Page 1
50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-048
Single-Package Rooftop Units
Electric Cooling with Electric Heat Option
Installation, Start-Up and
Service Instructions
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS .................. 1
INSTALLATION ............................ 1-31
Step 1 — Provide Unit Support .............. 1
• ROOF CURB
• ALTERNATE UNIT SUPPORT
Step 2 — Rig and Place Unit ................. 8
• POSITIONING
• ROOF MOUNT
Step 3 — Field Fabricate Ductwork ...........11
Step 4 — Make Unit Duct Connections .......11
Step5—TrapCondensate Drain .............11
Step 6 — Controls Options ..................12
• CONSTANT VOLUME APPLICATIONS
• VARIABLE AIR VOLUME (VAV)
APPLICATIONS
Step 7 — Make Electrical Connections .......15
• POWER WIRING
• FIELD POWER SUPPLY
• FIELD CONTROL WIRING
Step 8 — Make Outdoor-Air Inlet
Adjustments ...............................25
• ECONOMIZER
• ECONOMIZER SETTINGS
Step 9 — Position Power Exhaust/
Barometric Relief Damper Hood .............29
Step 10 — Install Accessories ...............30
START-UP ................................32-42
SERVICE ..................................42-45
TROUBLESHOOTING ......................46-51
START-UP CHECKLIST ...............CL-1, CL-2
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of air-conditioning equipment
can be hazardous due to system pressure and electrical components. Only trained andqualified service personnel should
install, repair, or service air-conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions of cleaning coils and filters and replacing filters. All
other operations should be performed by trained service personnel. When working on air-conditioning equipment, observe precautions in the literature, tags and labels attached
to the unit, and other safety precautions that may apply.
Follow all safety codes.W earsafetyglasses and work gloves.
Use quenching cloth for unbrazing operations. Have fire extinguishers available for all brazing operations.
IMPORTANT — READ BEFORE INSTALLING
IMPORTANT: Due to upgrades in unit control software and hardware, units produced currently are slightly
different than original design units. The unit control
software (which has changed) is designated with a sticker
on the unit control board, chip U8 (the large chip in
the center of the board), which states the software Version number. Version 1.0 is the original version. Version 2.0 is the current version. Differences in installation, configuration, and start-up procedures in this
manual will be identified by Version number.
INSTALLATION
Step 1 — Provide Unit Support
All panels must be in place when rigging. Unit is not
designed for handling by fork truck.
ROOF CURB — Assemble and install accessory roof curb
in accordance with instructions shipped with the curb. Accessory roof curb and information required to field fabricate
a roof curb or horizontal adapter are shown in Fig. 1 and 2.
Install insulation, cant strips, roofing, and counter flashing
as shown. Ductwork can be secured to roof curb before unit
is set in place.
IMPORTANT: The gasketing of the unit to the roof
curb is critical for a leak-proof seal. Install gasket supplied with the roof curb as shown in Fig. 1. Improperly applied gasket can result in air leaks and poor unit
performance.
Curb should be level. This is necessary to permit unit drain
to function properly. Unit leveling tolerance is shown in
Fig 1 and 2. Refer to Accessory Roof Curb Installation Instructions for additional information as required. When accessory roof curb is used, unit may be installed on class A,
B, or C roof covering material.
ALTERNATEUNITSUPPORT—When the curb or adapter
cannot be used, support unit with sleepers using unit curb or
adapter support area. If sleepers cannot be used, support long
sides of unit (refer to Fig. 3-6) with a minimum number of
equally spaced 4-in. x 4-in. pads as follows:
50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-034 units require 3 pads on each side;
50EJ,EK,EW,EY038-048 require 4 pads on each side. Unit
may sag if supported by corners only.
Before performing service or maintenance operations on
unit, turn offmain power switch to unit. Electrical shock
could cause personal injury.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1
Tab 1b
PC 111 Catalog No. 535-006 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50E-3SI Pg 1 8-96 Replaces: 50E-1SI
Page 2
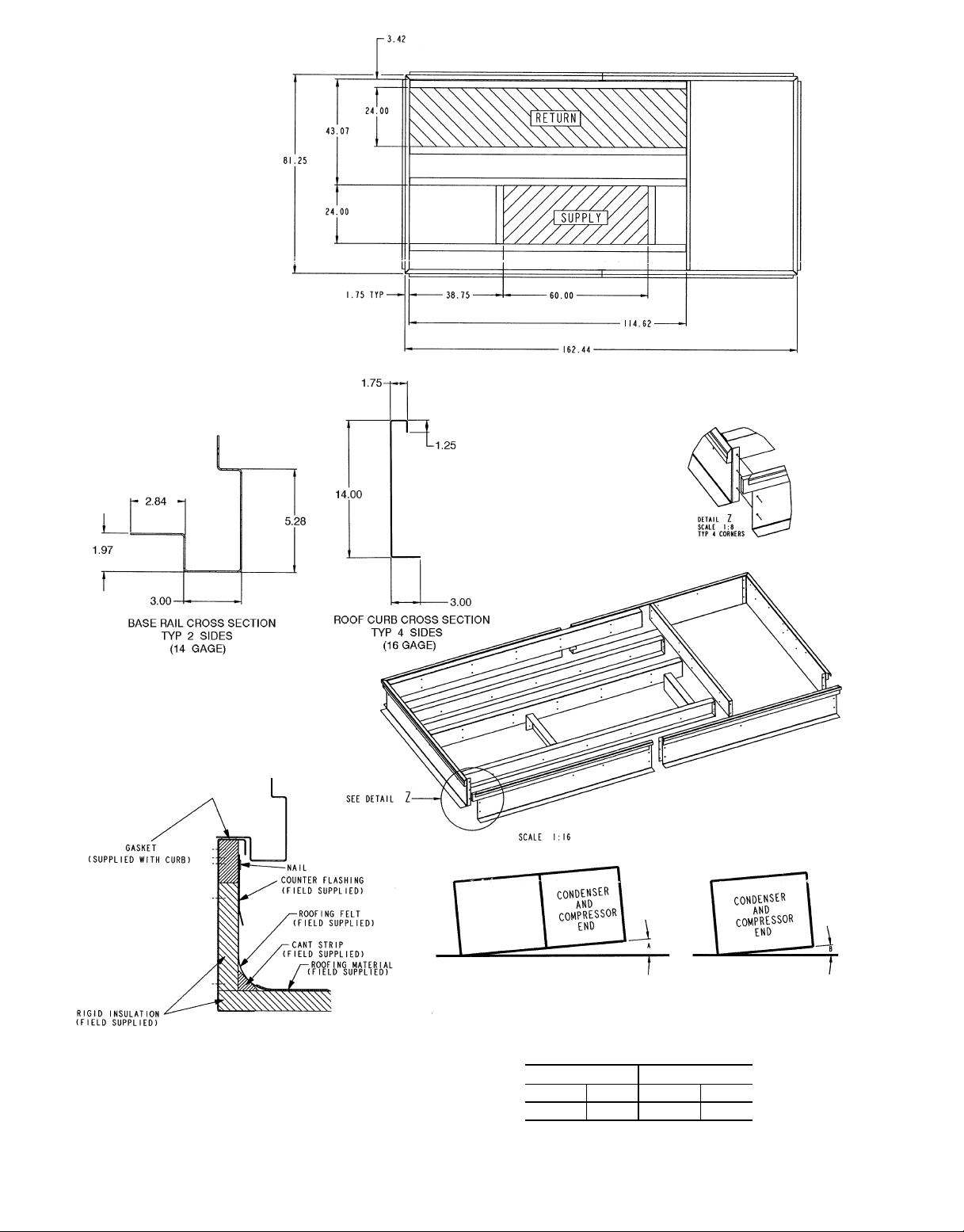
NOTE: To prevent standing water in the drain pan of the indoor section
and the heat exchangers, UNIT CAN ONLY BE PITCHED AS SHOWN.
NOTES:
1. Unlessotherwisespecified,alldimensions are to outside of part.
2. Roof curb accessory is shipped disassembled.
3. All roof curb parts are to be 16 ga galvanized steel.
4. Dimensions are in inches.
Fig. 1 — Roof Curb (Sizes 024-034)
UNIT LEVELING TOLERANCES DIMENSIONS*
*From edge of unit to horizontal.
(Degrees and Inches)
AB
Deg. in. Deg. in.
1.0 2.9 .50 .75
2
Page 3
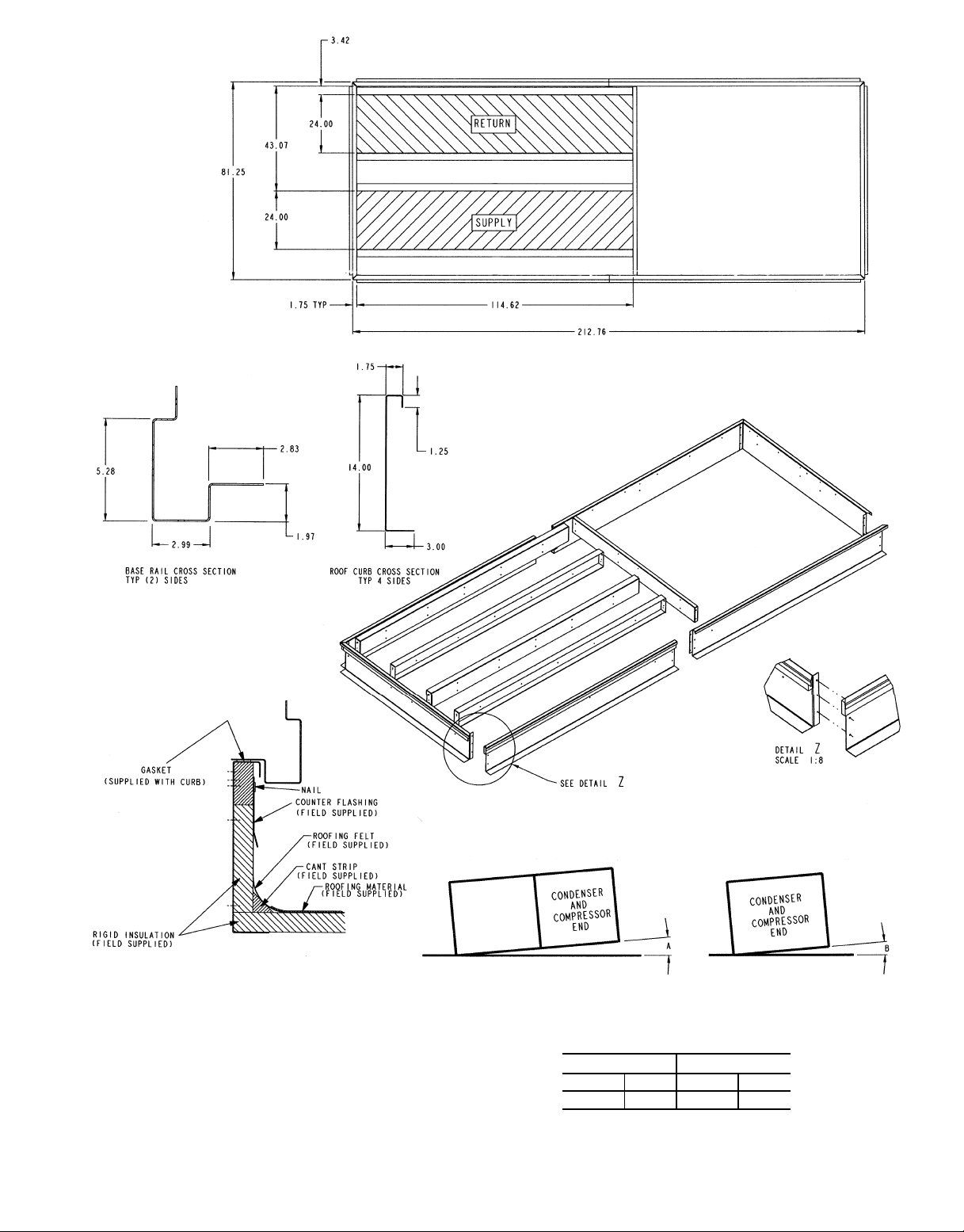
NOTES:
1. Unlessotherwisespecified,alldimensions are to outside of part.
2. Roof curb accessory is shipped disassembled.
3. All roof curb parts are to be 16 ga galvanized steel.
4. Dimensions are in inches.
Fig. 2 — Roof Curb (Sizes 038-048)
NOTE: To prevent standing water in the drain pan of the indoor section and the
heat exchangers, UNIT CAN ONLY BE PITCHED AS SHOWN.
UNIT LEVELING TOLERANCES DIMENSIONS*
*From edge of unit to horizontal.
(Degrees and Inches)
AB
Deg. in. Deg. in.
1.0 2.9 .50 .75
3
Page 4
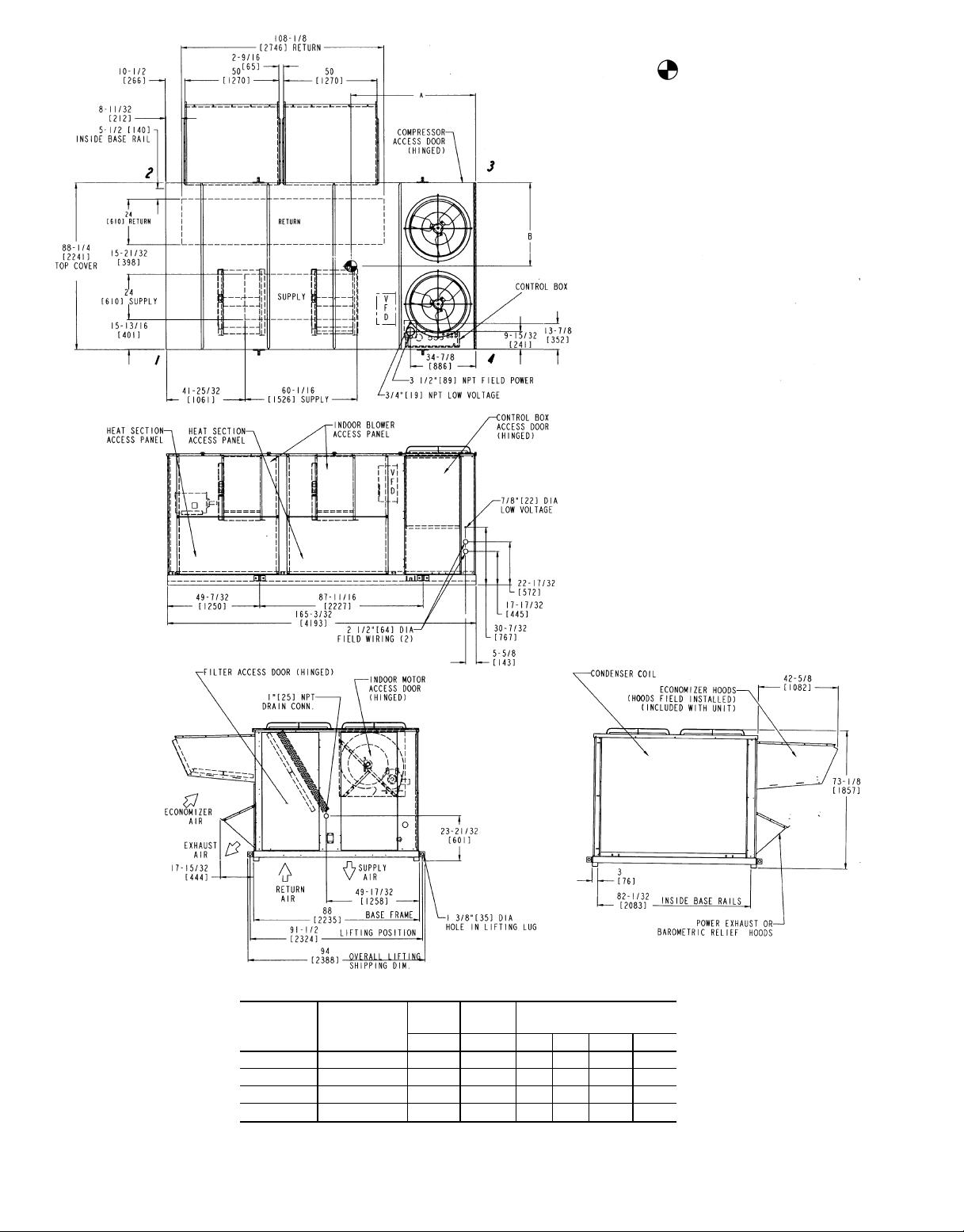
NOTES:
1. Weights include economizer (Std)
2. Center of gravity.
3. Do not locate adjacent units with discharge facing economizer inlet. Minimum clearances to be:
Adjacent Units: 158-09
Top of Units: No overhang
Condenser Coil: 48-09
Economizer Side: 68-09
Filter Access Side: 108-09 (for removal of evaporator coil)
4. For smaller service and operational
clearances, contact Carrier Application Engineering department.
5. Bottom ducts designed to be attached
toaccessoryroof curb. If unitismounted
on dunnage, it is recommended the
ductsbe supported by cross braces as
done on accessory roof curb.
6. Dimensions are in inches. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
7. For units with electric heat, a fieldsupplied 90° elbow must be installed
in the supply ductwork below the unit
discharge.
LEGEND
VFD — Variable Frequency Drive
UNIT SIZE
50EJ/EK
OPERATING
WEIGHT
(lb)
024 4016 5-11
028 4102 5- 8
030 4102 5- 8
034 4102 5- 8
AB
ft-in. ft-in. 1 2 3 4
3
⁄83-511⁄16823 914 1199 1080
1
⁄23-75⁄8844 859 1210 1189
1
⁄23-75⁄8844 859 1210 1189
1
⁄23-75⁄8844 859 1210 1189
CORNER WEIGHT
Fig. 3 — Base Unit Dimensions, 50EJ/EK024-034
4
(lb)
Page 5
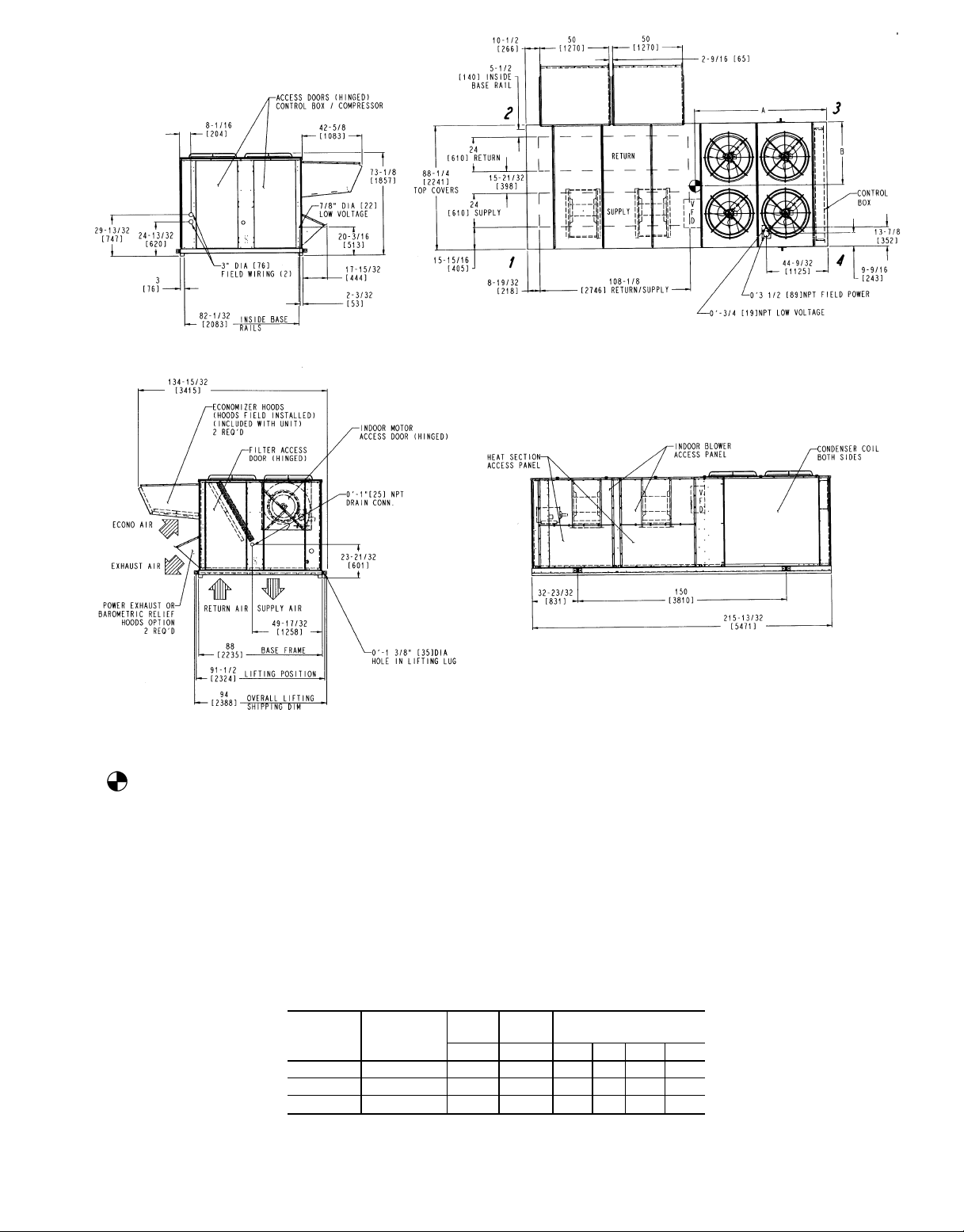
NOTES:
1. Weights include economizer (Std)
2. Center of gravity.
3. Do not locate adjacent units with discharge facing economizer inlet. Minimum clearances to be:
Adjacent Units: 158-09
Top of Units: No overhang
Condenser Coil: 48-09
Economizer Side: 68-09
Filter Access Side: 108-09 (for removal of evaporator coil)
4. For smaller service and operational clearances, contact Carrier Application Engineering department.
5. Bottom ducts designed to be attached to accessory roof curb. If unit is
mountedondunnage,itisrecommendedtheductsbesupportedbycross
braces as done on accessory roof curb.
6. Dimensions are in inches. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
7. For units with electric heat, a field-supplied 90° elbow must be installed
in the supply ductwork below the unit discharge.
LEGEND
VFD — Variable Frequency Drive
UNIT SIZE
50E
OPERATING
WEIGHT
(lb)
J038 4282 7-7
J/K044 4508 7-3
J048 4795 7-2
AB
ft-in. ft-in. 1 2 3 4
5
⁄163-101⁄2961 858 1162 1302
13
⁄163-111⁄2973 868 1258 1409
3
⁄163-103⁄321007 915 1368 1505
CORNER WEIGHT
(lb)
Fig. 4 — Base Unit Dimensions, 50EJ038-048 and 50EK044
5
Page 6
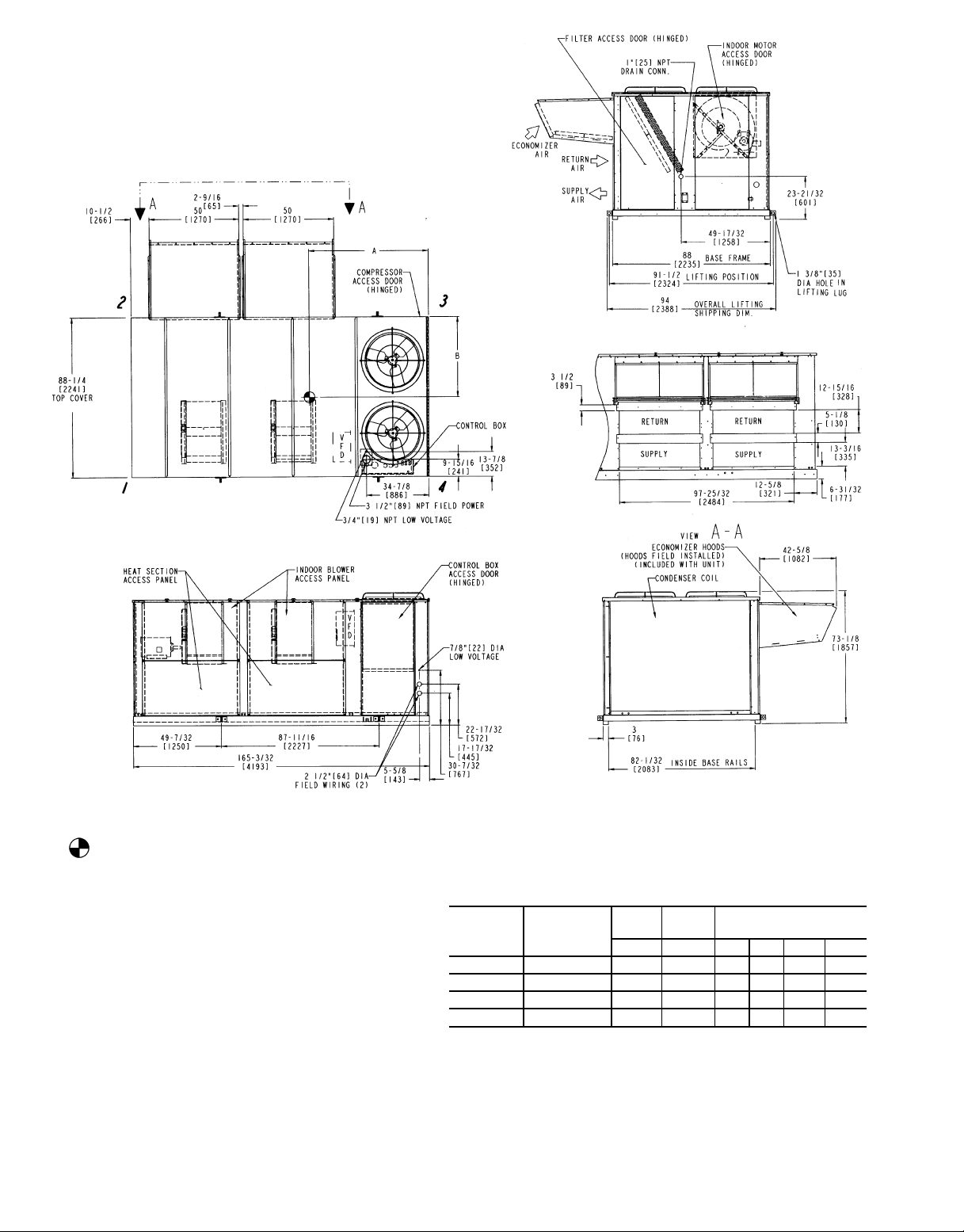
NOTES:
1. Weights include economizer (Std)
2. Center of gravity.
3. Donotlocateadjacent units with discharge facing economizer inlet. Minimum clearances to be:
Adjacent Units: 158-09
Top of Units: No overhang
Condenser Coil: 48-09
Economizer Side: 68-09
Filter Access Side: 108-09 (for removal of evaporator
coil)
4. For smaller service and operational clearances, contact Carrier Application Engineering department.
5. Dimensions are in inches. Dimensions in [ ] are in
millimeters.
6. For units equipped with electric heat, a field-supplied
90° elbow must be installed in the supply ductwork below the unit discharge.
7. For side-supply/return applications, a single return and
supply ductwork connection is recommended for covering both return and both supply openings.
Fig. 5 — Base Unit Dimensions, 50EW/EY024-034
UNIT SIZE
50EW/EY
OPERATING
WEIGHT
(lb)
024 4016 5-11
028 4102 5- 8
030 4102 5- 8
034 4102 5- 8
6
LEGEND
VFD — Variable Frequency Drive
AB
CORNER WEIGHT
(lb)
ft-in. ft-in. 1 2 3 4
3
⁄83-511⁄16823 914 1199 1080
1
⁄23-75⁄8844 859 1210 1189
1
⁄23-75⁄8844 859 1210 1189
1
⁄23-75⁄8844 859 1210 1189
Page 7
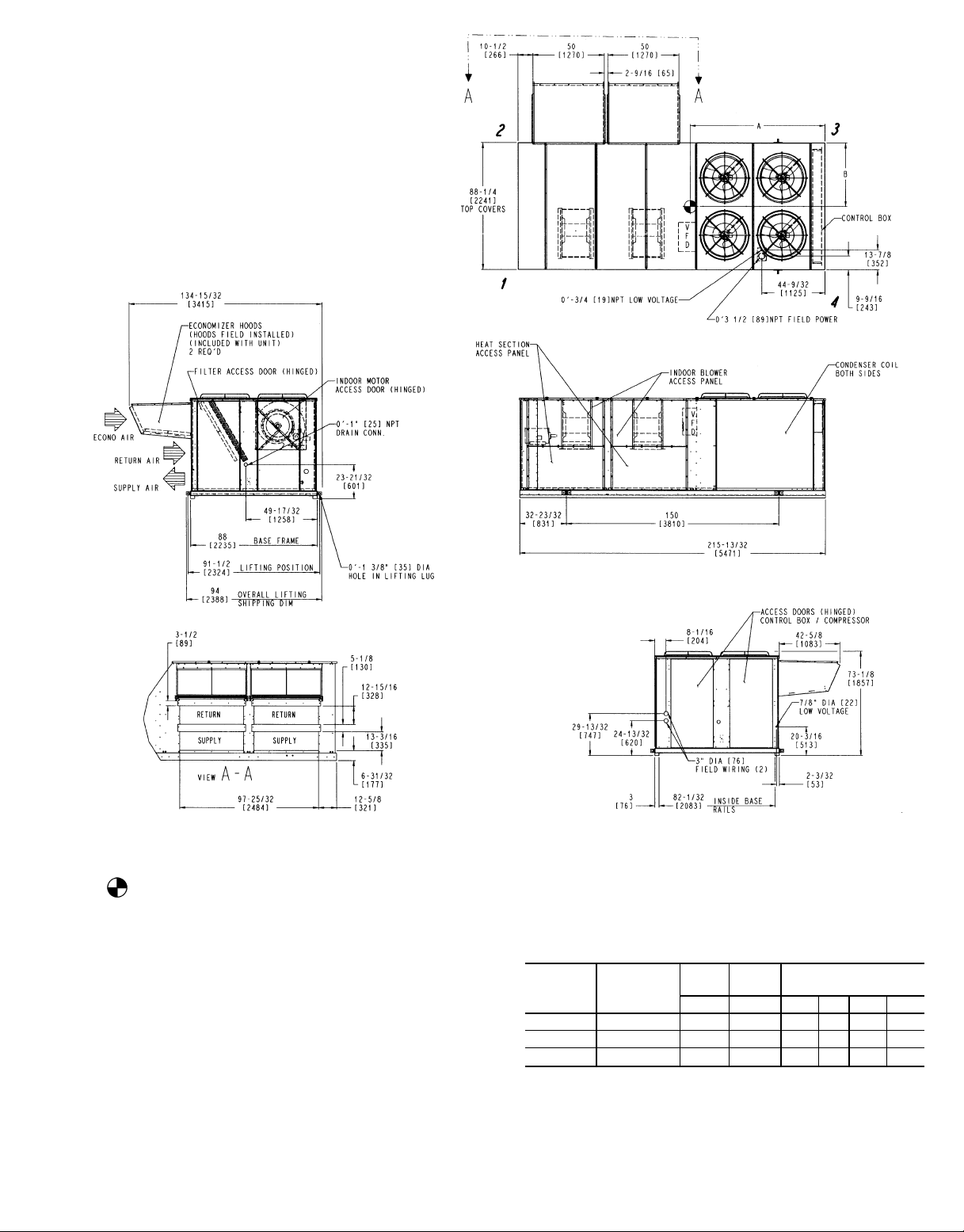
NOTES:
1. Weights include economizer (Std)
2. Center of gravity.
3. Do not locate adjacent units with discharge facing economizer inlet.
Minimum clearances to be:
Adjacent Units: 158-09
Top of Units: No overhang
Condenser Coil: 48-09
Economizer Side: 68-09
Filter Access Side: 108-09 (for removal of evaporator coil)
4. For smaller service and operational clearances, contact Carrier
Application Engineering department.
5. Dimensions are in inches. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
6. For units equipped with electric heat, a field-supplied 90° elbow must
be installed in the supply ductwork below the unit discharge.
7. For side-supply/return applications, a single return and supply ductwork connection is recommended for covering both return and both
supply air openings.
Fig. 6 — Base Unit Dimensions, 50EW038-048 and 50EY044
UNIT SIZE
50E
W038 4282 7-7
W/Y044 4508 7-3
W048 4795 7-2
7
OPERATING
WEIGHT
(lb)
LEGEND
VFD — Variable Frequency Drive
AB
CORNER WEIGHT
(lb)
ft-in. ft-in. 1 2 3 4
5
⁄163-101⁄2961 858 1162 1302
13
⁄163-111⁄2973 868 1258 1409
3
⁄163-103⁄321007 915 1368 1505
Page 8
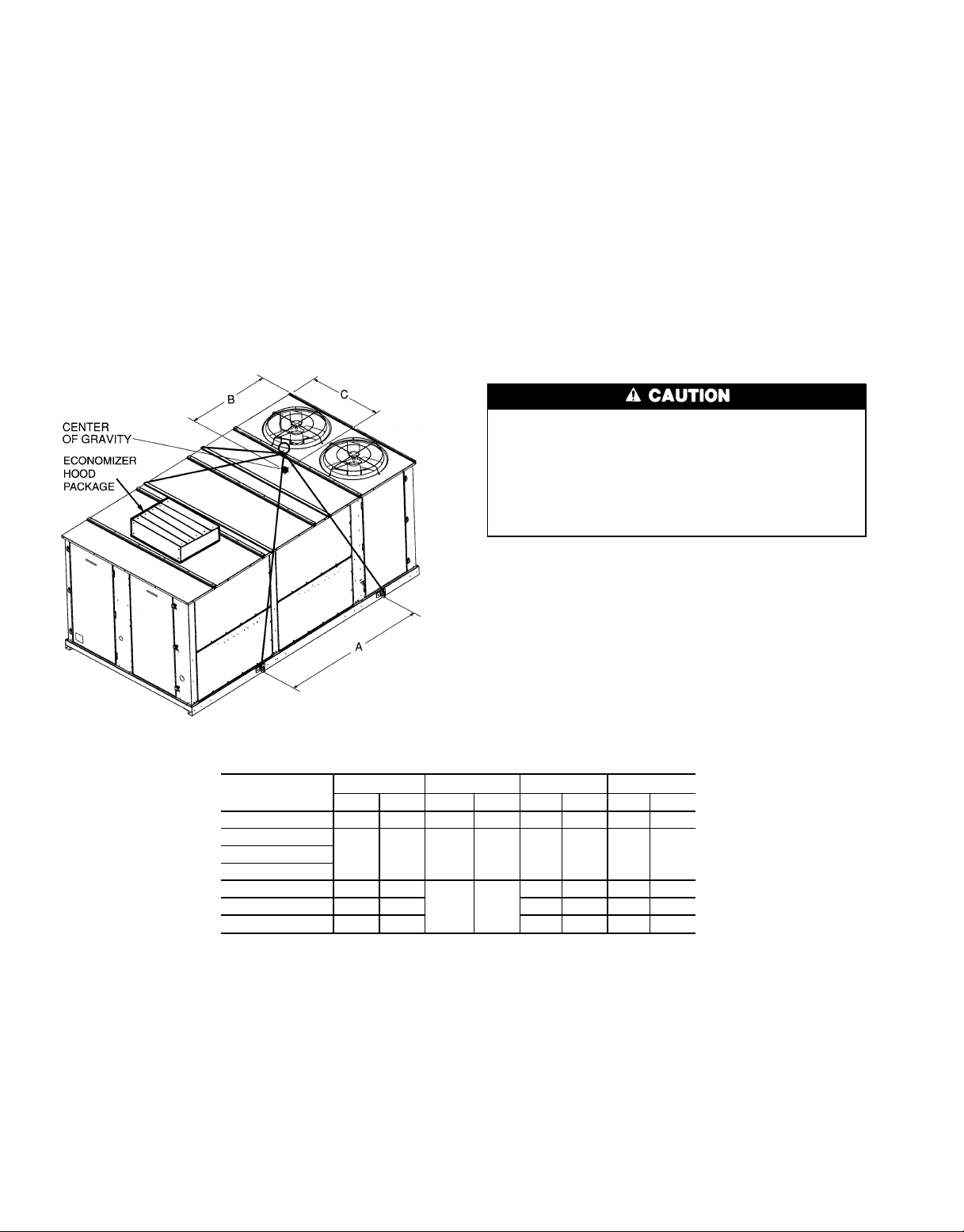
Step2 — Rig and Place Unit — Inspect unit for trans-
portation damage. File any claim with transportation agency.
Keep unit upright, and do not drop. Use spreader bars over
unit to prevent sling or cable damage. Rollers may be used
to move unit across a roof. Level by using unit frame as a
reference; leveling tolerance is shown in Fig. 1 and 2. See
Fig. 7 for additional information. Unit weight is shown in
Table 1.
NOTE: On retrofit jobs, ductwork may be attached to old
unit instead of roof curb. Be careful not to damage ductwork
when removing unit. Attach existing ductwork to roof curb
instead of unit.
Four lifting lugs are provided on the unit base rails as shown
in Fig. 7. Refer to rigging instructions on unit.
POSITIONING — Provide clearance around and above unit
for airflow, safety, and service access (Fig. 3-6).
Do not install unit in an indoor location. Do not locate air
inlets near exhaust vents or other sources of contaminated
air.
Although unit is weatherproof, guard against water from
higher level runoff and overhangs.
NOTICE TO RIGGERS:
ALL PANELS MUST BE IN PLACE
WHEN RIGGING.
NOTE: Rig with four cables and spread with two
92 in. (2337 mm) spreader bars. Maintain a distance of 74 in. (1880 mm) from top of unit to
eyehook.
NOTE:
Add 32 lb (14.5 kg) for domestic crating.
Add 312 lb (142 kg) for export crating (024-034 units).
Add 346 lb (157 kg) for export crating (038-048 units).
Add 250 lb (113 kg) for power exhaust.
Add 220 lb (100 kg) for copper condenser coil (024-034 units).
Add 285 lb (129 kg) for copper condenser coil (038-044 units).
Add 380 lb (172 kg) for copper condenser coil (048 unit).
MODEL
50EJ/EK/EW/EY
024 4016 1822 87.68 2227 71.4 1814 41.7 1059
028
034
038* 4282 1942
044 4508 2045 87.8 2230 46.5 1181
048* 4795 2175 86.2 2189 46.1 1171
*Sizes 038 and 048 are 50EJ,EW units only.
WEIGHT A B C
lb kg in. mm in. mm in. mm
4102 1860 87.68 2227 68.5 1740 43.6 1107030
91.3 2319 46.5 1181
150 3810
Fig. 7 — Rigging Label
8
Page 9
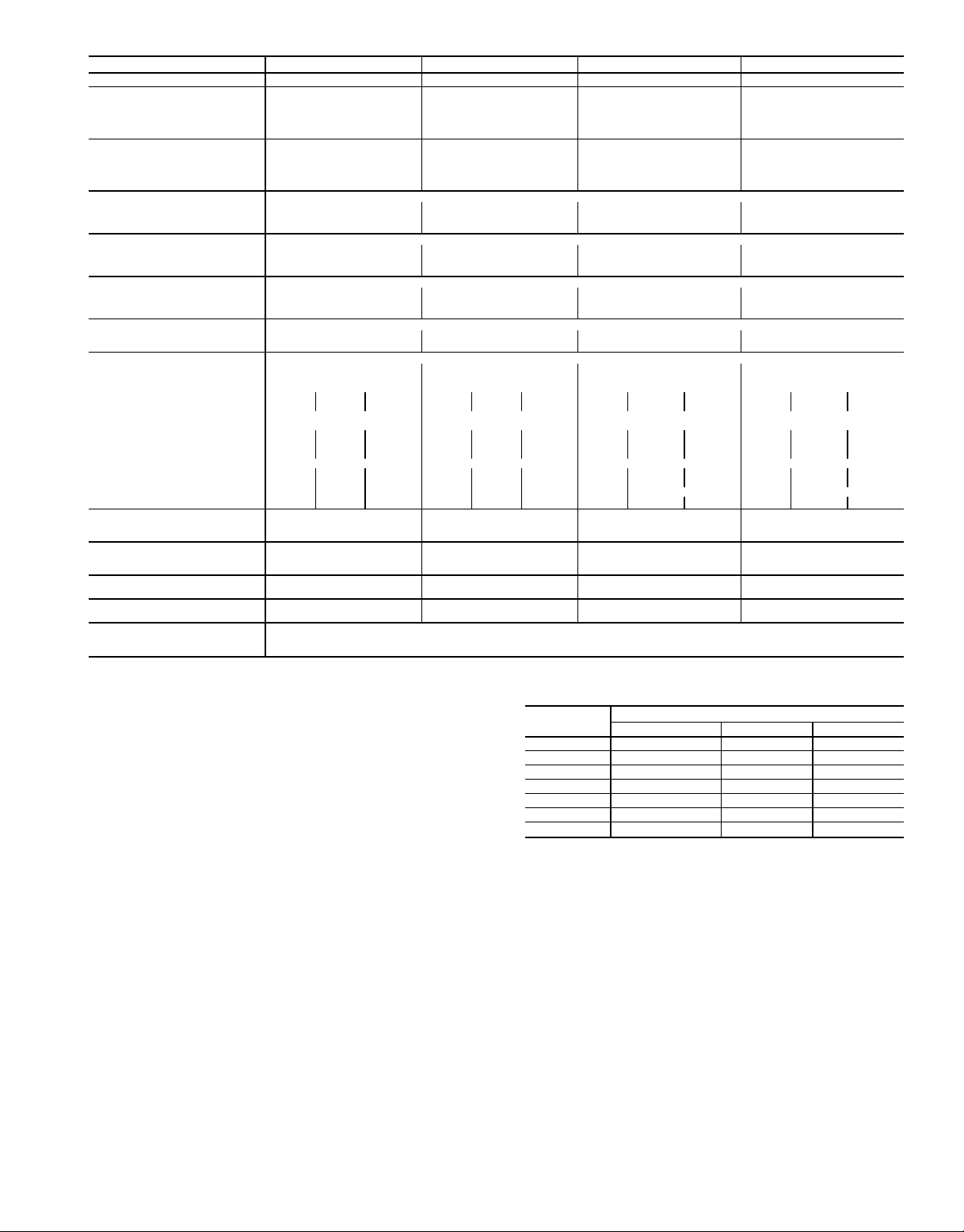
Table 1 — Physical Data
UNIT 50EJ,EK,EW,EY 024 028 030 034
NOMINAL CAPACITY (tons) 20 25 27 30
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb)*
Unit
Al/Al† 4016 4102 4102 4102
Al/Cu† 4236 4322 4322 4322
Roof Curb (14-in. curb) 365 365 365 365
COMPRESSOR
Type Ckt 1 06D328 06D328 06D537 06D537
Ckt 2 06D818 06D328 06D328 06D537
Number of Refrigerant Circuits 22 2 2
Oil (oz) (Ckt1, Ckt 2) 115, 88 115 ea. 115 ea. 115 ea.
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-22
Operating Charge (lb-oz)
Circuit 1** 25-0 25-0 25-0 25-0
Circuit 2 31-0 25-0 25-0 25-0
CONDENSER COIL Cross-Hatched
Quantity 11 1 1
Rows...Fins/in. 4...15 4...15 4...15 4...15
Total Face Area (sq ft) 33.3 33.3 33.3 33.3
CONDENSER FAN Propeller Type
Nominal Cfm 13,420 13,420 13,420 13,420
Quantity...Diameter (in.) 2...30 2...30 2...30 2...30
Motor Hp (1075 Rpm) 11 1 1
EVAPORATOR COIL Cross-Hatched
Rows...Fins/in. 4...15 4...15 4...15 4...15
Total Face Area (sq ft) 31.7 31.7 31.7 31.7
EVAPORATOR FAN Centrifugal Type
Quantity...Size (in.) 2...20x15 2...20x15 2...20x15 2..20x15
Type Drive Belt Belt Belt Belt
Nominal Cfm 8,000 10,000 11,000 12,000
Motor Hp 5 10†† 15 7.5 10†† 15 10 15†† 20 10 15†† 20
Motor Frame Size S184T S215T S254T S213T S215T S254T S215T S254T S256T S215T S254T S256T
Motor Bearing Type Ball Ball Ball Ball
Maximum Allowable Rpm 1200 1200 1200 1200
Motor Pulley Pitch Diameter 4.6 6.6 6.9 4.9 6.1 7.1 6.6 6.7 7.5 6.4 6.9 7.5
Nominal Motor Shaft Diameter (in.) 1
Fan Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 11.1 12.5 11.1 11.1 11.1 11.1 13.7 11.1 11.1 12.5 11.1 11.1
Nominal Fan Shaft Diameter (in.) 111⁄
Belt, Quantity...Type 1...BX59 1...BX60 1...5VX590 1...BX56 1...BX56 1...5VX590 1...BX62 1...5VX590 1...5VX600 1...BX60 1...5VX590 1...5VX600
Belt, Length (in.) 62 63 59 59 59 59 65 59 60 63 59 60
Pulley Center Line Distance (in.) 16.0-18.7 15.6-18.4 15.0-17.9 15.6-18.4 15.6-18.4 15.0-17.9 15.6-18.4 15.0-17.9 15.6-18.4 15.0-17.9
Factory Speed Setting (rpm) 725 924 1088 773 962 1119 843 1056 1182 896 1088 1182
HIGH-PRESSURE SWITCH (psig)
Cutout 426 426 426 426
Reset (Auto.) 320 320 320 320
LOW-PRESSURE SWITCH (psig)
Cutout 77 7 7
Reset (Auto.) 22 22 22 22
RETURN-AIR FILTERS
Quantity...Size (in.) 10...20x24x2 10...20x24x2 10...20x24x2 10...20x24x2
OUTDOOR-AIR FILTERS 8...16x25 8...16x25 8...16x25 8...16x25
Quantity...Size (in.) 4...20x25 4...20x25 4...20x25 4...20x25
POWER EXHAUST Direct Drive, 3-Speed, Single-Phase Motor (Factory-Wired For High Speed) and Forward Curved Fan
Motor, Quantity...Hp 4...1
Fan, Diameter...Width (in.) 11...10
1
⁄
8
13⁄
8
15⁄
8
13⁄
8
16
LEGEND
Al — Aluminum
Cu — Copper
*Weightof unit does not includevariable frequencydrive (VFD), barometric relief, orpower
exhaust. If a VAV unit (a VFD is installed), add the VFD weight in the table at right.
†Evaporator coil fin material/condenser coil fin material.
**Sizes 024-034: Circuit 1uses the lower portion ofcondenser coil,Circuit 2 uses the upper
portion. Sizes 038-048: Circuit 1 uses the left condenser coil, Circuit 2 the right.All units
have intertwined evaporator coils.
††Motor and drive shown will deliver approximately 2.5 in. wg net external static. For more
drive information, see Table 2.
3
⁄89 Copper Tubes, Aluminum Lanced or Copper Fins
3
⁄89 Copper Tubes, Aluminum or Copper Plate Fins, Intertwined Circuits
13⁄
8
15⁄
8
13⁄
8
15⁄
8
15⁄
8
111⁄
16
NOTES:
1. See Table 2 for evaporator fan motor data.
2. Sizes 038 and 048 are 50EJ,EW units only.
VFD
(Hp)
111⁄
16
VFD WEIGHTS (lb)
208/230 v 460 v 575 v
5 20 22 60
7.5 51 37 64
10 51 61 64
15 61 63 109
20 63 111 109
25 105 112 174
30 172 118 180
13⁄
8
15⁄
8
15⁄
8
111⁄
16
9
Page 10
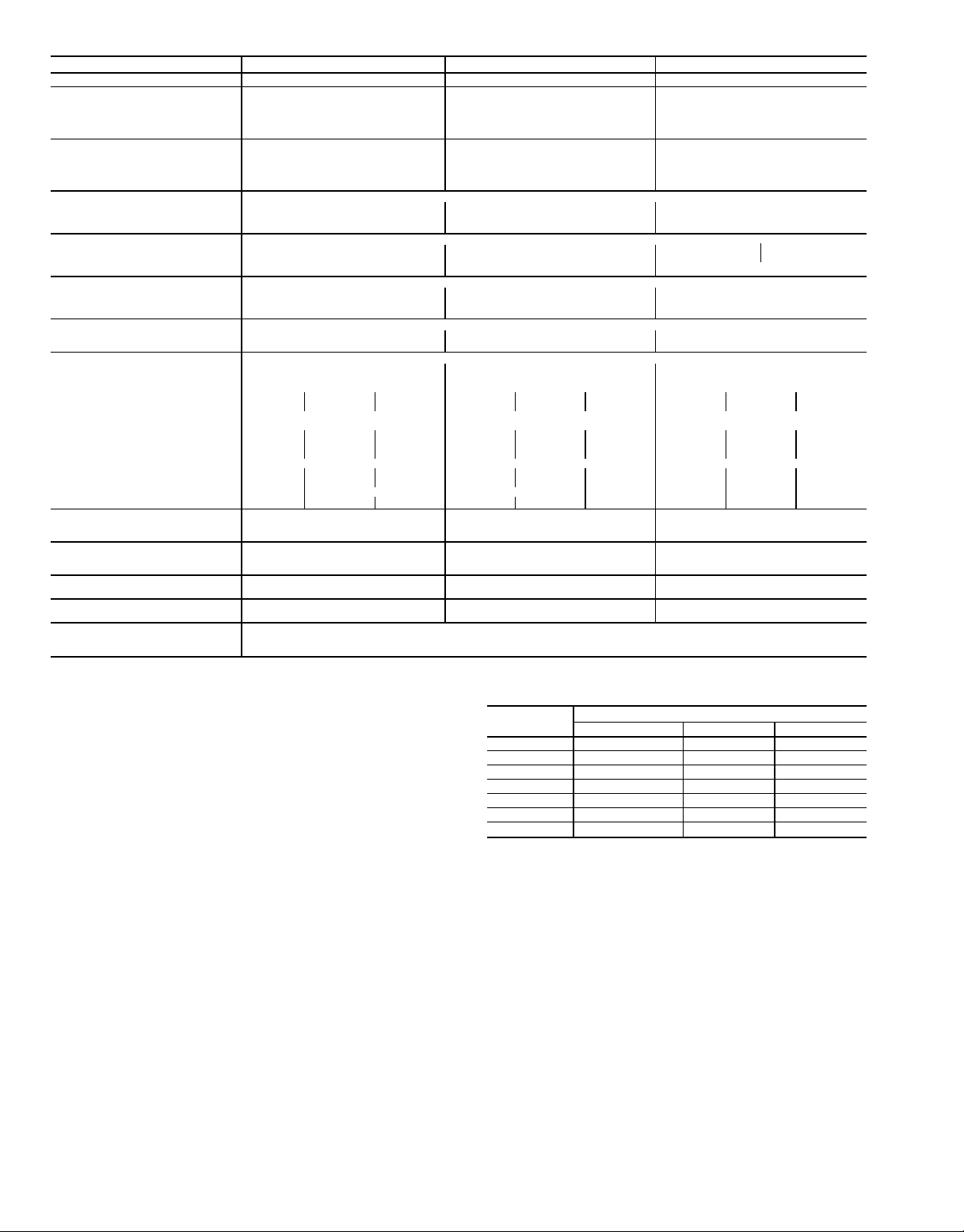
Table 1 — Physical Data (cont)
UNIT 50EJ,EK,EW,EY 038 044 048
NOMINAL CAPACITY (tons) 35 40 45
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb)*
Unit
Al/Al† 4282 4508 4795
Al/Cu† 4567 4793 5175
Roof Curb (14-in. curb) 410 410 410
COMPRESSOR
Type Ckt 1 06D537 06EA250 06EA265
Ckt 2 06D537 06EA250 06EA250
Number of Refrigerant Circuits 22 2
Oil (oz) (Ckt1, Ckt 2) 115 ea. 224 ea. 304, 224
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-22
Operating Charge (lb-oz)
Circuit 1** 34-0 35-0 41-0
Circuit 2 34-0 35-0 41-0
CONDENSER COIL Cross-Hatched
Quantity 2211
Rows...Fins/in. 3...15 3...15 4...15 3...15
Total Face Area (sq ft) 58.3 58.3 66.7
CONDENSER FAN Propeller Type
Nominal Cfm 27,064 27,064 27,064
Quantity...Diameter (in.) 4...30 4...30 4...30
Motor Hp (1075 Rpm) 11 1
EVAPORATOR COIL Cross-Hatched
Rows...Fins/in. 3...15 3...15 4...15
Total Face Area (sq ft) 34.7 34.7 34.7
EVAPORATOR FAN Centrifugal Type
Quantity...Size (in.) 2..20x15 2...20x15 2...20x15
Type Drive Belt Belt Belt
Nominal Cfm 14,000 16,000 18,000
Motor Hp 10 15†† 20 15 20†† 25 20 25†† 30
Motor Frame Size S215T S254T S256T S254T S256T S284T S256T S284T S286T
Motor Bearing Type Ball Ball Ball
Maximum Allowable Rpm 1200 1200 1200
Motor Pulley Pitch Diameter 4.1 6.9 7.5 6.9 8.1 9.1 5.3 5.9 7.5
Nominal Motor Shaft Diameter (in.) 1
Fan Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 9.1 12.5 12.5 12.5 13.7 13.7 9.1 9.1 11.1
Nominal Fan Shaft Diameter (in.) 111⁄
Belt, Quantity...Type 1...BX51 1...5VX630 1...5VX650 1...5VX630 1...5VX670 2...5VX680 1...5VX550 2...5VX560 2...5VX610
Belt, Length (in.) 54 63 65 63 67 68 55 56 59
Pulley Center Line Distance (in.) 15.6-18.4 15.0-17.9 15.0-17.9 14.6-17.6 15.0-17.9 14.6-17.6 14.6-17.6
Factory Speed Setting (rpm) 788 966 1050 1066 1035 1162 1019 1135 1182
HIGH-PRESSURE SWITCH (psig)
Cutout 426 426 426
Reset (Auto.) 320 320 320
LOW-PRESSURE SWITCH (psig)
Cutout 77 7
Reset (Auto.) 22 22 22
RETURN-AIR FILTERS
Quantity...Size (in.) 10...20x24x2 10...20x24x2 10..20x24x2
OUTDOOR-AIR FILTERS 8...16x25 8...16x25 8...16x25
Quantity...Size (in.) 4...20x25 4...20x25 4...20x25
POWER EXHAUST Direct Drive, 3-Speed, Single-Phase Motor (Factory-Wired For High Speed) and Forward Curved Fan
Motor, Quantity...Hp 4...1
Fan, Diameter...Width (in.) 11...10
3
⁄
8
15⁄
8
16
15⁄
8
LEGEND
Al — Aluminum
Cu — Copper
*Weightof unit does not includevariable frequencydrive (VFD), barometric relief, orpower
exhaust. If a VAV unit (a VFD is installed), add the VFD weight in the table at right.
†Evaporator coil fin material/condenser coil fin material.
**Sizes 024-034: Circuit 1uses the lower portion ofcondenser coil,Circuit 2 uses the upper
portion. Sizes 038-048: Circuit 1 uses the left condenser coil, Circuit 2 the right.All units
have intertwined evaporator coils.
††Motor and drive shown will deliver approximately 2.5 in. wg net external static. For more
drive information, see Table 2.
3
⁄89 Copper Tubes, Aluminum Lanced or Copper Fins
3
⁄89 Copper Tubes, Aluminum or Copper Plate Fins, Intertwined Circuits
15⁄
8
NOTES:
1. See Table 2 for optional evaporator fan motor data.
2. Sizes 038 and 048 are 50EJ,EW units only.
VFD
(Hp)
111⁄
15⁄
8
16
11⁄
8
15⁄
8
VFD WEIGHTS (lb)
208/230 v 460 v 575 v
5 20 22 60
7.5 51 37 64
10 51 61 64
15 61 63 109
20 63 111 109
25 105 112 174
30 172 118 180
111⁄
17⁄
8
16
17⁄
8
10
Page 11
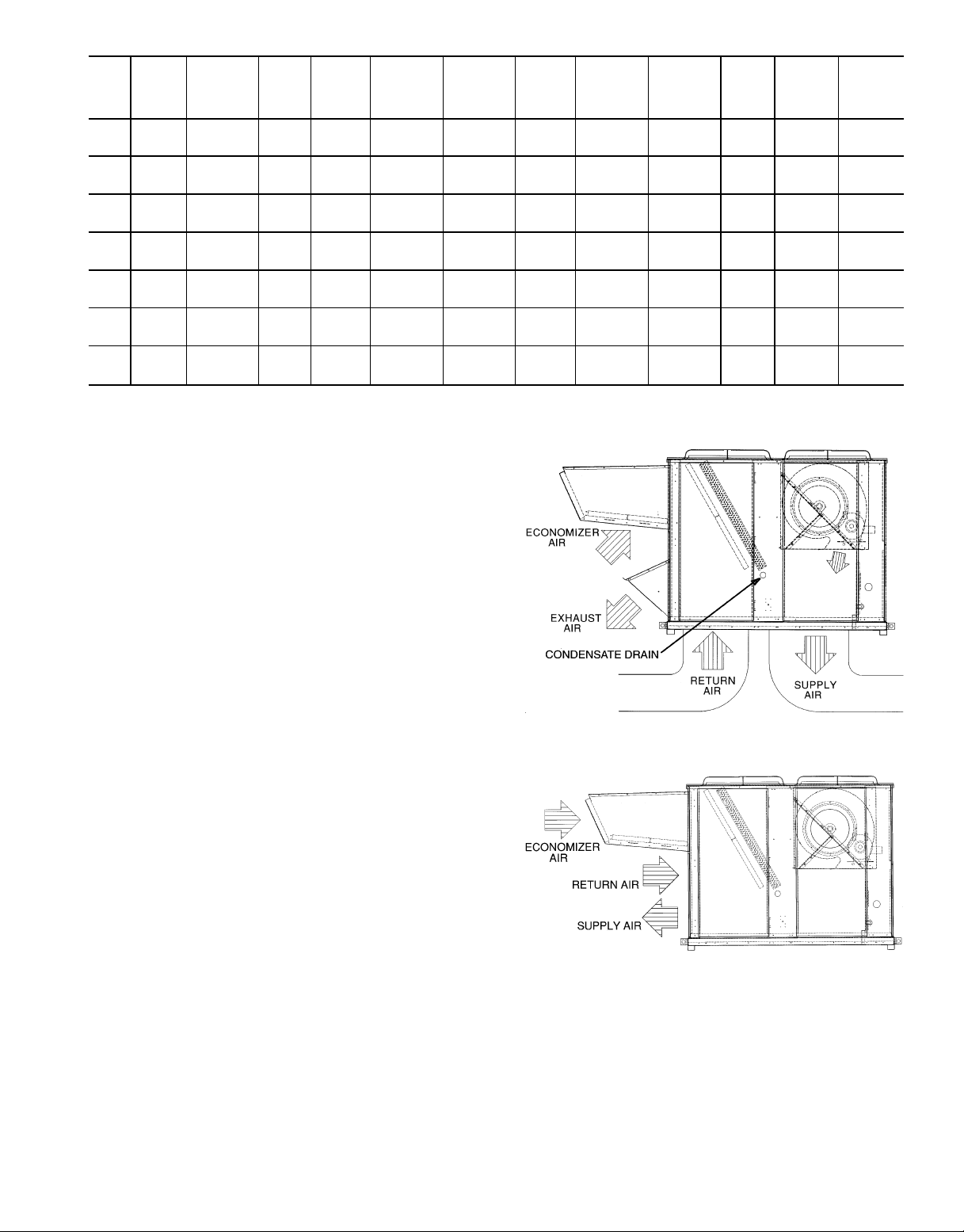
Table 2 — Evaporator Fan Motor Data
UNIT
MOTOR
SIZE
024
028
030
034
038
044
048
NOTE: Motor shaft speed is 1750 rpm. The fan shaft diameter is 1
HP
10 1.38 924 BK72 6.6 None-1.375 1B5V124 12.5 B-1.6875 BX60 63 7.05
15 1.62 1088 1B5V68 6.9 B-1.625 1B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 5VX590 59 9.38
7.5 1.38 773 BK55H 4.9 H-1.375 1B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 BX56 59 6.87
10 1.38 962 BK67H 6.1 H-1.375 1B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 BX56 59 7.26
15 1.62 1119 1B5V70 7.1 B-1.625 1B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 5VX590 59 9.17
10 1.38 843 BK72 6.6 None-1.375 1B5V136 13.7 B-1.6875 BX62 65 6.96
15 1.62 1056 1B5V66 6.7 B-1.625 1B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 5VX590 59 9.60
20 1.62 1182 1B5V74 7.5 B-1.625 1B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 5VX600 60 11.67
10 1.38 896 BK70H 6.4 H-1.375 1B5V124 12.5 B-1.6875 BX60 63 7.20
15 1.62 1088 1B5V68 6.9 B-1.625 1B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 5VX590 59 9.38
20 1.62 1182 1B5V74 7.5 B-1.625 1B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 5VX600 60 11.17
10 1.38 788 2BK47 4.1 None-1.375 2B5V90 9.1 B-1.6875 BX51 54 5.49
15 1.62 966 1B5V68 6.9 B-1.625 1B5V124 12.5 B-1.6875 5VX630 63 9.22
20 1.62 1050 1B5V74 7.5 B-1.625 1B5V124 12.5 B-1.6875 5VX650 65 10.02
15 1.62 966 1B5V68 6.9 B-1.625 1B5V124 12.5 B-1.6875 5VX630 63 9.54
20 1.62 1035 1B5V80 8.1 B-1.625 1B5V136 13.7 B-1.6875 5VX670 67 10.37
25 1.88 1162 1B5V90 9.1 B-1.875 1B5V136 13.7 B-1.6875 5VX680 68 10.88
20 1.62 1019 2B5V52 5.3 B-1.625 2B5V90 9.1 B-1.6875 5VX550 55 7.93
25 1.88 1135 2B5V58 5.9 B-1.875 2B5V90 9.1 B-1.6875 5VX560 56 8.66
30 1.88 1182 2B5V76 7.5 B-1.875 2B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 5VX610 59 9.07
MOTOR
SHAFT
DIAMETER
(in.)
5 1.12 725 BK52 4.6 None-1.125 1B5V110 11.1 B-1.6875 BX59 62 5.02
FAN
SHAFT
SPEED
(rpm)
MOTOR
SHEAVE
MOTOR
SHEAVE
PITCH
DIAMETER
(in.)
11
BUSHING
DIAMETER
⁄16inches.
ROOF MOUNT — Check building codes for weight distribution requirements.
(in.)
FAN
SHEAVE
FAN
SHEAVE
PITCH
DIAMETER
(in.)
BUSHING
DIAMETER
(in.)
BELT
OUTSIDE
BELT
LENGTH
BELT
TENSION
(Lb @
.24 in.)
Step 3 — Field Fabricate Ductwork — Secure all
ducts to building structure. Use flexible duct connectors between unit and ducts as required. Insulate and weatherproof
all external ductwork, joints, and roof openings with counter
flashing and mastic in accordance with applicable codes.
Ducts passing through an unconditioned space must be
insulated and covered with a vapor barrier.
To attach ductwork to roof curb, insert ductwork approximately 10 to 11 in. up into the curb. Connect ductwork to
14-gage roof curb material using sheet metal screw driven
from inside the duct.
The units with electric heat require a 1-in. clearance for
the first 24 in. of ductwork.
NOTE: A 90-degree elbow must be provided in the ductwork to comply with UL (Underwriters’ Laboratories) codes
for use with electric heat.
Outlet grilles must not lie directly below unit discharge.
Step 4 — Make Unit Duct Connections
50EJ,EK UNITS — Unit is shipped for through-the-bottom
duct connections. Ductwork openings are shown in Fig. 3
and 4. Attach all ductwork to roof curb. Air distribution
is shown in Fig. 8. Refer to installation instructions shipped
with accessory roof curb for more information.
50EW,EY UNITS — Remove shipping covers from supply
and return air openings. Attach field-supplied ductwork to
unit. Use a single duct over both return openings and a single
duct over both supply openings. See Fig. 5 and 6 for duct
opening dimensions. Secure all ducts to the building structure. See Fig. 9. Use flexible duct connectors between unit
and ducts as required.
Install accessory barometric relief or power exhaust in the
field-fabricated return ductwork. Refer to Position Power
Exhaust/Barometric Relief Damper Hood Section on
page 29 for more information.
Step5—TrapCondensate Drain — See Fig. 3-6
and 10 for drain location. Condensate drain is open to the
atmosphere and must be trapped. Install a trapped drain at
Fig. 8 — Air Distribution — Thru-the-Bottom
Fig. 9 — Air Distribution — Thru-the-Side
the drain location. One 1-in. FPT coupling is provided inside unit evaporator section for condensate drain connection. A trap at least 4-in. deep must be used. Trap must be
installed to prevent freeze-up.
Condensate pans are sloped so that water will completely
drain from the condensate pan to comply with indoor air quality guidelines.
11
Page 12
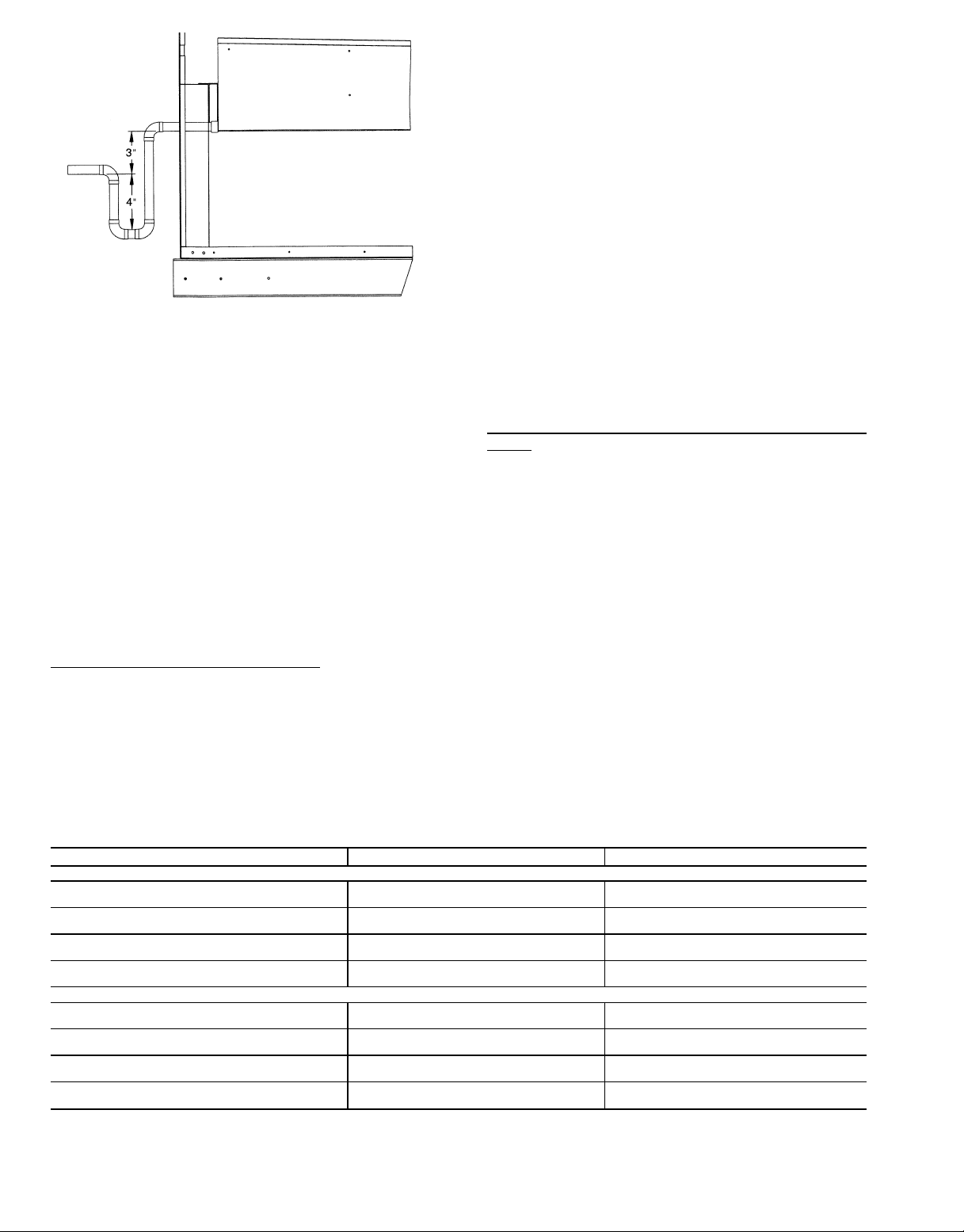
Fig. 10 — Condensate Drain Connections
(Typical Roof Curb or Slab Mount Shown)
Step 6 — Controls Options — The control options
that the units can provide are based on the following parameters: CV (constant volume) or VAV (variable air volume)
operation; stand-alone unit with field-supplied sensors installed (CV or VAV); as a system via the Carrier Comfort
System (TEMP or VVT); optional electronic expansion board
installed (CV or VAV); linked to the Carrier Comfort Network; and availability of a computer and software (Comfort
Works, Building Supervisor, and Service Tool) to access the
base control board. See Table 3.
NOTE: Access to the base control board allows unit occupancy schedules, unit timeclock, and various set points to be
changed from their factory-defined default settings.
CONSTANT VOLUME APPLICATIONS — The standard
CV unit is capable of being operated with either a Carrierapproved thermostat or a field-supplied sensor. (See Price
Pages for ordering information.)
Features with Thermostat Control of Unit
• two-stage heating (if installed)
• two-stage cooling
• control of unit using Y1, Y2, W1, W2, and G thermostat
inputs
• control of the indoor fan
• outdoor air temperature/supply air temperature monitoring
• control of an outdoor air condenser fan based on outdoor
air temperature
• control of modulating economizer damper to provide free
cooling when outdoor conditions are suitable, using supply air temperature as a control point
• control of the economizer damper and indoor fan to obtain
unoccupied free cooling
• provide power exhaust output to an external power exhaust controller
• support a field test for field checkout
• control of 2 stages of CV power exhaust
• compressor Time Guardt (power up and minimum offand
on times)
Additional features are provided by accessing the standard unit control board via software with a computer. These
features are:
• electronic expansion board features (if installed)
• compressor lockout during low supply air temperature
• control board diagnostics
• ability to change supply air set point (economizer control)
• ability to change high outdoor air temperature lockout set
point (economizer control)
• ability to change power exhaust set points
NOTE: A CV unit without a thermostat requires a field-
supplied sensor for operation.
Features with Sensor Control of Unit (Stand-Alone Appli-
cations — Unit control is limited to CV unoccupied default
set points, 90 F for cooling, 55 F for heating. There are
3 sensor options available:
• T-57 sensor will monitor room temperature
• T-55 sensor will monitor room temperature and provide
unoccupied override capability (1 hour)
• T-56 sensor will monitor room temperature, provide un-
occupied override capability (1 hour), and provide a temperature offset of 5° F.
Standard features are:
• support of remote occupied/unoccupied input to start and
stop the unit
• cooling capacity control of 3 stages using economizer and
2 compressors to maintain space temperature to an occupied or unoccupied set point
• enable heating (if installed) or cooling during unoccupied
periods as required to maintain space temperature within
the unoccupied set points
• adjustment of space temperature set points of ± 5° F when
using a T-56 sensor
Table 3 — Controls Options and Configurations (Non-Thermostat Applications)
UNIT CONFIGURATION DEFAULT COOLING DEFAULT HEATING
UNITS RUNNING VERSION 1.0 UNIT CONTROL SOFTWARE
CV or VAV Unit with SPT Sensor
CV Unit with SPT Sensor and Remote
Start/Stop Switch
VAV Unit Remote Start/Switch Only
VAV Unit with SPT Sensor and Remote
Start/Stop Switch
UNITS RUNNING VERSION 2.0 UNIT CONTROL SOFTWARE
CV or VAV Unit with SPT Sensor
CV Unit with SPT Sensor and Remote
Start/Stop Switch
VAV Unit Remote Start/Stop Switch Only
VAV Unit with SPT Sensor and Remote
Start/Stop Switch
CV — Constant Volume SAT — Supply-Air Temperature
NA — Not Available SPT — Space Temperature
RAT — Return-Air Temperature VAV — Variable Air Volume
LEGEND
Unoccupied Cooling — 90 F (SPT)
Occupied Cooling — NA
Unoccupied Cooling — 90 F (SPT)
Occupied Cooling — 78 F (SPT)
Unoccupied Cooling — NA
Occupied Cooling — 55 F (SAT)
Unoccupied Cooling — 90 F (SPT)
Occupied Cooling — 55 F (SAT)
Unoccupied Cooling — 90 F (SPT)
Occupied Cooling — NA
Unoccupied Cooling — 90 F (SPT)
Occupied Cooling — 78 F (SPT)
Unoccupied Cooling — 90 F (RAT)
Occupied Cooling — 55 F (SAT)
Unoccupied Cooling — 90 F (SPT)
Occupied Cooling — 55 F (SAT)
Unoccupied Heating — 55 F (SPT)
Occupied Heating — NA
Unoccupied Heating — 55 F (SPT)
Occupied Heating — 68 F (SPT)
Unoccupied Heating — NA
Occupied Heating — NA
Unoccupied Heating — 55 F (SPT)
Occupied Heating — NA
Unoccupied Heating — 55 F (SPT)
Occupied Heating — NA
Unoccupied Heating — 55 F (SPT)
Occupied Heating — 68 F (SPT)
Unoccupied Heating — 55 F (RAT)
Occupied Heating — 68 F (RAT)*
Unoccupied Heating — 55 F (SPT)
Occupied Heating — 68 F (RAT)*
*With DIP Switch No. 5 configured to OPEN (Occupied Heat Enabled).
NOTE: Space temperature sensor and remote stop/switch are field-supplied.
12
Page 13
Features with sensor control of unit with computer access
are:
• 365 day timeclock with backup (supports minute, hour,
day of week, date, month, and year)
• daylight savings time function
• occupancy control with 8 periods for unit operation
• holiday table containing up to 18 holiday schedules
• ability to initiate timed override from T-55 or T-56 sensors
• ability to use multiple space temperature sensors to average the space temperature
• supply air temperature reset for the supply air temperature
set point
• temperature compensated start to calculate early start times
before occupancy
• access to the Display, Maintenance, Configuration, Service, and Set Point data table through network software
When the unit is equipped with a field-supplied space temperature sensor and a remote contact closure (remote start/
stop) on the base control board, the occupied default set points
will monitor unit operation. The occupied default set points
are 78 F cooling and 68 F heating (if electric heat is installed). See Fig. 11 for remote start/stop wiring.
NOTE: For units which have not had the base unit control
board accessed via software to set an occupancy schedule,
the remote start/stop closure will allow the unit to operate in
the pre-configured occupied default set points (based on returnair temperature) of 78 F cooling and 68 F heating. Without
this feature, the unit will control to the unoccupied default
set points of 90 F cooling and 55 F heating (if electric heat
is installed).
An electronic expansion board may be field-installed to
provide the following features:
• control of modulating economizer damper to maintain
indoor air quality (IAQ) when outdoor conditions are
suitable
• provide discrete inputs for fan status, filter status, field-
applied status, and demand limit
• provide an output for the external alarm light indicator
When the unit is connected to the CCN (Carrier Comfort
Network), the following expansion board features can be
utilized.
• perform Demand Limit functions based on CCN loadshed
commands or the state of the discrete input
• alarm monitoring of all key parameters
• CCN protocol
• provides power exhaust fire outputs for direct control of
modulated power exhaust stages during fire or smoke modes
• smoke control modes including evacuation, smoke purge,
pressurization, and fire shutdown (modulating power exhaust required)
• provides CCN IAQ participation
See Carrier TEMP or VVTt (Variable Volume and Temperature) literature for complete TEMP (single zone) or VVT
(multi-zone) application information.
or during unexpected power outages. For complete Carrier
Comfort System (CCS) or Carrier Comfort Network (CCN)
features and benefits, refer to the product literature.
VARIABLE AIR VOLUME (VAV) APPLICATIONS
Features with Stand-Alone Applications — A VAV unit is
capable of providing unoccupied cooling controlling to a
90 F return-air temperature utilizing the factory-supplied returnair thermistor located below the return-air damper in the returnair section for unit control. The unit will provide unoccupied
heating (if electric heat is installed) controlling to a 55 F
return-air temperature. Also provided is a morning warm-up
which is initiated by the Occupied mode (if electric heat is
installed) and continues until the return-air temperature rises
to 68 F. The unit will provide occupied cooling with a default temperature of 55 F for the supply air. The supply-air
temperature is measured by the supply-air thermistor, located in the indoor fan compartment.
Standard features of a VAV unit with a remote start/stop
switch are:
• control of an outdoor condenser fan based upon outdoor
air temperature
• control of modulating economizer to provide free cooling
when outdoor conditions are suitable, using supply air temperature as a set point
• support of remote occupied/unoccupied input to start or
stop the unit
• provide power exhaust output to an external power exhaust controller
• support supply air temperature reset to offset supply air
set point
• support a field test for field check out
• support linkage to DAV systems
• cooling capacity control of 6 stages plus economizer with
compressors and unloaders to maintain supply air temperature set point during occupied periods
• control of one stage of heat to maintain supply air temperature at supply air set point during occupied periods
• provide a variable frequency drive high voltage relay output to enable VFD
• control of heat interlock relay
With the addition of a remote start/stop switch heating or
cooling is enabled during unoccupied periods as required to
maintain space temperature to within unoccupied set points.
Features with Sensor Control of Unit (Network Applications) — The base control board provides, as standard, a connection for use with a Carrier VVT system and can also be
integrated into a Carrier Comfort Network.
When the unit is accessed via a PC equipped with Comfort Works, Building Supervisor, or Service Tool, the following features can be accessed:
• on-board timeclock can be programmed
• occupancy schedules can be programmed
• unit set points can be changed
• alarms can be monitored
This access is available on the base control board via a
RJ-11 phone jack or a 3-wire connection to the communication bus. See Fig. 12. The timeclock has a 10-hour minimum
back-up time to provide for unit power off for servicing unit
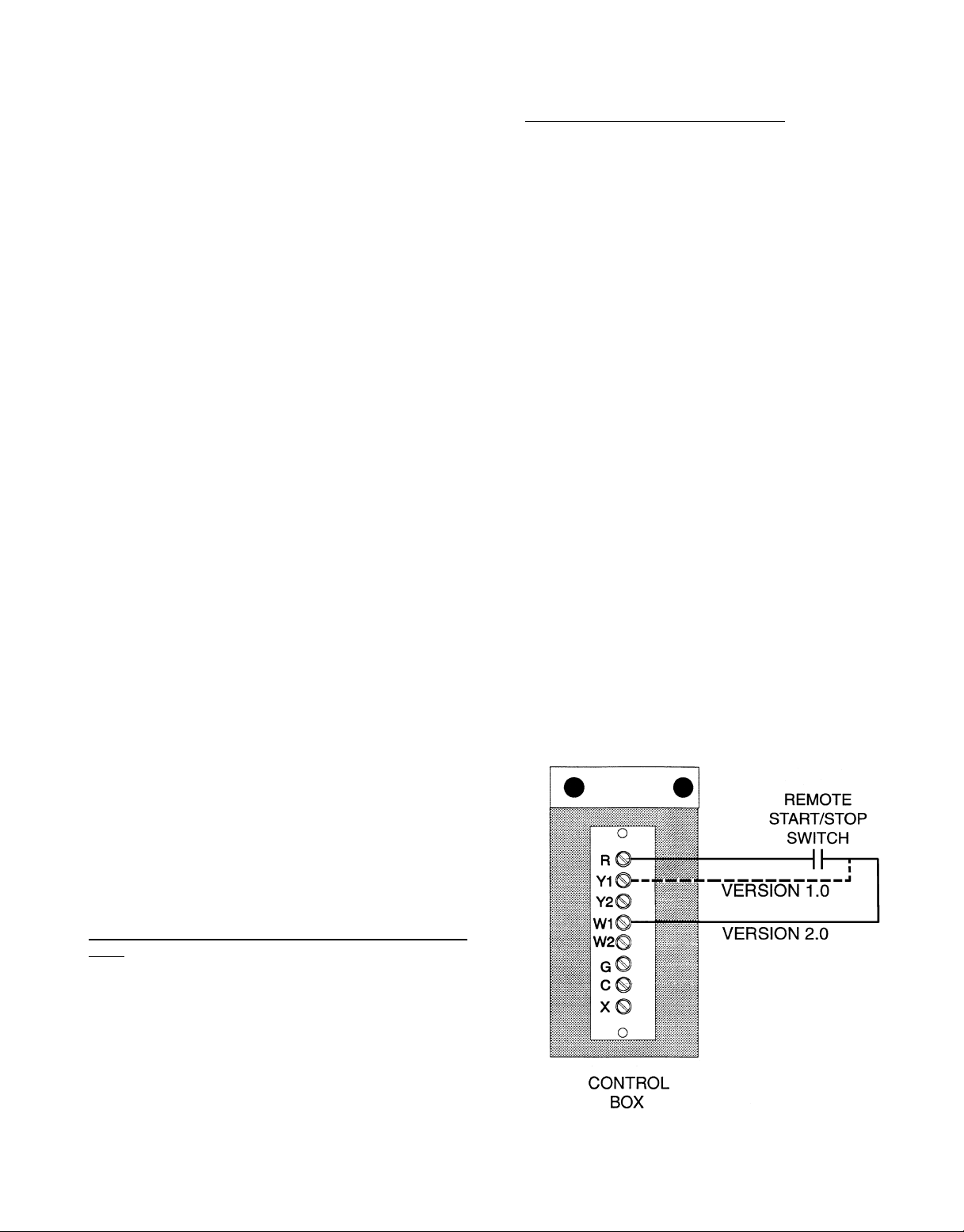
NOTE: On units running Version 1.0 of the Unit Control Software, the remote
start/stop switch is connected to R and Y1. On units running Version 2.0 of the
Unit Control Software, the remote start/stop switch is connected to R and W1.
Fig. 11 — Field Control Remote Start/Stop
13
Page 14
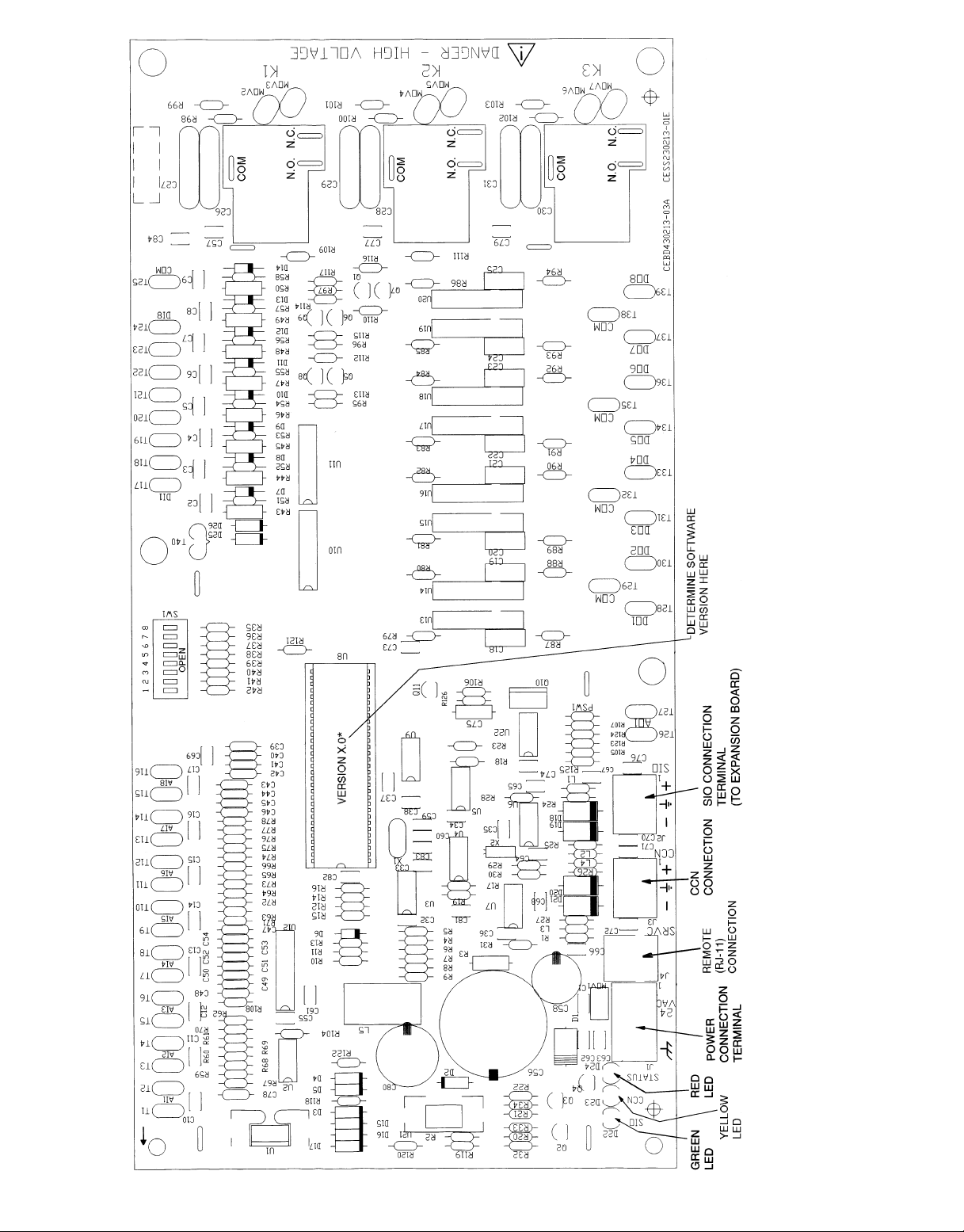
LEGEND
CCN — Carrier Comfort Network R—Relay
COM — Common SIO — Serial Input/Output
D—Diode SW — Switch
N.C. — Normally Closed T—Terminal
N.O. — Normally Open
*Where X is the unit control software version (1 or 2).
Fig. 12 — Control Board Diagram
14
Page 15
For units running Version1.0 of the unit control software,
network access software is required to enable occupied heating. For units running Version 2.0 of the unit control software, occupied heating is enabled or disabled by the position of DIP switch no. 5.
Additional features may be provided with electronic access to Unit Control Board. These features are:
• control board diagnostics
• compressor time guard override (power up, minimum off
and on times)
• compressor lockout during low supply-air temperature
• electronic expansion board features (if installed)
• field test capability
• control of the economizer damper and indoor fan to op-
tion unoccupied free cooling
• 365 day timeclock with backup (supports minute, hour, day,
month, and year)
• holiday table containing up to 18 holiday schedules
• occupancy control with 8 periods for unit operation
• support a set of display, maintenance, configuration, serv-
ice, and set point data tables for interface with Building
Supervisor, Comfort Works, or Service Tool
When a VAV unit with a space temperature sensor is accessed via a computer, the following additional features are
available:
• ability to initiate timed override from T-55 sensors
• ability to use multiple space temperature sensors to aver-
age space temperature
• temperature compensated start to calculate early start time
before occupancy
• provide space temperature reset to reset the supply air set
point upward when the temperature falls below the occupied cooling set point
An electronic expansion board may be field-installed to
provide the following features:
• fan status
• filter status
• field-applied status
• demand limiting
• IAQ sensor
• OAQ sensor
• alarm light
When the unit is connected to the CCN (Carrier Comfort
Network), the following expansion board features can be
utilized:
• CCN IAQ (indoor air quality) participation
• CCN OAQ (outdoor air quality) participation
• CCN demand limit participation
• fire unit shutdown
• fire pressurization
• fire evacuation
• fire smoke purge
• modulated power exhaust override
Afield-supplied space temperature sensor can be added to
provide the following:
• T-57 sensor will monitor room temperature
• T-55 sensor will monitor room temperature and provide
unoccupied override capability (1 hour)
When the unit is equipped with a field-supplied space temperature sensor and a remote contact closure (remote start/
stop), the occupied default set points will monitor unit operation. The occupied default set points are 55 F (supply air)
cooling and 68 F (space temperature) heating (if electric heat
is installed). See Fig. 11 for remote start/stop wiring.
NOTE: For units without a space temperature sensor and which
have not had the base unit control board accessed via software to set an occupancy schedule, the remote start/stop closure will allow the unit to operate in the pre-configured occupied default set points of 55 F (supply-air temperature)
cooling and 68 F (return-air temperature) heating. Without
an occupancy schedule, the unit will control to the unoccupied default set points of 90 F (return air) cooling and 55 F
(return air) heating (if electric heat is installed).
Features with Network Applications — The base control board
provides, as standard, a connection for use with a Carrier
Comfort System and can also be integrated into a Carrier
Comfort Network. When the unit is accessed via a PC equipped
with Comfort Works, Building Supervisor, or Service Tool
software, the following features can be accessed:
• on-board timeclock can be programmed
• occupancy schedules can be programmed
• unit set points can be changed
• alarms can be monitored
This access is available on the base control board via a
RJ-11 phone jack or a 3-wire connection to the communication bus. See Fig. 12. The timeclock has a 10-hour minimum back-up time to provide for unit power off for servicing unit or during unexpected power outages. For complete
Carrier Comfort System (CCS) or Carrier Comfort Network
(CCN) features and benefits, refer to the product literature.
Step 7 — Make Electrical Connections
POWER WIRING — Units are factory wired for the voltage
shown on the unit nameplate. The main terminal block is
suitable for use with aluminum or copper wires and is sized
for single-point electric heat.
When installing units, provide a disconnect per NEC (Na-
tional Electrical Code) of adequate size (MOCP [maximum
overcurrent protection] of unit is on the informative plate).
All field wiring must comply with NEC and all local codes.
Size wire based on MCA (minimum circuit amps) on the
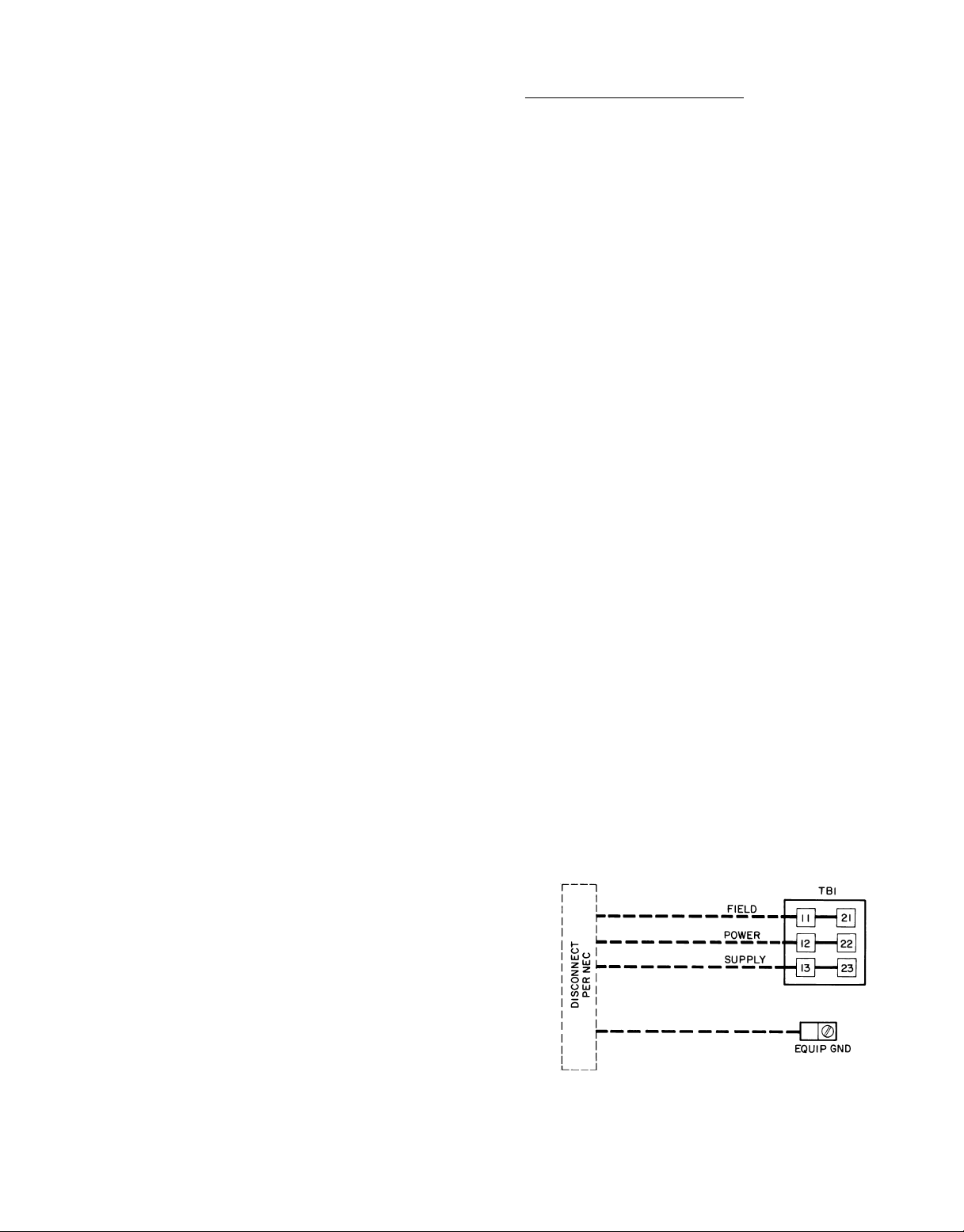
unit informative plate. See Fig. 13 for power wiring connections to the unit power terminal block and equipment ground.
The main power terminal block is suitable for use with
aluminum or copper wire. See Fig. 13. Units have circuit
breakers for compressors, fan motors, and control circuit. If
required by local codes, provide an additional disconnect,
per NEC and local codes requirements, of adequate size
(Table 4). Whenever external electrical sources are used, unit
must be electrically grounded in accordance with local codes,
or in absence of local codes, with NEC, ANSI (American
National Standards Institute) C1-latest year.
All field wiring must comply with NEC and local code
requirements.
FIELD POWER SUPPLY — Unit is factory wired for volt-
age shown on nameplate. See Table 4 for electrical data.
Field wiring can be brought into the unit from bottom
(through basepan and roof curb) or through side of unit (corner post next to control box).
EQUIP — Equipment
GND — Ground
NEC — National Electrical Code
TB — Terminal Block
NOTE: Maximum wire size for TB1 is 500 MCM.
Fig. 13 — Field Power Wiring Connections
15
LEGEND
Page 16
A31⁄2-in. NPT coupling for field power wiring and a
3
⁄4-in. NPT coupling for 24-v control wiring are provided in
basepan. In the side post, there are two 21⁄2-in. (024-034) or
3-in. (038-048) knockouts for the field power wiring. See
Fig. 3-6. If control wiring is to be brought in through the
side of unit, a7⁄8-in. diameter hole is provided in the condenser side post next to the control box.
If disconnect box is mounted to corner post, be careful
not to drill any screws into the condenser coil.
Routing Through Bottom of Unit — If wiring is brought in
through bottom of unit, use field-supplied watertight conduit
to run power wiring from basepan out through bottom
31⁄2-in. hole to the disconnect box and back into unit to the
main control box.
1
Use strain relief going into control box through 2
⁄2-in.
diameter hole provided. After wires are in unit control box,
connect to power terminal block (see Power Wiring section
on this page 15).
Low-voltage wiring must be run in watertight conduit from
the basepan to control box and through
7
⁄8-in. diameter hole
provided in bottom of unit control box. Field-supplied strain
relief must be used going into the box. After wiring is in
control box, make connections to proper terminals on terminal blocks (see Field Control Wiringsection on this page).
Install conduit connector in unit basepan or side panel openings provided. Route power and ground lines through connector to connections in unit control box as shown on unit
wiring diagram and Fig. 13.
Routing Through Side of Unit — Route power wiring in
field-supplied watertight conduit into unit through 21⁄2-or
3-in. hole. Strain relief (field supplied) must be used in hole.
See Fig. 13.
Use field-supplied strain relief going into control box through
1
⁄2- or 3-in. diameter hole provided. After wires are in unit
2
control box, connect to power terminal block (see Power Wiring section on page 15).
Bring low-voltage control wiring through factory-drilled
7
⁄8-in. diameter hole in condenser side post. Use strain relief
going into7⁄8-in. diameter hole in bottom of unit control box.
After wiring is in control box, make connection to proper
terminals on terminal blocks (see Field Control Wiring section on this page).
IMPORTANT: THE VAV (variable air volume) units
incorporateVFD (variable frequency drives) which generate, use, and can radiate radio frequency energy. If
units are not installed and used in accordance with these
instructions, they may cause radio interference. They
have been tested and found to comply with limits of a
Class A computing device as defined by FCC (Federal
Communications Commission) regulations, Subpart J
of Part 15, which are designed to provide reasonable
protection against such interference when operated in
a commercial environment.
The unit must be electrically grounded in accordance
with local codes and NEC ANSI/NFPA 70 (National Fire
Protection Association).
Operating voltage to compressor must be within voltage
range indicated on unit nameplate. On 3-phase units, voltages between phases must be balanced within 2% and the
current must be balanced within 10%.
Use the formula in Table 4 to determine the percentage of
voltage imbalance.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance
is more than 2%, contact your local electric utility company immediately.
Unit failure as a result of operation on improper line voltage or excessive phase imbalance constitutes abuse and may
cause damage to electrical components.
On 208/230-v units, transformer no. 1 is wired for 230-v.
If 208/230-v unit is to be run with 208-v power supply, the
transformer must be rewired as follows:
1. Remove cap from red (208-v) wire.
2. Remove cap from spliced orange (230-v) wire. Discon-
nect orange wire from black unit power wire.
3. Cap orange wire.
4. Splice red wire and black unit power wire. Cap wires.
IMPORTANT: Be certain unused wires are capped.
Failure to do so may damage the transformers.
FIELD CONTROL WIRING — Install either a Carrierapproved accessory thermostat or a CCN (Carrier Comfort
Network) compatible temperature sensor.Thermostats are used
on CV (constant volume) units only. Control box diagrams
are shown in Fig. 14 and 15.
Thermostat Wiring (CV Only) — Install a Carrier-approved
accessory thermostat assembly (per current price pages) according to the installation instructions included with the accessory or these instructions. Locate thermostat assembly on
a solid wall in the conditioned space to sense average
temperature.
Route thermostat cable or equivalent single leads of colored wire from subbase terminals to low-voltage connections as shown on unit label wiring diagram and in Fig. 16.
NOTE: For wire runs up to 50 ft, use no. 18 AWG (American Wire Gage) insulated wire (35 C minimum). For 50 to
75 ft, use no. 16 AWG insulated wire (35 C minimum). For
over 75 ft, use no. 14 AWG insulated wire (35 C minimum).
All wire larger than no. 18 AWG cannot be directly connected to the thermostat and will require a junction box and
splice at the thermostat.
Set heat anticipators settings to 0.1 for all voltages. Settings may be changed slightly to provide a greater degree of
comfort for a particular installation.
Sensor Wiring (CV or VAV) — The temperature sensor is
wired into the unit control board. See Fig. 17.
The unit is controlled with a T55, T56 (CV only), or T57
zone sensor. Terminal TH on the sensor is connected to T1
of the base module board. Terminal COM on the sensor is
connected to T2 on the base module board. If a T56 set point
override sensor is used, the override connection SW on the
sensor is connected to T3 on the base module board.
VAV units using Version 1.0 of the unit control software
may operate without a space temperature sensor during occupied schedules, but unit will not provide unoccupied heating or cooling.
VAV Units — VAV units require a field-supplied heat interlock relay (HIR) to drive the air terminal wide open when in
heat mode. The HIR part number is HN61KK041.
Remote Field Control (Units Running Version 1.0 of Unit
Control Software) — A switch closure across terminals R
and Y1 on TB-3 will initiate the Occupied mode. This can
be done manually as well as through a field-supplied
timeclock.
16
Page 17
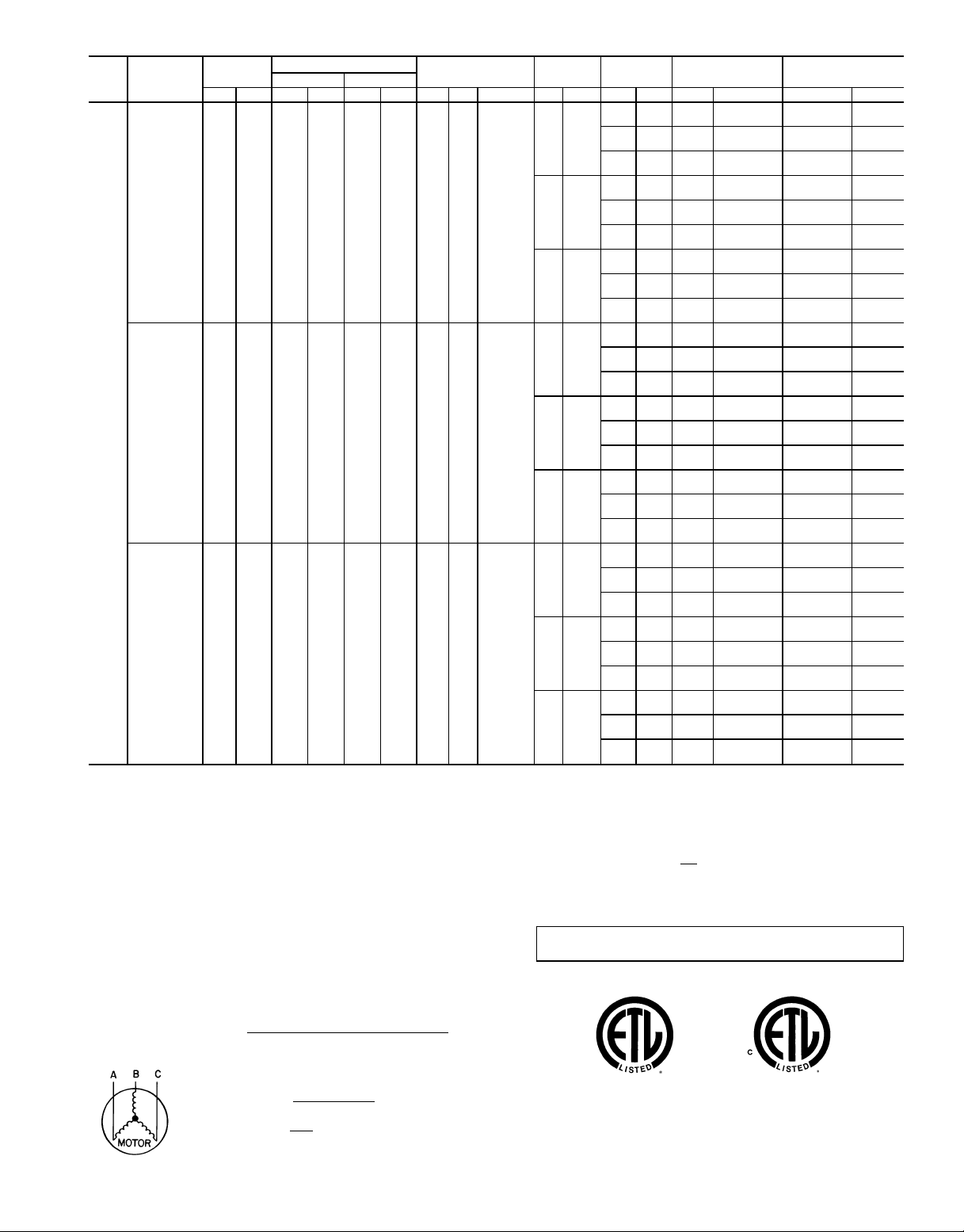
Table 4 — Electrical Data — 50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-048
NOMINAL
UNIT
VOLTAGE
SIZE
(3 Ph 60 Hz)
208/230 187 254 39.1 228 25.6 160 2 1 5.3
024
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
NEC — National Electrical Code
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Heater capacity (kW) is based on heater voltage of 208 v, 240 v, 480 v, and 575 v.
If power distribution voltage to unit varies from rated heater voltage, heater kW will
vary accordingly.
†Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC requirements formultimotor and combination load equipment (referto NEC Articles 430 and 440), theovercurrent protective device forthe
unit shall be fuse or HACR breaker. The Canadian units may be fuse or circuit
breaker.
2. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater than
2%.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
EXAMPLE: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
460 414 508 19.9 114 11.5 80 2 1 2.7
575 518 632 16.0 91 9.6 64 2 1 2.4
Use the following formula to determine the percent of voltage imbalance.
VOLTAGE
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA RLA LRA Qty Hp FLA (ea) Hp FLA FLA LRA kW FLA MCA MOCP†
LEGEND
max voltage deviation from average voltage
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
COMPRESSOR
No. 1 No. 2
average voltage
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
=
3
= 457
OFM IFM
5
10
15
5 7.6
10 14
15 21
5 6.1
10 11
15 17
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 457 − 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 − 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 − 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum
allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is more than 2%,
contact your local electric utility company immediately.
3. MCA calculation for units with electric heaters over 50 kW = (1.25 x IFM amps) +
(1.00 x heater FLA).
POWER
EXHAUST
— — — — 101.8/100.3 125/125
23.6 41.6 — — 125.4/123.9 150/150
16.7/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 114.7/127.3 125/150
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 144.2/156.8 150/175
15.2
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 171.0/192.2 200/225
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 200.5/221.7 225/225
— — — — 115.9/113.1 150/150
23.6 41.6 — — 139.5/136.7 175/175
30.8/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 132.3/143.3 150/150
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 161.8/172.8 175/175
28.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 188.6/208.2 220/225
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 218.1/237.7 250/250
— — — — 131.3/127.1 150/150
23.6 41.6 — — 154.9/150.7 175/175
46.2/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 151.6/160.8 175/175
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 181.1/190.3 200/200
42.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 207.9/225.7 250/250
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 237.4/255.2 275/275
— — — — 49.4 60
12.6 23.6 — — 62.0 80
— — 36 43.3 63.6 70
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 79.4 80
— — 72 86.6 96.1 110
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 111.9 125
— — — — 55.8 70
12.6 23.6 — — 68.4 80
— — 36 43.3 71.6 80
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 87.4 90
— — 72 86.6 104.1 110
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 119.9 125
— — — — 62.8 80
12.6 23.6 — — 75.4 90
— — 36 43.3 80.4 90
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 96.1 100
— — 72 86.6 112.9 125
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 128.6 150
— — — — 40.5 50
12.6 23.6 — — 53.1 60
— — 36 34.6 50.9 60
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 66.7 70
— — 72 69.3 76.9 80
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 92.7 100
— — — — 45.4 60
12.6 23.6 — — 58.0 70
— — 36 34.6 57.1 60
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 72.8 80
— — 72 69.3 83.0 90
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 98.8 100
— — — — 51.4 60
12.6 23.6 — — 64.0 80
— — 36 34.6 64.6 70
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 80.3 90
— — 72 69.3 90.5 100
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 106.3 110
= 1.53%
7
457
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
POWER SUPPLY
17
Page 18

