
EN
fx-570ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
User’s Guide
CASIO Worldwide Education Website
https://edu.casio.com
Manuals are available in multi languages at
https://world.casio.com/manual/calc/

Table of Contents
Before Using the Calculator.................................................... 4
About this Manual.................................................................................... 4
Initializing the Calculator..........................................................................4
Precautions..............................................................................................4
Safety Precautions..........................................................................................4
Handling Precautions......................................................................................5
Getting Started.........................................................................................5
Removing the Hard Case................................................................................5
Turning Power On and Off.............................................................................. 6
Adjusting Display Contrast..............................................................................6
Key Markings.................................................................................................. 6
Reading the Display........................................................................................7
Using Menus...................................................................................................9
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup.............................10
Calculation Mode................................................................................... 10
Configuring the Calculator Setup...........................................................10
Initializing Calculator Settings....................................................................... 14
Inputting Expressions and Values........................................16
Basic Input Rules...................................................................................16
Inputting with Natural Display................................................................ 17
√
Form Calculation Range.................................................................... 17
Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)....18
Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)...........................................19
Correcting and Clearing an Expression................................................. 19
Basic Calculations..................................................................20
Toggling Calculation Results..................................................................20
Fraction Calculations............................................................................. 21
Percent Calculations..............................................................................22
Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations............................22
Multi-Statements....................................................................................23
Using Engineering Notation................................................................... 23
Calculation History and Replay..............................................................24
Calculation History........................................................................................24
Replay...........................................................................................................24
Using Memory Functions....................................................................... 25
Answer Memory (Ans)...................................................................................25
Variables (A, B, C, D, E, F, M, X, Y).............................................................. 25
Independent Memory (M)..............................................................................26
Clearing the Contents of All Memories..........................................................26
1

Function Calculations............................................................27
Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e............................................................ 27
Trigonometric Functions........................................................................ 27
Hyperbolic Functions............................................................................. 27
Angle Unit Conversion........................................................................... 28
Exponential Functions............................................................................28
Logarithmic Functions............................................................................28
Power Functions and Power Root Functions.........................................29
Integration Calculations......................................................................... 30
Integration Calculation Precautions.............................................................. 31
Tips for Successful Integration Calculations................................................. 31
Differential Calculations......................................................................... 32
Differential Calculation Precautions.............................................................. 33
Σ Calculations........................................................................................ 33
Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion............................................ 34
Factorial Function (!)..............................................................................35
Absolute Value Function (Abs)...............................................................35
Random Number (Ran#)........................................................................35
Random Integer (RanInt#)..................................................................... 35
Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)............................................. 36
Rounding Function (Rnd).......................................................................36
Using CALC........................................................................................... 37
Using SOLVE.........................................................................................38
Solution Screen Contents............................................................................. 39
Continue Screen........................................................................................... 40
Scientific Constants............................................................................... 41
Metric Conversion..................................................................................43
Using Calculation Modes.......................................................45
Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)...............................................45
CMPLX Mode Calculation Examples............................................................ 46
Using a Command to Specify the Calculation Result Format....................... 46
Statistical Calculations (STAT)...............................................................46
Inputting Data................................................................................................47
Statistics Calculation Screen.........................................................................49
Using the Statistics Menu..............................................................................49
Calculating Estimated Values........................................................................54
Performing Normal Distribution Calculations................................................ 54
Base-n Calculations (BASE-N).............................................................. 55
Specifying the Number Mode of a Particular Input Value..............................57
Converting a Calculation Result to another Type of Value............................57
Logical and Negation Operations..................................................................57
Equation Calculations (EQN).................................................................59
Changing the Current Equation Type Setting................................................60
EQN Mode Calculation Examples.................................................................60
2

Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)................................................................61
Matrix Answer Memory................................................................................. 63
Assigning and Editing Matrix Variable Data.................................................. 63
Matrix Calculation Examples.........................................................................64
Creating a Numerical Table from a Function (TABLE)...........................65
Vector Calculations (VECTOR)..............................................................67
Vector Answer Memory.................................................................................68
Assigning and Editing Vector Variable Data..................................................68
Vector Calculation Examples........................................................................ 69
Technical Information............................................................ 71
Errors..................................................................................................... 71
Displaying the Location of an Error...............................................................71
Clearing the Error Message.......................................................................... 71
Error Messages.............................................................................................71
Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator... ...............................74
Replacing the Battery.............................................................................74
Calculation Priority Sequence................................................................75
Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision........................... 76
Calculation Range and Precision..................................................................76
Function Calculation Input Ranges and Precision........................................ 77
Specifications.........................................................................................79
Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator.......................................... 80
Frequently Asked Questions.................................................81
Frequently Asked Questions..................................................................81
3

Before Using the Calculator
About this Manual
• In no event shall CASIO Computer Co., Ltd. be liable to anyone for
special, collateral, incidental, or consequential damages in connection
with or arising out of the purchase or use of this product and items that
come with it.
• Moreover, CASIO Computer Co., Ltd. shall not be liable for any claim of
any kind whatsoever by any other party arising out of the use of this
product and the items that come with it.
• Unless specifically stated, all sample operations in this manual assume
that the calculator is in its initial default setup. Use the procedure under
"Initializing the Calculator" to return the calculator to its initial default
setup.
• The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
• The displays and illustrations (such as key markings) shown in this
manual are for illustrative purposes only, and may differ somewhat from
the actual items they represent.
• QR Code is a registered trademark of DENSO WAVE INCORPORATED
in Japan and in other countries.
• Company and product names used in this manual may be registered
trademarks or trademarks of their respective owners.
Initializing the Calculator
Perform the following procedure when you want to initialize the calculator
and return the calculation mode and setup to their initial default settings.
Note that this operation also clears all data currently in calculator memory.
(CLR) (All) (Yes)
Precautions
Be sure to read the following safety precautions before using the
calculator.
Safety Precautions
Battery
• Keep batteries out of the reach of small children.
4

• Use only the type of battery specified for this calculator in this
manual.
Handling Precautions
• Even if the calculator is operating normally, replace the battery
according to the schedule shown below. Continued use after the
specified number of years may result in abnormal operation. Replace
the battery immediately after display figures become dim.
fx-570ES PLUS: Every 2 years
fx-991ES PLUS: Every 3 years
• A dead battery can leak, causing damage to and malfunction of the
calculator. Never leave a dead battery in the calculator.
• The battery that comes with the calculator is for factory testing,
and it discharges slightly during shipment and storage. Because of
these reasons, its battery life may be shorter than normal.
• Do not use a nickel-based primary battery with this product.
Incompatibility between such batteries and product specifications can
result in shorter battery life and product malfunction.
• Avoid use and storage of the calculator in areas subjected to
temperature extremes, and large amounts of humidity and dust.
• Do not subject the calculator to excessive impact, pressure, or bending.
• Never try to take the calculator apart.
• Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the exterior of the calculator.
• Whenever discarding the calculator or batteries, be sure to do so in
accordance with the laws and regulations in your particular area.
Getting Started
Removing the Hard Case
Before using the calculator, slide its hard case downwards to remove it,
and then affix the hard case to the back of the calculator as shown in the
illustration below.
5

Turning Power On and Off
• Press
to turn on the calculator.
• Press (OFF) to turn off the calculator.
Note
• The calculator also will turn off automatically after approximately 10 minutes of nonuse. Press the
key to turn the calculator back on.
Adjusting Display Contrast
1. Press
2. Use and to adjust display contrast.
3. After the setting is the way you want, press
(SETUP) ( CONT ).
.
Important!
• If adjusting display contrast does not improve display readability, it probably means
that battery power is low. Replace the battery.
Key Markings
Pressing the
alternate function of the second key. The alternate function is indicated by
the text printed above the key.
or key followed by a second key performs the
(1) Keycap function (2) Alternate function
• Characters enclosed in brackets (┌ ┐) that are the same color as i are
used in the CMPLX Mode.
• Characters enclosed in brackets (┌ ┐) that are the same color as DEC,
HEX, BIN, and OCT are used in the BASE-N Mode.
• The following shows an example of how an alternate function operation
is represented in this manual.
6

Example: (sin-1)* 1
* Indicates the function that is accessed by the key operation (
) before it. Note that this is not part of the actual key operation
you perform.
• The following shows an example of how a key operation to select an onscreen menu item is represented in this manual.
Example: (COMP)
* Indicates the menu item that is selected by the number key
operation (
operation you perform.
• The cursor key is marked with four arrows, indicating direction, as
shown in the illustration nearby. In this manual, cursor key operation is
indicated as
) before it. Note that this is not part of the actual key
, , , and .
*
Reading the Display
The two-line display makes it possible to view both the input expression
and its result at the same time.
(1) Input expression
(2) Calculation result
(3) Indicators
• If a
means the displayed calculation result continues to the right. Use
and to scroll the calculation result display.
• If a indicator appears on the right side of the input expression, it
means the displayed calculation continues to the right. Use
to scroll the input expression display. Note that if you want to scroll the
input expression while both the and indicators are displayed, you
will need to press first and then use and to scroll.
indicator appears on the right side of the calculation result, it
and
7

Display indicators
This indicator: Means this:
The keypad has been shifted by pressing the
key. The keypad will unshift and this indicator will
disappear when you press a key.
The alpha input mode has been entered by
pressing the
be exited and this indicator will disappear when
you press a key.
M There is a value stored in independent memory.
The calculator is standing by for input of a variable
STO
RCL
STAT The calculator is in the STAT Mode.
CMPLX The calculator is in the CMPLX Mode.
name to assign a value to the variable. This
indicator appears after you press
The calculator is standing by for input of a variable
name to recall the variable's value. This indicator
appears after you press
key. The alpha input mode will
.
(STO).
MAT The calculator is in the MATRIX Mode.
VCT The calculator is in the VECTOR Mode.
The default angle unit is degrees.
The default angle unit is radians.
The default angle unit is grads.
FIX A fixed number of decimal places is in effect.
SCI A fixed number of significant digits is in effect.
Math Natural Display is selected as the display format.
8

Calculation history memory data is available and
can be replayed, or there is more data above/
below the current screen.
Disp
The display currently shows an intermediate result
of a multi-statement calculation.
Important!
• For some type of calculation that takes a long time to execute, the display may show
only the above indicators (without any value) while it performs the calculation
internally.
Using Menus
Some of the calculator's operations are performed using menus. Pressing
or , for example, will display a menu of applicable functions.
The following are the operations you should use to navigate between
menus.
• You can select a menu item by pressing the number key that
corresponds to the number to its left on the menu screen.
• The
another menu below the current one. The indicator means another
menu above. Use
• To close a menu without selecting anything, press .
indicator in the upper right corner of a menu means there is
and to switch between menus.
9

Calculation Modes and
Calculator Setup
Calculation Mode
Before starting a calculation, you must first enter the correct mode as
indicated in the table below.
When you want to perform this type of
operation:
General calculations
Complex number calculations
Statistical and regression calculations
Calculations involving specific number
systems (binary, octal, decimal, hexadecimal)
Equation solution
Matrix calculations
Generation of a numerical table based on an
expression
Perform this key
operation:
(COMP)
(CMPLX)
(STAT)
(BASE-N)
(EQN)
(MATRIX)
(TABLE)
Vector calculations
Note
• The initial default calculation mode is the COMP Mode.
(VECTOR)
Configuring the Calculator Setup
Pressing
control how the calculations are executed and displayed. The setup menu
has two screens, which you can jump between using and .
(SETUP) displays the setup menu, which you can use to
10
Underlined ( ___ ) settings are initial defaults.
Specifying the Display Format
To specify this
display format:
Natural Display
(MthIO-MathO)
Natural Display
(MthIO-LineO)
Linear Display
(LineIO)
Natural Display (MthIO-MathO, MthIO-LineO) causes fractions, irrational
numbers, and other expressions to be displayed as they are written on
paper.
MthIO-MathO displays input and calculation results using the same format
as they are written on paper.
MthIO-LineO displays input the same way as MthIO-MathO, but
calculation results are displayed in linear format.
Linear Display (LineIO) causes fractions and other expressions to be
displayed in a single line.
Perform this key operation:
(SETUP) (MthIO) (MathO)
(SETUP) (MthIO) (LineO)
(SETUP) (LineIO)
Examples:
MthIO-MathO
MthIO-LineO
(Number Format: Norm 1)
11

