Page 1

P
Prrrro
PP
G
Gu
GG
og
oo
uiiiid
uu
grrrra
gg
de
dd
am
aa
e
ee
mm
me
mm
mm
errrr’’’’ssss
ee
DOC--OEM6--ActiveX--US--06/00
Page 2

The information in this documentation is not contractual in
nature. It is subject to modification without notice.
The software described in this manual is supplied under a
user license. Its use, duplication, or reproduction on any
media whatsoever, except as provided for under the terms
of the license, is not authorized.
No part of the manual may be copied, reproduced or
transmitted by any means whatsoever (unless it is for the
purchaser’s personal use) without the written permission of
Teklynx International.
E 2000 Teklynx International Co.
All rights reserved
Windowstttt is a registered trademark of Microsoftâ Corpora-
tion.
IBM, PC, AT PS/2 are registered trademarks of International
Business Machines,Inc.
Page 3

Table of Contents
About this manual vii........................................
Welcome! vii............................................
The Programmer’s Guide vii..........................
Typographical conventions viii.........................
Discover ActiveX Automation
1
foryourlabelingsoftware Chapter1-1......................
Introduction Chapter 1 - 1..........................................
What is an ActiveX object? Chapter 1 - 2............................
What is the type library? Chapter 1 - 3..............................
Mechanisms Chapter 1 - 4..........................................
Server Activation Chapter 1 - 4.....................................
Create Object function Chapter 1 - 4.............................
GetObject function Chapter 1 - 5................................
New
function Chapter 1 - 6...........................................
Server Deactivation Chapter 1 - 7...................................
Quit method Chapter 1 - 8......................................
Data Type Chapter 1 - 8............................................
Application Object Chapter 1 - 8.................................
Document Object Chapter 1 - 9..................................
Collection Object Chapter 1 - 9..................................
Event management Chapter 1 - 11...................................
Handling an Ob ject’s Events Chapter 1 - 11.......................
Connecting a WithEvents variable to an object Chapter 1 - 13.....
Compatibility with the previous version Chapter 1 - 14...............
Particularity about access rights Chapter 1 - 14.......................
Page 4

Reference Guide Chapter 2 - 15.....................................
2
Hierarchy diagram Chapter 2 - 15....................................
Application Object Chapter 2 - 17....................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 18..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 23...................................
PrinterSystem Object Chapter 2 - 26.................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 26...................................
Options Object Chapter 2 - 29........................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 29..................................
Dialogs Collection Chapter 2 - 34.....................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 34..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 35...................................
Dialog Object Chapter 2 - 36.........................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 36..................................
Object
Methods Chapter 2 - 37..........................................
RecentFiles Collection Chapter 2 - 38.................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 38..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 39...................................
RecentFile Object Chapter 2 - 41.....................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 41..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 42...................................
Documents Collection Chapter 2 - 43.................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 43..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 44...................................
Document Object Chapter 2 - 46.....................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 46..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 50...................................
Database Object Chapter 2 - 54......................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 54..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 56...................................
Printer Object Chapter 2 - 58.........................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 58...................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 60..................................
Format Object Chapter 2 - 63........................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 63..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 67...................................
DocumentProperties Collection Chapter 2 - 68........................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 68..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 69...................................
DocumentProperty Object Chapter 2 - 70.............................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 70..................................
DocObjects Collection Chapter 2 - 72.................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 72..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 74...................................
Programmer’s Guideii
Page 5

DocObject Object Chapter 2 - 76.....................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 76..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 79...................................
Images Collection Chapter 2 - 80.....................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 80..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 80...................................
Image Object Chapter 2 - 82.........................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 82..................................
Barcodes Collection Chapter 2 - 84...................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 84..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 85...................................
Barcode Object Chapter 2 - 86.......................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 86..................................
Code2D Object Chapter 2 - 93.......................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 93..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 94...................................
Texts Collection Chapter 2 - 95.......................................
Object properties Chapter 2 - 95..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 95...................................
Text Object Chapter 2 - 97...........................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 97..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 99...................................
TextSelection Object Chapter 2 - 102..................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 102..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 103...................................
OLEObjects Collection Chapter 2 - 104.................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 104..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 104...................................
OLEObject Object Chapter 2 - 106.....................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 106..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 106...................................
Shapes Collection Chapter 2 - 108.....................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 108..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 109...................................
Shape Object Chapter 2 - 113.........................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 113..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 113...................................
Variables Collection Chapter 2 - 114...................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 114..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 116...................................
Variable Object Chapter 2 - 118.......................................
Object Porperties Chapter 2 - 118..................................
TableLoockups Collection Chapter 2 - 120..............................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 120..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 120...................................
TableLoockup Object Chapter 2 - 122..................................
iiiTable of Contents
Page 6

