CS5101A
CS5102A
16-bit, 100 kSps / 20 kSps A/D Converters
Features
z Monolithic CMOS A/D Converters
– Inherent Sampling Architecture
– 2-channel Input Multiplexer
– Flexible Serial Output Port
z Ultra-low Distortion
– S/(N+D): 92 dB
– TDH: 0.001%
z Conversion Time
– CS5101A: 8µs
– CS5102A: 40 µs
z Linearity Error: ±0.001% FS
– Guaranteed No Missing Codes
z Self-calibration Maintains Accuracy
– Accurate Over Time & Temperature
z Low Power Consumption
– CS5101A: 320 mW
– CS5102A: 44 mW
I
Description
The CS5101A and CS5102A are 16-bit monolithic
CMOS analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) capable of
100 kSps (5101A) and 20 kSps (5102A) throughput. The
CS5102A’s low power consumption of 44mW, coupled
with a power-down mode, makes it particularly suitable
for battery-powered operation .
On-chip self-calibration circuitry achieves nonlinearity of
±0.001% of FS and guarantees 16-bit, no missing cod es
over the entire specified temperature range. Superior linearity also leads to 92 dB S/(N+D) with harmonics below
-100 dB. Offset and full-scale errors are minimized during the calibration cycle, eliminating the need for ex ternal
trimming.
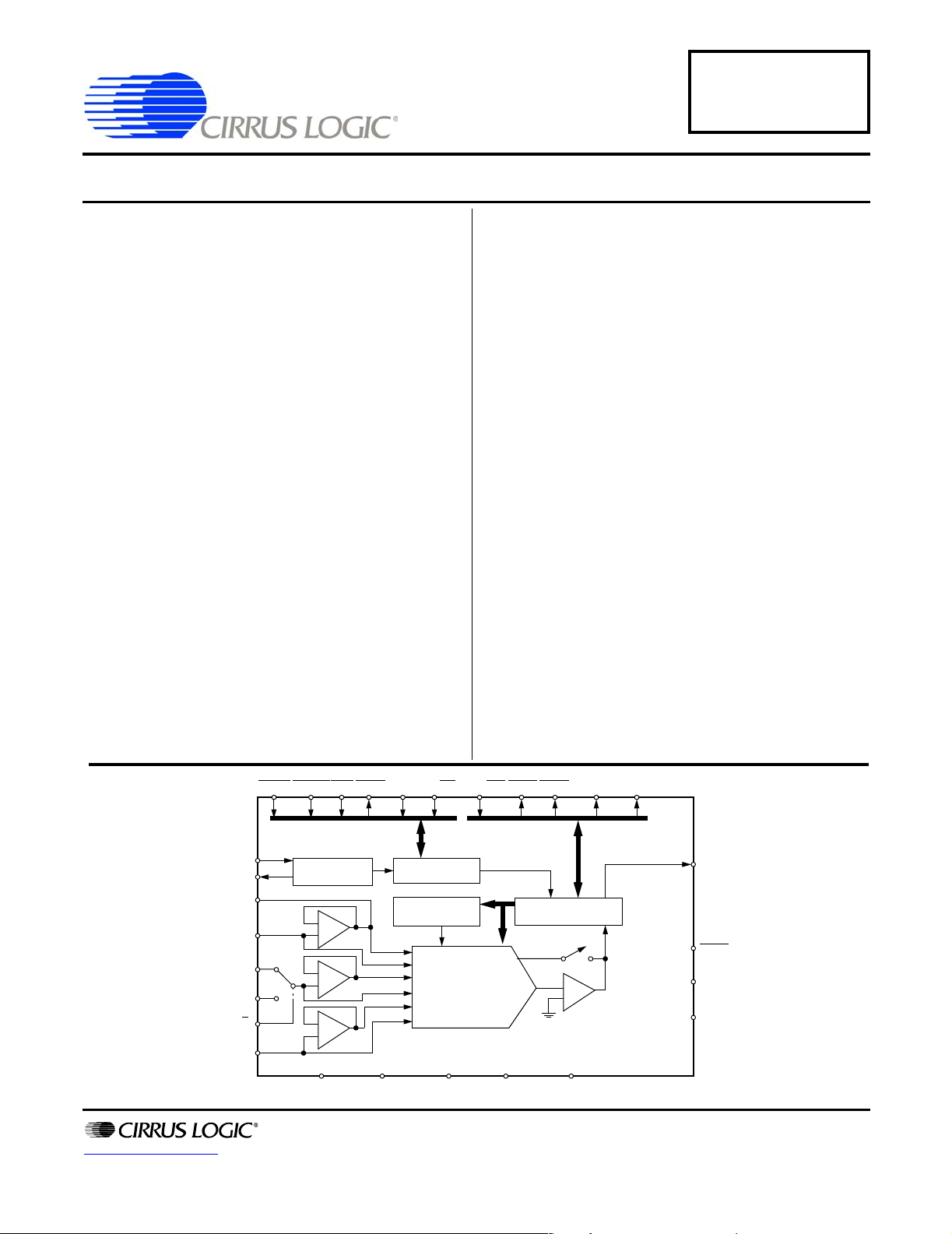
The CS5101A and CS5102A each consist of a 2-channel input multiplexer, DAC, conversion and calibration
microcontroller, clock generator, comparator, and serial
communications port. The inherent sampling architecture of the device eliminates the need for an external
track-and-hold amplifier.
The converters’ 16-bit data is output in serial form with
either binary or two’s complement coding. Three output
timing modes are available for easy interfacing to microcontrollers and shift registers. Unipolar and bipolar input
ranges are digitally selectable
ORDERING INFORMATION
See “Ordering Information” on page 38.
