Page 1

Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable
Installation
Release 2.7
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Guide
Text Part Number: OL-19105-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco HealthPresence, the Cisco logo, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco WebEx, DCE, and Welcome
to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco
Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco
Cisco
Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step,
Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort
MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase,
SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx
Cisco
Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0812R)
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide, Release 2.7
© 2002-2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS,
IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS,
logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone,
logo are registered trademarks of
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface vii
Audience vii
How This Guide Is Organized vii
Document Conventions viii
Related Documentation ix
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request ix
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
1 Overview 1-1
Operating System Requirements 1-1
JDK Patches for Solaris 8 1-1
JDK Patches for Solaris 9 1-2
KDC Patches 1-2
Network Registrar Requirements 1-2
Hardware Requirements 1-2
Types of Installations 1-4
2 Preparing to Install Components 2-1
Broadband Access Center for Cable Components 2-1
Installation and Startup Process 2-2
Broadband Access Center Database Requirements 2-5
File System Block Size 2-5
Large File Support 2-6
Installation Checklist 2-6
Installation 2-7
Installation Using the Graphical User Interface 2-7
Installing from the Command Line 2-8
CHAPTER
OL-19105-01
3 Installing Components 3-1
Installing Components Using the Graphical User Interface 3-1
Installing the Regional Distribution Unit 3-2
Installing Extensions on a Network Registrar Server 3-3
Installing Extensions 3-4
Configuring Extensions 3-5
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
iii
Page 4

Contents
Validating Extensions 3-6
Installing the Key Distribution Center 3-7
Installing the Device Provisioning Engine 3-8
Installing Components Using the CLI 3-8
Installing the Regional Distribution Unit 3-9
Installing Network Registrar Extensions 3-11
Installing the Key Distribution Center 3-14
Installing the Device Provisioning Engine 3-16
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
4 Installing in a Lab Environment 4-1
Installation Checklist 4-1
Installing in a Lab Environment Using the GUI 4-2
Installing in a Lab Environment Using the CLI 4-3
Configuring Network Registrar and a CMTS 4-6
5 Post-Installation Activities 5-1
Enabling a Network Registrar Spoofing DNS Server 5-1
Configuring the Syslog Utility to Receive Alerts from BACC 5-1
Uninstalling Broadband Access Center 5-2
Uninstalling BACC from the Graphical User Interface 5-3
Uninstalling BACC from the Console Mode 5-3
6 Upgrading Broadband Access Center for Cable 6-1
Before You Begin 6-2
Upgrading the RDU 6-2
Upgrading the Solaris DPE 6-2
CHAPTER
iv
Upgrading Hardware DPEs 6-4
Upgrading Network Registrar Extensions 6-5
Upgrading the KDC 6-5
Migrating the RDU Database 6-6
7 Setting Up a Device Provisioning Engine 7-1
Hardware DPE Setup Sequence 7-1
Connecting the Device Provisioning Engine 7-1
Configuring and Running a Terminal Emulation Program 7-2
Logging In 7-2
Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine for Data 7-3
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 5

Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine for Voice Technology 7-5
Setting Up Voice Technology 7-5
Controls Available 7-7
Debugging 7-7
Contents
APPENDIX
I
NDEX
A Network Registrar Configuration File Example A-1
Configuration Scripts A-1
Sample Script for DOCSIS Modems and Computers A-1
Sample Script for DOCSIS Modems and PacketCable MTAs A-2
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
v
Page 6

Contents
vi
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 7

Preface
Welcome to the Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7. This chapter provides
an outline of the other chapters in this guide, and demonstrates the styles and conventions used in the
guide.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Audience, page vii
• How This Guide Is Organized, page vii
• Document Conventions, page viii
• Related Documentation, page ix
• Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, page ix
Audience
This installation guide enables system integrators, network administrators, and network technicians to
install Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable, referred to as BACC throughout this installation guide,
on Solaris operating systems and to set up the Cisco device provisioning engine (DPE).
Note Within this installation guide you may encounter references to BACC. With two exceptions, these
references are actually referring to the BACC product. The exception are in those areas where you are
prompted to enter specific data that may also contain references to BACC and where references are made
to specific file, directory or pathnames.
In these instances, you must enter the characters exactly as they appear in this guide.
How This Guide Is Organized
This guide describes how to install BACC on Solaris operating system. The major sections of this guide
are described here:
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
vii
Page 8
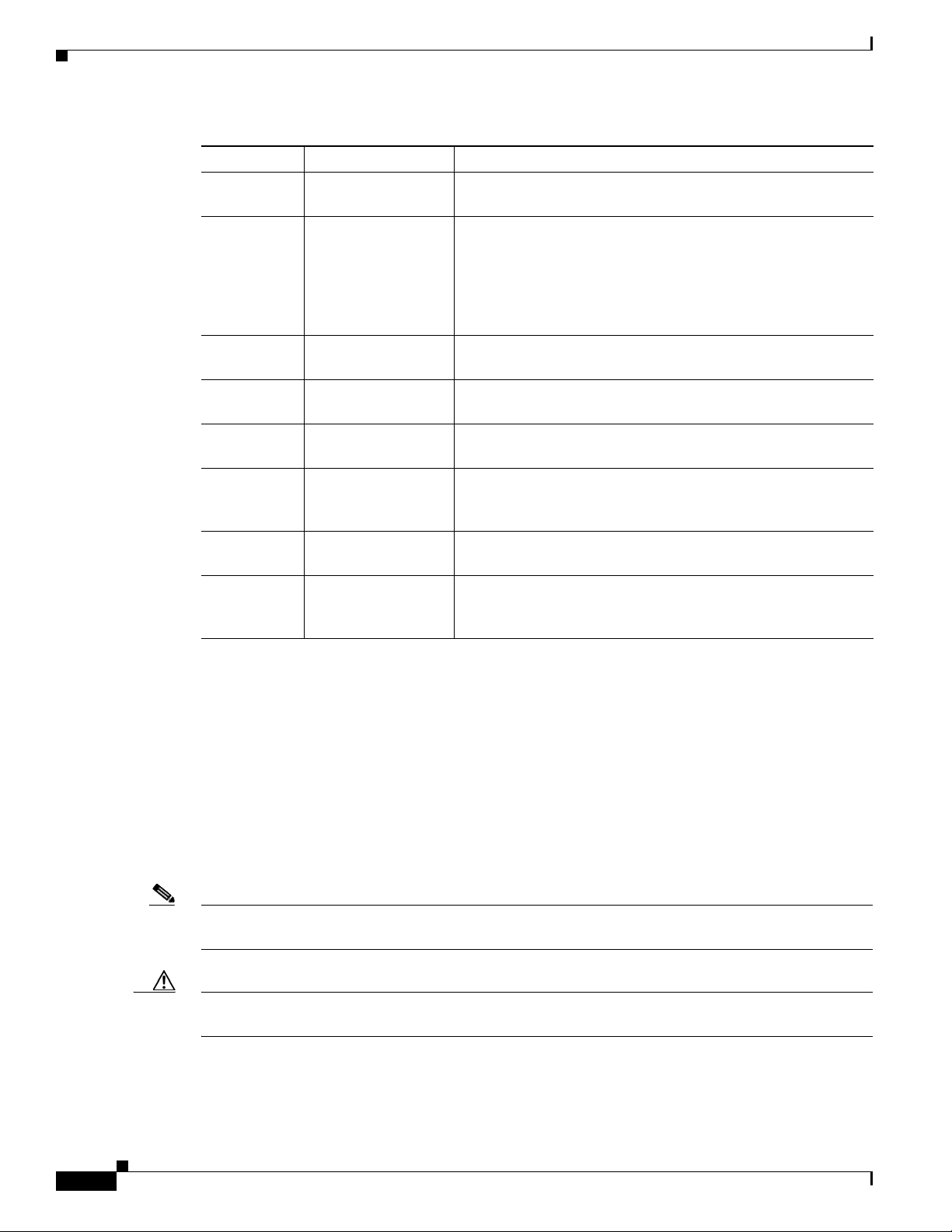
Preface
Section Title Description
Chapter 1 Overview Provides general requirements for a successful installation of
BACC.
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install
Components
Chapter 3 Installing
Components
Chapter 4 Installing in a Lab
Environment
Chapter 5 Post-Installation
Activities
Chapter 6 Upgrading
Broadband Access
Center for Cable
Chapter 7 Setting Up a Device
Provisioning Engine
Appendix A Network Registrar
Configuration File
Example
Describes considerations you need to take into account as you
prepare to install BACC. For example, it describes the
individual components of BACC, the order of operations for
installing the software, and the BACC database requirements. It
also describes initial steps for installing the software using
either a graphical user interface or a command line interface.
Describes how to install the individual components of BACC
using either the graphical user interface or the CLI.
Describes how to install a lab version of BACC using either the
graphical user interface or the CLI.
Describes those activities that are performed following
installation.
Describes the upgrade procedures performed on various BACC
components.
Describes how to configure a device provisioning engine
(DPE).
Shows examples of files used to configure Network Registrar
for high-speed data (HSD) and voice technology deployments.
Document Conventions
This guide uses the following conventions:
• Boldface is used for commands, keywords, and buttons.
• Italic is used for command input for which you supply values.
• Screen font is used for examples of information that are displayed on the screen.
• Boldface screen font is used for examples of information that you enter.
• UNIX paths are indicated as follows: /tools/list/connections.
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
publication.
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
viii
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 9

Preface
Related Documentation
Refer to these manuals for additional information:
• Release Notes for Broadband Access Center for Cable, Release 2.7
• Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide
• Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable CLI Reference Guide
• To support the DPE-590:
–
Device Provisioning Engine 590 Recovery CD-ROM Release Notes
–
Cisco Content Engine 500 Series Hardware Installation Guide
• To support the DPE-2115:
–
Device Provisioning Engine 2115 Recovery CD-ROM Release Notes
–
Installation and Setup Guide for the Cisco 1102 VLAN Policy Server
Caution Refer to this guide for port and connector identification and to perform hardware installation only. Do
not attempt to perform any of the configuration instructions found in that guide.
• Cisco Network Registrar User’s Guide
• Cisco Network Registrar CLI Reference
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional
information, see the monthly What’s
revised Cisco
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS
technical documentation, at:
New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and
Ve r si o n 2.0.
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
ix
Page 10

Preface
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
x
OL-19105-01
Page 11

Overview
Broadband Access Center for Cable (BACC) automates the process of configuring and provisioning
cable network devices. BACC interfaces with Cisco Network Registrar, which includes a high-speed
DHCP server for IP address management and a DNS server.
This chapter describes:
• Operating System Requirements, page 1-1
• Network Registrar Requirements, page 1-2
• Hardware Requirements, page 1-2
• Types of Installations, page 1-4
Operating System Requirements
You must install BACC on a computer running the Solaris 8 or 9 operating system. You must have the
correct type and number of patches installed on your system before you can install BACC.
CHAP T ER
1
JDK Patches for Solaris 8
The JDK patches recommended for successful BACC installation include:
• 112003-03 • 108773-18 • 111310-01
• 109147-31 • 111308-05 • 112438-03
• 108434-18 • 108435-18 • 113886-26
• 113887-26 • 111111-04 • 112396-02
• 110386-03 • 111023-03 • 111317-05
• 113648-03 • 115827-01 • 116602-01
• 108652-86 • 108921-22 • 108940-65
• 108987-14 • 108528-29 • 108989-02
• 108993-39 • 109326-16 • 110615-13
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
1-1
Page 12

Network Registrar Requirements
JDK Patches for Solaris 9
The JDK patches recommended for successful BACC installation include:
• 113886-26 • 113887-26
• 112785-44 • 113096-03
KDC Patches
The KDC patches required for successful BACC installation include:
• 112438-01
• 109326-06
Network Registrar Requirements
Chapter 1 Overview
Before you install BACC, be aware of these Cisco Network Registrar requirements:
• We recommend that you use Network Registrar 6.1.2.3 or higher with BACC 2.7.
• A Network Registrar DHCP server must be installed on a computer with Solaris 8 or 9.
• In a failover deployment of BACC, you must configure two redundant DHCP servers for failover.
• After you install BACC, ensure that Network Registrar scopes are configured to reflect failover
capability and the topology of the network on which BACC is installed.
For more information about configuring failover on Network Registrar servers, see the Network
Registrar User’s Guide.
Hardware Requirements
A BACC installation requires these servers:
• A regional distribution unit (RDU). This is the primary server in a BACC deployment. It contains
the central BACC database and manages the generation of configurations.
• One or more device provisioning engines (DPE). A Cisco device provisioning engine caches
provisioning information and handles all configuration requests including the transfer of
configuration files to devices. It is integrated with the Cisco Network Registrar DHCP server to
control the assignment of IP addresses. Multiple DPEs can communicate with a single DHCP server.
DPEs include factory installed software that enables provisioning, but you must perform some initial
set up.
1-2
Note The hardware installation procedures for the device provisioning engine are described in the following
guides:
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 13

