F-789SGA
SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR
USER INSTRUCTIONS
E-IE-455
ENGLISH

Contents
Display ...............................................................................................................P.2
Getting Started
Power On, Off ...........................................................................................P.3
Display Contrast Adjustment..................................................................... P.3
Mode Selection ..................................................................................... P.3-4
Application Function Menu (Apps Key) ................................................. P.4-5
Calculator Set-up Menu ........................................................................ P.5-7
Before Using the Calculator ......................................................................P.7
Inputting Expressions and Values
Input Capacity ...........................................................................................P.8
Input Editing.......................................................................................... P.8-10
Inputting and Display Result in Mathematics Mode...................................P.10
Input Range and Error Messages
Calculation Precision, Input Range ................................................... P.10-13
Order of Operations .......................................................................... P.14-15
Calculation Stacks...................................................................................P.15
Error Messages and Error Locator.................................................... P.15-16
Basic Calculations
Arithmetic Calculations............................................................................P.17
Memory Calculations......................................................................... P.17-18
Fraction Calculations...............................................................................P.19
Display Values Exchange ......................................................................P.20
Percentage Calculations .........................................................................P.21
Degree-Minutes-Seconds Calculations................................................... P.21
Replay & Multi-statements ......................................................................P.22
Constant Value Calculations ............................................................. P.23-26
Metric Conversions ........................................................................... P.27-28
Functional Scientific Calculations
Square, Root, Cube, Cube Root, Power, Power Root,
Reciprocal and Pi ....................................................................................P.28
Logarithm, Natural Logarithm, Antilogarithm and Logab.........................P.29
Angle Unit Conversion ............................................................................P.29
Trigonometry Calculations ......................................................................P.30
Permutation, Combination, Factorials and Random
Number Generation.................................................................................P.31
Produce (�) Calculation ..........................................................................P.32
Summation (∑) Calculation ....................................................................P.32
Maximum Value and Minimum Value Calculation .................................. P.32
Modulus After Division (Mod) Calculations ............................................P.33
Least Common Multiple and Greatest Common Divisor.......................... P.33
Prime Fractorization ................................................................................P.34
Quotient and Remainder Calculations ....................................................P.35
Coordinate Conversion ..................................................................... P.35-36
Absolute Value Calculation .....................................................................P.36
Engineering Notation...............................................................................P.36
Complex Number Calculations.......................................................... P.37-38
Base-n Calculations and Logical Calculations ........................................P.39
Statistical Calculations
Statistical Type Selection ........................................................................P.40
Statistical Data Input ...............................................................................P.41
Editing Statistical Sample Data ...............................................................P.41
Statistical Calculation Screen..................................................................P.42
Statistical Menu................................................................................. P.42-43
Statistical Calculation Example ......................................................... P.44-45
Distribution Calculations.................................................................... P.45-46
Equation Calculations............................................................................... P.47-49
Solve Function........................................................................................... P.49-50
CALC Function .......................................................................................... P.50-51
Differential Calculations ........................................................................... P.51-52
Integration Calculations ........................................................................... P.52-53
Matrix Calculations ................................................................................... P.53-58
Vector Calculations................................................................................... P.58-62
Function (x, y) Table Calculation ..................................................................P.63
Battery Replacement.......................................................................................P.64
Advice and Precautions ........................................................................... P.64-65
Specifications .................................................................................................P.65
1
How to Use the Slide Cover
Open or close the cover by sliding
as shown in the figure.
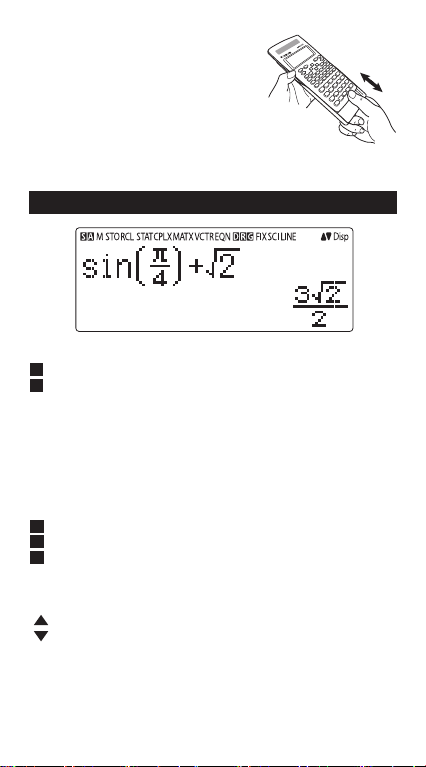
Display
<Status Indicators>
S : Shift key
A : Alpha key
M : Independent Memory
STO : Store Memory
RCL : Recall Memory
STAT : 1-Var & 2-Var Statistics Mode
CPLX : Complex Number Calculation Mode
MATX : Matrix Calculation Mode
VCTR : Vector Calculation Mode
EQN : Equation Calculation Mode
D : Degree Mode
R : Radian Mode
G : Gradient Mode
FIX : Fixed-decimal Setting
SCI : Scientific Notation
LINE : Line Display Mode
: Up Arrow
: Down Arrow
Disp : Multi-statements Display
2
Getting Started
Power On, Off
First time operation:
1. Remove the battery insulation tab to load the battery.
2. Press to initialize the
calculator.
Power ON: When is pressed.
Power OFF: are pressed.
