Page 1
fx-7400G PLUS
E
CASIO COMPUTER CO., LTD.
6-2, Hon-machi 1-chome
Shibuya-ku, Tokyo 151-8543, Japan
SA0212-A Printed in China
User’s Guide
E
fx-7400G PLUS
User’s Guide
RCA500487-1
http://world.casio.com/edu_e/
fx-7400G PLUS (English) Cover Black
Page 2
MENU
[OPTN]key
STAT
LIST
DRAW
List List_
On DrawOn
Off DrawOff
Dim Dim_
[PRGM]key
[VARS]key
GRPH
Fill Fill(
COM
V-WIN
GPH1 S-Gph1_
Seq Seq(
If If_
Xmin Xmin
GPH2 S-Gph2_
Then Then_
Xmax Xmax
GPH3 S-Gph3_
Min Min(
Else Else_
Xscl Xscl
Scat Scatter
Max Max(
I·End IfEnd
FACT
xy xyLine
Pie Pie
Stck StackedBar
Mean Mean(
Xfct Xfct
Med Median(
For For_
Yfct Yfct
Hist Hist
To _To_
STAT
Box MedBox
Sum Sum_
Step _Step_
X
N-Dis N-Dist
CALC
Next Next
n n
Simp Simp
oo
Int÷
_Int÷_
W·End
While_
Σx Σx
X Linear
Rmdr _Rmdr_
Whle
WhileEnd
Σx2 Σx2
Med Med-Med
STAT
Do Do
xσn xσn
X^2 Quad
x^ x^
Lp·W LpWhile_
y^ y^
CTL
xσn-1 x σn-1
Log Log
Prog Prog_
minX minX
Exp Exp
PROB
Rtrn Return
maxX maxX
Pwr Power
Bar Bar
Line LineG
Both Both
X! !
Brk Break
Y
LIST
nPr P
Stop Stop
pp
List1 List1
nCr C
Σy Σy
List2 List2
Ran# Ran#
JUMP
Σy2 Σy2
List3 List3
NUM
Lbl Lbl_
Σxy Σxy
List4 List4
Abs Abs_
Goto Goto_
yσn yσn
List5 List5
Int Int_
⇒⇒
List6 List6
Frac Frac_
Isz Isz_
yσn-1 y σn-1
MARK
Rnd Rnd
Dsz Dsz_
minY minY
Square
Intg Intg_
? ?
maxY maxY
× Cross
ANGL
^^
GRPH
• Dot
o o
a a
CALC
r r
CLR
b b
1VAR 1-Variable_
g g
Text ClrText
c c
2VAR 2-Variable_
o'''
Grph ClrGraph
List ClrList
r r
X LinearReg_
Pol( Pol(
DISP
Q1 Q1
Med Med-MedLine_
Rec( Rec(
Stat DrawStat
Med Med
X^2 QuadReg_
Grph DrawGraph
Q3 Q3
TABL
Mod Mod
Log LogReg_
Tabl DispTable
PTS
Exp ExpReg_
G-Con DrawTG-Con
x1 x1
Pwr PowerReg_
G-Plt DrawTG-Plt
y1 y1
LIST
REL
I/O
::
x2 x2
SRT-A SortA(
= =
SRT-D SortD(
%
Data
≠≠
y2 y2
GRPH
> >
x3 x3
SEL
DISP
%
Data
Sep.G
O
.
Lap
WIN
Sep.G
NormWin
Norm
O.Lap
< <
y3 y3
On G_SelOn_
>>
GRPH
Off G_SelOff_
<<
Send Send
(
Recv Receive(
Y Y
TYPE
Xt Xt
Y= Y=Type
Yt Yt
Parm ParamType
TABL
Strt F_Start
Y> Y>Type
End F_End
Y< Y<Type
pitch F_pitch
Y> Y >Type
Y< Y <Type
TABL
[SETUP]key
On T_SelOn_
Off T_SelOff_
Deg
Deg
[SHIFT]key
Rad
Rad
ZOOM
' '
Gra
Gra
Fact Factor_
" "
V-WIN
~ ~
V-Win ViewWindow_
* *
Sto StoV-Win
/ /
Rcl RclV-Win
# #
SKTCH
Fix
Fix_
Cls Cls
Sci
Sci_
GRPH
Norm
Norm
Y= Graph_Y=
Parm Graph(X,Y)=(
Auto
S-WindAuto
Y> Graph_Y>
Man
S-WindMan
Y< Graph_Y<
Rang VarRange
Y> Graph_Y >
List1
VarList1
Y< Graph_Y <
List2
VarList2
List3
VarList3
Plot
PLOT
LINE
Plot
P-On PlotOn
P-Off PlotOff
P-Chg PlotChg
[ALPHA]key
List4
VarList4
Line Line
F-Lin F-Line
' '
List5
VarList5
" ”
List6
VarList6
Hztl Horizontal_
Vert Vertical_
~ ~
d/dx d/dx(
Con
G-Connect
Plot
G-Plot
Ymin Ymin
Ymax Ymax
Yscl Yscl
Tmin Tmin
Tmax Tmax
Tpth Tptch
GUIDELINES LAID DOWN BY FCC RULES FOR USE OF THE UNIT IN THE U.S.A. (not applicable to other areas).
NOTICE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of
the following measures:
•Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
•Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
•Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
•Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could
void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Proper connectors must be used for connection to host computer and/or peripherals in order to
meet FCC emission limits.
Connector SB-62 Power Graphic Unit to Power Graphic Unit
Connector FA-123 Power Graphic Unit to PC for IBM/Macintosh Machine
Model Number: fx-7400G PLUS
Trade Name: CASIO COMPUTER CO., LTD.
Responsible party: CASIO, INC.
Address: 570 MT. PLEASANT AVENUE, DOVER, NEW JERSEY 07801
Telephone number: 973-361-5400
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IBM is a registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
Macintosh is a registered trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.
Declaration of Conformity
Important!
Please keep your manual and all information handy
for future reference.
FCC WARNING
CASIO ELECTRONICS CO., LTD.
Unit 6, 1000 North Circular Road,
London NW2 7JD, U.K.
Program Mode Command List
Page 3
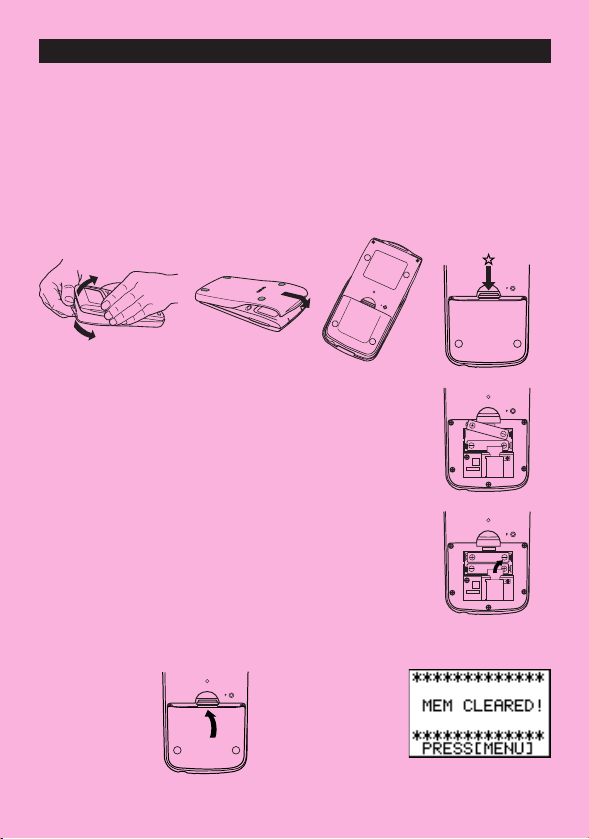
BEFORE USING THE CALCULATOR
FOR THE FIRST TIME ONLY...
This calculator does not contain any main batteries when you purchase it. Be sure to perform
the following procedure to load batteries, reset the calculator, and adjust the contrast before
trying to use the calculator for the first time.
1. Making sure that you do not accidently press the o key, attach the case to the calculator
and then turn the calculator over. Remove the back cover from the unit by pulling with your
finger at the point marked
2. Load the two batteries that come with calculator.
•Make sure that the positive (+) and negative (–) ends of
the batteries are facing correctly.
3. Remove the insulating sheet at the location marked
“BACK UP” by pulling in the direction indicated by the
arrow.
4. Replace the back cover and turn the calculator front side up, which should automatically
turn on power and perform the memory reset operation.
✩.
i
i
Page 4

5. Press m.
If the Main Menu shown to the right is not on the display,
pre ss the P but to n on th e b ac k of th e cal culator t o
perform memory reset.
P button
6. Use the cursor keys (
or simply press i to display the contrast adjustment screen.
7. Press d to make the figure on the screen lighter or e to make them darker.
8. After getting the contrast the way you want it, press m to return to the main menu.
ii
ii
f, c, d, e) to select the CONT icon and press w
Page 5

Handling Precautions
•Your calculator is made up of precision components. Never try to take it apart.
•Avoid dropping your calculator and subjecting it to strong impact.
•Do not store the calculator or leave it in areas exposed to high temperatures or humidity, or large
amounts of dust. When exposed to low temperatures, the calculator may require more time to display
results and may even fail to operate. Correct operation will resume once the calculator is brought back
to normal temperature.
• The display will go blank and keys will not operate during calculations. When you are operating the
keyboard, be sure to watch the display to make sure that all your key operations are being performed
correctly.
•Replace both the main power supply and the memory back up batteries once every 2 years regardless
of how much the calculator is used during that period. Never leave dead batteries in the battery compartment. They can leak and damage the unit.
•Keep batteries out of the reach of small children. If swallowed, consult with a physician immediately.
•Avoid using volatile liquids such as thinner or benzine to clean the unit. Wipe it with a soft, dry cloth, or
with a cloth that has been dipped in a solution of water and a neutral detergent and wrung out.
•In no event will the manufacturer and its suppliers be liable to you or any other person for any damages,
expenses, lost profits, lost savings or any other damages arising out of loss of data and/or formulas
arising out of malfunction, repairs, or battery replacement. The user should prepare physical records of
data to protect against such data loss.
•Never dispose of batteries, the liquid crystal panel, or other components by burning them.
•When the “Low battery!” message appears on the display, replace the main power supply batteries as
soon as possible.
•Be sure that the power switch is set to OFF when replacing batteries.
• If the calculator is exposed to a strong electrostatic charge, its memory contents may be damaged or
the keys may stop working. In such a case, perform the All Reset operation to clear the memory and
restore normal key operation.
•Note that strong vibration or impact during program execution can cause execution to stop or can
damage the calculator’s memory contents.
•Using the calculator near a television or radio can cause interference with TV or radio reception.
•Before assuming malfunction of the unit, be sure to carefully reread this manual and ensure that the
problem is not due to insufficient battery power, programming or operational errors.
iii
Page 6
Be sure to keep physical records of all important data!
The large memory capacity of the unit makes it possible to store large amounts of data. You should note,
however, that low battery power or incorrect replacement of the batteries that power the unit can cause
the data stored in memory to be corrupted or even lost entirely. Stored data can also be affected by
strong electrostatic charge or strong impact.
In no event shall CASIO Computer Co., Ltd. be liable to anyone for special, collateral, incidental, or
consequential damages in connection with or arising out of the purchase or use of these materials.
Moreover, CASIO Computer Co., Ltd. shall not be liable for any claim of any kind whatsoever against the
use of these materials by any other party.
• The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
•No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form without the express written consent of the
manufacturer.
• The options described in Chapter 9 of this manual may not be available in certain geographic areas.
For full details on availability in your area, contact your nearest CASIO dealer or distributor.
iv
Page 7

• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
••• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
•• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
•• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
fx-7400G PLUS
•• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
•• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
•• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
•• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
•• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
•• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
•• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
Page 8

Contents
Chapter 1 Getting Acquainted ...................................................... 1
1. Using the Main Menu ............................................................................ 2
2. Key Table ............................................................................................... 4
3. Key Markings ........................................................................................ 6
4. Selecting Modes ................................................................................... 6
Using the Set Up Screen ............................................................................... 6
Set Up Screen Function Key Menus ............................................................. 7
5. Display ....................................................................................................9
About the Display Screen .............................................................................. 9
About Menu Item Types ................................................................................. 9
Exponential Display ..................................................................................... 10
Special Display Formats .............................................................................. 11
Calculation Execution Screen...................................................................... 11
6. Contrast Adjustment .......................................................................... 11
7. When you keep having problems… .................................................. 12
Get the Calculator Back to its Original Mode Settings ................................ 12
Low Battery Message .................................................................................. 12
Chapter 2 Basic Calculations ..................................................... 13
1. Addition and Subtraction ................................................................... 14
2. Multiplication ...................................................................................... 14
3. Division .................................................................................................14
4. Quotient and Remainder Division ..................................................... 15
5. Mixed Calculations ............................................................................. 16
(1) Mixed Arithmetic Calculation Priority Sequence .................................... 16
(2) Parentheses Calculation Priority Sequence .......................................... 17
(3) Negative Values ..................................................................................... 17
(4) Exponential Expressions ....................................................................... 17
(5) Rounding ............................................................................................... 18
6. Other Useful Calculation Features .................................................... 18
(1) Answer Memory (Ans) ........................................................................... 18
(2) Consecutive Calculations ...................................................................... 18
(3) Replay .................................................................................................... 19
(4) Error Recovery ....................................................................................... 19
(5) Making Corrections ................................................................................ 20
7. Using Variables ................................................................................... 21
vi
Page 9

Contents
8. Fraction Calculations ......................................................................... 23
(1) Fraction Display and Input ..................................................................... 23
(2) Performing Fraction Calculations ........................................................... 23
(3) Changing the Fraction Simplification Mode ........................................... 25
9. Selecting Value Display Modes.......................................................... 27
10. Scientific Function Calculations ....................................................... 28
(1) Trigonometric Functions ........................................................................ 28
Setting the Default Angle Unit................................................................ 28
Converting Between Angle Units ........................................................... 29
Trigonometric Function Calculations ...................................................... 30
(2) Logarithmic and Exponential Function Calculations .............................. 30
(3) Other Functions ..................................................................................... 31
(4) Coordinate Conversion .......................................................................... 32
(5) Permutation and Combination ............................................................... 33
(6) Other Things to Remember ................................................................... 33
Multiplication Sign .................................................................................. 33
Calculation Priority Sequence ............................................................... 34
Using Multistatements ........................................................................... 34
Stacks .................................................................................................... 35
Errors ..................................................................................................... 36
How to Calculate Memory Usage .......................................................... 36
Memory Status (MEM) ........................................................................... 37
Clearing Memory Contents .................................................................... 37
Va riable Data (VARS) Menu .................................................................. 38
Chapter 3 Differential Calculations ............................................ 43
Chapter 4 Graphing ..................................................................... 47
1. Before Trying to Draw a Graph .......................................................... 48
Entering the Graph Mode ............................................................................ 48
2. View Window (V-Window) Settings.................................................... 48
Initializing and Standardizing the View Window .......................................... 50
View Window Memory ................................................................................. 51
3. Graph Function Operations ............................................................... 52
Specifying the Graph Type .......................................................................... 52
Storing Graph Functions ............................................................................. 52
Editing Functions in Memory ....................................................................... 54
Drawing a Graph ......................................................................................... 54
4. Drawing Graphs Manually.................................................................. 55
vii
Page 10

