Page 1
Container Refrigeration
OPERATION AND SERVICE
for
69NT40-561-001 to 199
Container Refrigeration Units
T--340 Rev B
Page 2

OPERATION AND SERVICE MANUAL
CONTAINER REFRIGERATION UNIT
Models
69NT40--561--001 to 199
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
PARAGRAPH NUMBER Page
GENERAL SAFETY NOTICES Safety--1............................................................
FIRST AID Safety--1............................................................................
OPERATING PRECAUTIONS Safety--1...........................................................
MAINTENANCE PRECAUTIONS Safety--1..........................................................
SPECIFIC WARNING AND CAUTION STATEMENTS Safety--1.......................................
INTRODUCTION 1--1..............................................................................
1.1 INTRODUCTION 1--1.....................................................................
1.2 CONFIGURATION IDENTIFICATION 1-- 1...................................................
1.3 FEATURE DESCRIPTIONS 1--1............................................................
1.3.1 Control Box 1--1......................................................................
1.3.2 Temperature Readout 1--1..............................................................
1.3.3 Pressure Readout 1--1.................................................................
1.3.4 Compressor 1--1......................................................................
1.3.5 Condenser Coil 1--1...................................................................
1.3.6 Evaporator 1--1.......................................................................
1.3.7 Evaporator Fan Operation 1--1..........................................................
1.3.8 Plate Set 1--1.........................................................................
1.4 OPTION DESCRIPTIONS 1--1.............................................................
1.4.1 Battery 1--1...........................................................................
1.4.2 Dehumidification 1--1..................................................................
1.4.3 USDA 1--1...........................................................................
1.4.4 Interrogator 1-- 1.......................................................................
1.4.5 Remote Monitoring 1--1................................................................
1.4.6 Communications Interface Module 1--2...................................................
1.4.7 Autotransformer 1--2...................................................................
1.4.8 Temperature Recorder 1--2.............................................................
1.4.9 Handles 1--2..........................................................................
1.4.10 Thermometer Port 1--2.................................................................
1.4.11 Water Cooling 1--2....................................................................
1.4.12 Back Panels 1--2......................................................................
1.4.13 460 Volt Cable 1--2....................................................................
1.4.14 230 Volt Cable 1--2....................................................................
1.4.15 Cable Restraint 1--2...................................................................
1.4.16 Upper Air (Fresh Air Make Up) 1--2......................................................
1.4.17 Lower Air (Fresh Air Make Up) 1--2......................................................
1.4.18 Labels 1--2...........................................................................
1.4.19 Controller 1--2
1.4.20 Condenser Grille 1--2..................................................................
1.4.21 Emergency Bypass 1--2................................................................
1.4.22 eAutoFresh 1--2.......................................................................
........................................................................
i T-340
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
PARAGRAPH NUMBER Page
DESCRIPTION 2--1...............................................................................
2.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 2--1.............................................................
2.1.1 Refrigeration Unit -- Front Section 2--1...................................................
2.1.2 Fresh Air Makeup Vent 2--1.............................................................
2.1.3 Evaporator Section 2--2................................................................
2.1.4 Compressor Section 2--3...............................................................
2.1.5 Air--Cooled Condenser Section 2--4......................................................
2.1.6 Water--Cooled Condenser Section 2--5...................................................
2.1.7 Control Box Section 2--6...............................................................
2.1.8 Communications Interface Module 2--6...................................................
2.2 REFRIGERATION SYSTEM DATA 2--7......................................................
2.3 ELECTRICAL DATA 2--8...................................................................
2.4 SAFETY AND PROTECTIVE DEVICES 2--9.................................................
2.5 REFRIGERATION CIRCUIT 2--10...........................................................
2.5.1 Standard Operation 2--10................................................................
2.5.2 Economized Operation 2--10.............................................................
2.5.3 Electronic Expansion Valve 2--10.........................................................
MICROPROCESSOR 3--1..........................................................................
3.1 TEMPERATURE CONTROL MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM 3--1..............................
3.1.1 Keypad 3--2..........................................................................
3.1.2 Display Module 3--2...................................................................
3.1.3 Controller 3--3........................................................................
3.2 CONTROLLER SOFTWARE 3--3...........................................................
3.2.1 Configuration Software (V ariables) 3--3...................................................
3.2.2 Operational Software (Function Codes) 3--3..............................................
3.3 CONTROLLER SEQUENCE AND MODES OF OPERATION 3-- 4...............................
3.3.1 Start up -- Compressor Phase Sequence 3--4.............................................
3.3.2 Start up -- Compressor Bump Start 3--4..................................................
3.3.3 Perishable Set Point Temperature -- Perishable Pulldown 3--4...............................
3.3.4 Perishable Set Point Temperature -- Standard Temperature Control Mode 3--4.................
3.3.5 Perishable Set Point Temperature -- Economy Fan Operation Mode 3--4......................
3.3.6 Perishable Set Point Temperature Control 3--4............................................
3.3.7 Perishable Mode Cooling -- Sequence of Operation 3--5....................................
3.3.8 Perishable Mode Heating -- Sequence of Operation 3--6....................................
3.3.9 Sequence of Operation -- Perishable Mode (Capacity Trim Heat) 3--6........................
3.3.10 Perishable Mode -- Dehumidification 3--6.................................................
3.3.11 Perishable, Dehumidification -- Bulb Mode 3--7............................................
3.3.12 Frozen Mode -- Pulldown 3--7...........................................................
3.3.13 Frozen Mode -- T emperature Control 3--7.................................................
3.3.14 Frozen Mode -- Standard 3--7...........................................................
3.3.15 Frozen Mode -- Heat Lockout Temperature 3--7...........................................
3.3.16 Frozen Mode -- Economy 3--7...........................................................
3.3.17 Frozen Mode Cooling -- Sequence of Operation 3--8.......................................
3.3.18 Defrost Interval 3--9
...................................................................
T-340
ii
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
PARAGRAPH NUMBER Page
3.3.19 Defrost Mode -- Sequence of Operation 3--9..............................................
3.4 PROTECTION MODES OF OPERATION 3--10................................................
3.4.1 Evaporator Fan Operation 3--10..........................................................
3.4.2 Failure Action 3--10.....................................................................
3.4.3 Generator Protection 3--10..............................................................
3.4.4 Compressor High Temperature, Low Pressure Protection 3--10...............................
3.4.5 Perishable Mode -- System Pressure Regulation 3--10.......................................
3.4.6 Condenser Fan Override 3--10...........................................................
3.5 CONTROLLER ALARMS 3--10..............................................................
3.6 UNIT PRE--TRIP DIAGNOSTICS 3--11.......................................................
3.7 DataCORDER 3-- 11........................................................................
3.7.1 Description 3--11.......................................................................
3.7.2 DataCORDER Software 3--1 1............................................................
3.7.3 Sensor Configuration (dCF02) 3--12......................................................
3.7.4 Logging Interval (dCF03) 3--12...........................................................
3.7.5 Thermistor Format (dCF04) 3--12.........................................................
3.7.6 Sampling Type (dCF05 & dCF06) 3--14...................................................
3.7.7 Alarm Configuration (dCF07 -- dCF10) 3--14...............................................
3.7.8 DataCORDER Power Up 3--14...........................................................
3.7.9 Pre--trip Data Recording 3--14............................................................
3.7.10 DataCORDER Communications 3--14.....................................................
3.7.11 USDA Cold Treatment 3--15.............................................................
3.7.12 USDA Cold Treatment Procedure 3--15...................................................
3.7.13 DataCORDER Alarms 3--16.............................................................
3.7.14 ISO Trip Header 3--16..................................................................
OPERATION 4--1.................................................................................
4.1 INSPECTION (Before Loading) 4--1.........................................................
4.2 CONNECT POWER 4--1..................................................................
4.2.1 Connection To 380/460 VAC Power 4--1..................................................
4.2.2 Connection To 190/230 VAC Power 4--1..................................................
4.3 ADJUST FRESH AIR MAKEUP VENT 4--1...................................................
4.3.1 Upper Fresh Air Makeup Vent 4--2.......................................................
4.3.2 Lower Fresh Air Makeup Vent 4--2.......................................................
4.3.3 Vent Position Sensor 4--2..............................................................
4.4 eAutoFresh OPERATION 4--3..............................................................
4.4.1 eAutoFresh Pre--Trip Inspection 4--3.....................................................
4.4.2 eAutoFresh Start--Up Procedure 4--3....................................................
4.4.3 eAutoFresh Operation 4--3.............................................................
4.4.4 eAutoFresh Modes of Operation 4--3.....................................................
4.5 CONNECT WA TER--COOLED CONDENSER 4--4............................................
4.5.1 Water--Cooled Condenser with Water Pressure Switch 4--4.................................
4.5.2 Water--Cooled Condenser with Condenser Fan Switch 4--4.................................
4.6 CONNECT REMOTE MONITORING RECEPTACLE 4--5......................................
iii T-340
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
PARAGRAPH NUMBER Page
4.7 STARTING AND STOPPING INSTRUCTIONS 4--5...........................................
4.7.1 Starting the Unit 4--5...................................................................
4.7.2 Stopping the Unit 4--5..................................................................
4.8 START--UP INSPECTION 4--5.............................................................
4.8.1 Physical Inspection 4--5................................................................
4.8.2 Check Controller Function Codes 4--5....................................................
4.8.3 Start T emperature Recorder 4--5........................................................
4.8.4 Complete Inspection 4-- 5...............................................................
4.9 PRE--TRIP DIAGNOSIS 4--5...............................................................
4.10 OBSERVE UNIT OPERATION 4--6.........................................................
4.10.1 Probe Diagnostic Logic 4--6............................................................
4.11 EMERGENCY BYPASS OPERATION 4--7...................................................
TROUBLESHOOTING 5--1.........................................................................
5.1 UNIT WILL NOT START OR STARTS THEN STOPS 5--1......................................
5.2 UNIT OPERATES LONG OR CONTINUOUSLY IN COOLING 5--1..............................
5.3 UNIT RUNS BUT HAS INSUFFICIENT COOLING 5--2........................................
5.4 UNIT WILL NOT HEAT OR HAS INSUFFICIENT HEATING 5--2................................
5.5 UNIT WILL NOT TERMINATE HEATING 5--2................................................
5.6 UNIT WILL NOT DEFROST PROPERLY 5--2................................................
5.7 UNIT WILL NOT DEFROST PROPERLY (Continued) 5--3.....................................
5.8 ABNORMAL PRESSURES 5-- 3............................................................
5.9 ABNORMAL NOISE OR VIBRATIONS 5--3..................................................
5.10 MICROPROCESSOR MALFUNCTION 5--3..................................................
5.11 NO EVAPORATOR AIR FLOW OR RESTRICTED AIR FLOW 5--4..............................
5.12 EAUTOFRESH NOT OPERATING 5--4......................................................
5.13 ELECTRONIC EXPANSION V ALVE MALFUNCTION 5--4......................................
5.14 AUTOTRANSFORMER MALFUNCTION 5--5................................................
5.15 WATER--COOLED CONDENSER OR WATER PRESSURE SWITCH 5--5.......................
5.16 COMPRESSOR OPERATING IN REVERSE 5--5.............................................
5.17 ABNORMAL TEMPERATURES 5--5........................................................
5.18 ABNORMAL CURRENTS 5--5..............................................................
SERVICE 6--1....................................................................................
6.1 SECTION LAYOUT 6--1...................................................................
6.2 MANIFOLD GAUGE SET 6--1..............................................................
6.3 REFRIGERATION SYSTEM SERVICE-UNITS WITH STANDARD PIPING (with Service Valves) 6--2
6.3.1 Service Connections 6--2...............................................................
6.3.2 Pumping Down the Unit 6--2............................................................
6.3.3 Refrigerant Leak Checking 6--3.........................................................
6.3.4 Evacuation and Dehydration 6--3........................................................
6.3.5 Refrigerant Charge 6-- 4................................................................
6.4 COMPRESSOR 6--4......................................................................
6.4.1 Removal and Replacement of Compressor 6--5...........................................
T-340
iv
Page 7

TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
PARAGRAPH NUMBER Page
6.5 HIGH PRESSURE SWITCH 6--6...........................................................
6.5.1 Checking High Pressure Switch 6--6.....................................................
6.5.2 Replacing High Pressure Switch 6--6.....................................................
6.6 CONDENSER COIL 6--6..................................................................
6.7 CONDENSER FAN AND MOTOR ASSEMBLY 6--6...........................................
6.8 WATER--COOLED CONDENSER CLEANING 6--7............................................
6.9 FILTER DRIER 6--9.......................................................................
6.10 EVAPORATOR COIL AND HEATER ASSEMBLY 6--9.........................................
6.10.1 Evaporator Coil Replacement 6--9.......................................................
6.10.2 Evaporator Heater Removal and Replacement 6--9........................................
6.11 EVAPORATOR FAN AND MOTOR ASSEMBLY 6--10..........................................
6.11.1 Replacing the Evaporator Fan Assembly 6--10.............................................
6.11.2 Disassemble the Evaporator Fan Assembly 6--10...........................................
6.11.3 Assemble the Evaporator Fan Assembly 6--10.............................................
6.12 EVAPORATOR SECTION CLEANING 6--11...................................................
6.13 eAutoFresh SERVICE 6--11.................................................................
6.13.1 Servicing the eAutoFresh Air Filter 6--1 1...................................................
6.13.2 Checking eAutoFresh Drive System 6--11.................................................
6.13.3 Checking the Controller 6--12............................................................
6.13.4 Servicing the eAutoFresh Drive System 6--12..............................................
6.14 ELECTRONIC EXPANSION VALVE 6-- 14.....................................................
6.14.1 Replacing Electronic Expansion Valve and Screen 6--14.....................................
6.15 ECONOMIZER EXPANSION VALVE 6--14....................................................
6.15.1 Valve Replacement 6--14................................................................
6.16 ECONOMIZER SOLENOID VALVE 6-- 15.....................................................
6.17 DIGITAL UNLOADER VALVE 6--15..........................................................
6.18 VALVE OVERRIDE CONTROLS 6--16........................................................
6.19 AUTOTRANSFORMER 6--18...............................................................
6.20 CONTROLLER 6-- 18.......................................................................
6.20.1 Handling Modules 6--18.................................................................
6.20.2 Controller Troubleshooting 6--18..........................................................
6.20.3 Controller Programming Procedure 6--19..................................................
6.20.4 Removing and Installing a Module 6--21...................................................
6.20.5 Battery Replacement 6--21..............................................................
6.21 VENT POSITION SENSOR SERVICE 6--21...................................................
6.22 TEMPERATURE SENSOR SERVICE 6--22...................................................
6.22.1 Sensor Checkout Procedure 6--22........................................................
6.22.2 Sensor Replacement 6--25..............................................................
6.22.3 Sensor Re-Installation 6--25.............................................................
6.23 ELECTRONIC PAR TLOW TEMPERATURE RECORDER 6--27..................................
6.24 MAINTENANCE OF PAINTED SURFACES 6--29..............................................
6.25 COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE MODULE INSTALLATION 6--29..............................
ELECTRICAL WIRING SCHEMATICS 7--1...........................................................
7.1 INTRODUCTION 7--1.....................................................................
v T-340
Page 8

LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
FIGURE NUMBER Page
Figure 2--1 Refrigeration Unit -- Front Section 2--1....................................................
Figure 2--2 Evaporator Section 2-- 2.................................................................
Figure 2--3 Compressor Section 2-- 3................................................................
Figure 2--4 Air--Cooled Condenser Section 2--4.......................................................
Figure 2--5 Water--Cooled Condenser Section 2--5....................................................
Figure 2--6 Control Box Section 2-- 6................................................................
Figure 2--7 Refrigeration Circuit Schematic -- Standard Operation 2--11...................................
Figure 2--8 Refrigeration Circuit Schematic -- Economized Operation 2--12................................
Figure 3--1 T emperature Control System 3--1.........................................................
Figure 3--2 Keypad 3--2...........................................................................
Figure 3--3 Display Module 3--3....................................................................
Figure 3--4 Control Module 3--3.....................................................................
Figure 3--5 Controller Operation -- Perishable Mode 3--5...............................................
Figure 3--6 Perishable Mode -- Cooling 3--5..........................................................
Figure 3--7 Perishable Mode Heating 3--6............................................................
Figure 3--8 Controller Operation -- Frozen Mode 3--8..................................................
Figure3--9FrozenMode 3-- 8......................................................................
Figure 3--10 Defrost 3--10..........................................................................
Figure 3--11 Standard Configuration Download Report 3--13.............................................
Figure 3--12 Data Reader 3--15......................................................................
Figure 4--1 Autotransformer 4--1....................................................................
Figure 4--2 Upper Fresh Air Make Up Flow Chart 4--2.................................................
Figure 4--3 Diagram of Emergency Bypass Connections 4--7...........................................
Figure 6--1 Manifold Gauge Set 6--1................................................................
Figure 6--2 R-134a Manifold Gauge/Hose Set 6--1....................................................
Figure 6--3 Service Valve 6-- 2......................................................................
Figure 6--4 Refrigeration System Service Connections 6--3.............................................
Figure 6--5 Compressor Kit 6--5....................................................................
Figure 6--6 High Pressure Switch Testing 6--6........................................................
Figure 6--7 Water-Cooled Condenser Cleaning - Forced Circulation 6--8.................................
Figure 6--8 Water-Cooled Condenser Cleaning - Gravity Circulation 6--8.................................
Figure 6--9 5+1 Heater Arrangement -- Omega Heater 6--9.............................................
Figure 6--10 Evaporator Fan Assembly 6--10..........................................................
Figure 6--11 Stepper Components 6--12..............................................................
Figure 6--12 Jumper Assembly 6-- 12.................................................................
Figure 6--13 Motor Cup Replacement 6--13...........................................................
Figure 6--14 Electronic Expansion Valve 6--14.........................................................
Figure 6--15 Economizer Expansion V alve 6--14.......................................................
Figure 6--16 Coil View of Economizer Solenoid Valve (ESV) 6--15........................................
Figure 6--17 View of Digital Unloader Valve (DUV) Assembly 6--15.......................................
Figure 6--18 Controller Section of the Control Box 6--19.................................................
Figure 6--19 Sensor Types
6--25.....................................................................
T-340
vi
Page 9

LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS (Continued)
FIGURE NUMBER Page
Figure 6--20 Sensor and Cable Splice 6--25...........................................................
Figure 6--21 Supply Sensor Positioning 6--26..........................................................
Figure 6--22 Return Sensor Positioning 6--26..........................................................
Figure 6--23 Evaporator Temperature Sensor Positioning 6--26..........................................
Figure 6--24 Compressor Discharge Temperature Sensor 6--27..........................................
Figure 6--25 Electronic Partlow Temperature Recorder 6--28.............................................
Figure 6--26 Communications Interface Installation 6--29................................................
Figure 7--1 LEGEND -- Standard Unit Configuration 7--2...............................................
Figure 7--2 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM -- Standard Unit Configuration 7--3..................................
Figure 7--3 LEGEND -- Configuration Includes Available Options
Figure 7--4 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM -- Configuration Includes Available Options
Figure 7--5 LEGEND -- Configuration Includes eAutoFresh & Emergency Bypass Options 7--6..............
Figure 7--6 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM -- Configuration Includes eAutoFresh & Emergency Bypass Options 7--7.
Figure 7--7 SCHEMATIC AND WIRING DIAGRAM -- Upper Vent Position Sensor (VPS) Option 7--8.........
Figure 7--8 SCHEMATIC AND WIRING DIAGRAM -- Lower Vent Position Sensor (VPS) Option 7--9.........
Figure 7--9 UNIT WIRING DIAGRAM -- Standard Unit Configuration with 3--Phase Condenser Fan Motors 7--10
Figure 7--10 UNIT WIRING DIAGRAM -- Configuration Includes 2 Phase Condenser Fan Motor
Figure 7--11 UNIT WIRING DIAGRAM -- Configuration Includes eAutoFresh & Emergency Bypass Options 7--14
(Except Vent Positioning System, eAutoFresh & Emergency Bypass Options) 7--4.............
(Except Vent Positioning System, eAutoFresh & Emergency Bypass Options) 7--5.............
and Optional Heater Arrangement 7--12...................................................
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE NUMBER Page
Table 2--1 Safety and Protective Devices 2--9.........................................................
Table 3--1 Keypad Function 3--2.....................................................................
Table 3--2 DataCORDER Configuration Variables 3--12..................................................
Table 3--3 DataCORDER Standard Configurations 3--14.................................................
Table 3--4 Controller Configuration Variables 3--17......................................................
Table 3--5 Controller Function Codes 3--18.............................................................
Table 3--6 Controller Alarm Indications 3--22...........................................................
Table 3--7 Controller Pre--trip Test Codes 3--27.........................................................
Table 3--8 DataCORDER Function Code Assignments 3--31..............................................
Table 3--9 DataCORDER Pre--trip Result Records 3--32.................................................
Table 3--10 DataCORDER Alarm Indications 3--33......................................................
Table 6--1 Valve Override Control Displays 6--17........................................................
Table 6--2 Sensor Resistance 6--23...................................................................
Table 6--3 Sensor Resistance (CPDS) 6--24............................................................
Table 6--4 Recommended Bolt Torque Values 6--29.....................................................
Table 6--5 R-134a Temperature - Pressure Chart 6--30..................................................
vii T-340
Page 10

SAFETY SUMMARY
GENERAL SAFETY NOTICES
The following general safety notices supplement specific warnings and cautions appearing elsewhere in this
manual. They are recommended precautions that must
be understood and applied during operation and maintenance of the equipment covered herein. The general
safety notices are presented in the following three sections labeled: First Aid, Operating Precautions and
Maintenance Precautions. A listing of the specific warnings and cautions appearing elsewhere in the manual
follows the general safety notices.
FIRST AID
An injury, no matter how slight, should never go unattended. Always obtain first aid or medical attention immediately.
OPERATING PRECAUTIONS
Always wear safety glasses.
Keep hands, clothing and tools clear of the evaporator
and condenser fans.
No work should be performed on the unit until all circuit
breakers and start-stop switches are turned off, and
power supply is disconnected.
In case of severe vibration or unusual noise, stop the
unit and investigate.
CAUTION - means to warn against potential hazard or
unsafe practice that couldresult inminor personal injury,
product or property damage.
The statements listed below are applicable to the refrigeration unit and appear elsewhere in this manual. These
recommended precautions must be understood and applied during operation and maintenance of the equipment covered herein.
DANGER
Never use air for leak testing. It has been determined that pressurized, mixtures of refrigerant and air can undergo combustion
when exposed to an ignition source.
WARNING
Beware of unannounced starting of the
evaporator and condenser fans. The unit
may cycle the fans and compressor unexpectedly as control requirements dictate.
MAINTENANCE PRECAUTIONS
Beware of unannounced starting of the evaporator and
condenser fans. Do not open the condenser fan grille or
evaporator access panels before turning power off, disconnecting and securing the power plug.
Be sure power is turned off before working on motors,
controllers, solenoid valves and electrical control
switches. Tag circuit breaker and power supply to prevent accidental energizing of circuit.
Do not bypass any electrical safety devices, e.g. bridging an overload, or using any sort of jumper wires. Problems with the system should be diagnosed, and any
necessary repairs performed by qualified service personnel.
When performing any arc welding on the unit or container, disconnect all wire harness connectors from the
modules in control boxes. Do not remove wire harness
from the modules unless you are grounded to the unit
frame with a static safe wrist strap.
In case of electrical fire, open circuit switch and extinguish with CO
SPECIFIC WARNING AND CAUTION STATEMENTS
To help identify the label hazards on the unit and explain
the level of awareness each one carries, an explanation
is given with the appropriate consequences:
DANGER - means an immediate hazard that WILL result in severe personal injury or death.
WARNING - means to warn against hazards or unsafe
conditions that COULD result in severe personal injury
or death.
(never use water).
2
WARNING
Do not attempt to remove power plug(s) be fore turning OFF start-stop switch (ST), unit
circuit breaker(s) and external power
source.
WARNING
Make sure the power plugs are clean and
dry before connecting to power receptacle.
WARNING
Make sure that the unit circuit breaker(s)
(CB-1 & CB-2) and the START-STOP switch
(ST) are in the “O” (OFF) position before
connecting to any electrical power source.
WARNING
Always turn OFF the unit circuit breakers
(CB-1 & CB-2) and disconnect main power
supply before working on moving parts.
Safety--1
T--340
Page 11

WARNING
CAUTION
Make sure power to the unit is OFF and
power plug disconnected before replacing
the compressor.
WARNING
Before disassembly of the compressor, be
sure to relieve the internal pressure very
carefully by slightly loosening the couplings to break the seal.
WARNING
Do not use a nitrogen cylinder without a
pressure regulator. Do not use oxygen in or
near a refrigeration system as an explosion
may occur.
WARNING
Do not open the condenser fan grille before
turning power OFF and disconnecting
power plug.
Charge wate r--cooled condense r or receiver according to nameplate specifications to
ensure optimal unit performance.
CAUTION
Do not remove wire harnesses from controller modules unless you are grounded to
the unit frame with a static safe wrist strap.
CAUTION
Unplug all controller module wire harness
connectors before performing arc welding
on any part of the container.
CAUTION
Do not attempt to use an ML2i PC card in an
ML3 equipped unit. The PC cards are physically different and will result in damage to
the controller.
WARNING
Oakite No. 32 is an acid. Be sure that the
acid is slowly added to the water. DO NOT
PUT WATER INTO THE ACID - thiswill cause
spattering and excessive heat.
WARNING
Wear rubber gloves and wash the solution
from the skin immediately if accidental contact occurs. Do not allow the solution to
splash onto concrete.
WARNING
Always turn OFF the unit circuit breakers
(CB-1 and CB-2) and disconnect main
power supply before working on moving
parts.
WARNING
Installation requires wiring to the main unit
circuit breaker, CB1. Make sure the power to
the unit is off and power plug disconnected
before beginning installation.
CAUTION
Pre-tr ip inspection should not be performed with critical temperature cargoes in
the containe r.
CAUTION
When Pre-Trip key is pressed, economy , dehumidification and bulb mode will be deactivated. At the completion of Pre-Trip activity, econom y, dehumidification and bulb
mode must be reactivated.
CAUTION
When condenser water flow isbelow 11 lpm
(3 gpm) or when water-cooled operation is
not in use, the CFS switch MUST be set to
position “1” or the unit will not operate
properly.
CAUTION
When a failure occurs during automatic
testing, the unit will suspend operation
awaiting operator intervention.
T--340
Safety--2
Page 12
CAUTION
CAUTION
When Pre-Trip test Auto 2 runs to completion without being interrupted, the unit will
terminate pre-trip and display “Auto 2”
“end.” The unit will suspend operationuntil
the user depresses the ENTER key!
CAUTION
Allowing the scroll compressor to operate
in reverse for more than two minutes willresult in internal compressor damage. Turn
the start-stop switch OFF immediately.
CAUTION
To prevent trapping liquid refrigerant in the
manifold gauge set besure set is brought to
suction pressure before disconnecting.
CAUTION
Take necessary steps (place plywood over
coil or use sling on motor) to prevent motor
from falling into condenser coil.
CAUTION
Do not remove wire harnesses from module
unless you are grounded to the unit frame
with a static safe wrist strap.
CAUTION
Unplug all module connectors before performing arc welding on any part of the container.
CAUTION
The unit must be OFF whenever a programming card is inserted or removed from the
controller programming port.
CAUTION
The scroll compressor achieves low suction pressure very quickly. Do not use the
compressor to evacuate the system below
0 psig. Never operate the compressor with
the suction or discharge service valves
closed (frontseated). Internal damage will
result from operating the compressor in a
deep vacuum.
Use care when cutting wire ties to avoid
nicking or cutting wires.
CAUTION
Do not allow moisture to enter wire splice
area as this may affect the sensor resistance.
Safety--3
T--340
Page 13

SECTION 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1 INTRODUCTION
The Carrier Transicold model 69NT40--561--001 to 199
series units are of lightweight aluminum frame
construction, designed to fit in the front of a container
and serve as the container’s front wall.
They are one piece, self--contained, all electric units,
which include cooling and heating systems to provide
precise temperature control.
The units are supplied with a complete charge of
refrigerant R--134a and compressor lubricating oil, and
are ready for operation upon installation. Forklift
pockets are provided for unit installation and removal.
The base unit operates on nominal 380/460 volt,
3--phase, 50/60 hertz (Hz) power. An optional
autotransformer may be fitted to allow operation on
nominal 190/230, 3--phase, 50/60 Hz power. Power for
the control system is provided by a transformer which
steps the supply power down to 18 and 24 volts, single
phase.
The controller is a Carrier Transicold Micro--Link 3
microprocessor. The controller will operate
automatically to select cooling, holding or heating as
required to maintain the desired set point temperature
within very close limits. The unit may also be equipped
with an electronic temperature recorder.
The controller has a keypad and display for viewing or
changing operating parameters. The display is also
equipped with lights to indicate various modes of
operation.
1.2 CONFIGURATION IDENTIFICATION
Unit identification information is provided on a plate
located to the left of the receiver or water--cooled
condenser, on the back wall of the condenser section.
The plate provides the unit model number, the unit serial
number and the unit parts identification number (PID).
The model number identifies the overall unit
configuration, while the PID number provides
information on specific optional equipment, factory
provisioned to allow for field installation of optional
equipment and differences in detailed parts.
1.3 FEATURE DESCRIPTIONS
1.3.1 Control Box
Units are equipped with either an aluminum or
composite material box, and may be fitted with a
lockable door.
1.3.2 Temperature Readout
The unit is fitted with suction and discharge temperature
sensors. The sensor readings may be viewed on the
controller display.
1.3.3 Pressure Readout
The unit is fitted with evaporator and discharge
transducers. The transducer readings may be viewed
on the controller display.
1.3.4 Compressor
The unit is fitted with a scroll compressor equipped with
suction and discharge service connections.
1.3.5 Condenser Coil
The unit is fitted with a four--row condenser coil using
7mm tubing.
1.3.6 Evaporator
Evaporator section is equipped with an electronic
expansion valve (EEV).
1.3.7 Evaporator Fan Operation
Units are equipped with three--phase evaporator fan
motors. Opening of an evaporator fan internal protector
will shut down the unit.
1.3.8 Plate Set
Each unit is equipped with a tethered set of wiring
schematics and wiring diagram plates. The plate sets
are ordered using a seven--digit base part number and a
two--digit dash number.
1.4 OPTION DESCRIPTIONS
Various options may be factory or field equipped to the
base unit. These options are listed in the tables and
described in the following subparagraphs.
1.4.1 Battery
The refrigeration controller may be fitted with standard
replaceable batteries or a rechargeable battery pack.
Rechargeable battery packs may be fitted in the
standard or in a secure location.
1.4.2 Dehumidification
The unit may be fitted with a humidity sensor. This
sensor allows setting of a humidity set point in the
controller. In dehumidification mode, the controller will
operate to reduce internal container moisture level.
1.4.3 USDA
The unit may be supplied with fittings for additional
temperature probes, which allow recording of USDA
Cold Treatment data by the integral DataCORDER
function of the Micro--Link refrigeration controller.
1.4.4 Interrogator
Units that use the DataCORDER function are fitted with
interrogator receptacles for connection of equipment to
download the recorded data. Two receptacles may be
fitted; one is accessible from the front of the container
and the other is mounted inside the container (with the
USDA receptacles).
1.4.5 Remote Monitoring
The unit may be fitted with a remote monitoring
receptacle. This item allows connection of remote
indicators for COOL, DEFROST and IN RANGE.
Unless otherwise indicated, the receptacle is mounted
at the control box location.
1--1 T--340
Page 14

