Page 1

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX
Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX are adaptable for all mobile professionals, from users on the move within an
office environment to nurses and doctors in a healthcare environment to associates working in the warehouse, on the sales floor,
or in a call center. Staff, nurses, doctors, educators, and IT personnel can be easily reached when mobile.
This guide provides information and guidance to help the network administrator deploy the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and
8821-EX in a wireless LAN environment.
Page 2
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
2
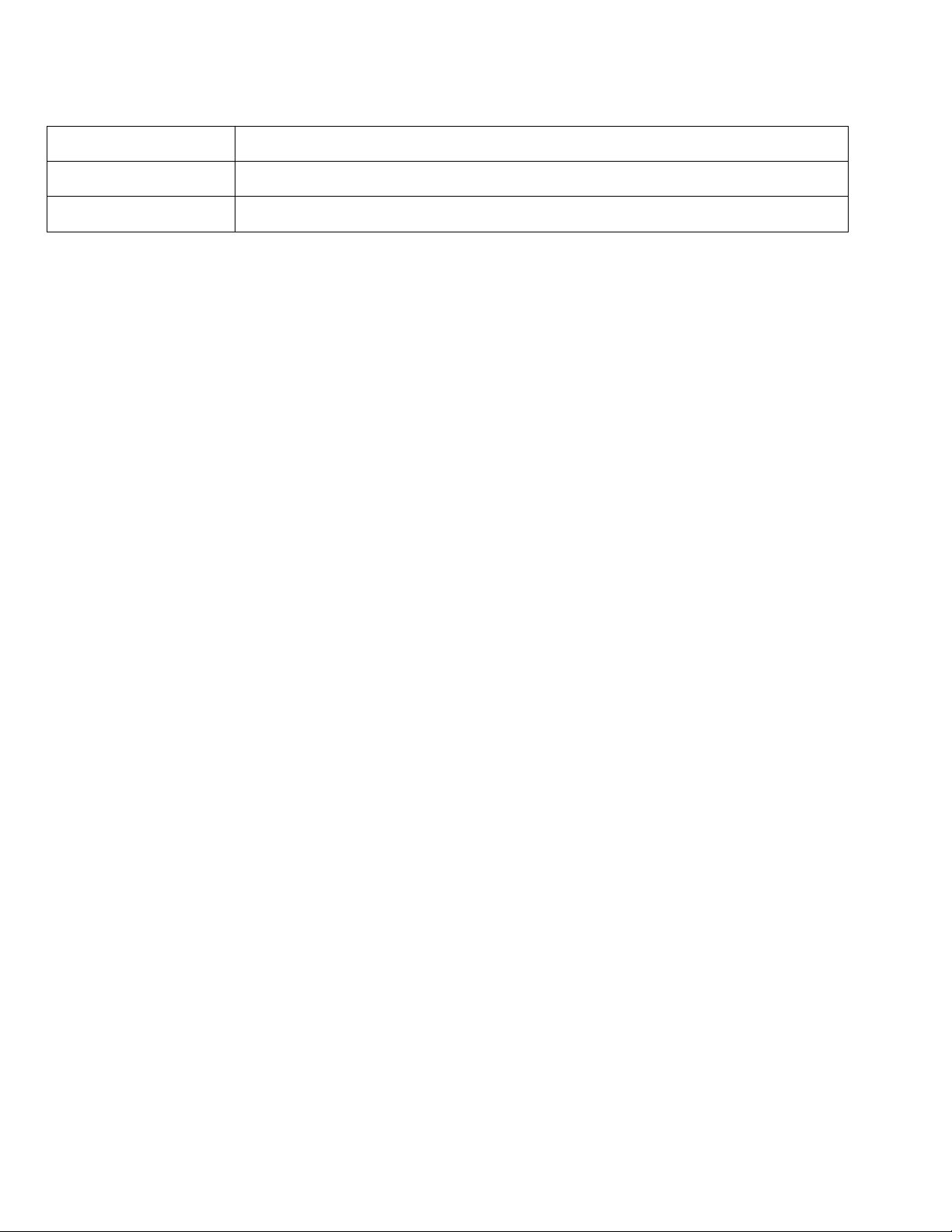
Revision History
Date
Comments
08/13/14
10.2(1) Release
08/17/16
11.0(2) Release
Page 3

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
3
Contents
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Overview ......................................................................................................................... 6!
Phone Models .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 6!
Requirements ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 6!
Site Survey .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 7!
Call Control ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 8!
Wireless LAN ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 8!
Protocols ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 12!
Wi-Fi ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 12!
Regulatory ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 15!
Bluetooth ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 16!
Languages ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 17!
8821-EX Certifications ......................................................................................................................................................................... 17!
Cleaning ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 18!
Accessories ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 19!
Wireless LAN Design .............................................................................................................................................................................. 20!
802.11 Network ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 20!
5 GHz (802.11a/n/ac) ........................................................................................................................................................................ 20!
2.4 GHz (802.11b/g/n) ...................................................................................................................................................................... 22!
Signal Strength and Coverage ........................................................................................................................................................... 23!
Data Rates ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 25!
Rugged Environments ....................................................................................................................................................................... 26!
Security .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 28!
Extensible Authentication Protocol - Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling (EAP-FAST) ................................................ 29!
Extensible Authentication Protocol - Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) ................................................................................... 30!
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) ..................................................................................................................... 32!
EAP and User Database Compatibility ............................................................................................................................................. 32!
Quality of Service (QoS) ....................................................................................................................................................................... 33!
Call Admission Control (CAC) ........................................................................................................................................................ 33!
Traffic Classification (TCLAS) ........................................................................................................................................................ 34!
QoS Basic Service Set (QBSS) ......................................................................................................................................................... 34!
Wired QoS ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 35!
Roaming ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 36!
Fast Secure Roaming (FSR) .............................................................................................................................................................. 36!
Interband Roaming ............................................................................................................................................................................ 37!
Scanning ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 38!
Power Management .............................................................................................................................................................................. 38!
Call Capacity ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 39!
Multicast ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 39!
Configuring the Cisco Wireless LAN .................................................................................................................................................... 40!
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller and Lightweight Access Points .......................................................................................................... 40!
802.11 Network Settings ................................................................................................................................................................... 41!
WLAN Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................. 51!
Controller Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................ 56!
Call Admission Control (CAC) ........................................................................................................................................................ 58!
Page 4

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
4
RF Profiles ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 61!
FlexConnect Groups ......................................................................................................................................................................... 63!
Multicast Direct ................................................................................................................................................................................ 63!
QoS Profiles ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 64!
Advanced Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................ 68!
Cisco Meraki Access Points .................................................................................................................................................................. 71!
Creating the Wireless Network ......................................................................................................................................................... 71!
SSID Configuration .......................................................................................................................................................................... 73!
Radio Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................... 77!
Traffic Shaping ................................................................................................................................................................................. 78!
Monitoring Clients ............................................................................................................................................................................ 79!
Cisco Autonomous Access Points ......................................................................................................................................................... 80!
802.11 Network Settings ................................................................................................................................................................... 80!
WLAN Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................. 84!
Call Admission Control (CAC) ........................................................................................................................................................ 94!
QoS Policies ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 95!
Power Management .......................................................................................................................................................................... 98!
Advanced Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................ 99!
Cisco Autonomous Access Point Sample Configuration .................................................................................................................. 99!
Configuring Cisco Call Control ........................................................................................................................................................... 104!
Cisco Unified Communications Manager ........................................................................................................................................... 104!
Device Pools ................................................................................................................................................................................... 104!
Phone Button Templates ................................................................................................................................................................. 105!
Security Profiles .............................................................................................................................................................................. 105!
SIP Profiles ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 107!
Common Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................ 107!
QoS Parameters ............................................................................................................................................................................... 107!
G.722 and iSAC Advertisement ..................................................................................................................................................... 108!
Audio Bit Rates ............................................................................................................................................................................... 108!
Wireless LAN Profiles .................................................................................................................................................................... 109!
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express ............................................................................................................................. 118!
Product Specific Configuration Options ............................................................................................................................................. 122!
Configuring the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX ........................................................................................................... 132!
Wi-Fi Profile Configuration ................................................................................................................................................................ 132!
Automatic Provisioning .................................................................................................................................................................. 132!
Local User Interface ........................................................................................................................................................................ 133!
Admin Webpage ............................................................................................................................................................................. 141!
Certificate Management ...................................................................................................................................................................... 144!
Manual Installation ......................................................................................................................................................................... 144!
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) ............................................................................................................................. 147!
Certificate Removal ........................................................................................................................................................................ 180!
Bluetooth Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................... 180!
Upgrading Firmware .......................................................................................................................................................................... 182!
Troubleshooting ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 183!
WLAN Signal Indicator ....................................................................................................................................................................... 183!
Neighbor List ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 184!
WLAN Statistics ................................................................................................................................................................................... 184!
Call Statistics ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 185!
Status Messages .................................................................................................................................................................................. 185!
Page 5

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
5
WLAN Diagnostics .............................................................................................................................................................................. 186!
Restoring Factory Defaults ................................................................................................................................................................. 187!
Phone Webpages ................................................................................................................................................................................. 188!
Device Information ......................................................................................................................................................................... 188!
Network Setup ................................................................................................................................................................................ 189!
Streaming Statistics ......................................................................................................................................................................... 190!
Device Logs .................................................................................................................................................................................... 191!
Capturing a Screenshot of the Phone Display .................................................................................................................................... 193!
Additional Documentation ................................................................................................................................................................... 194!
Page 6
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
6
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Overview
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX are the platforms that provide collaboration within enterprises. It brings
together the capabilities of Cisco Unified Communication applications, building upon the solid foundations of Cisco Unified
Communications devices, both wired and wireless.
Cisco’s implementation of 802.11 permits time sensitive applications such as voice and video to operate efficiently across
campus wide wireless LAN (WLAN) deployments. These extensions provide fast roaming capabilities and an almost seamless
flow of multimedia traffic, whilst maintaining security as the end user roams between access points.
It should be understood that WLAN uses unlicensed spectrum, and as a result it may experience interference from other devices
using the unlicensed spectrum. The proliferation of devices in the 2.4 GHz spectrum, such as Bluetooth headsets, Microwave
ovens, cordless consumer phones, means that the 2.4 GHz spectrum may contain more congestion than other spectrums. The 5
GHz spectrum has far fewer devices operating in this spectrum and is the preferred spectrum to operate the Cisco Wireless IP
Phone 8821 and 8821-EX in order to take advantage of the 802.11a/n/ac data rates available.
Despite the optimizations that Cisco has implemented in the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX, the use of unlicensed
spectrum means that uninterrupted communication can not be guaranteed, and there may be the possibility of voice gaps of up
to several seconds during conversations. Adherence to these deployment guidelines will reduce the likelihood of these voice
gaps being present, but there is always this possibility.
Through the use of unlicensed spectrum, and the inability to guarantee the delivery of messages to a WLAN device, the Cisco
Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX is not intended to be used as a medical device and should not be used to make clinical
decisions.
Phone Models
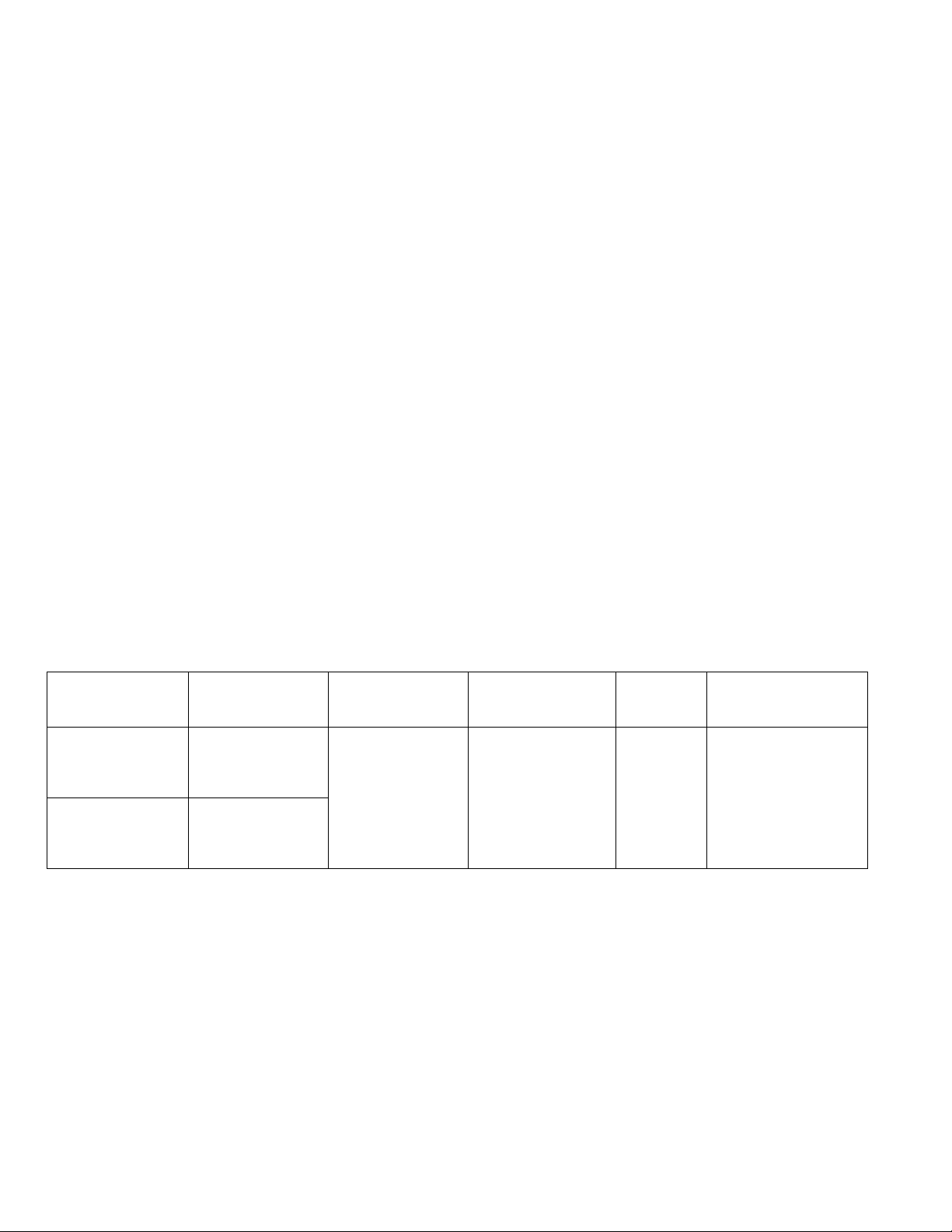
The following Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX models are available.
Below outlines the modes, frequency ranges and channels supported by each model.
Part Number
Description
Peak Antenna
Gain
Frequency
Ranges
Available
Channels
Channel Set
CP-8821-K9=
Cisco Wireless IP
Phone 8821
2.4 GHz = 2.4 dBi
5 GHz = 3.0 dBi
2.412 - 2.472 GHz
5.180 - 5.240 GHz
5.260 - 5.320 GHz
5.500 - 5.700 GHz
5.745 - 5.825 GHz
13
4
4
11
5
1-13
36,40,44,48
52,56,60,64
100-140
149,153,157,161,165
CP-8821-EX-K9=
Cisco Wireless IP
Phone 8821-EX
Note: 802.11j (channels 34, 38, 42, 46) are not supported.
Channel 14 for Japan is not supported.
Requirements
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX are IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac devices that provide voice communications.
The environment must be validated to ensure it meets the requirements to deploy the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821EX.
Page 7
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
7
Site Survey
Before deploying the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX into a production environment, a site survey must be
completed by a Cisco certified partner with the advanced wireless LAN specialization. During the site survey the RF spectrum
can be analyzed to determine which channels are usable in the desired band (5 GHz or 2.4 GHz). Typically there is less
interference in the 5 GHz band as well as more non-overlapping channels, so 5 GHz is the preferred band for operation and
even more highly recommended when the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX is to be used in a mission critical
environment. The site survey will include heatmaps showing the intended coverage plan for the location. The site survey will
also determine which access point platform type, antenna type, access point configuration (channel and transmit power) to use
at the location. It is recommended to select an access point with integrated antennas for non-rugged environments (e.g. office,
healthcare, education, hospitality) and an access point platform requiring external antennas for rugged environments (e.g.
manufacturing, warehouse, retail).
The wireless LAN must be validated to ensure it meets the requirements to deploy the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821EX.
Signal
The cell edge should be designed to -67 dBm where there is a 20-30% overlap of adjacent access points at that signal
level.
This ensures that the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX always have adequate signal and can hold a signal
long enough in order to roam seamlessly where signal based triggers are utilized vs. packet loss triggers.
Also need to ensure that the upstream signal from the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX meets the access
point’s receiver sensitivity for the transmitted data rate. Rule of thumb is to ensure that the received signal at the access
point is -67 dBm or higher.
It is recommended to design the cell size to ensure that the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX can hold a
signal for at least 5 seconds.
Channel Utilization
Channel Utilization levels should be kept under 40%.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX convert the 0-255 scale value to a percentage, so 105 would equate to
around 40% in the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
Noise
Noise levels should not exceed -92 dBm, which allows for a Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) of 25 dB where a -67 dBm
signal should be maintained.
Also need to ensure that the upstream signal from the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX meets the access
point’s signal to noise ratio for the transmitted data rate.
Packet Loss / Delay
Per voice guidelines, packet loss should not exceed 1% packet loss; otherwise voice quality can be degraded
significantly.
Jitter should be kept at a minimal (< 100 ms).
Retries
802.11 retransmissions should be less than 20%.
Multipath
Multipath should be kept to a minimal as this can create nulls and reduce signal levels.
Page 8
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
8
Call Control
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX utilize Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for call control with the following
applications.
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM)
Minimum = 9.1(2)
Recommended = 10.5(2), 11.0(1), 11.5(1)
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CUCME)
Minimum = 10.5
Recommended = 11.0 and later
• Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST)
Minimum = 10.5
Recommended = 11.0 and later
Note: Cisco Unified Communications Manager requires a device package to be installed or service release update in order to
enable Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX device support.
Device packages for Cisco Unified Communications Manager are available at the following location.
http://software.cisco.com/download/navigator.html?mdfid=278875240
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX utilize the fast track method utilizing the Cisco Unified IP Phone 9971 as the
reference model for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/voice_ip_comm/cucme/feature/phone_feature/phone_feature_support_guide.html#_Toc4
36645184
Wireless LAN
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX are supported on the following Cisco Wireless LAN solutions.
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Lightweight Access Points
Minimum = 8.0.121.0
Recommended = 8.0.135.0, 8.1.131.0, 8.2.121.0
• Cisco Meraki Access Points
• Cisco Autonomous Access Points
Minimum = 12.4(21a)JY
Recommended = 12.4(25d)JA2, 15.2(4)JB6, 15.3(3)JD
Note: Cisco Wireless LAN Controller release 8.0.121.0 or later is required if utilizing Flexconnect + Local Switching mode.
Access Points
Below are the Cisco Access Points that are supported.
Page 9

