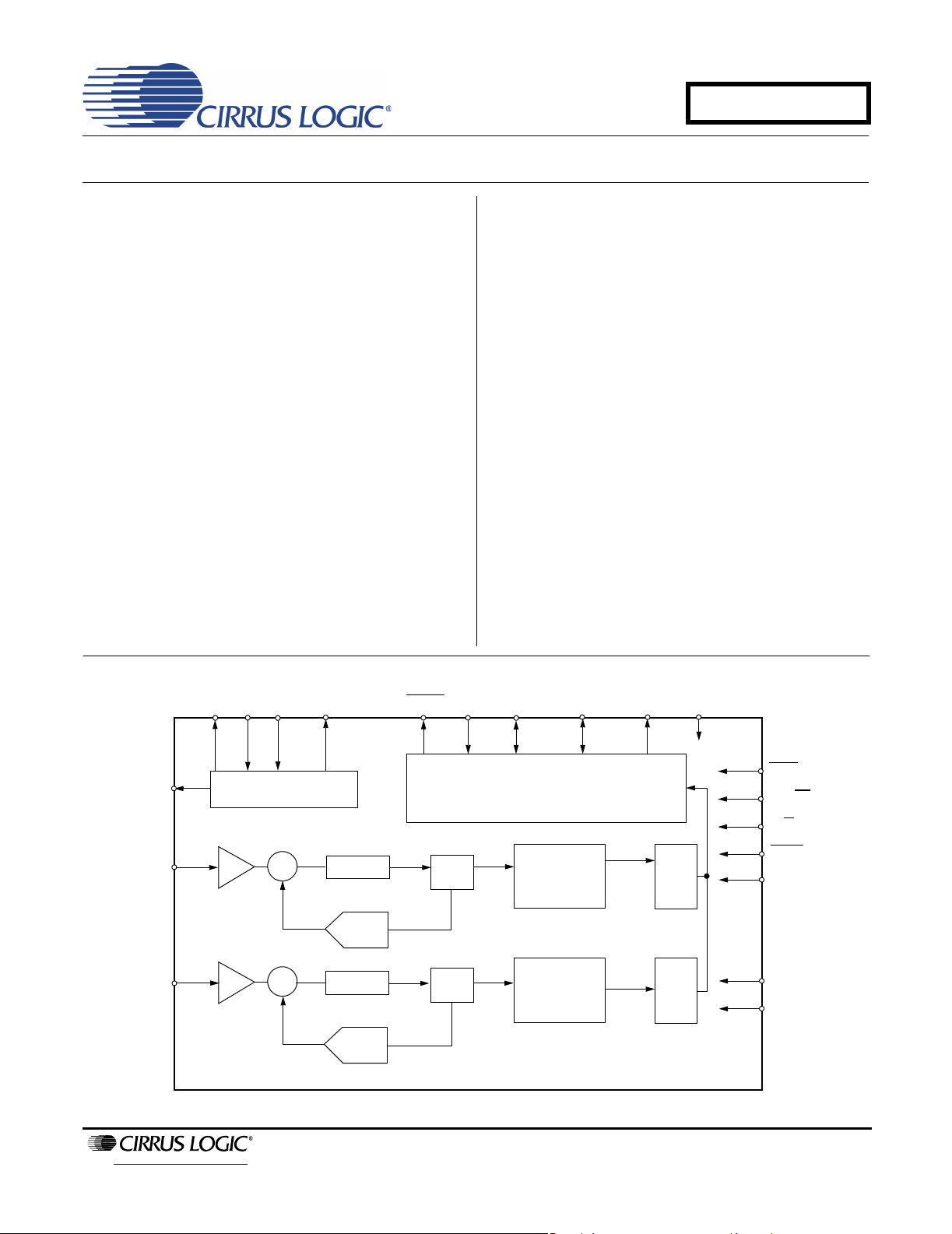
CS5351
108 dB, 192 kHz, Multi-bit Audio A/D Converter
Features
Advanced Multi-bit Delta-Sigma Architecture
24-bit Conversion
108 dB Dynamic Range
-98 dB THD+N
System Sampling Rates up to 192 kHz
135 mW Power Consumption
High-Pass Filter and DC Offset Calibration
Supports Logic Levels Between 5 and 2.5 V
Single-Ended Analog Inputs
Overflow Detection
Pin Compatible with the CS5361
General Description
The CS5351 is a complete analog-to-digital converter
for digital audio systems. It performs sampling, analogto-digital conversion, and anti-alias filtering. The device
generates 24-bit values for both left and right inputs in
serial form at sample rates up to 192 kHz per channel.
The CS5351 uses a 5th-order, multi-bit, delta-sigma
modulator followed by digital filtering and decimation,
which removes the need for an external anti-alias filter.
The ADC uses a differential architecture which provides
excellent noise rejection.
The CS5351 is ideal for audio systems requiring wide
dynamic range, negligible distortion, and low noise.
Such applications include A/V receivers, DVD-R, CD-R,
digital mixing consoles, and effects processors.
ORDERING INFORMATION
CS5351-KSZ, Lead Free -10° to 70°C 24-pin SOIC
CS5351-KZZ, Lead Free -10° to 70°C 24-pin TSSOP
CS5351-DZZ, Lead Free -40° to 85°C 24-pin TSSOP
CDB5351 Evaluation Board
VQ3
VQ1
FILT+
Voltage Reference
AINL
S/H
AINR
S/H
http://www.cirrus.com
VQ2
+
-
+
-
REFGND
LP Filter
DAC
LP Filter
DAC
OVFL
V
L
LRCK
SCLK
Serial Output Interface
Digital
ΔΣ
Decimation
Filter
ΔΣ
Digital
Decimation
Filter
Copyright © Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2007
(All Rights Reserved)
SDOUT MCLK
High
Pass
Filter
High
Pass
Filter
RST
I²S/LJ
M/S
HPF
MDIV
MODE0
MODE1
MAY '07
DS565F2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS ...................................................................................... 4
SPECIFIED OPERATING CONDITIONS .............................................................................................. 4
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ........................................................................................................ 4
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS (CS5351-KSZ/KZZ) ............................................................................. 5
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS (CS5351-DZZ) .................................................................................... 6
DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS .................................................................................................7
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS .............................................................................................. 10
DIGITAL CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................................................................ 10
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS ......................................................................................................... 10
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - SERIAL AUDIO PORT .............................................................. 11
2. PIN DESCRIPTIONS ............................................................................................................................ 14
3. TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM ................................................................................................... 15
4. APPLICATIONS ................................................................................................................................... 16
4.1 Operational Mode/Sample Rate Range Select .............................................................................. 16
4.2 System Clocking ............................................................................................................................ 16
4.2.1 Slave Mode ........................................................................................................................... 16
4.2.2 Master Mode ......................................................................................................................... 17
4.3 Power-Up Sequence ...................................................................................................................... 17
4.4 Analog Connections ....................................................................................................................... 18
4.5 High-Pass Filter and DC Offset Calibration ................................................................................... 18
4.6 Overflow Detection ......................................................................................................................... 19
4.6.1 OVFL Output Timing ............................................................................................................. 19
4.7 Grounding and Power Supply Decoupling ..................................................................................... 19
4.8 Synchronization of Multiple Devices .............................................................................................. 19
5. PARAMETER DEFINITIONS ................................................................................................................ 20
6. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS ................................................................................................................. 21
7. REVISION HISTORY ............................................................................................................................ 23
CS5351
2 DS565F2

LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. Single-Speed Mode Stopband Rejection ..................................................................................... 8
Figure 2. Single-Speed Mode Transition Band ........................................................................................... 8
Figure 3. Single-Speed Mode Transition Band (Detail) ............................................................................... 8
Figure 4. Single-Speed Mode Passband Ripple ......................................................................................... 8
Figure 5. Double-Speed Mode Stopband Rejection .................................................................................... 8
Figure 6. Double-Speed Mode Transition Band .......................................................................................... 8
Figure 7. Double-Speed Mode Transition Band (Detail) ............................................................................. 9
Figure 8. Double-Speed Mode Passband Ripple ........................................................................................ 9
Figure 9. Quad-Speed Mode Stopband Rejection ...................................................................................... 9
Figure 10. Quad-Speed Mode Transition Band .......................................................................................... 9
Figure 11. Quad-Speed Mode Transition Band (Detail) .............................................................................. 9
Figure 12. Quad-Speed Mode Passband Ripple ........................................................................................ 9
Figure 13. Master Mode, Left-Justified SAI ............................................................................................... 12
Figure 14. Slave Mode, Left-Justified SAI ................................................................................................. 12
Figure 15. Master Mode, I²S SAI ............................................................................................................... 12
Figure 16. Slave Mode, I²S SAI ................................................................................................................. 12
Figure 17. OVFL Output Timing ................................................................................................................ 12
Figure 18. Left-Justified Serial Audio Interface ......................................................................................... 13
Figure 19. I²S Serial Audio Interface ......................................................................................................... 13
Figure 20. OVFL Output Timing, I²S Format ............................................................................................. 13
Figure 21. OVFL Output Timing, Left-Justified Format ............................................................................. 13
Figure 22. Typical Connection Diagram .................................................................................................... 15
Figure 23. CS5351 Master Mode Clocking ............................................................................................... 17
Figure 24. CS5351 Recommended Analog Input Buffer ........................................................................... 18
CS5351
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. CS5351 Mode Control ................................................................................................................. 16
Table 2. CS5351 Slave Mode Clock Ratios .............................................................................................. 16
Table 3. CS5351 Common Master Clock Frequencies ............................................................................. 17
DS565F2 3
CS5351
1. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS
(All Min/Max characteristics and specifications are guaranteed over the Specified Operating Conditions. Typical
performance characteristics and specifications are derived from measurements taken at typical supply voltages
and T
= 25°C.)
A
SPECIFIED OPERATING CONDITIONS
(GND = 0 V, all voltages with respect to 0 V.)
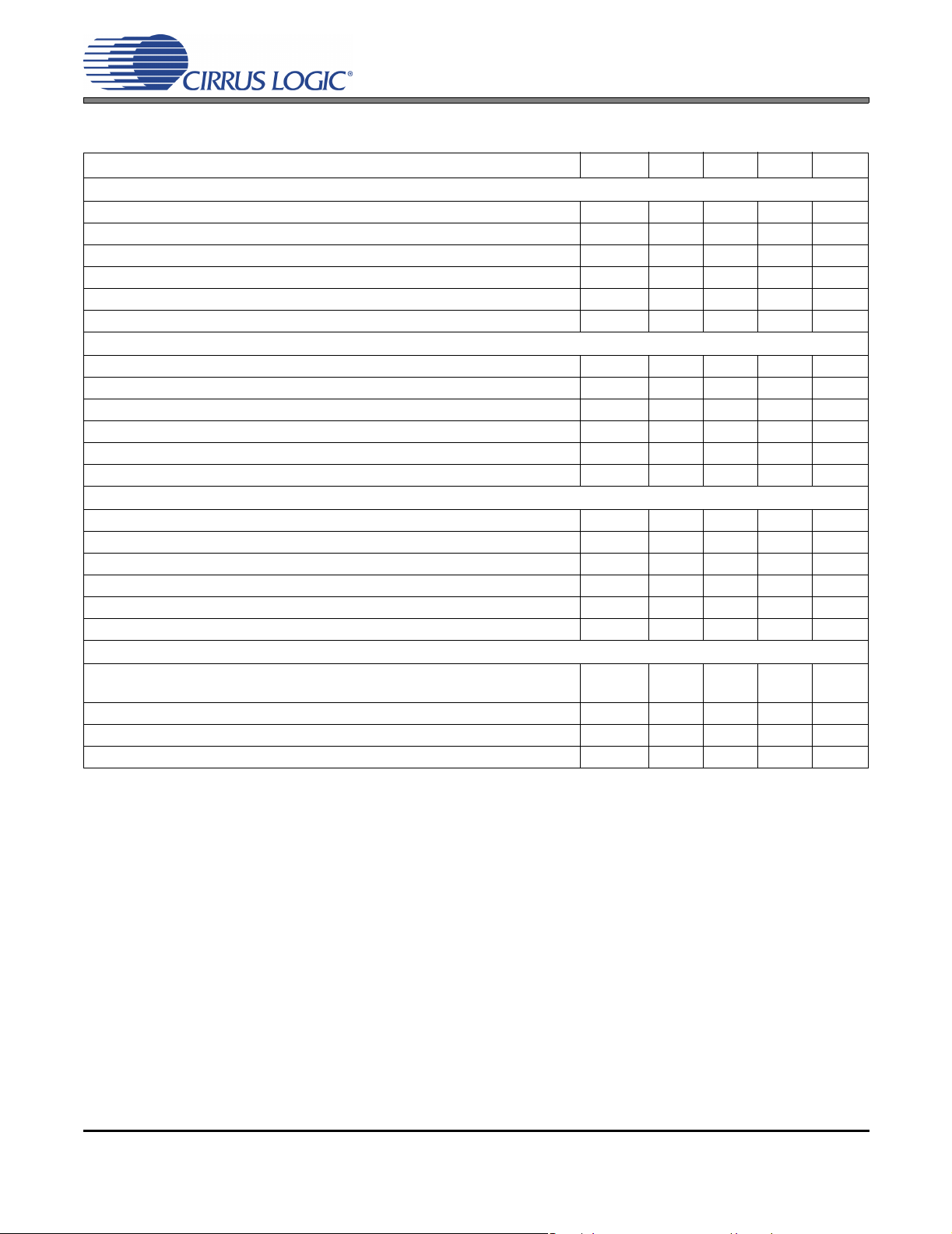
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
DC Power Supplies: Positive Analog
Positive Digital
Positive Logic
Ambient Operating Temperature Commercial (-KSZ/-KZZ)
Automotive (-DZZ)
VA
VD
VL
T
T
AC
AI
4.75
3.1
2.37
-10
-40
5.0
3.3
3.3
5.25
5.25
5.25
-
-
70
85
V
V
V
°C
°C
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(GND = 0 V, All voltages with respect to ground.) (Note 1)
Parameter Symbol Min Max Units
DC Power Supplies: Analog
Logic
Digital
Input Current (Note 2)
Analog Input Voltage (Note 3)
Digital Input Voltage (Note 3)
Ambient Operating Temperature (Power Applied)
Storage Temperature
V
T
