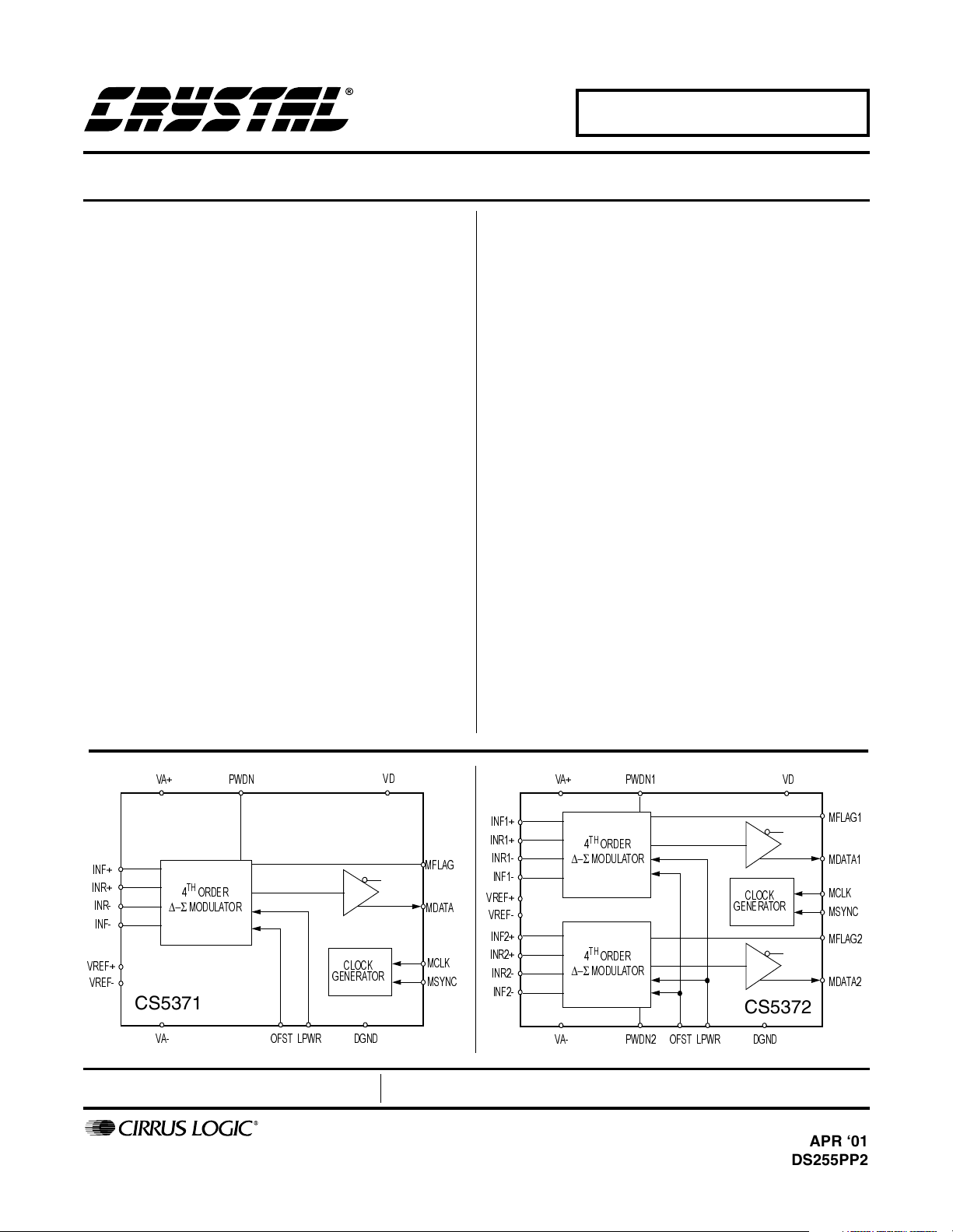
CS5371/CS5372
Low-Power High-Performance ∆Σ Modulators
Features
l Fourth-Order ∆Σ Architecture
l Clock Jitter Tolerant Architecture
l Input Voltage Range 5 V
l High Dynamic Range (SNR)
s 124 dB @ 411 Hz Bandwidth
s 121 dB @ 822 Hz Bandwidth
l Low Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
s -118 dB Typical, -112 dB Maximum
l Low Power Consumption
s Normal Mode: 25 mW per Channel
s Low Power Mode: 15 mW per Channel
l Small Footprint 24 Pin SSOP Package
l Single or Multi-Channel System Support
s 1 Channel System; CS5371
s 2 Channel System; CS5372
s 3 Channel System; CS5371 + CS5372
s 4 Channel System; CS5372 + CS5372
l Single or Dual Power Supply Configurations
s VA+ = +5 V; VA- = 0 V; VD = +3 V to +5 V
s VA+ = +2.5 V; VA- = -2.5 V; VD = +3 V to +5 V
s VA+ = +3 V; VA- = -3 V; VD = +3 V
p-p
(2.5 V
diff
)
Description
The CS5371 and CS5372 are one and two channel high
dynamic range, fourth-order ∆−Σ modulators intended
for geophysical and sonar applications. Used in combination with the CS5376 digital filter, a unique high
resolution A/D measurement system results.
The CS5371 and CS5372 provide higher dynamic range
and lower total harmonic distortion than our industry
standard CS5321 modulator, while consuming significantly less power per channel. The modulators generate
an oversampled serial bit stream at 512 kbits per second
when operated from a clock frequency of 2.048 MHz.
The CS5371 and CS5372 are available in a small 24-pin
SSOP package, providing exceptional performance in a
very small footprint.
In normal mode (LPWR = 0, MCLK = 2.048 MHz), power
consumption is 25 mW per channel, and in low power
mode (LPWR = 1, MCLK = 1.024MHz), power consumption is 15 mW per channel. Each modulator can be
independently powered down to 1 mW per channel, and
by halting the input clock the modulators enter a micropower state using only 10 µW per channel.
ORDERING INFORMATION
CS5371 - BS -40
CS5372 - BS -40
o
C to +85 oC 24-pin SSOP
o
C to +85 oC 24-pin SSOP
,1)
,15
,15
,1)
95()
95()
9$
∆−Σ
7+25'(5
02'8/$725
3:'1
&/2&.
*(1(5$725
CS5371
9$
2)67 /3:5 '*1'
Preliminary Product Information
P.O. Box 17847, Austin, Texas 78760
(512) 445 7222 FAX: (512) 445 7581
http://www.cirrus.com
9'
,1)
,15
0)/$*
0'$7$
0&/.
06<1&
,15
,1)
95()
95()
,1)
,15
,15
,1)
9$
7+25'(5
∆−Σ
02'8/$725
7+25'(5
∆−Σ
02'8/$725
3:'1
&/2&.
*(1(5$725
CS5372
3:'1
9$
This document contains information for a new product.
Cirrus Logic reserves the right to modify this product without notice.
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2001
(All Rights Reserved)
2)67 /3:5 '*1'
9'
0)/$*
0'$7$
0&/.
06<1&
0)/$*
0'$7$
APR ‘01
DS255PP2
1