Contents
5. Other Graphing Functions ................................................................. 58
Connect Type and Plot Type Graphs (D-Type)............................................. 58
Trace ............................................................................................................ 59
Scroll ........................................................................................................... 60
Overwrite ..................................................................................................... 60
Zoom ........................................................................................................... 62
Sketch Function ........................................................................................... 65
Chapter 5 Table & Graph .............................................................73
1. Storing a Function .............................................................................. 74
2. Deleting a Function ............................................................................ 74
3. Assigning Values to a Variable........................................................... 74
4. Generating a Numeric Table ............................................................... 76
5. Editing a Table ..................................................................................... 77
6. Graphing a Function ........................................................................... 77
7. Assigning Numeric Table Contents to a List .................................... 78
Chapter 6 List Function .............................................................. 79
List Data Linking ..................................................................................... 80
1. List Operations ................................................................................... 81
2. Editing and Rearranging Lists ........................................................... 82
Editing List Values ....................................................................................... 82
Sorting List Values ....................................................................................... 85
3. Manipulating List Data ....................................................................... 87
Accessing the List Data Manipulation Function Menu ................................. 87
4. Arithmetic Calculations Using Lists ................................................. 91
Error Messages ........................................................................................... 91
Inputting a List into a Calculation ................................................................ 91
Recalling List Contents ................................................................................ 93
Graphing a Function Using a List ................................................................ 93
Inputting Scientific Calculations into a List .................................................. 93
Performing Scientific Function Calculations Using a List ............................ 94
Chapter 7 Statistical Graphs and Calculations .........................95
1. Before Performing Statistical Calculations ...................................... 96
2. Statistical Calculation Examples ....................................................... 96
Inputting Data into Lists ............................................................................... 97
viii
Page 11

Contents
Plotting Data ................................................................................................ 97
Plotting a Scatter Diagram........................................................................... 98
Changing Graph Parameters....................................................................... 98
1. Graph draw/non-draw status (SELECT) .................................................. 98
2. General graph settings (SET) .................................................................. 99
Drawing an
Selecting the Regression Type .................................................................. 105
Displaying Statistical Calculation Results .................................................. 106
Graphing statistical calculation results ...................................................... 106
xy Line Graph ......................................................................... 105
3. Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data ........... 107
Histogram .................................................................................................. 107
Box Graph ................................................................................................. 107
Normal Distribution Curve ......................................................................... 108
Displaying Single-Variable Statistical Results ........................................... 108
Pie Chart ................................................................................................... 109
Stacked Bar Chart ..................................................................................... 110
Bar Graph .................................................................................................. 111
Line Graph ................................................................................................. 112
Bar Graph and Line Graph ........................................................................ 113
4. Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data........... 114
Linear Regression Graph .......................................................................... 114
Med-Med Graph ........................................................................................ 115
Quadratic Regression Graph..................................................................... 115
Logarithmic Regression Graph .................................................................. 116
Exponential Regression Graph.................................................................. 116
Power Regression Graph .......................................................................... 117
Displaying Paired-Variable Statistical Results ........................................... 118
Copying a Regression Graph Formula to the Graph Mode ....................... 118
Multiple Graphs ......................................................................................... 119
5. Manual Graphing .............................................................................. 120
Setting the Width of a Histogram ............................................................... 120
6. Performing Statistical Calculations................................................. 121
Single-Variable Statistical Calculations ..................................................... 122
Paired-Variable Statistical Calculations ..................................................... 122
Regression Calculation ............................................................................. 123
Estimated Value Calculation (
, )............................................................ 123
ix
Page 12

Contents
Chapter 8 Programming ........................................................... 125
1. Before Programming ........................................................................ 126
2. Programming Examples................................................................... 127
3. Debugging a Program ...................................................................... 132
4. Calculating the Number of Bytes Used by a Program ................... 132
5. Secret Function ................................................................................ 133
6. Searching for a File........................................................................... 134
7. Editing Program Contents ............................................................... 135
8. Deleting a Program ........................................................................... 138
9. Useful Program Commands............................................................. 139
10. Command Reference ........................................................................ 143
Command Index ........................................................................................ 143
Basic Operation Commands ..................................................................... 144
Program Commands (COM)...................................................................... 145
Program Control Commands (CTL) ........................................................... 149
Jump Commands (JUMP) ......................................................................... 151
Clear Commands (CLR) ............................................................................ 153
Display Commands (DISP)........................................................................ 153
Input / Output Commands (I/O) ................................................................. 154
Conditional Jump Relational Operators (REL) .......................................... 155
11. Text Display ....................................................................................... 156
12. Using Calculator Functions in Programs ....................................... 156
Using Graph Functions in a Program ........................................................ 156
Using Table & Graph Functions in a Program ........................................... 157
Using List Sort Functions in a Program ..................................................... 158
Using Statistical Calculations and Graphs in a Program ........................... 158
Performing Statistical Calculations ............................................................ 160
Chapter 9 Data Communications ............................................. 163
1. Connecting Two Units ...................................................................... 164
2. Connecting the Unit with a Personal Computer ............................. 165
3. Connecting the Unit with a CASIO Label Printer ........................... 166
4. Before Performing a Data Communication Operation ................... 167
5. Performing a Data Transfer Operation ............................................ 168
6. Screen Send Function ...................................................................... 172
7. Data Communications Precautions ................................................ 173
x
Page 13

Contents
Chapter 10 Program Library ..................................................... 175
1. Prime Factor Analysis ...................................................................... 176
2. Greatest Common Measure ............................................................. 178
t-Test Value ....................................................................................... 180
3.
4. Circle and Tangents.......................................................................... 182
5. Rotating a Figure .............................................................................. 189
Appendix ..................................................................................... 193
Appendix A Resetting the Calculator ................................................... 194
Appendix B Power Supply .................................................................... 196
Replacing Batteries ................................................................................... 196
About the Auto Power Off Function ........................................................... 199
Appendix C Error Message Table ......................................................... 200
Appendix D Input Ranges ..................................................................... 202
Appendix E Specifications .................................................................... 204
xi
Page 14

Contents
xii
Page 15
Chapter
Getting Acquainted
— Read This First!
The symbols in this manual indicate the
following messages.
: Important notes
: Notes
: Reference pages
P. 000
1
Page 16
Chapter 1 Getting Acquainted
1. Using the Main Menu
The main menu appears on the display whenever you turn on the calculator. It con-
tains a number of icons that let you select the mode (work area) for the type of
operation you want to perform. You can also make the Main Menu appear at any time
by pressing m.
The following explains the meaning of each icon.
Icon Meaning
Use this mode for arithmetic calculations and function calculations.
Use this mode to perform single-variable (standard deviation) and paired-variable (regression) statistical calculations, and to draw statistical graphs.
Use this mode for storing and editing numeric
data.
Use this mode to store graph functions and to
draw graphs using the functions.
Use this mode to store functions, to generate a
numeric table of different solutions as the values
assigned to variables in a function change, and
to draw graphs.
Use this mode to store programs in the program
area and to run programs.
Use this mode to transfer memory contents or
back-up data to another unit.
Use this mode to adjust the contrast of the display.
Use this mode to check how much memory is
used and remaining, to delete data from memory,
and to initialize (reset) the calculator.
2
Page 17

Getting Acquainted Chapter 1
uu
uTo enter a mode
uu
Example To enter the RUN Mode from the Main Menu
1. Press m to display the Main Menu.
2. Use d, e, f, and c to move the highlighting to the RUN icon.
3. Press w to enter the RUN Mode.
•You can also enter a mode without highlighting an icon in the Main Menu by
inputting the number marked in the lower right corner of the icon.
•When you enter a mode, up to four function key menu items appear at the bottom
of the display. Each menu item corresponds to the function key (1, 2, 3,
4) that is below the item. Some function menus have multiple pages. When this
happens, you should press [ to advance to the next menu page.
Example Menus
1234 1234
3
Page 18