VA
VL
VD
I
in
V
IND
T
stg
IN
A
-0.3
-0.3
-0.3
+6.0
+6.0
+6.0
-10 +10 mA
GND - 0.7 VA + 0.7 V
-0.7 VL + 0.7 V
-50 +95 °C
-65 +150 °C
V
V
V
Notes: 1. Operation beyond these limits may result in permanent damage to the device.
Normal operation is not guaranteed at these extremes.
2. Any pin except supplies. Transient currents of up to ±100 mA on the analog input pins will not cause
SCR latch-up.
3. The maximum over/under voltage is limited by the input current.
4 DS565F2
CS5351
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS (CS5351-KSZ/KZZ)
(Test conditions (unless otherwise specified): Input test signal is a 1 kHz sine wave; measurement bandwidth is
10 Hz to 20 kHz.)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Single-Speed Mode Fs = 48 kHz
Dynamic Range A-weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 4)
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
Double-Speed Mode Fs = 96 kHz
Dynamic Range A-weighted
unweighted
40 kHz bandwidth unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 4)
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
40 kHz bandwidth -1 dB
Quad-Speed Mode Fs = 192 kHz
Dynamic Range A-weighted
unweighted
40 kHz bandwidth unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 4)
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
40 kHz bandwidth -1 dB
THD+N
THD+N
THD+N
Dynamic Performance for All Modes
Interchannel Isolation - 95 - dB
DC Accuracy
Interchannel Gain Mismatch - 0.1 - dB
Gain Error -2 - 2 %
Gain Drift -100 - 100 ppm/°C
Offset Error HPF enabled
HPF disabled
Analog Input Characteristics
Full-scale Input Voltage 0.55*VA 0.56*VA .57*VA Vpp
Input Impedance 7.5 - - kΩ
Common Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR - 82 - dB
102
99
-
-
-
102
99
-
-
-
-
-
102
99
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
108
105
-98
-84
-44
108
105
102
-98
-84
-44
-95
108
105
102
-98
-84
-44
-95
-
-
-
-
-92
-
-
-
-
-
-92
-
-
-
-
-
-
-92
-
-
-
0
100
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
LSB
LSB
Notes: 4. Referred to the typical full-scale input voltage.
DS565F2 5
CS5351
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS (CS5351-DZZ)
(Test conditions (unless otherwise specified): Input test signal is a 1 kHz sine wave; measurement bandwidth is
10 Hz to 20 kHz.)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Single-Speed Mode Fs = 48 kHz
Dynamic Range A-weighted
unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 4)
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
Double-Speed Mode Fs = 96 kHz
Dynamic Range A-weighted
unweighted
40 kHz bandwidth unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 4)
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
40 kHz bandwidth -1 dB
Quad-Speed Mode Fs = 192 kHz
Dynamic Range A-weighted
unweighted
40 kHz bandwidth unweighted
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (Note 4)
-1 dB
-20 dB
-60 dB
40 kHz bandwidth -1 dB
THD+N
THD+N
THD+N
Dynamic Performance for All Modes
Interchannel Isolation - 95 - dB
DC Accuracy
Interchannel Gain Mismatch - 0.1 - dB
Gain Error -5 - 5 %
Gain Drift -100 - 100 ppm/°C
Offset Error HPF enabled
HPF disabled
Analog Input Characteristics
Full-scale Input Voltage 0.53*VA 0.56*VA 0.59*VA Vpp
Input Impedance 7.5 - - kΩ
Common Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR - 82 - dB
100
97
-
-
-
100
97
-
-
-
-
-
100
97
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
108
105
-98
-84
-44
108
105
102
-98
-84
-44
-95
108
105
102
-98
-84
-44
-95
-
-
-
-
-90
-
-
-
-
-
-90
-
-
-
-
-
-
-90
-
-
-
0
100
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
LSB
LSB
6 DS565F2
CS5351
DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Single-Speed Mode (2 kHz to 51 kHz sample rates)
Passband (-0.1 dB) (Note 5) 0-0.47Fs
Passband Ripple -0.1 - 0.035 dB
Stopband (Note 5) 0.58 - - Fs
Stopband Attenuation -95 - - dB
Total Group Delay (Fs = Output Sample Rate) t
Interchannel Phase Deviation - 0.0001 - Deg
gd
Double-Speed Mode (50 kHz to 102 kHz sample rates)
Passband (-0.1 dB) (Note 5) 0-0.45Fs
Passband Ripple -0.1 - 0.035 dB
Stopband (Note 5) 0.68 - - Fs
Stopband Attenuation -92 - - dB
Total Group Delay (Fs = Output Sample Rate) t
Interchannel Phase Deviation - 0.0001 - Deg
gd
Quad-Speed Mode (100 kHz to 204 kHz sample rates)
Passband (-0.1 dB) (Note 5) 0-0.24Fs
Passband Ripple -0.1 - 0.035 dB
Stopband (Note 5) 0.78 - - Fs
Stopband Attenuation -92 - - dB
Total Group Delay (Fs = Output Sample Rate) t
Interchannel Phase Deviation - 0.0001 - Deg
gd
High Pass Filter Characteristics
Frequency Response -3.0 dB
-0.13 dB (Note 6)
Phase Deviation @ 20 Hz (Note 6) -10-Deg
Passband Ripple --0dB
Filter Settling Time 10
Notes: 5. The filter frequency response scales precisely with Fs.
6. Response shown is for Fs equal to 48 kHz. Filter characteristics scale with Fs.
-12/Fs- s
-9/Fs- s
-5/Fs- s
-120-
5
/Fs s
-
Hz
Hz
DS565F2 7

