Page 1

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
This chapter explains how to configure Token Ring Inter-Switch Link (TRISL) on Cisco routers. The
chapter describes TRISL in the context of the Inter-Switch Link (ISL) protocol and the Token
Ring VLAN concept.
For a complete description of the Token Ring Inter-Switch Link commands in this chapter, refer to the
“Token Ring Inter-Switch Link Commands” chapter in the Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking
Command Reference (Volume 1 of 2). To locate documentation of other commands that appear in this
chapter, use the command reference master index or search online. For informati on on how Token Ring
VLANs are implemented on switches, refer to the Catalyst T oken Rin g Switching Implementat ion Guide,
the Catalyst 5000 Series T ok en Ring Confi gur ation Notes, the Catalyst 3900 Token Ring Switc hing Us er
Guide, and the Catalyst 3920 Token Ring Switching User Guide.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Technology Overview, page 145
• TRISL Configuration Task List, page 148
• Monitoring TRISL Statistics, page 153
• TRISL Configuration Examples, page 154
To identify the hardware platform or software image information associated with a feature, use the
Feature Navigator on Cisco.com to search for information about the feature or refer to the software
release notes for a specific release. For more information, see the “Identifying Platform Support for
Cisco IOS Software Features” section on page li in the “Using Cisco IOS Software” chapter.
Technology Overview
Cisco’s TRISL Implementation
This section contains information related to Cisco’s implementation of TRISL that you should
understand before you proceed to the “TRISL Configuration Task List” section on page 148.
ISL and TRISL
ISL is a Layer 2 protocol that enables switches and routers to transport Ethernet frames from multiple
VLANs across Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet links. Cisco’s TRISL protocol extends the ISL model
to include the transport of Token Ring frames from multiple VLANs across these same links.
78-11737-02
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-145
Page 2
Technology Overview
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
TRISL support on Cisco routers provides inter-VLAN routing and bridging across a 100-Mb
Fast Ethernet link. ISL and TRISL together provide routing and bridging between Token Ring and
Ethernet LANs, ELANS, and VLANs.
TRISL is supported on the following platforms with any one of the following port adapters:
• Cisco 7500 or Cisco 7200 series routers
–
Two-port Fast Ethernet/ISL 100BaseTX
–
Two-port Fast Ethernet/ISL 100BaseFX
–
One-port Fast Ethernet 100BaseTX
–
One-port Fast Ethernet 100BaseFX
• Cisco 4500 or 4700 series routers
–
NM-1FE
• Cisco 3600 or 2600 series routers
–
NM-1FE1CE1
–
NM-1FE1CT1
–
NM-1FE1R2W
–
NM-1FE2CE1
–
NM-1FE2CT1
–
NM-1FE2W
–
NM-2FE2W
Note The two-port Fast Ethernet/ISL port adapters support frame sizes u p to 17800 bytes and t he one-port
Fast Ethernet port adapters support a frame size of up to 1500 bytes.
TRISL provides the following capabilities and features, which will be described in the “TRISL
Configuration Task List” section on page 148 and the “TRISL Configuration Examples” section on
page 154:
• IP routing for source-routed and non-source-routed frames between TRISL VLANs and any LAN,
ELAN, or VLAN.
• IPX routing for source-routed and non-source-routed frames between TRISL VLANs and any
LANs, ELANs, or VLANs.
• Source-Route Bridging (SRB) between TRISL VLANs and SRB-capable LANs, ELANs, or
VLANs.
• Source-Route Transparent Bridging (SRT) between TRISL VLANs and SRT-capable LANs,
ELANs, or VLANs.
• Source-Route Translational Bridging (SR/TLB) between TRISL VLANs and Ethernet LANs,
ELANs, or VLANs.
• Duplicate Ring Protocol (DRiP), which prevents external loops that could result if the router’s
virtual ring number were duplicated el sewhere in the network.
BC-146
Note VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) is currently not supported for TRISL on the routers.
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
Page 3
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
S6813
Switch B
5
TrBRF 3
Token Ring VLANs
A VLAN is essentially a broadcast domain. In transparent bridging, there is only one type of broadcast
frame and, therefore, only one level of broadcast domain and one level of VLAN. In source routing,
however, there are two types of broadcast frames:
• Those that are confined to a single ring
• Those that traverse the bridged domain
Therefore, there are two levels of VLANs in a Token Ring switched network.
The first level is the Token Ring Concentrator Relay Function (TrCRF). At this level, the VLAN is a
logical ring and, as such, is assigned a ring number. On a Token Ring switch, the logical ring (TrCRF)
contains one or more physical ports. On a router , the logi cal ring (TrCRF) does not contain any physical
ports, but rather is used only in processing source-rou ted traffi c to terminate the routing information f ield
(RIF).
The second level is the Token Ring Bridge Relay Function (TrBRF). This is the parent VLAN to which
TrCRF VLANs are assigned. At this level, the VLAN is a logical bridge and, as such, is assigned a bridge
number. The logical bridge (TrBRF) contains the virtual ports that establish a connection between the
TrB RF a nd i t s TrC RFs . Th e TrB RF c a n be e xte nde d across a network of switches and routers via ISL,
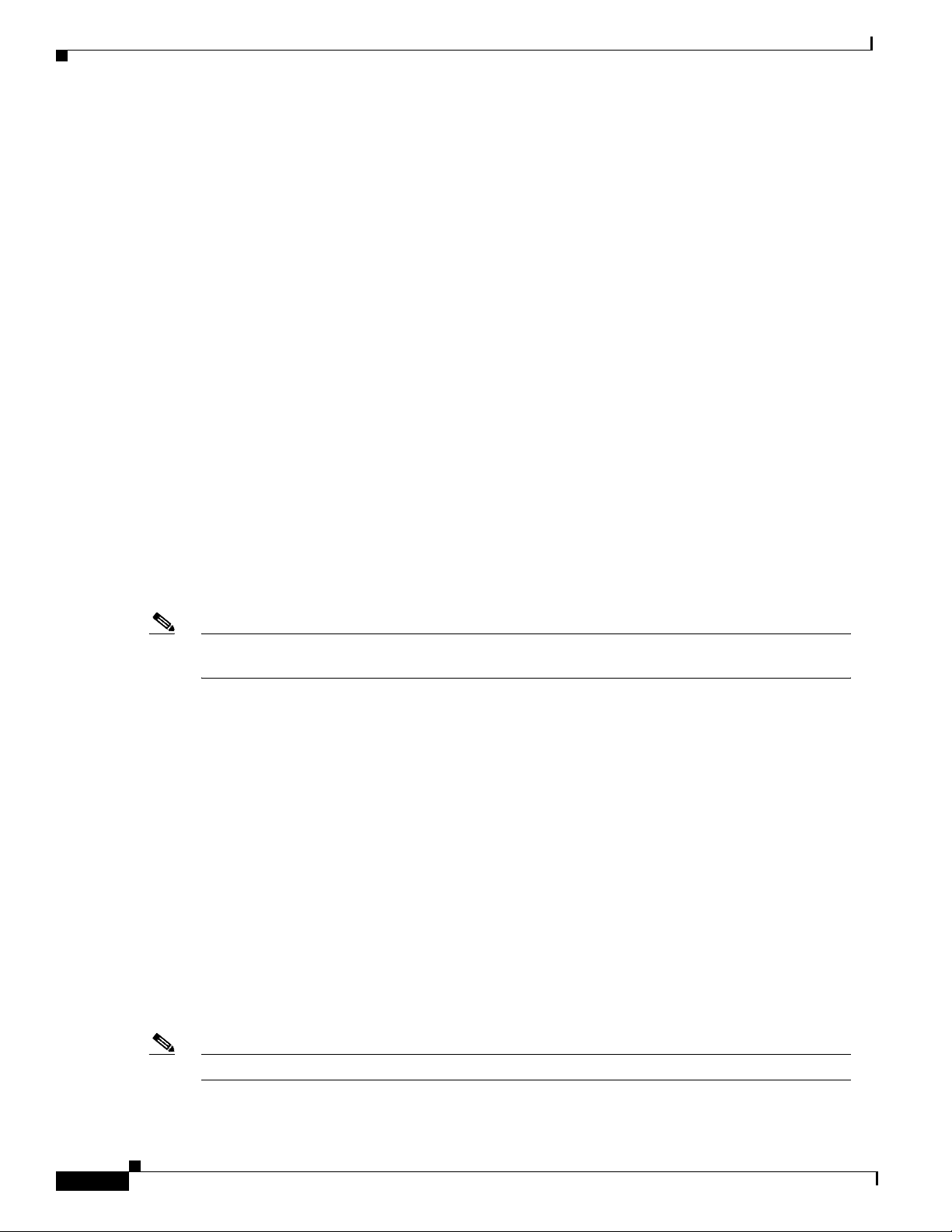
as shown in Figure 52.
Technology Overview
Figure 52 Physical View of Switches Interconnected via ISL
Switch A
TrCRF
400
TrBRF 3
ISL
TrCRF
350
TrCRF
200
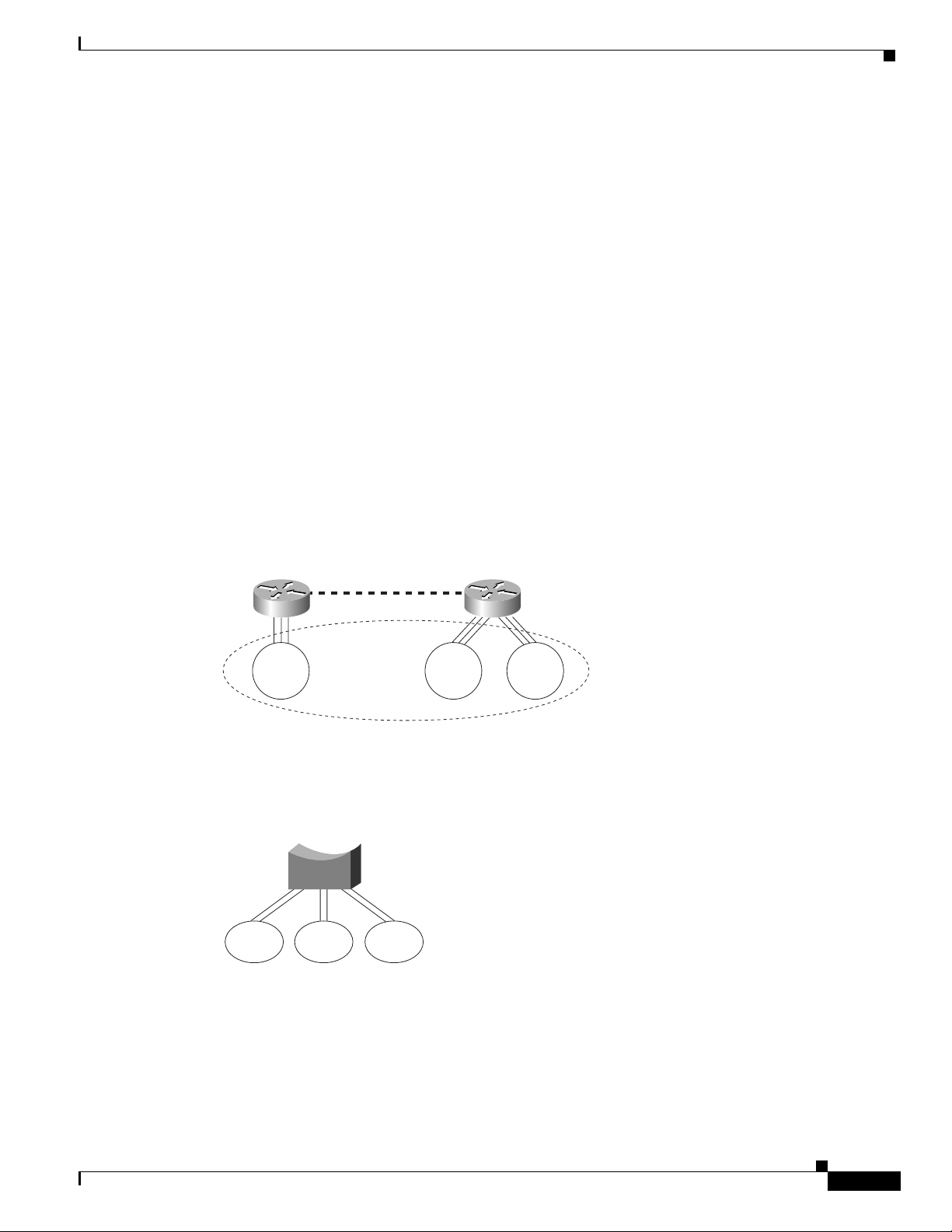
When you extend the T rBRF across an ISL link, you are essen tially e xtending the bridge across de vices,
as shown in Figure 53.
Figure 53 Logical View of Switches Interconnected via ISL
TrCRF
400
TrCRF
350
TrCRF
200
1859
78-11737-02
Therefore, if you use source-route bridging between the TrCRFs that belong to the TrBRF, only one hop
appears in the RIF.
Traffic is switched between the ports in a TrCRF and bridged via SRB or SRT between the TrCRFs in a
TrBRF.
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-147
Page 4
TRISL Configuration Task List
1
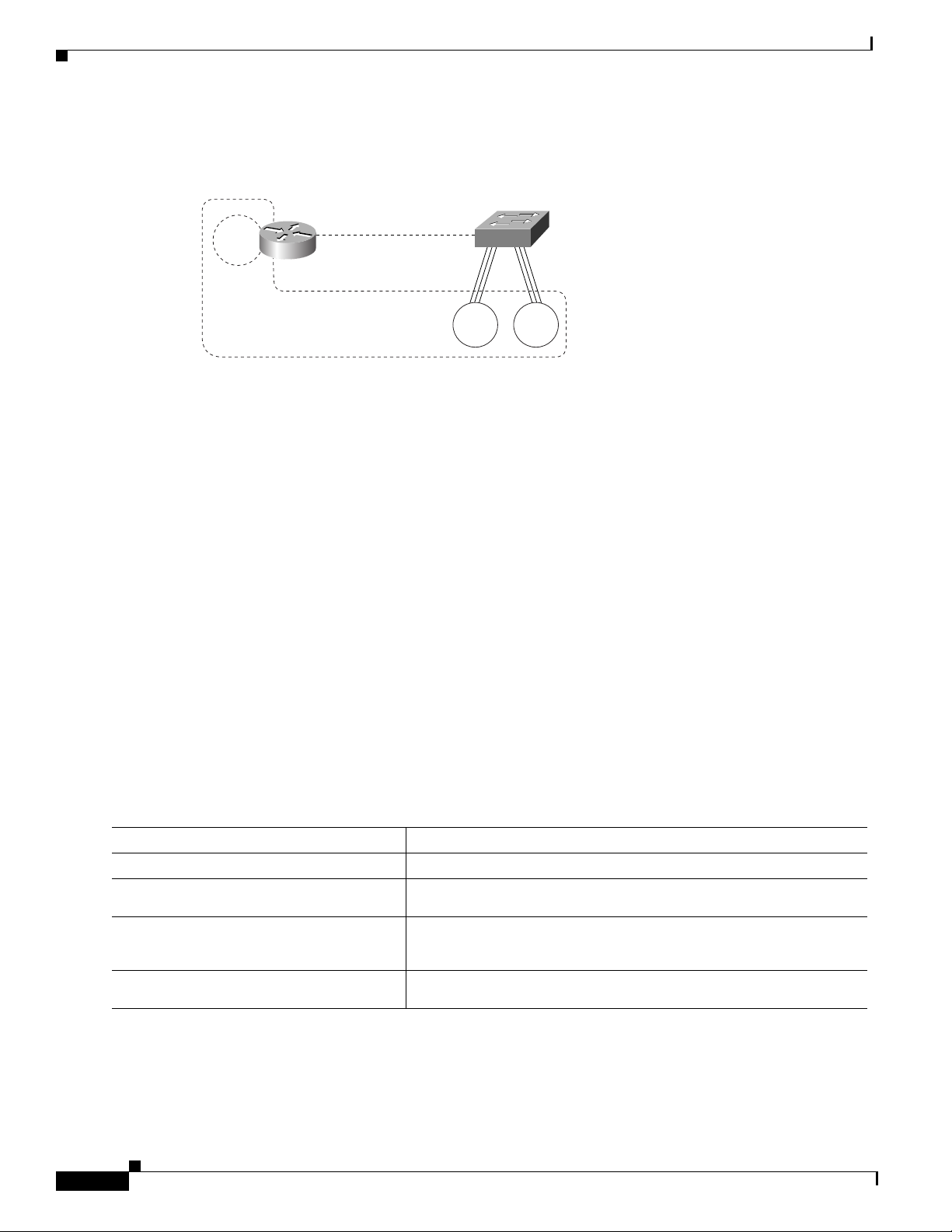
Figure 54 illustrates a TrBRF that contains TrCRFs on both a router and a switch.
Figure 54 TrCRFs in a TrBRF
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
TrCRF
TRISL
TrBRF