Object Properties Chapter 2 - 122..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 123...................................
Formulas Collection Chapter 2 - 125...................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 125..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 125...................................
Formula Object Chapter 2 - 127.......................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 127..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 128...................................
Dates Collection Chapter 2 - 129......................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 129..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 129...................................
Date Object Chapter 2 - 131..........................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 131..................................
Counters Collection Chapter 2 - 133...................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 133..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 133...................................
Counter Object Chapter 2 - 135.......................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 135..................................
FreeVariables Collection Chapter 2 - 139...............................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 139..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 140...................................
Free Object Chapter 2 - 141...........................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 141..................................
DatabaseVariables Collection Chapter 2 - 143..........................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 143..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 144...................................
FormVariables Collection Chapter 2 - 145..............................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 145..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 146...................................
Strings Collection Chapter 2 - 147.....................................
Object Properties Chapter 2 - 147..................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 147...................................
Document Events Chapter 2 - 149.....................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 149...................................
Application Events Chapter 2 - 151....................................
Object Methods Chapter 2 - 151...................................
Programmer’s Guideiv
Appendix Chapter 3 - 152.............................................
3
InformationonVisualC++DataType Chapter3-152.................
Index Chapitre 4 - 155.................................................
4
Page 7

About this manual
Welcome!
Welcome to the number one Windows based label design and
printing software. It provides the simplest, yet highest
performance solution f or your labeling requirements.
This version of this labeling software integrates the ActiveX
technology offering you the possibility toe easily create a
program to control your labeling software.
The
Programmer’s
Guide
The purpose of this manual is to help you program your own
application to control your labeling software. All you should know
about using ActiveX with your labeling software is described in
this manual. However, to get more information about the
ActiveX technology, refer to the Microsoft reference manuals.
The Programmer’s Guide is divided into three parts:
S Discover ActiveX for your labeling software:thispart
gives the bases for programming with ActiveX.
S Reference Guide: this part gives all the ob ject, method and
property definitions integrate d by your labeling software.
S Appendix: this part gives you information on Visual C++
Data Type.
Page 8

viii
Programmer’s Guide
Typographical conventions
This manual distinguishes dif ferent types of information by using
the following conv entions:
S terms taken f rom the interface itself, such as commands,
appear in bold;
S keys appear in small caps, as in the following example:
”Press the
SHIFT key”;
S numbered lists mean there is a procedure to follow;
S when the conjunction ”or” appears next to a paragraph it
means there is another procedure available for performing a
given task;
S When a menu command contains submenus, the menu name
followed by the command to select appears in bold. Thus,
”Choose File Open” means choose the File menu, then the
Open command.
This symbol provides tips for optimizing certain tasks, speeding
up the execution of commands, etc.
This symbol highlights important information about a particular
function or procedure.
This symbol highlights an example or an exercise.
Page 9

Discover ActiveX Automation for your labeling software
Introduction
Using ActiveX Automation, you can control almost anything
you create with your labeling software — even your labeling
software itself.
The ActiveX technology lets you easily integrate your labeling
software as a printing module or a designer module in your own
organization.
1
ActiveX is object oriented and all of the ActiveX objects are
programmable from any languages such as Visual Basic. So the
user can control his labeling software using your own program.
Your labeling software becomes the server and your program is
the client application.
Through this manual, you will find examples and references
using Visual Basic 6.0.
Page 10

Chapter 1 -- 2
What is an ActiveX object?
An ActiveX object is an instance of a class that exposes
properties, methods, and events to ActiveX clients. ActiveX
objects support the COM (Component Object Model) - Microsoft
technology. An ActiveX component is an application or library
that is able to create one or more ActiveX objects. In this case,
your labeling software exposes many objects that you can use to
create new applications and programming tools. Within your
labeling software, objects are organized hierarchically, with an
object named Application at the top of the hierarchy (see
Chapter 2 - 15: the hierarchy diagram).
Each ActiveX object has its own member function definition.
When the member functions are exposed, it makes the object
programmable by an ActiveX client. Three types of members can
be exposed for an object:
S Methods are actions that an object can p erform. For ex am-
ple, the Document object in your labeling software provides
a Close method that closes the current document.
S Properties are functions that a ccess information about the
state of an object. The Application object’s Visible property
determines whether the labeling software is visible or not.
S Events are actions recognized by an object, such as clicking
the mouse or pressing a key. You can write code to respond
to such actions. In Automation, an event is a method that is
called, rather than implemented, by an object (see also
Chapter 1 - 11).
Programmer’s Guide
Your labeling software often works with several instances of an
object which together make up a Collection object.For
example, since your labeling software is a multiple-document
interface (MDI), it might have multiple documents. To provide an
easy way to access and program the documents, your labeling
software exposes an object named Documents, which refers to
all of the already opened document objects. Documents is a
collection object.
A Collection object lets you work as a group with the objects it
manage (see Chapter 1 - 9).
All the methods, properties and events are defined in
Chapter 2 - 17: Refe re nce Guide.
Page 11

Discover ActiveX Automation for your labeling software
What is the type library?
The type library supplied by the labeling software is a file
(Lppx2.tlb) that describes the type of all the ActiveX objects.
The type library does not store objects, it stores type information. By accessing the type library, your application can
determine the characteristics of an object, such as the interfaces
supported by the object and the names and parameters.
This library helps you to write your program because it contains
all the definitions of object methods and properties that you can
access. Using this library you optimize your job.
ThenameofthistypelibraryisLabelManager2 with the
TK Labeling ActiveX 6.0 reference.
The procedures below show how to install and use the type
library with Visual Basic 6.0.
"""" To install the type library
1 Choose Project References.
2 Activate TK Labeling ActiveX 6.0 in the list of available ref-
erences then validate the d ialog box.
"""" To display the methods and properties
1 Use the Object Explorer by pressing the
2 In the library list, select LabelManager2.
Chapter 1 -- 3
F2 key.
"""" To use the type library
S While writing code, you have just to enter a period ”.” after
an object to get the associated methods and properties, or
after a method to get the associated properties.
Page 12