Chapter 1 Getting Acquainted
2. Key Table
Alpha Lock
Normally, once you press a and then a key to input an alphabetic character, the keyboard reverts to its primary functions immediately. If you press
! and then a, the keyboard locks in alpha input until you press a
again.
4
Page 19
Getting Acquainted Chapter 1
Trace Zoom
Page
6
6
45
24 31
23
Page
15
31
31
31
31
23
60
139
38
31
31
31
31
17
V-Window
30
17
Sketch
7
2
16
30
31
17
Page PagePagePagePage
30
82
21
20
82
14
60
14
18
17
30
21
PagePagePagePage
82
14
60
16
5
Page 20
Chapter 1 Getting Acquainted
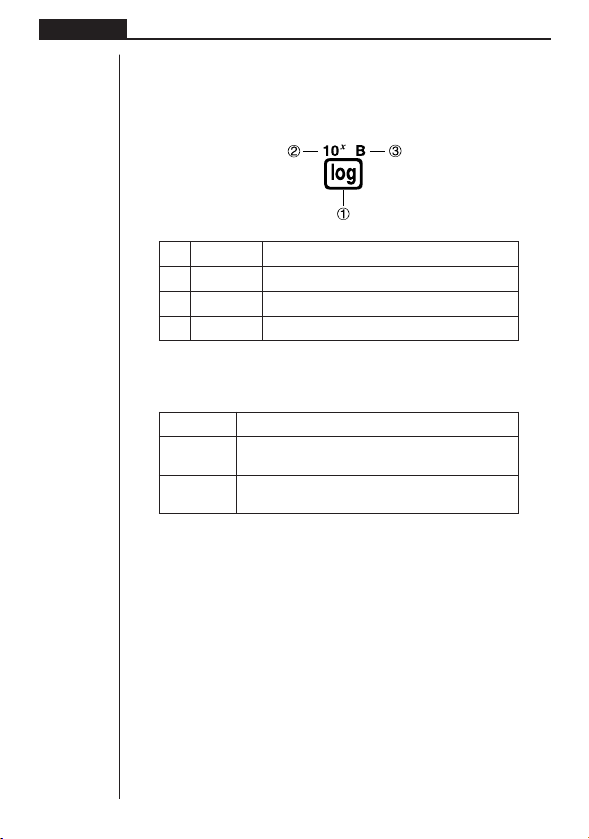
3. Key Markings
Many of the calculator’s keys are used to perform more than one function. The functions marked on the keyboard are color coded to help you find the one you need
quickly and easily.
Function Key Operation
1 log l
2 10
3 B al
The following describes the color coding used for key markings.
x
!l
Color Key Operation
Orange Press ! and then the key to perform the marked
RedPress a and then the key to perform the marked
function.
function.
4. Selecting Modes
kk
k Using the Set Up Screen
kk
The first thing that appears when you enter a mode is the mode’s set up screen,
which shows the current status of settings for the mode. The following procedure
shows how to change a set up.
uu
uTo change a mode set up
uu
1. Select the icon you want and press w enter a mode and display its initial screen.
Here we will enter the RUN Mode.
6
Page 21
Getting Acquainted Chapter 1
2. Press !Z to display the mode’s set up
screen.
• This set up screen is just one possible example. Actual set up screen contents will differ
according to the mode you are in and that
mode’s current settings.
3. Use the f and c cursor keys to move the highlighting to the item whose
setting you want to change.
4. Press the function key (1 to 4) that is marked with the setting you want to
make.
5. After you are finished making any changes you want, press Q to return to the
initial screen of the mode.
kk
k Set Up Screen Function Key Menus
kk
This section details the settings you can make using the function keys in the set up
display.
uu
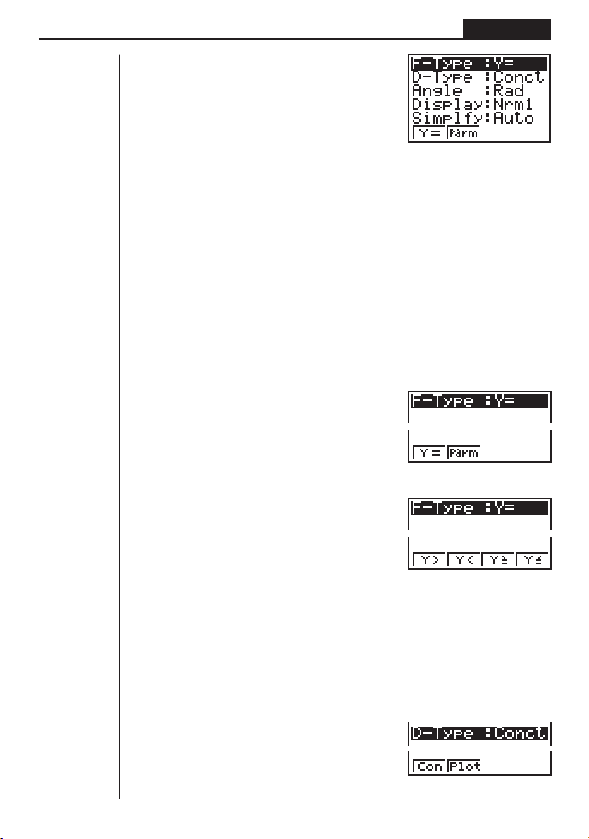
uGraph Function Type (F-Type)
uu
1234
1 (Y=) .......... Re ct ang ular coor di nat e
2 (Parm) ...... Parametric coordinate graphs
[
1 (Y>) .......... y > f( x) inequality graph
2 (Y<) .......... y < f( x) inequality graph
3 (Y≥) .......... y > f (x) inequality graph
4 (Y≤) .......... y < f (x) inequality graph
Press [ to return to the previous menu.
• The setting you make for F-Type determines the variable name that is input when
you press T.
uu
uGraph Draw Type (D-Type)
uu
1 (Con) ........ Connection of points plot-
2 (Plot) ......... Plotting of points on graph
graphs
ted on graph.
without connection.
1234[
1234[
1234
7
Page 22
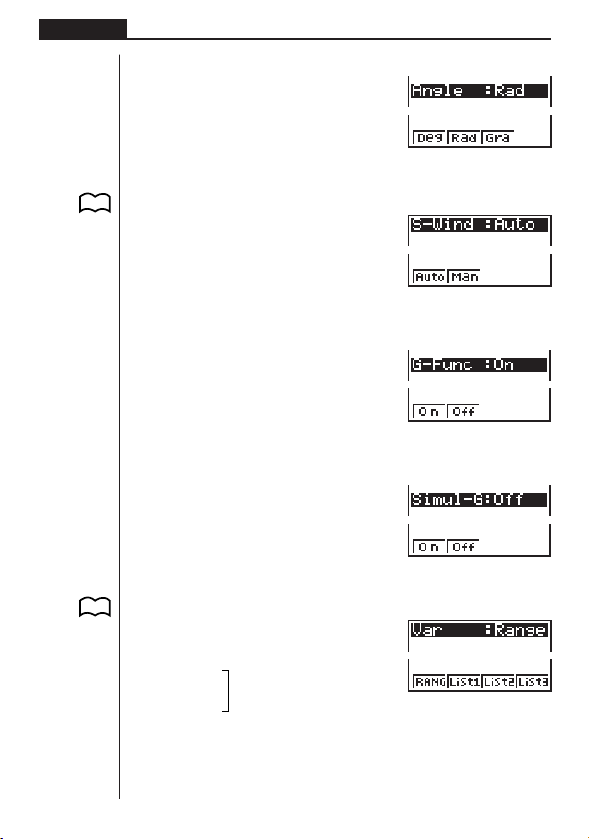
Chapter 1 Getting Acquainted
uu
uAngle unit (Angle)
uu
1 (Deg) ........ Sp ec if ie s degr ees as
2 (Rad) ........ Sp ec if ie s r ad ia ns as
3 (Gra) ......... Specifies grads as default.
uu
uStatistical Graph View Window Setting (S-Wind)
uu
P. 120
P. 120
P.75
1 (Auto)........ Automat ic setting of view
2 (Man) ........ Manu al set ti ng of vi ew
uu
uGraph Function Display (G-Func)
uu
1 (On) .......... Turns on display of function
2 (Off) .......... Turns off display of function
uu
uSimultaneous Graph Mode (Simul-G)
uu
1 (On) .......... Turn s on sim ul taneous
2 (Off) .......... Simultaneous graphing off
uu
uTable & Graph Generation Settings (Var)
uu
1 (RANG) .... Table generation and graph
2 (List1)
3 (List2)
4 (List3)
default.
default.
window values for statistical graph drawing.
window values for statistical graph drawing.
during graph drawing and
trace.
during graph drawing and
trace.
graphing of all functions in
memory.
(g ra ph s dr aw n on e- by one).
drawing using numeric table range.
Table generation and graph
....
drawing using list data.
1234
1234
1234
1234
1234[
8
Page 23
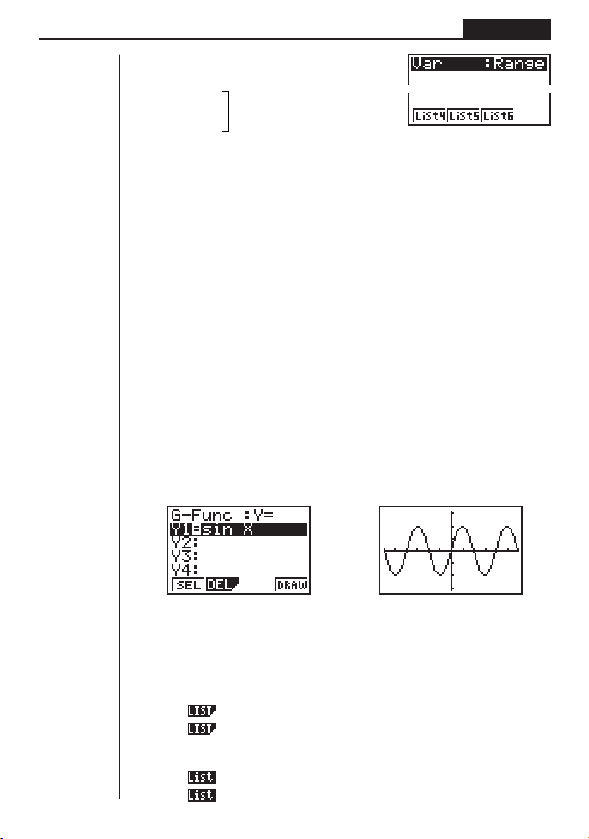
Getting Acquainted Chapter 1
[
1 (List4)
2 (List5)
3 (List6)
Press [ to return to the previous menu.
Other menus for set up (Display, Simplfy, Frac) are described in each applicable
section of this manual as they come up.
Table generation and graph
....
drawing using list data.
1234 [
Abbreviations
STAT ............... Statistics
PRGM ............. Program
CONT.............. Contrast
MEM ............... Memory
5. Display
kk
k About the Display Screen
kk
This calculator uses two types of display: a text display and a graphic display. The
text display can show 13 columns and six lines of characters, with the bottom line
used for the function key menu, while the graph display uses an area that measures
79 (W) × 47 (H) dots.
Text Display Graph Display
kk
k About Menu Item Types
kk
This calculator uses certain conventions to indicate the type of result you can expect
when you press a function key.
• Next Menu
Example:
Selecting displays a menu of list functions.
• Command Input
Example:
Selecting inputs the “List” command.
9
Page 24
Chapter 1 Getting Acquainted
• Direct Command Execution
Example:
Selecting executes the DRAW command.
kk
k Exponential Display
kk
The calculator normally displays values up to 10 digits long. Values that exceed this
limit are automatically converted to and displayed in exponential format. You can
specify one of two different ranges for automatic changeover to exponential display.
–2
Norm 1 ............ 10
Norm 2 ............ 10–9 (0.000000001) > |x|, |x| > 10
uu
uTo change the exponential display range
uu
1. Press !Z to display the Set Up Screen.
2. Use f and c to move the highlighting to “Display”.
3. Press 3 (Norm).
The exponential display range switches between Norm 1 and Norm 2 each time you
perform the above operation. There is no display indicator to show you which exponential display range is currently in effect, but you can always check it by seeing what
results the following calculation produces.
(0.01) > |x|, |x| > 10
10
10
Ab/caaw
(Norm 1)
(Norm 2)
All of the examples in this manual show calculation results using Norm 1.
For full details about the “Display”, see “Selecting Value Display Modes”.
P.27
uu
uHow to interpret exponential format
uu
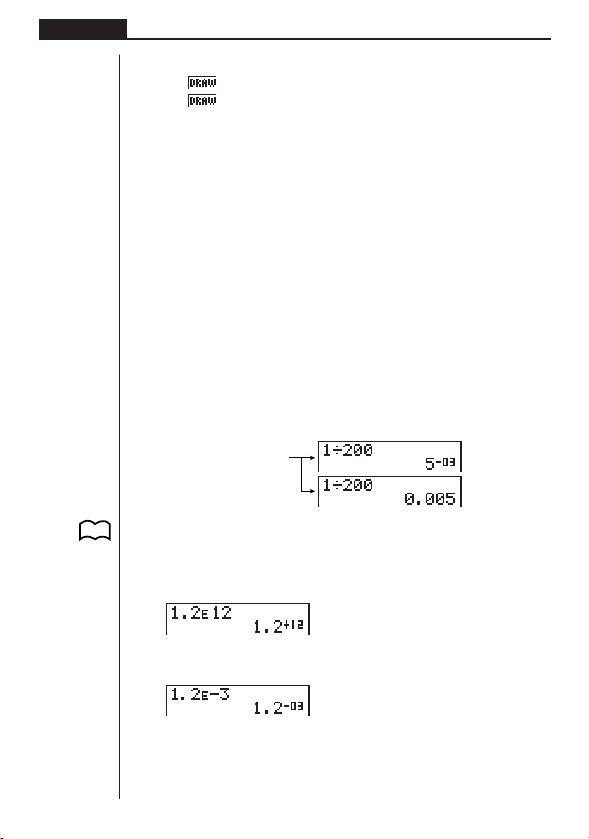
+12
1.2
indicates that the result is equivalent to 1.2 × 1012. This means that you should
move the decimal point in 1.2 twelve places to the right, because the exponent is
positive. This results in the value 1,200,000,000,000.
–03
1.2
indicates that the result is equivalent to 1.2 × 10–3. This means that you should
move the decimal point in 1.2 three places to the left, because the exponent is negative. This results in the value 0.0012.
10
Page 25
Getting Acquainted Chapter 1
kk
k Special Display Formats
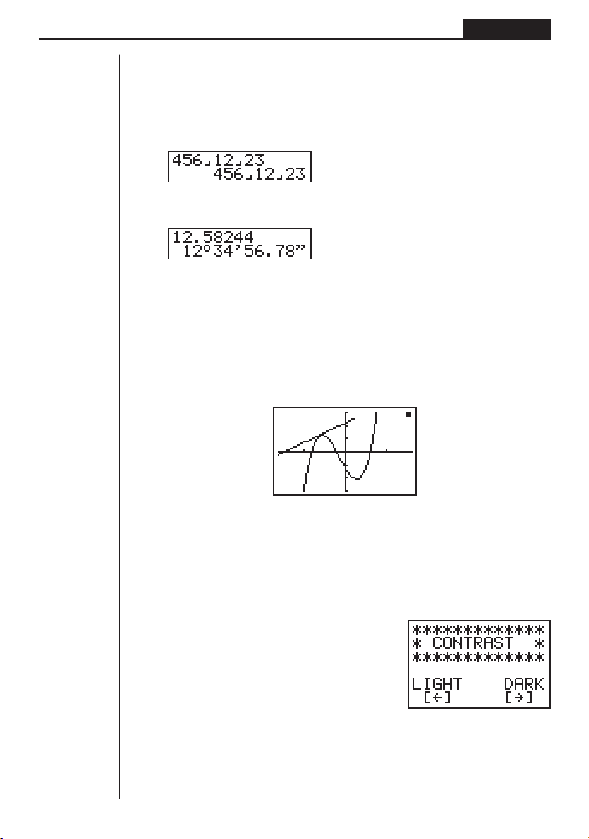
kk
This calculator uses special display formats to indicate fractions, and sexagesimal
values.
uu
uFractions
uu
.......... Indicates: 456
uu
uSexagesimal Values
uu
.......... Indicates: 12° 34’ 56.78"
•In addition to the above, this calculator also uses other indicators or symbols,
which are described in each applicable section of this manual as they come up.
kk
k Calculation Execution Screen
kk
Whenever the calculator is busy drawing a graph or executing a long, complex calculation or program, a black box (k) flashes in the upper right corner of the display.
This black box tells you that the calculator is performing an internal operation.
–––
12
23
6. Contrast Adjustment
Adjust the contrast whenever objects on the display appear dim or difficult to see.
uu
uTo display the contrast adjustment screen
uu
Highlight the CONT icon in the Main Menu and
then press w.
Press d to make the figures on the screen lighter or e to make them darker.
After getting the contrast the way you want it, press m to return to the main menu.
11
Page 26
Chapter 1 Getting Acquainted
7. When you keep having problems…
If you keep having problems when you are trying to perform operations, try the following before assuming that there is something wrong with the calculator.
kk
k Get the Calculator Back to its Original Mode Settings
kk
1. In the Main Menu, select the RUN icon and press w.
2. Press ! Z to display the Set Up Screen.
3. Highlight “Angle” and press 2 (Rad).
4. Highlight “Display” and press 3 (Norm) to select the exponential display range
P.6
P. 196
(Norm 1 or Norm 2) that you want to use.
5. Now enter the correct mode and perform your calculation again, monitoring the
results on the display.
kk
k Low Battery Message
kk
The low battery message appears while the main battery power is below a certain
level whenever you press o to turn power on or m to display the Main Menu.
o or m
If you continue using the calculator without replacing batteries, power will automatically turn off to protect memory contents. Once this happens, you will not be able to
turn power back on, and there is the danger that memory contents will be corrupted
or lost entirely.
About 3 seconds later
↓
12
Page 27