REFBUF
http://www.cirrus.com
HOLDSLEEPRST CODEBP/UP
12 28 2 5 16 17 8 9 11 15
XOUT
VREF
AIN1
AIN2
CH1/2
3
4
21
20
19
24
13
22
Clock
Generator
-
+
-
+
-
+
25 23
CLKIN
AGND
STBY
Calibration
Copyright © Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2005
CRS/FIN
Control
SRAM
16-Bit Charge
Redistribution
DAC
DGND VD- VD+VA-VA+
(All Rights Reserved)
TRK1
10
SSH/SDL
TRK2
Microcontroller
-
+
Comparator
716
SDATA
14
26
27
18
SCLK
TEST
SCKMOD
OUTMOD
AUG ‘05
DS45F5

CS5101A CS5102A
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. CHARACTERISTICS & SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................. 4
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS, CS5101A............................................................................... 4
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS, CS5101A.........................................................................6
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS, CS5102A............................................................................... 7
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS, CS5102A.........................................................................9
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS, ALL DEVICES ............................................................... 11
DIGITAL CHARACTERISTICS, ALL DEVICES......................................................................13
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS .....................................................................13
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS .........................................................................................14
2. OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................15
3. THEORY OF OPERATION .....................................................................................................15
3.1 Calibration . ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ................................................ 16
4. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................... 17
4.1 Initiating Conversions ....................................................................................................... 17
4.2 Tracking the Input ............................ ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ...................17
4.3 Master Clock .......... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ....................................... ......... 18
4.4 Asynchronous Sampling Considerations .........................................................................18
4.5 Analog Input Range/Coding Format ................................................................. ... ... ... ... ... 19
4.6 Output Mode Control ........................................................................................................19
4.6.1 Pipelined Data Transmission .............................................................................. 19
4.6.2 Register Burst Transmission (RBT) ....................................................................20
4.6.3 Synchronous Self-clocking (SSC) .................................... ... .... ... ... ......................20
4.6.4 Free Run (FRN) ..................................................................................................20
5. SYSTEM DESIGN USING THE CS5101A & CS5102A ......................................................... 22
5.1 System Initialization ...................... ... ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .... ...............22
5.2 Single-channel Operation ................................................................ .... ... ......................... 23
6. ANALOG CIRCUIT CONNECTIONS ...................................................................................... 23
6.1 Reference Considerations ...............................................................................................23
6.2 Analog Input Connection ................................. ....................................... ... ... .... ... ............24
6.3 Sleep Mode Operation .....................................................................................................24
6.4 Grounding & Power Supply Decoupling ............................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ......................... 25
7. CS5101A & CS5102A PERFORMANCE ............................................................................... 26
7.1 Differential Nonlinearity . ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ......................................26
7.2 FFT Tests and Windowing ...............................................................................................28
7.3 Sampling Distortion ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ...................................... ...... 30
7.4 Noise ...... ....................................... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... .........................31
7.5 Aperture Jitter .................................................................. .... ... ......................................... 31
7.6 Power Supply Rejection ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... ...................................... ... 32
8. PIN DESCRIPTIONS .............................................................................................................. 33
8.1 Power Supply Connections . ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ...................................... 33
8.2 Oscillator ...... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ............ 34
8.3 Digital Inputs .......................... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ... ................................34
8.4 Analog Inputs ............ .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ...................................... 35
8.5 Digital Outputs ................................................................. .... ... ......................................... 35
8.6 Analog Outputs .......................... ... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... .........................35
8.7 Miscellaneous ........................ .... ...................................... .... ... ... ...................................... 35
