The association of the gateway with a site is based on device mobility. Prior to Release 8.6.4, the association
of the gateway with a site was based on device mobility, that is, depending on the PSTN connection and the
subnet of the site. From Release 8.6.4, the device mobility is disabled for the gateways. The gateways must
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
40 OL-27022-01
Page 61

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
be associated with the site explicitly. For every PSTN connection you configure, you can associate the gateway
with the desired site using the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface on the PSTN Connections
> Add PSTN Connection > Device > Add Device page. Select the appropriate site in the Site Association
drop-down list. You can also edit the site associated with the gateway on the Connections > Devices > Edit
Device page.
Routing Calls Through Gateways
The calls are routed through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 sites based on the PSTN access settings at
Connections > Sites > Add Site > PSTN Access. Configuring the PSTN Access allows you to control the
routing of PSTN calls through various connection groups.
From Release 8.6.4, Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to route PSTN calls based on the call type for
each outside dial code. You can also configure multiple connection groups for routing PSTN calls and route
the calls based on the call type and outside dial code. During the First Time Setup, a default connection group
containing all the PSTN gateways that are configured will be in use until you change the PSTN Access settings
for your site. Configure the connection groups and their usage for each site using the Cisco Business Edition
3000 Administrative Interface. Connection groups are not exposed on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First
Time Setup Wizard. The connection groups are configured after the First Time Setup. Therefore, all the calls
will be routed correctly.
If you have upgraded the Cisco Business Edition 3000 from a lower version to Release 8.6.4, a system-generated
connection group is formed which includes all the gateways in that site before the upgrade. The naming
convention for this connection group is <<SiteName>> Connections. Each site will be associated to its
respective connection group. By default, the sites will use their connection groups. When a new site is created,
the All Connections connection group is created by the system and will be used as a default connection group.
While configuring a gateway, the Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to associate each gateway with a
site. By default, the internal gateway is associated with the central site of your system. New configuration
groups can be created using the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface corresponding to the
PSTN access of each site. All the calls from this site will be routed through the corresponding connection
group.
You can configure multiple outside dial codes for your system (System Settings > Dial Plan General tab).
Based on the dial code and the Class of Service available for the installed country pack, various routing options
are available. For information on the classes of services supported by your country pack, see .Table 3: Classes
of Service Supported Based on the Country Pack, on page 37
Cisco Business Edition 3000 PSTN access allows you to route calls based on the following criteria:
• Route all calls from the site through the same connection group
You can choose a single connection group through which all the calls from that particular site will be
routed. You can also view the dial plan pattern. By default, All Connections connection group will be
selected.
Note
If the system is upgraded from a previous version, the <<SiteName>> Connections
connection group will be selected by default for the Site that is inherited from the previous
release.
• Route calls from the site through different connection groups based on Outside Dial Code
You can choose the connection group through which all the calls will be routed from that site for each
outside dial code.
OL-27022-01 41
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 62

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
Note
This option is not available for a single outside dial code configured in the System
Settings > Dial Plan > General > Dialing Prefixes area.
• Route calls from the site through connection groups based on Outside Dial Code and call type
You can choose connection groups for each call type for every outside dial code configured on the
system. The call types available for your system depends on the country pack you have installed. For
more information about various call types supported by different countries, see Table 3: Classes of
Service Supported Based on the Country Pack, on page 37.
• Route using a custom dial plan
Click Edit Dial Plan or Edit SPA Dial Plan to customize the routing options based on your requirement.
If there is no SPA connection configured in the system, the Edit SPA Dial Plan option will not be present.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 also allows you to specify an outside dial code for redial and click-to-call features
for each site. If the user dials an E.164 number without an outside dial code, the calls will be routed using the
outside dial code as defined for the redial and click-to-call for each site.
Logical Partitioning
The Logical Partitioning feature is required for countries with telecom restrictions, such as India.
Logical Partitioning prevents toll bypass of the PSTN calls through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 for
countries that adhere to telecom regulations. Logical Partitioning is enabled in the Country Pack for countries
that have regulations.
The Logical Partitioning feature is not available for countries that do not have regulations. Currently, the
Logical Partitioning feature is enabled for India.
You can select one of the following features for Logical Partitioning:
• Default - Allows you to enable default policies such that each site can route calls using the local gateway.
This is a basic requirement for deployments and is provided by default.
• Custom - Allows you to choose the required gateways such that multiple sites located in the same trunk
area can share a common gateway. This allows provisioning of a Policy matrix between any sites.
Best Practices for Using DHCP for Acquiring IP Addresses, on page 32
Example of Typical Deployment Model, on page 53
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 75
Sites Settings, on page 329
Remote Management of Cisco Business Edition 3000 using Cisco OnPlus
Remote Management Services (RMS) simplifies the adoption and ongoing management of Cisco Business
Edition 3000, thereby enhancing the business benefits of your network resulting in reduced total cost of
ownership (TCO). Remote Management provisions the management of Cisco Business Edition 3000 remotely
over a Wide Area Network (WAN).
Cisco Business Edition 3000 is remotely monitored and managed using the Cisco OnPlus installed and deployed
at various customer locations. You can use the Cisco OnPlus to remotely access, configure, and troubleshoot
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
42 OL-27022-01
Page 63

the Cisco Business Edition 3000 device. The Cisco OnPlus device, Cisco ON100, provides a secured tunnel
for communicating with the Cisco Business Edition 3000.
The Cisco OnPlus allows you to perform the following:
• Continuously monitor and manage the system
• Allows the TAC or IT staff to deliver technical support and management
• Allow their trusted admin to better manage the Cisco Business Edition 3000 device
For more information on Cisco OnPlus, see the Cisco OnPlus Portal User Guide, available on Cisco.com at
http://www.cisco.com/web/partners/sell/smb/onplus/index.html.
Signing on to Cisco Business Edition 3000 using Cisco Onplus
This section describes how to access Cisco Business Edition 3000 device through a secured Cisco OnPlus
tunnel and troubleshoot issues from a remote location.
Procedure
Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Sign in to the Cisco OnPlus URL using your credentials. For example, http://www.cisco-onplus.com/ .
The Cisco OnPlus home page displays.
Select the registered Customer added to the Cisco OnPlus portal.
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 is discovered by Cisco ON100 in the portals overview page. For more
information on how to register customers to the Cisco OnPlus portal, see the Cisco OnPlus Portal User Guide
available at http://www.cisco.com/web/partners/sell/smb/onplus/index.html.
Select the Cisco Business Edition 3000 device from the portal list.
Note: If you cannot find Cisco Business Edition 3000 device, you can manually add Cisco Business Edition
3000 device to the Cisco OnPlus portal list. For more information on how to add a device manually, see the
Cisco OnPlus Portal User Guide.
Click the “i” (Device Information) icon to view the Cisco Business Edition 3000 product-specific configuration
details.
From the Info tab, you can verify the MAC address, serial number, PID-VID, and other configuration details
of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 device.
Click the Connect tab to connect to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 device through a secured HTTPS tunnel.
You can now access the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface that is displayed.
Note: Ensure that the Secure (HTTPS) connection is enabled to establish a secured connection to maintain
content-level security.
Sign in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administration Interface with your user name and password.
You can now manage your Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface remotely.
If you find a problem while accessing the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Interface, see Troubleshooting
Overview, on page 411
OL-27022-01 43
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 64

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
Usage Profiles
A usage profile allows you to configure most of the user settings for a phone in one place. You can edit an
existing usage profile, duplicate an existing usage profile to create a new profile, or add an entirely new usage
profile. Each usage profile has a unique name. After you configure your usage profiles, you can assign them
to users or to departments, so that the settings in the usage profile apply to the phones that belong to an
individual user or to a department.
In the usage profile, you can configure calling privileges for users, phone features, such as barge and Cisco
Extension Mobility, phone hardware functionality, phone applications that may display on the phone, and the
phone button template, which controls the order of the buttons and the feature buttons that display on the
phone.
You can configure a usage profile through the following methods:
• Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time
Setup Wizard (for initial deployment)
• On the Usage Profile page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (if you are not
using the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file during initial deployment)
• Under Users/Phones > Usage Profiles in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
(after initial deployment)
The usage profiles are not phone model specific; all settings that are available in the usage profile do not
support all phone models. Before you add or edit an existing usage profile and assign it to a user, determine
whether the phone model that is assigned to the user supports the features and functionality that is available
in the usage profile. If you configure a setting that is not supported by the phone, the phone ignores the value
in the configuration file, and the user cannot use the feature or functionality on the phone.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports a maximum of 30 usage profiles.Note
The usage profiles in the following table come with your system by default; that is, they display on the Usage
Profile page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (and in the Cisco Business Edition
3000 Administrative Interface, unless you delete them from the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup
Wizard). You can delete these usage profiles, you can edit these profiles, or you assign them to your users
without modification.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
44 OL-27022-01
Page 65