Chapter
Basic Calculations
In the RUN Mode you can perform arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) as well as calculations involving scientific functions.
1. Addition and Subtraction
2. Multiplication
3. Division
4. Quotient and Remainder Division
5. Mixed Calculations
6. Other Useful Calculation Features
7. Using Variables
8. Fraction Calculations
9. Selecting Value Display Modes
10. Scientific Function Calculations
2
Page 28
Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
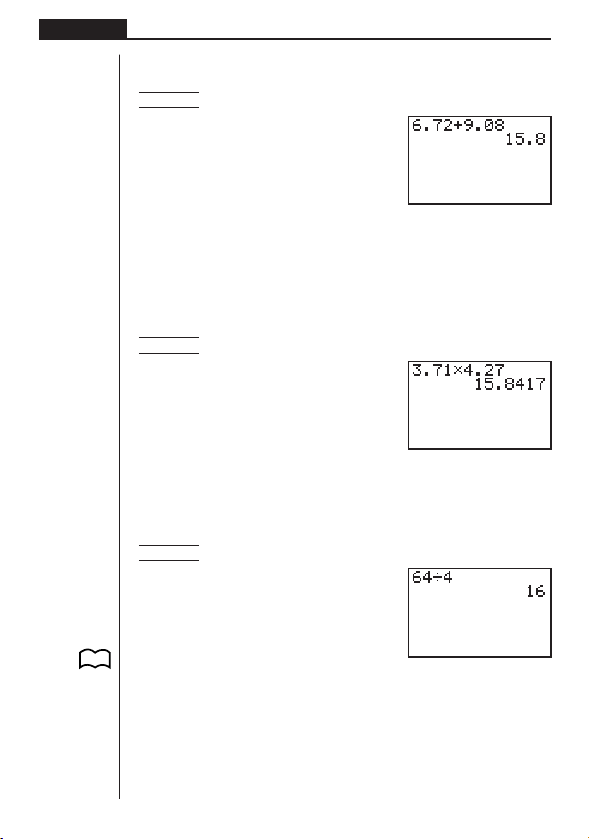
1. Addition and Subtraction
Example 6.72 + 9.08
g.hc+j.aiw
You can input the operation just as it is written. This capability is called “true algebraic logic.”
Be sure to press A to clear the display before starting a new calculation.
2. Multiplication
Example 3.71 × 4.27
Ad.hb*
e.chw
• The range of this calculator is –9.99999999 × 10
3. Division
Example 64 ÷ 4
Age/ew
99
to +9.99999999 × 1099.
P.17
Parentheses also come in handy when performing division. For full details on using
parentheses, see “Parentheses Calculation Priority Sequence”.
14
Page 29
Basic Calculations Chapter 2
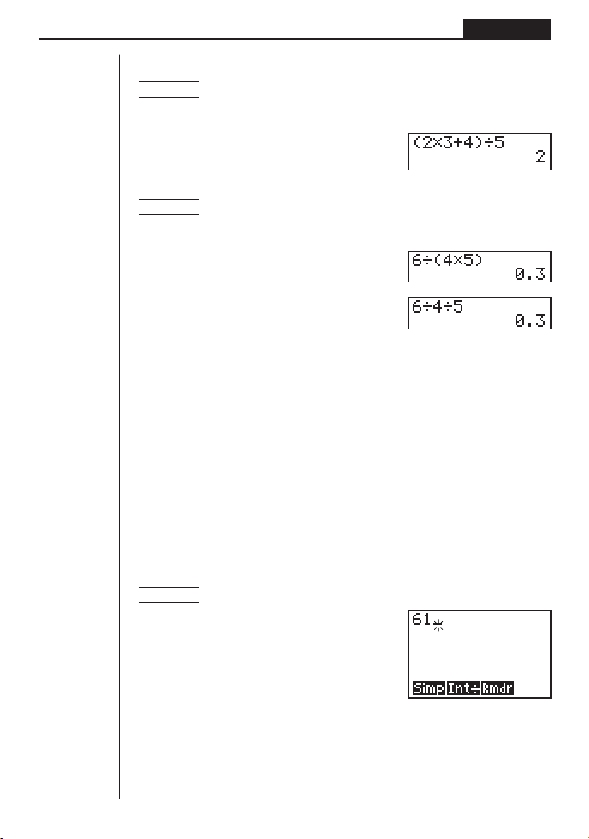
uu
uTo use parentheses in a calculation
uu
Example 1
You should input this calculation as: (2 × 3 + 4) ÷ 5
2 × 3 + 4
–––––––
5
A(c*d+e)/fw
Example 2 –––––
You can input this calculation as: 6 ÷ (4 × 5) or 6 ÷ 4 ÷ 5.
6
4 × 5
Ag/(e*f)w
Ag/e/fw
4. Quotient and Remainder Division
This calculator can produce either the quotient or the quotient and remainder of
division operations involving two integers. Use K to display the Option Menu for
the function key menu you need to perform quotient and remainder division.
Operation
Use the RUN Mode for quotient and remainder division.
Quotient Division ...... <integer>K2(CALC)2(Int÷)<integer>w
Reminder Division .... <integer>K2(CALC)3(Rmdr)<integer>w
uu
uTo perform quotient division
uu
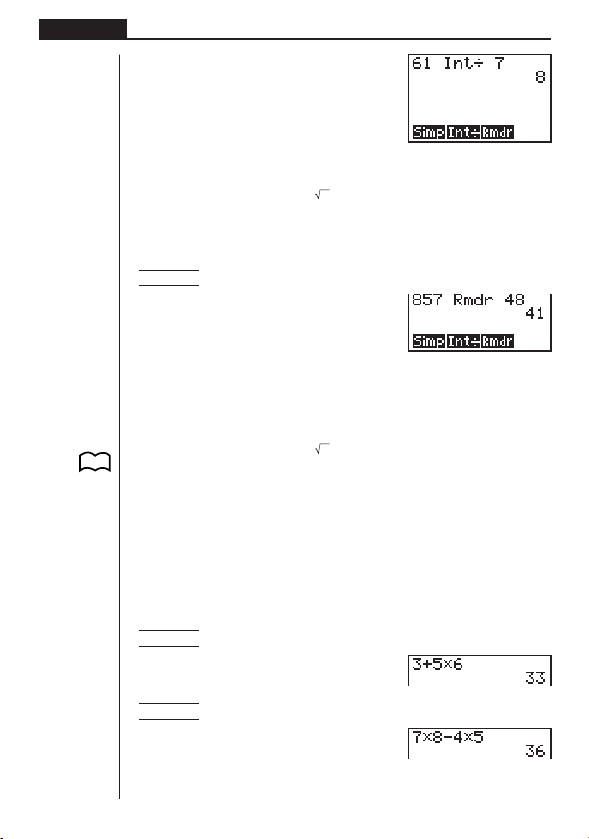
Example To display the quotient produced by 61 ÷ 7
AgbK2(CALC)
1 2 34
15
Page 30
Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
2(Int÷)hw
•Remember that you can use only integers in quotient division operations. You
cannot use expressions such as
part.
uu
uTo perform remainder division
uu
Example To display the remainder produced by 857 ÷ 48
ifh3(Rmdr)eiw
Press Q to clear the Option Menu after you finish your remainder and quotient
calculations.
•Remember that you can use only integers in remainder division operations. You
cannot use expressions such as
P.91
part.
•Quotient and remainder division can also be used with lists to divide a multiple
integers by each other in a single operation.
5. Mixed Calculations
(1) Mixed Arithmetic Calculation Priority Sequence
For mixed arithmetic calculations, the calculator automatically performs multiplication and division before addition and subtraction.
Example 1 3 + 5 × 6
Ad+f*gw
1 2 34
2 or sin60 because their results have a decimal
123 4
2 or sin60 because their results have a decimal
Example 2 7 × 8 – 4 × 5
Ah*i-e*fw
16
Page 31

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
(2) Parentheses Calculation Priority Sequence
Expressions enclosed inside parentheses are always given priority in a calculation.
Example 1 100 – (2 + 3) × 4
Abaa-(c+d)
*ew
Example 2 (7 – 2) × (8 + 5)
•A multiplication sign immediately in front of an open parenthesis can be omitted.
A(h-c)(i+f)
w
•Any closing parentheses at the end of a calculation can be omitted, no matter
how many there are.
Parentheses are always closed in the operation examples presented in this manual.
(3) Negative Values
Use the - key to input negative values.
Example 56 × (–12) ÷ (–2.5)
Afg*-bc/
-c.fw
(4) Exponential Expressions
Use the E key to input exponents.
Example (4.5 × 1075) × (–2.3 × 10
Ae.fEhf*-c.d
E-hjw
–79
)
The above shows what would appear when the exponential display range is set to
Norm 1. It stands for –1.035 × 10
P.10
–3
, which is –0.001035.
17
Page 32

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
(5) Rounding
Example 74 ÷ 3
Ahe/dw
The actual result of the above calculation is 24.66666666… (and so on to infinity),
which the calculator rounds off. The calculator’s internal capacity is 15 digits for the
values it uses for calculations, which avoids precision problems with consecutive
operations that use the result of the previous operation.
6. Other Useful Calculation Features
(1) Answer Memory (Ans)
Calculation results are automatically stored in the Answer Memory, which means
you can recall the results of the last calculation you performed at any time.
uu
uTo recall Answer Memory contents
uu
Press ! and then K (which is the shifted function of the - key).
This operation is represented as ! K throughout this manual.
Example To perform 3.56 + 8.41 and then divide 65.38 by the result
Ad.fg+i.ebw
gf.di/!Kw
(2) Consecutive Calculations
If the result of the last calculation is the first term of the next calculation, you can use
the result as it is on the display without recalling Answer Memory contents.
uu
uTo perform a consecutive calculation
uu
Example To perform 0.57 × 0.27, and then add 4.9672 to the results
Aa.fh*a.chw
+e.jghcw
18
Page 33

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
(3) Replay
While the result of a calculation is on the display, you can use d and e to move the
cursor to any position within the expression used to produce the result. This means
you can back up and correct mistakes without having to input the entire calculation.
You can also recall past calculations you have already cleared by pressing A.
Operation
The first press of e displays the cursor at the beginning of the expression, while
d displays the cursor at the end. Once the cursor is displayed, use e to move it
right and d to move it left.
uu
uTo use Replay to change an expression
uu
Example To calculate 4.12 × 6.4 and then change the calculation to 4.12 × 7.1
Ae.bc*g.ew
d
dddh.bw
Multi-Replay
Pressing A and then f or c sequentially recalls and displays past calculations.
(4) Error Recovery
Whenever an error message appears on the display, press d or e to re-display
the expression with the cursor located just past the part of the expression that caused
the error. You can then move the cursor and make necessary corrections before
executing the calculation again.
uu
uTo correct an expression that causes an error
uu
Example To recover from the error generated by performing 148 ÷ 0. × 3.37
instead of 148 ÷ 0.3 × 3.37
Abei/a.
*d.dhw
19
Page 34

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
d(You could also press e.)

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
ddddd

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
uu
uTo assign the same value to more than one variable
uu
Operation
<value or expression>aa<start variable name>a3(~)a<end variable
name>w
Example To assign the result of 2 to variables A, B, C, D, and E
A!9caaAa3(~)
aEw
uu
uTo clear the contents of all variables
uu
In the Main Menu, select the MEM icon and press w.
Select Memory Usage.
w
Press c to scroll the display until “Alpha” is highlighted.
ccccccc
1(DEL)
1 234
1 234
Press 1 (YES) to clear all variables or 4 (NO) to abort the clear operation without
clearing anything.
22
Page 37

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
8. Fraction Calculations
(1) Fraction Display and Input
Example 1 Display of
3
––
4
Example 2 Display of 3
Mixed fractions (such as 3 1/4) are input and displayed as:
integer{numerator{denominator.
Improper fractions (15/7) and proper fractions (such as 1/4) are input and displayed
as: numerator{denominator.
Use the $ key to input each part of a fraction.
uu
uTo input a fraction
uu
Operation
Proper Fraction or Improper Fraction Input: <numerator value>$<denominator value>
Mixed Fraction Input: <integer value>$<numerator value>$<denominator value>
Example To input 3
Press d$b$e.
Note that the maximum size of a fractional value is 10 digits, counting the integer,
numerator, and denominator digits and separator symbols. Any value longer than
10 digits is automatically converted to its equivalent decimal value.
1
––
4
1
––
4
(2) Performing Fraction Calculations
21
Example
uu
uTo convert between fraction and decimal values
uu
Operation
Fraction to Decimal Conversion: M
Decimal to Fraction Conversion: M
–– + 3 ––
54
Ac$f+d$b$ew
23
Page 38

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
Example To convert the result of the previous example to a decimal and
uu
uTo convert between proper and improper fractions
uu
Operation
Mixed Fraction to Improper Fraction Conversion: !/
Improper Fraction to Mixed Fraction Conversion: !/
Example To convert the result of the previous example to an improper
• The calculator automatically reduces the results of fraction calculations. You can
uu
uTo perform a mixed decimal and fraction calculation
uu
Example 5.2 ×
• The result of a calculation that mixes fractions and decimal values is always a
then back to a fraction
M
M
fraction and then back to a proper fraction
!/
!/
use the procedure described under “Changing the Fraction Simplification Mode”
below to specify manual fraction simplification.
1
––
Af.c*b$fw
decimal value.
5
uu
uTo use parentheses in a fraction calculation
uu
Example
24
12
–––––– + ––
117
–– + ––
34
Ab$(b$d+b$e)
+c$hw
Page 39

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
(3) Changing the Fraction Simplification Mode
The initial default of the calculator is automatic simplification of fractions produced
by fraction calculations. You can use the following operation to change the fraction
simplification mode to manual.
uu
uTo change the fraction simplification mode
uu
Example To change the fraction simplification mode to manual
!Z
(Displays the Set Up Screen.)
cccc2(Man)
1 2 34
When the fraction simplification is set to manual, you have to use the Option Menu to
simplify fractions. You can let the calculator select the divisor to use for simplification
or you can specify a divisor.
uu
uTo simplify using the calculator’s divisor
uu
Operation
Perform calculations after selecting the RUN icon in the Main Menu to enter the
RUN Mode.
To display the simplification menu: K2(CALC)
To select automatic simplification: 1(Simp)w
To specify the divisor for simplification*: 1(Simp) <Divisor>w
*You can specify only a positive integer as the divisor.
Example To perform the calculation 1 ––
Ab$g$ch+b$
b$jw
(The result that appears when using manual simplification is the least common multiple of the fractions used in the calculation.)
61
+ 1 –– and reduce the result
27 9
25
Page 40

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
K2(CALC)1(Simp)w
• F = 3 indicates that 3 is the divisor.
• The calculator automatically selects the smallest possible divisor for simplification.
Repeat the above operation to simplify again.
1(Simp)w
Try once again.
1(Simp)w
This display indicates that further simplification is impossible.
uu
uTo simplify using your own divisor
uu
ExampleTo perform the above calculation and then specify 9 as the divisor
to use for simplification
1(Simp)jw
1 234
1 234
1 234
1 234
• If the value you specify is invalid as a divisor for simplification, the calculator
automatically uses the lowest possible divisor.
26
Page 41

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
9. Selecting Value Display Modes
You can make specifications for three value display modes.
Fix Mode
This mode lets you specify the number of decimal places to be displayed.
Sci Mode
This mode lets you specify the number of significant digits to be displayed.
Norm 1/Norm 2 Mode
This mode determines at what point the display changes over to exponential display
format.
Display the Set Up Screen and use the f and c keys to highlight “Display”.
1234
uu
u To specify the number of decimal places (Fix)
uu
1. While the set-up screen is on the display, press 1 (Fix).
2. Press the function key that corresponds to the number of decimal places you
want to set (0 to 9).
•Press [ to display the next menu of numbers.
Example To specify two decimal places
1 234
1 (Fix)
123 4
3 (2)
Press the function key that corr espon ds to the
number of decimal places you want to specify.
•Displayed values are rounded off to the number of decimal places you specify.
•A number of decimal place specification remains in effect until you change the
Norm Mode setting.
27
Page 42

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
uu
u To specify the number of significant digits (Sci)
uu
1. While the set-up screen is on the display, press 2 (Sci).
2. Press the function key that corresponds to the number of significant digits you
want to set (0 to 9).
•Press [ to display the next menu of numbers.
Example To specify three significant digits
2 (Sci)
4 (3)
Press the function key that corr espon ds to the
number of significant digits you want to specify.
•Displayed values are rounded off to the number of significant digits you specify.
•Specifying 0 makes the number of significant digits 10.
•A number of significant digit specification remains in effect until you change the
Norm Mode setting.
uu
u To specify the exponential display range (Norm 1/Norm 2)
uu
Press 3 (Norm) to switch between Norm 1 and Norm 2.
Norm 1: 10
Norm 2: 10
–2
(0.01)>|x|, |x| >10
–9
(0.000000001)>|x|, |x| >10
10. Scientific Function Calculations
Use the RUN Mode to perform calculations that involve trigonometric functions and
other types of scientific functions.
1 2 34
1234
10
10
(1) Trigonometric Functions
Before performing a calculations that involves trigonometric functions, you should
first specify the default angle unit as degrees (°), radians (r), or grads (g).
kk
k Setting the Default Angle Unit
kk
The default angle unit for input values can be set using the set up screen. If you set
degrees (°) for example, inputting a value of 90 is automatically assumed to be 90°
The following shows the relationship between degrees, radians, and grads.
90° = π/2 radians = 100 grads
28
Page 43

