Page 1

GETTING STARTED GUIDE
Cisco Aironet 2800 Series Access Points
First Published: June 22, 2016
Page 2

1 About this Guide
2 About the Access Point
3 Safety Instructions
4 Unpacking
5 AP Views, Ports, and Connectors
6 Preparing the AP for Installation
7 Installation Overview
8 Performing a Pre-Installation Configuration
9 Mounting and Grounding the Access Point
10 Powering the Access Point
11 Configuring and Deploying the Access Point
12 Checking the Access Point LEDs
13 Miscellaneous Usage and Configuration Guidelines
15 Related Documentation
16 Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
17 Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
2
Page 3

1 About this Guide
This guide provides instructions on how to install your Cisco Aironet 2800I and 2800E series access
points and provides links to resources which can help you configure the access point. This guide
provides mounting instructions and limited troubleshooting procedures.
The 2800 series access point is referred to as access point or AP in this document.
2 About the Access Point
The Cisco Aironet 2800 Series Wi-Fi access points provide 802.11ac Wave 2 with Multi User MIMO
(MU MIMO). This AP series offers integrated and external antenna options, with a dedicated 5 GHz
radio and a flexible radio that can be configured as a 2.4 GHz radio (default) or as an additional
5 GHz radio. This access point supports a greater overall High Density Experience (HDX) which
provides mission-critical wireless to meet your performance needs. The access points support full
interoperability with leading 802.11ac clients, and support a mixed deployment with other access
points and controllers.
A full listing of the access point's features and specifications are provided in the Cisco Aironet 2800
Series Access Point Data Sheet, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/wireless/aironet-2800-series-access-points/datashee
t-c78-736497.html
Access Point Features
The 2800 series access point is a wireless controller-based product and supports:
• Integrated antennas on the 2802I access point model (AIR-AP2802I-x-K9)
• External antennas on the 2802E access point models (AIR-AP2802E-x-K9)
Note The ‘x’ in the model numbers represents the regulatory domain. For information on
supported regulatory domains, see the“AP Model Numbers and Regulatory Domains”
section on page 4.
• Flexible Radio Assignment, allowing for either manual configuration or for the APs to intelligently
determine the operating role of the integrated radios based on the available RF environment. The
AP can operate in the following modes:
–
2.4 GHz and 5 GHz role, where one radio serves clients in 2.4 GHz mode, while the other
serves clients in 5 GHz mode.
3
Page 4
–
Dual 5 GHz radio role, with both radios operating in the 5 GHz band, actively serving client
devices to maximize the benefits of 802.11ac Wave 2 and to increase client device capacity.
–
Wireless Security Monitoring and 5 GHz role, where one radio serves 5 GHz clients, while the
other radio scans both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz for wIPS attackers, CleanAir interferers, and
rogue devices.
• Multiuser Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO) technology with 3 spatial streams.
• Cross-AP Noise Reduction, a Cisco innovation that enables APs to intelligently collaborate in real
time about RF conditions so that users connect with optimized signal quality and performance.
• Optimized AP Roaming for ensuring that client devices associate with the AP in their coverage
range that offers the fastest data rate available.
• Cisco ClientLink 4.0 technology for improved downlink performance to all mobile devices,
including one-, two-, and three-spatial-stream devices up to 802.11ac Wave 1 and Wave 2. The
technology also improves battery life on mobile devices.
• Cisco CleanAir technology enhanced with 160MHz channel support. CleanAir delivers proactive,
high-speed spectrum intelligence across 20-, 40-, and 80-, and 160-MHz-wide channels to combat
performance problems arising from wireless interference.
• MIMO equalization capabilities, which optimize uplink performance and reliability by reducing
the impact of signal fade.
The AP supports the following operating modes:
• Centralized
• Sniffer
• FlexConnect
• Monitor Mode
• Service Provider Option 60 (DHCP Option 60)
AP Model Numbers and Regulatory Domains
AP Type Model Number Details
Access Point for indoor
environments, with internal
antennas
Access Point for indoor
environments, with external
antennas
4
AIR-AP2802I-x-K9 Dual-band, controller-based
802.11a/g/n/ac
AIR-AP2802E-x-K9
Page 5

You need to verify whether the AP model you have is approved for use in your country. To verify
approval and to identify the regulatory domain that corresponds to a particular country, visit
http://www.cisco.com/go/aironet/compliance. Not all regulatory domains have been approved. As and
when they are approved, this compliance list will be updated.
Antennas and Radios
The 2800 series access point contains a dedicated 5 GHz radio and a flexible radio that can be
configured as a 2.4 GHz radio (default) or as an additional 5 GHz radio. The 2800 series access point
configurations are:
• AIR-AP2802I-x-K9—One 2.4 GHz/5 GHz flexible radio and one 5 GHz radio.
• AIR-AP2802E-x-K9—One 2.4 GHz/5 GHz flexible radio and one 5 GHz radio. The are 4
dual-band dipole and a Smart antenna connector.
Internal Antennas
The 2802I has 12 cross polarized internal antennas.
External Antennas
The 2802E model is configured with up to four external dual-band dipole antennas, and two 2.4 GHz/
5 GHz dual-band radios. The radio and antennas support frequency bands 2400–2500 MHz and
5180–5865 MHz through a common dual-band RF interface. Features of the external dual-band
dipole antennas are:
• Four RTNC antenna connectors on the top of the access point
• Four TX/RX antennas
• Smart Antenna connector for connecting an external antenna
5
Page 6
Supported External Antennas
Part Number Description Gain
AIR-ANT2524DB-R/= Dipole Antenna, Black, with RP-TNC connectors. 2 dBi (2.4 GHz)
4 dBi (5 GHz)
AIR-ANT2524DG-R/= Dipole Antenna, Gray, with RP-TNC connectors. 2 dBi (2.4 GHz)
4 dBi (5 GHz)
AIR-ANT2524DW-R/= Dipole Antenna, White, with RP-TNC connectors. 2 dBi (2.4 GHz)
4 dBi (5 GHz)
AIR-ANT2535SDW-R Low Profile Antenna, White, with RP-TNC
connectors.
AIR-ANT2566P4W-R= Directional Antenna, 4-port, with RP-TNC
connectors.
AIR-ANT2524V4C-R= Ceiling Mount Omni Antenna, 4-port, with
RP-TNC connectors.
AIR-ANT2544V4M-R= Wall Mount Omni Antenna, 4-port, with RP-TNC
connectors.
AIR-ANT2566D4M-R= 60 Degree Patch Antenna, 4-port, with RP-TNC
connectors.
1. Available in all countries except Japan. Japan regulatory approval is pending.
2. For the USA, the UNII-1 channels can be used only indoors.
1 2
3 dBi (2.4 GHz)
5 dBi (5 GHz)
6 dBi (2.4 GHz)
6 dBi (5 GHz)
2 dBi (2.4 GHz)
4 dBi (5 GHz)
4 dBi (2.4 GHz)
4 dBi (5 GHz)
6 dBi (2.4 GHz)
6 dBi (5 GHz)
Cisco also provides the following external antenna accessories:
• 5 ft Low Loss RF cable with RP-TNC and N-type Connectors (AIR-CAB005LL-R-N/=). You will
need four of these.
• 2 ft Smart Antenna Connector to RP-TNC Connectors (AIR-CAB002-DART-R=).
6
Page 7

3 Safety Instructions
Translated versions of the following safety warnings are provided in the translated safety warnings
document that is shipped with your access point. The translated warnings are also in the Translate d
Safety Warnings for Cisco Aironet Access Points, which is available on Cisco.com.
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury.
Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical
circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. Use the
statement number provided at the end of each warning to locate its translation in the
translated safety warnings that accompanied this device.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source.
Statement 1004
Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes.
Statement 1074
This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent)
protection. Ensure that the protective device is rated not greater than:
20A.
Statement 1005
Statement 1071
Warning
Warning
Do not operate your wireless network device near unshielded blasting caps or in an
explosive environment unless the device has been modified to be especially qualified for
such use.
In order to comply with FCC radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, antennas should be
located at a minimum of 12 inches (30 cm) or more from the body of all persons.
Statement 332
Statement 245B
7
Page 8