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
9
Note: The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX are supported with the Cisco AP3600 when the internal 802.11a/b/g/n
radio is utilized, however is not supported if the 802.11ac module (AIR-RM3000AC) for the Cisco AP3600 is installed.
The table below lists the modes that are supported by each Cisco Access Point.
Cisco AP
Series
802.11a
802.11b
802.11g
802.11n
802.11ac
Lightweight
Autonomous
600
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
No
Page 10
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
10
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX are currently supported on the Cisco Meraki MR18, MR24, MR26, MR32,
MR34, MR42, MR52, MR53 indoor access point platforms and the Cisco Meraki MR72 outdoor access point platform only.
700
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
700W
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1040
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1130
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Yes
1140
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1240
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Yes
1250
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1260
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1600
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1700
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
1810
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
1810W
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
1830
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
1850
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
2600
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
2700
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
2800
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
3500
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
3600
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes (with
AIRRM3000AC
module)
Yes
Yes
3700
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
3800
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
890
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Page 11

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
11
https://meraki.cisco.com/products/wireless#models
The Cisco Meraki MR12, MR16, and Z1 access point platforms are not certified for use with Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and
8821-EX deployments.
Note: VoWLAN is not currently supported in conjunction with outdoor MESH technology (1500 series).
Limited support is provided when using 3rd party access points as there are no interoperability tests performed for 3rd party
access points.
However the user should have basic functionality when connected to a Wi-Fi compliant access point.
Some of the key features are the following:
• 5 GHz (802.11a/n/ac)
• Wi-Fi Protected Access v2 (WPA2+AES)
• Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM)
• Traffic Specification (TSPEC)
• Traffic Classification (TCLAS)
• Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP)
• Class of Service (CoS / 802.1p)
• QoS Basic Service Set (QBSS)
Antenna Systems
Some of the Cisco Access Points require or allow external antennas.
Please refer to the following URL for the list of supported antennas and how these external antennas should be mounted.
Page 12
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
12
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/wireless/aironet-antennasaccessories/product_data_sheet09186a008008883b.html
All indoor Cisco Meraki access points have internal antennas and all outdoor Cisco Meraki access points require external
antennas.
https://meraki.cisco.com/products/wireless/antennas-power
3rd party antennas are not supported, as there is no interoperability testing performed against 3rd party antennas including
Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) and Leaky Coaxial Systems.
Please refer to the following URL for more info on Cisco Wireless LAN over Distributed Antenna Systems.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/wireless/aironet-1130-ag-series/positioning_statement_c07-565470.html
Note: Cisco Access Points with integrated internal antennas (other than the W series) are to be mounted on the ceiling as they
have omni-directional antennas and are not designed to be wall mounted.
Protocols
Supported voice and wireless LAN protocols include the following:
• 802.11a,b,d,e,g,h,i,n,r,ac
• Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM)
• Traffic Specification (TSPEC)
• Traffic Classification (TCLAS)
• Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP)
• Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
• Real Time Protocol (RTP)
• G.722, G.711, iSAC, iLBC, G.729
• Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
Wi-Fi
The following table lists the data rates, ranges, and receiver sensitivity info for Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
5 GHz Specifications
5 GHz - 802.11a
Data Rate
Modulation
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power = 14 dBm
(Depends on region)
6 Mbps
OFDM - BPSK
-94 dBm
9 Mbps
OFDM - BPSK
-93 dBm
12 Mbps
OFDM - QPSK
-92 dBm
18 Mbps
OFDM - QPSK
-89 dBm
24 Mbps
OFDM - 16 QAM
-86 dBm
Page 13

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
13
36 Mbps
OFDM - 16 QAM
-83 dBm
48 Mbps
OFDM - 64 QAM
-78 dBm
54 Mbps
OFDM - 64 QAM
-76 dBm
5 GHz - 802.11n (HT20)
Data Rate
Modulation
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power = 13 dBm
(Depends on region)
7 Mbps (MCS 0)
OFDM - BPSK
-94 dBm
14 Mbps (MCS 1)
OFDM - QPSK
-91 dBm
21 Mbps (MCS 2)
OFDM - QPSK
-89 dBm
29 Mbps (MCS 3)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-86 dBm
43 Mbps (MCS 4)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-82 dBm
58 Mbps (MCS 5)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-77 dBm
65 Mbps (MCS 6)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-76 dBm
72 Mbps (MCS 7)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-74 dBm
5 GHz - 802.11n (HT40)
Data Rate
Modulation
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power = 13 dBm
(Depends on region)
15 Mbps (MCS 0)
OFDM - BPSK
-91 dBm
30 Mbps (MCS 1)
OFDM - QPSK
-88 dBm
45 Mbps (MCS 2)
OFDM - QPSK
-86 dBm
60 Mbps (MCS 3)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-83 dBm
90 Mbps (MCS 4)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-79 dBm
120 Mbps (MCS 5)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-75 dBm
135 Mbps (MCS 6)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-73 dBm
150 Mbps (MCS 7)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-72 dBm
5 GHz - 802.11ac (VHT20)
Data Rate
Modulation
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power = 12 dBm
(Depends on region)
7 Mbps (MCS 0)
OFDM - BPSK
-93 dBm
14 Mbps (MCS 1)
OFDM - QPSK
-90 dBm
21 Mbps (MCS 2)
OFDM - QPSK
-87 dBm
29 Mbps (MCS 3)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-84 dBm
43 Mbps (MCS 4)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-81 dBm
58 Mbps (MCS 5)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-76 dBm
65 Mbps (MCS 6)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-75 dBm
72 Mbps (MCS 7)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-74 dBm
87 Mbps (MCS 8)
OFDM – 256 QAM
-70 dBm
5 GHz - 802.11ac (VHT40)
Data Rate
Modulation
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power = 12 dBm
(Depends on region)
15 Mbps (MCS 0)
OFDM - BPSK
-90 dBm
30 Mbps (MCS 1)
OFDM - QPSK
-87 dBm
45 Mbps (MCS 2)
OFDM - QPSK
-85 dBm
60 Mbps (MCS 3)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-82 dBm
90 Mbps (MCS 4)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-79 dBm
120 Mbps (MCS 5)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-73 dBm
135 Mbps (MCS 6)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-72 dBm
150 Mbps (MCS 7)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-72dBm
Page 14
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
14
2.4 GHz Specifications
2.4 GHz - 802.11b
Data Rate
Modulation
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power = 17 dBm
(Depends on region)
1 Mbps
DSSS - BPSK
-98 dBm
2 Mbps
DSSS - QPSK
-96 dBm
5.5 Mbps
DSSS - CCK
-93 dBm
11 Mbps
DSSS - CCK
-91 dBm
2.4 GHz - 802.11g
Data Rate
Modulation
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power = 14 dBm
(Depends on region)
6 Mbps
OFDM - BPSK
-95 dBm
9 Mbps
OFDM - BPSK
-94 dBm
12 Mbps
OFDM - QPSK
-93 dBm
18 Mbps
OFDM - QPSK
-90 dBm
24 Mbps
OFDM - 16 QAM
-87 dBm
36 Mbps
OFDM - 16 QAM
-84 dBm
48 Mbps
OFDM - 64 QAM
-79 dBm
54 Mbps
OFDM - 64 QAM
-77 dBm
2.4 GHz - 802.11n (HT20)
Data Rate
Modulation
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power = 13 dBm
(Depends on region)
7 Mbps (MCS 0)
OFDM - BPSK
-95 dBm
14 Mbps (MCS 1)
OFDM - QPSK
-92 dBm
21 Mbps (MCS 2)
OFDM - QPSK
-90 dBm
29 Mbps (MCS 3)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-87 dBm
43 Mbps (MCS 4)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-83 dBm
58 Mbps (MCS 5)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-78 dBm
65 Mbps (MCS 6)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-77 dBm
72 Mbps (MCS 7)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-75 dBm
180 Mbps (MCS 8)
OFDM – 256 QAM
-67 dBm
200 Mbps (MCS 9)
OFDM – 256 QAM
-66 dBm
5 GHz - 802.11ac (VHT80)
Data Rate
Modulation
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power = 12 dBm
(Depends on region)
33 Mbps (MCS 0)
OFDM - BPSK
-87 dBm
65 Mbps (MCS 1)
OFDM - QPSK
-83 dBm
98 Mbps (MCS 2)
OFDM - QPSK
-81 dBm
130 Mbps (MCS 3)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-78 dBm
195 Mbps (MCS 4)
OFDM - 16 QAM
-75 dBm
260 Mbps (MCS 5)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-73 dBm
293 Mbps (MCS 6)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-68 dBm
325 Mbps (MCS 7)
OFDM - 64 QAM
-68 dBm
390 Mbps (MCS 8)
OFDM – 256 QAM
-64 dBm
433 Mbps (MCS 9)
OFDM – 256 QAM
-62 dBm
Page 15

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
15
Note: Receiver sensitivity is the minimum signal needed to decode a packet at a certain data rate.
The above values are pure radio specifications and do not account for the gain of the single integrated antenna.
To achieve 802.11n/ac connectivity, it is recommended that the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX be within 100 feet
of the access point.
Regulatory
World Mode (802.11d) allows a client to be used in different regions, where the client can adapt to using the channels and
transmit powers advertised by the access point in the local environment.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX operate best when the access point is 802.11d enabled, where it can determine
which channels and transmit powers to use per the local region.
Enable World Mode (802.11d) for the corresponding country where the access point is located.
Some 5 GHz channels are also used by radar technology, which requires that the 802.11 client and access point be 802.11h
compliant if utilizing those radar frequencies (DFS channels). 802.11h requires 802.11d to be enabled.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will passively scan DFS channels first before engaging in active scans of those
channels.
If 802.11d is not enabled, then the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX can attempt to connect to the access point using
reduced transmit power.
Below are the countries and their 802.11d codes that are supported by the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
Australia (AU)
Iceland (IS)
Poland (PL)
Austria (AT)
India (IN)
Portugal (PT)
Bahrain (BH)
Ireland (IE)
Puerto Rico (PR)
Belgium (BE)
Israel (IL)
Romania (RO)
Brazil (BR)
Italy (IT)
Russian Federation (RU)
Bulgaria (BG)
Japan (JP)
Saudi Arabia (SA)
Canada (CA)
Korea (KR)
Serbia (RS)
Chile (CL)
Latvia (LV)
Singapore (SG)
Colombia (CO)
Liechtenstein (LI)
Slovakia (SK)
Costa Rica (CR)
Lithuania (LT)
Slovenia (SI)
Croatia (HR)
Luxembourg (LU)
South Africa (ZA)
Cyprus (CY)
Macau (MO)
Spain (ES)
Czech Republic (CZ)
Macedonia (MK)
Sweden (SE)
Denmark (DK)
Malta (MT)
Switzerland (CH)
Dominican Republic (DO)
Mexico (MX)
Taiwan (TW)
Ecuador (EC)
Monaco (MC)
Thailand (TH)
Egypt (EG)
Montenegro (ME)
Turkey (TR)
Estonia (EE)
Netherlands (NL)
Ukraine (UA)
Finland (FI)
New Zealand (NZ)
United Arab Emirates (AE)
France (FR)
Nigeria (NG)
United Kingdom (GB)
Germany (DE)
Norway (NO)
United States (US)
Gibraltar (GI)
Panama (PA)
Uruguay (UY)
Greece (GR)
Paraguay (PY)
Vietnam (VN)
Hong Kong (HK)
Peru (PE)
Hungary (HU)
Philippines (PH)
Page 16

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
16
Note: Compliance information is available on the Cisco Product Approval Status web site at the following URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/cse/prdapp/jsp/externalsearch.do?action=externalsearch&page=EXTERNAL_SEARCH
Bluetooth
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX support Bluetooth 3.0 technology allowing for wireless headset communications.
Bluetooth enables low bandwidth wireless connections within a range of 30 feet, however it is recommended to keep the
Bluetooth device within 10 feet of the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
Up to ten headsets can be paired, where the previously connected headset is given priority.
The Bluetooth device does not need to be within direct line-of-sight of the phone, but barriers, such as walls, doors, etc. can
potentially impact the quality.
Bluetooth utilizes the 2.4 GHz frequency just like 802.11b/g/n and many other devices (e.g. microwave ovens, cordless phones,
etc.), so the Bluetooth quality can potentially be interfered with due to using this unlicensed frequency.
Bluetooth Profiles
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX support the following Bluetooth profiles.
Hands-Free Profile (HFP)
With Bluetooth Hands-Free Profile (HFP) support, the following features can be available if supported by the Bluetooth
headset.
• Ring
• Answer a call
• End a call
• Volume Control
• Last Number Redial
• Call Waiting
• Divert / Reject
• 3 way calling (Hold & Accept and Release & Accept)
• Speed Dialing
Phone Book Access Profile (PBAP)
Phone Book Access Profile (PBAP) support enables the exchange of phone book objects between devices.
For more information, refer to the documentation from the Bluetooth headset manufacturer.
Coexistence (802.11b/g/n + Bluetooth)
If using Coexistence where 802.11b/g/n and Bluetooth are used simultaneously, then there are some limitations and deployment
requirements to be considered as they both utilize the 2.4 GHz frequency range.
Capacity
Page 17

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
17
When using Coexistence (802.11b/g/n + Bluetooth), call capacity is reduced due to the utilization of CTS to protect the
802.11g/n and Bluetooth transmissions.
Multicast Audio
Multicast audio from Push To Talk (PTT), Music on Hold (MMOH) and other applications are not supported when
using Coexistence.
Voice Quality
Depending on the current data rate configuration, CTS may be sent to protect the Bluetooth transmissions when using
Coexistence.
In some environments, 6 Mbps may need to be enabled.
Note: It is recommended to use 802.11a/n/ac if using Bluetooth due to 802.11b/g/n and Bluetooth both utilizing 2.4 GHz, but
also due to the above limitations.
Languages
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX currently support the following languages.
The corresponding locale package must be installed to enable support for that language. English is the default language on the
phone.
Download the locale packages from the Localization page at the following URL:
http://software.cisco.com/download/navigator.html?mdfid=278875240
8821-EX Certifications
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821-EX is certified for Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Class I Division 2 and
Atmospheres Explosibles (ATEX) Class I Zone 2.
Arabic
French
Polish
Bulgarian
German
Portuguese
Catalan
Greek
Romanian
Chinese
Hebrew
Russian
Croatian
Hungarian
Serbian
Czech
Italian
Slovak
Danish
Japanese
Slovenian
Dutch
Korean
Spanish
English
Latvian
Swedish
Estonian
Lithuanian
Thai
Finnish
Norwegian
Turkish
Page 18