9. PARAMETER DEFINITIONS .................................................................................................. 36
10. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS ..................................................................................................... 37
11. ORDERING INFORMATION ................................................................................................ 38
12. ENVIRONMENTAL, MANUFACTURING, & HANDLING INFORMATION ........... ...............38
13. REVISIONS ..........................................................................................................................39
2 DS45F5

CS5101A CS5102A
LIST OF FIGURES
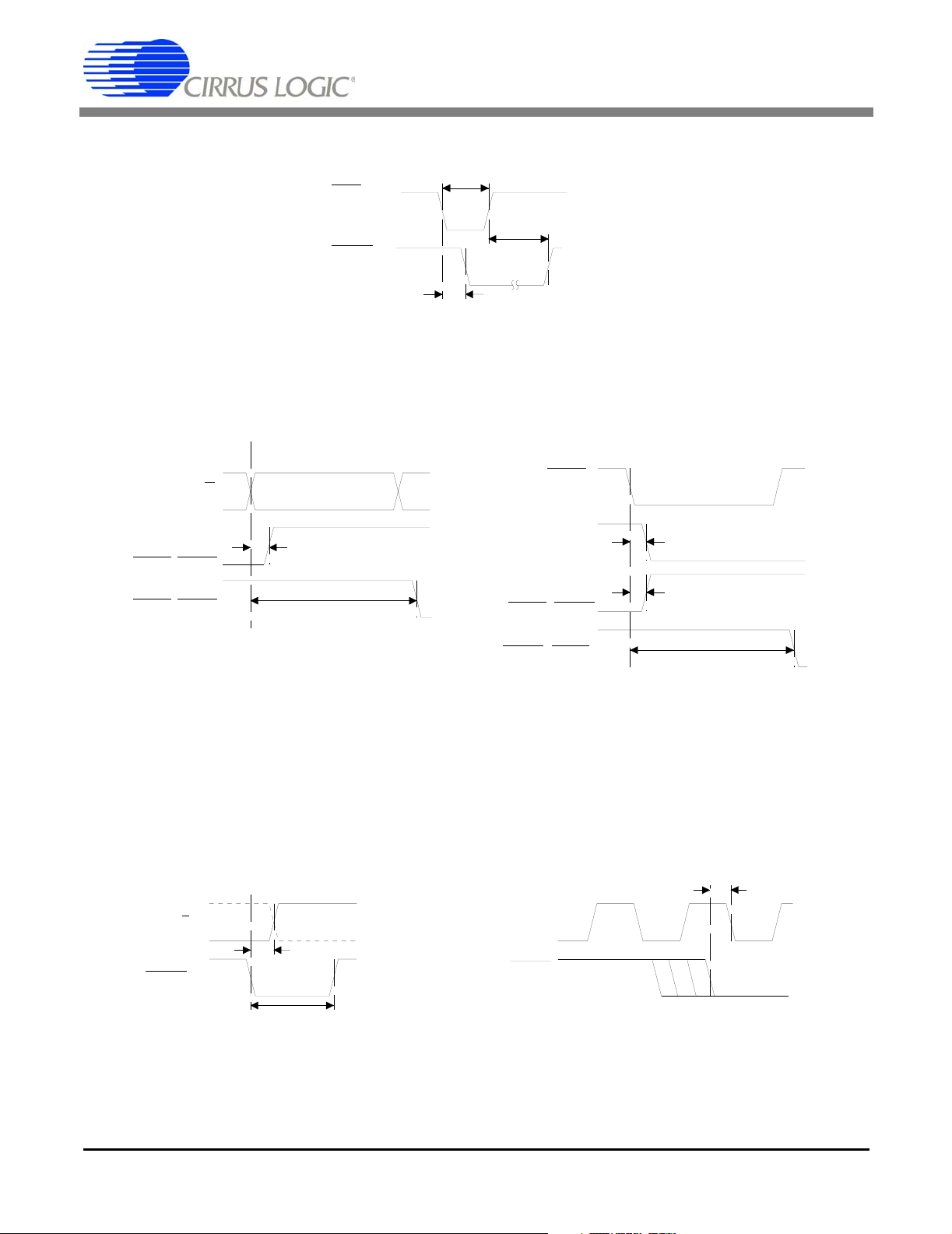
Figure 1. Reset, Calibration, and Control Timing .......................................................................... 10
Figure 2. Serial Communication Timing........................................................................................12
Figure 3. Coarse Charge Input Buffers & Charge Redistribution DAC . ... ... ... .... ... ... ......................15
Figure 4. Coarse/Fine Charge Control .......................................................................................... 18
Figure 5. Pipelined Data Transmission (PDT) Mode Timing......................................................... 20
Figure 6. Register Burst Transmission (RBT) Mode Timing..........................................................21
Figure 7. Synchronous Self-clocking (SSC) Mode Timing ............................................................ 21
Figure 8. Free Run (FRN) Mode Timing........................................................................................21
Figure 9. CS5101A/CS5102A System Connection Diagram... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ................................ 22
Figure 10. Power-up Reset Circuit ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ................................... 23
Figure 11. Reference Connections................................................................................................24
Figure 12. Charge Settling Time ...................................................................................................24
Figure 13. CS5101A DNL Plot - Ambient Temperature at 25 °C .................................................. 27
Figure 14. CS5101A DNL Plot - Ambient Temperature at 138 °C ................................................ 27
Figure 15. CS5102A DNL Plot - Ambient Temperature at 25 °C .................................................. 27
Figure 16. CS5102A DNL Plot - Ambient Temperature at 138 °C ................................................ 27
Figure 17. CS5101A DNL Error Distribution..................................................................................28
Figure 18. CS5102A DNL Error Distribution..................................................................................28
Figure 19. CS5101A FFT (SSC Mode, 1-Channel)....................................................................... 29
Figure 20. CS5101A FFT (SSC Mode, 1-Channel)....................................................................... 29
Figure 21. CS5102A FFT (SSC Mode, 1-Channel)....................................................................... 29
Figure 22. CS5102A FFT (SSC Mode, 1-Channle)....................................................................... 29
Figure 23. CS5101A Histogram Plot of 8192 Conversion Inputs .................................................. 31
Figure 24. CS5102A Histogram Plot of 8192 Conversion Inputs .................................................. 31
Figure 25. Power Supply Rejection...............................................................................................32
Figure 26. CS5101A & CS5102A 28-pin PLCC Pinout ................................................................. 33
Figure 27. 28-Pin PLCC Mechanical Drawing............................................................................... 37
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. Output Coding ................................................................................................................. 19
Table 2. Output Mode Control....................................................................................................... 19
DS45F5 3
CS5101A CS5102A
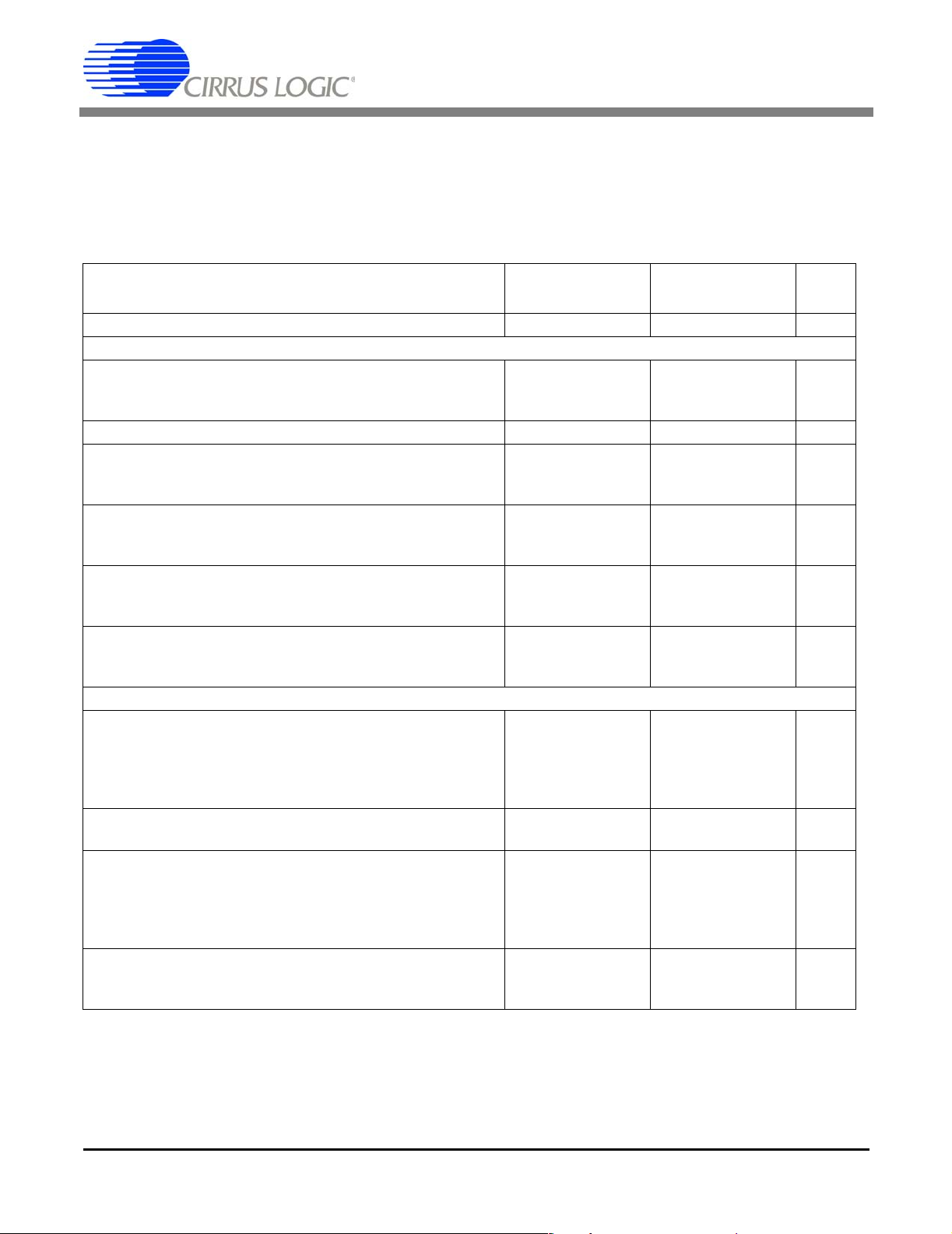
1. CHARACTERISTICS & SPECIFICATIONS
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS, CS5101A
(TA = TMIN to TMAX; VA+, VD+ = 5V; VA-, VD- = -5V; VREF = 4.5V; Full-scale Input sine wave, 1 kHz; CLKIN = 8 MHz; fs =
100 kSps; Bipolar Mode; FRN Mode; AIN1 and AIN2 tied together, each channel tested separately; Analog Source Impedance
= 50 Ω with 1000 pF to AGND unless otherwise specified)
CS5101A-J CS5101A-B
Parameter*
Specified Temperature Range 0 to +70 -40 to +85 ºC
Accuracy
±¼
±1
±1
±1
±2
±2
±1
±2
±2
±2
±1
±1
±1
100
102
88
91
90
92
30
32
35
70
0.003
0.002
±4
±3
±5
±4
±5
±3
±4
±3
Differential Input Range -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Differential Linearity (Note 3)
Full-scale Error -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Unipolar Offset -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Bipolar Offset -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Bipolar Negative Full-scale Error -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Dynamic Performance (Bipolar Mode)
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise (Note 1)
1-kHz Input -J
-B
12-kHz Input -J
-B
Total Harmonic Distortion -J
-B
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (Note 1)
0 dB Input -J
-B
-60 dB Input -J
-B
Noise (Note 4)
Unipolar Mode
Bipolar Mode
0.002
-
0.001
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
96
98
85
85
--0.002
0.001--
87
90
-
-
-
-
±¼
±1
±1
±1
±2
±2
±1
±2
±2
±1
±1
±1
±1
100
102
88
91
90
92
30
32
35
70
0.003
0.002
-
±4
±3
-
±5
±4
-
±5
±3
-
±4
±3
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.002
-
0.001
-
-
16 --16--Bits
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
96
98
85
85
--0.002
0.001--
87
90
-
-
-
-
UnitMin Typ Max Min Typ Max
%FS
%FS
∆LSB
-
LSB
LSB
∆LSB
LSB
LSB
∆LSB
LSB
LSB
∆LSB
LSB
LSB
∆LSB
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
dB
dB
dB
dB
%
%
dB
dB
dB
dB
µV
rms
µVrms
Notes: 1. Applies after calibration at any temperature within the specified temperature range.