Caution The fasteners you use to mount an access point on a ceiling must be capable of
maintaining a minimum pullout force of 20 lbs (9 kg) and must use all 4 indented holes
on the mounting bracket.
Caution This product and all interconnected equipment must be installed indoors within the same
building, including the associated LAN connections as defined by Environment A of the
IEEE 802.af Standard.
Note The access point is suitable for use in environmental air space in accordance with section
300.22.C of the National Electrical Code and sections 2-128, 12-010(3), and 12-100 of the
Canadian Electrical Code, Part 1, C22.1. You should not install the power supply or power
injector in air handling spaces.
Note Use only with listed ITE equipment.
4 Unpacking
To unpack the access point, follow these steps:
Step 1 Unpack and remove the access point and the accessory kit from the shipping box.
Step 2 Return any packing material to the shipping container and save it for future use.
Step 3 Verify that you have received the items listed below. If any item is missing or damaged, contact
your Cisco representative or reseller for instructions.
–
The access point
–
Mounting bracket (selected when you ordered the access point)
–
Adjustable ceiling-rail clip (selected when you ordered the access point)
8
Page 9
354571
1
2
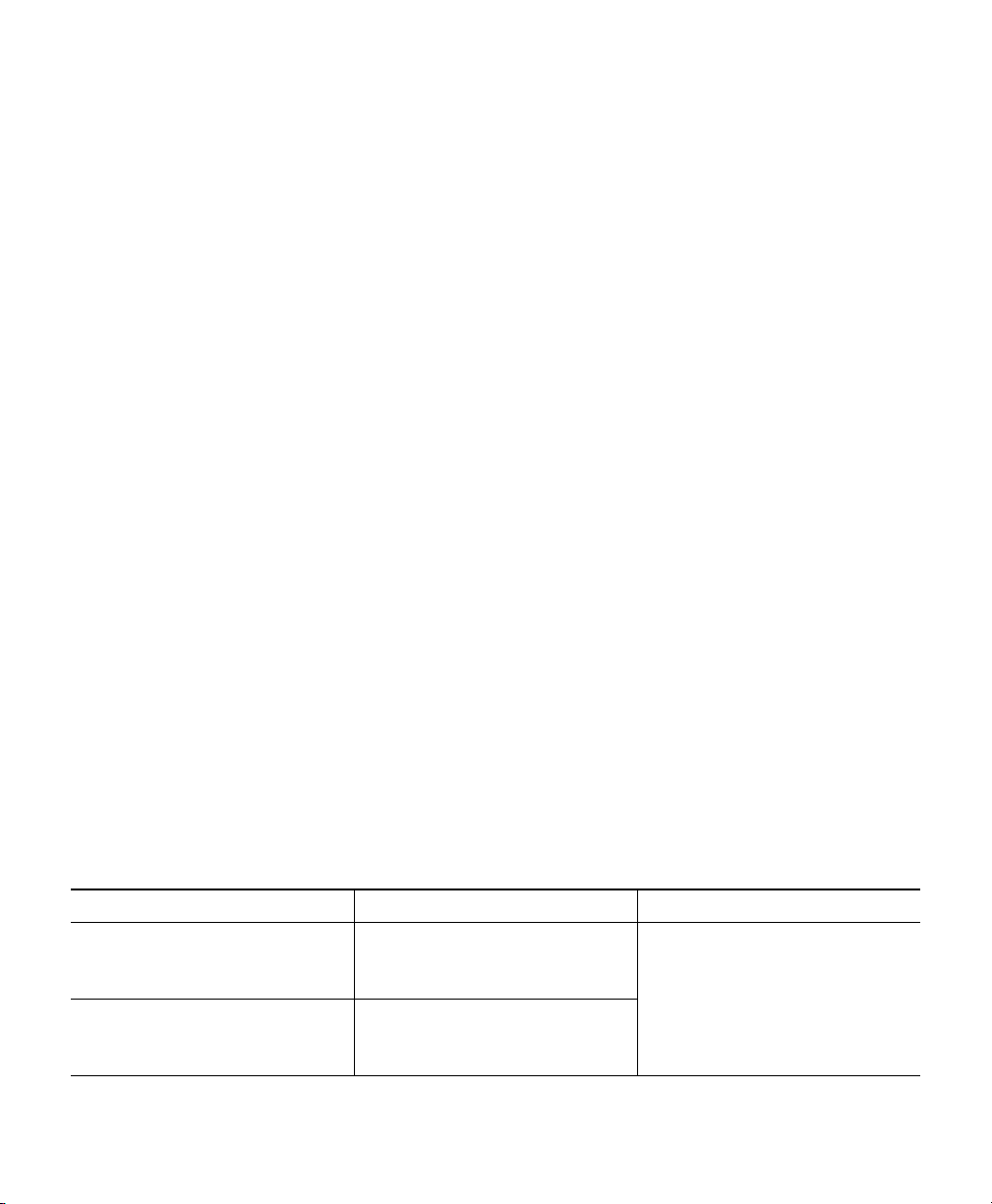
5 AP Views, Ports, and Connectors