Auto Power off Function:
When the calculator is not used for approximately 7
minutes, it will automatically power off.
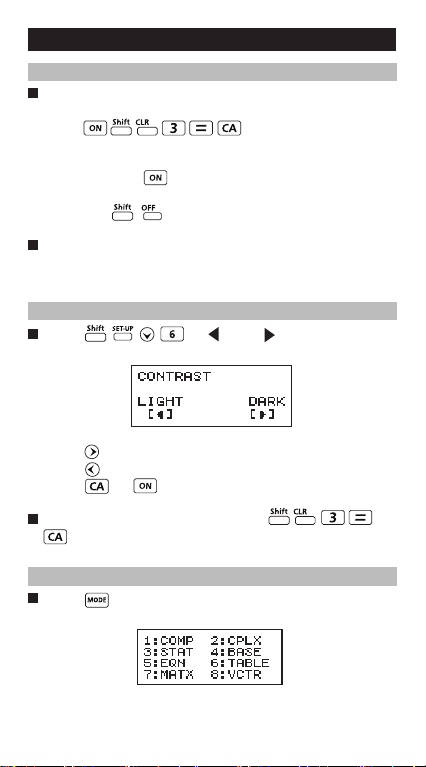
Display Contrast Adjustment
Press (6: CONT ), to enter the
Display Contrast Adjustment screen.
Press to darken the display contrast.
Press to lighten the display contrast.
Press or to confirm and clear the screen.
To initialize the LCD contrast, press
outside the Display Contrast Adjustment screen.
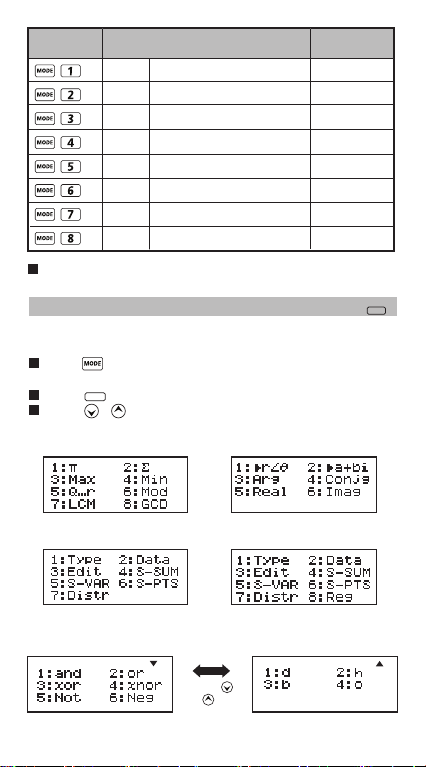
Mode Selection
Press to enter the Calculation Mode Selection
screen.
3
Operation
Mode
COMP Normal calculations
CPLX
Complex number calculation
Statistical and regression
STAT
calculations
Calculations involving specific
BASE
number systems
EQN Equation solution EQN
TABLE Function table generation
MATX Matrix calculations MATX
VCTR Vector calculations VCTR
Indicator
CPLX
STAT
LCD
The default mode is COMP mode.
Application Function Menu (Apps Key)
The Apps menu contains mathematical functions. In each
Calculation Mode, the listed functions are different.
Press and corresponding number to enter the calculation
mode.
Apps
Press to enter the Apps menu.
Press / for next / previous pages.
i) COMP Mode ii) CPLX Mode
iii) STAT Mode
In SD mode In REG mode
iv) BASE Mode
Apps
Press [ ]
or [ ] key
4
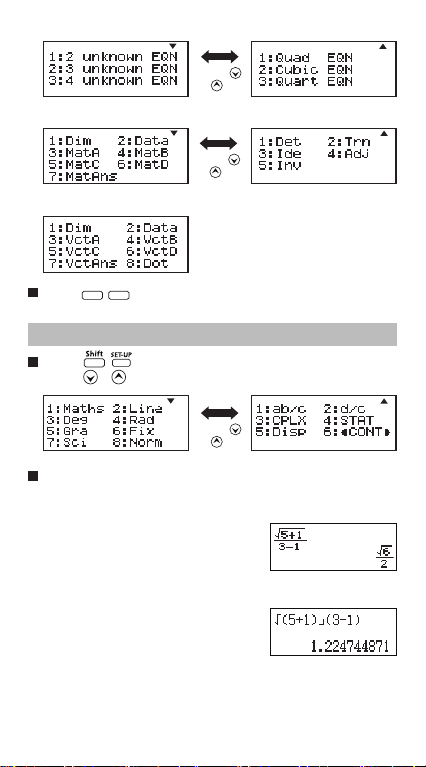
v) EQN Mode
Press [ ]
or [ ] key
vi) MATX Mode
Press [ ]
or [ ] key
vii) VCTR Mode
Apps Apps
Press to exit the Apps menu.