2. Total drift over specified temperature range after calibration at power-up, at 25
3. Minimum resolution for which no missing codes is guaranteed over the specified temperature range.
4. Wideband noise aliased into the baseband, referred to the input.
* Refer to Parameter Definitions (immediately following the pin descriptions at the end of this data sheet.
4 DS45F5
º C.
CS5101A CS5102A
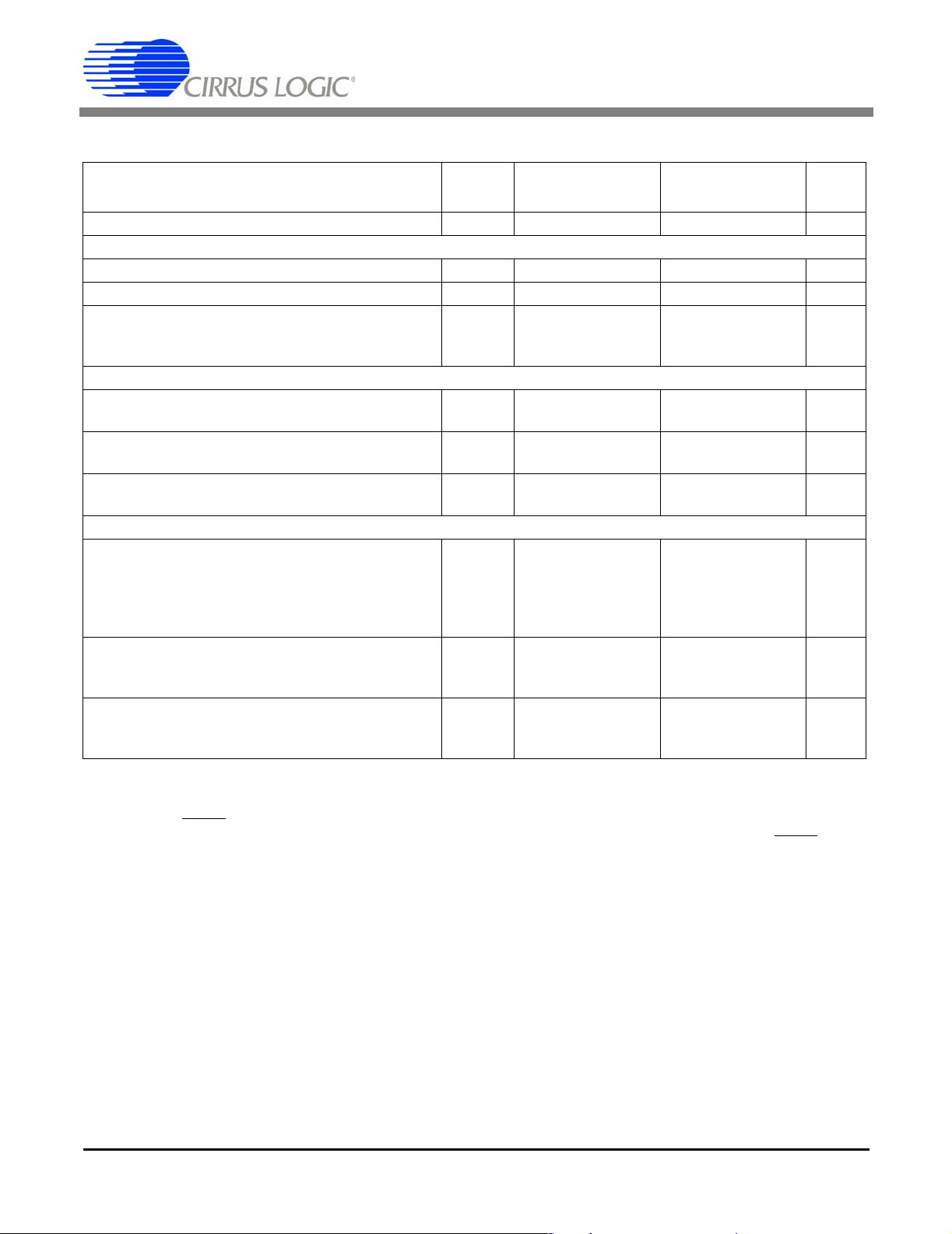
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS, CS5101A (Continued)
CS5101A-J CS5101A-B
Parameter* Symbol
Specified Te mperature Range - 0 to +70 -40 to +85 ºC
Analog Input
Aperture Time - - 25 - - 25 - ns
Aperture Jitter -
- 100 - - 100 - ps
Input Capacitance (Note 5)
Unipolar Mode
Bipolar Mode
-
-
--320
200
425
265
-
320
-
200
425
265
Conversion and Throughput
Conversion Time (Note 6)
t
c
- - 8.12 - - 8.12 µs
Acquisition Time (Note 7)
t
a
- - 1.88 - - 1.88 µs
Throughput (Note 8)
f
tp
100 - - 100 - - kSps
Power Supplies
Power Supply Current (Note 9)
Positive Analog
Negative Analog
(SLEEP High) Positive Digital
Negative Digital
21
I
+
A
I
-
A
I
+
D
I
-
D
21
-
-21
-
11
-
-11
-
28
-28
15
-15
-
-21
11
-
-11
-
28
-28
15
-15
Power Consumption (Note 9, Note 10)
(SLEEP High)
(SLEEP Low)
P
do
P
ds
--3201430
-
-
3201430-mW
-
Power Supply Rejection (Note 11)
Positive Supplies
Negative Supplies
PSR
PSR
-
84
-
84
-
-
-
84
-
84
UnitMin Typ Max Min Typ Max
mA
mA
mA
mA
mW
-
-
pF
pF
dB
dB
Notes:
5. Applies only in the track mode. When converting or calibrating, inpu t capacitance will not exceed 30 pF.
6. Conversion time scales directly to the master clock speed. The times shown are for synchronous, internal loopback
(FRN) mode) with 8.0 MHz CLKIN. In PDT, RBT, and SSC modes, asynchronous delay between the falling edge
HOLD and the start of conversion may add to the apparent conversion time. This delay will not exceed 1.5
of
master clock cycles + 10 ns. In PDT, RBT, and SSC modes, CLKIN can be increased as long as the
rate is 100 kHz max.