Figure 1 Face of the 2802I Model
Status LED
1
Location of the ports and connectors on
2
the head of the AP.
9
Page 10
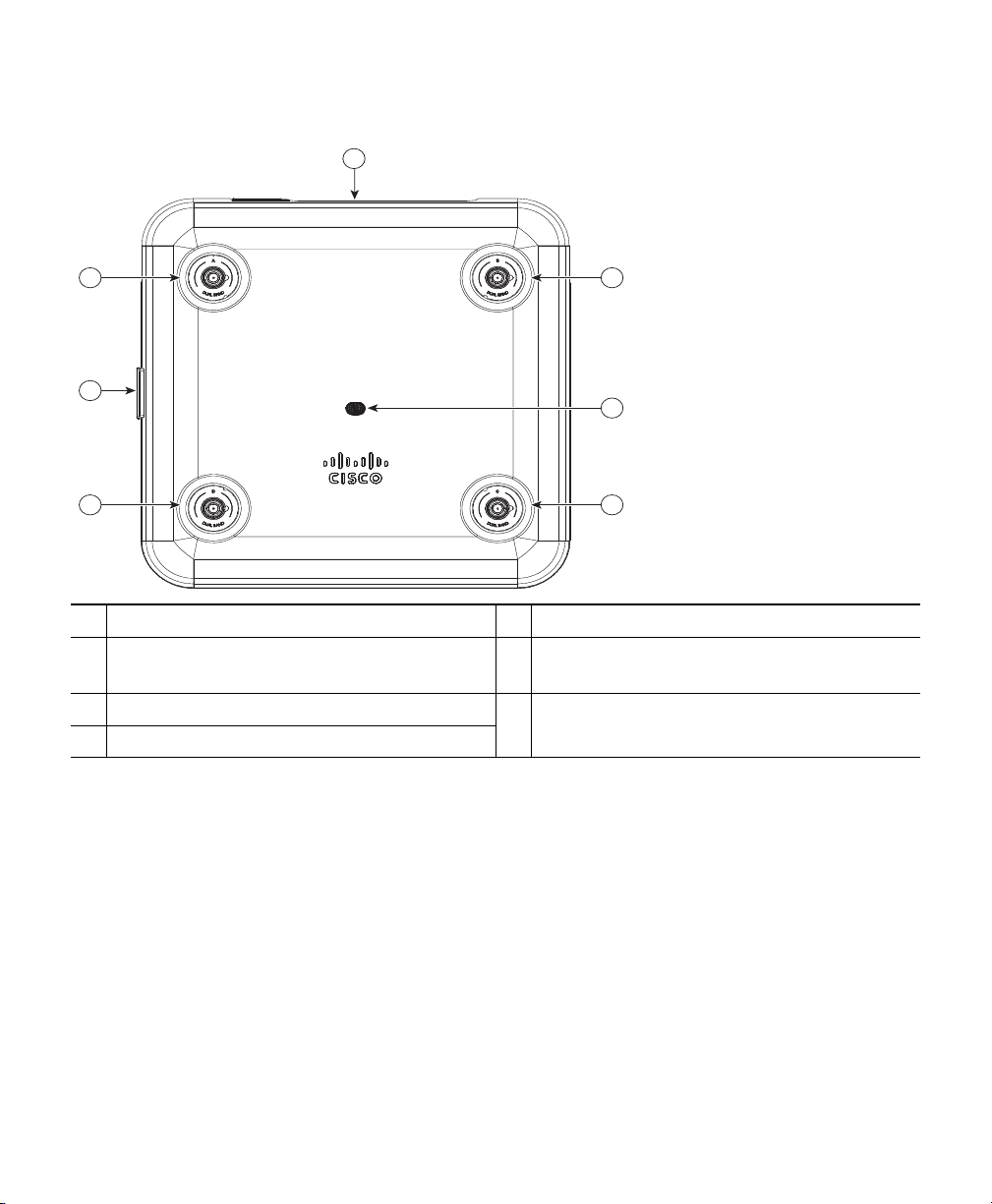
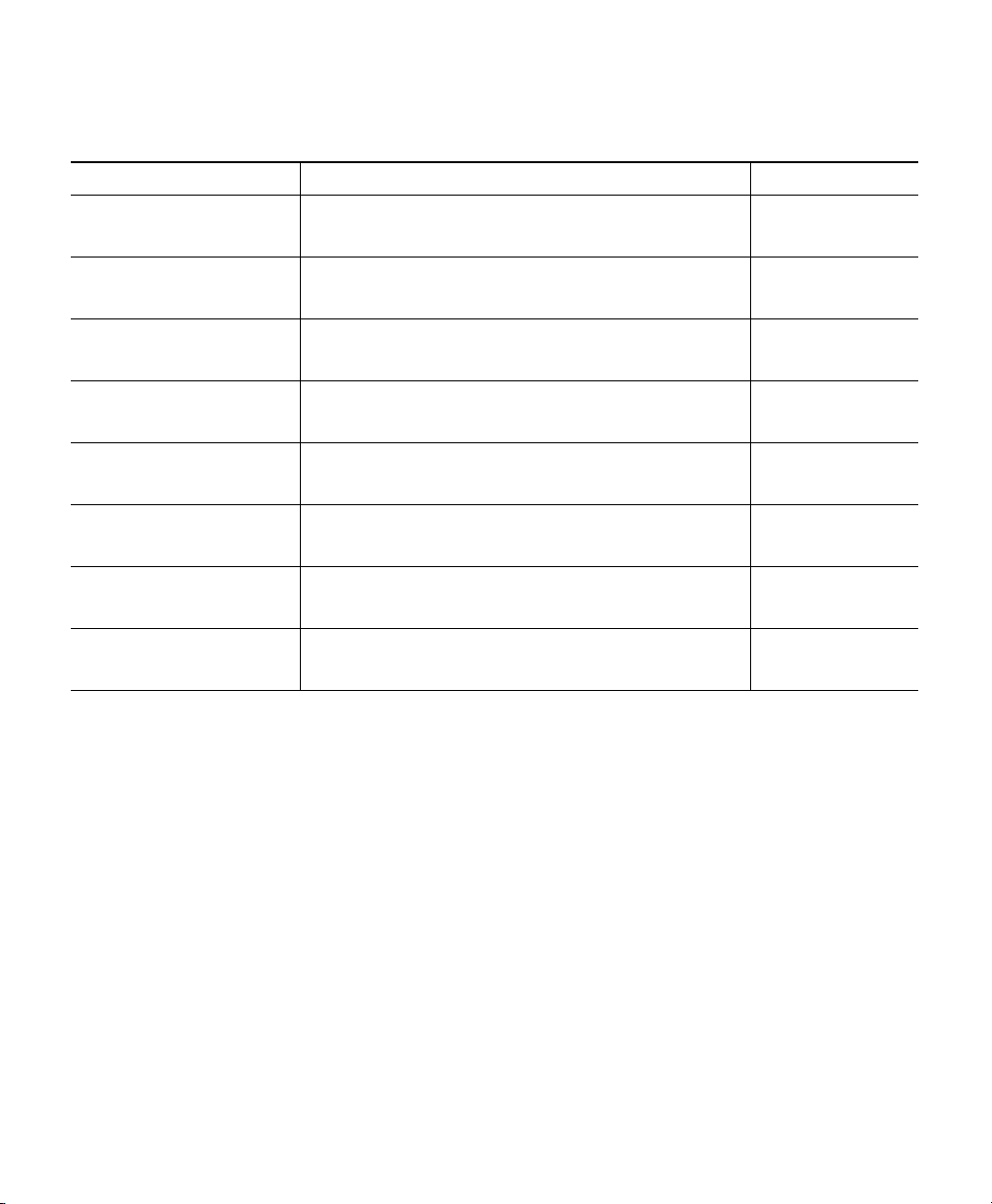
Figure 2 Face of the 2802E Model
354569
1
7
6
4
2
3
5
Dual-band antenna connector A
1
Dual-band antenna connector B
2
Status LED
5
Location of the ports and connectors on the
6
head of the AP
Dual-band antenna connector C
3
Dual-band antenna connector D
4
Location of the Smart antenna connector
7
port on the right side of the AP
The ports and connections on the bottom of the access point are shown in Figure 3.
10
Page 11
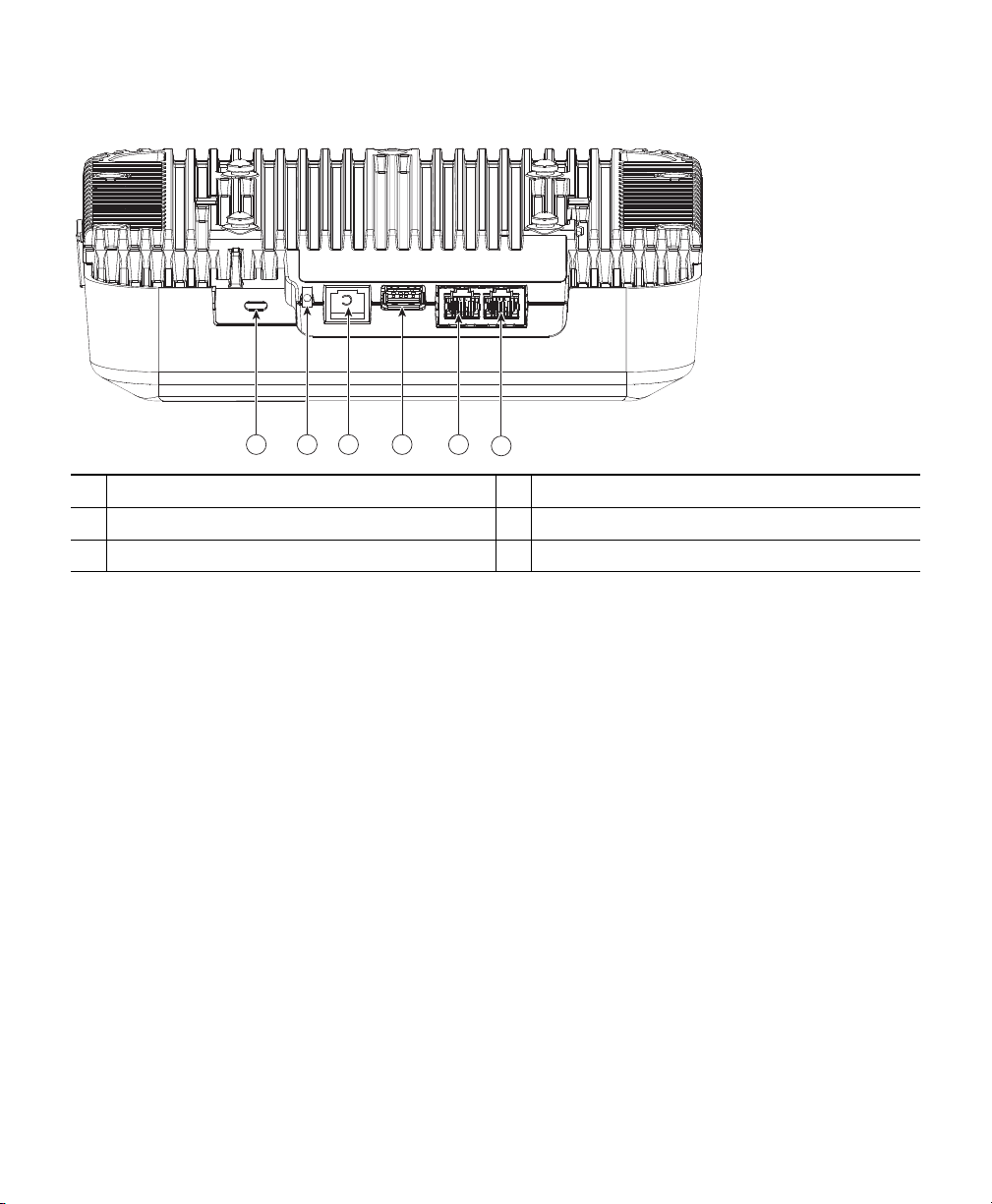
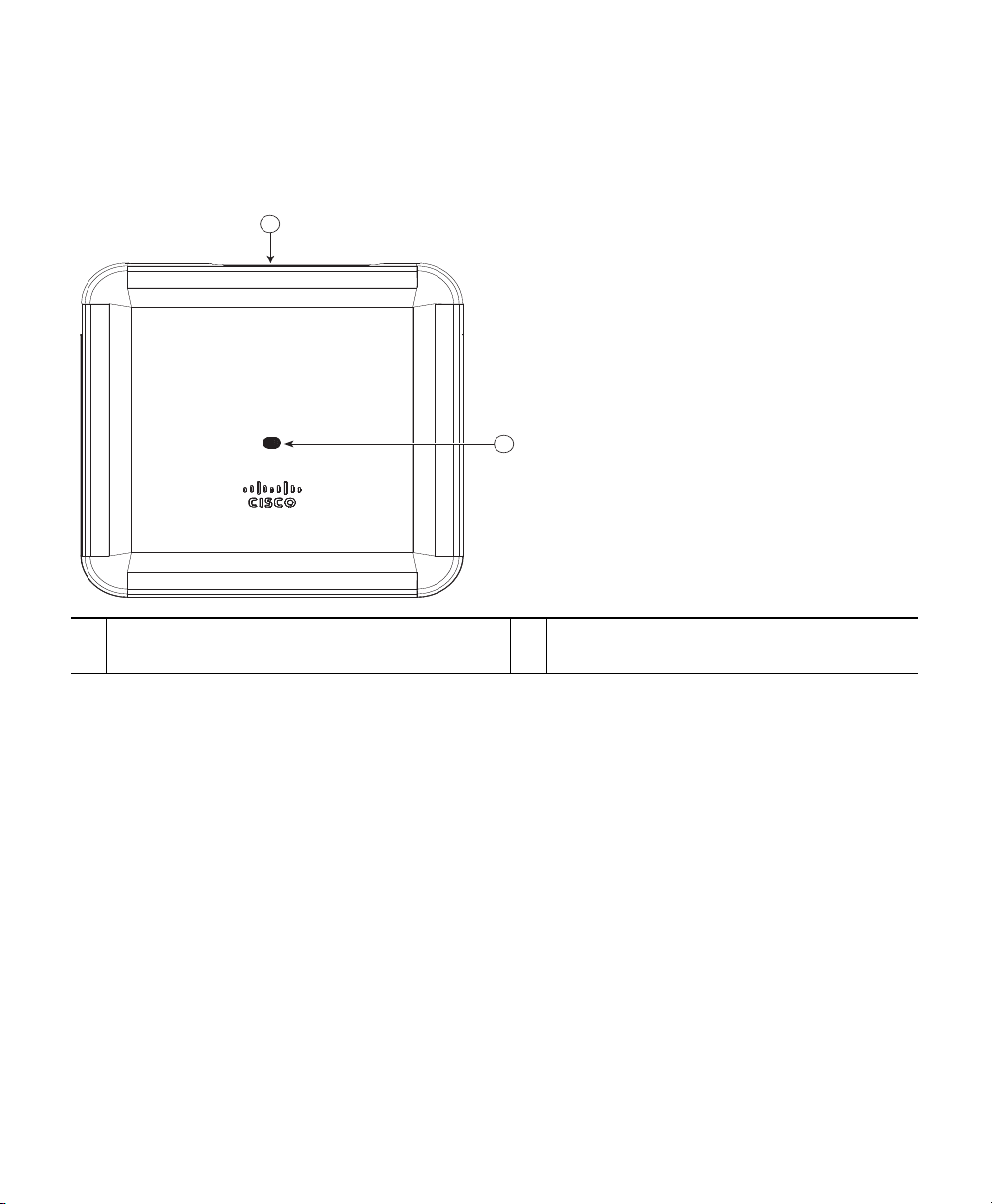
354570
1 2 3 4 5
6
Figure 3 Ports and Connectors on the Head of the 2802E Model
Kensington lock slot
1
Mode button
2
Console port
3
USB port
4
Gigabit Ethernet port
5
Gigabit Ethernet port
6
11
Page 12
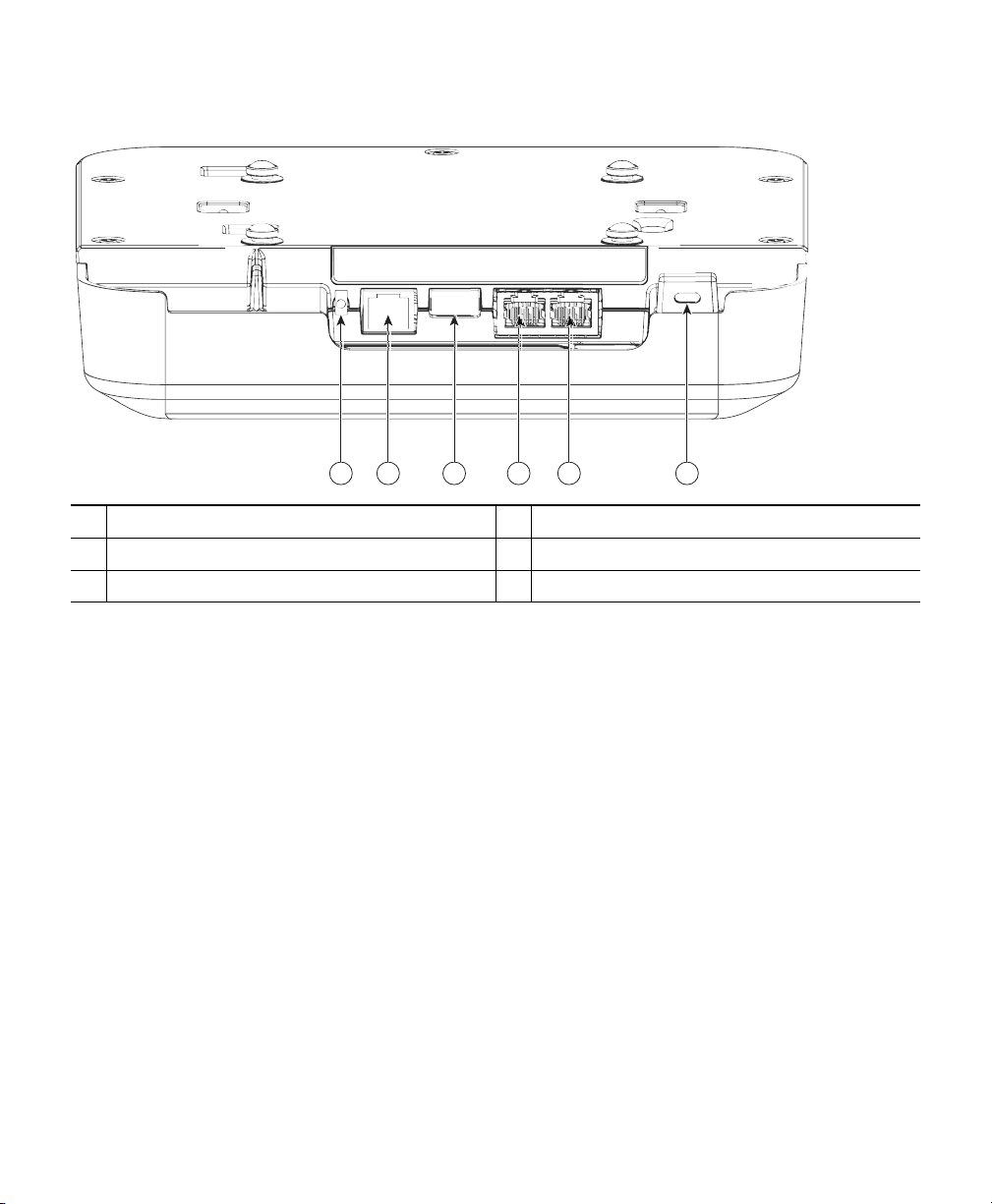
354625
1 2 3 4 5 6
Figure 4 Ports and Connectors on the Head of the 2802I Model
Mode button
1
Console port
2
USB port
3
Gigabit Ethernet port
4
Gigabit Ethernet port
5
Kensington lock slot
6
12
Page 13
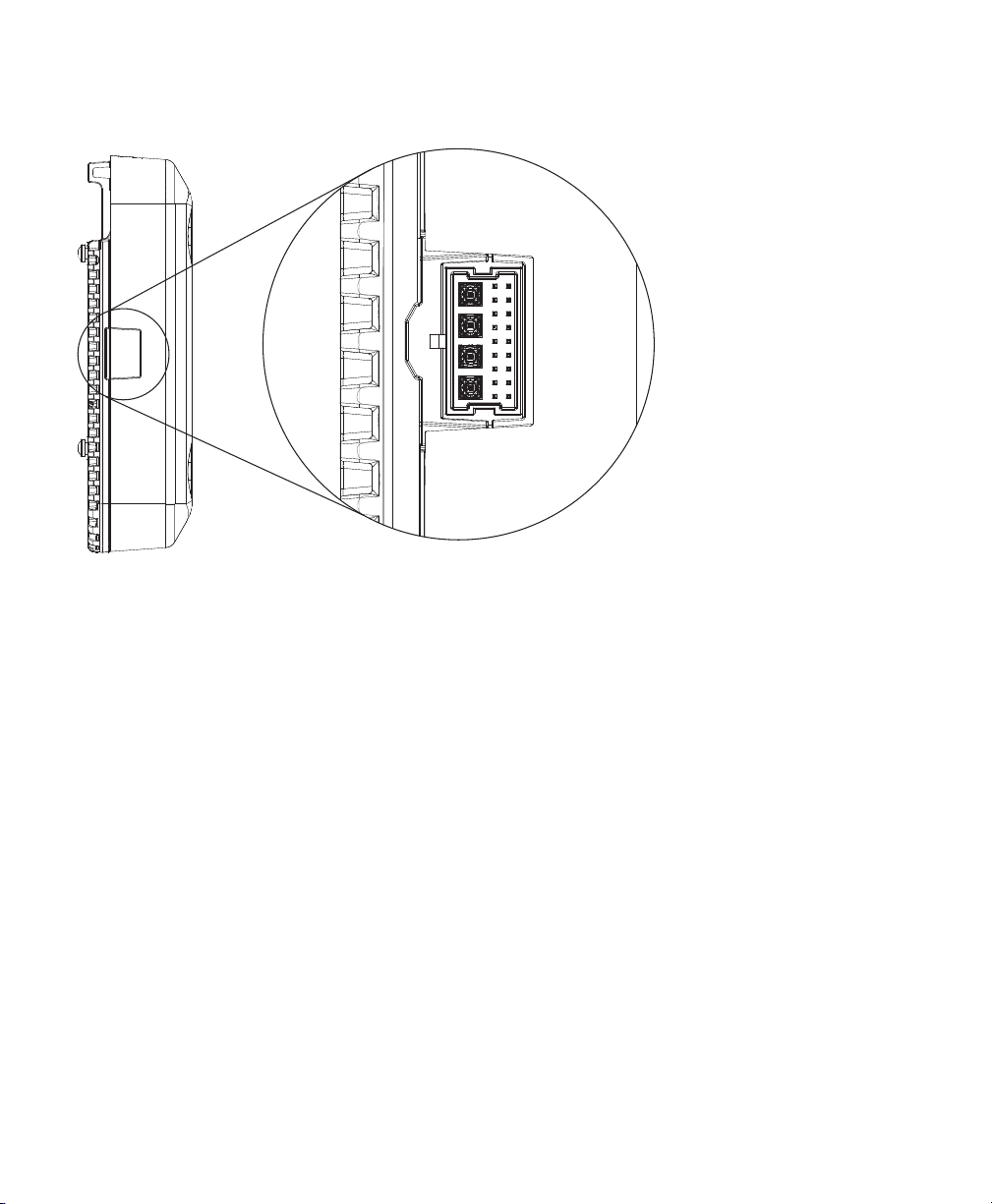
354568
Figure 5 Smart Antenna Connector on the Right Side of the 2802E Model
For more information on the Smart antenna connector, see the “What is a Smart Antenna connector?”
section on page 30.
13
Page 14

