
User’s Guide
Barcode Print +
ENG
Version 0

i
Copyright
Copyright © 2019 Brother Industries, Ltd. All rights reserved.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The software described in this document is
furnished under licence agreements. The software may be used or copied only in accordance with the terms
of those agreements. No part of this publication can be reproduced in any form or by any means without
prior written permission of Brother Industries, Ltd.
Trademarks
Brother is the trademark of Brother Industries, Ltd.
BarDIMM is a registered trademark of Jetmobile SAS.
QRCode is a trademark of DENSO WAVE INCORPORATED.
Other products and company names herein may be the trademarks of their respective owners.
Any trade names and product names of companies appearing on Brother products, related documents and
any other materials are all trademarks or registered trademarks of those respective companies.

ii
Table of Contents
1
Background 3
1.1 Overview ................................................................................................................................................. 3
1.2 Supported Brother Machines .................................................................................................................. 4
1.3 Supported Barcodes ............................................................................................................................... 4
2
Activation 5
3
Breakdown of Control Codes 6
3.1 1-D Barcodes .......................................................................................................................................... 6
3.2 PDF417 ................................................................................................................................................... 9
3.3 QRCode ................................................................................................................................................ 12
4
Overview of Barcode Types 14

3
1
1 Background
1.1 Overview
The Brother Barcode Print + software solution extends the barcode printing capability of Brother printers.
Features
• Uses the same BarDIMM commands as other printer vendors.
• Requires no additional hardware, such as a USB memory stick, compact flash card, or DIMM.
• Supports both 1D and 2D barcodes.
4
1
1.2 Supported Brother Machines
For a comprehensive list of all Brother machines compatible with Brother Barcode Print +, visit your local
Brother website.
1.3 Supported Barcodes
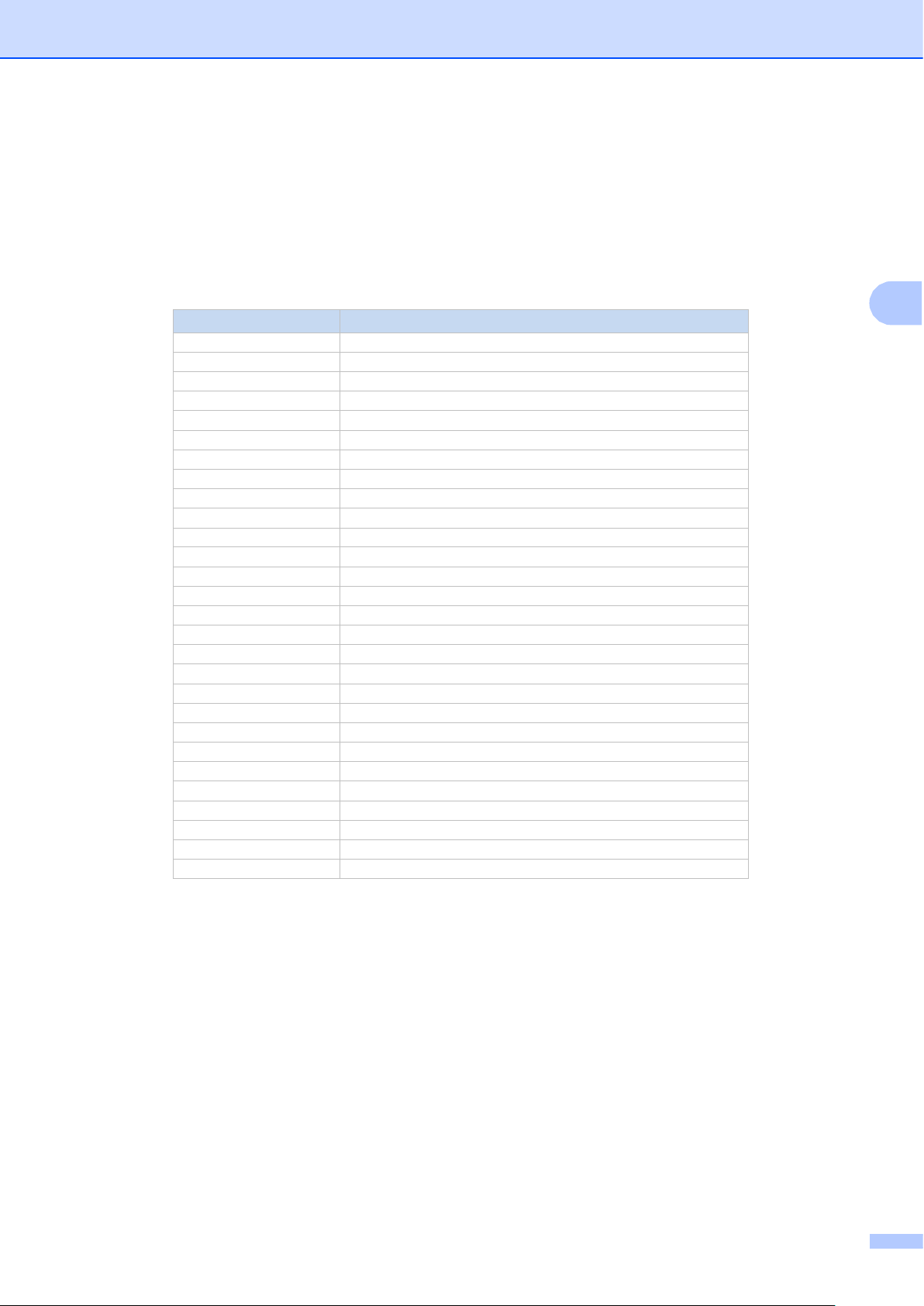
Brother Barcode Print + supports many popular 1D and 2D barcodes.
Barcode category
Details
CODABAR
CODABAR
Code 128
Code 128 A, B, C
Code 128
Code 128 with Auto-Switch
Code 25 (2 of 5)
