Page 1

PA-2400
C Library Manual
(Version 1.00 )
March 1998
Casio Computer Co., Ltd.
Copyright ©1998. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Table of Contents
Preface 4
Chapter 1. Supported Files 5
1.1 List of Dedicated Libraries 6
1.1.1 I/O Bootup Library Function 6
1.1.2 File Transfer Utility 6
1.1.3 File Check Utility 6
Chapter 2. I/O Bootup Library 7
2.1 Overview 7
2.2 Function 7
2.3 Detail of Function 9
iobox_chk 9
2.4 Source List 11
Chapter 3. File Transfer Utility 15
3.1 Overview 15
3.2 List of Functions 16
3.3 Communication Functions 17
3.4 Pathname Description Method 18
3.5 Rules of Describing Arguments 20
3.6 Conditoons on Communication Partner 21
3.6.1 Rules of Naming Files and Directory Paths 21
3.6.2 Specifying on Non-Existing File 21
3.6.3 /D (delete) Command Option 22
3.7 Setting Up Registry 22
3.7.1 Setup Items 22
3.7.2 Setting Up Registry with User Application 24
3.8 Termination Codes 26
3.9 Log File 29
3.10 Restrictions 30
3.11 Precautions 30
3.12 Details of Functions 31
FLCE /Y 31
FLCE /S 33
FLCE /R 35
FLCE /A 37
FLCE /D 39
FLCE /N 41
FLCE /T 42
FLCE (Idle Start) 43
2
Page 3

Chapter 4. File Check Utility 45
4.1 Overview 45
4.2 List of Functions 45
4.3 Pathname Describing Method 45
4.3.1 Description of Pathnames 45
4.3.2 Rules of Naming Files and Directory Paths 46
4.4 Rules of Describing Arguments 46
4.5 Functions 47
4.5.1 List File Generating Function 47
4.5.2 List File Comparison 48
4.6 Format of List Files 49
4.7 Syntax Analysis of Script Fil es 50
4.8 Error Messages/Codes 52
4.9 Restrictions 53
4.10 Details of Functions 54
FCHKCE /G 54
FCHKCE /C 56
3
Page 4
Preface
This manual describes the C language-dedicated library functions and utilities that run on the Casio
PA-2400 (hereinafter referred to as "H/PC", which stands for Handheld PC).
The PA-2400 uses the Windows CE operating system, and uses the Win32 API functions to generate
user application programs. However, more functions may be required if generating a business
application, etc.
The C language-dedicated library functions and utilities described in this manual are used to support
functions that are not supported by the API functions.
Information about the Win32 API functions can be retrieved using the Help function in the Windows
95 system.
Win32 API Function
C language dedicated library,
utility
(I/O bootup, FLCE, FCHKCE)
Available from
Microsoft
Available from
Casio
4
Page 5
1. Supported Files
The following files will be supported by the C-library functions and utilities described in this
document.
I/O Bootup Library
1) IOBOX1.H Function header file
2) IOBOX1.LIB Import library for linking
File Transfer Utility
1) FLCE.EXE Execution file
2) SND.LNK Shortcut for PA-2400-to-PA-2400 communication
3) RCV.LNK Shortcut for PA-2400-to-PA-2400 communication
4) IDLE.LNK Shortcut for idle
File Check Utility
1) FCHKCE.EXE Execution file
2) MAKE.LNK Shortcut for PA-2400-to-PA-2400 communication
3) CHECK.LNK Shortcut for downloading AP
Files that can be placed in any directory (shortcut)
Files that are required for building
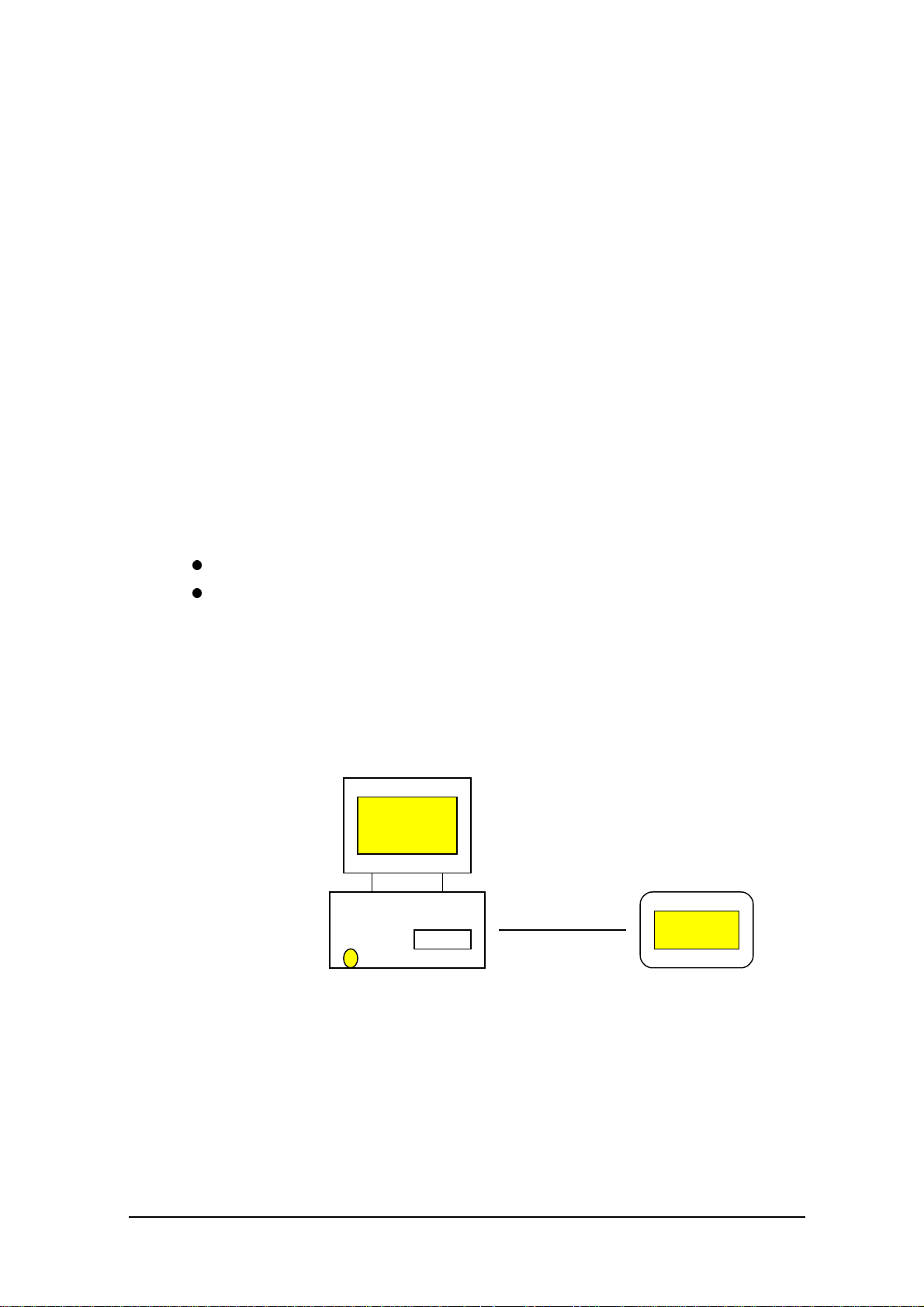
Each library function or utility can be made available to the user when the DLL/EXE file is copied
into the Windows directory on the PA-2400 (see the figure below).
Host PC
PA-2400
Copy
Fig.1.1 System configuration
5
Page 6