1.4.6 Communications Interface Module
The unit may be fitted with a communications interface
module. The communications interface module is a
slave module, which allows communication with a
master central monitoring station. The module will
respond to communication and return information over
the main power line. Refer to the ship master system
technical manual for further information.
1.4.7 Autotransformer
An autotransformer may be provided to allow operation
on 190/230, 3--phase, 50/60 Hz power. The
autotransformer raises the supply voltage to the
nominal 380/460 volt power required by the base unit.
The autotransformer may also be fitted with an
individual circuit breaker for the 230 volt power.
If the unit is equipped with an autotransformer and
communications module, the autotransformer will be
fitted with a transformer bridge unit (TBU) to assist in
communications.
1.4.8 Temperature Recorder
The unit may be fitted with an electronic temperature
recording device.
1.4.9 Handles
The unit may be equipped with handles to facilitate
access to stacked containers. These fixed handles are
located on either side of the unit.
1.4.10 Thermometer Port
The unit may be fitted with ports in the front of the frame
for insertion of a thermometer to measure supply and/or
return air temperature. If fitted, the port(s) will require a
cap and chain.
1.4.11 Water Cooling
The refrigeration system may be fitted with a
water--cooled condenser. The condenser is constructed
using copper--nickel tube for sea water applications.
The water--cooled condenser is in series with the air
cooled condenser and replaces the standard unit
receiver. When operating on the water--cooled
condenser, the condenser fan is deactivated by a water
pressure switch or condenser fan switch.
1.4.12 Back Panels
Aluminum back panels may have access doors and/or
hinge mounting.
1.4.13 460 Volt Cable
Various power cable and plug designs are available for
the main 460 volt supply . The plug options tailor the
cables to each customer’s requirements.
1.4.14 230 Volt Cable
Units equipped with an autotransformer require an
additional power cable for connection to the 230 volt
source. V arious power cable and plug designs are
available. The plug options tailor the cables to each
customer’s requirements.
1.4.15 Cable Restraint
Various designs are available for storage of the power
cables. These options are variations of the compressor
section cable guard.
1.4.16 Upper Air (Fresh Air Make Up)
The unit may be fitted with an upper fresh air makeup
assembly. The fresh air makeup assembly is available
with a vent positioning sensor (VPS) and may also be
fitted with screens.
1.4.17 Lower Air (Fresh Air Make Up)
The unit may be fitted with a lower fresh air makeup
assembly. The fresh air makeup assembly is available
with a vent positioning sensor (VPS) and may also be
fitted with screens.
1.4.18 Labels
Safety Instruction and Function Code listing labels
differ, depending on the options installed. Labels
available with additional languages are listed in the parts
list.
1.4.19 Controller
Two replacement controllers are available:
1. Remanufactured -- Controller is the equivalent of a
new OEM controller and is supplied with a 12--month
warranty.
2. Repaired -- Controller has had previous faults repaired and upgraded with the latest software.
Note: Repaired controllers are NOT to be used for
warranty repairs; only full OEM Remanufactured
controllers are to be used.
Controllers will be factory--equipped with the latest
version of operational software, but will NOT be
configured for a specific model number and will need to
be configured at the time of installation or sale.
1.4.20 Condenser Grille
Two styles of condenser grilles are available: direct
bolted grilles and hinged grilles.
1.4.21 Emergency Bypass
The optional Emergency Bypass switch (EB) functions
to bypass the controller in the event of controller failure.
1.4.22 eAutoFresh
The optional eAutoFresh venting system moderates the
atmospheric level inside the container unit in response
to cargo respiration.
T--340
1--2
Page 15
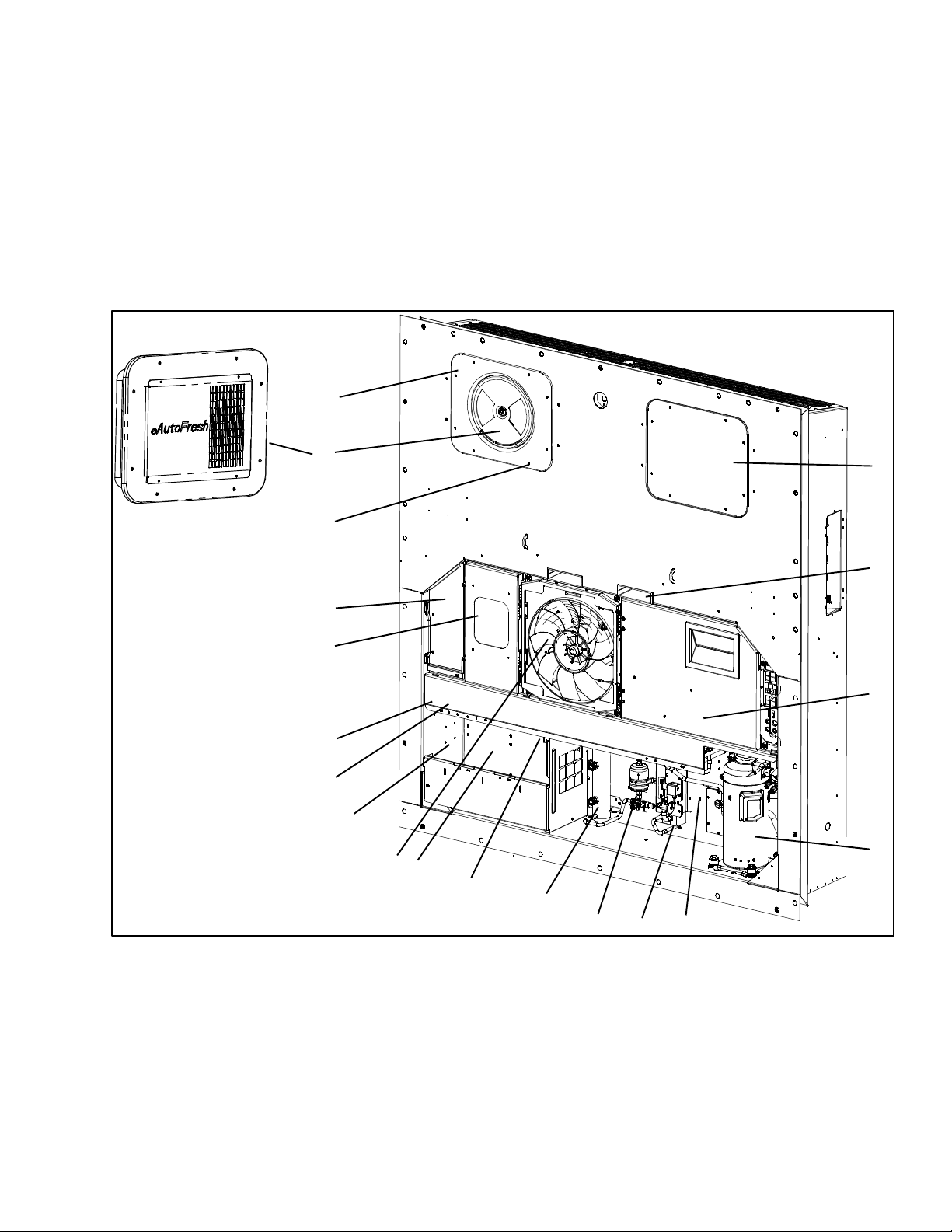
SECTION 2
DESCRIPTION
2.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1.1 Refrigeration Unit -- Front Section
The unit is designed so that the majority of the components are accessible from the front (see Figure 2--1).
The unit model number, serial number and parts identification number can be found on the serial plate to the left
of the receiver or water--cooled condenser on the back
wall of the condenser section.
19
2.1.2 Fresh Air Makeup Vent
The function of the upper or lower makeup air vent is to
provide ventilation for commodities that require fresh air
circulation. A manually operated venting system is located in the upper left access panel.
The optional eAutoFresh vent system is to moderate the
atmospheric level in the container in response to cargo
respiration. When transporting frozen cargo loads the
vent will be closed. The upper left access panel contains
the vent slide and motor assembly. It may be removed to
allow entry into the evaporator section where the CO
sensor and drive pack are located.
2
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
1. Access Panel (Evap. Fan #1)
2. Fork Lift Pockets
3. Control Box
4. Compressor
5. Ambient Sensor (AMBS)
6. Economizer
7. Filter Drier
8. Receiver or Water Cooled Condenser
9. Unit Serial Number, Model Number and
Parts Identification Number (PID) Plate
10. Power Cables and Plug (Location)
11. Condenser Fan
Figure 2--1 Refrigeration Unit -- Front Section
1
2
3
4
9
8
12. Autotransformer (Location)
13. TransFRESH Communications Connector
14. Interrogator Connector (Front left)
15. Temperature Recorder
16. Lower Fresh Air Makeup Vent Location
17. TIR (Transports Internationaux Routiers)
18. Upper Fresh Air Makeup Vent or eAutoFresh
19. Access Panel (Evap. Fan #2)
7
(Blank Cover Shown)
Sealing Provisions -- Typical All Panels
(Automatic Vent) panel
5
6
2--1
T-340
Page 16
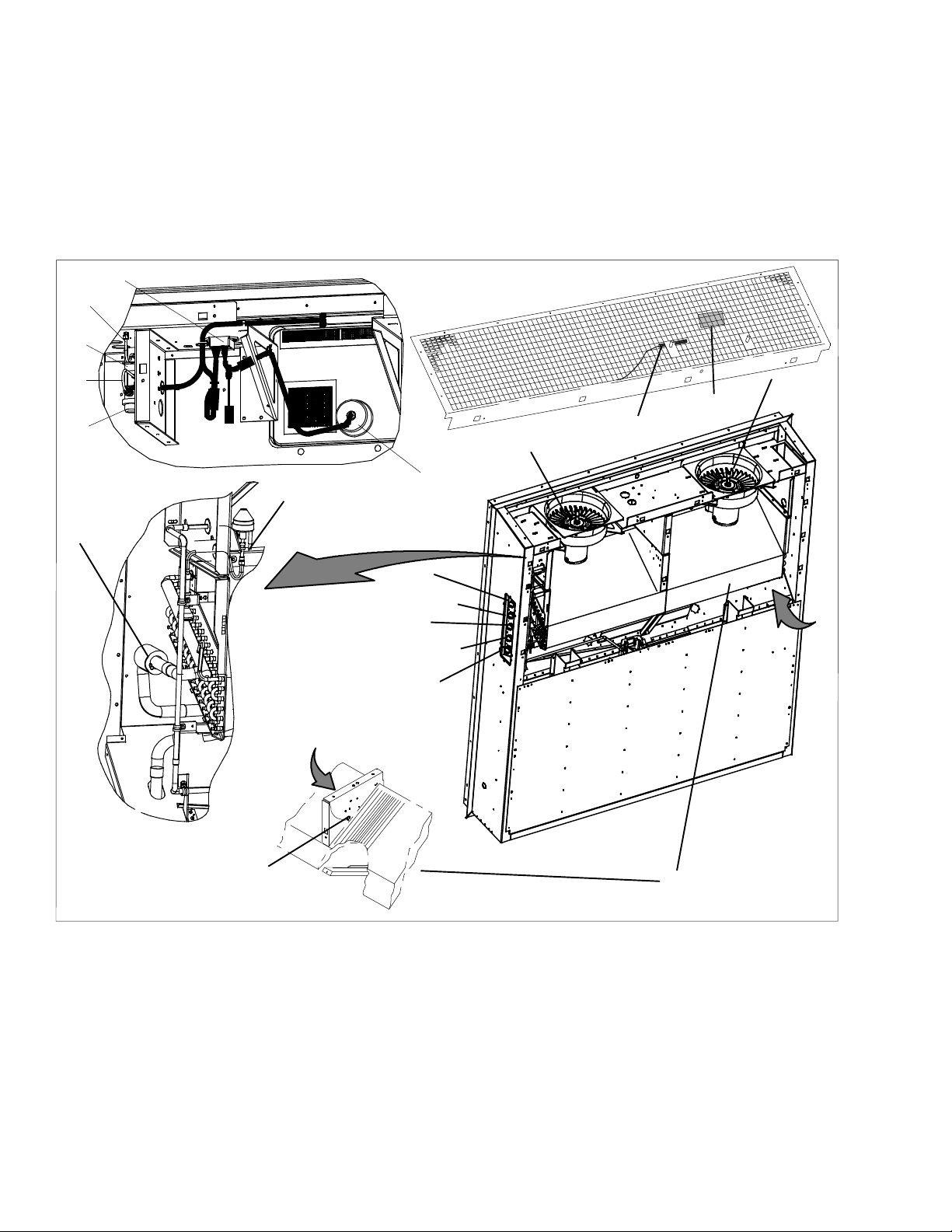
2.1.3 Evaporator Section
The evaporator section (Figure 2--2) contains the return
temperature sensor, humidity sensor, electronic expansion valve, dual speed evaporator fans (EM1 and EM2),
evaporator coil and heaters, defrost temperature sensor, heat termination thermostat and evaporator temperature sensors (ETS1 and ETS2).
The evaporator fans circulate air through the container
by pulling it in the top of the unit, directing it through the
evaporator coil, where it is heated or cooled, and
15
14
13
discharging it at the bottom.
If unit is equipped with eAutoFresh, system components are mounted in addition to the standard refrigeration unit components. The stepper motor component is
installed in the vent; the air filter, CO
motor drive and CO
sensing lines are installed on the
2
sensor, stepper
2
rib of the upper grill.
Most evaporator components are accessible by removing the upper rear panel (as shown in the illustration) or
by removing the evaporator fan access panels (see
Figure 2--1, Items 1 and 19.
12
10
11
4
3
2
1
9
16
21
20
19
6
18
17
7
8
1. Evaporator Fan Motor #1 (EM1)
2. Return Recorder Sensor/Temperature Sensor
(RRS/RTS)
3. Humidity Sensor (HS)
4. Evaporator Fan Motor #2 (EM2)
5. Evaporator Coil
6. Evaporator Coil Heaters (Underside of Coil)
7. Heater Termination Thermostat (HTT)
8. Defrost Temperature Sensor (DTS)
9. Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV)
10. Evaporator Temperature Sensors (Location)
(ETS1 and ETS2)
Figure 2--2 Evaporator Section
5
11. Air Filter
12. CO
13. CO
14. CO
Sensor Sensing Line
2
Sensor (COS)
2
Sensor Outlet Line
2
15. Stepper Motor Drive (SD)
16. Stepper Motor (AF)
17. Interrogator Connector (Rear) (ICR)
18. USDA Probe Receptacle PR2
19. USDA Probe Receptacle PR1
20. USDA Probe Receptacle PR3
21. Cargo Probe Receptacle PR4
2--2T-340
Page 17
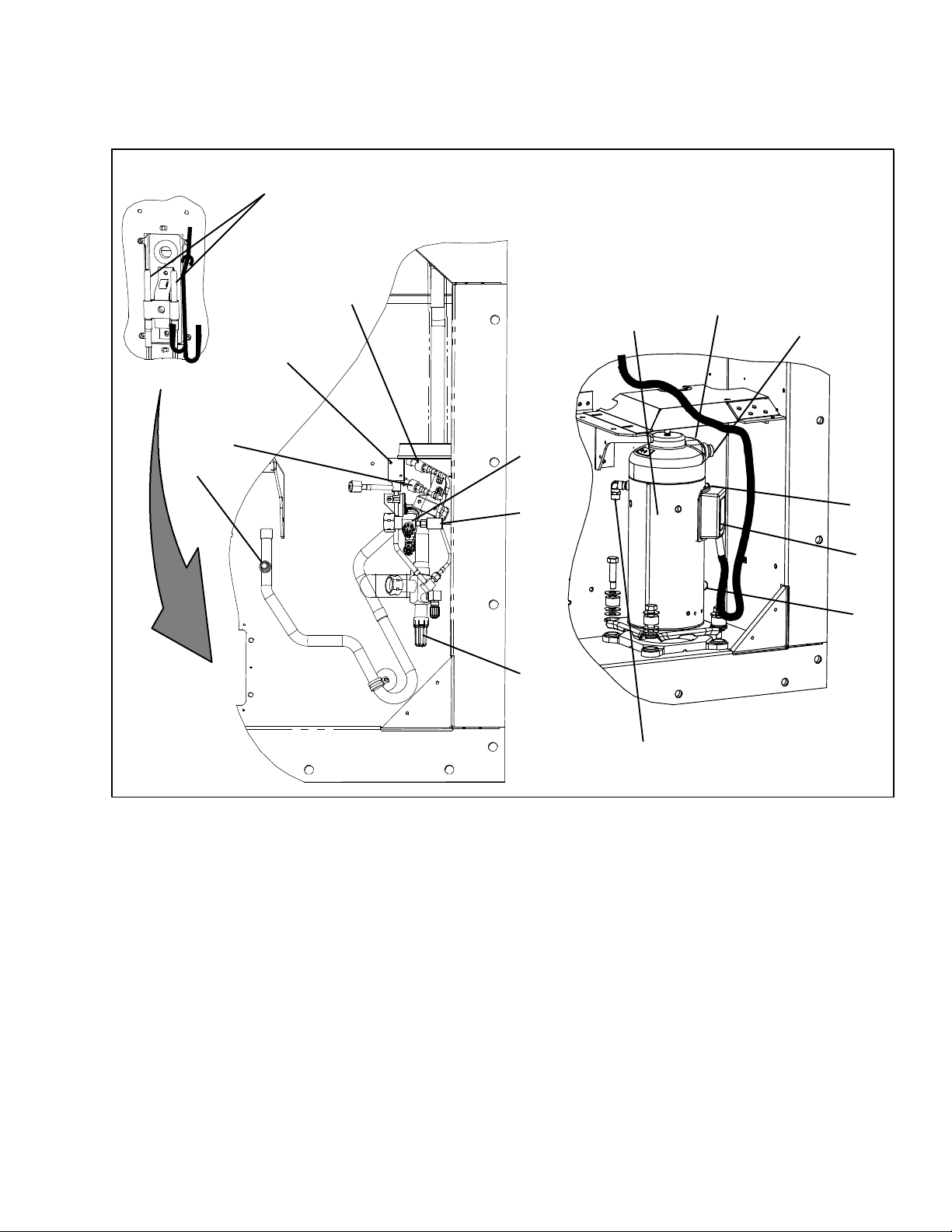
2.1.4 Compressor Section
The compressor section includes the compressor,
digital unloader valve (DUV), high pressure switch,
discharge pressure transducer (DPT), evaporator
15
pressure transducer (EPT) and the suction pressure
transducer (SPT).
The supply temperature sensor, supply recorder sensor
and ambient sensor are located to the left of the compressor.
11
1
10
9
12
8
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
1. Compressor
2. Compressor Discharge Temperature Sensor
(CPDS) (Location)
3. Discharge Connection
4. Suction Connection (Location)
5. Compressor Terminal Box
6. Oil Drain (Location)
7. Economizer Connection
8. Discharge Pressure Transducer (DPT)
Figure 2--3 Compressor Section
7
9. Suction Pressure Transducer (SPT)
10. Digital Unloader Valve (DUV)
11. Evaporator Pressure Transducer (EPT)
12. Discharge Service Valve
13. High Pressure Switch (HPS)
14. Suction Service Valve
15. Supply Temperature/Supply Recorder Sensor
Assembly (STS/SRS)
2--3
T-340
Page 18
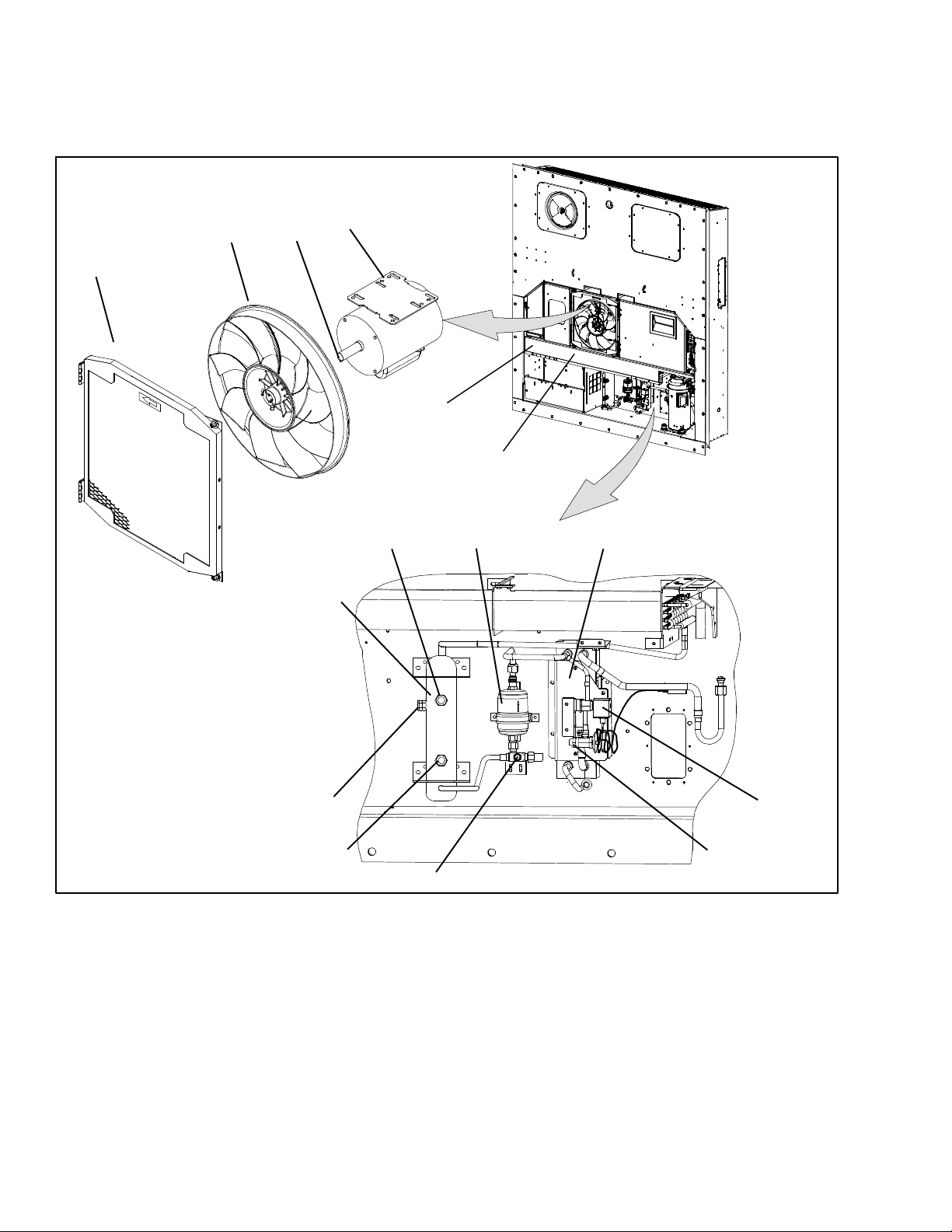
2.1.5 Air-- Cooled Condenser Section
The air--cooled condenser section (Figure 2--4)
consists of the condenser fan, condenser coil, receiver,
liquid line service valve, filter drier, fusible plug,
economizer, economizer expansion valve, economizer
solenoid valve (ESV), and sight glass/moisture
indicator.
The condenser fan pulls air through the bottom of the
coil and discharges it horizontally through the condenser fan grille.
2
1
3
4
5
6
89 10
7
1. Grille and Venturi Assembly
2. Condenser Fan
3. Key
4. Condenser Fan Motor
5. Condenser Coil
6. Condenser Coil Cover
7. Receiver
8. Sight Glass
15
14
13
9. Filter Drier
10. Economizer
11. Economizer Solenoid Valve (ESV)
12. Economizer Expansion Valve
13. Service Access Valve
14. Liquid Level/Moisture Indicator
15. Fusible Plug
Figure 2--4 Air--Cooled Condenser Section
2--4T-340
11
12
Page 19
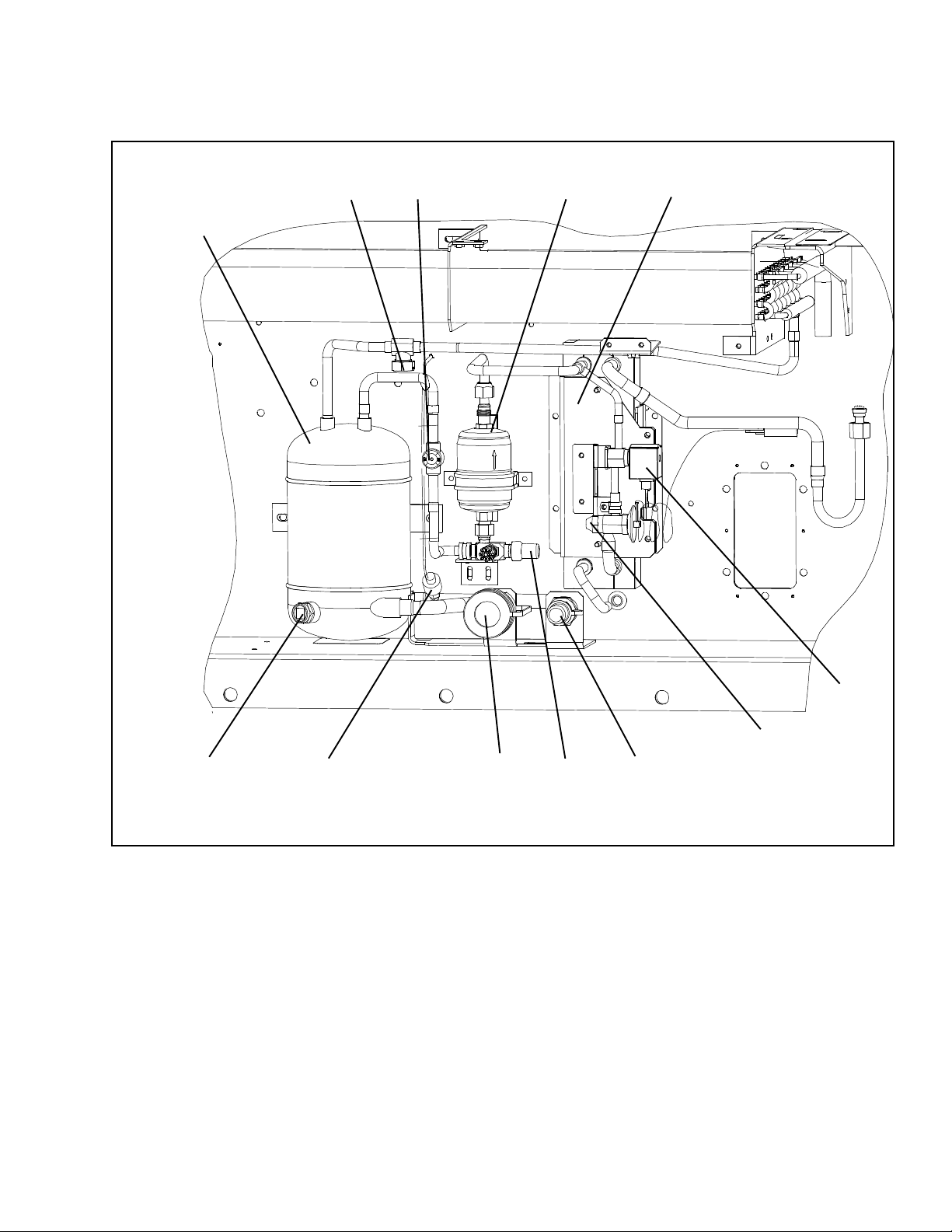
2.1.6 Water-- Cooled Condenser Section
The water--cooled condenser section (Figure 2--5) consists of a water--cooled condenser , sight glass, rupture
disc, filter drier, water couplings, water pressure switch,
economizer, economizer expansion valve, economizer
solenoid valve (ESV), and moisture/liquid indicator.
The water--cooled condenser replaces the standard unit
receiver.
23 4
1
5
12
1. Water--Cooled Condenser
2. Rupture Disc
3. Moisture/Liquid Indicator
4. Filter Drier
5. Economizer
6. Economizer Solenoid Valve (ESV)
11
Figure 2--5 Water--Cooled Condenser Section
10 9
7. Economizer Expansion Valve
8. Coupling (Water In)
9. Liquid Line Service Valve/Connection
10. Self Draining Coupling (Water Out)
11. Water Pressure Switch (WP)
12. Sight Glass
8
6
7
2--5
T-340
Page 20
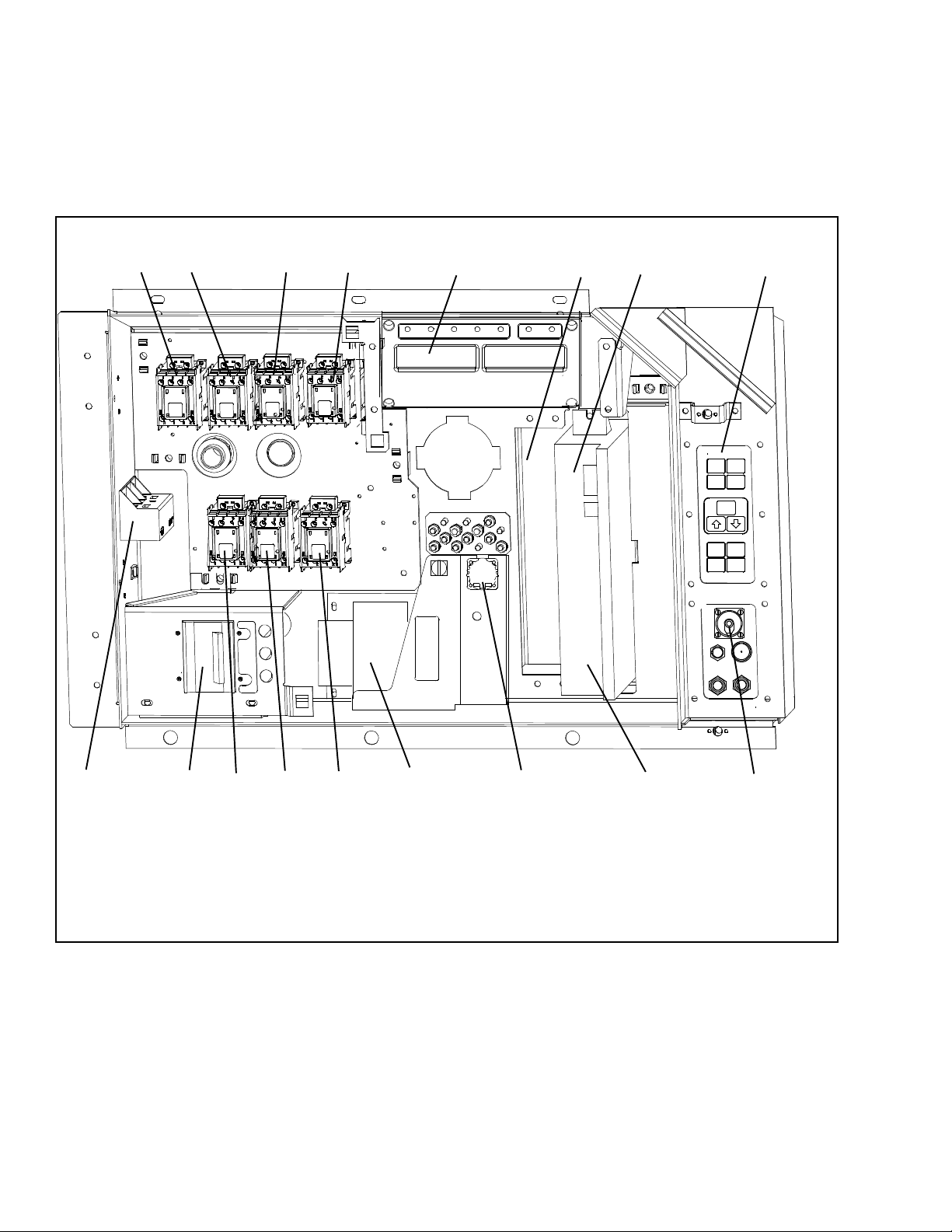
2.1.7 Control Box Section
2.1.8 Communications Interface Module
The control box (Figure 2--6) includes: the manual operation switches, circuit breaker (CB--1), compressor,
fan and heater contactors, control power transformer,
fuses, key pad, display module, current sensor module,
controller module and the communications interface
module.
1567
32
4
The optional communications interface module is a
slave module that allows communication with a master
central monitoring station. The module will respond to
communication and return information over the main
power line. Refer to the master central monitoring station technical manual for additional information.
8
15
1617 12
1. Compressor Contactor -- CH
2. Compressor Phase A Contactor -- PA
3. Compressor Phase B Contactor -- PB
4. Heater Contactor -- HR
5. Display Module
6. Communications Interface Module
7. Controller/DataCORDER Module (Controller)
8. Key Pad
9. Remote Monitoring Receptacle
14 13
Figure 2--6 Control Box Section
10
10. Controller Battery Pack (Standard Location)
1 1. Interrogator Connector (Box Location)
12. Control Transformer
13. High Speed Evaporator Fan Contactor -- EF
14. Low Speed Evaporator Fan Contactor -- ES
15. Condenser Fan Contactor -- CF
16. Circuit Breaker -- 460V
17. Current Sensor Module
2--6T-340
911
Page 21
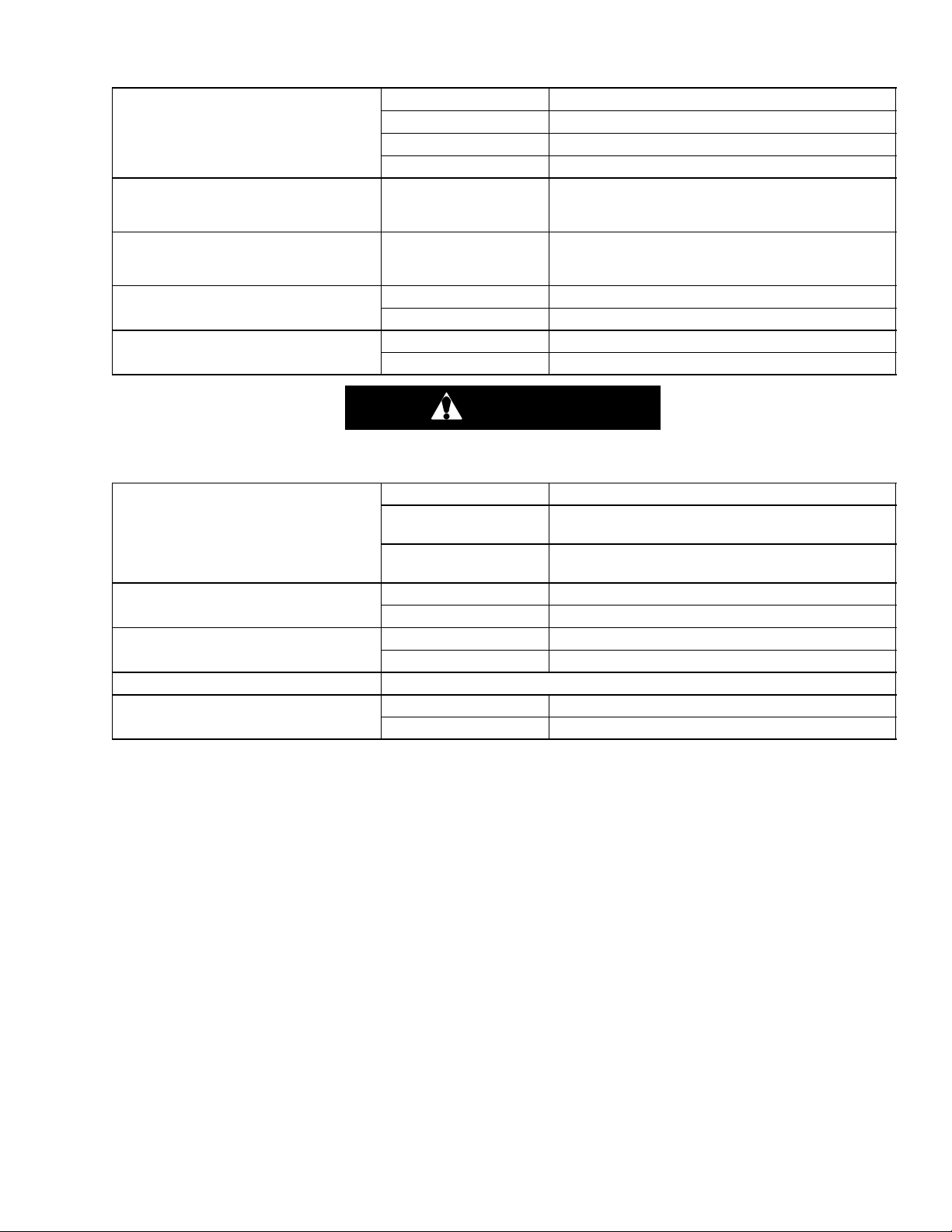
2.2 REFRIGERATION SYSTEM DATA
Model Number ZMD26KVE-- TFD --272
a. Compressor/Motor
Assembly
b. Electronic Expansion Valve
Superheat (Evaporator)
c. Economizer Expansion
Valve Superheat
d. Heater Termination Thermostat
e. High Pressure Switch
Weight (With Oil) 42.9 kg (95 lb)
Approved Oil Uniqema Emkarate RL--32--3MAF
Oil Charge 1774 ml (60 ounces)
Verify at --18_C
(0F) container box
temperature
Verify at --18_C
(0F) container box
temperature
Opens 54_ (+/-- 3) C = 130_ (+/-- 5) F
Closes 38_ (+/-- 4) C = 100_ (+/-- 7) F
Cutout 25 (+/-- 1.0) kg/cm2= 350 (+/-- 10) psig
Cut--In 18 (+/-- 0.7) kg/cm2= 250 (+/-- 10) psig
4.4to6.7_C(8to12_F)
4.4to11.1_C(8to20_F)
CAUTION
Charge wa t e r--cooled condenser or receiver according to nameplate specifications to ensure
optimal unit per for m ance.
Unit Configuration Charge R e quir ements
Water--Cooled
f. Refrigerant Charge -- R--134a
g. Fusible Plug
h. Rupture Disc
i. Unit Weight Refer to unit model number plate.
j. Water Pressure Switch
Condenser
Receiver
Melting point 99_C = (210_F)
Torque 6.2to6.9mkg(45to50ft--lbs)
Bursts at 35 +/-- 5% kg/cm2= (500 +/-- 5% psig)
Torque 6.2to6.9mkg(45to50ft--lbs)
Cut--In 0.5 +/-- 0.2 kg/cm2(7 +/-- 3 psig)
Cutout 1.6 +/-- 0.4 kg/cm2(22 +/-- 5 psig)
5.44 kg
(12 lbs)
4.99 kg
(11 lbs)
2--7
T-340
Page 22
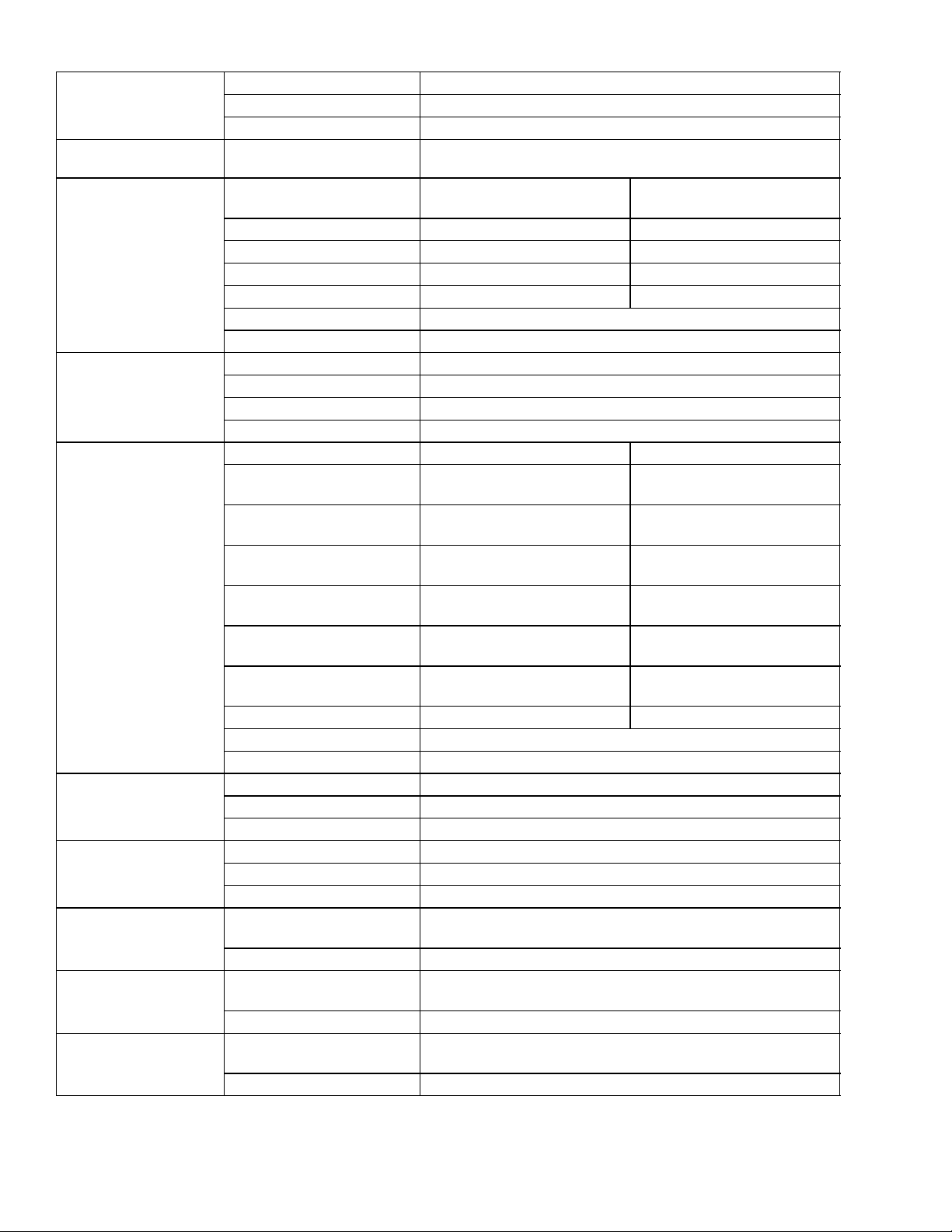
2.3 ELECTRICAL DATA
a. Circuit Breaker
b. Compressor
Motor
c. Condenser Fan
Motor
d. Evaporator Coil
Heaters
e. Evaporator Fan
Motor(s)
f. Fuses
g. Vent Positioning
Sensor
h. Solenoid V alv e
Coils (ESV)
24 VDC
i. DUV Coils
12 VDC
j. EEV Nominal
Resistance
CB--1 Trips at 29 amps
CB--2 (50 amp) Trips at 62.5 amps
CB--2 (70 amp) Trips at 87.5 amps
Full Load Amps (FLA) 13 amps @ 460 VAC
380 VAC, Single Phase,
50 Hz
460 VAC, Single Phase,
60 Hz
Full Load Amps 1.3 amps 1.6 amps
Horsepower 0.43 hp 0.75 hp
Rotations Per Minute 1425 rpm 1725 rpm
Voltage and Frequency 360 -- 460 VAC +/-- 2.5 Hz 400 -- 500 VAC +/-- 2.5 Hz
Bearing Lubrication Factory lubricated, additional grease not required.
Rotation Counter--clockwise when viewed from shaft end.
Number of Heaters 6
Rating 750 watts +5/--10% each @ 230 VAC
Resistance (cold) 66.8 to 77.2 ohms @ 20_C(68_F)
Type Sheath
380 VAC/3 PH/50 Hz 460 VAC/3 PH/60 Hz
Full Load Amps
High Speed
Full Load Amps
Low Speed
Nominal Horsepower
High Speed
Nominal Horsepower
Low Speed
Rotations Per Minute
High Speed
Rotations Per Minute
Low Speed
1.0 1.2
0.6 0.6
0.49 0.84
0.06 0.11
2850 rpm 3450 rpm
1425 rpm 1725 rpm
Voltage and Frequency 360 -- 460 VAC +/-- 1.25 Hz 400 -- 500 VAC +/-- 1.5 Hz
Bearing Lubrication Factory lubricated, additional grease not required
Rotation CW when viewed from shaft end
Control Circuit 7.5 amps (F3A,F3B)
Controller/DataCORDER 5amps(F1&F2)
Emergency Bypass 10 amps (FEB)
Electrical Output 0.5 VDC to 4.5 VDC over 90 degree range
Supply Voltage 5 VDC +/-- 10%
Supply Current 5mA(typical)
Nominal Resistance @
77_F(25_C)
7.7 ohms +/-- 5%
Maximum Current Draw 0.7 amps
Nominal Resistance @
77_F(20_C)
14.8 ohms +/-- 5%
Maximum Current Draw 929 mA
Coil Feed to Ground
(Gray Wire)
47 ohms
Coil Feed to Coil Feed 95 ohms
2--8T-340
Page 23
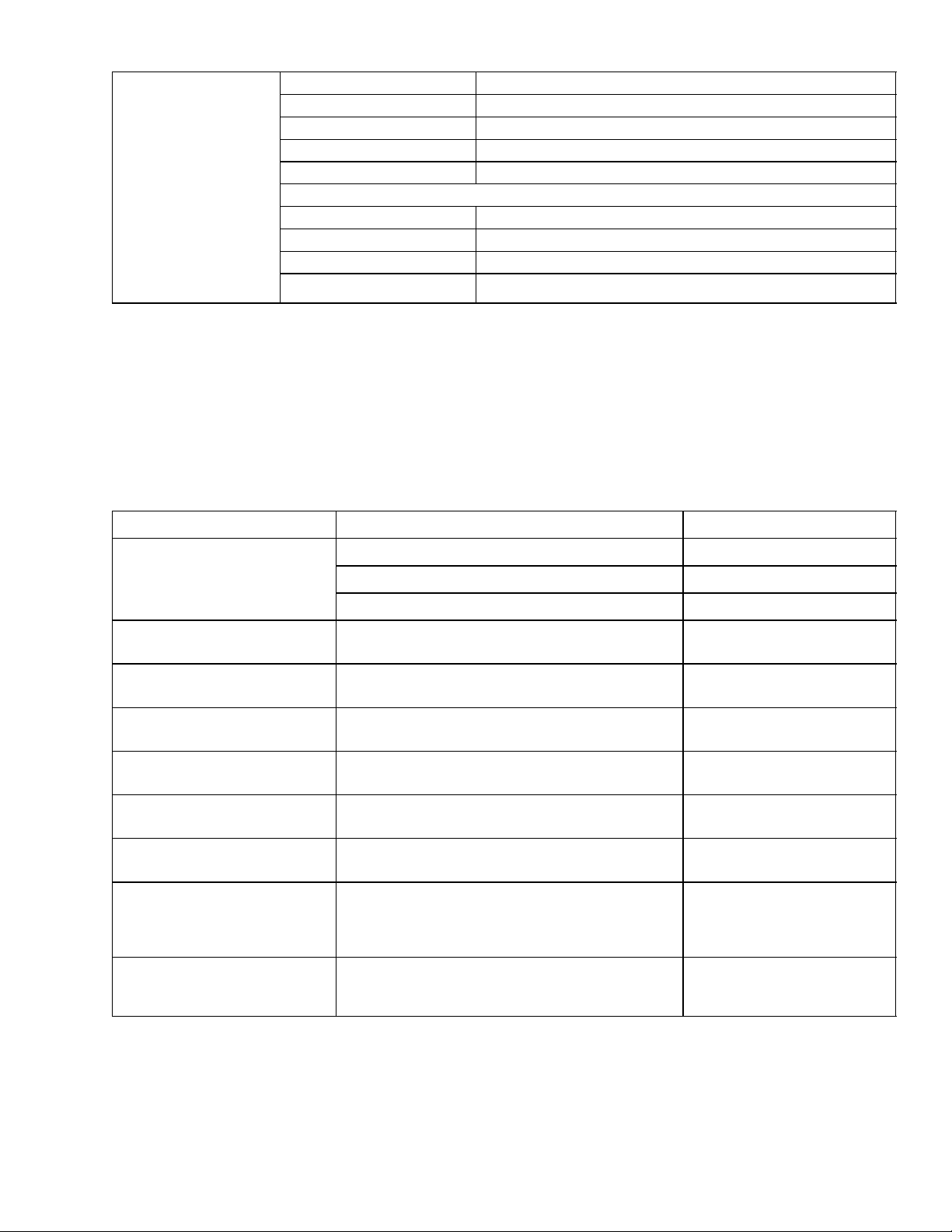
Section 2.3 -- ELECTRICAL DAT A--CONTINUED
Orange wire Power
Red wire Output
Brown wire Ground
Input voltage 5VDC
k. Humidity Sensor
Output voltage 0to3.3VDC
Output voltage readings verses relative humidity (RH) percentage:
30% 0.99 V
50% 1.65 V
70% 2.31 V
90% 2.97 V
2.4 SAFETY AND PROTECTIVE DEVICES
Unit components are protected from damage by safety
and protective devices listed in Table 2--1. These devices monitor the unit operating conditions and open a
set of electrical contacts when an unsafe condition occurs.
Open safety switch contacts on either or both of devices
IP--CP or HPS will shut down the compressor.
Table 2--1 Safety and Protective Devices
Open safety switch contacts on device IP--CM will shut
down the condenser fan motor.
The entire refrigeration unit will shut down if one of the
following safety devices open: (a) circuit breaker(s); (b)
fuse (F3A/F3B, 7.5A); or (c) evaporator fan motor internal protector(s) -- (IP).
UNSAFE CONDITION
DEVICE DEVICE SETTING
Circuit Breaker (CB--1) -- Manual Reset Tripsat29amps(460VAC)
Excessive current draw Circuit B reak er (CB--2, 50 a mp) -- Manual Reset Trips at 62.5 amps (230 VAC)
Circuit B reak er (CB--2, 70 a mp) -- Manual Reset Trips at 87.5 amps (230 VAC)
Excessive current draw in the
control circuit
Excessive current draw by the
controller
Excessive current draw by the
Emergency Bypass module
Excessive condenser fan
motor winding temperature
Excessive compressor motor
winding temperature
Excessive evaporator fan
motor(s) winding temperature
Abnormal pressures/temperatures in the high refrigerant
side
Abnormally high discharge
pressure
Fuse(F3A&F3B) 7.5 amp rating
Fuse (F1 & F2) 5 amp rating
Fuse (FEB) 10 amp rating
Internal Protector (IP--CM) -- Automatic Reset N/A
Internal Protector (IP--CP) -- Automatic Reset N/A
Internal Protector(s) (IP--EM) -- Automatic Reset N/A
FusiblePlug--UsedontheReceiver
Rupture Disc -- Used on the Water--Cooled Con-
99_C = (210_F)
35 kg/cm
2
= (500 psig)
denser
High Pressure Switch (HPS)
Opens at 25 kg/cm
(350 psig)
2
2--9
T-340
Page 24