Chapter 1 Overview
Hardware Requirements
• For the DPE-590, refer to the Cisco Content Engine 500 Series Hardware Installation Guide. This
can be found at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/app_ntwk_services/waas/ce/ce500/installation/guide/
ce500hig.html
• For the DPE-2115, refer to the Installation and Setup Guide for the Cisco 1102 VLAN Policy Server.
This can be found at:
www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps2136/
products_installation_and_configuration_guide_book09186a00801f0d02.html
• A key distribution center (KDC). The KDC and the DPE registration services handle the
authentication of all voice technology media terminal adapters (MTAs). When a lab installation is
performed, the KDC is installed on the lab computer. For performance reasons however, in a
component installation, the KDC should be installed on a separate server.
Note The KDC is required only when configuring a system to support voice technology
operations.
• One or more Cisco Network Registrar servers. Network Registrar provides Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) functionality. Implementing
dynamic DNS (DDNS) within Network Registrar, increases the number of servers you need to
deploy.
Table 1-1 describes the hardware requirements for each server.
Ta b l e 1-1 Hardware Recommendations per Provisioning Group
# Subscribers Server
Min. #
Servers
Recommended #
Servers
1
Server Class
10000 DPE 1 2 SUN V210 1GHz
CNR 1 2 SUN V210 1GHz 1 1 GB
KDC 1 - SUN V210 1GHz 1 1 GB
25000 DPE 1 2 SUN V210 1GHz
CNR 1 2 SUN V210 1GHz 1 1 GB
KDC 1 - SUN V210 1GHz 2 2 GB
100000 DPE 1 2 SUN V210 1GHz
CNR 1 2 SUN V210 1GHz 2 2 GB
KDC 1 - SUN V210 1GHz 2 2 GB
250000 DPE 2 2 SUN V210 1GHz
CNR 2 2 SUN V210 1GHz 2 2 GB
KDC - - NA
3
500000 DPE 2 2 SUN V210 1GHz
CNR 2 2 SUN V210 1GHz 2 2 GB
KDC - - NA
3
#
Processors
2
2
2
2
1 1 GB
1 1 GB
2 2 GB
2 2 GB
Memory
- -
2
2 2 GB
- -
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
1-3
Page 14
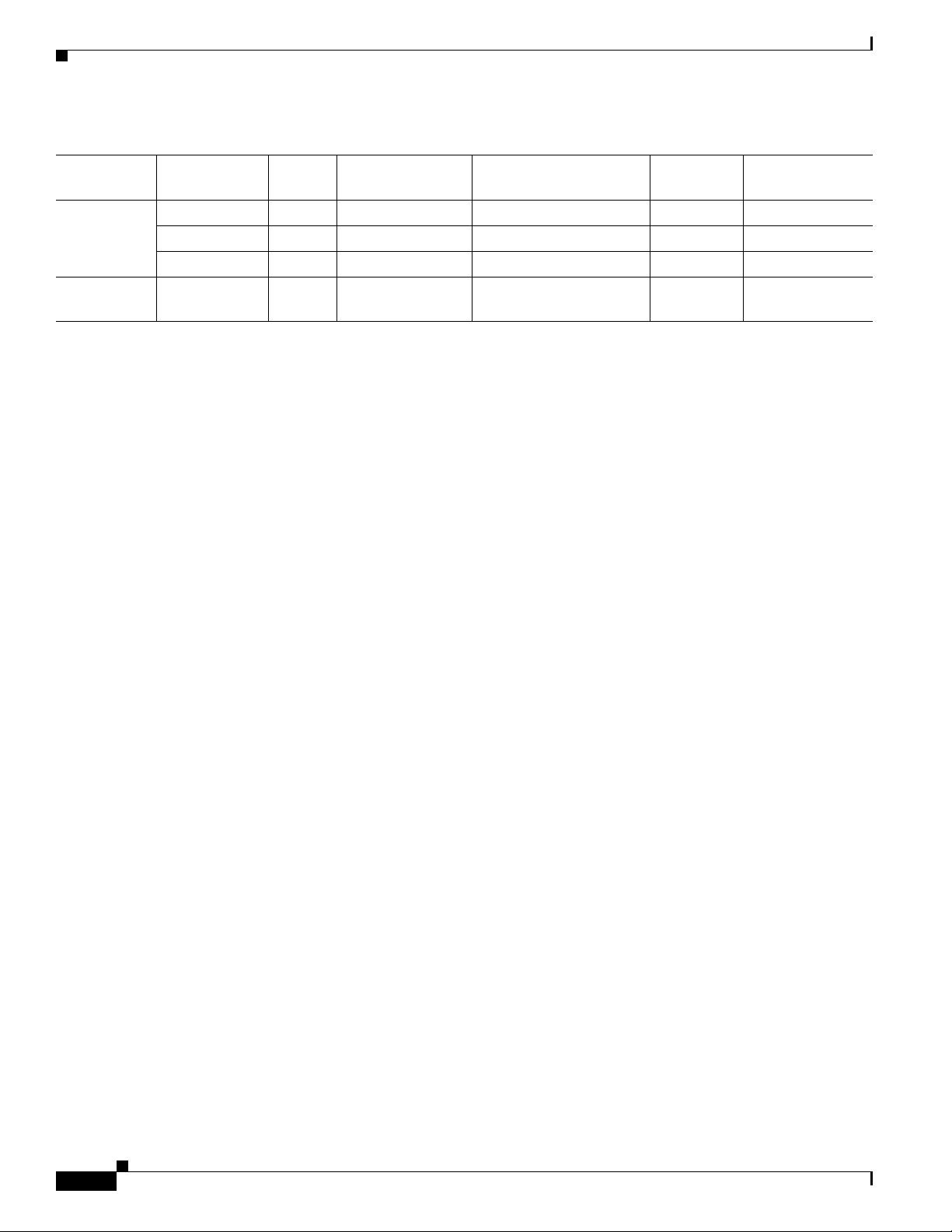
Types of Installations
Table 1-1 Hardware Recommendations per Provisioning Group (continued)
Chapter 1 Overview
Min. #
# Subscribers Server
Servers
1 million DPE 2 2 SUN V210 1GHz
CNR 2 2 SUN V210 1GHz 2 2 GB or 4 GB
KDC - - NA
Lab Install Single server
1 1 SUN V210 1GHz 1 1 GB
Recommended #
Servers
1
Server Class
3
#
Processors Memory
2
2 2 GB or 4 GB
4
4
- -
for all
1. The number of recommended servers is based on the average subscriber with two devices (1 cable modem and 1 PC).
2. With BACC 2.6.1 and later releases, the non-appliance Sun DPE can be replaced with a DPE-2115 single 3.06 Ghz CPU and 2 GB memory, which yields
equal or better performance.
3. Only 100000 MTA devices are currently supported per provisioning group.
4. 2 GB for configuration files that are less than or equal to 1.5 KB and 4 GB for configuration files that are more than 1.5 KB.
Types of Installations
This guide discusses two types of installation:
• Individual component installation—The installation program enables you to install one or more
individual components of BACC. The individual components are the RDU, Cisco Network Registrar
extensions, the Solaris device provisioning engine (DPE), and the KDC. Refer to
“Installing Components” for specifics about installing the individual components.
• Lab installation—The installation program enables you to install BACC for use in a laboratory
environment for demonstration or evaluation prior to deploying BACC into a full network
implementation. Refer to
Chapter 4, “Installing in a Lab Environment” for more information.
You can install BACC from the installation program’s graphical user interface (GUI) or from the
command line.
Chapter 3,
1-4
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 15