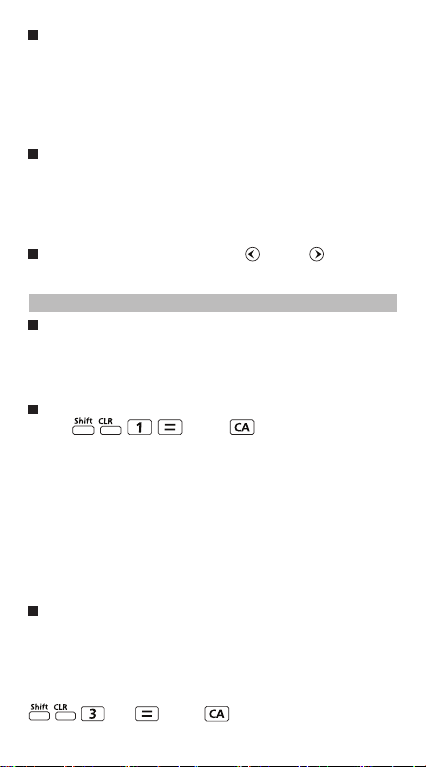
Calculator Set-up Menu
Press to enter the Calculator Set-up Menu;
press / for next / previous page.
Press [ ]
or [ ] key
To select the calculator input & output format [1] Maths
or [2] Line
[1] Maths – (Mathematics mode):
The majority of calculation input
and output (e.g. Fraction, pi,
square root number) are shown in
Mathematics textbook format.
[2] Line – (Line mode): The majority
of calculation input and output are
shown in the line format. The
“LINE” icon will be shown.
For the STAT, EQN, MATX, VCTR mode, the Input & Display
format will switch to Line mode automatically.
Mathematics mode
Line mode
LINE
5

To select the angle unit [3] Deg, [4] Rad or [5] Gra
[3] Deg: Angle unit in Degree
[4] Rad: Angle unit in Radian
[5] Gra: Angle unit in Gradient
90º = radians = 100grads
To select display digit or notation [6] Fix, [7] Sci or
[8] Norm
[6] Fix: Fixed Decimal, [Fix 0~9?] appears, specify the
number of decimal places by pressing [0] – [9].
Example: 220 ÷ 7 = 31.4286 (FIX 4)
= 31.43 (FIX 2)
[7] Sci: Scientific Notation, [Sci 0~9?] appears, specify
the number of significant digits by pressing [0] – [9].
Example: 220 ÷ 7 = 3.1429x10
= 3.143x10
1
(SCI 5)
1
(SCI 4)
[8] Norm: Exponential Notation, [Norm 1~2?] appears,
specify the exponential notation format by pressing [1]
or [2].
Norm 1: Exponential notation is automatically used for
integer values with more than 10 digits and decimal
values with more than TWO decimal points.
Norm 2: Exponential notation is automatically used for
integer values with more than 10 digits and decimal
values with more than NINE decimal places.
Example: 1 ÷ 1000 = 1x10-3 (Norm 1)
= 0.001 (Norm 2)
To select the fraction format [1] a b/c or [2] d/c
[1] a b/c: specify Mixed fraction display
[2] d/c: specify Improper fraction display
To select the complex number display format [3]
CLPX ([1] a+bi or [2] r< )
[1] a+bi: specify Rectangular Coordinates
[2] r< : specify Polar Coordinates
6
To select the statistical display format [4] STAT
([1] ON or [2] OFF)
[1] ON: Show FREQ (Frequency) Column in Statistical
Data Input Screen
[2] OFF: Hide FREQ (Frequency) Column in Statistical
Data Input Screen
To select the decimal point display format [5] Disp
([1] Dot or [2] Comma)
[1] Dot: specify dot format for Decimal point result display
[2] Comma: specify comma format for Decimal point
result display
To Adjust Display contrast [6] CONT
Refer to the “Display Contrast Adjustment” section.
Before Using the Calculator
Check the current Calculation Mode
Be sure to check the status indicators that indicate the
current calculation mode (COMP, STAT, TABLE), display
formats setting, and angle unit setting (Deg, Rad, Gra).
Return to initial setup
Press (YES) to return the initial
calculator setup:
Calculation mode : COMP
Input/Output Format : Maths
Angle unit : Deg
Display Digits : Norm 1
Fraction Display Format : d/c
Statistical Data Input : OFF
Decimal Point format : Dot
This action will not clear the variable memories.
Initialize the calculator
When you are not sure of the current calculator setting, you
are recommended to initialize the calculator (resets
calculation mode to "COMP", angle unit to "Degree", clears
replay and variable memories, and resets LCD contrast) by
performing the following key operations:
(All) (YES) .
7
Inputting Expressions and Values
Input Capacity
F-789SGA allows you to input a single calculation with up to 99
bytes. Normally, one byte is used each time you press one of
the numeric keys, arithmetic keys, scientific function keys or
. Some functions require 4 – 13bytes. , , and the
direction keys will not use up any bytes.
When the remaining input capacity is less than 10bytes, the
input cursor will change from “ ” to “ ” signaling that the
memory is running now.
Input Editing
New Input begins on the left of display. When the input data
is more than 15 characters (Line Mode) / 16 characters
(Math mode), the line will scroll to the right consecutively.
You can scroll back to the left by using and to review
the input.
In Line mode, press to let the cursor jump to the
beginning of input, press to jump to the end.
In Mathematics mode, press to let the cursor jump to the
beginning of input when it is at the end of the input
calculation. Or press to let the cursor jump to the end of
input when it is at the beginning of the input calculation.