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. CHARACTERISTICS/SPECIFICATIONS....................................................... 4
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS .................................................................. 4
5.0 AND 3.0 V DIGITAL CHARACTERISTICS ........................................... 6
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ............................................................. 6
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................ 7
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION. ........................................................................... 8
3. MODULATOR PERFORMANCE.................................................................. 10
3.1. Full Scale Signal Performance......................................................... 10
3.2. Noise Performance .......................................................................... 10
4. SIGNAL INPUTS ......................................................................................... 10
4.1. Differential Inputs - INR+/-, INF+/- ................................................... 10
4.2. Anti-Alias Filters ............................................................................... 11
4.3. Input Impedance .............................................................................. 11
4.4. Maximum Signal Levels ................................................................... 12
5. INPUT OFFSET ........................................................................................... 12
5.1. Offset Enable - OFST....................................................................... 12
5.2. Offset Drift ........................................................................................ 12
6. VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUTS .............................................................. 12
6.1. Voltage Reference Configurations ................................................... 13
6.2. VREF Input Impedance .................................................................... 13
6.3. Gain Accuracy .................................................................................. 14
6.4. Gain Drift .......................................................................................... 14
7. DIGITAL FILTER INTERFACE .................................................................... 14
7.1. Modulator Clock - MCLK .................................................................. 14
7.2. Modulator Data - MDATA................................................................. 14
7.3. Modulator Sync - MSYNC ................................................................ 15
7.4. Modulator Flag - MFLAG.................................................................. 15
8. POWER MODES ......................................................................................... 15
8.1. Normal Power Mode ........................................................................ 15
8.2. Low Power Mode - LPWR ................................................................ 16
8.3. Power Down Mode - PWDN............................................................. 16
8.4. Micro Power Mode ........................................................................... 16
9. POWER SUPPLY ........................................................................................ 16
9.1. Power Supply Configurations ........................................................... 16
9.2. Power Supply Bypassing ................................................................. 16
9.3. SCR Latch-up Considerations.......................................................... 16
9.4. DC-DC Converter Considerations.................................................... 17
9.5. Power Supply Rejection ................................................................... 17
10. PIN DESCRIPTION - CS5371 ..................................................................... 18
11. PIN DESCRIPTION - CS5372 ..................................................................... 20
12. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS ............................................................................ 22
CS5371/CS5372
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For a complete listing of Direct Sales, Distributor, and Sales Representative contacts, visit the Cirrus Logic web site at:
http://www.cirrus.com/corporate/contacts/
Preliminary product information describes products which are in production, but for which full characterization data is not yet available. Advance product information describes products which are in development and subject to development changes. Cirrus Logic, Inc. has made best efforts to ensure that the information
contained in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject to change without notice and is provided “AS IS” without warranty of
any kind (express or implied). No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus Logic, Inc. for the use of this information, nor for infringements of patents or other rights
of third parties. This document is the property of Cirrus Logic, Inc. and implies no license under patents, copyrights, trademarks, or trade secrets. No part of
this publication may be copied, reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photographic, or
otherwise) without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. Items from any Cirrus Logic website or disk may be printed for use by the user. However, no
part of the printout or electronic files may be copied, reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical,
photographic, or otherwise) without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc.Furthermore, no part of this publication may be used as a basis for manufacture
or sale of any items without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. The names of products of Cirrus Logic, Inc. or other vendors and suppliers appearing
in this document may be trademarks or service marks of their respective owners which may be registered in some jurisdictions. A list of Cirrus Logic, Inc. trademarks and service marks can be found at http://www.cirrus.com.
2 DS255PP2
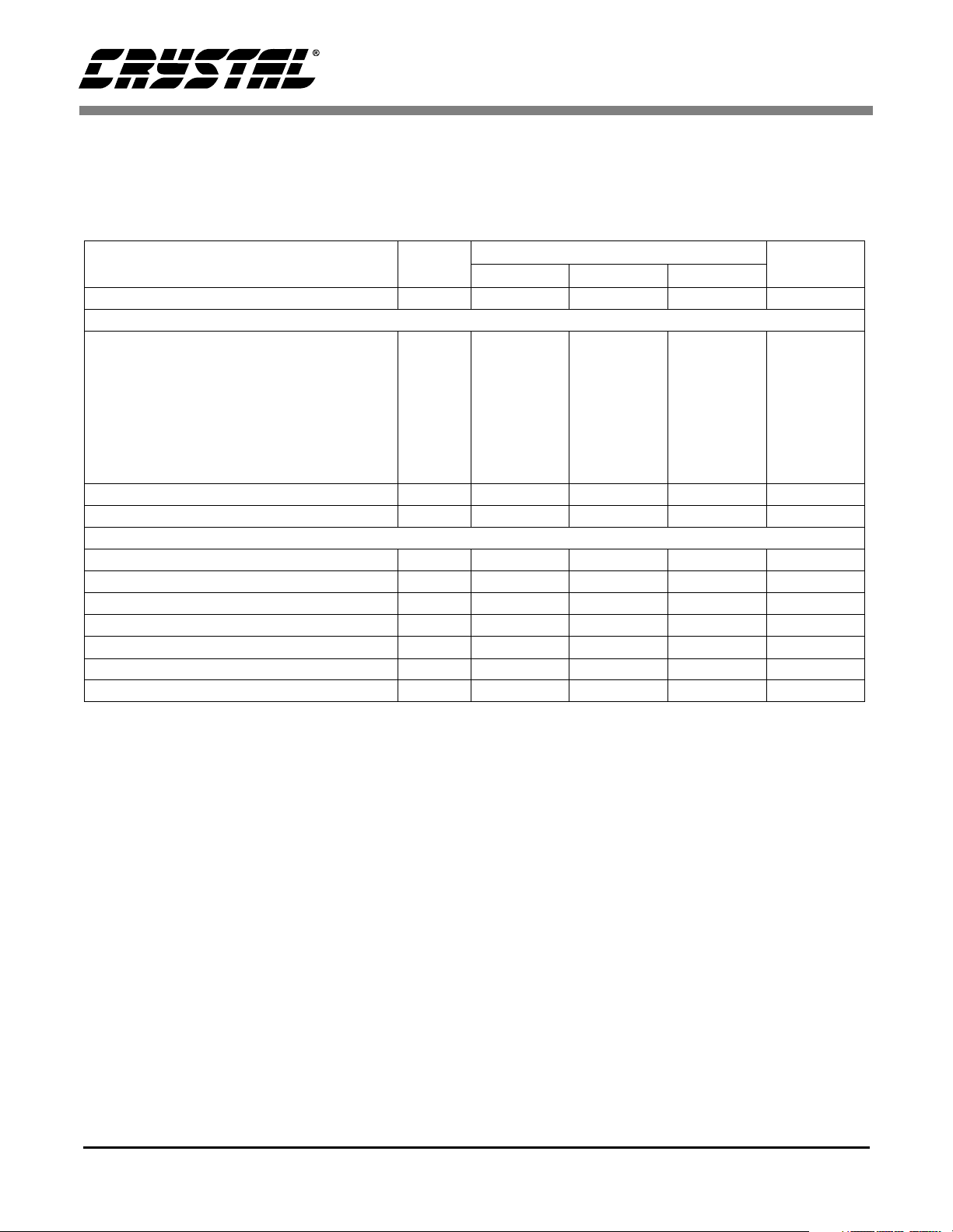
1. CHARACTERISTICS/SPECIFICATIONS
CS5371/CS5372
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS Notes:T
VD = 3 V ± 5%; DGND = 0 V; MCLK = 2.048 MHz; LPWR = 0; VREF+/- = 2.5V (VREF- = -2.5 V; VREF+ = 0 V);
Devices are connected as shown in Figure 3, the System Connection Diagram, unless otherwise specified.
Parameter Symbol
Specified Temperature Range T
Dynamic Performance
Dynamic Range (Note 1)
OFST = 1 0 Hz to 1644 Hz
0 Hz to 822 Hz
0 Hz to 411 Hz
0 Hz to 206 Hz
0 Hz to 103 Hz
0 Hz to 51.5 Hz
0 Hz to 25.75 Hz
Total Harmonic Distortion (Note 2) THD - -118 -112 dB
Intermodulation Distortion (Note 3) IMD - -115 - dB
DC Accuracy
Channel to Channel Gain Variation CGV - 1 - %
Full Scale Error (Note 4) FSE - 1 - %
Full Scale Drift (Notes 4 and 5) TC
Offset (Notes 4) V
Offset after Calibration (Note 6) - ±1 - µV
Offset Calibration Range (Note 7) - 100 - %F.S.
Offset Drift (Notes 4 and 5) TC
Notes: 1. Dynamic Range defined as 20log( (RMS full scale) / (RMS idle noise) )
2. Tested with full scale input signal of 31.25 Hz; OWR = 1000 sps; OFST = 0 or OFST = 1.
3. Characterized with input signals of 31.25 Hz and 52.63 Hz, each 6 dB down from full scale, OWR =
1000 sps.
4. Specification is for the parameter over the specified temperature range and is for the CS5371/CS5372
devices only and does not include the effects of external components.
5. Specifications are guaranteed by design and/or characterization.
6. The offset after calibration specification applies to the effective offset voltage for a full scale input to the
CS5371/CS5372 modulator, but is measured from the output digital codes from the CS5376.
7. The CS5371/CS5372 offset calibration is performed digitally and includes full scale range. Calibration
offsets greater than ± 5% of full scale will begin to subtract from the dynamic range.
= -40 °C to +85 °C; VA+ = 2.5 V ± 5%; VA- = -2.5 V ± 5%;
A
CS5371-BS / CS5372-BS
A
SNR
FS
ZSE
ZSE
-40 - +85 °C
-
-
121
-
-
-
-
- 5 - ppm/°C
-1-mV
-1-µV/°C
109
121
124
127
130
133
136
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
UnitMin Typ Max
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
DS255PP2 3
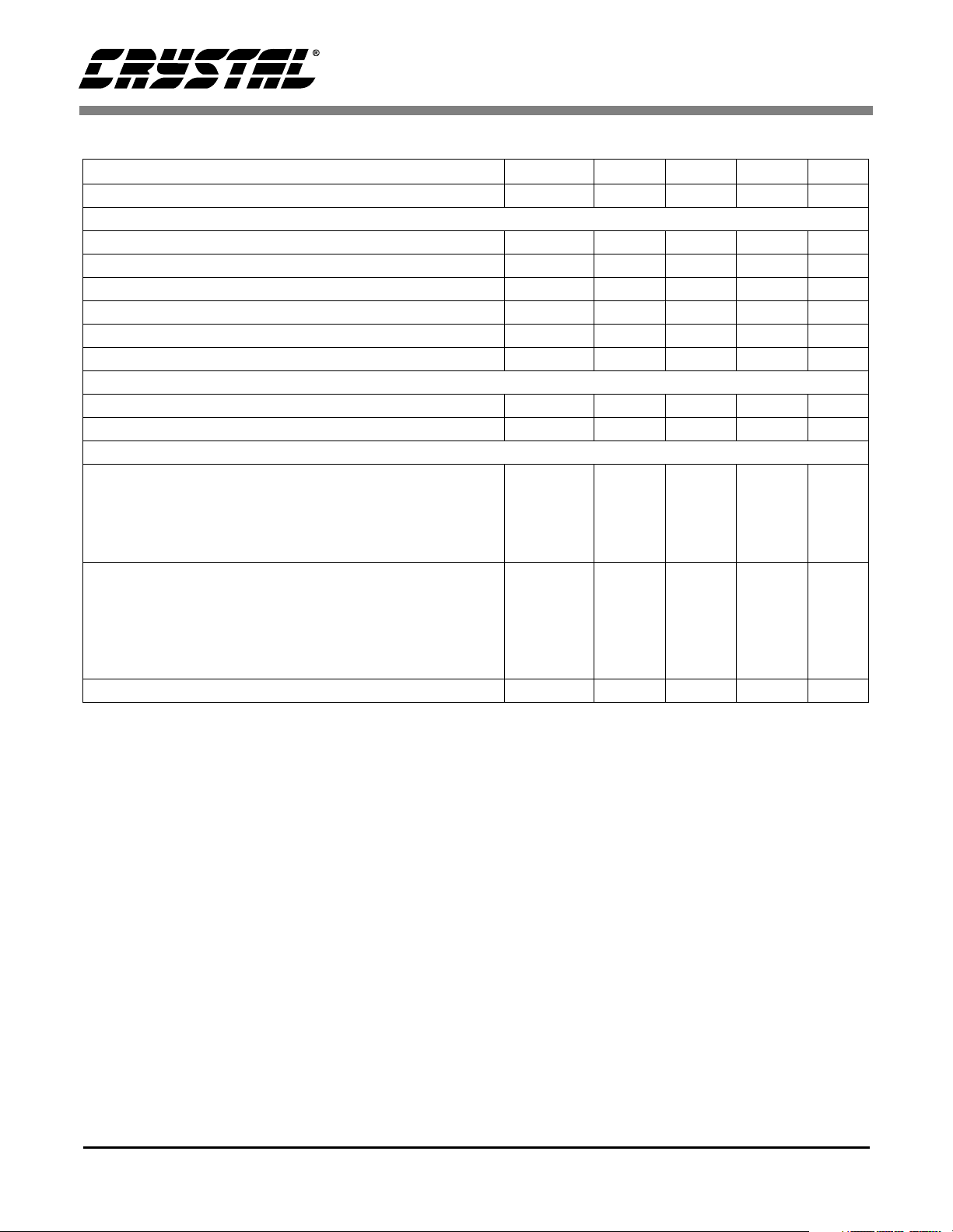
CS5371/CS5372
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Specified Temperature Range T
Input Characteristics
Input Signal Frequencies (Note 8) BW DC - 1644 Hz
Input Voltage Range (Note 9) VIN - - 5 V
Input Over-range Voltage Tolerance (Note 9) I
Input Signal plus Common Mode VA- - VA+ V
Common Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR - 90 - dB
Channel Crosstalk, CS5372 only CXT - -120 - dB
Voltage Reference Input
VREF (VREF+) - (VREF-) - 2.5 - V
VREF Current - - 120 µA
Power Supplies
DC Power Supply Currents (Note 10 and 11)
LPWR = 0; MCLK = 2.048 MHz Analog
Digital
LPWR = 1; MCLK = 1.024 MHz Analog
Digital
Power Down
CS5371 PWDN = 1
PWDN = 1, MCLK = 0
CS5372 PWDN1 or PWDN2 = 1
PWDN1 = PWDN2 = 1
PWDN1 = PWDN2 = 1; MCLK = 0
Power Supply Rejection DC - 128 kHz (Note 12) PSRR - 90 - dB
A
OVR
VA
VD
VA
VD
P
D
-40 - +85 °C
5--%F.S.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
5.0
0.1
3.0
0.1
1
10
25
1
10
7.0
0.2
4.5
0.2
-
-
-
-
-
mA
mA
mA
mA
mW
µW
mW
mW
µW
p-p
Notes: 8. The upper bandwidth limit is determined by the CS5376 digital filter. A simple single pole anti-alias filter
with a -3 dB frequency at (MCLK / 256) should be placed in front of each channel.
9. The input voltage range is for the configuration depicted in Figure 3, the System Connection Diagram,
and applies to signal frequencies from DC to the stop-band frequency selected in the CS5376.
10. Per channel. All outputs unloaded. All digital inputs forced to VD or GND respectively.
11. In Low Power Mode LPWR = 1, the Master Clock MCLK is reduced to 1.024 MHz. This reduces the
signal bandwidth by a factor of 2.
12. Tested with a 100 mVp-p sine wave applied separately to each supply.
4 DS255PP2
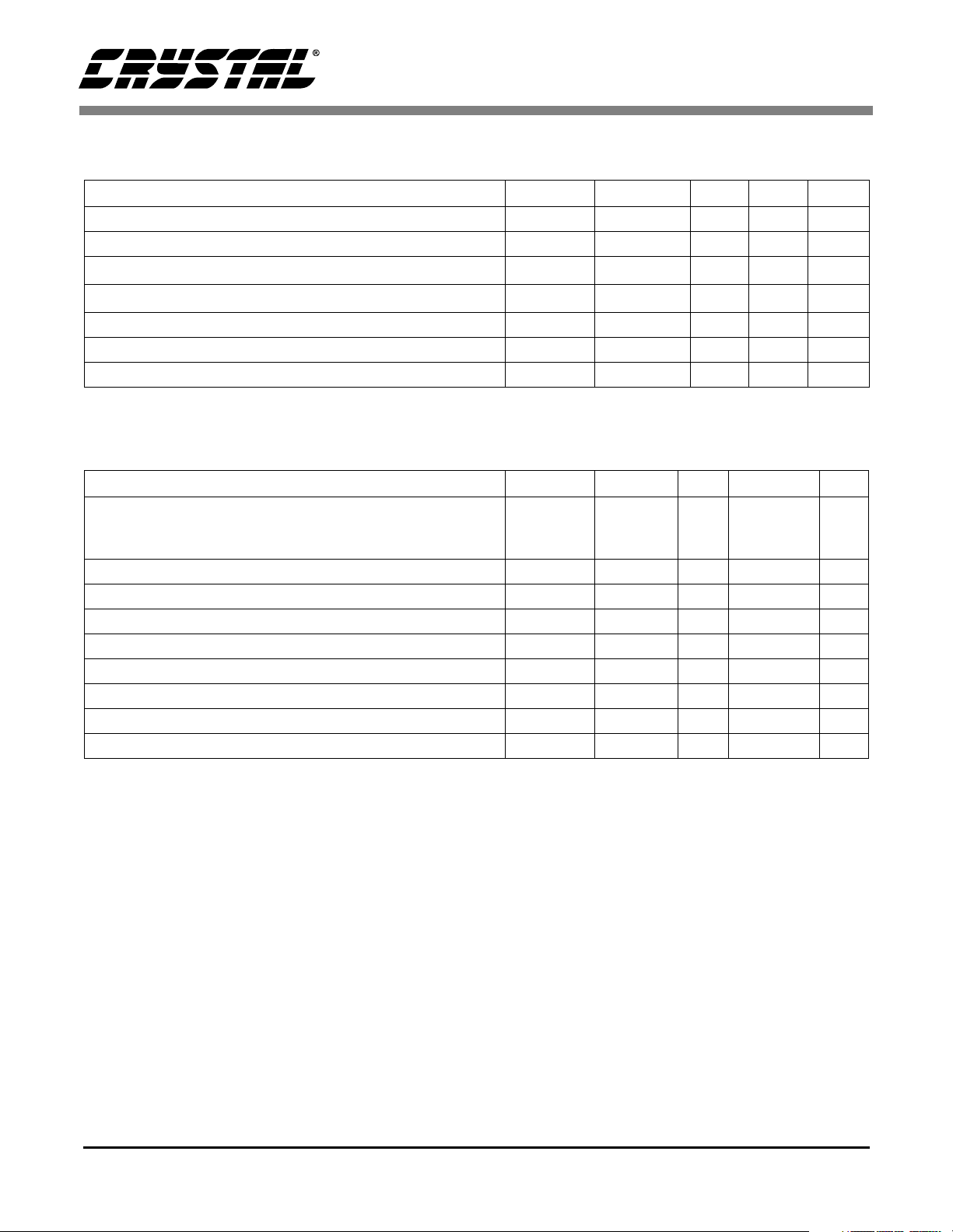
CS5371/CS5372
5.0 AND 3.0 V DIGITAL CHARACTERISTICS Notes:T
= 25 °C; VA+, VD = 5 V ± 5% or 3 V ±
A
5%; AGND, DGND = 0 V; All voltages with respect to DGND.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
High-Level Input Voltage V
Low-Level Input Voltage V
High-Level Output Voltage I
Low-Level Output Voltage I
= -5.0 mA V
out
= 5.0 mA V
out
Input Leakage Current I
3-State Leakage Current I
Digital Output Pin Capacitance C
IH
IL
OH
OL
in
OZ
out
0.6 * VD - VD V
0.0 - 0.8 V
(VD) - 1.0 - - V
--0.4V
-±1±10µA
--±10µA
-9-pF
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS Notes:DGND = 0 V
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
DC Power Supplies (Note 13 and 14) Positive Digital
Positive Analog
Negative Analog
Input Current, Any Pin Except Supplies (Note 15 and 16) I
Input Current, Supplies (Note 16) I
Output Current I
Power Dissipation (Note 17) PDN - - 500 mW
Analog Input Voltage All Analog Pins V
Digital Input Voltage All Digital Pins V
Ambient Operating Temperature T
Storage Temperature T
VD
VA+
VA-
IN
IN
OUT
INA
IND
A
stg
-0.3
-0.3
+0.3
-
-
-
+6.0
+6.0
-3.3
--±10mA
--±50mA
--±25mA
- 0.3 - (VA+) + 0.3 V
-0.3 - (VD) + 0.3 V
-40 - 85 °C
-65 - 150 °C
V
V
V
Notes: 13. VA+ and VA- must satisfy {(VA+) - (VA-)} < +6.6 V.
14. VD and VA- must satisfy {(VD) - (VA-)} < +7.6 V.
15. Includes continuous over-voltage conditions at the analog input (AIN) pins.
16. Transient current of up to 100 mA can be safely tolerated without SCR latch-up.
17. Total power dissipation, including all input and output currents.
DS255PP2 5
CS5371/CS5372
2.7 V
0.3 V
t
fallin
t
risein
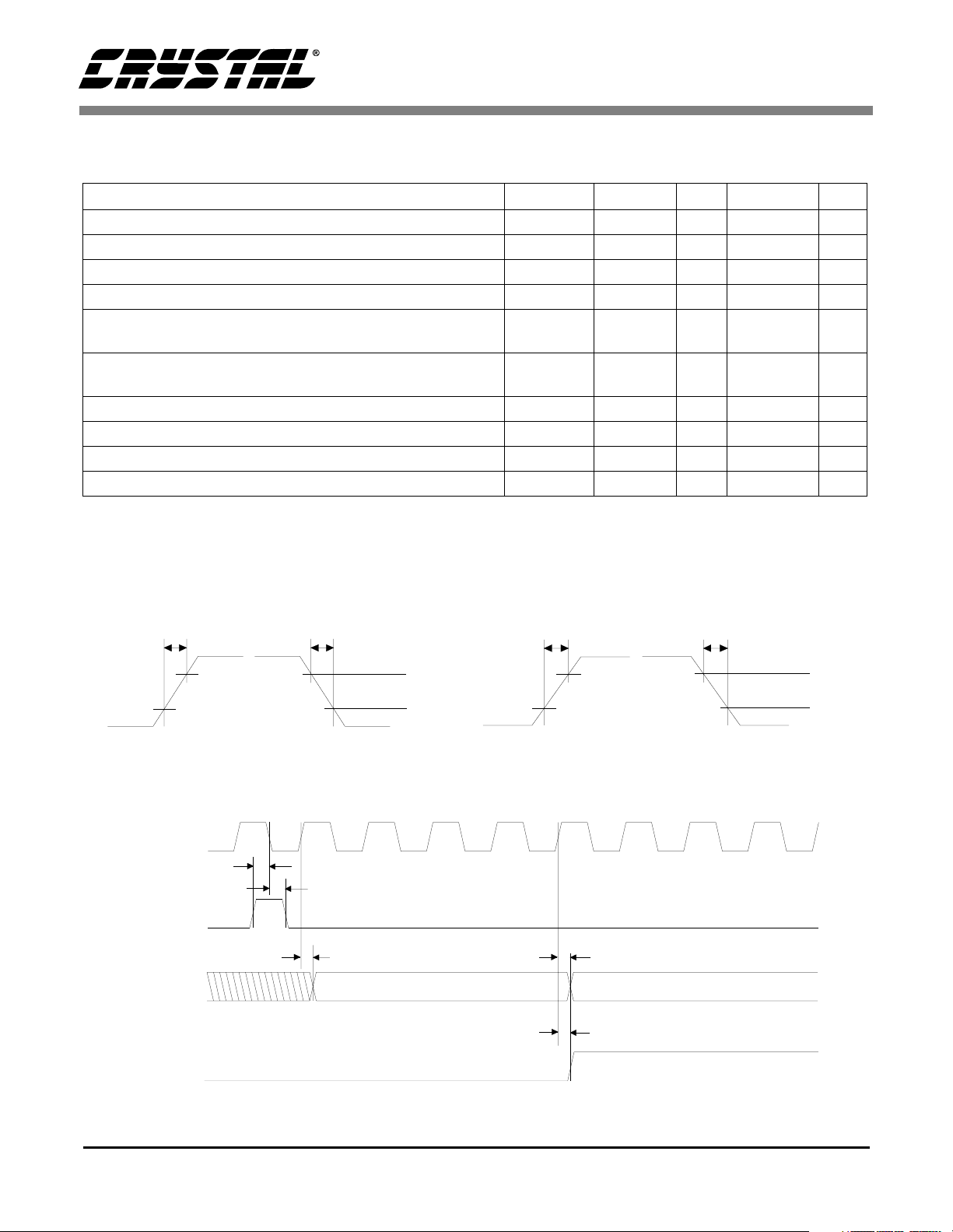
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS Notes:T
5%; VD = 3 V ± 5%; Inputs: Logic 0 = 0 V, Logic 1 = VD; C
= -40 °C to +85 °C; VA+ = +2.5 V ± 5% VA- = -2.5 V ±
A
= 50 pF
L
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
MCLK Frequency (Note 18) f
c
0.1 2.048 2.2 MHz
MCLK Duty Cycle 40 - 60 %
MCLK Jitter (In-band, Aliased in-band) - - 300 ps
MCLK Jitter (Out-of-band) - - 1 ns
Rise Times: Any Digital Input (Note 19)
Any Digital Output
Fall Times: Any Digital Input (Note 19)
Any Digital Output
MSYNC Setup Time to MCLK falling (Note 20) t
MSYNC Hold Time after MCLK falling t
MCLK rising to Valid MFLAG t
MCLK rising to Valid MDATA t
t
risein
t
riseout
t
fallin
t
fallout
mss
msh
mfh
mdv
-
-
-
-
20 - - ns
20 - - ns
-3565ns
-6090ns
50
50
-
50
100
-
50
100
Notes: 18. If MCLK is removed, the CS5372 enters a micro power state.
19. Excludes MCLK input, MCLK should be driven with a signal having rise/fall times of 25 ns or faster.
20. MSYNC latched on MCLK falling edge, data output on next MCLK rising edge.
ns
ns
ns
ns
MCLK
MSYNC
MDATA
MFLAG
t
mss
t
msh
t
mdv
Figure 1. Rise and Fall Times
VALID DATA
t
riseo ut
t
mdv
t
mfh
VALID DATA
t
fallout
2.7 V
0.3 V
Figure 2. CS5372 Interface Timing
6 DS255PP2

