Page 1

f
x-100MS
f
(
x-115MS
User’s Guide 2
Additional Functions)
kfx-912MS owners
Please be sure to read the important notice of this manual.
(fx-912MS)
E
http://world.casio.com/edu_e/
Page 2

Important!
Please keep your manual and all information handy for
future reference.
CASIO ELECTRONICS CO., LTD.
Unit 6, 1000 North Circular Road,
London NW2 7JD, U.K.
Page 3

Contents
Before getting started... .......................... 2
kModes .................................................................... 2
Mathematical Expression Calculations
and Editing Functions ............................ 3
kReplay Copy........................................................... 3
kCALC Memory ....................................................... 4
kSOLVE Function .................................................... 4
Scientific Function Calculations............ 5
kInputting Engineering Symbols .............................. 5
Complex Number Calculations .............. 7
kAbsolute Value and Argument Calculation............. 8
kRectangular Form ↔ Polar Form Display .............. 8
kConjugate of a Complex Number .......................... 9
Base-n Calculations ................................ 9
Statistical Calculations ......................... 11
Normal Distribution .................................................. 11
Differential Calculations ....................... 12
Integration Calculations ....................... 13
Power Supply ......................................... 14
Specifications ........................................ 16
See the “fx-95MS/fx-100MS/fx-115MS/fx-570MS/fx991MS User’s Guide” for details about the following items.
Removing and Replacing the Calculator’s Cover/
Safety Precautions/ Handling Precautions/
Tw o -line Display/
Before getting started... (except for “Modes”)/
Basic Calculations/ Memory Calculations/
Scientific Function Calculations/ Equation Calculations/
Statistical Calculations/ Technical Information
E-1
Page 4
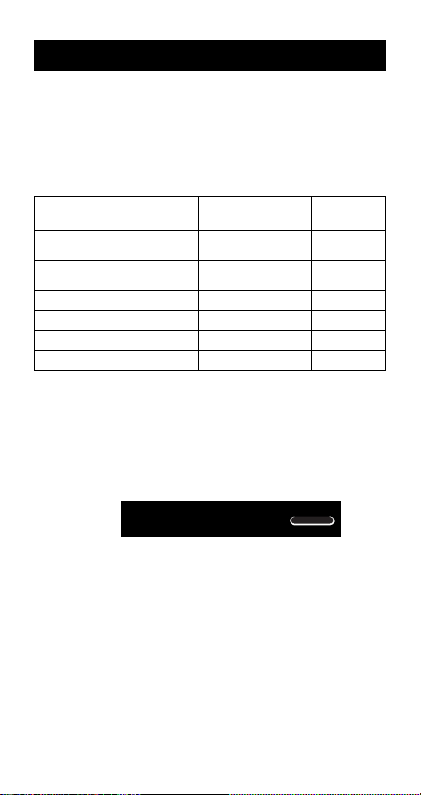
Before getting started...
k Modes
Before starting a calculation, you must first enter the correct
mode as indicated in the table below.
• The following table shows the modes and required
operations for the fx-100MS and fx-115MS.
fx-100MS and fx-115MS Modes
To perform this type of Perform this To enter
calculation: key operation: this mode:
Basic arithmetic
calculations
Complex number
calculations
Standard deviation
Regression calculations
Base-n calculations
Solution of equations
• Pressing the F key more than three times displays
additional setup screens. Setup screens are described
where they are actually used to change the calculator
setup.
• In this manual, the name of the mode you need to enter
in order to perform the calculations being described is
indicated in the main title of each section.
Example:
Complex Number
Calculations
Note!
• To return the calculation mode and setup to the initial
defaults shown below, press
Calculation Mode: COMP
Angle Unit: Deg
Exponential Display Format: Norm 1, Eng OFF
Complex Number Display Format:
Fraction Display Format: ab/c
Decimal Point Character: Dot
F 1 COMP
F 2 CMPLX
F F 1
F F 2
F F 3
F F F 1
SD
REG
BASE
EQN
CMPLX
A B 2(Mode) =.
a+bi
E-2
Page 5