Code 25 Interleaved
Code 39 (3 of 9)
Code 39
Code 39 (3 of 9)
Code 39 + Chk Encode Space Before Data
Code 39 (3 of 9)
Code 39 + Mod 43Chk
Code 39 (3 of 9)
Code 39 Encode Space Before Data
Code 93
Code 93
Code 93
Code 93 Extended
EAN/JAN
EAN/JAN-13, EAN/JAN-13 +2
EAN/JAN
EAN/JAN-13 +5
EAN/JAN
EAN/JAN-8, EAN/JAN-8 +2
EAN/JAN
EAN/JAN-8 +5
EAN/JAN
GS1-128 (UCC/EAN 128)
GS1 DataBar
Standard, Limited, Expanded, Truncated, and Stacked
Interleave 25 (2 of 5)
Interleave 25 + Chk
MSI Plessey
MSI Plessey + Chk 10 and Chk 11
PDF-417
PDF-417 and Macro PDF-417
PostNet
PostNet 9 and PostNet 5
QR Code
QR Code
QR Code
Model 1
QR Code
Model 2
Swiss QR Code
Swiss QR Code
UPC
UPC-A, UPC-A +2, and UPC-A +5
UPC
UPC-E (UPC-E0 and UPC-E1)
UPC
UPC-E +2 and UPC-E +5
USPS
ZIP+4 PostNet 11
For a comprehensive list of all the barcodes compatible with Brother Barcode Print +, visit your local Brother
website.

5
2
2 Activation
To activate the Barcode Print + solution, send a valid licence file to the target machine using the Brother
Software Licence Management Tool. If you do not have a valid licence file (in LIC format), contact your local
Brother office.
You can download the tool from support.brother.com.
NOTE
To successfully send licence files to the target machines, make sure that:
• The target machines are correctly set up, connected to a local network, and available.
• The target machines have the latest firmware installed. To update your machine’s firmware, go to
support.brother.com and download the Firmware Update Tool.
• You know the target machines’ passwords. You can activate more than one machine using the
same software solution if the target machines have a common password, or if they are not
password-protected.
1. Run the Brother Software Licence Management Tool.
2. The tool lists the Brother machines on your network. Double-click the machines you want to select for
activation, and then click the Activate button.
• If no machines are listed: Click the Search button to update the list.
• If the machines you want are not in the list: Go to Search > Add Machine.
3. The Licence Selection window appears. Select the correct software solution licence file (LIC file) for
your target machines.
NOTE
If you were provided with 20-digit licence codes, you can use them instead of the LIC file.
4. If the machines are password-protected, enter the password, and then click OK.
5. Make sure the information in the Confirmation dialog box is correct, and then click the Activate button.
When the activation is complete, the newly activated machines will be rebooted, and the log file will be
saved in the tool’s folder.
NOTE
For more information, see the Brother Software Licence Management Tool User’s Guide at
support.brother.com.