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
uu
uTo set the default angle unit
uu
Example To change the angle unit from radians to degrees
!Z
cc1(Deg)
1 234
•Once you change the angle unit setting, it remains in effect until you change it
again using the set up screen. You also should check the set up screen to find out
what the current angle unit setting is.
kk
k Converting Between Angle Units
kk
You can use the following procedure to input a value using an angle unit that is not
the current default angle unit. Then when you press w, the value will be converted
to the default angle unit.
uu
uTo convert between angle units
uu
Example To convert 4.25 radians to degrees while degrees are set as the
default angle unit
Ae.cfK[
2(ANGL)2(r)w
1 2 34
1 2 34
29
Page 44

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
kk
k Trigonometric Function Calculations
kk
P.29
Always make sure that the default angle unit is set to the required default before
performing trigonometric function calculations.
uu
uTo perform trigonometric function calculations
uu
Example 1 sin (63° 52' 41")
Default angle unit: Degrees
!Zcc1(Deg)Q
sgdK[2(ANGL)[1(° ' ")fc1(° ' ")eb1(° ' ")w
Example 2
Default angle unit: Radians
Example 3 tan(–35grad)
Default angle unit: Grads
(2) Logarithmic and Exponential Function Calculations
•A base 10 logarithm (common logarithm) is normally written as log10 or log.
•A base e () logarithm (natural logarithm) is normally
written as loge or ln.
Note that certain publications use “log” to refer to base
take care to watch for what type of notation is being used in the publications you are
working with. This calculator and manual use “log” to mean base 10 and “ln” for base
π
sec (–– rad) = ––––––––––
3
!Zcc2(Rad)Q
b/c(!7/d)w
!Zcc3(Gra)Q
t-dfw
1
1 + ––– = 2.71828...
lim
n
n→∞
cos (––rad)
n
Result: 0.897859012
1
π
3
Result: 2
Result: –0.6128007881
e logarithms, so you must
e.
30
Page 45

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
uu
uTo perform logarithmic/exponential function calculations
uu
Example 1 log1.23
lb.cdw
Example 2 ln90
Ijaw
Example 3 To calculate the anti-logarithm of common logarithm 1.23 (10
!0b.cdw
Example 4 To calculate the anti-logarithm of natural logarithm 4.5 (e
!ee.fw
Example 5 (–3)4 = (–3) × (–3) × (–3) × (–3)
(-d)Mew
Example 67123
h!qbcdw
(3) Other Functions
Example Operation Display
+ =
3.65028154 !92+!95w 3.6502815425
(–3)2 = (–3) × (– 3) = 9 (-3)xw 9
2
= –(3 × 3) = –9 -3xw – 9
–3
1
––––––––––– = 12
11
––– – –––
34
8! (= 1 × 2 × 3 × .... × 8)
= 40320 8K4(PROB)1(
3
Random number generation K4(PROB)
(pseudo random number 4(Ran#) w (Ex.) 0.4810497011
between 0 and 1.)
= 42
(3!X-4!X)
!Xw 12
!#(36*42*49)w
Result: 0.0899051114
Result: 4.49980967
Result: 16.98243652
4.5
Result: 90.0171313
Result: 81
Result: 1.988647795
x!)w 40320
1.23
)
)
4236 × 42 × 49
31
Page 46

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
Example Operation Display
What is the absolute value of
the common logarithm of3?
3
log
= 0.1249387366
|
|
4
What is the integer part of K[1(NUM)
7800
––––– ?
96
What is the decimal part of K[1(NUM)
7800
––––– ?
96
200 ÷ 6= 200/6w 33.33333333
× 3= *3w 100
Round the value used 200/6w 33.33333333
for internal calculations K[1(NUM)4(Rnd)w 33.33333333
to 11 digits* *3w 99.99999999
What is the nearest integer K[1(NUM)[1(Intg)
not exceeding – 3.5? -3.5w – 4
*When a Fix (number of decimal places) or Sci (number of significant digits) is in effect, Rnd
rounds the value used for internal calculations in accordance with the current Fix or Sci
specification. In effect, this makes the internal value match the displayed value.
(4) Coordinate Conversion
uu
u Rectangular Coordinates
uu
4
K[1(NUM)
1(Abs)l(3/4)w 0.1249387366
2(Int)(7800/96)w 81
3(Frac)(7800/96)w 0.25
uu
u Polar Coordinates
uu
•With polar coordinates, θ can be calculated and displayed within a range of
θ
< 180° (radians and grads have same range).
–180°<
Example To calculate r and
!Zcc1(Deg)Q
K[2(ANGL)[[
1(Pol()14,20.7)w Ans
32
Operation Display
θ
°
when x = 14 and y = 20.7
–
24.989
1
2–55.928–→ 55.92839019 (
–
→ 24.98979792 (r)
θ
)
Page 47

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
Example To calculate x and y when r = 25 and θ = 56°
!Zcc1(Deg)Q
K[2(ANGL)[[
2(Rec()25,56)w Ans
(5) Permutation and Combination
Operation Display
uu
u Permutation
uu
n! n!
nPr = ––––– nCr = –––––––
(n – r)! r! (n – r)!
uu
u Combination
uu
–
13.979–→ 13.97982259 (x)
1
2–20.725–→ 20.72593931 (y)
Example To calculate the possible number of different arrangements
10P4 = 5040 10K4(PROB)
Example To calculate the possible number of different combinations of
10C4 = 210 10K4(PROB)
using 4 items selected from 10 items
Formula Operation Display
nPr)4w 5040
2(
4 items selected from 10 items
Formula Operation Display
nCr)4w 210
3(
(6) Other Things to Remember
kk
k Multiplication Sign
kk
You can leave out the multiplication sign in any of the following cases.
•In front of the following scientific functions:
sin, cos, tan, sin
Seq, Min, Max, Mean, Median, List, Dim, Sum
Examples: 2 sin30, 10log1.2, 2
•In front of constants, variable names, Ans memory contents.
Examples: 2π, 2AB, 3Ans, 6X, etc.
•In front of an open parenthesis.
Examples: 3(5 + 6), (A + 1)(B –1)
–1
, cos–1, tan–1, log, In, 10x, ex, , 3, Pol(x, y), Rec(r, θ), d/dx,
3, etc.
33
Page 48

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
kk
k Calculation Priority Sequence
kk
The calculation priority sequence is the order that the calculator performs operations. Note the following rules about calculation priority sequence.
•Expressions contained in parentheses are performed first.
•When two or more expressions have the same priority, they are executed from
right to left.
Example 2 + 3 × (log sin2π2 + 6.8) = 22.07101691 (angle unit = Rad)
3
5
6
The following is a complete list of operations in the sequence they are performed.
1. Coordinate transformation: (Pol (
List: Fill, Seq, Min, Max, Mean, Median, SortA, SortD
2. Type A functions (value input followed by function):
sexagesimal input: ° ’ ”
3. Powers: ^ (
4. Fraction input: a
5. Multiplication operations where the multiplication sign before π or a variable is
omitted: 2π; 5A; 3sinx; etc.
6. Type B functions (function followed by value input):
7. Multiplication operations where the multiplication sign before a scientific function
is omitted: 2
8. Permutation: nPr; combination: nCr
9. Multiplication; division; integer division; remainder division
10. Addition; subtraction
11. Relational operators: =,
y
x
x
); roots:
b
/c
, 3, log, In, ex, 10x, sin, cos, tan, sin–1, cos–1, tan–1, (–), Dim, Sum
3; Alog2; etc.
1
2
4
, >, <, ≥, ≤
GG
G
GG
x, y), Rec (r,
θ
); differential calculations: d/dx(;
2
x
, x–1, x!
kk
k Using Multistatements
kk
Multistatements are formed by connecting a number of individual statements for
sequential execution. You can use multistatements in manual calculations and in
programmed calculations. There are two different ways that you can use to connect
statements to form multistatements.
• Colon (:)
Statements that are connected with colons are executed from left to right, without
stopping.
34
Page 49

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
Invalid
^^
^)
^^
Intermediate result at point
where “^” is used.
•Display Result Command (
When execution reaches the end of a statement followed by a display result command, execution stops and the result up to that point appears on the display. You
can resume execution by pressing the w key.
uu
uTo use multistatements
uu
Example 6.9 × 123 = 848.7
123 ÷ 3.2 = 38.4375
AbcdaaA
!W[[3(:)
g.j*aA!W[2(^)
aA/d.cw
w
•Note that the final result of a multistatement is always displayed, regardless of
whether it ends with a display result command.
•You cannot construct a multistatement in which one statement directly uses the
result of the previous statement.
Example 123 × 456: × 5
kk
k Stacks
kk
When the calculator performs a calculation, it temporarily stores certain information
in memory areas called a “stacks” where it can later recall the information when it is
necessary.
There are actually two stacks: a 10-level numeric stack and a 26-level command
stack. The following example shows how data is stored in the stacks.
Numeric stack
Command stack
A calculation can become so complex that it requires too much stack memory and
cause a stack error (Stk ERROR) when you try to execute it. If this happens, try
simplifying your calculation or breaking it down into separate parts. See “How to
P.36
Calculate Memory Usage” for details on how much memory is taken up by various
commands.
35
Page 50

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
kk
k Errors
kk
An error message appears on the display and calculation stops whenever the calculator detects some problem. Press A to clear the error message.
The following is a list of all the error messages and what they mean.
Ma ERROR - (Mathematical Error)
•A value outside the range of ±9.99999999 × 10
lation, or an attempt was made to store such a value in memory.
•An attempt was made to input a value that exceeds the range of the scientific
function being used.
•An attempt was made to perform an illegal statistical operation.
Stk ERROR - (Stack Error)
• The calculation being performed caused the capacity of one of the stacks to be
exceeded.
Syn ERROR - (Syntax Error)
•An attempt to use an illegal syntax.
Arg ERROR - (Argument Error)
•An attempt to use an illegal argument with a scientific function.
Dim ERROR - (Dimension Error)
•An attempt to perform an operation with two or more lists when the dimensions of
the lists do not match.
P.200
In addition to the above, there are also a Mem ERROR and Go ERROR. See “Error
Message Table” for details.
kk
k How to Calculate Memory Usage
kk
Some key operations take up one byte of memory each, while others take up two
bytes.
1-byte operations: 1, 2, 3, ..., sin, cos, tan, log, In,
2-byte operations:
d/dx(, Xmin, If, For, Return, DrawGraph, SortA(, Sum, etc.
99
was generated during a calcu-
, π, etc.
36
Page 51

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
kk
k Memory Status (MEM)
kk
You can check how much memory is used for storage for each type of data. You can
also see how many bytes of memory are still available for storage.
uu
uTo check the memory status
uu
1. In the Main Menu, select the MEM icon and press w.
2. Press w again to display the memory status screen.
Number of bytes still free
3. Use f and c to move the highlighting and view the amount of memory (in
bytes) used for storage of each type of data.
The following table shows all of the data types that appear on the memory status
screen.
Data type Meaning
Program Program data
Stat Statistical calculations and graphs
List List data
Y= Graph functions
Draw Graph drawing conditions (View Window,
V-WinView Window memory data
Table Table & Graph data
Alpha Alpha memory data
enlargement/reduction factor, graph screen)
kk
k Clearing Memory Contents
kk
uu
uTo clear all data within a specific data type
uu
1. In the memory status screen, use c and f to move the highlighting to the
data type whose data you want to clear.
37
Page 52

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
2. Press 1 (DEL).
1(DEL)
3. Press 1 (YES) to clear the data or 4 (NO) to abort the operation without
clearing anything.
kk
k Va riable Data (VARS) Menu
kk
You can use the variable data menu to recall the data listed below.
•View Window values
•Enlargement/reduction factor
• Single-variable/paired-variable statistical data
•Graph functions
•Table & Graph table range and table contents
To recall variable data, press J to display the variable data menu.
J
1 (V-WIN) .... View Window values
2 (FACT)......
[
1 (STAT) ...... Single/paired-variable statistical data
2 (GRPH) .... Graph functions stored in the GRAPH Mode
3 (TABL) ...... Table & Graph function table range and table contents
Press [ to return to the previous menu.
x and y-axis enlargement/reduction factor
1 234
1234[
1234 [
uu
uTo recall View Window values
uu
Pressing 1 (V-WIN) while the variable data menu is on the screen displays a View
Window value menu.
1 (V-WIN)
1234 [
38
Page 53

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
1 (Xmin) ....... x-axis minimum
2 (Xmax)......
3 (Xscl) ........
[
1 (Ymin) ....... y-axis minimum
2 (Ymax)......
3 (Yscl) ........
[
1 (Tmin) ....... Minimum of T
2 (Tmax) ...... Maximum of T
3 (Tpth) ........ Pitch of T
Press [ to return to the previous menu.
uu
uTo recall enlargement and reduction factors
uu
Pressing 2 (FACT) while the variable data menu is on the screen displays an
enlargement/reduction factor menu.
2(FACT)
1 (Xfct) ......... x-axis enlargement/reduction factor
2 (Yfct) .........
x-axis maximum
x-axis scale
1234 [
y-axis maximum
y-axis scale
1234 [
1234[
y-axis enlargement/reduction factor
uu
uTo recall single/paired-variable statistical data
uu
Pressing [ and then 1 (STAT) while the variable data menu is on the screen
displays a statistical data menu.
[1(STAT)
1 (X) ............ Single/paired-variable
2 (Y) ............ Paired-variable
3 (GRPH) .... Statistical graph data menu
4 (PTS) ........ Summary point data menu
x-data menu
y-data menu
1234[
39
Page 54

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
The following menu appears whenever you press 1 (X), while the statistical data
menu is on the display.
1 (X)
1 (n) ............. Number of data
o) ............. Mean of x data
2 (
x) ........... Sum of x data
3 (Σ
2
x
) .......... x data sum of squares
4 (Σ
[
1 (xσn) ......... x data population standard deviation
xσn-1) ....... x data samp le sta nda rd
2 (
3 (minX) .......
4 (maxX)......
Press [ to return to the previous menu.
The following menu appears whenever you press 2 (Y) while the statistical data
menu is on the display.
2 (Y)
deviation
x data minimum value
x data maximum value
1234[
1234[
1 (p) ............. Mean of y data
y) ........... Sum of y data
2 (Σ
2
y
) .......... y data sum of squares
3 (Σ
xy) ......... x data and y data sum of products
4 (Σ
[
1 (yσn) ......... y data population standard deviation
yσn-1) ....... y data sample standard deviation
2 (
3 (minY) .......
4 (maxY)......
Press [ to return to the previous menu.
40
y data minimum value
y data maximum value
1234[
1234[
Page 55