2.5 REFRIGERATION CIRCUIT
2.5.1 Standard Operation
Starting at the compressor, (see Figure 2--7, upper
schematic) the suction gas is compressed to a higher
pressure and temperature.
The refrigerant gas flows through the discharge line and
continues into the air-- cooled condenser. When operating with the air--cooled condenser active, air flowing
across the coil fins and tubes cools the gas to saturation
temperature. By removing latent heat, the gas condenses to a high pressure/high temperature liquid and
flows to the receiver, which stores the additional charge
necessary for low temperature operation.
When operating with the water--cooled condenser active (see Figure 2--7, lower schematic), the refrigerant
gas passes through the air--cooled condenser and enters the water--cooled condenser shell. The water flowing inside the tubing cools the gas to saturation temperature in the same manner as the air passing over the
air--cooled condenser. The refrigerant condenses on
the outside of the tubes and exits as a high temperature
liquid. The water--cooled condenser also acts as a receiver, storing refrigerant for low temperature operation.
The liquid refrigerant continues through the liquid line,
the filter drier (which keeps refrigerant clean and dry)
and the economizer (not active during standard operation) to the electronic expansion valve. As the liquid refrigerant passes through the variable orifice of the expansion valve, some of it vaporizes into a gas (flash
gas). Heat is absorbed from the return air by the balance
of the liquid, causing it to vaporize in the evaporator coil.
The vapor then flows through the suction tube back to
the compressor.
On systems fitted with a water pressure switch, the condenser fan will be off when there is sufficient pressure to
open the switch. If water pressure drops below the
switch cut out setting, the condenser fan will automatically start.
During the standard mode of operation, the normally
closed digital unloader valve (DUV) controls the system
refrigerant flow and capacity by loading and unloading
the compressor in frequent discrete time intervals. If the
system capacity has been decreased to the lowest allowable capacity with the DUV, the unit will enter a trim
heat mode of operation, during which the controller will
pulse the evaporator heaters in sequence with the compressor digital signal in order to absorb the excess capacity.
2.5.2 Economized Operation
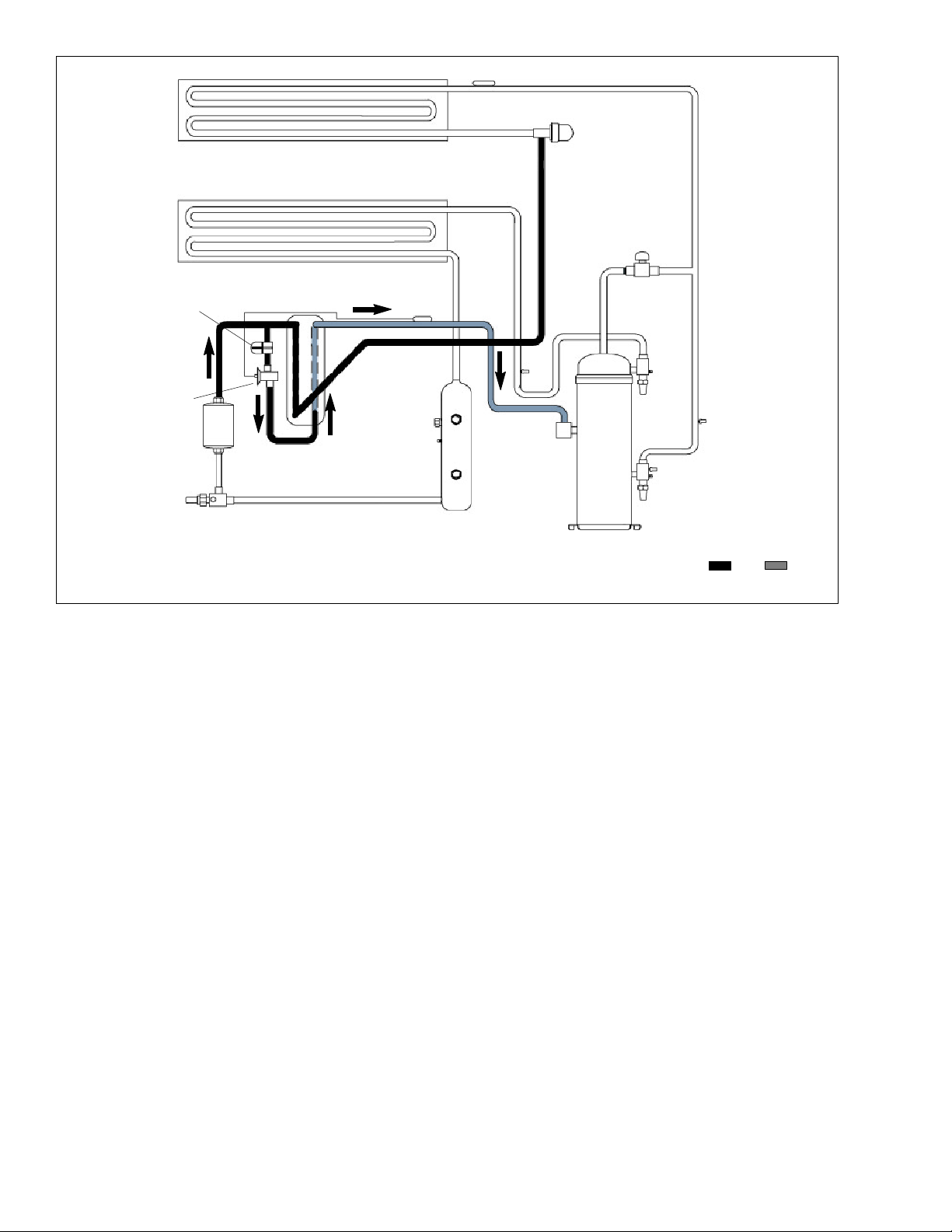
In the economized mode, (see Figure 2--8) the frozen
and pull down capacity of the unit is increased by subcooling the liquid refrigerant entering the electronic expansion valve. Overall efficiency is increased because
the gas leaving the economizer enters the compressor
at a higher pressure, therefore requiring less energy to
compress it to the required condensing conditions.
Liquid refrigerant for use in the economizer circuit istaken from the main liquid line as it leaves the filter drier.
The flow is activated when the controller energizes the
economizer solenoid valve (ESV).
The liquid refrigerant flows through the ESV to the expansion valve internal passages, absorbing heat from
the liquid refrigerant flowing to the electronic expansion
valve. The resultant “medium” temperature/pressure
gas enters the compressor at the economizer port fitting.
When the air temperature falls to 2.0_C(3.6_F) above
set point, the DUV unloads the compressor’s scroll and
begins to reduce the capacity of the unit. Percentage of
the unit capacity is accessed through code select 01
(Cd01). For example, if Cd01 displays 70, it indicates
that the compressor is operating unloaded with the DUV
engaged 30% of the time.
2.5.3 Electronic Expansion Valve
The microprocessor controls the superheat leaving the
evaporator via the electronic expansion valve (EEV),
based on inputs from the evaporator pressure transducer (EPT). The microprocessor transmits electronic
pulses to the EEV stepper motor, which opens or closes
the valve orifice to maintain the superheat set point.
2--10T-340
Page 25
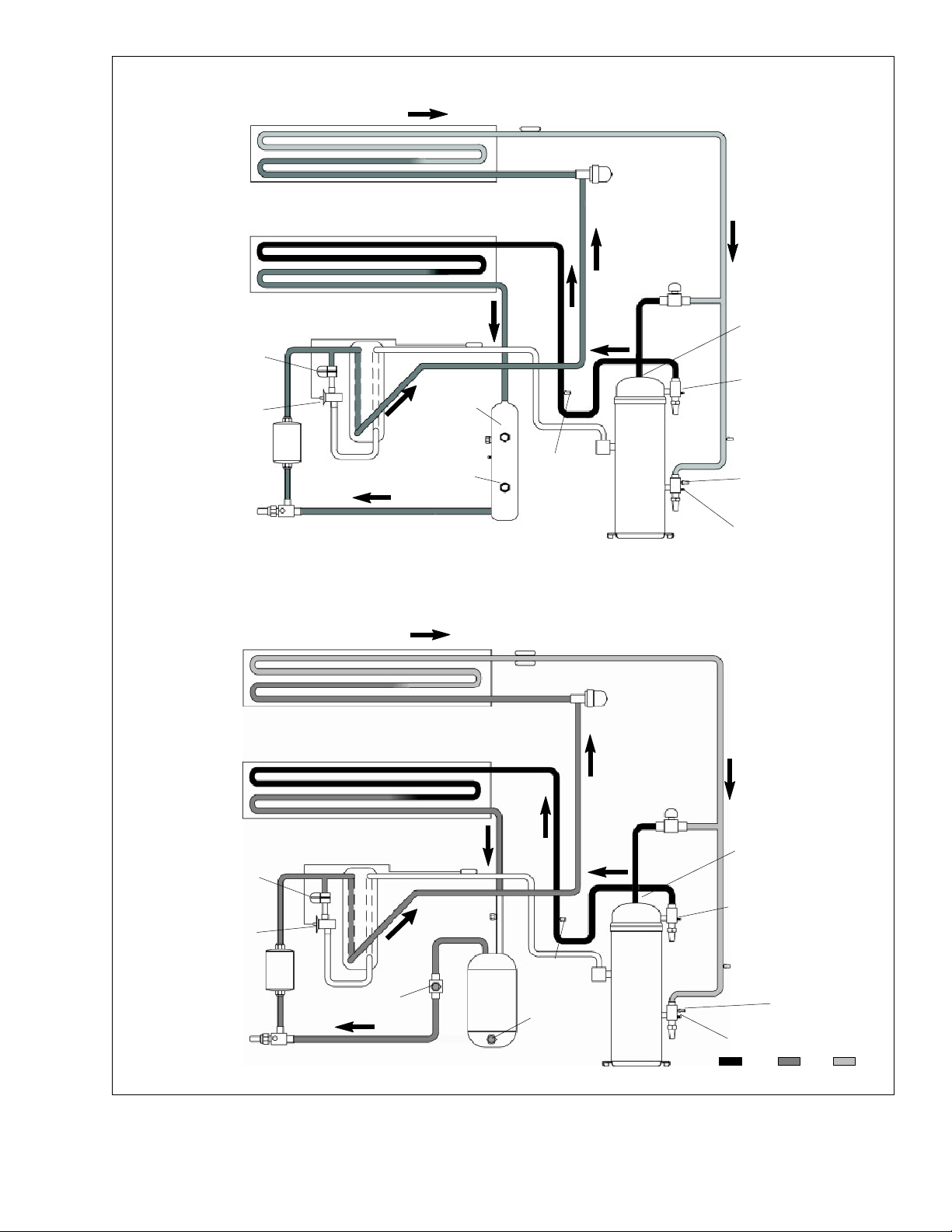
ECONOMIZER
SOLENOID
VALV E
ECONOMIZER
TXV
FILTER
DRIER
LIQUID LINE
SERVICE
VALV E
STANDARD OPERATION WITH RECEIVER
EVAPORATOR
CONDENSER
ECONOMIZER
ECON.
TXV
SENSING
BULB
SIGHT
GLASS
LIQUID LEVEL/
MOISTURE
INDICATOR
COMBO
ETS1 AND 2
RECEIVER
DISCHARGE
PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
ELECTRONIC
EXPANSION
VALV E
DIGITAL
UNLOADER
VALV E
COMPRESSOR
DISCHARGE
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DISCHARGE
SERVICE
VALV E
EVAPORATOR
PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
SUCTION
PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
SUCTION
SERVICE
VALV E
STANDARD OPERATION WITH W ATER--COOLED CONDENSER
ECONOMIZER
SOLENOID
VALV E
ECONOMIZER
TXV
FILTER
DRIER
LIQUID LINE
SERVICE
VALV E
EVAPORATOR
CONDENSER
ECONOMIZER
MOISTURE
INDICATOR
WATER-- COOLE D
ETS1 AND 2
CONDENSER
DISCHARGE
PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
SIGHT
GLASS
ELECTRONIC
EXPANSION
VALV E
DIGITAL
UNLOADER
VALV E
COMPRESSOR
DISCHARGE LIQUID
DISCHARGE
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DISCHARGE
SERVICE
VALV E
EVAPORATOR
PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
SUCTION
PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
SUCTION
SERVICE
VALV E
SUCTION
Figure 2--7 Refrigeration Circuit Schematic -- Standard Operation
2--11
T-340
Page 26
ECONOMIZER
SOLENOID
VALV E
ECONOMIZER
TXV
LIQUID LINE
SERVICE
VALV E
ECONOMIZER
ECON.
TXV
SENSING
BULB
RECEIVER
ELECTRONIC
EXPANSION
VALV E
COMPRESSOR
Figure 2--8 Refrigeration Circuit Schematic -- Economized Operation
LIQUID
ECONOMIZER
PRESSURE
2--12T-340
Page 27
SECTION 3
MICROPROCESSOR
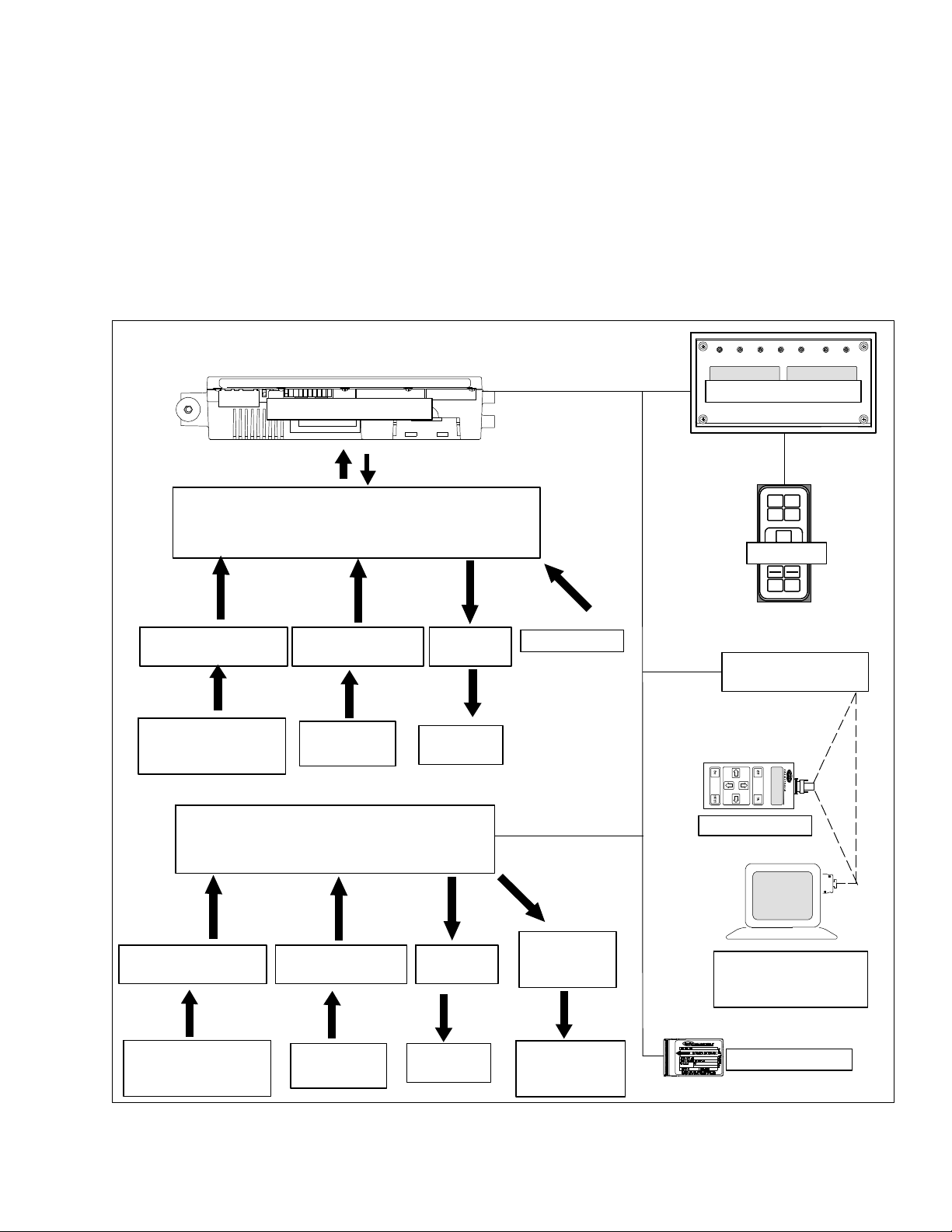
3.1 TEMPERATURE CONTROL
MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM
The temperature control Micro--Link 3 microprocessor
system (see Figure 3--1) consists of a keypad, display
module, the control module (controller) and interconnecting wiring. The controller houses the temperature
control software and the DataCORDER software. The
temperature control software functions to operate the
unit components as required to provide the desired cargo temperature and humidity. The DataCORDER software functions to record unit operating parameters and
CONTROL MODULE
TEMPERATURE CONTROL SOFTWARE
cargo temperature parameters for future retrieval. Coverage of the temperature control software begins with paragraph 3.2. Coverage of the DataCORDER software is
provided in paragraph 3.7.
The keypad and display module serve to provide user
access and readouts for both of the controller functions,
temperature control and DataCORDER. The functions
are accessed by keypad selections and viewed on the
display module. The components are designed to permit ease of installation and removal.
DISPLAY MODULE
KEYPAD
CONFIGURATION
SOFTWARE
CONFIGURATION
VARIABLE
(CnF##)
DataCORDER SOFTWARE
CONFIGURATION
SOFTWARE
CONFIGURATION
VARIABLE
(dCF## read only)
OPERATIONAL
SOFTWARE
FUNCTION
CODE (Cd)
OPERATIONAL
SOFTWARE
FUNCTION
CODE (dC)
ALARMS
(AL<70)
TO
DISPLAY
ALARMS
(AL>68)
TO
DISPLAY
PRE--TRIP
DATA
STORAGE
MEMORY
TO
DISPLAY
(Scrollback)
INTERROGATION
CONNECTOR
DATAREADER
Computer Device
With DataLINE
Software
PCMCIA CARD
Figure 3--1 Temperature Control System
3--1
T-340
Page 28
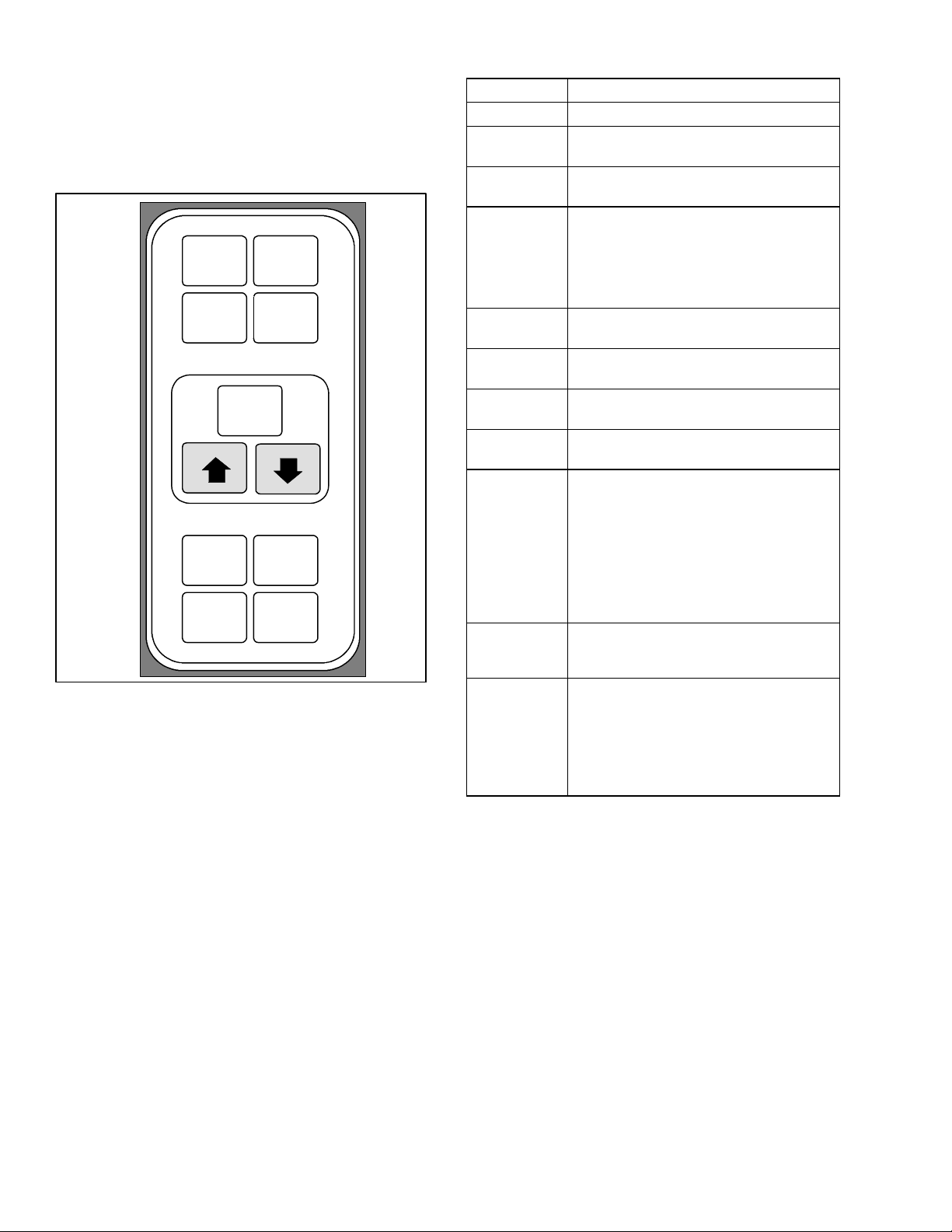
3.1.1 Keypad
Table 3--1 Keypad Function
The keypad (Figure 3--2) is mounted on the right--hand
side of the control box. The keypad consists of eleven
push button switches that act as the user’s interface
with the controller. Descriptions of the switch functions
are provided in Table 3--1.
1
3
2
4
5
6
8
10
1. Code Select
2. Pre--trip
3. Alarm List
4. Manual Defrost/
Interval
7
9
11
6. UP Arrow
7. DOWN Arrow
8. Return/Supply
9. Celsius/Fahrenheit
10. Battery Power
Figure 3--2 Keypad
3.1.2 Display Module
The display module (Figure 3--3) consists of two 5--digit
displays and seven indicator lights. The indicator lights
include:
1. Cool -- White or Blue LED: Energized when the refrigerant compressor is energized.
2. Heat -- Orange LED: Energized to indicate heater operation in the heat or defrost mode.
3. Defrost -- Orange LED: Energized when the unit is in
the defrost mode.
4. In--Range -- Green LED: Ene rgized whe n the control led tempe rature probe is within specified tolerance
of set point.
KEY
FUNCTION
Code Select Accesses function codes.
Pre--trip
Alarm List
Manual
Defrost/
Interval
Displays the pre--trip selection menu.
Discontinues pre--trip in progress.
Displays alarm list and clears the
alarm queue.
Displays selected defrost mode. Depressing and holding the Defrost interval key for five (5) seconds will initiate defrost using the same logic as
if the optional manual defrost switch
was toggled on.
Enter
Arrow Up
Arrow Down
Return/
Supply
Confirms a selection or saves a
selection to the controller.
Change or scroll a selection upward
Pre--trip advance or test interruption.
Change or scroll a selection downward. Pre--trip repeat backward.
Displays non--controlling probe temperature (momentary display).
Displays alternate English/Metric
scale (momentary display). When set
to F, pressure is displayed in psig and
Celsius /
Fahrenheit
vacuum in “/hg.” “P” appears after the
value to indicate psig and “i” appears
for inches of mercury.
When set to C, pressure readings are
in bars. “b” appears after the value to
indicate bars.
Battery
Power
Initiate battery backup mode to allow
set point and function code selection
if AC power is not connected.
This key is pressed to switch the
functions from the temperature software to the DataCORDER Software.
ALT. Mode
The remaining keys function the
same as described above except the
readings or changes are made to the
DataCORDER programming.
NOTE
The controlling probe in the perishable range
will be the SUPPLY air probe and the controlling
probe in the frozen range will be the RETURN
air probe.
5. Supply -- Yellow LED: Energized when the supply air
probe is used for control. When this LED is illuminated, the temperature displayed in the AIR TEMPERATURE display is the reading at the supply air
probe. This LED will flash if dehumidification or humidification is enabled.
6. Return -- Yellow LED: Energized when the return air
probe is used for control. When this LED is illuminated, the temperature displayed in the AIR TEMPERATURE display is the reading at the return air
probe. This LED will flash if dehumidification or humidification is enabled.
7. Alarm -- Red LED: Energized when there is an active
or an inactive shutdown alarm in the alarm queue.
3--2T-340
Page 29
COOL HEAT DEFROST IN RANGE ALARM SUPPLY RETURN
SETPOINT/Code AIR TEMPERATURE/Data
Figure 3--3 Display Module
3.1.3 Controller
CAUTION
Do not remove wire harnesses from controller modules unless you are grounded to
the unit frame with a static safe wrist strap.
CAUTION
Unplug all controller module wire harness
connectors before performing arc welding
on any part of the container.
CAUTION
Do not attempt to use an ML2i PC card in an
ML3 equipped unit. The PC cards are physically different and will result in damage to
the controller.
NOTE
Do not attempt to service the controller modules. Breaking the seal will void the warranty.
The Micro--Link 3 controller is a dual module microprocessor as shown in Figure 3--4. It is fitted with test
points, harness connectors and a software card programming port.
3.2 CONTROLLER SOFTWARE
The controller software is a custom designed program
that is subdivided into configuration software and operational software. The controller software performs the following functions:
a. Control supply or return air temperature to required
limits, provide modulated refrigeration operation,
economized operation, unloaded operation, electric
heat control and defrost. Defrost is performed to clear
buildup of frost and ice and ensure proper air flow
across the coil.
b. Provide default independent readouts of set point and
supply or return air temperatures.
c. Provide ability to read and (if applicable) modify the
configuration software variables, operating software
Function Codes and Alarm Code indications.
d. Provide a Pre--trip step--by--step checkout of refrig-
eration unit performance including: proper component operation, electronic and refrigeration control
operation, heater operation, probe calibration, pressure limiting and current limiting settings.
e. Provide battery--powered ability to access or change
selected codes and set point without AC power
connected.
f. Provide the ability to reprogram the software through
the use of a memory card.
3.2.1 Configuration Software (Variables)
The configuration software is a variable listing of the
components available for use by the operational software. This software is factory installed in accordance
with the equipment fitted and options listed on the original purchase order. Changes to the configuration software are required only when a new controller has been
installed or a physical change has been made to the unit
such as the addition or removal of an option. A configuration variable list is provided in Table 3--4. Change to
the factory--installed configuration software is achieved
via a configuration card or by communications.
3.2.2 Operational Software (Function Codes)
The operational software is the actual operation programming of the controller which activates or deactivates components in accordance with current unit operating conditions and operator selected modes of
operation.
1. Mounting Screw
2. Micro--Link 3 Control/DataCORDER Module
3. Connectors
4. Test Points
Figure 3--4 Control Module
5. Fuses
6. Control Circuit Power Connection
7. Software Programming Port
8. Battery Pack (Standard Location)
3--3
812 33 3 3 345 67
T-340
Page 30

The programming is divided into function codes. Some
of the codes are read only while the remaining codes
may be user configured. The value of the user configurable codes can be assigned in accordance with user desired mode of operation. A list of the function codes is
provided in Table 3--5.
To access the function codes, perform the following:
a. Press the CODE SELECT key, then press an arrow
key until the left window displays the desired code
number.
b. The right window will display the value of this item for
five seconds before returning to the normal display
mode.
c. If a longer time is desired, press the ENTER key to ex-
tendthetimetofiveminutes.
3.3 CONTROLLER SEQUENCE AND MODES OF
OPERATION
General operation sequences for cooling, heating and
defrost are provided in the following sub--paragraphs.
Schematic representation of controller action is
provided in Figure 3--5.
The operational software responds to various inputs.
These inputs come from the temperature and pressure
sensors, the temperature set point, the settings of the
configuration variables and the function code assignments. The action taken by the operational software will
change if any one of the inputs change. Overall interaction of the inputs is described as a “mode” of operation.
The modes of operation include perishable (chill) mode
and frozen mode. Descriptions of the controller interaction and modes of operation are provided in the following
sub paragraphs.
3.3.1 Start up -- Compressor Phase Sequence
The controller logic will check for proper phase sequencing and compressor rotation. If sequencing is allowing
the compressor and three--phase evaporator fan motor
to rotate in the wrong direction, the controller will energize or de--energize relay TCP as required (see Figure
7--2). Relay TCP will switch its contacts, energizing or
de--energizing relays PA and PB. Relay PA is wired to
energize the circuits(s) on L1, L2 and L3. Relay PB is
wired to energize the circuit(s) on L3, L2, and L1, thus
providing reverse rotation.
3.3.2 Start up -- Compressor Bump Start
The controller logic will initiate a compressor bump start
procedure to clear refrigerant from the compressor. If
suction and discharge pressures have equalized, the
compressor will perform three compressor bump starts.
A compressor bump start may occur after a defrost has
been completed.
During the procedure, the EEV will close. Relays TS,
TQ, TN, TE, TV will be de--energized (opened). The result of this action will close the ESV and shut all fans off.
The compressor will start for 1 second, then pause for
five seconds. This sequence will be repeated two additional times. After the final bump start the unit will pre-position the EEV to correct starting position pause and
startup.
3.3.3 Perishable Set Point Temperature --
Perishable Pulldown
When cooling from a temperature that is more than
2.5_C(4.5_F) above set point, the system will be in the
perishable pulldown mode in economized operation.
However, pressure and current limit functions may restrict the valve if either exceeds the preset value.
3.3.4 Perishable Set Point Temperature -Standard Temperature Control Mode
The unit is capable of maintaining supply air temperature to within +/ --0.2_C (+/--0.36_F) of set point. Supply
air temperature is controlled by positioning of the electronic expansion valve (EEV), cycling of the digital unloader valve (DUV), cycling of the compressor and cycling of the heaters.
Once set point is reached, the unit will transition to the
perishable steady state mode. This results in unloaded
operation by cycling the DUV to limit capacity and maintain steady temperature control.
If the controller has determined that cooling is not required or the controller logic determines suction pressure is at the low pressure limit, the unit will transition to
the perishable idle mode. The compressor is turned off
and the evaporator fans continue to run to circulate air
throughout the container. If temperature rises above set
point +0.2_C, the unit will transition back to the perishable steady state mode
If the temperature drops to 0.5_C(0.9_F) below set
point, the unit will transition to the perishable heating
mode and the heaters will be energized. The unit will
transition back to the perishable idle mode when the
temperature rises to 0.2_C(0.4_F) below the set point
and the heaters will de--energize.
3.3.5 Perishable Set Point Temperature -Economy Fa n Oper ation Mode
The economy mode is an extension of the standard
mode. The mode is activated when the setting of function code Cd34 is “ON.” Economy mode is provided for
power saving purposes. Economy mode could be utilized in the transportation of temperature--tolerant cargo
or non--respiration items which do not require high airflow for removing respiration heat. There is no active
display indicator that economy mode has been activated. To check for economy mode, perform a manual
display of code Cd34.
In order to achieve economy mode, a perishable set
point must be selected prior to activation. When economy mode is active, the evaporator fans will be controlled as follows:
At the start of each cooling or heating cycle, the evaporator fans will run in high speed for three minutes. They
will then be switched to low speed any time the supply
air temperature is within +/- - 0.2_C (0.36_F) of the set
point and the return air temperature is less than or equal
to the supply air temperature +3_C(5.4_F). The fans will
continue to run in low speed for one hour. At the end of
the hour, the evaporator fans will switch back to high
speed and the cycle will be repeated. If bulb mode is active, the economy fan activity will be overridden.
3.3.6 Perishable Set Point Temperature Cont rol
With configuration variable CnF26 (Heat Lockout Temperature) set to -- 10_C the perishable mode of operation
is active with set points above --10_C(+14_F). With the
variable set to -- 5_C, the perishable mode is active above --5_C(+23_F). Refer to Table 3--4.
When in the perishable mode, the controller maintains
the supply air temperature at set point, the SUPPLY indicator light will be illuminated on the display module
and the default reading on the display window will be the
supply temperature sensor reading.
3--4T-340
Page 31

FALLING
TEMPERA TURE
RISING
TEMPERA TURE
+2.5_C
(4.5_F)
MODULATED
UNLOADED
COOLING
MODULATED
UNLOADED
COOLING
+0.20_C
SET POINT
AIR CIRCULATION
--0.20_C
AIR CIRCULATION
-- 0 . 5 _C
(0.9_F)
HEATING
NOTE 1: TEMPERATURE INDICATIONS ARE ABOVE OR BELOW SET POINT.
NOTE 2: ECONOMIZED UNLOADED COOLING OCCURS IF RETURN TEMPERATURE
IS GREATER THAN SET POINT PLUS 1.9
IS GREATER THAN 70%. IF BOTH CONDITIONS ARE NOT MET, STANDARD
UNLOADED COOLING OCCURS.
_C AND IF CAPACITY MODULATION
HEATING
Figure 3--5 Controller Operation -- Perishable Mode
When the supply air temperature enters the in--range
temperature tolerance (as selected at function code
Cd30), the in--range light will energize.
3.3.7 Perishable Mode Cooling -- Sequence of
Operation
NOTE
In the Standard Perishable Mode of Operation,
the evaporator motors run in high speed. In the
Economy Perishable Mode, the fan speed is
varied.
a. With supply air temperature above set point and de-
creasing, the unit will cool with the condenser fan
motor (CF), compressor motor (CH), evaporator fan
motors (EF) energized and the COOL light illuminated. (See Figure 3--6). Also, if current or pressure
limiting is not active, the controller will close contacts
TS to open the economizer solenoid valve (ESV) and
place the unit in economized operation.
b. When the air temperature decreases to a predeter-
mined tolerance above set point, the in--range light is
illuminated.
ENERGIZED
DE--ENERGIZED
ST
HPS
IP-- EM1
F
HTT
IP-- CM
TS
IP-- EM2
ESV
TC
TN
TH
24 VOLT POWER
CF
EF
TV
TE
HR
CH
ES
EF
NOTE: The EEV and DUV are independently operated by the microprocessor. For full diagrams and legend, see Section 7.
Figure 3--6 Perishable Mode -- Cooling
3--5
T-340
Page 32

c. As the air temperature continues to fall, unloaded
cooling starts approximately 2.5_C(4.5_F) above set
point. (See Figure 3--5). When unloaded cool starts,
the EEV control will transition from a full cool superheat set point to a lower modulated cool superheat
set point. Once unloading starts, the EEV controls
evaporator superheat based on the system duty
cycle where instantaneous superheat will vary . When
the return air has fallen to within 1.9_C(3.4_F) of set
point temperature and the average capacity of the
system has fallen below 70%, the unit will open contacts TS and close the ESV.
d. The controller monitors the supply air. Once the sup-
ply air falls below set point, the controller periodically
records the supply air temperature, set point and
time. A calculation is then performed to determine
temperature drift from set point over time. If the calculation determines cooling is no longer required, contacts TC and TN are opened to de--energize compressor motor and condenser fan motor. In addition
the controller will close the EEV. Perishable heat
mode is locked disabled for five minutes. The cool
light is also de--energized.
e. The evaporator fan motors continue to run to circulate
air throughout the container. The in--range light remains illuminated as long as the supply air is within
tolerance of set point.
f. If the return air temperature increases to 1.0_C
(1.8_F) above set point and three minutes have
elapsed, contacts TC and TN close to restart the
compressor and condenser fan motors in standard
mode (non--economized) operation. The cool light is
also illuminated.
g. If the average system capacity has risen to 100% dur-
ing unloaded cooling and three minutes has elapsed,
relay TS will energize and open the ESV, placing the
unit in economized mode.
h. If the supply air increases more than 2.5_C(4.5_F)
above set point temperature, the microprocessor will
transition the evaporator superheat control from
modulation back to full cool control.
3.3.8 Perishable Mode Heating -- Sequence of
Operation
a. If the air temperature decreases 0.5_C(0.9_F) below
set point, the system enters the heating mode. (See
Figure 3--5). The controller closes contacts TH (see
Figure 3--7) to allow power flow through the heat termination thermostat (HTT) to energize the heaters
(HR). The HEAT light is also illuminated. The evaporator fans continue to run to circulate air throughout
the container.
b. When the temperature rises to 0.2_C(0.4_F) below
set point, contacts TH open to de--energize the heaters. The HEAT light is also de--energized. The evaporator fans continue to run to circulate air throughout
the container.
c. The safety heater termination thermostat (HTT) is at-
tached to an evaporator coil circuit and will open the
heating circuit if overheating occurs.
ENERGIZED
DE--ENERGIZED
ST
HPS
IP-- EM1
F
HTT
IP-- CM
TS
IP-- EM2
ESV
TC
TN
TH
24 VOLT POWER
TV
EF ES
TE
HR
CH
CF
EF
NOTE: The EEV and DUV are independently operated by the microprocessor. For full diagrams and legend, see Section 7.
Figure 3--7 Perishable Mode Heating
3.3.9 Sequence of Operation -- Perishable Mode
(Capacity Trim Heat)
If the system capacity has been decreased to the lowest
allowable capacity and conditions exist that warrant maximum temperature stability the controller will pulse the HR
relay to energize the evaporator heaters in sequence with
the compressor digital signal. Trim heat is enabled only if
(12.77_C < set point < 15.55_C [54.99_F < set point <
59.99_F]) and (--6.67_C < ambient temperature < 1.66 _C
[19.99_F < ambient temperature < 34.99_F]).
3.3.10 Perishable Mode -- Dehumidification
The dehumidification mode is provided to reduce the humidity levels inside the container. The mode is activated
when a humidity value is set at function code Cd33. The
display module SUPPLY LED will flash ON and OFF every second to indicate that the dehumidification mode is
active. Once the Mode is active and the following conditions are satisfied, the controller will activate the heat
relay to begin dehumidification.
1. The humidity sensor reading is above the set point.
2. The unit is in the perishable steady state mode and
supply air temperature is less than 0.2_C (0.36_F)
above set point.
3. The heater debounce timer (three minutes) has
timed out.
4. Heater termination thermostat (HTT) is closed.
If the above conditions are true the evaporator fans will
switch from high to low speed operation. The evaporator
fan speed will switch every hour thereafter as long as all
conditions are met (see Bulb Mode section for different
evaporator fan speed options). If any condition except
item (1) becomes false OR if the relative humidity
sensed is 2% below the dehumidification set point, the
high speed evaporator fans will be energized.
Power is applied to the defrost heaters in the dehumidification mode. This added heat load causes the controller
to open the ESV to match the increased heat load while
still holding the supply air temperature very close to the
set point.
Opening the ESV reduces the temperature of the
evaporator coil surface, which increases the rate at
which water is condensed from the passing air .
3--6T-340
Page 33

Removing water from the air reduces the relative
humidity. When the relative humidity sensed is 2%
below the set point, the controller de--energizes the heat
relay. The controller will continue to cycle heating to
maintain relative humidity below the selected set point.
If the mode is terminated by a condition other than the
humidity sensor, e.g., an out--of--range or compressor
shutdown condition, the heat relay is de--energized
immediately.
Two timers are activated in the dehumidification mode
to prevent rapid cycling and consequent contactor wear.
They are:
1. Heater debounce timer (three minutes).
2. Out--of--range timer (five minutes).
The heater debounce timer is started whenever the
heater contactor status is changed. The heat contactor
remains energized (or de--energized) for at least three
minutes even if the set point criteria are satisfied.
The out--of--range timer is started to maintain heater operation during a temporary out--of--range condition. If
the supply air temperature remains outside of the user
selected in--range setting for more than five minutes, the
heaters will be de--energized to allow the system to recover. The out--of--range timer starts as soon as the
temperature exceeds the in--range tolerance value set
by function code Cd30.
3.3.11 Perishable, Dehumidification -- Bulb Mode
Bulb mode is an extension of the dehumidification
mode, which allows changes to the evaporator fan
speed and/or defrost termination set points.
Bulb mode is active when configuration code Cd35 is set
to “Bulb.” Once the bulb mode is activated, the user may
then change the dehumidification mode evaporator fan
operation from the default (speed alternates from low to
high each hour) to constant low or constant high speed.
This is done by toggling function code Cd36 from its
default of “alt” to “Lo” or “Hi” as desired. If low speed
evaporator fan operation is selected, this gives the user
the additional capability of selecting dehumidification
set points from 60 to 95% (instead of the normal 65 to
95%).
In addition, if bulb mode is active, function code Cd37
may be set to override the previous defrost termination
thermostat settings. (Refer to paragraph 3.3.19) The
temperature at which the defrost termination thermostat
will be considered “open” may be changed [in 0.1_C
(0.2_F) increments] to any value between 25.6_C
(78_F) and 4_C (39.2_F). The temperature at which the
defrost termination thermostat is considered closed for
interval timer start or demand defrost is 10_C for “open”
values from 25.6_C(78_F) down to a 10_C setting. For
“open” values lower than 10_C, the “closed” values will
decrease to the same value as the “open” setting. Bulb
mode is terminated when:
1. Bulb mode code Cd35 is set to “Nor.”
2. Dehumidification code Cd33 is set to “Off.”
3. The user changes the set point to one that is in the
frozen range.
When bulb mode is disabled by any of the above, the
evaporator fan operation for dehumidification reverts to
“alt” and the DTS termination setting resets to the value
determined by controller configuration variable CnF41.
3.3.12 Frozen Mode -- Pulldown
Schematic representation of controller action is
provided in Figure 3--8. When cooling from a temperature that is more than 2.5_C(4.5_F) above set point, the
system will be in the frozen pulldown mode. It will transition to economized operation. However, pressure and
current limit functions may restrict the valve, if either exceeds the preset value.
3.3.13 Frozen Mode -- Temperature Control
When in the frozen mode, the controller maintains the
return air temperature at set point, the RETURN indicator light will be illuminated on the display module and the
default reading on the display window will be the return
air probe reading.
When the return air temperature enters the in--range
temperature tolerance as selected at function code
Cd30, the in--range light will energize.
3.3.14 Frozen Mode -- Standard
Frozen range cargos are not sensitive to minor temperature changes. The method of temperature control
employed in this range takes advantage of this to greatly
improve the energy efficiency of the unit. Temperature
control in the frozen range is accomplished by cycling
the compressor on and off as the load demand requires.
Once set point is reached, the unit will transition to the
frozen steady state mode (economized operation).
When temperature drops to set point minus 0.2_C and
the compressor has run for at least five minutes, the unit
will transition to the frozen idle mode. The compressor is
turned off and the evaporator fans continue to run to circulate air throughout the container. If temperature rises
above set point +0.2_C, the unit will transition back to
the frozen steady state mode.
3.3.15 Frozen Mode -- Heat Lockout Temperature
With configuration variable CnF26 (Heat Lockout Temperature) set to --10_C the frozen mode of operation is
active with set points at or below --10_C(+14_F). With
the variable set to --5_C, the frozen mode is active at or
below --5_C(+23_F).
If the temperature drops 10_C below set point, the unit
will transition to the frozen “heating” mode, in which the
evaporator fans are brought to high speed. The unit will
transition back to the frozen steady state mode when
the temperature rises back to the transition point.
3.3.16 Frozen Mode -- Economy
In order to activate economy frozen mode operation, a
frozen set point temperature must be selected. The
economy mode is active when function code Cd34 is set
to “ON.” When economy mode frozen is active, the system will perform normal frozen mode operations except
that the entire refrigeration system, excluding the controller, will be turned off when the control temperature is
less than or equal to the set point --2_C. After an off-cycle period of 60 minutes, the unit will turn on high
speed evaporator fans for three minutes, and then
check the control temperature. If the control temperature is greater than or equal to the set point +0.2_C, the
unit will restart the refrigeration system and continue to
cool until the previously mentioned off--cycle temperature criteria are met. If the control temperature is less
than the set point +0.2_C, the unit will turn off the evaporator fans and restart another 60 minute off--cycle.
3--7
T-340
Page 34

FALLING
TEMPERATURE
RISING
TEMPERATURE
ECONOMIZED
COOLING
+0.2_C
SET POINT
SET POINT
-- 0 . 2 _C
AIR CIRCULATION
NOTE: TEMPERATURES INDICATIONS ARE ABOVE OR BELOW SET POINT
Figure 3--8 Controller Operation -- Frozen Mode
3.3.17 Frozen Mode Cooling -- Sequence of
Operation
a. When the supply air temperature is above set point
and decreasing, the unit will transition to economized
cooling with the condenser fan motor (CF), compressor motor (CH), economizer solenoid valve
(ESV), low speed evaporator fan motors (ES) energized and the COOL light illuminated. (See
Figure 3--9).
b. When the air temperature decreases to a predeter-
mined tolerance above set point, the in--range light is
illuminated.
c. When the return air temperature decreases to 0.2_C
(0.4_F) below set point, contacts TC, TS and TN are
opened to de--energize the compressor, economizer
solenoid valve and condenser fan motor. The cool
light is also de--energized. The EEV will close.
d. The evaporator fan motors continue to run in low
speed to circulate air throughout the container. The
in--range light remains illuminated as long as the return air is within tolerance of set point.
e. If return air temperature drops to 10_C(18_F) or
more below set point, the evaporator fans increase to
high speed.
f. When the return air temperature increases to 0.2_C
(0.4_F) above set point and three minutes have
elapsed, the EEV opens and contacts TC, TS and TN
close to restart the compressor, open the ESV and
restart the condenser fan motor. The cool light is
illuminated.
ENERGIZED
DE--ENERGIZED
ST
HPS
IP-- EM1
F
HTT
IP-- CM
TS
IP-- EM2
ESV
TC
TN
TH
24 VOLT POWER
TV
EF
TE
HR
CH
CF
ES
EF
NOTE: The EEV and DUV are independently operated
by the microprocessor. For full diagrams and legend,
see Section 7.
Figure 3--9 Frozen Mode
3--8T-340
Page 35