1.1 List of Dedicated Libraries
1.1.1 I/O Bootup Library Function
Table 1.1 I/O Bootup libraru function
No. Function Description Page
1 iobox_chk Monitoring the connection status of I/O BOX 9
1.1.2 File Transfer Utility
Table 1.2 File transfer utility
No. Function (command) Description Page
1 FLCE /Y Communication environment setup/Idle start 31
2 FLCE /S File transmission 33
3 FLCE /R File reception 35
4 FLCE /A File transmission (append) 37
5 FLCE /D File deletion 39
6 FLCE /N File move/File name modification 41
7 FLCE /T Time transmission 42
1.1.3 File Check Utility
Table 1.3 File check utility
No. Function(Command) Description Page
1 FCHKCE /G Generation of a list file 54
2 FCHKCE /C Comparison of list files 56
6
Page 7
2. I/O Bootup Library
2.1 Overview
The I/O bootup library monitors the connection status of the dedicated I/O Box and notifies the user
of the status.
2.2 Function
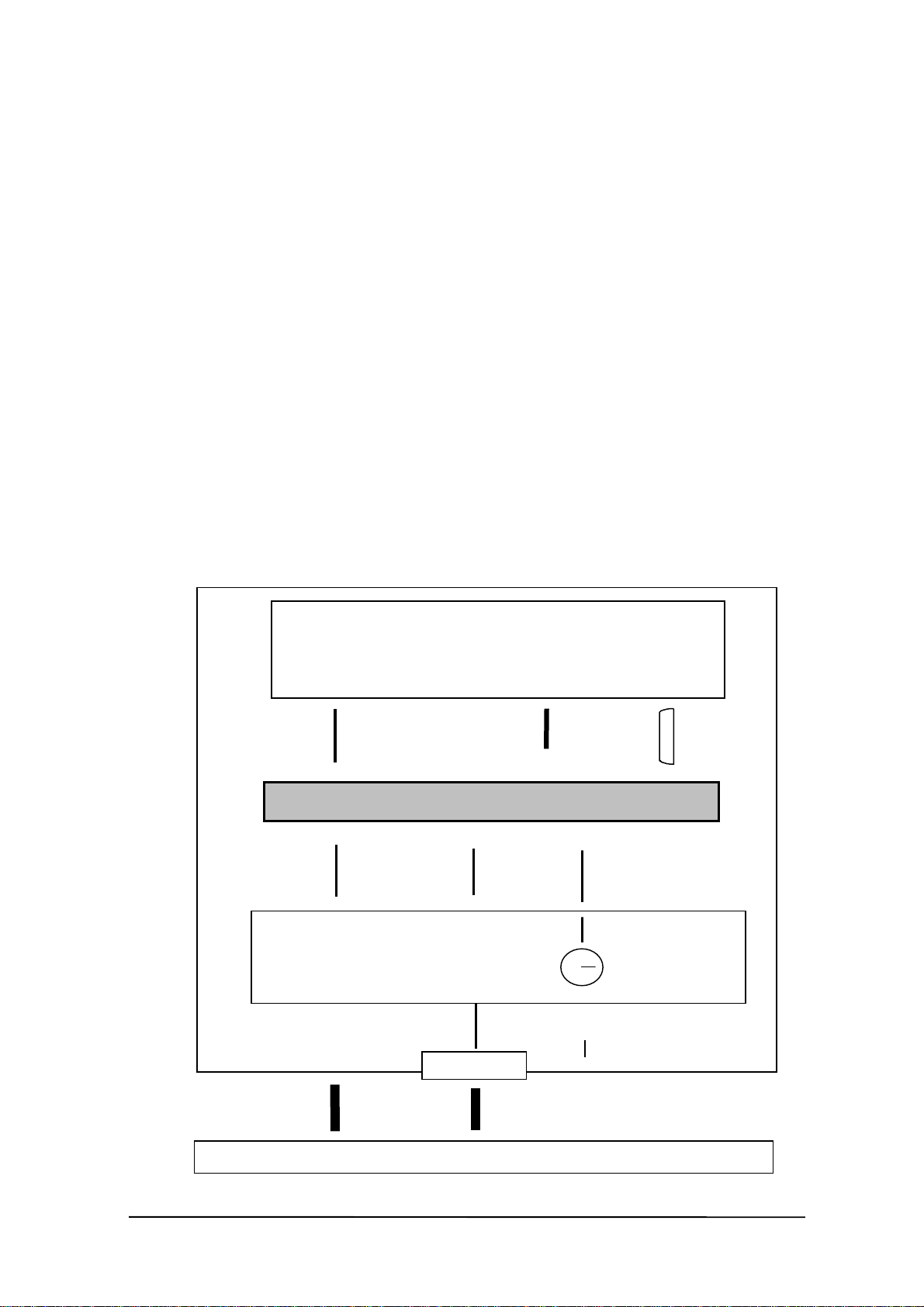
This library supports only one function, iobox_chk(). The iobox_chk() function monitors and
detects, for a specified period, whether I/O Box is mounted, and returns the result (mounting
detected, time-out error, or error). Each time this function is used, it is necessary to also execute
"Permit interrupt, Wait for interrupt and time-out, and Prohibit interrupt". The following diagram
shows the range covered by this library.
Fig. 2.1
PA-2400
User Application
(1) iobox_chk ( TIME_OUT_SEC ) ;
(5) Return
Detection, Timeout
Error
IOBOX1.DLL
I/O PORT: 0
(2) Mounting
(4) Timeout
I/O Box
(3) I/O Box ON Signal
7
Page 8

Because the interrupt signals are detected by their signal levels, they can be detected even if the
order of and 2) is changed. (The connection status can be detected whether this function is
called before or after I/O Box is mounted, unless a time-out occurs.)
8
Page 9

2.3 Details of Function
iobox_chk
< Description >
Monitors the connection status between two PA-2400 terminals and I/O Box for a specified period
of time and returns the result.
< Format >
int iobox_chk ( DWORD time_out );
< Parameter >
DWORD time_out : Maximum time to monitor the connection status (1 to 4,294,967,295 (ms) )
No time-out = INFINITE
(4,294,967,295 (ms) equals to INFINITE.)
< Return value >
int
< Return code >
0 : Connection detected
1 : Time-out
-1 : Used exclusively by other program
Other : Function call fails.
< Include file >
iobox1.h
< Remarks >
If the main program calls this function, it must subsequently acquire a return from this function.
If the main program is terminated without acquiring a return, it can no longer be called on and
after the next call, since the interrupt event object of I/O Box that has been generated in this
function is not closed. (In order to restore it to normal operation, it is necessary to reset the
whole system.)
To avoid this problem set a short time-out for this function call and always receive the return of
time-out, then execute the cancellation process if, for example, programming the cancellation
process after waiting for connection.
If the system power is turned off while this function is in the process of waiting for connection to I/O
Box , the monitoring operation can be resumed from the state that immediately preceded the point
9
Page 10

where the system power was turned off by the Power-ON resume function.
A disconnection from I/O Box should be judged by means of a communication error that is detected
by the user application or a time-out return error with this function after the PA-2400 is connected to
I/O Box.
Always include iobox1.lib with the import library to be used for developing user applications.
10
Page 11

2.4 Source List
This section introduces the IOBOX1.C program and its reference sources, and show a list of
environment variables.
// windows ce iobox sample file
#include <windows.h>
#include <commctrl.h>
#include "iobox1.h"
VOID ioProc( void);
TCHAR szAppName[ ] = TEXT("Hello Windows CE");
TCHAR szTitle[ ] = TEXT("PA-2400 I/O BOX TEST");
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND, UINT, WPARAM, LPARAM);
HINSTANCE hInst = NULL;
HWND hWndCB = NULL;
HANDLE hWnd;
HANDLE h;
const int WINDOW_WIDTH = 480;
const int WINDOW_HEIGHT = 214;
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPWSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow )
{
// HWND hWnd;
MSG msg;
WNDCLASS wc;
wc.style = 0L;
wc.lpfnWndProc = (WNDPROC) WndProc;
wc.cbClsExtra = 0;
11
Page 12

wc.cbWndExtra = 0;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.hIcon = NULL;
wc.hCursor = NULL;
wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH) GetStockObject(WHITE_BRUSH);
wc.lpszMenuName = NULL;
wc.lpszClassName = szAppName;
RegisterClass(&wc);
InitCommonControls(); // Initialize common controls - command bar
hInst = hInstance; // Save handle to create command bar
hWnd = CreateWindow(szAppName, // Class
szTitle, // Title
WS_OVERLAPPED, // Style
100, // x-position
50, // y-position
WINDOW_WIDTH/2, // x-size
WINDOW_HEIGHT/2, // y-size
NULL, // Parent handle
NULL, // Menu handle
hInstance, // Instance handle
NULL); // Creation
ShowWindow(hWnd, SW_SHOW);
UpdateWindow(hWnd);
while ( GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return(msg.wParam);
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message,
WPARAM uParam, LPARAM lParam )
12
Page 13

{
HDC hdc;
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
RECT rect;
DWORD ThreadID;
switch (message)
{
case WM_CREATE:
sndPlaySound(TEXT("OpenProg"), SND_NODEFAULT | SND_ASYNC);
hWndCB = CommandBar_Create(hInst, hWnd, 1);
CommandBar_AddAdornments( hWndCB, 0L, 0L);
return 0;
case WM_PAINT:
hdc = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
GetClientRect(hWnd, &rect);
rect.top += CommandBar_Height(hWndCB);
DrawText(hdc, TEXT("Hello Windows CE!"), -1, &rect,
DT_SINGLELINE | DT_CENTER | DT_VCENTER);
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
return 0;
case WM_LBUTTONDOWN:
h = CreateThread(NULL, 0, ( LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)ioProc, NULL, 0,
( LPDWORD)&ThreadID); return 0;
case WM_USER:
switch( ( int)uParam) {
case 0:
MessageBox( hWnd, TEXT( "Connected!") , TEXT( "MessageBox"), MB_OK);
break;
case 1:
MessageBox( hWnd, TEXT( "Time Out!") , TEXT( "MessageBox"),
MB_OK); break;
case -1:
MessageBox( hWnd, TEXT( "Other program is using!") ,
TEXT( "MessageBox"), MB_OK); break;
13
Page 14

default:
MessageBox( hWnd, TEXT( "Function call Failed!") , TEXT( "MessageBox"),
MB_OK); break;
}
// TerminateThread( h,0); // Close because thread is no longer required.
// ExitThread( 0L);
CloseHandle( h);
return 0;
case WM_CLOSE:
sndPlaySound(TEXT("Close"), SND_NODEFAULT | SND_ASYNC);
DestroyWindow(hWnd);
return 0;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
return 0;
default:
return (DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, uParam, lParam));
}
return (0);
}
VOID ioProc()
{
int ret;
// ret=iobox_chk( INFINITE); // Wait for infinite
ret=iobox_chk( 5*1000); // Wait for 5 seconds
PostMessage( hWnd, WM_USER, ret, 0L);
}
// End of Hello Windows CE program.
14
Page 15