UNIT
SIZE
028
Table 4 — Electrical Data — 50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-048 (cont)
NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
(3 Ph 60 Hz)
208/230 187 254 39.1 228 39.1 228 2 1 5.3
460 414 508 19.9 114 19.9 114 2 1 2.7
575 518 632 16.0 91 16.0 91 2 1 2.4
VOLTAGE
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA RLA LRA Qty Hp FLA (ea) Hp FLA FLA LRA kW FLA MCA MOCP†
COMPRESSOR
No. 1 No. 2
OFM IFM
24.2/
7.5
22.0
30.8/
10
28.0
46.2/
15
42.0
7.5 11
10 14
15 21
7.5 9
10 11
15 17
POWER
EXHAUST
— — — — 122.8/120.6 150/150
23.6 41.6 — — 146.4/144.2 175/175
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 124.1/135.8 150/150
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 153.6/165.3 175/175
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 180.4/200.7 200/225
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 209.9/230.2 225/250
— — — — 129.4/126.6 150/150
23.6 41.6 — — 153.0/150.2 175/175
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 132.3/143.3 150/150
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 161.8/172.8 175/175
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 188.6/208.2 200/225
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 218.1/237.7 225/250
— — — — 144.8/140.6 175/175
23.6 41.6 — — 168.4/164.2 200/200
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 151.6/160.8 175/175
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 181.1/190.3 200/200
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 207.9/225.7 250/250
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 237.4/255.2 275/275
— — — — 61.2 80
12.6 23.6 — — 73.8 90
— — 36 43.3 67.9 70
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 83.6 90
— — 72 86.6 100.4 110
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 116.1 125
— — — — 64.2 80
12.6 23.6 — — 76.8 90
— — 36 43.3 71.6 80
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 87.4 90
— — 72 86.6 104.1 110
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 119.9 125
— — — — 71.2 90
12.6 23.6 — — 83.8 100
— — 36 43.3 80.4 90
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 96.1 100
— — 72 86.6 112.9 125
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 128.6 150
— — — — 49.8 60
12.6 23.6 — — 62.4 70
— — 36 34.6 54.6 60
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 70.3 80
— — 72 69.3 80.5 90
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 96.3 100
— — — — 51.8 60
12.6 23.6 — — 64.4 80
— — 36 34.6 57.1 60
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 72.8 80
— — 72 69.3 83.0 90
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 98.8 100
— — — — 57.8 70
12.6 23.6 — — 70.4 80
— — 36 34.6 64.6 70
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 80.3 90
— — 72 69.3 90.5 100
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 106.3 110
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
POWER SUPPLY
18
Page 19