3.3.18 Defrost Interval
Controller function code Cd27 sets two modes for defrost initiation, either user--selected timed intervals or
automatic control. The user--selected values are 3, 6, 9,
12, 24 hours or AUTO. Some units may be configured to
allow defrost to be disabled altogether. In this case, a
user--selected value of OFF will be available. The factory default for defrost is AUTO. Refer to Table 3--5.
In perishable mode, perishable--pulldown mode, or
frozen--pulldown mode, automatic defrost starts with an
initial defrost set to three hours and then adjusts the interval to the next defrost based on the accumulation of
ice on the evaporator coil. In this way, defrosts are
scheduled to occur only when necessary.
Once set point has been reached in frozen operation,
the automatic selection will set the time interval to
12 hours for the first two defrosts once the return probe
is reading below the frozen set point and then adjust to
24 hours thereafter.
All defrost interval times reflect the number of compressor runtime hours since the last defrost de--ice cycle.
The minimum defrost interval under the automatic setting is three hours while the maximum is 24. In frozen
mode the amount of wall--clock time necessary to accumulate a given amount of defrost interval time will exceed the defrost interval time by a factor of two to three
depending on the compressor duty--cycle. Defrost interval time is not accumulated in any mode until the defrost
termination sensor reads less than 10_C(50_F).
If defrost does not terminate correctly and temperature
reaches set point of the heat termination thermostat
(HTT), the thermostat will open to de--energize the heaters. If termination does not occur within two hours,the
controller will terminate defrost. An alarm will be activated to inform of a possible DTS failure.
If probe check (controller function code CnF31) is configured to SPECIAL, the unit will proceed to the next operation (snap freeze or terminate defrost). If the code is
configured to STANDARD, the unit will perform a probe
check. The purpose of the probe check is to detect malfunctions in the sensed temperature. If probe check
fails, the system will run for eight minutes to validate. At
the end of eight minutes, probe alarms will be set or
cleared based on the conditions seen.
When the return air falls to 7_C(45_F), the controller en-
sures that the defrost temperature sensor (DTS) reading has dropped to 10_C or below. If it has not, a DTS
failure alarm is given and the defrost mode is operated
by the return temperature sensor (RTS).
If controller function code CnF33 is configured to snap
freeze, the controller will sequence to this operation.
The snap freeze consists of running the compressor
without the evaporator fans in operation for a period of 4
minutes at 100% capacity . When the snap freeze is
completed, defrost is formally terminated.
3.3.19 Defrost Mode -- Sequence of Operation
The defrost cycle may consist of up to three distinct operations. The first is de--icing of the coil, the second is a
probe check cycle and the third is snap freeze. Defrost
may be initiated by any one of the following methods:
1. The manual defrost function (also manual defrost
switch function, if equipped) is initiated by the user
through the use of the keypad or manual defrost
switch. The manual defrost function is ended by use
of the DTS.
NOTE
The Manual Defrost / Interval key can be used
to initiate a manual defrost.
Manual Defrost/Interval key operation:
Depressing and holding the Manual Defrost / Interval key for five seconds will initiate defrost. If
the Manual Defrost / Interval key is released in
less than five seconds, defrost interval (code
27) shall be displayed.
2. The user sends a def ros t command by
communications.
3. The defrost interval timer (controller function code
Cd27) reaches the defrost interval set by the user.
4. The controller probe diagnostic logic determines that
a probe check is necessary based on the temperature
values currently reported by the supply and return
probes.
5. If the controller is programmed with the Demand Defrost option and the option is set to “IN” the unit will
enter defrost if it has been in operation for more than
2.5 hours without reaching set point.
6. The system is actively in a compressor suction pressure or high pressure ratio protection mode and reduced the average system capacity below a predetermined threshold value.
Defrost may be initiated any time the defrost temperature sensor reading falls below the controller defrost termination thermostat set point. Defrost will terminate
when the defrost temperature sensor reading rises
above the defrost termination thermostat set point. The
defrost termination thermostat is not a physical component. It is a controller setting that acts as a thermostat, “closing” (allowing defrost) when the defrost temperature sensor reading is below the set point and
“opening” (terminating or preventing defrost) when the
sensor temperature reading is above set point. When
the unit is operating in bulb mode (refer to paragraph
3.3.11), special settings may be applicable.
If the controller is programmed with the Lower DTT setting option, the defrost termination thermostat set point
may be configured to the default of 25.6_C(78_F) or
lowered to 18_C(64_F). When a request for defrost is
made through the manual defrost switch, communications or probe check the unit will enter defrost if the defrost temperature thermostat reading is at or below the
defrost termination thermostat setting. Defrost will terminate when the defrost temperature sensor reading
rises above the defrost termination thermostat setting.
When a request for defrost is made with the defrost interval timer or by demand defrost, the defrost temperature setting must be below 10_C(50_F).
When the defrost mode is initiated, the controller closes
the EEV, opens contacts TC, TN and TE (or TV) to de-energize the compressor, condenser fan and evaporator fans. The COOL light is also de--energized. The controller then closes contacts TH to supply power to the
heaters. The defrost light is illuminated. When the defrost temperature sensor reading rises to the defrost termination thermostat setting, the de--icing operation is
terminated.
3--9
T-340
Page 36

ENERGIZED
DE--ENERGIZED
ST
HPS
IP-- EM1
F
HTT
IP-- CM
TS
IP-- EM2
ESV
TC
TN
TH
24 VOLT POWER
CF
TV
EF ES
TE
HR
PB
EF
NOTE: The EEV and DUV are independently operated by the microprocessor. For full diagrams and legend, see Section 7.
Figure 3--10 Defrost
3.4 PROTECTION MODES OF OPERATION
3.4.1 Evaporator Fan Operation
Opening of an evaporator fan internal protector will shut
down the unit.
3.4.2 Failure Action
Function code Cd29 may be operator set to select action the controller will take upon system failure. The factory default is full system shutdown. Refer to Table 3--5.
3.4.3 Generator Protection
Function codes Cd31(Stagger Start, Offset Time) and
Cd32 (Current Limit) may be operator set to control start
up sequence of multiple units and operating current
draw. The factory default allows on demand starting (no
delay) of units and normal current draw. Refer to
Table 3--5.
3.4.4 Compressor High Temperature, Low
Pressure Protection
The controller monitors compressor discharge pressure, and temperature and suction pressure. If discharge pressure or temperature rises above the allowed
limit or suction pressure falls below the allowed limit, the
compressor will be cycled off and on every 3 minutes.
Condenser and evaporator fans continue to operate
during the compressor off cycle.
If high compressor dome temperature occurs, the controller will allow additional refrigerant to be released into
the system in order to provide cooling to the evaporator
coil and compressor dome. The controller is alerted to
high compressor dome temperatures via the CPDS
when the ambient temperature is greater than 43.3_C,
the return air temperature is less than --17.5_C and if the
compressor discharge temperature is greater than
1 17.7_C.
Dome temperature control logic will disengage when return air temperature and ambient temperature return to
allowed limits or when compressor turns off.
If the suction pressure low limit is triggered, the DUV will
energize to raise the suction pressure.
3.4.5 Perishable Mode -- System Pressure
Regulation
In perishable mode, system pressures may need to be
regulated at ambient temperatures of 20_C(68_F) and
below. Once below this ambient temperature, the condenser fan may cycle on and off based on limits imposed
for discharge pressure. For extremely cold ambient
temperatures, --18_C(0_F), heater cycling may occur
within normal system operation based on discharge
pressure limits.
3.4.6 Condenser Fan Override
When configuration variable CnF17 (Discharge T emperature Sensor) is set to “In” and CnF48 (Condenser
Fan Switch Override) is set to “On”, the condenser fan
switch override logic is activated. If condenser cooling
water pressure is sufficient to open the water pressure
switch (de--energizing the condenser fan) when water
flow or pressure conditions are not maintaining discharge temperature, the logic will energize the condenser fan as follows:
1. If the DUV is less than 80% open when the controller
calls for it to be100% open, the condenser fan is energized. When the DUV is 100% open, the fan will
de--energize.
2. If DPT reading is invalid or out of range (AL 65), the
condenser fan is energized and will remain energized until system power is cycled.
3. If the system is running on condenser fan override
and the high pressure switch opens, the condenser
fan is energized and will remain energized until the
system power is cycled.
3.5 CONTROLLER ALARMS
Alarm display is an independent controller software
function. If an operating parameter is outside of expected range or a component does not return the correct signals back to the controller, an alarm is generated. A listing of the alarms is provided in Table 3--6,
page 3--22.
The alarm philosophy balances the protection of the refrigeration unit and that of the refrigerated cargo. The
action taken when an error isdetected always considers
the survival of the cargo. Rechecks are made to confirm
that an error actually exists.
Some alarms requiring compressor shutdown have
time delays before and after to try to keep the compressor on line. An example is alarm code “LO,” (low main
voltage), when a voltage drop of over 25%occurs, an indication is given on the display, but the unit will continue
to run.
When an Alarm Occurs:
a. The red alarm light will illuminate for alarm code num-
bers 15, 17, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, and 27.
b. If a detectable problem exists, its alarm code will be
alternately displayed with the set point on the left
display.
c. The user should scroll through the alarm list to deter-
mine what alarms exist or have existed. Alarms must
be diagnosed and corrected before Alarm List can be
cleared.
To Display Alarm Codes:
a. While in the Default Display mode, press the ALARM
LIST key. This accesses the Alarm List Display Mode,
which displays any alarms archived in the alarm
queue.
3--10T-340
Page 37

b. The alarm queue stores up to 16 alarms in the se-
quence in which they occurred. The user may scroll
through the list by depressing an ARROW key.
c. The left display will show “AL##,” where ## is the
alarm number sequentially in the queue.
d. The right display will show the actual alarm code.
“AA##” will display for an active alarm, where “##” is
the alarm code. Or “IA##” will display for an inactive
alarm, See Table 3--6, page 3--22.
e. “END” is displayed to indicate the end of the alarm list
if any alarms are active.
f. “CLEAr” is displayed if all alarms are inactive. The
alarm queue may then be cleared by pressing the ENTER key. The alarm list will clear and “ -- -- -- -- -- ” will
be displayed.
Note:
AL26 is active when all of the sensors are not
responding. Check the connector at the back of
the controller; if it is loose or unplugged, reconnect it, then run a pre- -trip test (P5) to clear
AL26.
3.6 UNIT PRE--TRIP DIAGNOSTICS
Pre--trip Diagnostics is an independent controller function that suspends normal refrigeration controller activities and provides preprogrammed test routines. The
test routines include Auto Mode testing, which automatically preforms a pre programmed sequence of tests, or
Manual Mode testing, which allows the operator to select and run any of the individual tests.
CAUTION
Pre--trip inspection should not be pe rformed with critical temperature cargoes in
the containe r.
CAUTION
When Pre--trip key is pressed, economy, dehumidification and bulb mode will be deactivated. At the completion of Pre--trip activity, econom y, dehumidification and bulb
mode must be reactivated.
Testing may be initiated by use of the keypad or via communication, but when initiated by communication the
controller will execute the entire battery of tests (auto
mode).
At the end of a pre--trip test, the message “P,” “rSLts”
(pretest results) will be displayed. Pressing the ENTER
key will allow the user to see the results for all subtests.
The results will be displayed as “PASS” or “FAIL” for all
the tests run to completion.
3.7 DataCORDER
3.7.1 Description
The Carrier Transicold “DataCORDER” software is integrated into the controller and serves to eliminate the
temperature recorder and paper chart. The DataCORDER functions may be accessed by keypad selections
and viewed on the display module. The unit is also fitted
with interrogation connections (see Figure 3--1) which
may be used with the Carrier Transicold Data Reader to
down load data. A personal computer with Carrier
Transicold DataLINE software may also be used to
download data and configure settings. The DataCORDER consists of:
Configuration Software
Operational Software
Data Storage Memory
Real Time Clock (with internal battery backup)
Six Thermistor Inputs
Interrogation Connections
Power Supply (battery pack)
The DataCORDER performs the following functions:
a. Logs data at 15, 30, 60 or 120 minute intervals and
stores two years of data (based on one hour interval).
b. Records and displays alarms on the display module.
c. Records results of pre--trip testing.
d. Records DataCORDER and temperature control
software generated data and events as follows:
Container ID Change
Software Upgrades
Alarm Activity
Battery Low (battery pack)
Data Retrieval
Defrost Start and End
Dehumidification Start and End
Power Loss (with and without battery pack)
Power Up (with and without battery pack)
Remote Probe Temperatures in the Container
(USDA Cold treatment and Cargo probe recording)
Return Air Temperature
Set Point Change
Supply Air Temperature
Real Time Clock Battery (internal battery) Replacement
Real Time Clock Modification
Trip Start
ISO Trip Header (When entered via Interrogation
program)
Economy Mode Start and End
“Auto 1/Auto 2/Auto 3” Pre--trip Start and End
Bulb Mode Start
Bulb Mode Changes
Bulb Mode End
USDA Trip Comment
Humidification Start and End
USDA Probe Calibration
Fresh Air Vent Position
3.7.2 DataCORDER Software
A detailed description of the pre--trip tests and test
codes is provided in Table 3--7, page 3--27. detailed operating instructions are provided in paragraph 4.9.
The DataCORDER Software is subdivided into the Operational Software, Configuration Software, and the
Data Memory.
3--11
T-340
Page 38

a. Operational Software
The Operational Software reads and interprets inputs
for use by the Configuration Software. The inputs are labeled Function Codes. Controller functions (see
Table 3--8, page 3--31) which the operator may access
to examine the current input data or stored data. To access these codes, do the following:
1. Press the ALT. MODE and CODE SELECT keys.
2. Press an arrow key until the left window displays the
desired code number. The right window will display
the value of this item for five seconds before returning to the normal display mode.
3. If a longer display time is desired, press the ENTER
key to extend the display time to five minutes.
b. Configuration Software
The configuration software controls the recording and
alarm functions of the DataCORDER. Reprogramming
to the factory--installed configuration is achieved via a
configuration card. Changes to the unit DataCORDER
configuration may be made using the DataLINE
interrogation software. Alisting of the configuration variables is provided in Table 3--2. Descriptions of DataCORDER operation for each variable setting are provided in the following paragraphs.
3.7.3 Sensor Configuration (dCF02)
Two modes of operation may be configured, the Standard Mode and the Generic Mode.
a. Standard Mode
In the standard mode, the user may configure the DataCORDER to record data using one of seven standard
configurations. The seven standard configuration variables, with their descriptions, are listed in Table 3--3.
The inputs of the six thermistors (supply, return, USDA
#1, #2, #3 and cargo probe) and the humidity sensor input will be generated by the DataCORDER. See
Figure 3--11.
NOTE
The DataCORDER software uses the supply
and return recorder
sensors (SRS, RRS). The
temperature control software uses the supply
and return temperature
sensors (STS, RTS).
b. Generic Mode
The generic recording mode allows user selection of the
network data points to be recorded. The user may select
up to a total of eight data points for recording. A list of the
data points available for recording follows. Changing the
configuration to generic and selecting which data points
to record may be doneusing the Carrier Transicold Data
Retrieval Program.
1. Control mode
2. Control temperature
3. Frequency
4. Humidity
5. Phase A current
6. Phase B current
7. Phase C current
8. Main voltage
9. Evaporator expansion valve percentage
10. Discrete outputs (Bit mapped -- require special
handling if used)
1 1. Discrete inputs (Bit mapped -- require special
handling if used)
12. Ambient sensor
13. Evaporator temperature sensor
14. Compressor discharge sensor
15. Return temperature sensor (RTS)
16. Supply temperature sensor (STS)
17. Defrost temperature sensor
18. Discharge pressure transducer
19. Suction pressure transducer
20. Condenser pressure transducer
21. Vent position sensor (VPS)
3.7.4 Logging Interval (dCF03)
The user may select four different time intervals between data recordings. Data is logged at exact intervals
in accordance with the real time clock. The clock is factory set at Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
3.7.5 Thermistor Format (dCF04)
The user may configure the format in which the thermistor readings are recorded. The short resolution is a 1
byte format and the long resolution is a 2 byte format.
The short requires less memory and records temperature with variable resolutions depending on temperature
range. The long records temperature in 0.01_C
(0.02_F) steps for the entire range.
CONFIGURATION NO.
dCF01 (Future Use) -- -- -- -dCF02 Sensor Configuration 2 2,5,6,9,54,64,94
dCF03 Logging Interval (Minutes) 60 15,30,60,120
dCF04 Thermistor Format Short Long
dCF05 Thermistor Sampling Type A A,b,C
dCF06 Controlled Atmosphere/Humidity Sampling Type A A,b
dCF07 Alarm Configuration USDA Sensor 1 A Auto, On, Off
dCF08 Alarm Configuration USDA Sensor 2 A Auto, On, Off
dCF09 Alarm Configuration USDA Sensor 3 A Auto, On, Off
dCF10 Alarm Configuration Cargo Sensor A Auto, On, Off
Table 3--2 DataCORDER Configuration Variables
TITLE DEFAULT OPTION
3--12T-340
Page 39

Raw Data Report for ABC1234567
May 31, 2007 to Jun 04, 2007
System Configuration at the Time of Interrogation:
Interrogated On May 05, 2007
Extracted by DataLINE Rev 1.0.0
Controller Software: 5327
Controller Serial #: 04163552
Bill of Lading #: 1
Origin: Origin Date:
Destination: Discharge Date:
Comment: DataLINE Tool
Probe Calibration Readings: USDA1: 0.0 USDA2: 0.0 USDA3: 0.0 Cargo: 0.0
Temperature Units: Centigrade
________________________________________________________________________________________
May 31, 2007
Setpoint: 1.66, Container : Serial : 04189552
9 Sensors Logged at 15 Minute Interval
Sensor Format Resolution
Figure 3--11 Standard Configuration Download Report
3--13
T-340
Page 40

Table 3--3 DataCORDER Standard Configurations
communication when an interrogation cable is
plugged into an interrogation receptacle.
Standard
Config.
2 sensors
(dCF02=2)
5 sensors
(dCF02=5)
6 sensors
(dCF02=6)
9 sensors
(dCF02=9)
6 sensors
(dCF02=54)
7 sensors
(dCF02=64)
10 sensors
(dCF02=94)
3.7.6 Sampling Type (dCF05 & dCF06)
Three types of data sampling are available: average,
snapshot and USDA. When configured to average, the average of readings taken every minute over the recording
period is recorded. When configured to snapshot, the sensor reading at the log interval time is recorded. When
USDA is configured, the supply and return temperature
readings are averaged and the three USDA probe readings are snapshot.
3.7.7 Alarm Configuration (dCF07 -- dCF10)
The USDA and cargo probe alarms may be configured
to OFF, ON or AUTO.
If a probe alarm is configured to OFF, the alarm for this
probe is always disabled.
If a probe alarm is configured to ON, the associated
alarm is always enabled.
If the probes are configured to AUTO, they act as a
group. This function is designed to assist users who
keep their DataCORDER configured for USDA recording, but do not install the probes for every trip. If all the
probes are disconnected, no alarms are activated. As
soon as one of the probes is installed, all of the alarms
are enabled and the remaining probes that are not
installed will give active alarm indications.
3.7.8 DataCORDER Power Up
The DataCORDER may be powered up in any one of
four ways:
1. Normal AC power: The DataCORDER is powered
up when the unit is turned on via the stop--start
switch.
2. Controller DC battery pack power: If a battery packis
installed, the DataCORDER will power up for
2 thermistor inputs (supply & return)
2 thermistor inputs (supply & return)
3 USDA thermistor inputs
2 thermistor inputs (supply & return)
3 USDA thermistor inputs
1 humidity input
Not Applicable
2 thermistor inputs (supply & return)
3 USDA thermistor inputs
1 cargo probe (thermistor input)
2 thermistor inputs (supply & return)
3 USDA thermistor inputs
1 humidity input
1 cargo probe (thermistor input)
2 thermistor inputs (supply & return)
3 USDA thermistor inputs
1 humidity input
1 cargo probe (thermistor input)
3 C.A. inputs (NOT APPLICABLE)
Description
3. External DC battery pack power: A 12 volt battery
pack may also be plugged into the back of the
interrogation cable, which is then plugged into an
interrogation port. No controller battery pack is
required with this method.
4. Real Time Clock demand: If the DataCORDER is
equipped with a charged battery pack and AC power
is not present, the DataCORDER will power up when
the real time clock indicates that a data recording
should take place. When the DataCORDER is finished recording, it will power down.
During DataCORDER power--up, while using battery-pack power, the controller will perform a hardware voltage check on the battery . If the hardware check passes,
the controller will energize and perform a software battery voltage check before DataCORDER logging. If either test fails, the real time clock battery power--up will
be disabled until the next AC power cycle. Further DataCORDER temperature logging will be prohibited until
that time.
An alarm will be generated when the battery voltage
transitions from good to bad indicating that the battery
pack needs recharging. If the alarm condition persists
for more than 24 hours on continuous AC power, the
battery pack needs replacement.
3.7.9 Pre--trip Data Recording
The DataCORDER will record the initiation of a pre--trip
test (refer to paragraph 3.6) and the results of each of
the tests included in pre--trip. The data is time--stamped
and may be extracted via the Data Retrieval program.
Refer to Table 3--9 for a description of the data stored in
the DataCORDER for each corresponding Pre--trip test.
3.7.10 DataCORDER Communications
Data retrieval from the DataCORDER can be accomplished by using one of the following: DataReader,
DataLINE or a communications interface module.
NOTE
A DataReader, DataLINE or a communications
interface module display of Communication
Failed is caused by faulty data transfer between
the DataCORDER and the data retrieval device. Common causes include:
1. Bad cable or connection between
DataCORDER and data retrieval device.
2. PC communication port(s) unavailable or
misassigned.
3. Chart Recorder Fuse (FCR) blown.
Configuration identification for the models covered
herein may be obtained on the Container Products
Group Information Center by authorized Carrier Transicold Service Centers.
a. DataReader
The Carrier Transicold Data Reader (see Figure 3--12)
is a simple to operate handheld device designed to extract data from the DataCORDER and upload it to a PC.
The Data Reader has the ability to store multiple data
files. Refer to Data Retrieval manual 62-- 10629 fo r a
more detailed explanation of the DataReader.
3--14T-340
Page 41

DataReader
1
8
7
6
1. OFF
2. ON
3. UP Arrow
4. RIGHT Arrow
2
3
4
5
5. ENTER
6. Escape
7. DOWN Arrow
8. LEFT Arrow
Figure 3--12 Data Reader
b. DataBANK™ Card
The DataBANK™ card is a PCMCIA card that interfaces
with the controller through the programming slot and
can download the data at a much faster rate, when
compared to the PC or DataReader. Files downloaded
to DataBANK card files are accessible through an Omni
PC Card Drive. The files can then be viewed using the
DataLINE software.
c. DataLINE
The DataLINE software for a personal computer is supplied on both floppy disks and CD. This software allows
interrogation, configuration variable assignment,
screen view of the data, hard copy report generation,
cold treatment probe calibration and file management.
Refer to Data Retrieval manual 62--10629 for a more
detailed explanation of the DataLINE interrogation software. The DataLINE manual may be found on the internet at www.container.carrier.com.
d. Communications Interface Module
The communications interface module is a slave module, which allows communication with a master central
monitoring station. The module will respond to communication and return information over the main power line.
With a communications interface module installed, all
functions and selectable features that are accessible at
the unit may be performed at the master station. Retrieval of all DataCORDER reports may also be performed. Refer to the master system technical manual
for further information.
3.7.11 USDA Cold Treatment
Sustained cold temperature has been employed as an
effective postharvest method for the control of Mediterranean and certain other tropical fruit flies. Exposing infested fruit to temperatures of 2.2_C(36_F) or below for
specific periods results in the mortality of the various
stages of this group of insects.
In response to the demand to replace fumigation with
this environmentally sound process, Carrier has integrated Cold Treatment capability into its microprocessor
system. These units have the ability to maintain supply
air temperature within one quarter degree Celsius of set
point and record minute changes in product temperature within the DataCORDER memory, thus meeting
USDA criteria. Information on USDA is provided in the
following sub--paragraphs.
a. USDA Recording
A special type of recording is used for USDA cold treatment purposes. Cold treatment recording requires three
remote temperature probes be placed at prescribed
locations in the cargo. Provision is made to connect
these probes to the DataCORDER via receptacles located at the rear left--hand side of the unit. Four or five
receptacles are provided. The four 3--pin receptacles
are for the probes. The 5--pin receptacle is the rear connection for the Interrogator. The probe receptacles are
sized to accept plugs with tricam coupling locking devices. A label on the back panel of the unit shows which
receptacle is used for each probe.
The standard DataCORDER report displays the supply
and return air temperatures. The cold treatment report
displays USDA #1, #2, #3 and the supply and return air
temperatures. Cold treatment recording is backed up by
a battery so recording can continue if AC power is lost.
b. USDA/ Message Trip Comment
A special feature in DataLINE allows the user to enter a
USDA (or other) message in the header of a data report.
The maximum message length is 78 characters. Only
one message will be recorded per day.
3.7.12 USDA Cold Treatment Procedure
The following is a summary of the steps required to initiate a USDA Cold T reatment:
a. Calibrate the three USDA probes by ice bathing the
probes and performing the calibration function with
the DataReader or DataLINE. This calibration procedure determines the probe offsets and stores them in
the controller for use in generating the cold treatment
report. Refer to the Data Retrieval manual 62--10629
for more details.
b. Pre--cool the container to the treatment temperature
or below.
c. Install the DataCORDER module battery pack (if not
already installed).
d. Place the three probes. The probes are placed into
the pulp of the product (at the locations defined in the
following table) as the product is loaded.
3--15
T-340
Page 42

Sensor 1
Place in pulp of the product located next
to the return air intake.
Place in pulp of the product five feet
from the end of the load for 40 foot con-
Sensor 2
tainers, or three feet from the end of the
load for 20 foot containers. This probe
should be placed in a center carton at
one--half the height of the load.
Place in pulp of product five feet from
the end of the load for 40 foot containers
Sensor 3
or three feet from the end of the load for
20 foot containers. This probe should be
placed in a carton at a side wall at one-half the height of the load.
e. To initiate USDA recording, connect the personal
computer and perform the configuration as follows,
using the DataLINE software:
1. Enter ISO header information.
2. Enter a trip comment if desired.
3. Configure the DataCORDER for five probes (s, r, P1,
P2, P3) (dcf02=5).
4. Configure the logging interval for one hour.
5. Set the sensor configuration to “USDA.”
6. Configure for two byte memory storage format
(dcf04=LONG).
7. Perform a “trip start.”
3.7.13 DataCORDER Alarms
The alarm display is an independent DataCORDER
function. If an operating parameter is outside of the expected range or a component does not return the correct values to the DataCORDER, an alarm is generated.
The DataCORDER contains a buffer of up to eight
alarms. A listing of the DataCORDER alarms is provided in Table 3--10, page 3--33. Refer to paragraph
3.7.7 for configuration information.
To display alarm codes:
a. While in the Default Display mode, press the ALT.
MODE & ALARM LIST keys. This accesses the DataCORDER Alarm List Display Mode, which displays
any alarms stored in the alarm queue.
b. To scroll to the end of the alarm list, press the UP AR-
ROW. Depressing the DOWN ARROW key will scroll
the list backward.
c. The left display will show “AL#” where # is the alarms
number in the queue. The right display will show
“AA##,” if the alarm is active, where ## is the alarm
number. “IA##,” will show if the alarm is inactive
d. “END” is displayed to indicate the end of the alarm list
if any alarms are active. “CLEAr” is displayed if all the
alarms in the list are inactive.
e. If no alarms are active, the alarm queue may be
cleared. The exception to this rule is the DataCORDER alarm queue Full alarm (AL91), which does not
have to be inactive in order to clear the alarm list. To
clear the alarm list:
1. Press the ALT. MODE & ALARM LIST keys.
2. Press the UP/DOWN ARROW key until “CLEAr” is
displayed.
3. Press the ENTER key. The alarm list will clear and
“-- -- -- -- -- ” will be displayed.
4. Press the ALARM LIST key. “AL” will show on the left
display and “-- -- -- -- -- ” on the right display when
there are no alarms in the list.
5. Upon clearing of the alarm queue, the alarm light will
be turned off.
3.7.14 ISO Trip Header
DataLINE provides the user with an interface to view/
modify current settings of the ISO trip header through
the ISO Trip Header screen.
The ISO Trip Header screen is displayed when the user
clicks on the “ISO Trip Header” button in the “Trip Functions” Group Box on the System T ools screen.
F9 function -- Provides the user with a shortcut for manually triggering the refresh operation. Before sending
modified parameter values, the user must ensure that a
successful connection is established with the controller.
If the connection is established with the DataCORDER,
the current contents of the ISO Trip Header from the DataCORDER will be displayed in each field. If the connection is not established with the DataCORDER, all fields
on the screen will be displayed as “Xs.” If at any time during the display of the ISO Trip Header screen the connection is not established or is lost, the user is alerted to
the status of the connection.
After modifying the values and ensuring a successful
connection has been made with the DataCORDER,
click on the “Send” button to send the modified parameter values.
The maximum allowed length of the ISO Trip Header is
128 characters. If the user tries to refresh the screen or
close the utility without sending the changes made on
the screen to the DataCORDER, the user is alerted with
a message.
3--16T-340
Page 43

Table 3--4 Controller Configuration Variables
CONFIGURATION
NUMBER
TITLE DEFAULT OPTION
CnF02 Evaporator Fan Speed dS (Dual) SS (Single)
CnF03 Control Sensors FOUr duAL
CnF04 Dehumidification Mode On OFF
CnF08 Single Phase/3--Phase Evaporator Fan Motor 1Ph 3Ph
CnF09 Refrigerant Selection r134a r744
CnF11 Defrost “Off” Selection noOFF OFF
CnF15 Discharge Temperature Sensor Out In
CnF16 DataCORDER Present On (Yes) (Not Allowed)
CnF17 Discharge Pressure Sensor Out (No) In (Yes)
CnF18 Heater Old (Low Watt) nEW (High Watt)
CnF20 Suction Pressure Sensor Out (No) In (Yes)
CnF22 Economy Mode Option OFF Std, Full
CnF23 Defrost Interval Timer Save Option noSAv SAv
CnF24 Advanced Pre--trip Enhanced T est Series Option Auto Auto2, Auto 3
CnF25 Pre--trip Test Points/Results Recording Option rSLtS dAtA
CnF26 Heat Lockout Change Option Set to --10C Set to --5C
CnF27 Suction Temperature Display Option Out In
CnF28 Bulb Mode Option NOr bULb
CnF31 Probe Check Option SPEC Std
CnF32 Single Evaporator Fan Option 2EF0 (Not Allowed)
CnF33 Snap Freeze Option OFF SnAP
CnF34 Degree Celsius Lockout Option bOth F
CnF37 Electronic T emperature Recorder rEtUR SUPPL, bOth
CnF41 Lower DTT Setting Out In
CnF44 eAutoFresh Enabled Out LO, UP
CnF45 Low Humidity Enabled Out In
CnF47 Fresh Air Vent Position Sensor OFF UP , LOW , CUStOM
CnF49 DataCORDER Configuration Restore OFF On
CnF50 Enhanced Bulb Mode Selection OFF Bulb, dEHUM
CnF51 Timed Defrost Disable 0 0--out, 1--in
CnF52 Oil Return Algorithm 1 0--out, 1--in
CnF53 Water Cool Oil Return Logic 0 0--out, 1--in
CnF55 TXV Boost Relay 0 0--out, 1--in
CnF56 TXV Boost Circuit 0 0--out, 1--in
CnF59 Electronic Expansion Valve 0 0--none, 1--EC,
2--KE, 3-- NA
CnF60 Compressor--Cycle Perishable Cooling 0 0--out, 1--in
CnF61 ACT ASC Control Enable 0 0--out, 1--in
CnF62 Extended Temperature Control Enable 0 0-- on, 1--in
CnF63 CCPC Pre--trip/Tripstart Default State 0 0--on, 1-- off
Note: Configuration numbers not listed are not used in this application. These items may appear when loading
configuration software to the controller but changes will not be recognized by the controller programming.
3--17
T-340
Page 44

Table 3--5 Controller Function Codes
(Sheet 1 of 4)
Code
No.
TITLE DESCRIPTION
Note: If the function is not applicable, the displa y will read “ -- -- -- -- --”
Display Only Functions
Cd01
Cd03
Cd04
Cd05
Cd06
Cd07 Main Power Voltage The main supply voltage is displayed.
Cd08
Cd09
Cd10
Cd1 1
Cd12
Cd14
Cd15
Cd16
Cd18 Software Revision # The software revision number is displayed.
Cd19 Battery Check
Cd20 Config/Model #
Cd21 Capacity Mode The mode of operation is displayed (Unloaded -- Standard -- Economized).
Cd22 Compressor State The status of the compressor is displayed (Off, On).
Digital Unloader
Valve Closed (%)
Compressor Motor
Current
Line Current,
Phase A
Line Current,
Phase B
Line Current,
Phase C
Main Power
Frequency
Ambient
Temperature
Evaporator T emperature Sensor
Compressor Discharge Temperature
Compressor Suction
Pressure
Compressor Discharge Pressure
Digital Unloader
Val v e
Compressor Motor
Hour Meter/Unit Run
Time Hour Meter
Displays the DUV percent closed. The right display reads 100% when the valve is
fully closed. The valve will usually be at 10% on start up of the unit except in very
high ambient temperatures.
The current sensor measures current draw in lines L1 & L2 by all of the high voltage components. It also measures current draw in compressor motor leg T3. The
compressor leg T3 current is displayed.
The current sensor measures current on two legs. The third unmeasured leg is calculated based on a current algorithm. The current measured is used for control and
diagnostic purposes. For control processing, the highest of the Phase A and B current values is used for current limiting purposes. For diagnostic processing, the current draws areused to monitor component energization. Whenever a heater or a motor is turned ON or OFF, the current draw increase/reduction for that activity is measured. The current draw is then tested to determine if it falls within the expected range
of values for the component. Failure of this test will result in a pre--trip failure or a control alarm indication.
The value of the main power frequency is displayed in Hertz. The frequency displayed will be halved if either fuse F1 or F2 is bad (alarm code AL21).
The ambient sensor reading is displayed.
Evaporator temperature sensor reading is shown on the right display.
Compressor discharge temperature sensor reading, using compressor dome temperature, is displayed.
Reading for evaporator pressure transducer (EPT) is shown on the left display;
Press ENTER at Cd12 to show reading for compressor suction port pressure on
right display.
Compressor discharges pressure transducer reading is displayed.
The status of the valve is displayed (Open -- Closed).
This code displays the compressor motor hours. User can view unit run time by
pressing the ENTER key while in Cd16. Total hours are recorded in increments of
10 hours (i.e., 3000 hours is displayed as 300).
The Compressor Motor Hour Meter display can be reset to 0 by pressing and
holding the ENTER key for 5 seconds. The Unit Run Time Hour Meter cannot be
reset.
This code checks the Controller/DataCORDER battery pack. While the test is running, “btest” will flash on the right display, followed by the result. “PASS” will be displayed for battery voltages greater than 7.0 volts. “F AIL” will be displayed for battery
voltages between 4.5 and 7.0 volts, and “-- -- -- -- -- ” will be displayed for battery voltages less than 4.5 volts. After the result is displayed for four seconds, “btest” will
again be displayed, and the user may continue to scroll through the various codes.
This code indicates the dash number of the model for which the Controller is configured (i.e., if the unit is a 69NT40--551--100, the display will show “51100”). To
display controller configuration database information, press ENTER. Values in
“CFYYMMDD” format are displayed if the controller was configured with a configuration card or with a valid OEM serial port configuration update; YYMMDD represents the publication date of the model configuration database.
3--18T-340
Page 45

Table 3--5 Controller Function Codes (Sheet 2 of 4)
Cd23
Cd25
Cd26
Evaporator Fan Displays the current evaporator fan state (high, low or off).
Compressor Run
Time Remaining
Until Defrost
Defrost T emperature
Sensor Reading
This code displays the time remaining until the unit goes into defrost (in tenths of
an hour). This value is based on the actual accumulated compressor running
time.
Defrost temperature sensor reading is displayed.
Configurable Functions
NOTE
Function codes Cd27 through Cd37 are user--selectable functions. The operator can change the value of
these functions to meet the operational needs of the container.
There are two modes for defrost initiation: user--selected timed intervals or automatic
control. The user--selected values are (OFF), 3, 6, 9, 12, 24 hours or AUTO. The factory default is AUTO. Automatic defrost starts with an initial defrost at three hours,
then the interval to the next defrost is adjusted based on the accumulation of ice on
the evaporator coil. Following a start--up or after termination of a defrost, the time will
not begin counting down until the defrost temperature sensor (DTS) reading falls below set point. If the reading of DTS rises above set point any time during the timer
count down, the interval is reset and the countdown begins over. If DTS fails, alarm
code AL60 is activated and control switches over to the the return temperature sensor. The controller will act in the same manner as with the DTS except the return temperature sensor reading will be used.
Defrost Interval Timer Value (Configuration variable CnF23): If the softwareis configured to “SAv” (save) for this option, the value of the defrost interval timer will besaved
at power down and restored at power up. This option prevents short power interruptions from resetting an almost expired defrost interval, and possibly delaying a
needed defrost cycle.
Cd27
Defrost Interval
(Hours or Automatic)
Cd28
Cd29
Cd30 In--Range Tolerance
Cd31
Cd32
Temperature Units
(C or F)
Failure Action
(Mode)
Stagger Start Offset
Time (Seconds)
Current Limit
(Amperes)
NOTE
The defrost interval timer counts only during compressor run time.
This code determines the temperature units (C or F) that will be used for all temperature displays. The user selects C or F by selecting function code Cd28 and
pushing the ENTER key. The factory default value is Celsius units.
NOTE
This function code will display “ --- --- --- --- --- “ if Configuration Variable CnF34 is
set to F.
If all of the control sensors are out of range (alarm code AL26) or there is a probe
circuit calibration failure (alarm code AL27), the unit will enter the shutdown state
defined by this setting. The user selects one of four possible actions as follows:
A -- Full Cooling (Compressor is on, economized operation.)
B -- Partial Cooling (Compressor is on, standard operation.)
C -- Evaporator Fan Only (Evaporator fans on high speed, not applicable with frozen
set points.)
D -- Full System Shutdown -- Factory Default (Shut down every component in the
unit.)
The in--range tolerance will determine the band of temperatures around the set
point which will be designated as in--range. If the control temperature is in--range,
the in--range light will be illuminated. There are four possible values:
1 = +/-- 0.5C (+/-- 0.9F)
2 = +/-- 1.0C (+/-- 1.8F)
3 = +/-- 1.5C (+/-- 2.7F)
4 = +/-- 2.0C (+/-- 3.6F) -- Factory Default
The stagger start offset time is the amount of time that the unit will delay at start-up, thus allowing multiple units to stagger their control initiation when all units are
powered up together. The eight possible offset values are:
0 (Factory Default), 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 or 21 seconds
The current limit is the maximum current draw allowed on any phase at any time. Limiting the unit’s current reduces the load on the main power supply. When desirable,
the limit can be lowered. Note, however, that capacity is also reduced. The five values
for 460 VAC operation are: 15, 17, 19, 21, or 23 amperes. The factory default setting
is 21 amperes.
3--19
T-340
Page 46

Perishable Mode
Cd33
Dehumidification
Control (% RH)
Cd34
Economy Mode
(On--Off)
Cd35 Bulb Mode
Cd36
Evaporator Speed
Select
Defrost T ermination
Cd37
Temperature Setting
(Bulb Mode)
Cd38
Cd39
Cd40
Secondary Supply
Temperature Sensor
Secondary Return
Temperature Sensor
Container Identification Number
Cd41 Valve Override
Cd43 eAutoFresh Mode
Cd44 eAutoFresh Values
Cd45
Fresh Air Vent
Position Sensor
Table 3--5 Controller Function Codes (Sheet 3 of 4)
Relative humidity set point is available only on units configured for dehumidification.
When the mode is activated, the control probe LED flashes on and off every second
to alert the user. If not configured, the mode is permanently deactivated and
“-- -- -- -- -- ” will display. The value can be set to “OFF,” “TEST,” or a range of 65 to
95% relative humidity in increments of 1%. [If bulb mode is active (code Cd35) and
“Lo” speed evaporator motors are selected (code Cd36), then set point ranges from
60 to 95%.] When “TEST” is selected or test set point is entered, the heat LED should
illuminate, indicating that dehumidification mode is activated. After a period of five
minutes in the “TEST” mode has elapsed, the previously selected mode is reinstated.
Economy mode is a user selectable mode of operation provided for power saving
purposes.
Bulb mode is a user selectable mode of operation that is an extension of dehumidification control (Cd33). If dehumidification is set to “Off,” code Cd35 will display “Nor” and the user will be unable to change it. After a dehumidification set
point has been selected and entered for code Cd33, the user may change code
Cd35 to “bulb.” After bulb has been selected and entered, the user may utilize
function codes Cd36 and Cd37 to make the desired changes.
This code is enabled only if in the dehumidification mode (code Cd33) and bulb
mode (Cd35) has been set to “bulb.” If these conditions are not met, “alt” will be
displayed (indicating that the evaporator fans will alternate their speed) and the
display cannot be changed. If a dehumidification set point has been selected
along with bulb mode, “alt” may be selected for alternating speed, “Lo” for low
speed evaporator fan only, or “Hi” for high speed evaporator fan only. If a setting
other than “alt” has been selected and bulb mode is deactivated in any manner ,
the selection reverts back to “alt.”
This code, as with function code Cd36, is used in conjunction with bulb mode and
dehumidification. If bulb mode is active, this code allows the user to change the
temperature above which defrost will terminate. It allows the user to change the
setting within a range of 4_C to 25.6_Cin0.1_C(0.2_F) increments. This value is
changed using the UP/DOWN ARROW keys, followed by the ENTER key when
the desired value is displayed. If bulb mode is deactivated, the DTS setting returns to the default.
Display Only Functions -- Continued
Code Cd38 will display the current supply recorder sensor (SRS) reading for units
configured for four probes. If the unit is configured with a DataCORDER, Cd38
will display “-- -- -- -- -- .” If the DataCORDER suffers a failure, (AL55) Cd38 will
display the supply recorder sensor reading.
Code Cd39 will display the current return recorder sensor (RRS) reading for units
configured for four probes. If the unit is configured with a DataCORDER, Cd39
will display “-- -- -- -- -- .” If the DataCORDER suffers a failure, (AL55) Cd39 will
display the return recorder sensor reading.
Code Cd40 is configured at commissioning to read a valid container identification
number. The reading will not display alpha characters; only the numeric portion of
the number will display.
SERVICE FUNCTION: This code is used for troubleshooting, and allows manual
positioning of the economizer solenoid valve, electronic expansion valve, and digital unloader valve. Provides readings such as: Percent Capacity, EEV, Capacity
Mode, LIV and DUV. Refer to paragraph 6.18 for operating instructions.
Code Cd43 is used to select the mode of operation for the eAutoFresh slides. As-
sociated parameters can also be selected from submenus: OFF , USER, DELAY,
TEST and gASLM (refer to section 4.4.4 for description of operational parameters). If the unit is not configured for eAutoFresh, Cd43 will display “-- -- -- -- -- .”
Code Cd44 displays the eAutoFresh CO2and O2values (CO2 and O2) and CO
and O2limits (CO2LIM and O2LIM), respectively. If the unit is not configured for
eAutoFresh, Cd44 will display “ -- -- -- -- -- .”
Unless AL50 is active or CnF47 is OFF, the fresh air flow (CMH/CFM) is
displayed. This function code will automatically activate for 30 seconds and
display when a vent position change occurs.
2
3--20T-340
Page 47