CHAP T ER
Preparing to Install Components
This chapter provides the information you need to prepare for a successful Broadband Access Center for
Cable (BACC) component installation, including these topics:
• Broadband Access Center for Cable Components, page 2-1
• Installation and Startup Process, page 2-2
• Broadband Access Center Database Requirements, page 2-5
• Installation Checklist, page 2-6
• Installation, page 2-7
Broadband Access Center for Cable Components
The BACC component installation program prompts you to install one or more of these components:
• Regional distribution unit (RDU). The RDU is the primary server in the BACC provisioning system.
You should install the RDU on a Solaris 8 or Solaris 9 server that meets the requirements described
in the
“Hardware Requirements” section on page 1-2. The RDU performs these functions:
–
Manages the generation of device configurations.
2
OL-19105-01
–
Acts as a clearinghouse through which all application programming interface (API) requests
must pass.
–
Manages the BACC system.
• Network Registrar extensions. These extensions are the link between BACC and Network Registrar.
Install this component on all Network Registrar servers in your BACC environment. If you are
deploying BACC in a failover environment, you must also install the extensions on the failover
servers.
Note We recommend that you install the BACC Network Registrar extensions on a server running
Network Registrar 6.1.2.3 or higher.
• Device Provisioning Engine (DPE). BACC supports the deployment of a DPE on Solaris Sparc
computers running Solaris 8 or Solaris 9.
Note The DPE component now requires licenses to be installed at the RDU. If you have not yet
received your licenses, contact your Cisco Systems representative before proceeding.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
2-1
Page 16
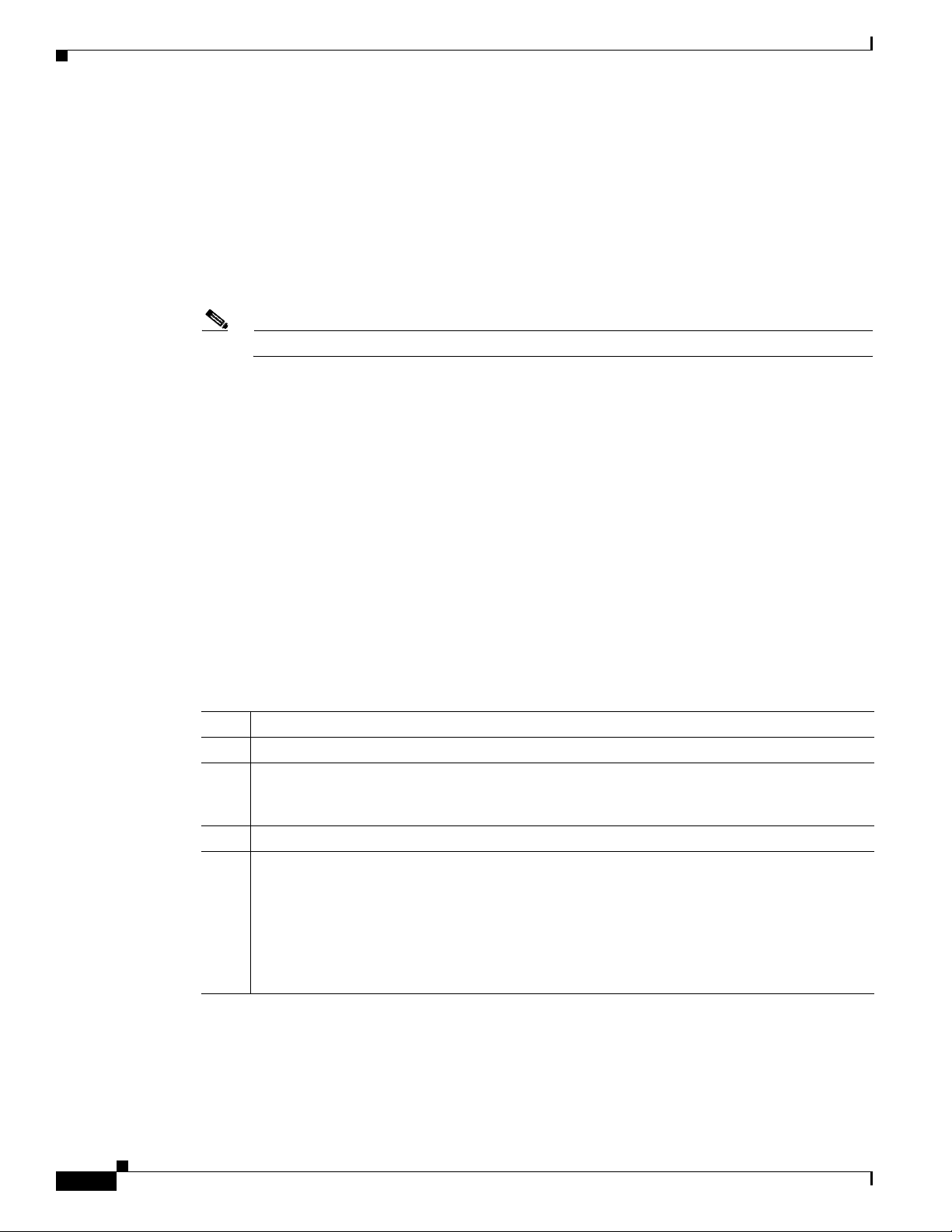
Installation and Startup Process
If, during DPE installation, the installation program detects the presence of a TFTP server running
on the same computer that the DPE being installed on, the installation is immediately terminated
and an error message appears on screen.
• Key Distribution Center (KDC). For maximum performance and segmentation of the network, you
may install one KDC instance per provisioning group. The KDC, along with the DPE registration
service, handles the authentication of all PacketCable voice technology MTAs. When a laboratory
installation is performed, the KDC is installed on the lab computer. For performance reasons
however, in a component installation, the KDC should be installed on a separate server. The KDC
component requires a license.
Note The KDC and DPE have service keys that are required to allow them to communicate.
Although the component installation program supports installing the components on the same computer,
in practice, you are likely to run the program on several different computers as described in these
sections:
1. Installing the RDU on a Solaris 8 or 9 server.
2. Installing the Network Registrar extensions on a Network Registrar server or servers.
3. Installing the DPE on Solaris Sparc computers running Solaris 8 or Solaris 9.
4. Installing the KDC server.
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install Components
Installation and Startup Process
To ensure a smooth installation and startup process, complete the order of operations as listed in
Table 2-1.
Ta b l e 2-1 Installation and Startup Process
Item Description
1. Determine which components you are installing and on what computers.
2. Verify the file system block size of the directory in which you intend to install the BACC
database and database transaction log files. See the
Requirements” section on page 2-5.
3. Review the installation checklist. See the “Installation Checklist” section on page 2-6.
4. Install a DPE. When you install the DPE, ensure that you have this information available:
• Home Directory location
• Data Directory location
After Solaris DPE installation is complete, you must configure the DPE using the command line
interface (CLI). Refer to the Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable CLI Reference Guide
for these configuration instructions.
“Broadband Access Center Database
2-2
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 17
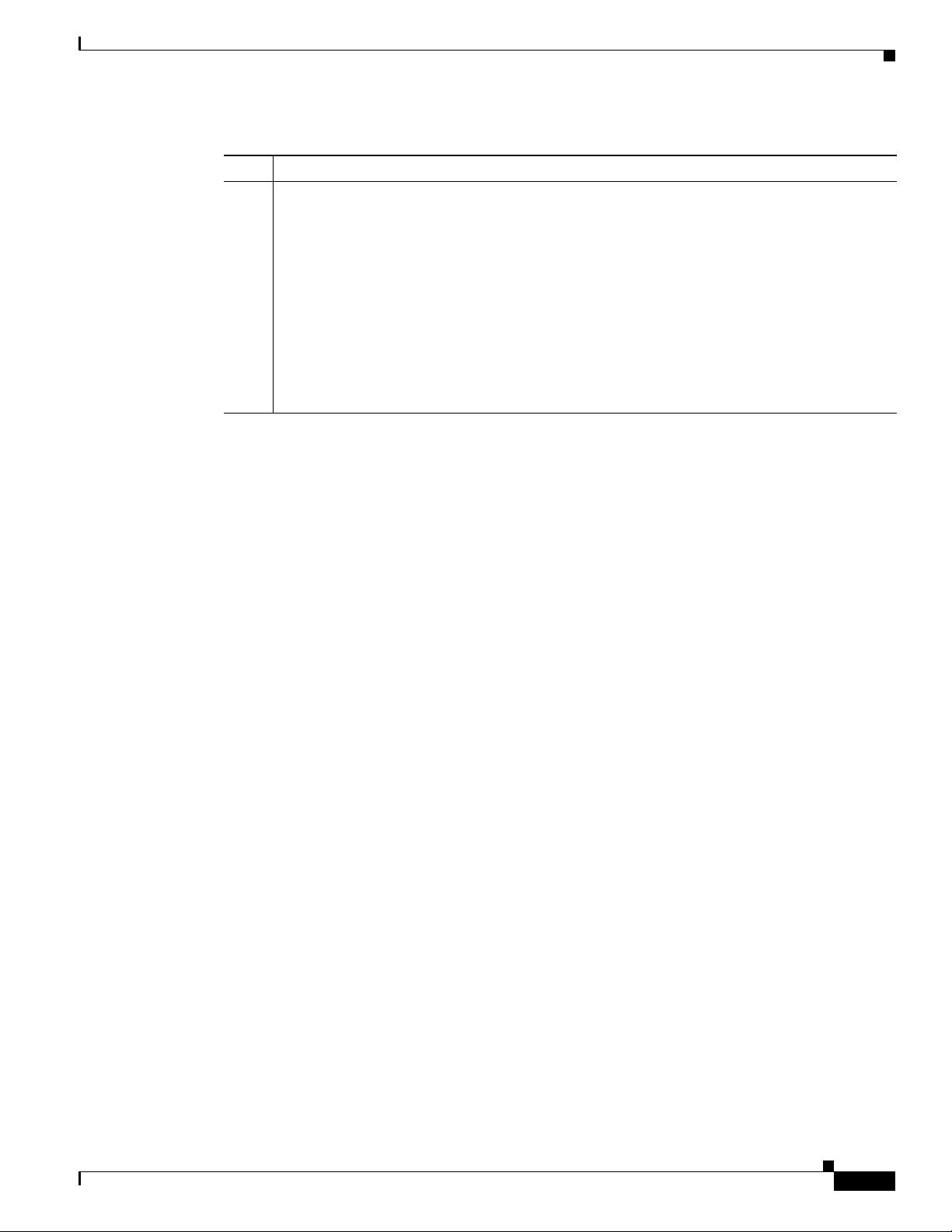
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install Components
Table 2-1 Installation and Startup Process (continued)
Item Description
5. Install the RDU. When you install the RDU, ensure that you:
• Obtain a valid BACC license key for each technology that you provision.
• Configure the syslog file for alerts. See the “Configuring the Syslog Utility to Receive
Alerts from BACC” section on page 5-1.
• Verify that the RDU is running by starting the administrators user interface. For more
information, see the Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide.
• Change the BACC administrator’s password. For more information, see the Broadband
Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide.
Note The existence of a text file called log.txt indicates that errors occurred during the
Installation and Startup Process
installation process. This text file is located under the <BACC_HOME> directory.
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
2-3
Page 18
Installation and Startup Process
Table 2-1 Installation and Startup Process (continued)
Item Description
6. Install and configure Network Registrar, if it is not already installed on your systems. We
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install Components
recommend that you use Network Registrar 6.1.2.3 or higher. For more information, see the
Network Registrar Installation Guide.
• When you install Network Registrar Local Cluster (LCCM), ensure that you:
a. Obtain a valid Network Registrar license key for local cluster.
b. On all Network Registrar local cluster servers, install the BACC extensions for the
product. For more information see the
Server” section on page 3-3.
c. Configure Network Registrar, including its extensions. Specifically, you need to
configure scopes, policies, client-classes, and scope selection tags. For more
information, see the
“Configuring Extensions” section on page 3-5, and also see the
Network Registrar User’s Guide.
d. Configure the syslog on the Network Registrar for alerts and debugging information.
See the
“Configuring the Syslog Utility to Receive Alerts from BACC” section on
page 5-1.
e. Validate the installation by connecting to the administrative user interface and viewing
the administrator’s user interface. For more information, see the Cisco Broadband
Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide.
“Installing Extensions on a Network Registrar
• When you install Network Registrar Regional Cluster (RCCM), ensure that you:
a. Identify the master server for Network Registrar Regional Installation, which
administers all the configured CNR local clusters. This server can be Solaris or
Windows or Linux. However, we recommend that you have the Solaris Operating
System on the CNR Regional Server.
b. Obtain a valid central-cluster license key for the CNR Regional Server.
c. After you install the BACC extensions for the product on all CNR local servers,
replicate the local data into regional and pull the “Replica Address Space”. For more
information see the Network Registrar User’s Guide.
d. Alternatively, you can also create subnets, client-classes, policies, and so on at RCCM
and push them to the required LCCM DHCP server. For more information, see the
Network Registrar User’s Guide.
e. Configure this CNR Regional CCM Server’s IP address, port number, and login details
into the RDU defaults for IP Reservation support. For more information, see the Cisco
Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide.
Note Network Registrar Release Version prior to 6.1 does not support Regional Cluster,
Hence BACC’s IP Lease Reservation Support feature cannot be used.
2-4
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 19
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install Components
Table 2-1 Installation and Startup Process (continued)
Item Description
7. Install and configure the KDC. When you install the KDC, ensure that you have this
information available:
• A valid license for KDC.
• KDC realm—Identified by a unique name, the KDC realm consists of a KDC, and the
clients and servers registered to that KDC.
Note The realm must match the certificate chain at the KDC.
• KDC FQDN—This is the fully qualified domain name on which the KDC server is located.
• KDC interface address—This is the interface (generally the IP address of the KDC server)
on which the KDC listens for requests.
Note During installation it may be necessary to install several Solaris patches on your
Note If you decide to terminate the BACC installation after the operating system database has been
installed, you must uninstall it before attempting to reinstall the product. If you do not do this,
and rerun the installation program, you cannot change the location of either the
<BACC_DATA> and <BACC_DBLOG> directories.
Broadband Access Center Database Requirements
computer. The installation program will display a complete list of patches that are
required. Should patch installation become necessary, refer to the Sun Microsystems
website to download the required patches.
Broadband Access Center Database Requirements
Before you install BACC, be aware of these database considerations:
• File system block size
• Support for large files
File System Block Size
For optimum performance and reliability of the BACC database, configure the file system or systems
that contain the database files and database log files with an 8 KB block size or greater. If your system
configuration does not support an 8 KB block size, then configure the block size in multiples of 8 KB;
for example, 16 KB or 32 KB.
The installation program prompts you to specify a directory in which to install database files and
database log files. These directories are identified in BACC with system variables, <BACC_DATA> and
<BACC_DBLOG> respectively.
To verify that a directory resides on a file system with a minimum 8 KB block size, follow these steps:
Step 1 Run the UNIX mount command without any parameters to determine on which file system device the
directory resides. The default directory is /var/CSCObpr. For example:
/var on /dev/dsk/c0t0d0s4 read/write/setuid/intr/largefiles/onerror=panic/dev=2200004 on
Mon Nov 26 08:07:53
OL-19105-01
In this example, the file system device is /dev/dsk/c0t0d0s4.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
2-5
Page 20
Installation Checklist
Step 2 To determine the file system block size, use the df command. For example:
# df -g /dev/dsk/c0t0d0s4
Example output from the df command is as follows:
/var (/dev/dsk/c0t0d0s4 ): 8192 block size 1024 frag size
961240 total blocks 851210 free blocks 755086 available 243712 total files
239730 free files 35651588 filesys id
ufs fstype 0x00000004 flag 255 filename length
In this example, the block size is 8192 bytes, which is 8 KB. The block size of the selected directory,
therefore, is correct.
Large File Support
Ensure that the file system in which you place database files is configured to support files above 2 GB.
To verify large file support:
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install Components
Step 1 Run the UNIX mount command without parameters.
Step 2 Note whether the intended file system contains the keyword largefiles.
An example output of the mount command is:
/var on /dev/dsk/c0t0d0s4 read/write/setuid/intr/largefiles/onerror=panic/dev=2200004 on
Mon Nov 26 08:07:53
In this example, the output contains the keyword largefiles. This file system, therefore, can support files
greater that than 2 GB.
Installation Checklist
Before you run the installation software, use this checklist to ensure that you are ready:
• Verify the prerequisite system hardware and software requirements described in Chapter 1,
“Overview”
• Determine the home directory (<BACC_HOME>) in which you want to install the BACC
component or components. The default directory is /opt/CSCObpr.
Note Cisco Systems recommends that yo have at least 350 MB of disk space available.
2-6
• Ensure that you have root access to the computers where you intend to install BACC components.
• Have your BACC license key or keys at hand. You need a valid license key for each technology that
you want to provision with BACC.
• For the RDU, determine where you want to install the data directory (<BACC_DATA>) and the
database transaction logs (<BACC_DBLOG>). (The default directory is /var/CSCObpr.)
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 21
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install Components
Note Cisco recommends that you install the database transaction logs on a different physical disk than either
the home directory or the data directory.
• For the RDU, select the shared secret password that BACC servers on your network use as a token
to authenticate communication with one another. The shared secret password is the same for all
BACC servers on your network.
• We recommend that Network Registrar 6.1.2.3 or higher is installed and running on any servers
where you are installing BACC extensions.
• For extensions, determine the name of provisioning group to which the Network Registrar server
belongs.
• For Network Registrar extensions, determine where you want to install the data directory
(<BACC_DATA>).
• Verify that you have the necessary Network Registrar configuration files, (See Appendix A,
“Network Registrar Configuration File Example” for an example of these configuration files.)
• Verify that you have the necessary KDC servers available.
Installation
Note If you interrupt the installation program after it begins copying files, you may have to manually clean up
the locations of copied files.
Installation
The initial steps in the BACC installation program are identical regardless of the BACC component you
are installing. This section describes how to work with the installation program and the initial
installation steps.
You install BACC using either the graphical user interface (GUI) or the command line interface (CLI).
Both of these interfaces are supplied with BACC.
Installation Using the Graphical User Interface
To install BACC using the graphical interface:
Step 1 Using an X-Windows client, log in as root on the computer on which you intend to install the BACC
component.
Step 2 At the Solaris system prompt, navigate to the directory containing the setup.bin file. If you are using the
BACC CD-ROM, you will find setup.bin located at the root of your CD-ROM drive.
Step 3 Enter this command to start the installation program:
> setup.bin
OL-19105-01
The installation program verifies that you have installed the required patches to the Solaris operating
system. When the verification is complete, the Welcome screen appears.
Step 4 Click Next. The Choose Installation Type screen appears.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
2-7
Page 22
Installation
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install Components
Step 5 Select one of the two installation types:
• Individual Components—This option enables you to install an RDU, Network Registrar extensions, the
DPE, or the KDC. See these sections for the appropriate installation instructions:
–
Installing the Regional Distribution Unit, page 3-2
–
Installing Extensions on a Network Registrar Server, page 3-3
–
Installing the Key Distribution Center, page 3-7
–
Installing the Device Provisioning Engine, page 3-8
• Lab—This option enables you to install the software in a laboratory environment. See Chapter 4,
“Installing in a Lab Environment” in this guide.
Step 6 Click Next. Depending on the option you selected in the preceding step, either the Installation
Components screen appears, or you begin the lab installation.
Note You must select one of the displayed installation components before you can proceed with the
installation.
Installing from the Command Line
To perform the initial installation procedure from the command line:
Step 1 Log into the intended BACC host as root.
Step 2 At the Solaris system prompt, change directory to your CD-ROM drive or other installation media. The
installation program, setup.bin, is at the root of this drive.
Step 3 Enter this command to start the installation program:
> setup.bin -console
The installation program verifies that you have installed the required patches to the Solaris operating
system. When the verification is complete, the program displays welcome information.
Step 4 Press Enter to continue. The program prompts you to choose the installation type. You can choose to
install:
• Individual components
• Lab installation
Step 5 To choose individual components, enter C; or, to choose Lab installation, enter L. For example:
Choose Installation
Choose the type of BPR installation you want to install.
2-8
The Lab installation will store all components in the chosen destination.
Otherwise, you can select individual components and destinations.
Enter C for individual components or L for lab [C]:c
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 23

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install Components
The program prompts you to confirm the installation type.
Step 6 Press y and then Enter to continue.
At this point you must decide which installation you want to perform. To install individual components
go to the
“Installing Components Using the CLI” section on page 3-8. To install in a lab environment go
to the “Installing in a Lab Environment Using the CLI” section on page 4-3.
Installation
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
2-9
Page 24

Installation
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install Components
2-10
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 25

CHAP T ER
3
Installing Components
This chapter explains the procedures you must follow to correctly install Broadband Access Center for
Cable (BACC) components in a Solaris operating system environment.
This chapter contains these topics:
• Installing Components Using the Graphical User Interface, page 3-1
• Installing Components Using the CLI, page 3-8
Installing Components Using the Graphical User Interface
This section explains the procedures that you follow to install one or more of components of BACC using
the GUI.
You can choose to install one or all of these components:
• Regional distribution unit (RDU). Refer to Installing the Regional Distribution Unit, page 3-2 for
further information.
• Network Registrar extensions. Refer to Installing Extensions on a Network Registrar Server,
page 3-3 for further information.
• Key Distribution Center (KDC). Refer to Installing the Key Distribution Center, page 3-7 for further
information.
OL-19105-01
• Device Provisioning Engine (DPE). Refer to Installing the Device Provisioning Engine, page 3-8 for
further information.
For more information about each component see the “Broadband Access Center for Cable Components”
section on page 2-1.
Before you begin any of these procedures, you must complete the initial installation procedure described
in the
“Installation and Startup Process” section on page 2-2.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
3-1
Page 26

Installing Components Using the Graphical User Interface
Installing the Regional Distribution Unit
Install the RDU server on a Solaris 8 server that meets the requirements described in the “Hardware
Requirements” section on page 1-2.
To install the RDU server, complete the steps described in the “Installation and Startup Process” section
on page 2-2, then follow these steps:
Step 1 Click Next. The Home Directory Destination screen appears. The default directory is /opt/CSCObpr.
Step 2 Accept the default directory or enter a new directory. You can use the Browse button to select a new
directory.
Step 3 Click Next. The installation program displays the Create Directory dialog box. Click Yes to continue.
The Data Directory Destination screen appears. The default directory is /var/CSCObpr.
Step 4 Accept the default directory or enter a new directory. You can use the Browse button to select a new
directory.
Chapter 3 Installing Components
Note By default, the installation program installs the data directory (BPR_DATA) on a different
directory than the home directory (BPR_HOME). Cisco Systems recommends that the data
directory be on a different physical disk than the home directory; for example
/var/disk0/CSCObpr. However, you can install the data directory on the same disk as the home
directory.
The directory specified becomes the top-level directory under which the installation program
creates a number of subdirectories; for example, /var/disk0/CSCObpr/rdu/db.
Step 5 Click Next. The installation program displays the Create Directory dialog box. Click Yes to continue.
The Database Transaction Logs screen appears.
Step 6 Enter the pathname for the directory in which you want the transaction logs (BPR_DBLOG) installed.
The default directory is /var/CSCObpr.
Note By default, the installation program installs the database transaction logs directory
(BPR_DBLOG) in the same directory as the data directory (BPR_DATA). Cisco Systems
recommends that you locate the database transaction logs directory on the fastest disk on the
system; for example, /var/disk1/CSCObpr. You also should ensure that the disk has 1 GB of
space available.
The directory specified becomes the top-level directory under which the installation program
creates a number of subdirectories.
3-2
Step 7 Accept the default directory or enter a new directory. You can use the Browse button to select a new
directory.
Step 8 Click Next. The installation program displays the Create Directory dialog box. Click Ye s to continue.
The Regional Distribution Unit Host/Port screen appears.
Step 9 Accept the default listening port number or enter a new port number. The default port is 49187.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 27

Chapter 3 Installing Components
Note The installation program obtains the IP address of the RDU automatically. You do not need to
Caution If you change the default listening port value, ensure that the new value does not conflict with
Step 10 Click Next. The Shared Secret Password screen appears.
Step 11 Enter and confirm the shared secret password.
Note The RDU, DPEs, and Network Registrar extension points all use the same shared secret. This is
Installing Components Using the Graphical User Interface
enter this value.
any existing port assignments. Also, ensure that you configure all DPEs and Network
Registrar servers with the correct RDU port number. See the Broadband Provisioning
Registrar Administrator’s Guide for information about configuring the DPE and Network
Registrar extensions.
a character string, or token, that is used to authenticate communication.
Step 12 Click Next. The Installation Parameters screen appears. This screen identifies the values that you have
entered in the previous screens. To modify any of the values entered:
a. Click Back until the desired screen appears.
b. Make the necessary changes.
c. Click Next repeatedly until you return to this screen.
Step 13 Click Next. When the installation is complete, the Installation Summary screen appears. Click Finish to
exit the installation program.
Note You must configure your license keys using the administrator’s user interface. Refer to the Cisco
Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide for additional information.
Installing Extensions on a Network Registrar Server
You install BACC extensions on a Network Registrar server. If you are deploying BACC in a failover
environment, you also must install the extensions on the failover servers. After you install extensions,
you need to configure them.
The remainder of this section explains how to install, configure, and validate these extensions.
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
3-3
Page 28