MthIO-LineO
(Number Format: Norm 2)
LineIO
(Number Format: Norm 1)
Note
• The calculator switches to Linear Display automatically whenever you enter the STAT,
BASE-N, MATRIX, or VECTOR Mode.
Specifying the Default Angle Unit
To specify this as the
Perform this key operation:
default angle unit:
Degrees
Radians
Grads
(SETUP) (Deg)
(SETUP) (Rad)
(SETUP) (Gra)
90°= π/2 radians = 100 grads
Specifying the Number Format
Specifies the number of digits for display of a calculation result.
To specify this: Perform this key operation:
Number of Decimal
(SETUP) (Fix) -
Places
Number of Significant
Digits
Exponential Display
Range
(SETUP) (Sci) -
(SETUP) (Norm) (Norm 1) or
(Norm 2)
12

Fix: The value you specify (from 0 to 9) controls the number of decimal
places for displayed calculation results. Calculation results are rounded off
to the specified digit before being displayed.
Example: (LineIO) 100 ÷ 7 = 14.286 (Fix 3)
14.29 (Fix 2)
Sci: The value you specify (from 0 to 9) controls the number of significant
digits for displayed calculation results. Calculation results are rounded off
to the specified digit before being displayed.
Example: (LineIO) 1 ÷ 7 = 1.4286 × 10-1 (Sci 5)
1.429 × 10-1 (Sci 4)
1.428571429 × 10-1 (Sci 0)
Norm: Selecting one of the two available settings (Norm 1, Norm 2)
determines the range in which results will be displayed in exponential
format. Outside the specified range, results are displayed using non-
exponential format.
Norm 1: 10-2 > |x|, |x| ≧ 10
Norm 2: 10-9 > |x|, |x| ≧ 10
10
10
Example: (LineIO) 1 ÷ 200 = 5 × 10-3 (Norm 1)
0.005 (Norm 2)
Specifying the Fraction Display Format
To specify this
fraction display
Perform this key operation:
format:
Mixed
Improper
(SETUP) (ab/c)
(SETUP) (d/c)
Specifying the Complex Number Format
To specify this
complex number
Perform this key operation:
format:
Rectangular
(SETUP) (CMPLX) (a+bi)
Coordinates
Polar Coordinates
(SETUP) (CMPLX) (r∠θ)
13

Specifying the Stat Format
Specifies whether or not to display a FREQ (frequency) column in the
STAT Mode Statistics Editor.
To specify this: Perform this key operation:
Show FREQ Column
Hide FREQ Column
(SETUP) (STAT) (ON)
(SETUP) (STAT) (OFF)
Specifying the Decimal Point Display Format
Specifies whether to display a dot or a comma for the calculation result
decimal point. A dot is always displayed during input.
To specify this
decimal point
Perform this key operation:
display format:
Dot (.)
Comma (,)
Note
(SETUP) (Disp) (Dot)
(SETUP) (Disp) (Comma)
• When dot is selected as the decimal point, the separator for multiple results is a
comma (,). When comma is selected, the separator is a semicolon (;).
Adjusting Display Contrast
(SETUP) ( CONT )
See "Getting Started" for details.
Initializing Calculator Settings
Perform the following procedure to initialize the calculator, which returns
the calculation mode to COMP and returns all other settings, including
setup menu settings, to their initial defaults.
(CLR) (Setup) (Yes)
This setting: Is initialized to this:
Calculation Mode COMP
Display Format MthIO-MathO
14

Angle Unit Deg
Number Format Norm 1
Fraction Display
Format
Complex Number
Format
Stat Format OFF
Decimal Point Dot
d/c
a+bi
15

Inputting Expressions and
Values
Basic Input Rules
Calculations can be input in the same form as they are written. When you
press
automatically and the result will appear on the display.
Example 1: 4 × sin30 × (30 + 10 × 3) = 120
the priority sequence of the input calculation will be evaluated
*1 Input of the closing parenthesis is required for sin, sinh, and other
functions that include parentheses.
*2 These multiplication symbols (×) can be omitted. A multiplication
symbol can be omitted when it occurs immediately before an opening
parenthesis, immediately before sin or other function that includes
parentheses, immediately before the Ran# (random number) function,
or immediately before a variable (A, B, C, D, E, F, M, X, Y), scientific
constants, π or e.
*3 The closing parenthesis immediately before the
omitted.
Example 2: Input example omitting
above example.
30 30 10 3
4
*2
and
operation can be
*3
operations in the
Note
• If the calculation becomes longer than the screen width during input, the screen will
scroll automatically to the right and the
this happens, you can scroll back to the left by using
• When Linear Display is selected, pressing
beginning of the calculation, while will jump to the end.
indicator will appear on the display. When
and to move the cursor.
will cause the cursor to jump to the
16

• When Natural Display is selected, pressing while the cursor is at the end of the
input calculation will cause it to jump to the beginning, while pressing
cursor is at the beginning will cause it to jump to the end.
• You can input up to 99 bytes for a calculation. Each numeral, symbol, or function
normally uses one byte. Some functions require three to 13 bytes.
• The cursor will change shape to
remaining. If this happens, end calculation input and then press
when there are 10 bytes or less of allowed input
while the
.
Inputting with Natural Display
Selecting Natural Display makes it possible to input and display fractions
and certain functions (log,
Abs) just as they are written in your textbook.
, , , , , , , , , ∫, d/dx, Σ,
Example:
1 + √
(MthIO-MathO)
2
2 2 1 2
Important!
• Certain types of expressions can cause the height of an input expression to be greater
than one display line. The maximum allowable height of an input expression is two
display screens (31 dots × 2). Further input will become impossible if the height of the
calculation you are inputting exceeds the allowable limit.
• Nesting of functions and parentheses is allowed. Further input will become impossible
if you nest too many functions and/or parentheses. If this happens, divide the
calculation into multiple parts and calculate each part separately.
Note
2 + √2
• When you press and obtain a calculation result using Natural Display, part of the
expression you input may be cut off. If you need to view the entire input expression
again, press
Form Calculation Range
√
and then use and to scroll the input expression.
Results that include square root symbols can have up to two terms (an
integer term is also counted as a term).
*
d√e
, √ form calculation
f
When a calculation result takes the form ±
a√b
±
c
results are displayed using formats like those shown below.
17

± a√b, ± d ± a√b,
*
The ranges of the coefficients (a, b, c, d, e, f) are as shown below.
1 ≦ a < 100, 1 < b < 1000, 1 ≦ c < 100
0 ≦ d < 100, 0 ≦ e < 1000, 1 ≦ f < 100
(a, b, c, d, e, f are integers)
Example:
10√2 + 15 × 3√3 = 45√3 + 10√2 √ form
99√
999 = 3129.089165 (= 297√111) decimal form
± a'√b ± d'√e
c'
Using Values and Expressions as
Arguments (Natural Display only)
A value or an expression that you have already input can be used as the
7
argument of a function. After you have input
make it the argument of √
Example: To input 1 +
As shown above, the value or expression to the right of the cursor after
(INS) are pressed becomes the argument of the function that is
specified next. The range encompassed as the argument is everything up
to the first open parenthesis to the right, if there is one, or everything up to
the first function to the right (sin(30), log2(4), etc.)
This capability can be used with the following functions:
( ), , , ( ), ( ), ( ),
( ), ( ), , , ( ), (Abs).
, resulting in
7
and then change it to 1 +
6
√
1
, for example, you can
6
7
.
6
7
(MthIO-MathO)
√
6
7 6
(INS)
,
18

Overwrite Input Mode (Linear
Display only)
You can select either insert or overwrite as the input mode, but only while
Linear Display is selected. In the overwrite mode, text you input replaces
the text at the current cursor location. You can toggle between the insert
and overwrite modes by performing the operations:
cursor appears as " " in the insert mode and as " " in the overwrite
mode.
Note
• Natural Display always uses the insert mode, so changing display format from Linear
Display to Natural Display will automatically switch to the insert mode.
(INS). The
Correcting and Clearing an
Expression
To delete a single character or function:
Move the cursor so it is directly to the right of the character or function you
want to delete, and then press
In the overwrite mode, move the cursor so it is directly under the character
or function you want to delete, and then press
To insert a character or function into a calculation:
Use
insert the character or function and then input it. Be sure always to use the
insert mode if Linear Display is selected.
To clear all of the calculation you are inputting:
Press
and to move the cursor to the location where you want to
.
.
.
19

Basic Calculations
Use the
basic calculations.
key to enter the COMP Mode when you want to perform
(COMP)
Toggling Calculation Results
While Natural Display is selected, each press of will toggle the
currently displayed calculation result between its fraction form and decimal
form, its √ form and decimal form, or its π form and decimal form.
1
Example 1: π ÷ 6 =
π = 0.5235987756 (MthIO-MathO)
6
1
(π) 6
Example 2: (√2 + 2) × √3 = √6 + 2√3 = 5.913591358 (MthIO-MathO)
2 2 3
While Linear Display is selected, each press of
currently displayed calculation result between its decimal form and fraction
form.
1
Example 3: 1 ÷ 5 = 0.2 =
4
1
=
Example 4: 1 -
= 0.2 (LineIO)
5
5
(LineIO)
5
1
5
π
6
√6 + 2√3 5.913591358
will toggle the
0.5235987756
0.2 1 5
4 5
1
20
1 5 0.2

Important!
• Depending on the type of calculation result that is on the display when you press the
key, the conversion process may take some time to perform.
• With certain calculation results, pressing the
value.
• You cannot switch from decimal form to mixed fraction form if the total number of digits
used in the mixed fraction (including integer, numerator, denominator, and separator
symbols) is greater than 10.
Note
• With Natural Display (MathO), inputting one of the following calculations and then
pressing
calculation that results in a √
Pressing
result. The √
instead of will display the calculation result in decimal form: a
form or π form expression, a division calculation.
after that will switch to the fraction form or π form of the calculation
form of the result will not appear in this case.
key will not convert the displayed
Fraction Calculations
Note that the input method for fractions is different, depending upon
whether you are using Natural Display or Linear Display.
2
1
Example 1:
+
3
(MthIO-MathO) 2
Example 2: 4 - 3
(MthIO-MathO) 4
7
=
2
6
or
(LineIO) 2
1
1
=
2
2
3 1 2
2 3 1 2
3 1 2 7 6
( ) 3 1 2
7
6
7
6
1
2
(LineIO) 4
Note
• Mixing fractions and decimal values in a calculation while Linear Display is selected
will cause the result to be displayed as a decimal value.
• Results of calculations that mix fraction and decimal values are always decimal.
3 1 2 1 2
21