TRISL Configuration Task List
To configure and monitor TRISL in your network, perform one or more of the following tasks:
• Configuring IP Routing over TRISL, page 148
• Configuring Hot Standby Router Protocol over TRISL, page 149
• Configuring IPX Routing over TRISL, page 150
• Configuring Source-Route Bridging over TRISL, page 151
• Configuring Source-Route Transparent Bridging over TRISL, page 151
• Configuring Source-Route Translational Bridging over TRISL, page 152
See the “TRISL Configuration Examples” section on page 154 for examples.
TrCRF
Switch
TrCRF
1183
Configuring IP Routing over TRISL
The IP routing over TRISL VLANs feature e xtends IP routin g capabilities to inclu de support for routing
IP frame types in VLAN configurations. To configure IP routing over TRISL, use the following
commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
BC-148
Router(config)# ip routing
Router(config)# interface type
slot/port.subinterface-number
Router(config-if)# encapsulation
tr-isl trbrf-vlan vlanid bridge-num
bridge-number
Router(config-if)# ip address
ip-address mask
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
Enables IP routing on the router.
Specifies the subinterface on which TRISL will be used.
Defines the encapsulation format, and specifies the VLAN identifier.
Sets a primary IP address for an interface.
78-11737-02
Page 5
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
You can configure TRISL to route source-routed traffic by enabling the collection and use of RIF
information on a TRISL subinterface. This creates a “pseudoring” to terminate the RIF path on a ring.
Without RIF i nformation, a packet could not be bridged across a source-route brid ged network connected
to this interface.
To route source-routed traffic, use the following additional commands in interface configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Router(config-if)# multiring
trcrf-vlan vlanid ring
Router(config-if)# multiring
{protocol-keyword [all-routes |
spanning | all | other]}
Note TRISL encapsulation must be specified for a subinterface before an IP address can be assigned to that
subinterface.
TRISL Configuration Task List
Creates a pseudoring to terminate the RIF and assigns it to a VLAN.
ring-number
Enables collection and use of RIF information with routed protocols.
Configuring Hot Standby Router Protocol over TRISL
The Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) provides fault tolerance and enhanced routing performance
for IP networks. HSRP allows Cisco routers to monitor each other’s operational status and very quickly
assume packet forwarding responsibility in the event the current forwarding device in the HSRP group
fails or is taken do wn for maintenance. The standb y mechanism remai ns transparent to the attached hosts
and can be deployed on any LAN type. With multiple hot-standby groups, routers can simultaneously
provide redundant backup and perform load-sharing across different IP subsets.
To configure HSRP over TRISL between VLANs, use the following commands beginning in global
configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Router(config)# interface type
slot/port subinterface-number
Router(config-if)# encapsulation
tr-isl trbrf-vlan vlanid bridge-num
bridge-number
Router(config-if)# ip address
ip-address mask [secondary]
Router(config-if)# standby
[group-number] ip
[ip-address [secondary]]
Specifies the subinterface on which ISL will be used.
Defines the encapsulation format, and specify the VLAN identifier.
Specifies the IP address for the subnet on which ISL will be used.
Enables HSRP.
78-11737-02
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-149
Page 6
TRISL Configuration Task List
T o customize hot standb y group attributes, use one of the follo wing commands in interface conf iguration
mode, as needed:
Command Purpose
Router(config-if)# standby [group-number]
timers hellotime holdtime
Router(config-if)# standby [group-number]
priority priority
Router(config-if)# standby [group-number]
preempt
Configures the time between hello packets and the hold time before
other routers declare the active router to be down.
Sets the hot standby priority used to choose the active router.
Specifies that if the local router has priority over the current active
router, the local router should attempt to take its place as the active
router.
Router(config-if)# standby [group-number]
track type-number [interface-priority].
Configures the interface to track other interfaces, so that if one of th e
other interfaces goes down, the hot standby priority for the device is
lowered.
Router(config-if)# standby [group-number]
authentication string
Enables the automatic spanning-tree function on a group of bridged
interfaces.
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
Configuring IPX Routing over TRISL
The IPX Routing over ISL VLANs feature extends Novell NetWare routing capabilities to include
support for routing all standard IPX encapsulations for Token Ring frame types in VLAN configurations.
Users with Novell NetW are en vironments can configure either SAP or SN AP encapsulations to be routed
using the TRISL encapsulation across VLAN boundaries.
Netware users can now configure consolidated VLAN routing over a single VLAN trunking interface.
With configurable Token Ring encapsulation protocols on a per VLAN basis, u sers have the flexibility
of using VLANs regardless of their NetWare Token Ring encapsulation. Encapsulation types and
corresponding framing types are described in the “Configuring Novell IPX” chapter of the Cisco IOS
AppleTalk and Novell IPX Configuration Guide.
Note Only one type of IPX encapsulation can be configured per VLAN (subinterface). The IPX
encapsulation used must be the same within any particular subnet. A single encapsulation must be
used by all NetWare systems that belong to the same LAN.
To configure Cisco IOS software to route IPX on a router with connected VLANs, use the following
commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Router(config)# ipx routing [node]
Router(config)# interface type
slot/port.subinterface-number
Router(config-if)# encapsulation
tr-isl trbrf-vlan vlanid bridge-num
bridge-number
Router(config-if)# ipx encapsulation
encapsulation-type
Router(config-if)# ipx network
network number
Enables IPX routing globally.
Specifies the subinterface on which TRISL will be used.
Defines the encapsulation for TRISL.
Specifies the IPX encapsulation.
Specifies the IPX network.
BC-150
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
Page 7