6 Preparing the AP for Installation
Before you mount and deploy your access point, we recommend that you perform a site survey (or use
the site planning tool) to determine the best location to install your access point.
You should have the following information about your wireless network available:
• Access point locations.
• Access point mounting options: below a suspended ceiling, on a flat horizontal surface, or on a
desktop.
Note You can mount the access point above a suspended ceiling but you must purchase
additional mounting hardware: See “Mounting and Grounding the Access Point” section
on page 19 for additional information.
• Access point power options: PoE+ or Cisco Power Injector AIR-PWRINJ6=.
Cisco recommends that you make a site map showing access point locations so that you can record the
device MAC addresses from each location and return them to the person who is planning or managing
your wireless network.
7 Installation Overview
Installing the access point involves these operations:
Step 1 Performing a Pre-Installation Configuration, page 15 (optional)
Step 2 Mounting and Grounding the Access Point, page 19
Step 3 Powering the Access Point, page 21
Step 4 Preparing the AP for Installation, page 14
14
Page 15

8 Performing a Pre-Installation Configuration
The following procedures ensure that your access point installation and initial operation go as
expected. This procedure is optional.
Note Performing a pre-installation configuration is an optional procedure. If your network
controller is properly configured, you can install your access point in its final location and
connect it to the network from there. See the “Deploying the Access Point on the Wireless
Network” section on page 23 for details.
The following Pre-Installation Configuration procedure given does not include configuring Link
Aggregation. For information on configuring Link Aggregation, see the Cisco Wireless LAN
Controller Configuration Guide, Release 8.2, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-2/config-guide/b_cg82.html
The pre-installation configuration setup is illustrated in Figure 6.
15
Page 16