Table 4 — Electrical Data — 50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-048 (cont)
NOMINAL
UNIT
VOLTAGE
SIZE
(3 Ph 60 Hz)
208/230 187 254 57.1 266 39.1 228 2 1 5.3
030
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
NEC — National Electrical Code
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Heater capacity (kW) is based on heater voltage of 208 v, 240 v, 480 v, and 575 v.
If power distribution voltage to unit varies from rated heater voltage, heater kW will
vary accordingly.
†Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC requirements formultimotor and combination load equipment (referto NEC Articles 430 and 440), theovercurrent protective device forthe
unit shall be fuse or HACR breaker. The Canadian units may be fuse or circuit
breaker.
2. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater than
2%.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
EXAMPLE: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
460 414 508 25.6 120 19.9 114 2 1 2.7
575 518 632 20.5 96 16.0 91 2 1 2.4
Use the following formula to determine the percent of voltage imbalance.
VOLTAGE
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA RLA LRA Qty Hp FLA (ea) Hp FLA FLA LRA kW FLA MCA MOCP†
LEGEND
max voltage deviation from average voltage
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
COMPRESSOR
No. 1 No. 2
average voltage
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
=
3
= 457
OFM IFM
10
15
20
10 14
15 21
20 27
10 11
15 17
20 22
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 457 − 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 − 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 − 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum
allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is more than 2%,
contact your local electric utility company immediately.
3. MCA calculation for units with electric heaters over 50 kW = (1.25 x IFM amps) +
(1.00 x heater FLA).
POWER
EXHAUST
— — — — 151.9/149.1 200/200
23.6 41.6 — — 175.5/172.7 225/225
30.8/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 151.9/149.1 200/200
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 175.5/172.8 225/225
28.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 188.6/208.2 200/225
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 218.1/237.7 225/250
— — — — 167.3/163.1 200/200
23.6 41.6 — — 190.9/186.7 225/225
46.2/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 167.3/163.1 200/200
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 190.9/186.7 225/225
42.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 207.9/225.7 250/250
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 237.4/255.2 275/275
— — — — 180.5/175.1 225/225
23.6 41.6 — — 204.1/198.7 250/250
59.4/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 180.5/175.1 225/225
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 204.1/198.7 250/250
54.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 224.4/240.7 275/275
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.2/173.2 253.9/270.2 300/300
— — — — 71.3 90
12.6 23.6 — — 83.9 100
— — 36 43.3 71.6 90
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 87.4 100
— — 72 86.6 104.1 110
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 119.9 125
— — — — 78.3 100
12.6 23.6 — — 90.9 110
— — 36 43.3 80.4 100
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 96.1 110
— — 72 86.6 112.9 125
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 128.6 150
− — — — 84.3 100
12.6 23.6 — — 96.9 110
— — 36 43.3 87.9 100
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 103.6 110
— — 72 86.6 120.4 125
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 136.1 150
— — — — 57.4 70
12.6 23.6 — — 70.0 90
— — 36 34.6 57.4 70
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 72.8 90
— — 72 69.3 83.0 90
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 98.8 100
— — — — 63.4 80
12.6 23.6 — — 76.0 90
— — 36 34.6 64.6 80
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 80.3 90
— — 72 69.3 90.5 100
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 106.3 110
— — — — 68.4 80
12.6 23.6 — — 81.0 100
— — 36 34.6 70.8 80
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 86.6 100
— — 72 69.3 96.8 110
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 112.5 125
= 1.53%
7
457
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
POWER SUPPLY
19
Page 20