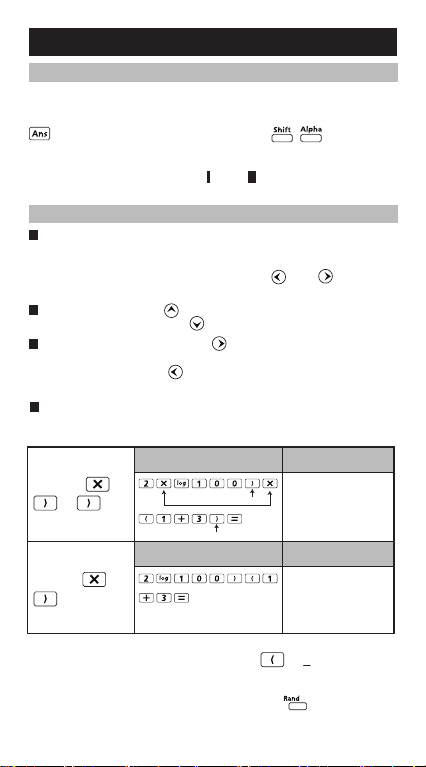
Omit the multiplication sign and final close parenthesis.
Example: 2 x log 100 x (1+3) = 16
Operation 1: Display 1
Including *1,
*2, *3
*1
3
Operation 2: Display 2
Omitting *1,
*3
*1. Omit multiplication sign (x)
- Input before an open parentheses : 1 x (2+3)
- Input before scientific functions that includes parentheses:
2 x cos(30)
- Input before Random number function
- Input before Variable (A, B, C, D, X, Y, M), π, θ
8
2xlog(100) x (1+3)
*2
2log(100)(1+3)
16
16
*2. Scientific functions come with the open parenthesis.
Example: sin(, cos(, Pol(, LCM(…. You need to input the
argument and the close parenthesis .
*3. Omit the last close parenthesis before the , , ,
and .
Insert and Overwrite Input mode
In Line mode, you can use INSERT or overwrite mode for
inputting.
- In Insert mode (Default input mode), the cursor is a
vertical flashing line “ ” for inserting a new character.
- In Overwrite mode, press key to switch the cursor
to a flashing horizontal “ _ ” and replace the character at
the current cursor position.
In Mathematics mode, you can only use the Insert mode.
Whenever the display format changes from Line mode to
Mathematics mode, it will automatically switch to the Insert mode.
Deleting and Correcting an Expression
In Insert mode: Move the cursor to the right of the character or
function that needs to be deleted, then press .
In Overwrite mode: Move the cursor under the character or
function being deleted, then press .
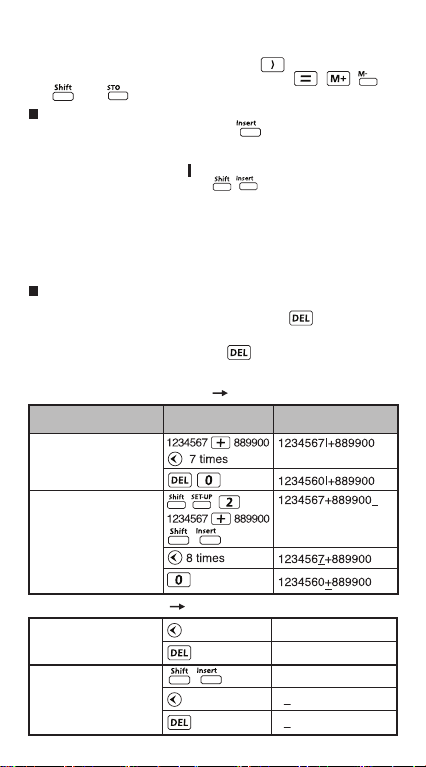
Example: 1234567 + 889900
(1) Replace an entry (1234567 1234560)
Mode Setting
Method 1: Line/Maths
mode - Insert mode
Method 2: Line mode Overwrite mode
Key In operation
Display (input Line only)
(2) Deletion (1234567 134567)
Method 1: Line/Maths
mode - Insert mode
Method 2: Line mode -
Overwrite mode
12times
13times
12|34567+889900
1|34567+889900
1234567+889900_
1234567+889900
134567+889900
9
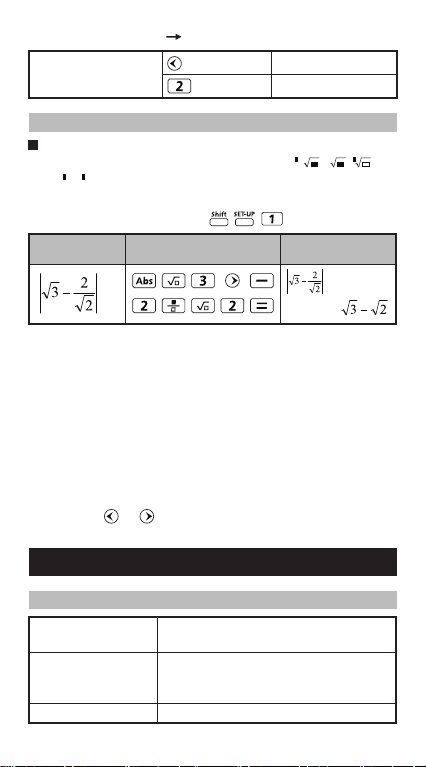
(3) Insertion (889900 2889900)
Line/Maths mode -
Insert mode
6times
1234567+|889900
1234567+2|889900
Inputting and Display Result in Mathematics Mode
In Mathematic Mode, the input and display result of
fraction or certain functions (log, x
2
, x3, x , , 3 , , x-1,
10 , e , Abs) is shown in Handwriting/Mathematics
format.