Figure 6 Pre-Installation Configuration Setup
Controller
Layer 3
devices
Link Aggregation Link Aggregation
Cisco Aironet
access points
354066
To perform pre-installation configuration, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Make sure that the Cisco wireless LAN controller DS port is connected to the network. Use
the CLI, web-browser interface, or Cisco WCS procedures as described in the appropriate
Cisco wireless LAN controller guide.
a. Make sure that access points have Layer 3 connectivity to the Cisco wireless LAN controller
Management and AP-Manager Interface.
b. Configure the switch to which your access point is to attach. See the Cisco Wireless LAN
Controller Configuration Guide for the release you are using, for additional information.
c. Set the Cisco wireless LAN controller as the master so that new access points always join with
it.
d. Make sure DHCP is enabled on the network. The access point must receive its IP address
through DHCP.
e. CAPWAP UDP ports must not be blocked in the network.
f. The access point must be able to find the IP address of the controller. This can be
accomplished using DHCP, DNS, or IP subnet broadcast. This guide describes the DHCP
method to convey the controller IP address. For other methods, refer to the product
16
Page 17

documentation. See also the “Configuring DHCP Option 43” section on page 28 for more
information.
Note The access point requires a gigabit Ethernet (GbE) link to prevent the Ethernet port from
becoming a bottleneck for traffic because wireless traffic speeds exceed transmit speeds
of a 10/100 Ethernet port.
Step 2 Apply power to the access point. See Powering the Access Point, page 21.
a. As the access point attempts to connect to the controller, the LEDs cycle through a green, red,
and amber sequence, which can take up to 5 minutes.
Note If the access point remains in this mode for more than five minutes, the access point is
unable to find the Master Cisco wireless LAN controller. Check the connection between
the access point and the Cisco wireless LAN controller and be sure that they are on the
same subnet.
b. If the access point shuts down, check the power source.
c. After the access point finds the Cisco wireless LAN controller, it attempts to download the
new operating system code if the access point code version differs from the Cisco wireless
LAN controller code version. While this is happening, the Status LED blinks amber.
d. If the operating system download is successful, the access point reboots.
Step 3 Configure the access point if required. Use the controller CLI, controller GUI, or Cisco Prime
Infrastructure to customize the access-point-specific 802.11ac network settings.
Step 4 If the pre-installation configuration is successful, the Status LED is green indicating normal
operation. Disconnect the access point and mount it at the location at which you intend to
deploy it on the wireless network.
Step 5 If your access point does not indicate normal operation, turn it off and repeat the
pre-installation configuration.
17
Page 18

Note When you are installing a Layer 3 access point on a different subnet than the Cisco
wireless LAN controller, be sure that a DHCP server is reachable from the subnet on
which you will be installing the access point, and that the subnet has a route back to
the Cisco wireless LAN controller. Also be sure that the route back to the Cisco
wireless LAN controller has destination UDP ports 5246 and 5247 open for CAPWAP
communications. Ensure that the route back to the primary, secondary, and tertiary
wireless LAN controller allows IP packet fragments. Finally, be sure that if address
translation is used, that the access point and the Cisco wireless LAN controller have
a static 1-to-1 NAT to an outside address. (Port Address Translation is not
supported.)
18
Page 19

9 Mounting and Grounding the Access Point
Cisco Aironet 2800 series access points can be mounted in several configurations – on a suspended
ceiling, on a hard ceiling or wall, on an electrical or network box, and above a suspended ceiling.
Go to the following URL for access point mounting instructions:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/access_point/mounting/guide/apmount.html
The standard mounting hardware supported by the AP is listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Brackets and Clips for Mounting the AP
Part Number Description
Brackets
Clips AIR-AP-T-RAIL-R Ceiling Grid Clip (Recessed mounting)
1. Mount the AP using no less than four screw holes on a bracket.
1
AIR-AP-BRACKET-1 Low-profile bracket
(This is the default option)
AIR-AP-BRACKET-2 Universal bracket
(This is the default option)
AIR-AP-T-RAIL-F Ceiling Grid Clip (Flush mounting)
AIR-CHNL-ADAPTER Optional adapter for channel-rail ceiling grid profile.
When mounting the AP in areas where there is a possibility of the AP being knocked off the mounting
bracket, use the lock hasp on the back of the AP (see Figure 7) to lock it to the bracket.
19
Page 20

Figure 7 Locking the AP to the Bracket
Position of the hasps for the locks on the back of the 2802I and 2802E models
1
20
Page 21

10 Powering the Access Point
The AP can be powered through only Power-over-Ethernet (PoE), using:
• 802.3at Cisco Power Injector AIR-PWRINJ6=
• Any 802.3at (25.5 W) compliant switch port
11 Configuring and Deploying the Access Point
This section describes how to connect the access point to a wireless LAN controller. Because the
configuration process takes place on the controller, see the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
Configuration Guide for additional information.
The information in this section does not include configuring Link Aggregation. For information on
configuring Link Aggregation, see the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, Release
8.2, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-1/configuration-guide/b_cg81.html
The Controller Discovery Process
The access point uses standard Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points Protocol
(CAPWAP) to communicate between the controller and other wireless access points on the network.
CAPWAP is a standard, inter-operable protocol which enables an access controller to manage a
collection of wireless termination points. The discovery process using CAPWAP is identical to the
Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) used with previous Cisco Aironet access points.
LWAPP-enabled access points are compatible with CAPWAP, and conversion to a CAPWAP controller
is seamless. Deployments can combine CAPWAP and LWAPP software on the controllers.
The functionality provided by the controller does not change except for customers who have Layer 2
deployments, which CAPWAP does not support.
In a CAPWAP environment, a wireless access point discovers a controller by using CAPWAP discovery
mechanisms and then sends it a CAPWAP join request. The controller sends the access point a
CAPWAP join response allowing the access point to join the controller. When the access point joins
the controller, the controller manages its configuration, firmware, control transactions, and data
transactions.
21
Page 22

Note For additional information about the discovery process and CAPWAP, see the Cisco Wireless
LAN Controller Software Configuration Guide. This document is available on Cisco.com.
Note CAPWAP support is provided in controller software release 5.2 or later. However, your
controller must be running the release that supports 2800 series access points, as specified in
the access point data sheet.
Note You cannot edit or query any access point using the controller CLI if the name of the access
point contains a space.
Note Make sure that the controller is set to the current time. If the controller is set to a time that
has already occurred, the access point might not join the controller because its certificate may
not be valid for that time.
Access points must be discovered by a controller before they can become an active part of the network.
The access point supports these controller discovery processes:
• Layer 3 CAPWAP discovery—Can occur on different subnets than the access point and uses IP
addresses and UDP packets rather than MAC addresses used by Layer 2 discovery.
• Locally stored controller IP address discovery—If the access point was previously joined to a
controller, the IP addresses of the primary, secondary, and tertiary controllers are stored in the
access point non-volatile memory. This process of storing controller IP addresses on an access
point for later deployment is called priming the access point. For more information about priming,
see the “Performing a Pre-Installation Configuration” section on page 15.
• DHCP server discovery—This feature uses DHCP option 43 to provide controller IP addresses to
the access points. Cisco switches support a DHCP server option that is typically used for this
capability. For more information about DHCP option 43, see the “Configuring DHCP Option 43”
section on page 28.
• DNS discovery—The access point can discover controllers through your domain name server
(DNS). For the access point to do so, you must configure your DNS to return controller IP
addresses in response to CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.localdomain, where localdomain is
the access point domain name. Configuring the CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER provides
backwards compatibility in an existing customer deployment. When an access point receives an IP
22
Page 23