• Fractions in calculation results are displayed after being reduced to their lowest terms.
To switch a calculation result between improper fraction and mixed
fraction form:
Perform the following key operation:
To switch a calculation result between fraction and decimal form:
Press
.
(a
bcd
)
c
Percent Calculations
Inputting a value and pressing
become a percent.
Example 1: 150 × 20% = 30
150
Example 2: Calculate what percentage of 880 is 660 (75%)
660
Example 3: Increase 2500 by 15% (2875)
2500
Example 4: Decrease 3500 by 25% (2625)
3500
2500 15 (%) 2875
3500 25 (%) 2625
20 (%) 30
880 (%) 75
(%) causes the input value to
Degree, Minute, Second
(Sexagesimal) Calculations
You can perform calculations using sexagesimal values, and convert
values between sexagesimal and decimal.
Performing an addition or subtraction operation between sexagesimal
values, or a multiplication or division operation between a sexagesimal
value and a decimal value will cause the result to be displayed as a
sexagesimal value.
You also can convert between sexagesimal and decimal.
The following is the input format for a sexagesimal value: {degrees}
{minutes} {seconds} .
22

Note
• You must always input something for the degrees and minutes, even if they are zero.
Example 1: 2°20’30” + 39’30” = 3°00’00”
2
20 30 0 39 30 3°0’0”
Example 2: Convert 2°15’18” to its decimal equivalent.
2
15 18 2°15’18”
(Converts sexagesimal to decimal.)
(Converts decimal to sexagesimal.)
2.255
2°15’18”
Multi-Statements
You can use the colon character (:) to connect two or more expressions
and execute them in sequence from left to right when you press
Example: 3 + 3 : 3 × 3
3 (:) 3 3 6
3
.
Using Engineering Notation
A simple key operation transforms a displayed value to engineering
notation.
9
Example 1: Transform the value 1234 to engineering notation, shifting the
decimal point to the right.
1234
Example 2: Transform the value 123 to engineering notation, shifting the
decimal point to the left.
123
(←) 0.123×10
23
1234
1.234×10
1234×10
123
3
0
3

(←) 0.000123×10
Calculation History and Replay
Calculation History
In the COMP, CMPLX, or BASE-N Mode, the calculator remembers up to
approximately 200 bytes of data for the newest calculation.
You can scroll through calculation history contents using
Example:
and .
6
1 + 1 = 2
2 + 2 = 4
3 + 3 = 6
(Scrolls back.)
(Scrolls back again.)
Note
• Calculation history data is all cleared whenever you press , when you change to a
different calculation mode, when you change the display format, or whenever you
perform the following operations:
(CLR) (All) (Yes).
1 1 2
2
2 4
3
3 6
(CLR) (Setup) (Yes),
Replay
While a calculation result is on the display, you can press
edit the expression you used for the previous calculation.
or to
4
2
Example: 4 × 3 + 2 = 14
4 × 3 - 7 = 5
(Continuing)
4
3 2 14
7 5
24

Using Memory Functions
Answer Memory (Ans)
The last calculation result obtained is stored in Ans (answer) memory.
Ans memory contents are updated whenever a new calculation result is
displayed.
Answer Memory contents are updated whenever you execute a calculation
using any one of the following keys: , , , (M-), ,
(STO).
Answer Memory can hold up to 15 digits.
Example 1: To divide the result of 3 × 4 by 30 (LineIO)
4 12
3
(Continuing)
Example 2: To perform the calculations shown below:
123 456 579
(Continuing) 789
30
Variables (A, B, C, D, E, F, M, X, Y)
Your calculator has nine preset variables named A, B, C, D, E, F, M, X,
and Y.
You can assign values to variables and use the variables in calculations.
Example:
To assign the result of 3 + 5 to variable A
3
5 (STO) (A) 8
To multiply the contents of variable A by 10
(Continuing)
(A) 10 80
25

To recall the contents of variable A
(Continuing)
To clear the contents of variable A
0 (STO) (A) 0
(A) 8
Independent Memory (M)
You can add calculation results to or subtract results from independent
memory.
The "M" indicator appears on the display when there is any value other
than zero stored in independent memory.
Example:
To clear the contents of M
0
To add the result of 10 × 5 to M
(Continuing) 10 5 50
(STO) (M) 0
To subtract the result of 10 + 5 from M
(Continuing) 10 5 (M-) 15
To recall the contents of M
(Continuing) (M) 35
Note
• Variable M is used for independent memory.
Clearing the Contents of All Memories
Ans memory, independent memory, and variable contents are retained
even if you press
calculator.
Perform the following procedure when you want to clear the contents of all
memories.
, change the calculation mode, or turn off the
(CLR) (Memory) (Yes)
26

Function Calculations
Use the
function calculations.
Note: Using functions can slow down a calculation, which may delay
display of the result. Do not perform any subsequent operation while
waiting for the calculation result to appear. To interrupt an ongoing
calculation before its result appears, press
key to enter the COMP Mode when you want to perform
(COMP)
.
Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
π is displayed as 3.141592654, but π = 3.14159265358980 is used for
internal calculations.
e is displayed as 2.718281828, but e = 2.71828182845904 is used for
internal calculations.
Trigonometric Functions
Specify the angle unit before performing calculations.
Example 1: sin 30° = 0.5 (LineIO) (Angle unit: Deg)
30 0.5
Example 2: sin-1 0.5 = 30° (LineIO) (Angle unit: Deg)
(sin-1) 0 5 30
Hyperbolic Functions
Input a function from the menu that appears when you press
The angle unit setting does not affect calculations.
.
Example 1: sinh 1 = 1.175201194
27

(sinh) 1 1.175201194
Example 2: cosh-1 1 = 0
(cosh-1) 1 0
Angle Unit Conversion
°, r, g : These functions specify the angle unit. ° specifies degrees,
radians, and g grads.
Input a function from the menu that appears when you perform the
following key operation:
Example: π/2 radians = 90°, 50 grads = 45° (Angle unit: Deg)
(π) 2 (DRG ) (r)
50
(DRG ).
(DRG ) (g) 45
r
Exponential Functions
Note that the input method is different depending upon whether you are
using Natural Display or Linear Display.
Example: To calculate e5 × 2 to three significant digits (Sci 3)
(SETUP) (Sci)
90
(MthlO-MathO) ( ) 5 2 2.97×10
(LinelO)
( ) 5 2 2.97×10
Logarithmic Functions
Use the
Base 10 is the default setting if you do not input anything for a.
The
selected. In this case, you must input a value for the base.
Example 1: log10 1000 = log 1000 = 3
Example 2: log2 16 = 4
key to input logab as log (a,b).
key also can be used for input, but only while Natural Display is
1000 3
2
2
28

2 (,) 16 4
(MthIO-MathO, MthIO-LineO)
Example 3: log2(43) = 6 (MthIO-MathO, MthIO-LineO)
2 (x3)
Example 4: log2(4)3 = 8 (MthIO-MathO, MthIO-LineO)
2 4 (x3)
Example 5: To calculate ln 90 (= loge 90) to three significant digits (Sci 3)
(SETUP) (Sci)
2 16 4
90
4.50×10
Power Functions and Power Root
Functions
6
8
0
Note that the input methods for
depending upon whether you are using Natural Display or Linear Display.
Example 1: 1.2 × 103 = 1200 (MthIO-MathO)
Example 2: (1 + 1)
Example 3: (52)3 = 15625
Example 4: 5√32 = 2
(MthlO-MathO)
2+2
= 16 (MthIO-MathO)
1 1 2 2 16
5 (x3)
, , , and are different
2 10 3 1200
1
( ) 5 32 2
15625
(LinelO) 5
Example 5: To calculate √2 × 3 (= 3√2 = 4.242640687...) to three decimal
places (Fix 3)
( ) 32 2
(SETUP) (Fix)
29

(MthIO-MathO) 2 3√2
4.243
(LineIO)
2 3 4.243
Example 6: 3√5 + 3√-27 = -1.290024053
(LineIO)
( ) 5
( ) 27
-1.290024053
1
Example 7:
Note
• The following functions cannot be input in consecutive sequence: x2, x3, , x-1. If you
input 2
press the
• x2, x3, x-1 can be used in complex number calculations.
= 12
1
1
-
3
4
(LineIO)
, for example, the final will be ignored. To input 2
key, and then press (MthIO-MathO).
3 4 12
2
2
, input 2 ,
Integration Calculations
Function for performing numerical integration using the Gauss-Kronrod
method.
Natural Display input syntax is ∫
is ∫ (f (x), a, b, tol).
tol specifies tolerance, which becomes 1 × 10-5 when nothing is input for
tol.
e
Example 1: ∫
ln(x) = 1
1
(MthIO-MathO)
(X) 1 (e)
(LineIO)
(X) (,) 1 (,)
b
f (x)dx, while Linear Display input syntax
a
(e)
1
1
30

Example 2: ∫(
1
, 1, 5, 1 × 10-7) = 0.8 (LineIO)
2
x
1 (X) (,) 1 (,) 5
(,)
Example 3: ∫
1
π
(sin x + cos x)2 dx = π (tol: Not specified) (MthIO-MathO)
0
7
(Angle unit: Rad)
(X) (X)
0
(π)
Integration Calculation Precautions
• Integration calculation can be performed in the COMP Mode only.
• The following cannot be used in f(x), a, b, or tol: Pol, Rec, ∫, d/dx, Σ.
• When using a trigonometric function in f(x), specify Rad as the angle
unit.
• A smaller tol value increases precision, but it also increases calculation
time. When specifying tol, use value that is 1 × 10
• Integration normally requires considerable time to perform.
• Depending on the content of f(x) and the region of integration,
calculation error that exceeds the tolerance may be generated, causing
the calculator to display an error message.
• The content of f(x), positive/negative values within the integration
interval, and the interval to be integrated can cause large error in the
resulting integration values. (Examples: When there are parts with
discontinuous points or abrupt change. When the integration interval is
too wide.) In such cases dividing the integration interval into parts and
performing the calculation may improve calculation accuracy.
-14
or greater.
0.8
π
Tips for Successful Integration Calculations
When a periodic function or integration interval results in positive
and negative f(x) function values
Perform separate integrations for each cycle, or for the positive part and
the negative part, and then combine the results.
31

(1) Positive Part
(2) Negative Part
When integration values fluctuate widely due to minute shifts in the
integration interval
Divide the integration interval into multiple parts (in a way that breaks
areas of wide fluctuation into small parts), perform integration on each
part, and then combine the results.
Differential Calculations
Function for approximation of the derivative based on the central
difference method.
d
Natural Display input syntax is
(f (x)) |
dx
, while Linear Display input
x=a
d
syntax is
(f (x), a, tol).
dx
tol specifies tolerance, which becomes 1 × 10
-10
when nothing is input for
tol.
Example 1: To obtain the derivative at point x = π/2 for the function y =
sin(x) (Angle unit: Rad)
(MthIO-MathO)
( ) (X)
(π) 2
(LineIO)
( ) (X) (,)
(π) 2
0
0
Example 2:
( ) 3 (X) 5 (X)
d
(3x2 - 5x + 2, 2, 1 × 10
dx
2
(,) 1 12
-12
) = 7 (LineIO)
2 (,)
32
7

Differential Calculation Precautions
• Differential calculation can be performed in the COMP Mode only.
• The following cannot be used in f(x), a, b, or tol: Pol, Rec, ∫, d/dx, Σ.
• When using a trigonometric function in f(x), specify Rad as the angle
unit.
• A smaller tol value increases precision, but it also increases calculation
time. When specifying tol, use value that is 1 × 10
• If convergence to a solution cannot be found when tol input is omitted,
the tol value will be adjusted automatically to determine the solution.
• Non-consecutive points, abrupt fluctuation, extremely large or small
points, inflection points, and the inclusion of points that cannot be
differentiated, or a differential point or differential calculation result that
approaches zero can cause poor precision or error.
-14
or greater.
Σ Calculations
Function that, for a specified range of f(x), determines sum
(f(x)) = f(a) + f(a + 1) + f(a + 2) + ⋯ + f(b).
Natural Display input syntax is
is ∑(f(x), a, b).
a and b are integers that can be specified within the range of -1 × 1010 < a
≦ b < 1 × 1010.
Example: (x + 1) = 20
(MthIO-MathO)
( ) (X) 1 1 5 20
(LineIO)
( ) (X) 1 (,) 1
(f(x)), while Linear Display input syntax
(,) 5
20
Note
• The following cannot be used in f(x), a, or b: Pol, Rec, ∫, d/dx, Σ.
33