MATHEMATICS MODE:
DisplayKey in operationExample
NOTE
(1) Some input expressions cause the height of a
calculation expression to be greater than one display
screen. Maximum input capacity: 2 display screens
(31 dots x 2).
(2) Calculator memory limits how many functions or
parentheses can be input in any single expression. In
this case, divide the expression into multiple parts
and calculate separately.
(3) If part of the expression you input is cut off after
calculation and in the result display screen, you can
press or to view the full expression.
Input Range and Error Messages
Calculation Precision, Input Range
Number of Digits for
Internal Calculation
Precision
Calculation Range
Up to 18 digits
±1 at the 10th digit for a single calculation.
±1 at the least significant for exponential
display
–99
to ±9.999999999 × 1099 or 0
±1 × 10
10
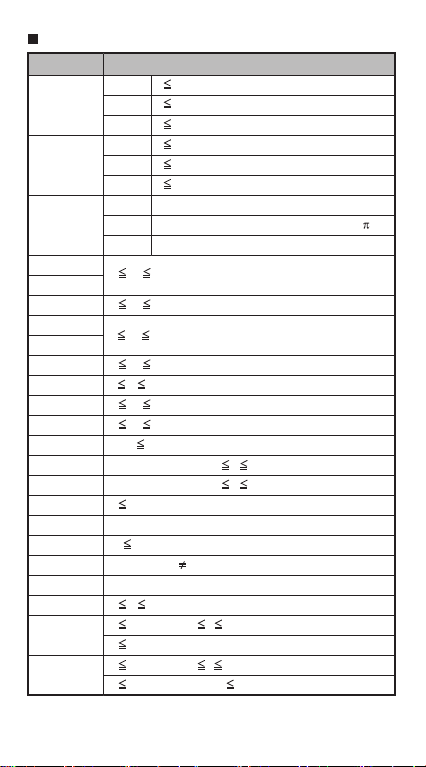
Function Calculation Input Ranges
Input RangeFunctions
9
10
9
10
99
99
99
99
-1
99
99
x 230.258 509 2
100
33
,x 0
10
, 0 r n (n,r are integers)
100
100
or 1 n!/(n-r)! < 1x10
sinx
cosx
tanx
-1
sin
-1
cos
-1
tan
sinhx
coshx
sinh
cosh
tanhx
tanh
logx/lnx
10
x
e
√x
2
x
3
x
-1
x
3
√x
x!
nPr
nCr
DEG 0 |x| <9×10
RAD 0 |x| <157 079 632.7
GRA 0 |x| <1x10
DEG 0 |x| <9×10
RAD 0 |x| <157 079 632.7
GRA 0 |x| <1x10
DEG Same as sinx, except when |x| =(2n-1)×90
RAD Same as sinx, except when |x| =(2n-1)× /2
GRA Same as sinx, except when |x| =(2n-1)×100
x
0 |x| 1
x
x
0 |x| 9.999 999 999x10
0 |x| 230 258 509 2
-1
0 |x| 4.999 999 999x10
x
-1
1 x 4.999 999 999x10
x
0 |x| 9.999 999 999x10
-1
0 |x| 9.999 999 999x10
x
0< x 9.999 999 999x10
x
-9.999 999 999 x1099 x 99.999 999 99
-9.999 999 999 x10
0 x <1x10
50
|x|<1x10
|x| 2.154 434 69x10
100
|x|<1x10
100
|x|<1x10
0 x 69 (x is an integer)
0 n < 1x10
1 {n!/((n-r)!} < 1x10
0 n < 1x1010, 0 r n (n,r are integers)
1 n!/r! < 1x10
100
11
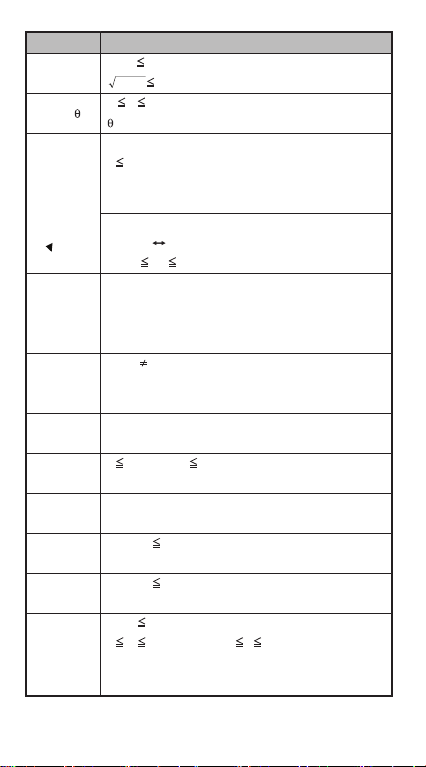
Pol(x,y)
Rec(r, )
°′ ″
°′ ″
^(xy)
x
√y
a b/c
i~Rand(a,b)
Rand
LCM(x,y,z)
GCD(x,y,z)
Q…r(x,y)
Input RangeFunctions
|x|,|y| 9.999 999 999x10
x2+y2 9.999 999 999x10
0 r 9.999 999 999x10
99
99
99
: Same as sinx
|a|,b,c <1x10
100
0 b,c
The display seconds value is subject to an error of
+/-1 at the second decimal place
100
|x|<1x10
Deciaml Sexagesimal Conversions
0°0′0″ |x| 9999999°59′59″
100
x>0: -1x10
< ylog x < 100
x=0: y>0
x<0: y=n,m/(2n+1) (m,n are integers)
However: -1x10
y>0: x 0, –1x10
100
<ylog|x|<100
100
<1/x logy<100
y=0:x>0
y<0:x=2n+1,(2n+1)/m (m≠0;m,n are integers)
Total of integer, numerator, and denominator must be
10 digits or less (including division marks).