CS5371/CS5372
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION.
The CS5371 and CS5372 are one and two channel
fourth-order ∆−Σ modulators, optimized for extremely high resolution measurement of signals between DC and 1644 Hz. They are designed to be
used with the CS5376 low power multi-channel
decimation filter. Figure 3 on page 8 shows a fourchannel system connection diagram for two
CS5372 and one CS5376.
High Performance
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators have exceptional
performance characteristics. Modulator dynamic
range (SNR) is 124 dB over a 411 Hz bandwidth,
with total harmonic distortion (THD) of -118 dB.
Low Power Consumption
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators have very low
power consumption. Power consumption is only
25 mW per channel in normal mode (LPWR=0,
MCLK=2.048 MHz), and 15 mW per channel in
low power mode (LPWR=1, MCLK=1.024 MHz).
An independently selectable power-down mode
(PWDN=1) can be used to disable a modulator and
reduces its power consumption to 1 mW. If MCLK
is then halted (MCLK=0), the modulator enters a
micropower state using only 10 µW per channel.
Small Package Size
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators are available in a
very small 24-pin SSOP package approximately
8 mm x 8 mm in size. The CS5372 has two modulator channels per package to increase board layout
density even further.
Multi-Channel System Support
Combining the CS5371 and CS5372 modulators
with the CS5376 digital filter permits multiple
channel system configurations to be supported.
1 Channel - CS5371, CS5376
2 Channel - CS5372, CS5376
3 Channel - CS5371, CS5372, CS5376
4 Channel - CS5372, CS5372, CS5376
Differential Analog Signal Inputs
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators have differential
analog inputs capable of measuring signals up to
5.0 V peak-to-peak (2.5 V fully differential) when
using a 2.5 V voltage reference. The inputs will
tolerate a 5% over-range voltage and continue operating at full specification.
Digital Filter Interface
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators are designed to
operate with the CS5376 digital filter. The CS5376
generates the modulator clock and synchronization
signal inputs (MCLK and MSYNC), while receiving the modulator data and over-range flag outputs
(MDATA and MFLAG). The modulators produce
an oversampled ∆−Σ serial bit stream at 512 kbits
per second when operated from a 2.048 MHz modulator clock.
Multiple Power Supply Configurations
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators support multiple
power supply configurations. They can run from
single or dual supplies in the following configurations:
s VA+ = +5V; VA- = 0V; VD = +3V to +5V
s VA+ = +2.5V; VA- = -2.5V; VD = +3V to +5V
s VA+ = +3V; VA- = -3V; VD = +3V
DS255PP2 7