7. The CS5101A requires 6 clock cycles of coarse charge, followed by a minimum of 1.125 µs of fine charge. FRN
mode allows 9 cycles for fine charge which provides for the minimum 1.125 µs with an 8MHz clock, however; in
PDT, RBT, or SSC modes and at clock frequencies of 8 MHz or less, fine charge may be less than 9 clock cycles.
This reflects the typical specification (6 clock cycles + 1.125 µs).
8. Throughput is the sum of the acquisition and conversion times. It will vary in accordance with conditions affecting
acquisition and conversion times, as described above.
9. All outputs unloaded. All inputs at VD+ or DGND.
10. Power consumption in the sleep mode applies with no master clock applied (CLKIN held high or low).
11. With 300 mV p-p, 1-kHz ripple applied to each supply separately in the bipolar mode. Rejection improves by 6 dB
in the unipolar mode to 90 dB. Figure 25 shows a plot of typical power supply rejection versus frequency.
HOLD sample
DS45F5 5
CS5101A CS5102A
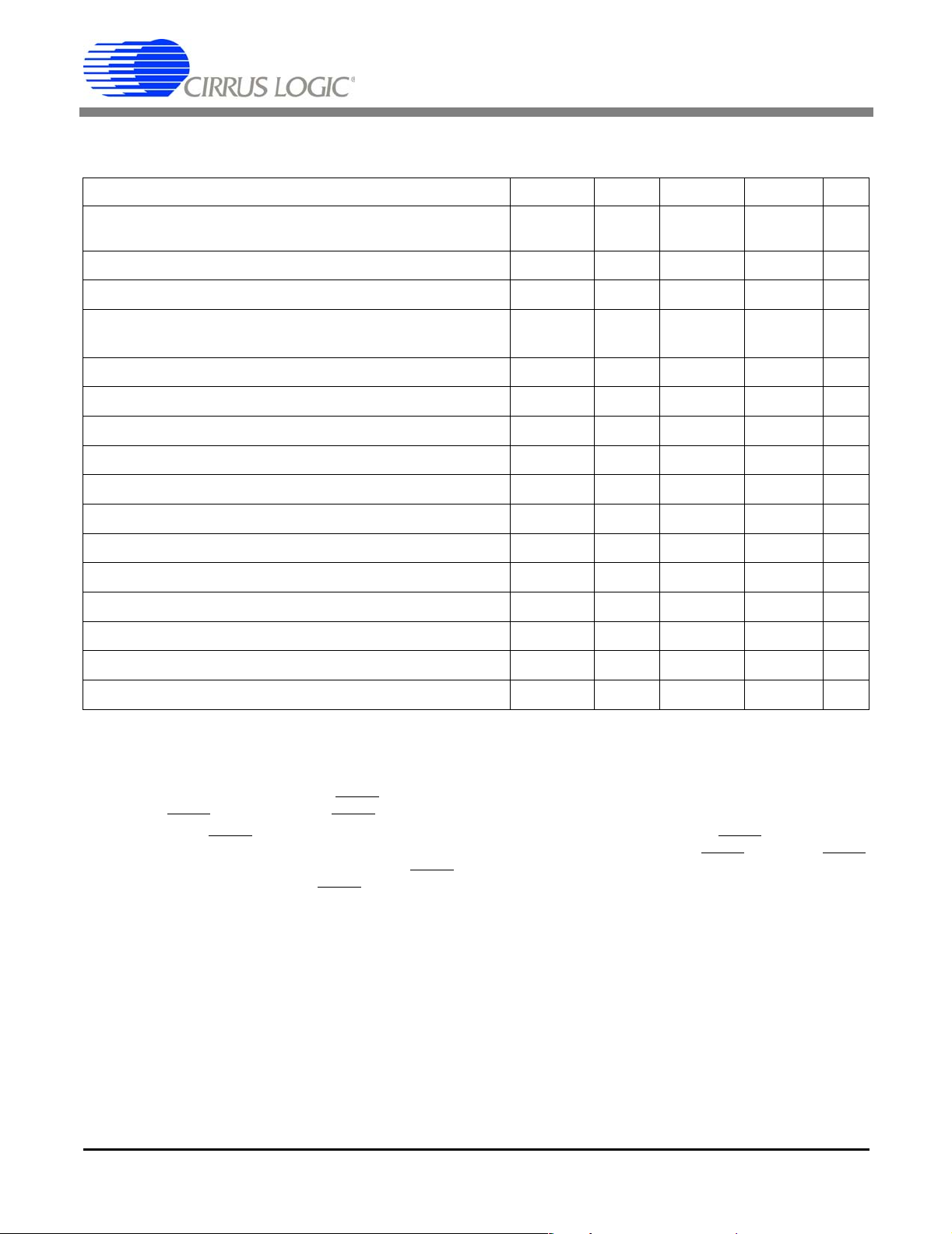
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS, CS5101A
(TA = TMIN to TMAX; VA+, VD+ = 5V ±10%; VA-, VD- = -5V ±10%; Inputs: Logic 0 = 0V, Logic 1 = VD+; CL = 50 pF).
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
CLKIN Period
t
clk
CLKIN Low Time t
CLKIN High Time t
clkl
clkh
Crystal Frequency (Note 12)
f
xtal
SLEEP Rising to Oscillator Stable (Note 13) - - 2 - ms
108 - 10,000 ns
37.5 - - ns
37.5 - - ns
2.0 - 9.216 MHz
RST Pulse Width t
RST to STBY falling t
RST Rising to STBY Rising t
CH1/2 Edge to TRK1, TRK2 Rising (Note 14) t
CH1/2 Edge to TRK1, TRK2 Falling (Note 14) t
HOLD to SSH Falling (Note 15) t
HOLD to TRK1, TRK2 Falling (Note 15) t
HOLD to TRK1, TRK2, SSH Rising (Note 15) t
HOLD Pulse Width (Note 16) t
HOLD to CH1/2 Edge (Note 15) t
HOLD Falling to CLKIN Falling (Note 16) t
rst
drrs
cal
drsh1
dfsh4
dfsh2
dfsh1
drsh
hold
dhlri
hcf
150 - - ns
-100 -ns
- 1 1,528,160 - t
clk
-80 -ns
--68t
+260 ns
clk
-60 -ns
66t
clk
-68t
+260 ns
clk
-120 -ns
1t
+20 - 63t
clk
15 - 64t
95 - 1t
clk
clk
+10 ns
clk
ns
ns
Notes: 12. External loading capacitors are required to allow the crystal to oscillate. Maximum crystal frequency is 8.0 MHz in
FRN mode (100 kSps).