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
18
Certification ensures that the equipment is fit for its intended purpose and that adequate information is supplied with it to ensure
that it can be used safely.
Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Class I Division 2
Laws and regulations in most municipalities, states, and provinces in North America require certain products to be tested to a
specific standard or group of standards when they are to be classified safe when used in an explosive environment.
In North America, hazardous locations have traditionally been defined by the following combination of Class and Division:
• Class I - A location where a quantity of flammable gas or vapor, sufficient to produce an explosive or ignitable
mixture, may be present in the air.
• Class II - A location made hazardous by the presence of combustible elements.
• Class III - A location made hazardous by the presence of easily ignitable fibers in the air.
• Division 1 - A location where a classified hazard is likely to exist.
• Division 2 - A location where a classified hazard does not normally exist but is possible under abnormal conditions.
More recently in North America, for Class I hazards, locations can be classified under the zone system as defined by the
IEC/ATEX mentioned below.
Atmospheres Explosibles (ATEX) Class I Zone 2
Equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres must comply with ATEX Directive
94/9/EC.
Areas classified into zones must be protected from effective sources of ignition.
Locations where explosive gas atmospheres are likely to be present are divided into IEC/EU-defined Zones (Class I Zone 0, 1, 2
for locations with flammable gases or vapors and Class II Zone 20, 21, 22 for locations with combustible dust or ignitable
fibers).
Class I
• Zone 0 - An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is continuously present or present for long periods.
• Zone 1 - An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is likely to occur in normal operation.
• Zone 2 - An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere does not normally exist, or if they do occur, will exist only for
a short period of time.
Class II
• Zone 20 – An area in which an ignitable concentrations of combustible dust or ignitable fibers/flyings are present
continuously or for long periods of time under normal operating conditions.
• Zone 21 - An area in which an ignitable concentrations of combustible dust or ignitable fibers/flyings are likely to exist
under normal operating conditions.
• Zone 22 - An area in which an ignitable concentrations of combustible dust or ignitable fibers/flyings are not likely to
exist under normal operating conditions.
Cleaning
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX are IP67 rated, which is designed to provide protection from dust, liquid
splashes and moisture.
This allows the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX to be cleaned, sanitized without the possibility of damaging the
unit.
Page 19

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
19
A moist cloth can be used for simple cleaning; however Caviwipes and Saniwipes are the recommended choice for thoroughly
cleaning the phone.
Caviwipes and Saniwipes contain up to 17% Isopropanol. Any cleaning solution containing a higher degree of Isopropanol
including pure Isopropanol or an alternative alcohol based liquid could potentially damage the phone.
Carry cases can additionally help protect the phone further and provide drop protection.
Accessories
The following accessories are available for the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
• Batteries
• Phone Power Supply
• Belt Holster
• Leather Case
• Desktop Charger
• Multicharger
3rd Party Accessories
Only the 3rd party accessories listed below are certified for use with the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
• Headsets Apple (www.apple.com)
Jabra (www.jabra.com)
Plantronics (www.plantronics.com)
Sennheiser (www.sennheiser.com)
• USB to Ethernet Dongles Apple USB 2.0 Ethernet Adapter (www.apple.com)
Page 20
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
20
Belkin B2B048 USB 3.0 Gigabit Ethernet Adapter (www.belkin.com)
D-Link DUB-E100 USB 2.0 Fast Ethernet Adapter (www.dlink.com)
Linksys USB3GIG USB 3.0 Gigabit Ethernet Adapter (www.linksys.com)
Linksys USB300M USB 2.0 Ethernet Adapter (www.linksys.com)
Wireless LAN Design
The following network design guidelines must be followed in order to accommodate for adequate coverage, call capacity and
seamless roaming for the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
802.11 Network
Use the following guidelines to assist with deploying and configuring the wireless LAN.
5 GHz (802.11a/n/ac)
5 GHz is the recommended frequency band to utilize for operation of the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
In general, it is recommended for access points to utilize automatic channel selection instead of manually assigning channels to
access points.
If there is an intermittent interferer, then the access point or access points serving that area may need to have a channel statically
assigned.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX support Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) and Transmit Power Control
(TPC) from 802.11h, which are required when using channels operating at 5.260 - 5.720 GHz, which are 15 of the 24 possible
channels.
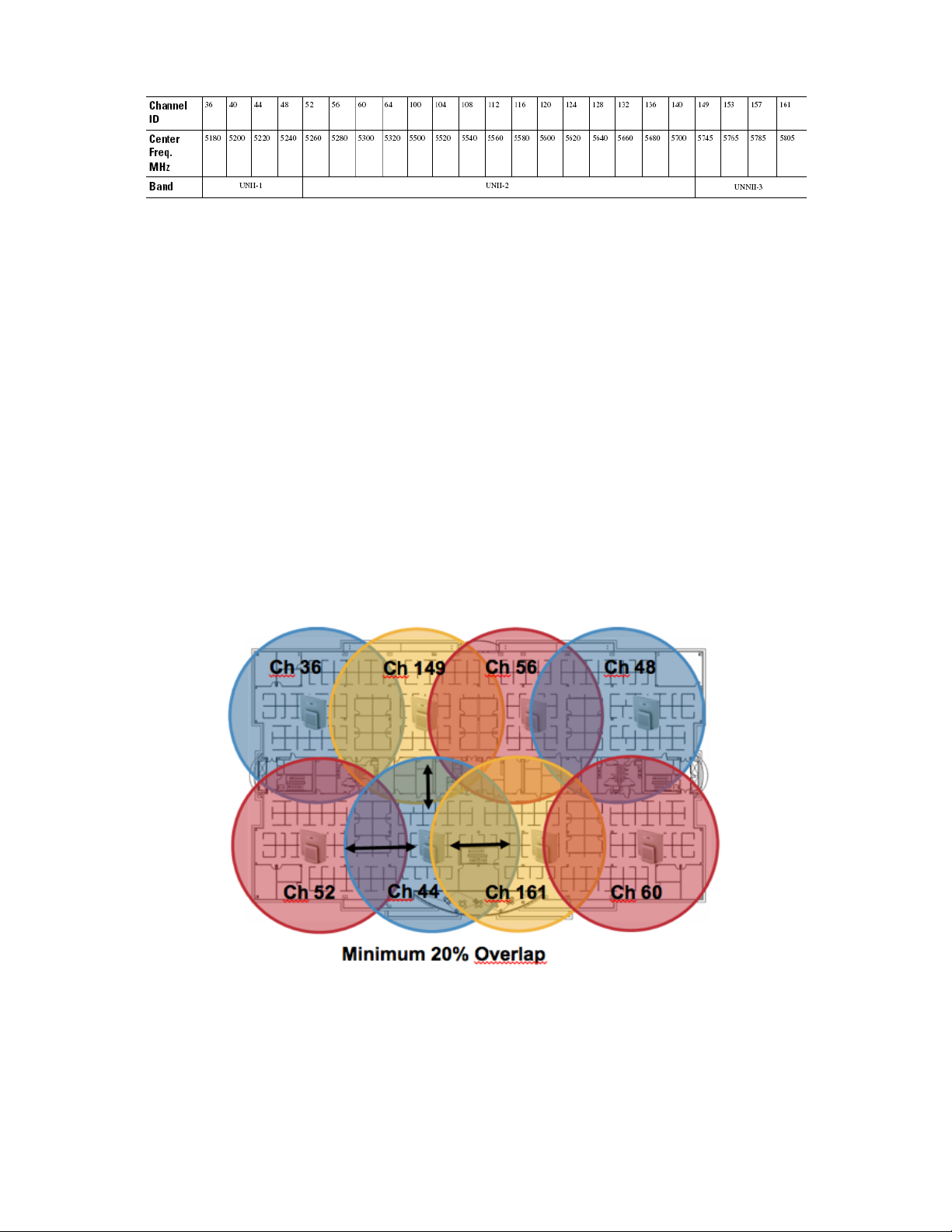
Need to ensure there is at least 20 percent overlap with adjacent channels when deploying the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821
and 8821-EX in an 802.11a/n/ac environment, which allows for seamless roaming. For critical areas, it is recommended to
increase the overlap (30% or more) to ensure that there can be at least 2 access points available with -67 dBm or better, while
the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX also meet the access point’s receiver sensitivity (required signal level for the
current data rate).
Page 21
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
21
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS)
DFS dynamically instructs a transmitter to switch to another channel whenever radar signal is detected. If the access point
detects radar, the radio on the access point goes on hold for at least 60 seconds while the access point passively scans for
another usable channel.
TPC allows the client and access point to exchange information, so that the client can dynamically adjust the transmit power.
The client uses only enough energy to maintain association to the access point at a given data rate. As a result, the client
contributes less to adjacent cell interference, which allows for more densely deployed, high-performance wireless LANs.
If there are repeated radar events detected by the access point (just or falsely), determine if the radar signals are impacting a
single channel (narrowband) or multiple channels (wideband), then potentially disable use of that channel or channels in the
wireless LAN.
The presence of an access point on a non-DFS channel can help minimize voice interruptions.
In case of radar activity, have at least one access point per area that uses a non-DFS channel (UNII-1). This ensures that a
channel is available when an access point’s radio is in its hold-off period while scanning for a new usable channel.
A UNII-3 channel (5.745 - 5.825 GHz) can optionally be used if available.
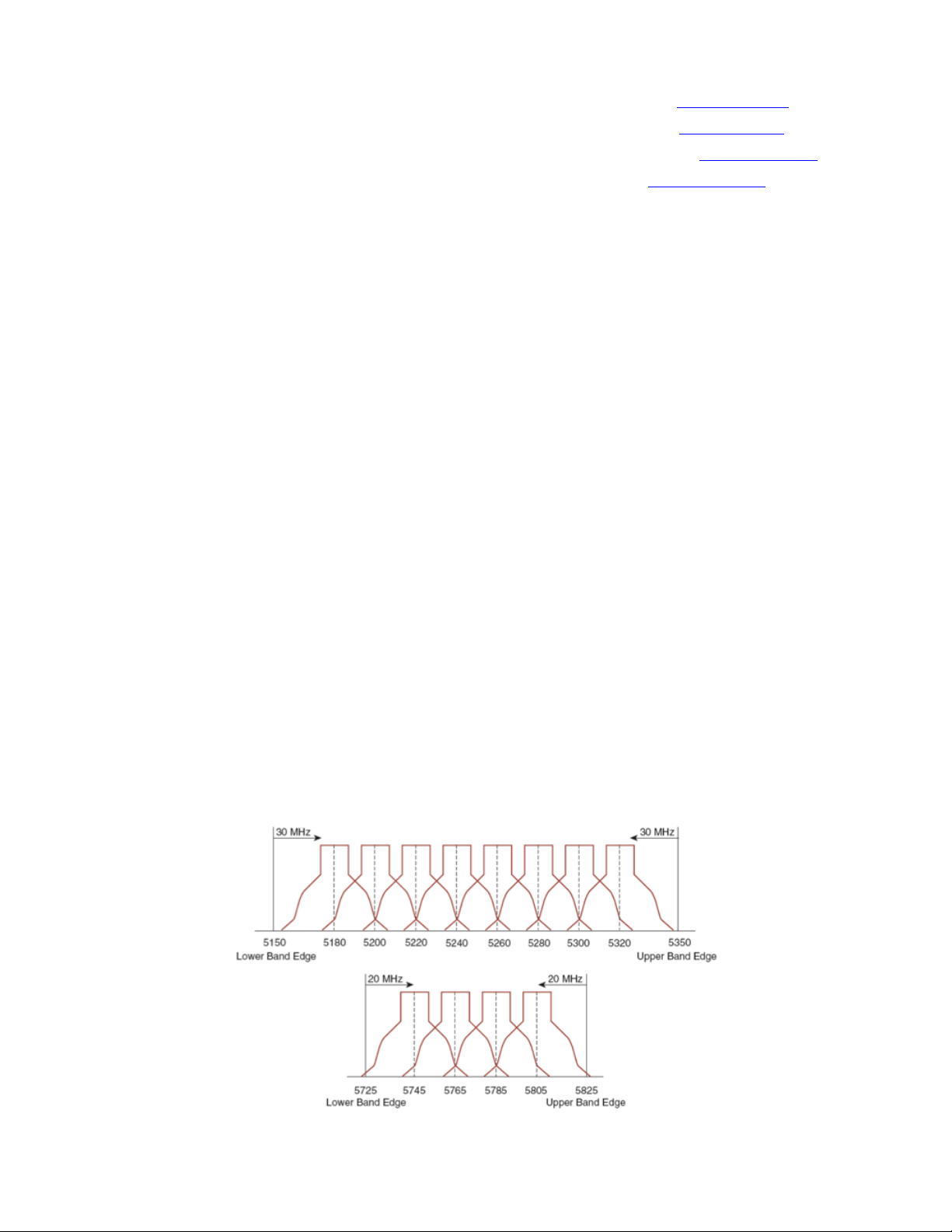
Below is a sample 5 GHz wireless LAN deployment.
For 5 GHz, 21 channels are available in the Americas, 16 channels in Europe, and 19 channels in Japan.
Where UNII-3 is available, it is recommended to use UNII-1, UNII-2, and UNII-3 only to utilize a 12 channel set.
If planning to use UNII-2 extended channels (channels 100 - 140), it is recommended to disable UNII-2 (channels 52-64) on the
access point to avoid having so many channels enabled.
Having many 5 GHz channels enabled in the wireless LAN can delay discovery of new access points.
Page 22
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
22
2.4 GHz (802.11b/g/n)
In general, it is recommended for access points to utilize automatic channel selection instead of manually assigning channels to
access points.
If there is an intermittent interferer, then the access point or access points serving that area may need to have a channel statically
assigned.
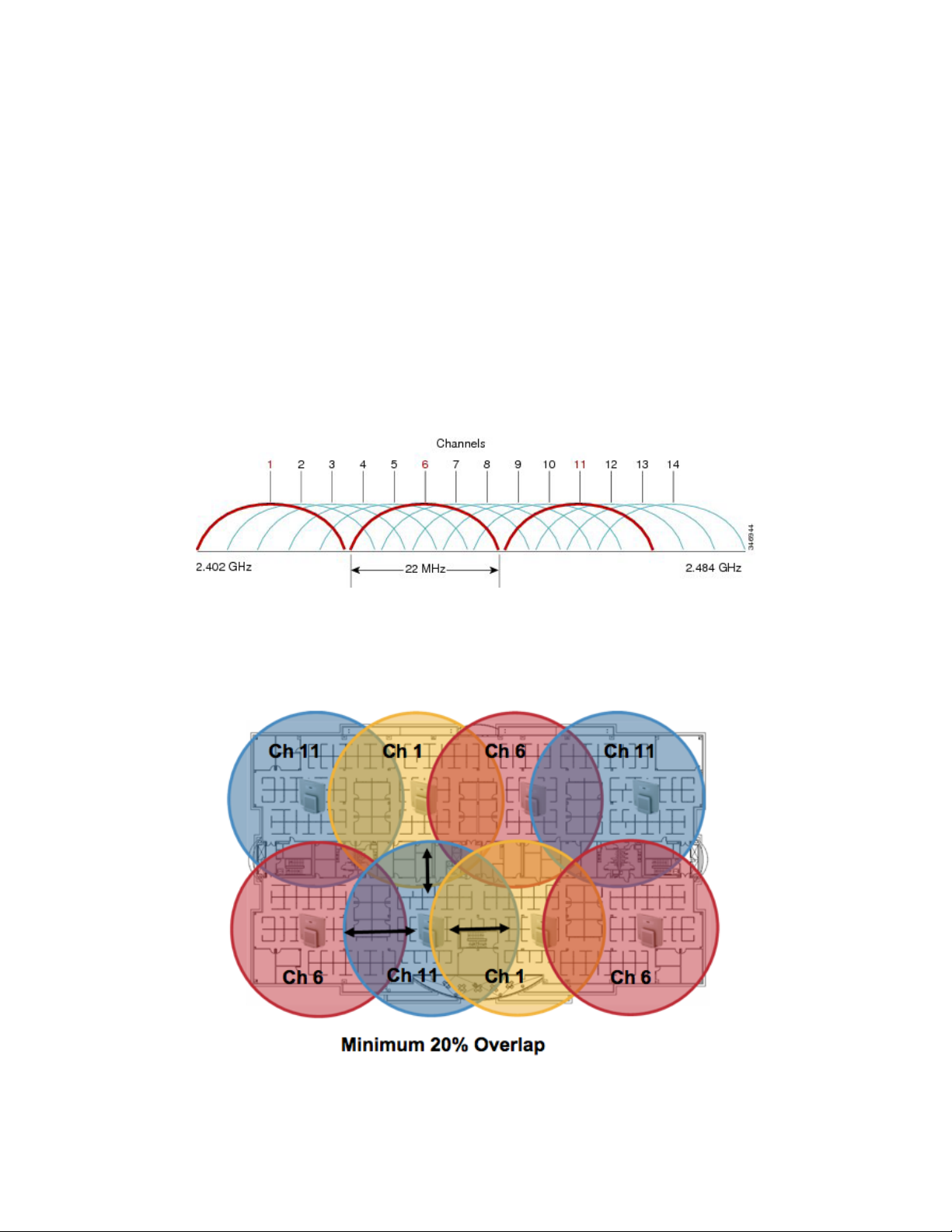
In a 2.4 GHz (802.11b/g/n) environment, only non-overlapping channels must be utilized when deploying VoWLAN. Nonoverlapping channels have 22 MHz of separation and are at least 5 channels apart.
There are only 3 non-overlapping channels in the 2.4 GHz frequency range (channels 1, 6, 11).
Non-overlapping channels must be used and allow at least 20 percent overlap with adjacent channels when deploying the Cisco
Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX in an 802.11b/g/n environment, which allows for seamless roaming.
Using an overlapping channel set such as 1, 5, 9, 13 is not a supported configuration.
Below is a sample 2.4 GHz wireless LAN deployment.
Page 23
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
23
Signal Strength and Coverage
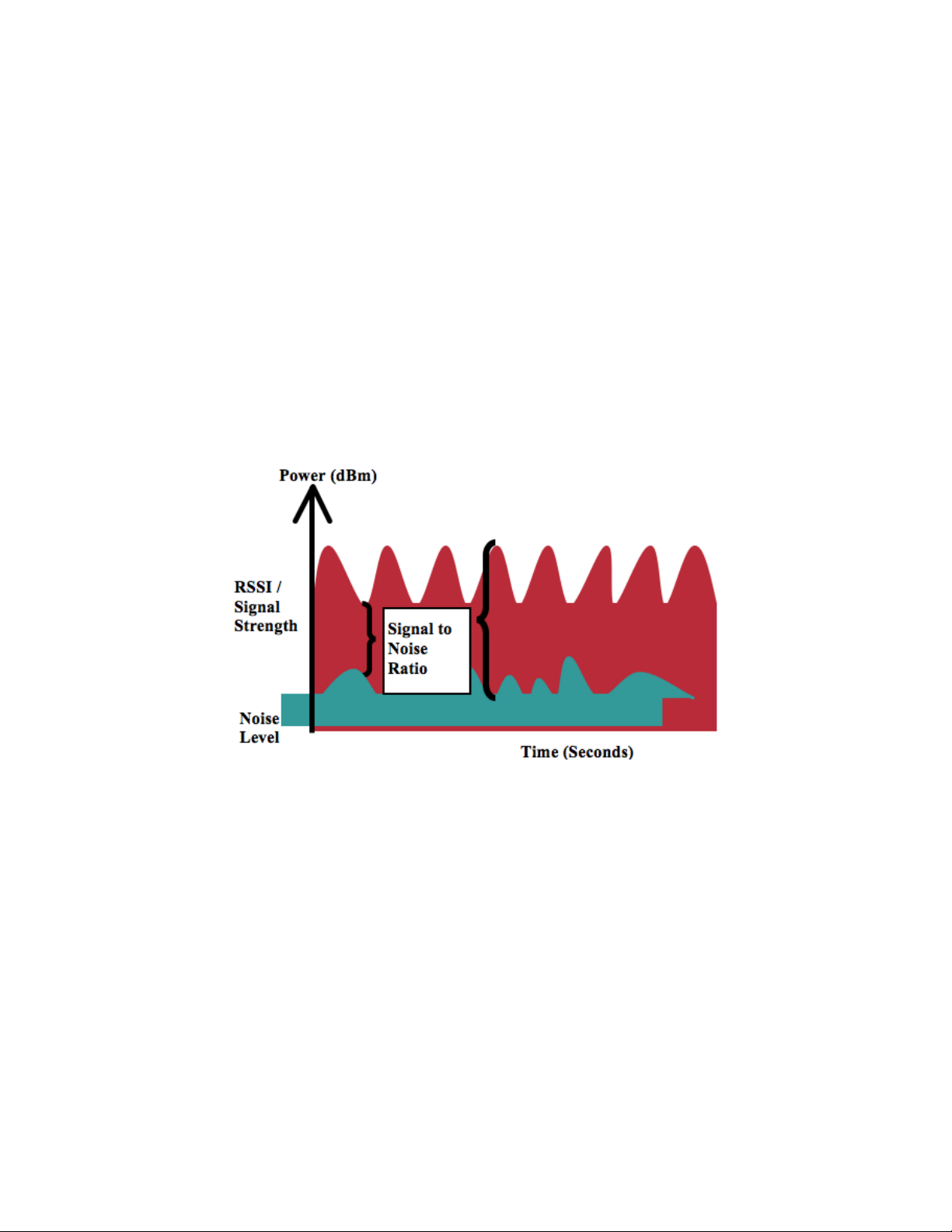
To ensure acceptable voice quality, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX should always have a signal of -67 dBm or
higher when using 5 GHz or 2.4 GHz, while the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX also meet the access point’s
receiver sensitivity required signal level for the transmitted data rate.
Ensure the Packet Error Rate (PER) is no higher than 1%.
A minimum Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) of 25 dB = -92 dBm noise level with -67 dBm signal should be maintained.
It is recommended to have at least two access points on non-overlapping channels with at least -67 dBm signal with the 25 dB
SNR to provide redundancy.
To achieve maximum capacity and throughput, the wireless LAN should be designed to 24 Mbps. Higher data rates can
optionally be enabled for other applications other than voice only that can take advantage of these higher data rates.
Recommended to set the minimum data rate to 11 Mbps or 12 Mbps for 2.4 GHz (dependent upon 802.11b client support
policy) and 12 Mbps for 5 GHz, which should also be the only rate configured as a mandatory / basic rate.
In some environments, 6 Mbps may need to be enabled as a mandatory / basic rate.
Due to the above requirements, a single channel plan should not be deployed.
When designing the placement of access points, be sure that all key areas have adequate coverage (signal).
Typical wireless LAN deployments for data only applications do not provide coverage for some areas where VoWLAN service
is necessary such as elevators, stairways, and outside corridors.
Microwave ovens, 2.4 GHz cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, or other electronic equipment operating in the 2.4 GHz band
will interfere with the Wireless LAN.
Microwave ovens operate on 2450 MHz, which is between channels 8 and 9 of 802.11b/g/n. Some microwaves are shielded
more than others and that shielding reduces the spread of the energy. Microwave energy can impact channel 11, and some
microwaves can affect the entire frequency range (channels 1 through 11). To avoid microwave interference, select channel 1
for use with access points that are located near microwaves.
Most microwave ovens, Bluetooth, and frequency hopping devices do not have the same effect on the 5 GHz frequency. The
802.11a/n/ac technology provides more non-overlapping channels and typically lower initial RF utilization. For voice
deployments, it is suggested to use 802.11a/n/ac for voice and use 802.11b/g/n for data.
However there are products that also utilize the non-licensed 5 GHz frequency (e.g. 5.8 GHz cordless phones, which can impact
UNII-3 channels).
Page 24

