Page 1
For fx-9860G Series/GRAPH 85 Series
Physium
Application
User’s Guide
E
http://edu.casio.com
Page 2

Contents
1Physium Overview
2Starting Up Physium
3Periodic Table
4 Fundamental Physical Constants
5Calling Physium Functions from an eActivity
6 Precautions
Contents
20051201
Page 3

1-1
Physium Overview
1 Physium Overview
• The Physium application provides you with the following capabilities.
Periodic Table of Elements
• The application can be used to display periodic table of elements.
•Table shows element atomic number, atomic symbol, atomic weight, etc.
•Elements can be search for based on element name, atomic symbol, atomic number or
atomic weight.
Fundamental Physical Constants
• The application can be used to display fundamental physical constants, which are
grouped for easy referencing.
•Physical constants can be edited and saved as required.
•Physical constants can be stored in Alpha memory and used in the RUN
•
MAT mode.
20051201
Page 4

Starting Up Physium
2-1
2 Starting Up Physium
1. From the Main Menu, enter the PHYSIUM mode.
2. This displays an initial screen like the one shown below.
Cursor
3. Use f and c to move the highlighting and select the type of information you want
(Periodic Table or Fundamental Physical Constants).
4. Press w to display the information you selected in step 3 (Periodic Table or
Fundamental Physical Constants).
PHYSIUM mode
20051201
Page 5
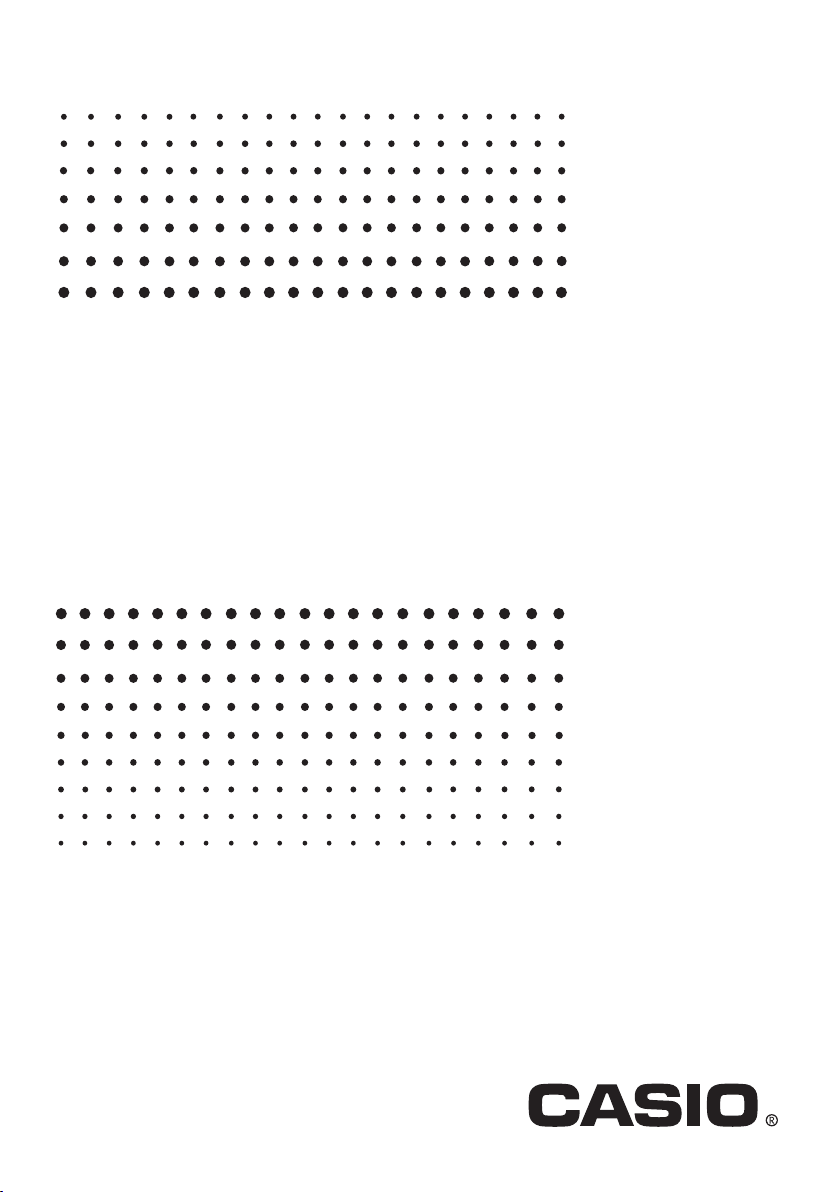
3-1
Periodic Table
3 Periodic Table
kk
k Periodic Table Screen
kk
Period Number
Group Number
Cursor
•Group numbers run along top of the screen, while period numbers run down the left.
• Lanthanoids are indicated as L`, while actinoids are indicated as A`.
112
•
•Use f, c, d, and e to move the cursor around the screen.
115
Uub to
Uup are indicated as ``.
1(MINI) .......................... Displays the periodic table MINI screen.
6 (DETAIL) (or w) ....... Displays a dialog box with details about the element where
the cursor is located. If L` or A` is selected, pressing this