CS5351
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
Amplitude (dB)
-90
-100
-110
-120
-130
-140
0.00.10.20.30.40.50.60.70.80.91.0
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
Amplitude (dB)
-90
-100
-110
-120
-130
-140
0.40 0.42 0.44 0.46 0.48 0.50 0.52 0.54 0.56 0.58 0.60
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Figure 1. Single-Speed Mode Stopband Rejection Figure 2. Single-Speed Mode Transition Band
0
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
Amplitude (dB)
-6
-7
-8
-9
-10
0.45 0.46 0.47 0.48 0.49 0.50 0.51 0.52 0.53 0.54 0.55
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
0.10
0.08
0.05
0.03
0.00
Amplitude (dB)
-0.03
-0.05
-0.08
-0.10
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0. 35 0.40 0.45 0.50
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Figure 3. Single-Speed Mode Transition Band (Detail) Figure 4. Single-Speed Mode Passband Ripple
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
Amplitude (dB)
-90
-100
-110
-120
-130
-140
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
Amplitude (dB)
-90
-100
-110
-120
-130
-140
0.40 0.43 0.45 0.48 0.50 0.53 0.55 0.58 0.60 0.63 0.65 0.68 0.70
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Figure 5. Double-Speed Mode Stopband Rejection Figure 6. Double-Speed Mode Transition Band
8 DS565F2