Rectangular-Polar Coordinate
Conversion
Pol converts rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates, while Rec
converts polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates.
(1) Rectangular Coordinates (Rec)
(2) Polar Coordinates (Pol)
Specify the angle unit before performing calculations.
The calculation result for r and θ and for x and y are each assigned
respectively to variables X and Y.
Calculation result θ is displayed in the range of -180° < θ ≦ 180°.
Example 1: To convert rectangular coordinates (√2, √2) to polar
coordinates (Angle unit: Deg)
(MthIO-MathO)
(Pol) 2 (,) 2
(LineIO)
(Pol) 2 (,) 2
r = 2, θ = 45
r = 2
θ = 45
Example 2: To convert polar coordinates (√2, 45°) to rectangular
coordinates (Angle unit: Deg)
(MthIO-MathO)
(Rec) 2 (,) 45 X = 1, Y = 1
34

Factorial Function (!)
Generate three 3-digit random numbers.
The random 3-digit decimal values are converted to 3-digit
integer values by multiplying by 1000.
Example: (5 + 3)! = 40320
5 3 (x!)
40320
Absolute Value Function (Abs)
Note that the input method is different depending upon whether you are
using Natural Display or Linear Display.
Example: |2 - 7| × 2 = 10
(MthIO-MathO)
(Abs) 2 7 2 10
(LineIO)
(Abs) 2 7 2 10
Random Number (Ran#)
Function that generates a pseudo random number in the range of 0.000 to
0.999.
The result is displayed as a fraction when Natural Display is selected.
Example:
1000 (Ran#) 634
92
175
(Results shown here are for illustrative purposes only. Actual results will
differ.)
Random Integer (RanInt#)
For input of the function of the form RanInt#(a, b), which generates a
random integer within the range of a to b.
Example:
To generate random integers in the range of 1 to 6
35

(RanInt) 1 (,) 6 2
(Results shown here are for illustrative purposes only. Actual results will
differ.)
Permutation (nPr) and Combination
(nCr)
Example: To determine the number of permutations and combinations
possible when selecting four people from a group of 10.
6
1
Permutations: 10
Combinations: 10
(nPr) 4
(nCr) 4
5040
210
Rounding Function (Rnd)
The argument of this function is made a decimal value and then rounded
in accordance with the current number of display digits setting (Norm, Fix,
or Sci).
With Norm 1 or Norm 2, the argument is rounded off to 10 digits.
With Fix and Sci, the argument is rounded off to the specified digit.
When Fix 3 is the display digits setting, for example, the result of 10 ÷ 3 is
displayed as 3.333, while the calculator maintains a value of
3.33333333333333 (15 digits) internally for calculation.
In the case of Rnd(10÷3) = 3.333 (with Fix 3), both the displayed value
and the calculator’s internal value become 3.333.
Because of this a series of calculations will produce different results
depending on whether Rnd is used (Rnd(10÷3) × 3 = 9.999) or not used
(10 ÷ 3 × 3 = 10.000).
Example: To perform the following calculations when Fix 3 is selected for
the number of display digits: 10 ÷ 3 × 3 and Rnd(10 ÷ 3) × 3 (LineIO)
(SETUP) (Fix)
10 3 3 10.000
(Rnd) 10 3 3 9.999
36

Using CALC
CALC lets you save calculation expressions that contain variables, which
you can then recall and execute in the COMP Mode and the CMPLX
Mode.
The following describes the types of expressions you can save with CALC.
• Expressions: 2X + 3Y, 2AX + 3BX + C, A + Bi
• Multi-statements: X + Y : X(X + Y)
• Equations with a single variable on the left and an expression including
variables on the right: A = B + C, Y = X2 + X + 3
(Use
To start a CALC operation after inputting an expression, press the
key.
Example 1: To store 3A + B and then substitute the following values to
perform the calculation: (A, B) = (5, 10), (7, 20)
(=) to input the equals sign of the equality.)
3
(A) (B)
(1) Prompts for input of a value for A
10
5
(or )
(2) Current value of A
7 20
To exit CALC:
Example 2: To store A+Bi and then determine √3 + i, 1 + √3i using polar
coordinates (r∠θ) (Angle Unit: Deg)
37

(CMPLX)
(A) (B) (i)
(CMPLX) ( r∠θ)
3 1 2∠30
(or ) 1 3 2∠60
To exit CALC:
Note
• During the time from when you press until you exit CALC by pressing , you
should use Linear Display input procedures for input.
Using SOLVE
SOLVE uses Newton's method to approximate the solution of equations.
Note that SOLVE can be used in the COMP Mode only.
The following describes the types of equations whose solutions can be
obtained using SOLVE.
• Equations that include variable X: X2 + 2X - 2, Y = X + 5, X = sin(M),
X + 3 = B + C
SOLVE solves for X. An expression like X2 + 2X - 2 is treated as X2 + 2X
- 2 = 0.
• Equations input using the following syntax: {equation}, {solution
variable}
SOLVE solves for Y, for example, when an equation is input as: Y = X +
5, Y
Important!
• If an equation contains input functions that include an open parenthesis (such as sin
and log), do not omit the closing parenthesis.
• The following functions are not allowed inside of an equation: ∫, d/dx, Σ, Pol, Rec.
Example: To solve y = ax2 + b for x when y = 0, a = 1, and b = -2
(Y) (=)
(A) (X) (B)
38

(1) Prompts for input of a value for Y
1 2
0
Input an initial value for X (Here, input 1):
(SOLVE)
(2) Current value of Y
(3) Current value of X
1
Solution Screen
To exit SOLVE:
Note
• During the time from when you press (SOLVE) until you exit SOLVE by
pressing
Important!
• Depending on what you input for the initial value for X (solution variable), SOLVE may
not be able to obtain solutions. If this happens, try changing the initial value so they
are closer to the solution.
• SOLVE may not be able to determine the correct solution, even when one exists.
• SOLVE uses Newton's method, so even if there are multiple solutions, only one of
them will be returned.
• Due to limitations in Newton's method, solutions tend to be difficult to obtain for
equations like the following: y = sin(x), y = ex, y = √x.
, you should use Linear Display input procedures for input.
Solution Screen Contents
Solutions are always displayed in decimal form.
39

(1) Equation (The equation you input.)
(2) Variable solved for
(3) Solution
(4) (Left Side) - (Right Side) result
"(Left Side) - (Right Side) result" shows the result when the right side of
the equation is subtracted from the left side, after assigning the obtained
value to the variable being solved for. The closer this result is to zero, the
higher the accuracy of the solution.
Continue Screen
SOLVE performs convergence a preset number of times. If it cannot find a
solution, it displays a confirmation screen that shows "Continue: [=]",
asking if you want to continue.
Press
Example: To solve y = x2 - x + 1 for x when y = 3, 7, and 13.
to continue or to cancel the SOLVE operation.
(Y) (=)
(X) (X) 1
Input an initial value for X (Here, input 1):
(SOLVE)
3
1
40

7
13
Scientific Constants
Your calculator comes with 40 built-in scientific constants that can be used
in any mode besides BASE-N.
Each scientific constant is displayed as a unique symbol (such as π),
which can be used inside of calculations.
To input a scientific constant into a calculation, press
and then input the two-digit number that corresponds to the constant you
want.
(CONST)
Example 1: To input the scientific constant C0 (speed of light in a
vacuum), and display its value
(CONST)
(C0)
Example 2: To calculate C0 =
1 (CONST) (ε0)
(CONST) (μ0)
1
(MthIO-MathO)
√
ε0μ
0
The following shows the two-digit numbers for each of the scientific
constants.
01: (mp) proton mass 02: (mn) neutron mass
03: (me) electron mass
05: (a0) Bohr radius 06: (h) Planck constant
04: (mμ) muon mass
41

07: (μN) nuclear magneton 08: (μB) Bohr magneton
09: (
) Planck
10: (α) fine-structure constant
constant, rationalized
11: (re) classical electron radius
12: (λC) Compton wavelength
14: (λCp) proton Compton
13: (γp) proton gyromagnetic ratio
wavelength
15: (λCn) neutron Compton
16: (R∞) Rydberg constant
wavelength
17: (u) atomic mass unit
18: (μp) proton magnetic moment
19: (μe) electron magnetic
20: (μn) neutron magnetic moment
moment
21: (μμ) muon magnetic moment
22: (F) Faraday constant
23: (e) elementary charge 24: (NA) Avogadro constant
25: (k) Boltzmann constant
26: (Vm) molar volume of ideal
gas (237.15K, 100kPa)
27: (R) molar gas constant 28: (C0) speed of light in vacuum
29: (C1) first radiation constant 30: (C2) second radiation constant
31: (σ) Stefan-Boltzmann constant 32: (ε0) electric constant
33: (μ0) magnetic constant 34: (Φ0) magnetic flux quantum
35: (g) standard acceleration of
36: (G0) conductance quantum
gravity
37: (Z0) characteristic impedance
38: (t) Celsius temperature
of vacuum
39: (G) Newtonian constant of
40: (atm) standard atmosphere
gravitation
• The values are based on CODATA (2014) recommended values.
42

Metric Conversion
The calculator's built-in metric conversion commands make it simple to
convert values from one unit to another. You can use the metric
conversion commands in any calculation mode except for BASE-N and
TABLE.
To input a metric conversion command into a calculation, press
(CONV) and then input the two-digit number that corresponds to the
command you want.
Example 1: To convert 5 cm into inches (LineIO)
5 (CONV)
(cm in)
Example 2: To convert 100 g into ounces (LineIO)
100 (CONV) (g oz)
Example 3: To convert -31°C into Fahrenheit (LineIO)
31 (CONV) (°C °F)
The following shows the two-digit numbers for each of the metric
conversion commands.
01: in
05: yd
cm 02: cm in 03: ft m 04: m ft
m 06: m yd 07: mile km 08: km mile
09: n mile
13: gal (US)
m 10: m n mile 11: acre m
ℓ 14: ℓ gal (US) 15: gal (UK) ℓ 16: ℓ gal (UK)
43
2
12: m2acre

17: pc km 18: km pc 19: km/h m/s 20: m/s km/h
21: oz
25: atm
29: hp
33: kgf • m
37: °F
g 22: g oz 23: lb kg 24: kg lb
Pa 26: Pa atm 27: mmHg Pa 28: Pa mmHg
kW 30: kW hp 31: kgf/cm2Pa 32: Pa kgf/cm
J 34: J kgf • m 35: lbf/in2kPa 36: kPa lbf/in
°C 38: °C °F 39: J cal 40: cal J
Conversion formula data is based on the "NIST Special Publication 811
(2008)".
Note
• The J cal command performs conversion for values at a temperature of 15°C.
2
2
44