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
24
The Cisco Unified Network Control System (NCS) can be utilized to verify signal strength and coverage.
Page 25
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
25
Data Rates
It is recommended to disable rates below 12 Mbps for 5 GHz deployments and below 12 Mbps for 2.4 GHz deployments where
capacity and range are factored in for best results.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX both have a single antenna, therefore it supports up to MCS 7 data rates for
802.11n (up t to 150 Mbps) and up to MCS 9 data rates for 802.11ac (up to 433 Mbps).
Higher MCS rates can be left enabled for other 802.11n/ac clients, which are utilizing the same band frequency and utilize
MIMO (multiple input / multiple output) antenna technology, which can take advantage of those higher rates.
If 802.11b clients are not allowed in the wireless network, then it is strongly recommended to disable the data rates below 12
Mbps. This will eliminate the need to send CTS frames for 802.11g/n protection as 802.11b clients can not detect these OFDM
frames.
When 802.11b clients exist in the wireless network, then an 802.11b rate must be enabled and only an 802.11b rate can be
configured as a mandatory / basic rate.
The recommended data rate configurations are the following:
802.11 Mode
Mandatory
Data Rates
Supported
Data Rates
Disabled
Data Rates
802.11a/n/ac
12 Mbps
18-54 Mbps,
VHT MCS 1 - MCS 9
6, 9 Mbps,
VHT MCS 0
802.11a/n
12 Mbps
18-54 Mbps,
HT MCS 1 - MCS 7
(HT MCS 8 - MCS 23)
6, 9 Mbps,
HT MCS 0
802.11g/n
12 Mbps
18-54 Mbps,
HT MCS 1 - MCS 7
(HT MCS 8 - MCS 23)
1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11 Mbps,
HT MCS 0
802.11b/g/n
11 Mbps
12-54 Mbps,
HT MCS 1 - MCS 7
(HT MCS 8 - MCS 23)
1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9 Mbps,
HT MCS 0
802.11a
12 Mbps
18-54 Mbps
6, 9 Mbps
802.11g
12 Mbps
18-54 Mbps
1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11 Mbps
802.11b/g
11 Mbps
12-54 Mbps
1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9 Mbps
802.11b
11 Mbps
None
1, 2, 5.5 Mbps
For a voice only application, data rates higher than 24 Mbps can optionally be enabled or disabled, but there is no advantage
from a capacity or throughput perspective and enabling these rates could potentially increase the number of retries for a data
frame.
Other applications such as video may be able to benefit from having these higher data rates enabled.
To preserve high capacity and throughput, data rates of 24 Mbps and higher should be enabled.
If deploying in an environment where excessive retries may be a concern, then a limited set of the data rates can be used (e.g.
12, 24, 54, MCS 1, MCS 4, MCS 7), where the lowest enabled rate is the mandatory / basic rate.
For rugged environments or deployments requiring maximum range, it is recommended to enable 6 Mbps as a mandatory /
basic rate.
Page 26

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
26
Note: Some environments may require that a lower data rate be enabled due to use of legacy clients, environmental factors or
maximum range is required.
Set only the lowest data rate enabled as the single mandatory / basic rate. Multicast packets will be sent at the highest
mandatory / basic data rate enabled.
Note that capacity and throughput are reduced when lower rates are enabled.
Rugged Environments
When deploying the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX in a rugged environment (e.g. manufacturing, warehouse,
retail), additional tuning on top of the standard design recommendations may be necessary.
Below are the key items to focus on when deploying a wireless LAN in a rugged environment.
Access Point and Antenna Selection
For rugged environments, it is recommended to select an access point platform that requires external antennas (e.g.
Cisco 1602e, 2602e, 3502e, 3602e, and 3702e Series Access Points). It is also important to ensure an antenna type is
selected which can operate well in rugged environments.
Access Point Placement
It is crucial that line of sight to the access point’s antennas is maximized by minimizing any obstructions between the
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 or 8821-EX and the access point. Ensure that the access point and/or antennas are not
mounted behind any obstruction or on or near a metal or glass surface.
If access points with integrated internal antennas are to be used in some areas (other than the W series), then it is
recommended to mount those access points on the ceiling as they have omni-directional antennas and are not designed
to be wall mounted.
Frequency Band
As always, it is recommended to use 5 GHz. Use of 2.4 GHz, especially when 802.11b rates are enabled, may not work
well.
For the 5 GHz channel set, it is recommended to use a 8 or 12 channel plan only; disable UNII-2 extended channels if
possible.
Data Rates
The standard recommended data rate set may not work well if multipath is present at an elevated level.
Therefore, it is recommended to enable lower data rates (e.g. 6 Mbps) to operate better in such an environment.
If using for voice only, then data rates above 24 Mbps can be disabled to increase first transmission success. If the
same band is also used for data, video or other applications, then is suggested to keep the higher data rates enabled.
Transmit Power
Due to the potential of elevated multipath in rugged environments, the transmit power of the access point and Cisco
Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX should also be restricted. This is more important if planning to deploy 2.4 GHz
in a rugged environment.
If using auto transmit power, the access point transmit power can be configured to use a specified range (maximum and
minimum power levels) to prevent the access point from transmitting too hot as well as too weak (e.g. 5 GHz maximum
of 16 dBm and minimum of 11 dBm).
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will utilize the access point’s current transmit power setting to
determine what transmit power it uses for transmitted frames when DTPC is enabled in the access point’s
configuration.
Fast Roaming
Page 27

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
27
It is recommended to utilize 802.11r / Fast Transition (FT) for fast roaming. Enabling 802.11r (FT) also reduces the
number of frames in the handshake when roaming to only two frames. Reducing the number of frames during a roam,
increases the chances of roam success.
When using 802.1x authentication, it is important to use the recommended EAPOL key settings.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Need to ensure that DSCP values are preserved throughout the wired network, so that the WMM UP tag for voice,
video, and call control frames can be set correctly.
Beamforming
If using Cisco 802.11n capable access points, then Beamforming (ClientLink) should be enabled, which can help with
client reception.
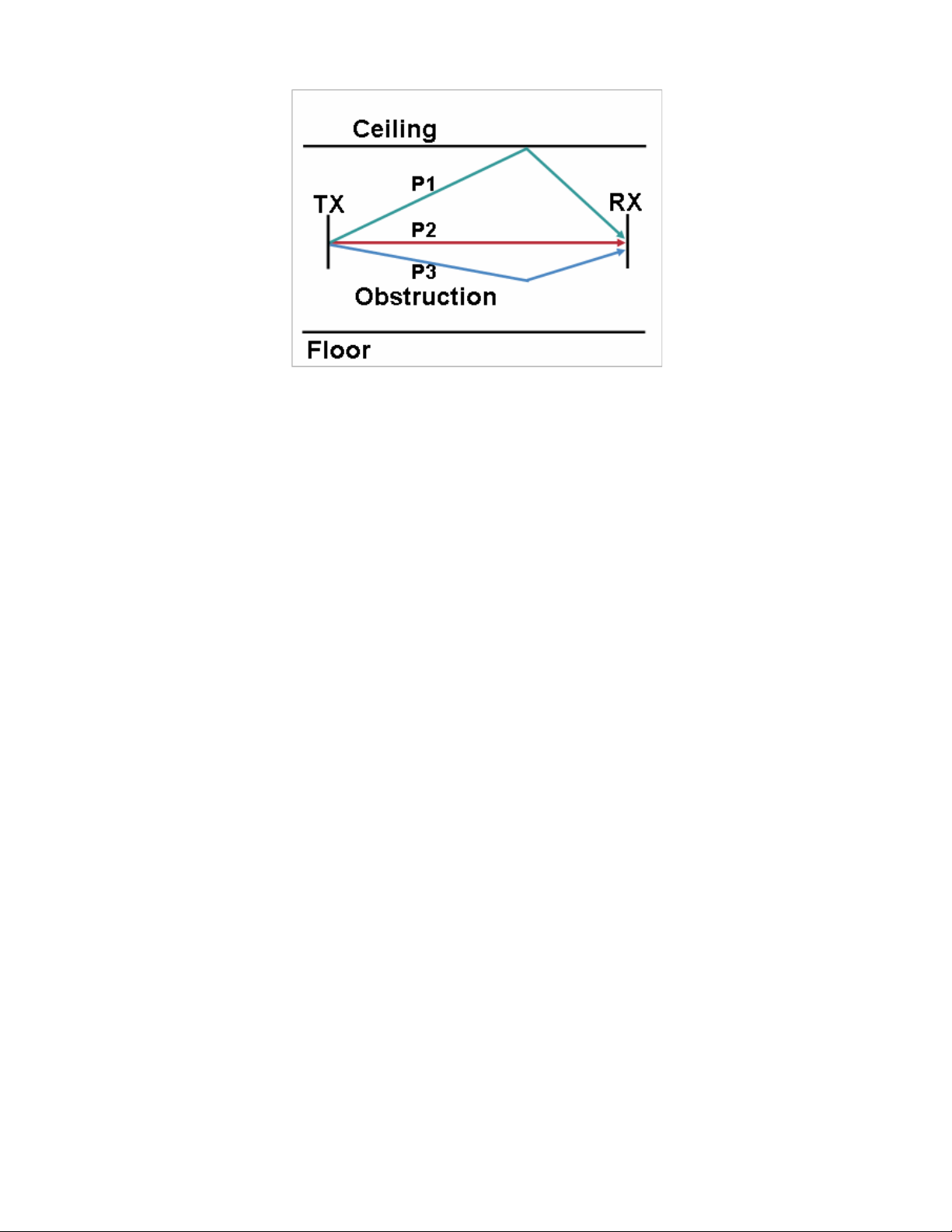
Multipath
Multipath occurs when RF signals take multiple paths from a source to a destination.
A part of the signal goes to the destination while another part bounces off an obstruction, then goes on to the destination. As a
result, part of the signal encounters delay and travels a longer path to the destination, which creates signal energy loss.
When the different waveforms combine, they cause distortion and affect the decoding capability of the receiver, as the signal
quality is poor.
Multipath can exist in environments where there are reflective surfaces (e.g. metal, glass, etc.). Avoid mounting access points
on these surfaces.
Below is a list of multipath effects:
Data Corruption
Occurs when multipath is so severe that the receiver is unable to detect the transmitted information.
Signal Nulling
Occurs when the reflected waves arrive exactly out of phase with the main signal and cancel the main signal
completely.
Increased Signal Amplitude
Occurs when the reflected waves arrive in phase with the main signal and add on to the main signal thereby increasing
the signal strength.
Decreased Signal Amplitude
Occurs when the reflected waves arrive out of phase to some extent with the main signal thereby reducing the signal
amplitude.
Page 28
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
28
Use of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), which is used by 802.11a/n/ac and 802.11g/n, can help to reduce
issues seen in high multipath environments.
If using 802.11b in a high multipath environment, lower data rates should be used in those areas (e.g. 1 and 2 Mbps).
Use of antenna diversity can also help in such environments.
Security
When deploying a wireless LAN, security is essential.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX support the following wireless security features.
WLAN Authentication
• WPA2 (802.1x authentication + AES or TKIP encryption)
• WPA (802.1x authentication + TKIP or AES encryption)
• WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared key + AES encryption)
• WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared key + TKIP encryption)
• EAP-FAST (Extensible Authentication Protocol - Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling)
• EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol - Transport Layer Security)
• PEAP-GTC (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol - Generic Token Card)
• PEAP-MSCHAPv2 (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol - Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication
Protocol version 2)
• 802.11r / Fast Transition (FT)
• CCKM (Cisco Centralized Key Management)
• None
WLAN Encryption
• AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
• TKIP / MIC (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol / Message Integrity Check)
• WEP (Wired Equivalent Protocol) 40/64 and 104/128 bit
Page 29