• Mode indicators appear in the upper part of the display,
except for the BASE indicators, which appear in the
exponent part of the display.
• Engineering symbols are automatically turned off while
the calculator is the BASE Mode.
•You cannot make changes to the angle unit or other
display format (Disp) settings while the calculator is in
the BASE Mode.
• The COMP, CMPLX, SD, and REG modes can be used
in combination with the angle unit settings.
•Be sure to check the current calculation mode (SD, REG,
COMP, CMPLX) and angle unit setting (Deg, Rad, Gra)
before beginning a calculation.
Mathematical Expression
Calculations and Editing
COMP
Functions
Use the F key to enter the COMP Mode when you
want to perform mathematical expression calculations
or edit expressions.
COMP ............................................................
k Replay Copy
Replay copy lets you recall multiple expressions from replay
so they are connected as a multi-statement on the screen.
• Example:
Replay memory contents:
1 + 1
2 + 2
3 + 3
4 + 4
5 + 5
6 + 6
Multi-statement: 4 + 4:5 + 5:6 + 6
[ and ] to display the expression 4 + 4.
Use
A [(COPY).
Press
E-3
F 1
Page 6

•You can also edit expressions on the display and perform other multi-statement operations. For more details
about using multi-statements, see “Multi-statements” in
the separate “User’s Guide.”
• Only the expressions in replay memory starting from the
currently displayed expression and continuing to the last
expression are copied. Anything before the displayed
expression is not copied.
k CALC Memory
• CALC memory lets you temporarily store a mathematical
expression that you need to perform a number of times
using different values. Once you store an expression,
you can recall it, input values for its variables, and
calculate a result quickly and easily.
•You can store a single mathematical expression, with up
to 79 steps. Note that CALC memory can be used in the
COMP Mode and CMPLX Mode only.
• The variable input screen shows the values currently
assigned to the variables.
• Example: Calculate the result for Y = X
when X = 7 (Result: 58), and when X = 8 (Result: 76).
(Input the function.)
COMP
CMPLX
2
+ 3X – 12
p y p u p x K + 3 p x , 12
(Store the expression.) C
(Input 7 for X? prompt.) 7 =
(Input 8 for X? prompt.) C 8 =
• Note that the expression you store is cleared whenever
you start another operation, change to another mode, or
turn off the calculator.
k SOLVE Function
The SOLVE function lets you solve an expression using
variable values you want, without the need to transform or
simply the expression.
• Example: C is the time it would take for an object thrown
straight up with initial velocity A to reach height B.
E-4
Page 7

Use the formula below to calculate initial velocity A for a
height of B = 14 meters and a time of C = 2 seconds.
Gravitational acceleration is D = 9.8 m/s
(Result: A =
B AC – DC
16.8
1
2
)
2
2
.
p 2 p u p 1 - p k ,
R 1 \ 2 T - p h - p k K
A I
(B?) 14 =
(A?) ]
(C?) 2 =
(D?) 9 l 8 =
[ [
(A?) A I
• The SOLVE function finds approximations based on
Newton’s method, which means that error can occur.
Certain expressions or initial values may result in error
without convergence of results.
• If an expression does not include an equals sign (=), the
SOLVE function produces a solution for expression = 0.
Scientific Function
COMP
Calculations
Use the F key to enter the COMP Mode when you
want to perform basic arithmetic calculations.
COMP ............................................................
k Inputting Engineering Symbols
COMP EQN
•Turning on engineering symbols makes it possible for
you to use engineering symbols inside your calculations.
E-5
F 1
CMPLX
Page 8
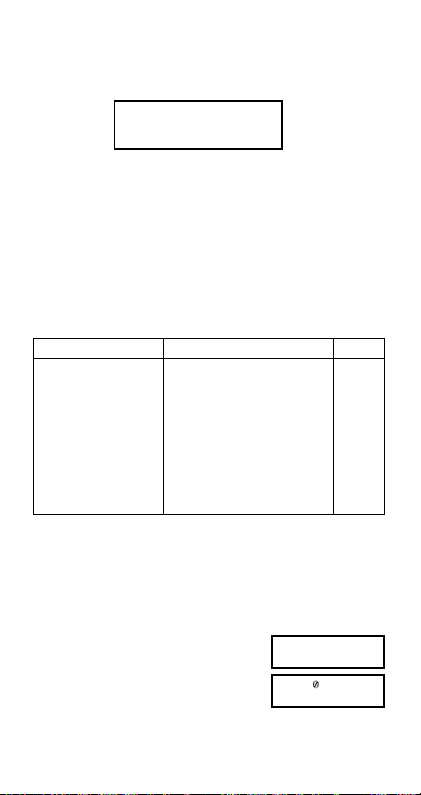
•To turn engineering symbols on and off, press the F
key a number of times until you reach the setup screen
shown below.
Disp
1
•Press 1. On the engineering symbol setting screen that
appears, press the number key (
sponds to the setting you want to use.
1(Eng ON): Engineering symbols on (indicated by
2(Eng OFF): Engineering symbols off (no “Eng”
“Eng” on the display)
• The following are the nine symbols that can be used
when engineering symbols are turned on.
To input this symbol:
k (kilo)
M (Mega) A M 10
G (Giga) A g 10
T (Tera) A t 10
m (milli) A m 10
µ (micro) A N 10
n (nano) A n 10
p (pico) A p 10
f (femto) A f 10
• For displayed values, the calculator selects the engineering symbol that makes the numeric part of the value fall
within the range of 1 to 1000.
• Engineering symbols cannot be used when inputting fractions.
• Example: 9 10 = 0.9 m (milli)
When engineering symbols are turned on, even standard (non-engineering)
indicator)
Perform this key operation: Unit
.....
F
1
calculation results are displayed using engineering symbols.
1 or 2) that corre-
A k 10
(Disp)
1
9 \ 10 =
E-6
9 ⫼1 m
900.
3
6
9
12
–3
–6
–9
–12
–15
Eng
0.
Page 9