Table 3--5 Controller Function Codes (Sheet 4 of 4)
Cd46
Cd47
Cd48
Cd49
Airflow Display Units
Variable Economy
Temperature Setting
Dehumidification Parameter Selection
Days Since Last
Successful Pre--trip
Cd50 CCPC Disabled
Automatic Cold
Cd51
Treatment
Parameter Selection
This code displays the airflow units to be displayed for Cd 45. Options are CF,
CM or bOth (dependent on the setting of Cd28 or pressing of the C/F key).
Code Cd47 is used with optional economy mode. The values are 0.5_C--4.0_C.
The default is 3.0C. If the unit is not configured for economy mode, “-- ---- --” will be
displayed.
Code Cd48 is used both when dehumidification set point is set above 65% RH
and below 64% RH. When dehumidification set point is set above 65% RH, select
goes to LO if it had been set to hi. When dehumidification set point is set below
64% RH, select goes to Alt if it had been set to LO.
Code Cd49 will display the time period (days) since the last successful pre--trip
completion. Press ENTER repeatedly to display last pre--trip completion in Auto,
Auto 1 and Auto 2 modes.
Code 50 allows selection of CCPC mode. The user can press ENTER, then arrow
keys, then ENTER again to enable (On) or suspend (OFF) CCPC mode. If CCPC
operation is On, it may be suspended due to one of the following conditions:
“SEtPt” =Set point is too low.
“CAHUM”= CA or humidity control is active
“ACT”=ACT is active.
“FAIL”=Return temperature probe has failed.
“PrtrP”=Pre--trip is active.
“C LIM”= Cool limit logic is active.
“PULL”=Unit is in pulldown mode.
Code Cd51 initially displays countdown timer increments of 1 day, 1 hour with the
temperature default. Pressing ENTER allows selection of within the current menu
and proceeds to the next menu. After five seconds of no activity, the display reverts to normal system display, but retains the parameters previously selected.
“ACt” = “On,” “Off” or “---- ----”. The default is Off.
“trEAt”=C /F in 0.1 degree increments. The default is 0.0_C.
“DAyS”= “0--99” increments of 1. The default is 0.
“ProbE”=probe positions (example 12_4) . The default is -- ---- --.
“SPnEW”= C /F in 0.1 degree increments. The default is 10.0_C.
Automatic Set point
Cd53
Change Mode
Parameter Selection
Cd54
Cd55
Electronic Expansion Valve Status
Discharge Superheat
Water Pressure
Cd58
Switch/Condenser
FanSwitchStateor
Override Logic State
Cd59 Pump Down Logic
Code Cd53 initially displays countdown timer increments of 1 day, 1 hour with the
temperature default. Pressing ENTER allows selection of within the current menu
and proceeds to the next menu. After five seconds of no activity, the display reverts to normal system display, but retains the parameters previously selected.
“ASC”=“On” or “Off” The default is Off.
“NSC”=“1--2”
“SP 0”=C /F in 0.1 degree increments. The default is 10.0_C.
“DAY 0”= “0--99” increments of 1. The default is 1.
“SP 1”=C /F in 0.1 degree increments. The default is 10.0_C.
“DAY 1”= “0--99” increments of 1. The default is 1.
“SP 2”=C /F in 0.1 degree increments. The default is 10.0_C.
Reading for evaporator superheat is shown on the right display. Press ENTER at
Cd54 to show reading for EEV position (in %) on left display.
Code Cd55 will display the discharge superheat values in C /F as calculated by
the discharge temperature minus the discharge saturation temperature as calculated from discharge pressure. “-- ------ --” will be displayed if the selection is not valid.
Code Cd58 will display “CLOSE” if the WPS or CFS switch contacts are closed or
that these options are not installed. “OPEn” is displayed when the WPS or CFS
switch contacts are open. When the WPS/CFS Override Logic is “TRUE”, the
right display will flash on all units.
Code Cd59 allows operation of the pump down logic control. The display will flash
between “STArT PdN” and “PrESS EnTEr”. Once the operator confirms continuation of the sequence, pump down logic begins. If the pump down logic is completed within 20 minutes, the unit will turn off and the display will flash “P dN
DOnE” and “SHUT OFF”. The operator must shut off the unit. If the pump down
logic is not completed within 20 minutes, the unit will return to its previous control
condition.
3--21
T-340
Page 48

Code
No.
AL03
AL05
AL06
Loss of Superheat
Control
Manual Defrost
Switch Failure
Keypad or Harness
Failure
TITLE DESCRIPTION
Fresh Air Vent Open
AL07
withFrozenSet
Point
AL08
High Compressor
Pressure Ratio
AL10 CO2Sensor Failure
AL14
AL16
AL17
AL18
AL19
AL20
Phase Sequence
Failure -- Electronic
Compressor Current
High
Phase Sequence
Failure -- Pressure
Discharge Pressure
High
Discharge Temperature High
Control Circuit Fuse
Open (24 VAC)
Table 3--6 Controller Alarm Indications (Sheet 1 of 5)
Alarm 03 is triggered if superheat operates below 1.66_C(3_F) for five minutes
continuously while the compressor is running and the EEV is at 0% open. The
alarm will trigger off when superheat has remained above 1.66_C(3_F) for five
minutes continuously while the compressor is running.
Alarm 05 is triggered if the controller detects continuous Manual Defrost Switch
action for five minutes or more. The alarm will only trigger off when the unit is
power cycled.
Alarm 06 is triggered if the controller detects continuous keypad button activity
for five minutes or more. The alarm will only trigger off when the unit is power
cycled.
Alarm 07 is triggered if the VPS is reading greater than 0 CMH based on the
function code display value and a frozen set point is active.
If AL 50 is active, AL 07 will not be generated.
The alarm will go inactive if the VPS reading transitions to 0 CMH, the set point
transitions to the perishable range, or an AL50 is active.
Alarm 08 is triggered when the controller detects that the discharge pressure to
suction pressure ratio is too high. The alarm triggers shut down of the compressor, which will restart in normal staging logic, after three minutes.
Alarm 10 is triggered when the CO2sensor voltage is operating outside of the 0.9
v to 4.7 v range, or if the sensor is out of range. This is a display alarm and has
no associated failure action.
Alarm 14 is triggered if the electronic phase detection system is unable to determine the correct phase relationship. AL 14 is also triggered if electronic phase
sequence detection was successful and conclusive, but unit is miswired. The
miswiring causes increased suction pressure and decreased discharge pressure
when the compressor is running; these conditions are present only when the
compressor is energized in the direction opposite of that indicated by electronic
phase sequence detection. If the system is unable to determine the proper relationship, alarm 14 will remain active. Additional information on phase detection
may be displayed at Function Code Cd41. If the right most digit of Code Cd41 is
3 or 4, this indicates incorrect motor or sensor wiring. If the right most digit is 5,
this indicates a failed current sensor assembly.
Alarm 16 is triggered if compressor current draw is 15% over calculated maximum for 10 minutes out of the last hour. The alarm is display only and will trigger
off when the compressor operates for one hour without over current.
Alarm 17 is triggered if a compressor start in both directions fails to generate sufficient pressure differential. The controller will attempt restart every 20 minutes
and deactivate the alarm if successful. This alarm triggers failure action C (evaporator fan only) or D (all machinery off) of Function Code Cd29 if the unit has a
perishable set point. Failure action D (all machinery off) is triggered if the unit has
a frozen set point.
Alarm 18 is triggered if discharge pressure is 10% over calculated maximum for
10 minutes within the last hour. The alarm is display only and will trigger off when
the compressor operates for one hour without overpressure.
Alarm 19 is triggered if discharge temperature exceeds 135_C (275_F) for
10 minutes within the last hour. The alarm is display only and will trigger off when
the compressor operates for one hour without over temperature.
Alarm 20 is triggered by control power fuse (F3A, F3B) opening and will cause
the software shutdown of all control units. This alarm will remain active until the
fuse is replaced.
3--22T-340
Page 49

AL21
AL22
Micro Circuit Fuse
Open (18 VAC)
Evaporator Fan
Motor Safety
AL23 Loss of Phase B
AL24
AL25
Compressor Motor
Safety
Condenser Fan Motor Safety
All Supply and Re-
AL26
turn temperature
Control Sensors
Failure
AL27
AL28
A/D Accuracy Failure
Low Suction Pressure
AL29 AutoFresh Failure
AL50
Fresh Air Position
Sensor (VPS)
AL51 Alarm List Failure
AL52 Alarm List Full
Table 3--6 Controller Alarm Indications (Sheet 2 of 5)
Alarm 21 is triggered by one of the fuses (F1/F2) being opened on 18 VAC power
supply to the controller. Temperature control will be maintained by cycling the
compressor.
Alarm 22 responds to the evaporator motor internal protectors. The alarm is triggered by opening of the internal protector. It will disable all control units until the
motor protector resets.
Alarm 23 is triggered if low current draw is detected on phase B and IPCP, HPS
or IPEM is not tripped. If the compressor should be running, the controller will initiate a start up every five minutes and trigger off if current reappears. If the evaporator fan motors only should be running, the alarm will trigger off if current reappears. This alarm triggers failure action C (evaporator fan only) or D (all machinery off) of Function Code Cd29 if the unit has a perishable set point. Failure action D (all machinery off) is triggered if the unit has a frozen set point.
Alarm 24 is triggered when compressor is not drawing any current. It also triggers
failure action “C” or “D” set by function Code 29 for perishable set point, or “D” for
frozen set point. If the compressor should be running, the controller will initiate a
start up every five minutes and trigger off, if current reappears. This alarm will remain active until compressor draws current.
Alarm 25 is triggered by the opening of the condenser motor internal protector
and will disable all control units except for the evaporator fans. This alarm will remain active until the motor protector resets. This alarm triggers failure action C
(evaporator fan only) or D (all machinery off) of Function Code Cd29 if the unit
has a perishable set point. Failure action D (all machinery off) is triggered if the
unit has a frozen set point.
Alarm 26 is triggered if the controller determines that all of the control sensors
are out--of--range. This can occur for box temperatures outside the range of
-- 5 0 _Cto+70_C(--58_F to +158_F). This alarm triggers the failure action code
set by Function Code Cd29.
The controller has a built--in Analog to Digital (A--D) converter, used to convert
analog readings (i.e. temperature sensors, current sensors, etc.) to digital readings. The controller continuously performs calibration tests on the A--D converter.
If the A--D converter fails to calibrate for 30 consecutive seconds, this alarm is
activated.This alarm will be inactivated as soon as the A--D converter calibrates.
Alarm 28 is triggered if evaporator pressure is invalid. This alarm triggers shut
down of the compressor off for three minutes. This alarm will be inactivated when
suction pressure rises above 2 psia for three continuous minutes.
Alarm 29 is triggered if CO2 or O2 level is outside of the limit range and the vent
position is at 100% for longer than 90 minutes. Alarm LED will be activated and
user intervention is required. The alarm is triggered off when atmospheric conditions are within limit settings.
Alarm 50 is activated whenever the sensor is outside the valid range. There is a
four--minute adjustment period where the user can change the vent position without generating an alarm event. The sensor requires four minutes of no movement
to confirm stability. If the vent position changes at any point beyond the four-minute adjustment period, the sensor will generate an alarm event. The alarm is
triggered off when the unit power cycles and the sensor is within valid range.
During start--up diagnostics, the EEPROM is examined to determine validity of its
contents. This is done by testing the set point and the alarm list. If the contents
are invalid, alarm 51 is activated. During control processing, any operation involving alarm list activity that results in an error will cause alarm 51 to be activated.
Alarm 51 is a “display only” alarm and is not written into the alarm list. Pressing
the ENTER key when “CLEAr” is displayed will result in an attempt to clear the
alarm list. If that action is successful (all alarms are inactive), alarm 51 will be
reset.
Alarm 52 is activated whenever the alarm list is determined to be full at start--up
or after recording an alarm in the list. Alarm 52 is displayed, but is not recorded in
the alarm list. This alarm can be reset by clearing the alarm list. This can be done
only if all alarms written in the list are inactive.
3--23
T-340
Page 50

AL53
Battery Pack Failure
Supply Temperature
AL54
Sensor Failure
(STS)
AL55 I/O Failure
Return Temperature
AL56
Sensor Failure
(RTS)
Table 3--6 Controller Alarm Indications (Sheet 3 of 5)
Alarm 53 is caused by the battery pack charge being too low to provide sufficient
power for battery--backed recording. If this alarm occurs on start up, allow a unit
fitted with rechargeable batteries to operate for up to 24 hours to charge rechargeable batteries sufficiently to deactivate the alarm.
Alarm 53 is also activated when there is no battery pack installed in the controller. To clear the alarm until another battery pack is installed, press ENTER and
ALT simultaneously at the startup of Cd19.
Alarm 54 is activated by an invalid supply temperature sensor (STS) reading that
is sensed outside the range of --50 to +70_C(--58_F to +158_F) or if the probe
check logic has determined there is a fault with this sensor. If alarm 54 is activated and the primary supply is the control sensor, the supply recorder sensor
(SRS) will be used for control if the unit is so equipped. If the unit does not have
a supply recorder sensor, and AL54 is activated, the return temperature sensor
(RTS) reading minus 2C will be used for control.
NOTE
The P5 Pre--trip test must be run to deactivate the alarm.
This alarm activates to indicate I/O functions have failed and require
replacement.
Alarm 56 is activated by an invalid return temperature sensor (RTS) reading that
is outside the range of --50_ to +70_C(--58_F to +158_F).Ifalarm56isactivated
and the primary return is the control sensor, the return recorder sensor (RRS) will
be used for control if the unit is so equipped. If the unit is not equipped with a return recorder sensor or it fails, the supply temperature sensor (STS) will be used
for control.
AL57
AL58
AL59
AL60
Ambient Temperature Sensor Failure
Compressor High
Pressure Safety
Heater Termination
Thermostat (HTT)
Defrost T emperature
Sensor Failure
AL61 Heaters Failure
AL63 Current Over Limit
AL64
Discharge Temperature Over Limit
NOTE
The P5 Pre--trip test must be run to deactivate the alarm.
Alarm 57 is triggered by an ambient temperature reading outside the valid range
from --50_ to +70_C(--58_F to +158_F).
Alarm 58 is triggered when the compressor high discharge pressure safety switch
remains open for at least one minute. This alarm will remain active until the pressure switch resets, at which time the compressor will restart.
Alarm 59 is triggered when the heat termination thermostat switch is opened (except when defrost sensor alarm is active). This alarm will remain active until the
heat termination thermostat closes.
Alarm 60 is an indication of a probable failure of the defrost temperature sensor
(DTS). It is triggered by the opening of the heat termination thermostat (HTT) or
the failure of the DTS to go above set point within two hours of defrost initiation.
After one--half hour with a frozen range set point, or one--half hour of continuous
compressor run time, if the return air falls below 7_C(45_F), the controller
checks to ensure the DTS reading has dropped to 10_C or below. If not, a DTS
failure alarm is given and the defrost mode is operated using the return temperature sensor. The defrost mode will be terminated after one hour by the controller.
Alarm 61 is triggered by detection of improper amperage resulting from heater
activation or deactivation. Each phase of the power source is checked for proper
amperage. This alarm is a display alarm with no resulting failure action and will
be reset by a proper amp draw of the heater .
Alarm 63 is triggered by the current limiting system. If the compressor is ON and
current limiting procedures cannot maintain a current level below the user selected limit, the current limit alarm is activated. This alarm is a display alarm and
is inactivated by power cycling the unit, changing the current limit via the code
select Cd32, or if the current decreases below the activation level.
Alarm 64 is triggered if the discharge temperature sensed is outside the range of
-- 6 0 _C(--76_F) to 175_C (347_F), or if the sensor is out of range. This is a dis-
play alarm and has no associated failure action.
3--24T-340
Page 51

AL65
AL66
AL67
AL68
AL69
Discharge Pressure
Transducer Failure
Evaporator Pressure
Transducer/Suction
Pressure Transducer
Out of Range
Humidity Sensor
Failure
Condenser Pressure
Sensor Fault
Primary Evaporator
Temperature Sensor
Out of Range
Table 3--6 Controller Alarm Indications (Sheet 4 of 5)
Alarm 65 is triggered if a compressor discharge transducer is out of range.
This is a display alarm and has no associated failure action.
Alarm 66 is triggered if an evaporator pressure transducer (EPT) is less than 0.2
volts or greater than 4.95 volts.
Occasionally, readings for normally operating evaporator pressure transducers
may drift. When this occurs, the SPT will be used to control both the EEV and
DUV. If the unit operates “in range” within 30 minutes, the EEV and DUV will be
controlled by the SPT. If not, the unit will return to normal operation and Alarm 66
will be activated. If the SPT assumes control of the EEV and DUV, Alarm 66 will
be activated after the next Trip Start has begun. Pre--trip 5--9 is used to detect
the failed transducer. A successful Pre--trip 5--9 will return the EEV and DUV to
normal operation.
For the SPT to assume control of the unit, the unit must not be operating “in
range” in addition to ALL 5 of the following conditions:
1. Unit is operating in frozen mode.
2. Unit has operated “in range” one time since the last Trip Start.
3. Both EPT and SPT are valid.
4. Both EPT readings are within +/-- 0.5_C(0.9_F) of each other.
5. Absolute difference between evaporator pressure and suction pressure readings
is greater than 3.175.
Alarm is triggered off when evaporator pressure sensor is back in range.
Alarm 67 is triggered by a humidity sensor reading outside the valid range of 0%
to 100% relative humidity. If alarm AL67 is triggered when the dehumidification
mode is activated, then the dehumidification mode will be deactivated.
Alarm 68 is triggered when the Condenser Pressure Sensor is out of range. This
is a display alarm and has no associated failure action.
Alarm 69 is triggered when the primary evaporator temperature sensor (ETS1) is
out of range. The controller switches to use of the secondary evaporator temperature sensor (ETS2). This is a display alarm and triggered off when ETS1 is back
within range.
3--25
T-340
Page 52

Table 3--6 Controller Alarm Indications (Sheet 5 of 5)
NOTE
If the controller is configured for four probes without a DataCORDER, the DataCORDER alarms AL70 and
AL71 will be processed as Controller alarms AL70 and AL71. Refer to Table 3--10, page 3--33.
The controller performs self--check routines. If an internal failure occurs, an
“ERR” alarm will appear on the display. This is an indication the controller needs
to be replaced.
ERROR DESCRIPTION
ERR 0--RAM failure Indicates that the controller working memory has failed.
ERR
#
Entr
StPt
LO
Internal
Microprocessor
Failure
Enter Set point
(Press Arrow &
Enter)
Low Main V oltage
(Function Codes
Cd27--38 disabled
and NO alarm
stored.)
ERR 1--Program Memory
failure
ERR 2--Watchdog
time--out
ERR 3--N/A N/A
ERR 4--N/A N/A
ERR 5--A--D failure
ERR 6--IO Board failure Internal program/update failure.
ERR 7--Controller failure Internal version/firmware incompatible.
ERR 8--DataCORDER
failure
ERR 9--Controller failure Internal controller memory failure.
In the event that a failure occurs and the display cannot be updated, the status
LED will indicate the appropriate ERR code using Morse code as shown below.
ERR0to9
E R R 0 = . . -- . . -- . -- -- -- -- -ERR1 = . .--. .--. . -------ERR2 = . .--. .--. . . -- -- --
ERR3 = . .--. .--. . . . -- --
ERR4= . .--. .--. ....--
ERR5= . .--. .--. .....
ERR6= . .--. .--. --....
ERR7 = . .--. .--. -- -- . . .
ERR8 = . .--. .--. -- ----. .
E R R 9 = . . -- . . -- . -- -- -- -- .
The controller is prompting the operator to enter a set point.
This message will be alternately displayed with the set point whenever the supply
voltage is less than 75% of its proper value.
Indicates a problem with the controller program.
The controller program has entered a mode whereby
the controller program has stopped executing.
The controller’s Analog to Digital (A--D) converter has
failed.
Internal DataCORDER memory failure.
3--26T-340
Page 53

Table 3--7 Controller Pre--trip Test Codes (Sheet 1 of 4)
Code
No.
TITLE DESCRIPTION
“Auto” or “Auto1” menu includes the: P0, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6 and rSLts. “Auto2” menu includes P0, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9, P10 and rSLts. “Auto3” menu includes P0, P1,
P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 and P8.
P0--0 Pre--trip Initiated
P1--0 Heaters Turned On
P1--1 Heaters Turned Off
P2--0 Condenser Fan On
P2--1 Condenser Fan Off
Low Speed
P3
Evaporator Fans
Low Speed
P3--0
Evaporator Fan
Motors On
Low Speed
P3--1
Evaporator Fan
Motors Off
High Speed
P4--0
Evaporator Fan
Motors On
High Speed
P4--1
Evaporator Fan
Motors Off
NOTE
All lights and display segments will be energized for five seconds at the start of
the pre--trip. Since the unit cannot recognize lights and display failures, there are
no test codes or results associated with this phase of pre--trip.
Setup: Heater must start in the OFF condition, and then be turned on. A current
draw test is done after 15 seconds.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if current draw change is within the range specified.
Setup: Heater must start in the ON condition, and then be turned off. A current
draw test is done after 10 seconds.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if current draw change is within the range specified.
Requirements: Water pressure switch or condenser fan switch input must be
closed.
Setup: Condenser fan is turned ON, a current draw test is done after
15 seconds.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if current draw change is within the range specified.
Setup: Condenser fan is turned OFF, a current draw test is done after
10 seconds.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if current draw change is within the range specified.
Requirements: The unit must be equipped with a low speed evaporator fan, as
determined by the Evaporator Fan speed select configuration variable.
Setup: The High Speed Evaporator fans will be turned on for 10 seconds, then
off for two seconds, then the low speed evaporator fans are turned on. A current
draw test is done after 60 seconds.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if change in current draw is within the range specified.
Setup: The Low Speed Evaporator fan is turned off, a current draw test is done
after 10 seconds.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if change in current draw is within the range specified.
Setup: The high speed evaporator fan is turned on, a current draw test is done
after 60 seconds.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if change in current draw is within the range specified.
Setup: The high speed evaporator fan is turned off, a current draw test is done
after 10 seconds.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if change in current draw is within the range specified.
3--27
T-340
Page 54

P5--0
Supply/Return
Probe Test
Table 3--7 Controller Pre--trip Test Codes (Sheet 2 of 4)
Setup: The High Speed Evaporator Fan is turned on and run for eight minutes,
with all other outputs de--energized.
Pass/Fail Criteria: A temperature comparison is made between the return and
supply probes.
NOTE
If this test fails, “P5--0” and “FAIL” willbe displayed. If both Probe tests (this
test and the PRIMARY/ SECONDARY) pass, the display will read “P5”
“PASS.”
Requirements: For units equipped with secondary supply probe only.
Pass/Fail Criteria: The temperature difference between supply temperature sensor
(STS) and supply recorder sensor (SRS) probe is compared.
P5--1 Supply Probe Test
P5--2 Return Probe Test
P5--3
Evaporator Fan
Direction Test
Primary .vs Sec-
P5--7
ondary Evaporator
Temperature
Sensor Test
NOTE
If this test fails, “P5--1” and “FAIL” will be displayed. If both Probe tests (this
and the SUPPLY/RETURN TEST) pass, because of the multiple tests, the
display will read “P 5” “PASS.”
Requirements: For units equipped with secondary return probe only.
Pass/Fail Criteria: The temperature difference between return temperature sensor
(RTS) and return temperature sensor (RRS) probe is compared.
NOTES
1. If this test fails, “P5--2” and “FAIL” will be displayed. If both Probe tests
(this test and the SUPPLY/RETURN) pass, because of the multiple
tests, the display will read “P 5,” “PASS.”
2. The results of Pre--trip tests 5--0, 5--1 and 5--2 will be used to activate or
clear control probe alarms.
Requirements: Test P5--0 must pass before this test is run.
Setup: While the evaporator is running on high speed, the temperature differen-
tial between supply temperature sensor (STS) and return temperature sensor
(RTS) probes is measured, with and without heaters energized.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if differential of STS is 0.25 degree C higher than
RTS.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if secondary evaporator temperature sensor (ETS2) is
within +/-- 0.5 degree C of the primary evaporator temperature sensor (ETS1).
P5--8
P5--9
P5--10
P5--11
P5--12
Suction Pressure
Transducer Test
Suction (Evaporator) Pressure Transducer Test
Humidity Sensor
Controller Configuration Verification
Tes t
Humidity Sensor
Installation Verification Test
Humidity Sensor
Range Check Test
Requirements: Test P5--7 must pass before this test is run.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if suction pressure transducer (SPT) is within +/-- 0 psi
of saturation pressure at current evaporator temperature. Also passes if suction
pressure transducer (SPT) is within +/-- 1 psi of discharge pressure 6 hours after a
power interruption.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if suction pressure transducer (SPT) is within +/-- 1.5
psi of the evaporator pressure transducer (EPT).
Requirements: Test P5--9 must pass before this test is run.
Test is skipped if controller is not configured for the humidity sensor and the
voltage is less than 0.20 volts.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if controller configuration has the humidity sensor installed. Fails if controller is not configured for humidity sensor and the voltage is
greater than 0.20 volts.
Requirements: Test P5--10 must pass before this test is run.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if voltage is greater than 0.20 volts for the humidity
sensor. Fails if voltage is less than 0.20 volts for the humidity sensor.
Requirements: Test P5--11 must pass before this test is run.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes if the voltage for the humidity sensor is between 0.66
volts and 4 volts. Fails if voltage is outside of the 0.66 volt to 4 volt range.
3--28T-340
Page 55

Table 3--7 Controller Pre--trip Test Codes (Sheet 3 of 4)
P6--0
P6--1
P6--2
P6--3
P6--4
Discharge
Thermistor Test
Suction
Thermistor Test
Discharge Pressure
Sensor Test
Suction Pressure
Sensor Test
Compressor Current Draw Test
If alarm 64 is activated any time during the first 45 second period of Step 1, the
test fails.
Alarm is activated if suction temperature is outside of the valid range of --60_C
(--76_F) to 150_C (302_F) any time during the first 45 second period of Step 1,
the test fails.
If alarm 65 is activated any time during the first 45 second period of Step 1, the
test fails.
If alarm 66 is activated, the test fails.
Compressor current is tested before and 10 seconds after start up. If current
does not increase, the test fails. P6--7 is run at the end of P6--4. If this test fails,
P6--6 is skipped.
NOTE
P6--6 through P6--10 tests are conducted by changing the status of each individual valve and comparing
suction pressure change and/or compressor current change with predetermined values. The tests will
cause the compressor and condenser fans to cycle on and off as needed to generate the pressure required
for the individual pre--trip sub tests. The compressor will start in order to build discharge pressure, followed
by a compressor pump down sequence. At the conclusion of the compressor pump down sequence, the
compressor will shut down and the valve test will start.
P6--6
P6--7
P6--10
Economizer
Val v e Tes t
Digital Unloader
Val v e Tes t
Electronic
Expansion Valve
Tes t
Passes if suction pressure increases a minimum of 4 psi when the valve opens
for 15 seconds.
Passes if pressure and current changes are within 3 seconds of DUV switch signal and either the pressure change or the current draw change is above 5 psi or
above 1.5A, respectively.
Pass/Fail Criteria: The test records the suction pressure during the open valve
position and passes if the suction pressure increase is above 3 psi when the
valve opens for 10 seconds.
NOTE
P7--0 & P8 are included with “Auto2 & Auto 3” only . P9--0 through P10 are included with “Auto2” only.
NOTE
This test is skipped if the sensed ambient temperature is less than 7_C
(45_F), the return air temperature is less than --17.8_C(0_F), the water
pressure switch is open or the condenser fan switch is open.
P7--0
P7--1
High Pressure
Switch Open
High Pressure
Switch Closed
Setup: With the unit running, the condenser fan is turned off and a 900 second
(15 minute) timer is started. The right display shows the value of the initial
sensor configured and valid out of the discharge pressure, CPC pressure, discharge temperature.
Pass/Fail Criteria:The test fails immediately if:
--all three sensors are not configured or are invalid.
--the ambient temperature or return air temperature sensors
are invalid at the start of the test.
The test fails if:
--the high pressure switch if open at the start of the test.
--the high pressure switch fails to open within 15 minutes.
--a valid discharge temperature exceeds 137.78_C (280_F).
--a valid discharge pressure or valid condensing pressure
exceeds 390 psig.
The test passes if the high pressure switch opens within the 15 minute time limit
and before any of the valid and configured sensors exceed their limits.
Requirements: Test P7--0 must pass for this test to execute. Setup: The condenser fan is started and a 60 second timer is started.
Pass/Fail Criteria: Passes the test if the high pressure switch (HPS) closes
within the 60 second time limit, otherwise, it fails.
3--29
T-340
Page 56

P8--0
P8--1
P8--2
Perishable Mode
Heat Test
Perishable Mode
Pulldown Test
Perishable Mode
Maintain Temperature Test
Table 3--7 Controller Pre--trip Test Codes (Sheet 4 of 4)
Setup: If the container temperature is below 15.6_C(60_F), the set point is
changed to 15.6_C, and a 180--minute timer is started. The left display will read
“P8--0.” The control will then heat the container until 15.6_C is reached. If the
container temperature is above 15.6_C at the start of the test, then the test proceeds immediately to test P8--1 and the left display will change to “P8--1.”
Pass/Fail Criteria: The test fails if the 180 minute timer expires before the control temperature reaches set point. The display will read “P8--0,” “FAIL.”
Requirements: Control temperature must be at least 15.6_C(60_F).
Setup: The set point is changed to 0_C(32_F), and a 180--minute timer is
started. The left display will read “P8--1,” the right display will show the supply air
temperature. The unit will then start to pull down the temperature to the 0C set
point.
Pass/Fail Criteria: The test passes if the container temperature reaches set
point before the 180 minute timer expires.
Requirements: Test P8--1 must pass for this test to execute. This test is
skipped if the DataCORDER is not configured or not available.
Setup: A 15--minute timer is started. The unit will be required to minimize control
temperature error (supply temperature minus set point) until the timer expires.
The control temperature will be sampled at least once each minute starting at the
beginning of P8--2.
Pass/Fail Criteria: If the average recorded temperature is within +/-- 1.0_C
(1.8_F) of set point, the test passes. If the average temperature is outside of the
tolerance range or if the DataCORDER supply temperature probe is invalid, the
test fails and and the control probe temperature will be recorded as --50.0_C.
P8--2 will auto--repeat by starting P8--0 over.
P9--0 Defrost T est
P10--0
P10--1
Frozen Mode
Heat Test
Frozen Mode
Pulldown Test
Frozen Mode
P10--2
Maintain
Temperature Test
Setup: The defrost temperature sensor (DTS) reading will be displayed on the
left display. The right display will show the supply air temperature. The unit will
run FULL COOL for 30 minutes maximum until the DTT is considered closed.
Once the DTT is considered closed, the unit simulates defrost by running the
heaters for up to two hours, or until the DTT is considered open.
Pass/Fail Criteria: The test fails if: the DTT is not considered closed after the
30 minutes of full cooling, HTT opens when DTT is considered closed or if return
air temperature rises above 49_C (120_F).
Setup: If the container temperature is below 7.2_C(45_F), the set point is
changed to 7.2_C and a 180--minute timer is started. The control will then be
placed in the equivalent of normal heating. If the container temperature is above
7.2_C at the start of the test, then the test proceeds immediately to test 10--1.
During this test, the control temperature will be shown in the right display.
Pass/Fail Criteria: The test fails if the 180--minute timer expires before the control temperate reaches set point --0.3_C (0.17_F). If the test fails it will not auto-repeat. There is no pass display for this test. Once the control temperature
reaches set point, the test proceeds to test 10--1
Requirements: Control temperature must be at least 7.2_C(45_F)
Setup: The set point is changed to --17.8_C(0_F). The system will then attempt
to pull down the control temperature to set point using normal frozen mode cooling. During this test, the control temperate will be shown on the right display.
Pass/Fail Criteria: If the control temperature does not reach set point --0.3_C
(0.17_F) before the 180--minute timer expires the test fails and will auto--repeat
by starting P10--0 over.
Requirements: Test P10--1 must pass for this test to execute. This test is
skipped if the DataCORDER is not configured or not available.
Setup: A 15--minute timer is started. The unit will be required to minimize return
probe temperature error (supply temperature minus set point) until the timer expires. The return probe temperature will be sampled at least once each minute
starting at the beginning of P10--2.
Pass/Fail Criteria: If the average recorded temperature is within +/-- 1.6_C
(+/-- 2.9) of set point, the test passes. If the average temperature is outside of
the tolerance range or if the DataCORDER return temperature probe is invalid,
the test fails and the control probe temperature will be recorded as --50.0_C.
P10--2 will auto--repeat by starting P10--0 over.
3--30T-340
Page 57

Table 3--8 DataCORDER Function Code Assignments
NOTE
Inapplicable Functions Display “-- -- -- -- -- ”
To Access: Press ALT. MODE key
Code
No.
dC1
dC2
dC3--5
dC6--13
dC14
dC15--19 Future Expansion These codes are for future expansion, and are not in use at this time.
dC20--24
dC25 Future Expansion This code is for future expansion, and is not in use at this time.
dC26,27 S/N, Left 4, Right 4
dC28 Minimum Days Left
dC29 Days Stored Number of days of data that are currently stored in the DataCORDER.
dC30
dC31 Battery Test
dC32 Time: Hour, Minute Current time on the real time clock (RTC) in the DataCORDER.
dC33 Date: Month, Day Current date (month and day) on the RTC in the DataCORDER.
dC34 Date: Year Current year on the RTC in the DataCORDER.
dC35
Recorder Supply
Temperature
Recorder Return
Temperature
USDA 1,2,3 Temperatures
Network Data
Points 1--8
CargoProbe4Temperature
Temperature Sensors 1--5 Calibration
Date of Last Trip
start
Cargo Probe 4
Calibration
TITLE DESCRIPTION
Current reading of the supply recorder sensor.
Current reading of the return recorder sensor.
Current readings of the three USDA probes.
Current values of the network data points (as configured). Data point 1
(Code 6) is generally the humidity sensor and its value is obtained from the
controller once every minute.
Current reading of the cargo probe #4.
Current calibration offset values for each of the five probes: supply, return,
USDA #1, #2, and #3. These values are entered via the interrogation program.
The DataCORDER serial number consists of eight characters. Function
code dC26 contains the first four characters. Function code dC27 contains
the last four characters. (This serial number is the same as the controller
serial number.)
An approximation of the number of logging days remaining until the DataCORDER starts to overwrite the existing data.
The date when a Trip Start was initiated by the user. In addition, if the system
goes without power for seven continuous days or longer, a trip start will automatically be generated on the next AC power up. Press and hold “ENTER”
key for five seconds to initiate a “Trip Start.”
Shows the current status of the optional battery pack.
PAS S : Battery pack is fully charged.
FAIL: Battery pack voltage is low.
Current calibration value for the Cargo Probe. This value is an input via the
interrogation program.
3--31
T-340
Page 58

Table 3--9 DataCORDER Pre--trip Result Records
Test
No.
TITLE DATA
1--0 Heater On Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Change in current for Phase A, B and C
1--1 Heater Off Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Change in currents for Phase A, B and C
2--0 Condenser Fan On
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Water pressure switch (WPS) -- Open/Closed,
Change in currents for Phase A, B and C
2--1 Condenser Fan Off Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Change in currents for Phase A, B and C
3--0
3--1
4--0
4--1
Low Speed Evaporator Fan
On
Low Speed Evaporator Fan
Off
High Speed Evaporator Fan
On
High Speed Evaporator Fan
Off
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Change in currents for Phase A, B and C
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Change in currents for Phase A, B and C
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Change in currents for Phase A, B and C
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Change in currents for Phase A, B and C
5--0 Supply/Return Probe Test Pass/Fail/Skip Result, STS, RTS, SRS and RRS
5--1
5--2
Secondary Supply Probe
(SRS)Test
Secondary Return Probe
(RRS) Test
Pass/Fail/Skip
Pass/Fail/Skip
6--0 Discharge Thermistor Test Pass/Fail/Skip
6--1 Suction Thermistor Test Pass/Fail/Skip
6--2
Discharge Pressure Sensor
Tes t
Pass/Fail/Skip
6--3 Suction Pressure Sensor Test Pass/Fail/Skip
6--4
Compressor Current Draw
Tes t
Pass/Fail/Skip
6--6 Economizer Valve Test Pass/Fail/Skip
6--7 Digital Unloader Valve Test Pass/Fail/Skip
7--0 High Pressure Switch Closed
7--1 High Pressure Switch Open
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, AMBS, DPT or CPT (if equipped)
Input values that component opens
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, STS, DPT or CPT (if equipped)
Input values that component closes
8--0 Perishable Mode Heat Test Pass/Fail/Skip Result, STS, time it takes to heat to 16_C(60_F)
8--1
8--2
9--0 Defrost Test
Perishable Mode Pulldown
Tes t
Perishable Mode Maintain
Tes t
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, STS, time it takes to pull down to 0_C(32_F)
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Averaged DataCORDER supply temperature
(SRS) over last recording interval.
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, DTS reading at end of test, line voltage, line
frequency, time in defrost.
10--0 Frozen Mode Heat Test Pass/Fail/Skip Result, STS, time unit is in heat.
10--1 Frozen Mode Pulldown Test Pass/Fail/Skip Result, STS, time to pull down unit to --17.8_C(0_F).
10--2 Frozen Mode Maintain Test
Pass/Fail/Skip Result, Averaged DataCORDER return temperature
(RRS) over last recording interval.
3--32T-340
Page 59

Table 3--10 DataCORDER Alarm Indications
To Access: Press ALT. MODE key
Code No. TITLE DESCRIPTION
The supply recorder sensor reading is outside of the range of --50_Cto
Recorder Supply
dAL70
dAL71
dAL72--74
dAL75
dAL76, 77 Future Expansion These alarms are for future expansion and are not in use at this time.
dAL78--85
dAL86 R TC Battery Low
dAL87 RTC Failure
dAL88
dAL89 Flash Memory Error
dAL90 Future Expansion This alarm is for future expansion, and is not in use at this time.
dAL91 Alarm List Full The DataCORDER alarm queue is determined to be full (eight alarms).
Temperature Out of
Range
Recorder Return
Temperature Out of
Range
USDA Temperatures
1, 2, 3 Out of Range
Cargo Probe 4 Out of
Range
Network Data Point
1 -- 8 Out of Range
DataCORDER
EEPROM Failure
70_C(--58_F to +158_F), or the probe check logic has determined there is
a fault with this sensor.
NOTE
The P5 Pre--trip test must be run to inactivate the alarm.
The return recorder sensor reading is outside of the range of --50_Cto
70_C(--58_F to +158_F), or the probe check logic has determined there is
a fault with this sensor.
NOTE
The P5 Pre--trip test must be run to inactivate the alarm.
The USDA probe temperature reading is outside of --50_Cto70_C
(--58_F to +158_F) range.
The cargo probe temperature reading is outside of --50_Cto70_C
(--58_F to +158_F) range.
The network data point is outside of its specified range. The DataCORDER is configured by default to record the supply and return recorder sensors. The DataCORDER may be configured to record up to eight additional network data points. An alarm number (AL78 to AL85) is assigned to
each configured point. When an alarm occurs, the DataCORDER must be
interrogated to identify the data point assigned. When a humidity sensor is
installed, it is usually assigned to AL78.
The real time clock (RTC) backup battery is too low to adequately maintain the RTC reading.
An invalid time has been detected. Either the DataCorder run time hour
and minute have not changed at the start of the hour, or the real time
clock (RTC) time has gained or lost more than 2 minutes in the hour. This
situation may be corrected by cycling the power, setting the clock or meeting the above criteria for an hour.
A write of critical DataCORDER information to the EEPROM has failed.
An error has been detected in the process of writing daily data to the non-volatile FLASH memory.
3--33
T-340
Page 60