13. With an 8.0 MHz crystal, two 10 pF loading capacitors and a 10 MΩ parallel resistor (see Figure 9).
14. These timings are for FRN mode.
15. SSH only works correctly if
HOLD rises to 64t
16. When
HOLD goes low, the analog sample is captured immediately. To start conversion, HOLD must be latched
by a falling edge of CLLKIN. Conversion will begin on the next rising edge of CLKIN after
is operated synchronous to CLKIN, the
if CLKIN falls 95 ns after HOLD falls. This ensures that the HOLD pulse will meet the minimum specification for t
clk
HOLD falling edge is within +15 to +30 ns of CH1/2 edge or if CH1/2 edge occurs after
after HOLD has fallen. These timings are for PDT and RBT modes.
HOLD is latched. If HOLD
HOLD pulse width may be as narrow as 150 ns for all CLKIN frequencies
hcf
.
6 DS45F5
CS5101A CS5102A
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS, CS5102A
(TA = TMIN to TMAX; VA+, VD+ = 5V; VA-, VD- = -5V; VREF = 4.5V; Full-scale Input Sine Wave, 200 Hz; CLKIN = 1.6 MHz;
fs = 20 kSps; Bipolar Mode; FRN Mode; AIN1 and AIN2 tied together, each channel tested separately; Analog Source
Impedance = 50 Ω with 1000 pF to AGND unless otherwise specified)
CS5102A-J CS5102A-B
Parameter*
Specified Te mperature Range 0 to +70 -40 to +85 ºC
Accuracy
±¼
±2
±2
±1
±1
±1
±1
±1
±1
±2
±2
±2
±2
102
90
92
30
32
35
70
0.003
0.0015
-
±4
±3
-
±4
±3
-
±4
±3
-
±4
±3
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Differential Input Range -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Differential Linearity (Note 3)
Full-scale Error -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Unipolar Offset -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Bipolar Offset -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Bipolar Negative Full-scale Error -J (Note 1)
-B
Drift (Note 2)
Dynamic Performance (Bipolar Mode)
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise (Note 1)
-J
-B
Total Harmonic Distortion -J
-B
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (Note 1)
0 dB Input -J
-B
-60 dB Input -J
-B
Noise (Note 4)
Unipolar Mode
Bipolar Mode
0.002
-
0.001
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
9698100
--0.002
0.001--
87
90
-
-
-
-
±¼
±2
±2
±1
±1
±1
±1
±1
±1
±1
±2
±2
±1
102
90
92
30
32
35
70
0.003
0.0015
-
±4
±3
-
±4
±3
-
±4
±3
-
±4
±3
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.002
-
0.001
-
-
16 --16--Bits
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
9698100
--0.002
0.001--
87
90
-
-
-
-
UnitMin Typ Max Min Typ Max
%FS
%FS
∆LSB
LSB
LSB
∆LSB
LSB
LSB
∆LSB
LSB
LSB
∆LSB
LSB
LSB
∆LSB
dB
dB
%
%
dB
dB
dB
dB
µV
rms
µVrms
* Refer to Parameter Definitions (immediately following the pin descriptions at the end of this data sheet.
DS45F5 7
ANALOG CHARACTERISTICS, CS5102A (Continued)
CS5102A-J CS5102-B
CS5101A CS5102A
Parameter* Symbol
UnitMin Typ Max Min Typ Max
Specified Te mperature Range - 0 to +70 -40 to +85 ºC
Analog Input
Aperture Time - - 30 - - 30 - ns
Aperture Jitter -
- 100 - - 100 - ps
Input Capacitance (Note 5)
Unipolar Mode
Bipolar Mode
-
-
--320
200
425
265
--320
200
425
265
pF
pF
Conversion and Throughput
Conversion Time (Note 17) t
Acquisition Time (Note 18) t
Throughput (Note 19) f
c
a
tp
- - 40.625 - - 40.625 µs
- - 9.375 - - 9.375 µs
20 - - 20 - - kSps
Power Supplies
Power Supply Current (Note 20)
Positive Analog
Negative Analog
(SLEEP High) Positive Digital
Negative Digital
2.4
I
+
A
I
-
A
I
+
D
I
-
D
2.4
-
-2.4
-
2.5
-
-1.5
-
3.5
-3.5
3.5
-2.5
-
-2.4
-
2.5
-
-1.5
-
3.5
-3.5
3.5
-2.5
mA
mA
mA
mA
Power Consumption (Note 10, Note 20)
(SLEEP High)
(SLEEP Low)
P
do
P
ds
-
44
-
65
1
-
-
44
-
1
65
mW
-
mW
Power Supply Rejection (Note 21)
Positive Supplies
Negative Supplies
PSR
PSR
-
84
-
84
-
-
-
84
-
84
-
-
dB
dB
Notes:
17. Conversion time scales directly to the master clock speed. The times shown are for synchronous, internal loopback
(FRN) mode. In PDT, RBT, and SSC modes, asynchronous delay between the falling edge of
of conversion may add to the apparent conversion time. This delay will not exceed 1 master clock cycle + 140 ns.
18. The CS5102A requires 6 clock cycles of coarse charge, followed by a minimum of 5.625 µs of fine charge. FRN
mode allows 9 cycles for fine charge which provides for the minimum 5.625 µs with a 1.6 MHz clock, however; in
PDT, RBT, or SSC modes and at clock frequencies of less than 1.6 MHz, fine charge may be less than 9 clock
cycles.
19. Throughput is the sum of the acquisition and conversion times. It will vary in accordance with conditions affecting
acquisition and conversion times, as described above.
20. All outputs unloaded. All inputs at VD+ or DGND. See table below for power dissipation versus clock frequency.
21. With 300 mV p-p, 1-kHz ripple applied to each supply separately in the bipolar mode. Rejection improves by 6 dB
in the unipolar mode to 90 dB. Figure 25 shows a plot of typical power supply rejection versus frequency.
HOLD and the start
Typical Power (mW) CLKIN (MHz)
34 0.8
37 1.0
39 1.2
41 1.4
44 1.6
8 DS45F5
CS5101A CS5102A
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS, CS5102A
(TA = TMIN to TMAX; VA+, VD+ = 5V ±10%; VA-, VD- = -5V ±10%; Inputs: Logic 0 = 0V, Logic 1 = VD+; CL = 50 pF).