Using Calculation Modes
Complex Number Calculations
(CMPLX)
To perform complex number calculations, first press
enter the CMPLX Mode.
You can use either rectangular coordinates (a+bi) or polar coordinates
(r∠θ) to input complex numbers.
Complex number calculation results are displayed in accordance with the
complex number format setting on the setup menu.
Example 1: (2 + 6i) ÷ (2i) = 3 - i (Complex number format: a+bi)
2 6 (i) 2 (i) 3-i
Example 2: 2∠45 = √2 + √2i (MthIO-MathO) (Angle unit: Deg)
(Complex number format: a+bi)
(CMPLX) to
2
Example 3: √2 + √2i = 2∠45 (MthIO-MathO) (Angle unit: Deg)
(Complex number format: r∠θ)
2 2 (i)
Note
• If you are planning to perform input and display of the calculation result in polar
coordinate format, specify the angle unit before starting the calculation.
• The θ value of the calculation result is displayed in the range of -180° < θ ≦ 180°.
• Display of the calculation result while Linear Display is selected will show a and bi (or r
and θ) on separate lines.
(∠) 45
√2+√2i
2∠45
45

CMPLX Mode Calculation Examples
1
Example 1: (1 - i)-1 =
+bi)
Example 2: (1 + i)2 + (1 - i)2 = 0 (MthIO-MathO)
1
+
i (MthIO-MathO) (Complex number format: a
2
2
1 (i)
1
1
+
i
2
2
1 (i) 1 (i)
Example 3: To obtain the conjugate complex number of 2 + 3i
(Complex number format: a+bi)
(CMPLX) (Conjg) 2 3 (i) 2-3i
Example 4: To obtain the absolute value and argument of 1 + i (MthIO-
MathO) (Angle unit: Deg)
Absolute Value (Abs):
(Abs) 1 (i)
Argument (arg):
(CMPLX) (arg) 1 (i)
Using a Command to Specify the Calculation
Result Format
0
√2
45
Either of two special commands (
of a calculation to specify the display format of the calculation results.
The command overrides the calculator's complex number format setting.
Example: √2 + √2i = 2∠45, 2∠45 = √2 + √2i (MthIO-MathO) (Angle unit:
Deg)
2 2 (i) (CMPLX)
2
(∠) 45 (CMPLX) ( a+bi) √2+√2i
r∠θ or a+bi) can be input at the end
( r∠θ)
2∠45
Statistical Calculations (STAT)
To start a statistical calculation, perform the key operation
to enter the STAT Mode and then use the screen that appears to select the
type of calculation you want to perform.
(STAT)
46

To select this type of statistical calculation:
(Regression formula shown in parentheses)
Press this key:
Single-variable (X)
Paired-variable (X, Y), linear regression
(y = A + Bx)
Paired-variable (X, Y), quadratic regression
(y = A + Bx + Cx2)
Paired-variable (X, Y), logarithmic regression
(y = A + Blnx)
Paired-variable (X, Y), e exponential
regression
(y = A eBx)
Paired-variable (X, Y), ab exponential
regression
(y = ABx)
(1-VAR)
(A+BX)
(_+CX2)
(ln X)
(e∧X)
(A•B∧X)
Paired-variable (X, Y), power regression
(A•X∧B)
(y = AxB)
Paired-variable (X, Y), inverse regression
(1/X)
(y = A + B/x)
Pressing any of the above keys (
Note
• When you want to change the calculation type after entering the STAT Mode, perform
the key operation
screen.
(STAT) (Type) to display the calculation type selection
to ) displays the Statistics Editor.
Inputting Data
Use the Statistics Editor to input data. Perform the following key operation
to display the Statistics Editor:
(STAT) (Data).
47

The Statistics Editor provides 80 rows for data input when there is an X
column only, 40 rows when there are X and FREQ columns or X and Y
columns, or 26 rows when there are X, Y, and FREQ columns.
Note
• Use the FREQ (frequency) column to input the quantity (frequency) of identical data
items. Display of the FREQ column can be turned on (displayed) or off (not displayed)
using the Stat Format setting on the setup menu.
Example 1: To select linear regression and input the following data:
(170, 66), (173, 68), (179, 75)
(STAT) (A+BX)
170 173 179
66 68 75
Important!
• All data currently input in the Statistics Editor is deleted whenever you exit the STAT
Mode, switch between the single-variable and a paired-variable statistical calculation
type, or change the Stat Format setting on the setup menu.
• The following operations are not supported by the Statistics Editor:
(M-), (STO). Pol, Rec, and multi-statements also cannot be input with the
Statistics Editor.
,
To change the data in a cell:
In the Statistics Editor, move the cursor to the cell that contains the data
you want to change, input the new data, and then press
.
To delete a line:
In the Statistics Editor, move the cursor to the line that you want to delete
and then press
.
To insert a line:
In the Statistics Editor, move the cursor to the location where you want to
insert the line and then perform the following key operation:
(STAT) (Edit) (Ins).
48

To delete all Statistics Editor contents:
Single-variable Statistics
Paired-variables Statistics
In the Statistics Editor, perform the following key operation:
(STAT) (Edit) (Del-A).
Statistics Calculation Screen
The Statistics Calculation Screen is for performing statistical calculations
with the data you input with the Statistics Editor. Pressing the key
while the Statistics Editor is displayed switches to the Statistics Calculation
Screen.
Using the Statistics Menu
While the Statistics Calculation Screen is on the display, press
(STAT) to display the Statistics Menu.
The content to the Statistics Menu depends on whether the currently
selected statistical operation type uses a single variable or paired
variables.
Statistics Menu Items
Common Items
Select this menu
item:
(Type) Display the calculation type selection screen
(Data) Display the Statistics Editor
(Sum)
When you want to obtain this:
Display the Sum sub-menu of commands for
calculating sums
49

(Var)
Display the Var sub-menu of commands for
calculating the mean, standard deviation, etc.
Display the Distr sub-menu of commands for
Single-variable:
(Distr)
normal distribution calculations
• For more information, see "Performing
Normal Distribution Calculations".
Display the Reg sub-menu of commands for
regression calculations
Paired-variable:
(Reg)
• For details see "Commands when Linear
Regression Calculation (A+BX) Is Selected"
and "Commands when Quadratic Regression
Calculation (_+CX2) Is Selected".
Display the MinMax sub-menu of commands
(MinMax)
for obtaining maximum and minimum values
Single-variable (1-VAR) Statistical Calculation Commands
Sum Sub-menu (
(STAT) (Sum))
Select this menu
When you want to obtain this:
item:
(∑x2)
(∑x)
Var Sub-menu (
Sum of squares of the sample data
Sum of the sample data
(STAT) (Var))
Select this menu
When you want to obtain this:
item:
(n)
Number of samples
(x) Mean of the sample data
(σx) Population standard deviation
(sx) Sample standard deviation
50

Distr Sub-menu ( (STAT) (Distr))
(P()
This menu can be used to calculate the
(Q()
probability of standard normal distribution.
(R()
• For details see "Performing Normal
Distribution Calculations".
( t)
MinMax Sub-menu (
(STAT) (MinMax))
Select this menu
When you want to obtain this:
item:
(minX) Minimum value
(maxX) Maximum value
Commands when Linear Regression Calculation (A+BX) Is Selected
Sum Sub-menu (
(STAT) (Sum))
Select this menu
When you want to obtain this:
item:
(∑x2)
(∑x)
(∑y2)
(∑y)
(∑xy)
(∑x3)
(∑x2y)
(∑x4)
Sum of squares of the X-data
Sum of the X-data
Sum of squares of the Y-data
Sum of the Y-data
Sum of products of the X-data and Y-data
Sum of cubes of the X-data
Sum of (X-data squares × Y-data)
Sum of biquadrate of the X-data
51

Var Sub-menu ( (STAT) (Var))
Select this menu
When you want to obtain this:
item:
(n)
Number of samples
(x) Mean of the X-data
(σx) Population standard deviation of the X-data
(sx) Sample standard deviation of the X-data
(y) Mean of the Y-data
(σy) Population standard deviation of the Y-data
(sy) Sample standard deviation of the Y-data
Reg Sub-menu (
(STAT) (Reg))
Select this menu
When you want to obtain this:
item:
(A) Regression coefficient constant term A
(B) Regression coefficient B
(r) Correlation coefficient r
(xˆ)
(yˆ)
MinMax Sub-menu (
Estimated value of X
Estimated value of Y
(STAT) (MinMax))
Select this menu
When you want to obtain this:
item:
(minX) Minimum value of the X-data
(maxX) Maximum value of the X-data
(minY) Minimum value of the Y-data
(maxY) Maximum value of the Y-data
52

Commands when Quadratic Regression Calculation (_+CX2) Is
Mean: 3, Population Standard Deviation: 1.154700538
Selected
Reg Sub-menu ( (STAT) (Reg))
Select this menu
When you want to obtain this:
item:
(A) Regression coefficient constant term A
Linear coefficient B of the regression
(B)
coefficients
Quadratic coefficient C of the regression
(C)
coefficients
(xˆ1) Estimated value of x
(xˆ2) Estimated value of x
1
2
(yˆ) Estimated value of y
Note
• xˆ, xˆ1, xˆ2 and yˆ are not variables. They are commands of the type that take an
argument immediately before them. See "Calculating Estimated Values" for more
information.
Example 2: To input the single-variable data x = {1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4,
5}, using the FREQ column to specify the number of repeats for each
items ({xn; freqn} = {1;1, 2;2, 3;3, 4;2, 5;1}), and calculate the mean and
population standard deviation.
(SETUP) (STAT) (ON)
(STAT) (1-VAR)
1
2 3 4 5
1 2 3 2
(STAT) (Var) (x) 3
(STAT) (Var) (σx)
1.154700538
Results:
Example 3: To calculate the linear regression and logarithmic regression
correlation coefficients for the following paired-variable data and determine
the regression formula for the strongest correlation: (x, y) = (20, 3150),
53

(110, 7310), (200, 8800), (290, 9310). Specify Fix 3 (three decimal places)
Linear Regression Correlation Coefficient: 0.923
Logarithmic Regression Correlation Coefficient: 0.998
Logarithmic Regression Formula: y = -3857.984 + 2357.532lnx
for results.
(SETUP) (STAT) (OFF)
(SETUP) (Fix)
(STAT) (A+BX)
20
110 200 290
3150 7310 8800 9310
(STAT) (Reg) (r)
(STAT) (Type) (ln X)
(STAT) (Reg) (r)
(STAT) (Reg) (A) -3857.984
(STAT) (Reg) (B) 2357.532
Results:
0.923
0.998
Calculating Estimated Values
Based on the regression formula obtained by paired-variable statistical
calculation, the estimated value of y can be calculated for a given x-value.
The corresponding x-value (two values, x1 and x2, in the case of quadratic
regression) also can be calculated for a value of y in the regression
formula.
Example 4: To determine the estimate value for x when y = -130 in the
regression formula produced by logarithmic regression of the data in
Example 3. Specify Fix 3 for the result. (Perform the following operation
after completing the operations in Example 3.)
130 (STAT) (Reg) (xˆ)
Important!
• Regression coefficient, correlation coefficient, and estimated value calculations can
take considerable time when there are a large number of data items.
Performing Normal Distribution Calculations
While single-variable statistical calculation is selected, you can perform
normal distribution calculation using the functions shown below from the
54
4.861

menu that appears when you perform the following key operation:
Normalized variate ( t): -0.762
P(t): 0.223
(STAT) (Distr).
P, Q, R: These functions take the argument t and determine a probability
of standard normal distribution as illustrated below.
t: This function is preceded by the argument X, and determines the
normalized variate X
Example 5: For the single variable data {xn; freqn} = {0;1, 1;2, 2;1, 3;2, 4;2,
5;2, 6;3, 7;4, 9;2, 10;1}, to determine the normalized variate (
3, and P(t) at that point up to three decimal places (Fix 3).
(SETUP) (STAT) (ON)
t =
X - x
.
σx
t) when x =
(SETUP) (Fix)
(STAT) (1-VAR)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 10
0
1 2 1 2 2 2 3 4 2 1
3 (STAT) (Distr) ( t)
(STAT) (Distr) (P()
Results:
Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
Press
perform calculations using decimal, hexadecimal, binary, and/or octal
values.
(BASE-N) to enter the BASE-N Mode when you want to
55