Table 4: Default usage profiles
ConsiderationsType
Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
Standard
Manager
Consider applying this usage profile to most of your users. If you use the default values in
the usage profile:
• The user can place and receive local and internal calls; if the site where the phone
resides allows these types of calls.
• The user can make emergency calls to the local center that handles emergencies for
the municipality; if the site where the phone resides allows emergency calls.
• The user can use barge if the phone supports barge; barge allows a user to interrupt
a call without permission from other participants on the call.
• The user can use call pickup if the phone supports call pickup; call pickup allows the
user to pick up calls for another user.
• The user can create speed dials if the phone has 3 or more buttons on it.
• The user can use the speakerphone and a headset if the phone supports that
functionality.
Consider applying this usage profile to the managers in the company. If you use the default
values in the usage profile:
• The user can place and receive all types of calls, including long distance and
international calls; if the site where the phone resides allows these types of calls.
• The user can make emergency calls to the local center that handles emergencies for
the municipality; if the site where the phone resides allows emergency calls.
Assistants
• The user can use barge, call pickup, and call park if the phone supports these features.
Call park allows a user to park a call on one phone and then pick up the call on another
phone.
• The user can create speed dials if the phone has 3 or more buttons on it.
• The user can use the speakerphone and a headset if the phone supports that
functionality.
Consider applying this usage profile to the assistants that support the managers in the
company. If you use the default values in the usage profile:
• The user can place and receive internal, local, toll free, and long distance calls; if the
site where the phone resides allows these types of calls.
• The user can make emergency calls to the local center that handles emergencies for
the municipality; if the site where the phone resides allows emergency calls.
• The user can use barge and call pickup if the phone supports these features.
• The user can create speed dials if the phone has 3 or more buttons on it.
• The user can use the speakerphone and a headset if the phone supports that
functionality.
OL-27022-01 45
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 66

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
ConsiderationsType
Power
Common Area
Consider applying this usage profile to the users that assist with administering the system;
for example, to the IT support staff. If you use the default values in the usage profile:
• The user can place and receive internal, local, toll free, and long distance calls; if the
site where the phone resides allows these types of calls.
• The user can make emergency calls to the local center that handles emergencies for
the municipality; if the site where the phone resides allows emergency calls.
• The user can use barge and call pickup if the phone supports these features.
• The user can create speed dials if the phone has 3 or more buttons on it.
• The user can use the speakerphone and a headset if the phone supports that
functionality.
Consider applying this usage profile to departments, which are for phones that are used in
public spaces, such as break rooms. If you use the default values in the usage profile:
• On the public space phone, the user that can place and receive internal calls.
• The user can make emergency calls to the local center that handles emergencies for
the municipality; if the site where the phone resides allows emergency calling.
• On the public space phone, the user can use barge if the phone supports this feature.
• As the administrator, you can add speed dials if the public space phone has 3 or more
buttons on it.
• On the public space phone, the user can use the speakerphone and a headset if the
phone supports that functionality.
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 75
Usage Profiles, on page 44
Checklists for Users, Departments, Lines, and Phones, on page 139
Users, Departments, Phones, and Lines
Phones, users, and lines are closely related in Cisco Business Edition 3000. A user, which is an employee
from the company, uses the usage profile on a phone that is supported in Cisco Business Edition 3000. Because
phones and users are closely related, you cannot configure a phone without first configuring a user or department
that has an extension (line) from the dial plan assigned to it.
In the Cisco Business Edition 3000 system, a user becomes an owner of a phone when you assign the user
extension to line 1 on the phone. If the user is an owner of the phone, the phone uses the usage profile that is
assigned to the user.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
46 OL-27022-01
Page 67

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
A department is a special kind of user that is reserved for public-space phones; this user is reserved for
Tip
phones in cafeterias, lobbies, and break rooms . A public-space phone cannot support Reach Me Anywhere.
You do not configure passwords or phone PINs for departments, unlike users (Users/Phones > Users).
Example of How User or Department Ownership Works for a Phone
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
If you have not already done so, add the user or department configuration; for example, add the user by
selecting Users/Phones > Users (or Department) in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
• When you add the user or department, you must assign a usage profile that you want to be available to
the phone.
• When you add the user or department, assign an extension to the user or department, based on the dial
plan that is set up for your system.
Add the phone and assign the extension to line 1 on the phone.
The user or department becomes the owner of the phone, and a user can use the features and functionality
from the usage profile on the phone if the phone supports the functionality.
You can create a shared line between an IP phone and an analog phone using the same user extension.Tip
Note
Refer to http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/vg224/software/configuration/guide/
scgvoip.html for information on VG224 configuration.
On the User or Department page, you create lines for the user or department based on the dial plan that you
set up; for example, if your dial plan is set up for 4-digit dialing with an extension range of 2000-2999, you
can assign an extension such as 2555 to the user or department. You can set up to 6 extensions in a prioritized
list for each user or department. The usage profile that you assign to the user or department applies to all
extensions that are in the prioritized list.
You assign user extensions (lines) to the phone on the Phone page. You can set up to 6 lines as a prioritized
list on the Phone page, even if the phone does not support 6 lines. For each line, you can define Call Forward
All and External Caller ID.
The phone button template that is configured in the usage profile determines the order of line buttons and the
types of functionality that displays next to the line buttons on the phone; for example, for all lines except line
1, which must be a line because of user-phone ownership, you can designate a line as a speed dial, line, or
feature button (Mobility and Meet-Me Conference). When the phone button template that is configured in the
usage profile designates the buttons as lines, the system orders the lines that are assigned on the Phone page
based on the prioritized list, with the first line being designated for line 1, the second line in the list being
used for the next button on the phone that is designated as line 2. In the Usage Profile, you must establish the
purpose for all line buttons on the phone, even when the phone does not support all the line buttons.
The users can create up to 48 speed dials in a prioritized list in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences
Interface, even when the phone does not support 48 speed dials.
Note
The number of speed dial keys that can be created is dependent on the model of phone and whether
key expansion modules are connected to the phone.
OL-27022-01 47
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 68

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
Significant Behavior of SIP Trunk
SIP trunk exhibits significant behavior while processing PSTN calls in Cisco Business Edition 3000.
The SIP trunk supports the following features:
• Basic Outgoing/Incoming Call
• Early and Delayed Offer
• PRACK
• Session Timers
• PAI and RPID for Identity
• DTMF using RFC 2833, KPML, and Unsolicited Notify
• Hold/Resume, Transfer, Conference, Forwarding
• Diversion Header
• MWI
• Options Ping
The following sections details the behavior of SIP trunk specific to Cisco Business Edition 3000.
• Incoming 302 Moved Temporarily, on page 48
• Incoming OOD REFER Message Handling, on page 49
• Calling Party Transformation, on page 49
• Connected Party Transformation, on page 50
Incoming 302 Moved Temporarily
The SIP service provider sends 302 message to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 to reach to SIP Uniform
Resource Identifier (URI) as specified in the Contact header field. By default, the SIP trunk will use the
Redirect by Application feature to reroute the PSTN calls. The SIP trunk checks the class of service and the
privilege of the calling user before redirecting the calls.
In a SIP environment, the two possible ways of forwarding or redirecting a call are sending SIP 302 Moved
Temporarily with one or more Contact: headers as response to an INVITE or are sending a new INVITE to
the new destination.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 sends an INVITE to the new destination upon reception of 302 Moved temporarily
but it cannot generate such a response. The 302 Moved temporarily response is received when call forward
is enabled on a SIP endpoint.
The service provider can be configured to react in different ways when a SIP call is forwarded or redirected
by one of the call legs. Most often, a SIP peer sends a SIP response 302 Moved temporarily with the new
destination URI appearing in the Contact: header of the message.
Similar to Call Transfer Supplementary service, the service provider can be configured to pass along the 302
Moved Temporarily to the originating call leg or to react to it and send a new INVITE on behalf of the
forwarded (FWED) party.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
48 OL-27022-01
Page 69