CS5351
0
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
Amplitude (dB)
-6
-7
-8
-9
-10
0.40 0.43 0.45 0.48 0.50 0.53 0.55
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
0.10
0.08
0.05
0.03
0.00
Amplitude (dB)
-0.03
-0.05
-0.08
-0.10
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0. 20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Figure 7. Double-Speed Mode Transition Band (Detail) Figure 8. Double-Speed Mode Passband Ripple
Amplitude (dB)
Amplitude (dB)
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Figure 9. Quad-Speed Mode Stopband Rejection Figure 10. Quad-Speed Mode Transition Band
Amplitude (dB)
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Amplitude (dB)
Frequency (normalized to Fs)
Figure 11. Quad-Speed Mode Transition Band (Detail) Figure 12. Quad-Speed Mode Passband Ripple
DS565F2 9

CS5351
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(GND = 0 V, all voltages with respect to ground. MCLK=12.288 MHz; Master Mode)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Power Supply Current VA = 5 V
(Normal Operation) VL,VD = 5 V
VL,VD = 3.3 V
Power Supply Current VA = 5 V
(Power-Down Mode) (Note 7) VL,VD = 5 V
Power Consumption
(Normal Operation) VA, VD, VL = 5 V
VA = 5 V, VL, VD = 3.3 V
(Power-Down Mode)
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (1 kHz) (Note 8) PSRR - 65 - dB
V
Nominal Voltage
Q
Maximum allowable DC current source/sink
Filt+ Nominal Voltage
Maximum allowable DC current source/sink
Output Impedance
Output Impedance
I
A
I
D
I
D
I
A
I
D
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
17.5
22
14.5
100
100
198
135
1
2.5
25
0.01
5
15
0.01
21.5
27.5
17
-
-
243
161
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
mW
mW
mW
mA
mA
mA
μA
μA
V
kΩ
mA
V
kΩ
mA
Notes: 7. Power Down Mode is defined as RST
= Low with all clocks and data lines held static.
8. Valid with the recommended capacitor values on FILT+ and VQ as shown in the Typical Connection
Diagram.
DIGITAL CHARACTERISTICS
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Units
High-Level Input Voltage (% of VL) V
Low-Level Input Voltage (% of VL) V
High-Level Output Voltage at I
Low-Level Output Voltage at Io = 100 μA(% of VL)V
Current Sink I
OVFL
Input Leakage Current (all pins except SCLK and LRCK) I
Input Leakage Current (SCLK and LRCK) I
= 100 μA(% of VL)V
o
IH
IL
OH
OL
ovfl
in
in
70% - - V
--30%V
70% - - V
--15%V
--4.0mA
-10 - 10 μA
-25 - 25 μA
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Allowable Junction Temperature
Junction to Ambient Thermal Impedance
(Multi-layer PCB) TSSOP
(Multi-layer PCB) SOIC
(Single-layer PCB) TSSOP
(Single-layer PCB) SOIC
θ
JA-TM
θ
JA-SM
θ
JA-TS
θ
JA-SS
--135
-
-
-
-
105
70
60
80
°C
-
-
-
-
°C/W
°C/W
°C/W
°C/W
10 DS565F2

CS5351
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - SERIAL AUDIO PORT
(Logic "0" = GND = 0 V; Logic "1" = VL, CL = 20 pF)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Output Sample Rate Single-Speed Mode
Double-Speed Mode
Quad-Speed Mode
OVFL to LRCK edge setup time
OVFL to LRCK edge hold time
OVFL time-out on overrange condition
Fs = 44.1, 88.2, 176.4 kHz
Fs = 48, 96, 192 kHz
MCLK Specifications
MCLK Period t
MCLK Pulse Duty Cycle 40 50 60 %
Master Mode
SCLK falling to LRCK t
SCLK falling to SDOUT valid t
SCLK Duty Cycle - 50 - %
Slave Mode
Single-Speed
Output Sample Rate Fs 2 - 51 kHz
LRCK Duty Cycle 405060%
SCLK Period t
SCLK Duty Cycle 455055%
SCLK falling to SDOUT valid t
SCLK falling to LRCK edge t
Double-Speed
Output Sample Rate Fs 50 - 102 kHz
LRCK Duty Cycle 405060%
SCLK Period t
SCLK Duty Cycle 455055%
SCLK falling to SDOUT valid t
SCLK falling to LRCK edge t
Quad-Speed
Output Sample Rate Fs 100 - 204 kHz
LRCK Duty Cycle 405060%
SCLK Period t
SCLK Duty Cycle 455055%
SCLK falling to SDOUT valid t
SCLK falling to LRCK edge t
Fs
Fs
Fs
t
setup
t
hold
clkw
mslr
sdo
sclkw
dss
slrd
sclkw
dss
slrd
sclkw
dss
slrd
100
16/f
1/f
2
50
sclk
sclk
-
-
-
-
-
51
102
204
--s
--s
740
680
-
-
38 - 1953 ns
-20 - 20 ns
0 - 32 ns
153 - - ns
- - 32 ns
-20 - 20 ns
153 - - ns
- - 32 ns
-20 - 20 ns
77 - - ns
- - 32 ns
-8 - 3 ns
kHz
kHz
kHz
ms
ms
DS565F2 11

CS5351
SCLK output
LRCK
output
SDOUT
Figure 13. Master Mode, Left-Justified SAI Figure 14. Slave Mode, Left-Justified SAI
SCLK input
LRCK input
CLK input
t
ms l r
LRCK input
t
sdo
MSB MSB-1
SDOUT
SCLK input
t
srdl
t
dss
t
sclkw
LRCK input
t
srdl
MSB MSB- 1 MSB-2
t
srdl
t
dss
t
sclkw
t
sclkw
t
dss
SDOUT
MSB
Figure 15. Master Mode, I²S SAI Figure 16. Slave Mode, I²S SAI
MSB-1
SDOUT
LRCK
t
setup
t
hold
OVFL
Figure 17. OVFL Output Timing
MSB
MSB-1
12 DS565F2

CS5351
LRCK
SCLK
SDATA 23 22 7 6 23 22
Left Channel Right Channel
23 225432108 7654321089 9
Figure 18. Left-Justified Serial Audio Interface
LRCK
SCLK
SDATA 23 22 8 7 23 22
Left Channel Right Channel
23 226543210 8765432109 9
Figure 19. I²S Serial Audio Interface
LRCK
SCLK
OVFL
LRC K
SCLK
OVFL
OVFL_R OVFL_L OVFL_R
Figure 20. OVFL Output Timing, I²S Format
OV FL_R OVF L_L OV FL_R
Figure 21. OVFL Output Timing, Left-Justified Format
DS565F2 13