Positive:
Negative:
Positive:
Negative:
The initial default number mode when you enter the BASE-N Mode is
0000000000000000 ≦ x ≦ 0111111111111111
1000000000000000 ≦ x ≦ 1111111111111111
00000000000 ≦ x ≦ 17777777777
20000000000 ≦ x ≦ 37777777777
decimal, which means input and calculation results use the decimal
number format.
Press one of the following keys to switch number modes:
(DEC) for
decimal, (HEX) for hexadecimal, (BIN) for binary, or (OCT) for
octal.
Example 1: To enter the BASE-N Mode, switch to the binary mode, and
calculate 112 + 1
2
(BASE-N)
(BIN)
11 1
Example 2: Continuing from above, switch to the hexadecimal mode and
calculate 1F16 + 1
16
(HEX) 1 (F) 1
Example 3: Continuing from above, switch to the octal mode and
calculate 78 + 1
8
(OCT) 7 1
Note
• Use the following keys to input the letters A through F for hexadecimal values:
(A), (B), (C), (D), (E), (F).
• In the BASE-N Mode, input of fractional (decimal) values and exponents is not
supported. If a calculation result has a fractional part, it is cut off.
• The input and output ranges is 16 bits for binary values, and 32 bits for other types of•
values. The following shows details about input and output ranges.
Base-n Mode
Binary
Octal
Input/Output Ranges
56

Positive:
Negative:
Decimal
00000000 ≦ x ≦ 7FFFFFFF
80000000 ≦ x ≦ FFFFFFFF
Hexadecimal
-2147483648 ≦ x ≦ 2147483647
Specifying the Number Mode of a Particular Input
Value
You can input a special command immediately following a value to specify
the number mode of that value. The special commands are: d (decimal), h
(hexadecimal), b (binary), and o (octal).
Example: To calculate 1010 + 1016 + 102 + 108 and display the result as a
decimal value
(DEC) (BASE) (d) 10
(BASE) (h) 10
(BASE) (b) 10
(BASE) (o) 10 36
Converting a Calculation Result to another Type of
Value
You can use any one of the following key operations to convert the
currently displayed calculation result to another type of value:
(decimal), (HEX) (hexadecimal), (BIN) (binary), (OCT) (octal).
Example: To calculate 1510 × 3710 in the decimal mode, and then convert
the result to hexadecimal, binary, and octal
(DEC) 15 37 555
(HEX) 0000022B
(BIN) 0000001000101011
(OCT) 00000001053
(DEC)
Logical and Negation Operations
Your calculator provides you with logical operators (and, or, xor, xnor) and
functions (Not, Neg) for logical and negation operations on binary values.
Use the menu that appears when you press
logical operators and functions.
57
(BASE) to input these

Press this key: When you want to input this:
(and)
(or)
(xor)
(xnor)
(Not)
(Neg)
Logical operator "and" (logical product),
which returns the result of a bitwise AND
Logical operator "or" (logical sum), which
returns the result of a bitwise OR
Logical operator "xor" (exclusive logical
sum), which returns the result of a bitwise
XOR
Logical operator "xnor" (exclusive
negative logical sum), which returns the
result of a bitwise XNOR
"Not(" function, which returns the result of
a bitwise complement
"Neg(" function, which returns the result of
a two's complement
All of the following examples are performed in the binary mode (
(BIN)).
Example 1: To determine the logical AND of 10102 and 11002 (10102 and
11002)
1010 (BASE) (and) 1100 0000000000001000
Example 2: To determine the logical OR of 10112 and 110102 (10112 or
110102)
1011 (BASE) (or) 11010 0000000000011011
Example 3: To determine the logical XOR of 10102 and 11002 (10102 xor
11002)
1010 (BASE) (xor) 1100 0000000000000110
Example 4: To determine the logical XNOR of 11112 and 1012 (11112 xnor
1012)
1111 (BASE) (xnor) 101 1111111111110101
Example 5: To determine the bitwise complement of 10102 (Not(10102))
58

(BASE) (Not) 1010 1111111111110101
Example 6: To negate (take the two's complement) of 101101
(Neg(1011012))
2
(BASE) (Neg) 101101 1111111111010011
Note
• In the case of a negative binary, octal or hexadecimal value, the calculator converts
the value to binary, takes the two's complement, and then converts back to the original
number base. For decimal (base-10) values, the calculator merely adds a minus sign.
Equation Calculations (EQN)
You can use the following procedure in the EQN Mode to solve
simultaneous linear equations with two or three unknowns, quadratic
equations, and cubic equations.
1. Press
(EQN) to enter the EQN Mode.
2. On the menu that appears, select an equation type.
To select this
Press this key:
calculation type:
Simultaneous linear
equations with two
(anX + bnY = cn)
unknowns
Simultaneous linear
equations with three
(anX + bnY + cnZ = dn)
unknowns
Quadratic equation
Cubic equation
(aX2 + bX + c = 0)
(aX3 + bX2 + cX + d = 0)
3. Use the Coefficient Editor that appears to input coefficient values.
59

• To solve 2x2 + x - 3 = 0, for example, press in step 2, and then
input the following for the coefficients (a = 2, b = 1, c = -3): 2
1
3 .
• To change a coefficient value you already have input, move the cursor
to the appropriate cell, input the new value, and then press .
• Pressing
Important!
• The following operations are not supported by the Coefficient Editor: ,
(M-), (STO). Pol, Rec, and multi-statements also cannot be input
with the Coefficient Editor.
will clear all of the coefficients to zero.
4. After all the values are the way you want, press
.
• This will display a solution. Each press of will display another
solution. Pressing while the final solution is displayed will return to
the Coefficient Editor.
• You can scroll between the solutions using the and keys.
• To return to the Coefficient Editor while any solution is displayed,
press
Note
• Even if Natural Display is selected, the solutions of simultaneous linear equations are
not displayed using any form that includes √
• Values cannot be converted to engineering notation on the solution screen.
.
.
Changing the Current Equation Type Setting
Press
appears. Changing the equation type causes the values of all Coefficient
Editor coefficients to change to zero.
(EQN) and then select an equation type from the menu that
EQN Mode Calculation Examples
Example 1: x + 2y = 3, 2x + 3y = 4
(EQN) (anX + bnY = cn)
1
2 3
2 3 4
Example 2: x - y + z = 2, x + y - z = 0, -x + y + z = 4
60
(X=) -1
(Y=) 2

(EQN) (anX + bnY + cnZ = dn)
1
1 1 1 0
1 1 2
1 1 1 4
(X=) 1
(Y=) 2
(Z=) 3
Example 3: x2 + x +
Example 4: x2 - 2√2x + 2 = 0 (MthIO-MathO)
Example 5: x3 - 2x2 - x + 2 = 0
3
= 0 (MthIO-MathO)
4
(EQN) (aX2 + bX + c = 0)
1
1 3 4
(EQN) (aX2 + bX + c = 0)
1
(EQN) (aX3 + bX2 + cX + d = 0)
1
2 2 2 (X=) √2
2 1 2
(X1=) -
(X2=) -
(X1=) -1
(X2=) 2
(X3=) 1
1
√2
+
-
2
√2
2
i
i
2
1
2
Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
Use the MATRIX Mode to perform calculations involving matrices of up to
3 rows by 3 columns. To perform a matrix calculation, you first assign data
to special matrix variables (MatA, MatB, MatC), and then use the variables
in the calculation as shown in the example below.
Example 1: To assign to MatA and to MatB, and then
perform the following calculations:
+ (MatA+MatB)
61
× (MatA×MatB),

1. Press (MATRIX) to enter the MATRIX Mode.
2. Press (MatA) (2×2).
• This will display the Matrix Editor for input of the elements of the 2 × 2
matrix you specified for MatA.
(1) "A" stands for "MatA".
3. Input the elements of MatA: 2
4. Perform the following key operation:
(MATRIX) (Data) (MatB) (2×2).
• This will display the Matrix Editor for input of the elements of the 2 × 2
matrix you specified for MatB.
5. Input the elements of MatB: 2
6. Press to advance to the calculation screen, and perform the first
calculation (MatA×MatB):
(MATRIX) (MatA) (MATRIX) (MatB) .
• This will display the MatAns screen with the calculation results.
Note: "MatAns" stands for "Matrix Answer Memory". See "Matrix Answer
Memory" for more information.
1 1 1 .
1 1 2 .
(2) "Ans" stands for "MatAns".
7. Perform the next calculation (MatA+MatB):
(MATRIX) (MatA) (MATRIX) (MatB) .
62

Matrix Answer Memory
Whenever the result of a calculation executed in the MATRIX Mode is a
matrix, the MatAns screen will appear with the result. The result also will
be assigned to a variable named "MatAns".
The MatAns variable can be used in calculations as described below.
• To insert the MatAns variable into a calculation, perform the following
key operation: (MATRIX) (MatAns).
• Pressing any one of the following keys while the MatAns screen is
displayed will switch automatically to the calculation screen:
, ,
, , , , (x3). The calculation screen will show the
MatAns variable followed by the operator or function for the key you
pressed.
Assigning and Editing Matrix Variable Data
Important!
• The following operations are not supported by the Matrix Editor: , (M-),
(STO). Pol, Rec, and multi-statements also cannot be input with the Matrix
Editor.
To assign new data to a matrix variable:
1. Press
(MATRIX) (Dim), and then, on the menu that
appears, select the matrix variable to which you want to assign data.
2. On the next menu that appears, select dimension (m×n).
3. Use the Matrix Editor that appears to input the elements of the matrix.
Example 2: To assign to MatC
(MATRIX)
(Dim) (MatC) (2×3)
1
0 1 0 1 1
To edit the elements of a matrix variable:
1. Press (MATRIX) (Data), and then, on the menu that
appears, select the matrix variable you want to edit.
2. Use the Matrix Editor that appears to edit the elements of the matrix.
• Move the cursor to the cell that contains the element you want to
change, input the new value, and then press
.
To copy matrix variable (or MatAns) contents:
1. Use the Matrix Editor to display the matrix you want to copy.
63

• If you want to copy MatA, for example, perform the following key
operation: (MATRIX) (Data) (MatA).
• If you want to copy MatAns contents, perform the following to display
the MatAns screen:
2. Press (STO), and then perform one of the following key
operations to specify the copy destination: (MatA), (MatB), or
(MatC).
• This will display the Matrix Editor with the contents of the copy
destination.
(MATRIX) (MatAns) .
Matrix Calculation Examples
The following examples use MatA =
Example 1, and MatC =
Example 3: 3 × MatA (Matrix Scalar Multiplication).
3 (MATRIX) (MatA)
Example 4: Obtain the determinant of MatA (det(MatA)).
(MATRIX) (MatA)
Example 5: Obtain the transposition of MatC (Trn(MatC)).
(MATRIX) (MatC)
Example 6: Obtain the inverse matrix of MatA (MatA-1).
Note: You cannot use for this input. Use the key to input
from Example 2.
(MATRIX) (det)
(MATRIX) (Trn)
and MatB = from
"-1"
1
.
(MATRIX) (MatA)
Example 7: Obtain the absolute value of each element of MatB
(Abs(MatB)).
(Abs) (MATRIX) (MatB)
Example 8: Determine the square and cube of MatA (MatA2, MatA3).
Note: You cannot use
(x3) to specify cubing.
for this input. Use to specify squaring, and
64