3. File Transfer Utility
3.1 Overview
This file utility performs file transfer either between a PC and PA-2400 or between two PA-2400
terminals. The dedicated up/download utility should be running on this PC. As a result, functions
that can be implemented by this utility depend on the up/download utility dedicated for the host PC,
as well as the file transfer protocol used between two FLCEs.
For this operation the following I/O interfaces can be used:
(For more information about the hardware configuration of the I/O Box system, refer to the
Hardware Manual.)
1) RS-232C
Interface via the 16-pin cable (using the communication cable supplied with PA-2400)
Direct interface to the host PC
2) IrDA 1.0
Interface to the host PC via the master or satellite I/O Box
Interface between two H/PCs
15
Page 16
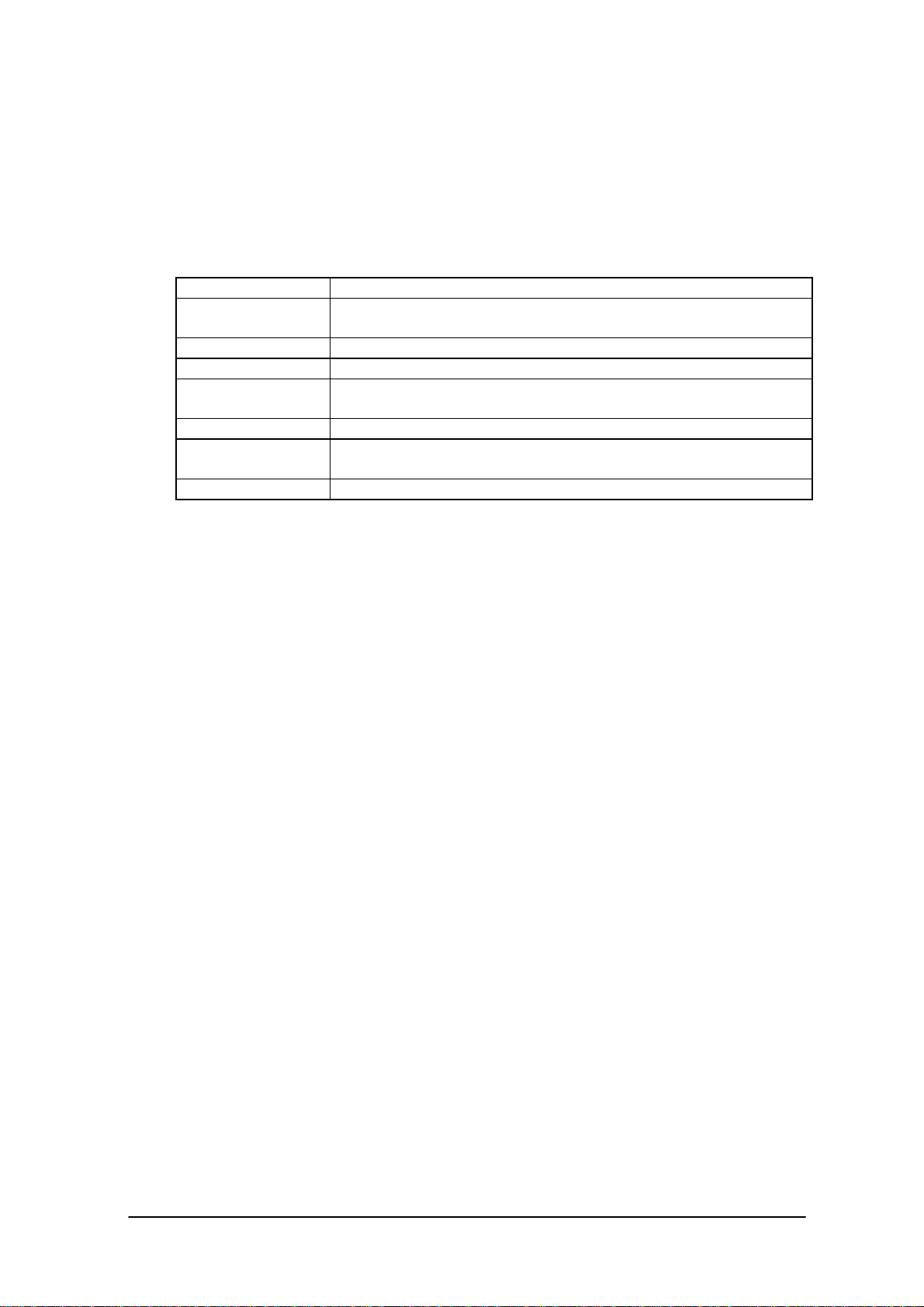
3.2 List of Functions
With this file transfer utility the following functions related to the file transfer protocol can be
specified:
Table 3.1 List of Functions
Function Description
Communication
environment setup
File transmission Transfers a file from the local machine to the communication partner.
File reception Receives a file from the communication partner.
File transmission
(append)
File deletion Deletes a file or directory existing on the communication partner.
File move/File name
modification
Time transmission Sets the system date and time of the communication partner.
Sets the device, baud rate, and communication mode to be used for
communication.
Appends a file existing on the local machine to a file existing on the
communication partner.
Moves or modifies the name of a file existing on the communication
partner.
16
Page 17
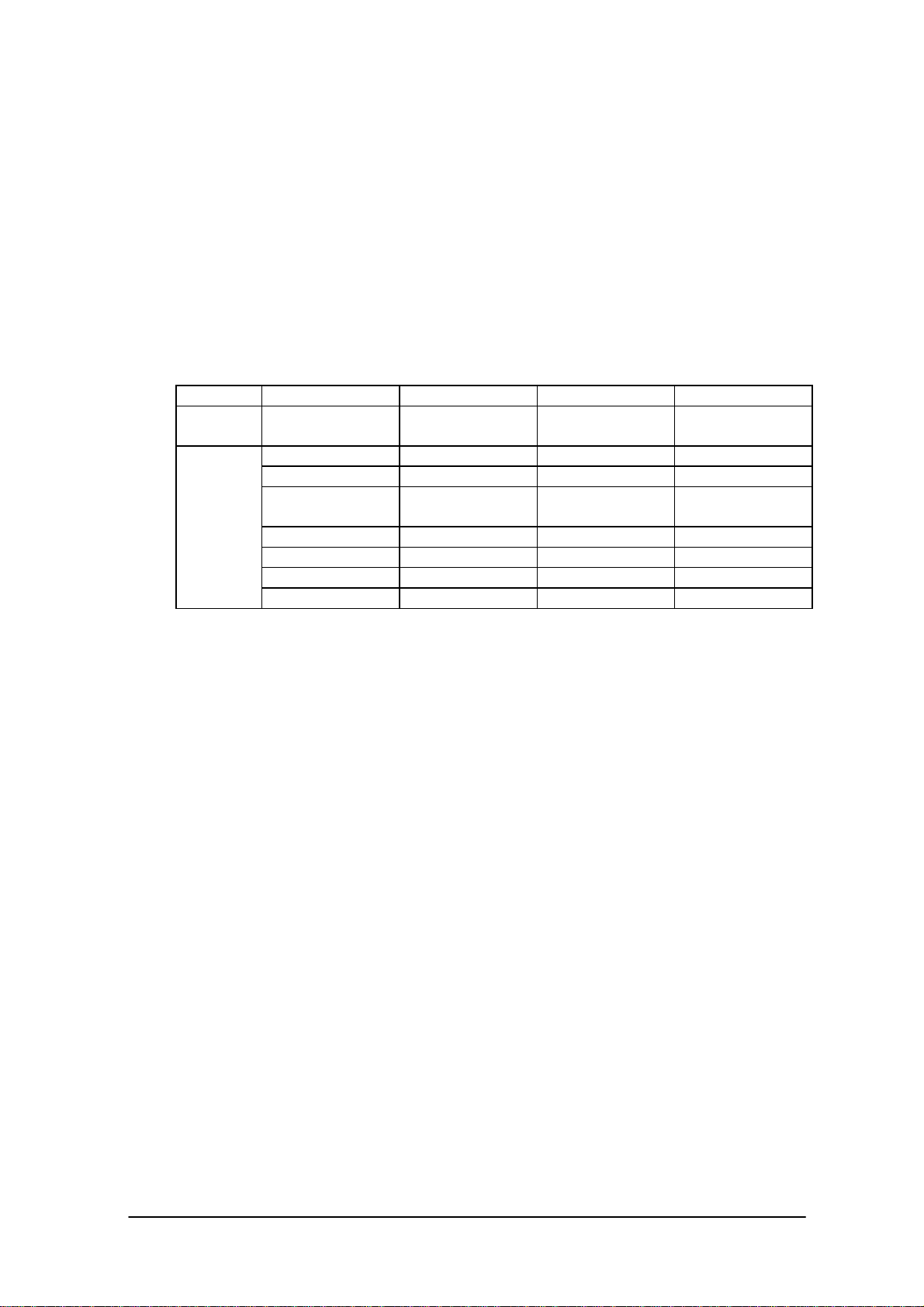
3.3 Communication Functions
Operational specifications for the FLCE should be made by initiating an appropriate command
together with the following arguments. A maximum of twenty commands can be described at one
time, and they will be processed sequentially in the order in which they are described. If a command
encounters an error, communication is immediately terminated from the error and subsequent
commands will no longer be processed.
When the communication environment setup command is not specified, the default value is used.
Table 3.2 Types of Arguments
Type Function Command Applicable Option Example of Input
Setup
command
Operation
command
Communication
environment setup
File transmission / S O, R / SOR
File reception / R O, R / ROR
File transmission
(append)
File deletion / D O, R / D
File move / N None / N
Time transmission / T None / T
Idle start None Script file name
/Y={device, baud
rate, mode}
/ A None / A
None /Y={IrDA,
115200, }
Outline of Options
O (Overwrite) : Specification of forced overwrite of a read-only file
If this option is specified, even a read-only file will be overwritten.
If an overwrite of a read-only file is attempted and this option is not specified, this function will
be abnormally terminated.
The attribute of a source file will be duplicated onto a target file which has been overwritten.
R (Recursive call):
All the files that exist under the specified directory are used as the objective of processing. If the
specified directory has any sub-directories, the files in these sub-directories are also included as
the objective of processing. The hierarchical directory system has a maximum depth of sixteen
levels.If this option is not specified, only a file that is designated by its pathname will be the
objective of processing.
17
Page 18