CS5351
2. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
RST 124FILT+
M/S 223REFGND
LRCK 322VQ3
SCLK 421AINR
MCLK 520VQ2
VD 619VA
GND 718GND
VL 817VQ1
SDOUT 916AINL
MDIV 10 15 OVFL
HPF 11 14 M1
I²S/LJ 12 13 M0
Pin Name # Pin Description
RST 1 Reset (Input) - The device enters a low power mode when low.
M/S
LRCK
SCLK 4 Serial Clock (Input/Output) - Serial clock for the serial audio interface.
MCLK 5 Master Clock (Input) - Clock source for the delta-sigma modulator and digital filters.
VD 6 Digital Power (Input) - Positive power supply for the digital section.
GND
VL 8 Logic Power (Input) - Positive power for the digital input/output.
SDOUT 9 Serial Audio Data Output (Output) - Output for two’s complement serial audio data.
MDIV 10 MCLK Divider (Input) - Enables a master clock divide by two function.
HPF
I²S/LJ
M0
M1
OVFL 15 Overflow (Output, open drain) - Detects an overflow condition on both left and right channels.
AINL
AINR
VQ1
VQ2
VQ3
VA 19 Analog Power (Input) - Positive power supply for the analog section.
REF_GND 23 Reference Ground (Input) - Ground reference for the internal sampling circuits.
FILT+ 24 Positive Voltage Reference (Output) - Positive reference voltage for the internal sampling circuits.
2 Master/Slave Mode (Input) - Selects operation as either clock master or slave.
3 Left Right Clock (Input/Output) - Determines which channel, Left or Right, is currently active on the
serial audio data line.
7
Ground (Input) - Ground reference. Must be connected to analog ground.
18
11 High Pass Filter Enable (Input) - Enables the Digital High-Pass Filter.
12 Serial Audio Interface Format Select (Input) -Selects either the Left-Justified or I²S format for the SAI.
13
Mode Selection (Input) - Determines the operational mode of the device.
14
1621Analog Inputs (Input) - The full-scale analog input level is specified in the Analog Characteristics speci-
fication table.
17
2022Quiescent Voltage (Output) - Filter connection for the internal quiescent reference voltage.
14 DS565F2

3. TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
CS5351
+5V
47μF
+5 V to 3.3 V
+
+
Analog
Input
Buffer
(Figure 24)
1μF
0.01 μF
+
1μF
0.01 μF
FILT+
REFGND
AINL
VQ1
VQ3
VQ2
AINR
*
Ω
5.1
VA V
CS5351
A/D CONVERTER
0.01 μF0.01 μF
+
1μF
+5V to 2.5V
0.01 μF
D
L
V
VL
10 kΩ
OVFL
RST
2
I
S/LJ
M/S
HPF
M0
Power Down
and Mode
Settings
M1
MDIV
SDOUT
Audio Data
Processor
LRCK
Timing Logic
and Clock
GND
SCLK
MCLK
GND
* Resistor may only be used
if VD is derived from VA. If
used, do not drive any other
logic from VD
Figure 22. Typical Connection Diagram
DS565F2 15

4. APPLICATIONS
4.1 Operational Mode/Sample Rate Range Select
The output sample rate, Fs, can be adjusted from 2 kHz to 204 kHz. The CS5351 must be set to the proper
speed mode via the mode pins, M1 and M0. Refer to Table 1.
M1 (Pin 14) M0 (Pin 13) MODE Output Sample Rate (Fs)
00
01
10
11
4.2 System Clocking
The device supports operation in either Master Mode, where the left/right and serial clocks are synchronously generated on-chip, or Slave Mode, which requires external generation of the left/right and serial clocks.
The device also includes a master clock divider in Master Mode where the master clock will be internally
divided prior to any other internal circuitry when MDIV is enabled, set to logic 1. In Slave Mode, the MDIV
pin needs to be disabled, set to logic 0.
Single-Speed Mode 2 kHz - 51 kHz
Double-Speed Mode 50 kHz - 102 kHz
Quad-Speed Mode 100 kHz - 204 kHz
Reserved
Table 1. CS5351 Mode Control
CS5351
4.2.1 Slave Mode
LRCK and SCLK operate as inputs in Slave Mode. The left/right clock must be synchronously derived
from the master clock and be equal to Fs. It is also recommended that the serial clock be synchronously
derived from the master clock and be equal to 64x Fs to maximize system performance. Refer to Table 2
for required clock ratios.
Single-Speed Mode
Fs = 2 kHz to 51 kHz
MCLK/LRCK Ratio 256x, 512x 128x, 256x 128x
SCLK/LRCK Ratio 32x, 64x, 128x 32x, 64x 32x, 64x
Table 2. CS5351 Slave Mode Clock Ratios
Double-Speed Mode
Fs = 50 kHz to 102 kHz
Quad-Speed Mode
Fs = 100 kHz to 204 kHz
16 DS565F2

4.2.2 Master Mode
In Master Mode, LRCK and SCLK operate as outputs. The left/right and serial clocks are internally derived
from the master clock with the left/right clock equal to Fs and the serial clock equal to 64x Fs, as shown
in Figure 23. Refer to Table 3 for common master clock frequencies.
CS5351
MCLK
÷ 1
÷ 2
SAMPLE RATE (kHz)
32 8.192 16.384
44.1 11.2896 22.5792
48 12.288 24.576
64 8.192 16.384
88.2 11.2896 22.5792
96 12.288 24.576
176.4 11.2896 22.5792
192 12.288 24.576
Table 3. CS5351 Common Master Clock Frequencies
÷ 256
÷ 128
÷ 64
Single
Speed
Double
Speed
Quad
Speed
0
1
÷ 4
MDIV
÷ 2
÷ 1
Figure 23. CS5351 Master Mode Clocking
MDIV = 0
MCLK (MHz)
Single
Speed
Double
Speed
Speed
Quad
00
01
10
M0M1
00
01
10
MDIV = 1
MCLK (MHz)
LRCK Output
(Equal to Fs)
SCLK Output
4.3 Power-Up Sequence
Reliable power-up can be accomplished by keeping the device in reset until the power supplies, clocks and
configuration pins are stable. It is also recommended that reset be enabled if the analog or digital supplies
drop below the minimum specified operating voltages to prevent power glitch related issues.
The internal reference voltage must be stable for the device to produce valid data. Therefore, there is a delay between the release of reset and the generation of valid output due to the finite output impedance of
FILT+ and the presence of the external capacitance.
DS565F2 17