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
In Redirect by Application configuration, the SIP trunk passes the control to Redirecting Application layer
for handling the rerouting. The Rerouting Calling Search Space configured on SIP trunk is passed to allow
further check on class of service and privilege of the calling user for redirection to the new Contact. To set
these parameters, refer to Connection Type: SIP Trunk, on page 283.
The Redirect by Application feature of the SIP trunk allows the Cisco Business Edition 3000 to do the
following:
• Apply digit analysis to the redirected contacts to ensure that the calls are routed correctly
• Prevent DOS attack by limiting the number of redirection (recursive redirection) that a service parameter
can set
• Allow other features to be invoked while the redirection is taking place
Calls get redirected to a restricted phone number (such as an international number) due to handling redirection
at the stack level to route the calls without blocking. This behavior occurs when the Redirect by Application
check box is not checked in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
Note
In case of multiple redirections before final redirection over SIP trunk, the maximum of two Redirection
headers will be sent over SIP trunk, that is the original called party and last called party information.
Incoming OOD REFER Message Handling
Out-of-dialog REFER (OOD-R) enables remote applications to establish calls by sending a REFER message
to Cisco Business Edition 3000 without an initial INVITE. After the REFER is sent, the remainder of the call
setup is independent of the application and the media stream does not flow through the application. The
application using OOD-R triggers a call setup request that specifies the Referee address in the Request-URI
and the Refer-Target in the Refer-To header.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 handles the incoming REFER from a SIP trunk service provider.
Calling search spaces determine the partitions that calling devices can search when they attempt to complete
a call. The out-of-dialog calling search space is used when a Cisco refers a call (B) that is coming into SIP
user (A) to a third party (C) when no involvement of SIP user (A) exists. In this case, the system uses the
out-of-dialog calling search space of SIP user (A). The third party (C) is either an internal extension or an
auto attendant client.
CUBE on Cisco ISR8xx, the session border element in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 SIP trunking solution,
does not support the OOD REFER inter-operability. The service provider cannot send OOD REFER through
CUBE on Cisco ISR8xx through Cisco Business Edition 3000.
Calling Party Transformation
The mid-call SIP messages, namely reINVITEs, UPDATE or 200 OK sent from the calling party direction
on SIP Trunk from Cisco Business Edition 3000, carry the URI identity containing a number in user portion.
This occurs during Hold/Resume and Transfer, which results in transactions inside a SIP dialog.
By default, the Cisco Business Edition 3000 sends configured extension number only, while expected number
for inter-operability with the SIP service provider is the DID or full number (for example: Office code +
Subscriber code).
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 preconfigures the Calling party Transformation on SIP Trunk used to connect
to the session border elements.
OL-27022-01 49
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 70

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
By provisioning the Calling Party Transformations feature for a SIP Trunk, the SIP dialogs established as
part of outbound SIP Trunk calls always use the transformation for upsizing the number sent in P-Asserted
ID or Remote Party ID headers of an outbound SIP message.
Note
For the calling party transformation to function correctly, ensure that the External Caller ID is defined for
the user. You can edit the External Caller ID on Users/Phones > Users > Edit User > General page.
Connected Party Transformation
The backward direction SIP messages namely 183, 200 Ok or mid-call UPDATE/INVITE messages from the
connected party SIP trunk on Cisco Business Edition 3000 carry the URI identity containing a number in user
portion.
By default, the Cisco Business Edition 3000 sends configured extension number only, while the expected
number for inter-operability with the SIP service provider is the DID or full number (for example: Office
code + Subscriber code).
To send the full number (DID) on SIP trunk, the Cisco Business Edition 3000 preconfigures the Connected
Party Transformation on SIP trunk used to connect to the session border element. By provisioning the Connected
Party Transformation feature for a SIP trunk, the SIP dialogs established as part of inbound SIP trunk calls
always use the transformation for upsizing the number sent in PAI/RPID headers of an outbound SIP message.
Note
For the connected party transformation to function correctly, ensure that the External Caller ID is defined
for the user. You can edit the External Caller ID on Users/Phones > Users > Edit User > General page.
Attendant Group
Note
The Attendant Group page allows you to add or remove attendant console users who will be associated with
all the phones in the phone list of Cisco Business Edition 3000 (choose Users/Phones > Attendant Group).
You can add until ten users to the Attendant Group. The system displays an error message when you click to
add more than ten users.
You must have administrator account, browser access, and Internet access to add or remove users.
Attendant Group requires an additional enhanced user license for each group member. If the number of
licenses is insufficient, a new user will not get associated to the Attendant Group.
Attendant Group has an Available list of users, which displays all the users in the Cisco Business Edition
3000 who are not associated with Attendant Group, and a Selected list, which displays all users who are
associated to Attendant Group. You can move users from Available to Selected to associate a user to Attendant
Group.
After adding a user to the Selected list you must save the user in the Selected list. You can also remove users
from the Selected list. The users removed from the Selected list are moved to the Available list. For more
information, see (Setting Up Attendant Group, on page 151 and Attendant Group Settings, on page 173).
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
50 OL-27022-01
Page 71

Hunt Lists
Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
A hunt list consists of a group of extensions that can answer calls. You set up hunt lists for the purpose of
distributing calls amongst the users that belong to the group. For example, if the company does not have a
receptionist and several users must answer calls, consider setting up a hunt list to ensure that calls are evenly
distributed amongst the users that belong to the hunt list. For example, if several administrative assistants
must share the call load for several managers, consider setting up a hunt list to ensure that all calls are answered
quickly. You configure hunt lists on the Hunt Lists page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface. (select Users/Phones > Hunt Lists).You can create as many hunt lists as you want.
Extensions in a hunt list can belong to users or departments. You can assign any user or department extension
to a hunt list, but only those extensions that are assigned to phones can actually answer the calls. An extension
may belong to more than one hunt list.
Pilot extensions for hunt lists must be in the extension range(s), but pilot extensions do not get assigned to
users or departments.
For the members (extensions) that belong to the group, you can select one of the following distribution methods:
Note
Note
An idle member is not servicing any calls. An available member is on an active call but is available to
accept a new call. A busy member cannot accept calls.
• Top Down—Cisco Business Edition 3000 distributes a call to idle or available members (extensions)
starting from the first idle or available member of a hunt list to the last idle or available member.
• Circular—Cisco Business Edition 3000 distributes a call to idle or available members starting from the
(n+1)th member of a hunt list, where the nth member is the member to which Cisco Business Edition
3000 most recently extended a call. If the nth member is the last member of a hunt list, Cisco Business
Edition 3000 distributes a call starting from the top of the hunt list.
• Longest Idle Time—Cisco Business Edition 3000 only distributes a call to idle members, starting from
the longest idle member to the least idle member of a hunt list.
• Broadcast—Cisco Business Edition 3000 distributes a call to all idle or available members of a hunt list
simultaneously.
Do not put extensions that are shared lines in a hunt list that uses the Broadcast distribution algorithm.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 cannot display shared lines correctly on the phone if the extensions are
members of a hunt list that uses the Broadcast distribution algorithm.
Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Operator, on page 152
Call Pickup Groups
In the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, you can add, edit, and delete call pickup groups.
The system defines a call pickup group as a group of users or departments that is designed to pick up calls to
any user or department within this group or in an associated group. A user or department can be associated
with multiple pickup groups. Each group has a unique number, known as a Group Pickup Number, which
OL-27022-01 51
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 72

Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Business Edition 3000
allows any authorized user or department to pick up a call by entering this number. For authorization, the user
or department must be in either the same or an associated pickup group and should know the Group Pickup
Number.
Upon migration from a previous version to the current version of Cisco Business Edition 3000, all users or
departments are added to a default pickup group. Currently, Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports multiple
call pickup groups, which allows user to associate a list of users or departments to pickup groups either by
site or by company functional area. To make use of this feature, user can now assign the user or department
to different pickup groups based on the site or functional area.
Soft clients like webex connect and cucirtx do not support multiple call pickup groups.Note
To pick up a call, the user or department must use the phone’s buttons or softkeys to dial the extension given
in the dial plan. The softkey is generated if call pickup is enabled in the user or department usage profile.
For information about the types of softkeys that are available, see the following topics:
• GPickUp, on page 52
• OPickUp, on page 52
Note
Tip
GPickUp
Short for Group Pickup, this softkey is used to selectively pick up calls coming into a device that is a member
of the same pickup group. This softkey can be used to pick up calls across multiple call pickup groups.
OPickUp
Short for Other Group Call Pickup, this softkey is used to answer a call that is ringing on an extension outside
the user’s or department’s pickup group. However, both these phones must belong to associated pickup groups.
The order of pickup depends on the priority that is assigned to these associated pickup groups.
Usually, within the same group, the longest alerting call (longest ringing time) gets picked up first if
multiple incoming calls occur in that group. For Other Group Call Pickup, priority takes precedence over
the ringing time if multiple associated pickup groups are configured.
Call Pickup Group configuration settings allow you to configure the call pickup group including the group
name and extension length. You can use the Call Pickup Group page to configure multiple call pickup groups.
The number of pickup groups is limited by the feature code selected on the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First
Time Setup Wizard.
There can be a maximum of 20 call pickup groups in a 3-digit dial plan and 100 pickup groups in 4-digit
or higher dial plan.
Table 22: Settings on the Add or Edit Call Pickup Group Page, on page 165 describes how to add or edit a
call pickup group on the Call Pickup Groups page (Users/Phones > Call Pickup Groups).
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
52 OL-27022-01
Page 73

Example of Typical Deployment Model
The following illustration shows an example of a typical deployment model that includes the central site, two
remote sites, and the teleworker site. The central site includes the gateway, server, several routers, a Cisco
VG224 Analog Phone Gateway, and IP and analog phones. The remote sites include phones and routers. For
more information on the example, see the following sections.
Figure 4: Example of a typical deployment model
Example of Typical Deployment Model
Table 5: Components of a typical deployment model
DescriptionNumber
Central Site1
Router2
Router with VPN3
Cisco Business Edition 3000 Server4
Cisco VG224 Analog Phone Gateway5
Cisco 2901 Integrated Services Router (ISR) (Gateway)6
Dual E1/TI connection7
Service Provider (Telecommunications Company)8
Internet9
Teleworkers Site10
OL-27022-01 53
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 74