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
29
Note: Shared Key authentication is not supported.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX also support the following additional security features.
• Image authentication
• Device authentication
• File authentication
• Signaling authentication
• Secure Cisco Unified SRST
• Media encryption (SRTP)
• Signaling encryption (TLS)
• Certificate authority proxy function (CAPF)
• Secure profiles
• Encrypted configuration files
• Settings Access (can limit user access to configuration menus)
Extensible Authentication Protocol - Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling (EAP-FAST)
Extensible Authentication Protocol - Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling (EAP-FAST) encrypts EAP transactions
within a Transport Level Security (TLS) tunnel between the access point and the Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service
(RADIUS) server such as the Cisco Access Control Server (ACS) or Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE).
The TLS tunnel uses Protected Access Credentials (PACs) for authentication between the client (the Cisco Wireless IP Phone
8821 and 8821-EX) and the RADIUS server. The server sends an Authority ID (AID) to the client, which in turn selects the
appropriate PAC. The client returns a PAC-Opaque to the RADIUS server. The server decrypts the PAC with its master-key.
Both endpoints now have the PAC key and a TLS tunnel is created. EAP-FAST supports automatic PAC provisioning, but it
must enable don the RADIUS server.
To enable EAP-FAST, a certificate must be installed on to the RADIUS server.
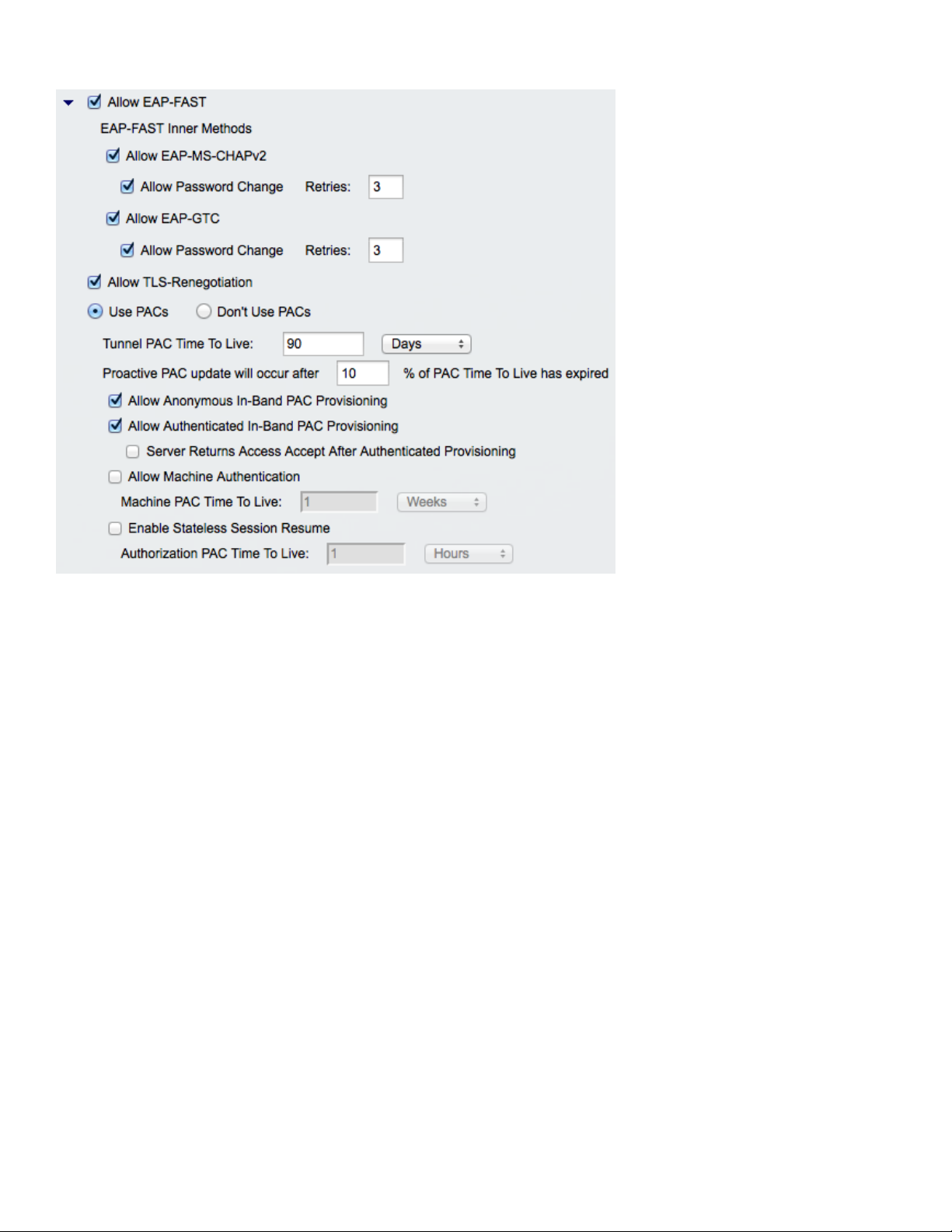
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX currently support automatic provisioning of the PAC only, so enable Allow
anonymous in-band PAC provisioning on the RADIUS server as shown below.
Both EAP-GTC and EAP-MSCHAPv2 must be enabled when Allow anonymous in-band PAC provisioning is enabled.
EAP-FAST requires that a user account be created on the authentication server.
Page 30
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
30
If anonymous PAC provisioning is not allowed in the production wireless LAN environment then a staging RADIUS server can
be setup for initial PAC provisioning of the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
This requires that the staging RADIUS server be setup as a slave EAP-FAST server and components are replicated from the
product master EAP-FAST server, which include user and group database and EAP-FAST master key and policy info.
Ensure the production master EAP-FAST RADIUS server is setup to send the EAP-FAST master keys and policies to the
staging slave EAP-FAST RADIUS server, which will then allow the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX to use the
provisioned PAC in the production environment where Allow anonymous in-band PAC provisioning is disabled.
When it is time to renew the PAC, then authenticated in-band PAC provisioning will be used, so ensure that Allow
authenticated in-band PAC provisioning is enabled.
Ensure that the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX has connected to the network during the grace period to ensure it
can use its existing PAC created either using the active or retired master key in order to get issued a new PAC.
Is recommended to only have the staging wireless LAN pointed to the staging RADIUS server and to disable the staging access
point radios when not being used.
Extensible Authentication Protocol - Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS)
Extensible Authentication Protocol - Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) is using the TLS protocol with PKI to secure
communications to the authentication server.
TLS provides a way to use certificates for both user and server authentication and for dynamic session key generation.
A certificate is required to be installed.
EAP-TLS provides excellent security, but requires client certificate management.
Page 31

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
31
EAP-TLS may also require a user account to be created on the authentication server matching the common name of the
certificate imported into the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 or 8821-EX.
It is recommended to use a complex password for this user account and that EAP-TLS is the only EAP type enabled on the
RADIUS server.
Page 32

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
32
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) uses server-side public key certificates to authenticate clients by creating
an encrypted SSL/TLS tunnel between the client and the authentication server.
The ensuing exchange of authentication information is then encrypted and user credentials are safe from eavesdropping.
PEAP-GTC and PEAP-MSCHAPv2 are supported inner authentication protocols.
PEAP requires that a user account be created on the authentication server.
The authentication server can be validated via importing a certificate into the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
For more information on Cisco Secure Access Control System (ACS) and Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), refer to the
following links.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/secure-access-control-system/datasheet-listing.html
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/identity-services-engine/datasheet-listing.html
EAP and User Database Compatibility
The following chart displays the EAP and database configurations supported by the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821EX.
Database Type
EAP-FAST
(Phase Zero)
EAP-TLS
PEAP-GTC
PEAP-MSCHAPv2
Cisco ACS
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Windows SAM
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Windows AD
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
LDAP
No
Yes
Yes
No
ODBC
(ACS for Windows Only)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Page 33

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
33
LEAP Proxy RADIUS
Server
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
All Token Servers
No
No
No
No
Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service enables queuing to ensure high priority for voice traffic.
To enable proper queuing for voice and call control traffic use the following guidelines.
• Ensure that WMM is enabled on the access point.
• Create a QoS policy on the access point giving priority to voice and call control traffic.
Traffic Type
DSCP
802.1p
WMM UP
Port Range
Voice
EF (46)
5 6 UDP 16384 - 32767
Call Control
CS3 (24)
3 4 TCP 5060 - 5061
• Be sure that voice and call control packets have the proper QoS markings and other protocols are not using the same
QoS markings.
• Enable Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) preservation on the Cisco IOS switch.
For more information about TCP and UDP ports used by the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX and the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, refer to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager TCP and UDP Port Usage document at this
URL:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/voice_ip_comm/cucm/port/10_0_1/CUCM_BK_T537717B_00_tcp-port-usage-guide-
100.html
Call Admission Control (CAC)
Call Admission Control can be enabled on the access point.
• Enable Call Admission Control (CAC) / Wi-Fi MultiMedia Traffic Specifications (TSPEC) for Voice
• Set the desired maximum RF bandwidth that is allocated for voice traffic (default = 75%)
• Set the bandwidth that is reserved for roaming voice clients (default = 6%)
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will specify 12 Mbps for the PHY rate to be used for TSPEC.
Pre-Call Admission Control
If Call Admission Control is enabled on the access point, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will send an Add
Traffic Stream (ADDTS) to the access point to request bandwidth in order to place or receive a call.
Page 34

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
34
If the AP sends an ADDTS successful message then the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 or 8821-EX establishes the call.
If the access point rejects the call and the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 or 8821-EX has no other access point to roam to, then
the phone will display Network Busy.
If the admission is refused for an inbound call there is no messaging from the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 or 8821-EX to
inform the remote endpoint that there is insufficient bandwidth to establish the call, so the call can continue to ring out within
the system until the remote user terminates the call.
Roaming Admission Control
During a call, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX measure Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) and Packet
Error Rate (PER) values for the current and all available access points to make roaming decisions.
If the original access point where the call was established had Call Admission Control enabled, then the Cisco Wireless IP
Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will send an ADDTS request during the roam to the new access point, which embedded in the
reassociation request frame.
Traffic Classification (TCLAS)
Traffic Classification (TCLAS) helps to ensure that the access point properly classifies voice packets.
Without proper classification, voice packets will be treated as best effort, which will defeat the purpose of TSPEC and QoS in
general.
TCP and UDP port information will be used to set the UP (User Priority) value.
The previous method of classification depends upon preservation of DSCP value throughout the network, where the DSCP
value maps to a particular queue (BE, BK, VI, VO).
However, the DSCP values are not always preserved as this can be viewed as a security risk.
Using port based QoS policies is inadequate for CAPWAP based wireless LAN solutions as all data packets use the same UDP
port (CAPWAP = UDP 5246) and the access point uses the outside QoS marking to determine which queue the packets should
be placed in.
With TCLAS, DSCP preservation is not a requirement.
Call Admission Control must be enabled on the access point in order to enable TCLAS.
TCLAS will be negotiated within the ADDTS packets, which are used to request bandwidth in order to place or receive a call.
QoS Basic Service Set (QBSS)
There are three different versions of QoS Basic Service Set (QBSS) that the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX
support.
The first version from Cisco was on a 0-100 scale and was not based on clear channel assessment (CCA), so it does not account
for channel utilization, but only the 802.11 traffic traversing that individual access point’s radio. So it does not account for
other 802.11 energy or interferers using the same frequencies.
QBSS is also a part of 802.11e, which is on a 0-255 scale and is CCA based. So this gives a true representation on how busy
the channel is. The max threshold is also defined on the client side, which is set to 105.
The second version from Cisco is based on the 802.11e version, but allows the default max threshold of 105 to be optionally
configured.
Each version of QBSS can be optionally be configured on the access point.
Page 35

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
35
Wired QoS
Configure QoS settings and policies for the necessary network devices.
Configuring Cisco Switch Ports for WLAN Devices
Configure the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Access Point switch ports as well as any uplink switch ports.
If utilizing Cisco IOS Switches, use the following switch port configurations.
Enable COS trust for Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
mls qos
!
interface X
mls qos trust cos
Enable DSCP trust for Cisco Access Points
mls qos
!
interface X
mls qos trust dscp
If utilizing Cisco Meraki MS Switches, reference the Cisco Meraki MS Switch VoIP Deployment Guide.
https://meraki.cisco.com/lib/pdf/meraki_whitepaper_msvoip.pdf
Note: When using the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, DSCP trust must be implemented or must trust the UDP data ports used
by the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller (CAPWAP = UDP 5246 and 5247) on all interfaces where wireless packets will traverse
to ensure QoS markings are correctly set.
Configuring Cisco Switch Ports for Wired IP Phones
Enable the Cisco wired IP phone switch ports for Cisco phone trust.
Below is a sample switch configuration:
mls qos
!
Interface X
mls qos trust device cisco-phone
mls qos trust dscp
Page 36

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
36
Roaming
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX default to Auto for the 802.11 mode, which allows the Cisco Wireless IP
Phone 8821 and 8821-EX to connect to either 5 GHz or 2.4 GHz and enables interband roaming support.
802.11r / Fast Transition (FT) is the recommended deployment model for all environment types where frequent roaming occurs.
802.1x authentication is required in order to utilize CCKM.
802.1x without 802.11r (FT) or CCKM can introduce delay during roaming due to its requirement for full re-authentication.
WPA and WPA2 introduce additional transient keys and can lengthen roaming time.
When 802.11r (FT) or CCKM is utilized, roaming times can be reduced from 400-500 ms to less than 100 ms, where that
transition time from one access point to another will not be audible to the user.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX support 802.11r (FT) with WPA2 (AES) or WPA2-PSK (AES) and CCKM
with WPA2 (AES or TKIP) and WPA (TKIP or AES).
Authentication
Roaming Time
WPA/WPA2 Personal
150 ms
WPA/WPA2 Enterprise
300 ms
802.11r (FT)
< 100 ms
CCKM
< 100 ms
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX manage the scanning and roaming events.
The roaming trigger for the majority of roams should be due to meeting the required RSSI differential based on the current
RSSI, which results in seamless roaming (no voice interruptions).
For seamless roaming to occur, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX must be associated to an access point for at
least 3 seconds, otherwise roams can occur based on packet loss (max tx retransmissions or missed beacons).
Roaming based on RSSI may not occur if the current signal has met the strong RSSI threshold.
Fast Secure Roaming (FSR)
802.11r / Fast Transition (FT) is the recommended deployment model for all environment types where frequent roaming occurs.
Cisco Centralized Key Management (CCKM) is also supported, but requires 802.1x authentication.
802.11r (FT) and CCKM enable fast secure roaming and limits the off-network time to keep audio gaps at a minimum when on
call.
802.1x or PSK without 802.11r (FT) and 802.1x without CCKM can introduce delay during roaming due to its requirement for
full re-authentication. WPA and WPA2 introduce additional transient keys and can lengthen roaming time.
802.11r (FT) and CCKM centralizes the key management and reduces the number of key exchanges.
When 802.11r (FT) or CCKM is utilized, roaming times can be reduced from 400-500 ms to less than 100 ms, where that
transition time from one access point to another will not be audible to the user.
There are two methods of 802.11r (FT) roaming.
Page 37