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
Note The default IPX encapsulation format for Token Ring in Cisco IOS routers is SAP. Therefore, you
only need to explicitly configure the IPX encapsulation type if your Token Ring network requires
SNAP encapsulation instead of SAP.
When routing source-routed traffic for specific VLANs, use the following additional commands in
interface configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Router(config-if)# multiring
trcrf-vlan vlanid
ring-number
Router(config-if)# multiring
{protocol-keyword [all-routes |
spanning | all | other]}
trcrf-ring
Creates a pseudoring to terminate the RIF and assign it to a VLAN.
Enables collection and use of RIF information with routed protocols.
Configuring Source-Route Bridging over TRISL
TRISL Configuration Task List
To configure SRB over TRISL, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Router(config)# source-bridge
ring-group vring-num
Router(config)# interface type
slot/port.subinterface-number
Router(config-if)# encapsulation
tr-isl trbrf-vlan vlanid bridge-num
bridge-number
Router(config-if)# source-bridge
trcrf-vlan vlanid ring-group
ring-number
Configures a virtual ring for the router.
Specifies the subinterface on which TRISL will be used.
Defines the encapsulation for TRISL.
Attaches a TrCRF VLAN identifier to the router’s virtual ring.
Configuring Source-Route Transparent Bridging over TRISL
To configure transparent bridging over TRISL, use the following command beginning in global
configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Router(config)# interface type
slot/port.subinterface-number
Router(config-if)# encapsulation
tr-isl trbrf-vlan vlanid bridge-num
bridge-number
Router(config-if)# bridge-group
bridge-group number
Specifies the subinterface on which TRISL will be used.
Defines the encapsulation for TRISL.
Specifies the bridge group to which the TRISL subinterface belongs.
78-11737-02
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-151
Page 8
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
TRISL Configuration Task List
Configuring Source-Route Translational Bridging over TRISL
T o conf i gure source-r oute translat ional bridgi ng ov er TRISL, use the following commands beginning in
global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Router(config)# source-bridge ring-group vring-num
Router(config)# source-bridge transparent ring-group
pseudoring bridge-number tb-group [oui]
Router(config)# interface type
slot/port.subinterface-number
Router(config-if)# encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan
vlanid bridge-num bridge-number
Router(config-if)# source-bridge trcrf-vlan vlanid
ring-group ring-number
Configures a virtual ring for the router.
Enables bridging between transparent bridging and
source-route bridging.
Specifies the subinterface on which TRISL will be
used.
Defines the encapsulation for TRISL.
Assigns a VLAN ID to the router’s virtual ring.
Note For a complete description of SR/TLB, including configuring translation compatibility with IBM
8209 bridges and configuring Token Ring LLC2 to Ethernet Type II (0x80d5) and Token Ring LLC2
to Ethernet 802.3 LLC2 (standard) translations, please refer to the “Configuring Source-Route
Bridging” chapter in this publication and “Source-Route Bridging Commands” chapter in the Cisco
IOS Bridging and IBM Command Reference (Volume 1 of 2).
Configuring Automatic Spanning Tree
The automatic spanning-tree function supports automatic resolution of spanning trees i n SRB network s,
which provides a single path for spanning explorer frames to traverse from a given node in the network
to another. Spanning explorer frames have a single-route broadcast indicator set in the routing
information field. Port identif iers consist of ri ng numbers and bridge numbers associated with the ports.
The spanning-tree algorithm for SRB does n ot suppor t Topology Change Notification Bridge Protocol
Data Unit (BPDU).
Although the automatic spanning-tree function can be configured with Source-Route Translational
Bridging (SR/TLB), the SRB domain and transparent bridging domain have separate spanning trees.
Each Token Ring interface can belong to only one spanning tree. Only one bridge group can run the
automatic spanning-tree function at a time.
To create a bridge group that runs an automatic spanning-tree function compatible with the IBM SRB
spanning-tree implementation, use the following command in global configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config)# bridge bridge-group
protocol ibm
Creates a bridge group that runs the automatic spanning-tree function.
BC-152
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
Page 9