key displays the transition element screen.
J ................................... Returns to the Physium initial screen.
uu
u Details Dialog Box
uu
Atomic Symbol
Atomic Number
Atomic Weight
Element Name
Attributes
• The details dialog box shows the element atomic number, atomic symbol, element name,
atomic weight, and attributes for the element that was selected on the periodic table
screen.
•Brackets ([ ]) indicate atomic weight of a well-known isotope. The element names for
these isotopes are followed by an asterisk (`).
J(or w or o) ........... Closes the dialog box.
20051201
Page 6
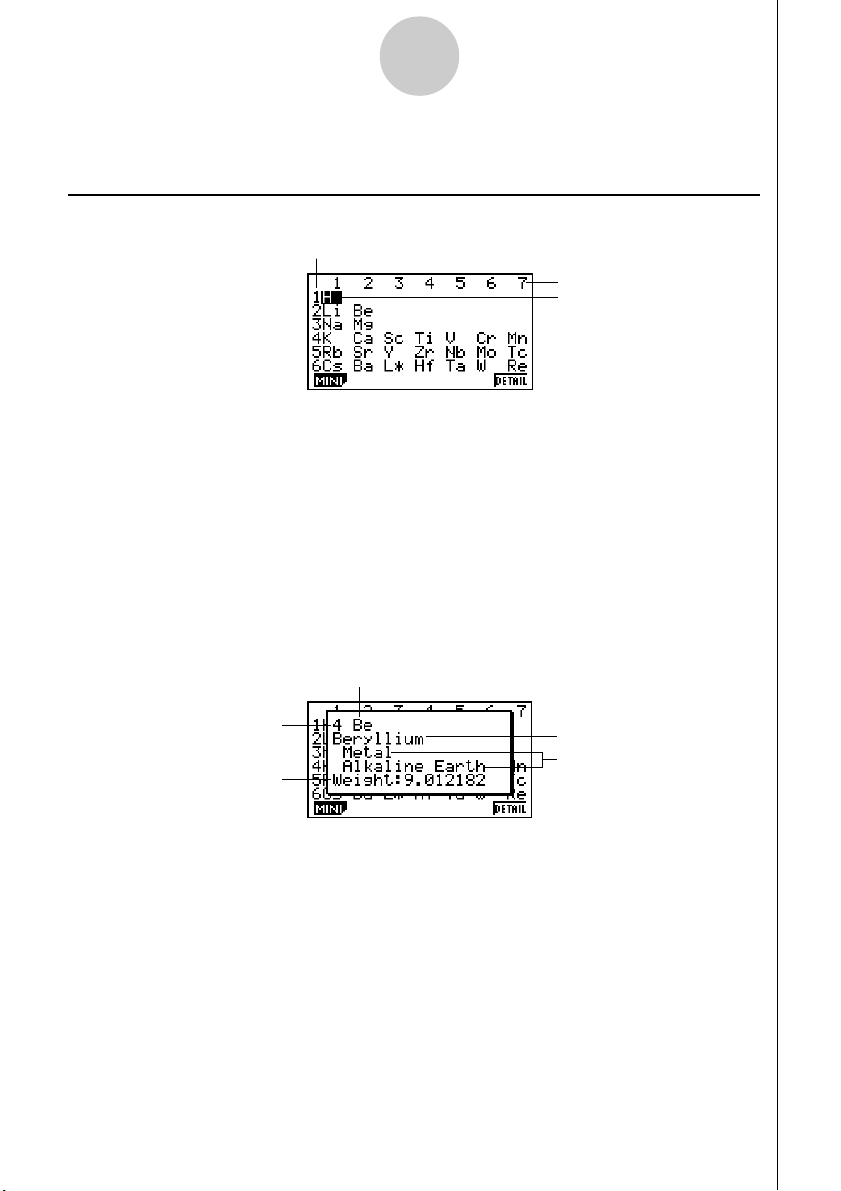
3-2
Periodic Table
uu
u Lanthanoids Screen and Actinoids Screen
uu
Cursor
•Pressing 6(DETAIL) (or w) while L` or A` is selected on the periodic table screen
will display the transition element screen.
•Use f, c, d, and e to move the cursor around the screen.
6(DETAIL) (or w) ........ Displays a dialog box with details about the element where
the cursor is located.
J ................................... Returns to the periodic table screen.
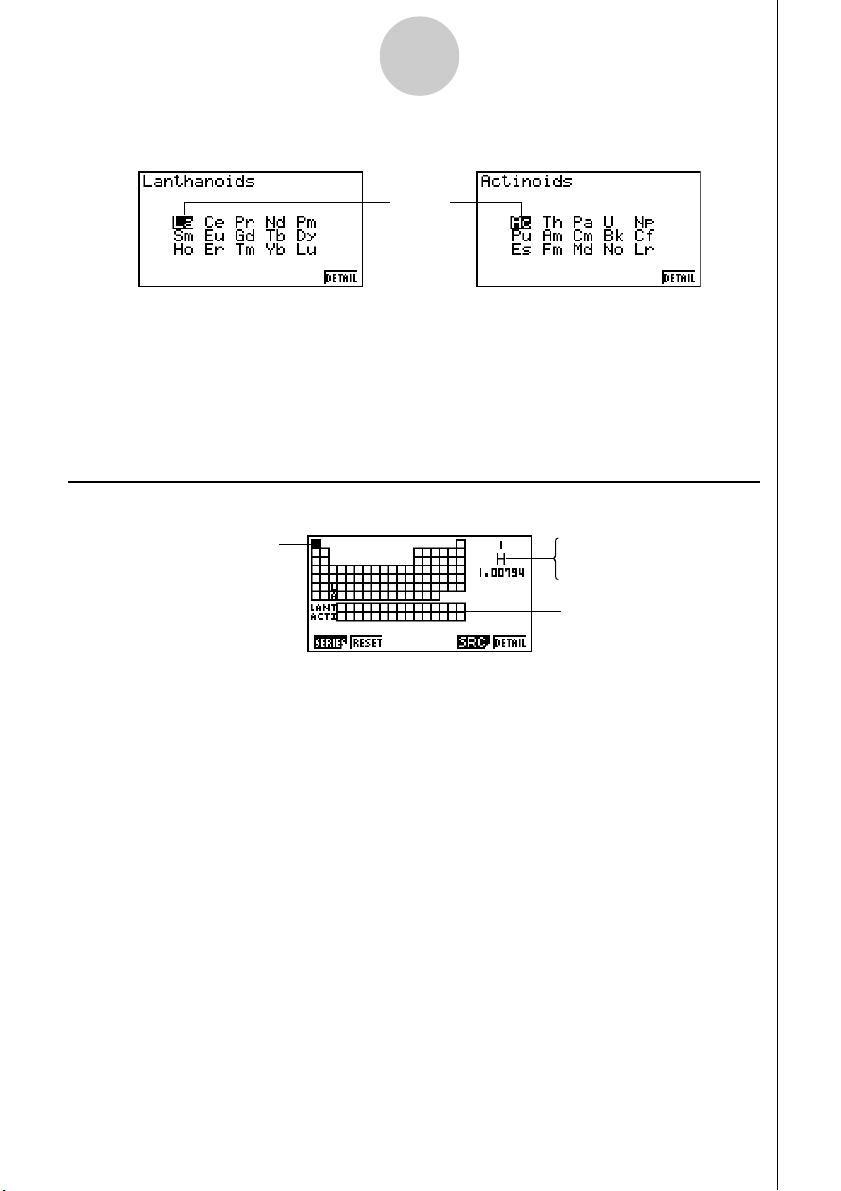
kk
k Mini Table Screen
kk
Cursor
Atomic Number
Atomic Symbol
Atomic Weight
Lanthanoids
Actinoids
• The mini table screen shows a compressed version of the periodic table, with cells that
represent each element.
• The information in the upper right corner of the screen shows the atomic number, atomic
symbol, and atomic weight for the element where the cursor is currently located in the
table.
•Transition elements (lanthanoids and actinoids) are shown below the periodic table
(LANT, ACTI).
•When a lanthanoid is selected, the information in the upper right shows the corresponding
atomic number (57 to 71), “Lant.” for the atomic symbol, and blank for the atomic weight.
When an actinoid is selected, the information shows the corresponding atomic number
(89 to 103), “Acti.” for the atomic symbol, and blank for the atomic weight.
•Use f, c, d, and e to move the cursor around the screen.
20051201
Page 7