Example of Typical Deployment Model
Central site (Example)
The previous illustration shows that the central site is where your server, gateway, and the majority of your
phones/users are located. To use fax or analog phones at the central site, the Cisco VG224 Analog Phone
Gateway is set up specifically for the central site. The gateway allows access to the PSTN through a dual
T1/E1 connection that is provided by the service provider (telecommunications company).
Although not included in the previous illustration, a switch exists between the server and the Cisco Unified
IP Phones.
DescriptionNumber
Remote Site 111
Router with VPN12
Cisco VG224 Analog Phone Gateway13
Dedicated WAN link14
Remote Site 215
Router16
Cisco VG224 Analog Phone Gateway17
Teleworker site (Example)
The previous illustration shows that the teleworker site has phones and personal computers that connect to
the central site through the Internet. A router that supports VPN connects the teleworker site to the central
site.
Quality of service (QoS) may not be available for the teleworker site.Tip
Remote site 1 (Example)
The previous illustration shows that remote site 1 connects to the central site through a router that supports
VPN (and connects to the Internet). Analog phones and fax are used at remote site 1, so the Cisco VG224
Analog Phone Gateway is set up for these phones and functionality specifically for this site. Fewer phones
are included in remote site 1 than at the central site.
Remote site 2 (Example)
The previous illustration shows that remote site 2 connects to the central site through a dedicated WAN link.
Analog phones are used at remote site 2, so the Cisco VG224 Analog Phone Gateway is set up to support the
analog phones at this site.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
54 OL-27022-01
Page 75

CHAPTER 2
Frequently Asked Questions
This chapter contains a list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) and the answers to those questions. Use
this chapter in conjunction with other chapters in this guide.
Q.
I cannot access the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard. Why not?
A.
Verify that you have set up the network correctly. See the following sections:
• Using a Cable to Set Up Server Access to the Network, on page 127
• Using the Cisco Network Configuration USB Flash Drive, on page 128
Your server comes preinstalled with the default IP address of 192.168.1.250. The default
Tip
username is admin. The default password is BE-3000. Perform one of the procedures in the
preceding bullets so that the server is recognized on the network.
Q.
How do I sign in to the interfaces?
A.
To sign in to the interfaces, see one of the following sections:
• Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, on page 67
• Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, on page 67
• Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface, on page 68
Cisco Business Edition 3000 uses HTTPS, so you must accept the certificate for the server during
Tip
the login process before you can access the GUI. If you need assistance with accepting the certificate
for the server, review your browser documentation.
Q.
What browsers are supported?
A.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 supports the following operating system browsers on your server:
• Microsoft Internet Explorer (IE) 8 when running on Microsoft Windows XP or Windows 7
OL-27022-01 55
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 76

• Firefox 8.x when running on Microsoft Windows XP, Windows 7, or Apple Mac OS X
• Safari 4.x when running on Apple Mac OS X
Note
Cisco Business Edition 3000 does not support the buttons or browser options in your browser. Do
not use the browser buttons or browser options (for example, the Back button) when you perform
configuration tasks.
Q.
Does this product provide accessibility?
A.
The administrative interfaces provide functionality for you that allows you to access buttons or icons
on a page without using a mouse. You can perform the following procedures from any point on the page
so that you do not have to scroll or tab through various settings.
• Accessing the Icons on the Page, on page 68
• Accessing the Buttons On the Page, on page 69
Q.
What kind of security is provided?
A.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 uses HTTPS, so you must accept the certificate for the server during the login
process before you can access the GUIs. If you need assistance with accepting the certificate for the server,
review your browser documentation. Cisco Business Edition 3000 encrypts the passwords for all administrator
and users.
Caution
The secure shell username and password that is assigned in the Administrator page in the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (System Settings > Administrator) is sent to the
phone in clear text because there is no phone encryption supported with Cisco Business Edition
3000; the configuration file that is sent to the phone does not include any encrypted values. Do not
configure these secure shell username and password unless Cisco Technical Assistance Center
(TAC) tells you to do so.
Q.
How do I view the version of software?
A.
You can view the version of Cisco Business Edition 3000 software that is running on your system by
clicking About in the upper, right corner of the GUIs. In addition, in the Restart/Shutdown page in the
Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, you can view the active and inactive versions
that are on your system. The active version is the version of software that you are currently running on
your system; the active version matches the version that displays in the About dialog box. The inactive
version, if available, is the last version of software that was running on the system before an upgrade.
To close the About box, click outside of the box.Tip
Q.
How do I access online help?
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
56 OL-27022-01
Page 77

A.
When you access online help in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, you can view
the field descriptions for each page that displays in the GUI. In addition, in the online help for Cisco
Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, you can access some troubleshooting information for
your system. To access online help documentation in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface, click Help that displays in the upper right corner of each page.
Q.
What is a country pack, and where do I install it?
A.
If your locale or country is not supported by default, as indicated in the Country/Locale page in the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, you can install a Cisco-provided country pack, which
includes the dial plan, phone and network tones, and language to support a country. You can only install
the country pack during the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard. You can only install
one country pack, and you cannot apply a country pack and select an option from the defaults.
Obtain the country pack from www.cisco.com. If you plan to upload it to the system from a USB flash
drive, copy the file to the USB flash drive.
The Country/Locale page allows you to set up the support for the following items:
• The locale, which is the language that displays for text in the online help, in the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface,
and the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface; the locale also impacts the tones
that are used for the phones and gateway.
The locale that you select impacts all users in the system; for example, all phones use the same
network tones, and all users view the same language in the GUIs.
• The country where the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server is located. The country that you select
determines the dial plan that is used by the system.
The gateway only supports English text, so English is the language that is used for all gateway CLI
commands. If you must reimage the server, the text during the installation displays in English.
For more information, see Country/Locale Settings, on page 197.
Q.
What is a locale?
A.
A locale is the language that displays:
• In the online help
• In the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard
• In the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
• In the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface
• On the phones
The locale also provide localized tones that are used for the phones and gateway.
The locale that you select impacts all users in the system; for example, all phones use the same network
tones, and all users view the same language in the GUIs and on the phones.
Some phases, including trademarks, display in English only. To obtain the latest localized text and tones,
apply a locale update through the Upgrade page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface after the update is available.
OL-27022-01 57
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 78

Cisco recommends that all users set their supported browsers to the locale so that the text displays as
expected. Cisco does not support other browser controls, including the Print, Back, Forward, Refresh
buttons, with any Cisco Business Edition 3000 GUIs.
Note
If you change the browser to the locale after you log into the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First
Time Setup Wizard, close and reopen the browser so that the language displays as you expect.
When you configure the system, use only characters from the Modern Latin Alphabet or use Arabic
Tip
numerals. For example, you can enter A-Z, a-z, 1, 2, 3 and some special characters.
For more information, see the following sections:
• Country/Locale Settings, on page 197
• Upgrade of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 software failed
Q.
How do I update the administrator username and password?
A.
The Change Password page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard allows you to
set the administrator username and password for your system. Administrators can perform all tasks in
the Cisco Business Edition 3000 GUIs, including but not limited to adding phones, users, and monitoring
the system. Anyone with access to this username and password can make updates in the GUIs.
The default username is admin. The default password is BE-3000. For security purposes, Cisco
Tip
requires that you change the default password that comes with your system. Enter values that are
difficult to guess, and remember your new username and password because the password does not
display in the Password page.
To change the administrator username and password after you complete the Cisco Business Edition 3000
First Time Setup Wizard, select System Settings > Administrator.
Individual users with administrative privileges, as indicated in the User page in the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, should use their username and passwords that are established in
the User page.
Q.
What is a strong password?
A.
A non-trivial password meets the following criteria:
• Contains three of the four allowable characteristics: uppercase character, lowercase character,
number, symbol.
• Does not include a character or number more than three times consecutively.
• Does not repeat or include the alias, username, or extension.
• Does not contain 3 consecutive characters or numbers (for example, passwords such as 654 or
ABC).
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
58 OL-27022-01
Page 79