A P
J
9 ⫼1 m
900.
0.9
Complex Number
CMPLX
Calculations
Use the F key to enter the CMPLX Mode when you
want to perform calculations that include complex
numbers.
CMPLX ...........................................................
• The current angle unit setting (Deg, Rad, Gra) affects
CMPLX Mode calculations. You can store an expression in CALC memory while in the CMPLX Mode.
• Note that you can use variables A, B, C, and M only in
the CMPLX Mode. Variables D, E, F, X, and Y are used
by the calculator, which frequently changes their values.
You should not use these variables in your expressions.
•The indicator “R↔I” in the upper right corner of a
calculation result display indicates a complex number
result. Press
real part and imaginary part of the result.
•You can use the replay function in the CMPLX Mode.
Since complex numbers are stored in replay memory in
the CMPLX Mode, however, more memory than normal
is used up.
• Example: (23
(Real part 6) 2 + 3 i + 4 + 5 i =
(Imaginary part 8i) A r
A r to toggle the display between the
i)(45i)
6
8
i
F 2
E-7
Page 10

k Absolute Value and Argument
Calculation
Supposing the imaginary number expressed by the
rectangular form
Gaussian plane, you can determine the absolute value (
and argument (
is r⬔.
• Example 1: To determine the absolute value (
argument (
(r 5) A A R 3 + 4 i T =
(
53.13010235
• The complex number can also be input using the polar
form
r⬔
• Example 2:
z = a + bi is represented as a point in the
) of the complex number. The polar form
) of 3+4i (Angle unit: Deg)
Imaginary axis
°) A a R 3 + 4 i T =
.
2 ⬔ 45 1 i
(Angle unit: Deg)
(r = 5, =
Real axis
L 2 A Q 45 =
r) and
53.13010235
A r
k Rectangular Form ↔ Polar Form
Display
You can use the operation described below to convert a
rectangular form complex number to its polar form, and a
polar form complex number to its rectangular form. Press
A r to toggle the display between the absolute value
(
r) and argument (
• Example: 1
(Angle unit: Deg)
).
i ↔ 1.414213562 ⬔ 45
1 + i A Y = A r
L 2 A Q 45 A Z = A r
E-8
r)
°)
Page 11