4.4 Analog Connections
The analog modulator samples the input at 6.144 MHz. The digital filter will reject signals within the stopband of the filter. However, there is no rejection for input signals which are (n
band frequency, where n=0,1,2,...Refer to Figure 24 which shows the suggested filter that will attenuate any
noise energy at 6.144 MHz, in addition to providing the optimum source impedance for the modulators. The
use of capacitors which have a large voltage coefficient (such as general purpose ceramics) must be avoided since these can degrade signal linearity.
1 μF
100 kΩ
100 kΩ
CS5351
× 6.144 MHz) the digital pass-
634 Ω
470 pF
C0G
-
+
91 Ω
-
+
1 μF
2700 pF
C0G
0.01 μF
CS5351
AINL
VQ1
VQ3
100 kΩ
+
100 kΩ
1 μF
Figure 24. CS5351 Recommended Analog Input Buffer
470 pF
C0G
4.5 High-Pass Filter and DC Offset Calibration
The operational amplifiers in the input circuitry driving the CS5351 may generate a small DC offset into the
A/D converter. The CS5351 includes a high pass filter after the decimator to remove any DC offset which
could result in recording a DC level, possibly yielding "clicks" when switching between devices in a multichannel system.
The high pass filter continuously subtracts a measure of the DC offset from the output of the decimation
filter. If the HPF
and this DC offset will continue to be subtracted from the conversion result. This feature makes it possible
to perform a system DC offset calibration by:
Running the CS5351 with the high pass filter enabled until the filter settles. See the Digital Filter Characteristics for filter settling time.
pin is taken high during normal operation, the current value of the DC offset register is frozen
91 Ω
634 Ω
2700 pF
C0G
VQ2
AINR
Disabling the high pass filter and freezing the stored DC offset.
A system calibration performed in this way will eliminate offsets anywhere in the signal path between the
calibration point and the CS5351.
18 DS565F2

4.6 Overflow Detection
The CS5351 includes overflow detection on both the left and right channels. This time multiplexed information is presented as open drain, active low on pin 15, OVFL
logical low as soon as an overrange condition in either channel is detected. The data will remain low as
specified in the Switching Characteristics - Serial Audio Port section. This ensures sufficient time to detect
an overrange condition regardless of the speed mode. After the timeout, the OVFL_L and OVFL_R data will
return to a logical high if there has not been any other overrange condition detected. Please note that an
overrange condition on either channel will restart the timeout period for both channels.
4.6.1 OVFL Output Timing
In Left-Justified format, the OVFL pin is updated one SCLK period after an LRCK transition. In I²S format,
the OVFL
cases the OVFL
mat, the rising edge of LRCK would latch the right channel overflow status, and the falling edge of LRCK
would latch the left channel overflow status. In I²S format, the falling edge of LRCK would latch the right
channel overflow status and the rising edge of LRCK would latch the left channel overflow status.
pin is updated two SCLK periods after an LRCK transition. Refer to Figures 23 and 24. In both
data can be easily demultiplexed by using the LRCK to latch the data. In left-justified for-
4.7 Grounding and Power Supply Decoupling
As with any high-resolution converter, the CS5351 requires careful attention to power supply and grounding
arrangements if its potential performance is to be realized. Figure 22 shows the recommended power arrangements, with VA and VL connected to clean supplies. VD, which powers the digital filter, may be run
from the system logic supply or may be powered from the analog supply via a resistor. In this case, no additional devices should be powered from VD. Decoupling capacitors should be as near to the ADC as possible, with the low value ceramic capacitor being the nearest. All signals, especially clocks, should be kept
away from the FILT+ and VQ pins in order to avoid unwanted coupling into the modulators. The FILT+ and
VQ decoupling capacitors, particularly the 0.01 µF, must be positioned to minimize the electrical path from
FILT+ and REFGND. The CDB5351 evaluation board demonstrates the optimum layout and power supply
arrangements. To minimize digital noise, connect the ADC digital outputs only to CMOS inputs.
CS5351
. The OVFL_L and OVFL_R data will go to a
4.8 Synchronization of Multiple Devices
In systems where multiple ADCs are required, care must be taken to achieve simultaneous sampling. To
ensure synchronous sampling, the MCLK and LRCK must be the same for all of the CS5351’s in the system.
If only one master clock source is needed, one solution is to place one CS5351 in Master Mode, and slave
all of the other CS5351’s to the one master. If multiple master clock sources are needed, a possible solution
would be to supply all clocks from the same external source and time the CS5351 reset with the inactive
edge of MCLK. This will ensure that all converters begin sampling on the same clock edge.
DS565F2 19

5. PARAMETER DEFINITIONS
Dynamic Range
The ratio of the rms value of the signal to the rms sum of all other spectral components over the specified
bandwidth. Dynamic Range is a signal-to-noise ratio measurement over the specified bandwidth made
with a -60 dBFS signal. 60 dB is added to resulting measurement to refer the measurement to full-scale.
This technique ensures that the distortion components are below the noise level and do not affect the
measurement. This measurement technique has been accepted by the Audio Engineering Society,
AES17-1991, and the Electronic Industries Association of Japan, EIAJ CP-307. Expressed in decibels.
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
The ratio of the rms value of the signal to the rms sum of all other spectral components over the specified
bandwidth (typically 10 Hz to 20 kHz), including distortion components. Expressed in decibels. Measured
at -1 and -20 dBFS as suggested in AES17-1991 Annex A.
Frequency Response
A measure of the amplitude response variation from 10 Hz to 20 kHz relative to the amplitude response
at 1 kHz. Units in decibels.
Interchannel Isolation
A measure of crosstalk between the left and right channels. Measured for each channel at the converter's
output with no signal to the input under test and a full-scale signal applied to the other channel. Units in
decibels.
CS5351
Interchannel Gain Mismatch
The gain difference between left and right channels. Units in decibels.
Gain Error
The deviation from the nominal full-scale analog output for a full-scale digital input.
Gain Drift
The change in gain value with temperature. Units in ppm/°C.
Offset Error
The deviation of the mid-scale transition (111...111 to 000...000) from the ideal. Units in mV.
20 DS565F2

6. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS 24L SOIC (300 MIL BODY) PACKAGE DRAWING
1
b
CS5351
HE
c
SEATING
PLANE
D
A
e
A1
INCHES MILLIMETERS
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
A 0.093 0.104 2.35 2.65
A1 0.004 0.012 0.10 0.30
B 0.013 0.020 0.33 0.51
C 0.009 0.013 0.23 0.32
D 0.598 0.614 15.20 15.60
E 0.291 0.299 7.40 7.60
e 0.040 0.060 1.02 1.52
H 0.394 0.419 10.00 10.65
L 0.016 0.050 0.40 1.27
∝
0° 8° 0° 8°
∝
L
DS565F2 21

CS5351
24L TSSOP (4.4 mm BODY) PACKAGE DRAWING
N
1
23
TOP VIEW
D
E
e
2
b
SIDE VIEW
A2
A1
A
SEATING
PLANE
L
1
E1
END VIEW
INCHES MILLIMETERS NOTE
DIM MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
A -- -- 0.043 -- -- 1.10
A1 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.05 -- 0.15
A2 0.03346 0.0354 0.037 0.85 0.90 0.95
b 0.00748 0.0096 0.012 0.19 0.245 0.30 2,3
D 0.303 0.307 0.311 7.70 7.80 7.90 1
E 0.248 0.2519 0.256 6.30 6.40 6.50
E1 0.169 0.1732 0.177 4.30 4.40 4.50 1
e -- 0.026 BSC -- -- 0.65 BSC --
L 0.020 0.024 0.028 0.50 0.60 0.70
µ
0° 4° 8° 0° 4° 8°
JEDEC #: MO-153
Controlling Dimension is Millimeters.
Notes:
1. “D” and “E1” are reference datums and do not included mold flash or protrusions, but do include mold
mismatch and are measured at the parting line, mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed 0.20 mm per
side.
2. Dimension “b” does not include dambar protrusion/intrusion. Allowable dambar protrusion shall be
0.13 mm total in excess of “b” dimension at maximum material condition. Dambar intrusion shall not reduce dimension “b” by more than 0.07 mm at least material condition.
3. These dimensions apply to the flat section of the lead between 0.10 and 0.25 mm from lead tips.
∝
22 DS565F2

7. REVISION HISTORY
Release Changes
PP2 Preliminary datasheet.
F1 Improve Gain Error specification under Analog Characteristics.
Specify Full-scale Input Voltage in terms of VA under Analog Characteristics.
Update Differential Input Impedance under Analog Characteristics.
Increase maximum Power-Supply Current, IA, under DC Electrical Characteristics.
Reduce maximum Power Consumption under DC Electrical Characteristics.
Update FILT+ Output Impedance specification under DC Electrical Characteristics.
Extend maximum Fs in Single-Speed Mode to 51 kHz.
Extend maximum Fs in Double-Speed Mode to 102 kHz.
Extend maximum Fs in Quad-Speed Mode to 204 kHz.
Decrease maximum SCLK falling to LRCK edge specification in Quad-Speed Mode.
Replace minimum MCLK high/low timing specifications with duty cycle specification.
Replace minimum SCLK high/low timing specifications with duty cycle specification.
Replace recommended analog input buffer with new input buffer topology.
F2
Updated ordering information.
CS5351
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For all product questions and inquiries, contact a Cirrus Logic Sales Representative.
To find the one nearest you, go to www.cirrus.com.
IMPORTANT NOTICE
Cirrus Logic, Inc. and its subsidiaries ("Cirrus") believe that the information contained in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject
to change without notice and is provided "AS IS" without warranty of any kind (express or implied). Customers are advised to obtain the latest version of relevant
information to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold subject to the terms and conditions of sale
supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those pertaining to warranty, indemnification, and limitation of liability. No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus
for the use of this information, including use of this information as the basis for manufacture or sale of any items, or for infringement of patents or other rights of third
parties. This document is the property of Cirrus and by furnishing this information, Cirrus grants no license, express or impli ed under any patents, mask work rights,
copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets or other intellectual property rights. Cirrus owns the copyrights associated with the information contained herein and gives consent for copies to be made of the information only for use within your organization with respect to Cirrus integrated circuits or other products of Cirrus. This consent
does not extend to other copying such as copying for general distribution, advertising or promotional purposes, or for creating any work for resale.
CERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL APPLICATIONS”). CIRRUS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE
IN AIRCRAFT SYSTEMS, MILITARY APPLICATIONS, PRODUCTS SURGICALLY IMPLANTED INTO THE BODY, AUTOMOTIVE SAFETY OR SECURITY DEVICES, LIFE SUPPORT PRODUCTS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD TO BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK AND CIRRUS DISCLAIMS AND MAKES NO WARRANTY, EXPRESS, STATUTORY OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH REGARD TO ANY CIRRUS PRODUCT
THAT IS USED IN SUCH A MANNER. IF THE CUSTOMER OR CUSTOMER’S CUSTOMER USES OR PERMITS THE USE OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS, CUSTOMER AGREES, BY SUCH USE, TO FULLY INDEMNIFY CIRRUS, ITS OFFICERS, DIRECTORS, EMPLOYEES, DISTRIBUTORS AND
OTHER AGENTS FROM ANY AND ALL LIABILITY, INCLUDING ATTORNEYS’ FEES AND COSTS, THAT MAY RESULT FROM OR ARISE IN CONNECTION
WITH THESE USES.
Cirrus Logic, Cirrus, and the Cirrus Logic logo designs are trademarks of Cirrus Logic, Inc. All other brand and product names in this document may be trademarks
or service marks of their respective owners.
DS565F2 23
 Loading...
Loading...