3.4 Pathname Description Method
1) Enclose every pathname in a pair of parentheses. A pathname must have a length of 255
characters or less including the two parentheses. A 2-byte code character is counted as one
character.
Example: FLCE /S "casio data*.dat" "d:data"
2) Pathnames must be described in accordance with the path naming rule supported by the OS of
the machine on which the specified path is to be placed.
3) Observe the following rule on drive letters when describing pathnames:
Describe a pathname on the H/PC so it begins with the root directory, without including
a drive letter. (This rule should also be applied when the pathname of a file or directory on
the H/PC is specified from the up/down utility for a host PC.)
If a pathname with a drive letter is specified from the communication partner, the drive
letter will be ignored by the FLCE on the host PC. (In other words, this pathname
specification is treated as being equal to a specification that begins with the root directory
without a drive letter.)
If the communication partner (PC, etc.) runs under an OS that requires drive letter
specification, and if the H/PC needs to describe the pathname of a file or directory on the
partner side, always attach an appropriate drive letter.
However, as an exception to 2) above, if the communication partner side designates a device on the
Windows CE machine for retrieving the format or other disk information, define a drive letter as
follows. These setups can be modified as required by making the appropriate description in the
registry.
Default setting : Internal RAM
PC card
Table 3.3 Summary of drive letter handling
Pathname specification on WindowsCEPathname specification on other
Specify a file or
directory
Specify a device Follows the above mentioned rule. Depends on the OS.
Not required (ignored if described) Depends on the OS.
C: (Define the boot drive as C: to comply with the
specifications of the PC/AT machine.)
D:
machine
Drive letters D and E are used for external storage devices.
Note:
Identification between multiple PC cards depends on the Windows CE OS specifications. Directory
names of multiple PC cards are determined according to the order in which they were inserted into
18
Page 19

each slot, for example, "Storage Card" and "Storage Card2", thus no differentiation is made
between these two cards in terms of device type. This is why neither of the cards can be assigned a
fixed drive letter.
Reference:
Windows CE has no concept of a drive letter. Accordingly, an additional drive is assigned a
directory directly under the root directory.
Example:
Internal RAM
"My Documents" Internal RAM
General directory Internal RAM
"Storage Card" PC card
19
Page 20

3.5 Rules of Describing Arguments
Separate each parameter by inserting a space after each piece.
Only one /Y command can be described immediately after "FLCE" (it can also be eliminated).
A maximum of twenty operation commands can be described after the necessary parameters.
Correct start-up example 1:
FLCE^/Y={COM1, 115200,}^/SO^"datadata.dat"^"datadata2.dat"^"c:data"
^/D^"c:casio0623.dat"
^ : Space code
Correct start-up example 2 (with the /Y command being eliminated) :
FLCE /SO "datadata.dat" "datadata2.dat" "c:data" /D "c:casio
0623.dat"
Incorrect start-up example 2 (with the /Y command not immediately after FLCE):
FLCE /SO "datadata.dat" "datadata2.dat" "c:data" /Y={COM1, 115200, } /D
"c:casio0623.dat"
For commands and options both uppercase and lowercase characters can be used.
The order in which options are specified does not matter.
Example of specification for command and option:
/soR
/SOR
An option must be specified so it immediately follows a command without inserting a space.
Multiple options must be specified without separating them by a space.
Example specification for command and option:
Correct : /RRO
Incorrect : /R RO
Incorrect : /RR O
20
Page 21

3.6 Conditions on Communication Partner
3.6.1 Rules of Naming Files and Directory Paths
Specify the pathname of a file or directory on the communication partner according to the naming
rule of the communication partner-side OS.
Table 3.4
Communication
partner
Windows95
/Windows NT
DOS O X Required (Error, if omitted)
Windows CE O O Not required (Ignored, if specified)
O : Specification permitted
X : Results in an invalid pathname and termination from error, if specified.
8.3 format Long file name Drive letter
O O Required (Error, if omitted)
3.6.2 Specifying on Non-existing File
If the pathname of a file or directory which does not exist on the communication partner side, the
following processing is performed;
Table 3.5
Communication partner Reception Delete Move Transmission, transmission
(append)
Windows 95/Windows NT A C B D
DOS A C B D
Windows CE A C B D
A: Abnormally terminated if any of the multiple pathnames specified does not exist (even a file
that actually exists will not be transferred).
B: Abnormally terminated if the specified pathname does not exist (transfer is not achieved).
C: If the specified pathname includes a path that does not exist, that path will be ignored (existing
pathnames will be processed).
D: A new file will be created.
21
Page 22

3.6.3 /D (delete) Command Option
These options (O: Forced deletion, R: Recursive call) of the delete command may not have a
corresponding operation provided on the communication partner side.
If this is the case, use this command without an option.
Table 3.6
Communication partner O option R option
Windows 95/Windows NT O O
DOS X X
Windows CE O O
O: Corresponds (specification permitted)
X: Does not correspond (specification prohibited)
3.7 Setting Up Registry
By writing a value in the registry it is possible to modify the default value of the communication
environment, etc. However, use the command line argument (/Y) to specify the communication line
or baud rate during normal use. Use this registry setup only if the default values require
modification. In other cases, where the drive letter definition requires modification, create the key
(item) of a drive letter and describe on the key the pathname of a device which will be defined
according to the specification.
If the registry has been set up, it will be remain valid until it is modified or the system is cold-started.
For a key (item) that is not set in the registry or a key (item) that has an incorrect setup the original
default value will be used.
3.7.1 Setup Items
Default if the RS-232C baud rate registry has no setup: 19200 bps
Default if the IrDA baud rate registry has no setup : 115.2 Kbps
Default if the communication line specification (232C= COM1 or IrDA) registry has no setup:
IrDA
Default if the drive letter definition registry has no setup value:
C (Object Store of internal RAM)
D Storage Card (storage card)
22
Page 23

Default if the command-to-response interval time-out registry has no setup : 30 seconds
Registry position
HKEY_CURRENT_USERFLCE
Contents
Key name Type Value
BAUD DWORD Baud rate
DEVNM STRING Communication line (I/O device)
DRIVEA
DRIVEB
DRIVEC
STRING Path of a device defined as drive a:
STRING Path of a device defined as drive b:
STRING Path of a device defined as drive c:
: :
DRIVEZ
STRING Path of a device defined as drive z:
RECVWAIT DWORD Command-to-response interval time-out (second)
Possible values for communication line and baud rate setups
Communication line : COM1, IrDA
Baud rate : For RS-232C; 9600, 14400, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200
: For IrDA; 9600, 38400, 115200
Any of the above listed baud rates can be set to either line.(only permitted baud rates can be set,
otherwise an error will result.)
Path to a device
A path to a device should be specified by the directory name to which the device is assigned.
Example: Object Store of the internal RAM
PC card or Compact Flash Storage Card
Command-to-response interval time-out
Specify the time-out limit in seconds. If a value greater than 32768 (8000h) is specified, the
default value (30 seconds) will be used instead.
23
Page 24

3.7.2 Setting Up Registry with User Application
Modify the registry as required from your application while referencing the following sample
program.
/***********************************************/
/* Registry Registration Program */
/***********************************************/
#include <windows.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <commctrl.h>
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPWSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow )
{
HKEY hKey1; // Open Handle
LONG lReg1; // Result code
DWORD Disp1; // Create or Open disposition
int err;
constwchar_tSubKey1[] = TEXT( "FLCE");// Key for FLCE
constwchar_tName[] = TEXT( "RECVWAIT");
// Name for the command-to-response interval time-out
constDWORDValue = 1800L;
// Time-out value to be set (seconds)
err=TRUE;
// Open the registry key
lReg1=RegCreateKeyEx( HKEY_CURRENT_USER, SubKey1, 0, NULL, 0, 0, 0,
&hKey1, &Disp1);
if( lReg1 == ERROR_SUCCESS) {
// Set the value
lReg1=RegSetValueEx( hKey1, Name, 0, REG_DWORD, ( const BYTE
*)&Value, sizeof( Value)); if( lReg1 != ERROR_SUCCESS)
// Close the registry key.
lReg1=RegCloseKey( hKey1);
if( lReg1 != ERROR_SUCCESS)
err=FALSE;
24
Page 25

err=FALSE;
}
else {
err=FALSE;
}
if( err==TRUE)
MessageBox( NULL, TEXT( "Success setting registry!") , TEXT( "This is
MessageBox"), MB_OK);
else
MessageBox( NULL, TEXT( "Fail setting registry!") , TEXT( "This is
MessageBox"), MB_OK);
return( err);
}
25
Page 26