CS5371/CS5372
+3 V
Channel 1
VREF
~
~Channel 2
220
100 µF
+3 V
100 µF
Ω
1k
Ω
1k
Ω
1k
Ω
1k
Ω
1k
Ω
1k
Ω
1k
Ω
1k
Ω
0.01µF
0.01 µF
COG
0.01 µF
COG
0.01 µF
0.01
0.01 µF
X7R
X7R
0.01 µF
VA+ VD+
INRI+
INFI+
µ
F
INFI-
INRI-
M
F
LAG1
MDATA1
MFLAG2
MDATA2
CS5372
INR2+
INF2+
INF2-
INR2-
VREF+
VREF-
VA- DGND
MCLK
MSYNC
OFST
LPWR
PWDN1
PWDN2
+3 V
100 µF
MFLAG1
MDATA1
MFLAG2
MDATA2
MCLK
MSYNC
GPIO4
GPIO5
GPIO6
GPIO7
CS5376
-3 V
VA+ VD+
VREF-
VREF+
Ω
1k
Ω
1k
0.01 µF
~Channel 3
~Channel 4
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
-3 V
100 µF
0.01 µF
COG X7R
0.01 µF
0.01 µF
COG X7R
0.01 µF
INRI+
INFI+
INFI-
INRI-
INR2+
INF2+
INF2-
INR2-
MSYNC
PWDN1
PWDN2
CS5372
MFLAG1
MDATA1
MFLAG2
MDATA2
VA- DGND
MCLK
OFST
LPWR
MFLAG3
MDATA3
MFLAG4
MDATA4
Figure 3. System Connection Diagram
8 DS255PP2