6
3
3 Breakdown of Control Codes
3.1 1-D Barcodes
Each barcode comprises a sequence of PCL commands and control codes. Control code parameters can be
customised to change the code’s size, shape, and content.
Example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
ESC(s
0p
30v
,,,b
,,,s
h
24600T
123456789123
Barcode Print PCL Command
Barcode Data
#
Name
Parameter
Comments
1
Escape code
ESC(s
ESC is ASCII value 27
2
Human-readable information
#p
Default value = 0p
3
Barcode height
#v
Default value = 0v
4
Barcode width
#b
Default value = ,,,b
5
Barcode space width
#s
Default value = ,,,s
6
Human-readable text font
#h
Default value = h
7
Barcode name
PCL_BARCODE_NAMET
See Overview of Barcode Types
8
Barcode data
N/A
User-defined information
NOTE
• To ensure good readability, each barcode must be programmed correctly.
• If the “b” and “s” parameters are identical, the “s” parameter does not need to be specified.
• Do not use decimal values (e.g. “1.5”).
3.1.2 Human-readable information (“p”)
Specifies if a caption is printed with the barcode.
ESC(s0p
30v,,,b,,,sh24600T123456789123
Value
Description
0
Default (print)
1
Do not print human-readable text
2
Embed human-readable text
3
Half-embed human-readable text
4
Print human-readable text under the code

7
3
3.1.3 Barcode height (“v”)
Specifies the barcode height in 1/60th of an inch.
ESC(s0p
30v,,,b,,,sh24600T123456789123
In this example, 30/60th means that the barcode height will be 0.5 in. (12.7 mm).
3.1.4 Barcode width (“b”)
Specifies the width of barcode bars.
ESC(s0p
30v,,,b,,,sh24600T123456789123
This setting affects the total barcode width. To print smaller barcodes, specify smaller values.
For 1D codes, four values need to be specified in 1/600th of an inch:
1. First (thin) bar width
2. Second bar width
3. Third bar width
4. Fourth bar width
Alternatively, default values (“,,,”) can be used. The “ESC(s0p30v,,,b…” sequence will then give the
same output as “ESC(s0p30v8,16,24,32b…”.
Example
For UPC-A barcodes to be printed correctly, four different bar thicknesses are required.
The output will vary depending on the specified values:
Greater Values
Smaller Values
NOTE
Not all barcode readers may be able to read small barcodes.
3.1.5 Barcode space width (“s”)
Specifies the width of the spaces between bars in a barcode.
ESC(s0p
30v,,,b,,,sh24600T123456789123
For 1D codes, four values need to be specified in 1/600th of an inch:
1. First (thin) space width
2. Second space width
3. Third space width
4. Fourth space width

8
3
3.1.6 Human-readable text font (“h”)
Specifies the font used for barcode captions.
ESC(s0p
30v,,,b,,,sh24600T123456789123
Value
Description
0 (or no value)
Default (Courier)
1
Letter gothic
2
Universe
3
Universe condensed
5
OCR-B
3.1.7 Barcode type (“T”)
Specifies the barcode type.
ESC(s0p
30v,,,b,,,sh24600T123456789123
For more information, see Overview of Barcode Types.
3.1.8 Barcode data
The actual user-defined information.
ESC(s0p
30v,,,b,,,sh24600T123456789123
ASCII control code characters (ASCII code 0–30) can be specified for Code93 Extended, Code128A, and
Code128 With-AutoSwitch as follows:
ESC
&p#X
<00>
Where:
# is the number of control code characters
<00> is an example control code character
Example
To specify two ASCII control code characters “0” and “1” with Code 128A, use: 24850TESC&p2X<00><01>