3.8 Termination Codes
The FLCE returns one of the codes listed in Table 3.7 as the termination code if communication is
complete. Upper-level programs should perform an appropriate action to reference these values.
The communication function may return a code other than that described in the termination codes
list. Such a code is received from the communication partner and specific (i.e. outside the standard
protocol) to the software used on the communication partner side.
For information about these codes refer to the functional specifications of LMWIN, etc.
Passing of termination code
A termination code will be returned as a return value from Winmain. Upper-level programs
should reference this return value using GetExitCodeProcess().
List of termination codes
A category code (upper byte) indicates the error category, and an error detail code (lower byte)
indicates the detail of the error.
Category codes are defined as follows:
00h Normal termination
DCh to F8h Normal termination and notification of termination. Upper-level programs
should take an action that is appropriate to each definition.
01h Protocol error
02h File-related error
0Fh Argument-related error
A0h Communication line-related error
26
Page 27

Table 3.7 List of Termination Codes
Error code
Categ
ory
code
Detail
code
Meaning Possible cause Remedy
00h 00h Normally terminated Normal. DCh
to
F5h
00h Normally terminated Formatting of drive a:
between 'A' and 'Z' is
specified from the partner
Refer to Section 3.10
station. (For drive letter
definitions, refer to
Section 2.2.)
F6h 00h Normally terminated Power-off is specified from
Turn off the power.
the partner station.
F7h 00h Normally terminated. Resetting the power is
Refer to Section 3.10.
specified from the partner
station.
F8h 00h Terminated due to
interruption.
Communication is
terminated because the
Resume communication
as required.
break key is pressed on the
local station or partner
station.
01h 00h Protocol error. Data anomaly (data error
occurred on the
communication line).
Check the
communication line
connection.
02h 80h File not found. Non-existent file is specified. Check the specified file
or directory.
02h 81h Current directory delete
error.
An attempt has been made
to delete the current
Check the objective
directory of deletion.
directory.
02h 82h File write error Write to the file is not
possible.
02h 83h File read error. Read from the file is not
possible.
02h 84h Read only access error An attempt has been made
to overwrite or delete the
read-only file.
0Fh 01h Argument parameter
error
Incorrect argument
description.
0Fh 02h Argument too long Argument portion of the
command line is too long.
Check if the file is
ready to be written to
Check if the file is
ready to be read from.
Specify another file
name or cancel the
read-only attribute.
Check the argument
parameter.
Reduce the length of
the argument including
FLCE to 255 characters
or less.
0Fh 80h Reception data analysis
anomaly
Data analysis is impossible
due to a loss of reception
data.
Check the cable
connection and
mounting condition of
the H/PC on I/O Box
0Fh FFh System error Insufficient system resource. Increase the system
resource, then reboot
the system.
A0h 10h Communication port
open error
One of the other programs
is using COM1 or IrDA,
or FLCE is already initiated.
Terminate the program
that is using COM1 or
IrDA.
27
Page 28

A0h 20h Line break error or
IrDA duplicate open
error
A0h 30h Connection-wait time-
out error.
Either the cable was
unplugged during
communication or the IrDA
connection is broken (where
Check the cable
connection and
mounting condition of
the H/PC on I/O Box.
the H/PC is unmounted from
I/O Box).
IrDA port is already open. Terminate the other
program that is using
IrDA.
Connection was not
established within 1 minute
of start-up.
Check the cable
connection or check if
the IrDA is ready for
communication.
28
Page 29

3.9 Log File
The FLCE will create a log file to record communication logs.
Log File Name
The current log file name is fixed to "FLCE.LOG".
This specification cannot be modified. Therefore, if the current log file needs to be stored, use
another file name.
Location of Log File
A log file is created under the "Windows" directory.
Method of Creation
Even if a log file already exists, a new log file is created (i.e. overwrites the old one).
Append to the existing log file is not attempted.
If a new file cannot be created, log file creation is aborted.
If an argument of a command parameter includes an error, a log file will not be created.
A log file starts to be created at the point in time when communication with the partner begins.
Format
1st line Version information of FLCE.EXE will be outputted.
2nd line Version information (1 byte) of the protocol will be outputted.The first version is
"1".
3rd line Communication partner machine code (maximum 3 bytes) will be outputted.
AT .... IBM-PC compatible machine
4th line Session ID information will be outputted.
This will be outputted in a hexadecimal number (Example: 0x0000).
5th line Last event information will be outputted.
6th line Last phase information will be outputted.
7th line Last status information will be outputted.
Outputted as a hexadecimal number (Example: 0x0000).
8th line Last transmission file name will be outputted.
9th line Last reception file name will be outputted. Output will consist of the above nine
lines
Since with lines 2 through 4 the information acquired from the communication partner is
outputted, this line will be outputted as a blank line for a log file on one of the H/PCs that
operates in the PC emulation mode for communication between two H/PCs.
One line must be less than 80 bytes in length. Therefore, if a file name inserted in the 8-th or 9th
line requires 65 bytes or more (15 bytes are used for the item name), characters on and after the
65th byte will not be outputted.
29
Page 30

3.10 Restrictions
The file transfer utility is subject to the following restrictions:
The FLCE does not support communication with a 3-pin interface or PCMCIA card.
The COM1 port and IrDA port cannot be used concurrently, since they must use the same
hardware. Before initiating the FLCE, terminate the other program that is using the COM1 or
IrDA port.
As the return value from the FLCE the termination codes which request formatting of a drive or
resetting of the machine are defined. However, Windows CE Ver2.0 does not support this
function. If this function is required, incorporate it into the user application.
Because of the Windows CE specifications some of the files contained in the
Windows folder cannot be duplicated.
3.11 Precautions
Under the state where the file transfer utility is operating, if a file is transmitted out or received
in a folder that is opened by the Explorer, the transfer speed is reduced considerably.
To avoid this close the folder that was opened by the Explorer and that contains the file to be
transmitted before initiating the file transfer utility. Otherwise create a folder, other than the
one opened by the Explorer, for file reception.
If attempting H/PC-to-H/PC communication always use the AC adapter.
While the file transfer utility is operating, do not press the reset switch.
If the baud rate is set to 38400 or 96000 bps for the IrDA port, the file transfer utility will
temporarily overwrite the registry value when it is initiated and will restore the previous value
when it is terminated. Therefore, if the system power is reset in mid-course, the modified
registry value is retained.
(However, if it is set to 115200 bps, modification of the registry value will not take place.)
If the system power is reset in mid-course by mistake, initiate the file transfer utility again.
This restores the registry value before modification.
Modified registry: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEcommIrDABaud
30
Page 31

3.12 Details of Functions
FLCE /Y
< Description >
Used to set up the device, baud rate, and communication mode used for communication.
If this command is omitted, the default value {IrDA, 115200, } is used.
Any of the parameters can be omitted. If this is done, the default value for each parameter will
be used.
Always insert this command directly after FLCE. Placing it in another place will result in a
parameter error.
< Format >
FLCE /Y={ [<device>], [<baud rate>], [<mode>] }
(Parameters in [ ] can be omitted.)
< Parameter >
Device Select either "IrDA" or "COM1".
Baud rate If "IrDA" is selected - The following baud rates can be selected.
9600, 38400, 115200
(Irrespective of the selected baud rate communication at 9600 bps is allowed if
using the IrDA protocol.)
If "COM1" is selected - The following baud rates can be selected for RS-232C
communication.
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200
Combinations other than those described above are not permitted and will cause
a parameter error.
Mode "H" - H/PC-to-H/PC command specification mode (Connection-wait time-out
is 1 minute.)
This option is used by one side which specifies the operation command when
performing communication between two H/PCs.
(The FLCE on the communication partner H/PC should operate in the idle start
mode.)
"I" - Normal mode (Connection-wait time-out is infinite.)
Only "H" or "I" can be specified.
31
Page 32

If mode specification is omitted, the normal mode with the connection-wait time out set to 1 minute is automatically specified.
Table 3.8
Start Communication partner
Idle (including script) PC (I/O Box)/HT
Designation of operation
command
Examples:
FLCE /Y={COM1, 115200, } /S "casio*.dat" "d:casiodat"
Communication is performed using the RS-232C port at a baud rate of 115.2 Kbps. (Connectionwait time-out is 1 minute.)
FLCE /Y={, , I} /S "casio*.dat" "d:casiodat"
Communication is performed through command specification with the device name and the baud
PC (I/O Box)
HT Mode
Connection-wait time-out
1 minute Infinite
No mode
specification
specification,
"H"
Mode
specification
, "I"
-
rate is default-set.(Connection-wait time-out is infinite.)
FLCE /Y={, , H} /S "casio*.dat" "d:casiodat"
Communication is performed between two host PCs through comm and specification with the device
name and the baud rate is default-set.(Connection-wait time-out is 1 minute.)
FLCE /Y={, , I}
Communication is performed in the idle mode with the device name and the baud rate is default-set.
(Connection-wait time-out is 1 minute.)
FLCE /Y={, , } /S "casio*.dat" "d:casiodat"
Communication is performed under the same conditions (using default values) when "/Y" is omitted.
32
Page 33