UNIT
SIZE
034
Table 4 — Electrical Data — 50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-048 (cont)
NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
(3 Ph 60 Hz)
208/230 187 254 57.1 266 57.1 266 2 1 5.3
460 414 508 25.6 120 25.6 120 2 1 2.7
575 518 632 20.5 96 20.5 96 2 1 2.4
VOLTAGE
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA RLA LRA Qty Hp FLA (ea) Hp FLA FLA LRA kW FLA MCA MOCP†
COMPRESSOR
No. 1 No. 2
OFM IFM
30.8/
10
28.0
46.2/
15
42.0
59.4/
20
54.0
10 14
15 21
20 27
10 11
15 17
20 22
POWER
EXHAUST
— — — — 169.9/167.1 225/200
23.6 41.6 — — 193.5/190.7 250/225
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 169.9/167.1 225/200
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 193.5/190.7 250/225
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 188.6/208.2 225/225
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 218.1/237.7 250/250
— — — — 185.3/181.1 225/225
23.6 41.6 — — 208.9/204.7 250/250
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 185.3/181.1 225/225
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 208.9/204.7 250/250
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 207.9/225.7 250/250
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 237.4/255.2 275/275
— — — — 198.5/193.1 250/250
23.6 41.6 — — 222.1/216.7 275/250
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 198.5/193.1 250/250
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 222.1/216.7 275/250
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 224.4/240.7 275/275
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 253.9/270.2 300/300
— — — — 77.0 100
12.6 23.6 — — 89.6 110
— — 36 43.3 77.0 100
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 89.6 110
— — 72 86.6 104.1 110
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 119.9 125
— — — — 84.0 100
12.6 23.6 — — 96.6 110
— — 36 43.3 84.0 100
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 96.6 110
— — 72 86.6 112.9 125
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 128.6 150
— — — — 90.0 110
12.6 23.6 — — 102.6 125
— — 36 43.3 90.0 110
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 103.6 125
— — 72 86.6 120.4 125
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 136.1 150
— — — — 61.9 80
12.6 23.6 — — 74.5 90
— — 36 34.6 61.9 70
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 74.5 90
— — 72 69.3 83.0 90
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 98.8 100
— — — — 67.9 80
12.6 23.6 — — 80.5 100
— — 36 34.6 67.9 80
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 80.5 100
— — 72 69.3 90.5 100
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 106.3 110
— — — — 72.9 90
12.6 23.6 — — 85.5 100
— — 36 34.6 72.9 90
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 86.6 100
— — 72 69.3 96.8 110
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 112.5 125
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
POWER SUPPLY
20
Page 21