SECTION 4
OPERATION
4.1 INSPECTION (Before Loading)
WARNING
Beware of unannounced starting of the
evaporator and condenser fans. The unit
may cycle the fans and compressor unexpectedly as control requirements dictate.
a. Check inside for the following:
1. Check channels or “T” bar floor for cleanliness.
Channels must be free of debris for proper air circulation.
2. Check container panels, insulation and door seals
for damage. Effect permanent or temporary repairs.
3. Visually check evaporator fan motor mounting bolts
for proper securement (refer to paragraph 6.11).
4. Check for visible corrosion on the evaporator stator
and fan deck (refer to paragraph 6.12).
5. Check for dirt or grease on evaporator fans or fan
deck and clean if necessary.
6. Check evaporator coil for cleanliness or obstructions. Wash with fresh water.
7. Check defrost drain pans and drain lines for obstructions and clear if necessary. W ash with fresh water.
8. Check panels on refrigeration unit for loose bolts and
condition of panels. Make sure TIR devices are in
place on access panels.
b. Check condenser coil for cleanliness. Wash with
fresh water.
c. Open control box door. Check for loose electrical con-
nections or hardware.
d. Check color of moisture--liquid indicator.
2. Plug the 460 VAC (yellow) cable into a de--energized
380/460 VAC, 3--phase power source. Energize the
power source. Place circuit breaker (CB--1) in position “I” (ON). Close and secure control box door.
4.2.2 Connection To 190/230 VAC Power
An autotransformer (Figure 4--1) is required to allow operation on nominal 230 volt power. It is fitted with a 230
VAC cable and a receptacle to accept the standard 460
VAC power plug. The 230 volt cable is black in color
while the 460 volt cable is yellow. The transformer may
also be equipped with a circuit breaker (CB--2). The
transformer is a step up transformer that will provide
380/460 VAC, 3--phase, 50/60 Hz power to the unit
when the 230 VAC power cable is connected to a
190/230 VAC, 3--phase power source.
1. Make sure that the start--stop switch (ST, on control
panel) and circuit breakers CB--1 (in the control box
and CB--2 (on the transformer) are in position “0”
(OFF). Plug in and lock the 460 VAC power plug at the
receptacle on the transformer.
2. Plug the 230 VAC (black) cable into a de--energized
190/230 VAC, 3--phase power source. Energize the
power source. Set circuit breakers CB--1 and CB--2 to
position “I” (ON). Close and secure control box door.
2
1
3
4.2 CONNECT POWER
WARNING
Do not attempt to remove power plug(s) be fore turning OFF start--stop switch (ST),
unit circuit breaker(s) and external power
source.
WARNING
Make sure the power plugs are clean and
dry before connecting to power receptacle.
4.2.1 Connection To 380/460 VAC Power
1. Make sure start--stop switch (ST, on control panel)
and circuit breaker (CB--1, in the control box) are in
position “0” (OFF).
1. Dual Voltage Modular Autotransformer
2. Circuit Breaker (CB--2) 230--Volt
3. 460 VAC Power Receptacle
Figure 4--1 Autotransformer
4.3 ADJUST FRESH AIR MAKEUP VENT
The purpose of the fresh air makeup vent is to provide
ventilation for commodities that require fresh air circulation. The vent must be closed when transporting frozen
foods.
Air exchange depends on static pressure differential,
which will vary depending on the container and how the
container is loaded.
Units may be equipped with a vent position sensor
(VPS). The VPS determines the position of the fresh air
vent and sends data to the controller display.
4--1
T-340
Page 61

4.3.1 Upper Fresh Air Makeup Vent
Two slots and a stop are designed into the Upper Fresh
Air disc for air flow adjustments. The first slot allows for a
0 to 30% air flow; the second slot allows for a30 to 100%
air flow. To adjust the percentage of air flow , loosen the
wing nut and rotate the disc until the desired percentage
of air flow matches with the arrow . Tighten the wing nut.
To clear the gap between the slots, loosen the wing nut
until the disc clears the stop.
Figure 4--2 gives air exchange values for an empty container. Higher values can be expected for a fully loaded
container.
AIR
FLOW
(CMH)
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 102030405060708090
AIR
FLOW
(CMH)
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 102030405060708090
50HZ
PERCENT OPEN
60HZ
PERCENT OPEN
TBAR
11/2”
TBAR
25/8”
TBAR 3”
100
100
TBAR
11/2”
TBAR
25/8”
TBAR 3”
Figure 4--2 Upper Fresh Air Make Up Flow Chart
4.3.2 Lower Fresh Air Makeup Vent
a. Full Open or Closed Positions
Maximum air flow is achieved by loosening the wing
nuts and moving the cover to the maximum open
position (100% position). The closed position is 0% air
flow position. The operator may also adjust the opening
to increase or decrease the air flow volume to meet the
required air flow.
b. Reduced Flow for Lower Fresh Air Makeup
NOTE
In order to prevent inaccurate display readings
on units equipped with a Vent Position Sensor
(VPS), ensure that the rack and pinion drive of
the VPS is not disrupted when adjusting the air
makeup vent.
NOTE
Do not loosen the hex nut beyond its stop. Doing so may cause inaccurate display readings
and errors in DataCORDER reports.
Similar to the Upper Fresh Air Makeup vent, two slots
and a stop are designed into the Lower Fresh Air slide
for air flow adjustments. The first slot allows for a 0 to
25% air flow; the second slot allows for a 25 to 100% air
flow. To adjust the percentage of air flow, loosen the hex
nut and rotate the disc until the desired percentage of air
flow matches with the arrow. Tighten the hex nut. To
clear the gap between the slots, loosen the hex nut until
the disc clears the stop.
On some models the air slide is supplied with two
adjustableair control discs. The fresh air makeup canbe
adjusted for 15, 35, 50 or 75 cubic meters per hour
(CMH). The air flow has been established at 60 Hz
power and 2--1/2 inch T bar and with 15 mm (0.6 inch)
H
O external static above free blow.
2
Loosen the hex nut, adjust each disc to the required air
flow, then tighten hex nut.
NOTE
The main air slide is in the fully closed position
during reduced air flow operation when
equipped with air control discs.
c. Air Sampling for Carbon Dioxide (CO
) Level
2
Loosen hex nuts and move the cover until the arrow on
the cover is aligned with the “atmosphere sampling port”
label. Tighten the hex nuts and attach a 3/8 in. hose to
the sampling port.
If the internal atmosphere content has reached an
unacceptable level, the operator may adjust the disc
opening to meet the required air flow volume to ventilate
the container.
4.3.3 Vent Position Sensor
The VPS allows the user to determine the position of the
fresh air vent via Function Code 45. This function code
is accessible via the Code Select key.
The vent position will display for 30 seconds whenever
motion corresponding to 5 CMH (3 CFM) or greater is
detected. It will scroll in intervals of 5 CMH (3 CFM).
Scrolling to Function Code 45 will display the Fresh Air
Vent Position.
The position of the vent will be recorded in the
DataCORDER whenever the unit is running under AC
power and any of the following:
Trip start
On every power cycle
Midnight
Manual changes greater than 5 CMH (3 CFM)
remaining in the new position for at least 4 minutes
T-340 4--2
Page 62

NOTE
The user has four minutes to make necessary
adjustments to the vent setting. This time
calculation begins on the initial movement of
the sensor. The vent can be moved to any
position within the four minutes. On completion
of the first four minutes, the vent is required to
remain stable for the next four minutes. If vent
position changes are detected during the
four--minute stability period, an alarm will be
generated. This provides the user with the
ability to change the vent setting without
generating multiple events in the
DataCORDER.
4.4 eAutoFresh OPERATION
The eAutoFresh system allows the opening and closing
of the mechanical air vent slide. The opening and
closing of the slide is determined by the mode selected
through function code Cd43.
Upon power up, the controller will fully close the
eAutoFresh air vent. Nine seconds after power up, the
controller will check if there is a carbon dioxide (CO
sensor connected. When a CO2sensor is detected, the
controller will enable access to the Gas Limit mode of
operation. If no sensor is detected, the only modes of
operation available will be Test, User, and Delay . The
controller will then resume operation in the last mode of
operation before power interruption.
4.4.1 eAutoFresh Pre--Trip Inspection
Pre--trip testing of the eAutoFresh system is performed
during Pre--Trip test P0. Operatio n of the system may be
observed during this test.
Upon initiation of Pre--Trip P0, the current state will be
saved and the vent will fully close. This will be followed
by two sequences of opening to 100% and returning to
the closed position. No other eAutoFresh mode of
operation will be available until the two cycles of opening
and closing have completed. Upon termination of the
test, the vent will open to the previous state and
operation will return to the previous mode.
If the last mode was gASLM, the vent will open to the
preset FLO setting, the controller will start taking new
readings and control based on those readings.
4.4.2 eAutoFresh Start--Up Procedure
To start the system, do the following:
a. Press the “CODE SELECT” key (see Figure 3--2).
b. Press the “UP or DOWN“ arrow key until “CD43“ is
displayed, then press “ENTER”.
c. Press the “UP or DOWN“ arrow key to access the de-
sired mode of operation. When the mode operation is
displayed press t he enter key to access the submenu
parameters.
4.4.3 eAutoFresh Operation
The modes of operation are: OFF, USER, TEST,
DELAY, and GASLIMIT. Each mode of operation has
submenus with selectable parameters. Not all
parameters are available in each submenu.
Operational Parameters
FLO indicates the opening to which the slide will move
based on the stored value in CMH (in increments of 5) or
CFM depending on the selection of Cd46 (Airflow display units), Cd28 (Metric/Imperial) or the pressing of the
deg C/F key. CFM is displayed as CF, CMH is displayed
as CM.
tIM is the time delay prior to the door opening. The time
range is from 1 to 72 hrs in 1 hr increments.
CO2LM is the maximum level of carbon dioxide that is
allowed for the cargo. The range is from 0% to 19% in
1% increments, the default setting is 10.
O2LM is the minimum level of O
that is allowed for the
2
cargo. The range is from 2% to 20% in 1% increments,
the default setting is 10.
Rtn is an offset value used to expand the return air temperature value to compensate for the fresh air entering
the container. The allowable range is from 0.6C to 2.8C
2)
or 1.0_Fto5.0_F in 0.1 degree increments the default
setting is 2.8_C(5_F).
4.4.4 eAutoFresh Modes of Operation
NOTE
When setting any mode of operation, complete
the entire process to ensure all parameters are
set.
a. OFF
A setting of OFF will disable all automatic venting
operations. The eAutoFresh vent will be driven fully
closed and the eAutoFresh opening set to 0 CMH in
function code Cd44. This is the default mode whenever
a frozen mode of operation has been selected. When
the frozen set point is selected, the current eAutoFresh
setting is saved. The vent position will restore when a
perishable set point is selected.
b. USER
The USER mode provides ventilation for commodities
that require fresh air circulation. The flow rate can be
accessed through the submenu if a perishable set point
has been selected. To set the flow rate, press the
ENTER key to activate the selection mode. When FLO
appears in the left hand window, use the UP or DOWN
arrow key to scroll to the desired opening. The range is
from 0 to 220CM (0 to 129CF) in increments of 5. Press
the ENTER key to set the value and begin operation.
c. TEST
TEST mode allows the operator to test the movement of
the mechanical slide air vent and calibrate the carbon
dioxide sensor.
4--3
T-340
Page 63

tESt -- When “tESt” appears in the left window, press the
ENTER key to begin the test. The eAutoFresh slide will
open fully and then return to the closed position. The
test may be observed by the operator to ensure proper
operation of the vent. After completion of the TEST, the
unit will return to the previous mode of operation.
NOTE
It is recommended that the calibration procedure only be performed during pre--trip or when
the container has been fully vented.
CAL will attempt to calibrate the carbon dioxide sensor.
When “CAL“ mode is selected the display will flash
“CAL“. The operator is to hold the “ENTER“ key for 5
seconds. The display will stop flashing and read “CAL“
for 5 seconds. The microprocessor will read the CO
value, and then compare that value to a known zero
value. If the sensor is within the calibration parameter
range, the microprocessor will determine the
appropriate offset for the sensor. If the sensor is outside
of this range, for example if the container is loaded or
has a high level of CO
the controller will flash “NOCAL“
2,
for 5 seconds then revert to the previous mode of
operation.
d. DELAY
In DELAY mode, the operation of the eAutoFresh
system will be delayed for a set amount of time. This
allows time for the cargo to reach set point. In DELAY
mode, the eAutoFresh vent will open to the stored (FLO)
value when the return air temperature sensor is at or
below set point plus the return offset value (rtn) or the
delay time (tIM), whichever comes first. The
eAutoFresh vent will be fully closed when return air
temperature sensor is greater than the set point plus the
offset temperature (rtn).
To set the unit in Delay mode, scroll until “DELAY“
appears in the left window, press the ENTER key to
activate the submenu. The first selection is the amount
of time (tIM) for the delay. Select the amount of time for
the delay by using the UP and DOWN arrow keys. The
range is from 1 to 72 hours in 1 hour increments. Press
the ENTER key to set the value and move to the FLO
rate. Use the UP or DOWN arrow key to scroll to the
desired FLO rate. The range is from 0 to 220CM (0 to
129CF) in increments of 5 and 3 respectively. Press the
ENTER key to set the value and move to the return
temperature offset. Use the UP or DOWN arrow key to
scroll to the desired rtn rate. The range of offset is from
0.6_Cto2.8_C(1.0_Fto2.8_F) in 0.1 degree
increments. Press the ENTER key to set the value and
begin operation.
e. GAS LIMIT (gASLM)
In GAS LIMIT mode, access to the submenu is available
provided a perishable set point has been selected, and a
valid reading is detected from the carbon dioxide
sensor. In “Gas limit” mode the microprocessor will
monitor and limit the amount of carbon dioxide within the
container by opening and closing the eAutoFresh vent.
The vent will open to the (FLO) setting once the unit has
completed initial temperature pull down or if the cargo
temperature is within 5_C of set point and the carbon
dioxide level has reached the max limit or if the Oxygen
level has reached the lower limit. After the first 15
minutes of the vent opening the controller will again
evaluate the level of CO
first 15 minutes the gas limit values are satisfied, the
, and/or O2levels. If after the
2
vent will close, if either gas limit has not been satisfied
within 15 minutes the air exchange vent will open in 10
CMH increments every 15 minutes until both gas
concentrations are satisfied. Once all limits are satisfied
the vent will return to the closed position. If conditions
are not met with slide open 100% for 90 minutes Alarm
29 will be activated.
To operate in Gas Limit mode, scroll until gASLM
appears in the left window, press the ENTER key to
activate the submenu. The first selection is the
maximum carbon dioxide (CO2LM). Select the max
level by using the UP and DOWN arrow keys. The range
is from 0 to 19% in 1% increments. Press the ENTER
key to set the value and move to the minimum Oxygen
level (O2LM). The range is from 2 to 20% in 1%
increments. Press the ENTER key to set the value and
move to the FLO rate. Use the UP or DOWN arrow key
2
to scroll to the desired FLO rate. The range is from 0 to
220CM (0 to 129CF) in increments of 5 and 3
respectively. Press the ENTER key to set the value and
begin operation.
4.5 CONNECT WATER--COOLED CONDENSER
The water--cooled condenser is used when cooling water is available and heating the surrounding air is objectionable, such as in a ship’s hold. If water--cooled operation is desired, connect in accordance with the following
subparagraphs.
4.5.1 Water-- Cooled Condenser with Water
Pressure Switch
a. Connect the water supply line to the inlet side of con-
denser and the discharge line to the outlet side of the
condenser. (See Figure 2--5.)
b. Maintain a flow rate of 11 to 26 liters per minute (3 to 7
gallons per minute). The water pressure switch will
open to de--energize the condenser fan relay. The
condenser fan motor willstop andwill remain stopped
until the water pressure switch closes.
c. To shift to air--cooled condenser operation, discon-
nect the water supply and the discharge line to the
water--cooled condenser. The refrigeration unit will
shift to air--cooled condenser operation when the water pressure switch closes.
4.5.2 Water-- Cooled Condenser with Condenser
Fan Switch
a. Connect the water supply line to the inlet side of con-
denser and the discharge line to the outlet side of the
condenser. (See Figure 2--5.)
b.Maintainaflowrateof11to26lpm(3to7gpm).
c. Set the condenser fan switch to position “O.” This will
de--energize the condenser fan relay. The condenser
fan motor will stop and remain stopped until the CFS
switch is set to position “I.”
CAUTION
When condenser water flow isbelow 11 lpm
(3 gpm) or when water--cooled operation is
not in use, the CFS switch MUST be set to
position “1” or the unit will not operate
properly.
d. To shift to air--cooled condenser operation, stop the
unit, set the CFS switch to position ”I” and restart the
unit. Disconnect the water lines to the water--cooled
condenser.
T-340 4--4
Page 64

4.6 CONNECT REMOTE MONITORING
RECEPTACLE
If remote monitoring is required, connect remote monitor plug at unit receptacle. When the remote monitor
plug is connected to the remote monitoring receptacle,
the following remote circuits are energized:
CIRCUIT
Sockets B to A Energizes remote cool light
Sockets C to A Energizes remote defrost light
Sockets D to A Energizes remote in--range light
4.7 STARTING AND STOPPING INSTRUCTIONS
FUNCTION
WARNING
Make sure that the unit circuit breaker(s)
(CB--1 & CB--2) and the START--STOP
switch (ST) are in the “O” (OFF) position before connecting to any electrical power
source.
4.7.1 Starting the Unit
a. With power properly applied, the fresh air vent posi-
tion set and (if required) the water--cooled condenser
connected (refer to paragraphs 4.2, 4.3 & 4.5), place
the START--STOP switch to “I” (ON).
NOTE
The electronic phase detection system will
check for proper compressor rotation within the
first 30 seconds. If rotation is not correct, the
compressor will be stopped and restarted in the
opposite direction. If the compressor is producing unusually loud and continuous noise after
the first 30 seconds of operation, stop the unit
and investigate.
b. The Controller Function Codes for the container ID
(Cd40), software version (Cd18) and unit model number (Cd20) will be displayed in sequence.
c. Continue with Start Up Inspection, paragraph 4.8.
4.7.2 Stopping the Unit
To stop the unit, place the ST ART--STOP switch in position “0” (OFF).
4.8 START--UP INSPECTION
4.8.1 Physical Inspection
Check rotation of condenser and evaporator fans.
4.8.2 Check Controller Function Codes
Check, and if required, reset controller Function Codes
(Cd27 through Cd39) in accordance with desired operating parameters. Refer to Table 3--5.
4.8.3 Start T emperature Recorder
Partlow Recorders
a. Open recorder door and check battery of electronic
recorder. Be sure key is returned to storage clip of
mechanical recorder.
b. Lift stylus (pen) by pulling the marking tip outward un-
til the stylus arm snaps into it’s retracted position.
c. Install new chart, making sure chart is under the four
corner tabs. Lower the stylus until it has madecontact
with the chart. Close and secure door.
DataCORDER
a. Check and, if required, set the DataCORDER Config-
uration in accordance with desired recording parameter. Refer to paragraph 3.7.3.
b. Enter a “Trip Start.” To enter a “Trip Start,” do the fol-
lowing:
1. Depress the ALT MODE key. When the left display
shows, dC, depress the ENTER key.
2. Scroll to Code dC30.
3. Depress and hold the ENTER key for five seconds.
4. The “Trip Start” event will be entered in the DataCORDER.
4.8.4 Complete Inspection
Allow unit to run for five minutes to stabilize conditions
and perform a pre--trip diagnosis in accordance with the
following paragraph.
4.9 PRE--TRIP DIAGNOSIS
CAUTION
Pre--trip inspection should not be performed with critical temperature cargoes in
the container.
CAUTION
When Pre--Trip key is pressed, economy,
dehumidification and bulb mode will be
deactivated. At the completion of Pre--Trip
activity, economy, dehumidification and
bulb mode must be reactivated.
Pre--Trip diagnosis provides automatic testing of the
unit components using internal measurements and
comparison logic. The program will provide a “PASS” or
“FAIL” display to indicate test results.
The testing begins with access to a pre--trip selection
menu. The user may have the option of selecting one of
two automatic tests. These tests will automatically
perform a series of individual pre--trip tests. The user
may also scroll down to select any of the individual tests.
When only the short sequence is configured, it will
appear as “AUtO” in the display. Otherwise “AUtO1” will
indicate the short sequence and “AUtO2” will indicate
the long sequence. The test short sequence will run
tests P0 through P6. The long test sequence will run
tests P0 through P10.
A detailed description of the pre--trip test codes is listed
in Table 3--7, page 3--27. If no selection is made, the
pre--trip menu selection process will terminate
automatically. However, dehumidification and bulb
mode must be reactivated manually if required.
Scrolling down to the “rSLts” code and pressing ENTER
will allow the user to scroll through the results of the last
pre--trip testing run. If nopre--testing has been run (or an
individual test has not been run) since the unit was
powered up, “-- ---- --” will be displayed.
4--5
T-340
Page 65

To start a pre--trip test, do the following:
NOTE
1. Prior to starting tests, verify that unit
voltage (Function Code Cd07) is within
tolerance and unit amperage draw
(Function Codes Cd04, Cd05, Cd06) are
within expected limits. Otherwise, tests
may fail incorrectly.
2. All alarms must be rectified and cleared
before starting tests.
3. Pre--trip may also be initiated via
communications. The operation is the
same as for the keypad initiation described
below except that should a test fail, the
pre--trip mode will automatically terminate.
When initiated via communications, a test
may not be interrupted with an arrow key,
but the pre--trip mode can be terminated
with the PRE--TRIP key.
a. Press the PRE--TRIP key. This accesses a test
selection menu.
b. TO RUN AN AUTOMATIC TEST : Scroll through the
selections by pressing the UP ARROW or DOWN
ARROW keys to display AUTO, AUTO 1, AUTO 2 or
AUTO 3 as desired, then press the ENTER key.
1. The unit will execute the series of tests without any
need for direct user interface. These tests vary in
length, depending on the component under test.
2. While tests are running, “P#--#” will appear on the left
display; the #’s indicate the test number and sub--test.
The right display will show a countdown time in
minutes and seconds, indicating the amount of time
remaining in the test.
CAUTION
When a failure occurs during automatic
testing, the unit will suspend operation
awaiting operator intervention.
When an automatic test fails, it will be repeated once.
A repeated test failure will cause “FAIL” to be shown
on the right display, with the corresponding test number to the left. The user may then press the DOWN
ARROW to repeat the test, the UP ARROW to skip to
the next test or the PRE--TRIP key to terminate testing. The unit will wait indefinitely or until the user
manually enters a command.
CAUTION
When Pre--Trip test Auto 2 runs to completion without being interrupted, the unit will
terminate pre--trip and display “Auto 2”
“end.” The unit will suspend operationuntil
the user depresses the ENTER key!
When an Auto 1 runs to completion without a failure,
the unit will exit the pre--trip mode and return to normal control operation. However, dehumidification and
bulb mode must be reactivated manually if required.
c. TO RUN AN INDIVIDUAL TEST: Scroll through the
selections by pressing the UP ARROW or DOWN
ARROW keys to display an individual test code.
Pressing ENTER when the desired test code is
displayed.
1. Individually selected tests, other than the
LED/Display test, will perform the operations
necessary to verify the operation of the component.
At the conclusion, PASS or FAIL will be displayed.
This message will remain displayed for up to three
minutes, during which time a user may select
another test. If the three minute time period expires,
the unit will terminate pre--trip and return to control
mode operation.
2. While the tests are being executed, the user may
terminate the pre--trip diagnostics by pressing and
holding the PRE--TRIP key. The unit will then resume
normal operation. If the user decides to terminate a
test but remain at the test selection menu, the user
may press the UP ARROW key. When this is done,
all test outputs will be de--energized and the test
selection menu will be displayed.
3. Throughout the duration of any pre--trip test (except
the P--7 high pressure switch tests), the current and
pressure limiting processes are active. The current
limiting process only is active for P--7.
d. Pre--Trip Test Results
At the end of the pre--trip test selection menu, the message “P,” “rSLts” (pre--trip results) will be displayed.
Pressing the ENTER key will allow the user to see the
results for all subtests (i.e., 1--0, 1--1, etc). The results
will be displayed as “PASS” or “FAIL” for all the tests run
to completion since power up. If a test has not been run
since power up, “-- -- -- -- -- ” will be displayed. Once all
pre--test activity is completed, dehumidification and
bulb mode must be reactivated manually if required.
4.10 OBSERVE UNIT OPERATION
4.10.1 Probe Diagnostic Logic
For units configured with four temperature probes,
which include the supply and return temperature probes
and the supply and return DataCORDER probes, the
controller continuously performs probe diagnosis testing that compares the four probes. If the diagnosis result
indicates a problem exists, the controller will perform a
probe check to identify which probe or probes are in error.
a. Probe Diagnostic Logic
In the perishable mode of operation, both pairs of supply
and return probes are monitored for probe
disagreement. Probe disagreement is considered a
difference of 0.5_C(0.9_F) or greater between the
supply air sensors and/or a difference of 2.0_C(3.6_F)
between the return air sensors. Probe disagreement
found in either pair can trigger a defrost probe check.
In the frozen mode of operation, only the controlling
probes are considered. Disagreement of the controlling
probes can trigger a defrost probe check, which will
occur when the difference between the sensors are
greater than 2.0_C(3.6_F). Normally, the controlling
probes are the return probes but if both return probes
are invalidated, the supply probes are used for control
purposes. Probe disagreement of the non--controlling
probe pair will not trigger a defrost probe check.
If the supply probes agree and return probes agree, all
supply and return sensors are valid and the unit returns
to normal control.
T-340 4--6
Page 66

If supply probes disagree and the return probes agree,
then invalidate the worst supply probe. If the probe
check is run as part of Pre--trip P--5, an alarm will be
triggered for the invalidated probe. If it is a run time defrost probe check, the invalidated probe will be passed
over and no alarm will be triggered. However , if the best
supply probe is greater than 1.2_C(2.2_F) difference
with respect to its return probes, the best supply probe is
also invalidated. If unit is in perishable operation, a
probe alarm will be triggered for both supply probes.
If the supply probes agree and return probes disagree,
invalidate the worst return probe. If the probe check is
being run as part of Pre--trip P--5, an alarm will be
triggered for the invalidated probe. If it is a run time defrost probe check, the invalidated probe will be passed
over and no alarm will be necessary. If the best return
probe is greater than 1.2_C(2.2_F) difference with re-
spect to its supply probes, then the best return probe is
also invalidated. If unit is in perishable operation, a
probe alarm will be triggered for both return probes.
b. Probe Check Procedure
A probe check diagnostic procedure is executed during
Pre--trip P--5. A defrost cycle probe check may be
accomplished at the end of defrost by energizing the
evaporator motors for eight minutes at the end of the
normal defrost. The defrost light will remain on during
this period. If supply probes are within limits and return
probes are within limits, the unit will return to normal
control.
4.11 EMERGENCY BYPASS OPERATION
To place the unit in the emergency bypass mode:
1. Locate the connection diagram and connectors for
the emergency bypass (EB) sensors behind the top
left side of the compressor.
2. Disconnect the emergency bypass connector from
the controller connector and attach it to the emergency bypass module connector. See Figure 4--3.
3. Locate the wire tire located at the EB switch in the
control box.
4. Cut the wire tie, then place the EB switch in the On
position.
5. Place the Mode Switch (MS) in the Full Cool position
to enable the system for cooling.
6. Manually control container air temperature by cycling the Mode switch between Full Cool and evaporator Fans Only.
To operate the fans only, the MODE switch must be in
the FANS ONLY position and the EMERGENCY
BYPASS switch must be in the Bypass position.
The EBS module uses the system’ssafety devices (high
pressure switch, motor internal protectors, and heat
termination thermostat) to protect the system while in
Emergency Bypass Mode.
CAUTION
The unit will remain in the full cooling mode
as long as the EB switch is in the On position and the Mode Switch is in the Full Cool
position. If the cargo can be damaged by
low temperatures, the operator must monitor container temperature and manually
cycle operation as required to maintain
temperature within required limits.
When the Emergency Bypass switch is in the Bypass
position, the EBS will be enabled. With the Mode switch
in Full Cool mode, the following will occur
simultaneously:
a. The EBS switch will enable EBS input.
b. The phase detection circuit will detect the phase
rotation and close to provide power to the compressor
contactor.
c. The condenser fan contact will close to energize the
condenser contactor and provide power to the condenser fan motor.
d. The evaporator fan contact will close to energize the
high speed evaporator contactor and provide power
to the evaporator fan motor.
e. The EBS electronic module will operate the EEV to
control superheat.
To return the unit to normal operation:
1. Locate the connectors behind the compressor.
2. Disconnect the Emergency Bypass connector from
the EBS module connector and reconnect it to the
controller connector. See Figure 4--3.
3. Inside the control box, place the EB switch in the Off
position.
4. Re-install the wire tie at the switch mounting.
EMERGENCY BYPASS
CONNECTOR
Figure 4--3 Diagram of Emergency Bypass
Connections
4--7
T-340
Page 67

SECTION 5
TROUBLESHOOTING
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
5.1 UNIT WILL NOT START OR STARTS THEN STOPS
External power source OFF Turn on
No power to unit
Loss of control power
Component(s) not operating
Compressor hums, but does not
start
Start--Stop switch OFF or defective Check
Circuit breaker tripped or OFF Check
Autotransformer not connected 4.2.2
Circuit breaker OFF or defective Check
Control transformer defective Replace
Fuse (F3A/F3B) blown Check
Start--Stop switch OFF or defective Check
Evaporator fan motor internal protector open 6.11
Condenser fan motor internal protector open 6.7
Compressor internal protector open 6.4
High pressure switch open 5.8
Heat termination thermostat open Replace
Malfunction of current sensor Replace
Low line voltage Check
Single phasing Check
Shorted or grounded motor windings 6.4
Compressor seized 6.4
REMEDY/
REFERENCE
SECTION
5.2 UNIT OPERA TES LONG OR CONTINUOUSLY IN COOLING
Container
Refrigeration system
Hot load Normal
Defective box insulation or air leak Repair
Shortage of refrigerant 6.3
Evaporator coil covered with ice 5.6
Evaporator coil plugged with debris 6.10
Evaporator fan(s) rotating backwards 6.10/6.11
Air bypass around evaporator coil Check
Controller set too low Reset
Compressor service valves or liquid line shutoff valve
partially closed
Dirty condenser 6.6
Compressor worn 6.4
Current limit (function code Cd32) set to wrong value 3.4.3
Economizer solenoid valve malfunction 6.18
Digital unloader valve stuck open Replace
Electronic expansion valve Replace
Open valves
completely
5--1
T-340
Page 68

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
5.3 UNIT RUNS BUT HAS INSUFFICIENT COOLING
Abnormal pressures 5.8
Abnormal temperatures 5.17
Abnormal currents 5.18
Controller malfunction 5.10
Refrigeration system
5.4 UNIT WILL NOT HEAT OR HAS INSUFFICIENT HEATING
No operation of any kind
No control power
Unit will not heat or has insufficient heat
Evaporator fan or motor defective 6.11
Compressor service valves or liquid line shutoff valve
partially closed
Frost on coil 5.11
Digital unloader valve stuck open Replace
Electronic expansion valve Replace
Start--Stop switch OFF or defective Check
Circuit breaker OFF or defective Check
External power source OFF Turn ON
Circuit breaker or fuse defective Replace
Control Transformer defective Replace
Evaporator fan internal motor protector open 6.11
Heat relay defective Check
Heater termination thermostat open 6.10
Heater(s) defective 6.10
Heater contactor or coil defective Replace
Evaporator fan motor(s) defective or rotating backwards 6.10/6.11
Evaporator fan motor contactor defective Replace
Controller malfunction 5.10
Defective wiring Replace
Loose terminal connections Tighten
Low line voltage 2.3
REMEDY/
REFERENCE
SECTION
Open valves
completely
5.5 UNIT WILL NOT TERMINATE HEATING
Controller improperly set Reset
Unit fails to stop heating
5.6 UNIT WILL NOT DEFROST PROPERLY
Will not initiate defrost
automatically
Will not initiate defrost
manually
Initiates but relay (DR) drops out Low line voltage 2.3
Controller malfunction 5.10
Heater termination thermostat remains closed along with
the heat relay
Defrost timer malfunction (Cd27) Table 3--5
Loose terminal connections Tighten
Defective wiring Replace
Defrost temperature sensor defective or heat termination
thermostat open
Heater contactor or coil defective Replace
Manual defrost switch defective Replace
Keypad is defective Replace
Defrost temperature sensor open Replace
5--2T-340
6.10
Replace
Page 69

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
5.7 UNIT WILL NOT DEFROST PROPERLY (Continued)
REMEDY/
REFERENCE
SECTION
Initiates but does not defrost
Frequent defrost Wet load Normal
5.8 ABNORMAL PRESSURES
High discharge pressure
Low suction pressure
Suction and discharge pressures tend to equalize when unit
is operating
Heater contactor or coil defective Replace
Heater(s) burned out 6.10
Condenser coil dirty 6.6
Condenser fan rotating backwards 6.7
Condenser fan inoperative 6.7
Refrigerant overcharge or noncondensibles 6.3
Discharge service valve partially closed Open
Electronic expansion valve (EEV) control malfunction Replace
Incorrect software and/or controller configuration Check
Failed suction pressure transducer (SPT) or evaporator
pressure transducer (EPT)
Suction service valve partially closed Open
Filter drier partially plugged 6.9
Low refrigerant charge 6.3
No evaporator air flow or restricted air flow 6.10
Excessive frost on evaporator coil 5.6
Evaporator fan(s) rotating backwards 6.11.3
EEV control malfunction Replace
Failed digital unloader valve (DUV) Replace
Compressor operating in reverse 5.16
Compressor cycling/stopped Check
Failed digital unloader valve (DUV) Replace
Replace
5.9 ABNORMAL NOISE OR VIBRATIONS
Compressor start up after an extended shutdown
Brief chattering when manually shut down
Compressor
Condenser or Evaporator Fan
5.10 MICROPROCESSOR MALFUNCTION
Will not control
Compressor operating in reverse 5.16
Loose mounting bolts or worn resilient mounts Tighten/Replace
Loose upper mounting 6.4.1
Liquid slugging 6.14
Bent, loose or striking venturi Check
Worn motor bearings 6.7/6.11
Bent motor shaft 6.7/6.1 1
Incorrect software and/or controller configuration Check
Defective sensor 6.22
Defective wiring Check
Low refrigerant charge 6.3
Normal
5--3
T-340
Page 70

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
5.11 NO EVAPORATOR AIR FLOW OR RESTRICTED AIR FLOW
REMEDY/
REFERENCE
SECTION
Evaporator coil blocked
No or partial evaporator air flow
5.12 EAUTOFRESH NOT OPERATING
Vent not opening
Gas Limit mode unavailable
Unable to calibrate CO2sensor
Code 44 displays “----------”
Frost on coil 5.6
Dirty coil 6.10
Evaporator fan motor internal protector open 6.11
Evaporator fan motor(s) defective 6.11
Evaporator fan(s) loose or defective 6.11
Evaporator fan contactor defective Replace
Unit not Configured for eAutoFresh Operation No action
Code 43 in Off mode 4.4.2
Wiring disconnected Check wiring
Stepper drive defective 6.13.2
Stepper motor defective 6.13.4
Unit operating in frozen mode 4.4.4
Check CO2sensor 4.4.4
Wiring disconnected Check wiring
Unit operating in frozen mode 4.4.4
“Enter“ Key not held for sufficient length of time 4.4.4
CO2outside of acceptable levels Check
Check CO2sensor 4.4.4
Unit not Configured for eAutoFresh Operation No action
Check CO2sensor 4.4.4
5.13 ELECTRONIC EXPANSION VALVE MALFUNCTION
Incorrect software and/or controller configuration Check
Failed suction pressure transducer (SPT) or evaporator
pressure transducer (EPT)
Suction service valve partially closed Open
Filter drier partially plugged 6.9
Low suction pressure
High suction pressure with low
superheat
Liquid slugging in compressor
Low refrigerant charge 6.3
No evaporator air flow or restricted air flow 6.10
Excessive frost on evaporator coil 5.6
Evaporator fan(s) rotating backwards 6.11.3
EEV control malfunction 6.14
Failed digital unloader valve (DUV) Replace
Loose or insufficiently clamped sensor Replace
Foreign material in valve 6.14
Failed suction pressure transducer (SPT) or evaporator
pressure transducer (EPT)
EEV control malfunction Replace
Improperly seated powerhead
Failed suction pressure transducer (SPT) or evaporator
pressure transducer (EPT)
Failed EEV Replace
Replace
Replace
Ensure powerhead is locked
and in place
Replace
5--4T-340
Page 71

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
5.14 AUTOTRANSFORMER MALFUNCTION
Circuit breaker (CB--1 or CB--2) tripped Check
Unit will not start
5.15 WATER--COOLED CONDENSER OR WATER PRESSURE SWITCH
Autotransformer defective 6.19
Power source not turned ON Check
460 VAC power plug is not inserted into the receptacle 4.2.2
REMEDY/
REFERENCE
SECTION
High discharge pressure
Condenser fan starts and stops
5.16 COMPRESSOR OPERATING IN REVERSE
The compressor may start in reverse for up to 10 seconds to determine correct phase rotation if
required for phase detection.
Allowing the scroll compressor to operate in reverse for more than two minutes will result in internal
compressor damage. Turn the start--stop switch OFF immediately.
Electrical
5.17 ABNORMAL TEMPERATURES
High discharge temperature
Dirty coil
Noncondensibles
Water pressure switch malfunction Check
Water supply interruption Check
NOTE
CAUTION
Incorrect wiring of compressor
Incorrect wiring of compressor contactor(s)
Incorrect wiring of current sensor
Condenser coil dirty 6.6
Condenser fan rotating backwards 6.7
Condenser fan inoperative 6.7
Refrigerant overcharge or noncondensibles 6.3
Discharge service valve partially closed Open
Electronic expansion valve (EEV) control malfunction Replace
Failed suction pressure transducer (SPT) or evaporator
pressure transducer (EPT)
Discharge temperature sensor drifting high Replace
Failed economizer expansion valve, economizer coil, or
economizer solenoid valve
Plugged economizer expansion valve, economizer coil, or
economizer solenoid valve
Loose or insufficiently clamped sensor Replace
6.8
Check
Replace
Replace
Replace
5.18 ABNORMAL CURRENTS
Unit reads abnormal currents Current sensor wiring Check
5--5
T-340
Page 72

SECTION 6
SERVICE
NOTE
Use a refrigerant recovery system whenever removing refrigerant. When working with refrigerants you must
comply with all local government environmental laws. In the U.S.A., refer to EPA section 608.
A R-134a manifold gauge/hose set with self-sealing ho-
DANGER
Never use air for leak testing. It has been determined that pressurized, mixtures of refrigerant and air can undergo combustion
when exposed to an ignition source.
6.1 SECTION LAYOUT
Service procedures are provided herein beginning with
refrigeration system service, then refrigeration system
component service, electrical system service, temperature recorder service and general service. Refer to the
Table of Contents to locate specific topics.
6.2 MANIFOLD GAUGE SET
The manifold gauge set (see Figure 6--1) is used to
determine system operating pressure, add refrigerant
charge, and to equalize or evacuate the system.
ses (see Figure 6--2) is required for service of the models covered within this manual. The manifold gauge/
hose set is available from Carrier Transicold. (Carrier
Transicold part number 07-00294-00, which includes
items 1 through 6, Figure 6--2.) T operform service using
the manifold gage/hose set, do the following:
Preparing Manifold Gauge/Hose Set For Use:
If the manifold gauge/hose set is new or was
exposed to the atmosphere, it will need to be evacuated to remove contaminants and air as follows:
1. Back seat (turn counterclockwise) both field service
couplings (see Figure 6--2) and midseat both hand
valves.
2. Connect the yellow hose to a vacuum pump and refrigerant 134a cylinder.
1
2
1
67
5
3
4
1. Opened (Backseated) Hand Valve
2. Suction Pressure Gauge
3. Discharge Pressure Gauge
4. Closed (Frontseated) Hand Valve
5. Connection to high side of system
6. Connection to either:
a. Refrigerant cylinder OR
b. Oil Container
7. Connection to low side of system
Figure 6--1 Manifold Gauge Set
When the suction pressure hand valve is frontseated
(turned all the way in), the suction (low) pressure can be
checked. When the discharge pressure hand valve is
frontseated, the discharge (high) pressure can be
checked. When both valves are open (all the way out),
high pressure vapor will flow into the low side. When the
suction pressure valve is open and the discharge pressure valve shut, the system can be charged. Oil can also
be added to the system.
To Low Side
Access Valve
7
3
To High Side
Access Valve
2
4
8
5
3
5
6
1. Manifold Gauge Set
2. RED Refrigeration and/or Evacuation Hose
(SAE J2196/R-134a)
3. Hose Fitting (0.5-16 Acme)
4. YELLOW Refrigeration and/or Evacuation Hose
(SAE J2196/R-134a)
5. Hose Fitting with O-ring (M14 x 1.5)
6. High Side Field Service Coupling (Red Knob)
7. BLUE Refrigeration and/or Evacuation Hose
(SAE J2196/R-134a)
8. Low Side Field Service Coupling (Blue Knob)
Figure 6--2 R-134a Manifold Gauge/Hose Set
3. Evacuate to 10 inches of vacuum and then charge
with R-134a to a slightly positive pressure of 0.1 kg/
2
cm
(1.0 psig).
4. Front seat both manifold gauge set valves and disconnect from cylinder. The gauge set is now ready
for use.
6--1
T-340
Page 73