10
0 a<1x10
, 0 b<1x1010 (a,b should be positive
integers or 0)
Result generates a 3 digits pseudo random
number(0.000~0.999)
0<x, y, z 9.999 999 999x10
Default result when x, y, z=0
0<x, y, z 9.999 999 999x10
Default result when x, y, z=0
0<x,y 9.999 999 999x10
12
(positive integers)
12
(positive integers)
12
(positive integers)
0 Q 999 999 9999, 0 r 999 999 9999 (Q,r are
integers)
Default result when x=0
12
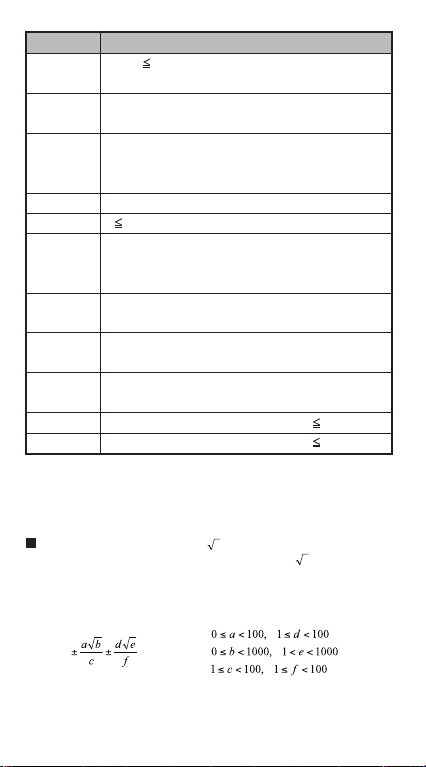
Input RangeFunctions
Mod(x,y)
Single-variable
Paired-variable
ABS
Pfact
BIN
0<|x,y| 9.999999999x10
Default result=x when y=0
100
|x|<1x10
|FREQ|
100
<1x10
100
|x|<1x10
100
|y|<1x10
|FREQ|
100
<1x10
100
|x|<1x10
x 9999999999 (positive integers)
0~ 0111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
Positive:
Negative:
1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000~
12
1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
Positive: 0~2147483647
DEC
Negative: -2147483648~-1
Positive: 0~177 7777 7777
OCT
Negative: 200 0000 0000~377 7777 7777
Positive: 0~7FFF FFFF
HEX
∑ (f(x),a, b)
∏ (f(x),a, b)
Negative: 8000 0000~FFFF FFFF
a and b are integers in the range of –1 • 10^10 < a b <1 • 10^10.
a and b are integers in the range of –1 • 10^10 < a b <1 • 10^10.
• Errors are cumulative in the case of consecutive
calculations, this is also true as internal consecutive
calculation are performed in the case of ^(x
y
), x√y, 3√, x!,
nPr, nCr , etc. and may become large.
Display of results using
Calculation results may be displayed using in all of the
following cases:
1. When intermediate and final calculation results are
displayed in the following form:
2. When the number of terms in the intermediate and final
calculation result is one or two.
13
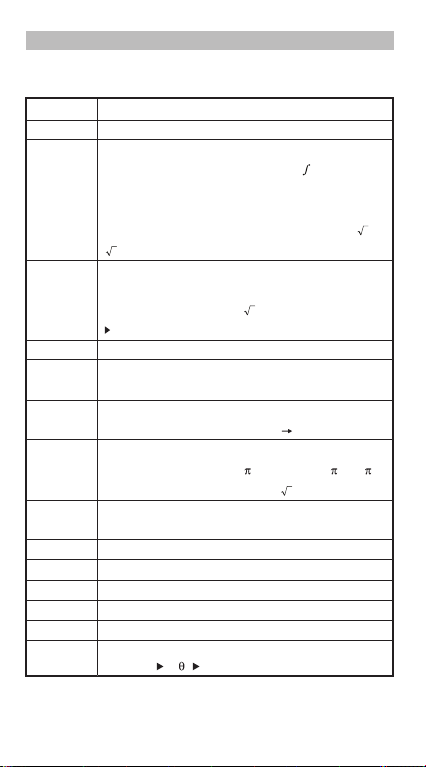
Order of Operations
This calculator will automatically determine the operation
priority of each individual command as follows:-
1st Priority
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
6th
7th
8th
9th
10th
11th
12th
13th
14th
15th
Recall memory (A, B, C, D, E, F, 0-9), Rand
Calculation within parentheses ( ).
Function with parenthesis that request the input
argument to the right Pol(, Rec(, d/dx, dx, P(, Q(, R(,
Det(, Trn(, Ide(, Adj(, Inv(, Arg(, Conjg(, Real(, Imag(,
sin(, cos(, tan(, sin
tanh(, sinh
3
(, Abs(, ROUND(, LCM(, GCD(, Q…r(, i~Rand(,
Functions that come after the input value preceded by
values, powers, power roots:
x2, x3, x–1, x!, ° ’ ”, °, r, g, ^(, x (, Percent %, logab, EXP,
t
Fractions: a b/c, d/c
Prefix symbol: (–) (negative sign), base-n symbols
(d, h, b, o, Neg, Not)
Statistical estimated value calculation:
Metric conversion commands (cm in, etc)
Multiplication where sign is omitted: Multiplication sign
omitted immediately before , e, variables (2 , 5A, A,
etc.), functions with parentheses (2 (3), Asin(30), etc.)