Table 4 — Electrical Data — 50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-048 (cont)
NOMINAL
UNIT
VOLTAGE
SIZE
(3 Ph 60 Hz)
208/230 187 254 57.1 266 57.1 266 4 1 5.3
038
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
NEC — National Electrical Code
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Heater capacity (kW) is based on heater voltage of 208 v, 240 v, 480 v, and 575 v.
If power distribution voltage to unit varies from rated heater voltage, heater kW will
vary accordingly.
†Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC requirements formultimotor and combination load equipment (referto NEC Articles 430 and 440), theovercurrent protective device forthe
unit shall be fuse or HACR breaker. The Canadian units may be fuse or circuit
breaker.
2. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater than
2%.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
EXAMPLE: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
460 414 508 25.6 120 25.6 120 4 1 2.7
575 518 632 20.5 96 20.5 96 4 1 2.4
Use the following formula to determine the percent of voltage imbalance.
VOLTAGE
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA RLA LRA Qty Hp FLA (ea) Hp FLA FLA LRA kW FLA MCA MOCP†
LEGEND
max voltage deviation from average voltage
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
COMPRESSOR
No. 1 No. 2
average voltage
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
=
3
= 457
OFM IFM
10
15
20
10 14
15 21
20 27
10 11
15 17
20 22
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 457 − 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 − 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 − 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum
allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is more than 2%,
contact your local electric utility company immediately.
3. MCA calculation for units with electric heaters over 50 kW = (1.25 x IFM amps) +
(1.00 x heater FLA).
POWER
EXHAUST
— — — — 180.5/177.7 225/225
23.6 41.6 — — 204.1/201.3 250/250
30.8/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 180.5/177.7 225/225
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 204.1/201.3 250/250
28.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 188.6/208.2 225/225
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 218.1/237.7 250/250
— — — — 195.9/191.7 250/225
23.6 41.6 — — 219.5/215.3 275/250
46.2/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 195.9/191.7 250/225
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 219.5/215.3 275/250
42.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 207.9/225.7 250/250
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 237.4/255.2 275/275
— — — — 209.1/203.7 250/250
23.6 41.6 — — 232.7/227.3 275/275
59.4/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 209.1/203.7 250/250
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 232.7/227.3 275/275
54.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 224.4/240.7 275/275
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 253.9/270.2 300/300
— — — — 82.4 100
12.6 23.6 — — 95.0 110
— — 36 43.3 82.4 100
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 95.0 110
— — 72 86.6 104.1 110
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 119.9 125
— — — — 89.4 110
12.6 23.6 — — 102.0 125
— — 36 43.3 89.4 110
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 102.0 125
— — 72 86.6 112.9 125
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 128.6 150
— — — — 95.4 110
12.6 23.6 — — 108.0 125
— — 36 43.3 95.4 110
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 108.0 125
— — 72 86.6 120.4 125
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 136.1 150
— — — — 66.7 80
12.6 23.6 — — 79.3 90
— — 36 34.6 66.7 80
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 79.3 90
— — 72 69.3 83.0 90
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 98.8 100
— — — — 72.7 90
12.6 23.6 — — 85.3 100
— — 36 34.6 72.7 80
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 85.3 100
— — 72 69.3 90.5 100
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 106.3 110
— — — — 77.7 90
12.6 23.6 — — 90.3 110
— — 36 34.6 77.7 90
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 90.3 110
— — 72 69.3 96.8 110
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 112.5 125
= 1.53%
7
457
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
POWER SUPPLY
21
Page 22

UNIT
SIZE
044
Table 4 — Electrical Data — 50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-048 (cont)
NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
(3 Ph 60 Hz)
208/230 187 254 69.2 345 69.2 345 4 1 5.3
460 414 508 28.8 173 28.8 173 4 1 2.7
575 518 632 26.7 120 26.7 120 4 1 2.4
VOLTAGE
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA RLA LRA Qty Hp FLA (ea) Hp FLA FLA LRA kW FLA MCA MOCP†
COMPRESSOR
No. 1 No. 2
OFM IFM
46.2/
15
42.0
59.4/
20
54.0
74.8/
25
68.0
15 21
20 27
25 34
15 17
20 22
25 27
POWER
EXHAUST
— — — — 223.1/218.9 275/275
23.6 41.6 — — 246.7/242.5 300/300
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 223.1/218.9 275/275
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 246.7/242.5 300/300
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 223.1/225.7 275/275
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 246.7/255.2 300/300
— — — — 236.3/230.9 300/300
23.6 41.6 — — 259.9/254.5 300/300
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 236.3/230.9 300/300
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 259.9/254.5 300/300
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 236.3/240.7 300/300
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 259.9/270.2 300/300
— — — — 251.7/244.9 300/300
23.6 41.6 — — 275.3/268.5 300/300
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 251.7/244.9 300/300
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 275.3/268.5 300/300
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 251.7/258.2 300/300
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.2/173.2 275.3/287.7 300/300
— — — — 96.6 125
12.6 23.6 — — 109.2 125
— — 36 43.3 96.6 125
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 109.2 125
— — 72 86.6 112.9 125
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 128.6 150
— — — — 102.6 125
12.6 23.6 — — 115.2 125
— — 36 43.3 102.6 125
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 115.2 125
— — 72 86.6 120.4 150
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 136.1 150
− — — — 109.6 125
12.6 23.6 — — 122.2 150
— — 36 43.3 109.6 125
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 122.2 150
— — 72 86.6 129.1 150
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 144.9 175
— — — — 86.7 110
12.6 23.6 — — 99.3 125
— — 36 34.6 86.7 110
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 99.3 125
— — 72 69.3 91.4 110
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 106.3 125
— — — — 91.7 110
12.6 23.6 — — 104.3 125
— — 36 34.6 91.7 110
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 104.3 125
— — 72 69.3 96.8 125
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 112.5 125
— — — — 96.7 110
12.6 23.6 — — 109.3 125
— — 36 34.6 96.7 110
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 109.3 125
— — 72 69.3 103.0 125
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 118.8 125
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
POWER SUPPLY
22
Page 23

Table 3 — Electrical Data — 50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-048 (cont)
NOMINAL
UNIT
VOLTAGE
SIZE
(3 Ph 60 Hz)
208/230 187 254 82.1 446 69.2 345 4 1 5.3
048
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
NEC — National Electrical Code
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Heater capacity (kW) is based on heater voltage of 208 v, 240 v, 480 v, and 575 v.
If power distribution voltage to unit varies from rated heater voltage, heater kW will
vary accordingly.
†Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC requirements formultimotor and combination load equipment (referto NEC Articles 430 and 440), theovercurrent protective device forthe
unit shall be fuse or HACR breaker. The Canadian units may be fuse or circuit
breaker.
2. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater than
2%.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
EXAMPLE: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
460 414 508 42.3 223 28.8 173 4 1 2.7
575 518 632 34.6 164 26.7 120 4 1 2.4
Use the following formula to determine the percent of voltage imbalance.
VOLTAGE
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA RLA LRA Qty Hp FLA (ea) Hp FLA FLA LRA kW FLA MCA MOCP†
LEGEND
max voltage deviation from average voltage
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
COMPRESSOR
No. 1 No. 2
average voltage
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
=
3
= 457
OFM IFM
20
25
30
20 27
25 34
30 40
20 22
25 27
30 32
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 457 − 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 − 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 − 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum
allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is more than 2%,
contact your local electric utility company immediately.
3. MCA calculation for units with electric heaters over 50 kW = (1.25 x IFM amps) +
(1.00 x heater FLA).
POWER
EXHAUST
— — — — 252.4/247.0 300/300
23.6 41.6 — — 276.0/270.6 300/300
59.4/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 252.4/247.0 300/300
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 276.0/270.6 300/300
54.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 252.4/247.0 300/300
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 276.0/270.6 300/300
— — — — 267.8/261.0 300/300
23.6 41.6 — — 291.4/284.6 300/300
74.8/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 267.8/261.0 300/300
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 291.4/284.6 300/300
68.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 267.8/261.0 300/300
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.1/173.2 291.4/284.6 300/300
— — — — 281.0/273.0 300/300
23.6 41.6 — — 304.6/296.6 350/300
88.0/
— — 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 281.0/273.0 300/300
23.6 41.6 29/36 75.1/ 86.6 304.6/296.6 350/300
80.0
— — 59/72 150.1/173.2 281.0/273.0 300/300
23.6 41.6 59/72 150.2/173.2 304.6/296.6 350/300
— — — — 119.5 150
12.6 23.6 — — 132.1 150
— — 36 43.3 119.5 150
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 132.1 150
— — 72 86.6 120.4 150
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 136.1 150
— — — — 126.5 150
12.6 23.6 — — 139.1 175
— — 36 43.3 126.5 150
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 139.1 175
— — 72 86.6 129.1 150
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 144.9 175
− — — — 132.5 150
12.6 23.6 — — 145.1 175
— — 36 43.3 132.5 150
12.6 23.6 36 43.3 145.1 175
— — 72 86.6 136.6 175
12.6 23.6 72 86.6 152.4 175
— — — — 101.6 125
12.6 23.6 — — 114.2 125
— — 36 34.6 101.6 125
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 114.2 125
— — 72 69.3 101.6 125
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 114.2 125
— — — — 106.6 125
12.6 23.6 — — 119.2 150
— — 36 34.6 106.6 125
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 119.2 150
— — 72 69.3 106.6 125
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 119.2 150
— — — — 111.6 125
12.6 23.6 — — 124.2 150
— — 36 34.6 111.6 125
12.6 23.6 36 34.6 124.2 150
— — 72 69.3 111.6 125
12.6 23.6 72 69.3 124.2 150
= 1.53%
7
457
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
POWER SUPPLY
23
Page 24

DIP — Dual In-Line Package
PEC − Power Exhaust Controller
Fig. 14 — Control Box Diagram (Sizes 024-034)
DIP — Dual In-Line Package
PEC — Power Exhaust Controller
Fig. 15 — Control Box Diagram (Sizes 038-048)
24
Page 25

NOTE: On units running Version 1.0 of
theunit control software,the remote start/
stop switch is connected to R and Y1.
Conductors and drain wire must be 20 AWG minimum
stranded, tinned copper. Individual conductors must be insulated with PVC, PVC/nylon, vinyl, Teflon, or polyethylene. An aluminum/polyester 100% foil shield and an outer
jacket of PVC, PVC/nylon, chrome vinyl, or Teflon with a
minimum operating temperature range of −20 C to 60 C
(−4 F to 140 F) is required. Table 5 lists cables that meet the
requirements.
Table 5 — CCN Connection Approved
Shielded Cables
MANUFACTURER CABLE PART NO.
Alpha 2413 or 5463
American A22503
Belden 8772
Columbia 02525
IMPORTANT: When connecting the CCN communication bus to a system element, use a color coding system for the entire network to simplify installation and
checkout. See Table 6.
Fig. 16 — Field Control Thermostat Wiring
NOTE:Sensor part numbersare
as follows:
T55 — HH51BX001
T56 — HH51BX004
T57 — CEC01215303-01
Fig. 17 — Field Control Temperature
Sensor Wiring
Remote Field Control (Units Running Version 2.0 of Unit
Control Software) — A switch closure across terminals R
and W1 on TB-3 will initiate the Occupied mode. This can
be done manually as well as through a field-supplied
timeclock.
Service Tool, Building Supervisor, and Comfort Works —
Access to the control board can be achieved through the terminal marked CCN via a 3-wire bus.
IMPORTANT: Default bus address is 0. Default element number is 1. Refer to CCN literature for information on network addressing or changing CCN communication defaults.
Carrier Comfort Network Interface — The 50E units can be
connected to the CCN. The communication bus wiring is supplied and installed in the field. Wiring consists of shielded,
3-conductor cable with drain wire.
The system elements are connected to the communication
bus in a daisy chain arrangement. The positive pin of each
system element communication connector must be wired to
the positive pins of the system element on either side of it,
the negative pins must be wired to the negative pins, and the
signal pins must be wired to signal ground pins. Wiring connections for CCN should be made at the 3-pin plug (CCN
located at the base board. Consult CCN literature for further
information.
Table 6 — Color Code Recommendations
SIGNAL
TYPE
Positive (+) RED 1
Ground WHITE 2
Negative (−) BLACK 3
CCN BUS CONDUCTOR
INSULATION COLOR
CCN PLUG
PIN NO.
NOTE: If a cable with a different color scheme is selected,
a similar color code should be adopted for the entire network.
At each system element, the shields of the communication bus cables must be tied together. If the communication
bus is entirely within one building, the resulting continuous
shield must be connected to a ground at one point only.If
the communication bus cable exits from one building and
enters another, the shields must be connected to grounds at
the lightning suppressor in each building where the cable
enters or exits the building (one point per building only).
To connect the unit to the network:
1. Turn off power to the control box.
2. Cut the CCN wire and strip the ends of the red (+), white
(ground), and black (−) conductors. (If a different
network color scheme is used, substitute appropriate colors.)
3. Remove the 3-pin male plug from the base module in the
main control box, and connect the wires as follows:
a. Insert and secure the red (+) wire to terminal 1 of the
3-pin plug.
b. Insert and secure the white (ground) wire to ter-
minal 2 of the 3-pin plug.
c. Insert and secure the black (−) wire to terminal 3 of
the 3-pin plug.
4. Insert the plug into the existing 3-pin mating connector
on the base module in the main control box.
Step 8 — Make Outdoor-Air Inlet Adjustments
ECONOMIZER
NOTE: If accessory power exhaust or barometric relief pack-
ages are being added to the unit, install power exhaust or
barometric relief before installing economizer hoods.
Economizer Hood Assembly — The economizer hood is
shipped in a package secured to the outside of the unit and
must be field-assembled. There are 2 hoods on every unit.
The 50EW/EY units are side supply and side return. The return duct limits access to economizer filters from below. Filter tracks (mounting angle without tabs) must be installed
correctly to allow access to economizer filters from each side.
Perform the following procedure to assemble the economizer hood.
25
Page 26