Chapter 1 -- 4
Mechanisms
Your labeling software offers you two main objects: the
Application object that is at the top of the hierarchy and the
Document object. These main objects provide access to the
subordinated objects (see Chapter 2 - 15: the hierarchy
diagram).
The first step to activate the server is the main object creation,
in this case, the Application object.
The last step is the deactivation of the server with the Quit
method.
Server Activation
SeveralmethodsareavailabletocreateanActiveXobject.
Programmer’s Guide
Create Object function
Note
This function creates and returns a reference to the Application
object.
Syntax CreateObject(server name)
Defines an object variable. This object variable is meant to contain the object reference. Dim as Object creates a link at execution.
Dim MyApp as Object
Set MyApp = CreateObject(”Lppx2.Application”)
This code launches the application that creates the object. In this
case, the labeling software. As soon as the object is created, you
reference it in the code with the object variable that you have
defined, i.e. MyApp.
If you define an object variable with “As Object”, a variable
containing a reference for any object type is created. However,
the access to an object via this variable is realized by a late
bind, i.e. the link is create d during the execution of your program. To create an object variable that induces an early bind,
i.e. a link during the compilation of your program, define the
object variable with a specific identifier (see below).
Page 13
Discover ActiveX Automation for your labeling software
For example, you can define and create the reference using the
code below:
Dim MyApp As Lppx2.Application
Set MyApp = CreateObject(”Lppx2.Application”)
The variable reference creating an early bind increases the
performance but must only contain one reference.
Chapter 1 -- 5
GetObject function
Note
This function returns a reference to an ActiveX object from a file.
Syntax GetObject([pathname],[server name])
The syntax of the GetObject function includes the following
arguments:
Item Description
pathname Optional. Variable of Variant
type (String). Complete pathname with the name of the
file containing the object to
get. If you don’t define the
pathname, you have to define
the server name.
servername Optional. Variable of Variant
type (String). Name of the
application that gives the
object.
Use the GetObject function to access an ActiveX object from a
file and to assign this object, an object variable. Use the Set
instruction to assign the object that is returned by the GetOb-
ject functionattheobjectvariable(seebelow).
Below are several examples showing the variations of the
GetObject syntax.
Note
Dim MyDoc As Object
Set MyDoc = GetObject(”c:\ProgramFile\document.lab”)
When this code is executed, the application associated with the
pathname argument is launched and the object included in the
file is activated.
In the case where the server automation is already loaded in
the system memory, the ActiveX mechanism selects it, then the
document is activated.
Page 14

Chapter 1 -- 6
Programmer’s Guide
Intheexamplebelow,theservernameisspecified.Usethis
parameter if you have several versions of your labeling software
to open the document.lab with the correct version.
Dim MyApp As Object
Set MyApp = GetObject (”c:\ProgramFile\document.lab”,”Lppx2.Application”)
Note that in the example below the Visual Basic for Application
expression GetObject(,”Lppx2.Application) will fail unless the
Application (the labeling software) is already running. If the
Application is not already running, a new instance will not be
launched.
Dim MyApp As Object
Set MyApp = GetObject (,”Lppx2.Application”)
In this ex ample, the variation of the GetObject syntax varies
from the previous example in that a new instance of the application will always be launched even if the application is already
running. This variation is equivalent to a CreateObject statement.
Dim MyApp As Object
Set MyApp = GetObject (””,”Lppx2.Application”)
New function
The key word New can only be used if you work with the Type
Library (see: What is the type library).
New assigns an object reference to a variable or to a property.
Syntax
SetMyApp={[New]objectexpression}
This example demonstrates reation of the MyApp object that
represents Application. This is the standard access to get the
subordinated objects of Application.
Dim MyApp As LabelManager2.Application
Set MyApp = New LabelManager2.Application
Page 15
Discover ActiveX Automation for your labeling software
The syntax of the Set instruction contains the following items:
Item Description
objectvar Nameofthevariableorprop-
erty.
Chapter 1 -- 7
New Optional. This key word is
Note
The objectvar must have an object type compatible with the
object to which it is assigned.
Server Deactivation
The last step of y our program is the deactivation of the server
with the Quit method.
To correctly deactivate the server, you must:
a. Close all the documents with the CloseAll method on the
Documents collection.
b. Call the Quit method of the Application object. This method
meanstheprocessisended.
c. Ask Visual Basic to delete the Application f rom the system
memory by setting the value of the variable to Nothing.
generally used in the declarations to allow the implicit creationofanobject.Usedwith
Set, the New key word
creates a new instance of the
class. If the objectvar argument contains a reference to
an object, this reference is
lost when a new association is
created.
Page 16