6.3 REFRIGERATION SYSTEM SERVICE-UNITS
WITH STANDARD PIPING (with Service
Valves)
6.3.1 Service Connections
The compressor suction, compressor discharge, and
the liquid line service valves (see Figure 6--3) are provided with a double seat and an access valve which enables servicing of the compressor and refrigerant lines.
Turning the valve stem clockwise (all the way forward)
will frontseat the valve to close off the line connection
and open a path to the access valve. Turning the stem
counterclockwise (all the way out) will backseat the
valve to open the line connection and close off the path
to the access valve.
With the valve stem midway between frontseat and
backseat, both of the service valve connections are
open to the access valve path.
For example, the valve stem is first fully backseated
when connecting a manifold gauge to measure pressure. Then, the valve is opened 1/4 to 1/2 turn to measure the pressure.
b. Midseat both hand valves on the manifold gauge set
and allow the pressure in the manifold gauge set to be
drawn down to low side pressure. This returns any liquid that may be in the high side hose to the system.
c. Backseat the low side service valve. Backseat both
field service couplings and frontseat both manifold
hand valves. Remove the couplings from the access
valves.
d. Install both service valve stem caps and service port
caps (finger-tight only).
6.3.2 Pumping Down the Unit
To service the filter drier, economizer, expansion valves,
economizer solenoid valve, digital unloader valve or
evaporator coil, pump the refrigerant into the high side
as follows:
CAUTION
2
1
6
1. Line Connection
2. Access Valve
3. Stem Cap
4. Valve stem
To connect the manifold gauge/hose set for reading
pressures, do the following:
a. Remove service valve stem cap and check to make
sure it is backseated. Remove access valve cap.
(See Figure 6--3).
b. Connect the field service coupling (see Figure 6--2) to
the access valve.
c. Turn the field service coupling knob clockwise, which
will open the system to the gauge set.
d. To read system pressures, slightly midseat the ser-
vice valve.
e. Repeat the procedure to connect the other side of the
gauge set.
5
5. Compressor Or Filter
Drier Inlet Connection
6. Valve (Frontseated)
7. Valve (Backseated)
Figure 6--3 Service Valve
4
3
7
The scroll compressor achieves low suction pressure very quickly. Do not use the
compressor to evacuate the system below
0 psig. Never operate the compressor with
the suction or discharge service valves
closed (frontseated). Internal damage will
result from operating the compressor in a
deep vacuum.
a. Attach manifold gauge set to the compressor suction
and discharge service valves. Refer to paragraph 6.2.
b. Start the unit and run in the frozen mode (controller
set below -10_C(14_F)for10to15minutes.
c. Check function code Cd21 (refer to paragraph 3.2.2).
The economizer solenoid valve should be open. If
not, continue to run until the valve opens.
d. Frontseat the liquid line service valve. Place start-
stop switch in the OFF position when the suction
reaches a positive pressure of 0.1 bar (1.4 psig).
e. Frontseat the suction and discharge service valves.
The refrigerant will be trapped between the compressor discharge service valves and the liquid line valve.
f. Before opening up any part of the system, a slight
positive pressure shouldbe indicated on the pressure
gauge. Remove power from the unit before opening
any part of the system. If a vacuum is indicated, emit
refrigerant by cracking the liquid line valve momentarily to build up a slight positive pressure.
CAUTION
To prevent trapping liquid refrigerant in the
manifold gauge set besure set is brought to
suction pressure before disconnecting.
Removing the Manifold Gauge Set:
a. While the compressor is still ON, backseat the high
side service valve.
g. When opening up the refrigerant system, certain
parts may frost. Allow the part to warm to ambient
temperature before dismantling. This avoids internal
condensation which puts moisture in the system.
h. After repairs have been made, be sure to perform a
refrigerant leak check (refer to paragraph 6.3.3), and
evacuate and dehydrate the low side (refer to
paragraph 6.3.4).
i. Check refrigerant charge (refer to paragraph 6.3.5).
6--2T-340
Page 74

6.3.3 Refrigerant Leak Checking
DANGER
Never use air for leak testing. It has been determined that pressurized, mixtures of refrigerant and air can undergo combustion
when exposed to an ignition source.
1
2
3
4
5
a. The recommended procedure for finding leaks in a
system is with a R-134a electronic leak detector.
Testing joints with soapsuds is satisfactory only for
locating large leaks.
b. If the system is without refrigerant, charge the system
with refrigerant 134a to build up pressure between 2.1
to 3.5 bar (30.5 to 50.8 psig). To ensure complete
pressurization of the system, refrigerant should be
charged at the compressor suction valve and the liquid line service valve. Remove refrigerant cylinder
and leak-check all connections.
NOTE
Only refrigerant 134a should be used to pressurize the system. Any other gas or vapor will
contaminate the system, which will require
additional purging and evacuation of the system.
c. If required, remove refrigerant using a refrigerant
recovery system and repair any leaks. Check for
leaks.
d. Evacuate and dehydrate the unit. (Refer to paragraph
6.3.4.)
e. Charge unit per paragraph 6.3.5.
6.3.4 Evacuation and Dehydration
General
Moisture is detrimental to refrigeration syst ems. The
presence of moisture in a refrigeration system can have
many undesirable effects. The most common are copper plating, acid sludge formation, “freezing-up” of
metering devices by free water, and formation of acids,
resulting in metal corrosion.
Preparation
a. Evacuate and dehydrate only after pressure leak test.
b. Essential tools to properly evacuate and dehydrate
any system include a vacuum pump (8 m
3
/hr = 5 cfm
volume displacement) and an electronic vacuum
gauge. (The pump is available from Carrier Transicold, part number 07-00176-11.)
c. If possible, keep the ambient temperature above
15.6_C(60_F) to speed evaporation of moisture. If
the ambient temperature is lower than 15.6_C
(60_F), ice might form before moisture removal is
complete. Heat lamps or alternate sources of heat
may be used to raise the syst em temperature.
d. Additional time may be saved during a complete sys-
tem pump down by replacing the filter drier with asection of copper tubing and the appropriate fittings.
Installation of a new drier may be performed during
the charging procedure.
D
S
10
8
6
9
7
1. Liquid Service
Connection
2. Receiver or Water
Cooled Condenser
3. Compressor
4. Discharge Service
Connection
5. Suction Service
Connection
6. Vacuum Pump
7. Electronic Vacuum
Gauge
8. Manifold Gauge Set
9. Refrigerant Cylinder
10. Reclaimer
Figure 6--4 Refrigeration System Service
Connections
Procedure - Complete System
NOTE
Refer to Partial System procedure for information pertaining to partial system evacuation and
dehydration.
a. Remove all refrigerant using a refrigerant recovery
system.
b. The recommended method to evacuate and dehy-
drate the system is to connect evacuation hoses at
the compressor suction and liquid line service valve
(see Figure 6--4). Be sure the service hoses are
suited for evacuation purposes.
c. Test the evacuation setup for leaks by backseating
the unit service valves and drawing a deep vacuum
with the vacuum pump and gauge valves open. Shut
off the pump and check to see if the vacuum holds.
Repair leaks if necessary.
d. Midseat the refrigerant system service valves.
e. Open the vacuum pump and electronic vacuum
gauge valves, if they are not already open. Start the
vacuum pump. Evacuate unit until the electronic vac-
uum gauge indicates 2000 microns. Close the elec-
tronic vacuum gauge and vacuum pump valves. Shut
off the vacuum pump. Wait a few minutes to be sure
the vacuum holds.
f. Break the vacuum with clean dry refrigerant 134a gas.
Raise system pressure to roughly 0.14 bar (2 psig),
monitoring it with the compound gauge.
g. Remove refrigerant using a refrigerant recovery sys-
tem.
6--3
T-340
Page 75

h. Repeat steps e. and f. one time.
i. Remove the copper tubing and change the filter drier.
Evacuate unit to 500 microns. Close the electronic
vacuum gauge and vacuum pump valves. Shut off the
vacuum pump. Wait five minutes to see if vacuum
holds. This procedure checks for residual moisture
and/or leaks.
j. With a vacuum still in the unit, the refrigerant charge
may be drawn into the system from a refrigerant container on weight scales.
Procedure - Partial System
a. If refrigerant charge has been removed from the low
side only, evacuate the low side by connecting the
evacuation set-up at the compressor suction valve
and the liquid service valve but leave the service
valves frontseated until evacuation is completed.
b. Once evacuation has been completed and the pump
has been isolated, fully backseat the service valves to
isolate the service connections and then continue
with checking and, if required, adding refrigerant in
accordance with normal procedures.
6.3.5 Refrigerant Charge
Checking the Refrigerant Charge
NOTE
Use a refrigerant recovery system whenever
removing refrigerant. When working with refrigerants you must comply with all local government environmental laws. In the U.S.A., refer to
EPA Section 608.
NOTE
It may be necessary to finish charging unit
through suction service valve in gas form, due
to pressure rise in high side of the system.
d. Backseat manual liquid line valve (to close off gauge
port). Close liquid valve on cylinder.
e. Start unit in cooling mode. Run for approximately 10
minutes and check the refrigerant charge.
Adding Refrigerant to System (Partial Charge)
a. Examine the unit refrigerant system for any evidence
of leaks. Repair as necessary. (Refer to paragraph
6.3.3.).
b. Maintain the conditions outlined in paragraph 6.3.5.
c. Fully backseat the suction service valve and remove
the service port cap.
d. Connect charging line between suction service valve
port and cylinder of refrigerant R-134a. Open VAPOR
valve.
e. Partially frontseat (turn clockwise) the suction service
valve and slowly add charge until the refrigerant
appears at the proper level. Be careful not to frontseat
the suction valve fully, if the compressor is operated in
a vacuum, internal damage may result.
6.4 COMPRESSOR
a. Connect the gauge manifold to the compressor dis-
charge and suction service valves. For units operating on a water cooled condenser, change over to air
cooled operation.
b. Bring the container temperature to approximately
0_C(32_F) or below. Then set the controller set point
to -25_C (-13_F).
c. Partially block the condenser coil inlet air. Increase the
area blocked until the compressor discharge pressure
is raised to approximately 12.8 bar (185 psig).
d. On units equipped with a receiver, the level should be
between the glasses. On units equipped with a watercooled condenser, the level should be at the center of
the glass. If the refrigerant level is not correct, continue with the following paragraphs to add or remove refrigerant as required.
Adding Refrigerant to System (Full Charge)
a. Evacuate unit and leave in deep vacuum. (Refer to
paragraph 6.3.4.)
b. Place cylinder of R-134a on scale and connect charg-
ing line from cylinder to liquid line valve. Purge charging line at liquid line valve and then note weight of cylinder and refrigerant.
c. Open liquid valve on cylinder. Open liquid line valve
half-way and allow the liquid refrigerant to flow into
the unit until the correct weight of refrigerant (refer to
paragraph 2.2) has been added as indicated by
scales.
WARNING
Make sure power to the unit is OFF and
power plug disconnected before replacing
the compressor.
WARNING
Before disassembly of the compressor, be
sure to relieve the internal pressure very
carefully by slightly loosening the couplings to break the seal.
CAUTION
The scroll compressor achieves low suction pressure very quickly. Do not use the
compressor to evacuate the system below
0 psig. Never operate the compressor with
the suction or discharge service valves
closed (frontseated). Internal damage will
result from operating the compressor in a
deep vacuum.
6--4T-340
Page 76

6.4.1 Removal and Replacement of Compressor
a. Turn the unit ON and run it in full cool mode for 10
minutes.
NOTE
If the compressor is not operational, front--seat
the suction and discharge service valves and
go to step f. below.
p. Torque the four base--mounting screws to 6.2 mkg
(45 ft--lbs).
3
4
2
1
5
b. Frontseat the manual liquid line valve and allow the
unit to pull--down to 0.1 kg/cm
2
(1 psig).
c. Turn the unit start--stop switch (ST) and unit circuit
breaker (CB--1) OFF, and disconnect power to the
unit.
d. Frontseat the discharge and suction service valves.
e. Remove all remaining refrigerant from the com-
pressor using a refrigerant recovery system.
f. Remove the compressor terminal cover, disconnect
the ground wire and pull the cable plug from the compressor terminals. Install the terminal cover back
after removing the power cable.
NOTE
Inspect the power cable (plug) terminals to ensure they are not deformed or have any signs of
heat or arcing. If any damage is noted, replace
the power cable.
g. Remove the Rotalock fittings from the suction and
discharge service connections, and uncouple the
unloader and economizer lines from the compressor.
h. Cut the dome temperature sensor wires. The re-
placement compressor comes with a dome temperature sensor already assembled.
i. Remove and save the compressor base mounting
bolts. Discard the 4 top resilient mounts and washers.
j. Remove (slide out) the old compressor from the unit.
k. Inspect compressor base plate for wear. Replace, if
necessary.
l. Wire tie the compressor base plate to the com-
pressor, and slide the new compressor into the unit.
Refer to Figure 6--5.
NOTE
DO NOT add any oil to the replacement compressor. Replacement compressor is shipped
with full oil charge of 60 oz.
m. Cut and discard the wire ties used to hold the base
plate to the compressor.
n. Place the new SST washers on each side of the resi-
lient mounts, and the new Mylar washer on the bottom of it as shown in Figure 6--5. Install the four base
mounting bolts loosely.
o. Place the new Teflon seals at the compressor suc-
tion and discharge ports as well as the O--rings at the
unloader and economizer line connection ports.
Hand tighten all four connections.
11
2
12
6
7
8
7
9
10
1. Compressor
2. Teflon Seal for Valve
Connection (2)
3. O--Ring (Unloader
Connection)
4. Compressor Dis-charge Temperature
Sensor
5. O--Ring (Economizer
Connection)
7. SST Washers
8. Resilient Mount
9. Mylar Washers
10. Wire Ties
1 1. Power Cable Gasket
12. Ground Connection
Screw
13. Power Cable
Lubricant -- Krytox
(Not Shown)
6. Base Mounting Bolts
Figure 6--5 Compressor Kit
q. Torque the compressor ports / connections to:
Service Valve / Connection
Suction and Discharge
Rotalocks
Torque Value
108.5 to 135.5 Nm
(80to100ft--lbs.)
Unloader connection 24.5to27Nm
(18to20ft--lbs.)
Economized connection 32.5to35Nm
(24to26ft--lbs.)
r. Connect (butt--splice and heat shrink) the new com-
pressor dome temperature sensor with the old
sensor wires removed in step h. Wire--tie any loose
wiring as appropriate.
s. Evacuate the compressor to 1000 microns if the unit
was pumped down before the replaced compressor
was removed. Otherwise, evacuate the complete
unit and charge it with R--134a refrigerant (see Sections 6.3.4 and 6.3.5).
t. Open the compressor terminal cover and connect
the compressor power cable following the steps below:
u. Liberally coat the orange gasket surfaces with the
Krytox lubricant.
v. Install the orange gasket part onto the compressor
fusite with the grooved or threaded side out. Ensure
that the gasket is seated onto the fusite base.
6--5
T-340
Page 77

w. Coat the inside of the power plug (female) connector
pins with the Krytox lubricant, and insert the plug
onto the compressor terminal connections. Make
sure, the orange gasket has bottomed out onto the
fusite and it fits securely onto the terminal pins while
fully inserted into the orange plug.
x. Connect the green ground wire to the grounding tab
located inside the terminal box of the compressor using the self--tapping grounding screw. Close the
compressor terminal box using the terminal cover removed in step 20 above.
y. Backseat all service valves, connect the power to the
unit and run it for at least 20 minutes.
z. Perform a leak check of the system.
6.5 HIGH PRESSURE SWITCH
6.5.1 Checking High Pressure Switch
f. Open cylinder valve. Slowly close bleed-off valve to
increase pressure on switch. The switch should open
at a static pressure up to 25 kg/cm
light is used, light will go out. If an ohmmeter is used,
the meter will indicate open circuit.
g. Slowly open bleed-off valve to decrease the pressure.
The switch should close at 18 kg/cm
6.5.2 Replacing High Pressure Switch
a. Remove the refrigerant charge.
b. Disconnect wiring from defective switch. The high
pressure switch is located on the discharge connection or line and is removed by turning counterclockwise.
c. Install a new high pressure switch after verifying
switch settings.
d. Evacuate, dehydrate and recharge system.
e. Start unit, verify refrigeration charge and oil level.
2
(350 psig). If a
2
(250 psig).
WARNING
Do not use a nitrogen cylinder without a
pressure regulator. Do not use oxygen in or
near a refrigeration system as an explosion
may occur.
NOTE
The high pressure switch is non-adjustable.
a. Remove switch as outlined in paragraph 6.5.2.
b. Connect ohmmeter or continuity light across switch
terminals. Ohm meter will indicate no resistance or
continuity light will be illuminated if the switch closed
after relieving compressor pressure.
c. Connect hose to a cylinder of dry nitrogen. (See
Figure 6--6.
1
2
4
5
6.6 CONDENSER COIL
The condenser consists of a series of parallel copper
tubes expanded into copper fins. The condenser coil
must be cleaned with fresh water or steam so the air flow
is not restricted. To replace the coil, do the following:
WARNING
Do not open the condenser fan grille before
turning power OFF and disconnecting
power plug.
a. Using a refrigerant reclaim system, remove the refrig-
erant charge.
b. Remove the condenser coil guard.
c. Unsolder discharge line and remove the line to the
receiver or water-cooled condenser.
d. Remove coil mounting hardware andremove the coil.
e. Install replacement coil and solder connections.
f. Leak-check the coil connections per paragraph 6.3.3.
Evacuate the unit then charge the unit with refrigerant.
6.7 CONDENSER FAN AND MOTOR ASSEMBLY
3
1. Cylinder Valve
and Gauge
2. Pressure Regulator
3. Nitrogen Cylinder
Figure 6--6 High Pressure Switch Testing
d. Set nitrogen pressure regulator at 26.4 kg/cm
psig) with bleed-off valve closed.
e. Close valve on cylinder and open bleed-off valve.
6
4. Pressure Gauge
(0 to 36 kg/cm
0 to 400 psig)
5. Bleed-Off Valve
6. 1/4 inch Connection
2
=
2
(375
WARNING
Do not open condenser fan grille before
turning power OFF and disconnecting
power plug.
The condenser fan rotates counter-clockwise (viewed
from front of unit), pulls air through the condenser coil,
and discharges horizontally through the front of the unit.
To replace motor assembly:
a. Open condenser fan screen guard.
b. Loosen two square head set screws on fan. (Thread
sealer has been applied to set screws at installation.)
c. Disconnect wiring connector.
6--6T-340
Page 78

CAUTION
Take necessary steps (place plywood over
coil or use sling on motor) to prevent motor
from falling into condenser coil.
2. Oakite Composition No. 32, available as a liquid in
cases, each containing 3.785 liters (4 U.S. gallon)
bottles and also in carboys of 52.6 kg (1 16 lbs) net.
3. Fresh clean water.
4. Acid proof pump and containers or bottles with rubber
hose.
d. Remove motor mounting hardware and replace the
motor. It is recommended that new locknuts be used
when replacing motor.
e. Connect the wiring connector.
f. Install fan loosely on motor shaft (hub side in). DO
NOT USE FORCE. If necessary, tap the hub only, not
the hub nuts or bolts. Install venturi. Apply “Loctite H”
to fan set screws. Adjust fan within venturi so that the
outer edge of the fan is within 2.0 +/- 0.07 mm (0.08”
+/- 0.03”) from the outside of the orifice opening. Spin
fan by hand to check clearance.
g. Close and secure condenser fan screen guard.
6.8 W ATER--COOLED CONDENSER CLEANING
The water-cooled condenser is of the shell and coil type
with water circulating through the cupro-nickel coil. The
refrigerant vapor is admitted to the shell side and is condensed on the outer surface of the coil.
Rust, scale and slime on the water-cooling surfaces
inside of the coil interfere with the transfer of heat,
reduce system capacity, cause higher head pressures
and increase the load on the system.
By checking the leaving water temperature and the
actual condensing temperature, it can be determined if
the condenser coil is becoming dirty. A larger than normal difference between leaving condensing water temperature and actual condensing temperature, coupled
with a small difference in temperature of entering and
leaving condensing water , is an indication of a dirty condensing coil.
To find the approximate condensing temperature, with
the unit running in the cooling mode, install a gauge 0 to
36.2 kg/cm
charge service valve.
Example: Discharge pressure is 10.3 kg/cm2(146.4
psig). Referring to Table 6--5 (R-134a pressure/ temperature chart), the 10.3 kg/cm
verts to 43_C(110_F).
If the water-cooled condenser is dirty, it may be cleaned
and de-scaled by the following procedure:
a. Turn unit off and disconnect main power .
b. Disconnect water pressure switch tubing by loosen-
ing the two flare nuts. Install one-quarter inch flare
cap on water-cooled condenser inlet tube (replaces
tubing flare nut). De-scale tubing if necessary.
What You Will Need:
1. Oakite Aluminum Cleaner® 164, available as a powder in 20 kg (44 lb) pails and 205 kg (450 lb) drums.
2
(0 to 500 psig) on the compressor dis-
2
(146.4 psig) value con-
NOTE
When Oakite Compound No. 32 is used for the
first time, the local Oakite Technical Service
representative should be called in for
suggestions in planning the procedure. The
representative will advise the reader on how to
do the work with a minimum dismantling of
equipment: how to estimate the time and
amount of compound required; how to prepare
the solution; how to control and conclude the
de-scaling operation by rinsing and neutralizing
equipment before putting it back into service.
The representative’s knowledge of metals,
types of scale, water conditions and de-scaling
techniques will be highly useful.
Summary of Procedure:
1. Drain water from condenser tubing circuit.
2. Clean water tubes with Oakite Aluminum Cleaner®
164 to remove mud and slime.
3. Flush.
4. De-scale water tubes with Oakite No. 32 to remove
scale.
5. Flush.
6. Neutralize.
7. Flush.
8. Put unit back in service under normal load and check
head (discharge) pressure.
Detailed Procedure:
1. Drain and flush the water circuit of the condenser
coil. If scale on the tube inner surfaces is accompanied by slime, a thorough cleaning is necessary
before de-scaling process can be accomplished.
2. To remove slime or mud, use Aluminum Cleaner®
164. Mixed 170 grams (6 ounces) per 3.785 liters (1
U.S. gallon) of water. Mix cleaner in one half the
volume of water , while stirring, and then add remaining water. Warm this solution and circulate through
the tubes until all slime and mud has been removed.
3. After cleaning, flush tubes thoroughly with fresh
clean water.
4. Prepare a 15% by volume solution for de-scaling, by
diluting Oakite Compound No. 32 with water. This is
accomplished by slowly adding 0.47 liter (1 U.S. pint)
of the acid (Oakite No. 32) to 2.8 liters (3 U.S. quarts)
of water.
6--7
T-340
Page 79

WARNING
Oakite No. 32 is an acid. Be sure that the
acid is slowly added to the water. DO NOT
PUT WATER INTO THE ACID - thiswill cause
spattering and excessive heat.
WARNING
1
5
2
Wear rubber gloves and wash the solution
from the skin immediately if accidental contact occurs. Do not allow the solution to
splash onto concrete.
5. Fill the tubes with this solution by filling from the bottom. See Figure 6--7.
7
6
4
3
2
1
1. Pump support
2. Tank
3. Suction
4. Pump
5. Priming Connection
(Centrifugal pump
50 gpm at 35’ head)
6. Globe valves
Figure 6--7 Water-Cooled Condenser Cleaning -
5
11
12
7. Vent
8. Close vent pipe valve
when pump is running
9. Condenser
10. Remove water
regulating valve
1 1. Return
12. Fine mesh screen
Forced Circulation
8
9
10
4
3’ to 4’
3
1.Fill condenser with
cleaning solution. Do
not add solution more
rapidly than vent can
exhaust gases caused
by chemical action.
Figure 6--8 Water-Cooled Condenser Cleaning -
Gravity Circulation
7. The time required for de-scaling will vary, depending
upon the extent of the deposits. One way to determine when de-scaling has been completed is to
titrate the solution periodically , using titrating equipment provided free by the Oakite Technical Service
representative. As scale is being dissolved, titrate
readings will indicate that the Oakite No. 32 solution
is losing strength. When the reading remains
constant for a reasonable time, this is an indication
that scale has been dissolved.
8. When de-scaling is complete, drain the solution and
flush thoroughly with water.
If condenser cooling water is not being used as
drinking water or is not re-circulated in a closed or
tower system, neutralizing is not necessary.
2. Approximately 5’
3. Condenser
4. Vent pipe
5. 1” pipe
NOTE
NOTE
It is important to provide a vent at the top for
escaping gas.
6. Allow the Oakite No. 32 solution to soak in the tube
coils for several hours, periodically pump-circulating
it with an acid-proof pump.
An alternate method may be used whereby a pail
(see Figure 6--8) filled with the solution and attached
to the coils by a hose can serve the same purpose by
filling and draining. The solution must contact the
scale at every point for thorough de-scaling. Air
pockets in the solution should be avoided by regularly opening the vent to release gas. Keep flames
away from the vent gases.
9. Following the water flush, circulate a 56.7 gram (2
ounce) per 3.785 liter (1 U.S. gallon) solution of
Oakite Aluminum Cleaner® 164 thru the tubes to
neutralize. Drain this solution.
10.Flush the tubes thoroughly with fresh water.
1 1.Put the unit back in service and operate under nor-
mal load. Check the head pressure. If normal, a thorough de-scaling has been achieved.
What You Can Do For Further Help:
Contact the Engineering and Service Department of the
OAKITE PRODUCTS CO., 675 Central Avenue, New
Providence, NJ 07974 U.S.A. (or visit www.oakite.com)
for the name and address of the service representative
in your area.
6--8T-340
Page 80

6.9 FILTER DRIER
On units equipped with a water-cooled condenser, if the
sight glass appears to be flashing or bubbles are
constantly moving through the sight glass, the unit may
have a low refrigerant charge or the filter drier could be
partially plugged.
a. To check filter drier,
1. Test for a restricted or plugged filter drier by feeling
the liquid line inlet and outlet connections of the drier
cartridge. If the outlet side feels cooler than the inlet
side, then the filter drier should be changed.
2. Check the moisture-liquid indicator if the indicator
shows a high level of moisture, the filter drier should
be replaced.
b. To replace filter drier,
1. Pump down the unit (refer to paragraph 6.3.2). Evacuate if unit is not equipped with service valves. Then
replace filter drier.
2. Evacuate the low side in accordance with paragraph
6.3.4.
3. After unit is in operation, inspect for moisture in system and check charge.
6.10 EVAPORATOR COIL AND HEATER
ASSEMBLY
The evaporator section, including the coil, should be
cleaned regularly. The preferred cleaning fluid is fresh
water or steam. Another recommended cleaner is
Oakite 202 or similar, following manufacturer’s instruc-
tions.
The two drain pan hoses are routed behind the condenser fan motor and compressor. The drain pan line(s)
must be open to ensure adequate drainage.
6.10.1 Evaporator Coil Replacement
a. Pump unit down. (Refer to paragraph 6.3.2.) Evacua-
te if unit is not equipped with service valves. Refer to
paragraph 6.3.4.
b. With power OFF and power plug removed, remove
the screws securing the panel covering the evaporator section (upper panel).
c. Disconnect the defrost heater wiring.
d. Remove the mounting hardware from the coil.
e. Unsolder the two coil connections, one at the distribu-
tor and the other at the coil header.
f. Disconnect the defrost temperature sensor (see
Figure 2--2) from the coil.
g. Remove middle coil support.
h. After defective coil is removed from unit, remove
defrost heaters and install on replacement coil.
i. Install coil assembly by reversing above steps.
j. Leak check connections. Evacuate and add refriger-
ant charge.
6.10.2 Evaporator Heater Removal and
Replacement
The heaters are wired directly back to the contactor and
if a heater failure occurs during a trip, the heater set
containing that heater may be disconnected at the
contactor.
The next pre-trip will detect that a heater set has been
disconnected and indicate that the failed heater should
be replaced. To remove a heater, do the following:
a. Before servicing unit, make sure the unit circuit break-
ers (CB-1 and CB-2) and the start-stop switch (ST)
are in the OFF position, and that the power plug is disconnected.
b. Remove the upper back panel.
c. Determine which heater(s) need replacing by check-
ing resistance of each heater set. Refer to paragraph
2.3 for heater resistance values. Once the set containing the failed heater is determined, cut the splice
connection and retest to determine the actual failed
heater(s).
d. Remove hold-down clamp securing heater(s) to coil.
e. Lift the bent end of the heater (with the opposite end
down and away from coil). Move heater to the side
enough to clear the heater end support and remove.
To replace a heater, do steps a through e in reverse.
Optional 5+1 Heater Arrangement Heater Removal
and Replacement
Complete steps a. through e. noted above, then remove straight and Omega heaters:
f. To remove straight heater,
1. Locate holding clips positioned at the ends of the
heater element.
2. Rotate clips toward the center of the container unit.
3. Lift heater slightly up and out to remove.
g. To remove Omega heater (see Figure 6--9)
1. Remove the two tube clamps located near the top of
the heater element.
2. Locate holding clips positioned at the bottom of the
heater element and rotate slightly toward the center
of the container unit.
3. Carefully pull heater out to remove.
1
2
3
1. Omega Heater
2. Tube Clamps (2)
3. Holding Clips (2)
Figure 6--9 5+1 Heater Arrangement -- Omega
Heater
6--9
T-340
Page 81

6.11 EVAPORATOR FAN AND MOTOR ASSEMBLY
The evaporator fans circulate air throughout the container by pulling air in the top of the unit. The air isforced
through the evaporator coil where it is either heated or
cooled and then discharged out the bottom of the refrigeration unit into the container. The fan motor bearings
are factory lubricated and do not require additional
grease.
6.11.1 Replacing the Evaporator Fan Assembly
WARNING
b. Apply Loctite to the 1/4-20 x 3/4 long bolts and torque
to 0.81 mkg (70 inch-pounds).
c. Place one 5/8 flat washer on the shoulder of the fan
motor shaft. Insert the key in the keyway and lubricate
the fan motor shaft and threads with a graphite-oil
solution (such as Never-seez).
d. Install the fan onto the motor shaft. Place one 5/8 flat
washer with a 5/8-18 locknut onto the motor shaft and
torque to 40 foot-pounds.
Always turn OFF the unit circuit breakers
(CB-1 and CB-2) and disconnect main
power supply before working on moving
parts.
a. Remove upper access panel (see Figure 2--2) by
removing mounting bolts and TIR locking device.
Reach inside of unit and remove the Ty-Rap securing
the wire harness loop. Disconnect the connector by
twisting to unlock and pulling to separate.
b. Loosen four 1/4-20 clamp bolts that are located on the
underside of the fan deck at the sides of the fan
assembly. Slide the loosened clamps back from the
fan assembly.
c. Slide the fan assembly out from the unit and place on
asturdyworksurface.
6.11.2 Disassemble the Evaporator Fan Assembly
a. Attach a spanner wrench to the two 1/4-20 holes
located in the fan hub. Loosen the 5/8-18 shaft nut by
holding the spanner wrench stationary and turning
the 5/8-18 nut counter-clockwise (see Figure 6--10).
b. Remove the spanner wrench. Use a universal wheel
puller and remove the fan from the shaft. Remove the
washers and key.
c. Remove the four 1/4-20 x 3/4 long bolts that are
located under the fan that support the motor and stator housing. Remove the motor and plastic spacer.
6.11.3 Assemble the Evaporator Fan Assembly
a. Assemble the motor and plastic spacer onto the stator.
NOTE
When removing the black nylon evaporator fan
blade, care must be taken to assure that the
blade is not damaged. In the past, it was a common practice to insert a screwdriver between
the fan blades to keep it from turning. This practice can no longer be used, as the blade is made
up of a material that will be damaged. It is recommended that an impact wrench be used
when removing the blade. Do not use the impact wrench when reinstalling, as galling of the
stainless steel shaft can occur.
3
2
1
7
8
1. Stator
2. Flat washer, 5/8
3. Locknut, 5/8-18
4. Impeller Fan
Figure 6--10 Evaporator Fan Assembly
e. Install the evaporator fan assembly in reverse order
of removal. Torque the four 1/4-20 clamp bolts to
0.81 mkg (70 inch-pounds). Connect the wiring connector.
f. Replace access panel making sure that panel does
not leak. Make sure that the TIR locking device is
lockwired.
5. Screw, 1/4
6. Flat washer, 1/4
7. Mylar Protector
8. Evaporator Motor
2
4
5
6
6--10T-340
Page 82

6.12 EVAPORATOR SECTION CLEANING
Cleaning Procedure:
Containers and Container units that are exposed to
certain fumigants may develop visible surface
corrosion. This corrosion will show up as a white powder
found on the inside of the container and on the reefer
unit evaporator stator and fan deck.
Analyses by Carrier Transicold environmental
specialists have identified the white powder as
consisting predominantly of aluminum oxide. Aluminum
oxide is a coarse crystalline deposit most likely the result
of surface corrosion on the aluminum parts within the
container. If left untreated over time, it may build up in
thickness and eventually flake as a light--weight white
powder.
The surface corrosion of aluminum is brought about by
exposure to chemicals such as sulfur dioxide and
possibly other fumigants that are commonly used for
fumigation and protection of some perishable cargo
such as grapes, for example. Fumigation is the process
by which a chemical is released into an enclosed area to
eliminate infestations of insects, termites, rodents,
weeds and soil--born disease.
Typically any aluminum oxide that becomes detached
from evaporator fan stators will be blown into the wet
evaporator coil where it will be caught and then flushed
out of the unit during routine defrost cycles.
However, it is still highly recommended that after
carrying cargo subject to fumigation procedures, that
the inside of the unit be thoroughly cleansed prior to
reuse.
Carrier Transicold has identified a fully biodegradable
and environmentally safe alkaline cleaning agent
(Tri--Pow’r® HD) for the unit. This will assist in helping to
remove the corrosive fumigation chemicals and
dislodging of the corrosive elements.
a. Remove the upper evaporator access panel inside of
the unit.
b. Spray the surface with water before applying the
cleaning solution. This helps the cleaner work better.
c. Liberally apply the prepared cleaner solution (5 parts
water and 1 part cleaner).
d. Allow the cleaner to soak in for 5 to 7 minutes.
e. Assess area for rinsing. Follow all local regulations re-
garding disposal of waste water.
f. Thoroughly rinse the cleaner and surrounding area,
floor, etc. When rinsing where heavy foaming solution
is present, it is very important to take the time to thoroughly rinse the equipment and surroundings.
g. Always rinse the empty coil cleaner bottle, cap tightly
and dispose of properly .
6.13 eAutoFresh SERVICE
6.13.1 Servicing the eAutoFresh Air Filter
Removing the Air Sample Filter Element
When replacing the air sample filter element it can be
accessed in two ways: through the eAutoFresh side
evaporator access panel (item 11, Figure 2--2) or
through the inside of the container by lowering the upper
evaporator panel.
a. By hand, unscrew and remove the filter cup from the
bottom of the air sample filter assembly.
b. Remove the filter element from the filter assembly.
This cleaner is available from the Carrier Transicold
Performance Parts Group (PPG) and can be ordered
through any of the PPG locations; Part Number
NU4371--88.
As a general safety precaution, before using this
product, refer to and retain the Material Safety Data
(MSDS) sheet. This document can be found at:
www.nucalgon.com/products/coil_cleaners_tripower.htm
Prior to Cleaning:
-- Always wear goggles, gloves and work boots.
-- Avoid contact with skin and clothing, and avoid
breathing mists.
-- When mixing, add water to the sprayer first, then the
cleaner.
-- ALW AYS provide for proper ventilation when cleaning
indoor evaporator coils (rear doors must be open).
-- Be aware of surroundings -- food, plants, etc., and the
potential for human exposure.
-- Always read directions and follow recommended
dilution ratios. More is not always better. Using
non--diluted cleaner is not recommended.
c. Install the air sample filter element by reversing the
above steps.
6.13.2 Checking eAutoFresh Drive System
Checking the Auto Slide
a. Checking with ohmmeter, disconnect the four pin con-
nector to the stepper motor. With a reliable digital
ohmmeter, check the winding resistance. In normal
ambient, the motor should have 72 to 84 ohms measured on the red/green (a--b terminals) and on the
white/black (c--d terminals) leads. If an infinite or zero
reading occurs, check connections or replace the motor. If near normal or normal reading occurs, proceed
to Section 6.13.3 to check out the controller.
b. Checking with SMA--12 portable stepper drive tester
The SMA--12 portable stepper drive tester (Carrier
Transicold P/N 07--00375--00) is a battery operated
stepper drive which will open and close the auto slide,
which allows a more thorough check of the motor.
To check operation:
1. Stop the unit, disconnect the four pin connector from
the stepper drive to the stepper motor (see
Figure 6--11) and attach the SMA--12 stepper drive to
the connector going to the motor.
6--11
T-340
Page 83

1
2
1. Stepper Drive (SD)
2. Stepper Motor (AF)
Figure 6--11 Stepper Components
2. Set the SMA--12 pulse per second (PPS) to one PPS
and either open or close valve. Each LED should light
sequentially until all four are lit. Any LED failing to light
indicates an open on that leg which indicates a poor
connection or an open coil. Repair or replace as required to achieve proper operation.
3. Set the step rate to 200 PPS on the SMA--12. Press
open or close while watching slide mechanism for
movement, this is an indication that the motor is working.
4. If the slide moves in the above procedure but fails to
move when connected in the unit (refer to “Checking
the Drive Module” in the section that follows.)
Checking the Drive Module
a. Turn unit OFF.
b. Disconnect the four pin connector to the motor.
c. With voltmeterset to read 24volts AC, attach the pos-
itive lead to the drive module outlet pin A (wire 1A) of
the four pin connector and the negative lead to the B
pin(wire1B).
d. Turn ON unit, and watch the volt meter. After a short
delay, the reading should rise to approximately 12
volts.
e. Repeat for pins C and D (wires 2 A and 2 B).
f. If only one set of pins reads a voltage, check connec-
tions and retest.
g. If the retest reads out the same, the drive module or
controller is faulty.
h. If no voltage is present in any step, the output from the
controller to the drive module may be faulty, and will
require checking the connections and wires from the
controller to the drive module. Refer to section 6.13.3
i. To replace the drive module, disconnect all connect-
ors, unscrew from mounting, and replace with a NEW
drive module in reverse order.
6.13.3 Checking the Controller
a. Turn the unit OFF.
b. Disconnect the six pin connector to the stepper drive
from the controller.
c. With the voltmeter set to read 50 volts DC, attach the
positive lead to outlet pin A of the six pin connector,
and the negative lead to pin B or TP--9 of the controller.
d. Turn ON the unit for 40 seconds, and watch the volt-
meter. There should be approximately 24 to 32 VDC
shownonpinA.
e. There should be zero volts on pin B.
f. After a short delay, the reading should rise to approx-
imately 24 to 32 VDC on pin E.
g. Pins C and D will have zero to 5 volts transistor logic
(TTL) signals present, however, this can only be
checked with the connector assembled as this is an
open collector type circuit.
By checking the outputs on A, B and E it can be verified
that the controller is supplying power to the drive
module. To be thorough, and if it is desired, the signals
on pins C and D can be checked as follows:
1. Install a jumper assembly (Carrier part number
07--00408--00) to connect the drive module and con-
troller connectors as shown in Figure 6--12.
2. Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to test con-
nector socket C and negative lead to socket B, and
run as before by resetting unit.
3. Repeat for sockets D and B.
Controller
Connector (EC)
Drive Module
Connector (SD)
A
B
C
D
E
Test
Connector
Jumper
A
B
C
D
E
Figure 6--12 Jumper Assembly
There should be approximately five volts DC on sockets
“C” and “D” (S1 and S2) when measured as above. If not
the connections or controller is faulty. If any of these pins
are not consistent, the connections or controller is
suspect. Check and replace as required.
6.13.4 Servicing the eAutoFresh Drive System
To replace the drive motor assembly, do the following:
a. Remove bolts holding eAutoFresh Panel (3,
Figure 6--13) to the front of the unit. Reach in and cut
tie wrap (2) and disconnect motor connector (1).
Bring panel to work area.
b. Remove four screws (12) fastening the grille (11).
c. Remove six screws (9) fastening the rails (6 and 7),
the slide plate (8) and the gasket plate (10). Set com-
ponents aside for reassembly.
d. Remove the four screws (5) fastening the motor cup
(4) to the panel. Cut sealer on outside and inside of
motor cup assembly. Push out the motor cup as-
semble from the rear of the panel.
e. Mount replacement motor cup assembly in the panel
using original screws. Torque screws to 0.29 mkg (25
+/-- 1 Inch pounds)
f. Reapply sealer to inside and outside of motor cup as-
sembly.
g. Mount upper & lower rails, slide plate and gasket plate
using original hardware. Apply thread sealant and
torque screws to 0.29 mkg (25 +/-- 1 Inch pounds)
6--12T-340
Page 84

h. Mount grille assembly using original hardware. Apply
thread sealant and torque screws to 0.29 mkg (25 +/-1 Inch pounds)
i. Reconnect the motor connector.
1
2
j. Replace the bolts that secure the eAutoFresh Panel
to the front of the unit.
k. Carry out functional test. Refer to section 4.4.4 step
c.
3
5
1
7
6
4
98
1110
12
1. Connector
2. Tie Wrap
3. eAutoFresh Panel
4. Cup, Motor
5. Motor Cup Screws
6. Rail, Top
7. Rail, Bottom
8. Plate, Slide
9. Rail Screws
10. Plate, Gasket
11. Grille
12. Grill Screws
Figure 6--13 Motor Cup Replacement
6--13
T-340
Page 85

6.14 ELECTRONIC EXPANSION VALVE
The electronic expansion valve (EEV) is an automatic
device which maintains required superheat of the refrigerant gas leaving the evaporator. The valve functions
are: (a) automatic response of refrigerant flow to match
the evaporator load and (b) prevention of liquid refrigerant entering the compressor. Unless the valve is defective, it seldom requires any maintenance. See
Figure 6--14.
3. Replace filter drier.
4. Evacuate to 500 microns by placing vacuum pump
on liquid line and suction service valve.
5. Open liquid line service valve and check refrigerant
level.
6. Check superheat. (Refer to Section 2.2).
7. Check unit operation by running Pre--trip (Refer to
Section 3.7).
1
2
3
FLOW
DIRECTION
1. Coil Boot
2. Coil
3. Electronic Expansion Valve
Figure 6 --14 Electronic Expansion Valve
6.14.1 Replacing Electronic Expansion Valve and
Screen
a. Removing an EEV
1. Pump down the compressor (refer to paragraph
6.3.2) and frontseat both suction and discharge
valves.
2. Turn unit power off and remove power from the unit.
3. Remove coil.
4. VALVE REMOVAL: The preferred method of remov-
ing the valve is to cut the connection between the
brazed section and the valve, using a small tube cutter. Remove valve.
Alternately, use a wet rag to keep valve cool. Heat inlet and outlet connections to valve body and remove
valve.
5. Clean the valve stem with mild cleaner, if necessary.
b. Installing an EEV
1. Reverse steps 1 through 4 above to install a new
valve. Install valve and screen with cone of screen
pointing into liquid line at inlet to the valve.
2. During installation, make sure the EEV coil is
snapped down fully, and the coil retention tab is properly seated in one of the valve body dimples. Also,
ensure that coil boot is properly fitted over valve
body. See Figure 6--14.
6.15 ECONOMIZER EXPANSION VALVE
The economizer expansion valve can be found in
Figure 2--4 (Item 12). The economizer expansion valve
is an automatic device that maintains constant superheat of the refrigerant gas leaving at the point of bulb attachment, regardless of suction pressure.
Unless the valve is defective, it seldom requires maintenance other than periodic inspection to ensure that the
thermal bulb is tightly secured to the suction line and
wrapped with insulating compound.
6.15.1 Valve Replacement
a. Removing an Expansion V alve
NOTE
The economizer expansion valve is a hermetic
valve and does not have adjustable superheat
(See Figure 6--15).
1
2
1. Inlet
2. Outlet
Figure 6--15 Economizer Expansion Valve
1. Pump down the compressor (refer to paragraph
6.3.2) and frontseat both suction and discharge
valves. Evacuate if unit is not equipped with service
valves. Refer to paragraph 6.3.4.
2. Turn unit power off and remove power from the unit.
3. Remove cushion clamps located on the inlet and outlet lines.
4. Remove insulation (Presstite) from expansion valve
bulb.
5. Unstrap the bulb, located on the economizer line.
6. VALVE REMOVAL: The preferred method of removing the valve is to cut the connection between the
brazed section and the valve, using a small tube cutter. Remove valve.
Alternately, use a wet rag to keep valve cool. Heat inlet and outlet connections to valve body and remove
valve.
6--14T-340
Page 86