•You select rectangular form (a+bi) or polar form (r⬔)
for display of complex number calculation results.
...
F
1(Disp) r
1(a+bi):Rectangular form
2(r⬔
): Polar form (indicated by “r⬔” on the display)
k Conjugate of a Complex Number
For any complex number z where z = a+bi, its conjugate
(
z) is z = a–bi.
• Example: To determine the conjugate of the complex
number 1.23 + 2.34
i (Result:
1.23 – 2.34
i)
A S R 1 l 23 + 2 l 34 i T =
A r
Base-n Calculations
Use the F key to enter the BASE Mode when you
want to perform calculations using Base-
BASE ........................................................
• In addition to decimal values, calculations can be
performed using binary, octal and hexadecimal values.
•You can specify the default number system to be applied
to all input and displayed values, and the number system
for individual values as you input them.
•You cannot use scientific functions in binary, octal,
decimal, and hexadecimal calculations. You cannot input
values that include decimal part and an exponent.
• If you input a value that includes a decimal part, the unit
automatically cuts off the decimal part.
• Negative binary, octal, and hexadecimal values are
produced by taking the two’s complement.
E-9
BASE
n values.
F F 3
Page 12
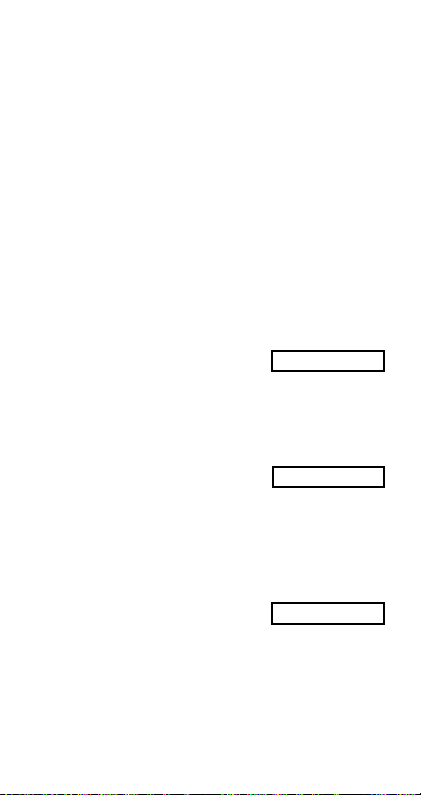
•You can use the following logical operators between
0.
o
values in Base-n calculations: and (logical product), or
(logical sum), xor (exclusive or), xnor (exclusive nor),
Not (bitwise complement), and Neg (negation).
• The following are the allowable ranges for each of the
available number systems.
Binary 1000000000 ⬉
Octal 4000000000 ⬉
x ⬉ 1111111111
0 ⬉
x ⬉ 0111111111
x ⬉ 7777777777
0 ⬉
x ⬉ 3777777777
Decimal –2147483648 ⬉ x ⬉ 2147483647
Hexadecimal 80000000 ⬉
x ⬉ FFFFFFFF
0 ⬉
x ⬉ 7FFFFFFF
• Example 1: To perform the following calculation and
produce a binary result:
10111
110102
2
Binary mode: t b
110001
2
0.
10111 + 11010 =
• Example 2: To perform the following calculation and
produce an octal result:
7654
÷ 12
8
516
10
8
Octal mode: t o
l l l 4
l l l 1
(o) 7654 \
(d) 12 =
• Example 3: To perform the following calculation and
produce a hexadecimal and a decimal result:
120
or 11012
16
Hexadecimal mode: t h
12d
301
16
10
0.
120 l 2 (or)
l l l 3
(b)
1101 =
Decimal mode: K
b
H
E-10
Page 13

• Example 4: To c on vert the value 2210 to its binary, octal, and hexadecimal equivalents.
Binary mode: t b
l l l 1(d) 22 =
Octal mode: o
Hexadecimal mode: h
• Example 5: To convert the value 51310 to its binary
equivalent.
Binary mode: t b
l l l 1(d) 513 =
•You may not be able to convert a value from a number
system whose calculation range is greater than the calculation range of the resulting number system.
• The message “Math ERROR” indicates that the result
has too many digits (overflow).
(101102 , 268 , 16
10110.
26.
16.
aMthERROR
16
0.
0.
)
b
b
o
H
b
b
Statistical
Calculations
Normal Distribution
Use the F key to enter the SD Mode when you want
to perform a calculation involving normal distribution.
SD ...........................................................
• Press A D, which produces the screen shown below.
P
( Q ( R ( →
1
2 3
E-11
t
4
SD
REG
SD
F F 1
Page 14

•Input a value from 1 to 4 to select the probability
distribution calculation you want to perform.
P(t)R(t)Q(t)
• Example: To determine the normalized variate (→t) for
x = 53 and normal probability distribution P(t) for the
following data: 55, 54, 51, 55, 53, 53, 54, 52
(
→
t =
0.284747398
, P(t) =
0.38974
55
A D 1(
)
S 54 S 51 S 55 S
53 S S 54 S 52 S
53 A D 4(
P(
) D 0.28 F =
→
t) =
Differential
COMP
Calculations
The procedure described below obtains the derivative of
a function.
F key to enter the COMP Mode when you
Use the
want to perform a calculation involving differentials.
COMP ............................................................
• Three inputs are required for the differential expression:
the function of variable
ferential coefficient is calculated, and the change in
x, the point (a) at which the dif-
x (∆x).
A J expression P a P ∆x T
• Example: To determine the derivative at point x = 2 for
the function
crease in
A J
2
y = 3x
– 5x + 2, when the increase or de-
x is ∆x = 2 × 10
3
–4
(Result: 7)
p x K , 5 p x + 2 P 2 P
E-12
F 1
2 e D 4 T =
Page 15