Basic Calculations Chapter 2
The following menu appears whenever you press 3 (GRPH) while the statistical
data menu is on the display.
3 (GRPH)
1234[
1(a)-3(c) ... Statistical graph regression coefficient and multinomial coeffi-
4 (
[
1 (Q1) .......... First quartile
2 (Med) ........ Median of input data
3 (Q3) .......... Third quartile
4 (Mod) ........ Mode of input data
Press [ to return to the previous menu.
The following menu appears whenever you press 4 (PTS) while the statistical data
menu is on the display.
4 (PTS)
1(x1)-4(y2) ..... Coordinates of summary points
[
1(x3)-2(y3) ..... Coordinates of summary points
Press [ to return to the previous menu.
cients
r) ............. Statistical graph correlation coefficient
1234[
1234[
1234[
uu
uTo recall graph functions
uu
Pressing [ and then 2 (GRPH) while the variable data menu is on the screen
displays a graph function menu.
[2 (GRPH)
1234 [
41
Page 56

Chapter 2 Basic Calculations
Input a storage area number and then press one of the following function keys to
recall the corresponding graph function stored in that storage area.
1 (Y) ............ Rectangular coordinate or inequality function
2 (Xt) ........... Parametric graph function Xt
3 (Yt) ........... Parametric graph function Yt
uu
uTo recall Table & Graph table range and table content data
uu
Pressing [ and then 3 (TABL) while the variable data menu is on the screen
displays a Table & Graph data menu.
[3(TABL)
1 (Strt) ......... Table range start value (F Start command)
2 (End) ........ Table range end value (F End command)
3 (Pitch) ....... Table value increment (F Pitch command)
1234 [
42
Page 57

Chapter
Differential Calculations
3
Page 58

Chapter 3 Differential Calculations
•To perform differential calculations, first display the Option Menu, and then input
the values shown in the formula below.
K2(CALC)[
d/dx) f(x),a,∆ x)
1(
Increase/decrease of
Point for which you want to determine the derivative
d/dx ( f (x), a, ∆x) ⇒ ––– f (a)
The differentiation for this type of calculation is defined as:
f '(a) = lim –––––––––––––
∆x→0
f '(a)
infinitesimal
f (a + ∆x) – f (a)
–––––––––––––
In this definition,
the neighborhood of f ' (a) calculated as:
In order to provide the best precision possible, this unit employs central difference to
perform differential calculations. The following illustrates central difference.
d
dx
f (a + ∆x) – f (a)
∆x
is replaced by a
∆x
x
sufficiently small
∆x, with the value in
The slopes of point a and point a + ∆x, and of point a and point a – ∆x in function
y = f(x) are as follows:
f (a + ∆x) – f (a) ∆y f (a) – f (a – ∆x) ∇y
––––––––––––– = ––– , ––––––––––––– = –––
∆x ∆x ∆x ∇x
In the above, ∆
difference.To calculate derivatives, the unit takes the average between the value of
y/∆x and ∇y/∇x, thereby providing higher precision for derivatives.
∆
44
y/∆x is called the forward difference, while ∇y/∇x is the backward
Page 59

Differential Calculations Chapter 3
This average, which is called the
1 f (a + ∆x) – f (a) f (a) – f (a – ∆x)
––––––––––––– + –––––––––––––
f '(a) = ––
2 ∆x ∆x
f (a + ∆x) – f (a – ∆x)
= –––––––––––––––––
2∆x
uu
uTo perform a differential calculation
uu
central difference
, is expressed as:
Example To determine the derivative at point x = 3 for the function
Input the function
Input point
Input ∆x, which is the increase/decrease of x.
• In the function f(x), only X can be used as a variable in expressions. Other variables (A through Z) are treated as constants, and the value currently assigned to
that variable is applied during the calculation.
•Input of ∆
lator automatically uses a value for ∆
which you specified as the point for which you wanted to determine the derivative.
•Discontinuous points or sections with drastic fluctuation can adversely affect precision or even cause an error.
•Note that you cannot use differential calculation inside of a differential calculation
term.
3
y = x
+ 4x2 + x – 6, when the increase/decrease of x is defined as
x = 1E – 5
∆
f(x).
AK2(CALC)[1(
TMd+eTx
+T-g,
d/dx)
x = a for which you want to determine the derivative.
d,
bE-f)
w
x and the closing parenthesis can be omitted. If you omit ∆x, the calcu-
x that is appropriate for the value of x = a,
45
Page 60

Chapter 3 Differential Calculations
•Pressing A during calculation of a differential (while the cursor is not shown
on the display) interrupts the calculation.
•Always perform trigonometric differentials using radians (Rad Mode) as the
angle unit.
46
Page 61

Chapter
Graphing
A collection of versatile graphing tools plus a large 79 × 47-dot
display makes it easy to draw a variety of function graphs quickly
and easily. This calculator is capable of drawing the following types
of graphs.
•Rectangular coordinate (Y =) graphs
•Parametric graphs
•Inequality graphs
•A selection of graph commands also makes it possible to incorporate graphing into programs.
1. Before Trying to Draw a Graph
2. View Window (V-Window) Settings
3. Graph Function Operations
4. Drawing Graphs Manually
5. Other Graphing Functions
4
Page 62

Chapter 4 Graphing
1. Before Trying to Draw a Graph
kk
k Entering the Graph Mode
kk
On the Main Menu, select the GRAPH icon and enter the GRAPH Mode. When you
do, the Graph Function (G-Func) menu appears on the display. You can use this
menu to store, edit, and recall functions and to draw their graphs.
Use
f
and c to change selection.
1 (SEL) ........ Draw/non-draw status
2 (DEL) ........ Graph delete
4 (DRAW) .... Draws graph
Memory area
123 4
2. View Window (V-Window) Settings
Use the View Window to specify the range of the x-and y-axes, and to set the spac-
ing between the increments on each axis. You should always set the View Window
parameters you want to use before drawing a graph. Press ! 3 to display the
View Window.
1. Press !3 to display the View Window.
!3(V-Window)
1234
1 (INIT) ........ View Window initial settings
2 (TRIG) ...... View Window initial settings using specified angle unit
3 (Sto) ......... Store View Window settings to View Window memory.
4 (Rcl) ..........Recall View Window settings from View Window memory.
Xmin................ Minimum
Xmax............... Maximum
Xscl ................. Spacing of
x-axis value
x-axis value
x-axis increments
48
Page 63

Graphing Chapter 4
2. Input a value for a parameter and press w. The calculator automatically selects
the next parameter for input.
•You can also select a parameter using the c and f keys.
Ymin................ Minimum y-axis value
Ymax............... Maximum
Yscl ................. Spacing of
The following illustration shows the meaning of each of these parameters.
y-axis value
y-axis increments
X scl
Y min
Y max
Y scl
(x, y)
X max
X min
3. Input a value for a parameter and press w. The calculator automatically selects
the next parameter for input.
• There are actually nine View Window parameters. The remaining three parameters appear on the display when you move the highlighting down past the Y
scale parameter by inputting values and pressing c.
Tmin ................ T minimum values
Tmax ............... T maximum values
Tptch ............... T pitch
The following illustration shows the meaning of each of these parameters.
ptch
min
max
(
X, Y
)
49
Page 64

Chapter 4 Graphing
4. To exit the View Window, press Q.
•Pressing w without inputting any value also exits the View Window.
• The following is the input range for View Window parameters.
–9.99E+97 to 9.999E+97
•You can input parameter values up to 7 digits long. Values greater than 10
less than 10
tive sign) plus a 2-digit exponent.
• The only keys that enabled while the View Window is on the display are: a to
j, ., E, -, f, c, d, e, +, -, *, /, (, ), ! 7,
Q. You can use - or - to input negative values.
• The existing value remains unchanged if you input a value outside the allowable range or in the case of illegal input (negative sign only without a value).
•Inputting a View Window range so the min value is greater than the max value,
causes the axis to be inverted.
•You can input expressions (such as 2π) as View Window parameters.
•When the View Window setting does not allow display of the axes, the scale for
y-axis is indicated on either the left or right edge of the display, while that for
the
the x-axis is indicated on either the top or bottom edge.
•When View Window values are changed, the graph display is cleared and the
newly set axes only are displayed.
•View Window setting may cause irregular scale spacing.
•Setting maximum and minimum values that create too wide of a View Window
range can result in a graph made up of disconnected lines (because portions of
the graph run off the screen), or in graphs that are inaccurate.
• The point of deflection sometimes exceeds the capabilities of the display with
graphs that change drastically as they approach the point of deflection.
•Setting maximum and minimum values that create to narrow of a View Window
range can result in an error (Ma ERROR).
kk
k Initializing and Standardizing the View Window
kk
uu
uTo initialize the View Window
uu
a. Press !3 (V-Window) 1 (INIT) to initialize the View Window to the following
settings.
Xmin = –3.9 Ymin = –2.3
Xmax = 3.9 Ymax = 2.3
Xscl = 1 Yscl = 1
-1
, are automatically converted to a 4-digit mantissa (including nega-
6
or
50
Page 65

Graphing Chapter 4
b. Press ! 3 (V-Window) 2 (TRIG) to initialize the View Window to the follow-
ing settings.
Deg Mode
Xmin = –360 Ymin = –1.6
Xmax = 360 Ymax = 1.6
Xscl = 90 Yscl = 0.5
Rad Mode
Xmin = –6.28318
Xmax = 6.28318
Xscl = 1.57079
Gra Mode
Xmin = –400
Xmax = 400
Xscl = 100
• The settings for Ymin, Ymax, Ypitch, Tmin, Tmax, and Tpitch remain unchanged
when you press 2 (TRIG).
kk
k View Window Memory
kk
You can store a set of View Window settings in View Window memory for recall when
you need them.
uu
uTo save View Window settings
uu
While the View Window setting screen is on the display, press 3 (Sto) to save the
current settings.
•Whenever you save View Window settings, any settings previously stored in
memory are replaced.
uu
uTo recall View Window settings
uu
While the View Window setting screen is on the display, press 4 (Rcl) to recall the
View Window settings stored in memory.
•Whenever you recall View Window settings, the settings on the View Window are
replaced by the recalled settings.
•You can change View Window settings in a program using the following syntax.
View Window [Xmin value], [Xmax value], [Xscl value],
[Ymin value], [Ymax value], [Yscl value],
[Tmin value], [Tmax value], [Tptch value]
51
Page 66

Chapter 4 Graphing
3. Graph Function Operations
You can store up to 10 functions in memory. Functions in memory can be edited,
recalled, and graphed. The types of functions that can be stored in memory are:
rectangular coordinate functions, parametric functions, and inequalities.
kk
k Specifying the Graph Type
kk
Before you can store a graph function in memory, you must first specify its graph
type.
1. While the Graph Function Menu is on the display, press [ to display a Graph
Type Menu.
[
1 (Y =) ......... Rectangular coordinate graph
2 (Parm) ...... Parametric graph
[
1 (Y >) ......... Y > f (x) inequality
2 (Y <) ......... Y <
3 (Y ≥) ......... Y >
4 (Y ≤) ......... Y <
Press [ to return to the previous menu
2. Press the function key that corresponds to the graph type you want to specify.
kk
k Storing Graph Functions
kk
uu
uTo store a rectangular coordinate function (Y =)
uu
Example To store the following expression in memory area Y1:
[1(Y =)
(Specifies rectangular coordinate
expression.)
cTx-f
(Inputs expression.)
w
(Stores expression.)
52
y = 2 x
2
– 5
f
(x) inequality
f
(x) inequality
f
(x) inequality
1234[
1234[
Page 67

Graphing Chapter 4
•You will not be able to store the expression in an area that already contains a
parametric function. Select another area to store your expression or delete the
existing parametric function first. This also applies when storing inequalities.
uu
uTo store a parametric function
uu
Example To store the following functions in memory areas Xt2 and Yt2:
x = 3 sin T
y = 3 cos T
[2(Parm)
(Specifies parametric expression.)
dsTw
(Inputs and stores x expression.)
dcTw
(Inputs and stores y expression.)
•You will not be able to store the expression in an area that already contains a
rectangular coordinate expression or inequality. Select another area to store your
expression or delete the existing expression first.
uu
uTo store an inequality
uu
Example To store the following inequality in memory area Y3:
2
y > x
– 2x – 6
[[1(Y>)
(Specifies an inequality.)
Tx-cT-g
(Inputs expression.)
w
(Stores expression.)
53
Page 68

Chapter 4 Graphing
kk
k Editing Functions in Memory
kk
uu
uTo edit a function in memory
uu
Example To change the expression in memory area Y1 from y = 2x2 – 5
e
(Displays cursor.)
eeeed
(Changes contents.)
w
(Stores new graph function.)
uu
uTo delete a function
uu
1. While the Graph Function Menu is on the display, press f or c to display the
cursor and move the highlighting to the area that contains the function you want
to delete.
2. Press 2 (DEL).
3. Press 1 (YES) to delete the function or 4 (NO) to abort the procedure without
deleting anything.
kk
k Drawing a Graph
kk
Before actually drawing a graph, you should first make the draw/non-draw status.
uu
uTo specify the draw/non-draw status of a graph
uu
You can specify which functions out of those stored in memory should be used for a
draw operation.
•Graphs for which there is no draw/non-draw status specification are not drawn.
Example To select the following functions for drawing:
2
y = 2x
– 3
to
y = 2x
Y1 :
t2: x = 3 sin T
X
Y
t2: y = 3 cos T
1 234
2
– 5
54
Page 69

Graphing Chapter 4
Use the following View Window parameters.
Xmin = –5 Ymin = –5
Xmax = 5 Ymax = 5
Xscl = 1 Yscl = 1
ccc
(Select a memory area that contains a
function for which you want to specify
non-draw.)
1 234
1(SEL)
(Specify non-draw.)
1234
Unhighlights
4(DRAW) or w
(Draws the graphs.)
•Pressing u or A returns to the Graph Function Menu.
•A parametric graph will appear coarse if the settings you make in the View
Window cause the pitch value to be too large, relative to the differential between the min and max settings. If the settings you make cause the pitch value
to be too small relative to the differential between the min and max settings, on
the other hand, the graph will take a very long time to draw.
4. Drawing Graphs Manually
After you select the RUN icon in the Main Menu and enter the RUN Mode, you can
draw graphs manually. First press ! 4 (SKTCH) 2 (GRPH) to recall the Graph
Command Menu, and then input the graph function.
!4(SKTCH)2(GRPH)
1 (Y =) ......... Rectangular coordinate graph
2(Parm) ....... Parametric graph
1234[
55
Page 70