Chapter 1 -- 8
Quit method
Data Type
Programmer’s Guide
The Quit method is used to end the process. Before using this
method, you must close all the documents.
Thefollowingexampleshowshowtodeactivatetheserver.Use
the CloseAll method on the Documents collection to close all
the documents. Then, use the Quit method on the Application
object to end the process. At the end, the Set instruction delete
the Application from the system memory.
MyApp.Documents.CloseAll False
MyApp.Quit
Set MyApp = Nothing
There are three data types corresponding to the three main
objects: Application, Document and Collection.
Application Object
The Application object represents the labeling software. The
Application object contains the properties and the methods that
return the first level objects. For example, the ActiveDocument
property returns a Document object.
"""" Using the Application object
To return the Application object, use the Application property.
The following sample shows how to display the path defined for
the labeling software.
Dim MyApp As LabelManager2.Application
Set MyApp = New LabelManager2.Application
MsgBox MyApp.Path
Most of the properties and methods that return the common user
interface objects, such as the active document (ActiveDocu-
ment property), can be used without the identifier of the
Application object by using the With keyword.
Page 17

Discover ActiveX Automation for your labeling software
Dim MyApp As LabelManager2.Application
...
With MyApp
.ActiveDocument
.Print
end With
The properties and methods that can be used without the
Application object are called “global.”
S To display the global properties and methods in the object
explorer (
displayed in the Classes zone.
F2 key), click on global at the beginning of the list
Chapter 1 -- 9
Document Object
Collection Object
Note
The Document object represents an open document. Each open
document in the labeling software is represented by a Docu-
ment object. This object has members (properties, methods,
and events) that you can use to manipulate the document.
You can access the current document if there is an open
document by using the ActiveDocument prope rty of the
Application object.
All open documents that belong to the documents collection are
represented by the Documents object. You can find a particular
document by moving through this collection.
A Collection object is an ordered set of items that can be
referred to a unit.
The Collection object provides a convenient way to refer to a
related group of items as a single object. The items, or members, in a collection need only be related by the fact that they
exist in the collection. Members or items of a collection don’t
have to share the same data type (see Chapter 1 - 8).
A collection can be created the same way other objects are
created. For example:
Dim X As New Collection
Once a collection is created, members can be added using the
Add method and removed using the Remove method. Specific
members can be returned from the collection using the Item
method, while the entire collection can be returned using the For
Each...Next statement.
Page 18
Chapter 1 -- 10
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Collection methods
Methods for collection are described in the following table. The
Item method is required; other methods are optional.
Method name Return type Description
Add VT_DISPATCH
or VT_EMPTY
Item Varies with
type of collection
Remove VT_EMPTY Removesanitemfroma
Adds an item to a collection. Returns VT_DISPATCH
if object is created (object
cannot exist outside the