address and DNS information from a DHCP server, it contacts the DNS to resolve
CISCO-CAPWAP-CONTROLLER.localdomain. When the DNS sends a list of controller IP
addresses, the access point sends discovery requests to the controllers.
Deploying the Access Point on the Wireless Network
After you have mounted the access point, follow these steps to deploy it on the wireless network:
Step 1 Connect and power up the access point.
Step 2 Observe the access point LED (for LED descriptions, see “Checking the Access Point LEDs”
section on page 24).
a. When you power up the access point, it begins a power-up sequence that you can verify by
observing the access point LED. If the power-up sequence is successful, the discovery and join
process begins. During this process, the LED blinks sequentially green, red, and off. When the
access point has joined a controller, the LED is chirping green if no clients are associated or
green if one or more clients are associated.
b. If the LED is not on, the access point is most likely not receiving power.
c. If the LED blinks sequentially for more than 5 minutes, the access point is unable to find its
primary, secondary, and tertiary Cisco wireless LAN controller. Check the connection
between the access point and the Cisco wireless LAN controller, and be sure the access point
and the Cisco wireless LAN controller are either on the same subnet or that the access point
has a route back to its primary, secondary, and tertiary Cisco wireless LAN controller. Also,
if the access point is not on the same subnet as the Cisco wireless LAN controller, be sure that
there is a properly configured DHCP server on the same subnet as the access point. See the
“Configuring DHCP Option 43” section on page 28 for additional information.
Step 3 Reconfigure the Cisco wireless LAN controller so that it is not the Master.
Note A Master Cisco wireless LAN controller should be used only for configuring access
points and not in a working network.
23
Page 24

12 Checking the Access Point LEDs
The location of the access point status LED is shown in Figure 2.
Note Regarding LED status colors, it is expected that there will be small variations in color intensity
and hue from unit to unit. This is within the normal range of the LED manufacturer’s
specifications and is not a defect.
The access point status LED indicates various conditions and are described in Table 2.
Table 2 LED Status Indications
Message
Ty pe
Association status Chirping Green Normal operating condition, but no wireless
Boot loader status Green Executing boot loader
Boot loader error Red Boot loader signing verification failure
Operating status Blinking amber Software upgrade in progress
Access point operating
system errors
LED State Message
Meaning
client associated
Green Normal operating condition, at least one wireless
client association
Cycling through green,
red, and amber
Rapidly cycling
through red, green,
amber, and off.
Cycling through red,
green, amber, and off
Discovery/join process in progress
Access point location command invoked from
controller web interface.
General warning; insufficient inline power
24
Page 25

13 Miscellaneous Usage and Configuration Guidelines
Using the Mode Button
Using the Mode button (see Figure 3) you can:
• Reset the AP to the default factory-shipped configuration.
• Clear the AP internal storage, including all configuration files.
To use the mode button, press, and keep pressed, the mode button on the access point during the
AP boot cycle. Wait until the AP status LED changes to Amber. During this, the AP console shows a
seconds counter, counting the number of seconds the mode button is pressed. Then:
• To reset the AP to the default factory-shipped configuration, keep the mode button pressed for less
than 20 seconds. The AP configuration files are cleared.
This resets all configuration settings to factory defaults, including passwords, WEP keys, the IP
address, and the SSID.
• To clear the AP internal storage, including all configuration files and the regulatory domain
configuration, keep the mode button pressed for more than 20 seconds, but less than 60 seconds.
The AP status LED changes from Amber to Red, and all the files in the AP storage directory are
cleared.
If you keep the mode button pressed for more than 60 seconds, the mode button is assumed faulty and
no changes are made.
25
Page 26

Troubleshooting the Access Point to Cisco Controller Join Process
Note Ensure that your controller is running the latest Cisco Wireless Controller Software Release
as specified in the access point data sheet.
Access points can fail to join a controller for many reasons: a RADIUS authorization is pending;
self-signed certificates are not enabled on the controller; the access point and the controller regulatory
domains don’t match, and so on.
Controller software enables you to configure the access points to send all CAPWAP-related errors to
a syslog server. You do not need to enable any debug commands on the controller because all of the
CAPWAP error messages can be viewed from the syslog server itself.
The state of the access point is not maintained on the controller until it receives a CAPWAP join
request from the access point. Therefore, it can be difficult to determine why the CAPWAP discovery
request from a certain access point was rejected. In order to troubleshoot such joining problems
without enabling CAPWAP debug commands on the controller, the controller collects information for
all access points that send a discovery message to it and maintains information for any access points
that have successfully joined it.
The controller collects all join-related information for each access point that sends a CAPWAP
discovery request to the controller. Collection begins with the first discovery message received from
the access point and ends with the last configuration payload sent from the controller to the access
point.
You can view join-related information for up to three times the maximum number of access points
supported by the platform for the 2500 series controllers and the Controller Network Module within
the Cisco 28/37/28xx Series Integrated Services Routers.
Note The maximum number of access points varies for the Cisco WiSM2, depending on which
controller software release is being used.
When the controller is maintaining join-related information for the maximum number of access points,
it does not collect information for any more access points.
An access point sends all syslog messages to IP address 255.255.255.255 by default when any of the
following conditions are met:
• An access point running software release 8.2.110.0 or later has been newly deployed.
26
Page 27

• An existing access point running software release 8.2.110.0 or later has been reset after clearing
the configuration.
If any of these conditions are met and the access point has not yet joined a controller, you can also
configure a DHCP server to return a syslog server IP address to the access point using option 7 on the
server. The access point then starts sending all syslog messages to this IP address.
When the access point joins a controller for the first time, the controller sends the global syslog server
IP address (the default is 255.255.255.255) to the access point. After that, the access point sends all
syslog messages to this IP address until it is overridden by one of the following scenarios:
• The access point is still connected to the same controller, and the global syslog server IP address
configuration on the controller has been changed using the config ap syslog host global
syslog_server_IP_address command. In this case, the controller sends the new global syslog server
IP address to the access point.
• The access point is still connected to the same controller, and a specific syslog server IP address
has been configured for the access point on the controller using the config ap syslog host specific
Cisco_AP syslog_server_IP_address command. In this case, the controller sends the new specific
syslog server IP address to the access point.
• The access point is disconnected from the controller and joins another controller. In this case, the
new controller sends its global syslog server IP address to the access point.
• Whenever a new syslog server IP address overrides the existing syslog server IP address, the old
address is erased from persistent storage, and the new address is stored in its place. The access
point also starts sending all syslog messages to the new IP address provided the access point can
reach the syslog server IP address.
You can configure the syslog server for access points and view the access point join information only
from the controller CLI.
Important Information for Controller-based Deployments
Keep these guidelines in mind when you use 2802 series access points:
• The access point can only communicate with Cisco wireless LAN controllers.
• The access point does not support Wireless Domain Services (WDS) and cannot communicate with
WDS devices. However, the controller provides functionality equivalent to WDS when the access
point joins it.
• CAPWAP does not support Layer 2. The access point must get an IP address and discover the
controller using Layer 3, DHCP, DNS, or IP subnet broadcast.
• The access point console port is enabled for monitoring and debug purposes. All configuration
commands are disabled when the access point is connected to a controller.
27
Page 28

Configuring DHCP Option 43
You can use DHCP Option 43 to provide a list of controller IP addresses to the access points, enabling
them to find and join a controller.
The following is a DHCP Option 43 configuration example on a Windows 2003 Enterprise DHCP
server for use with Cisco Aironet lightweight access points. For other DHCP server implementations,
consult product documentation for configuring DHCP Option 43. In Option 43, you should use the
IP address of the controller management interface.
Note DHCP Option 43 is limited to one access point type per DHCP pool. You must configure a
separate DHCP pool for each access point type.
The 2800 series access point uses the type-length-value (TLV) format for DHCP Option 43. DHCP
servers must be programmed to return the option based on the access point DHCP Vendor Class
Identifier (VCI) string (DHCP Option 43). The VCI string for the 2800 series access point is:
Cisco AP c2800
The format of the TLV block is listed below:
• Type: 0xf1 (decimal 241)
• Length: Number of controller IP addresses * 4
• Value: List of WLC management interfaces
To configure DHCP Option 43 in the embedded Cisco IOS DHCP server, follow these steps:
Step 1 Enter configuration mode at the Cisco IOS CLI.
Step 2 Create the DHCP pool, including the necessary parameters such as default router and name
server. A DHCP scope example is as follows:
ip dhcp pool <pool name>
network <IP Network> <Netmask>
default-router <Default router>
dns-server <DNS Server>
Where:
<pool name> is the name of the DHCP pool, such as AP2802
<IP Network> is the network IP address where the controller resides, such as
10.0.15.1
28
Page 29

<Netmask> is the subnet mask, such as 255.255.255.0
<Default router> is the IP address of the default router, such as 10.0.0.1
<DNS Server> is the IP address of the DNS server, such as 10.0.10.2
Step 3 Add the option 43 line using the following syntax:
option 43 hex <hex string>
The hex string is assembled by concatenating the TLV values shown below:
Type + Length + Value
Type is always f1(hex). Length is the number of controller management IP addresses times 4
in hex. Valu e is the IP address of the controller listed sequentially in hex.
For example, suppose that there are two controllers with management interface IP addresses,
10.126.126.2 and 10.127.127.2. The type is f1(hex). The length is 2 * 4 = 8 = 08 (hex). The IP
addresses translate to 0a7e7e02 and 0a7f7f02. Assembling the string then yields
f1080a7e7e020a7f7f02. The resulting Cisco IOS command added to the DHCP scope is option 43 hex
f1080a7e7e020a7f7f02.
29
Page 30