Chapter 4 Graphing
[
1 (Y >) ......... Y > f (x) inequality
2 (Y <) ......... Y <
3 (Y ≥) ......... Y >
4 (Y ≤) ......... Y <
Press [ to return to the previous menu.
uu
uTo graph using rectangular coordinates (Y =)
uu
You can graph functions that can be expressed in the format y = f(x).
Example To graph y = 2x2 + 3x – 4
1. In the set-up screen, specify the appropriate graph type for F-Type.
!Z1(Y =)Q
2. Input the rectangular coordinate (Y =) expression.
A!4(SKTCH)1(Cls)w
2(GRPH)1(Y =)
cTx+dT-e
3. Press w to draw the graph.
w
f
(x) inequality
f
(x) inequality
f
(x) inequality
Use the following View Window parameters.
Xmin = –5 Ymin = –10
Xmax = 5 Ymax = 10
Xscl = 2 Yscl = 5
1234[
•You can draw graphs of the following built-in scientific functions.
• sin x • cos x • tan x • sin–1 x • cos–1 x
• tan–1 x • • x
x
• 10
x
• e
2
• log x • l nx
–1
• x
3
•
View Window settings are made automatically for built-in graphs.
56
Page 71

Graphing Chapter 4
uu
uTo graph parametric functions
uu
You can graph parametric functions that can be expressed in the following format.
(X, Y) = (
f (T), g(T))
Example To graph the following parametric functions:
x = 7 cos T – 2 cos 3T
y = 7 sin T – 2 sin 3T
Use the following View Window parameters.
Xmin = –20 Ymin = –12
Xmax = 20 Ymax = 12
Xscl = 5 Yscl = 5
Tmin = 0 Tmax = 2π
Tptch = π÷36
1. In the set-up screen, specify the appropriate graph type for F-Type.
!Z2(Parm)
2. Set the default angle unit to radians (Rad).
cc2(Rad)Q
3. Input the parametric functions.
A!4(SKTCH)1(Cls)w
2(GRPH)2(Parm)
hcT-ccdT,
hsT-csdT)
4. Press w to draw the graph.
w
uu
uTo graph inequalities
uu
You can graph inequalities that can be expressed in the following four formats.
•
y > f
(x)
y < f
(x)
•
y > f
(x)
•
y < f
(x)
•
57
Page 72

Chapter 4 Graphing
Example To graph the inequality y > x2 – 2x – 6
1. In the set-up screen, specify the appropriate graph type for F-Type.
!Z[1(Y>)Q
2. Input the inequality.
A!4(SKTCH)1(Cls)w
2(GRPH)[1(Y>)
Tx-cT-g
3. Press w to draw the graph.
w
5. Other Graphing Functions
The functions described in this section tell you how to read the x- and y-coordinates
at a given point, and how to zoom in and zoom out on a graph.
• These functions can be used with rectangular coordinate, parametric, and inequality graphs only.
kk
k Connect Type and Plot Type Graphs (D-Type)
kk
P.7
You can use the D-Type setting of the set-up screen to specify one of two graph
types.
•Connect type (Conct)
Points are plotted and connected by lines to create a curve.
• Plot
Points are plotted without being connected.
Use the following View Window parameters.
Xmin = –6 Ymin = –10
Xmax = 6 Ymax = 10
Xscl = 1 Yscl = 5
58
Page 73

Graphing Chapter 4
kk
k Trace
kk
With trace, you can move a flashing pointer along a graph with the f, c, d, and
e cursor keys and obtain readouts of coordinates at each point. The following
shows the different types of coordinate readouts produced by trace.
•Rectangular Coordinate Graph • Parametric Function Graph
•Inequality Graph
uu
uTo use trace to read coordinates
uu
Example To determine the points of intersection for graphs produced by
1. After drawing the graphs, press 1 (TRCE) to display the pointer in the center of
the following functions:
2
y = x
– 3
Y1:
y = –x + 2
Y2:
Use the following View Window parameters.
Xmin = –5 Ymin = –10
Xmax = 5 Ymax = 10
Xscl = 1 Yscl = 2
the graph.
1(TRCE)
• The pointer may not be visible on the graph when you press 1 (TRCE).
2. Use d to move the pointer to the first intersection.
~ d
d
x/y
coordinate values
59
Page 74

Chapter 4 Graphing
•Pressing d and e moves the pointer along the graph. Holding down either
key moves the pointer at high speed.
3. Use f and c to move the pointer between the two graphs.
4. Use e to move the pointer to the other intersection.
e
•To quit the trace operation, press 1 (TRCE) again.
uu
uScrolling
uu
When the graph you are tracing runs off the display along either the x- or y-axis,
pressing the e or d cursor key causes the screen to scroll in the corresponding
direction eight dots.
•You can scroll only rectangular coordinate and inequality graphs while tracing.
You cannot scroll parametric function graphs.
•Trace can be used only immediately after a graph is drawn. It cannot be used
after changing the settings of a graph.
•You cannot incorporate trace into a program.
•You can use trace on a graph that was drawn as the result of an output command (^), which is indicated by the “-Disp-” indicator on the screen.
kk
k Scroll
kk
You can scroll a graph along its x- or y-axis. Each time you press f, c, d, or
e, the graph scrolls 12 dots in the corresponding direction.
~ e
kk
k Overwrite
kk
Using the following syntax to input a graph causes multiple versions of the graph to
be drawn using the specified values. All versions of the graph appear on the display
at the same time.
<function with one variable> , ! [ <variable name> ! =
<value> , <value> , .... <value> ! ] w
60
Page 75

Graphing Chapter 4
Example To graph y = Ax2 – 3, substituting 3, 1, and –1 for the value of A
Use the following View Window parameters.
Xmin = –5 Ymin = –10
Xmax = 5 Ymax = 10
Xscl = 1 Yscl = 2
[1(Y =)
(Specifies graph type.)
aATx-d,
![aA!=d,
b,-b!]w
(Stores expression.)
4(DRAW) or w
(Draws graph.)
• The function that is input using the above syntax can have only one variable.
•You cannot use X, Y or T as the variable name.
•You cannot assign a variable to the variable in the function.
P.8
•When the set-up screen’s Simul-G item is set to “On,” the graphs for all the variables are drawn simultaneously.
1234
↓
↓
61
Page 76

Chapter 4 Graphing
kk
k Zoom
kk
The zoom feature lets you enlarge and reduce a graph on the display.
uu
uBefore using zoom
uu
Immediately after drawing a graph, press !2 (ZOOM) to display the Zoom Menu.
!2(ZOOM)
1 (BOX) ....... Graph enlargement using box zoom
2 (FACT)...... Displays screen for specification of zoom factors
3 (IN) ........... Enlarges graph using zoom factors
4 (OUT) ....... Reduces graph using zoom factors
[
1234[
1 (ORIG)...... Original size
Press [ to return to the previous menu
uu
uTo use box zoom
uu
With box zoom, you draw a box on the display to specify a portion of the graph, and
then enlarge the contents of the box.
Example To use box zoom to enlarge a portion of the graph y = (x + 5)
1. After graphing the function, press !2 (ZOOM).
62
x + 4) (x + 3)
(
Use the following View Window parameters.
Xmin = –8 Ymin = –4
Xmax = 8 Ymax = 2
Xscl = 2 Yscl = 1
!2(ZOOM)
1 234[
1 234
Page 77

Graphing Chapter 4
2. Press 1 (BOX), and then use the cursor keys (d, e, f , c) to move the
pointer to the location of one of the corners of the box you want to draw on the
screen. Press w to specify the location of the corner.
1(BOX)
d ~ dw
3. Use the cursor keys to move the pointer to the location of the corner that is diagonally across from the first corner.
~ f d ~ d
f
4. Press w to specify the location of the second corner. When you do, the part of
the graph inside the box is immediately enlarged so it fills the entire screen.
w
•To return to the original graph, press 2 (ZOOM) [ 1 (ORIG).
•Nothing happens if you try to locate the second corner at the same location or
directly above the first corner.
•You can use box zoom for any type of graph.
uu
uTo use factor zoom
uu
With factor zoom, you can zoom in or zoom out on the display, with the current
pointer location being at the center of the new display.
•Use the cursor keys (d, e, f, c) to move the pointer around the display.
Example Graph the two functions below, and enlarge them five times in
order to determine whether or not they are tangential:
y = (x + 4) (x + 1) (x – 3)
Y1:
y = 3x + 22
Y2:
63
Page 78

Chapter 4 Graphing
1. After graphing the functions, press !2 (ZOOM), and the pointer appears on
the screen.
!2(ZOOM)
2. Use the cursor keys (d , e, f, c) to move the pointer to the location that
you want to be the center of the new display.
d
3. Press 2 (FACT) to display the factor specification screen, and input the factor
for the x- and y-axes.
2(FACT)
fwfw
4. Press Q to return to the graphs, and then press 3 (IN) to enlarge them.
Q3(IN)
Use the following View Window parameters.
Xmin = –8 Ymin = –30
Xmax = 8 Ymax = 30
Xscl = 5 Yscl = 10
~ d f ~ f
1 2 34
This enlarged screen makes it clear that the graphs of the two expressions are not
tangential.
•Note that the above procedure can also be used to reduce the size of a graph
(zoom out). In step 4, press 4 (OUT).
64
Page 79

Graphing Chapter 4
• The above procedure automatically converts the
dow values to 1/5 of their original settings.
•You can repeat the factor zoom procedure more than once to further enlarge or
reduce the graph.
uu
uTo initialize the zoom factor
uu
Press ! 2 (ZOOM) 2 (FACT) 1 (INIT) to initialize the zoom factor to the
following settings.
Xfct = 2 Yfct = 2
•You can use the following syntax to incorporate a factor zoom operation into a
program.
Factor <X factor>, <Y factor>
•You can use factor zoom for any type of graph.
kk
k Sketch Function
kk
The sketch function lets you draw lines and graphs on an existing graph.
•Note that Sketch function operation in the STAT, GRAPH or TABLE Mode is
different from Sketch function operation in the RUN or PRGM Mode.
uu
uBefore using the Sketch Function
uu
Press ! 4 (SKTCH) to display the sketch menu.
In the STAT, GRAPH or TABLE Mode
!4(SKTCH)
x-range and y-range View Win-
1 (Cls) ..........Clears drawn line and point
3 (PLOT)...... Displays plot menu
4 (LINE) ....... Displays line menu
[
1 (Vert) ........ Vertical line
2 (Hztl) ......... Horizontal line
Press [ to return to the previous menu
In the RUN or PRGM Mode
!4(SKTCH)
1 2 34[
1234[
1234[
65
Page 80

Chapter 4 Graphing
[
•Other menu items are identical to those in the STAT, GRAPH, TABLE Mode menu.
The Sketch function lets you draw lines and plot points on a graph that is already on
the screen.
All the examples in this section that show operations in the STAT, GRAPH or TABLE
Mode are based on the assumption that the following function has already been
graphed in the GRAPH Mode.
Memory Area Y1:
The following are the View Window parameters used when drawing the graph.
uu
uTo plot points
uu
In the STAT, GRAPH or TABLE Mode
Example To plot a point on the graph of y = x(x + 2)(x – 2)
1. After graphing the function, display the sketch menu and perform the following
operation to cause the pointer to appear on the graph screen.
!4(SKTCH)3(PLOT)1(Plot)
2. Use the cursor keys (f, c, d, e) to move the pointer the locations of the
points you want to plot and press w to plot.
•You can plot as many points as you want.
e ~ ef ~ f
w
1234
y = x(x + 2)(x – 2)
Xmin = –5 Ymin = –5
Xmax = 5 Ymax = 5
Xscl = 1 Yscl = 1
•The current x- and y-coordinate values are assigned respectively to variables X
and Y.
66
Page 81

Graphing Chapter 4
In the RUN or PRGM Mode
The following is the syntax for plotting points in these modes.
x-coordinate>, <y-coordinate>
Plot <
Example To plot a point at (2, 2)
Use the following View Window parameters.
Xmin = –5 Ymin = –10
Xmax = 5 Ymax = 10
Xscl = 1 Yscl = 2
1. After entering the RUN Mode, display the sketch menu and perform the following
operation.
!4(SKTCH)1(Cls)w
3(PLOT)1(Plot)c,c
2. Press w.
ww
•You can use the cursor keys (f, c, d, e) to move the pointer around the
screen.
• If you do not specify coordinates, the pointer is located in the center of the
graph screen when it appears on the display.
• If the coordinates you specify are outside the range of the View Window parameters, the pointer will not be on the graph screen when it appears on the display.
•The current
x- and y-coordinate values are assigned respectively to variables X
and Y.
67
Page 82

Chapter 4 Graphing
uu
uTo turn plot points on and off in the STAT, GRAPH and TABLE Modes
uu
• To turn a plot point on
1. After drawing a graph, display the sketch menu and then perform the following
operation to make the pointer appear at the center of the screen.
!4(SKTCH)3(PLOT)2(P-On)
2. Use the cursor keys (f, c, d, e) to move the pointer to the location where
you want to plot a point and then press w.
• To turn a plot point off
Perform the same procedure as described under “To turn a plot point on” above,
except press 3 (P-Off) in place of 2 (P-On).
• To change the on/off status of a plot point
Perform the same procedure as described under “To turn a plot point on” above,
except press 4 (P-Chg) in place of 2 (P-On).
uu
uTo turn plot points on and off in the RUN or PRGM Mode
uu
The following are the syntax for turning plot points on and off in these modes.
• To turn a plot point on
x-coordinate>, <y-coordinate>
PlotOn <
• To turn a plot point off
x-coordinate>, <y-coordinate>
PlotOff <
• To change the on/off status of a plot point
x-coordinate>, <y-coordinate>
PlotChg <
68
Page 83

Graphing Chapter 4
uu
uTo draw a line between two plotted points
uu
In the STAT, GRAPH or TABLE Mode
Example To draw a line between the two points of inflection on the graph
1. After graphing the function, display the sketch menu and perform the following
operation to cause the pointer to appear on the graph screen.
2. Use the cursor keys (f, c, d, e) to move the pointer to one of the points of
inflection and press w to plot it.
3. Use the cursor keys to move the pointer to the other point of inflection.
4. Display the sketch menu and perform the following operation to draw a line between the two points.
y = x(x + 2)(x – 2)
of
Use the same View Window parameters as in the example on page
66.
!4(SKTCH)3(PLOT)1(Plot)
d ~ df ~ f
w
e ~ ec ~ c
!4(SKTCH)4(LINE)1(Line)
69
Page 84