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
37
Over the Air
The client communicates directly with the target access point using 802.11 authentication with the FT authentication
algorithm.
Over the Distribution
The client communicates with the target access point through the current access point. The communication between
the client and the target access point is carried in FT action frames between the client and the current access point via
the WLAN controller.
802.11r (FT) utilizing the Over the Air method is the recommended fast secure roaming model to deploy.
Since the 802.11r (FT) plus Over the Distribution method requires connectivity to the currently associated access point, this
method may not work well if the phone is not always able to communicate with the current access point as well as the target
access point, which could occur in non-open environments if line of sight to both the current access point and the target access
point can not be retained when a roaming event occurs.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX support 802.11r (FT) with WPA2-PSK or WPA2 and CCKM with WPA2 or
WPA.
FSR Type
Authentication
Key Management
Encryption
802.11r (FT)
PSK
WPA2
AES
802.11r (FT)
EAP-FAST
WPA2
AES
802.11r (FT)
EAP-TLS
WPA2
AES
802.11r (FT)
PEAP-GTC
WPA2
AES
802.11r (FT)
PEAP-MSCHAPv2
WPA2
AES
CCKM
EAP-FAST
WPA2, WPA
AES, TKIP
CCKM
EAP-TLS
WPA2, WPA
AES, TKIP
CCKM
PEAP-GTC
WPA2, WPA
AES, TKIP
CCKM
PEAP-MSCHAPv2
WPA2, WPA
AES, TKIP
Interband Roaming
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX default to Auto for the frequency band mode, which enables interband
roaming and currently gives preference to the strongest signal. Typically this will give preference to 2.4 GHz over 5 GHz due
to 2.4 GHz having a stronger signal in general assuming the power levels are the same.
At power on, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will scan all 2.4 and 5 GHz channels when in Auto mode, then
attempt to associate to an access point for the configured network if available.
If configured for 5 GHz only or 2.4 GHz only mode, then just those channels are scanned.
It is recommended to perform a spectrum analysis to ensure that the desired bands can be enabled in order to perform interband
roaming.
Page 38

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
38
Scanning
There are three different scan modes (Continuous, Auto, Single AP), which can be configured for the Cisco Wireless IP Phone
8821 and 8821-EX in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
When using multiple access points where seamless roaming is required, Continuous (default) or Auto scan mode should be
enabled (Single AP scan mode should not be used if multiple access points exist).
Continuous scan mode is the default scan mode, which enables seamless roaming while also conserving battery life.
When on an active call with Continuous or Auto scan mode enabled, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will be
continuously scanning regardless of the current call state (idle or on call) or current access point signal level (RSSI).
When in idle (not on an active call) and Continuous scan mode is enabled, then the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821EX will also be continuously scanning.
When in idle with Auto scan mode, scans will only occur when the pre-defined RSSI threshold is held for the pre-defined
duration.
Continuous scan mode is recommended for environments where frequent roams occur or where smaller cells (pico cells) exist.
Continuous scan mode can also help with location tracking.
If using only one access point, select Single AP mode on the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX to reduce scanning
and optimize battery life.
Power Management
When the access point supports the Cisco Client Extensions (CCX) proxy ARP information element, the idle battery life will be
optimized. Proxy ARP allows the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX to remain in sleep mode longer versus waking
up at each Delivery Traffic Indicator Message (DTIM) period to check for incoming broadcasts.
To optimize battery life, the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will utilize either U-APSD or PS-POLL power save
methods depending on whether Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM) is enabled in the Access Point configuration or not.
If the access point does not support CCX or proxy ARP is not enabled, then the idle battery life will be up to fifty percent less.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX primarily use U-APSD when in idle or on call.
Null Power Save (PS-NULL) frames are utilized for off-channel scanning.
Wireless LAN is automatically disabled temporarily when Ethernet is connected by docking the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821
or 8821-EX when a USB to Ethernet dongle is attached, but will be automatically re-enabled once Ethernet is disconnected.
Use of a supported USB to Ethernet dongle is for initial provisioning purposes only and not to convert the Cisco Wireless IP
Phone 8821 or 8821-EX to a wired IP phone.
Delivery Traffic Indicator Message (DTIM)
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX can use the DTIM period to schedule wakeup periods to check for broadcast
and multicast packets as well as any unicast packets.
If proxy ARP is enabled, then the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX do not have to wake up at DTIM.
For optimal battery life and performance, is recommended to set the DTIM period to 2 with a beacon period of 100 ms.
The DTIM period is a tradeoff between battery life and multicast performance.
Broadcast and multicast traffic will be queued until the DTIM period when there are power save enabled clients associated to
the access point, so DTIM will determine how quickly these packets can be delivered to the client. If using multicast
applications, a shorter DTIM period can be used.
When multiple multicast streams exist on the wireless LAN frequently, then it is recommended to set the DTIM period to 1.
Page 39

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
39
Dynamic Transmit Power Control (DTPC)
To ensure packets are exchanged successfully between the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 or 8821-EX and the access point,
Dynamic Transmit Power Control (DTPC) should be enabled.
DTPC prevents one-way audio when RF traffic is heard in one direction only.
If the access point does not support DTPC, then the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will use the highest available
transmit power depending on the current channel and data rate.
The access point’s radio transmit power should not have a transmit power greater than what the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821
and 8821-EX can support.
Call Capacity
Design the network to accommodate the desired call capacity.
The Cisco Access Point can support up to 27 bi-directional voice streams for both 802.11a/n/ac and 802.11g/n at a data rate of
24 Mbps or higher. To achieve this capacity, there must be minimal wireless LAN background traffic and initial radio frequency
(RF) utilization.
The number of calls may vary depending on the data rate, initial channel utilization, and the environment.
Audio Only Calls
Below lists the maximum number of audio only calls (single bi-directional voice stream) supported per access point / channel.
Max # of
Streams
Audio Codec
Audio
Bit Rate
802.11 Mode
Data Rate
13
G.722 / G.711
64 Kbps
802.11a/n or 802.11g/n +
Bluetooth Disabled
6 Mbps
20
G.722 / G.711
64 Kbps
802.11a/n or 802.11g/n +
Bluetooth Disabled
12 Mbps
27
G.722 / G.711
64 Kbps
802.11a/n/ac or 802.11g/n
+ Bluetooth Disabled
24 Mbps or higher
Multicast
When enabling multicast in the wireless LAN, performance and capacity must be considered.
If there is an associated client that is in power save mode, then all multicast packets will be queued until the DTIM period.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX utilize active mode primarily, but if there is an associated client that is in
power save mode, then all multicast packets will be queued until the DTIM period.
With multicast, there is no guarantee that the packet will be received the by the client.
The multicast traffic will be sent at the highest mandatory / basic data rate enabled on the access point, so will want to ensure
that only the lowest enabled rate is configured as the only mandatory / basic rate.
The client will send the IGMP join request to receive that multicast stream. The client will send the IGMP leave when the
session is to be ended.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX support the IGMP query feature, which can be used to reduce the amount of
multicast traffic on the wireless LAN when not necessary.
Ensure that IGMP snooping is also enabled on all switches.
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
Page 40

40
Note: If using Coexistence where 802.11b/g/n and Bluetooth are being used simultaneously, then multicast voice is not
supported.
Configuring the Cisco Wireless LAN
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller and Lightweight Access Points
When configuring the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller and Lightweight Access Points, use the following guidelines:
• Ensure 802.11r (FT) or CCKM is Enabled
• Set Quality of Service (QoS) to Platinum
• Set the WMM Policy to Required
• Ensure Session Timeout is enabled and configured correctly
• Ensure Aironet IE is Enabled
• Set DTPC Support to Enabled
• Disable P2P (Peer to Peer) Blocking Action
• Ensure Client Exclusion is configured correctly
• Disable DHCP Address Assignment Required
• Set MFP Client Protection to Optional or Disabled
• Set the DTIM Period to 2
• Set Client Load Balancing to Disabled
• Set Client Band Select to Disabled
• Set IGMP Snooping to Enabled
• Enable Symmetric Mobile Tunneling Mode if Layer 3 mobility is utilized
• Enable ClientLink if utilizing Cisco 802.11n capable Access Points
• Configure the Data Rates as necessary
• Enable CCX Location Measurement
• Configure Auto RF as necessary
• Set Admission Control Mandatory to Enabled for Voice
• Set Load Based CAC to Enabled for Voice
• Enable Traffic Stream Metrics for Voice
• Set Admission Control Mandatory to Disabled for Video
• Set EDCA Profile to Voice Optimized or Voice and Video Optimized
• Set Enable Low Latency MAC to Disabled
• Ensure that Power Constraint is Disabled
• Enable Channel Announcement and Channel Quiet Mode
• Configure the High Throughput Data Rates as necessary
Page 41

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
41
• Configure the Frame Aggregation settings
• Enable CleanAir if utilizing Cisco Access Points with CleanAir technology
• Configure Multicast Direct Feature as necessary
• Set the 802.1p tag to 5 for the Platinum QoS profile
802.11 Network Settings
It is recommended to have the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX operate on the 5 GHz band only due to have many
channels available and not as many interferers as the 2.4 GHz band has.
If wanting to use 5 GHz, ensure the 802.11a/n/ac network status is Enabled.
Set the Beacon Period to 100 ms.
Ensure DTPC Support is enabled.
If using Cisco 802.11n capable Access Points, ensure ClientLink is enabled.
With the current releases, Maximum Allowed Clients can be configured.
Recommended to set 12 Mbps as the mandatory (basic) rate and 18 Mbps and higher as supported (optional) rates; however
some environments may require 6 Mbps to be enabled as a mandatory (basic) rate.
Enable CCX Location Measurement.
If wanting to use 2.4 GHz, ensure the 802.11b/g/n network status and 802.11g is enabled.
Set the Beacon Period to 100 ms.
Short Preamble should be Enabled in the 2.4 GHz radio configuration setting on the access point when no legacy clients that
require a long preamble are present in the wireless LAN. By using the short preamble instead of long preamble, the wireless
network performance is improved.
Ensure DTPC Support is enabled.
If using Cisco 802.11n capable Access Points, ensure ClientLink is enabled.
With the current releases, Maximum Allowed Clients can be configured.
Page 42

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
42
Recommended to set 12 Mbps as the mandatory (basic) rate and 18 Mbps and higher as supported (optional) rates assuming that
there will not be any 802.11b only clients that will connect to the wireless LAN; however some environments may require 6
Mbps to be enabled as a mandatory (basic) rate.
If 802.11b clients exist, then 11 Mbps should be set as the mandatory (basic) rate and 12 Mbps and higher as supported
(optional).
Enable CCX Location Measurement.
Beamforming (ClientLink)
Enable ClientLink if using Cisco 802.11n capable Access Points.
For releases prior to 7.2.103.0, ClientLink can be enabled globally via the 802.11 Global Parameters section or on individual
access points via the access point’s 802.11 radio configuration page.
As of release 7.2.103.0, ClientLink is no longer configurable via the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller’s web interface and is
only configurable via command line.
With releases 7.2.103.0 and later use the following commands to enable the beamforming feature globally for all access points
or for individual access point radios.
(Cisco Controller) >config 802.11a beamforming global enable
(Cisco Controller) >config 802.11a beamforming ap <ap_name> enable
(Cisco Controller) >config 802.11b beamforming global enable
(Cisco Controller) >config 802.11b beamforming ap <ap_name> enable
The current status of the beamforming feature can be displayed by using the following command.
(Cisco Controller) >show 802.11a
(Cisco Controller) >show 802.11b
Page 43

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
43
Legacy Tx Beamforming setting.................... Enabled
Auto RF (RRM)
When using the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller it is recommended to enable Auto RF to manage the channel and transmit
power settings.
Configure the access point transmit power level assignment method for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which frequency band
is to be utilized.
If using automatic power level assignment, a maximum and minimum power level can be specified.
Page 44

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
44
If using 5 GHz, it is recommended to enable up to 12 channels only to avoid any potential delay of access point discovery due
to having to scan many channels.
The 5 GHz channel width can be configured for 20 MHz or 40 MHz if using Cisco 802.11n Access Points and 20 MHz, 40
MHz, or 80 MHz if using Cisco 802.11ac Access Points.
If using 2.4 GHz, only channels 1, 6, and 11 should be enabled in the DCA list.
It is recommended to configure the 2.4 GHz channel for 20 MHz even if using Cisco 802.11n Access Points capable of 40 MHz
due to the limited number of channels available in 2.4 GHz.
Page 45

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
45
Individual access points can be configured to override the global setting to use dynamic channel and transmit power assignment
for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which frequency band is to be utilized.
Other access points enabled can be enabled for Auto RF and workaround the access points that are statically configured.
This may be necessary if there is an intermittent interferer present in an area.
The 5 GHz channel width can be configured for 20 MHz or 40 MHz if using Cisco 802.11n Access Points and 20 MHz, 40
MHz, or 80 MHz if using Cisco 802.11ac Access Points.
It is recommended to use channel bonding only if using 5 GHz.
Page 46

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
46
Client Roaming
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX do not utilize the RF parameters in the Client Roaming section of the Cisco
Wireless LAN Controller as scanning and roaming is managed independently by the phone itself.
EDCA Parameters
Set the EDCA profile for Voice Optimized and disable Low Latency MAC for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which
frequency band is to be utilized.
Low Latency MAC (LLM) reduces the number of retransmissions to 2-3 per packet depending on the access point platform, so
it can cause issues if multiple data rates are enabled.
LLM is not supported on the Cisco 802.11n/ac Access Points.
DFS (802.11h)
In the DFS (802.11h) configuration, channel announcement and quiet mode should be enabled.
Power Constraint should be left un-configured or set to 0 dB as DTPC will be used by the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and
8821-EX to control the transmission power.
In later versions of the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller it does not allow both TPC (Power Constraint) and DTPC (Dynamic
Transmit Power Control) to be enabled simultaneously.
Channel Announcement and Channel Quiet Mode should be enabled.
Page 47

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
47
High Throughput (802.11n/ac)
The 802.11n data rates can be configured per radio (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz).
802.11ac data rates are applicable to 5 GHz only.
Ensure that WMM is enabled and WPA2(AES) is configured in order to utilize 802.11n/ac data rates.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX support HT MCS 0 - MCS 7 and VHT MCS 0 - MCS 9 data rates only, but
higher MCS rates can optionally be enabled if there are other 802.11n/ac clients utilizing the same band frequency that include
MIMO antenna technology, which can take advantage of the those higher data rates.
It is recommended to disable MCS 0.
Frame Aggregation
Frame aggregation is a process of packaging multiple MAC Protocol Data Units (MPDUs) or MAC Service Data Units
(MSDUs) together to reduce the overheads where in turn throughput and capacity can be optimized.
Aggregation of MAC Protocol Data Unit (A-MPDU) requires the use of block acknowledgements.
It is recommended to adjust the A-MPDU and A-MSDU settings to the following to optimize the experience with the Cisco
Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
A-MPDU
User Priority 0, 3, 4, 5 = Enabled
User Priority 1, 2, 6, 7 = Disabled
A-MSDU
User Priority 1, 2 = Enabled
User Priority 0, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 = Disabled
Page 48