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
CLKIN Period (Note 22) t
CLKIN Low Time t
CLKIN High Time t
Crystal Frequency (Note 22, Note 23) f
clk
clkl
clkh
xtal
SLEEP Rising to Oscillator Stable (Note 24) - - 20 - ms
0.5 - 10 µs
200 - - ns
200 - - ns
0.9 1.6 2.0 MHz
RST Pulse Width t
RST to STBY falling t
RST Rising to STBY Rising t
CH1/2 Edge to TRK1, TRK2 Rising (Note 25) t
CH1/2 Edge to TRK1, TRK2 Falling (Note 25) t
HOLD to SSH Falling (Note 26) t
HOLD to TRK1, TRK2 Falling (Note 26) t
HOLD to TRK1, TRK2, SSH Rising (Note 26) t
HOLD Pulse Width (Note 27) t
HOLD to CH1/2 Edge (Note 26) t
HOLD Falling to CLKIN Falling (Note 27) t
Notes: 22. Minimum CLKIN period is 0.625 ms in FRN mode (20 kSps).
23. External loading capacitors are required to allow the crystal to oscillate. Maximum crystal frequency is 1.6 MHz in
FRN mode (20 kSps).
24. With a 2.0 MHz crystal, two 33 pF loading capacitors and a 10 MΩ parallel resistor (see Figure 9).
25. These timings are for FRN mode.
26. SSH only works correctly if
HOLD rises to 64t
27. When
HOLD goes low, the analog sample is captured immediately. To start conversion, HOLD must be latched
by a falling edge of CLLKIN. Conversion will begin on the next rising edge of CLKIN after
is operated synchronous to CLKIN, the HOLD pulse width may be as narrow as 150 ns for all CLKIN frequencies
if CLKIN falls 55 ns after
clk
HOLD falling edge is within +15 to +30 ns of CH1/2 edge or if CH1/2 edge occurs after
after HOLD has fallen. These timings are for PDT and RBT modes.
HOLD falls. This ensures that the HOLD pulse will meet the minimum specification for t
rst
drrs
cal
drsh1
dfsh4
dfsh2
dfsh1
drsh
hold
dhlri
hcf
150 - - ns
-100 -ns
- 2,882,040 - t
clk
-80 -ns
--68t
+260 ns
clk
-60 -ns
66t
clk
-68t
+260 ns
clk
-120 -ns
1t
+20 - 63t
clk
15 - 64t
55 - 1t
clk
clk
+10 ns
clk
ns
ns
HOLD is latched. If HOLD
hcf
.
DS45F5 9
t
rst
RST
STBY
t
drrs
Reset and Calibration Timing
t
CS5101A CS5102A
cal
CH1/2
TRK1,TRK2
TRK1,TRK2
CH1/2
HOLD
HOLD
SSH/SDL
t
drsh1
t
dfsh4
SSH,TRK1,TRK2
TRK1,TRK2
a. FRN Mode b. PDT, RBT Mode
t
dfsh2
t
drsh
t
dfsh1
Control Output Timing
t
dhlri
CLKIN
HOLD
t
hcf
t
hold
Channel Selection Timing Start Conversion Timing
Figure 1. Reset, Calibration, and Control Timing
10 DS45F5
CS5101A CS5102A
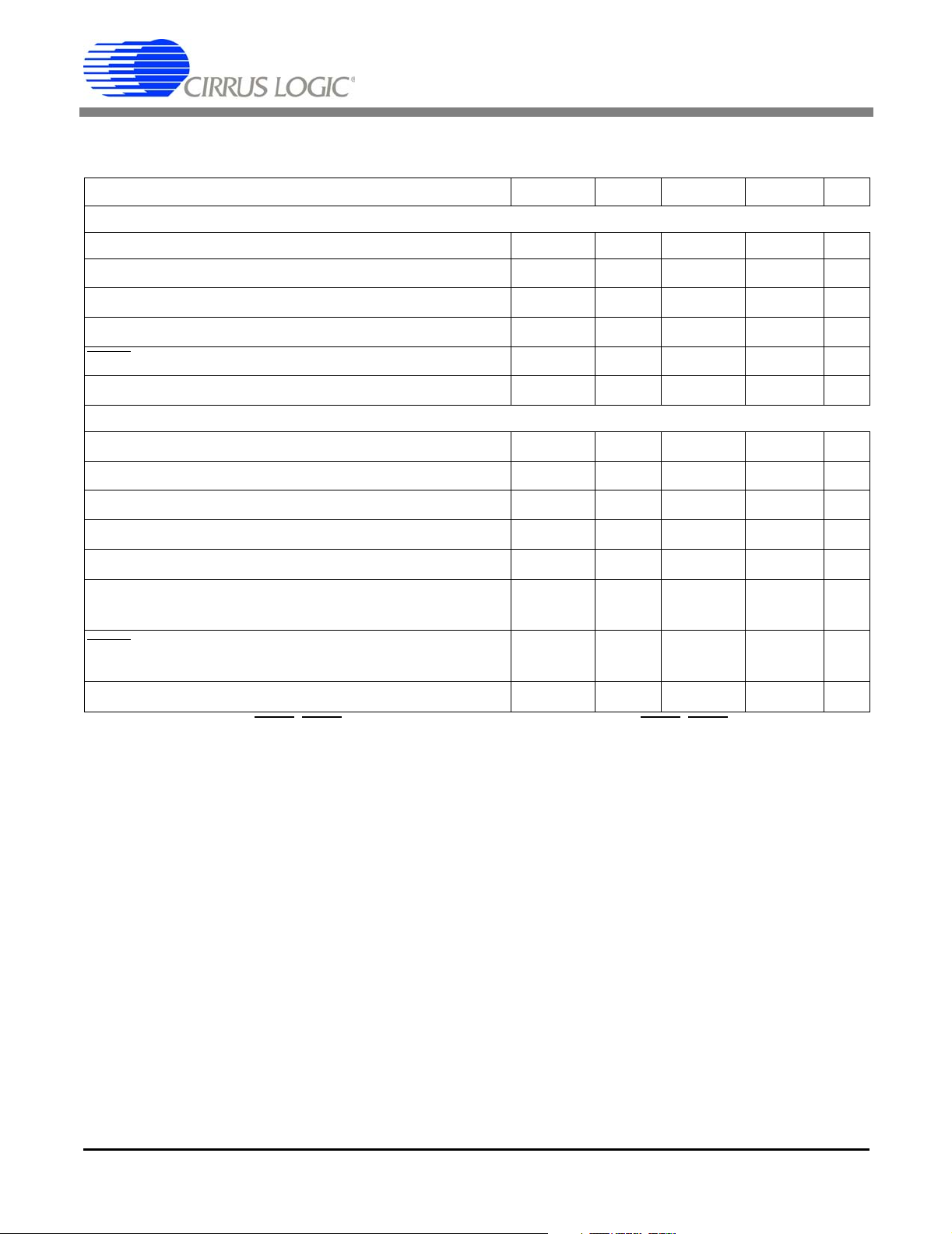
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS, ALL DEVICES
(TA = TMIN to TMAX; VA+, VD+ = 5V ±10%; VA-, VD- = -5V ±10%; Inputs: Logic 0 = 0V, Logic 1 = VD+; CL = 50 pF).