Chapter 4 Graphing
uu
uTo draw a line in the STAT, GRAPH and TABLE Modes
uu
Example To draw a line between two points of inflection on the graph of
1. After graphing the function, display the sketch menu and perform the following
operation to cause the pointer to appear on the graph screen.
!4(SKTCH)4(LINE)2(F-Lin)
2. Use the cursor keys (f, c, d, e) to move the pointer to one of the points of
inflection and press w.
d ~ df ~ f
w
3. Use the cursor keys to move the pointer to the other point of inflection and press
w to draw the line.
e ~ ec ~ c
w
uu
uTo draw a line in the RUN or PRGM Mode
uu
The following is the syntax for drawing lines in these modes.
F-Line <
x-coordinate 1>, <y-coordinate 1>, <x-coordinate 2>, <y-coordinate 2>
y = x(x + 2)(x – 2)
70
Page 85

Graphing Chapter 4
In the RUN or PRGM Mode
Example To draw a line perpendicular to the x-axis from point (x, y) = (2, 6)
1. After drawing the graph, use the procedure under “To plot points” to move the
2. Display the sketch menu and perform the following operation to draw a straight
• The above draws a straight line between the current pointer location and the
uu
uTo draw vertical and horizontal lines
uu
The procedures presented here draw vertical and horizontal lines that pass through
a specific coordinate.
In the STAT, GRAPH or TABLE Mode
Example To draw a vertical line on the graph of y = x(x + 2)(x – 2)
1. After graphing the function, display the sketch menu and perform the following
on the graph
Use the following View Window parameters:
Xmin = –2 Ymin = –2
Xmax = 5 Ymax = 10
Xscl = 1 Yscl = 2
x, y) = (2, 0), then use the cursor key (f) to move the pointer on the
pointer to (
y = 3x.
graph
u
!4(SKTCH)3(PLOT)1(Plot)
c,awwf~f
line between the two points.
u
!4(SKTCH)4(LINE)1(Line)w
previous pointer location.
operation to display the pointer and draw a vertical line through its current location.
!4(SKTCH)[1(Vert)
y = 3x
71
Page 86

Chapter 4 Graphing
2. Use the d and e cursor keys to move the line left and right, and press w to
draw the line at the current location.
e ~ ew
•To draw a horizontal line, simply press 2 (Hztl) in place of 1 (Vert), and use
the f and c cursor keys to move the horizontal line on the display.
In the RUN or PRGM Mode
The following is the syntax for drawing vertical and horizontal lines in these modes.
• To draw a vertical line
x-coordinate>
Vertical <
• To draw a horizontal line
Horizontal <
uu
uTo clear drawn lines and points
uu
The following operation clears all drawn lines and points from the screen.
In the STAT, GRAPH or TABLE Mode
Lines and points drawn using sketch menu functions are temporary. Display the
sketch menu and press 1 (Cls) to clear drawn lines and points, leaving only the
original graph.
In the RUN or PRGM Mode
The following is the syntax for clearing drawn lines and points, as well as the graph
itself.
Cls
y-coordinate>
72
Page 87

Chapter
Table & Graph
The Table & Graph menu makes it possible to generate numeric
tables from functions stored in memory. You can also use multiple
functions to generate tables. Since Table & Graph uses the same
list of functions that the GRAPH Mode uses for graphing, there is
no need to input the same functions in different modes.
•You can specify the range and increment of values assigned to
variables for table value generation.
•You can assign list values to variables.
•In addition to graphing of stored functions, you can also plot table
values generated by Table & Graph itself.
•Table values can be assigned to a list.
1. Storing a Function
2. Deleting a Function
3. Assigning Values to a Variable
4. Generating a Numeric Table
5. Editing a Table
6. Graphing a Function
7. Assigning Numeric Table Contents to a List
5
Page 88

Chapter 5 Table and Graph
To enter the Table Mode, press m to display the Main Menu, use the cursor keys to
select the TABLE icon, and then press w.
This is the initial Table Mode screen. To generate a table, you must first specify the
variable range.
The menu at the bottom of the display looks like the one shown here when the Var
item of the set-up screen is set to a list name (indicating that variable values should
P.8
be obtained from a list).
1. Storing a Function
Example To store the function y = 3 x2 – 2 in memory area Y1
Use f and c to move the highlighting in the TABLE Mode function list to the
memory area where you want to store the function. Next, input the function and
press w to store it.
2. Deleting a Function
Use f and c to move the highlighting to the memory area that contains the
function you want to delete.
Press 2 (DEL).
Press 1 (YES) to delete the selected function or 4 (NO) to abort the delete
operation without deleting anything.
P.52
The procedures for storing and deleting functions are identical to those used in the
GRAPH Mode.
3. Assigning Values to a Variable
You can use either one of two methods to assign values to a variable: automatic
assignment within a specified range, and assignment of values from a list. The standard default method is automatic assignment within a specified range.
74
Page 89

Table and Graph Chapter 5
uu
uTo assign values automatically within a specified range
uu
ExampleTo assign values from –3 to 3, in increments of 1 (seven values
To interrupt automatic assignment of variables and return to the function storage
screen, press Q.
uu
uTo assign values from a list
uu
Press ! Z to display the set-up screen.
If necessary, you can press [ to display a menu of other lists (4, 5, 6). The following shows the operation required to select List 6.
total)
3(RANG)
-dwdwbw
Strt: ................. Variable x start value
End: ................ Variable x end value
ptch: ................ Variable x value change
!Z
[3(List6)
123 4
After making the set-up screen setting you want, press Q to return to the Function
List. Note that the [RANG] item does not appear in the function key menu at the
bottom of the screen when a list is selected for assignment of variable values.
75
Page 90

Chapter 5 Table and Graph
4. Generating a Numeric Table
Before actually generating a numeric table, you must first select the functions you
want to use.
Use the f and c cursor keys to move the highlighting to the function you want to
use and then press 1 (SEL) to select it.
The “=” symbols of selected functions are highlighted on the display. You can select
more than one function for table generation.
In this display, Y1 and Y3 are selected.
Press 4 (TABL) or w to generate a numeric table.
•In this example, values are assigned automatically.
This display shows the generated numeric table. Though this example display shows
only the values for function Y1, values for function Y3 were also generated.
Each cell can hold up to six digits (negative sign takes up one digit).
You can move the cursor around the table using the cursor (f, c, d, e) keys.
The following points apply to cursor position and movement.
• The value contained in the currently selected cell appears at the bottom of the
display, with all current display attributes (number of decimal place, number of
significant digit, and exponential display range settings) applied.
•Moving the cursor off the screen causes the table to scroll when there are cells
off the top, bottom, left, or right .
•When the cursor is located in any function value cell (Y1, Y2, etc.), the function is
shown at the top of the display.
• If you change a value in column X, the corresponding function value is automatically updated using the new value for X.
1234
To return to the Function List, press 1 (FORM).
76
Page 91

Table and Graph Chapter 5
5. Editing a Table
You can use the editing screen to add lines to or delete lines from an existing table.
Press 2 (ROW) to display the Table Editing Menu.
2(ROW)
1234
1 (DEL) ........ Deletes line where cursor is located.
2 (INS) ......... Inserts new line where cursor is located.
3 (ADD) ....... Insert new line below line where cursor is located.
6. Graphing a Function
You can use the two following function keys to produce a graph using the numeric
table currently on the screen.
3 (G-CON) ... Graph with connected plot points
4 (G-PLT)..... Graph with plotted points (unconnected)
•Note that you can also produce a G-PLT (4) graph by pressing w while a
numeric table is on the screen.
Example To graph the function Y1 = 2X, whose table of numeric values is
currently on the screen
1234
4(G-PLT)
3(G-CON)
77
Page 92

Chapter 5 Table and Graph
Graphing a table whose values were generated using more than one function causes
the graphs of all the functions to be drawn at the same time. You can set
P.48
axis parameters using the View Window.
Press u or A to return to the numeric table screen from a graph. Pressing u
again goes back to the graph. You can use u to switch between the graph and its
table as long as you do not clear the graph.
7. Assigning Numeric Table Contents to
a List
You can assign a column of values from a table into a list. Simply use d and e to
move the cursor into the column whose values you want to copy. The cursor can be
in any row of the column. The copy operation is performed by pressing K to display the Option Menu, and then pressing 2 (LMEM).
K1(LIST)2(LMEM)
Use the first function menu to copy the column’s values to List 1 (1) to List 4 (4).
To copy to List 5 or List 6, press [ and then 1 (List 5) or 2 (List 6).
x- and y-
1234[
78
Page 93

Chapter
List Function
A list is a kind of container that you can use to store multiple data items.
This calculator lets you have up to six lists in memory, and their
contents can be used in arithmetic calculations, statistical calculations and for graphing.
Element number Display range Cell
List 1 List 2 List 3 List 4 List 5 List 6
1 56 1107 3.5 40
2 37 275 6 00
3 21 4122 2.1 00
4 69 887 4.4 20
5 40 16298 3 00
6 48 3248 6.8 30
7 93 64338 2 90
8 30 12849 8.7 00
••••••
••••••
••••••
••••••
1. List Operations
2. Editing and Rearranging Lists
3. Manipulating List Data
4. Arithmetic Calculations Using Lists
Column
6
List name
Row
Page 94

Chapter 6 List Function
kk
k List Data Linking
kk
List operation
Example:
List 1 + List 2
{1, 2, 3} + {4, 5, 6}
List 1 + 3
GraphOperation
List internal operations
a
w
80
LIST
List data can be assigned to a
variable for generation of a table
(defined using set-up screen).
Table
K
1(LIST)
2(LMEM)
Graphing with
list data
Example:
Y1=List 1X
Copying table result to a list
Specific selected data can
be copied to a list.
Page 95

List Function Chapter 6
1. List Operations
Select the LIST icon in the Main Menu and enter the LIST Mode to input data into a
list and to manipulate list data.
uu
uTo input values one-by-one
uu
Use d and e to move between lists, and f and c to move between cells
inside of a list.
The screen automatically scrolls when the cursor is located at the edge of the screen.
For our example, we will start by locating the cursor in Cell 1 of List 1.
1. Input a value and press w to store it in the list.
dw
2. The cursor automatically moves down to the next cell for input.
Let’s continue our example by inputting the values 4 and 5.
ewfw
81
Page 96

Chapter 6 List Function
uu
uTo batch input a series of values
uu
1. Use f to move the cursor to the list name.
ffff
2. Use d or e to move the cursor to another list.
e
3. Press !{, and then input the values you want, pressing , between each
one. Press !} after inputting the final value.
!{g,h,i!}
4. Press w to store all of the values in your list.
w
•Remember that a comma separates values, so you should not input a comma
after the final value of the set you are inputting.
Right: {34, 53, 78}
Wrong: {34, 53, 78,}
2. Editing and Rearranging Lists
kk
k Editing List Values
kk
uu
uTo change a cell value
uu
Use d or e to move the cursor to the cell whose value you want to change. Input
the new value and press w to replace the old data with the new one.
82
Page 97

List Function Chapter 6
uu
uTo delete a cell
uu
1. Use d, e, f, or c to move the cursor to the cell you want to delete.
cd
2. Press [ to display the Cell Operation Menu.
[
1 234
3. Press 1 (DEL) to delete the selected cell and cause everything below it to be
shifted up.
1(DEL)
•Note that the above cell delete operation does not affect cells in other lists. If
the data in the list whose cell you delete is somehow related to the data in
neighboring lists, deleting a cell can cause related values to become misaligned.
uu
uTo delete all cells in a list
uu
1. Use d, e , f or c to move the cursor to the name of the list whose cells
you want to delete.
83
Page 98

Chapter 6 List Function
2. Press [ to display the Cell Operation Menu (if it is not already displayed).
[
3. Press 2 (DEL-A). The function menu changes to confirm whether you really
want to delete all the cells in the list.
2(DEL-A)
4. Press 1 (YES) to delete all the cells in the selected list or 4 (NO) to abort the
delete operation without deleting anything.
1(YES)
uu
uTo insert a new cell
uu
Use d, e, f, or c to move the cursor to the location where you want to insert
the new cell. In this example, we will reinsert a cell containing the value 4, which we
deleted above.
1. Press [ to display the Cell Operation Menu (if it is not already displayed).
2. Press 3 (INS) to insert a new cell, which contains a value of 0, causing every-
thing below it to be shifted down.
3(INS)
1 2 34
1 234
123 4
84
Page 99

List Function Chapter 6
3. Input the value you want into the new cell (4 in our example) and press w.
ew
•Note that the above cell insert operation does not affect cells in other lists. If the
data in the list where you insert a cel l is somehow related to the data in
neighboring lists, inserting a cell can cause related values to become misaligned.
kk
k Sorting List Values
kk
You can sort lists into either ascending order or descending order. The current cursor location does not matter in the following procedures.
uu
uTo sort a single list
uu
Ascending order
1. While the lists are on the screen, press [ to display the Operation Menu and
then press 1 (SRT-A).
[1(SRT-A)
2. The prompt “How Many Lists? (H)” appears to ask how many lists you want to
sort. Here we will input 1 to indicate we want to sort only one list.
bw
3. In response to the “Select List (L)” prompt, input the number of the list you want to
sort. Here we will input 2 to specify sorting of List 2.
cw
The values in List 2 are sorted into ascending order.
85
Page 100

Chapter 6 List Function
Descending order
Use the same procedure as that for the ascending order sort. The only difference is
that you should press 2 (SRT-D) in place of 1 (SRT-A).
uu
uTo sort multiple lists
uu
You can link multiple lists together for a sort so that all of their cells are rearranged in
accordance with the sorting of a base list. The base list is sorted into either ascending order or descending order, while the cells of the linked lists are arranged so that
the relative relationship of all the rows is maintained.
Ascending order
1. While the lists are on the screen, press 1 (SRT-A).
1(SRT-A)
2. The prompt “How Many Lists? (H)” appears to ask how many lists you want to
sort. Here we will sort one base list linked to one other list, so we should input 2.
cw
3. In response to the “Select Base List (B)” prompt, input the number of the list you
want to sort into ascending order. Here we will specify List 1.
bw
4. In response to the “Select Second List (L)” prompt, input the number of the list
you want to link to the base list. Here we will specify List 2.
cw
The values in List 1 are sorted into ascending order, and the cells of List 2 are also
rearranged to keep the same relationship with the List 1 cells.
Descending order
Use the same procedure as that for the ascending order sort. The only difference is
86
that you should press 2 (SRT-D) in place of 1 (SRT-A).
 Loading...
Loading...