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
To enable the automatic spanning-tree function for a specified group of bridged interfaces in SRB or
SR/TLB, use the following command in interface configuration mode:
Command Purpose
Router(config-if)# source-bridge
spanning bridge-group
Enables the automatic spanning-tree function on a group of bridged int erf aces.
Monitoring TRISL Statistics
You can collect, clear, and display statistical information about the network.
The Duplicate Ring Protocol (DRiP) runs on Cisco routers and switches that support switched VLAN
networking and is used to identify active Token Ring VLANs (TrCRFs).
DRiP maintains the status of TrCRFs and uses this information to determine whether there are multiple
TrCRFs active in a TrBRF.
DRiP information is used for the following:
• All-routes explorer filtering
DRiP information is used in conjunction with the local configuration to determine which of the
TrCRFs configured within a TrBRF have active ports. This information is used on the base switch
to correctly filter all-routes explorers and on the ISL module to discard AREs that have already been
on an attached ring.
Monitoring TRISL Statistics
• Detecting the configuration of duplicate TrCRFs across routers and switches, which would cause a
TrCRF to be distributed across ISL trunks
DRiP information is used in conjunction with the local configuration information to determine
which TrCRFs are already active on the switches. If a T rCRF is enabled on more than one switch or
router, the ports associated with the TrCRF are disabled on all switches. A router will not disable
the internal ring used for SRB and for routing source-ro uted traffic. Ins tead, the r outer gen erates the
following error message to indicate that two identical TrCRFs exist:
DRIP conflict with CRF <vlan-id>
To show or clear DRiP or VLAN statistics, use one or all the following command in privileged EXEC
mode:
Command Purpose
Router# clear drip counters
Router# clear vlan statistics
Clears DRiP counters.
Removes VLAN statistics from any statically configured or system
configured entries.
Router# show drip
Router# show vlans
Note When DRiP counters are cleared, the counter is reset to 0. Incrementing of DRiP counters indicates
Displays DRiP information.
Displays a summary of VLAN subinterfaces.
that the router is receiving packets across the TrBRF.
78-11737-02
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-153
Page 10