collection) or VT_EMPTY if
no object is created (object
can exist outside the collection).
Returns the ind icated item
in the collection. Required.
The Item method may
take one or more arguments to indicate the element within the collection
to return. This method is
the default member for the
collection object.
collection. Uses indexing
arguments in the same way
as the Item method.
The Item method takes one or more arguments to indicate the
index. Indexes can be numbers or strings.
Because Item is the default method, you could write either:
MyObject.Item(3).Name
-Or-
MyObject(3).Name
"""" Count Property
Returns a Long (long integer) containing the number of objects
in a collection. Read-only.
Page 19
Discover ActiveX Automation for your labeling software
Event management
When a program detects that something has happened, it can
notify its clients. For example, if a stock ticker program detects a
change in the price of a stock, it can notify all clients of the
change. This notification process is referred to as firing an event.
Chapter 1 -- 11
Handling an
Object’s
Events
Get or set properties.
Call methods.
Client
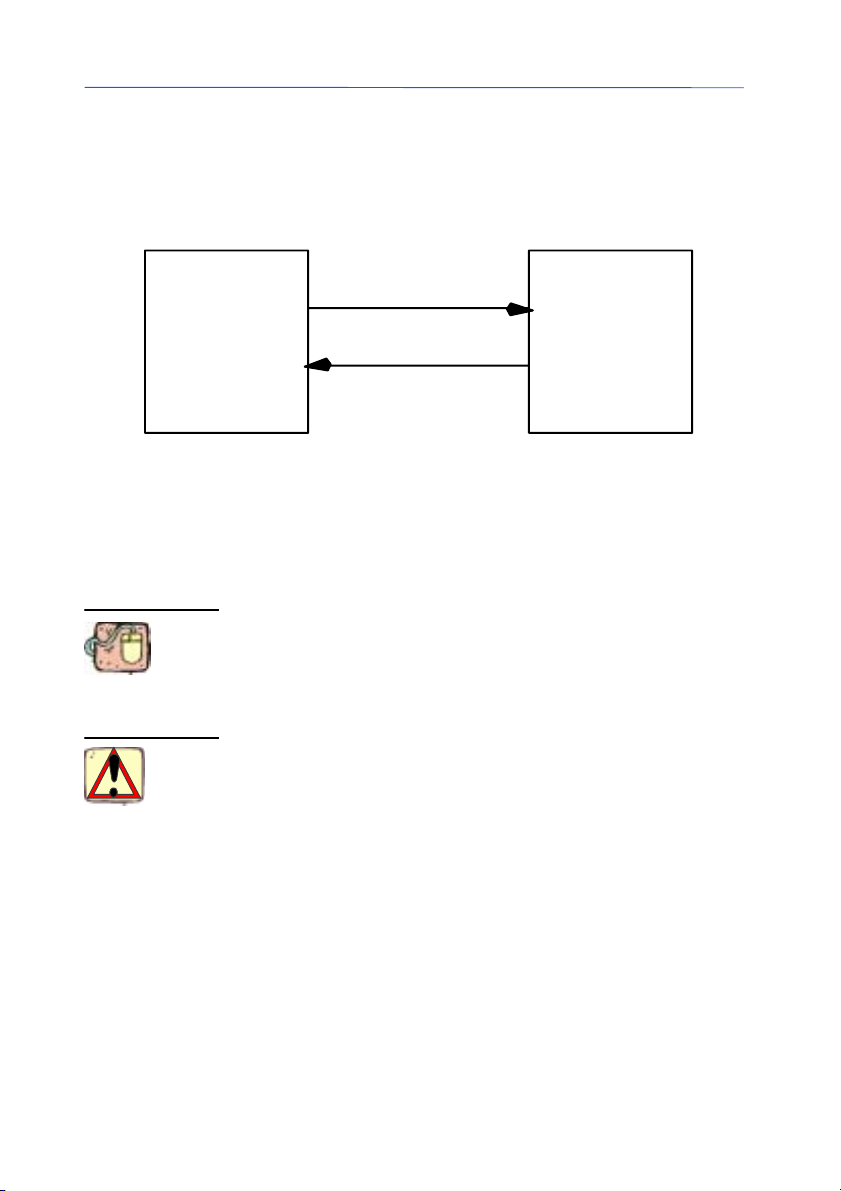
Fire events
Figure 1 Interaction between the Client and
the Labeling software
An object that triggers events is called an event source.To
handle the events triggered by an event source, you can declare
a variable of the object’s class using the WithEvents keyword.
For example, to handle the ProgressPrinting event of a Docu-
ment, place the following code in the Declarations section:
Option Explicit
Private WithEvents MyDoc As LabelManager2.Document
Private mblnCancel As Boolean
In this case, the client application must set the EnableEvents
property of the application to True in order to trigger the events.
The WithEvents keyword specifies that the variable MyDoc will
be used to handle an object’s events. You specify the kind of
object by supplying the name of the class from which the object
will be created.
Server: Lppx2
(event source)
Application
Document
Events
The variable MyDoc is declared in the Declarations section
because WithEvents variables must be module-level variables.
Thisistrueregardlessofthetypeofmoduleyouplacethemin.
The variable mblnCancel will be used to cancel the LongTask
method.
"""" Limitations on WithEvents variables
You should be aware of the following limitations on the use of
WithEvents variables:
Page 20
Chapter 1 -- 12
Programmer’s Guide
S A WithEvents variable cannot be a generic object variable.
Thatis,youcannotdeclareitAsObject-youmustspecify
the class name when you declare the variable.
S You cannot declare a WithEvents variable As New. The
event source object must be explicitly created and assigned
to the WithEvents variable.
S You cannot declare WithEvents variables in a standard mod-
ule. You can declare them only in class modules, form modules, and other modules that define classes.
S You cannot create arrays of WithEvents variables.
"""" Writing code to handle an event
As soon as you declare a variable WithEvents,thevariable
name appears in the left-hand drop down of the module’s code
window. When you select MyDoc,theDocument class events
will appear in the right-hand drop down, as shown in Figure 2
below:
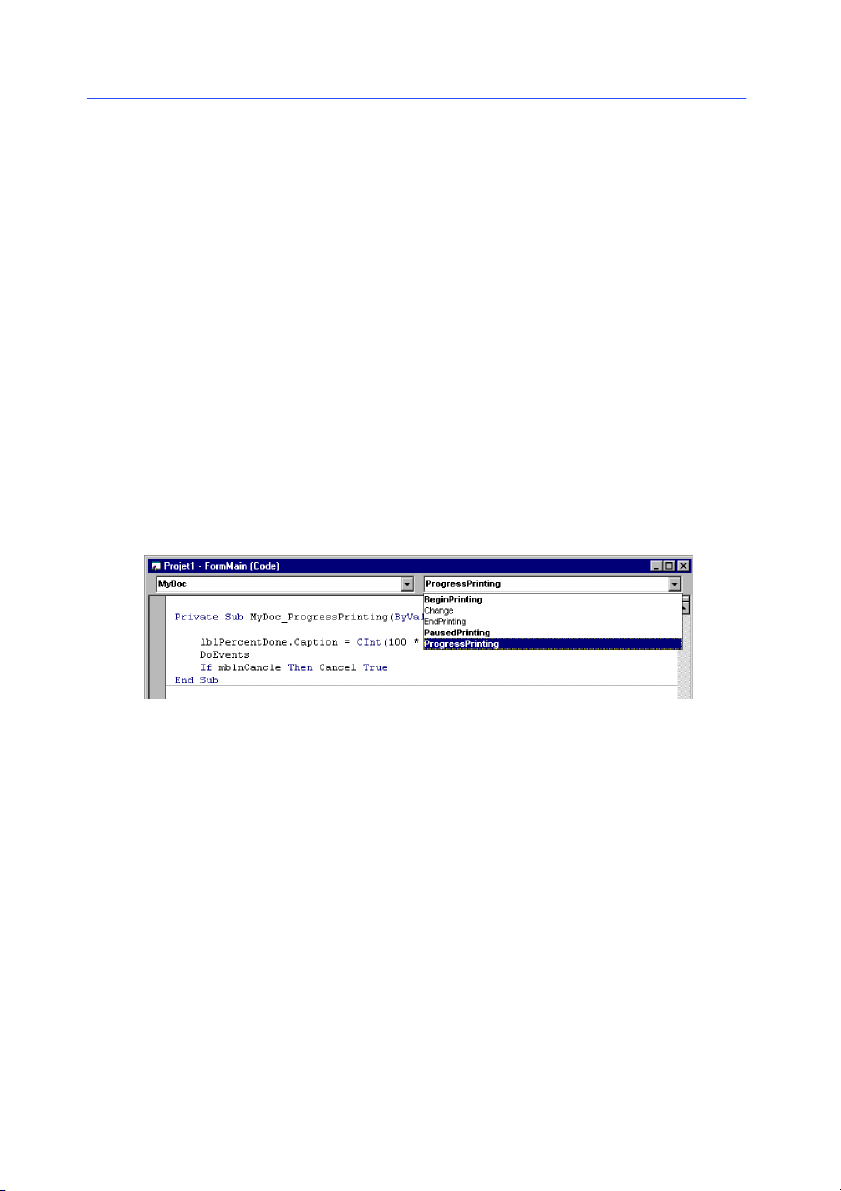
Figure 2 An event associated with a WithEvents variable
Selecting an event will display the corresponding event
procedure, with the prefix MyDoc_. All the event procedures
associated with a WithEvents variable will have the variable
name as a prefix.
Page 21