14 FAQs
What is Flexible Radio Assignment?
The Flexible Radio Assignment (FRA) feature automatically detects when a high number of devices
are connected to a network and changes the dual radios in the access point from 2.4 GHz/5 GHz to
5 GHz/5 GHz to serve more clients. The access point performs this function while still monitoring the
network for security threats and RF Interference that may affect performance. Flexible Radio
Assignment improves mobile user experience for high-density networks.
FRA has the following different modes of operation:
•Default operating mode—Serving clients on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radios.
•Dual 5 GHz Mode—Serving clients on both 5 GHz radios.
•Wireless Security Monitoring—Scanning both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radios for security threats while
also serving 5 GHz clients.
What is a Smart Antenna connector?
The 2802E model has a Smart antenna connector (see Figure 8), which is connected directly to the
flexible radio. Without a supported external antenna connected to the Smart Antenna connector, the
flexible radio can stay only in 2.4 GHz mode. If an external antenna is connected, the flexible radio
can be used in the full Flexible Radio Assignment mode, allowing dual 5 GHz and Wireless Security
Monitoring modes.
To connect to any supported RP-TNC connector-type external antenna to the Smart antenna
connector, use the DART cable connector AIR-CAB002-DART-R= (see Figure 9), which is to be
procured separately from Cisco.
30
Page 31

Figure 8 Smart Antenna Connector on 2802E Model
Figure 9 AIR-CAB002-DART-R= DART Connector
How Does Auto-Link Aggregation work with the 2800?
The 2800 AP supports automatic Link Aggregation (LAG) across its Ethernet and AUX ports. This
provides up to 2 Gbps of uplink speed to the access point.
The following Cisco switching series support LAG with the 2800 AP:
• Catalyst 3850 / all models (non-CA mode)
• Catalyst 3650 / all models (non-CA mode)
• Catalyst 4500/Sup-8E
• Catalyst 6500/Sup 720 or newer
31
Page 32

What is a ClientLink 4.0? How is it different from Tx-Beamforming?
Cisco ClientLink 4.0 is a beamforming capability built into Cisco Aironet wireless LAN access points.
When the access point concentrates signals toward the receiving client, that client is better able to hear
the AP’s transmission, and so throughput is greater. ClientLink also enhances performance in the
uplink (client-to-AP) direction, so that the AP can also better hear the client communications. The
result is improved performance in both directions, and doesn’t require any special capabilities in the
client device to work.
ClientLink works with all client technologies. It makes sure each client type always operates at the best
possible rate, as determined by the 802.11 access technology supported, network conditions, and the
distance of the client from the Wi-Fi AP. ClientLink helps maintain maximum client rates.
Can the USB port be used?
The USB port does not have any software support at this time.
15 Related Documentation
All user documentation for the Cisco Aironet 2800 series access point is available at the following
URL:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/wireless/aironet-2800-series-access-points/tsd-products-suppor
t-series-home.html
For detailed information and guidelines for configuring and deploying your access point in a wireless
network, see the following documentation:
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, Release 8.2, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-2/config-guide/b_cg82.html
• Cisco Aironet 2800 Series Access Point Deployment Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/technotes/8-3/b_cisco_aironet_series_2
800_3800_access_point_deployment_guide.html
32
Page 33

Tested To Comply
With FCC Standards
FOR HOME OR OFFICE USE
16 Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
This section provides declarations of conformity and regulatory information for the Cisco Aironet
2800 Series Access Points. You can find additional information at this URL:
www.cisco.com/go/aironet/compliance
Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission Declaration of Conformity Statement
Access Point Models Certification Number
AIR-AP2802I-B-K9 LDK102100
AIR-AP2802E-B-K9 LDK102099
Manufacturer:
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
This device complies with Part 15 rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits of a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and radiates radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference. However, there is no guarantee that
33
Page 34

interference will not occur. If this equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to correct the
interference by one of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician.
Caution The Part 15 radio device operates on a non-interference basis with other devices operating
at this frequency when using the integrated antennas. Any changes or modification to the
product not expressly approved by Cisco could void the user’s authority to operate this
device.
VCCI Statement for Japan
Warning
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control
Council for Interference from Information Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this
is used near a radio or television receiver in a domestic environment, it may
cause radio interference. Install and use the equipment according to the
instruction manual.
Page 35

03-6434-6500
208697
Guidelines for Operating Cisco Aironet Access Points in Japan
This section provides guidelines for avoiding interference when operating Cisco Aironet access points
in Japan. These guidelines are provided in both Japanese and English.
Japanese Translation
English Translation
This equipment operates in the same frequency bandwidth as industrial, scientific, and medical devices
such as microwave ovens and mobile object identification (RF-ID) systems (licensed premises radio
stations and unlicensed specified low-power radio stations) used in factory production lines.
1. Before using this equipment, make sure that no premises radio stations or specified low-power
radio stations of RF-ID are used in the vicinity.
2. If this equipment causes RF interference to a premises radio station of RF-ID, promptly change
the frequency or stop using the device; contact the number below and ask for recommendations
on avoiding radio interference, such as setting partitions.
3. If this equipment causes RF interference to a specified low-power radio station of RF-ID, contact
the number below.
Contact Number: 03-6434-6500
35
Page 36

Statement 371—Power Cable and AC Adapter
English Translation
When installing the product, please use the provided or designated connection cables/power cables/AC
adaptors. Using any other cables/adaptors could cause a malfunction or a fire. Electrical Appliance and
Material Safety Law prohibits the use of UL-certified cables (that have the “UL” shown on the code)
for any other electrical devices than products designated by CISCO. The use of cables that are certified
by Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law (that have “PSE” shown on the code) is not limited
to CISCO-designated products.
36
Page 37

Industry Canada
Access Point Models Certification Number
AIR-AP2802I-A-K9 2461B-102100
AIR-AP2802E-A-K9 2461B-102099
Canadian Compliance Statement
This device complies with Industry Canada licence-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to
the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this device must
accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil ne doit
pas produire de brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique
subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
Under Industry Canada regulations, this radio transmitter may only operate using an antenna of a type
and maximum (or lesser) gain approved for the transmitter by Industry Canada. To reduce potential
radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be so chosen that the equivalent
isotropically radiated power (e.i.r.p.) is not more than that necessary for successful communication.
Conformément à la réglementation d'Industrie Canada, le présent émetteur radio peut fonctionner
avec une antenne d'un type et d'un gain maximal (ou inférieur) approuvé pour l'émetteur par Industrie
Canada. Dans le but de réduire les risques de brouillage radioélectrique à l'intention des autres
utilisateurs, il faut choisir le type d'antenne et son gain de sorte que la puissance isotrope rayonnée
équivalente (p.i.r.e.) ne dépasse pas l'intensité nécessaire à l'établissement d'une communication
satisfaisante.
This radio transmitter has been approved by Industry Canada to operate with the antenna types listed
below with the maximum permissible gain and required antenna impedance for each antenna type
indicated. Antenna types not included in this list, having a gain greater than the maximum gain
indicated for that type, are strictly prohibited for use with this device.
Le présent émetteur radio a été approuvé par Industrie Canada pour fonctionner avec les types
d'antenne énumérés ci-dessous et ayant un gain admissible maximal et l'impédance requise pour
chaque type d'antenne. Les types d'antenne non inclus dans cette liste, ou dont le gain est supérieur au
gain maximal indiqué, sont strictement interdits pour l'exploitation de l'émetteur.
37
Page 38

Antenna Type Antenna Gain Antenna Impedance
Dual-band Omni 2/4 dBi 50 ohms
Dual-band Dipole 2/4 dBi 50 ohms
Dual-Band Directional 6/6 dBi 50 ohms
Operation in the band 5150-5250 MHz is only for indoor use to reduce the potential for harmful
interference to co-channel mobile satellite systems.
La bande 5 150-5 250 MHz est réservés uniquement pour une utilisation à l'intérieur afin de réduire
les risques de brouillage préjudiciable aux systèmes de satellites mobiles utilisant les mêmes canaux.
Users are advised that high-power radars are allocated as primary users (i.e. priority users) of the
bands 5250-5350 MHz and 5650-5850 MHz and that these radars could cause interference and/or
damage to LE-LAN devices.
Les utilisateurs êtes avisés que les utilisateurs de radars de haute puissance sont désignés utilisateurs
principaux (c.-à-d., qu'ils ont la priorité) pour les bandes 5 250-5 350 MHz et 5 650-5 850 MHz et
que ces radars pourraient causer du brouillage et/ou des dommages aux dispositifs LAN-EL.
European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein
Access Point Models:
AIR-AP2802I-E-K9
AIR-AP2802E-E-K9
38
Page 39

Declaration of Conformity with regard to the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC & Medical Directive 93/42/EEC
39
Page 40

The following standards were applied:
EMC—EN 301.489-1 v1.9.2; EN 301.489-17 v2.2.1
Health & Safety—EN60950-1: 2006; EN 50285: 2002
Radio—EN 300 328 v 1.8.1; EN 301.893 v 1.7.1
The conformity assessment procedure referred to in Article 10.4 and Annex III of Directive 1999/5/EC
has been followed.
Page 41