FLCE /S
< Description >
Used to transmit a file on the local machine to the communication partner side.
If an identical file name exists in the destination directory of the partner side, it will be
overwritten.
If the directory that is specified as the destination directory does not exist, it will be
automatically created.
The progress of file transfer will be displayed.
File pathnames will be processed in order from the left of the command line. If any of the file
pathnames to be transmitted do not exist on the local machine side, the FLCE is immediately
terminated by an error, and file pathnames placed at the right of that pathname will no longer be
transmitted.
< Format >
FLCE /S[<Option>] <Transmission file pathname> [<Transmission file pathname>] [...]
<Pathname of destination directory>
(Parameters in [ ] can be omitted.)
< Parameter >
Option O: Specification of forced overwrite of a read-only file
If this option is specified, even a read-only file will be overwritten.
If an overwrite is attempted for a read-only file and this option is not specified, this
function will be abnormally terminated.
R: Recursive call
All the files that exist under the directory specified by the transmission file
pathname are used as the objective of file transfer.
If the specified directory has any sub-directories, they will be also included in the
destination directories for the file transmission.
The hierarchical directory system has a maximum depth of sixteen levels.
Even if this option is specified, the transmission file pathname should be specified
by the full pathname.
If this option is not specified, only a file that is designated by the transmission file
pathname can be the objective of processing.
Transmission file pathname
Specify a file that exists on the local machine side by its full pathname.
33
Page 34

To specify all files enter "*.*" as the file name.
A wild card can be used for the file name.
Directory names or file names can be described using 2-byte code characters.
Destination directory pathname
As the last input parameter of this command describe the destination directory name
of the communication partner side. If the specified directory does not exist, it will be
automatically created by the specified name.
Enter a "" as the delimiter of the directory name. If this specifications not made a
parameter error will result.
A wild card can be used for the file name.
Directory names can be described using 2-byte code characters.
Name the destination side directory pathname in accordance with the naming rule of
the communication partner-side OS.
< Examples >
FLCE /S "casio*.dat" "d:casiodat"
This transfers a file that is located in the "casio" directory of the local machine which has a "DAT"
extension to the "d:casiodat" directory of the communication partner side.
FLCE /SR "casio*.dat" "d:casiodat"
This transfers all files under the "casio" directory (including the sub-directories) of the local machine
which have a "DAT" extension to the "d:casiodat" directory of the communication partner side.
34
Page 35

FLCE /R
< Description >
Uses a pathname request to specify a file that exists on the communication partner side, then
receive the file.
If an identical file name exists in the reception directory of the local machine side, it will be
overwritten.
If the directory that is specified as the reception directory does not exist, it will be
automatically created.
The progress of file transfer will be displayed.
< Format >
FLCE /R[<Option>] <Request file pathname> [<Request file pathname >] [...] <Reception
directory pathname>
(Parameters in [ ] can be omitted.)
< Parameter >
Option O: Specification of forced overwrite of a read-only file
If this option is specified, even a read-only file will be overwritten.
If an overwrite is attempted on a read-only file and this option is not specified, this
function will be abnormally terminated.
R: Recursive call
All the files that exist under the directory specified by the transmission file
pathname are used as the objective of file transfer. If the specified directory has any
sub-directories, they will also be included in the destination directories for file
transmission.
Even if this option is specified, the transmission file pathname should be specified
by the full pathname.
Request file pathname
Specify an objective file of reception that exists on the communication partner side
by its full pathname.
To specify all files enter "*.*" as the file name.
A wild card can be used for the file name.
Directory names or file names can be described using 2-byte code characters.
Specify the request file pathname according to the naming rule of the
communication partner-side OS.
35
Page 36

Destination directory pathname
As the last input parameter of this command describe the destination directory name
of the communication partner side.
If the specified directory does not exist, it will be automatically created by the
specified name.
Enter a "" as the delimiter of the directory name. If this specifications not made a
parameter error will result.
Directory names can be described using 2-byte code characters.
< Examples >
FLCE /R "a:12*.dat" "d:casio*.*" "casio data"
This transfers all files under the "12" directory of the drive A: which have a "DAT" extension and
all files under the "casio" of the drive D: of communication partner side to the "casio data" directory
of the local machine side.
FLCE /RR "a:12*.dat" "d:casio*.*" "casio data"
This transfers all files under the "12" directory (including the sub-directories) of the drive A: which
have a "DAT"extension and all files under the "casio" directory (including the sub-directories) of the
drive D: of communication partner side to the "casio data" directory of the local machine side.
36
Page 37
FLCE /A
< Description >
Used to transmit the contents of a file that exists on the local machine side and specified by the
append file pathname to the communication partner side, and append the contents to a file that
exists on the communication partner side.
If a file specified by the target file pathname does not exist on the communication partner
side, it will be automatically created.
The date and time of the target file will be set to the current system date and time of a
machine where the target file is processed for the appending operation.
If the file transfer fails in mid-course, the target file restores the condition that existed before
communication started.
File data will be appended as binary data. (If the target file is terminated by an EOF code, the
data will be appended after the EOF code.)
The progress of file transfer will be displayed.
If a transmission file pathname that does not exist on the local machine side is specified, the
FLCE is immediately terminated by an error. If this is occurs, even files that exist will not be
transmitted.
< Format >
FLCE /A <Appended file pathname> <Target file pathname>
< Parameter >
Appended file pathname
Specify an objective file of transmission that exists on the local machine side by its full
pathname.
A wild card cannot be used for the file name.
Directory names or file names can be described using 2-byte code characters.
Target file pathname
Specify a file that is the target of append and that exists on the communication partner side by
its full pathname. If the specified file does not exist, it will be automatically created by
the specified file name.
A wild card cannot be used for the file name.
Directory names can be described using 2-byte code characters.
Create the target file pathname in accordance with the naming rule of the communication
partner-side OS.
37
Page 38

< Examples >
FLCE /A "MYcasio.dat " "b:yourmaster.dat"
This appends the contents of the "casio.dat" file to the "master.dat" file on the communication
partner side.
38
Page 39

FLCE /D
< Description >
Used to delete a specified file or directory that exists on the communication partner side.
< Format >
FLCE /D[<Option>] <Deleted pathname> [<Deleted pathname>] [...]
(Parameters in [ ] can be omitted.)
< Parameter >
Option O: Specification of forced overwrite of a read-only file
If this option is specified, even a read-only file will be deleted.
If a deletion is attempted for a read-only file and this option is not specified, this
function will be abnormally terminated.
R: Recursive call
All the files that exist under the directory specified by the deleted file pathname are
used as the objective of file deletion.
If the specified directory has any sub-directories, they will also be included in the
objectives of deletion.
The hierarchical directory system has a maximum depth of sixteen levels.
If this option is specified, the deleted file pathname should be specified by the full
pathname.
If this option is not specified, only a file that is designated by the deleted file
pathname can be the objective of deletion.
Deleted file pathname
Without the R option
Specify an objective file of deletion that exists on the communication partner side by
its full pathname. A wild card can be used for the file name.
To specify all files enter "*.*" as the file name.
With the R option
Specify an objective file of deletion that exists on the communication partner side by
its full pathname.
Enter a "" as the delimiter of the directory name.
Directory names or file names can be described using 2-byte code characters.
Specify the request file pathname according to the naming rule of the
communication partner-side OS.
39
Page 40

< Examples >
FLCE /D "a:12*.dat" "b:casio970613.dat"
This deletes files under "a:12*.dat" and "b:casio970613.dat" of the communication partner
side.
FLCE /DR "a:casio"
This deletes all files and directories under the "a:casio" directory of the communication partner
side.
40
Page 41

FLCE /N
< Description >
Used to move a file that is specified by the move source pathname and that exists on the
communication partner side to the move destination-side path.
Specify a file name for the move destination-side pathname. The move source file will be
saved by the specified file name on the move destination side. The progress of file transfer
will also be displayed.
< Format >
FLCE /N <Move source pathname> <Move destination pathname>
< Parameter >
Move source pathname
Specify a file that is the objective of the move and that exists on the communication partner side
by its full pathname.
A wild card cannot be used for the file name.
Directory names or file names can be described using 2-byte code characters.
Name the move source path in accordance with the naming rule of the communication
partner-side OS.
Move destination pathname
Specify the destination path on the communication partner side by its full pathname.
If the specified source file name differs from the destination file name, the source file name will
be changed to the destination file name after the transfer.
If the directory that is specified by the destination pathname does not exist, it will be
automatically created.
A wild card cannot be used for the file name.
Directory names or file names can be described using 2-byte code characters.
Name the move destination path in accordance with the naming rule of the communication
partner-side OS.
< Examples >
FLCE /N "a:12kk.dat" "a:casiokk.dat"
This moves the "a:12kk.dat" file to "a:casiokk.dat" on the communication partner side.
FLCE /N "a:12kk.dat" "a:casiosj.dat"
This modifies the "a:12kk.dat" file to the "a:casiosj.dat" file on the communication
partner side.
41
Page 42

FLCE /T
< Description >
This function transmits the system date and time of the local machine to the communication
partner side to set its system date and time. The transmitted date and time is a local time.
Depending on the communication line condition, a few seconds of error may result.
< Format >
FLCE /T
< Parameter >
None
< Examples >
FLCE /SR "casio ap*.*" "casio ap" /T
Transfers all files under the "casio ap" directory (including sub-directories) of the local machine to
the "casio ap" directory of the communication partner side, then the date and time of the
communication partner machine is set.
42
Page 43