3-3
Periodic Table
1(SERIES) 1(METAL) ................. Highlights the cells of elements whose metallicity
makes them metals.
2(TRANS) ................. Highlights the cells of elements whose metallicity
makes them transition elements.
3(A-MET) .................. Highlights the cells of elements that are in the
Alkali Metals category.
4(A-EAR) ..................Highlights the cells of elements that are in the
Alkaline Earth Metal category.
5(HALGN) .................Highlights the cells of elements that are in the
Halogens category.
6(g)1(n-GAS) ....... Highlights the cells of elements that are in the
Noble Gases category.
6(g)2(n-METL) ..... Highlights the cells of elements whose metallicity
makes them non-metals.
6(g)3(R-EAR) ....... Highlights the cells of elements that are in the
Rare Earth category.
2(RESET) ....................................... Clears highlighting from the mini table screen.
5(SRC) 1(NAME) ........................ Displays a dialog box to search for an element
name.
2(SYMBL) ...................... Displays a dialog box to search for an atomic
symbol.
3(No.) ............................. Displays a dialog box to search for an atomic
number.
4(WEIGH) ...................... Displays a dialog box to search for an atomic
weight.
6(DETAIL)(or w) .......................... Displays a dialog box with details about the
element where the cursor is located. Note that
the dialog box does not appear when a
lanthanoid or actinoid is selected.
J .................................................... Returns to the periodic table screen.
20051201
Page 8