CS5371/CS5372
Figure 4. 1024 Point FFT plot with a 31.25 Hz
input at Full Scale, ten averages
-200
-180
-160
-140
-120
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
0 50 100 150 2 00 2 50 300 350 40 0 4 50 5 00
dB
Hz
S/N = 124.0 dB
S/D = 119.0 dB
3. MODULATOR PERFORMANCE
Figures 4 and 5 illustrate the spectral performance
of the CS5371/CS5372 modulators when combined with the CS5376 digital filter. The plots
were created from ten averaged 1024 point FFTs.
3.1. Full Scale Signal Performance
Figure 4 illustrates the full-scale signal performance of the CS5371/CS5372 modulators and
CS5376 digital filter using a 31.25 Hz input signal
and a 1000 sps output word rate. The outstanding
full-scale signal characteristics of the
CS5371/CS5372 modulators are shown, with no
harmonic components exceeding -120 dB. Analysis of this data set yields a signal-to-noise ratio
(SNR) of 124.0 dB and a signal-to-distortion ratio
(SDR) of 119.0 dB. Note that the full-scale signal
peak in Figure 4 shows a slightly reduced amplitude due to spectral smearing associated with the
FFT windowing function, and is a purely digital
phenomenon.
3.2. Noise Performance
Figure 5 illustrates the noise performance of the
CS5371/CS5372 modulators and CS5376 digital
filter using a 31.25 Hz -24 dB input signal and a
1000 sps output word rate. The outstanding noise
characteristics of the CS5371/CS5372 modulators
are shown, with the averaged noise components
consistently below the -150 dB level. Analysis of
this data set yields a dynamic range of 124.7 dB.
Note that the 0.7 dB variation between the signalto-noise calculation in Figure 4 and the dynamic
range calculation in Figure 5 is not modulator dependent and results from jitter in the test signal
generator when producing a full scale output, as evidenced by the skirt surrounding the signal peak below the -140 dB level in Figure 4.
4. SIGNAL INPUTS
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators use a switched
capacitor architecture for the analog signal inputs,
which has increased jitter tolerance relative to continuous time signal input stages.
4.1. Differential Inputs - INR+/-, INF+/-
The analog signal inputs are differential and use
four pins: INR+, INR-, INF+, and INF-. The positive inputs, INR+ and INF+, are connected to the
positive half of the differential signal, while the
negative inputs, INR- and INF-, are connected to
DS255PP2 9
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
dB
-120
-140
-160
-180
-200
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 40 0 450 500
Dynamic Range = 124.7 dB
Hz
Figure 5. 1024 Point FFT plot with a 31.25 Hz
input at -24 dB, ten averages

CS5371/CS5372
the negative half. The INR+ and INR- pins are
switched capacitor ‘rough charge’ inputs for the
INF+ and INF- fine input pins.
The full scale analog signal span is defined by the
voltage applied across the VREF+ and VREFpins. A 2.5 volt reference input sets full scale signals as 5 volts peak-to-peak, or 2.5 volts fully differential. Differential inputs increase the dynamic
range of small signals, reducing the gain requirements for input amplifier stages by a factor of two
relative to single ended analog inputs.
4.2. Anti-Alias Filters
The CS5371/CS5372 modulator inputs must be
bandwidth limited to ensure modulator loop stability and to prevent aliased high-frequency signals.
The modulators are 4th order and so are conditionally stable, and can be adversely affected by high
amplitude out-of-band signals. Also, aliasing effects degrade modulator performance if the analog
inputs are not bandwidth limited since out-of-band
signals can appear in the measurement bandwidth.
The use of a simple single pole low-pass anti-alias
filter on the differential inputs ensures out-of-band
signals are eliminated.
Sampling Frequency = MCLK / 4 = 512 kHz
-3 dB Filter Corner = Sample Freq / 64 = 8 kHz
RC filter = 8 kHz = 1 / [ 2π * (2 * R
diff
) * C
diff
It should be noted that when using low power mode
(LPWR=1 and MCLK=1.024 MHz) the modulator
sampling clock is 256 kHz, so the -3 dB filter corner should be scaled down to 4 kHz.
MCLK Frequency = 1.024 MHz
Sampling Frequency = MCLK / 4 = 256 kHz
-3 dB Filter Corner = Sample Freq / 64 = 4 kHz
RC filter = 4 kHz = 1 / [ 2π * (2 * R
diff
) * C
diff
Figure 3 illustrates the CS5372/CS5376 system
connections with input anti-alias filter components.
Filter components on the rough and fine pins
should be identical values for optimum performance, with the capacitor values a minimum of
0.01 µF. The rough input can use either X7R or
C0G capacitors, while the fine input requires C0G
type capacitors for optimal linearity. Using X7R
capacitors on the fine inputs will degrade signal to
distortion performance up to 8 dB.
4.3. Input Impedance
]
]
Anti-alias filtering may be accomplished actively
in an amplifier stage ahead of the CS5371/CS5372
modulator, or passively using an RC filter across
the differential rough and fine analog inputs. An
RC filter is recommended, even when using an amplifier stage, as it minimizes the ‘charge kick’ that
the driving amplifier sees as switched capacitor
sampling is performed.
The -3 dB corner of the input anti-alias filter should
be set to the internal modulator sampling clock divided by 64. The modulator sampling clock is a division by 4 of the modulator clock, MCLK. With
MCLK=2.048 MHz the modulator sampling clock
is 512 kHz, requiring an input filter with a -3 dB
corner at 8 kHz.
MCLK Frequency = 2.048 MHz
10 DS255PP2
Due to the dynamic switched-capacitor input architecture the input current required from the analog
signal source, and thus the input impedance of the
analog input pins, changes any time MCLK is
changed. The input impedance of the rough charge
inputs, INR+ and INR-, is [1 / (f * C)] where f is the
modulator clock frequency, MCLK, and C is the internal sampling capacitor. A 2.048 MHz modulator clock yields a rough input impedance of
approximately [1 / (2.048 MHz)*(20 pF)], or about
24 kohms.
Internal to the modulator the rough charge inputs
pre-charge the sampling capacitor used by the fine
inputs, therefore the effective input impedance of
the fine inputs is orders of magnitude above the impedance of the rough inputs.