FLCE (Idle Start)
< Description >
Passes the request right to the communication partner side and operates according to the function
that is requested by the partner.
If starting up the local machine with this mode, only the /Y command can be specified.
(If this is done, the normal mode instead of the idle start mode is entered. In other cases, if a
script file name is specified, a parameter error results and the function is terminated from the
error.)
Do not designate "H" as the mode parameter when specifying the "/Y" command.
(If "H" is designated a parameter error results and the function is terminated from the error.)
This function will be normally terminated by the reception of a termination command except
if a script file name is specified.
If a script file name is specified, communication will be performed according to the contents
of the script file that exists on the communication partner side.
If a script file name that does not exist on the communication partner side is specified, an error
code will be returned.
However, with H/PC-to-H/PC communication, a script file will not be processed. Therefore,
it will be ignored if specified.
< Format >
FLCE [/Y= { [Device], [Baud rate], [Mode] } ] [Script file name]
< Parameter >
Script file name
Specify a script file name that exists on the communication partner side. Always enclose a
script file name in quotation marks.
< Example >
Descriptions of parameters, such as those for file specification, are eliminated in this example.
In addition, assume the local machine is H/PC.
Connection with PC
FLCE
Communication partner: Up/down utility for host PC (command specification mode)
43
Page 44

FLCE "casio.scr"
Communication partner: Up/down utility for host PC (server mode)
FLCE /Y={COM1, , } "casio.scr"
Communication partner: Connected via cable to the up/down utility for host PC
H/PC-to-H/PC connection
FLCE
Communication partner: FLCE /Y= { , ,H } /S
FLCE
Communication partner: FLCE /Y= { , ,H } /R
FLCE /Y={, 9600, }
Communication partner: FLCE /Y= { , ,H } /R
44
Page 45

4. File Check Utility
4.1 Overview
The file check utility is used to check if an objective file has been successfully installed on the
partner-side H/PC. This function has the capability to detect an installation error irrespective of the
file transfer method used.
The transfer method involves a file transferred either between a host PC and H/PC or between two
H/PCs. It also includes copy operations from the card.
The term, "host PC", includes a personal computer (PC) and an H/PC which emulates the operation
of a PC.
4.2 List of Functions
The file check utility includes the following functions.
Table 4.1 List of Functions
Function Description
List file generation Generates a list file required for file checks.
List file comparison Compares list files.
4.3 Pathname Describing Method
4.3.1 Description of Pathnames
Always enclose a pathname in a pair of quotation marks. One pathname must be 255 characters
or less including the two quotation marks. A 2-byte code character is counted as one character.
Example: FCHKCE /G "casio data*.dat" "d:data" "casio data"
Pathnames should be described in accordance with the path naming rule supported by the OS of
the machine on which the specified path is to be placed.
Observe the following rule for drive letters if describing pathnames:
Specify a pathname on the H/PC so in begins with the root directory (my HT) and do not
include a drive letter.
If a pathname with a drive letter is specified, the drive letter will be ignored by the FCHKCE on
the H/PC side. (This pathname specification is treated equal to a specification from the root
directory without a drive letter.)
If the communication partner (PC, etc.) runs on an OS that requires drive letter specification,
and if the H/PC requires the pathname of a file or directory on the partner side to be specified,
always attach the appropriate drive letter.
45
Page 46

4.3.2 Rules of Naming Files and Directory Paths
Table 4.2
8.3 Format Long File Name Drive letter
Windows 95/Windows NT O O Required (Error, if omitted)
DOS O X Required (Error, if omitted)
Windows CE O O
O : Specification permitted
X : If specified, results in an invalid pathname and termination by error.
4.4 Rules of Describing Arguments
The total number of characters must be 255 characters or less including "FCHKCE".
If at least one incorrect parameter, such as an incorrect description, an incorrect command, or an
option that is not permitted to make a specification to the command, exists, the file check utility
is not initiated but is terminated by the error.
Separate the parameters by inserting a space (1-byte) between two parameters.
The /G option or /C option should be placed immediately after "FCHKCE".
To specify multiple transmission source file names, separate the pathnames with a space
(1-byte).
Example of Correct Start-up :
FCHKCE^/G^"casio datadata1.dat"^"casio datadata2.dat"^"d:data"^"casio
data"
^ : Space code
FCHKCE^/G^/SC^"casio datafchkce.scr"^"casio data"
FCHKCE^/C^"casio data"
Example of Incorrect Start-up (no /G or /C option):
FCHKCE "casio datadata1.dat" "casio datadata2.dat" "d:data" "casio data"
Uppercase and lowercase characters can be used for commands and options.
The order in which options other than /G or /C are specified does not matter.
Example of specification for command and option:
1) FCHKCE /g /r /AO
2) FCHKCE /G /ao /R
46
Page 47

4.5 Functions
4.5.1 List File Generating Function
If the names of files to be transferred (copied) from the H/PC are specified, this function will
create a list of files to be transferred (copied) and a list file that contains the checksum data
calculated from all the files to be transferred. Furthermore, the checksum data of this list file is
also generated.The name of a list file created with this function is set to "FCHK.LOG".
If the list file is successfully created, a "0" return value will be passed to this function as the
program termination code. If list file creation fails, this function receives a return value that is
not "0" and is abnormally terminated. In either case a history file is generated.
(FCHKG.HIS is created in [FCHK.LOG File output Directory name]).
The history file is generated to track the process of creating a list file. The user must transmit
(copy) the list file generated by this function to the partner station (child machine side) when
performing any file transfer (file copy).
Information to be set in the list file includes:
1) File size
2) Date and time of update
3) Transfer (copy) destination pathname (file name)
4) Number of transferred (copied) files
5) Checksum data of all the transferred (copied) files
6) Checksum data of list file
The checksum data of all the transferred (copied) files consists of the result in which each piece
of double-word data in all the objective files is XORed sequentially from beginning to end.
However, the checksum data of a list file is generated to obtain the sum of each double-word
contained in the list file, then a value is calculated that offsets the sum to zero. Use this offset
value as the checksum data.
The checksum data will be outputted as a list file as follows:
FILE_CHECKSUM=HHHHLLLL ( HHHH: HIGH-WORD / LLLL: LOW-WORD )
LIST_CHECKSUM=HHHHLLLL ( HHHH: HIGH-WORD / LLLL: LOW-WORD )
If an error occurs while generating the checksum of the list file (FCHK.LOG) which has
already been generated, the list file will be aborted. However, a generated list file will not be
deleted even if an error occurs during the analysis of command parameters.
47
Page 48

4.5.2 List File Comparison
With this function the following comparison will be made:
Comparison between the file information transferred (copied) from the partner station (parent
machine) and the contents of the list file (FCHK.LOG)
Comparison between the checksum data of the list file and the result of checksum calculation
performed again for the list file
Comparison between the checksum data included in the list file and the result of checksum
calculation performed again for all the entire files that were transmitted (copied).
If list file comparison is successfully completed, a "0" return value will be passed to this
function as the program termination code. If list file comparison fails, this function receives a
return value that is not "0" and is abnormally terminated. In either case a history file is
generated (FCHKC.HIS is created in [FCHK.LOG file pathname]).
The history file is generated as track the process of comparing the transmitted (copied) file and
the list file.
The objective information to be compared in the files includes:
1) File size
2) Date and time of update
3) Transfer (copy) destination pathname (file name)
4) Number of transferred (copied) files
5) Checksum data of all the transferred (copied) files
6) Checksum data of list file
The checksum data of all the transferred (copied) files consists of the result in which each piece
of double-word data in all the objective files is XORed sequentially from beginning to end.
However, the checksum data of a list file is generated to obtain the sum of each double-word
contained in the list file, then a value is calculated that offsets the sum to zero.
Use this offset value as the checksum data.
48
Page 49

4.6 Format of List Files
The format of list files to be generated with the file check utility is shown below.
<
FCHKLOG> :: = <FILENO> <FILEINFO> <FILECHECKSUM> <LISTCHECKSUM> null
<FILENO> :: = FILE_NO= <dec_num> <LS>
<FILEINFO> :: = <INFO> <LS>
<INFO> :: = <PATH> SP <SIZE> SP <DATE>
<LS> :: = CR
<FILECHECKSUM> :: = FILE_CHECKSUM= <hex_char> <LS>
<LISTCHECKSUM> :: = LIST_CHECKSUM= <hex_char> <LS>
<dec_num> :: = decimal number
<hex_char> ::= hexadecimal number represented by characters.
Example:
FILE_NO=3
“A:8AP¥MENU.EXE” 12345 19960728-063030
“A:8CONFIG.SYS” 1000 19960308-205820
“A:8AUTOEXEC.BAT” 512 19960206-234010
FILE_CHECKSUM=XXXXXXXX
LIST_CHECKSUM=XXXXXXXX
49
Page 50