Installing Components Using the Graphical User Interface
Installing Extensions
Before you install the Network Registrar extensions, complete the steps described in the “Installation
and Startup Process” section on page 2-2. To install the extensions:
Step 1 On the Installation Components screen, select the Cisco Network Registrar extension points option, then
click Next to continue; the Home Directory Destination screen appears.
Note The installation program now validates your Network Registrar (CNR) installation. We
recommend that you have CNR version 6.1.2.3 or higher. If the required version is not installed,
the installation process is terminated and you must upgrade to the required Network Registrar
version before proceeding.
Step 2 Enter the pathname for the home directory, or click the Browse button to locate the desired directory.
Note The installation program does not ask for the home directory when it identifies that you are
installing BACC components on a computer that already has a BACC component installed on it.
Chapter 3 Installing Components
Step 3 Click Next. The installation program performs some validation and, prompts you to create the directory,
if necessary, before the Data Directory Destination screen appears.
Step 4 Accept the default directory or enter a new directory. You can use the Browse button to select a new
directory.
Note By default, the installation program installs the data directory (BPR_DATA) on a different
directory than the home directory (BPR_HOME). Cisco Systems recommends that the data
directory be on a different physical disk than the home directory; for example,
/var/disk0/CSCObpr. However, you can install the data directory on the same disk as the home
directory.
Step 5 Click Next. The Regional Distribution Unit Host/Port screen appears.
Step 6 Enter the IP address (or hostname) and the listening port of the host where the RDU software is installed.
By default, the name of the local host appears in the RDU IP Address field. The RDU uses the listening
port to communicate with the DPEs and Network Registrar extension points.
Step 7 Click Next. The Cisco Network Registrar Extension Point Provisioning Group screen appears.
Step 8 Enter the name of the extension point provisioning group.
Step 9 Click Next. The PacketCable Panel screen appears.
Step 10 Determine if you need to install the voice technology option and click:
3-4
• Ye s button if you want to install the voice technology option. The PacketCable Properties screen
appears.
• No if you do not have a valid license key for this technology. After clicking No, go to step
number
Step 11 Enter the appropriate information into the fields shown.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
12.
OL-19105-01
Page 29

Chapter 3 Installing Components
Field Name Description
Kerberos Realm Name Specifies, using a unique name, the Kerberos realm. This must match the
IP Address of Primary
DHCP Server
IP Address of Primary DNS
Server
IP Address of Secondary
DHCP Server
IP Address of Secondary
DNS Server
Step 12 Click Next. The Shared Secret Password screen appears.
Step 13 Enter and confirm the shared secret password.
Installing Components Using the Graphical User Interface
realm set at the associated components.
Specifies the IP address of the voice technology primary DHCP server.
Specifies the IP address of the computer which is running the primary
DNS server.
Specifies the IP address of the voice technology secondary DHCP server.
Specifies the IP address of the computer which is running the secondary
DNS server; if that server is being used.
Note Use the shared secret password specified during the RDU installation.
Step 14 Click Next. The Installation Parameters screen appears. This screen identifies the values that you have
entered in the previous screens. To modify any of the values entered click Back until the desired screen
appears.
Step 15 Click Next. When the installation is complete, the Installed Components Summary screen appears. Click
Finish to exit the installation program.
Configuring Extensions
After you install the BACC extensions to Network Registrar, you must configure the extensions. The
procedure described in this section makes these assumptions:
• The BACC component is installed in /opt/CSCObpr.
• Network Registrar is installed in /opt/nwreg2.
• The Network Registrar username is admin and the password is changeme.
To configure extensions, follow these steps:
Step 1 Log in as root to the Network Registrar server.
Step 2 At the command line, enter these commands:
<NR_HOME>/usrbin/nrcmd -N admin -P changeme -b <
<BACC_HOME>/cnr_ep/bin/bpr_cnr_enable_extpts.nrcmd
OL-19105-01
Step 3 Enter these commands to reload the Network Registrar server:
/etc/init.d/nwreglocal stop
/etc/init.d/nwreglocal start
Alternatively, you can enter this command to reload the DHCP server alone:
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
3-5
Page 30

Installing Components Using the Graphical User Interface
<NR_HOME>/usrbin/nrcmd -N admin -P changeme "dhcp reload"
Caution Be aware that you also must configure client-classes, scope selection tags, policies, and scopes before
you can use the Network Registrar server. See the Network Registrar User’s Guide for information about
configuring these entities.
Validating Extensions
In the nrcmd program, run the following command and verify the output is the same:
nrcmd> extension list
100 Ok
dexdropras:
entry = dexdropras
file = libdexextension.so
init-args =
init-entry =
lang = Dex
preClientLookup:
entry = bprClientLookup
file = libbprextensions.so
init-args = BACC_HOME=/opt/CSCObpr,BACC_DATA=/var/CSCObpr
init-entry = bprInit
lang = Dex
prePacketEncode:
entry = bprExecuteExtension
file = libbprextensions.so
init-args =
init-entry =
lang = Dex
Chapter 3 Installing Components
3-6
Note The <BACC_HOME> and <BACC_DATA> values may be different in your installation.
Also in the nrcmd program, run the following command and verify the output is the same:
nrcmd> dhcp listextensions
100 Ok
post-packet-decode: dexdropras
pre-packet-encode: prePacketEncode
pre-client-lookup: preClientLookup
post-client-lookup:
post-send-packet:
pre-dns-add-forward:
check-lease-acceptable:
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 31

Chapter 3 Installing Components
Installing the Key Distribution Center
To install the Key Distribution Center (KDC), complete the steps described in the “Installation and
Startup Process” section on page 2-2, then follow these steps:
Step 1 On the Installation Components screen, select the Key Distribution Center option, then click Next to
continue; the Home Directory Destination screen appears.
Step 2 Enter the pathname for the home directory, or click the Browse button to locate the desired directory.
Note The installation program does not ask for the home directory when it identifies that you are
installing BACC components on a computer that already has a BACC component installed on it.
Step 3 Click Next. The installation program performs some validation and, prompts you to create the directory,
if necessary, before displaying the Data Directory Destination screen.
Step 4 Click Next and the Key Distribution Center Realm Name screen appears.
Installing Components Using the Graphical User Interface
Step 5 Enter the appropriate information into the fields shown.
Field Name Description
KDC Realm Specifies, using a unique name, the Kerberos realm. This must match the
realm set at the associated components.
KDC FQDN Identifies the fully qualified domain name on which the KDC server is
located.
KDC Interface Address Specifies the interface (generally the IP address of the KDC server) on
which the KDC listens for requests.
Step 6 Click Next and the KDC Service Key and DPE screen appears.
Note The KDC requires a password for each DPE. Th is pas s word mus t be entered at the corresponding
DPE and MUST match that entered for the KDC otherwise the DPE will not operate.
Step 7 Enter a 6 to 20 character password (see the example below) and the fully qualified domain name
(FQDN), for each DPE, and then click Add. Continue to add additional DPEs as necessary.
Example KDC Password
12345678901234567890
OL-19105-01
Step 8 Click Next when you are done. The Installation Parameters screen appears.
Step 9 After verifying that the parameters are correct, click Next to install BACC, or Back to modify the
parameters. When installation is complete, the Installation Summary screen appears.
Step 10 Click Finish to end the installation process and exit the installation program.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
3-7
Page 32

Installing Components Using the CLI
Caution After installing the KDC, you must install your licenses, and the chain of certificates, or the KDC will
not start.
Installing the Device Provisioning Engine
To install the DPE, complete the steps described in the “Installation and Startup Process” section on
page 2-2, then follow these steps:
Step 1 On the Installation Components screen, select the Device Provisioning Engine option, then click Next
to continue; the Home Directory Destination screen appears.
Step 2 Enter the pathname for the home directory, or click the Browse button to locate the desired directory.
Step 3 Click Next. The installation program performs some validation and, prompts you to create the directory,
if necessary, before displaying the Data Directory Destination screen.
Chapter 3 Installing Components
Step 4 Click Next, when you are done. The Installation Parameters screen appears.
Step 5 After verifying that the parameters are correct, click Next to install the DPE, or Back to modify the
parameters. When installation is complete, the Installation Summary screen appears.
Step 6 Click Finish to end the installation process and exit the installation program.
Installing Components Using the CLI
This section explains the procedures that you follow to install one or more of components of BACC using
the CLI.
Refer to these sections for installation instructions:
• Installing the Regional Distribution Unit, page 3-9
• Installing Network Registrar Extensions, page 3-11
• Installing the Key Distribution Center, page 3-14
• Installing the Device Provisioning Engine, page 3-16
For more information about each component see the “Broadband Access Center for Cable Components”
section on page 2-1.
Before you begin any of these procedures, you must complete the initial installation procedure. For more
information, see the
“Installing from the Command Line” section on page 2-8.
3-8
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 33

Chapter 3 Installing Components
Installing the Regional Distribution Unit
To install an RDU, complete the steps described in the “Installing from the Command Line” section on
page 2-8. Then, follow these steps:
Step 1 When the installation program prompts you to select one or more components, enter y and press Enter
at the Regional Distribution Unit (RDU) (y/n/?) prompt. The program then asks if you want to install
Cisco Network Registrar extension points, the DPE, and the KDC.
Step 2 To skip installing either the extension points or the KDC, press n and Enter for each option.
You can choose to install these options at a later date. See the “Installing Network Registrar Extensions”
section on page 3-11 for additional information.
For example:
Installation Components
Select one or more components to install BPR.
Regional distribution unit (RDU) (y/n/?) [no] y
Cisco Network Registrar extension points (y/n/?) [no] n
Device Provisioning Engine (DPE) (y/n/?) [no] n
Key Distribution Center (KDC) (y/n?) [no] n
Installing Components Using the CLI
The program prompts you to confirm the components that you want to install.
Step 3 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to start individual component validation.
Step 4 Press Enter to continue. For example:
Starting the individual component installation parameters validation.
Press Enter to Continue or 'q' to Quit:
Validating the individual component installation parameters - Please wait.
The program prompts you to enter the home directory destination.
Step 5 To accept the default directory, /opt/CSCObpr, press Enter; or enter another directory. For example:
Home Directory Destination
Home Directory Destination [/opt/CSCObpr]
The program asks you to confirm the directory.
Step 6 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the data directory destination.
Step 7 To accept the default directory, /var/CSCObpr, press Enter; or enter another directory. For example:
Data Directory Destination
Data Directory Destination [/var/CSCObpr]/var/disk0/CSCObpr
The program then asks you to confirm the directory.
OL-19105-01
Note By default, the installation program installs the data directory (BPR_DATA) on a different
directory than the home directory (BPR_HOME). Cisco Systems recommends that the data
directory be on a different physical disk than the home directory; for example,
/var/disk0/CSCObpr. However, you can install the data directory on the same disk as the home
directory.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
3-9
Page 34

Installing Components Using the CLI
Step 8 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the database transaction logs
destination.
Step 9 To accept the default directory, /var/CSCObpr, press Enter; or enter another directory. For example:
Database Transaction Logs Destination
Logs Directory Destination
Logs Directory Destination [/var/CSCObpr] /var/disk1/CSCObpr
The program then asks you to confirm the directory.
Note By default, the installation program installs the database transaction logs directory
(BPR_DBLOG) in the same directory as the data directory (BPR_DATA). Cisco Systems
recommends that you locate the database transaction logs directory on the fastest disk on the
system and that you ensure that the disk has 1 GB of space available.
The directory specified becomes the top-level directory under which the installation program
creates a number of subdirectories.
Chapter 3 Installing Components
Step 10 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the listening port for the RDU.
Step 11 To accept the default value, 49187, press Enter; or enter another port number. For example:
Regional Distribution Unit Host/Port
Enter the IP address and the listening port of the regional distribution
unit(RDU)associated with this installation.
Enter the Host/IP address and address of the listening port for the RDU and RDU Listening
Port [49187]
Note The installation program obtains the IP address of the RDU automatically. You do not need to
enter this value.
The program then prompts you to confirm the listening port number.
Note The RDU listens on all interfaces. The listening port is the port number that the RDU uses to
communicate with other BACC components, such as DPEs and Network Registrar extension
points.
Step 12 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the shared secret password.
Note You must use the same shared secret password for all RDUs, DPEs, and Network Registrar
extension points in your network. The default password is secret.
3-10
Step 13 Enter the password that you want to use for authentication among BACC servers. For example:
Shared Secret Password
Enter the password to be used for authentication
among the BPR servers.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 35

Chapter 3 Installing Components
If you are performing a lab installation, then the password will be used for all the
servers. If this is a component installation, then the password you enter must be the
same as the components previously installed.
Enter the Shared Secret Password [secret] changeme
The program prompts you to confirm the password.
Step 14 Enter the password again and press y to continue. The program displays the installation parameters you
have selected. For example:
The Component Installation will use the following parameters
to install the RDU component:
Home directory:/opt/CSCObpr
Data directory:/var/disk0/CSCObpr
Logs directory:/var/disk1/CSCObpr
RDU Port:49187
Step 15 Press y to install the RDU component. The program displays a message when the installation is
complete.
Installing Components Using the CLI
Caution You must configure your license keys using the administrator’s user interface. Refer to the Cisco
Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide for further information.
Installing Network Registrar Extensions
Before you install Network Registrar extensions, complete the steps described in the “Installing from the
Command Line” section on page 2-8 and ensure that Network Registrar is running. To install the
extensions:
Step 1 When the installation program prompts you to select one or more components, press y and Enter at
Cisco Network Registrar extension points (y/n/?).
To skip installing an RDU, the DPE, and the KDC, press n and Enter for these options.
For example:
Installation Components
Select one or more components to install BPR.
Regional distribution unit (RDU) (y/n/?) [no] n
Cisco Network Registrar extension points (y/n/?) [no] y
Device Provisioning Engine (DPE) (y/n/?) [no] n
Key Distribution Center (KDC) (y/n?) [no] n
OL-19105-01
The program prompts you to confirm the components that you want to install.
Step 2 Press y and Enter to continue. The program displays a message that it is starting individual component
validation.
Step 3 Press Enter to continue. For example:
Starting the individual component installation parameters validation.
Press Enter to Continue or 'q' to Quit:
Validating the individual component installation parameters - Please wait.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
3-11
Page 36