Permutations, combinations: nPr, nCr
Complex number polar coordinate symbol (<)
.
Dot:
Multiplication and division:
Addition and subtraction:
Logical AND (and)
Logical OR, XOR, XNOR (or, xor, xnor)
Calculation ending instruction: =, M+, M- STO (store
memory), r< , a+bi
–1
(, cos–1(, tan–1(, sinh(, cosh(,
–1
(, cosh–1(, tanh–1(, log(, ln(, e^(, 10^(, (,
x, y, x1, x2
ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ
×, ÷
+, –
14

In the same precedence level, calculations are performed
from left to right.
Operations enclosed within parentheses are performed first.
When a calculation contains an argument that is a negative
number, the negative number must be enclosed within the
parentheses.
Example:
2
–2
(–2)
When same priority commands are mixed into one
calculation:
= –4
2
= 4
Example 1:
1 ÷ 2 = 0.1591549431
Example 2:
2 A
1 ÷ 2A =
1
4
Calculation Stacks
This calculator uses memory areas, called “stacks”, to
temporarily store numeric value (numbers) commands (+, –,
x…) and functions according to their precedence during
calculations.
The numeric stack has 10 levels and the command stack has
128 levels. A stack error [Stack ERROR] occurs whenever
you try to perform a calculation that exceeds the capacity of
stacks.
Calculations are performed in sequence according to “Order
of Operations”. After the calculation is performed, the stored
stack values will be released.
Error Messages and Error Locator
The calculator is locked up when an error message is shown on
the display indicating the cause of the error.
Press to clear the error message, then return to the
initial display of the latest mode.
Press or to display the input expression with the
cursor positioned next to the error.
Press to clear the error message, replay memory history
and return to the initial display of the latest mode.
15
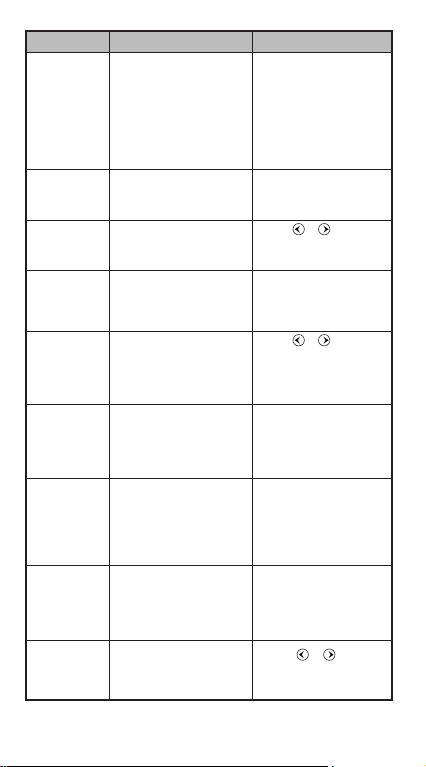
Error Message
Math ERROR
Stack ERROR
Syntax ERROR
Insufficient
MEM
Dimension
ERROR
(only in Matrix
or Vector)
Can’t Solve
ERROR
(only in SOLVE
function)
Variable
ERROR
(only in SOLVE
function)
Time Out
ERROR
(only in
Differential or
integration
Calculations
Argument
ERROR
Cause Action
• The intermediate or final
result is outside the
allowable calculation range.
• An attempt to perform a
calculation using a value
that exceeds the allowable
input range.
• An attempt to perform an
illogical operation (division
by zero, etc.)
• The capacity of the numeric
stack or operator stack is
exceeded.
• An attempt to perform an
illegal mathematical
operation.
• The calculation result of
Function Table mode
parameters caused more
than 30 x-values to be
generated for a table
• The dimension (row colum)
is over.
• An attempt to perform an
illegal matrix/vector
operation.
• The calculator could not
obtain a solution.
• Equation is not a correct
equation.
• Equation does not include
variable X.
• The solution variable is not
similar to the specified
variable in the expression.
• The calculation ends
without the ending condition
being fulfilled.
• Improper use of an
argument.
• Check the input values and
make sure they are all
within the allowable
ranges, Pay special
attention to values in any
using memory areas
• Simplify the calculation.
• Divide the calculation into
two or more separate
parts.
• Press or to display
the cursor at the location
of the error, make
appropriate corrections
• Narrow the table
calculation range by
changing the start, end,
and step values, and try
again.
• Press or to display
the location of the cause of
an error and make
required corrections.
• Check for errors in the
equation that you input.
• Input a value for the
solution variable that is
close to the expected
solution and try again.
• Correct the equation to
include variable X.
• Correct the equation to
match the solution variable
and expression.
(refer to P.49)
• Revise the ending condition
and try again.
(refer P.51)
• Press or to display
the location of the cause of
an error and make required
corrections.