NOTE: Before assembly of the economizer hood, check along
the outer edges of the economizer assembly for any seal strip
protruding past the flanges. Trim the excess seal strip so that
it is flush with the economizer assembly flanges.
1. Apply black seal strip (provided in package) to outside
top-edge of hood sides. Wrap seal strip over edge to cover
top flange (4 hood sides). Make sure seal strip covers
screw holes. Allow strip to overhang
1
⁄8-in. past the end
opposite the mounting flange. See Fig. 18.
2. Assemble hood sides, top, and cross member with gasketed screws provided. See Fig. 19.
3. Attach 10 green speed clips (provided) to hood top.
4. Apply black seal strip (provided) to mounting flanges of
hood sides being sure to cover mounting holes. See
Fig. 20.
NOTE: Each hood assembly has a slotted side that should
be adjacent to the other hood when mounted to the unit.
5. Apply black seal strip (provided) to hood top mounting
flange. Seal strip of hood top mounting flange must press
tightly against seal strip of hood side mounting flanges.
See Fig. 21.
6. Add gray foam strip (provided in package) to cross members on bottom tray. See Fig. 22.
7. Place gray foam strip (provided) on inside of slotted hood
side between filter and cross member opposite the mounting end. See Fig. 23.
8. Attach gray foam strip (provided) to block-off baffle on
outer face of flange. See Fig. 24.
9. Remove the screws on each end and along top of damper
assembly of unit. Remove top 2 screws on each side of
filter panel under damper assembly. Set hood assembly
in place and attach to unit using these screws.
10. Attach accessory enthalpy bracket on hood side furthest
from control box end. Locate bracket on inside upper
right-hand corner of economizer hood using hood mounting holes. Mount outdoor-airthermistor to enthalpy bracket
(if purchased). Attach and wire enthalpy assembly. Place
quick connects on enthalpy wires.
11. Remove screws along bottom of damper assembly. Locate and mount blockoff baffle using these screws.
12. Assemble 2 filter tracks side-by-side with the assembled ends together.
13. Attach mounting angle (without tabs) to the assembled
end of the filter track. See Fig. 25.
14. Attach 6 green speed clips (provided) to mounting angles.
Engagement section of clip faces inside of rack.
TOP
FLANGE
BLACK
SEAL
STRIP
HOOD SIDE
Fig. 18 — Adding Seal Strip to
Top of Hood Sides
NOTE: Left side economizer hood has mounting angle without tabs and filter
track assembled end on the opposite side.
Fig. 19 — Economizer Hood Assembly
(Right-Side Economizer Hood Shown)
MOUNTING
FLANGE
HOOD SIDE
Fig. 20 — Adding Seal Strip to
Mounting Flange of Hood Sides
15. Attach remaining mounting angle (with tabs) to other
end of the filter track with no. 10 screws provided. See
Fig. 26.
16. Place filter track assembly in bottom of hood by placing
tabbed end into slotted side (with tab on bottom) and
attaching opposite end to hood with speed clips and gasketed screws provided. Tabs can be hand bent after they
have been inserted into the side.
NOTE: The filter track assembly end with screws should
face away from the other hood when mounted on the unit.
NOTE: Tabs from both filter tracks will be in the same
space.After one filter track has been inserted into board,
bend the tabs so they will not interfere with installation
of the second hood.
17. Attach black seal strip (provided) to filter cover. Seal
strip should be applied to the center of the large flange
making sure to cover holes. See Fig. 27.
18. Slide two 20 x 25-in. filters into cross members of hood
assembly.Attach filter cover over filters with screws and
speed clips provided.
26
Page 27

HOOD SIDE
HOOD TOP
BLOCKOFF BAFFLE
Fig. 21 — Adding Seal Strip to
Hood Top Mounting Flange
GRAY FOAM STRIP
CROSS MEMBER
Fig. 22 — Adding Foam Strip to Cross Member
GRAY FOAM STRIP
Fig. 24 — Adding Foam Strip to Blockoff Baffle
MOUNTING ANGLE
(WITHOUT TABS)
FILTER TRACK
ASSEMBLY
Fig. 25 — Mounting Angle (Without Tabs)
Attached to Filter Track Assembly
HOOD SIDE
(SLOTTED)
HOOD
TOP
Fig. 23 — Adding Foam Strip to Hood Side
27
MOUNTING ANGLE
(WITH TABS)
Fig. 26 — Mounting Angle (With Tabs)
Attached to Filter Track Assembly
Page 28

Minimum Damper Position Setting — Setting of the outdoor air damper position is performed in conjunction with a
shortened version of the field-run test. This is performed by
first opening DIP (Dual In-Line Package) switch no. 6 then
no. 4. See Fig. 17 and Table 7.
The outdoor-air damper closes. The control allows 90 seconds for the damper to close in case it is in the full open
position. Next, the indoor-fan contactor will energize. The
outdoor-air damper will remain at 0% for 30 seconds. It will
then move to the 10% position for another 30 seconds. This
will be repeated at every 10% increment for 30 seconds until
the damper reaches 100% open. Close DIP switch no. 6 during the 30 seconds immediately after the desired outdoor air
minimum damper position. The 30-second time period is to
allow time where DIP switch no. 6 can be closed. The default value of the minimum outdoor air damper position is
20%. If the desired minimum position is 30%, allow the damper
BLACK SEAL STRIP
(CENTERED)
FILTER COVER
position to go to 10% for 30 seconds, then 20% for 30 seconds, and when it reaches 30% close DIP switch no. 6 during the 30-second period following the 30% position.
The minimum outdoor air damper position is now set.
ECONOMIZER SETTINGS
Accessory Enthalpy Control (Fig. 28) — The control
(HH57AC077) is mounted in the economizer hood. See
Fig. 19. The enthalpy setting adjustment is on the enthalpy
control. For maximum benefit of outdoor air, set enthalpy
control to A. See Fig. 29 and 30.
Accessory Differential Enthalpy Control — The control
(HH57AC077), in conjunction with the accessory enthalpy
sensor (HH57AC078), controls economizer operation according to the differential enthalpy. The control is mounted
in the economizer hood. The sensor is mounted in the return
duct (50EJ/EK) or return air plenum (50EW/EY).
Fig. 27 — Attaching Seal Strip
to Filter Cover
HH57AC077
ENTHALPY CONTROL
NOTE: Switches shown in high enthalpy state. Terminals 2 and 3 close on enthalpy decrease.
Fig. 29 — Wire Connections for Solid State
Enthalpy Control (HH57AC077)
CONTROL
CURVE
CONTROL POINT
(APPROX. DEG.)
A 73 (23)
B 70 (21)
C 67 (19)
D 63 (17)
AT 50% RH
C7400A1004
+
HH57AC078
ENTHALPY SENSOR
(USED WITH ENTHALPY
CONTROL FOR DIFFERENTIAL
ENTHALPY OPERATION)
Fig. 28 — Differential Enthalpy Control
and Sensor
RH — Relative Humidity
Fig. 30 — Psychrometric Chart for
Enthalpy Control
28
Page 29

Step 9 — Position Power Exhaust/Barometric
ReliefDamper Hood —
been made and adjusted at the factory. The power exhaust
blowers and barometric relief dampers are shipped assembled and tilted back into the unit for shipping. Brackets
and extra screws are shipped in shrink wrap around the dampers. If ordered, each unit will have 4 power exhaust blowers
and motors or 4 barometric relief dampers.
1. Remove 9 screws holding each damper assembly in place.
See Fig. 31. Each damper assembly is secured with 3 screws
on each side and 3 screws along the bottom. Save screws.
2. Pivot each damper assembly outward until edges of damper
assembly rest against inside wall of unit.
Be careful when tilting blower assembly. Hoods
and blowers are heavy and can cause injury if
dropped.
3. Secure each damper assembly to unit with 6 screws across
top (3 screws provided) and bottom (3 screws from
Step 1) of damper.
All electrical connections have
4. With screws saved from Step 1, install brackets on each
side of damper assembly.
5. Remove tape from damper blades.
VAV DUCT PRESSURE TRANSDUCER — The VAV duct
pressure transducer (VAVinverter pressure transducer) is located behind the filter access door on the lower inner panel.
See Fig. 32. A section of
1
⁄4-in. plastic tubing must be run
from the high-pressure tap on the differential pressure switch
and connected to a tap in the supply-air duct. The tap is usually located
2
⁄3of the way out on the main supply duct. Re-
move plug button in panel to route tubing.
VAV BUILDING PRESSURE TRANSDUCER — The VAV
building pressure transducer (modulating power exhaust pressure transducer) is located behind the filter access door on
the inner panel. See Fig. 32. A section of1⁄4-in. plastic tubing must be run from the high-pressure tap on the differential pressure switch to the conditioned space. The pressure
tube must be terminated in the conditioned space where a
constant pressure is required. This location is usually in an
entrance lobby so that the building exterior doors will open
and close properly. Remove plug button in panel to route
tubing.
NOTES:
1. Unless otherwise specified, all dimensions are to outside of part.
2. Dimensions are in inches.
Fig. 31 — Barometric Relief Damper and Power
Exhaust Mounting Details
29
Page 30

VAV — Variable Air Volume
Fig. 32 — Pressure Transducer Locations
Step10 — InstallAccessories — After all the factory-
installed options have been adjusted, install all fieldinstalled accessories. Refer to the accessory installation instructions included with each accessory.
MOTORMASTERt III SENSOR LOCATION — Motormaster III sensor locations are shown in Fig. 33A-33C. Refer to the Motormaster III installation instructions for wiring
and installation information.
Fig. 33A — Motormaster III Sensor Location
(Sizes 024-034)
30
Page 31

Fig. 33B — MotormasterT III Sensor Location
(Sizes 038 and 044)
Fig. 33C — Motormaster III Sensor Location
(Size 048)
31
Page 32

START-UP
Use the following information and Start-Up Checklist on
page CL-1 to check out unit PRIOR to start-up.
Unit Preparation — Check that unit has been installed
in accordance with these installation instructions and applicable codes.
CompressorMounting — Loosen the compressor hold-
down bolts until sidewise movement of the washer under
each holddown bolt head can be obtained. Do not loosen
completely as bolts are self-locking and will maintain
adjustment.
Service Valves — Ensure that the suction, discharge,
and liquid line service valves are open. Damage to the compressor could result if they are left closed.
Internal Wiring — Check all electrical connections in
unit control boxes; tighten as required.
Refrigerant Service Ports — Each refrigerant sys-
tem has one suction port located in the top of the compressor
motor casing. All units also have one service port on the liquid line valve and one on the compressor discharge valve.
Be sure that caps on the ports are tight.
VariableFrequencyDrive (VFD) — The variable fre-
quency drives are factory set. These settings include factoryinstalled jumpers and software configurations. The only
configured set point is duct static pressure. An Operation Manual
is shipped with each VAV unit. This manual should be
used if the drive needs to be customized for a particular
application.
To set the duct static pressure, perform the following steps.
The factory setting is zero. The duct transducer has a range
from 0 to 5 in. wg. The transducer output is 2 to 10 vdc,
therefore, 0 to 5 in. wg is proportional to the 2 to 10 vdc and
must be expressed to the VFD in terms of percentage of the
frequency range. To do this, refer to Table 7. The set point
value is a percentage of the maximum output frequency. Locate the duct static pressure closest to that desired and use
the corresponding set point value. If necessary, interpolation
between duct static pressures is permissible.
To set the VFD, the VFD must be powered up, however,
since it is located near the indoor air fan, operation of the
fan is not desirable. To disable the fan, perform the following procedure:
1. Open the indoor fan circuit breaker.
2. Remove the jumper between CC and ST on the terminal
strip of the VFD (see Fig. 34).
3. Close the indoor fan circuit breaker.The VFD now is powered but the fan will not operate.
4. On the front of the VFD is a keypad and display which
will be used to enter the set point. To access this field,
press ‘‘SETUP’’key,then press the ‘‘SETUP’’key 6 times
to scroll to the sixth parameter, which will display
‘‘Sr1.’’ This is the VFD set point listed in Table 7.
5. Press the ‘‘READ/WRITE’’ key. The set point value will
be displayed. Use the up-arrow or down-arrow key to adjust the set point value to the value desired.
6. Press the ‘‘READ/WRITE’’ key again to enter the new
value.
7. Open the indoor fan circuit breaker.
8. Replace the jumper between CC and ST on the terminal
strip of the VFD.
9. Close the indoor fan circuit breaker, the VFD now is powered and the fan will operate.
NOTE: Any field measurement of supply fan amps must be
taken with an RMS meter between the fan circuit breaker
and fan contactor (upstream of VFD).
Table 7 — VFD Set Point
PRESSURE
(in. wg)
0.00 2.0 12.0
0.25 2.4 14.4
0.50 2.8 16.8
0.75 3.2 19.2
1.00 3.6 21.6
1.25 4.0 24.0
1.50 4.4 26.4
1.75 4.8 28.8
2.00 5.2 31.2
2.25 5.6 33.6
2.50 6.0 36.0
2.75 6.4 38.4
3.00 6.8 40.8
3.25 7.2 43.2
3.50 7.6 45.6
VFD — Variable Frequency Drive
VOLTAGE
(vdc)
VFD
SET POINT
NOTE: Terminal strip is located inside the VFD (Variable Frequency
Drive) at the bottom.
Fig. 34 — VFD Factory-Installed Jumpers
32
Page 33

Power Exhaust — The optional non-modulating power
exhaust (CV only) is a two-stage design where the operation
of the exhaust fans is linked to economizer position. When
the supply fan is running and the economizer is 25% open,
the base module closes contacts, activating 2 exhaust fans.
When the economizer position reaches 75% open, the base
module activates the other 2 exhaust fans. The fans will turn
off when the economizer closes below the same points. The
economizer position set points that trigger the exhaust fans
can be modified, but only through use of the Service Tool,
Comfort Works, or Building Supervisor Software. If singlestage operation is desired, adjust the economizer set points
to identical values at the desired point to activate all exhaust
fans.
The optional modulating power exhaust (VAV standard,
CV optional) is controlled by a modular electronic sequencer system. This system consists of a model R353 signal input module and 4 model S353 staging modules. The
signal input module receivesa0to10vdcsignal from the
building pressure transducer, which is mounted adjacent to
the supply static transducer behind the filter access panel.
The modules are mounted just below the unit control board.
The left module is the R353, and the 4 modules on the right
are S353 modules for stages 1 through 4. On the unit wiring
label, the R353 is designated PESC, and the S353 modules
are designated PES1 through PES4.
The building pressure transducer range is −0.5 to
+0.5 in. wg. It is powered bya0to10vdcsignal. A factoryinstalled hose at the ‘‘Lo’’ connection leads to atmosphere,
and a field-supplied hose must be connected to the ‘‘Hi’’connection and led into the building to a point where building
pressure is to be controlled. There is a plug button in the
bulkhead just above the transducers, for use in leading the
hoses into the building via the return air ductwork.
There are 3 adjustments at the R353 module, all of which
have been factory set. In the center of the circuit board is a
set of 4 pins with a jumper, labeled J2. This determines the
mode of operation. The bottom 2 pins must be jumpered for
direct operation. Direct operation means that the staging modules are activated in sequence as the input signal
increases.
At the upper right corner of the board is a set of 5 pins and
jumper, which determines the time constant for the control.
The time constant is the delay in response built into the controls. The jumper should be on the middle or bottom 2 pins,
for the maximum time constant. The delay can be decreased,
if desired, by moving the jumper progressively upward, always jumpering adjacent pins.
At the lower left corner of the board below the terminal
strip is a resistor marked R27. This must be removed in order to obtain the 0 to 10 vdc signal output. There will not be
a resistor on a factory-supplied module, but a resistor may
be present on a replacement module and must be removed.
The R353 module has a terminal block with 7 connections available for wiring. The 2 right-hand terminals are for
the 24 vac and common connections. The next 2 terminals
are for the 0 to 10 vdc signal. Consult the wiring label for
wire identification if replacing the module. The 3 left-hand
terminals are not used for this application.
The S353 module has an LED (light-emitting diode), a set
of 4 jumper pins, and 2 potentiometers. The LED will light
whenever the module is activated, providing a visual indication of the number of exhaust fans running. The jumper
pins are arranged in a square format. Two jumpers are used
to determine the mode of operation (direct or reverse). The
2 jumpers must be arranged horizontally for direct action
(factory set).
At the top of the module are 2 potentiometers. The left
potentiometer adjusts the offset.The right potentiometer adjusts differential. The potentiometers are factory set for a
nominal 0 in. wg building pressure.
The offset set point is defined as the point at which a mod-
ule turns off a fan, and is measured in terms of percent of the
input signal. For control purposes, 0 offset is at an arbitrary
‘‘floor’’ which is established at 10% of the input signal, or
1 vdc. In this example, the first stage will turn off at 30%
(3 vdc), and the offset potentiometer will be set at 20%. The
second stage will turn off at 50% signal (5 vdc), and the offset potentiometer will be set at 40%. The fourth stage is at
the maximum 75% offset, which equates to 85% signal or
8.5 vdc. The offset potentiometer is calibrated in 10%
increments.
Table 8 relates building pressure to signal level.
Table 8 — Potentiometer Signal Levels
BUILDING PRESSURE
(in. wg)
−0.50 2
−0.25 4
0.00 6
0.25 8
0.50 10
SIGNAL LEVEL
(vdc)
If the building pressure is controlled at 0 in. wg, offset of
the first stage should be set at 50%, which equates to 60%
of the input signal, or 6 vdc. The other stages can then be set
as desired between 50% and 75%.
The default offset set points for modulating power exhaust are shown in Table 9.
Table 9 — Power Exhaust Default Set Points
STAGE OFFSET
1 50% 3% 6.0 6.3 0.00
2 55% 3% 6.5 6.8 0.06
3 60% 3% 7.0 7.3 0.12
4 64% 3% 7.4 7.7 0.18
DIFFE-
RENTIAL
OFF
VOLTAGEONVOLTAGE
OFF
STATIC
PRESSURE
(in. wg)
The differential set point is the difference between the
turn off point and the turn on point for each module. It also
is calibrated in terms of percent of input signal, and has a
range of 1% to 7%. The differential potentiometer is calibrated in 1% increments, and is factory set at approximately
3%. It is recommended to leave the set point at 3%, to minimize cycling of the fans.
The offset and differential potentioments have been factory set for atmosphereic pressure. Do not change these settings until there is some experience with the building. In most
cases the factory settings will be satisfactory. However, if
the building pressure is not being maintained as desired, then
some minor adjusting on a trial and error basis can be made.
Direct Digital Controls DIP Switch Configuration —
configured for each application. The DDC board is configured through the DIP switches located on the board. There
are 8 DIP switches which configure 8 different applications
of the DDC. See Tables10Aand 10B. DIP switch 1 is on the
left of the block. DIP switch 8 is on the right of the block.
To open a DIP switch, push the switch up with suitable tool
(small-blade screwdriver). To close a DIP switch, push the
switch down. Factory settings are shown in Tables 11A
and 11B.
The Direct Digital Control (DDC) board must be
33
Page 34

Table 10A — DIP Switch Configuration (Version 1.0 of Unit Control Software)
SETTING 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
OPEN VAV
CLOSED CV TSTAT
LEGEND
CCN — Carrier Comfort Network
CV — Constant Volume
I/O — Input/Output
POS. — Position
TSTAT — Thermostat
VAV — Variable Air Volume
CCN/
Sensors
Expansion
I/O Board
Base Board
Only
Field
Test
ON
Field
Test
OFF
Modulated
Power
Exhaust
CV
Power
Exhaust
Time Guard Override
ON/ Set Min.
Damper Pos. ON
Time Guard Override
OFF/ Set Min.
Damper Pos. OFF
NOTES:
1. The Factory Test DIP switch should not be enabled in the field.
2. The OPEN side of the DIP switch is marked ‘‘OPEN.’’ When the
rocker switch is on the ‘‘OPEN’’ side of the switch, the switch is
open.
3. If DIP switch no. 1 is open, DIP switch no. 2 is ignored, since VAV
units control to supply-air temperature.
Gas Heat Factory Test ON
Electric Heat Factory Test OFF
Table 10B — DIP Switch Configuration (Version 2.0 of Unit Control Software)
SETTING 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
VAV — Space Sensor
Installed
OPEN VAV
CV — CCN or Sensors
VAV — No Space Sensor
CLOSED CV
LEGEND
CCN — Carrier Comfort Network
CV — Constant Volume
VAV — Variable Air Volume
Used
CV — Thermostat
Expansion
Board
Base Control
Board Only
Field Test
ON
Field Test
OFF
VAV —
Occupied
Heat
Enabled
CV —
Modulated
Power
Exhaust
VAV —
Occupied
Heat
Disabled
CV —
Constant
Volume
Power
Exhaust
NOTES:
1. The OPEN side of the DIP switch is marked ‘‘OPEN.’’ When the
rocker switch is on the ‘‘OPEN’’ side of the switch, the switch is
OPEN.
2. The configuration of DIP switches 2 and 5 are dependent on DIP
switch 1. If DIP switch 1 is set to OPEN (VAVoperation), then DIP
switches 2 and 5 will configure CV functions.
3. When the unit is field-tested (DIP switch 4 to OPEN), the function
of DIP switch 6 changes and it is used to set the minimum damper
position.
Time Guard Override
Time Guard Override
ON
IN CONJUNCTION
WITH FIELD TEST
— Set Minimum
Damper Position
OFF
Gas Heat
Electric Heat
Heat Pump
Operation
Air Conditioner
Operation
Table 11A — DIP Switch Factory Settings (Version 1.0 of Unit Control Software)
UNIT 12345678
50EJ/EW Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed
50EK/EY Open Closed Closed Closed Open Closed Closed Closed
Table 11B — DIP Switch Factory Settings (Version 2.0 of Unit Control Software)
UNIT 12345678
50EJ/EW Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed
50EK/EY Open Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed
34
Page 35

DIPswitch configurations for Version1.0 of the Unit Con-
trol Software are as follows:
• DIP switch 1 configures the unit to operate as a variable
air volume (VAV) or constant volume (CV) unit
• DIP switch 2 configures what type of sensors or thermostats are used with the unit
• DIP switch 3 configures the DDC for use with the electronic expansion board
• DIP switch 4 is used to field test the unit
• DIP switch 5 configures the unit to use constant volume or
modulated power exhaust
• DIP switch 6 configures the Time Guardt override and the
minimum damper position
• DIP switch 7 configures the unit for gas heat or electric
heat
• DIP switch 8 is used to factory test the unit
The DIP switch configurations for Version 2.0 of the unit
control software are as follows:
• DIP switch 1 configures the unit to operate as a VAV or
CV unit
• DIP switch 2 configures the unit to use a space sensor (VAV
units) or a thermostat (CV units)
• DIP switch 3 configures the DDC for use with an electronic expansion board
• DIP switch 4 is used to field test the unit
• DIP switch 5 is used to enable occupied heating (V AV units)
or specify the type of power exhaust (CV units)
• DIP switch 6 configures the Time Guard override and, when
used with the field test function, sets the minimum damper
position
• DIP switch 7 configures the unit for gas heat or electric
heat
• DIP switch 8 configures the unit for heat pump or air conditioner operation
CrankcaseHeater(s) — Heater(s) is energized as long
as there is power to the unit, except when the compressors
are operating.
IMPORTANT: Unit power must be on for 24 hours
prior to start-up. Otherwise, damage to compressor may
result.
EvaporatorFan — Fan belt and fixed pulleys are factory-
installed. See Tables 12-14 for Fan Performance Data. See
Table 15 for Air Quantity Limits. See Table 16 for Motor
Limitation data. Be sure that fans rotate in the proper direction. Static pressure drop for power exhaust, barometric
relief damper, and electric heat is negligible. To alter fan performance, see Evaporator Fan Performance Adjustment section on page 43.
Condenser Fans and Motors — Fans and motors
are factory set. Refer to Condenser-Fan Adjustment section
(page 44) as required.
Return-Air Filters — Check that correct filters are in-
stalled in filter tracks. See Table 1. Do not operate unit without return-air filters.
Filter Replacement — To replace filters, open filter
access door (marked with label). Remove inner access panel.
Remove plastic filter retainer in between filter tracks by sliding and pulling outward. Remove first filter by sliding it out
of the opening in filter track. Locate filter removal tool, which
is shipped next to the return air dampers. Use the filter removal tool to remove the remaining filters.
Outdoor-AirInlet Screens — Outdoor-air inlet screens
must be in place before operating unit.
EconomizerAdjustment— Remove filter access panel.
Check that outdoor-air damper is closed and return-air damper
is open.
Economizer operation and adjustment is described in Sequence of Operation and Make Outdoor Air Inlet Adjustments sections (this page and page 25), respectively.
Sequence of Operation
NOTE: Unit is shipped with default values that can be changed
through Service Tool or CCN software.
COOLING, CONSTANT VOLUME (CV) UNITS — On
power up, the control module will activate the initialization
software. The initialization software reads DIP switch no. 1
position to determine CV or VAV operation. Next, DIP switch
no. 2 is read to determine if the control is TSTAT or sensor
type operation. The initialization sequence: clears all alarms
and alerts; re-maps the input/output database for CV operation; sets maximum heat stages to 2; and sets maximum cool
stages to 3. The control module reads DIP switch no. 3 and
determines if the unit will use expansion mode operation.
The TSTAT function performs a thermostat based control
by monitoring Y1, Y2, W1, W2 and G inputs. These functions control stages: cool1, cool2, heat1, heat2, and the indoor fan respectively. If the TSTAT function is not selected,
the control module determines the occupancy state based on
the system time schedules or with remote occupied/unoccupied
input. If Temperature Compensated Start is active, the unit
will be controlled as in the Occupied mode. User defined set
points are shown in Table 17.
Occupied or unoccupied comfort set points must be selected. Use of the space temperature offset input can also be
configured. The control module will set appropriate operating mode and fan control. The control module will turn on
indoor fan if in Occupied mode or if the unit is in Unoccupied mode and the space temperature is outside of the unoccupied comfort set points (Unoccupied Heat or Unoccupied Cool). The control module will then monitor space
temperature against comfort set points and control heating
or cooling stages as required. If the system is in the Occupied mode, the economizer will operate as required. If the
system is in Unoccupied mode, the system will perform night
time free cool and IAQ (indoor air quality) pre-occupancy
purge as required (when functions are enabled via software).
Whenever the DX (direct expansion) cooling is requested,
the outdoor fan will operate.
35
Page 36