Installing Components Using the CLI
The program prompts you to enter the home directory destination.
Step 4 To accept the default home directory destination, /opt/CSCObpr/, press Enter; or enter another
directory. For example:
Home Directory Destination
Home Directory Destination [/opt/CSCObpr]
The program then asks you to confirm the directory.
Step 5 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the data directory destination
Step 6 To accept the default directory, /var/CSCObpr, press Enter; or enter another directory. For example:
Data Directory Destination
Data Directory Destination [/var/CSCObpr] /var/disk0/CSCObpr
Note By default, the installation program installs the data directory (BPR_DATA) on a different
directory than the home directory (BPR_HOME). Cisco Systems recommends that the data
directory be on a different physical disk than the home directory; for example
/var/disk0/CSCObpr. However, you can install the data directory on the same disk as the home
directory.
Chapter 3 Installing Components
Step 7 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the host IP address and the listening
port of the RDU.
Step 8 Enter the IP address (or hostname) and listening port of the host where the RDU software is installed.
The program prompts you to confirm this information. For example:
Regional Distribution Unit Host/Port
Enter the IP address and the listening port of the regional distribution unit (RDU)
associated with this installation.
Enter the Host/IP address and address of the listening port for the RDU.
RDU IP Address [doc-u5.cisco.com] 10.10.10.2
RDU Listening Port [49187]
========== Confirmation ==========
RDU Host:10.10.10.2
RDU Port:49187
Is this correct (y/n/q/?) [yes] y
Step 9 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the name of the extension point
provisioning group.
Step 10 Enter the name of the Network Registrar extension point group. For example:
Cisco Network Registrar Extension Point Provisioning Group
Enter the Cisco Network Registrar extension point provisioning group.
3-12
This a required field. The value you specify must contain only alphanumeric
characters without spaces and not exceed 10 characters in length. You can use
the BPR command-line tool to change this value after you complete this
installation.
Extension Point Provisioning Group [] group1
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 37

Chapter 3 Installing Components
Step 11 Press y and Enter to continue. The program then lets you decide if you are going to be provisioning voice
technology devices. For example:
Are you going to use a device(s) that supports PacketCable voice technology?
If you are going to use PacketCable devices we need some more info.
Enter Yes to Install PacketCable and No if you do not want Packetcable
installed [No]: yes
Step 12 Press y if you are using voice technology devices or n if you are not. If you are not using voice
technology devices, you will be prompted to enter a shared secret password as described in Step 14. If
you press y, the program will prompt you to enter several voice technology properties. For example:
Enter KDC Realm Name ACME.COM
Enter the IP Address of the Primary DHCP Server. 10.10.10.1
Enter the IP Address of the Primary DNS Server. 10.10.10.3
Enter the IP Address of the Secondary DHCP Server. 10.10.10.2
Enter the IP Address of the Secondary DNS Server. 10.10.10.4
Step 13 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the shared secret password.
Installing Components Using the CLI
Note You must use the same shared secret password for all BACC servers on your network.
Step 14 Enter the password that you want to use for authentication among BACC servers. For example:
Shared Secret Password
Enter the password to be used for authentication
among the BPR servers.
If you are performing a lab installation, then the password will be used for all the
servers. If this is a component installation, then the password you enter must be the
same as the components previously installed.
Enter the Shared Secret Password [secret] changeme
The program prompts you to confirm the password.
Step 15 Enter the password again.
Step 16 Press y and Enter to continue. The program then displays the installation parameters you have selected.
For example:
Installation Parameters
This screen shows the installation parameters that you have chosen:
========== Confirmation ==========
The Component Installation will use the following parameters
to install the NR Extension Points component:
OL-19105-01
Home directory:/opt/CSCObpr
Data directory:/var/disk0/CSCObpr
NR extension point provisioning group:group1
Step 17 Press y and Enter to install the Network Registrar extensions. The program displays a message when
the installation is complete.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
3-13
Page 38

Installing Components Using the CLI
Step 18 To configure the extensions complete the procedure described in the “Configuring Extensions” section
on page 3-5.
Installing the Key Distribution Center
To install the KDC:
Step 1 When the installation program prompts you to select one or more components, press y and Enter at Key
Distribution Center (KDC) (y/n/?).
To skip installing an RDU and Network Registrar extension points, enter n and Enter for these options.
For example:
Installation Components
Select one or more components to install BPR.
Regional distribution unit (RDU) (y/n/?) [no] n
Cisco Network Registrar extension points (y/n/?) [no] n
Device Provisioning Engine (DPE) (y/n/?) [no] n
Key Distribution Center (KDC) (y/n/?) [yes] y
Chapter 3 Installing Components
The program prompts you to confirm the components that you want to install.
Step 2 Press y and Enter to continue. The program displays a message that it is starting individual component
validation.
Step 3 When validation is complete, the program prompts you to enter the home directory destination.
Validation involves checking to verify that the correct patches have been installed. If they are not, error
messages appear on screen.
Step 4 To accept the default home directory destination, /opt/CSCObpr/, press Enter, or enter another directory.
For example:
Home Directory Destination
Home Directory Destination [/opt/CSCObpr]
Choosing yes will create the directory during the installation. Choosing no will allow a
different directory to be chosen.
The directory /opt/CSCObpr does not exist. Create it? (y/n/?) [yes]
Step 5 When validation is complete, the program prompts you to enter the data directory destination.
Step 6 To accept the default data directory destination, /var/CSCObpr/, press Enter, or enter another directory.
For example:
Data Directory Destination
Data Directory Destination [/var/CSCObpr]
Choosing yes will create the directory during the installation. Choosing no will allow
a different directory to be chosen.
The directory /var/CSCObpr does not exist. Create it? (y/n/?) [yes]
3-14
The program prompts you to confirm the components that you want to install.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 39

Chapter 3 Installing Components
Step 7 Press y and Enter to create the directory and continue. The program prompts you to enter the KDC realm
name. For example:
Key Distribution Center (KDC) Realm Name
Enter the Kerberos realm name for the KDC:
The realm name should be consistent with the realm you give to DPEs in this provisioning
group.
KDC Interface Address [10.10.10.5]
KDC FQDN [acme_u6.acme.com]
KDC Realm [ACME.COM]
The program prompts you to confirm the realm name.
Step 8 Press y and Enter to confirm your entry and continue. The program prompts you to enter the KDC
service key and the DPE panel. For example:
KDC Service Key and DPE Panel
Please Enter the Necessary Info
Enter Password Here [] 12345678901234567890
Enter Your DPE FQDN [] dpe1.cisco.com
Installing Components Using the CLI
Note Please be aware that the service key consists of 48 characters. If all are not entered the service
key will be invalid.
Step 9 The program prompts you to enter the information for another DPE. Press y and enter to add another
DPE, or press n and enter to continue.
Note The installation program uses the same voice technology shared key for all DPEs.
Step 10 Press y and Enter to continue. The program displays the installation parameters that you selected. For
example:
Installation Parameters
This screen shows the installation parameters that you have chosen:
========== Confirmation ==========
The Component Installation will use the following parameters
to install the KDC component:
KDC realm name: ACME.COM
Home directory: /opt/CSCObpr
Data directory: /var/CSCObpr
Step 11 Press y and Enter to install the KDC. The program displays a message when the installation is complete.
OL-19105-01
Caution After installing the KDC, you must install your licenses and the chain of certificates or the KDC will not
start.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
3-15
Page 40

Installing Components Using the CLI
Installing the Device Provisioning Engine
To install the DPE:
Step 1 When the installation program prompts you to select one or more components, press y and Enter at
Device Provisioning Engine (y/n/?).
To skip installing an RDU and Network Registrar extension points, enter n and Enter for these options.
For example:
Installation Components
Select one or more components to install BPR.
Regional distribution unit (RDU) (y/n/?) [no] n
Cisco Network Registrar extension points (y/n/?) [no] n
Device Provisioning Engine (DPE) (y/n/?) [yes] y
Key Distribution Center (KDC) (y/n/?) [no] n
The program prompts you to confirm the components that you want to install.
Step 2 Press y and Enter to continue. The program displays a message that it is starting individual component
validation. Press Enter to continue
Step 3 When validation is complete, the program prompts you to enter the home directory destination.
Validation involves checking to verify that the correct patches have been installed. If they are not, error
messages appear on screen.
Step 4 To accept the default home directory destination, /opt/CSCObpr/, press Enter, or enter another directory.
For example:
Home Directory Destination
Chapter 3 Installing Components
Home Directory Destination [/opt/CSCObpr]
Choosing yes will create the directory during the installation. Choosing no will allow a
different directory to be chosen.
The directory /opt/CSCObpr does not exist. Create it? (y/n/?) [yes]
Step 5 When validation is complete, the program prompts you to enter the data directory destination.
Step 6 To accept the default data directory destination, /var/CSCObpr/, press Enter, or enter another directory.
For example:
Data Directory Destination
Data Directory Destination [/var/CSCObpr]
Choosing yes will create the directory during the installation. Choosing no will allow
a different directory to be chosen.
The directory /var/CSCObpr does not exist. Create it? (y/n/?) [yes]
The program prompts you to confirm the components that you want to install.
Step 7 Press y and Enter to create the directory and continue. The program displays the installation parameters
that you selected. For example:
Installation Parameters
This screen shows the installation parameters that you have chosen:
3-16
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 41

Chapter 3 Installing Components
========== Confirmation ==========
The Component Installation will use the following parameters
to install the DPE component:
Home directory: /opt/CSCObpr
Data directory: /var/CSCObpr
Step 8 Press y and Enter to install the DPE. The program displays a message when the installation is complete.
Installing Components Using the CLI
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
3-17
Page 42

Installing Components Using the CLI
Chapter 3 Installing Components
3-18
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 43

Installing in a Lab Environment
This chapter describes how to install BACC in a lab environment to demonstrate product functionality
and how to configure a CMTS and Network Registrar to support BACC.
When you install Broadband Access Center for Cable (BACC) in a lab environment, the installation
program installs all components on a single server. The lab installation program involves fewer steps
than the component installation and automates much of the configuration. When you complete the
installation, however, you need to perform some setup on a cable modem termination system (CMTS)
and on Network Registrar.
The lab installation program is designed to keep the installation and configuration as simple as possible
by using a predefined overall system configuration.
The lab installation program uses predefined default values for the installation that assume a specific
network configuration.
Installation Checklist
CHAP T ER
4
You can install BACC in a lab environment on a single computer running the Solaris 8 or 9 operating
system. Before you run the installation program, use this checklist to ensure that you are ready:
• Verify the prerequisite system hardware and software requirements described in Chapter 1,
“Overview.”
• Have your BACC evaluation license key or keys at hand. You need a valid license key for each
technology that you want to provision with BACC.
• Ensure that you have root access to the computers where you intend to install BACC.
• Verify that Network Registrar is installed and running on the server. We recommend that you use
Network Registrar 6.1.2.3 or higher.
• Determine the destination directory in which you want to install BACC.
Note Cisco Systems recommends that you have at least 350 MB of disk space available.
• For extensions, determine the name of provisioning group to which the Network Registrar server
belongs.
• Verify that you have the necessary Network Registrar configuration files. See Appendix A,
“Network Registrar Configuration File Example” for an example of these configuration files.
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
4-1
Page 44

Installing in a Lab Environment Using the GUI
Installing in a Lab Environment Using the GUI
The lab installation prompts for this information:
• BACC destination directory
• Network Registrar administrator username and password
• Shared secret password
During a lab installation, a set of predetermined default values are used as a network configuration.
To install BACC in a lab environment, complete these steps:
Step 1 Complete steps 1 through 4 in the “Installation Using the Graphical User Interface” section on page 2-7.
Step 2 Click Lab when the Choose Installation Type screen appears.
Step 3 Click Next. The lab installation program automatically checks to see if it detects a TFTP server.
Caution When installing BACC on a Solaris server, both the Solaris and Network Registrar TFTP
servers must be disabled.
Chapter 4 Installing in a Lab Environment
Provided that a TFTP server is not detected, a PacketCable voice technology screen appears.
Step 4 Determine if you need to install the voice technology option and click:
• Ye s button if you want to install the voice technology option
• No if you do not have a valid license key for this technology.
Step 5 Click Next and the Destination Directory screen appears.
Step 6 Enter the pathname of the location where you want to install BACC.
Step 7 Click Next. The installation program verifies that the selected installation directory exists and, if it does
not, prompts you to automatically create it. The installation program also confirms that the required disk
space is available, and then the Cisco Network Registrar Username and Password screen appears.
Step 8 Enter the Network Registrar administrative username and password.
Step 9 Click Next. The Key Distribution Center Realm Name screen appears.
Step 10 If the default KDC realm name is inappropriate, enter desired KDC Realm, FQDN, and interface address
name.
Step 11 Click Next. The PacketCable Properties screen appears.
Note If you did not select the voice technology option from the PacketCable Panel, this screen will
not appear.
Step 12 Enter the appropriate information into the fields shown.
4-2
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 45

Chapter 4 Installing in a Lab Environment
Field Name Description
Kerberos Realm Name Specifies, using a unique name, the Kerberos realm. This must match the
IP Address of Primary
DHCP Server
IP Address of Primary DNS
Server
IP Address of Secondary
DHCP Server
IP Address of Secondary
DNS Server
Step 13 The Shared Secret Password screen appears.
Step 14 Enter and confirm the shared secret password. This password is a token that a BACC server uses to
authenticate communication with other BACC servers.
Step 15 Click Next and the Lab Installation Parameters screen appears. This screen identifies the values that you
have entered in the previous screens. To modify any of the values entered:
Installing in a Lab Environment Using the CLI
realm set at the associated components.
Specifies the IP address of the voice technology primary DHCP server.
Specifies the IP address of the computer which is running the primary
DNS server.
Specifies the IP address of the voice technology secondary DHCP server.
Specifies the IP address of the computer which is running the secondary
DNS server; if that server is being used.
a. Click Back until the desired screen appears.
b. Make the necessary changes.
c. Click Next repeatedly until you return to this screen.
Step 16 Click Next and the lab version of BACC is installed. When installation is complete, the Installation
Summary screen appears.
Step 17 Click Finish and BACC is completely installed in your lab environment.
Note You use the administrator’s user interface to configure your license keys. Refer to the Cisco Broadband
Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide for additional information.
Caution After installation is complete, you must install your licenses and the chain of certificates or the KDC
will not start.
Installing in a Lab Environment Using the CLI
The lab installation prompts for this information:
OL-19105-01
• BACC destination directory
• Network Registrar administrator username and password
• Shared secret password
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
4-3
Page 46

Installing in a Lab Environment Using the CLI
To install BACC in a lab environment, complete the steps described in the “Installing from the Command
Line” section on page 2-8:
Step 1 The program displays this message:
Are you going to use a device(s) that supports Packetcable voice technology?
If you are going to use Packetcable devices we need some more info.
Enter Yes to Install Packetcable and No if you don’t want Packetcable
installed [No]: Yes
Step 2 Enter Ye s and press Enter. A confirmation message appears.
Step 3 Answer the confirmation question appropriately and press Enter. The program displays this message.
Validating LAB settings...
The program then prompts you to enter the destination directory.
Step 4 To accept the default directory, /opt/CSCObpr, press Enter. For example:
Destination Directory
Directory path for BACC_HOME
Chapter 4 Installing in a Lab Environment
Location BACC_HOME
Installation Directory [/opt/CSCObpr]
The program then asks you to confirm the directory.
Step 5 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the Cisco Network Registrar username
and password.
Step 6 To enter a Network Registrar username and password:
a. Enter a valid administrator username and password.
b. Enter the password again to confirm it.
For example:
Cisco Network Registrar Username and Password
Enter the administrator username and password for the NR server.
Enter the username and password for the NR server to be used in the lab
installation. You must confirm the NR password.
Network Registrar adminstrator Username [admin] admin
Network Registrar adminstrator Password [] changeme
Confirm Network Registrar Password [] changeme
The program then redisplays the administrator username, password, and password confirmation. It then
prompts you to confirm this information.
Step 7 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the KDC realm name. The realm name
must be the same one used with all of the DPEs in the provisioning group. For example:
Enter the Kerberos realm name for the KDC
4-4
The realm name should be consistent with the realm you give to DPEs in this
provisioning group.
KDC Interface Address:
KDC FQDN:
KDC Realm:
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 47