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
PDT & RBT Modes
SCLK Input Pulse Period t
SCLK Input Pulse Width Low t
SCLK Input Pulse Width High t
SCLK Input Falling to SDATA Valid t
HOLD
Falling to SDATA Valid PDT Mode t
TRK1, TRK2 Falling to SDATA Valid (Note 28) t
FRN & SSC Modes
sclk
sclkl
sclkh
dss
dhs
dts
200 - - ns
50 - - ns
50 - - ns
-100150ns
-140230ns
-65125ns
SCLK Output Pulse Width Low t
SCLK Output Pulse Width High t
SDATA Valid Before Rising SCLK t
SDATA Valid After RIsing SCLK t
st
SDL Falling to 1
Rising SCLK
Last Rising SCLK to SDL Rising CS5101A
CS5102A
HOLD
Falling to 1st Falling SCLK CS5101A
CS5102A
CH1/2 Edge to 1
st
Falling SCLK
slkl
slkh
t
rsclk
t
rsdl
t
rsdl
t
hfs
t
hfs
t
dhlri
ss
sh
-2t
-2t
2t
-100 - - ns
clk
2t
-100 - - ns
clk
66t
clk
-
-
6t
clk
6t
clk
-7t
2t
2t
2t
clk
clk
clk
clk
clk
-
-
clk
-t
-t
68t
+260 ns
clk
2t
+165
clk
+200
2t
clk
8t
+165
clk
+200
8t
clk
64t
clk
ns
ns
t
clk
clk
clk
Notes: 28. Only valid for TRK1, TRK2 falling when SCLK is low. If SCLK is high when TRK1, TRK2 falls, then SDATA is
valid t
time after the next falling SCLK.
dss
DS45F5 11
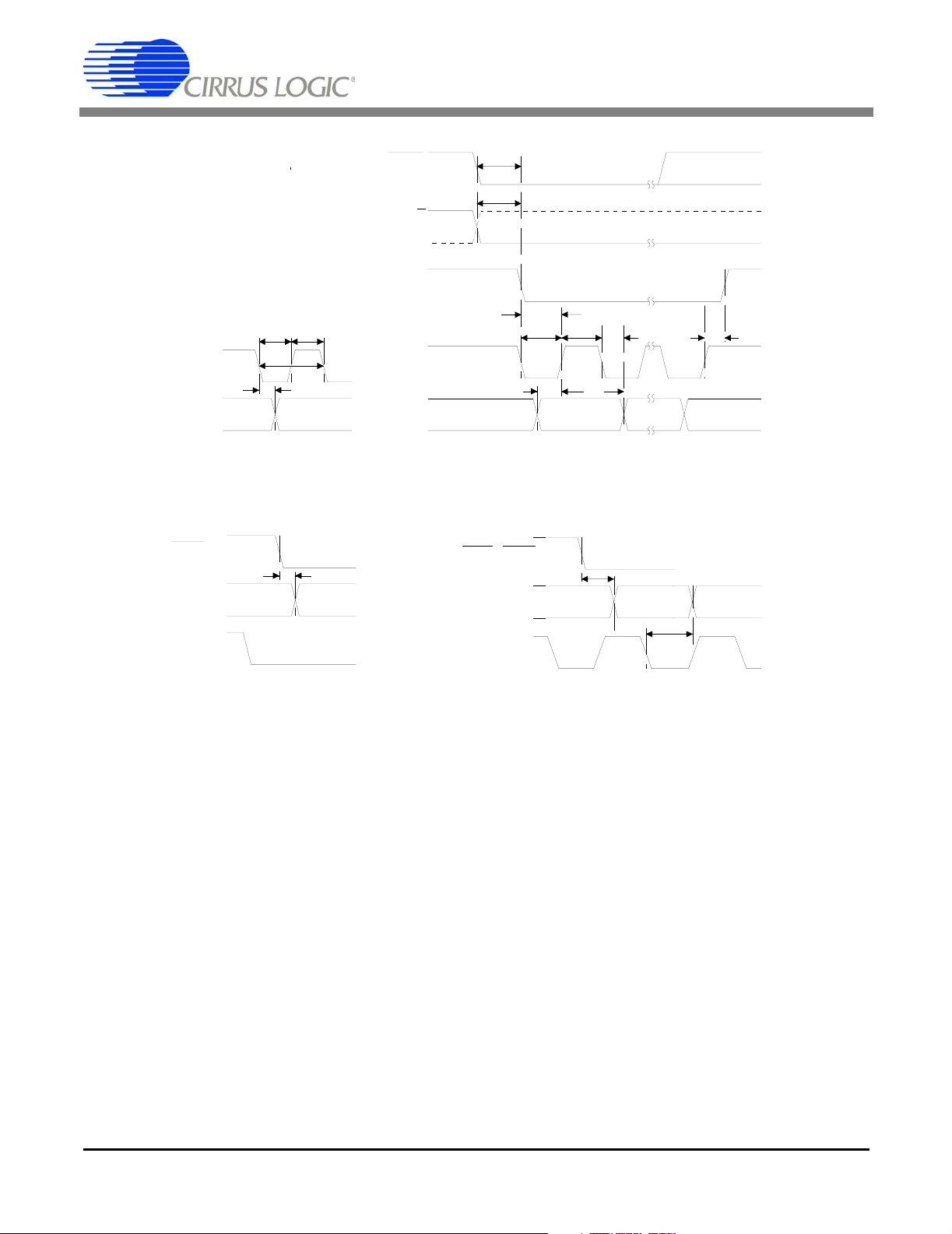
CS5101A CS5102A
t
HOLD
CH1/2
SSH/SDL
t
sclkltsclkh
SCLK
t
SCLK
SDATA
t
dss
sclk
SDATA
a. SCLK Input (PDT & RBT Modes) b. SCLK Output (FRN & SSC Modes)
Serial Data Timing
hfs
t
chfs
t
rsclk
t
t
t
ss
slkl
slkh
MSB
t
sh
t
dss
LSB
t
rsdl
HOLD
SDATA
SCLK
t
dhs
MSB
TRK1, TRK2
SDATA
SCLK
t
dts
MSB
t
dss
MSB-1
a. Pipelined Data Transmission (PDT) b. Register Burst Transmission (RBT)
Data Transmission Timing
Figure 2. Serial Communication Timing
12 DS45F5
 Loading...
Loading...