Q.
Why do I need licenses? How do I install and view the licenses on my system?
A.
Cisco User Connect Licensing (UCL) is a user-based licensing model where the number of users and
phones that are added to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 system get tracked and licensed for use. Several
license types exist, but be aware that you may not be able to add a phone or enable certain features, such
as voicemail, unless you install licenses. Your system comes with a 5 starter licenses.
The Manage Licenses page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard and in the
Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface allows you to perform such tasks as installing
licenses and viewing details about installed licenses, including the license version, the type of licenses,
and the number of licenses that you used and available.
For more information, see the following sections:
• Cisco User Connect Licensing, on page 95
• License Settings, on page 241
Q.
How do I find, add, update, delete, and copy configuration?
A.
You can add your configuration through the following methods:
• Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file during the initial deployment. Click
Automatic Setup and upload the file through the desktop or through a USB flash drive. (See
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page 75).
• Through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard during the initial deployment
(if you do not plan to use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file) - Add your data, and click
Next or Back in the GUI.
• Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file to add users and phones in bulk after the
initial deployment. (See Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, on page
75).
• Through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface after initial deployment. The
following sections describe how to find, delete, add, edit, and copy your configuration in the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface:
• Finding Your Configuration, on page 69
• Deleting Your Configuration, on page 70
• Adding Your Configuration, on page 71
• Editing Your Configuration, on page 71
• Copying (Duplicating) Configuration, on page 72
When add your add and edit your configuration, use only characters from the Modern Latin Alphabet
Tip
or use Arabic numerals. For example, you can enter A-Z, a-z, 1, 2,3 and some special characters.
Q.
When can I not perform configuration tasks?
OL-27022-01 59
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 80

A.
You cannot perform configuration tasks under the following circumstances:
• After a backup has started
• After a restore has started; that is, the restoration of data has begun
• When the system is creating the export file during configuration export
• After an upgrade has started
Alert your users when any of these tasks are in progress. Your users cannot update the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface under these circumstances.
If another administrator starts these tasks in another browser session, you can manage the tasks that are
in progress by clicking Assume Control when the button is presented in your browser session.
Q.
How do I configure my gateway?
A.
See the following sections:
• Configuring the Gateway for the First Time, on
page 133
• Editing the Gateway Configuration, on page 135
• Deleting the Gateway, on page 137
Q.
What is the Post-Setup Wizard?
A.
After you log in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface for the first time, the
Post-Setup wizard displays. Cisco Business Edition 3000 displays the Post-Setup Wizard to ensure that
you perform the most critical tasks immediately after the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup
Wizard completes. The Post-Setup wizard allows you to perform the following tasks:
• Immediately import users and phones in bulk from the Cisco Provided .xls Data Configuration file
If you selected automatic setup during the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard,
uploaded the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, and included users and phones in the
configuration file, the Post-Setup wizard allows you to import the users and phones immediately
after you log in to the GUI. After you import the users and phones, the system displays status of
the import. If errors are reported, you can save the error report to a .csv file so that you can track
the and correct the issues after the Post-Setup wizard completes.
• Immediately obtain the CLI commands that you must issue on the gateway
The Post-Setup wizard displays the CLI commands that you must issue on the external gateway.
You can copy the commands directly onto the gateway if it is in enable mode, or you can save the
commands to a file. (If you save to a text file, verify the text after you save it. The text should
replicate the text from the GUI.)
• Perform other recommended tasks, such as backups
The last page of the Post-Setup wizard displays tasks that Cisco recommends that you perform
before you perform any other tasks in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
For more information, see the following sections:
• Post-Setup Wizard, on page 253
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
60 OL-27022-01
Page 81

• Checklists for Users, Departments, Lines, and Phones, on page 139
• Checklists for Configuring the Gateway, on page 133
Q.
How do I upgrade software?
A.
The Upgrade page (Maintenance > Upgrade) in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface allows you to upload a valid file to upgrade the software that is running on your server. To
upgrade your software, you can use either a DVD or SFTP server that has the upgrade file on it. You
can use the Upgrade page to install ISO images for new releases, locale updates, device packs, phone
firmware loads, updates for dial plans, or other Cisco-issued patches (.cop files) that are required for
your Cisco Business Edition 3000 system.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 prevents you (and users) from making configuration changes during the
upgrade.
For more information, see the following sections:
• Upgrading Cisco Business Edition 3000
• Reverting to a Previous Version of Cisco Business Edition 3000, on page 160
• Upgrade Settings, on page 365
Q.
How do I perform a backup of data?
A.
Running a backup ensures that you store your important data to a remote location, such as a USB hard
drive or SFTP server. To restore data after a system failure, for example, if you must reinstall or replace
a server, you must have access to a backup tar file that matches the Cisco Business Edition 3000 software
version that is running on your server. To run a backup, select Maintenance > Backup, which allows
you to immediately back up your data.
For more information, see the following sections:
• Backing Up Your Data, on page 157
• Backup Settings, on page 181
Q.
When would I need to restore my data?
A.
The Restore page (Maintenance > Restore) in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
allows you to upload a backup tar file to restore data if you have a system failure; for example, you must
replace your server or reinstall your server because of a system failure. Do not reinstall your server or
replace your server unless your technical support team indicates that you must do so.
For more information, see Backing Up and Restoring License Files, on page 104.
Q.
What are call detail records (CDRs), and how do I export them?
A.
Call detail records (CDRs), which display under the Call Detail Reports page, provide important data
about calls, including the date and time for the call, who made the call, and the reason why the call ended.
CDRs store information about the devices of the call and other call control/routing aspects. Call detail
records are automatically generated with Cisco Business Edition 3000; you do not need to perform any
tasks for the system to generate these types of records. When a call is placed or received, the system
automatically generates a call detail record when the call is terminated. In addition, the system generates
OL-27022-01 61
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 82

a record when significant changes occur to a given call, such as ending the call, transferring the call,
redirecting the call, and splitting the call.
From the Call Details Reports page, you can generate a summary report, generate a report that provides
detailed information about your calls, or export your CDR data. When you export CDR data, consider
the following information:
• Cisco Business Edition 3000 exports all data that is available on CDRs to a .csv file. Cisco Business
Edition 3000 uses the same CDR framework as Cisco Unified Communications Manager, so the
.csv file contains information that does not apply to Cisco Business Edition 3000, including
information on RSVP, MLPP, video, and partitions.
• If you open and review the .csv file for any reason, you are viewing the same information that is
available with Cisco Unified Communications Manager. To analyze your CDR data, refer to the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Call Detail Records Administration Guide, which is
available in English only. (You must have an understanding of Cisco Unified Communications
Manager in order to understand the information that is provided in this document.)
Note
For information on call termination cause codes, refer to the Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Call Detail Records Administration Guide.
For information, see Call Detail Reports, on page 185.
Q.
Can I export my configuration? Where can I import it?
A.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 allows you to export some of your configuration data through the
Configuration Export page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. When you
export your configuration data, the system creates a tar file that contains most of the data that your system
is using. Before you export your data, review the following information:
• The export creates a tar file that includes the data that you configured for the system. The tar file
does not include passwords, call detail records, or any configuration that is related to voicemail.
You can export the tar file to a USB flash drive or a SFTP server.
Because Cisco Business Edition 3000 uses Cisco Unified Communications Manager for call
processing, the tar file includes Cisco Unified Communications Manager data that is used to make
call processing work. Most of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager data that is included
in the tar file does not display in the GUIs for Cisco Business Edition 3000.
For more information, see the following sections:
• Exporting Your Data and Importing to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition
5000, on page 160
• Configuration Export Settings, on page 201
Q.
When is the server going to automatically restart? How do I manually restart the server?
A.
After you complete the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, the server automatically
reboots. After the reboot completes, you can log in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
62 OL-27022-01
Page 83

In the Restart/Shutdown page (Maintenance > Restart/Shutdown) in the Cisco Business Edition 3000
Administrative Interface, you can restart (reboot) the server or shut down the server.
To stop all processes on the server and then have the server restart, click Restart. When you restart the
server, calls in progress may drop because the phones unregister from the system, re-register with the system,
and then restart.
When you click Shutdown, the server stops all processes, shuts down, and does not restart. When you shut
down the server, calls in progress drop because the phones unregister from the system, power down, and do
not restart.
Caution
During a restart, the server may be unavailable for more than 10 minutes, and you cannot update
any pages.
The server automatically restarts under the following circumstances:
• After you complete the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard
• When you update the time zone on the Date/Time page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000
Administrative Interface (System Settings > Date/Time)
• When you make updates to the Network Settings section on the Network page in the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (Connections > Network)
• When you revert to a previous version of software
• When you upgrade the software
Caution
Cisco recommends that you do not press the power button on the server to shut down or to restart
the server unless you absolutely must do so. If you do so, you may accidentally corrupt the file
system, which may prevent you from being able to reboot your server.
Q.
How do I restart the phones?
A.
If you restart the Cisco Business Edition 3000 server, all phones that are configured in the system
automatically restart; that is, they power down and then immediately boot up. In the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, select Maintenance > Restart/Shutdown. To restart specific
phones, you (or the user) must press the appropriate reset key sequence on the phones themselves, as
indicated in the phone documentation. (The user can also unplug and plug the phone back into the
network.)
Q.
How do I know whether the phone is registered?
A.
After you configure the phone and connect it to the network, the phone attempts to connect (or register)
to Cisco Business Edition 3000. When the phone attempts to register, the phone displays a message. (If
the phone is working as expected, it is registered to the Cisco Business Edition 3000.)
The Edit Phone page (Users > Users/Phones) in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
displays the registration status for the phones. You must click the phone configuration in the Search
Phones page to display the Edit Phone page.
Q.
How do I log out users from Cisco Extension Mobility-enabled phones?
OL-27022-01 63
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 84