4.7 Syntax Analysis of Script Files
If a script file name is specified when generating a list file, the syntax of the script file is analyzed as
follows before generating the list file.
The specifications of the script file syntax is given below.
<SCRIPT FILE> :: = <COMMANDS>
<COMMANDS> :: = <COMMANDS> <COMMAND> | null
<COMMAND> :: = ?/? <CMDBODY> <LS>
<CMDBODY> :: = <APPEND>
| <CHILD_PROC>
| <DELETE>
| <FORMAT>
| <BEEP>
| <RENAME>
| <RECEIVE>
| <SEND>
| <PRINT>
| <TIME_ADJUST>
| <END_SESSION>
<APPEND> :: = <APPEND_CMD> <APPEND_OPTION> <SP> <PATHNAME_PAIR>
<CHILD_PROC> :: = <CHILD_PROC_CMD> <SP> <CMD_PARAMETER>
<FORMAT> :: = <FORMAT_CMD> <SP> <DRIVE>
<BEEP> :: = <BEEP_CMD>
<RENAME> :: = <RENAME_CMD> <SP> <PATHNAME_PAIR>
<RECEIVE> :: = <RECEIVE_CMD> <OPTIONS> <SP> <PATHNAME_LIST>
<SEND> :: = <SEND_CMD> <OPTION> <SP> <PATHNAME_LIST>
<PRINT> :: = <PRINT_CMD> <SP> <STRING>
<TIME_ADJUST> :: = <TIME_CMD> <SP> <TIME_VALUE>
<END_SESSION> :: = <END_CMD> <PARAM>
<APPEND_CMD> :: = 'A'
<CHILD_PROC_CMD> :: = 'C'
<FORMAT_CMD> :: = 'F'
<BEEP_CMD> :: = 'B'
<RENAME_CMD> :: = 'N'
<RECEIVE_CMD> :: = 'R'
<SEND_CMD> :: = 'S'
<PRINT_CMD> :: = 'P'
50
Page 51

<TIME_CMD> :: = 'T'
<END_CMD> :: = '/'
<PATHNAME_PAIR> :: = <PATHNAME> <DELM> <PATHNAME>
<CMD_PARAMETER> :: = <CMD_NAME> <STRING>
<CMD_NAME> :: = <PATHNAME>
<PATHNAME_LIST> :: = <PATHNAME> <DELM> <PATHNAME_LIST> | <PATHNAME>
<DRIVE> :: = <DRIVE_LETTER> ':'
<TIME_VALUE> :: = <DATE> <TIME>
<OPTIONS> :: = <OPTIONS> <OPTION> | null
<OPTION> :: = <RECURSIVE_OPTION> | <UPDATE_OPTION>
<RECURSIVE_OPTION> :: = 'R'
<UPDATE_OPTION> :: = 'U'
<APPEND_OPTION>::='S' | 'R'
<STRING> :: = ""<CHARS>""
<DELM> :: = <SP>
<LS> :: = CR | <SP>
<SP> :: = <SP> SP | SP
<PARAM> :: = <SP> <NUMBER>
With this file check utility <CMD_BODY> is searched in the objective script file. If <SEND> (='S' :
See Note is found in the <CMD_BODY>, <PATHNAME_LIST> line that follows, <SEND> is
determined to be the destination pathname and a list file (FCHK.LOG) is generated.
Other <CMD_BODY> lines not accompanying <SEND> will be ignored in the list file generation.
Note :
The commands and options that can be the objective of generating a list file are given below.
1) "/S"
2) "/SO"
3) "/SR"
4) "/SOR"
5) "/SRO"
51
Page 52

4.8 Error Messages/Codes
Code Message Meaning Remedy
The making of a list file completed.
00
The contents of the list file agreed.
Specified path name not found.
01
The list file making error.
02
FCHK.LOG not found.
03
The contents of the list file didn’t
04
agree. (The path name discords)
The contents of the list file didn’t
05
agree. (The size discords)
The contents of the list file didn’t
06
agree. (The date/the time discord)
The contents of the list file didn’t
07
agree.
(All the file check-sum data
discord).
The contents of the list file didn’t
08
agree.
(The list file check-sum data
discord)
A script file not found
09
The script file syntax error
0A
The list file read error
0B
It is an unjust option.
0C
The parameter error.
0D
Script file read error
10
It crossed limitation on the script
11
file size.
It crossed limitation on the number
12
of the log files.
13 The output path name of the
specified list file wasn’t found out.
Normal termination No problem
File name specified by the list
file does not exist.
Physical error occurs during list
file creation.
List file (FCHK.LOG) could not
be found by the list file check.
Verification result of list file
checks is not matched.
(No path name matched)
Verification result of list file
checks is not matched
(No size matched)
Verification result of list file
checks is not matched
(No date/time matched)
Verification result of list file
checks is not matched. (No all
file check-sum matched)
Verification result of list file
checks is not matched (No
check-sum data of the list files
matched)
Script file with the specified file
name was not found.
Specified script file includes a
syntax error.
Physical error occurs during list
file check when the list file
(FCHK.LOG) was being read.
Start-up option is illegal. Review the start-up option.
Specified parameter has an
error.
Error occurs in the process of
reading a script file.
The size of specified script file
is 32,001 bytes or greater.
There are 65,001 files or more
that can be used as the log files.
Output destination path name of
the specified FCHK.LOG file
was not found.
Specify an existing
pathname or file name.
Try to execute the same
program again
Specify the directory where
the list file is located
Try to execute the file check
utility again from the
beginning.
Try to execute the file check
utility again from the
beginning.
Try to execute the file check
utility again from the
beginning.
Try to execute the file check
utility again from the
beginning.
Try to execute the file check
utility again from the
beginning.
Specify the directory where
the script file is located.
Rewrite the script file
correctly.
Try to execute the same
program again.
Review the specified
parameter.
Try to execute the same
program again.
Reduce the script file size to
32,000 bytes or less.
Reduce the number of
objective files to be logged
to 65,000 files or less
Specify a directory that
actually exists.
52
Page 53

4.9 Restrictions
Because of the Windows CE specifications some of the files contained in the Windowsfolder
cannot be duplicated. As a result, they will not be listed in the list file.
53
Page 54

4.10 Details of Functions
FCHKCE /G
< Description >
If the names of files to be transferred (copied) from the H/PC are specified, this function will create
a list of files to be transferred (copied) and a list file that contains the checksum data calculated from
all the files to be transferred. It also calculates the checksum data of this list file.
The maximum number of objective files that can be logged is 65,000.
The maximum size of a script file is 3,200 bytes.
< Format >
FCHKCE /G [</Option>] <file name list or script file name > <Destination directory name >
[<FCHK.LOG file output directory name>]
(Parameters in [ ] can be omitted.)
< Parameter >
Option /SC: Specification of a script file name
The objective script file is specified by this parameter to indicate the file name.
FCHKCE.EXE will analyze the file names to be transmitted against the contents of
this script file and then create a list file.
/R: Specification of recursive call
All the files that exist under the directory specified by the parameter of the file
pathname are used as the objective of creating a list file. If the specified directory has
sub-directories, files located in them are also used as the objective of creating a list
file.
The hierarchical directory system has a maximum depth of sixteen levels.
If this option is not specified, only files that are designated by the file names list can
be the objective of list file creation.
/AO: Append output
If the FCHK.LOG file exists in the directory specified by [FCHK.LOG file output
directory name], a log file will be created and appended to the FCHK.LOG file.
If the FCHK.LOG file does not exist in the directory specified by [FCHK.LOG file
output directory name], a new log file will be created.
(However, if the specified directory itself does not exist, this function will be
54
Page 55

abnormally terminated.)
This append output is achieved in such a simple way that a new list file is appended
to the end of an existing list file. If part of the existing list file needs to be modified,
create a list file again instead of performing this append output.
File name list or script file name
Describe the list of files to be transmitted (copied). These files should be located on the
transmission (copy) source side. As the last input parameter of this command describe
the destination directory name of the communication partner side. If the specified
directory does not exist, it will be automatically created under the specified name. If
specifying multiple transmission (copy) source file names, separate the pathnames with
a space (1-byte).
A wild card can be used for the file name.
If the /SC option is specified, also specify the pathname of the script file.
Destination directory name
Specify the destination directory name of the file transmission(copy).
Specify the directory name in accordance with the naming rule of the OS used on the
transmission (copy) destination side.
Add a "" to the end of the directory name as the delimiter.
FCHK.LOG file output directory name
Specify the output destination directory name of the FCHK.LOG file.
Specify the directory name in accordance with the naming rule of the OS on the local
machine side.
Add a "" to the end of the directory name as the delimiter.
If this parameter is omitted, the FCHK.LOG file will be created in the current
directory.
< Return value >
Return code (refer to the attached sheet).
55
Page 56

FCHKCE /C
< Description >
This function will perform the following comparisons: a comparison between the file information
transferred (copied) from the partner station (parent machine) and the contents of the list file
(FCHK.LOG), a comparison between the checksum data of the list file and the result of checksum
calculation performed again for the list file, and a comparison between the checksum data included
in the list file and the result of checksum calculation performed again for all the files that were
transmitted (copied).
There can be a maximum of 65,000 objective files for comparison.
< Format >
FCHKCE /C [</Option>] <FCHK.LOG file pathname >
(Parameters in [ ] can be omitted.)
< Parameter >
Option /D: Does not compare the update data.
Generally, the update date/time will be automatically changed to the current time of
the H/PC if file transfer is performed through the Explorer of the H/PC. Set this
option to omit the update date/time from the objective of comparison.
(A copy operation performed between the FLCE and PC card will not update the
date/time.)
FCHK.LOG file pathname
Specify the pathname of the FCHK.LOG list file in accordance with the naming
rule of the OS.
< Return value >
Return code (refer to the attached sheet).
56
 Loading...
Loading...