3-4
Periodic Table
uu
u Mini Table Details Dialog Box
uu
• The mini table details dialog box is the same as the details dialog box described under
“Details Dialog Box” on page 3-1.
• The mini table details dialog box shows details for the element where the cursor is
currently located on the mini table. Note that the cursor cannot be used to select a LANTI
or ACTI cell.
J(or w or o) ........... Closes the dialog box.
uu
u Searching for an Element Name
uu
1. On the mini table screen, press 5(SRC) and then 1(NAME).
• This will display an element name search dialog box.
2. Enter up to nine characters for the element name you want to search for.
• The screen will change to show all elements whose names start with the character(s)
you input.
3. Use f and c to select the element name you want.
4. Press w to return to the mini table screen, with the cursor located at the element you
selected in step 3.
•“Nothing” will appear on the screen if no element name corresponds to the character(s)
you input.
•To close the dialog box and return to the mini table screen without searching for anything,
press J.
uu
u Searching for an Atomic Symbol
uu
1. On the mini table screen, press 5(SRC) and then 2(SYMBL).
• This will display an atomic symbol search dialog box.
20051201
Page 9

3-5
Periodic Table
2. Enter up to nine characters for the atomic symbol you want to search for.
• The screen will change to show all elements whose atomic symbols start with the
character(s) you input.
3. Use f and c to select the atomic symbol you want.
4. Press w to return to the mini table screen, with the cursor located at the element you
selected in step 3.
•“Nothing” will appear on the screen if no element name corresponds to the character(s)
you input.
•To close the dialog box and return to the mini table screen without searching for anything,
press J.
uu
u Atomic Number Search
uu
1. On the mini table screen, press 5(SRC) and then 3(No.).
• This will display an atomic number search dialog box.
2. Enter up to three digits for the atomic number you want to search for.
3. Press w to return to the mini table screen, with the cursor located at the element that
corresponds to the atomic number you input in step 2.
• If there is no element that corresponds to the atomic number you input, pressing w will
return to the mini table screen with the cursor at the same location it was when you
started this procedure.
•To close the dialog box and return to the mini table screen without searching for anything,
press J.
20051201
Page 10

3-6
Periodic Table
uu
u Atomic Weight Search
uu
1. On the mini table screen, press 5(SRC) and then 4(WEIGH).
• This will display an atomic weight search dialog box.
2. Enter a value up nine digits long (including numbers and decimal point) for the atomic
weight you want to search for.
• The screen will change to show all elements whose atomic weight corresponds to the
numbers you input.
3. Use f and c to select the atomic weight you want.
4. Press w to return to the mini table screen, with the cursor located at the element you
selected in step 3.
•“Nothing” will appear on the screen if no atomic weight corresponds to the number(s) you
input.
•To close the dialog box and return to the mini table screen without searching for anything,
press J.
20051201
20060601
Page 11