CS5371/CS5372
4.4. Maximum Signal Levels
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators are 4th order and
are therefore conditionally stable, and may go into
an oscillatory condition if the analog inputs overrange beyond full scale by more than 5%. If an unstable condition is detected, the modulators collapse to a 1st order system until loop stability is
achieved. During this time, the MFLAG pin transitions from low to high signaling the CS5376 digital filter to set an error bit in the digital output
word. The analog input signal must be reduced to
within the full scale range of the converter for at
least 32 MCLK cycles for the modulators to recover from an unstable condition.
5. INPUT OFFSET
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators are ∆−Σ type and
so can produce ‘idle tones’ in the passband when
the input signal is a steady state DC signal within
about ±50 mV of the common mode input voltage.
Idle tones result from patterns in the output bitstream and appear in the measurement spectrum
about -135 dB down from full scale.
Idle tones can be eliminated by adding 100 mV or
more of differential DC offset to the modulator inputs. The added offset should be applied differentially to the inputs, common mode offsets do not
affect idle tones.
5.1. Offset Enable - OFST
If the analog inputs are within ±50 mV of the common mode voltage when no signal is present, the
OFST pin can be used to eliminate idle tones.
When OFST=1, +100 mV of differential offset is
added to the modulator analog inputs to push the
idle tones out of the measurement bandwidth. Care
should be taken that when OFST is active, offset
voltages generated by external circuitry do not negate the internally added offset.
5.2. Offset Drift
Offset drift characteristics vary from part to part
and with changes in the power supply voltages. If
the CS5371/CS5372 is used in precision DC measurement applications where offset drift is to be
minimized, the power supplies should be well regulated.
For the lowest offset drift, the CS5371/CS5372
modulators should operate with an MCLK of
2.048 MHz. The offset drift rate is inversely proportional to clock frequency, with slower modulator clock rates exhibiting more offset drift.
Operating from an MCLK of 1.024 MHz results in
twice the offset drift rate compared to an MCLK of
2.048 MHz.
Because offset drift is not linear with temperature,
an exact drift rate per °C cannot be specified. The
CS5371/CS5372 modulators will exhibit approximately 5 ppm/°C of offset drift operating with an
MCLK of 2.048 MHz.
6. VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUTS
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators are designed to
operate with a 2.5 V voltage reference applied
across the VREF+ and VREF- pins to set the full
scale signal range of the analog inputs. A 2.5 V
voltage reference results in the highest dynamic
range and best signal-to-noise performance, though
smaller reference voltages may be used. When the
CS5371/CS5372 modulators are operated with a
2.5 V reference, the analog inputs measure full
scale signals of 5 volts peak-to-peak, or 2.5 volts
differential.
In a single supply power configuration the voltage
reference output should be connected to the
VREF+ pin with the VREF- pin connected to
ground. In a dual supply power configuration the
voltage reference should be powered from the VA+
and VA- supplies, with the modulator VREF+ pin
connected to the voltage reference output and the
DS255PP2 11

CS5371/CS5372
VREF- pin connected to VA-. Because most 2.5 V
voltage references require a power supply voltage
greater than 3 V to operate, when powering the
voltage reference from dual ±2.5 V or ±3.0 V supplies the reference voltage into the VREF+ pin is
defined relative to the VA- supply.
The selected voltage reference should produce less
than 1 µVrms of noise in the measurement bandwidth on the VREF+ pin. The CS5376 digital filter
output word rate selection determines the bandwidth over which voltage reference noise affects
the CS5371/CS5372 modulator dynamic range.
6.1. Voltage Reference Configurations
For a 2.5 V reference, the Linear Technology
LT1019-2.5 voltage reference yields low enough
noise if the output is filtered with a low pass RC fil-
ter as shown in Figure 6. The filtered version in
Figure 6 is acceptable for most spectral measurement applications, but a buffered version with lower source impedance, Figure 7, may be preferred
for DC measurement applications. The configuration shown in Figure 7 can use a Linear Technology LT1077 or similar low voltage op-amp to buffer
the voltage reference output.
6.2. VREF Input Impedance
Due to the dynamic switched-capacitor input architecture the input current required from the voltage
reference, and thus the input impedance of the
modulator VREF+ pin, will change any time
MCLK is changed. The input impedance of the
voltage reference input is calculated similar to the
analog signal input impedance as [1 / (f * C)]
where f is the modulator clock frequency, MCLK,
+3 V
-3 V
+3 V
-3 V
µ
10
F
0.1µF
2.5 REF
µ
10
0.1µF
F
Option A
200
Ω
0.1µF 68µF
To VREF+
+
To VREF -
Figure 6. 2.5 Voltage Reference Option A
µ
10
u
0.1µF
2.5 REF
µ
10
0.1µF
u
Option B
1k
10k
+
+
49.9
100µF
AL
100µF
AL
Ω
+
-
OPAMP
100
1k
Ω
0.1µF 68µF
Ω
To VREF+
+
Tant
To VREF -
Ω
Ω
Figure 7. 2.5 Voltage Reference Option B
12 DS255PP2

CS5371/CS5372
and C is the internal sampling capacitor. A
2.048 MHz MCLK yields a voltage reference input
impedance of approximately
[1 / (2.048 MHz)*(20 pF)], or about 24 kohms.
6.3. Gain Accuracy
Gain accuracy of the CS5371/CS5372 modulators
is affected by variation of the voltage reference input. A change in the voltage reference input impedance due to a change in MCLK could affect
gain accuracy when using the higher source impedance configuration of Figure 6. The VREF+ pin input impedance and the external low-pass filter
resistor create a resistive voltage divider for the
output reference voltage, reducing the effective
voltage reference input. If gain error is to be minimized, especially when MCLK is to be changed,
the voltage reference should have a low output impedance to minimize the effect of the resistive voltage divider. The buffered voltage reference
configuration of Figure 7 offers lower output impedance and more stable gain characteristics.
6.4. Gain Drift
Gain drift of the CS5371/CS5372 modulators due
to temperature is around 5 ppm/°C, and does not include the temperature drift characteristics of the external voltage reference. Gain drift is not affected
by the modulator sample rate or by power supply
variations.
7. DIGITAL FILTER INTERFACE
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators are designed to
operate with the CS5376 digital filter. The CS5376
generates the modulator clock and synchronization
signal inputs (MCLK and MSYNC), while receiving the modulator data and over-range flag outputs
(MDATA and MFLAG). The modulators produce
an oversampled ∆−Σ serial bit stream at 512 kbits
per second when operated from a 2.048 MHz modulator clock.
7.1. Modulator Clock - MCLK
For proper operation, the CS5371/CS5372 modulators must be provided with a CMOS compatible
clock on the MCLK pin. MCLK is internally divided by four to generate the modulator sampling
clock. MCLK must have less than 300 ps of inband jitter to maintain full performance specifications.
When used with the CS5376 digital filter, MCLK is
automatically generated and is typically
2.048 MHz or 1.024 MHz. MCLK can be generated by other means, using a crystal oscillator for example, and can run any rate between 100 kHz and
2.2 MHz. If MCLK is disabled, the modulators are
placed into a micro-power state. They are
equipped with loss of clock detection circuitry to
force power down if MCLK is removed.
The choice of MCLK frequency affects the performance of the CS5371/CS5372 modulators. They
exhibit the best dynamic range (SNR) performance
with faster MCLK rates because of increased oversampling of the analog input signal. The modulators exhibit the best total harmonic distortion
(THD) performance with slower MCLK rates because slower sampling allows more time to settle
the analog input signal.
7.2. Modulator Data - MDATA
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators output a ∆−Σ serial bitstream to the MDATA pin, with a one’s den-
sity proportional to the amplitude of the analog
input signal and a bit rate determined by the modulator sampling clock. The modulator sampling
clock is a divide by four of MCLK, so for a
2.048 MHz MCLK the modulator sampling clock
and MDATA output bit rate will be 512 kHz.
The MDATA output has a one’s density defined as
nominal 50% for no signal input, 86% for positive
full scale, and 14% for negative full scale. It has a
maximum positive over-range capability to 93%
and a maximum negative over-range capability to
DS255PP2 13