Table 12 — Fan Performance, 50EJ/EK024-034 — Vertical Discharge Units
FOR EW/EY UNITS, REDUCE NET AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE BY 0.3 IN. WG
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
4,000 322 0.77 401 1.09 466 1.43 523 1.78 575 2.13 622 2.50 666 2.87 707 3.25
5,000 361 1.14 433 1.50 494 1.86 548 2.23 598 2.62 643 3.00 686 3.40 726 3.80
6,000 403 1.62 468 2.01 526 2.41 577 2.81 624 3.21 668 3.62 709 4.04 748 4.46
7,000 448 2.22 508 2.65 561 3.08 609 3.50 654 3.93 696 4.37 736 4.81 773 5.25
8,000 495 2.97 549 3.42 599 3.88 645 4.33 687 4.79 727 5.25 765 5.71 801 6.18
8,250 507 3.18 560 3.64 609 4.10 654 4.56 696 5.02 735 5.49 773 5.96 809 6.43
9,000 543 3.85 593 4.34 639 4.82 682 5.30 723 5.78 761 6.27 797 6.76 832 7.24
10,000 592 4.90 638 5.41 682 5.91 722 6.42 760 6.93 797 7.44 832 7.95 865 8.46
11,000 642 6.10 685 6.64 725 7.17 764 7.70 800 8.24 835 8.77 868 9.30 900 9.84
12,000 693 7.48 733 8.04 771 8.60 807 9.15 841 9.71 874 10.26 906 10.82 937 11.38
12,500 718 8.23 757 8.80 794 9.37 829 9.94 862 10.51 895 11.08 926 11.64 956 12.21
13,000 744 9.03 781 9.62 817 10.20 851 10.78 884 11.36 915 11.93 946 12.51 975 13.09
13,750 783 10.32 818 10.92 852 11.52 885 12.12 917 12.71 947 13.31 977 13.90 1005 14.50
14,000 795 10.77 831 11.38 864 11.98 896 12.59 928 13.19 958 13.79 987 14.39 1015 14.99
15,000 847 12.71 880 13.34 912 13.96 943 14.59 972 15.21 1001 15.83 1029 16.45 1056 17.08
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
4,000 746 3.64 783 4.03 818 4.44 852 4.85 884 5.26 916 5.68 946 6.11 975 6.54
5,000 764 4.21 800 4.62 834 5.04 868 5.46 900 5.89 930 6.33 960 6.77 989 7.22
6,000 785 4.89 820 5.32 854 5.76 886 6.21 918 6.65 948 7.11 977 7.56 1006 8.02
7,000 809 5.70 843 6.16 876 6.61 908 7.08 939 7.54 968 8.01 997 8.49 1025 8.96
8,000 836 6.65 869 7.12 901 7.60 932 8.08 962 8.57 991 9.05 1019 9.55 1046 10.04
8,250 843 6.91 876 7.39 908 7.87 938 8.36 968 8.84 997 9.34 1025 9.83 1052 10.33
9,000 865 7.74 898 8.23 929 8.73 959 9.23 988 9.74 1016 10.24 1043 10.75 1070 11.27
10,000 897 8.98 928 9.49 958 10.01 987 10.53 1016 11.06 1043 11.58 1070 12.11 1096 12.64
11,000 931 10.37 961 10.91 990 11.45 1018 11.99 1046 12.54 1073 13.08 1099 13.63 1124 14.18
12,000 967 11.94 996 12.49 1024 13.06 1051 13.62 1078 14.18 1104 14.75 1129 15.31 1154 15.88
12,500 985 12.78 1014 13.35 1041 13.92 1068 14.49 1094 15.07 1120 15.64 1145 16.22 1169 16.80
13,000 1004 13.67 1032 14.25 1059 14.83 1086 15.42 1111 16.00 1137 16.59 1161 17.17 1185 17.76
13,750 1033 15.09 1060 15.69 1087 16.29 1112 16.88 1138 17.48 1162 18.08 1186 18.68 — —
14,000 1043 15.59 1070 16.19 1096 16.79 1122 17.40 1147 18.00 1171 18.60 1195 19.21 — —
15,000 1083 17.70 1109 18.32 1134 18.94 1159 19.56 1183 20.19 — — — — — —
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
4,000 1004 6.97 1032 7.41 1059 7.86
5,000 1017 7.67 1045 8.12 1072 8.58
6,000 1034 8.49 1061 8.96 1087 9.43
7,000 1052 9.44 1079 9.93 1105 10.42
8,000 1073 10.54 1099 11.04 1125 11.55
8,250 1079 10.84 1105 11.34 1130 11.85
9,000 1096 11.78 1122 12.30 1147 12.82
10,000 1122 13.18 1147 13.71 1171 14.25
11,000 1149 14.73 1173 15.29 1197 15.84
12,000 1178 16.45 1202 17.03 — —
12,500 1193 17.38 ————
13,000 ——————
13,750 ——————
14,000 ——————
15,000 ——————
AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
3.4 3.6 3.8
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
LEGEND
Bhp — Brake Horsepower
NOTES:
1. Fan performance is based on wet coils, economizer, roof curb,
cabinet losses, and clean 2-in. filters.
2. Conversion — Bhp to watts:
Watts =
3. VAV units will operate down to 70 cfm/ton.
Bhp x 746
Motor efficiency
36
Page 37

Table 13 — Fan Performance, 50EJ038,044 and 50EK044 — Vertical Discharge Units
For EW/EY UNITS, REDUCE NET AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE BY 0.5 IN. WG
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
8,000 448 2.18 498 2.87 544 3.25 589 3.64 631 4.04 671 4.44 710 4.86 747 5.27
9,000 492 2.87 537 3.68 580 4.09 621 4.50 660 4.92 698 5.35 734 5.78 769 6.22
10,000 537 3.69 578 4.63 617 5.07 655 5.50 692 5.95 727 6.39 761 6.85 795 7.30
11,000 582 4.65 620 5.75 657 6.20 692 6.66 726 7.13 759 7.60 792 8.07 823 8.55
12,000 629 5.75 664 7.02 698 7.50 730 7.98 763 8.47 794 8.96 824 9.45 854 9.95
13,000 675 7.00 708 8.48 739 8.98 770 9.48 800 9.99 830 10.50 859 11.01 887 11.53
14,000 722 8.42 753 10.11 782 10.63 811 11.16 840 11.69 868 12.22 895 12.75 922 13.29
15,000 770 10.00 798 11.94 826 12.48 853 13.03 880 13.57 907 14.13 932 14.68 958 15.24
16,000 817 11.76 844 13.96 870 14.53 896 15.09 922 15.66 947 16.23 971 16.81 995 17.38
17,000 865 13.70 890 16.19 915 16.78 940 17.37 964 17.95 988 18.54 1011 19.14 1034 19.73
18,000 913 15.83 937 18.64 961 19.25 984 19.85 1007 20.46 1030 21.07 1052 21.68 1074 22.30
19,000 961 18.16 984 21.32 1006 21.94 1029 22.56 1050 23.19 1072 23.82 1093 24.45 1115 25.08
20,000 1009 20.69 1031 24.22 1052 24.86 1074 25.50 1095 26.15 1115 26.80 1136 27.45 1156 28.10
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
8,000 783 5.70 818 6.13 852 6.56 884 7.00 916 7.45 947 7.90 978 8.36 1007 8.82
9,000 803 6.66 836 7.11 869 7.56 900 8.02 930 8.48 960 8.95 989 9.42 1018 9.90
10,000 827 7.77 858 8.23 889 8.70 919 9.18 948 9.66 977 10.15 1005 10.64 1032 11.13
11,000 854 9.03 884 9.51 913 10.00 941 10.50 969 11.00 997 11.50 1024 12.01 1050 12.52
12,000 883 10.45 911 10.96 939 11.47 967 11.98 993 12.50 1020 13.02 1046 13.54 1071 14.07
13,000 914 12.05 942 12.57 968 13.10 994 13.63 1020 14.17 1045 14.71 1070 15.25 1094 15.79
14,000 948 13.83 974 14.37 999 14.92 1024 15.47 1049 16.02 1073 16.58 1096 17.14 1120 17.70
15,000 983 15.80 1007 16.36 1032 16.92 1056 17.49 1079 18.06 1102 18.64 1125 19.21 1148 19.79
16,000 1019 17.96 1043 18.54 1066 19.13 1089 19.71 1111 20.30 1134 20.89 1156 21.49 1177 22.08
17,000 1057 20.33 1079 20.93 1102 21.53 1124 22.14 1145 22.75 1167 23.35 1188 23.97 — —
18,000 1096 22.91 1117 23.53 1138 24.15 1160 24.78 1180 25.40 — — — — — —
19,000 1135 25.72 1156 26.36 1176 26.99 1197 27.63 — — — — — — — —
20,000 1176 28.75 1196 29.41 — — — — — — — — — — — —
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
8,000 1036 9.29 1065 9.76 1092 10.24
9,000 1046 10.38 1073 10.87 1100 11.36
10,000 1059 11.63 1086 12.13 1112 12.64
11,000 1076 13.03 1102 13.55 1127 14.07
12,000 1096 14.60 1121 15.13 1145 15.67
13,000 1118 16.34 1142 16.89 1165 17.45
14,000 1143 18.26 1166 18.83 1188 19.40
15,000 1170 20.37 1192 20.96 — —
16,000 1199 22.68 ————
17,000 ——————
18,000 ——————
19,000 ——————
20,000 ——————
AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
3.4 3.6 3.8
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
LEGEND
Bhp — Brake Horsepower
NOTES:
1. Fan performance is based on wet coils, economizer, roof curb,
cabinet losses, and clean 2-in. filters.
2. Conversion − Bhp to watts:
Watts =
3. VAV units will operate down to 70 cfm/ton.
Bhp x 746
Motor efficiency
37
Page 38

Table 14 — Fan Performance, 50EJ048 — Vertical Discharge Units
FOR EW UNITS, REDUCE NET AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE BY 0.5 IN. WG
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
13,000 683 7.10 715 8.59 747 9.09 777 9.60 808 10.11 837 10.62 866 11.14 894 11.66
14,000 730 8.53 761 10.25 790 10.77 819 11.30 847 11.83 875 12.36 902 12.90 929 13.44
15,000 778 10.14 807 12.10 834 12.65 862 13.19 888 13.75 915 14.30 941 14.86 966 15.42
16,000 826 11.93 853 14.15 879 14.72 905 15.29 931 15.86 955 16.44 980 17.01 1004 17.59
17,000 875 13.90 900 16.42 925 17.01 949 17.60 973 18.19 997 18.78 1020 19.38 1043 19.98
18,000 923 16.06 947 18.90 971 19.51 994 20.12 1017 20.73 1039 21.34 1062 21.96 1084 22.58
19,000 972 18.42 995 21.61 1017 22.24 1039 22.87 1061 23.50 1083 24.13 1104 24.76 1125 25.40
20,000 1021 20.98 1042 24.55 1064 25.20 1085 25.85 1106 26.50 1126 27.15 1147 27.80 1167 28.46
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
13,000 921 12.18 948 12.71 975 13.24 1001 13.77 1026 14.30 1051 14.84 1076 15.39 1100 15.93
14,000 955 13.98 981 14.53 1006 15.08 1031 15.63 1056 16.18 1080 16.74 1103 17.30 1127 17.86
15,000 991 15.98 1015 16.54 1040 17.11 1063 17.68 1087 18.25 1110 18.83 1133 19.41 1155 19.99
16,000 1028 18.17 1051 18.76 1074 19.34 1097 19.93 1120 20.52 1142 21.12 1164 21.71 1185 22.31
17,000 1066 20.58 1089 21.18 1111 21.78 1133 22.39 1154 23.00 1175 23.61 1197 24.23 — —
18,000 1106 23.19 1127 23.82 1148 24.44 1169 25.07 1190 25.69 — — ————
19,000 1146 26.04 1166 26.68 1187 27.32 — — — — — — ————
20,000 1187 29.11 — — — — — — — — — — ————
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
13,000 1124 16.48 1148 17.03 1171 17.59
14,000 1150 18.43 1173 19.00 1195 19.57
15,000 1177 20.57 1199 21.16 — —
16,000 ——————
17,000 ——————
18,000 ——————
19,000 ——————
20,000 ——————
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
3.4 3.6 3.6
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
AVAILABLE EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
LEGEND
Bhp — Brake Horsepower
NOTES:
1. Fan performance is based on wet coils, economizer, roof curb,
cabinet losses, and clean 2-in. filters.
2. Conversion − Bhp to watts:
Watts =
3. VAV units will operate down to 70 cfm/ton.
Bhp x 746
Motor efficiency
UNIT
50EJ,EK,EW,EY
024 6,000 2000 6,000 10,000
028 7,500 2500 7,500 12,500
030 8,250 2750 8,250 13,750
034 9,000 3000 9,000 15,000
038 10,500 3500 10,500 17,500
044 12,000 4000 12,000 20,000
048 13,500 4500 13,500 22,500
LEGEND
CV — Constant Volume
VAV — Variable Air Volume
MINIMUM HEATING
CFM
Table 15 — Air Quantity Limits
MINIMUM COOLING
CFM (VAV)
MINIMUM COOLING
CFM (CV)
MAXIMUM
CFM
38
Page 39

STANDARD EFFICIENCY MOTORS
Nominal
Hp
5
7.5
10
15
20
25
30
Maximum
Bhp
5.9 17.94 16.99 — — 5,348 82.3
5.9 — — 8.50 5.78 5,240 84.0
8.7 25.52 24.36 — — 7,717 84.1
9.5 — — 13.30 9.63 8,549 82.9
10.2 26.93 25.50 — — 8,879 85.7
11.8 — — 14.75 11.33 10,284 85.6
15.3 42.84 40.80 — — 13,686 83.4
18.0 — — 24.00 18.00 15,891 84.5
22.4 59.36 56.00 — — 19,032 87.8
23.4 — — 29.25 22.82 19,950 87.5
28.9 76.30 72.83 — — 24,499 88.0
29.4 — — 37.04 28.69 25,181 87.1
35.6 92.56 87.81 — — 29,378 90.4
34.7 — — 42.80 n/a 29,316 88.3
Table 16 — Motor Limitations
Maximum Amps
208 230 460 575
Maximum
Watts
Motor
Efficiency
HIGH EFFICIENCY MOTORS
Nominal
Hp
5
7.5
10
15
20
25
30
LEGEND
BHP — Brake Horsepower
Maximum
Bhp
5.9 16.76 13.92 — — 5,030 87.5
5.9 — — 6.96 — 5,030 87.5
5.9 — — — 5.66 4,918 89.5
8.7 26.10 22.27 — — 7,334 88.5
9.5 — — 12.16 — 8,008 88.5
9.5 — — — 9.50 7,728 91.7
10.2 28.56 24.89 — — 8,502 89.5
11.8 — — 14.40 — 9,836 89.5
11.8 — — — 11.68 9,600 91.0
15.3 45.08 39.17 — — 12,543 91.0
18.0 — — 23.04 — 14,756 91.0
18.0 — — — 18.12 14,439 93.0
22.4 63.84 55.55 — — 18,363 91.0
23.4 — — 29.02 — 19,183 91.0
23.4 — — — 23.17 18,650 93.6
28.9 80.69 70.05 — — 23,511 91.7
29.4 — — 35.63 — 23,918 91.7
29.4 — — — 28.81 23,432 93.6
35.6 102.65 89.00 — — 28,742 92.4
34.7 — — 43.38 — 28,015 92.4
34.7 — — — 33.89 27,656 93.6
208 230 460 575
Maximum Amps
Maximum
Watts
NOTE: Extensive motor and electrical testing on the Carrier units has ensured
that the full horsepower range of the motor can be utilized with confidence.
Using your fan motors up to the horsepower ratings shown on the Motor Limitations table will not result in nuisance tripping or premature motor failure. Unit
warranty will not be affected.
Motor
Efficiency
Table 17 — User Defined Set Points
SET POINT FORMAT DESCRIPTION LIMITS DEFAULT
OHSP xx.xF Occupied Heat Set Point 55 to 80 F 68
OCSP xx.xF Occupied Cool Set Point 55 to 80 F 78
UHSP xx.xF Unoccupied Heat Set Point 40 to 80 F 55
UCSP xx.xF Unoccupied Cool Set Point 75 to 95 F 90
SASP xx.xF Supply Air Set Point 45 to 70 F 55
OATL xx.xF Hi OAT Lockout Temperature 55 to 75 F 65
NTLO xx.xF Unoccupied OAT Lockout Temperature 40 to 70 F 50
RTIO xx.x Reset Ratio 0 to 10 3
LIMT xx.x^F Reset Limit 0 to 20 F 10
MDP xxx% Minimum Damper Position 0 to 100% 20
IAQS xxxx IAQ Set Point 1 to 5000 650
UHDB xx.x^F Unoccupied Heating Deadband 0 to 10 1
UCDB xx.x^F Unoccupied Cooling Deadband 0 to 10 1
LTMP xx.xF Low Temp. Min. Position 0 to 100 10
HTMP xx.xF High Temp. Min. Position 0 to 100 35
PES1 xx.xF CV Power Exhaust Stage 1 Point 0 to 100 25
PES2 xx.xF CV Power Exhaust Stage 2 Point 0 to 100 75
CV — Constant Volume
IAQ — Indoor Air Quality
OAT — Outdoor Air Temperature
LEGEND
39
Page 40

The control module will operate economizer, run diagnostics to monitor alarms/alerts at all times, and respond to
CCN communications to perform any configured network
POC (product outboard control) functions such as time/
outdoor-airtemperature broadcast and global occupancy broadcast. When the optional expansion I/O board is employed, it
will: perform a periodic scan and maintain a database of expanded I/O points; perform Fire/Smoke control (power exhaust required); if in Occupied mode, perform IAQ control
and monitor the fan, filter, demand limit, and field-applied
status (with accessories).
If thermostats are used to energize the G input, the control
module will turn on the indoor fan without delay and open
the economizer dampers to minimum position. If thermostats are used to deenergize the G input, the control module
will turn offthe indoor fan without delay and close the economizer dampers.
When cooling, G must be energized before cooling can
operate. The control module determines if outdoor conditions are suitable for economizer cooling using the standard
outdoor air thermistor. For the economizer to function for
outside air cooling: the enthalpy must be below the enthalpy
set point; the outdoor-air temperature must be equal to or
less than the High Outdoor Air Temperature Lockout (default is 65 F); the SAT (supply-air temperature) thermistor
must not be in alarm; and the outdoor air reading is available. When these conditions are satisfied, the control module will use economizer as the first stage of cooling.
WhenY1 input is energized, the economizer will be modulated to maintain SAT at the defined set point. (The default
is 55 F.) When SAT is above the set point, the economizer
will be 100% open. When SAT is below the set point, the
economizer will modulate between minimum and 100% open
position. When Y2 is energized, the control module will turn
on compressor 1 and continue to modulate the economizer
as described above. If the Y2 remains energized and the SAT
reading remains above the set point for 15 minutes, compressor 2 will turn on. If Y2 is deenergized at any time, only
the last stage of compression that was energized will be turned
off.If outdoor conditions are not suitable for economizer cooling, the economizer will go to minimum position and cycle
compressors 1 and 2 based on demand from Y1 and Y2 respectively.The compressors will be locked out when the SAT
temperature is too low (less than 40 F for compressor 1 and
less than 45 F for compressor 2).After a compressor is locked
out, it can restart after normal time-guard period.
The Time Guardt function maintains a minimum off time
of 5 minutes, a minimum on time of 10 seconds, and a
minimum delay before starting the second compressor of
10 seconds.
When heating, the heat stages respond to the demand from
W1 and W2 of the thermostat input. Heating and cooling
will be mutually locked-out on demand on a first call basis.
The heating and the cooling functions cannot operate
simultaneously.
COOLING, VARIABLE VOLUME UNITS — On power up,
the control module will activate the initialization software.
The initialization software reads DIP switch no. 1 position
to determine CV or VAV operation. The initialization sequence: clears all alarms and alerts; re-maps the input/
output database for VAV operation; sets maximum heat stages
to 1; and sets maximum cool stages to 6. The control module
reads DIP switch no. 3 and determines if the unit will use
expansion mode operation. Power up takes a random time of
1 to 63 seconds plus 5 minutes the first time power is sent
to the control board after a power outage.
The control module will determine if an interface (linkage) is active and if the unit will operate in a Digital Air
Volume (DAV) mode. In a DAV system, the room terminals
are equipped with microprocessor controls that give
commands to the base unit module. If a linkage is active, the
control module will replace local comfort set points, space
and return air temperatures, and occupancy status with the
linkage data supplied.
The control module will determine occupancy status from
Time Schedules (if programmed), Remote Occupied/
Unoccupied input, global occupancy schedules, or DAV. If
temperature compensated start is active, the unit will be controlled as in the Occupied mode.
NOTE: The temperature compensated start is a period of time
calculated to bring the unit on while in Unoccupied mode to
reach the occupied set point when occupancy occurs.
The control module will set the appropriate operating mode
and fan control. The control module will turn on the VFD if
Occupied mode is evident. If in Unoccupied mode and a valid
space temperature reading is available (either from a sensor
or DAV), the control module will monitor SPT (space temperature) against unoccupied heat and cool set points. The
control module will start the VFD whenever SPT is outside
of the set points (Unoccupied Heat or Unoccupied Cool).
The VFD may also be started by nighttime thermostat via
remote Occupied/Unoccupied input or by a temperature compensated start algorithm. When the VFD is running in a normal mode, the control module will start heating or cooling
as required to maintain supply-air temperature at the supply
air set point plus the reset (when enabled). The reset value
is determined by SAT (supply-air temperature) reset and/or
space temperature reset algorithms. The reset is only available when enabled through software.
When cooling, the control module will energize the power
exhaust enable output to the external power exhaust controller (when power exhaust is used).
The control module will run continuous diagnostics for
alarms/alerts; respond to CCN (Carrier Comfort Network)
communications; perform any configured network POC (Product Outboard Control) functions such as time/outdoor air temperature broadcast and global broadcast; and perform Fire/
Smoke control.
HEATING, CONSTANT VOLUME (CV) UNITS — The
control module is powered by 24 vac. If the unit is controlled with a room sensor, the fan will run continuously in
the Occupied mode, with the outside-air damper in the minimum position. If the unit is controlled through a room thermostat (with FANset to AUTO), upon a call for heat the first
stage of heat is energized, the indoor-fan motor will turn on,
and the outdoor-air damper will move to the minimum position. Upon a call for additional heat (if the unit is equipped
with a two-stage heater), the second stage of heat is energized. When the call for heat is satisfied, the heaters will
deenergize. The indoor-fan motor will also deenergize (unless controlled by a room sensor) and the outdoor-air damper
will move to the closed position.
If the unit is controlled with a room sensor the fan will not
run in the unoccupied mode. Upon a call for heat, the first
stage of heat is energized, the indoor-fan motor will turn on,
and the outdoor air damper will move to the Unoccupied
IAQ position (generally set to zero in the unoccupied mode).
The IAQ feature is enabled through system software. Upon
a call for additional heat (if the unit is equipped with a twostage heater), the second stage of heat is energized. When
the call for heat is satisfied, the heaters and indoor-fan motor
will deenergize and the outdoor-air damper will move to the
closed position (if open).
HEATING, VARIABLE AIR VOLUME (VAV) UNITS —
The control board is powered by 24 vac. When there is a call
for heating (from Morning Warm-Up, Unoccupied, or Occupied modes), power is sent from the control module to
energize the first stage of electric heat. A field-supplied heat
40
Page 41

interlock relay signals for the air terminals to fully open. See
Fig. 35. In the Occupied mode, the indoor-fan motor will
operate continuously and the outdoor-air dampers will be in
the minimum position. In the Unoccupied mode, the indoorfan motor will be off, but will energize upon the call for heat.
The outdoor-air dampers will move to the IAQ unoccupied
position (generally set to zero in the Unoccupied mode). The
IAQ feature is enabled through system software. The duct
pressure sensor will signal to the variable frequency drive to
operate at full speed. Upon a call for additional heat (if the
unit is equipped with a two-stage heater), the second stage
of heat will be energized. When the call for heat is satisfied,
the heaters will deenergize.
NOTE: The HIR is not needed in a DAV system.
If the unit is in the Unoccupied mode, the indoor-fan motor will deenergize and the outdoor-air damper will move to
the closed position (if open).
MORNINGWARM-UP (VA VONLYWITH PC ACCESSED/
CCN OPERATION) — Morning warm-up occurs when the
control module has been programmed to turn on heat, prior
to the Occupied mode, to be ready for the occupancy. Morning warm-up is a condition in VAV systems that occurs when
the Temperature Compensated Start algorithm calculates a
biased occupied start time and the unit has a demand for heating. The warm-up will continue into the occupied period as
long as there is a need for heat. During warm-up, the unit
can continue heating into the occupied period, even if occupied heating is disabled. When the heating demand is satisfied, the warm-up condition will terminate. To increase or
decrease the heating demand, use the network access software to change the occupied heating set point.
NOTE: To utilize morning warm-up mode, the unit occupancy schedule must be accessed via Service Tool, Comfort
Works, or Building Supervisor software (units running Version 1.0 of unit control software).
MORNINGWARM-UP (VAV ONLYWITH STAND-ALONE
OPERATION) — When a unit running version 2.0 of the
unit control software operates in stand-alone mode, morning
warm-up occurs when the unit is energized in Occupied mode
and return-air temperature (RAT) is below 68 F. Warm-up
will not terminate until the RAT reaches 68 F. The heat interlock relay output is energized during morning warm-up.
(Afield-installed 24-vdc heat interlock relay is required.) The
output will be energized until the morning warm-up cycle is
complete. Refer to Fig. 35 for heat interlock relay wiring.
SPACE TEMPERATURE RESET (VAV ONLY) — An accessory space temperature sensor is required. Space temperature reset is used to reset the supply-air temperature set
point of a VAV system higher, as the space temperature falls
below the Occupied Cool set point. As the space temperature falls below the cool set point, the supply-air temperature will be reset upward as a function of the reset ratio. Reset ratio is expressed in degrees change in supply-air temperature
per degree of space temperature change. A reset limit will
exist which will limit the maximum number of degrees the
supply-air temperature may be raised. Both the reset ratio
and the reset limit are user definable. The sequence of operation is as follows:
1. The on/off status of the unit supply fan is determined.
2. If the fan is on, the sequence will check if the system is
in Occupied mode.
3. If the system is in Occupied mode, the sequence will de-
termine if the reset option is enabled.
4. If the reset option is enabled, the sequence will read the
space temperature and compare it to the Occupied Cool
set point. If the temperature is below the Occupied Cool
set point, the algorithm will compute the reset value and
compare this value against the reset limit. If it is greater
than the reset limit, the sequence will use the reset limit
as the reset value.
The field-supplied space temperature sensor input signal
(4 to 20 ma and 2 to 10 vdc) enables the space temperature
reset function. Refer to Fig. 36 for sensor wiring.
POWER EXHAUST OPERATION — The optional power
exhaust packages are factory- or field-installed with vertical
units and optionally installed in the return air ductwork for
horizontal applications. The standard (only offeredwith constant volume units) and modulating power exhaust (offered
on VAV units) are the 2 packages available. The modulating
power exhaust package is equipped with a field-adjustable
static pressure controller which will control up to 4 power
exhaust stages to maintain a building static pressure. The blue
sequencer located in the control box below the control board
can be adjusted by removing the covers and adjusting the set
point dial to the desired building pressure. The standard power
exhaust package controls up to 2 stages of power exhaust to
maintain building pressure. These power exhaust stages are
staged according to a percentage of the economizer damper
position. The default values are 25% for Stage 1 and 75%
for Stage 2. This package has set points that are adjustable
through software (such as Service Tool, Building Supervisor, or Comfort Works).
Fig. 35 — Heat Interlock Relay Wiring
Fig. 36 — Space Temperature Sensor Wiring
41
Page 42