Fundamental Physical Constants
4-1
4 Fundamental Physical Constants
kk
k Category Selection Screen
kk
b(Universal) ................... Displays a list of universal physical constants.
c(Electromagnetic) ........ Displays a list of electromagnetic physical constants.
d(Atomic & nuclear) ...... Displays a list of atomic and nuclear physical constants.
e(Physico-chemical) ...... Displays a list of physico-chemical physical constants.
f(Adopted values) ......... Displays a list of adopted values physical constants.
a(My Drawer) ................ Displays the “My Drawer” screen.
J ................................... Returns to the Physium initial screen.
kk
k Built-in Constants
kk
• The following is a list of the constants that this application includes as built-in fundamental
physical constants.
Category Quantity Value
Universal c : speed of light in vacuum 299792458
µ
0 : magnetic constant 1.25663706E–6
ε0 : electric constant 8.8541878E–12
Z0 : characteristic impedance of vacuum 376.7303135
G : Newtonian constant of gravitation 6.6742E–11
h : Planck constant 6.6260693E–34
H : Planck constant over 2 pi 1.0545716E–34
mp : Planck mass 2.17645E–8
lp : Planck length 1.61624E–35
tp : Planck time 5.39121E–44
Electromagnetic e : elementary charge 1.6021765E–19
φ
0 : magnetic flux quantum 2.0678337E–15
G0 : conductance quantum 7.74809173E–5
KJ : Josephson constant 4.83597879E14
RK : von Klitzing constant 25812.80745
µ
B : Bohr magneton 9.2740094E–24
µ
N : nuclear magneton 5.0507834E–27
20051201
Page 12

Fundamental Physical Constants
4-2
Category Quantity Value
Atomic & nuclearα : fine-structure constant 7.29735256E–3
R∞ : Rydberg constant 10973731.57
a0 : Bohr radius 5.2917721E–11
me : electron mass 9.1093826E–31
µ
e : electron magnetic moment –9.284764E–24
m
µ : muon mass 1.8835314E–28
µ
µ: muon magnetic moment –4.490447E–26
m
τ : tau mass 3.16777E–27
mp : proton mass 1.6726217E–27
µ
p : proton magnetic moment 1.4106067E–26
mn : neutron mass 1.6749272E–27
µ
n : neutron magnetic moment –9.662364E–27
Physico-chemical NA : Avogadro constant 6.0221415E23
mu : atomic mass constant 1.6605388E–27
F : Faraday constant 96485.3383
R : molar gas constant 8.314472
k : Boltzmann constant 1.3806505E–23
Vm : molar volume of ideal gas
(273.15 K, 101.325 kPa)
σ
: Stefan-Boltzmann constant 5.6704E–8
Adopted values KJ–90 : conventional value of Josephson
constant
RK–90 : conventional value of von Klitzing
constant
0.022413996
483597.9
25812.807
gn : standard acceleration of gravity 9.80665
20051201
Page 13

Fundamental Physical Constants
kk
k Constant List Screen
kk
• The constant list screen shows each constant in the format: Symbol = Value.
•Use f and c to move the highlighting to the constant you want to select.
1(EDIT) ......................... Enters the editing mode for editing the currently selected
2(STORE) ..................... Stores the currently selected constant in Alpha memory.
3(DETAIL) (or w) ........ Displays a dialog box with details about the currently
4(KEEP) ........................ Stores the currently selected constant in My Drawer.
5(INIT) ........................... Returns the currently selected constant to its initial default
6(A•InIT) ........................ Returns all constants to their initial default values.
J ................................... Returns to the category selection screen.
constant. The editing mode is also entered automatically
whenever a number key is pressed while a constant is
selected.
selected constant.
•Press 4(KEEP) causes the message “Complete!” to
appear on the display. Press J to clear the message
from the screen.
value.
4-3
kk
k My Drawer Screen
kk
•Pressing 4(KEEP) while the constant list screen is on the display will save the currently
selected constant to the My Drawer screen. The My Drawer screen displays constants in
the sequence they are saved.
2(STORE) ..................... Stores the currently selected constant in Alpha memory.
3(DETAIL) (or w) ........ Displays a dialog box with details about the currently
6(DEL) ........................... Deletes the currently selected constant.
J ................................... Returns to the category selection screen.
selected constant.
20051201
Page 14