Chapter 4 Installing in a Lab Environment
Step 8 Enter the appropriate KDC Interface Address, FQDN, and Realm information and then press Enter.
The program redisplays the KDC information and prompts you to confirm this information.
Step 9 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter PacketCable properties. For example:
Enter PacketCable properties
Enter KDC Realm Name
Enter IP Address for Primary DHCP []
Enter IP Address for Primary DNS []
Enter IP Address for Secondary DHCP []
Enter IP Address for Secondary DNS []
Step 10 Enter the appropriate voice technology information. Keep in mind that the KDC Realm name you enter
here must be the same as that entered in the previous screen.
Step 11 Press Enter; the program redisplays the PacketCable Properties information and prompts you to confirm
the information.
Step 12 Press y and Enter to continue. The program prompts you to enter the shared secret password. This
password is a token that a BACC server uses to authenticate communication with other BACC servers.
The default password is secret.
Step 13 Enter the password that you want to use for authentication among BACC servers. For example:
Shared Secret Password
Installing in a Lab Environment Using the CLI
Enter the password to be used for authentication
among the BPR servers.
If you are performing a lab installation, then the password will be used for
all the servers. If this is a component installation, then the password you
enter must be the same as the components previously installed.
Enter the Shared Secret Password [secret] secret
The program prompts you to confirm the password.
Step 14 Enter the password again and press y to continue. The program then displays the installation parameters
that you selected. For example:
Installation Parameters
This screen shows the installation parameters that you have chosen:
========== Confirmation ==========
The Lab/Demo Installation will install all components using the following
parameters:
Installation directory:/opt/CSCObpr
Is this correct (y/n/q/?) [yes]
Step 15 Press y and Enter to install the lab software. The program displays a message when the installation is
complete.
OL-19105-01
Note You use the administrator’s user interface to configure your license keys. Refer to the Cisco Broadband
Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide for additional information.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
4-5
Page 48

Configuring Network Registrar and a CMTS
Caution After installation is complete, you must install your licenses and the chain of certificates or the KDC
will not start.
Configuring Network Registrar and a CMTS
For BACC to function, you need to set up Network Registrar client-classes, policies, scopes, and
selection tags. You also need to perform some configuration of CMTS devices.
To configure Network Registrar and CMTS devices, complete these steps:
Step 1 Set up scopes on your Network Registrar server. For example:
<NR_HOME>/usrbin/nrcmd -N <USER_NAME> -P <PASSWORD> -b <
<BACC_HOME>/cnr_ep/samples/bpr_cnr_hsd_sample_config.nrcmd
Chapter 4 Installing in a Lab Environment
Note The <BACC_HOME>/cnr_ep/samples/bpr_cnr_hsd_sample_config.nrcmd command runs a
sample Network Registrar configuration script, which defines client-classes, policies, scopes,
selection tags and other related information. You must update this file to reflect the IP address
settings on your network. For more information about this file, see
“Network Registrar
Configuration File Example”. For more detailed information about defining client-classes,
policies, scopes, and selection tags, see the Network Registrar User’s Guide.
Step 2 Enable the cable interface or interfaces on your CMTS with the correct IP addresses and DHCP
helper-address. For example, you might edit the CMTS configuration as follows:
interface Cable3/0
ip address 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0
ip address 192.168.6.0 255.255.255.0 secondary
ip address 192.168.7.0 255.255.255.0 secondary
ip address 192.168.8.0 255.255.255.0 secondary
Note The IP addresses used here are identical to those in the sample script supplied with the BACC
product. You must edit these addresses to match your own IP address range. Do not attempt to
use these IP addresses in an operational environment.
no ip directed-broadcast
no keepalive
cable downstream annex B
cable downstream modulation 64qam
cable downstream interleave-depth 32
cable downstream frequency 477000000
cable upstream 0 frequency 26000000
cable upstream 0 power-level 0
no cable upstream 0 shutdown
cable dhcp-giaddr primary
cable helper-address <IP Address Of Your Network Registrar Server>
4-6
Note A sample configuration script file is included with the BACC product. This file, called
cmts_sample.cfg, is located in the <BACC_HOME>/cnr_ep/samples directory.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 49

Chapter 4 Installing in a Lab Environment
Step 3 To configure your CMTS to insert the DHCP relay agent information option in forwarded
BOOTREQUEST messages, use this Cisco IOS command:
ip dhcp relay information option
The default device detection logic in BACC uses DHCP option 82 information (relay-agent information)
to detect devices.
Step 4 To configure your CMTS so that it does not validate the relay agent information option in forwarded
BOOTREPLY messages, use this IOS command:
no ip dhcp relay information check
Configuring Network Registrar and a CMTS
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
4-7
Page 50

Configuring Network Registrar and a CMTS
Chapter 4 Installing in a Lab Environment
4-8
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 51

CHAP T ER
5
Post-Installation Activities
This chapter describes activities you can perform after installing BACC:
• Enabling a Network Registrar Spoofing DNS Server, page 5-1
• Configuring the Syslog Utility to Receive Alerts from BACC, page 5-1
• Uninstalling Broadband Access Center, page 5-2
Enabling a Network Registrar Spoofing DNS Server
A spoofing DNS server redirects all DNS requests to the same IP address. This can be used to enforce a
self-provisioning flow for a new subscriber.
For example, assume that a DNS host is dns.acme.com, and has an IP address of 10.10.10.5. Assume
also, that the Web server with the self-provisioning flow is 10.10.10.6.
On the DNS server, set the following in Network Registrar:
nrcmd> zone . delete
nrcmd> zone . create primary dns.acme.com postmaster.dns.acme.com
nrcmd> zone . addrr * a 10.10.10.6
nrcmd> save
nrcmd> dns reload
When DNS reloads, the changes will take effect.
On the DHCP server, set the following in Network Registrar:
nrcmd> policy unprovisioned setoption domain-name-servers 10.10.10.5
nrcmd> policy unprovisioned setoption domain-name acme.com
nrcmd> save
nrcmd> dhcp reload
Configuring the Syslog Utility to Receive Alerts from BACC
This section describes how to configure the syslog utility on both the Network Registrar extension points
and RDU server to receive alerts and debugging information from BACC.
Step 1 Log in as root on the Network Registrar server.
Step 2 At the command line, create the log file. For example:
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
5-1
Page 52

Uninstalling Broadband Access Center
touch /var/log/bpr.log
Step 3 Open the /etc/syslog.conf file with a text editor.
Step 4 Add this line to the /etc/syslog.conf file:
local6.info /var/log/bpr.log
Note You must insert one or more tabs between the local6:info and /var/log/bpr.log information.
Step 5 Save and close the /etc/syslog.conf file.
Step 6 To force the syslog utility to take the new configuration, at the command line enter these commands:
ps -ef | grep syslogd
root 217 1 0 Nov 26 ? 0:00 /usr/sbin/syslogd
kill -HUP 217
Note The pid in this example is 217, but may change when you run ps -ef | grep syslogd. Use the
correct output, from that command, as the input to kill -HUP.
Chapter 5 Post-Installation Activities
Syslog is now ready to receive alerts from BACC.
Uninstalling Broadband Access Center
The program described in this section uninstalls the RDU, Network Registrar extensions, the DPE, and
the KDC, but it does not uninstall the Network Registrar application. Prior to removing BACC you must
manually remove the BACC configuration on Network Registrar.
The uninstallation program removes all files located under the installation directory (the default
installation directory is /opt/CSCObpr). If the database is found under the installation directory, as is the
case in the lab installation program, the program displays a warning message that it is deleting the
database. You can exit from the uninstallation program at that time, or you can choose to proceed.
The uninstallation program also shuts down and removes these processes if they are detected: RDU,
KDC, SNMP Agent, JRun, BACC agent, and the DPE.
The uninstallation program does not remove files that were placed outside the installation directory. For
example, a component installation places the database and database transaction logs directories under
/var/CSCObpr. So theses files are not removed. The uninstallation program also does not remove any
files that are located under the Network Registrar directory.
Caution If you uninstall BACC after configuring your Network Registrar servers to use BACC extensions, your
network will no longer function correctly. You must uninstall BACC extensions in Network Registrar to
completely uninstall the BACC program.
5-2
There are two ways to remove BACC:
• Uninstalling BACC from the Graphical User Interface, page 5-3
• Uninstalling BACC from the Console Mode, page 5-3
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 53

Chapter 5 Post-Installation Activities
Uninstalling BACC from the Graphical User Interface
To uninstall BACC using the graphical user interface:
Step 1 Log in as root.
Step 2 Manually remove the configuration of the BACC extensions on the Network Registrar server. You can
do this from any server that has nrcmd installed and connectivity with Network Registrar.
Follow these steps:
a. To uninstall the BACC extensions from your Network Registrar configuration, use these commands:
<NR_HOME>/usrbin/nrcmd -N admin -P changeme -b <
<BACC_HOME>/cnr_ep/bin/bpr_cnr_disable_extpts.nrcmd
b. To reload your DHCP server, use these commands:
/etc/init.d/nwreglocal stop
/etc/init.d/nwreglocal start
Alternatively, enter this command:
<NR_HOME>/usrbin/nrcmd -N admin -P changeme "dhcp reload"
Uninstalling Broadband Access Center
c. To remove the BACC extensions from the Network Registrar extensions directory, use this
command:
rm -f <NR_HOME>/extensions/dhcp/dex/libbprextensions.so
Step 3 At the CLI prompt, enter:
<BACC_HOME>/_uninst/uninstall.bin
The uninstallation program’s Welcome screen appears.
Step 4 Click Next. The uninstallation program begins removing BACC files.
When the uninstallation is complete, the Cisco Broadband Provisioning Registrar was Uninstalled screen
appears.
Step 5 To exit the uninstallation program, click Finish.
Note Should the uninstallation program fail to successfully uninstall BACC, error messages will appear on
screen.
Uninstalling BACC from the Console Mode
To uninstall BACC from the console mode:
OL-19105-01
Note If you are uninstalling BACC from a lab installation, the database is automatically deleted based on your
confirmation. To prevent the accidental or unplanned deletion of the database, copy or back up the
database files and log files as instructed in the Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator’s
Guide.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
5-3
Page 54

Uninstalling Broadband Access Center
Step 1 Log in as root.
Step 2 Manually remove the configuration of the BACC extensions on the Network Registrar server. You can
do this from any server that has nrcmd installed and connectivity with Network Registrar. Follow these
steps:
a. To uninstall the BACC extensions from your Network Registrar configuration, use these commands:
<NR_HOME>/usrbin/nrcmd -N admin -P changeme -b <
<BACC_HOME>/cnr_ep/bin/bpr_cnr_disable_extpts.nrcmd
b. To reload your DHCP server, use these commands:
/etc/init.d/nwreglocal stop
/etc/init.d/nwreglocal start
Alternatively, enter this command:
<NR_HOME>/usrbin/nrcmd -N admin -P changeme "dhcp reload"
c. To remove the BACC extensions from the Network Registrar extensions directory, use this
command:
rm -f <NR_HOME>/extensions/dhcp/dex/libbprextensions.so
Chapter 5 Post-Installation Activities
Step 3 At the CLI prompt, enter:
<BACC_HOME>/_uninst/uninstall.bin -console
The following is displayed:
Welcome to the Uninstallation Program
Press Enter to uninstall Cisco Broadband Provisioning Registrar from your system.
Press Enter to Continue or 'q' to Quit:
Step 4 Press Enter to start the removal process. When uninstallation is complete these messages appear:
Cisco Broadband Provisioning Registrar was Uninstalled
Cisco Broadband Provisioning Registrar files were uninstalled successfully.
Press Enter to finish:
Step 5 Press Enter to exit the program.
5-4
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 55

Upgrading Broadband Access Center for Cable
This chapter describes how to upgrade a BACC 2.5.0.2 or higher installation to BACC 2.7. If you have
a BACC release preceding BACC 2.5.0.2, you must first upgrade your system to BACC 2.5.0.2 and then
complete this upgrade procedure.
Table 6-1 summarizes the order of upgrade and migration tasks required for BACC components for
different versions.
Ta b l e 6-1 Upgrading BACC components
Version RDU Solaris DPE
BACC 2.5.0.2
(Migration of
RDU database
required)
BACC 2.6.x
(Migration of
RDU database
required)
Run setup.bin.
At the end, the
installer
prompts you to
run the
migration tool.
Run setup.bin.
At the end, the
installer
prompts you to
run the
migration tool.
N/A Download the
Run the upgrade
script to
upgrade the
DPE.
Appliance
DPE-590
upgrade file and
run the DPE
patch process.
Download the
upgrade file and
run the DPE
patch process.
CHAP T ER
Appliance
DPE-2115
Download the
upgrade file and
run the DPE
patch process.
Download the
upgrade file and
run the DPE
patch process.
CNR-EP KDC
Run the upgrade
script to
upgrade the
CNR_EP.
Run the upgrade
script to
upgrade the
CNR_EP.
6
Run the upgrade
script to
upgrade the
KDC.
Run the upgrade
script to
upgrade the
KDC.
OL-19105-01
The BACC upgrade procedure requires that the components be updated in the exact order described
below. Performing the upgrade in any other order may result in errors during provisioning:
• Before You Begin, page 6-2
• Upgrading the RDU, page 6-2
• Upgrading the Solaris DPE, page 6-2
• Upgrading Hardware DPEs, page 6-4
• Upgrading Network Registrar Extensions, page 6-5
• Upgrading the KDC, page 6-5
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
6-1
Page 56

Before You Begin
Before You Begin
The following procedure is required before upgrading all components except the RDU.
Step 1 Untar the upgrade file(27upgrade.tar) onto the computer where the BACC components reside. For
example:
tar -xvf 27upgrade.tar
The component upgrade scripts are extracted to the patch27/bin upgrade folder.
Step 2 Run the backupDb.sh script to back up the RDU database files. See the Cisco Broadband Access Center
for Cable Administrator’s Guide for additional information.
Upgrading the RDU
To upgrade the RDU:
Chapter 6 Upgrading Broadband Access Center for Cable
Step 1 Run the setup.bin file normally associated with a new installation of BACC. The setup.bin file
automatically detects the previous installation.
Step 2 When the installation program prompts you to perform the database migration procedure, run the
migration script using the migrateDb.sh script as described in
Upgrading the Solaris DPE
Complete these steps to upgrade the installed Solaris DPE component from release 2.6.x to release 2.7:
Step 1 Run this script from the upgrade folder:
./27-upgrade-dpe.sh
Step 2 You must manually restart the agent to finish the upgrade process.
An output similar to this displays.
BPR Located
BPR Home directory is /opt/CSCObpr
Current version is 2.6.(x)
DPE Component Installed
Stopping the BPR Agent
BPR Agent is stopped.
Migrating the RDU Database, page 6-6.
6-2
BPR Agent stopped
Copying the Upgrade Files
Upgrading Package Information
Upgrade for BPR 2.7 Completed Successfully
Please start your BPR Agent to finish the upgrade Process
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 57