CS5371/CS5372
Table 1. Output coding for the CS5371/CS5372 and
CS5376 combination
Modulator Input
Signal
CS5376 Filter
Output Code
HEX Decimal
> + (VREF + 5%) Error Flag Possible
≈ + (VREF + 5%) 64CCCC +6606028
+VREF 5FFFFF +6291455
0V 000000 0
-VREF A00001 -6291455
≈ - (VREF + 5%) 9B3334 -6606028
> - (VREF + 5%) Error Flag Possible
7%. The one’s density of the MDATA output is defined as the ratio of ‘1’ bits to total bits in the serial
bitstream output, i.e. an 86% one’s density has, on
average, a ‘1’ value in 86 of every 100 output data
bits.
When operated with the CS5376 digital filter, the
full scale 24-bit output codes range from
0x5FFFFF (decimal 6,291,455) to 0xA00001 (decimal -6,291,455).
The MSYNC input is rising edge triggered and resets the internal MCLK counter-divider so the analog sampling instant occurs during a consistent
MCLK phase. It also sets the MDATA output timing so the bitstream can be properly sampled by the
CS5376 digital filter input.
7.4. Modulator Flag - MFLAG
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators are 4th order ∆−
Σ and are therefore conditionally stable. The mod-
ulators may go into an oscillatory condition if the
analog inputs are over-ranged more than 5% past
either positive or negative full scale.
If an unstable condition is detected, the modulators
collapse to a 1st order system until loop stability is
achieved. During this time, the MFLAG pin transitions from low to high to signal an error condition. The analog input signal must be reduced to
within the full scale range for at least 32 MCLK cycles for the modulator to recover from an unstable
condition.
Note that for a full scale input signal, 5 V
(2.5 V
) with VREF=2.5 V, the CS5371/CS5372
diff
and CS5376 chip set does not output a maximum
24-bit 2’s complement digital code of 0x7FFFFF
(digital 8,388,607), but instead a lower scaled value
to allow over-range capability. The CS5376 converts to full performance specification up to a positive over-range value of 0x64CCCC (decimal
6,606,028) and down to a negative over-range value of 0x9B3334 (decimal -6,606,028).
7.3. Modulator Sync - MSYNC
To synchronize the analog sampling instant and
timing of the digital output bitstream, the
CS5371/CS5372 modulators use an MSYNC signal. When using the CS5376 digital filter, MSYNC
is automatically generated from a SYNC signal input from the external system.
14 DS255PP2
p-p
The MFLAG output connects to a dedicated input
on the CS5376 digital filter, causing an error bit to
be set in the status portion of the digital output data
word when detected.
8. POWER MODES
Four power modes are available when using the
CS5371/CS5372 modulators. Normal power and
low power modes are operational modes, power
down and micro power modes are non-operational
standby modes.
8.1. Normal Power Mode
The normal operational mode for the modulators,
LPWR=0 and MCLK=2.048 MHz, provides the
best performance with power consumption of
25 mW per channel. This power mode is recommended when maximum conversion accuracy is required.

CS5371/CS5372
8.2. Low Power Mode - LPWR
The modulators have a low-power operational
mode, LPWR=1 and MCLK=1.024 MHz, that reduces power consumption to 15 mW per channel at
the expense of 3 dB of dynamic range. This operational mode is recommended when minimizing
power is more important than maximizing dynamic
range.
When operated with LPWR=1, the modulator sampling clock (MCLK / 4) must be restricted to rates
of 256 kHz or less, which requires MCLK to run at
1.024 MHz or less. Operating in low power mode
with modulator sample rates greater than 256 kHz
will significantly degrade total harmonic distortion
performance.
8.3. Power Down Mode - PWDN
The modulators have a power down mode,
PWDN=1 and MCLK=Active, that disables the operation of the selected modulator channel and reduces its power consumption to 1 mW. Each
modulator has an independent power down pin,
PWDN on the CS5371 and PWDN1, PWDN2 on
the CS5372. Note that when the modulators are
powered down and MCLK is active, the internal
clock generator is still drawing minimal currents.
8.4. Micro Power Mode
Standby power consumption of the modulators can
be minimized by placing them into a micro power
mode, PWDN=1 and MCLK=0. Micro power
mode requires setting the PWDN pin and halting
MCLK to remove the clock generator input current.
Micro power mode consumes only 10 µW of power.
The analog and digital circuitry is separated internally to enhance performance, therefore power
must be supplied to all three supply pins and the
digital ground pin must be referenced to system
ground.
9.1. Power Supply Configurations
The CS5371/CS5372 analog supplies can be powered by a single +5 V supply and analog ground, or
by dual supplies of + 2.5 V or + 3.0 V. When using
dual supplies, the positive and negative analog
power supplies must be equivalent in voltage but
opposite in polarity and must satisfy the following
conditions:
(VA+) - (VA-) < 6.6 volts
(VD) - (VA-) < 7.6 volts
These conditions permit several power supply configurations.
s VA+ = +5 V;VA- = 0 V;VD+ = +3 V to +5 V
s VA+ = +2.5 V;VA- = -2.5 V;VD+ = +3 V to +5 V
s VA+ = +3 V;VA- = -3 V;VD+ = +3 V
When used with the CS5376 digital filter the maximum voltage differential between the modulator
digital supply, VD, and the CS5376 digital supply,
VDD2, must be less than 0.3 V.
9.2. Power Supply Bypassing
The analog and digital supply pins, VA+, VA-, and
VD, should be decoupled to system ground with
0.01 µF and 10 µF capacitors, or with a single
0.1 µF capacitor. Bypass capacitors can be X7R,
tantalum, or any other dielectric types.
9.3. SCR Latch-up Considerations
9. POWER SUPPLY
The CS5371/CS5372 modulators have one positive
analog power supply pin, VA+, one negative analog power supply pin, VA-, one digital power supply pin, VD, and one digital ground pin, DGND.
DS255PP2 15
The VA- pin is tied to the CS5371/CS5372 substrate and should always be connected to the most
negative supply voltage to ensure SCR latch-up
does not occur. In general, latch-up may occur
when any pin voltage is 0.7 V or more below VA-.

CS5371/CS5372
When using dual power supplies, it is recommended to connect the VA- analog supply pin to system
ground using a reversed biased Schottky diode.
This configuration clamps the VA- pin a maximum
of 0.3 V above ground to ensure SCR latch-up does
not occur during power up. If the VA+ supply
ramps before the VA- supply, the VA- pin can be
pulled above ground through the CS5371/CS5372.
If the VA- supply pin is unintentionally pulled
0.7 V above the DGND pin, SCR latch-up can occur.
9.4. DC-DC Converter Considerations
Many measurement systems are battery powered
and utilize DC-DC converters to generate the necessary supply voltages for the system. To minimize the effects of interference, it is desirable to
operate the DC-DC converter at a frequency which
is rejected by the digital filter, or else synchronously to the modulator sample clock rate. A synchronous DC-DC converter whose operating frequency
is derived from MCLK minimizes the potential for
‘beat frequencies’ appearing in the
band.
measurement
9.5. Power Supply Rejection
Power supply rejection of the CS5371/CS5372
modulators is frequency dependent. The CS5376
digital filter rejects power supply noise for frequencies above the filter corner frequency. For frequencies between DC and the digital filter corner
frequency, power supply rejection is nearly constant at 90 dB.
16 DS255PP2