•You can omit input of
automatically substitutes an appropriate value for
you do not input one.
•Discontinuous points and extreme changes in the value
of x can cause inaccurate results and errors.
∆
x, if you want. The calculator
∆
x if
Integration
COMP
Calculations
The procedure described below obtains the definite integral
of a function.
Use the
F key to enter the COMP Mode when you
want to perform integration calculations.
COMP ............................................................
• The following four inputs are required for integration
calculations: a function with the variable
define the integration range of the definite integral; and
n, which is the number of partitions (equivalent to N =
n
2
) for integration using Simpson’s rule.
d expression P a P b P n F
• Example:
5
∫
(2x2 + 3x + 8) dx =
1
(Number of partitions n = 6)
d
150.6666667
2 p x K + 3 p x
8 P 1 P 5 P 6 T =
Note!
•You can specify an integer in the range of 1 to 9 as the
number of partitions, or you can skip input of the number
of partitions entirely, if you want.
•Internal integration calculations may take considerable
time to complete.
•Display contents are cleared while an integration
calculation is being performed internally.
E-13
F 1
x; a and b, which
+
Page 16

Power Supply
The type of battery you should use depends on the model
number of your calculator.
fx-115MS
The TWO WAY POWER system actually has two power
supplies: a solar cell and a G13 Type (LR44) button battery.
Normally, calculators equipped with a solar cell alone can
operate only when relatively bright light is present. The
TWO WAY POWER system, however, lets you continue
to use the calculator as long as there is enough light to
read the display.
•Replacing the Battery
Either of the following symptoms indicates battery power
is low, and that the battery should be replaced.
•Display figures are dim and difficult to read in areas
where there is little light available.
• Nothing appears on the display when you press the
5 key.
u To replace the battery
1 Remove the five screws that
hold the back cover in place
and then remove the back
cover.
2 Remove the old battery.
3 Wipe off the sides of new
battery with a dry, soft cloth.
Load it into the unit with the
positive
you can see it).
4 Replace the back cover and
secure it in place with the five
screws.
5 Press
step.
side facing up (so
k
5 to turn power on. Be sure not to skip this
Screw Screw
E-14
Page 17

fx-100MS
This calculator is powered by a single AA-size battery.
•Replacing the Battery
Dim figures on the display of the calculator indicate that
battery power is low. Continued use of the calculator when
the battery is low can result in improper operation.
Replace the battery as soon as possible when display
figures become dim.
• To replace the battery
1 Press A i to turn power off.
2 Remove the six screws that
hold the back cover in place
and then remove the back
cover.
3 Remove the old battery.
4 Load a new battery into the
unit with its positive k and
negative
correctly.
5 Replace the back cover and
secure it in place with the six
screws.
6 Press
ends facing
l
5 to turn power on.
Screw Screw
Auto Power Off
Calculator power automatically turns off if you do not
perform any operation for about six minutes. When this
happens, press
5 to turn power back on.
E-15
Page 18

Specifications
Power Supply:
fx-100MS: Single AA-size battery (R6P(SUM-3))
fx-115MS: Solar cell and a single G13 Type button
Battery Life:
fx-100MS: Approximately 17,000 hours continuous
fx-115MS: Approximately 3 years (1 hour use per day).
Dimensions:
fx-100MS: 20.0 (H)
fx-115MS: 12.7 (H)
Weight:
fx-100MS: 133 g (4.7 oz) including battery
fx-115MS: 105 g (3.7 oz) including battery
Power Consumption: 0.0002 W
Operating Temperature: 0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F)
battery (LR44)
display of flashing cursor.
Approximately 2 years when left with power
turned off.
҂ 78 (W) ҂ 155 (D) mm
13
/16 (H) ҂ 31/16 (W) ҂ 61/8 (D)
҂ 78 (W) ҂ 154.5 (D) mm
1
/2 (H) ҂ 31/16 (W) ҂ 61/16 (D)
Important notice for fx-912MS owners
The names fx-912MS (Japan domestic model name)
and fx-115MS (international model name) apply to the
same model. Owners of the fx-912MS should refer to
the description of fx-115MS.
E-16
Page 19

CASIO COMPUTER CO., LTD.
6-2, Hon-machi 1-chome
Shibuya-ku, Tokyo 151-8543, Japan
SA0206-D Printed in China
CA 310074C-1
 Loading...
Loading...