Chapter 6 Upgrading Broadband Access Center for Cable
Step 3 Run this command to verify that the output indicates it is BACC release 2.7:
# pkgparam CSCObpr VERSION
The version information returned should be 2.7.
Note The previous version of the file bpr.jar is renamed as bpr-2x.jar and is located in the
<BACC_HOME>/lib directory.
Step 4 Check the list of installed files. An output similar to this is displayed.
drwxr-xr-x 4 root smmsp 512 May 26 11:22 electric
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 11730913 May 26 11:22 bpr.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 116848 May 26 11:22 libosstatus.so
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 465392 May 26 11:22 libnative.so
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 827344 May 26 11:22 libInformManager.so
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 1983836 May 26 11:22 libbprextensions.so
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 30790 May 26 11:23 pkcerts.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 938940 May 26 11:23 libdb_java-4.1.so
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 840988 May 26 11:23 libdb-4.1.so
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 187162 May 26 11:23 sun_parser.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 28404 May 26 11:23 sun_jaxp.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 33428 May 26 11:23 sleepycat.jar
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 936631 May 26 11:23 bcprov.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 832960 May 26 11:23 libgcc_s.so.1
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 62624 May 26 11:23 TelnetD.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 8661944 May 26 11:23 libstdc++.so.5
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 285176 May 26 11:23 libscp_java01.so
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 849020 May 26 11:23 libscp01.so
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 185208 May 26 11:23 libmlog.so
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 529820 May 26 11:23 libcnrschema.so
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 2847640 May 26 11:23 libaic.so
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 217572 May 26 11:23 dnsjava-1.5.1.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 29411 May 26 11:23 comm.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 384820 May 26 11:23 cnrsdk.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 131919 May 26 11:23 xmlParserAPIs.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 1728861 May 26 11:23 xercesImpl.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 2370312 May 26 11:23 libssl.so.0.9.7
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 2328048 May 26 11:23 libnetsnmp.so.5
drwxr-xr-x 2 root smmsp 512 May 26 11:23 SnmpAgent
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 14475552 May 26 11:23 libcrypto.so.0.9.7
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 28404 May 26 11:23 jaxp.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 187162 May 26 11:23 crimson.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 1107051 May 26 11:23 AdventNetSnmp.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 801714 May 26 11:23 xalan.jar
-rwx------ 1 root smmsp 167588 May 26 11:23 libnativeCrypto.so
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 515746 May 26 11:23 adminui.war
-rw-r--r-- 1 root smmsp 84311 May 26 11:23 sampleui.war
Upgrading the Solaris DPE
OL-19105-01
Note The actual directory contents displayed in this procedure may differ, from those shown above, depending
on the components installed on the computer.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
6-3
Page 58

Upgrading Hardware DPEs
Upgrading Hardware DPEs
You may remotely patch your DPE devices, or if you have local access to these devices, you can fully
reimage them. Refer to the recovery CD-ROM release notes that accompanied the DPE device for the
required reimaging procedure.
Complete these steps to upgrade the DPE component to release 2.7:
Caution If the hardware DPE is rebooted or powered off while a patch is being applied, the device is left in an
unknown state and must be completely reimaged. Refer to either the DPE-590 or DPE-2115 Recovery
CD-ROM Release Notes that accompany the DPE device, for reimaging instructions.
Step 1 Open an FTP connection to each DPE to be patched and upload the patch bundle to the DPE. See step 3
for the appropriate DPE file name.
Note When opening the FTP connection, you must enter the username admin and the login password
chosen for the selected DPE.
Chapter 6 Upgrading Broadband Access Center for Cable
Step 2 After an FTP connection is established, change directory to ‘incoming’ using this command at the FTP
prompt:
cd incoming
This will locate the patch file so that the DPE can easily find it.
Step 3 Select the upgrade file corresponding to the BACC version currently running on your DPE and FTP it to
the DPE.
If you have this DPE
model...
Running this BACC
release...
Use this file to upgrade to BACC 2.7
DPE 590 BACC 2.5.0.2 dpe-590-2502to27-upgrade.bpr
BACC 2.6.x dpe-590-26xto27-upgrade.bpr
DPE-2115 BACC 2.5.0.2 dpe-2115-2502to27-upgrade.bpr
BACC 2.6.x dpe-2115-26xto27-upgrade.bpr
For example, you use this command to FTP the DPE-590 upgrade file from BACC 2.6.x to BACC 2.7:
bin
put dpe-590-26xto27-upgrade.bpr
Step 4 Log into each DPE, in the enable mode, and run the upgrade command. You are prompted to select the
2.7 upgrade file and apply it. After the upgrade is finished, the DPE will reboot.
Step 5 Log into each DPE, in the enable mode, and run the show version command. This should identify the
current version running on the DPE as BACC 2.7.
6-4
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 59

Chapter 6 Upgrading Broadband Access Center for Cable
Upgrading Network Registrar Extensions
Use this procedure to upgrade the Network Registrar extensions from BACC 2.5.0.2, or 2.6.x to
BACC
2.7:
Step 1 Run the 27-upgrade-cnrep.sh script.
Step 2 Stop the Network Registrar Server Agent when prompted.
The upgrade script automatically copies the upgraded extension point files into the required directories.
When complete, it prompts you to restart the Network Registrar Server Agent.
Step 3 Run this command to verify that the output indicates it is BACC release 2.7:
# pkgparam CSCObpr VERSION
The version information returned should be 2.7.
Step 4 Go to the /opt/CSCObpr/lib directory. Provided that the upgrade was successful, the directory content
should appear similar to the list for the Solaris DPE upgrade with the addition of the
libbprextensions-2x.so file.
Upgrading Network Registrar Extensions
Note The previous version of the file bpr.jar is renamed as bpr-2x.jar and is located in the
<BACC_HOME>/lib directory.
Step 5 If a second check is required to verify upgrade success, go to the $CNR_HOME/extensions/dhcp/dex
directory and verify that these files appear:
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root bin 6 0904 Oct 29 2003 libdexextension.so
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root other 1530628 Jul 22 12:43 libbprextensions-2x.so
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root other 1560748 Aug 11 12:49 libbprextensions.s
Note The actual directory contents displayed in this procedure may differ, from those shown above, depending
on the components installed on the computer.
Upgrading the KDC
Note BACC 2.7 KDC requires a new license. Please ensure that the correct license and certificates are
installed before you start the BACC agent.
OL-19105-01
Use this procedure to upgrade the KDC from BACC 2.5.0.2 or 2.6.x to BACC 2.7:
Step 1 Run the 27-upgrade-KDC.sh script.
Step 2 Manually start the BACC agent to complete the upgrade process.
Step 3 Run this command to verify that the output indicates it is BACC release 2.7:
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
6-5
Page 60

Migrating the RDU Database
# pkgparam CSCObpr VERSION
The version information returned should be 2.7.
Step 4 Go to the /opt/CSCObpr/kdc/internal/bin directory. Provided that the upgrade was successful, this
directory content should appear similar to this:
-r-x------ 1 root smmsp 1388 May 26 11:23 shutdownKDC.sh
-r-x------ 1 root smmsp 535 May 26 11:23 runKDC.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root smmsp 1023548 May 26 11:23 kdc
Note The actual directory content that is displayed may differ, from that shown above, depending on the
components installed on the computer.
Chapter 6 Upgrading Broadband Access Center for Cable
Migrating the RDU Database
The Regional Distribution Unit (RDU) database migration script lets you migrate your RDU database
from BACC 2.5.0.2 into BACC 2.7.
The migration script is automatically installed, and unpacked, whenever the BACC 2.7 installation
program (setup.bin) is run. The installation program unpacks the migration script file into the
<BACC_HOME>/migration directory. You run the RDU database migration script using the
migrateDb.sh script. This script migrates the BACC 2.5.0.2 or BACC 2.6.x database to BACC 2.7.
Note Prior to installing the new BACC version you must run the backupDb.sh script to back up the database
files. See the Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator’s Guide for additional
information.
After the migration is completed, run the verifyDb.sh script to check database consistency. Verification
is an optional step and may be skipped if shorter downtime for migration is critical.
Each time a migration is performed, information is recorded in a migration log file, which is stored in
<BACC_DATA>/rdu/logs directory. The migration.log file identifies which version of the database is
being migrated.
Start the RDU using “bprAgent start rdu” command and observe messages about successful initialization
in the rdu.log file.
6-6
Caution The RDU should not be started while migration is in progress; any attempt to restart the RDU results in
a series of error messages being written into the rdu.log file. These messages will indicate that database
migration is needed before the RDU can be restarted.
Migrating from BACC 2.5.0.2
When migrating from release 2.5.0.2, you must use command line parameters to specify the file system
directory for temporary storage when running the migrateDb.sh script. This script is located in the
<BACC_HOME>/migration directory.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 61

Chapter 6 Upgrading Broadband Access Center for Cable
When running this script, use this syntax:
./migrateDb.sh temp_dir
Where temp_dir identifies the temporary directory.
When performing this migration, you must allow for the available disk space required for temporary
storage. The available disk space must be at least the same as the size of the old database files. However,
for performance reasons, Cisco recommends that you locate this directory on a different disk from the
database and the database log files.
Internally, the migration process from BACC 2.5.0.2 is a two-step process. The first step, migration from
BACC 2.5.0.2 to BACC 2.6 generates a migration25to26.log file. The second part, from BACC 2.6 to
2.7 generates a migration26to27.log file.
• If migration is interrupted during the first part, from BACC 2.5.0.2 to BACC 2.6, migration restarts
from where it left off, and the same migration log continues to be used.
• If migration is interrupted during the second part, from BACC 2.6 to 2.7, migration restarts from the
beginning. The old migration log is renamed with a suffix with the timestamp and a new migration
log is created.
If migration is interrupted during the first part, and a clean restart of migration from BACC 2.5.0.2 is
required, you must:
Migrating the RDU Database
Step 1 Delete all files from the temporary directory.
Step 2 Rerun the database migration script.
Step 3 Start the RDU to initialize the database.
Step 4 Run the verifyDb.sh script to verify database consistency (optional).
Step 5 Restart the RDU after migration is complete and the database verified.
Migrating from BACC 2.6
When migrating 2.6.x, no command line parameter is needed.
Use this syntax:
./migrateDb.sh
Migrating from BACC 2.6 generates a migration26to27.log file.
Interrupting the migration from BACC 2.6.x to BACC 2.7 restarts the migration from the beginning. The
old migration log is renamed with a suffix with the timestamp and a new migration log is created.
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
6-7
Page 62

Migrating the RDU Database
Chapter 6 Upgrading Broadband Access Center for Cable
6-8
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 63

Setting Up a Device Provisioning Engine
A Cisco Device Provisioning Engine caches provisioning information and handles all configuration
requests including downloading configuration files to devices. It is integrated with the Cisco Network
Registrar DHCP server to control the assignment of IP addresses. Multiple DPEs can communicate with
a single DHCP server. DPEs come with factory installed software that enables provisioning, but you
must perform some initial configuration.
This chapter describes the setup procedure.
Hardware DPE Setup Sequence
Table 7-1 identifies the sequence of events for setting up a hardware DPE.
Ta b l e 7-1 DPE Setup Sequence
Item To do this . . . See this section...
1. Connect the DPE to the serial port of a
computer.
2. Configure and run a terminal emulation
program on the computer.
3. Log in to the DPE and change the login/enable
password.
4. Configure the DPE for data. Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine
5. Configure the DPE to support voice
technology.
6. Configure the DPE to support the CableHome
technology.
CHAP T ER
Connecting the Device Provisioning Engine,
page 7-1
Configuring and Running a Terminal
Emulation Program, page 7-2
Logging In, page 7-2
for Data, page 7-3
Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine
for Voice Technology, page 7-5
See the Cisco Broadband Access Center for
Cable Administrator’s Guide.
7
Connecting the Device Provisioning Engine
Each DPE comes with a console cable. To begin setting up the DPE, complete these steps:
Step 1 Attach one end of the cable to the console port of the DPE.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
7-1
Page 64

Chapter 7 Setting Up a Device Provisioning Engine
Logging In
Step 2 Attach the other end of the cable to the serial port on the computer that you want to use to configure the
DPE.
Step 3 Proceed to the “Configuring and Running a Terminal Emulation Program” section on page 7-2.
Configuring and Running a Terminal Emulation Program
You must configure and then run a terminal emulation program on the computer that you have connected
to the DPE.
To configure and run a terminal emulation program, complete these steps:
Step 1 Log in to the computer as root.
At the command line, enter the name of a terminal emulator. Choose a terminal emulation program that
enables communication with the DPE through the serial port on the host computer.
Step 2 Configure these settings on the terminal emulator:
• Speed:9600
• Data Bits:8
Step 3 Proceed to the “Logging In” section on page 7-2.
Logging In
Step 1 At the password prompt, enter the login password. The default user and enable passwords are changeme.
• Parity:None
• Stop Bits:1
• Flow Control:Hardware
When you have correctly configured the terminal emulation program, you are prompted to log in to the
DPE.
To log in to the DPE, complete these steps:
For example:
localhost BPR Device Provisioning Engine
User Access Verification
Password:
7-2
Note For security reasons, Cisco Systems strongly recommends that you change the original
password.
The system displays this user mode prompt:
localhost>
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 65

Chapter 7 Setting Up a Device Provisioning Engine
Step 2 Run the enable command to enter privileged mode. You must be working in privileged mode to
configure the DPE. For example:
localhost> enable
The system prompts you for the enable password.
Step 3 At the prompt, enter the enable password. The default is changeme.
The system displays this privileged mode prompt:
localhost#
Step 4 To change the login and enable password, as Cisco Systems recommends:
a. At the localhost# prompt, enter the password command. For example:
localhost# password
The system prompts you for the new password.
b. Enter the new password. The system prompts you to enter the new password again.
c. Re-enter the new password. The system displays a message that you successfully changed the
password.
Remember that this is your new log in password. If you want to change the privileged mode password,
use the enable password command.
Step 5 Proceed to the “Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine for Data” section on page 7-3.
Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine for Data
Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine for Data
To configure a DPE, have this information available:
• The static IP address that you want to assign to the DPE.
• The IP address or fully qualified domain name of the RDU for the DPE.
• The provisioning group or groups of which the DPE is part.
• The IP address of the default gateway on your network, if the default gateway is implemented on
your network.
• The host and domain names of the DPE.
Tip You can use the show run command to view the running configuration. A complete list of show
commands is available through the use of the show commands command. Refer to the Broadband
Access Center for Cable CLI Reference Guide for additional information.
Note The commands pertaining to security are only enabled when connected to the DPE serial port. Refer to
the Refer to the Broadband Access Center for Cable CLI Reference Guide for additional information.
To configure a DPE, complete these steps:
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
7-3
Page 66

Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine for Data
Step 1 Assign a static IP address and subnet mask to the first ethernet port on the DPE. For example, to assign
IP address 10.10.10.1 and the subnet mask 255.255.255.0, enter these commands:
localhost# interface ethernet 0 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
localhost# interface ethernet 0 ip enabled true
localhost# interface ethernet 0 provisioning enabled true
Note The values provided here are sample values only. Use values appropriate for your network.
Step 2 Enter the IP address for the RDU or its domain name if you are implementing DNS. Also, identify the
port on which the RDU is listening. The default listening port is 49187. For example:
localhost# dpe rdu-server 10.10.10.1 49187
Step 3 Specify the provisioning group or groups of which the DPE is part. Where appropriate, specify the
secondary provisioning group of which it is part. For example:
localhost# dpe provisioning-group primary group1
localhost# dpe provisioning-group secondary group2
Step 4 If your network topology has a default gateway IP address, enter that information. For example:
localhost# ip default-gateway 10.10.10.1
Chapter 7 Setting Up a Device Provisioning Engine
Step 5 To set up DNS for the DPE, enter the IP address of the DNS server. For example:
localhost# ip name-server 10.20.10.1
Note To enter more than one DNS server name, lists the servers with a space between each entry.
Step 6 Provide the DNS hostname and domain name for the DPE. For example:
localhost# hostname DPE1
localhost# ip domain-name example.com
Step 7 Configure the current time on the DPE. For example:
localhost# clock set 23:59:59 20 12 2003
Step 8 Set the shared secret password to be the same as that on the RDU.
Note This is one of the security related commands mentioned earlier in this chapter. This command
can only be run if the console is connected to the DPE serial port.
Step 9 For the configuration to take effect, you must reload the DPE. For example:
localhost# reload
After you reload the DPE, you can establish a Telnet session using the IP address of the DPE. Remember
to use the new login and enable password that you created in the
“Logging In” section on page 7-2.
7-4
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 67

Chapter 7 Setting Up a Device Provisioning Engine
Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine for Voice Technology
Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine for Voice Technology
This section describes those configuration activities that must be performed to properly set up a DPE to
support voice technology.
Note The tips provided in this section refer to the dpe.properties file, located in the
<BACC_HOME>/dpe/conf directory, for a lab installation of BAC. You change the properties specified,
as indicated in the tip, to enable the described feature. If you edit the properties, you must restart the
DPE.
Caution In the dpe.properties file, there should only be a single instance of each property described in these
tips.
Setting Up Voice Technology
Complete these steps to set up voice technology on your DPEs.
Step 1 Enter these commands to set the FQDN for each enabled DPE interface:
interface ethernet 0 provisioning fqdn <fqdn-value>
interface ethernet 1 provisioning fqdn <fqdn-value>
Tip dpe.properties: /server/provFQDNs=FQDN[IP address]:port. This could translate, for example,
into c3po.pcnet.cisco.com[10.10.10.5]:49186.
Note The FQDN is sent as the SNMPEntity in DHCP option 177 suboption 3.
Step 2 Enter these commands to configure voice technology at DPE:
packetcable registration kdc-service-key <password>
Note This is a protected mode security command, accessible only on the local console. The contents
of this property are only visible when logged into the local console.
Caution The DPE password entered using this CLI command must match the corresponding password used in
Keygen utility when generating Service Keys for KDC.
OL-19105-01
Tip dpe.properties: /pktcbl/regsvr/KDCServiceKey=(xx: ... xx) Where (xx: ... xx) represents a 24
byte randomly selected, colon separated, hexadecimal value; for example:
31:32:33:34:35:36:37:38:39:30:31:32:33:34:3 5:36:37:38:39:30:31:32:33:34.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
7-5
Page 68

Configuring a Device Provisioning Engine for Voice Technology
For a lab installation, the KDC and DPE are installed on the same host, and the installation program
automatically generates a random KDC service key for both the KDC and the DPE.
Step 3 Enter this command to control the choice of encryption algorithm for use during SNMPv3:
packetcable registration policy-privacy <value>
Note If you enter a value of zero (which is the default value) for this policy privacy, the MTA will
choose a privacy option for SNMPv3. Entering any non-zero value means Provisioning Server
will set its privacy option in SNMPv3 to a specific protocol. Although, at publication, DES is
the only privacy option supported by voice technology.
Tip dpe.properties: /pktcbl/regsvr/policyPrivacy=1 - This enables DES privacy.
Step 4 Enter this command to set the SNMP service key used for SNMPv3 cloning to the RDU.
packetcable snmp key-material <password>
Chapter 7 Setting Up a Device Provisioning Engine
Note This is a protected mode security command, accessible only on the local console. The contents
of this property are only visible when logged into the local console.
The default value for this command is <null>. Enter this default to turn SNMPv3 cloning off at this DPE.
Tip dpe.properties: to turn SNMPv3 cloning off, use /pktcbl/snmp/keyMaterial= to turn it on, use
/pktcbl/snmp/keyMaterial=<key>. For example, /pktcbl/snmp/keyMaterial=31:32:33:34:
35:36:37:38:39:30:31:32:33:34:35:36:37:38:39:30:31:32:33:34:35:36:37:38:39:30:31:32:33:
34:35:36:37:38:39:30:31:32:33:34:35:36
Caution Set this property, to the same 46 hexadecimal bytes that are used at the RDU (rdu.properties file located
in the <BACC_HOME>/rdu/conf directory) to enable SNMP cloning.
Step 5 Enter this command to enable the PacketCable voice technology.
packetcable enable
Note PacketCable provisioning is disabled at the DPE by default. If you change this property, you
must reboot the DPE for the new setting to take effect. Also, you can turn voice technology on
or off by entering either packetcable enable or no packetcable respectively.
7-6
Tip dpe.properties: /pktcbl/enable=enabled
Step 6 Run the dpe reload command.
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 69

Chapter 7 Setting Up a Device Provisioning Engine
Controls Available
These commands described in this section, provide additional configuration settings. Changing these
properties on the DPE-590 causes the change to take effect immediately, without a DPE restart. If you
are working with a lab install, and modify any DPE property, you must restart the DPE for the change
to take effect.
• packetcable registration encryption—This command optionally enables encryption of the MTA
configuration file.
Tip dpe.properties: /pktcbl/regsvr/configEncrypt=1
• no packetcable registration encryption—This command optionally disables encryption of the
MTA configuration file.
Tip dpe.properties: /pktcbl/regsvr/configEncrypt=0
• packetcable snmp timeout <timeout>—This command dynamically sets the number of seconds
that the DPE waits for a response to an SNMPv3 SET operation. The timeout is expressed in
seconds and the default value is 10 seconds.
Debugging
Tip dpe.properties: /pktcbl/snmp/timeout=1 and /pktcbl/snmp/timeout=10
Debugging
Step 1 Enter this command to collect all the log, property, and network configuration files on the DPE :
Step 2 Enter this command to check the status of both the DPE and voice technology settings:
Complete these steps to verify that your DPEs are operating properly after configuring them for
operation with voice technology.
support bundle state
This command places the collected log files in the /outgoing directory. From there, the bundle is
accessible using FTP.
show dpe
Example show dpe command output
BPR Agent is running
dpe is running
Version BPR 2.5 (cbpr_25_L_200302040515).
Caching 51970 device configs and 2 external files.
Received 312 cache hits and 0 misses.
Received 0 lease updates.
Connection status is Disconnected.
Sent 77 SNMP informs and 77 SNMP sets.
Received 77 MTA provisioning successful SNMP informs.
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
7-7
Page 70

Debugging
Chapter 7 Setting Up a Device Provisioning Engine
Received 0 MTA provisioning failed SNMP informs.
Running for 11 days 1 hours 59 mins 15 secs.
This command also checks if voice technology provisioning is running, and displays the current health
of the SNMPv3 service.
7-8
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 71

APPENDIX
Network Registrar Configuration File Example
This appendix describes the sample configuration files included with this installation. This file is typical
of the files you use during the BAC installation.
Configuration Scripts
This section describes sample configuration scripts that you can copy and use to work with your BAC
implementation. One exists for DOCSIS modems and computers, while another is available for DOCSIS
modems and PacketCable MTAs.
Sample Script for DOCSIS Modems and Computers
This sample configuration nrcmd script (bpr_cnr_hsd_sample_config.nrcmd) is used for a high-speed
data deployment of DOCSIS modems and computers, in a multiple host configuration with failover
protection. It is installed in this directory: <BACC_HOME>/cnr_ep/samples/.
These assumptions have been made to create this script:
A
OL-19105-01
• DHCP primary server IP address is: 192.168.0.32
• DNS primary server IP address is: 192.168.0.32
This sample script defines these objects:
• Scope selection tag objects for provisioned client-classes.
• Client-class objects for provisioned DOCSIS modems and computers.
• Policy objects for unprovisioned and provisioned devices. The only difference is that DNS servers
are not given to unprovisioned devices.
• Scope and scope policy objects for unprovisioned and provisioned DOCSIS modems and computers.
• Disable the TFTP server.
To run this script, in the Network Registrar nrcmd program, enter:
<NR_HOME>/usrbin/nrcmd -N <username> -P <password> -b < bpr_cnr_hsd_sample_config.nrcmd
Where:
• -N—identifies the username
• -P—identifies the password
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
A-1
Page 72

Appendix A Network Registrar Configuration File Example
Configuration Scripts
Sample Script for DOCSIS Modems and PacketCable MTAs
This sample configuration nrcmd script (bpr_cnr_pktcbl_sample_config.nrcmd) is used for a
high-speed data deployment of DOCSIS modems and PacketCable MTAs. A multiple host configuration
with failover protection is also used, and the script is also installed in the <BACC_HOME>/cnr_ep/
samples/ directory.
These assumptions have been made to create this script:
• DHCP primary server IP address is: 192.168.0.32
• DNS primary server IP address is: 192.168.0.32
This sample script defines objects similar to those described in the “Sample Script for DOCSIS Modems
and Computers” section on page A-1.
To run this script, in the Network Registrar nrcmd program, enter:
<NR_HOME>/usrbin/nrcmd -N <username> -P <password> -b < bpr_cnr_pktcbl_sample_config.nrcmd
A-2
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 73

INDEX
A
API
RDU 2-1
available disk space 4-1
B
BAC
administrator’s password 2-3
alert messages 5-1
installation 1-vii
graphical user interface 1-4
home and data directories 3-2, 3-4, 3-9, 3-12
server requirements 1-2
license key 2-3, 4-1
Solaris 8 1-1
Broadband Access Center
See BAC
C
cable modem termination system
See CMTS
Choose Installation Type screen 2-7, 4-2
Cisco Network Registrar
DHCP server 7-1
CMTS 4-6
device configuration 4-6
DHCP relay agent information 4-7
enabling the cable interface 4-6
IP addresses 4-6
Network Registrar 4-6
command line interface
installing components 3-8
commands
df 2-6
mount 2-5, 2-6
setup.bin 2-7
setup.bin -console 2-8
Configuration
extensions to Network Registrar 3-5
Network Registrar 3-6
configuration 2-1
Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification
(DOCSIS)
configurations 2-1
CSRC DPR
Solaris host 2-8
2-1
D
database
file locations 2-5
performance optimization 2-5
requirements 2-5
verifying large file support 2-6
Database Transaction Logs screen 3-2
Data Directory Destination screen 3-2, 3-4, 3-7, 3-8
Device Provisioning Engine
See DPE
DHCP
Network Registrar 1-2
settings for Network Registrar 5-1
OL-19105-01
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
IN-1
Page 74

Index
DNS
DNS server 5-1
enabling a spoofing server 5-1
for the DPE 7-4
Network Registrar 1-3
reload 5-1
server 7-4
DOCSIS
configuration management 2-1
Documentation 1-ix
conventions 1-viii
organization 1-vii
related documents 1-ix
Domain Name System
See DNS
DPE
commands
enable 7-3
enable password 7-3
password 7-3
communication with a single DHCP server 7-1
configuration 7-5
configuring a device 7-3
connections 7-1
downloading configuration files 7-1
dpe.properties file 7-5
/pktcbl/enable 7-6
/pktcbl/regsvr/configEncrypt=0 7-7
/pktcbl/regsvr/configEncrypt=1 7-7
/pktcbl/regsvr/KDCServiceKey 7-5
/pktcbl/regsvr/policyPrivacy 7-6
/pktcbl/snmp/keyMaterial 7-6
/pktcbl/snmp/timeout=1 7-7
/pktcbl/snmp/timeout=10 7-7
/server/provFQDNs 7-5
hardware requirements 1-2
logging in 7-2
service key and FQDN 3-7
set up sequence 7-1
terminal emulation program 7-2
Dynamic DNS
See DDNS 1-3
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol 1-3
See DHCP
F
failover deployment 1-2
extension points 1-2
G
graphical user interface 3-1
KDC installation 3-1
lab installation 4-2
Network Registrar extension installation 3-1
RDU installation 3-1, 3-2
H
hardware requirements
RDU 1-2
Home Directory Destination screen 3-2, 3-4, 3-7, 3-8
I
individual component validation 3-14, 3-16
installation 1-1
checklist 2-6, 4-1
exiting the program 3-3, 3-5
lab installations 4-1
operating system requirements 1-1
pathname 4-2
installation and startup process 2-2
Installation Components screen 3-4, 3-7, 3-8
Installation Parameters screen 3-3, 3-5, 3-7, 3-8
Installation Summary screen 3-3, 3-7, 3-8, 4-3
IN-2
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
Page 75

Index
installation types 1-4
individual component installation 1-4
lab installation 1-4
Installed Components Summary screen 3-5
IP addresses
of Primary DHCP Server 3-5, 4-3
of Primary DNS Server 3-5, 4-3
of Secondary DHCP Server 3-5, 4-3
of Secondary DNS Server 3-5, 4-3
J
JRun process, detecting 5-2
K
KDC
DPE registration service 1-3
FQDN 3-7, 4-2
hardware requirements 1-3
installation 2-2, 2-5, 3-7
interface address 3-7, 4-2
packetcable MTA authentication 2-2
realm name 3-4, 3-5, 3-7, 4-2, 4-3
KDC Service Key and DPE screen 3-7
Key Distribution Center
See KDC
L
Lab Installation Parameters screen 4-3
N
configuration script A-1
DHCP server 1-2, 5-1
extensions 2-1
installation
server extensions 3-3
installation validation 3-4
installing extensions 2-4, 3-9, 3-11
license key 2-4
reloading the server 3-5
server login 3-5
servers 1-3
upgrading 3-4
version 2-1
Network Registrar Extension Point Provisioning Group
screen
3-4
Network Registrar Username and Password screen 4-2
nrcmd cli A-2
nrcmd command line interface 4-6, A-1
P
Packet Cable Panel screen 3-4
Packet Cable Propertises screen 3-4
R
RDU
installation 2-3, 3-2, 3-9
primary BAC server 2-1
RDU agent 5-2
regional distribution unit
See RDU
Regional Distribution Unit Host/Port screen 3-2, 3-4
related documentation 1-ix
Network Registrar 1-2
administrative username and password 4-2
BAC requirements 1-2
configuration files 4-1
OL-19105-01
S
scope selection tag A-1
Shared Secret Password screen 3-3, 3-5, 4-3
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
IN-3
Page 76

Index
Solaris 1-vii
installing BAC 1-vii
setting up DPEs 1-vii
TFTP server 4-2
Solaris installation
checklist 2-6
Network Registrar requirements 1-2
operating system environment 3-1
RDU 2-1, 3-2
T
terminal emulation program 7-2
U
uninstall.bin 5-4
uninstall.bin directory 5-3
uninstalling 5-2
BAC 5-3
IN-4
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Installation Guide 2.7
OL-19105-01
 Loading...
Loading...