Discover ActiveX Automation for your labeling software
For example, add the following code to the
MyDoc_ProgressPrint event procedure:
Private Sub MyDoc_ProgressPrinting (ByVal Percent as
integer,Cancel as integer)
lblPercentDone.caption = CInt (100 * Percent) & “%”
DoEvents
If mblnCancel Then Cancel = True
End Sub
Whenever the ProgressPrinting event is raised, the event
procedure displays the percent complete in a Label control. The
DoEvent statement allows event processing to occur. The
module-level variable mblnCancel is set to True, and the
MyDoc_ProgressPrinting event then tests it and sets the
ByRef Cancel argument to True.
Chapter 1 -- 13
Connecting a WithEvents variable to an object
When you declare a variable WithEvents at design time, there
is no object associated with it. A WithEvents variable is just like
any other object variable. You hav e to create an object and
assign a reference to the object to the WithEvents variable.
Add the following code to the Form_Load event procedure to
create the LabelManager2.Application.
Private Sub Form_Load()
Set MyApp = New LabelManager2.Application
Set MyDoc = MyDoc.Documents.Add (”My Document”)
MyApp.EnableEvents = True
End Sub
When the code above is executed, Visual Basic creates a
LabelManager2.Application and a new document called “My
Document” then connects its events to the event procedures
associated with MyDoc. From that point on, whenever the
MyDoc raises its ProgressingPrinting event, the
MyDoc_PrintProgressing event procedure will be executed.
Page 22