A.
From the Phone Search page (Users/Phones > Phones) in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface, you can log out a Cisco Extension Mobility user that is logged into a Cisco Extension
Mobility-enabled phone. When the user is logged into the phone, the Logout link displays next to the
phone entry in the Search Phones page. (The Logout link ensures that you do not need to go to the phone
to manually log out the user.) Click the Logout link to log out the user from the phone.
Q.
How do I configure the system so that the call goes to the operator or to the auto attendant?
A.
See the following sections:
• Setting Up Auto Attendant, on page 151
• Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Auto Attendant, on page 152
• Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Auto Attendant if the Operator is Not
Available, on page 153
• Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Operator, on page 152
Q.
May I use auto attendant without using voicemail?
A.
Auto attendant and voicemail use the same internal components, but you may use auto attendant without
using voicemail. To use voicemail, you must perform configuration tasks, including installing a voicemail
license for each user that can use voicemail. Auto attendant requires that you perform configuration tasks,
but it does not require licensing.
You cannot use voicemail without also using the auto attendant functionality.Note
For more information, see the following sections:
• Voicemail, on page 10
• Auto Attendant, on page 13
• Setting Up Voicemail, on page 150
• Setting Up Auto Attendant, on page 151
• Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Auto Attendant, on page 152
• Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Auto Attendant if the Operator is Not
Available, on page 153
• Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Operator, on page 152
Q.
What is Cisco Web Dialer?
A.
Cisco Web Dialer allows a user to place calls to people in the corporate directory from Cisco Business
Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface. For example, Cisco Web Dialer uses hyperlinked telephone
numbers in a corporate directory to allow users to make calls from Cisco Business Edition 3000 User
Preferences Interface by clicking on the telephone number (extension) of the person that the user is
trying to call.
Cisco Web Dialer is turned on by default, and you cannot turn it off. It always displays in the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface for all users. To ensure that the user can call all
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
64 OL-27022-01
Page 85

employees in the corporate directory, verify that each user in Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface has an extension and phone assigned to him. (Only users with assigned extensions and phones
can be called through Cisco Web Dialer.)
Q.
How does a user update the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface?
A.
Remember that the settings that display in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface
depend on your configuration. If you set up all of the features that are available in the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface, the user can use the information in User Preferences Settings,
on page 393 to update their preferences.
Q.
How do I monitor and troubleshoot?
A.
You monitor the system by accessing the Monitoring menu in the Cisco Business Edition 3000
Administrative Interface. Under this menu, you can view a summary of the health of your system, view
a report for Cisco Extension Mobility usage in your system, view the call detail records that are being
generated by the system, and collect diagnostics for your system.
For more information, see the following topics:
• Troubleshooting from the Health Summary Page, on page 416
• Troubleshooting From the Diagnostics Page, on page 418
• Troubleshooting When You Cannot Access the Graphical User Interfaces, on page 419
• Troubleshooting Issues, on page 427
• Call Detail Reports, on page 185
• Cisco Extension Mobility Report, on page 199
Q.
MCS 7890-C1 will not power up. Why not?
A.
For more information about starting the MCS 7890-C1, see MCS 7890-C1 will not power up. Why not?,
on page 72.
Q.
How do I connect or disconnect a USB DVD drive to an MCS 7890-C1?
A.
To connect or disconnect a USB DVD drive to an MCS 7890-C1, perform the following procedures:
• Connecting a USB DVD Drive, on page 73
• Disconnecting a USB DVD Drive, on page 73
Q.
Is there a recovery disk available for MCS 7890-C1?
A.
No, MCS 7890-C1 does not support the use of a recovery disk.
In the event of a hardware failure, contact TAC for a replacement (RMA). If it is not a hardware failure,
you can reimage the system using the Cisco Business Edition 3000 DVD that ships with the unit and
then restore from backup. For information on how to reimage the MCS 7890-C1, refer to Reimaging an
MCS 7890-C1, on page 453.
Q.
How do I recover the system if I have lost the admin password?
OL-27022-01 65
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 86

A.
Reimage the system using the Cisco Business Edition 3000 DVD that ships with the unit and restore
from backup. For information on how to reimage the MCS 7890-C1, refer to Reimaging an MCS
7890-C1, on page 453.
Q.
How do I configure a Cisco Jabber client?
A.
Cisco Jabber clients are configured as Phones in the Phones configuration window, which can be accessed
by selecting Users/Phones > Phones. The Adding a Phone for a User, on page 141 procedure describes
how to add a phone within Cisco Business Edition 3000.
For configuration specific to Cisco Jabber clients, make sure to do the following:
• Choose Cisco Unified Services Client as the Phone Type
• Enter a unique name for the Cisco Jabber client in the Identifier field on the Add a Phone window.
The Identifier is the name that Cisco Business Edition 3000 assigns to the Cisco Jabber client. The
XML device configuration file that the TFTP service sends to the Cisco Jabber client during the
registration process is given the name you assign in this field.
Q.
How will internal users access Auto Attendant who has Voicemail enabled in their Usage Profiles?
A.
Perform the following procedure to reach auto attendant:
1
User A presses the voice mail box or dials the Auto Attendant pilot
extension.
The User A reaches the voice mailbox prompt.
2
User A dials “#” to reach Auto Attendant.
To sign in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 interfaces and to perform other configuration tasks, see the
following sections:
• Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, page 67
• Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, page 67
• Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface, page 68
• Accessing the Icons on the Page, page 68
• Accessing the Buttons On the Page, page 69
• Finding Your Configuration, page 69
• Deleting Your Configuration, page 70
• Adding Your Configuration, page 71
• Editing Your Configuration, page 71
• Copying (Duplicating) Configuration, page 72
• MCS 7890-C1 will not power up. Why not?, page 72
• Connecting a USB DVD Drive, page 73
• Disconnecting a USB DVD Drive, page 73
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
66 OL-27022-01
Page 87

Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard
Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard
Perform the following procedure to sign in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard.
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Before you sign in to the GUI for the first time, make sure that the server is recognized on your network.
Start a supported web browser. For a list of supported web browsers, see the Frequently Asked Questions,
on page 55.
In the address bar of the web browser, enter either of the following case-sensitive URLs:
• https://<IP address of the server>:8443/cucmadmin/dayonelaunch
• https:// <IP address of the server>:8443
Note
If the Cisco Business Edition 3000 link displays, click it.
Enter your username and password; then, click Sign In.
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard displays.
You can save and exit Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard at any time, even if the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard is not complete. After you log in again, the system remembers
where in the process you were when you logged off and continues with that step.
Note
The IP address that you enter depends on which procedure you performed to set up server access to
the network. If you used a cable to set up server access to the network, you may enter the default IP
address of the server. If you used the configure.xml file to set up server access to the network, you
enter the IP address that you assigned in the configure.xml file.
The default username is admin. The default password is BE-3000.Tip
After you complete the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, you cannot access it
again. After your initial deployment, you can update the majority of your settings and perform
maintenance-related tasks in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. (Some settings
cannot be changed, such as the country, locale, and default extension range.)
Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
Perform the following procedure to sign in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
Procedure
Step 1
OL-27022-01 67
Start a supported web browser.
For a list of supported browsers, see the Frequently Asked Questions, on page 55.
Note
You cannot sign in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface until after you have
completed the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 88

Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Make sure that you have set your browser to the same language that was selected in the Cisco Business Edition
3000 First Time Setup Wizard.
In the address bar of the web browser, enter one of the following case-sensitive URLs:
• https://<IP address or hostname of the Cisco Business Edition 3000
server>:8443/cucmadmin
• https://<IP address or hostname of the server>:8443
If the Cisco Business Edition 3000 link displays, click the link.
After the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface displays, enter your username and password;
then, click Sign In.
Signing in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface
All users that exist in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface can manage their user
preferences settings through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface if you give them the
URL for the page.
Before a user can log in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface, the user
Tip
configuration must exist in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. You can add the
user by entering the user data in the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, or you can create a user
in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface by selecting Users/Phones > Users.
The user can use the following procedure to browse into the server and log in to the Cisco Business Edition
3000 User Preferences Interface.
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Start a supported operating system browser.
For a list of supported browsers, see the Frequently Asked Questions, on page 55.
In the address bar of the web browser, enter the following case-sensitive URL:
https://<IP address or hostname of the Cisco Business Edition 3000
server>:8443/cucmuser
Enter your username and password; then, click Sign In.
Your default user and password are assigned to you by your system administrator.Tip
The Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface displays.
The first time that you sign into the interface, change your username and password, as described in the online
help for the Cisco Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface.
Accessing the Icons on the Page
Some of the pages include icons that display. To access these icons, perform the following procedure.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
68 OL-27022-01
Page 89