16
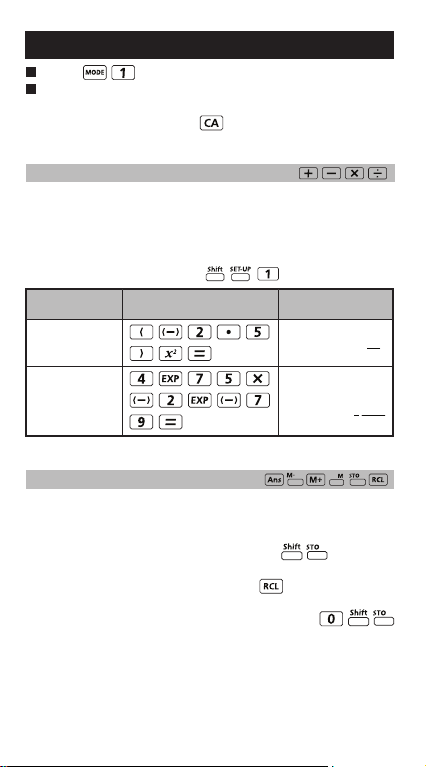
Basic Calculations
Press to enter COMP mode.
As the calculation is busy processing, the calculator
shows the message [PROCESSING] (without any
calculation result). Press key to interrupt the
calculating operation.
Arithmetic Calculations
• To calculate the negative values (exclude the negative
exponent) enclose then within the parentheses.
• This calculator supports 99 levels of parenthetical
expression.
MATHEMATICS MODE:
DisplayKey in operationExample
2
(-2.5)
(4 x 1075)(-2 x
-79
)
10
Memory Calculations
Memory Variables
• There are 19 memory variables (0 – 9, A – F, M, X and
Y), which store data, results, or dedicated values.
• Store values into memory by pressing + Memory
variable.
• Recall memory values by pressing + Memory
variable.
• Memory content can be cleared by pressing
+ Memory variable.
2
(-2.5)
75x
4
E
25
1250
4
1
17
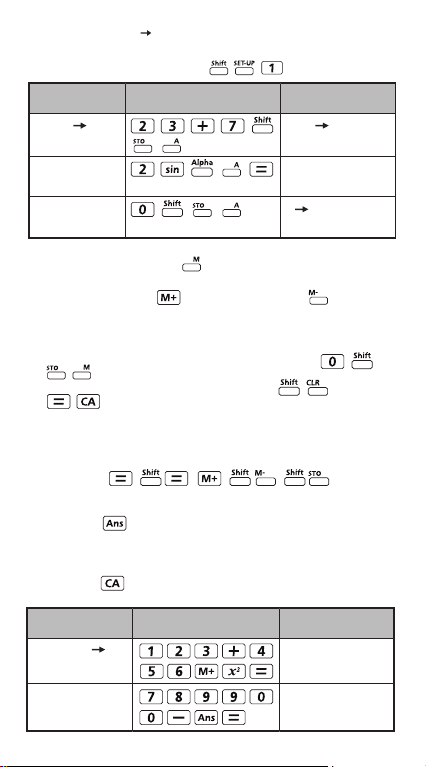
Example: 23 + 7 A (30 store into A), calculate 2 sinA
and clear memory A.
MATHEMATICS MODE:
Example
23 + 7 A
2 x sin A = 1
Clear memory
Independent Memory
• Independent memory uses the same memory area
as variable M. It is convenient for calculating cumulative
totals by pressing (add to memory) or (subtract
from memory).
• Memory contents are retained even when the calculator
is powered off.
• Clear independent memory (M) by pressing
• Clear all memory values by pressing 2(MCL)
.
Answer Memory
• The input values or the most recent calculation result will
be automatically stored into Answer memory whenever
you press , , , , . Answer
memory can hold up to 18 digits.
• Recall and use the latest stored Answer memory by
pressing .
• Answer memory is not updated when an error operation
has been performed.
• Answer memory contents can be maintained even after
pressing , changing the calculation mode, or turning
off the calculator.
Example
123 + 456 M+,
2
= 335,241
Ans
789900 – Ans =
454,659
18
DisplayKey in operation
23+7 A
30
2sin(A
1
0 A
0
DisplayKey in operation
2
Ans
335241
789900-Ans
454659
Fraction Calculations
The calculator supports Fraction calculation and the
conversions between Fraction, Decimal point, Mixed fraction
and Improper fraction.
• Specify the fraction calculation result display format by
selecting either mixed fraction ( ) or improper fraction
( ) in set-up menu.
• At the default setting, fractions are displayed as improper
fractions ( ).
• Mixed Fraction display results are only available after
selecting ( ) in the setup menu.
Improper Fraction
(d/c)
Maths Mode
Line Mode
Press to switch a calculation result between fraction and
decimal format.
Press to switch a calculation result between
improper fraction and mixed fraction format.
Results will be displayed in decimal format automatically
whenever the total digits of a fractional value (integer +
numerator + denominator + separator marks) exceeds 10.
When a fraction calculation is mixed with decimal values, the
result will be displayed in decimal format.
11
3
Mixed Fraction
(a b/c)
2
3
3
3_|2_|311_|3
Fraction Decimal point conversion
MATHEMATICS MODE:
DisplayKey in operationExample
5
7
1
1 + =
6
3
2
7
2.333333333
3
(Fraction Decimal)
2.333333333
(Decimal Mixed
Fraction)
1
2
3
1
1 +
2
1
1 +
2
1
1 +
2
5
6
5
6
2.333333333
5
6
7
3
1
2
3
19
 Loading...
Loading...