Chapter 1 -- 14
Programmer’s Guide
Compatibility with the previous version
This version is compatible with the previous version of the label
design software.
However, the labeling software includes new fe atures and certain
processes have changed.
To ensure your program can be executed with this version,
verify your code by referring to the User’s Guide for information
on the functions that have changed.
For example, the previous version of your labeling software uses
a simple-document interface (SDI) and, the ActiveDocument
property always refers to a document. This version is a multipledocument interface (MDI) and there isn’t always an open document. If you use this property, verify that there is an open document after the server is activated.
To remain compatible with the previous version :
S a document is automatically created at initialization,
S the Open method will close the current document (if one
exists), before a new document is created (The Close
method functions the same way).
However, if the Application object is visible, the user has control of the active document management. For example, if the
user closes the active document, a new document is not automatically created.
Particularity about access rights
Certain versions of the labeling software include a User
manager module. This module controls access to certain
functions of the labeling software.
For example, if calling a function through your ActiveX interface
fails, verify your rights in the User manager module. An error
message is displayed and provides information about the nature
oftheerror(seetheReference Guide, Chapter 2 - 24: Error
code table).
Page 23
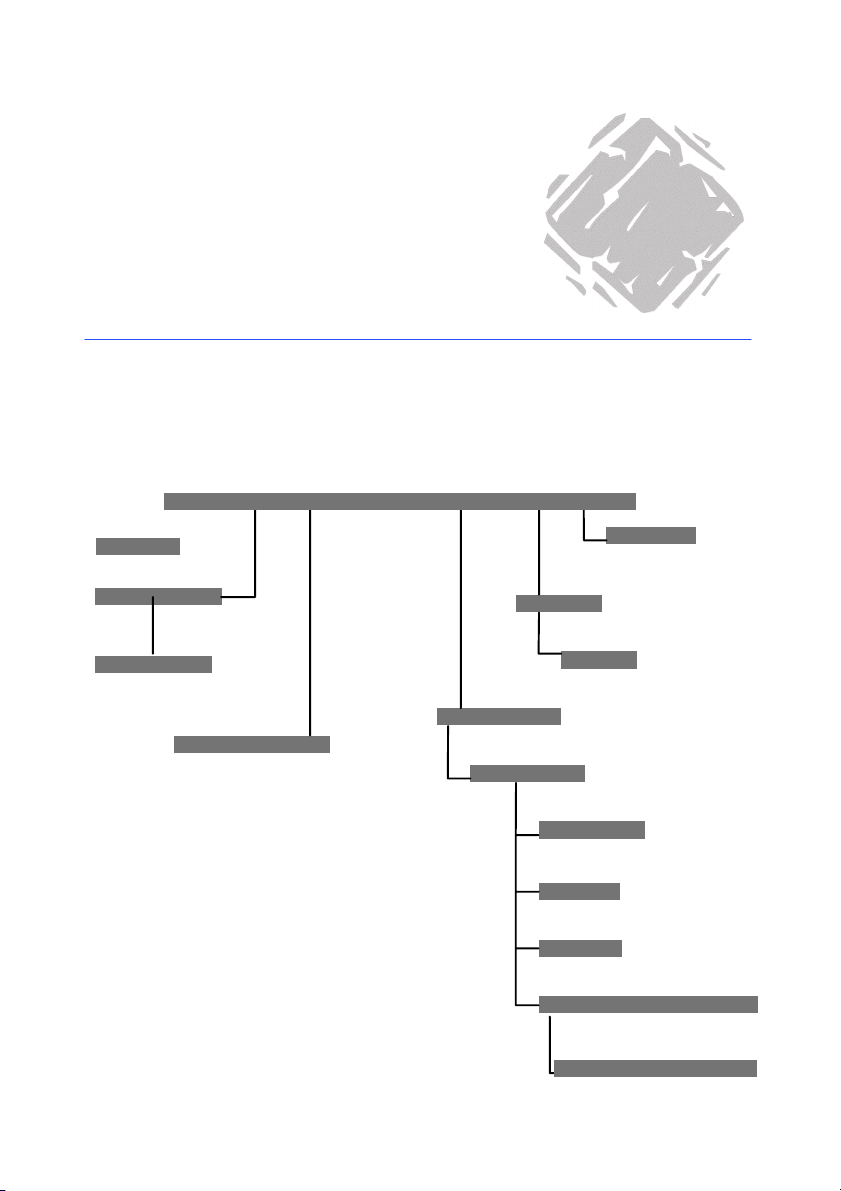
Reference Guide
Hierarchy diagram
The diagram below shows the object hierarchy:
Application .
2
Strings
RecentFiles