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
48
In the 7.0.116.0 release for the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, the default A-MPDU and A-MSDU configuration is the
following.
A-MPDU
User Priority 0, 4, 5 = Enabled
User Priority 1, 2, 3, 6, 7 = Disabled
A-MSDU
User Priority 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 = Enabled
User Priority 6, 7 = Disabled
Use the following commands to configure the A-MPDU and A-MSDU settings per the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821EX recommendations.
In order to configure the 5 GHz settings, the 802.11a network will need to be disabled first, then re-enabled after the changes
are complete.
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 0 enable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 3 enable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 4 enable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 5 enable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 1 disable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 2 disable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 6 disable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 7 disable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 1 enable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 2 enable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 0 disable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 3 disable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 4 disable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 5 disable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 6 disable
config 802.11a 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 7 disable
In order to configure the 2.4 GHz settings, the 802.11b/g network will need to be disabled first, then re-enabled after the
changes are complete.
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 0 enable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 3 enable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 4 enable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 5 enable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 1 disable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 2 disable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 6 disable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-mpdu tx priority 7 disable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 1 enable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 2 enable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 0 disable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 3 disable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 4 disable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 5 disable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 6 disable
config 802.11b 11nSupport a-msdu tx priority 7 disable
To view the current A-MPDU and A-MSDU configuration, enter either show 802.11a for 5 GHz or show 802.11b for 2.4 GHz.
Page 49

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
49
802.11n Status:
A-MPDU Tx:
Priority 0............................... Enabled
Priority 1............................... Disabled
Priority 2............................... Disabled
Priority 3............................... Enabled
Priority 4............................... Enabled
Priority 5............................... Enabled
Priority 6............................... Disabled
Priority 7............................... Disabled
A-MSDU Tx:
Priority 0............................... Disabled
Priority 1............................... Enabled
Priority 2............................... Enabled
Priority 3............................... Disabled
Priority 4............................... Disabled
Priority 5............................... Disabled
Priority 6............................... Disabled
Priority 7............................... Disabled
CleanAir
CleanAir should be Enabled when utilizing Cisco Access Points with CleanAir technology in order to detect any existing
interferers.
Page 50

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
50
Page 51

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
51
WLAN Settings
It is recommended to have a separate SSID for the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
However, if there is an existing SSID configured to support voice capable Cisco Wireless LAN endpoints already, then that
WLAN can be utilized instead.
The SSID to be used by the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX can be configured to only apply to a certain 802.11
radio type (e.g. 802.11a only).
It is recommended to have the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX operate on the 5 GHz band only due to have many
channels available and not as many interferers as the 2.4 GHz band has.
Ensure that the selected SSID is not utilized by any other wireless LANs as that could lead to failures when powering on or
during roaming; especially if a different security type is utilized.
To utilize 802.11r (FT) for fast secure roaming, check the box to enable Fast Transition.
Is recommended to uncheck Over the Distribution to utilize the Over the Air method instead of the Over the Distribution
System method.
Enable WPA2 policy with AES encryption then either FT 802.1x or FT PSK for authenticated key management type depending
on whether 802.1x or PSK is to be utilized.
Page 52

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
52
802.1x, CCKM and/or PSK may also be enabled if wanting to utilize the same SSID for various type of voice clients, where
some clients do not support 802.11r (FT) depending on whether 802.1x or PSK is being utilized.
To utilize CCKM for fast secure roaming, enable WPA2 policy with AES encryption and 802.1x + CCKM for authenticated
key management type.
Page 53

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
53
The WMM policy should be set to Required only if the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX or other WMM enabled
phones will be using this SSID.
If there are non-WMM clients existing in the WLAN, it is recommended to put those clients on another WLAN.
If non-other WMM clients must utilize the same SSID as the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX, then ensure the
WMM policy is set to Allowed.
Enabling WMM will enable the 802.11e version of QBSS. There are also the 7920 Client CAC and 7920 AP CAC options,
where 7920 Client CAC will enable Cisco version 1 and 7920 AP CAC enables Cisco version 2.
Page 54

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
54
Configure Enable Session Timeout as necessary per your requirements. It is recommended to either disable the session
timeout or extend the timeout (e.g. 24 hours / 86400 seconds) to avoid possible interruptions during audio calls. If disabled it
will avoid any potential interruptions altogether, but enabling session timeout can help to re-validate client credentials
periodically to ensure that the client is using valid credentials.
Enable Aironet Extensions (Aironet IE).
Peer to Peer (P2P) Blocking Action should be disabled.
Configure Client Exclusion as necessary.
The Maximum Allowed Clients Per AP Radio can be configured as necessary.
Off Channel Scanning Defer can be tuned to defer scanning for certain queues as well as the scan defer time.
If using best effort applications frequently (e.g. VPN, etc.) or if DSCP values for priority applications (e.g. voice, video, call
control) are not preserved to the access point, then is recommended to enable the lower priority queues (0-3) along with the
higher priority queues (4-7) to defer off channel scanning as well as potentially increasing the scan defer time.
DHCP Address Assignment Required should be disabled.
Management Frame Protection should be set to Optional or Disabled.
Use a DTIM Period of 2 with a beacon period of 100 ms.
Ensure Client Load Balancing and Client Band Select are disabled.
Media Session Snooping can be enabled to utilize SIP CAC.
It is recommended to set Re-anchor Roamed Voice Clients to disabled as this can cause brief interruptions with wireless LAN
connectivity when a call is terminated after performing an inter-controller roaming.
Page 55

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
55
AP Groups
AP Groups can be created to specify which WLANs / SSIDs are to be enabled and which interface they should be mapped to as
well as what RF Profile parameters should be used for the access points assigned to the AP Group.
On the WLANs tab, select the desired SSIDs and interfaces to map to then select Add.
Page 56

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
56
On the RF Profile tab, select the desired 802.11a or 802.11b RF Profile, then select Apply.
If changes are made after access points have joined the AP Group, then those access points will reboot once those changes are
made.
On the APs tab, select the desired access points then select Add APs.
Those access points will then reboot.
Controller Settings
Ensure the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller hostname is configured correctly.
Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
Page 57

57
Enable Link Aggregation (LAG) if utilizing multiple ports on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller.
Configure the desired AP multicast mode.
If utilizing multicast, then Enable Global Multicast Mode and Enable IGMP Snooping should be enabled.
If utilizing layer 3 mobility, then Symmetric Mobility Tunneling should be Enabled.
In the recent versions, Symmetric Mobility Tunneling is enabled by default and non-configurable.
Page 58

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
58
When multiple Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers are to be in the same mobility group, then the IP address and MAC address of
each Cisco Wireless LAN Controller should be added to the Static Mobility Group Members configuration.
Call Admission Control (CAC)
It is recommended to enable Admission Control Mandatory for Voice and configure the maximum bandwidth and reserved
roaming bandwidth percentages for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which frequency band is to be utilized.
The maximum bandwidth default setting for voice is 75% where 6% of that bandwidth is reserved for roaming clients.
Roaming clients are not limited to using the reserved roaming bandwidth, but roaming bandwidth is to reserve some bandwidth
for roaming clients in case all other bandwidth is utilized.
If CAC is to be enabled, will want to ensure Load-based CAC is enabled.
Load-based CAC will account for all energy on the channel.
SIP CAC can help ensure that downstream voice frames are prioritized correctly when a client does not support TSPEC.
Load based CAC logic is utilized with SIP CAC, so all 802.11 traffic and energy on the channel is accounted for to determine
available bandwidth.
Page 59

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
59
The access point has different methods for Call Admission Control when using SIP CAC depending on whether the client uses
TCP or UDP for SIP communications.
If the client uses TCP for SIP, then the access point will snoop the SIP packets when media session snooping is enabled on the
WLAN and will not forward the SIP frames upstream or downstream if there is not bandwidth available for the new voice
stream. This could potentially result in loss of registration to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
If the client uses UDP for SIP, then the access point will snoop the SIP packets when media session snooping is enabled on the
WLAN and will sent a 486 busy message to the client, which in turn can be interpreted as a Network Busy message and the
client could either roam to another access point or simply terminate the call setup for that session.
The Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX use TCP for SIP communications, therefore if the channel is busy where
another call can not be allowed, then the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX could potentially lose registration to the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager if SIP CAC is enabled.
Admission Control Mandatory for Video should be disabled.
Page 60

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
60
If Call Admission Control for voice is enabled, then the following configuration should be active, which can be displayed in the
show run-config.
Call Admission Control (CAC) configuration
Voice AC - Admission control (ACM)............ Enabled
Voice max RF bandwidth........................ 75
Voice reserved roaming bandwidth.............. 6
Voice load-based CAC mode..................... Enabled
Voice tspec inactivity timeout................ Disabled
Video AC - Admission control (ACM)............ Disabled
Voice Stream-Size............................. 84000
Voice Max-Streams............................. 2
Video max RF bandwidth........................ 25
Video reserved roaming bandwidth.............. 6
The voice stream-size and voice max-streams values can be adjusted as necessary by using the following command.
(Cisco Controller) >config 802.11a cac voice stream-size 84000 max-streams 2
Ensure QoS is setup correctly under the configuration, which can be displayed by using the following command.
(Cisco Controller) >show wlan <WLAN id>
Quality of Service............................... Platinum (voice)
WMM.............................................. Allowed
Page 61

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
61
Dot11-Phone Mode (7920).......................... ap-cac-limit
Wired Protocol................................... 802.1P (Tag=5)
In the Media settings, Unicast Video Redirect and Multicast Direct Enable should be enabled.
RF Profiles
RF Profiles can be created to specify which frequency bands, data rates, RRM settings, etc. a group of access points should use.
It is recommended to have the SSID used by the Cisco Wireless IP Phone and 8821 and 8821-EX to be applied to 5 GHz radios
only.
RF Profiles are applied to an AP group once created.
When creating an RF Profile, the RF Profile Name and Radio Policy must be defined.
Select 802.11a or 802.11b/g for the Radio Policy.
Page 62

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
62
On the 802.11 tab, configure the data rates as desired.
Is recommended to enable 12 Mbps as Mandatory and 18 Mbps and higher as Supported; however some environments may
require 6 Mbps to be enabled as a mandatory (basic) rate.
On the RRM tab, the Maximum Power Level Assignment and Minimum Power Level Assignment settings as well as other
TPC and Coverage Hole Detection settings can be configured.
On the High Density tab, Maximum Clients and Multicast Data Rates can be configured.
Page 63

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
63
FlexConnect Groups
All access points configured for FlexConnect mode need to be added to a FlexConnect Group.
If utilizing CCKM, then seamless roams can only occur when roaming to access points within the same FlexConnect Group.
Multicast Direct
In the Media Stream settings, Multicast Direct feature should be enabled.
Page 64

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
64
After Multicast Direct feature is enabled, then there will be an option to enable Multicast Direct in the QoS menu of the
WLAN configuration.
QoS Profiles
Configure the four QoS profiles (Platinum, Gold, Silver, Bronze), by selecting 802.1p as the protocol type and set the 802.1p
tag for each profile.
• Platinum = 5
• Gold = 4
• Silver = 2
• Bronze = 1
Page 65

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
65
Page 66

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
66
Page 67

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
67
Page 68

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
68
Note: The 802.1p tag mappings were changed with the 7.5.102.0 release.
Prior to the 7.5.102.0 release, Platinum = 6, Gold = 5, Silver = 3, Bronze = 1.
Advanced Settings
Advanced EAP Settings
Need to ensure that the advanced EAP settings in the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller are configured per the information below.
To view the EAP configuration on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and enter the following
command.
(Cisco Controller) >show advanced eap
EAP-Identity-Request Timeout (seconds)........... 30
EAP-Identity-Request Max Retries................. 2
EAP Key-Index for Dynamic WEP.................... 0
EAP Max-Login Ignore Identity Response........... enable
EAP-Request Timeout (seconds).................... 30
EAP-Request Max Retries.......................... 2
EAPOL-Key Timeout (milliseconds)...................... 400
Page 69

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
69
EAPOL-Key Max Retries............................ 4
If using 802.1x or WPA/WPA2, the EAP-Request Timeout on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller should be set to at least 20
seconds.
In later versions of Cisco Wireless LAN Controller software, the default EAP-Request Timeout was changed from 2 to 30
seconds.
To change the EAP-Request Timeout on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and enter the
following command.
(Cisco Controller) >config advanced eap request-timeout 30
If using WPA/WPA2 PSK then it is recommended to reduce the EAPOL-Key Timeout to 400 milliseconds from the
default of 1000 milliseconds with EAPOL-Key Max Retries set to 4 from the default of 2.
If using WPA/WPA2, then using the default values where the EAPOL-Key Timeout is set to 1000 milliseconds and
EAPOL-Key Max Retries are set to 2 should work fine, but is still recommended to set those values to 400 and 4
respectively.
The EAPOL-Key Timeout should not exceed 1 second (1000 milliseconds).
To change the EAPOL-Key Timeout on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and enter the
following command.
(Cisco Controller) >config advanced eap eapol-key-timeout 400
To change the EAPOL-Key Max Retries Timeout on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and
enter the following command.
(Cisco Controller) >config advanced eap eapol-key-retries 4
Auto-Immune
The Auto-Immune feature can optionally be enabled for protection against denial of service (DoS) attacks.
Although when this feature is enabled there can be interruptions introduced with voice over wireless LAN, therefore it is
recommended to disable the Auto-Immune feature on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller.
To view the Auto-Immune configuration on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and enter the
following command.
(Cisco Controller) >show wps summary
Auto-Immune
Auto-Immune.................................... Disabled
Client Exclusion Policy
Page 70

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
70
Excessive 802.11-association failures.......... Enabled
Excessive 802.11-authentication failures....... Enabled
Excessive 802.1x-authentication................ Enabled
IP-theft....................................... Enabled
Excessive Web authentication failure........... Enabled
Signature Policy
Signature Processing........................... Enabled
To disable the Auto-Immune feature on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and enter the
following command.
(Cisco Controller) >config wps auto-immune disable
CCKM Timestamp Tolerance
The default CCKM timestamp tolerance is set to 1000 ms.
It is recommended to adjust the CCKM timestamp tolerance to 5000 ms to optimize the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and
8821-EX roaming experience.
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan security wpa akm cckm timestamp-tolerance ?
<tolerance> Allow CCKM IE time-stamp tolerance <1000 to 5000> milliseconds; Default tolerance 1000 msecs
Use the following command to configure the CCKM timestamp tolerance per Cisco recommendations.
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan security wpa akm cckm timestamp-tolerance 5000 <WLAN id >
To confirm the change, enter show wlan <WLAN id>, where the following will be displayed.
CCKM tsf Tolerance............................... 5000
TKIP Countermeasure Holdoff Time
TKIP countermeasure mode can occur if the access point receives two Message Integrity Check (MIC) errors within a 60
second period. When this occurs, the access point will de-authenticate all TKIP clients associated to that 802.11 radio and
holdoff any clients for the countermeasure holdoff time (default = 60 seconds).
To change the TKIP countermeasure holdoff time on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and
enter the following command specifying the number of seconds and WLAN ID.
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan security tkip hold-down <nseconds> <wlan-id>
To confirm the change, enter show wlan <WLAN id>, where the following will be displayed.
Page 71

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
71
Tkip MIC Countermeasure Hold-down Timer....... 60
Cisco Meraki Access Points
When configuring Cisco Meraki access points, use the following guidelines:
• Enable 802.11r for WPA2-Enterprise or Pre-shared key
• Set Splash page to None
• Enable Bridge mode
• Enable VLAN tagging
• Set Band selection to 5 GHz band only
• Configure the Data Rates as necessary
• Configure Quality of Service (QoS)
Creating the Wireless Network
A wireless network must be created prior to adding any Cisco Meraki access points to provide WLAN service.
Select Create a new network from the drop-down menu.
Select Wireless for Network type then click Create.
Cisco Meraki access points can be claimed either by specifying the serial number or order number.
Page 72

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
72
Once claimed, those Cisco Meraki access points will then be listed in the available inventory.
Cisco Meraki access points can be claimed either by selecting Claim on the Create network or Organization > Configure >
Inventory pages.
Access points can also be claimed by selecting Add APs on the Wireless > Monitor > Access points page, then selecting
Claim.
Once claimed, Cisco Meraki access points can be added to the desired wireless network via the Organization > Configure >
Inventory page.
Access points can also be added to a wireless network by selecting Add APs on the Wireless > Monitor > Access points page.
Page 73

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
73
SSID Configuration
To create a SSID, select the desired network from the drop-down menu then select Wireless > Configure > SSIDs.
It is recommended to have a separate SSID for the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX; data clients and other type of
clients should utilize a different SSID and VLAN.
However, if there is an existing SSID configured to support voice capable Cisco Wireless LAN endpoints already, then that
WLAN can be utilized.
To set the SSID name, select Rename.
To enable the SSID, select Enabled from the drop-down menu.
Page 74