9
3
3.2 PDF417
3.2.1 Barcode composition
Each barcode comprises a sequence of PCL commands and control codes. Control code parameters can be
customised to change the code’s size, shape, and content. Each PDF417 barcode (also called “symbol”) can
consist of several modules.
Example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
ESC(s
0p
,,,v
,,,b
,,,s
24850T
123456789123
Barcode Print PCL Command
Barcode Data
#
Name
Parameter
Comments
1
Escape command
ESC(s
ESC is ASCII value 27
2
Error correction
#p
Default value = 0p
3
Barcode height
#v
Default value = ,,,v
4
Barcode (symbol) size
#b
Default value = ,,,b
5
Module size
#s
Default value = ,,,s
6
Barcode name
PCL_BARCODE_NAMET
▪ PDF417:
24850
▪ MacroPDF417:
24855
7
Barcode data
N/A
User-defined information
NOTE
• To ensure good readability, each barcode must be programmed correctly.
• Do not use decimal values (e.g. “1.5”).

10
3
3.2.2 Error Correction (“p”)
Specifies the error correction level or ratio against the data size.
ESC(s0p
,,,v,,,b,,,s24850T123456789123
Error Correction Level
Error Correction Data Code
0 2 1 4 2 8 3
16 4 32 5 64 6 128
7
256
8
512
You can also choose a value between 1000 and 1400 to define the error correction level in percent (0–
400%), based on the ratio between the size of the codeword and the data size.
3.2.3 Barcode height (“v”)
Specifies the barcode height.
ESC(s0p
,,,v,,,b,,,s24850T123456789123
1. (MacroPDF417 only) The number of blocks displayed as one column (default: 1)
Example
2v: If the number of blocks is three, the first column will show the first and second block, and the
second column will show the third block.
2. (MacroPDF417 only) Unused
3. Maximum block width (unit: 1/600th of an inch)
4. Maximum block height (unit: 1/600th of an inch)
3.2.4 Symbol size (“b”)
Specifies the PDF symbol size.
ESC(s0p
,,,v,,,b,,,s24850T123456789123
1. Maximum number of rows for the PDF symbol
2. Maximum number of columns for the PDF symbol
3. PDF symbol size control:
• 0: The size specified in 1 and 2 is set as the maximum for rows and columns (default)
• 1: The size specified in 1 and 2 is set as the mandatory values for rows and columns
4. PDF symbol content control:
• 0: The code is displayed with the stop pattern (default)
• 1: The code is displayed without the stop pattern

11
3
Display with the stop pattern
Display without the stop pattern
3.2.5 Module size (“s”)
Specifies the module size.
ESC(s0p
,,,v,,,b,,,s24850T123456789123
1. Module height to width ratio (1–10, default: 3)
2. Symbol length in the length to width ratio (default: 2)
3. Symbol width in the length to width ratio (default: 3)
4. Minimum module width (1–100, default: 10, unit: 1/100 of an inch)
Example
1,3,2,5s
(Module: square; Symbol length: 1.5 x width; Module width: 0.05 in.)
3.2.6 Barcode type (“T”)
Specifies the barcode type.
ESC(s0p
,,,v,,,b,,,s24850T123456789123
Value
Code Type
24850
PDF417
24855
MacroPDF417
3.2.7 Barcode data
The actual user-defined information:
ESC(s0p
,,,v,,,b,,,s24850T123456789123
ASCII control code characters (ASCII code 0–31) can be specified for PDF417 as follows:
ESC
&p#X
<00>
Where:
# is the number of control code characters
<00> is an example control code character
Example
To specify two ASCII code characters “0” and “1” with PDF417, use: 24850TESC&p2X<00><01>