TRISL Configuration Examples
TRISL Configuration Examples
The following sections provide TRISL configuration examples:
• IP Routing Non-Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface
Example, page 155
• IP Routing Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface Example,
page 156
• IP Routing Source-Route Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN Example,
page 157
• IP Routing Source-Routed Frames Between TRISL VLANs Example, page 158
• IPX Routing Non-Source-Routed Fram es Betwee n a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface
Example, page 159
• IPX Routing Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and a T oken Ring Interface Example,
page 160
• IPX Routing Source-Route Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN Example,
page 161
• IPX Routing Source-Routed Frames Between TRISL VLANs Example, page 162
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
• SRB Between Token Ring and TRISL VLAN Example, page 163
• SRB Between TRISL VLANs Example, page 164
• Transparent Bridging Between Token Ring and TRISL VLAN Example, page 166
• SR/TLB Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet Interface Example, page 167
• SR/TLB Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN Example, page 168
• TRISL with Fast EtherChannel Example, page 169
Note Because the VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) is not suppo rted on the router con f igured wit h TRISL, the
TrCRF configuration on the router must also be specified in the Catalyst 5000 switch configuration.
BC-154
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
Page 11

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
4
g
0
End station
TRISL Configuration Examples
IP Routing Non-Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface Example
Figure 55 illustrates IP routing between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring interface.
Figure 55 IP Routing Between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface
Catalyst 5000 switch
.4.4.1
Token
Ring 2
End station
Fast Ethernet 4/0.1
5.5.5.1
End station
5000
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
Token
Ring 1
End station
Token Rin
switch
module
T rCRF VLAN 4
Slot 5
Port 1
15423
The following is the configuration for the router:
ip routing
interface TokenRing 3/1
ip address 4.4.4.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface fastethernet4/0.1
ip address 5.5.5.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf 999 bridge-num 14
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with the Token Ring switch module in
slot 5. In this configuration, the Token Ring port 1 is assigned to the TrCRF VLAN 40.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ieee
set vlan 40 name trcrf40 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x1 mode srt
#add token port to trcrf 40
set vlan 40 5/1
set trunk 1/2 on
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
BC-155
Page 12

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
g
0
T
End station
TRISL Configuration Examples
IP Routing Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface Example
Figure 56 illustrates IP routing source-routed frames between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring
interface.
Figure 56 Routing Source-Routed Frames Betw een a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface
Catalyst 5000 switch
rCRF 200
100
4.4.4.1
End station
Token
Ring 2
Fast Ethernet 4/0.1
5.5.5.1
End station
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
End station
5500
Token
Ring 1
Token Rin
switch
module
T rCRF VLAN 4
Slot 5
Port 1
51883
The following is the configuration for the router:
ip routing
interface TokenRing 3/1
ip address 4.4.4.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface fastethernet4/0.1
ip address 5.5.5.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf 999 bridge-num 14
multiring trcrf-vlan 200 ring 100
multiring all
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with the Token Ring switch module in
slot 5. In this configuration, the Token Ring port 5/1 is assigned to the TrCRF VLAN 40.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
set vlan 200 name trcrf200 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x64 mode srb
set vlan 40 name trcrf40 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x1 mode srb
#add token port to trcrf 40
set vlan 40 5/1
set trunk 1/2 on
BC-156
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
Page 13