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
74
On the Wireless > Configure > Access control page, select WPA2-Enterprise to enable 802.1x authentication.
The Cisco Meraki authentication server or an external RADIUS server can be utilized when selecting WPA2-Enterprise.
The Cisco Meraki authentication server supports PEAP authentication and requires a valid email address.
Other authentication types (e.g. Pre-Shared Key) are available as well.
Ensure 802.11r is enabled.
Ensure Splash page is set to None to enable direct access.
Note: Cisco Meraki access points support 802.11r (FT) for fast secure roaming, but do not support Cisco Centralized Key
Management (CCKM).
If WPA2-Enterprise is enabled where the Cisco Meraki authentication server will be utilized as the RADIUS server, then a
user account must be created on the Network-wide > Configure > Users page, which the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and
8821-EX will be configured to use for 802.1x authentication.
Note: Cisco Meraki access points do not support EAP-FAST.
Page 75

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
75
On the Wireless > Configure > Access control page, recommend to enable Bridge mode, where the Cisco Wireless IP Phone
8821 and 8821-EX will obtain DHCP from the local LAN instead of the Cisco Meraki network; unless call control, other
endpoints, etc. are cloud-based.
Once Bridge mode is enabled, the VLAN tagging option will be available.
It is recommended to enable VLAN tagging for the SSID.
If VLAN tagging is utilized, ensure that the Cisco Meraki access point is connected to a switch port configured for trunk mode
allowing that VLAN.
If utilizing Cisco Meraki MS Switches, reference the Cisco Meraki MS Switch VoIP Deployment Guide.
https://meraki.cisco.com/lib/pdf/meraki_whitepaper_msvoip.pdf
If utilizing Cisco IOS Switches, use the following switch port configuration for ports that have Cisco Meraki access points
connected to enable 802.1q trunking.
Interface GigabitEthernet X
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport mode trunk
mls qos trust dscp
Page 76

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
76
On the Wireless > Configure > Access control page, the frequency band for the SSID to be used by the Cisco Wireless IP
Phone 8821 and 8821-EX can be configured as necessary.
It is recommended to select 5 GHz band only to have the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX operate on the 5 GHz
band due to have many channels available and not as many interferers as the 2.4 GHz band has.
If the 2.4 GHz band needs to be used due to increased distance, then Dual band operation (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) should be
selected. Do not utilize the Dual band operation with Band Steering option.
Is recommended to disable data rates below 12 Mbps unless a legacy 2.4 GHz client needs to be able to connect to the Wireless
LAN.
Cisco Meraki access points currently utilize a DTIM period of 1 with a beacon period of 100 ms; which both are nonconfigurable.
On the Wireless > Configure > SSID availability page, the SSID can be broadcasted by setting Visibility to Advertise this
SSID publicly.
Is recommended to set Per-AP Availability to This SSID is enabled on all APs.
A schedule for SSID availability can be configured as necessary, however it is recommended to set Scheduled Availability to
Disabled.
Page 77

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
77
Radio Settings
On the Wireless > Configure > Radio settings page, configure what radio transmit power and channel settings to use.
For the Radio power setting, it is recommended to select Enable power reduction on nearby APs as co-channel interference
can be potentially reduced. If wanting to use maximum radio power, then select Always use 100% power.
Can select whether to enable use of DFS channels or not via the Auto channel option.
The Default 5 GHz channel width is set to 80 MHz by default and that channel width will be utilized if the access point is
802.11ac capable. The Default 5 GHz channel width can also be set to use 20 MHz or 40 MHz.
If Channel width is set to Auto for an access point, then that access point will use the value specified for Default 5 GHz
channel width if applicable for that access point model.
The channel width can also be configured on a per access point basis overriding the default.
2.4 GHz radios utilize 20 MHz channel width and can not be configured for 40 MHz channels.
When using Cisco Meraki access points it is recommended to select Auto for the channel and transmit power.
Page 78

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
78
When Auto is selected for 2.4 GHz channels, only channels 1, 6, and 11 will be utilized.
Configure the access point transmit power level assignment method for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which frequency band
is to be utilized.
Individual access points can be configured with static channel and transmit power for either 5 or 2.4 GHz radios, which may be
necessary if there is an intermittent interferer present in an area. While other access points can be enabled for Auto and work
around the access points that are have static channel assignments.
Note: Cisco Meraki access points do not support Dynamic Transmit Power Control (DTPC), therefore the Cisco Wireless IP
Phone 8821 and 8821-EX will utilize the maximum transmit power supported for the current channel and data rate.
Traffic Shaping
On the Wireless > Configure > Firewall & traffic shaping page, traffic shaping rules can be defined.
To allow traffic shaping rules to be defined select Shape traffic on this SSID in the drop-down menu for Shape traffic.
Once Shape traffic on this SSID has been applied, then select Create a new rule to define Traffic shaping rules.
By default, Cisco Meraki access points currently tag voice frames marked with DSCP EF (46) as WMM UP 5 instead of WMM
UP 6 and call control frames marked with DSCP CS3 (24) as WMM UP 3 instead of WMM UP 4.
Page 79

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
79
Note: Cisco Meraki access points do not support Call Admission Control / Traffic Specification (TSPEC).
Monitoring Clients
On the Network-wide > Monitor > Clients page, client information and statistics can be displayed.
Page 80

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
80
Cisco Autonomous Access Points
When configuring Cisco Autonomous Access Points, use the following guidelines:
• Ensure 802.11r (FT) or CCKM is Enabled
• Configure the Data Rates as necessary
• Enable DTPC
• Configure Quality of Service (QoS)
• Set the WMM Policy to Required
• Ensure Aironet Extensions is Enabled
• Disable Public Secure Packet Forwarding (PSPF)
• Set IGMP Snooping to Enabled
802.11 Network Settings
It is recommended to have the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX operate on the 5 GHz band only due to have many
channels available and not as many interferers as the 2.4 GHz band has.
If wanting to use 5 GHz, ensure the 802.11a/n/ac network status is Enabled.
Page 81

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
81
Is recommended to enable 11r over air to enable fast secure roaming.
Recommended to set 12 Mbps as the mandatory (basic) rate and 18 Mbps and higher as supported (optional) rates; however
some environments may require 6 Mbps to be enabled as a mandatory (basic) rate.
If using 5 GHz, it is recommended to enable up to 12 channels only to avoid any potential delay of access point discovery due
to having to scan many channels.
For Cisco Autonomous Access Points, select Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) to use auto channel selection.
When DFS is enabled, enable at least one band (bands 1-4).
Can select band 1 only for the access point to use a UNII-1 channel (channel 36, 40, 44, or 48).
Individual access points can be configured to override the global setting to use dynamic channel and transmit power assignment
for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which frequency band is to be utilized.
Other access points enabled can be enabled for Auto RF and workaround the access points that are statically configured.
This may be necessary if there is an intermittent interferer present in an area.
The 5 GHz channel width can be configured for 20 MHz or 40 MHz if using Cisco 802.11n Access Points and 20 MHz, 40
MHz, or 80 MHz if using Cisco 802.11ac Access Points.
Ensure Client Power is configured properly. Do not use default setting of Max power for client power on Cisco Autonomous
Access Points as that will not advertise DTPC to the client.
Enable Dot11d for World Mode and configure the proper Country Code.
Ensure Aironet Extensions is enabled.
Set the Beacon Period to 100 ms and DTIM to 2.
Page 82

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
82
Page 83

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
83
If wanting to use 2.4 GHz, ensure the 802.11b/g/n network status and 802.11g is enabled.
Recommended to set 12 Mbps as the mandatory (basic) rate and 18 Mbps and higher as supported (optional) rates assuming that
there will not be any 802.11b only clients that will connect to the wireless LAN; however some environments may require 6
Mbps to be enabled as a mandatory (basic) rate.
If 802.11b clients exist, then 11 Mbps should be set as the mandatory (basic) rate and 12 Mbps and higher as supported
(optional).
Page 84

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
84
WLAN Settings
It is recommended to have a separate SSID for the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX.
However, if there is an existing SSID configured to support voice capable Cisco Wireless LAN endpoints already, then that
WLAN can be utilized instead.
The SSID to be used by the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX can be configured to only apply to a certain 802.11
radio type (e.g. 802.11a only).
Enable WPA2 key management.
Ensure either 11r or CCKM is enabled, where 11r is recommended.
Page 85

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
85
Page 86

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
86
Segment wireless voice and data into separate VLANs.
Ensure that Public Secure Packet Forwarding (PSPF) is not enabled for the voice VLAN as this will prevent clients from
communicating directly when associated to the same access point. If PSPF is enabled, then the result will be no way audio.
Page 87

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
87
Ensure AES is selected for encryption type.
Page 88

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
88
Configure the RADIUS servers to be used for authentication and accounting.
Page 89

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
89
Wireless Domain Services (WDS)
Wireless Domain Services should be utilized in the Cisco Autonomous Access Point environment, which is also required for
fast secure roaming.
Select one access point to be the primary WDS server and another to be the backup WDS server.
Configure the primary WDS server with the highest priority (e.g. 255) and the backup WDS server with a lower priority (e.g.
254).
Page 90

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
90
The Cisco Autonomous Access Points utilize Inter-Access Point Protocol (IAPP), which is a multicast protocol, therefore
should use a dedicated native VLAN for Cisco Autonomous Access Points.
For the native VLAN, it is recommended to not use VLAN 1 to ensure that IAPP packets are exchanged successfully.
Port security should be disabled on switch ports that Cisco Autonomous Access Points are directly connected to.
Server groups for Wireless Domain Services must be defined.
Page 91

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
91
First, define the server group to be used for infrastructure authentication.
Is recommended to use local RADIUS for infrastructure authentication.
If not using local RADIUS for infrastructure authentication, then need to ensure that all access points with Wireless Domain
Services enabled are configured in the RADIUS server.
Then, define the server group to be used for client authentication.
Will need to ensure that all access points with Wireless Domain Services enabled are configured in the RADIUS server.
Page 92

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
92
To utilize local RADIUS for infrastructure authentication, enable all authentication protocols.
Create a Network Access Server entry for the local access point.
Define the user account in which access points will be configured for to authenticate to the Wireless Domain Services enabled
access point.
Configure local RADIUS on each access point participating in Wireless Domain Services.
Page 93

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
93
Once the desired access points have been configured successfully to enable Wireless Domain Services, then all access points
including those serving as WDS servers need to be configured to be able to authenticate to the WDS servers.
Enable Participate in SWAN Infrastructure.
If using a single WDS server, then can specify the IP address of the WDS server; otherwise enable Auto Discovery.
Enter the Username and Password to be used to authenticate to the WDS server.
Page 94

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
94
Once the access point has been configured to authenticate to the WDS server, can check WDS Status to see the WDS server
state as well as how many access points are registered to the WDS server.
Call Admission Control (CAC)
Load-based CAC and support for multiple streams are not present on the Cisco Autonomous Access Points therefore it is not
recommended to enable CAC on Cisco Autonomous Access points.
Page 95

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
95
The Cisco Autonomous Access Point only allows for 1 stream and the stream size is not customizable, therefore SRTP and
barge will not work if CAC is enabled.
If enabling Admission Control for Voice or for Video on the Cisco Autonomous Access Point, the admission must be
unblocked on the SSID as well. In recent releases, the admission is unblocked by default.
dot11 ssid voice
vlan 3
authentication open eap eap_methods
authentication network-eap eap_methods
authentication key-management wpa version 2 dot11r
admit-traffic
QoS Policies
Configure the following QoS policy on the Cisco Autonomous Access Point to enable DSCP to CoS (WMM UP) mapping.
This allows packets to be placed into the proper queue as long as those packets are marked correctly when received at the access
point level.
Page 96

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
96
To enable QBSS, select Enable and check Dot11e.
If Dot11e is checked, then both CCA versions (802.11e and Cisco version 2) will be enabled.
Ensure IGMP Snooping is enabled.
Ensure Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM) is enabled.
Page 97

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
97
If enabling the Stream feature either directly or via selecting Optimized Voice for the radio access category in the QoS
configuration section, then use the defaults, where 5.5, 6, 11, 12 and 24 Mbps are enabled as nominal rates for 802.11b/g, 6, 12,
and 24 Mbps enabled for 802.11a and 6.5, 13, and 26 Mbps enabled for 802.11n.
If the Stream feature is enabled, ensure that only voice packets are being put into the voice queue. Signaling packets (SIP)
should be put into a separate queue. This can be ensured by setting up a QoS policy mapping the DSCP to the correct queue.
Page 98

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
98
Power Management
Proxy ARP can optimize idle battery life, by answering any ARP requests on behalf of the phone.
To enable Proxy ARP, set Client ARP Caching to Enable.
Also ensure that Forward ARP Requests to Radio Interfaces When Not All Client IP Addresses Are Known is checked.
Page 99

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
99
Advanced Settings
TKIP Countermeasure Holdoff Time
TKIP countermeasure mode can occur if the access point receives two Message Integrity Check (MIC) errors within a 60
second period. When this occurs, the access point will de-authenticate all TKIP clients associated to that 802.11 radio and
holdoff any clients for the countermeasure holdoff time (default = 60 seconds).
To change the TKIP countermeasure holdoff time on the Cisco Autonomous Access Point, telnet or SSH to the access point and
enter the following command specifying the number of seconds and WLAN ID.
Interface dot11radio X
countermeasure tkip hold-time <nseconds>
Cisco Autonomous Access Point Sample Configuration
version 15.3
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname ap-1
!
logging rate-limit console 9
!
aaa new-model
!
aaa group server radius rad_eap
server name 10.0.0.20
!
aaa group server radius rad_mac
!
aaa group server radius rad_acct
server name 10.0.0.20
!
aaa group server radius rad_admin
!
aaa group server tacacs+ tac_admin
!
aaa group server radius rad_pmip
!
aaa group server radius dummy
!
aaa group server radius WDS
server name 10.9.0.9
!
aaa group server radius Clients
server name 10.0.0.20
!
aaa authentication login default local
aaa authentication login eap_methods group rad_eap
aaa authentication login mac_methods local
Page 100

Cisco Wireless IP Phone 8821 and 8821-EX Wireless LAN Deployment Guide
100
aaa authentication login method_WDS group WDS
aaa authentication login method_Clients group Clients
aaa authorization exec default local
aaa accounting network acct_methods start-stop group rad_acct
!
aaa session-id common
clock timezone -0500 -5 0
clock summer-time -0400 recurring
no ip source-route
no ip cef
ip domain name cisco.com
ip name-server 10.0.0.30
ip name-server 10.0.0.31
!
dot11 pause-time 100
dot11 syslog
!
dot11 ssid data
vlan 2
authentication open eap eap_methods
authentication network-eap eap_methods
authentication key-management wpa version 2
!
dot11 ssid voice
vlan 3
authentication open eap eap_methods
authentication network-eap eap_methods
authentication key-management wpa version 2 dot11r
!
dot11 arp-cache optional
dot11 phone dot11e
!
no ipv6 cef
!
crypto pki trustpoint TP-self-signed-672874324
enrollment selfsigned
subject-name cn=IOS-Self-Signed-Certificate-672874324
revocation-check none
rsakeypair TP-self-signed-672874324
!
crypto pki certificate chain TP-self-signed-672874324
certificate self-signed 01
30820229 30820192 A0030201 02020101 300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 05050030
30312E30 2C060355 04031325 494F532D 53656C66 2D536967 6E65642D 43657274
69666963 6174652D 36373238 37343332 34301E17 0D313630 38303332 33303533
385A170D 32303031 30313030 30303030 5A303031 2E302C06 03550403 1325494F
532D5365 6C662D53 69676E65 642D4365 72746966 69636174 652D3637 32383734
33323430 819F300D 06092A86 4886F70D 01010105 0003818D 00308189 02818100
CB155DD1 3421B13F CD121F42 7A62D9F5 38EBC966 4420F38A 38DFAFF2 D43CD3B9
5F5A1B75 7910F9F5 6E9EDEF4 730942C7 17DC4CBC E5AE3E49 0AF79419 0BEF34BC
5DCEB4E2 FF2978CB C34D5AEE ED1DFB58 C7BF6592 61C1AD25 3EF87205 15EA58C2
0A5E2B15 7F08FAEA 5DA2BFA7 95E56C60 22C229C7 024A91D7 A4FEB50B 5425357F
02030100 01A35330 51300F06 03551D13 0101FF04 05300301 01FF301F 0603551D
23041830 168014FC 2FE6CF0E E0380A40 11381459 5D596E3E A684DA30 1D060355
1D0E0416 0414FC2F E6CF0EE0 380A4011 3814595D 596E3EA6 84DA300D 06092A86
4886F70D 01010505 00038181 0053F55B 5EBB1FE2 C849BC45 47D0E710 0200404E
 Loading...
Loading...