(MATRIX) (MatA)
(MATRIX) (MatA) (x3)
Creating a Numerical Table from a
Function (TABLE)
TABLE generates a numerical table for x and f(x) using an input f(x)
function.
Perform the following steps to generate a numerical table.
1. Press
2. Input a function in the format f(x), using the X variable.
• Be sure to input the X variable (
numerical table. Any variable other than X is handled as a constant.
• The following cannot be used in the function: Pol, Rec, ∫, d/dx, Σ.
3. In response to the prompts that appear, input the values you want to
use, pressing
For this prompt: Input this:
Start? Input the lower limit of X (Default = 1).
(TABLE) to enter the TABLE Mode.
(X)) when generating a
after each one.
End?
Input the upper limit of X (Default =
5).
Note: Make sure that the End value is
always greater than the Start value.
65

Input the increment step (Default = 1).
Note: The Step specifies by how
much the Start value should be
sequentially incremented as the
Step?
numerical table is generated. If you
specify Start = 1 and Step = 1, X
sequentially will be assigned the
values 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on to
generate the numerical table until the
End value is reached.
• Inputting the Step value and pressing
generates and displays the
numerical table in accordance with the parameters you specified.
• Pressing while the numerical table screen is displayed will return
to the function input screen in step 2.
Example: To generate a numerical table for the functions f(x) = x2 +
the range -1 ≦ x ≦ 1, incremented in steps of 0.5 (MthIO-MathO)
(TABLE)
1
2
for
(X) 1 2
1 1 0 5
Note
• You can use the numerical table screen for viewing values only. Table contents
cannot be edited.
• The numerical table generation operation causes the contents of variable X to be
changed.
• The specified Start, End, and Step values should produce a maximum of 30 X-
values for the numerical table being generated. Executing a numerical table
generation using a Start, End, and Step value combination that produces more than
30 X-values causes an error.
66

Important!
• The function you input for numerical table generation is deleted whenever you
display the setup menu in the TABLE Mode and switch between Natural Display
and Linear Display.
Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
Use the VECTOR Mode to perform 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional
vector calculations. To perform a vector calculation, you first assign data to
special vector variables (VctA, VctB, VctC), and then use the variables in
the calculation as shown in the example below.
Example 1: To assign (1, 2) to VctA and (3, 4) to VctB, and then perform
the following calculations: (1, 2) + (3, 4)
1. Press
(VECTOR) to enter the VECTOR Mode.
2. Press (VctA) (2).
• This will display the Vector Editor for input of the 2-dimensional vector
for VctA.
(1) "A" stands for "VctA".
3. Input the elements of VctA: 1
4. Perform the following key operation:
(VECTOR) (Data) (VctB) (2).
• This will display the Vector Editor for input of the 2-dimensional vector
for VctB.
5. Input the elements of VctB: 3
6. Press to advance to the calculation screen, and perform the
calculation (VctA+VctB):
(VECTOR) (VctA) (VECTOR) (VctB) .
• This will display the VctAns screen with the calculation results.
2 .
4 .
67
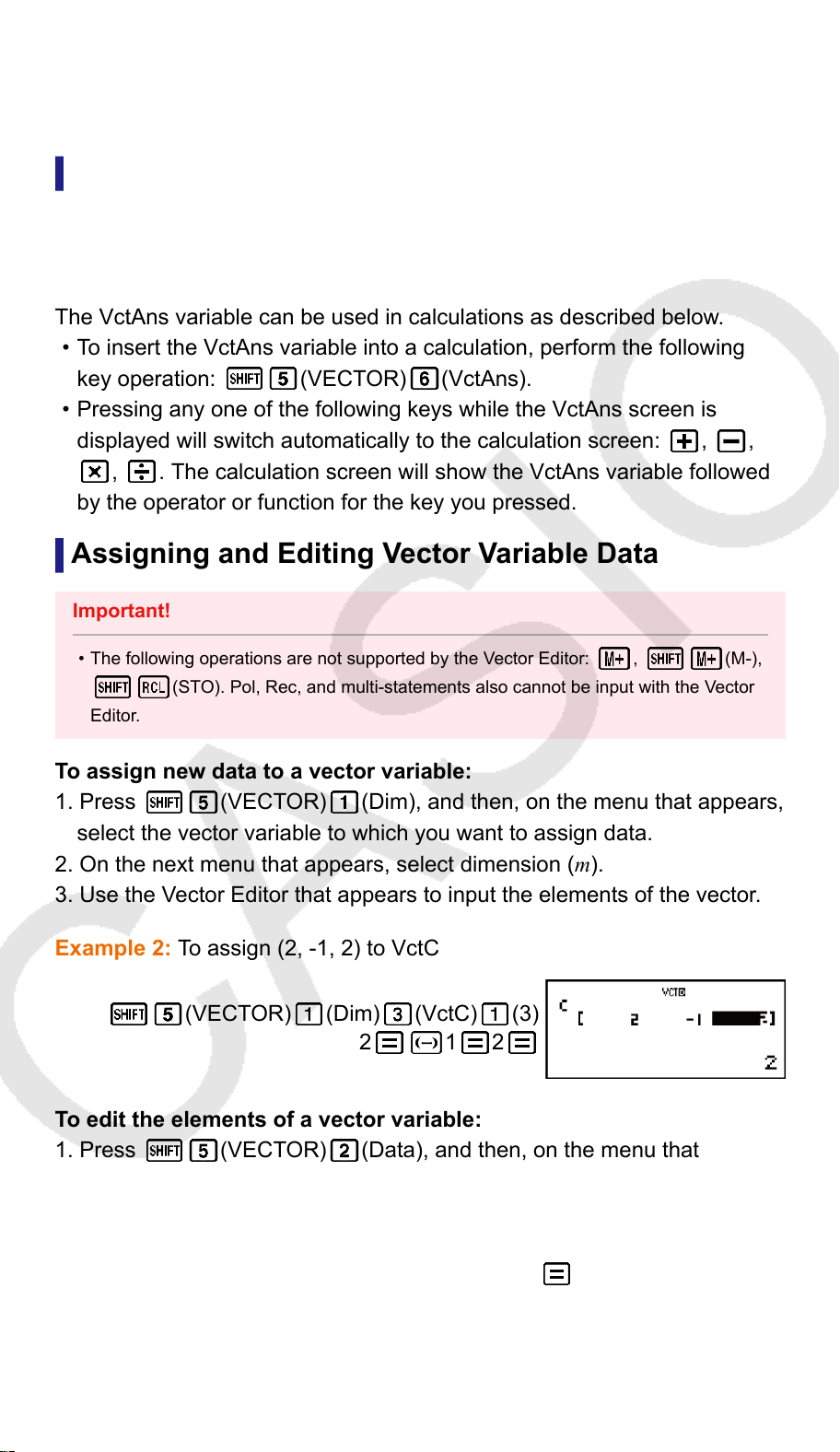
(2) "Ans" stands for "VctAns".
Note: "VctAns" stands for "Vector Answer Memory". See "Vector
Answer Memory" for more information.
Vector Answer Memory
Whenever the result of a calculation executed in the VECTOR Mode is a
vector, the VctAns screen will appear with the result. The result also will be
assigned to a variable named "VctAns".
The VctAns variable can be used in calculations as described below.
• To insert the VctAns variable into a calculation, perform the following
key operation:
(VECTOR) (VctAns).
• Pressing any one of the following keys while the VctAns screen is
displayed will switch automatically to the calculation screen: , ,
, . The calculation screen will show the VctAns variable followed
by the operator or function for the key you pressed.
Assigning and Editing Vector Variable Data
Important!
• The following operations are not supported by the Vector Editor: , (M-),
(STO). Pol, Rec, and multi-statements also cannot be input with the Vector
Editor.
To assign new data to a vector variable:
1. Press
(VECTOR) (Dim), and then, on the menu that appears,
select the vector variable to which you want to assign data.
2. On the next menu that appears, select dimension (m).
3. Use the Vector Editor that appears to input the elements of the vector.
Example 2: To assign (2, -1, 2) to VctC
(VECTOR) (Dim) (VctC) (3)
2
1 2
To edit the elements of a vector variable:
1. Press (VECTOR) (Data), and then, on the menu that
appears, select the vector variable you want to edit.
2. Use the Vector Editor that appears to edit the elements of the vector.
• Move the cursor to the cell that contains the element you want to
change, input the new value, and then press
.
To copy vector variable (or VctAns) contents:
1. Use the Vector Editor to display the vector you want to copy.
68

• If you want to copy VctA, for example, perform the following key
operation: (VECTOR) (Data) (VctA).
• If you want to copy VctAns contents, perform the following to display
the VctAns screen:
2. Press (STO), and then perform one of the following key
operations to specify the copy destination: (VctA), (VctB), or
(VctC).
• This will display the Vector Editor with the contents of the copy
destination.
(VECTOR) (VctAns) .
Vector Calculation Examples
The following examples use VctA = (1, 2) and VctB = (3, 4) from Example
1, and VctC = (2, -1, 2) from Example 2.
Example 3: 3 × VctA (Vector scalar multiplication), 3 × VctA - VctB
(Calculation example using VctAns)
3 (VECTOR) (VctA)
(VECTOR) (VctB)
Example 4: VctA • VctB (Vector dot product)
(VECTOR) (VctA)
(VECTOR) (Dot)
(VECTOR) (VctB)
Example 5: VctA × VctB (Vector cross product)
(VECTOR) (VctA)
(VECTOR) (VctB)
Example 6: Obtain the absolute values of VctC.
(Abs)
(VECTOR) (VctC)
69

Example 7: Determine the angle formed by VctA and VctB to three
decimal places (Fix 3). (Angle unit: Deg)
(cosθ =
(A∙B)
, which becomes θ = cos
|A||B|
(A∙B)
-1
|A||B|
)
(SETUP) (Fix)
(VECTOR) (VctA)
(VECTOR) (Dot)
(VECTOR) (VctB)
(Abs) (VECTOR) (VctA)
(Abs) (VECTOR) (VctB)
(cos-1)
70

Technical Information
Errors
The calculator will display an error message whenever an error occurs for
any reason during a calculation.
There are two ways to exit an error message display: Pressing
to display the location of the error, or pressing to clear the message
and calculation.
Displaying the Location of an Error
or
While an error message is displayed, press
calculation screen. The cursor will be positioned at the location where the
error occurred, ready for input. Make the necessary corrections to the
calculation and execute it again.
Example: When you input 14 ÷ 0 × 2 by mistake instead of 14 ÷ 10 ×
2 (MthIO-MathO)
14
0 2
or to return to the
(or )
1
Clearing the Error Message
While an error message is displayed, press
screen. Note that this also clears the calculation that contained the error.
to return to the calculation
Error Messages
Math ERROR
Cause:
• The intermediate or final result of the calculation you are performing
exceeds the allowable calculation range.
71

• Your input exceeds the allowable input range (particularly when using
functions).
• The calculation you are performing contains an illegal mathematical
operation (such as division by zero).
Action:
• Check the input values, reduce the number of digits, and try again.
• When using independent memory or a variable as the argument of a
function, make sure that the memory or variable value is within the
allowable range for the function.
Stack ERROR
Cause:
• The calculation you are performing has caused the capacity of the
numeric stack or the command stack to be exceeded.
• The calculation you are performing has caused the capacity of the
matrix or vector stack to be exceeded.
Action:
• Simplify the calculation expression so it does not exceed the capacity
of the stack.
• Try splitting the calculation into two or more parts.
Syntax ERROR
Cause:
• There is a problem with the format of the calculation you are
performing.
Action:
• Make necessary corrections.
Argument ERROR
Cause:
• There is a problem with the argument of the calculation you are
performing.
Action:
• Make necessary corrections.
Dimension ERROR (MATRIX and VECTOR Modes only)
Cause:
• The matrix or vector you are trying to use in a calculation was input
without specifying its dimension.
72