Procedure
Accessing the Buttons On the Page
Step 1
Step 2
Press Alt, press 1; then, press Tab. The cursor highlights the first icon from the left. To move to the next icon,
press Tab again.
Press Enter.
The system performs the function of the icon.
Accessing the Buttons On the Page
Most of the pages have buttons that display at the bottom of the page. To access these buttons, perform the
following procedure.
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Press Alt, press 2, and then press Tab. The cursor highlights the first button from the left. To move to the
next button, press Tab again.
Press Enter.
The system performs the function of the button.
Finding Your Configuration
Step 1
Step 2
You can search for your configuration in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, as described
in the following procedure.
Procedure
For items other than phones, users, departments, usage profiles, phone applications, and sites, click the menu
option to display the information. For example, to view your network settings or license information, click
Connections > Network or Maintenance > Manage Licenses. After you click the menu option, the
configuration page displays for these items.
For phones, users, departments, hunt lists, usage profiles, phone applications, and sites, multiple configurations
may exist for the items, so you can search for the specific configuration that you want to view. Navigate to
the Search page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface for the configuration that you
want to find.
• Users - Select Users/Phones > Users.
• Phones - Select Users/Phones > Phones.
• Departments - Select Users/Phones > Departments.
• Usage Profiles - Select Users/Phones > Usage Profiles.
• Phone Applications - Select Users/Phones > Phone Applications.
OL-27022-01 69
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 90

Deleting Your Configuration
• Hunt Lists - Select Users/Phones > Hunt Lists.
• Sites - Select Connections > Sites.
Tip
Step 3
To find all configured items in the system, ensure that the Filter dialog box and the field next to the Filter
drop-down list box are empty; go to Step 5.
Step 4
To filter or search for your configuration:
• To narrow your search to find a particular configuration, select a search parameter from the Filter
• To find a specific configuration, enter text in the field next to the Filter drop-down list box.
You can also search for call detail records, which provide you with monitoring data about calls, in the
Call Details Reports page (Monitoring > Call Details Reports).
drop-down list box.
Each search page allows you to filter on different criteria. For example, in the Users search page,
Tip
you can search by last name, user ID, and so on. In the Phones search page, you can search by
phone model and name of phone.
Step 5
Click Go.
All matching items display.
You can change the number of items that display on each page by choosing a different value from the Rows
per Page drop-down list box. You can reverse the sort order, by clicking the arrow in the column header.
Deleting Your Configuration
You can delete the entire configuration for users, phones, usage profiles, remote sites, hunt lists, and phone
applications in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. You can only delete one entry (one
record) at a time from the Cisco Business Edition 3000. For sites, you cannot delete the central site. In addition,
you cannot delete call detail records that display under Monitoring > Call Detail Reports in the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. The system automatically deletes call detail records after a
certain number of call detail records are generated (up to 2 months of CDRs are allowed).
Before you delete a usage profile that is assigned to users, reassign the users to a different usage profile. If
you delete a usage profile and do not reassign the users, the phone may not behave as the user expects.
Use the following procedure to delete a configured entry (record) from the Cisco Business Edition 3000.
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Find the item that you want to delete, as described in the Finding Your Configuration, on page 69.
For the item that you want to delete, click Delete.
A warning message displays.
Repeat this procedure to delete another configured item.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
70 OL-27022-01
Page 91

Adding Your Configuration
To add configuration for users, phones, usage profiles, sites, hunt lists, and phone applications in the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, perform the following procedure:
Procedure
Adding Your Configuration
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Navigate to the Search page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface for the type of item
that you want to add.
• Users—Select Users/Phones > Users.
• Phones—Select Users/Phones > Phones.
• Departments—Select Users/Phones > Departments.
• Usage Profiles—Select Users/Phones > Usage Profiles.
• Phone Applications—Select Users/Phones > Phone Applications.
• Hunt Lists—Select Users/Phones > Hunt Lists.
• Sites—Select Connections > Sites.
To add a new item, click Add <item> .
The Add page displays.
Make the necessary changes, and click OK.
Editing Your Configuration
To edit configuration in Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, perform the following procedure:
Procedure
Step 1
OL-27022-01 71
For users, phones, departments, hunt lists, usage profiles, phone applications, and sites, which each use a
Search page, navigate to the Search page in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface for the
type of item that you want to edit.
• Users - Select Users/Phones > Users.
• Phones - Select Users/Phones > Phones.
• Departments - Select Users/Phones > Departments.
• Usage Profiles - Select Users/Phones > Usage Profiles.
• Phone Applications - Select Users/Phones > Phone Applications.
• Hunt Lists - Select Users/Phones > Hunt Lists.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 92

Copying (Duplicating) Configuration
• Sites - Select Connections > Sites.
Step 2
Step 3
To edit an item, click Edit.
The Edit page displays. Make the necessary changes, and click Save.
You can edit the date and time for the server and phones, the network settings for the server, gateway
configuration information, dial plan, administrator username and password, and voice features that impact
the entire system through the System Settings menu; for example, to update the network settings for the server,
select Connections > Network. The configuration page displays where you can edit the information. After
you edit the information, click Save.
Copying (Duplicating) Configuration
You can copy (duplicate) the entire configuration from a usage profile so that you can easily add a new usage
profile. You can make a copy of the usage profile, easily modify the settings to retain any configuration that
you want to use, and then add the new usage profile to the GUI by using the following procedure. You cannot
copy more than one usage profile at a time.
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Find the usage profile that you want to copy, as described in the Finding Your Configuration, on page 69.
For the usage profile that you want to copy, click Duplicate.
The configuration displays where you can modify it. Make sure that you give the configuration a new name.
To add the new usage profile, click OK.
MCS 7890-C1 will not power up. Why not?
When starting the MCS 7890-C1 for the first time, or following a power outage, perform the following
procedure.
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
72 OL-27022-01
Move the MCS 7890-C1 back panel power switch to the on position (|).
The front power button illuminates, as shown in the following illustration. If the light fails to illuminate, press
the front power button.
Figure 5: MCS 7890-C1 power button
Page 93

Connecting a USB DVD Drive
Step 3
Perform the procedure described in the Frequently Asked Questions, on page 55.
Note
To shut down the MCS 7890-C1 gracefully, press the front power button once and release immediately.
If the system does not shut down using this method, press the front power button and hold for 5
seconds until the system is forced to power off.
Connecting a USB DVD Drive
To connect a USB DVD drive to the MCS 7890-C1, perform the following procedure:
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Connect the USB DVD drive to its power source.
Connect the USB DVD drive output to one of the USB input ports on the rear of the MCS 7890-C1.
Insert the install DVD into the USB DVD drive.
Disconnecting a USB DVD Drive
To disconnect a USB DVD drive from the MCS 7890-C1, perform the following procedure:
Procedure
Step 1
Step 2
OL-27022-01 73
Eject the DVD from the USB DVD drive. Store the DVD in an appropriate place.
Disconnect the USB DVD drive from the rear of the MCS 7890-C1.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 94

Disconnecting a USB DVD Drive
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
74 OL-27022-01
Page 95

CHAPTER 3
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data
Configuration File
This chapter contains information on the following topics:
• When You Can Use the Cisco-provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 75
• Considerations for Using the Cisco-provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 76
• Network Tab Settings, page 78
• Date and Time Tab Settings, page 80
• PSTN Gateway Tab Settings, page 80
• Dial Plan Tab Settings, page 81
• Block Rules Tab Settings, page 83
• Abbreviated Dialing Tab Settings, page 83
• Sites Tab Settings, page 84
• Usage Profiles Tab Settings, page 86
• Phones Tab Settings, page 89
• Users Tab Settings, page 91
When You Can Use the Cisco-provided .xls Data Configuration File
The data configuration file, which is a Cisco-provided .xls spreadsheet template where you can enter the
majority of your configuration data, provides the following support:
• Allows you to plan your configuration before you begin your first day of deployment.
• Allows you to insert users and phones in bulk through the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative
Interface after your initial deployment.
To quickly import (add) your configuration data to Cisco Business Edition 3000 after you plug in your Cisco
Business Edition 3000 server, you can enter your data and then upload the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration
file to the server from a USB flash drive or your desktop when you run the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First
OL-27022-01 75
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 96