10. PIN DESCRIPTION - CS5371
CS5371/CS5372
Rough Non-Inverting Input INR+
Fine Non-Inverting Input INF+
Fine Inverting Input INF-
Rough Inverting Input INR-
Positive Voltage Reference Input VREF+
Negative Voltage Reference Input VREF-
Negative Analog Power Supply VA-
Positive Analog Power Supply VA+
No Internal Connection NC
No Internal Connection NC
No Internal Connection NC
No Internal Connection NC
Power Supplies
VA + _ Positive Analog Power Supply, pin 8
Positive supply voltage.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
817
9
10
11
12 13
PWDN Power-down Enable
24
LPWR Low Power Mode Select
23
MFLAG Modulator Flag Output
22
MDATA Modulator Data Output
21
MSYNC Modulator Sync Input
20
MCLK Modulator Clock Input
19
18
VD Positive Digital Power Supply
DGND Digital Ground
NC No Internal Connection
16
NC No Internal Connection
15
OFST Offset Mode Select
14
VD Positive Digital Power Supply
_
VA -
Negative Analog Power Supply, pin 7
Negative supply voltage.
VD _ Positive Digital Power Supply, pin 13, 18
Positive supply voltage.
_
DGND
Digital Ground, pin 17
Analog Inputs
INR+ _ Rough Non-Inverting Input, pin 1
Rough non-inverting analog input. The rough input settles non-linear currents to improve
linearity on the fine input and reduce harmonic distortion.
INR- _ Rough Inverting Input, pin 4
Rough inverting analog input. The rough input settles non-linear currents to improve linearity
on the fine input and reduce harmonic distortion.
INF+ _ Fine Non-Inverting Input, pin 2
Fine non-inverting analog input.
DS255PP2 17

INF- _ Fine Inverting Input, pin 3
Fine inverting analog input.
VREF+ _ Positive Voltage Reference Input, pin 5
Input for an external +2.5 V voltage reference relative to VREF-.
_
VREF-
Negative Voltage Reference Input, pin 6
This pin must be tied to VA-.
Digital Inputs
MCLK _ Modulator Clock Input, pin 19
A CMOS compatible clock input for the modulator internal master clock, nominally 2.048
MHz with an amplitude equal to the VD digital power supply.
MSYNC _ Modulator Sync Input, pin 20
A low to high transition resets the internal clock phasing of the modulator. This assures the
sampling instant and modulator data output are synchronous to the external system.
CS5371/CS5372
OFST _ Offset Mode Select, pin 14
When high, adds approximately +100mV of offset to the analog inputs to guarantee any zero
input ∆−Σ idle tones are removed. When low, no offset is added.
LPWR
_
Low Power Mode Select, pin 23
When set high with MCLK operating at 1.024 MHz, modulator power dissipation is reduced to
15 mW per channel.
_
PWDN
Power-down Mode, pin 24
When high, the modulator is in power down mode and consumes 1mW. Halting MCLK while
in power down mode reduces modulator power dissipation to 10 µW.
Digital Outputs
MDATA _ Modulator Data Output, pin 21
Modulator data is output as a 1-bit serial data stream at a 512 kHz rate with an MCLK input of
2.048 MHz. Modulator data is output at a 256 kHz rate with an MCLK input of 1.024 MHz.
MFLAG _ Modulator Flag Output, pin 22
A high level output indicates the modulator is unstable due to an over-range on the analog
inputs.
18 DS255PP2

11. PIN DESCRIPTION - CS5372
CS5371/CS5372
Ch. 1 Rough Non-Inverting Input INR1+
Ch. 1 Fine Non-Inverting Input INF1+
Ch. 1 Fine Inverting Input INF1-
Ch. 1 Rough Inverting Input INR1-
Positive Voltage Reference Input VREF+
Negative Voltage Reference Input VREF-
Negative Analog Power Supply VA-
Positive Analog Power Supply VA+
Ch. 2 Rough Inverting Input INR2-
Ch. 2 Fine Inverting Input INF2-
Ch. 2 Fine Non-Inverting Input INF2+
Ch. 2 Rough Non-Inverting Input INR2+
Power Supplies
VA + _ Positive Analog Power Supply, pin 8
Positive supply voltage.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
817
9
10
11
12 13
PWDN1 Ch. 1 Power-down Enable
24
LPWR Low Power Mode Select
23
MFLAG1 Ch. 1 Modulator Flag Output
22
MDATA1 Ch. 1 Modulator Data Output
21
MSYNC Modulator Sync Input
20
MCLK Modulator Clock Input
19
18
VD Positive Digital Power Supply
DGND Digital Ground
MDATA2 Ch. 2 Modulator Data Output
16
MFLAG2 Ch. 2 Modulator Flag Output
15
OFST Offset Mode Select
14
PWDN2 Ch. 2 Power-down Enable
VA - _ Negative Analog Power Supply, pin 7
Negative supply voltage.
VD _ Positive Digital Power Supply, pin 18
Positive supply voltage.
DGND _ Digital Ground, pin 17
Analog Inputs
INR1+, INR2+ _ Channel 1 & 2 Rough Non-Inverting Inputs, pin 1, 12
Rough non-inverting analog inputs. The rough inputs settle non-linear currents to improve
linearity on the fine inputs and reduce harmonic distortion.
INR1-, INR2- _ Channel 1 & 2 Rough Inverting Inputs, pin 4, 9
Rough inverting analog inputs. The rough inputs settle non-linear currents to improve linearity
on the fine inputs and reduce harmonic distortion.
INF1+, INF2+ _ Channel 1 & 2 Fine Non-Inverting Input, pin 2, 11
Fine non-inverting analog inputs.
DS255PP2 19

INF1-, INF2- _ Channel 1 & 2 Fine Inverting Input, pin 3, 10
Fine inverting analog inputs.
VREF+ _ Positive Voltage Reference Input, pin 5
Input for an external +2.5V voltage reference relative to VREF-.
_
VREF-
Negative Voltage Reference Input, pin 6
This pin must be tied to VA-.
Digital Inputs
MCLK _ Modulator Clock Input, pin 19
A CMOS compatible clock input for the modulator internal master clock, nominally 2.048
MHz with an amplitude equal to the VD digital power supply.
MSYNC _ Modulator Sync Input, pin 20
A low to high transition resets the internal clock phasing of the modulator. This assures the
sampling instant and modulator data output are synchronous to the external system.
CS5371/CS5372
OFST _ Offset Mode Select, pin 14
When high, adds approximately +100mV of offset to the analog inputs to guarantee any zero
input ∆−Σ idle tones are removed. When low, no offset is added.
LPWR
_
Low Power Mode Select, pin 23
When set high with MCLK operating at 1.024 MHz, modulator power dissipation is reduced to
15 mW per channel.
_
PWDN1, PWDN2
Channel 1 & 2 Power-down Mode, pin 24, 13
When high, the modulator is in power down mode and consumes 1mW. Halting MCLK while
in power down mode reduces modulator power dissipation to 10 µW.
Digital Outputs
MDATA1, MDATA2 _ Modulator Data Output, pin 21, 16
Modulator data is output as a 1-bit serial data stream at a 512 kHz rate with an MCLK input of
2.048 MHz. Modulator data is output at a 256 kHz rate with an MCLK input of 1.024 MHz.
MFLAG1, MFLAG2 _ Modulator Flag, pin 22, 15
A high level output indicates the modulator is unstable due to an over-range on the analog
inputs.
20 DS255PP2

12. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
24 PIN SSOP PACKAGE DRAWING
N
CS5371/CS5372
1
23
TOP VIEW
D
E
e
INCHES MILLIMETERS
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
A -- 0.084 -- 2.13
A1 0.002 0.010 0.05 0.25
A2 0.064 0.074 1.62 1.88
b 0.009 0.015 0.22 0.38 2,3
D 0.311 0.335 7.90 8.50 1
E 0.291 0.323 7.40 8.20
E1 0.197 0.220 5.00 5.60 1
e 0.024 0.027 0.61 0.69
L 0.025 0.040 0.63 1.03
∝
0° 8° 0° 8°
2
b
SIDE VIEW
A2
A1
A
SEATING
PLANE
L
1
E1
END VIEW
NOTE
Notes: 1. “D” and “E1” are reference datums and do not included mold flash or protrusions, but do include mold
mismatch and are measured at the parting line, mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed 0.20 mm per
side.
2. Dimension “b” does not include dambar protrusion/intrusion. Allowable dambar protrusion shall be
0.13 mm total in excess of “b” dimension at maximum material condition. Dambar intrusion shall not
reduce dimension “b” by more than 0.07 mm at least material condition.
3. These dimensions apply to the flat section of the lead between 0.10 and 0.25 mm from lead tips.
DS255PP2 21

 Loading...
Loading...