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
n
n
5
Port 1
T
TRISL Configuration Examples
IP Routing Source-Route Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN Example
Figure 57 illustrates IP routing source-route frames between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL
VLAN.
Figure 57 IP Routing Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN
Catalyst
5000 switch
Ethernet
module
in slot 2
Token
Ring
TrCRF100
Slot 5
1
End statio
End statio
1884
Router A
100
rCRF 200
4.4.4.1
5.5.5.1
Ethernet ISL VLAN 12
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
5500
Token Ring
switch module
in slot 5
The following is the configuration for the router:
interface fastethernet4/0.1
ip address 5.5.5.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 999 bridge-num 14
multiring trcrf-vlan 200 ring 100
multiring all
!
interface fastethernet4/0.2
ip address 4.4.4.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation isl 12
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with t he Ethernet module i n slot 2 and a
Token Ring switch module in slot 5. In this configuration, the Token Ring port is assigned with TrCRF
VLAN 100 and the Ethernet port is assig ned with V LAN 12.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
set vlan 100 name trcrf100 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x1 mode srb
set vlan 200 name trcrf200 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x64 mode srb
set vlan 12 name eisl12 type ethernet
#add token port to trcrf 100
set vlan 100 5/1
#add ethernet
set vlan 12 2/1
set trunk 1/2 on
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
BC-157
Page 14

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
Catalyst
g
0
T
T
TRISL Configuration Examples
IP Routing Source-Routed Frames Between TRISL VLANs Example
Figure 58 illustrates IP routing source-routed frames between two TrBRF VLANs.
Figure 58 IP Routing Source-Routed Frames Between TrBRF VLANs
5000 switch
rCRF 200
Router
100
101
rCRF 300
5.5.5.1
4.4.4.1
Fast Ethernet 4/0.1
Fast Ethernet 4/0.2
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
TrBRF 998/Bridge 13
T rCRF VLAN 40
Token
Slot 5
Port 1
Ring
102
5500
Token
Ring
103
Token Rin
switch
module
TrCRF
VLAN 5
Slot 5
Port 2
End station
End station
51885
The following is the configuration for the router:
interface fastethernet4/0.1
ip address 5.5.5.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 999 bridge-num 14
multiring trcrf-vlan 200 ring 100
multiring all
!
interface fastethernet4/0.2
ip address 4.4.4.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 998 bridge-num 13
multiring trcrf-vlan 300 ring 101
multiring all
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with the Token Ring switch module in
slot 5. In this configuratio n, the Token Ring port attached to ring 102 is assigned with TrCRF VLAN 40
and the Token Ring port attached to ring 103 is assigned with TrCRF VLAN 50.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
set vlan 200 name trcrf200 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x64 mode srb
set vlan 40 name trcrf40 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x66 mode srb
set vlan 998 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xd stp ibm
set vlan 300 name trcrf300 type trcrf parent 998 ring 0x65 mode srb
set vlan 50 name trcrf50 type trcrf parent 998 ring 0x67 mode srb
#add token port to trcrf 40
set vlan 40 5/1
#add token port to trcrf 50
set vlan 50 5/2
set trunk 1/2 on
BC-158
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
Page 15

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
N
g
0
End station
TRISL Configuration Examples
IPX Routing Non-Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface Example
Figure 59 shows IPX routing non-source-routed frames between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring
interface.
Figure 59 IPX Routing Non-Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring
Interface Example
Catalyst 5000 switch
etwork 1
Token
Ring 2
End station
Fast Ethernet 4/0.1
Network 10
End station
5500
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
Token
Ring 1
End station
Token Rin
switch
module
T rCRF VLAN 4
Slot 5
Port 1
51886
The following is the configuration for the router:
ipx routing
interface TokenRing 3/1
ipx network 1
!
interface fastethernet4/0.1
ipx network 10
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf 999 bridge-num 14
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with the Token Ring switch module in
slot 5. In this configuration, the Token Ring port attached to ring 1 is assigned to the TrCRF VLAN 40.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ieee
set vlan 40 name trcrf40 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x1 mode srt
#add token port to trcrf 40
set vlan 40 5/1
set trunk 1/2 on
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
BC-159
Page 16

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
N
g
0
End station
TRISL Configuration Examples
IPX Routing Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface Example
Figure 60 shows IPX routing source-routed frames between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring interface.
Figure 60 IPX Routing Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and a Token Ring Interface
Catalyst 5000 switch
Fast Ethernet 4/0.1
Network 10
etwork 1
Token
Ring 2
End station
End station
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
End station
The following is the configuration for the router:
ipx routing
!
interface TokenRing 3/1
ipx network 1
multiring all
!
interface fastethernet4/0.1
ipx network 10
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf 999 bridge-num 14
multiring trcrf-vlan 200 ring 100
multiring all
5500
Token
Ring 1
Token Rin
switch
module
T rCRF VLAN 4
Slot 5
Port 1
51886
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with the Token Ring switch module in
slot 5. In this configuration, the Token Ring port attached to ring 1 is assigned to the TrCRF VLAN 40.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
set vlan 200 name trcrf200 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x64 mode srb
set vlan 40 name trcrf40 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x1 mode srb
#add token port to trcrf 40
set vlan 40 5/1
set trunk 1/2 on
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-160
78-11737-02
Page 17

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
n
n
Catalyst
T
TRISL Configuration Examples
IPX Routing Source-Route Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN Example
Figure 61 shows IPX routing source-route frames between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN.
Figure 61 IPX Routing Source-Routed Frames Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN
5000 switch
Ethernet
module
in slot 2
Token
Ring
TrCRF100
Slot 5
Port 1
End statio
End statio
51887
100
rCRF 20
Router A
Network 30
Network 10
Ethernet ISL VLAN 12
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
5500
Token Ring
switch module
in slot 5
The following is the configuration for the router:
ipx routing
interface fastethernet4/0.1
ipx network 10
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 999 bridge-num 14
multiring trcrf-vlan 20 ring 100
multiring all
!
interface fastethernet4/0.2
ipx network 30
encapsulation isl 12
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with t he Ethernet module i n slot 2 and a
Token Ring switch module in slot 5. In this configuration, the Token Ring port is assigned with TrCRF
VLAN 100 and the Ethernet port is assig ned with V LAN 12.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
set vlan 100 name trcrf100 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x1 mode srb
set vlan 20 name trcrf20 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x64 mode srb
set vlan 12 name default type eisl12
#add token port to trcrf 100
set vlan 100 5/1
#add ethernet
set vlan 12 2/1
set trunk 1/2 on
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
BC-161
Page 18