• You are trying to perform a calculation with matrices or vectors whose
dimensions do not allow that type of calculation.
Action:
• Specify the dimension of the matrix or vector and then perform the
calculation again.
• Check the dimensions specified for the matrices or vectors to see if
they are compatible with the calculation.
Variable ERROR (SOLVE feature only)
Cause:
• You did not specify a solution variable, and there is no X variable in
the equation you input.
• The solution variable that you specified is not included in the equation
you input.
Action:
• The equation you input must include an X variable when you do not
specify the solution variable.
• Specify a variable that is included in the equation you input as the
solution variable.
Can't Solve Error (SOLVE feature only)
Cause:
• The calculator could not obtain a solution.
Action:
• Check for errors in the equation that you input.
• Input a value for the solution variable that is close to the expected
solution and try again.
Insufficient MEM Error
Cause:
• The configuration of TABLE Mode parameters caused more than 30
X-values to be generated for a table.
Action:
• Narrow the table calculation range by changing the Start, End, and
Step values, and try again.
Time Out Error
Cause:
• The current differential or integration calculation ends without the
ending condition being fulfilled.
73

Action:
• Try increasing the tol value. Note that this also decreases solution
precision.
Before Assuming Malfunction of the
Calculator...
Perform the following steps whenever an error occurs during a calculation
or when calculation results are not what you expected. If one step does
not correct the problem, move on to the next step.
Note that you should make separate copies of important data before
performing these steps.
1. Check the calculation expression to make sure that it does not contain
any errors.
2. Make sure that you are using the correct mode for the type of
calculation you are trying to perform.
3. If the above steps do not correct your problem, press the
will cause the calculator to perform a routine that checks whether
calculation functions are operating correctly. If the calculator discovers
any abnormality, it automatically initializes the calculation mode and
clears memory contents. For details about initialized settings, see
"Configuring the Calculator Setup".
4. Initialize all modes and settings by performing the following
operation:
(CLR) (Setup) (Yes).
key. This
Replacing the Battery
The battery needs to be replaced after a specific number of years. Also,
replace the battery immediately after display figures become dim.
A low battery is indicated by a dim display, even if contrast is adjusted, or
by failure of figures to appear on the display immediately after you turn on
the calculator. If this happens, replace the battery with a new one.
Important!
• Removing the battery will cause all of the calculator’s memory contents to be deleted.
1. Press
2. On the back of the calculator, remove the screws and the cover.
(OFF) to turn off the calculator.
74

3. Remove the battery, and then load a new battery with its plus (+) and
minus (-) ends facing correctly.
4. Replace the cover.
5. Initialize the calculator: (CLR) (All) (Yes).
• Do not skip the above step!
Calculation Priority Sequence
The priority sequence of input calculations is evaluated in accordance with
the rules below.
When the priority of two expressions is the same, the calculation is
performed from left to right.
1 Parenthetical expressions
2
3
4 Fractions
5
6
7 Multiplication where the multiplication sign is omitted
Functions that require an argument to the right and a closing
parenthesis ")" following the argument
Functions that come after the input value (x2, x3, x-1, x!, °’ ”, °,
r
, g, %,
Negative sign ((-)), base-n symbols (d, h, b, o)
Metric conversion commands (cm
estimated values (xˆ, yˆ, xˆ1, xˆ2)
t), powers ( ), roots ( )
in, etc.), STAT Mode
75

8
9 Dot product (•)
10 Multiplication (×), division (÷)
11 Addition (+), subtraction (-)
12 and (logical operator)
13 or, xor, xnor (logical operators)
Note
• When squaring a negative value (such as -2), the value being squared must be
enclosed in parentheses (
the negative sign, inputting
appending a negative sign to the result.
• Always keep the priority sequence in mind, and enclose negative values in
parentheses when required.
Permutation (nPr), combination (nCr), complex number polar
coordinate symbol (∠)
2 ). Since x2 has a higher priority than
2 would result in the squaring of 2 and then
Calculation Ranges, Number of
Digits, and Precision
The calculation range, number of digits used for internal calculation, and
calculation precision depends on the type of calculation you are
performing.
Calculation Range and Precision
Calculation Range ±1 × 10
Number of Digits for
Internal Calculation
Precision
15 digits
In general, ±1 at the 10th digit for a single
calculation. Precision for exponential display is
±1 at the least significant digit. Errors are
-99
to ±9.999999999 × 1099 or 0
cumulative in the case of consecutive
calculations.
76

Function Calculation Input Ranges and Precision
Functions Input Range
Deg
0 ≦ |x| < 9 × 10
9
sinx
Rad
0 ≦ |x| < 157079632.7
cosx
Gra
0 ≦ |x| < 1 × 10
10
Same as sinx, except when |x| = (2n-1) ×
Deg
90.
Same as sinx, except when |x| = (2n-1) ×
tanx
Rad
π/2.
Same as sinx, except when |x| = (2n-1) ×
Gra
100.
sin-1x, cos-1x 0 ≦ |x| ≦ 1
tan-1x 0 ≦ |x| ≦ 9.999999999 × 10
99
sinhx, coshx 0 ≦ |x| ≦ 230.2585092
sinh-1x 0 ≦ |x| ≦ 4.999999999 × 10
cosh-1x 1 ≦ x ≦ 4.999999999 × 10
tanhx 0 ≦ |x| ≦ 9.999999999 × 10
tanh-1x 0 ≦ |x| ≦ 9.999999999 × 10
logx, lnx 0 < x ≦ 9.999999999 × 10
x
10
x
e
x 0 ≦ x < 1 × 10
√
2
x
-9.999999999 × 1099 ≦ x ≦ 99.99999999
-9.999999999 × 1099 ≦ x ≦ 230.2585092
100
|x| < 1 × 10
50
99
99
99
99
-1
-1
x
3
√
x |x| < 1 × 10
|x| < 1 × 10
100
100
77
; x ≠ 0

x! 0 ≦ x ≦ 69 (x is an integer)
nPr
nCr
Pol(x, y)
Rec(r, θ)
°’ ”
←
°’ ”
0 ≦ n < 1 × 1010, 0 ≦ r ≦ n (n, r are integers)
1 ≦ {n!/(n-r)!} < 1 × 10
100
0 ≦ n < 1 × 1010, 0 ≦ r ≦ n (n, r are integers)
1 ≦ n!/r! < 1 × 10
100
or 1 ≦ n!/(n-r)! < 1 × 10
|x|, |y| ≦ 9.999999999 × 10
√
x2 + y2 ≦ 9.999999999 × 10
0 ≦ r ≦ 9.999999999 × 10
99
99
99
100
θ: Same as sinx
a°b’c”: |a|, b, c < 1 × 10
100
; 0 ≦ b, c
The display seconds value is subject to an error
of ±1 at the second decimal place.
|x| < 1 × 10
100
Decimal ↔ Sexagesimal Conversions
0°0’0” ≦ |x| ≦ 9999999°59’59”
x > 0: -1 × 10
100
< ylogx < 100
x = 0: y > 0
y
x
x < 0: y = n,
m
(m, n are integers)
2n + 1
However: -1 × 10
y > 0: x ≠ 0, -1 × 10
x
y
√
y = 0: x > 0
y < 0: x = 2n+1,
100
< ylog |x| < 100
100
< 1/x logy < 100
2n + 1
(m ≠ 0; m, n are integers)
m
However: -1 × 10
100
< 1/x log |y| < 100
Total of integer, numerator, and denominator
a b/
c
must be 10 digits or less (including separator
symbol).
RanInt#(a, b) a < b; |a|, |b| < 1 × 1010; b - a < 1 × 10
10
• Precision is basically the same as that described under "Calculation
Range and Precision", above.
y, 3√ , x!, nPr, nCr type functions require consecutive internal
• xy, x√
calculation, which can cause accumulation of errors that occur with each
calculation.
78

• Error is cumulative and tends to be large in the vicinity of a function's
singular point and inflection point.
• The range for calculation results that can be displayed in π form when
using Natural Display is |x| < 106. Note, however, that internal calculation
error can make it impossible to display some calculation results in π
form. It also can cause calculation results that should be in decimal form
to appear in π form.
Specifications
fx-570ES PLUS
Power Requirements:
AAA-size battery R03 (UM-4) × 1
Approximate Battery Life:
2 years (based on one hour of operation per day)
Power Consumption:
0.0002 W
Operating Temperature:
0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F)
Dimensions:
13.8 (H) × 77 (W) × 161.5 (D) mm
1
/2" (H) × 3" (W) × 63/8" (D)
Approximate Weight:
105 g (3.7 oz) including the battery
fx-991ES PLUS
Power Requirements:
Built-in solar cell; button battery LR44 × 1
Approximate Battery Life:
3 years (based on one hour of operation per day)
Operating Temperature:
0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F)
Dimensions:
11.1 (H) × 77 (W) × 161.5 (D) mm
3
/8" (H) × 3" (W) × 63/8" (D)
79

Approximate Weight:
95 g (3.4 oz) including the battery
Verifying the Authenticity of Your
Calculator
Use the steps below to verify that your calculator is a genuine CASIO
calculator.
1. Press
2. Press .
• This displays the information below.
- Calculator ID number (24-character string)
- QR Code for accessing the Worldwide Education Service
(https://wes.casio.com/calc/)
3. Access the above site.
4. Follow the instructions on the display to verify the authenticity of your
calculator.
Press
.
to return to the mode menu.
80

Frequently Asked Questions
Example: (sin 30) + 15 (Angle Unit: Deg)
Frequently Asked Questions
■ How can I perform input and display results the same way I did on
a model that does not have Natural Textbook Format?
→ Perform the following key operation:
"Configuring the Calculator Setup" for more information.
■ How can I change a fraction form result to decimal form?
How can I change a fraction form result produced by a division
operation to decimal form?
→ See "Toggling Calculation Results" for the procedure.
■ What is the difference between Ans memory, independent memory,
and variable memory?
→ Each of these types of memory acts like "containers" for temporary
storage of a single value.
Ans Memory:
Stores the result of the last calculation performed. Use this memory to
carry the result of one calculation on to the next.
Independent Memory:
Use this memory to totalize the results of multiple calculations.
Variables:
This memory is helpful when you need to uses the same value multiple
times in one or more calculations.
(SETUP) (LineIO). See
■ What is the key operation to take me from the STAT Mode or TABLE
Mode to a mode where I can perform arithmetic calculations?
→ Press
■ How can I return the calculator to its initial default settings?
→ Perform the following key operation:
■ When I execute a function calculation, why do I get a calculation
result that is completely different from older CASIO calculator
models?
→ With a Natural Textbook Display model, the argument of a function that
uses parentheses must be followed by a closing parenthesis. Failing to
press
unwanted values or expressions to be included as part of the argument.
(COMP).
(CLR) (Setup) (Yes).
after the argument to close the parentheses may cause
81

0.707106781230 15
Older (S-V.P.A.M.) Model: 30 15 15.5
Natural Textbook Display Model:
Failure to press here as shown below will result in calculation of sin
45.
(LineIO) 30 15 15.5
82

© 2019 CASIO COMPUTER CO., LTD.
 Loading...
Loading...