Considerations for Using the Cisco-provided .xls Data Configuration File
Time Setup Wizard. If you upload the file, you bypass the configuration pages in the Cisco Business Edition
3000 First Time Setup Wizard, and the wizard immediately takes you to the Summary page where you can
confirm your data.
After the server restarts at the end of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, you can log
into the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface and verify that your data got added to Cisco
Business Edition 3000. If you include user and phone data in the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file,
the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface allows you to import the users and phones and then
informs you of import errors.
If you do not want to upload the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file when you run the Cisco
Tip
Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, consider entering your data in the file and using it as a
guide when you manually enter the information on the GUI pages.
For example, during your initial deployment, you inserted 25 users and phones; now, you must insert 25 more
users and phones. To accomplish this task, you can modify the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file
that you used for automatic setup during the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard or you
can obtain a new Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file and add your new users and phones to that new
spreadsheet.
Note
Be aware that when you download the localized spreadsheet on the Cisco Business Edition 3000, the
options in the Advanced Options drop-down menu for various functionalities may remain in English. Only
the non-technical texts and the non-reserved strings will be translated to the chosen locale. For example,
PRI 4ESS, PRI 5E8, SFTP, CentralSite, and Remote Site remains in English.
Note
Cisco recommends that all users set their supported browsers to the desired locale version that is available
in the installed country pack version, so that the text displays as expected.
Caution
Do not use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file to modify your configuration data. Cisco Business
Edition 3000 only supports the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file for the initial deployment and
for bulk insertion (adding) of users and phones after the initial deployment. For example, if you attempt
to update existing user and phone information through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, the
updates fail.
Considerations for Using the Cisco-provided .xls Data Configuration File
Before you complete the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, review the considerations in the following
sections:
• For Both the Initial Deployment and Bulk Insertion of Users and Phones After Initial Deployment, on
page 77
• For the Initial Deployment Only, on page 77
• For Bulk Insertion of Users and Phones After Initial Deployment, on page 78
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
76 OL-27022-01
Page 97

Considerations for Using the Cisco-provided .xls Data Configuration File
For Both the Initial Deployment and Bulk Insertion of Users and Phones After Initial Deployment
You must use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, which is a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. You
can rename the file, but do not change the .xls extension. The file is translated into multiple languages.
To include your configuration data, you can use any tool that supports the .xls format. When add your
Tip
data to the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, use only characters from the Modern Latin Alphabet
or use Arabic numerals. For example, you can enter A-Z, a-z, 1, 2,3 and some special characters.
Do not delete or change the order of the settings in the file. Do not rename the settings in the file. Do not add
more settings to the file. In these cases, the system cannot read the file.
Only add new tabs at the end of the file; for example, you may add a new tab at the end of the file to include
your notes. Do not delete or rename the tabs in the file. Do not change the order of the tabs in the file. In these
cases, the system cannot read the file.
Some configuration settings are not in the file. For settings that are not in the file, the system uses the default
values. To change the default values for these settings, you must access the Cisco Business Edition 3000
Administrative Interface and manually update the configuration.
Cisco Business Edition 3000 does not check the integrity of the configuration data until after the Cisco-provided
.xls data configuration file is inserted into the system.
For the Initial Deployment Only
When you use the file for automatic setup during the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard,
the system automatically uses the default values for the settings that are not considered mandatory in the file.
For the automatic setup to succeed, you must update the following settings in the file:
• Network tab - IP Address (Enter the IP address that you want the server to use after the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard completes. Do not enter the default IP address that comes with
the preinstalled server.)
• PSTN Gateway tab - IP Address or Obtain an IP Address Automatically (you must configure one of
these two options)
• Dial Plan tab - Extension Length (because you cannot change this value in the Cisco Business Edition
3000 Administrative Interface)
• If adding users and phones (optional) - You cannot add a phone unless you also add a user with a user
extension and assigned usage profile. After you add the user information under the User tab, add the
phone information under the Phone tab. Make sure that you assign a user extension from the User tab
to the Line cell under the Phone tab. If you do not do this task, the phone configuration does not get
added to the system.
• After you upload the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file and click Next in the Setup Mode page,
the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard displays a progress bar while the upload is
occurring. As the upload progresses, each page of the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup
Wizard displays with the data from the spreadsheet. If you click Cancel under the progress bar, you can
modify any data on the pages, and click Next until the FTS wizard displays the Summary page. If you
do not click Cancel, the Summary page displays after the upload completes. After the Summary page
displays, verify your data in the summary tabs.
OL-27022-01 77
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 98

Network Tab Settings
• The system validates most of the data from the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file when you
upload it in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard. User and phone configuration is
not validated until after the server restarts.
• If you add user and phone information to the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file for your initial
deployment, the Post-Setup wizard, which displays after you log in to the Cisco Business Edition 3000
Administrative Interface, allows you to insert the user and phone configuration immediately in the
system. (The configuration does not get inserted in the system until you click the button that initiates
the insertion.)
Warning
• USB Support, on page 5
Before you run the Cisco Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, you can copy
the configure.xml file, licenses, Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file,
Cisco-provided country pack, localized greeting for auto attendant, and music on hold
source audio file to a single USB flash drive. Insert the key, and then run the Cisco
Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard. After you run the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard and the server restarts, you may keep the USB
flash drive inserted in the server, which allows you to perform additional tasks, such as
uploading the greeting and music on hold source audio file to the Cisco Business Edition
3000 Administrative Interface.
For More Information
For Bulk Insertion of Users and Phones After Initial Deployment
If you use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file to insert phones and users in bulk after the initial
deployment, the system ignores all tabs except for the Users and Phones tabs.
To import users and phones in bulk after the initial deployment, you access the Search Users or Search Phones
pages in the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. (Click Import Users/Phones)
You cannot add a phone unless the following criteria are met:
• A user with an assigned extension is already configured in the system
• A user with an assigned extension is added to the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file (Make sure
that you select a usage profile for the user, too.)
• Always verify that the user and assigned extension exist. If you plan to add a phone through the
Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, make sure that you add at least one user extension to the
Line cell under the Phone tab. Otherwise, the phone configuration fails to get inserted into the system.
Network Tab Settings
The Network tab allows you to specify the hostname and IP address for the Cisco Business Edition 3000
server, the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS settings (if you plan to use DNS). To update the Link
Speed and MTU size, as described in the Network Settings, on page 245, select Connections > Network in
the Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
The following table describes the settings that display under the Network tab.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
78 OL-27022-01
Page 99

Table 6: Settings on the Network tab
Network Tab Settings
DescriptionSetting
System Host Name
System IP Address
Specify the hostname for the server. This value is an
alias that is assigned to an IPv4 address to identify
the server. The hostname cannot be more than 63
characters, can only contain alphanumeric characters
(a, b, 1, 2) and hyphen (-), and must start with a letter.
To use DNS, make sure that you map the IPv4
Tip
address of the Cisco Business Appliance
server to the hostname on the DNS server.
Cisco recommends that you update the DNS
server before you add the hostname or IP
address on the Network page.
You can only set a static IP address for the server.
Enter an IPv4 address that identifies the server on this
network.
The IP address must be in the format ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd
where ddd can be a value between 0 and 255 (except
0.0.0.0).
Caution
Do not enter the default IP address that
comes with your preinstalled server.
Instead, enter the IP address that you want
the server to use after the Cisco Business
Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard is
complete.
Media Resource IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
Enable DNS Resolution
Enter an IP address that identifies the internal gateway
on the network. The Media Resource IP address must
be in the same subnet as the System IP address.
Enter the subnet mask, which allows you to identify
the part of an IP address reserved for the network.
The subnet mask must be in the format
ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd where ddd can be a value between
0 and 255 (except 0.0.0.0).
Enter the default gateway, which represents a network
point that acts as the entrance to another network. The
default gateway must be in the format
ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd where ddd can be a value between
0 and 255 (except 0.0.0.0).
If you plan to use DNS for hostname resolution, select
Enable to configure your Domain Name System
(DNS) client and have one or more available DNS
servers.
OL-27022-01 79
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
Page 100

Date and Time Tab Settings
DescriptionSetting
Primary DNS Server
Alternate DNS Server
Domain
Date and Time Tab Settings
The Date and Time tab allows you to specify the country and time zone where your central site is located.
This tab does not allow you to configure the date and time for the server. To update the date and time for the
server, as described in the Date and Time Settings, on page 209, select System Settings > Date/Time in the
Cisco Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
The following table describes the settings for the Date and Time tab.
If you selected Enable for the Enable DNS Resolution
setting, enter the IP address of the primary DNS
server.The IP address must be in the format
ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd where ddd can be a value between
0 and 255 (except 0.0.0.0).
If you selected Enable for the Enable DNS Resolution
setting, enter the IP address of the secondary DNS
server (optional). The IP address must be in the format
ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd where ddd can be a value between
0 and 255 (except 0.0.0.0).
Enter the name of the domain where this node is
located.
Table 7: Settings on the Date and Time tab
Country
System Time Zone
PSTN Gateway Tab Settings
The PSTN Gateway tab allows you to configure basic settings for the gateway, including the hostname, IP
address, and the basic settings for the ports.
The following table describes the settings for the PSTN Gateway tab.
DescriptionSetting
Select the country that you want to configure for the
system. Select the country where your central site
(server) is located.
From the drop-down list box, select the time zone
that supports your central site. Time Zone comprises
a list of time zones for the selected region. Scroll
through the list to select the appropriate time zone.
Administration Guide for Cisco Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(4)
80 OL-27022-01
 Loading...
Loading...