CAPACITY CONTROL, COOLING — The cooling capacity staging tables are shown in Tables 18 and 19.
Table 18 — Cooling Capacity Staging Table
CV Units with 2 Compressors
STAGES 0
Compressor 1 Off Off On On
Compressor 2 Off Off Off On
NOTE:OnCVunitsthatrequire additional unloading, add suction pressure unloaders on Compressor 1 only.
1
ECONOMIZER
23
MOTORMASTERt III DEVICE — The Motormaster III
Solid-State Head Pressure Control is a field-installed accessory,fan speed control device actuated by a temperature sensor. The Motormaster III device is specifically designed for
use on Carrier equipment and controls the outdoor-fan motor speed in response to the saturated condensing temperature. For outdoor temperatures down to −20 F, the Motormaster III device maintains condensing temperature at
100 F.
SERVICE
Table 19 — Cooling Capacity Staging Table
VAV Units with 2 Compressors
and 2 Unloaders*
STAGES 0 123456
Compressor 1 OffOnOnOnOnOnOn
Unloader 1 Off On On Off On On Off
Unloader 2 Off On Off Off On Off Off
Compressor 2 Off Off Off Off On On On
*40 ton units have only 1 unloader.
FIELD TEST — The field test program is initiated by moving up DIP switch no. 4 to the OPEN position. The outdoorair damper will close. The control allows 90 seconds for the
damper to close in case it was in the full open position. Next,
the indoor-fan contactor will be energized, and the outsideair damper will begin to open to its default value of 20% and
stay at that position for a short period of time. The outdoorair damper will then open to its full open position and stay
at that position for a short period of time. The outdoor-air
damper will then close.
If the unit is equipped with power exhaust, stage 1 will be
energized for 5 seconds. If the unit is configured for stage 2
of power exhaust, stage 2 will be energized for 5 seconds
after the first stage is deenergized.
The first stage of heat will be energized for 30 seconds,
after which the second stage heat will be energized for an
additional 30 seconds. Heat is then deenergized.
The last step is the Cooling mode. Outdoor-fan contactor
no. 1 is energized. This is followed by each stage of cooling
energized with a 10-second delay between stages. After this
is complete, outdoor-fan contactor no. 2 is energized for
10 seconds.
The compressors will now deenergize, followed by the
outdoor-fan contactors and indoor-fan contactors.
The field test is then complete.
TIME GUARDt CIRCUIT — TheTimeGuard function (built
into the rooftop’s control module board) maintains a minimum off time of 5 minutes and a minimum on time of
10 seconds.
CRANKCASE HEATER — The unit main power supply must
remain on to provide crankcase heater operation. The crankcase heater in each compressor keeps oil free of refrigerant
while compressor is off.
HEAD PRESSURE CONTROL — Each unit has a fan cycling, outdoor thermostat to shut off outdoor-fan motor(s) at
55 F (one outdoor-fan motor on 024-034 units and 2 outdoorfan motors on 038-048 units). The head pressure control permits the unit to operate with correct condensing temperatures
down to 35 F outdoor-air temperature.
Before performing service or maintenance operations on
unit, turn off main power switch to unit. Turn off accessory heater power switch if applicable. Electrical shock
could cause personal injury.
ServiceAccess — All unit components can be reached
through clearly labelled hinged access doors. These doors
are not equipped with tiebacks, so if heavy duty servicing is
needed, either remove them or prop them open to prevent
accidental closure.
Each door is held closed with 3 latches. The latches are
secured to the unit with a single
See Fig. 37.
To open, loosen the latch bolt using a
the latch so it is not in contact with the door. Open the door.
To shut, reverse the above procedure.
NOTE: Disassembly of the top cover may be required under
special service circumstances. It is very important that the
orientation and position of the top cover be marked on the
unit prior to disassembly. This will allow proper replacement of the top cover onto the unit and prevent rainwater
from leaking into the unit.
IMPORTANT:After servicing is completed, make sure
door is closed and relatched properly,and that the latches
are tight. Failure to do so can result in water leakage
into the evaporator section of the unit.
Fig. 37 — Door Latch
1
⁄4-in.-20x1⁄2-in. long bolt.
7
⁄16-in. wrench. Pivot
42
Page 43

Cleaning— Inspect unit interior at beginning of each heat-
ing and cooling season and as operating conditions require.
Remove unit top panel and/or side panels for access to unit
interior.
EVAPORATOR COIL — Clean as required with a commercial coil cleaner.
CONDENSER COIL — Clean condenser coil annually and
as required by location and outdoor-air conditions. Inspect
coil monthly — clean as required.
CONDENSATE DRAIN — Check and clean each year at
start of cooling season. In winter, keep drains and traps dry.
FILTERS — Clean or replace at start of each heating and
cooling season, or more often if operating conditions require. Refer to Table 1 for type and size.
NOTE: The unit requires industrial grade throwaway filters
capable of withstanding face velocities up to 625 fpm.
OUTDOOR-AIR INLET SCREENS — Clean screens with
steam or hot water and a mild detergent. Do not use throwaway filters in place of screens.
Lubrication
COMPRESSORS — Each compressor is charged with the
correct amount of oil at the factory. The correct oil charge is
shown in Table 1. If oil is visible in the compressor sight
glass, check unit for operating readiness as described in Start-Up
section, then start the unit. Observe oil level and add oil, if
required, to bring oil level in compressor crankcase up to
between1⁄4and1⁄3of sight glass during steady operation.
1
If oil charge is above
until the compressor crankcase heater has been energized for
at least 24 hours with compressor off.
When additional oil or a complete charge is required, use
only Carrier-approved compressor oil:
Petroleum Specialties, Inc. .................Cryol 150
Texaco, Inc. .........................Capella WF-32
Witco Chemical Corp. ...................Suniso 3GS
⁄3sight glass, do not remove any oil
CONDENSERAND EVAPORATOR-FAN MOTOR BEARINGS — The condenser and evaporator-fan motors have
permanently-sealed bearings, so no field lubrication is
necessary.
Evaporator Fan Performance Adjustment
(Fig. 38) —
shown in Table 1 (factory speed setting).
To change fan speeds, change pulleys.
To align fan and motor pulleys:
1. Shut off unit power supply.
2. Loosen fan shaft pulley bushing.
3. Slide fan pulley along fan shaft.
4. Make angular alignment by loosening motor from mounting plate.
5. Retighten pulley.
IMPORTANT: Check to ensure that the unit drive
matches the duct static pressure in Tables 12 to 14.
Fan motor pulleys are factory set for speed
Evaporator Fan Service and Replacement
1. Turn off unit power.
2. Remove supply-air section panels.
3. Remove belt and blower pulley.
4. Loosen set screws in blower wheels.
5. Remove locking collars from bearings.
6. Remove shaft.
7. Remove venturi on opposite side of bearing.
8. Lift out wheel.
9. Reverse above procedure to reinstall fan.
10. Check and adjust belt tension as necessary.
IMPORTANT: Do not use reclaimed oil or oil that has
been exposed to the atmosphere. Refer to Carrier Standard Service Techniques Manual, Chapter 1, Refrigerants section, for procedures to add or remove oil.
FAN SHAFT BEARINGS — Lubricate the bearings at least
twice annually with suitable bearing grease. Do not over grease.
Typical lubricants are show below:
MANUFACTURER LUBRICANT
Texaco Regal AFB-2*
Mobil Mobilplex EP No. 1
Sunoco Prestige 42
Texaco Multifak 2
*Preferred lubricant because it contains rust and oxidation inhibitors.
Fig. 38 — Evaporator-Fan Pulley Alignment
and Adjustment
43
Page 44

Belt Tension Adjustment — To adjust belt tension:
1. Remove power to unit.
2. Remove motor mount nuts and bolts.
3. Loosen fan motor nuts. See Fig. 39.
4. Turn motor jacking bolts to move motor mounting plate
left or right for proper belt tension. A slight bow should
be present in the belt on the slack side of the drive while
running under full load.
5. Tighten nuts.
6. Adjust bolts and nut on mounting plate to secure motor
in fixed position. Recheck belt tension after 24 hours of
operation. Adjust as necessary.
Condenser-Fan Adjustment
1. Shut off unit power supply.
2. Remove fan guard.
3. Loosen fan hub setscrews.
4. Adjust fan height on shaft using a straightedge placed across
venturi and measure per Fig. 40.
5. Tighten setscrews and replace fan guard.
6. Turn on unit power.
Evaporator-Fan Motor Replacement
1. Shut off unit power supply.
2. Remove upper outside panel and open hinged door to
gain access to motor.
3. Fully retract motor plate adjusting bolts.
4. Loosen the 2 rear (nearest the evaporator coil) motor
plate nuts.
5. Remove the 2 front motor plate nuts and carriage bolts.
6. Slide motor plate to the rear (toward the coil) and remove fan belt(s).
7. Slide motor plate to the front and hand tighten one of
the rear motor plate nuts (tight enough to prevent the
motor plate from sliding back but loose enough to allow
the plate to pivot upward).
8. Pivot the front of the motor plate upward enough to allow access to the motor mounting hex bolts and secure
in place by inserting a prop.
9. Remove the nuts from the motor mounting hex bolts and
remove motor.
10. Reverse above steps to install new motor.
PowerFailure — Dampers have a spring return. In event
of power failure, dampers will return to fully closed position
until power is restored.
Refrigerant Charge — Amount of refrigerant charge
is listed on unit nameplate and in Table 1. Refer to Carrier
GTAC II; Module 5; Charging, Recovery,Recycling, and Reclamation section for charging methods and procedures.
Unit panels must be in place when unit is operating dur-
ing charging procedure.
NO CHARGE — Use standard evacuating techniques. After
evacuating system, weigh in the specified amount of refrigerant (refer to Table 1).
LOW CHARGE COOLING — Using appropriate cooling
charging chart (see Fig. 41 and 42), add or remove refrigerant until conditions of the appropriate chart are met. Note
that charging chart is different from those normally used.An
accurate pressure gage and temperature sensing device are
required. Measure liquid line pressure at the liquid line service valve using pressure gage. Connect temperature sensing
device to liquid line near the liquid line service valve and
insulate it so that outdoor ambient temperature does not affect reading. Indoor-air cfm must be within normal operating range of unit. Takeoutdoor ambient temperature and read
the suction pressure gage. Refer to appropriate chart to determine correct suction temperature. If intersection point on
chart is above the curve, add refrigerant. If intersection point
on chart is below curve, carefully recover some of the charge.
Recheck suction pressure as charge is adjusted.
Fig. 39 — Belt Tension Adjustment
Fig. 40 — Condenser-Fan Adjustment
Filter Drier — Replace whenever refrigerant system is
exposed to atmosphere.
Thermostatic Expansion Valve(TXV) — Each cir-
cuit has one. It is nonadjustable and is factory set to maintain 10 to 13° F superheat leaving the evaporator coil. Controls flow of liquid refrigerant to the evaporator coils.
Protective Devices
COMPRESSOR PROTECTION
Overcurrent — Each compressor has one manual reset, cali-
brated trip, magnetic circuit breaker. Do not bypass connections or increase the size of the circuit breaker to correct trouble.
Determine the cause and correct it before resetting the breaker.
Overtemperature — Each 06D type compressor (024-038 units
only) has an internal protector to protect it against excessively high discharge gas temperatures.
44
Page 45

Crankcase Heater — Each compressor has a crankcase heater
to prevent absorption of liquid refrigerant by oil in the crankcase when the compressor is idle. Since power for the crankcase heaters is drawn from the unit incoming power, main
unit power must be on for the heaters to be energized.
IMPORTANT: After a prolonged shutdown or service job, energize the crankcase heaters for 24 hours
before starting the compressors.
EVAPORATOR-FAN MOTOR PROTECTION — A manual reset, calibrated trip, magnetic circuit breaker protects
against overcurrent. Do not bypass connections or increase
the size of the breaker to correct trouble. Determine the cause
and correct it before resetting the breaker. If the evaporatorfan motor is replaced with a different horsepower motor, resizing of the circuit breaker is required. Contact Carrier Application Engineering.
CONDENSER-FAN MOTOR PROTECTION — Each
condenser-fan motor is internally protected against
overtemperature.
HIGH- AND LOW-PRESSURE SWITCHES — If either
switch trips, or if the compressor overtemperature switch activates, that refrigerant circuit will be automatically locked
out. To reset, manually move the thermostat setting.
FREEZE PROTECTION THERMOSTAT (FPT) — An FPT
is located on the evaporator coil for each circuit. It detects
frost build-up and turns offthe compressor, allowing the coil
to clear. Once the frost has melted, the compressor can be
reenergized.
Relief Devices — All units have relief devices to pro-
tect against damage from excessive pressures (i.e., fire). These
devices are installed on the suction line, liquid line, and on
the compressor.
Control Circuit, 24-V — This control circuit is pro-
tected against overcurrent by a 3.2-amp circuit breaker (CB4).
Breaker can be reset. If it trips, determine cause of trouble
before resetting.
Control Circuit, 115-V — This control circuit is pro-
tected against overcurrent by a 5.0-amp circuit breaker (CB3).
Breaker can be reset. If it trips, determine cause of trouble
before resetting.
Compressor Lockout Logic — If any of the safe-
ties trip, the circuit will automatically reset (providing the
safety has reset) and restart the compressor in 15 minutes. If
any of the safeties trip 3 times within a 90-minute period,
then the circuit will be locked out and will require manual
resetting by turning off either the unit disconnect or the control circuit breaker, or opening the thermostat.
Replacement Parts — A complete list of replacement
parts may be obtained from any Carrier distributor upon
request.
Fig. 41 — Cooling Charging Chart,
Sizes 024-034
Fig. 42 — Cooling Charging Chart,
Sizes 038-048
45
Page 46

TROUBLESHOOTING
Typical refrigerant circuiting diagrams are shown in Fig. 43-45.
LEGEND
FPS — Freeze Protection Switch
HPS — High-Pressure Switch
LPS — Low-Pressure Switch
Fig. 43 — Typical Refrigerant Circuiting
(50EJ,EK,EW,EY024-034)
46
Page 47

LEGEND
FPS — Freeze Protection Switch
HPS — High-Pressure Switch
LPS — Low-Pressure Switch
Fig. 44 — Typical Refrigerant Circuiting
(50EJ,EK,EW,EY038,044)
47
Page 48

LEGEND
FPS — Freeze Protection Switch
HPS — High-Pressure Switch
LPS — Low-Pressure Switch
Fig. 45 — Typical Refrigerant Circuiting
(50EJ,EW048)
48
Page 49

DiagnosticLEDs (Light-Emitting Diodes) — There
are 3 LEDs (red, yellow, and green) on the lower right hand
side of the control board. The red light is used to check
unit operation and alarms. A constant pulse is normal unit
operation. A series of quick blinks indicates an alarm. Refer
Table 20 — Control Board LED Alarms
to Table 20 below for a description of alarms. The yellow
LED blinks during transmission with the CCN (Carrier Comfort Network). The green LED blinks during transmission
with the expansion board.
LED
BLINKS
1 Normal Operation The expansion board and control board flash the red LED in one-
2 HF-13 Compressor 1 Safety The high or low pressure safety switch for compressor no. 1 has
3 HF-14 Compressor 2 Safety The high or low pressure safety switch for compressor no. 2 has
4 HF-15 Thermostat Failure The thermostat is calling for both heating and cooling at the
5 HF-05 SAT Thermistor Failure The supply-air temperature (SAT) sensor has failed. First check for
6 HF-06 OAT Thermistor Failure The outside-air temperature (OAT) sensor has failed. First check
7 HF-03 Space Temp. Sen. Failure The space temperature sensor has failed. First check for wiring
8 HF-12 RAT Thermistor Failure The return-air temperature (RAT) sensor has failed. Ensure that
9 SE-05 Loss of Communications
10 HF-16 Control Board Failure Generated when hardware has failed on control board. Replace
11 HF-17 Expansion Board Failure Generated when hardware has failed on the expansion board.
LEGEND
DIP — Dual In-Line Package
LED — Light-Emitting Diode
VAV — VariableAir Volume
ERROR
CODE
DESCRIPTION
with Expansion board
TROUBLESHOOTING
COMMENTS
second intervals when the board is operating properly.
opened for 3 seconds. The error will be cleared and compressor
no. 1 will be allowed to turn on in 15 minutes. If the safeties have
been tripped 3 times in 90 minutes, compressor no. 1 will be
locked out until the control board has been manually reset.
opened for 3 seconds. The error will be cleared and compressor
no. 2 will be allowed to turn on in 15 minutes. If the safeties have
been tripped 3 times in 90 minutes, compressor no. 2 will be
locked out until the control board has been manually reset.
same time. The unit will operate on a first call basis and will automatically reset.
wiring errors, then replace sensor.
for wiring errors, then replace sensor.
errors, then replace sensor.
the unit is a VAV unit. If NOT a VAV unit set DIP switch position 1
to the closed position and reset power. Then check for wiring
errors. Finally, replace sensor.
Communications between the expansion board and the control
board have been interrupted. Ensure that an expansion board
is installed and wired using the wire harness supplied with the
expansion module. If an expansion board is not used ensure that
DIP switch position 3 is in the closed position, and reset power.
the control board.
Replace the expansion board.
49
Page 50

Tables 21-23 show the input and output channel designations.
Table 21 — I/O Channel Designations
Base Module — CV
TERMINAL
NO.
T1-2 SPT (CCN) — 10KV Thermistor
T3-4 STO (CCN) — 10KV Thermistor
T5-6 OAT — 5KV Thermistor
T7-8 SAT — 5KV Thermistor
T9-10 —
T11-12 SAT Reset — AI (2-10 vdc)
T13-14 —
T15-16 —
T17-25 Y1 or Remote Start/Stop — DI (24 vac)
T18-25 Y2 — DI (24 vac)
T19-25 W1 — DI (24 vac)
T20-25 W2 — DI (24 vac)
T21-25 G — DI (24 vac)
T22-25 Compressor 1 Safety — DI (24 vac)
T23-25 Compressor 2 Safety — DI (24 vac)
T24-25 Outside Air Enthalpy — DI (24 vac)
T26-27 Economizer Pos. — AO (4-20 mA)
T28-29 Heat 1 Relay — DO (24 vac)
T30-29 Heat 2 Relay — DO (24 vac)
T31-32
T33-32 CV Power Exhaust2—DO(115vac)
T34-35 Condenser Fan — DO (115 vac)
T36-35 OFC2 — DO (115 vac)
T37-38 —
T39-38 —
K1 Indoor Fan Relay — DO (HV)
K2 Compr.1—DO(HV)
K3 Compr.2—DO(HV)
AI — Analog Input
AO — Analog Output
CCN — Carrier Comfort Network
CV — Constant Volume
DI — Direct Input
DO — Direct Output
HV — High Voltage
KV — Kilo-Ohms
OAT — Outdoor-Air Temperature
OFC — Outdoor Fan Contactor
RAT — Return-Air Temperature
SAT — Supply-Air Temperature
SPT — Space Temperature
STO — Space Temperature Offset
T—Terminal
VAV — Variable Air Volume
CV Power Exhaust 1/Modulating Pwr Exht — DO
(115 vac)
LEGEND
(Tables 21 and 22)
ASSIGNMENT
Table 22 — I/O Channel Designations
Base Module — VAV
TERMINAL
NO.
T1-2 SPT (CCN) — 10KV Thermistor
T3-4 RAT — 5KV Thermistor
T5-6 OAT — 5KV Thermistor
T7-8 SAT — 5KV Thermistor
T9-10 —
T11-12 SAT Reset — AI (2-10 vdc)
T13-14 —
T15-16 —
T17-25 Remote Start/Stop — DI (24 vac)
T18-25 —
T19-25 —
T20-25 —
T21-25 —
T22-25 Compressor 1 Safety — DI (24 vac)
T23-25 Compressor 2 Safety — DI (24 vac)
T24-25 Outside Air Enthalpy — DI (24 vac)
T26-27 Economizer Pos. — AO (4-20 mA)
T28-29 Heat 1 Relay — DO (115 vac)
T30-29 Heat Interlock Relay — DO (115 vac)
T31-32 Modulated Power Exhaust — DO (115 vac)
T33-32 —
T34-35 Condenser Fan — DO (115 vac)
T36-35 OFC2 — DO (115 vac)
T37-38 Unloader1—DO(115vac)
T39-38 Unloader2—DO(115vac)
K1 Indoor Fan Relay — DO (HV)
K2 Compr.1—DO(HV)
K3 Compr.2—DO(HV)
ASSIGNMENT
50
Page 51

Table 23 — I/O Channel Designations Expansion
Module — CV and VAV
TERMINAL
NO.
T1-2 —
T3-4 —
T5-6 —
T7-8 —
T9-10 —
T11-12 IAQ Indoor — AI (2-10 vdc)
T13-14 IAQ Outdoor — AI (2-10 vdc)
T15-16 —
T17-25 Fan Status — DI (24 vac)
T18-25 Filter Status — DI (24 vac)
T19-25 Field Applied Status — DI (24 vac)
T20-25 Demand Limit — DI (24 vac)
T21-25 Fire — Unit Shutdown — DI (24 vac)
T22-25 Fire — Pressurization — DI (24 vac)
T23-25 Fire — Evacuation — DI (24 vac)
T24-25 Fire — Smoke Purge — DI (24 vac)
T26-27 —
T28-29 —
T30-29 Alarm Light Indicator — DO (24 vac)
T31-32 Power Exhaust Fire #1 — DO (115 vac)
T33-32 Power Exhaust Fire #2 — DO (115 vac)
T34-35 Power Exhaust Fire #3 — DO (115 vac)
T36-35 Power Exhaust Fire #4 — DO (115 vac)
T37-38 —
T39-38 —
K1 —
K2 —
K3 —
LEGEND
AI — Analog Input
DI — Direct Input
DO — Direct Output
IAQ — Indoor Air Quality
T—Terminal
ASSIGNMENT
51
Page 52

Page 53

Page 54

PACKAGED SERVICE TRAINING
Our packaged service training programs provide an excellent way to increase your knowledge of the
equipment discussed in this manual. Product programs cover:
• Unit Familiarization
• Installation Overview
A large selection of product, theory, and skills programs is available. All programs include a video
cassette and/or slides and a companion booklet. Use these for self teaching or to conduct full training
sessions.
For a free Service Training Material Catalog (STM), call 1-800-962-9212. Ordering instructions are
included.
• Maintenance
• Operating Sequence
Copyright 1996 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1
Tab 1b
PC 111 Catalog No. 535-006 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50E-3SI Pg 54 8-96 Replaces: 50E-1SI
Page 55

START-UP CHECKLIST
MODEL NO.:
SOFTWARE VERSION (SEE FIG. 15)
DATE:
SERIAL NO.:
TECHNICIAN:
PRE-START-UP:
M VERIFY THAT DIP SWITCH SETTINGS ARE CORRECT
M VERIFY THAT ALL PACKING MATERIALS HAVE BEEN REMOVED FROM UNIT
M REMOVE ALL SHIPPING HOLDDOWN BOLTS AND BRACKETS PER INSTRUCTIONS
M VERIFY INSTALLATION OF ECONOMIZER HOOD
M VERIFY INSTALLATION OF ALL OPTIONS AND ACCESSORIES
M VERIFY THAT CONDENSATE CONNECTION IS INSTALLED PER INSTRUCTIONS
M VERIFY THAT ALL ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS AND TERMINALS ARE TIGHT
M CHECK THAT INDOOR-AIR FILTER IS CLEAN AND IN PLACE
M VERIFY THAT UNIT IS LEVEL WITHIN TOLERANCES
M CHECK FAN WHEELS AND PROPELLERS FOR LOCATION IN HOUSING/ORIFICE, AND VERIFY SET SCREW
IS TIGHT
M VERIFY THAT FAN SHEAVES ARE ALIGNED AND BELTS ARE PROPERLY TENSIONED
M VERIFY THAT SUCTION, DISCHARGE, AND LIQUID LINE SERVICE VALVES ON EACH CIRCUIT ARE OPEN
START-UP
ELECTRICAL
SUPPLY VOLTAGE L1-L2 L2-L3 L3-L1
COMPRESSOR AMPS — COMPRESSOR NO. 1 L1 L2 L3
— COMPRESSOR NO. 2 L1 L2 L3
SUPPLY FAN AMPS (CV) EXHAUST FAN AMPS
(VAV) *
*VAV fan supply amps reading must be taken with a true RMS meter for accurate readings.
ELECTRIC HEAT AMPS (IF SO EQUIPPED) L1 L2 L3
TEMPERATURES
OUTDOOR-AIR TEMPERATURE F DB (Dry-Bulb)
RETURN-AIR TEMPERATURE F DB F WB (Wet-Bulb)
COOLING SUPPLY AIR F
ELECTRIC HEAT SUPPLY AIR (IF SO EQUIPPED) F
PRESSURES
REFRIGERANT SUCTION CIRCUIT NO. 1 PSIG CIRCUIT NO. 2 PSIG
REFRIGERANT DISCHARGE CIRCUIT NO. 1 PSIG CIRCUIT NO. 2 PSIG
M VERIFY REFRIGERANT CHARGE USING CHARGING CHARTS ON PAGE 45
CL-1
Page 56

START-UP CHECKLIST (cont)
GENERAL
M ECONOMIZER MINIMUM VENT AND CHANGEOVER SETTINGS TO JOB REQUIREMENTS
M ENSURE DRIVES OPERATE WITHIN LIMITS OF FAN PERFORMANCE TABLES
HIGH-PRESSURE SWITCH SETTING
LOW-PRESSURE SWITCH SETTING
MOTOR PULLEY PART NUMBER
FAN PULLEY PART NUMBER
BELT PART NUMBER
BELT SIZE in.
FILTER QUANTITY
FILTER SIZES in.
ADDITIONAL NOTES:
PSIG
PSIG
Copyright 1996 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1
Tab 1b
PC 111 Catalog No. 535-006 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50E-3SI Pg CL-2 8-96 Replaces: 50E-1SI
CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Loading...
Loading...