This device also conforms to the EMC requirements of the Medical Devices Directive 93/42/EEC.
Note This equipment is intended to be used in all EU and EFTA countries. Outdoor use may be
restricted to certain frequencies and/or may require a license for operation. For more details,
contact Cisco Corporate Compliance.
The product carries the CE Mark:
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure
This section contains information on compliance with guidelines related to RF exposure.
Generic Discussion on RF Exposure
The Cisco products are designed to comply with the following national and international standards on
Human Exposure to Radio Frequencies:
• US 47 Code of Federal Regulations Part 2 Subpart J
• American National Standards Institute (ANSI) / Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers /
IEEE C 95.1 (99)
• International Commission on Non Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) 98
• Ministry of Health (Canada) Safety Code 6. Limits on Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Fields
in the range from 3kHz to 300 GHz
• Australia Radiation Protection Standard
To ensure compliance with various national and international Electromagnetic Field (EMF) standards,
the system should only be operated with Cisco approved antennas and accessories.
This Device Meets International Guidelines for Exposure to Radio Waves
The 2800 series device includes a radio transmitter and receiver. It is designed not to exceed the limits
for exposure to radio waves (radio frequency electromagnetic fields) recommended by international
guidelines. The guidelines were developed by an independent scientific organization (ICNIRP) and
include a substantial safety margin designed to ensure the safety of all persons, regardless of age and
health.
Page 42

As such the systems are designed to be operated as to avoid contact with the antennas by the end user.
It is recommended to set the system in a location where the antennas can remain at least a minimum
distance as specified from the user in accordance to the regulatory guidelines which are designed to
reduce the overall exposure of the user or operator.
Separation Distance
MPE Distance Limit
0.6 mW/cm
The World Health Organization has stated that present scientific information does not indicate the
need for any special precautions for the use of wireless devices. They recommend that if you are
interested in further reducing your exposure then you can easily do so by reorienting antennas away
from the user or placing he antennas at a greater separation distance then recommended.
2
30 cm (12 inches) 1.00 mW/cm
2
This Device Meets FCC Guidelines for Exposure to Radio Waves
The 2800 series device includes a radio transmitter and receiver. It is designed not to exceed the limits
for exposure to radio waves (radio frequency electromagnetic fields) as referenced in FCC Part 1.1310.
The guidelines are based on IEEE ANSI C 95.1 (92) and include a substantial safety margin designed
to ensure the safety of all persons, regardless of age and health.
As such the systems are designed to be operated as to avoid contact with the antennas by the end user.
It is recommended to set the system in a location where the antennas can remain at least a minimum
distance as specified from the user in accordance to the regulatory guidelines which are designed to
reduce the overall exposure of the user or operator.
The device has been tested and found compliant with the applicable regulations as part of the radio
certification process.
Separation Distance
MPE Distance Limit
0.6 mW/cm
The US Food and Drug Administration has stated that present scientific information does not indicate
the need for any special precautions for the use of wireless devices. The FCC recommends that if you
are interested in further reducing your exposure then you can easily do so by reorienting antennas
away from the user or placing the antennas at a greater separation distance then recommended or
lowering the transmitter power output.
2
30 cm (12 inches) 1.00 mW/cm
2
Page 43

This Device Meets the Industry Canada Guidelines for Exposure to Radio Waves
The 2800 series device includes a radio transmitter and receiver. It is designed not to exceed the limits
for exposure to radio waves (radio frequency electromagnetic fields) as referenced in Health Canada
Safety Code 6. The guidelines include a substantial safety margin designed into the limit to ensure the
safety of all persons, regardless of age and health.
As such the systems are designed to be operated as to avoid contact with the antennas by the end user.
It is recommended to set the system in a location where the antennas can remain at least a minimum
distance as specified from the user in accordance to the regulatory guidelines which are designed to
reduce the overall exposure of the user or operator.
Separation Distance
Frequency MPE Distance Limit
2.4 GHz
5GHz
Health Canada states that present scientific information does not indicate the need for any special
precautions for the use of wireless devices. They recommend that if you are interested in further
reducing your exposure you can easily do so by reorienting antennas away from the user, placing the
antennas at a greater separation distance than recommended, or lowering the transmitter power
output.
1.89 W/m
2.73 W/m
2
30 cm (12 inches) 5.4 W/m
2
9.2 W/m
2
2
Cet appareil est conforme aux directives internationales en matière d'exposition aux fréquences radioélectriques
Cet appareil de la gamme 2800 comprend un émetteur-récepteur radio. Il a été conçu de manière à
respecter les limites en matière d'exposition aux fréquences radioélectriques (champs
électromagnétiques de fréquence radio), recommandées dans le code de sécurité 6 de Santé Canada.
Ces directives intègrent une marge de sécurité importante destinée à assurer la sécurité de tous,
indépendamment de l'âge et de la santé.
Par conséquent, les systèmes sont conçus pour être exploités en évitant que l'utilisateur n'entre en
contact avec les antennes. Il est recommandé de poser le système là où les antennes sont à une distance
minimale telle que précisée par l'utilisateur conformément aux directives réglementaires qui sont
conçues pour réduire l'exposition générale de l'utilisateur ou de l'opérateur.
43
Page 44

Distance d'éloignement
Fréquence MPE Distance Limite
2.4 GHz
5GHz
Santé Canada affirme que la littérature scientifique actuelle n'indique pas qu'il faille prendre des
précautions particulières lors de l'utilisation d'un appareil sans fil. Si vous voulez réduire votre
exposition encore davantage, selon l'agence, vous pouvez facilement le faire en réorientant les antennes
afin qu'elles soient dirigées à l'écart de l'utilisateur, en les plaçant à une distance d'éloignement
supérieure à celle recommandée ou en réduisant la puissance de sortie de l'émetteur.
1.89 W/m
2.73 W/m
2
30 cm (12 inches) 5.4 W/m
2
9.2 W/m
2
2
Additional Information on RF Exposure
You can find additional information on the subject at the following links:
• Cisco Systems Spread Spectrum Radios and RF Safety white paper at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/cc/pd/witc/ao340ap/prodlit/rfhr_wi.htm
• FCC Bulletin 56: Questions and Answers about Biological Effects and Potential Hazards of Radio
Frequency Electromagnetic Fields
• FCC Bulletin 65: Evaluating Compliance with the FCC guidelines for Human Exposure to Radio
Frequency Electromagnetic Fields
You can obtain additional information from the following organizations:
• World Health Organization Internal Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection at this
URL: www.who.int/emf
• United Kingdom, National Radiological Protection Board at this URL: www.nrpb.org.uk
• Cellular Telecommunications Association at this URL: www.wow-com.com
• The Mobile Manufacturers Forum at this URL: www.mmfai.org
Administrative Rules for Cisco Aironet Access Points in Taiwan
This section provides administrative rules for operating Cisco Aironet access points in Taiwan. The
rules for all access points are provided in both Chinese and English.
44
Page 45

Chinese Translation
45
Page 46

English Translation
Administrative Rules for Low-power Radio-Frequency Devices
Article 12
For those low-power radio-frequency devices that have already received a type-approval, companies,
business units or users should not change its frequencies, increase its power or change its original
features and functions.
Article 14
The operation of the low-power radio-frequency devices is subject to the conditions that no harmful
interference is caused to aviation safety and authorized radio station; and if interference is caused, the
user must stop operating the device immediately and can't re-operate it until the harmful interference
is clear.
The authorized radio station means a radio-communication service operating in accordance with the
Communication Act.
The operation of the low-power radio-frequency devices is subject to the interference caused by the
operation of an authorized radio station, by another intentional or unintentional radiator, by
industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) equipment, or by an incidental radiator.
Chinese Translation
46
Page 47

English Translation
Low-power Radio-frequency Devices Technical Specifications
4.7 Unlicensed National Information Infrastructure
4.7.5 Within the 5.25-5.35 GHz band, U-NII devices will be restricted to indoor operations to
reduce any potential for harmful interference to co-channel MSS operations.
4.7.6 The U-NII devices shall accept any interference from legal communications and shall not
interfere the legal communications. If interference is caused, the user must stop operating
the device immediately and can't re-operate it until the harmful interference is clear.
4.7.7 Manufacturers of U-NII devices are responsible for ensuring frequency stability such that
an emission is maintained within the band of operation under all conditions of normal
operation as specified in the user manual.
Operation of Cisco Aironet Access Points in Brazil
This section contains special information for operation of Cisco Aironet access points in Brazil.
Access Point Models:
AIR-AP2802I-Z-K9
AIR-AP2802E-Z-K9
47
Page 48

Figure 10 Brazil Regulatory Information
Portuguese Translation
Este equipamento opera em caráter secundário, isto é, não tem direito a proteção contra interferência
prejudicial, mesmo de estações do mesmo tipo, e não pode causar interferência a sistemas operando
em caráter primário.
English Translation
This equipment operates on a secondary basis and consequently must accept harmful interference,
including interference from stations of the same kind. This equipment may not cause harmful
interference to systems operating on a primary basis.
Declaration of Conformity Statements
All the Declaration of Conformity statements related to this product can be found at the following
location: http://www.ciscofax.com
48
Page 49

17 Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service
Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a
service request, and gathering additional information, see What’s New in Cisco Product
Documentation.
To receive new and revised Cisco technical content directly to your desktop, you can subscribe to
the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation RSS feed. The RSS feeds are a free service.
18
© 2016 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks,
go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does
not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
49
Page 50

50
 Loading...
Loading...