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
End station
End station
g
Catalyst
0
T
T
TRISL Configuration Examples
IPX Routing Source-Routed Frames Between TRISL VLANs Example
Figure 62 shows IPX source-routed frames between TRISL VLANs.
Figure 62 IPX Routing Source-Routed Frames Between TRISL VLANs
rCRF 200
Router
100
101
rCRF 300
Network 10
Network 20
Fast Ethernet 4/0.1
Fast Ethernet 4/0.2
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
TrBRF 998/Bridge 13
TrCRF
VLAN 40
Slot 5
Port 1
The following is the configuration for the router:
ipx routing
interface fastethernet4/0.1
ipx network 10
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 999 bridge-num 14
multiring trcrf-vlan 200 ring 100
multiring all
!
interface fastethernet4/0.2
ipx network 20
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 998 bridge-num 13
multiring trcrf-vlan 300 ring 101
multiring all
Token
Ring
102
5000 switch
5500
Token
Ring
103
Token Rin
switch
module
TrCRF
VLAN 5
Slot 5
Port 2
51888
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with the Token Ring switch module in
slot 5. In this configuratio n, the Token Ring port attached to ring 102 is assigned with TrCRF VLAN 40
and the Token Ring port attached to ring 103 is assigned with TrCRF VLAN 50.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
set vlan 200 name trcrf200 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x64 mode srb
set vlan 40 name trcrf40 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x66 mode srb
set vlan 998 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xd stp ibm
set vlan 300 name trcrf300 type trcrf parent 998 ring 0x65 mode srb
set vlan 50 name trcrf50 type trcrf parent 998 ring 0x67 mode srb
#add token port to trcrf 40
set vlan 40 5/1
BC-162
78-11737-02
Page 19

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
Catalyst VLAN
le
T
#add token port to trcrf 50
set vlan 50 5/2
set trunk 1/2 on
SRB Between Token Ring and TRISL VLAN Example
Figure 63 illustrates SRB between a Token Ring interface on a router and a TRISL VLAN.
Figure 63 SRB Between a Token Ring Interface and TRISL VLAN
switch forwarding
TRISL VLAN traffic
5500
Ring
20
T rCRF VLAN 50
Slot 5
Port 1
Token
Token Ring
switch modu
rCRF 40
100
Router with
Fast Ethernet
adapter
Token
Ring
10
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
TRISL Configuration Examples
End station
End station
51889
The following is the configuration for the router with the Token Ring interface:
source-bridge ring-group 100
!
interface TokenRing3/1
ring speed 16
source-bridge 10 1 100
source-bridge spanning
!
interface fastethernet4/0.1
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 999 bridge-num 14
source-bridge trcrf-vlan 40 ring-group 100
source-bridge spanning
!
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch:
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
set vlan 40 name trcrf40 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x64 mode srb
set vlan 50 name trcrf50 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x14 mode srb
#add token port to trcrf 50
set vlan 50 5/1
78-11737-02
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-163
Page 20

TRISL Configuration Examples
End stationEnd station
Catalyst 5000 switch
T
T
0
SRB Between TRISL VLANs Example
Figure 64 illustrates SRB between two TrCRF VLANs.
Figure 64 SRB Between TRISL VLANs
Router with
Fast Ethernet
rCRF 102
101
adapter
Fast Ethernet 4/0.2
Fast Ethernet 4/0.1
TrBRF 998/Bridge 13
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
5500
Token
Ring
switch
module
rCRF 100
T rCRF VLAN 40
Slot 5
Port 1
Token
Ring 1
Token
Ring
10
TrCRF
VLAN 5
Slot 5
Port 2
51890
The following is the configuration for the router:
source-bridge ring-group 101
!
interface fastethernet4/0.1
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf 999 bridge-num 14
source-bridge trcrf-vlan 100 ring-group 101
source-bridge spanning
!
interface fastethernet4/0.2
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf 998 bridge-num 13
source-bridge trcrf-vlan 102 ring-group 101
source-bridge spanning
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with the Token Ring switch module in
slot 5. The Token Ring port on 5/1 is assigned to TrCRF VLAN 40 and the Token Ring port on 5/2 is
assigned to TrCRF VLAN 50.
In this configuration, the keyword name is optional and srb is the default mode.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
set vlan 100 name trcrf100 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x65 mode srb
set vlan 40 name trcrf40 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x1 mode srb
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
set vlan 998 name trbrf type trbrf bridge 0xd stp ibm
set vlan 102 name trcrf102 type trcrf parent 998 ring 0x65 mode srb
set vlan 50 name trcrf50 type trcrf parent 998 ring 0xa mode srb
BC-164
78-11737-02
Page 21

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
#add token port to trcrf 40
set vlan 40 5/1
#add token port to trcrf 50
set vlan 50 5/2
#enable trunk
set trunk 1/2 on
TRISL Configuration Examples
78-11737-02
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-165
Page 22

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
E
le
TRISL Configuration Examples
Transparent Bridging Between Token Ring and TRISL VLAN Example
Figure 65 illustrates transparent bridging between a router’s Token Ring interface and a TRISL VLAN.
Figure 65 Transparent Bridging Between Token Ring and TRISL VLAN
Catalyst VLAN
switch forwarding
Router with
Fast Ethernet
adapter
TrBRF 50/Bridge 11Fast Ethernet 0/0.1
TRISL VLAN traffic
5500
Token Ring
switch modu
Token
Ring
10
nd station
Token
End station
Ring
20
T rCRF VLAN 100
Slot 5
Port 1
51891
The following is the configuration for the router:
bridge 1 protocol ieee
!
interface Tokenring0
bridge-group 1
!
interface fastethernet0/0.1
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 50 bridge-num 11
bridge-group 1
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with a Token Ring switch module in
slot 5:
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 50 name trbrf50 type trbrf bridge 0xb stp ieee
set vlan 100 name trcrf100 type trcrf ring 0x14 parent 50 mode srt
#enable trunk
set trunk 1/2 on
#add token port to trcrf 100
set vlan 100 5/1
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-166
78-11737-02
Page 23