Fundamental Physical Constants
kk
k Editing a Constant
kk
1. Select the constant you want to edit, and then press 1(EDIT).
• This enters the editing mode.
2. Edit the constant as desired.
3. Press w.
• This saves the edited version of the constant.
•Even if you input more than 15 digits for a constant value, only the 15 most significant
digits are saved.
•A Syntax ERROR occurs if the resulting constant is the wrong format.
•An Ma ERROR occurs if the resulting constant is mathematically incorrect or illegal.
kk
k Saving a Constant to Alpha Memory
kk
4-4
1. Select the constant you want to save in Alpha memory and then press 2(STORE).
• This displays the “Store Alpha Mem.” dialog box.
2. Enter a letter that represents the Alpha memory where you want to store the constant.
3. Press w.
•Now when you recall the applicable Alpha memory in the RUN
will input the constant stored there.
20051201
•
MAT mode, the calculator
Page 15

Fundamental Physical Constants
kk
k Details Dialog Box
kk
•Selecting a constant and pressing 3(DETAIL) or w will display a dialog box with
details about the selected constant.
• The details dialog box shows the constant name, symbol, and unit.
kk
k Returning All Constants to their Initial Default Values
kk
•While the constant list screen is on the display, press 6(A•InIT) to display the Init All
dialog box.
4-5
Name
Symbol
Unit
•Press 1(Yes) to return all of the constants to their initial default values.
20051201
Page 16

Calling Physium Functions from an eActivity
5-1
5 Calling
You can call
eActivity file.
This section explains how to insert a Physium strip into an eActivity file, and how to use
inserted a Physium strip. For details about eActivity operations, see “Chapter 10 eActivity” in
the manual that comes with the calculator.
kk
k Inserting a Physium Strip into an eActivity File
kk
The following procedure assumes that the eActivity file into which you want to insert the
Physium strip is already open. For information about creating a new file and other basic
eActivity operations, see “Basic eActivity File Operation” (page 10-1-5) in the manual that
comes with the calculator.
uu
u To insert a Physium Strip into an eActivity file
uu
1. On the eActivity workspace screen, move the cursor the location where you want to insert
the Physium strip.
2. Press 2(STRP).
• This will display a dialog box with a list of insertable strips.
Physium
Physium
functions from an eActivity by including a “
Functions from an eActivity
Physium
strip” in the
3. Use f and c to move the highlighting to the Physium strip you want to insert.
20051201
20060601
Page 17

Calling Physium Functions from an eActivity
5-2
4. Press w.
• The strip is inserted above the line or the strip where the cursor is currently located.
5. Enter up to 16 characters for the strip title.
6. Press w to assign the title to the strip.
• This will highlight the strip.
•You can execute the strip here by pressing w. For details about operations that are
required when you execute a strip, see “Calling a Physium Function from a Physium
Strip” below.
kk
k Calling a Physium Function from a Physium Strip
kk
This section explains operations for Physium strip that can be inserted into an eActivity file.
The following procedure assumes that the applicable Physium strip has already been
inserted into an eActivity file that is currently open.
1. On the eActivity workspace screen, use the f and c keys to move the highlighting to
the Physium strip.
20051201
20060601
Page 18

Calling Physium Functions from an eActivity
5-3
2. Press w.
• This launches the Physium and displays the initial screen.
3. Perform the procedure under “Starting Up Physium” (page 2-1) from step 3.
4. To return to the eActivity workspace screen, press !a(').
uu
u Physium Strip Memory Capacity Precautions
uu
• For information about checking the current memory usage of each strip, see “10-5
eActivity File Memory Usage Screen” in the manual that comes with the calculator.
20051201
20060601
Page 19

6-1
Precautions
6 Precautions
•You can save screen captures of Physium screens and dialog box. For details, see “1-8
Using Screen Capture” in the manual that comes with the calculator.
•Note that the Catalog Function described in the manual that comes with the calculator is
not supported by Physium.
• The atomic weights in this application are based on those recommended by 2005 IUPAC
(International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry).
• The physical constants in this application are based on those recommended by the 2002
CODATA.
•A scientific constant in this application may be slightly different depending on the year it is
presented or books it is presented. Refer to appropriate information that fits your purpose
before use.
• The classification of rare earth elements may be slightly different from those in typical
textbooks or magazines in the USA.
• The classification of transition elements may be slightly different from those in typical
textbooks or magazines in the USA.
20051201
20060601
Page 20

CASIO COMPUTER CO., LTD.
6-2, Hon-machi 1-chome
Shibuya-ku, Tokyo 151-8543, Japan
SA0701-C
 Loading...
Loading...