7. Clean the valve stem with mild cleaner, if necessary.
x
b. Installing an Expansion Valve
1. The economizer valve should be wrapped in a
soaked cloth for brazing. Braze inlet connection to inlet line.
2. Braze inlet connection to inlet line.
3. Braze outlet connection to outlet line.
4. Reinstall the cushion clamps on inlet and outlet lines.
c. Replace filter drier.
d. Evacuate to 500 microns by placing vacuum pump
on liquid line and suction service valve.
5. Check superheat (see Section 2.2).
6.16 ECONOMIZER SOLENOID VALVE
a. Removing a Solenoid Valve Coil
1. Turn unit power off and remove power from the unit.
Disconnect leads.
2. Remove top screw and o--ring. Remove coil and
save mounting hardware, seals and spacer for reuse. (See Figure 6--16). Refer to step d. for valve coil
replacement.
1
2
3
d. Installing the Solenoid Valve Coil
1. Install the brass spacer on the valve stem.
2. Lubricate both o--rings with silicone provided in the
kit.
3. Install bottom coil o--ring on the valve stem.
4. Install the solenoid coil on the valve stem.
5. Place the top coil o--ring on the coil mounting screw
and secure the coil to the valve using a torque-wrench. Torque the screw to 25 lb--in.
6. Connect coil wires using butt--splices and heat-shrink tubing.
6.17 DIGITAL UNLOADER VALVE
a. Removing the DUV
1. Pump down the compressor (refer to paragraph
6.3.2) and frontseat both suction and discharge
valves. In the event the DUV is stuck open and compressor cannot pump down, remove charge.
2. Turn unit power off and remove power from the unit.
3. Loosen bolt on top of the DUV and remove coil
assembly.
NOTE
There is a loose steel spacer tube between the
top of the valve and the 12 VDC coil that needs
to be reinstalled into the solenoid valve coil.
When removing the coil, it may fall out when lifted from the valve body. Take care that the
spacer is not lost; the valve will not function correctly without it.
4
5
1. Slotted Screw
2. Top Coil (small) O--ring
3. Solenoid Coil, Enclosing Tube and Body
4. Bottom Coil (large) O--ring
5. Brass Spacer
Figure 6--16 Coil View of Econom iz e r Solenoid
Valve (ESV)
b. Removing the Solenoid Valve
1. Pump down the compressor (refer to paragraph
6.3.2) and frontseat both suction and discharge
valves.
2. VALVE REMOVAL: The preferred method of removing the solenoid valve is to cut the connection
between the brazed section and the valve, using a
small tube cutter. Remove valve.
Alternately, heat inlet and outlet connections to valve
body and remove valve.
3. Clean the valve stem with mild cleaner, if necessary.
c. Installing the Solenoid Valve
1. Fit the new solenoid valve into position and braze.
Use a wet rag to keep valve cool whenever brazing.
4. Remove clamps holding the DUV to the discharge
line.
5. Loosen the nuts attaching the DUV to the top of the
compressor.
6. VALVE REMOVAL: The preferred method of removing the solenoid valve is to cut the connection
between the brazed section and the valve, using a
small tube cutter. Remove valve. (See Figure 6--17).
Alternately, use a wet rag to keep valve cool. Heat
outlet connection to valve body and remove valve.
2
1
3
4
56
1. Sleeve
2. O--ring (hidden)
3. Screen Valve
Strainer
4. Tube
5. Solenoid Valve
Body
6. He
Nut, 1/2OD
Figure 6--17 View of Digita l Unloa der Valve (D U V)
Assembly
6--15
T-340
Page 87

7. Examine compressor and service valves. Ensure
that the o--ring is not stuck in the gland of the valve.
8. Discard the o--ring on the o--ring face seal connection.
b. Installing the Valve
1. Lubricate the gland shoulder area and o--ring with refrigerant oil.
2. Fit new valve in position and hand--tighten the o--ring
nut.
3. Use a wet rag to keep valve cool while brazing. Braze
DUV to service valve connection.
4. Reinstall and tighten the brackets that secure the
valve body to the discharge line.
5. Torque o--ring face seal connections to 18 to 20 ft-lbs.
6. Install the coil onto the valve body and tighten the attachment bolt.
NOTE
Confirm that the small spacer tube is inserted
into the coil prior to attaching it to the valve
body. The valve will not function correctly
without it.
7. Leak check and evacuate low side of unit as applicable. Refer to paragraph 6.3.4.
8. Open service valves.
6.18 VALVE OVERRIDE CONTROLS
Controller function code Cd41 is a configurable code
that allows timed operation of the automatic valves for
troubleshooting. Test sequences are provided in
Table 6--1. Capacity mode (CAP) allows alignment of
the economizer solenoid valve in the standard and
economized operating configurations. DUV Capacity
Modulation, % Setting (PCnt) and Electronic Expansion
V a lve (EEV) allows opening of the digital unloader valve
and electronic expansion valve, respectively, to various
percentages. If the unit is equipped with an LIV, the
Liquid Valve Setting allows the LIV to be automatically
controlled, or manually opened and closed.
The Override Timer (tIM) selection is also provided to
enter a time period of up to five minutes, during which
the override(s) are active. If the timer is active, valve
override selections will take place immediately. If the
timer is not active, changes will not take place for a few
seconds after the timer is started. When the timer times
out, override function is automatically terminated and
the valves return to normal machinery control. To operate the override, do the following:
a. Press the CODE SELECT key then press an AR-
ROW key until Cd41 is displayed in the left window.
The right window will display a controller communications code.
b. Press the ENTER key. The left display will show a test
name alternating with the test setting or time remaining. Use an ARROW key to scroll to the desired test.
Press the ENTER key and SELCt will appear in the
left display.
c. Use an ARROW key to scroll to the desired setting,
and then press the ENTER key. Selections available
for each of the tests are provided in the following
table.
d. If the timer is not operating, follow the above proce-
dure to display the timer. Use an ARROW key to scroll
to the desired time interval and press ENTER to start
the timer.
e. The above described sequence may be repeated
during the timer cycle to change to another override.
6--16T-340
Page 88

Table 6--1 Valve Override Control Displays
Left Display
Cd 41/SELCt
Controller Communications Codes
(Right Display)
tIM
(Override Timer)
PCnt
(% Setting -- DUV Capacity Modulation)
EEV
(% Setting -- Electronic Expansion Valve)
CAP
(Capacity Mode)
LIV (If Equipped)
(Liquid Injection Valve Setting)
Setting Codes (Right Display)
000(0 minutes/0 Seconds)
In 30 second increments to
500(5 minutes/ 0 seconds)
AUtO
(Normal Machinery Control)
0
3
6
10
25
50
100
AUtO
(Normal Machinery Control)
CLOSE (Closed)
0
3
6
10
25
50
100
AUtO
(Normal Control)
Std
UnLd
(Economizer = Closed)
ECOn
(Economizer = Open)
AUto
(Normal Control)
CLOSE (Closed)
OPEn (Open)
6--17
T-340
Page 89

6.19 AUTOTRANSFORMER
If the unit does not start, check the following:
a. Make sure the 460 VAC (yellow) power cable is
plugged into the receptacle (item 3, Figure 4--1) and
locked in place.
b. Make sure that circuit breakers CB-1 and CB-2 are in
the “ON” position. If the circuit breakers do not hold in,
check voltage supply.
c. There is no internal protector for this transformer
design, therefore, no checking of the internal protector is required.
d. Using a voltmeter, and with the primary supply circuit
ON, check the primary (input) voltage (460 VAC). Next,
check the secondary (output) voltage (230 VAC). The
transformer is defective if output voltage is not available.
6.20 CONTROLLER
6.20.1 Handling Modules
CAUTION
Do not remove wire harnesses from module
unless you are grounded to the unit frame
with a static safe wrist strap.
CAUTION
Unplug all module connectors before performing arc welding on any part of the container.
The guidelines and cautions provided herein should be
followed when handling the modules. These precautions and procedures should be implemented when
replacing a module, when doing any arc welding on the
unit, or when service to the refrigeration unit requires
handling and removal of a module.
a. Obtain a grounding wrist strap (Carrier Transicold
part number 07-00304-00) and a static dissipation
mat (Carrier Transicold part number 07-00277-00).
The wrist strap, when properly grounded, will dissipate any potential buildup on the body. The dissipation mat will provide a static-free work surface on
which to place and/or service the modules.
b. Disconnect and secure power to the unit.
c. Place strap on wrist and attach the ground end to any
exposed unpainted metal area on the refrigeration
unit frame (bolts, screws, etc.).
d. Carefully remove the module. Do not touch any of the
electrical connections if possible. Place the module
on the static mat.
e. The strap should be worn during any service work on
a module, even when it is placed on the mat.
6.20.2 Controller Troubleshooting
A group of test points (TP, see Figure 6--18) are provided on the controller for troubleshooting electrical circuits (see schematic diagram, section 7). A description
of the test points follows:
NOTE
Use a digital voltmeter to measure AC voltage
between TP’s and ground (TP9), except for
TP8.
TP1
This test point is not used in this application.
TP2
This test point enables the user to check if the high pressure switch (HPS) is open or closed.
TP3
This test point enables the user to check if the water
pressure switch (WP) contact is open or closed.
TP 4
This test point enables the user to check if the internal
protector for the condenser fan motor (IP-CM) is open or
closed.
TP 5
This test point enables the user to check if the internal
protectors for the evaporator fan motors (IP-EM1 or IPEM2) are open or closed.
TP 6 (IF EQUIPPED)
This test point enables the user to check if the controller
liquid injection valve relay (TQ) is open or closed.
TP 7
This test point enables the user to check if the controller
economizer solenoid valve relay (TS) is open or closed.
TP 8
This test point is not used in this application.
TP 9
This test point is the chassis (unit frame) ground connection.
TP 10
This test point enables the user to check if the heat termination thermostat (HTT) contact is open or closed.
6--18T-340
Page 90

12
1. Controller Software Programming Port
2. Mounting Screw
3. Controller
4. Test Points
Figure 6--18 Controlle r Section of the Control Box
6.20.3 Controller Programming Procedure
To load new software into the module, the programming
card is inserted into the programming/software port.
3
4
CAUTION
The unit must be OFF whenever a programming card is inserted or removed from the
controller programming port.
1. Turn unit OFF, via start-stop switch (ST).
2. Insert software/programming PCMCIA card containing the following (example) files into the programming/software port. (See Figure 6--18):
menuDDMM.ml3, this file allows the user to select a
file/program to upload into the controller.
cfYYMMDD.ml3, multi-configuration file.
3. Turn unit ON, via start-stop switch (ST).
If ruN COnFG is displayed, follow procedure
6.20.3.1 If Set UP is displayed, follow procedure
6.20.3.2.
6.20.3.1 Programming Procedure for
a. Procedure for loading operational software:
1. The display module will display the message ruN
2. Press the UP or DOWN arrow key until display
3. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
Software Versions Prior to 5328 and/or
Cards Without Updated Menu Option
(menu0111.ml)
COnFG. (If a defective card is beingused the display
will blink the message “bAd CArd.” Turn start-stop
switch OFF and remove the card.)
reads, LOAd 53XX for Scroll.
4. The display will alternate to between PrESS EntR
and rEV XXXX.
5. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
6. The display will show the message “Pro SoFt”. This
message will last for up to one minute.
7. The display module will go blank briefly, then read
“Pro donE” when the software loading has loaded. (If
a problem occurs while loading the software: the display will blink the message “Pro F AIL” or “bad 12V.”
Turn start-stop switch OFF and remove the card.)
8. Turn unit OFF, via start-stop switch (ST).
9. Remove the PCMCIA card from the programming/
software port and return the unit to normal operation
by placing the start-stop switch in the ON position.
10.Turn power on, and wait 15 seconds. The status LED
will flash quickly, and there will be no display. The
controller is loading the new software into memory.
This takes about 15 seconds.
When complete, the controller will reset and power
up normally.
1 1.Wait for default display, setpoint on the left, and con-
trol temperature on the right.
12.Confirm software is correct using keypad code select 18 to view Cd18 XXXX.
13.Turn power off. Operational software is loaded.
b. Procedure for loading configuration software:
1. Turn unit OFF using start-stop switch (ST).
2. Insert software/programming PCMCIA card containing the following (example) files into the programming/software port. (See Figure 6--18):
menuDDMM.ml3, this file allows the user to select
the file/program to upload into the controller.
cfYYMMDD.ml3, multi-configuration file
3. Turn unit ON using start-stop switch (ST).
4. The display module will display the message ruN
COnFG. (If a defective card is beingused the display
will blink the message “bAd CArd.” Turn start-stop
switch OFF and remove the card.)
5. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
6. The display module will go blank briefly and then display “551 00”, based on the operational software
installed.
7. Press the UP or DOWN ARROW key to scroll
through the list to obtain the proper model dash number. (If a defective card is being used, the display will
blink the message “bAd CArd.” Turn start-stop
switch OFF and remove the card.)
8. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
9. When the software loading has successfully completed, the display will show the message “EEPrM
donE.” (If a problem occurs while loading the software, the display will blink the message “Pro FAIL” or
“bad 12V .” Turn start-stop switch OFF and remove
the card.)
10.Turn unit OFF using start-stop switch (ST).
1 1.Remove the PCMCIA card from the programming/
software port and return the unit to normal operation
by placing the start-stop switch in the ON position.
12.Confirm correct model configuration using the keypad to choose code 20 (CD20). The model displayed
should match the unit serial number plate.
6--19
T-340
Page 91

6.20.3.2 Programming Procedure for
Software Versions 5328 and Later AND
With Updated Menu Option (menu0111.ml)
The updated menu option allows the operational software to be loaded, and time and container identification
to be set.
a. Procedure for loading operational software:
1. The display module will display the message Set UP.
2. Press the UP or DOWN arrow key until display
reads, LOAd 53XX for Scroll.
3. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
4. The display will alternate to between PrESS EntR
and rEV XXXX.
5. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
6. The display will show the message “Pro SoFt”. This
message will last for up to one minute.
7. The display module will go blank briefly, then read
“Pro donE” when the software loading has loaded. (If
a problem occurs while loading the software: the display will blink the message “Pro F AIL” or “bad 12V.”
Turn start-stop switch OFF and remove the card.)
8. Turn unit OFF, via start-stop switch (ST).
9. Remove the PCMCIA card from the programming/
software port and return the unit to normal operation
by placing the start-stop switch in the ON position.
10.Turn power on, and wait 15 seconds. The status LED
will flash quickly, and there will be no display. The
controller is loading the new software into memory.
This takes about 15 seconds.
When complete, the controller will reset and power
up normally.
1 1.Wait for default display, setpoint on the left, and con-
trol temperature on the right.
12.Confirm software is correct using keypad code se-
lect 18 to view Cd18 XXXX.
13.Turn power off. Operational software is loaded.
b. Procedure for loading configuration software:
1. Turn unit OFF using start-stop switch (ST).
2. Insert software/programming PCMCIA card contain-
ing the following (example) files into the programming/software port. (See Figure 6--18):
menuDDMM.ml3, this file allows the user to select
the file/program to upload into the controller.
cfYYMMDD.ml3, multi-configuration file
3. Turn unit ON using start-stop switch (ST).
4. Press the UP or DOWN arrow key until display reads
Set UP.
5. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
6. Press the UP or DOWN arrow key until display reads
XXXX the message ruN COnFG. (If a defective card
is being used the display will blink the message “bAd
CArd.” Turn start-stop switch OFF and remove the
card.)
7. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
8. The display module will go blank briefly and then display “551 00”, based on the operational software
installed.
9. Press the UP or DOWN ARROW key to scroll
through the list to obtain the proper model dash number. (If a defective card is being used, the display will
blink the message “bAd CArd.” Turn start-stop
switch OFF and remove the card.)
10.Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
1 1.When the software loading has successfully com-
pleted, the display will show the message “EEPrM
donE.” (If a problem occurs while loading the software, the display will blink the message “Pro FAIL” or
“bad 12V .” Turn start-stop switch OFF and remove
the card.)
12.Turn unit OFF using start-stop switch (ST).
13.Remove the PCMCIA card from the programming/
software port and return the unit to normal operation
by placing the start-stop switch in the ON position.
14.Confirm correct model configuration using the keypad to choose code 20 (CD20). The model displayed
should match the unit serial number plate.
c. Procedure for setting the date and time:
1. Press the UP or DOWN arrow key until display reads
Set TIM.
2. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
3. The first value to be modified is the date in YYYY
MM--DD format. The values will be entered from right
to left. Press the UP or DOWN ARROW key to increase or decrease the values. The ENTER key will
enter the information for the current field and move to
the next value; the CODE SELECT key will allow
modification of the previous value.
4. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
5. The next value to be modified is the time in HH MM
format. The values will be entered from right to left.
Press the UP or DOWN ARROW key to increase or
decrease the values. The ENTER key will enter the
information for the current field and move to the next
value; the CODE SELECT key will allow modification
of the previous value.
6. Press the ENTER key on the keypad. The date and
time will not be committed until start up procedures
are completed on the next power up.
d. Procedure for setting the container ID:
NOTE
The characters will be preset to the container ID
already on the controller. If none exist, the default will be AAAA0000000.
1. Press the UP or DOWN arrow key until display reads
Set ID.
2. Press the ENTER key on the keypad.
3. The values will be entered from right to left. Press the
UP or DOWN ARROW key to increase or decrease
the values. The ENTER key will enter the information
for the current field and move to the next value; the
CODE SELECT key will allow modification of the
previous value.
4. When the last value is entered, press the ENTER
key to enter the information to the controller; the
6--20T-340
Page 92

CODE SELECT key will allow modification of the
previous value.
6.20.4 Removing and Installing a Module
a. Removal:
1. Disconnect all front wire harness connectors and
move wiring out of way.
2. The lower controller mounting is slotted, loosen the
top mounting screw (see Figure 6--18) andlift up and
out.
3. Disconnect the back connectors and remove
module.
4. When removing the replacement module from its
packaging , note how it is packaged. When returning
the old module for service, place it in the packaging
in the same manner as the replacement. The packaging has been designed to protect the module from
both physical and electrostatic discharge damage
during storage and transit.
b.Installation:
Install the module by reversing the removal steps.
Torque values for mounting screws (item 2, see
Figure 6--18) are 0.23 mkg (20 inch-pounds). Torque
value for the connectors is 0.12 mkg (10 inch-pounds).
6.20.5 Battery Replacement
Standard Battery Location (Standard Cells):
a. Turn unit power OFF and disconnect power supply.
b. Slide bracket out and remove old batteries. (See
Figure 3--4, Item 8.)
c. Install new batteries and slide bracket into control box
slot.
CAUTION
Use care when cutting wire ties to avoid
nicking or cutting wires.
Standard Battery Location (Rechargeable Cells):
a. Turn unit power OFF and disconnect power supply.
b. Disconnect battery wire connector from control box.
c. Slide out and remove old battery and bracket. (See
Figure 3--4, Item 8.)
d. Slide new battery pack and bracket into the control
box slot.
e. Reconnect battery wire connector to control box and
replace wire ties that were removed.
Secure Battery Option (Rechargeable Cells Only):
a. Turn unit power OFF and disconnect power supply.
b. Open control box door and remove both the high volt-
age shield and clear plastic rain shield (if installed).
c. Disconnect the battery wires from the “KA” plug posi-
tions 14, 13, 1 1.
d. Using Driver Bit, Carrier Transicold part number
07--00418--00, remove the 4 screws securing the display module to the control box. Disconnect the ribbon
cable and set the display module aside.
NOTE
The battery wires must face toward the right.
e. Remove the old battery from the bracket and clean
bracket surface. Remove the protective backing from
the new battery and assemble to the bracket. Secure
battery by inserting the wire tie from the back of the
bracket around the battery, and back through the
bracket.
f. Reconnect the ribbon cable to display and re--install
the display.
g. Route the battery wires from the battery along the dis-
play harness and connect the red battery wire and
one end of the red jumper to “KA14,” the other end of
the red jumper wire to “KA1 1,” and the black wire to
“KA13.”
h. Replace wire ties that were removed.
6.21 VENT POSITION SENSOR SERVICE
The fresh air vent position sensor alarm (AL50) will occur if the sensor reading is not stable for four minutes or
if the sensor is outside of its valid range (shorted or
open). This can occur if the vent is loose or the panel is
defective. To confirm a defective panel, assure that the
wing nut is secure and then power cycle the unit. If the
alarm immediately reappears as active, the panel
should be replaced.
The alarm should immediately go inactive, check the
4-minute stability requirement. If the alarm reoccurs after the four minutes and the panel was known to have
been stable, then the sensor should be replaced.
In order to replace the VPS, the panel must be removed
and replaced with another upper fresh air panel
equipped with VPS.
Upon installation, a new vent position sensor assembly
requires calibration as follows:
1. Rotate the vent to the 0 CMH/ CFM position.
2. Code select 45 will automatically display. Press the
Enter key and hold for five seconds.
3. After the enter key has been pressed the display will
read CAL (for calibration).
4. Press the ALT MODE key and hold for five seconds.
5. After the calibration has been completed, Code 45 will
display 0 CMH / CFM.
a. Lower Vent Position Sensor Calibration
Calibration of the Lower VPS is only required when the
air makeup slide, motor or sensor has been repaired or
serviced.
The VPS is calibrated using the keypad:
1. Remove the two nuts that secure the air makeup
panel slide to the unit.
2. Rotate the gear clockwise until it stops.
3. Rotate the gear 1/4 turn counterclockwise.
4. Carefully reposition the slide onto the air makeup
panel, given that the gear is engaged with the rail and
has not moved.
5. Position slide panel to the fully closed position.
6. Code select Cd45 will automatically be shown on the
left display.
6--21
T-340
Page 93

7. Depress the ENTER key and hold for five seconds.
CAL for calibration is displayed.
8. Depress the ALT MODE key on the keypad and hold
for five seconds.
9. When calibration has been completed, Cd45 causes
0 CMH/CFM to be shown on the right display.
10.Secure the air makeup panel slide to the unit with the
two nuts; stake threads.
6.22 TEMPERATURE SENSOR SERVICE
Procedures for service of the return recorder, return
temperature, supply recorder, supply temperature, ambient, defrost temperature, evaporator temperature,
and compressor discharge temperature sensors are
provided in the following sub paragraphs.
6.22.1 Sensor Checkout Procedure
To check a sensor reading, do the following:
a. Remove the sensor and place in a 0_C(32_F)
ice-water bath. The ice-water bath is prepared by
filling an insulated container (of sufficient size to
completely immerse bulb) with ice cubes or chipped
ice, then filling voids between ice with water and
agitating until mixture reaches 0_C(32_F) measured
on a laboratory thermometer.
b. Start unit and check sensor reading on the control
panel. The reading should be 0_C(32_F). If the read-
ing is correct, reinstall sensor; if it is not, continue with
the following.
c. Turn unit OFF and disconnect power supply.
d. Refer to paragraph 6.20 and remove controller to gain
access to the sensor plugs.
e. Using the plug connector marked “EC” that is con-
nected to the back of the controller, locate the sensor
wires (RRS, RTS, SRS, STS, AMBS, DTS, or CPDS
as required). Follow those wires to the connector and
using the pins of the plug, measure the resistance.
Values are provided in Table 6--2 and Table 6--3.
Due to the variations and inaccuracies inohmmeters,
thermometers or other test equipment, a reading
within 2% of the chart value would indicate a good
sensor. If a sensor is defective, the resistance reading will usually be much higher or lower than the resistance values given.
6--22T-340
Page 94

Table 6--2 Sensor Resistance
Sensors AMBS, DTS, ETS, RRS, RTS, SRS, STS
°C °F Ohms °C °F Ohms °C °F Ohms °C °F Ohms
-- 4 0 -- 4 0 336,500 -- 7 . 8 18 49,060 24.4 76 10,250 56.7 134 2,809
--38.9 -- 3 8 312,600 -- 6 . 7 20 46,230 25.6 78 9,760 57.8 136 2,697
--37.8 -- 3 6 290,600 -- 5 . 6 22 43,580 26.7 80 9,299 58.9 138 2,590
--36.7 -- 3 4 270,300 -- 4 . 4 24 41,100 27.8 82 8,862 60.0 140 2,488
--35.6 -- 3 2 251,500 -- 3 . 3 26 38,780 28.9 84 8,449 61.1 142 2,390
--34.4 -- 3 0 234,200 -- 2 . 2 28 36,600 30.0 86 8,057 62.2 144 2,297
--33.3 -- 2 8 218,200 -- 1 . 1 30 34,560 31.1 88 7,686 63.3 146 2,208
--32.2 -- 2 6 203,400 0 32 32,650 32.2 90 7,334 64.4 148 2,124
--31.1 -- 2 4 189,700 1.1 34 30,850 33.3 92 7,000 65.6 150 2,042
-- 3 0 -- 2 2 177,000 2.2 36 29,170 34.4 94 6,684 68.3 155 1,855
--28.9 -- 2 0 165,200 3.3 38 27,590 35.6 96 6,384 71.1 160 1,687
--27.8 -- 1 8 154,300 4.4 40 26,100 36.7 98 6,099 73.9 165 1,537
--26.7 -- 1 6 144,200 5.5 42 24,700 37.8 100 5,828 76.7 170 1,402
--25.6 -- 1 4 134,800 6.6 44 23,390 38.9 102 5,571 79.4 175 1,281
--24.4 -- 1 2 126,100 7.7 46 22,160 40.0 104 5,327 82.2 180 1,171
--23.3 -- 1 0 1 18,100 8.9 48 20,990 41.1 106 5,095 85.0 185 1,072
--22.2 -- 8 1 10,500 10 50 19,900 42.2 108 4,874 87.8 190 983
--21.1 -- 6 103,600 11. 1 52 18,870 43.3 110 4,665 90.6 195 902
-- 2 0 -- 4 97,070 12.2 54 17,900 44.4 112 4,465 93.3 200 829
--18.9 -- 2 91,030 13.3 56 16,980 45.5 11 4 4,275 96.1 205 762
--17.8 0 85,400 14.4 58 16,120 46.7 116 4,095 98.9 210 702
--16.7 2 80,160 15.5 60 15,310 47.8 118 3,923 101.7 215 647
--15.6 4 75,270 16.6 62 14,540 48.9 120 3,759 104.4 220 598
--14.4 6 70,720 17.7 64 13,820 50.0 122 3,603 107.2 225 553
--13.3 8 66,460 18.9 66 13,130 51.1 124 3,454 110.0 230 51 1
--12.2 10 62,500 20.0 68 12,490 52.2 126 3,313 112.8 235 473
-- 1 1 . 1 12 58,790 21.1 70 11,880 53.3 128 3,177 115.6 240 438
--10.0 14 55,330 22.2 72 11,310 54.4 130 3,049 118.3 245 406
-- 8 . 9 16 52,090 23.3 74 10,760 55.6 132 2,926 121.1 250 378
6--23
T-340
Page 95

Table 6--3 Sensor Resistance (CPDS)
°C
-- 4 0 -- 4 0 2,889,600 36 96.8 53,887 11 2 233.6 4,204 188 370.4 706
-- 3 8 --36.4 2,532,872 38 100.4 49,656 114 237.2 3,977 190 374.0 697
-- 3 6 --32.8 2,225,078 40 104.0 45,812 116 240.8 3,759
-- 3 4 --29.2 1,957,446 42 107.6 42,294 118 244.4 3,550
-- 3 2 --25.6 1,724,386 44 111.2 39,078 120 248.0 3,354
-- 3 0 --22.0 1,522,200 46 114.8 36,145 122 251.6 3,173
-- 2 8 --18.4 1,345,074 48 118.4 33,445 124 255.2 3,004
-- 2 6 --14.8 1,190,945 50 122.0 30,985 126 258.8 2,850
-- 2 4 -- 1 1 . 2 1,056,140 52 125.6 28,724 128 262.4 2,711
-- 2 2 -- 7 . 6 938,045 54 129.2 26,651 130 266.0 2,580
-- 2 0 -- 4 . 0 834,716 56 132.8 27,750 132 269.6 2,454
-- 1 8 -- 0 . 4 743,581 58 136.4 23,005 134 273.2 2,335
-- 1 6 3.2 663,593 60 140.0 21,396 136 276.8 2,223
-- 1 4 6.8 593,030 62 143.6 19,909 138 280.4 2,119
-- 1 2 10.4 530,714 64 147.2 18,550 140 284.0 2,021
-- 1 0 14.0 475,743 66 150.8 17,294 142 287.6 1,928
-- 8 17.6 426,904 68 154.4 16,133 144 291.2 1,839
-- 6 21.2 383,706 70 158.0 15,067 146 294.8 1,753
-- 4 24.8 345,315 72 161.6 14,078 148 298.4 1,670
-- 2 28.4 31 1,165 74 165.2 13,158 150 302.0 1,591
10 50.0 171,165 86 186.8 8,918 162 323.6 1,193
12 53.6 155,574 88 190.4 8,376 164 327.2 1,142
14 57.2 141,590 90 194.0 7,869 166 330.8 1,096
16 60.8 129,000 92 197.6 7,404 168 334.4 1,054
18 64.4 117,656 94 201.2 6,972 170 338.0 1,014
20 68.0 107,439 96 204.8 6,571 172 341.6 975
22 71.6 98,194 98 208.4 6,197 174 345.2 938
24 75.2 89,916 100 212.0 5,848 176 348.8 902
26 78.8 82,310 102 215.6 5,529 178 352.4 867
28 82.4 75,473 104 219.2 5,233 180 356.0 834
30 83.0 69,281 106 222.8 4,953 182 359.6 798
32 89.6 63,648 108 226.4 4,692 184 363.2 764
34 93.2 58,531 110 230.0 4,446 186 366.8 733
°F Ohms °C °F Ohms °C °F Ohms °C °F Ohms
0 32.0 280,824 76 168.8 12,306 152 305.6 1,508
2 35.6 253,682 78 172.4 11,524 154 309.2 1,430
4 39.2 229,499 80 176.0 10,793 156 312.8 1,362
6 42.8 207,870 82 179.6 10,122 158 316.4 1,302
8 46.4 188,494 84 183.2 9,494 160 320.0 1,247
6--24T-340
Page 96

6.22.2 Sensor Replacement
a. Turn unit power OFF and disconnect power supply.
NOTE
Include white date code label when cutting out
and removing defective sensors. The label
could be required for warranty returns.
b. Cut cable. Slide the cap and grommet off a bulb type
sensor and save for reuse. Do not cut thegrommet.
c. Cut one wire of existing cable 40 mm (1-1/2 inches)
shorter than the other wire.
d. Cut replacement sensor wires (opposite colors) back
40 mm (1-1/2 inches). (See Figure 6--19.)
e. Strip back insulation on all wiring 6.3 mm (1/4 inch).
1
2
g. If required, slide the cap and grommet assembly onto
the replacement sensor.
h. Slip crimp fittings over dressed wires (keeping wire
colors together). Make sure wires are pushed into
crimp fittings as far as possible and crimp with crimping tool.
i. Solder spliced wires with a 60% tin and 40% lead
Rosincore solder.
j. Slide heat shrink tubing over each splice so that ends
of tubing cover both ends of crimp as shown in
Figure 6--20.
k. Heat tubing to shrink over splice. Make sure all seams
are sealed tightly against the wiring to prevent moisture seepage.
CAUTION
Do not allow moisture to enter wire splice
area as this may affect the sensor resistance.
3
Mounting Stud Type
12
3
Bulb Type
1. Sensor
2. 40 mm (1 1/2 in), 2 or 3 wires as required
3. 6.3 mm (1/4 in).
Figure 6--19 Sensor Types
f. Slide a large piece of heat shrink tubing over the
cable, and place the two small pieces of heat shrink
tubing, one over each wire, before adding crimp fittings as shown in Figure 6--20.
212
1
1. Cable
2. Sensor (Typical)
3. Large Heat Shrink
Tubing (1)
Figure 6--20 Sensor and Cable Splice
3
4
4. Heat Shrink
Tubing, 2 or 3
as required
l. Slide large heat shrink tubing over both splices and
shrink.
m.Position sensor in unit as shown in Figure 6--20 and
re-check sensor resistance.
n. Reinstall sensor (refer to paragraph 6.22.3).
NOTE
The P5 Pre-Trip test must be run to inactivate
probe alarms (refer to paragraph 4.9).
6.22.3 Sensor Re-Installation
Sensors STS and SRS
To properly position a supply sensor, the sensor must be
fully inserted into the probe holder. See Figure 6--21. Do
not allow heat shrink covering to contact the probe holder. For proper placement of the sensor, be sure to position the enlarged positioning section of the sensor
against the the side of the mounting clamp. This positioning will give the sensor the optimum amount of exposure to the supply air stream, andwill allow the controller
to operate correctly.
Sensors RRS and RTS
Reinstall the return sensor as shown in Figure 6--22. For
proper placement of the return sensor, be sure to position the enlarged positioning section of the sensor
against the the side of the mounting clamp.
Sensor DTS
The DTS sensor must have insulating material placed
completely over the sensor to ensure the coil metal temperature is sensed.
Sensors ETS1 and ETS2
The ETS1 and ETS2 sensors are located in a tube holder under insulation, as illustrated in Figure 6--23. When
the combo sensor is removed and reinstalled, it must be
placed in a tube holder by applying thermal grease. Insulating material must completely cover the sensor to
ensure the correct temperature is sensed.
6--25
T-340
Page 97

11
10
9
8
1. Supply Air Stream
2. Insulation
3. Back Panel
4. Supply Sensor
5. Mounting Clamp
6. Sensor Wires
7. Drip Loop
1
12
2
13
3
4
5
6
7
(2.5”)
8. Gasket Mounting Plate
9. Gasketed Support Plate
10. Gasketed Cover
11. TIR Bolt s
12. STS Probe
13. SRS Probe
Figure 6--21 Supply Sensor Positioning
1
1. Mounting Clamp 2. Return Sensor
Figure 6--22 Return Sensor Positioning
2
1.50 in.
(38.1cm)
4
3
1. Wire Tie
2. ETS1 and 2
Figure 6--23 Evaporator T emperature Sensor
2
1.00 in.
(25.4cm)
3. ETS Tube Holder
4. Insulation
Positioning
1
6--26T-340
Page 98

Sensor, CPDS
To replace the compressor discharge sensor (see
Figure 6--24) do the following:
a. Ensure the unit is disconnected from the power
source and that ST is in OFF position.
b. Remove the existing sensor. Clean all silicone sealer
and dielectric compound from the sensor well. Ensure well is clean and dry. Top of compressor, where
the sensor seals, must also be clean and dry .
SENSOR
SILICONE BEAD
SENSOR WELL
Figure 6--24 Compressor Discharge Temperature
Sensor
c. Using the syringe supplied with the replacement
sensor, squeeze all of the dielectric compound into
the sensor well.
d. Place a bead of the silicone sealer supplied with the
replacement sensor around the sensor sealing ring.
Insert sensor into the well with the leads parallel to the
suction fitting.
6.23 ELECTRONIC PARTLOW TEMPERATURE
RECORDER
The microprocessor--based temperature recorder is
designed to interface with the DataCORDER to log
temperature with time. The electronic recorder will
automatically record the return air, supply air, or both,
based on the setting of temperature controller
configuration code CnF37, refer to Table 3--4. The
recorder reads and records data from the controller in
present time, under normal operating conditions.
If the power has been OFF for more than thirty days, the
recorder will NOT re-synchronize (the chart will not
advance to present time), the pen tip will move to the
currently recorded temperature, and the recorder will
resume normal temperature recording.
If using the Electronic Partlow Recorder CTD part
number 12-00464-xx
Where xx= an even number (example: 12-00464-08)
The recorder will STOP when the power is OFF, and the
pen tip will remain at the last recorded temperature on
the chart. When power is applied, and the power off
period is less than thirty days, the recorder will retrieve
the logged data from the DataCORDER for the power
off period and record it onto the chart. Thereafter, the
recorder will resume normal temperature recording.
If the optional DataCORDER battery pack is being used
and the charge is too low to enable recording during the
power off period of less than thirty days, the pen tip will
move to below the inner chart ring for the period when
NO data was recorded by the DataCORDER.
If the power has been OFF for more than thirty days, the
recorder will NOT re-synchronize (the chart will not
advance to present time), the pen tip will move to the
currently recorded temperature, and the recorder will
resume normal temperature recording.
6.23.1 Replacing the Recorder
a. Turn power to the unit OFF .
b. Open the recorder door (item 1, see Figure 6--25).
c. Locate the connector below the recorder (item 6),
and squeeze the ears together to disconnect the
plug.
d. Remove the four mounting screws (item 8), and
remove the recorder.
e. Reconnect sensor (see Figure 6--20) and run a
Pretriptotest.
e. Install the new recorder by reversing the above
steps.
6--27
T-340
Page 99

1
2
3
4
10
9
8
7
1. Recorder Door
2. Change Chart
Button
3. Recorder Box
4. Pen Tip
5. Stylus Arm
Figure 6--25 Electronic Partlow Temperature Recorder
6.23.2 Rezeroing the Recording Thermometer
For Electronic Partlow Recorder CTD part number
12-00464-xx
Where xx= an odd number (example: 12-00464-03)
NOTE
Use chart CTD: part number 09-00128-00 (F),
part number 09-00128-01 (C).
a. Press the “Calibration” button (item 7, Figure 6--25)
on the bottom of the recorder. The pen tip will drive fully down scale, then move upscale to the chart ring at
-29_C (-20_F), and stop.
b. If the tip of the pen (item 4) is on the -29_C (-20_F)
chart ring, the recorder is in calibration, proceed to
step c. If the tip of the pen is NOT on the -29_C
(-20_F) chart ring, the operator must loosen the two
screws on the bottom of the stylus arm to adjust the
pen tip manually to the -29_C (-20_F) chart ring.
Tighten the screws when adjustment is complete.
5
6
6. Connector
7. Calibration Button
(Located underneath)
8. Mounting Screws,
#10-24 x 7/16 inches long
9. Hold Down Tab
10. Chart Retaining Nut
For Electronic Partlow Recorder CTD part number
12-00464-xx
Where xx= an even number (example: 12-00464-08)
NOTE
Use chart CTD part number 09-00128-00 (F),
part number 09-00128-01 (C).
a. Press the “Calibration” button (item 7, Figure 6--25)
on the bottom of the recorder. The pen tip will drive fully down scale, then move upscale to the chart ring at
0_C(32_F), and stop.
b. If the tip of the pen (item 4) is on the 0_C(32_F) chart
ring the recorder is in calibration, proceed to step c. If
the tip of the pen is NOT on the 0_C(32_F) chart ring,
the operator must loosen the two screws on the
bottom of the stylus arm to adjust the pen tip manually
to the 0_C(32_F) chart ring. Tighten the screws when
adjustment is complete.
c. Press the calibration button and the pen will position
itself to the correct temperature reading.
c. Press the calibration button and the pen will position
itself to the correct temperature reading.
6--28T-340
Page 100

6.24 MAINTENANCE OF PAINTED SURFACES
The refrigeration unit is protected by a special paint
system against the corrosive atmosphere in which it
normally operates. However, should the paint system
be damaged, the base metal can corrode. In order to
protect the refrigeration unit from the highly corrosive
sea atmosphere, or if the protective paint system is
scratched or damaged, clean area to bare metal using a
wire brush, emery paper or equivalent cleaning method.
Immediately following cleaning, apply two-part epoxy
paint to the area. and allow to dry. After the first coat
dries, apply a second coat.
6.25 COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE MODULE
INSTALLATION
a. CB1 is connected to the power system, see wiring
schematic. Ensure that the unit power is off AND
that the unit power plug is disconnected.
b. Open control box, see Figure 6--26 and remove low
voltage shield. Open high voltage shield.
c. If using factory provisioned wiring, remove the cir-
cuit breaker panel, with circuit breaker, from the
control box. Locate, wires CB21/CIA3, CB22/CIA5
and CB23/CIA7 that have been tied back in the wire
harness. Remove the protective heat shrink from
the ends of the wires.
d. Refit the circuit breaker panel.
e. Fit the new CIM into the unit.
f. Attach three wires CB21/CIA3, CB22/CIA5 and
CB23/CIA7 to the CIM at connection CIA.
g. Locate connectors CIA and CIB, remove plugs if re-
quired, and attach to the module.
h. Replace the low voltage shield.
Table 6--4 Recommended Bolt Torque Values
CB1
Figure 6--26 Communications Interface
Installation
Units that have been factory provisioned for installation
of a communication interface module (CIM) have the required wiring installed. If the unit is not factory provisioned, a provision wiring kit (Carrier T ransicold part
number 76-00685-00) must be installed. Installation instructions are packaged with the kit. To install the module, do the following:
Communications
interface Module
WARNING
Installation requires wiring to the main unit
circuit breaker, CB1. Make sure the power to
the unit is off and power plug disconnected
before beginning installation.
BOLT DIA.
#4
#6
#8
#10
1/4
5/16
3/8
7/16
1/2
9/16
5/8
3/4
NONFREE SPINNING (LOCKNUTS ETC.)
1/4
5/16
3/8
7/16
1/2
9/16
5/8
3/4
THREADS TORQUE Nm
FREE SPINNING
40
32
32
24
20
18
16
14
13
12
11
10
20
18
16
14
13
12
11
10
5.2 in-lbs
9.6 in-lbs
20 in-lbs
23 in-lbs
75 in-lbs
11 ft-lbs
20 ft-lbs
31 ft-lbs
43 ft-lbs
57 ft-lbs
92 ft-lbs
124 ft-lbs
82.5 in-lbs
145.2 in-lbs
22.0 ft-lbs
34.1 ft-lbs
47.3 ft-lbs
62.7 ft-lbs
101.2 ft-lbs
136.4 ft-lbs
0.6
1.1
2.0
2.5
8.4
15
28
42
59
78
127
171
9.3
16.4
23
47
65
86
139
188
6--29
T-340
 Loading...
Loading...