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
End station
g
0
5
T
TRISL Configuration Examples
SR/TLB Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet Interface Example
Figure 66 illustrates SR/T LB between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet interface.
Figure 66 SR/TLB Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet Interface
Catalyst 5000 switch
rCRF
200
Fast Ethernet 4/0.1
100
2/1
End station
End station
TrBRF 999/Bridge 14
End station
The following is the configuration for the router:
source-bridge ring-group 100
source-bridge transparent 100 101 6 1
!
interface Ethernet2/0
bridge-group 1
!
interface fastethernet4/0.1
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 999 bridge-num 14
source-bridge trcrf-vlan 200 ring-group 100
source-bridge spanning
!
bridge 1 protocol ieee
!
5500
Token
Ring
Token Rin
switch
module
T rCRF VLAN 4
Slot 5
Port 1
1892
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 switch with an Ethernet card in module 5 and
using port 1. The Token Ring port on 5/1 is assigned to TrCRF VLAN 40.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 name trbrf999 type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
set vlan 200 name trcrf200 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x64 mode srb
set vlan 40 name trcrf40 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x1 mode srb
#add token port to trcrf 40
set vlan 40 5/1
78-11737-02
#enable trunk
set trunk 1/2 on
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-167
Page 24

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
End station
End station
T
TRISL Configuration Examples
SR/TLB Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN Example
Figure 67 illustrates SR/TLB between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN.
Figure 67 SR/TLB Between a TRISL VLAN and an Ethernet ISL VLAN
Catalyst
5000 switch
Ethernet module
in slot 2, port 1
Token
Ring
101
TrCRF
VLAN 21
Slot 5
Port 1
51893
100
rCRF 20
Router A
Fast Ethernet 4/0.2
Fast Ethernet 4/0.1
Ethernet ISL VLAN 12
TrBRF 999/
Bridge 14
5500
Token Ring
switch module
in slot 5
The following is the configuration for the router:
source-bridge ring-group 100
source-bridge transparent 100 101 6 1
!
interface fastethernet4/0.1
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 999 bridge-num 14
source-bridge trcrf-vlan 20 ring-group 100
source-bridge spanning
!
interface fastethernet4/0.2
encapsulation isl 12
bridge-group 1
!
bridge 1 protocol ieee
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 swit ch wi th an Et he rnet mod ule in slo t 2 and a
Token Ring switch module in slot 5. In this configuration, the Token Ring port attached to ring 101 is
assigned to TrCRF VLAN 21, and the router’s virtual ring is assigned to TrCRF VLAN 20.
#vtp
set vtp domain trisl
set vtp mode server
set vtp v2 enable
#drip
set tokenring reduction enable
set tokenring distrib-crf disable
#vlans
set vlan 999 type trbrf bridge 0xe stp ibm
set vlan 20 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x64 mode srb
set vlan 21 type trcrf parent 999 ring 0x65 mode srb
#add token port to trcrf 21
set vlan 21 5/1
#add ethernet
set vlan 12 type ethernet
set vlan 12 2/1
set trunk 1/2 on
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-168
78-11737-02
Page 25

Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
C
TRISL with Fast EtherChannel Example
Figure 68 illustrates TRISL with Fast EtherChannel.
Figure 68 Sample Configuration of TRISL with Fast EtherChannel
Catalyst 5000 switch
5500
TRISL Configuration Examples
isco 7500 series
with FastEthernet
Token Ring
switch module
adapter
Token
Ring
Cisco 4500
series
Token
Ring
Cisco 4500
series
The following is the configuration for the Cisco 7500:
source-bridge ring-group 50
interface Port-channel1
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache distributed
hold-queue 300 in
interface Port-channel1.1
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 20 bridge-num 1
ip address 10.131.25.1 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
no ip directed-broadcast
source-bridge trcrf-vlan 23 ring-group 50
source-bridge spanning
interface Port-channel1.2
encapsulation tr-isl trbrf-vlan 30 bridge-num 2
ip address 10.131.24.1 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
no ip directed-broadcast
source-bridge trcrf-vlan 33 ring-group 50
source-bridge spanning
interface fastethernet4/1/0
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache distributed
channel-group 1
interface fastethernet4/1/1
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip route-cache distributed
channel-group 1
The following is the configuration for the Catalyst 5000 Switch:
78-11737-02
set vlan 10 name VLAN0010 type ethernet mtu 1500 said 100010 state active
set vlan 20 name VLAN0020 type trbrf mtu 4472 said 100020 state active bridge 0x1 stp
ieee
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
BC-169
Page 26

TRISL Configuration Examples
set vlan 30 name VLAN0030 type trbrf mtu 4472 said 100030 state active bridge 0x2 stp
ieee
set vlan 22 name VLAN0022 type trcrf mtu 4472 said 100022 state active parent 20 ring 0x1
mode srt aremaxhop 7 stemaxhop 7
set vlan 23 name VLAN0023 type trcrf mtu 4472 said 100023 state active parent 20 ring
0x32 mode srt aremaxhop 7 stemaxhop 7
set vlan 32 name VLAN0032 type trcrf mtu 4472 said 100032 state active parent 30 ring 0x2
mode srt aremaxhop 7 stemaxhop 7
set vlan 33 name VLAN0033 type trcrf mtu 4472 said 100033 state active parent 30 ring
0x32 mode srt aremaxhop 7 stemaxhop 7
set port channel 1/1-2 on
set trunk 1/1 on isl 1-1005
set trunk 1/2 on isl 1-1005
add token port to crf 22
set vlan 22 5/1
add token port to crf 32
set vlan 32 5/2
TRISL with Fast EtherChannel only runs on the Cisco 7500. The MTU size can be set to more than 1500
if all the members of the port channel interface are 2FE/ISL adapt ors. If, on the other hand, an y member
of the port channel interface is a non 2FE/ISL adaptor, then the MTU size is not configurable and
defaults to 1500 bytes. Also, only IP utilizes all four links. Spanning Tree Protocol must be disabled if
transparent bridging is confi gured on the FEC. The por t-channel interface is the routed interface. Do not
enable Layer 3 addresses on the physical Fast Ethernet interfaces. Do not assign bridge groups on the
physical Fast Ethernet interfaces because it creates loops. Also, you must disable Spanning Tree
Protocol if transparent bridging is configured on the FEC.
Configuring Token Ring Inter-Switch Link
BC-170
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
 Loading...
Loading...