12
3
3.3 QRCode
3.3.1 Barcode composition
Each barcode comprises a sequence of PCL commands and control codes. Control code parameters can be
customised to change the code’s size, shape, and content.
Example
1 2 3 4 5 6
ESC(s
0p
b
0s
24860T
123456789123
Barcode Print PCL Command
Barcode Data
#
Name
Parameter
Comments
1
Escape command
ESC(s
ESC is ASCII value 27
2
Error correction
#p
Default value = 0p
3
Barcode height
#b
Default value = b
4
Data type
#s
Default value = 0s
5
Barcode name
PCL_BARCODE_NAMET
▪ QRCode Model 1:
24860
▪ QRCode Model 2:
24861
▪ Swiss QRCode:
24862
6
Barcode data
N/A
User-defined information
NOTE
• To ensure good readability, each barcode must be programmed correctly.
• Do not use decimal values (e.g. “1.5”).
3.3.2 Error Correction (“p”)
Specifies the error correction level.
ESC(s0p
b0s24860T123456789123
Error Correction Level
Correction Ratio Against All Code Words
0 (Default)
M (~15%)
1
L (~7%)
2
M (~15%)
3
Q (~25%)
4
H (~30%)

13
3
3.3.3 Barcode height (“b”)
Specifies the maximum height of the small module (unit: 1/600th in.).
ESC(s0p
b0s24860T123456789123
3.3.4 Data type (“s”)
Specifies the barcode data type.
ESC(s0p
b0s24860T123456789123
Parameter
Barcode Data Type
0 (default)
Automatic (JIS/ShiftJIS)
1
Numerical (0–9)
2
Alphanumeric (0–9, uppercase A to Z, space $%*+-. /: )
3
Binary 8-bits/byte data (JIS 8-bit character set)
4
Kanji (Shift JIS values 8140h – 9FFCh and E040h – EAA4h)
Example
2s (Alphanumeric data)
3.2.5 Barcode type (“T”)
Specifies the barcode type.
ESC(s0p
b0s24860T123456789123
Value
Code Type
24860
QRCode Model1
24861
QRCode Model2
24862
Swiss QRCode
3.2.7 Barcode data
The actual user-defined information:
ESC(s0p
b0s24860T123456789123
ASCII control code characters (ASCII code 0–30) can be specified for QRCode as follows:
ESC
&p#X
<00>
Where:
# is the number of control code characters
<00> is an example control code character
Example
To specify two ASCII code characters “0” and “1” with QRCode, use: 24850TESC&p2X<00><01>

14
4
4 Overview of Barcode Types
Barcode Type
PCL
Barcode
Name
Barcode Sample
BOI:GTIN12-UPC-A
24600
B02:UPC-A +2
24601
B03:UPC-A +5
24602
B04:GTIN12-UPC-E
24610
B05:UPC-E +2
24611
B06:UPC-E +5
24612
B07:GTIN/EAN/JAN-8
24620
B08:EAN/JAN-8 +2
24621
B09:EAN/JAN-8 +5
24622
B10:GTIN/EAN/JAN-13
24630
B11:EAN/JAN-13 +2
24631
B12:EAN/JAN-13 +5
24632

15
4
Barcode Type
PCL
Barcode
Name
Barcode Sample
B13:25 (2 of 5)
Interleaved
24640
B14:25 Interleaved +
CHK
24641
B15:39 (3 of 9)
24670
B16:39 + CHK
24671
B17:39 (3of9) Encode
Space
24672
B18:39 + CHK Encode
Space
24673
B19:93
24690
B20:93 Extended
24691
B21:128 Autoswitch
24700
B22:128 A
24701
B23:128 B
24702
B24:128 C
24704
B25:GS1-128/EAN-UCC128
24720

16
4
Barcode Type
PCL
Barcode
Name
Barcode Sample
B26:CODABAR
24750
B27:CODABAR
+CHKmod16
24751
B28:MSI
24760
B29:MSI +CHK10
24761
B30:MSI+CHK10
+CHK10
24762
B31:MSI+CHK11+CHK10
24763
B32:ZIP+4 POSTNET 5
24770
B33:ZIP+4 POSTNET 9
24771
B34:ZIP+4 POSTNET 11
24772
B35:GS1 DataBar14/RSS-14
24810
B36:GS1 DataBar14/RSS Tru
24811
B37:GS1 DataBar14/RSS Sta
24812
B38:GS1 DataBar14/RSS Limited
24814

17
4
Barcode Type
PCL
Barcode
Name
Barcode Sample
B39:GS1 DataBar14/RSS Exp
24815
PDF417
24850
Macro PDF417
24855
B01:QRCode Model 1
24860
B02:QRCode Model 2
24861
B03:Swiss QR Code
24862

 Loading...
Loading...