RecentFile
PrinterSystem
Options
Dialogs
Dialog
Documents
Document
Database
Printer
Format
DocumentProperties
DocumentProperty
Page 24
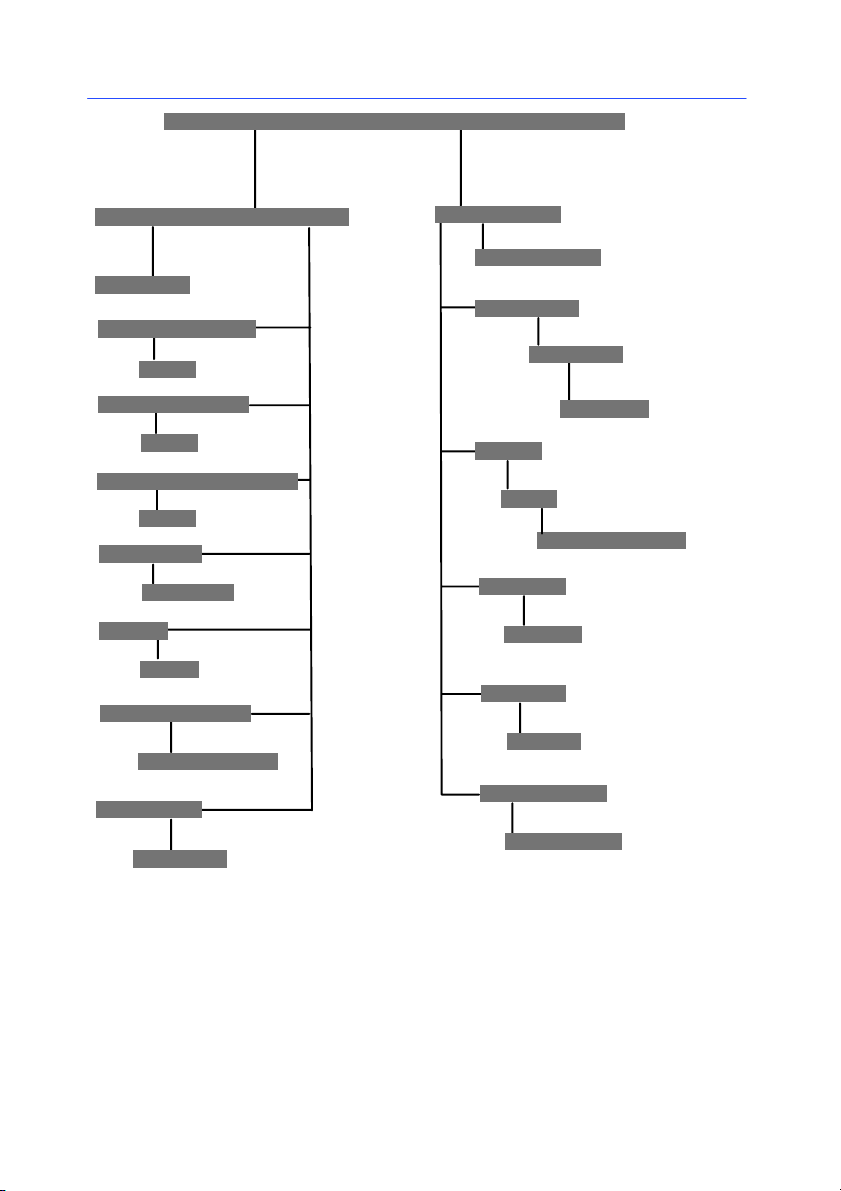
Chapter 2 -- 16
Programmer’s Guide
Document .
Variables .
Variable
FormVariables
Free
FreeVariables
Free
DatabaseVariables
Free
Counters
Counter
Dates
Date
TableLookups
TableLookup
Formulas
Formula
DocObjects
DocObjects
Barcodes
Barcode
Code2D
Texts
Text
TextSelection
Images
Image
Shapes
Shape
OLEObjects
OLEObject
Page 25
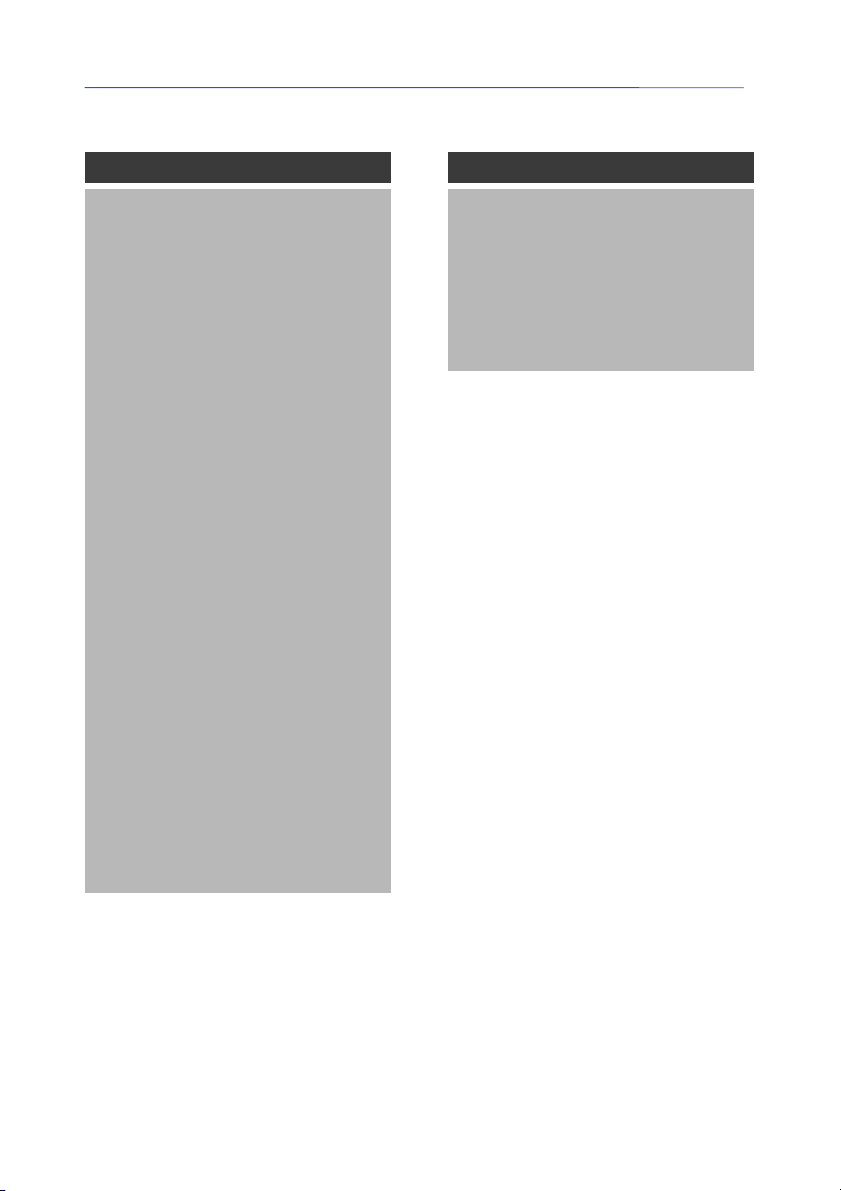
Reference Guide
Application Object
Properties Methods
ActiveDocument ErrorMessage
ActivePrinterName GetLastError
Application ShowHelp
Caption Move
DefaultFilePath Resize
Dialogs Quit
Documents
EnableEvents
FullName
Height
Left
Locked
Name (Default)
Options
Parent
Path
PrinterSystem
RecentFiles
Top
UserControl
Version
Visible
Width
Chapter 2 -- 17
Page 26

Chapter 2 -- 18
Object Properties
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Application.ActiveDocument
This property allows you to access the document object interface
(refer to the document which has the focus in the main
application).
Returns an error if no document in application.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or
"""" Application.ActivePrinterName
Returns the current pair <Printer, Port> of the active document,
if any, empty string if none.
Access Read-only.
Type VT_BSTR or
"""" Application.Application
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or
"""" Application.Caption
Returns or sets the caption text for the application window. To
change the caption of the application window into the default
text, set this property to an empty string (””).
Access Read/Write.
Document.
String.
object that represents the
Application.
Type VT_BSTR or
String.
Page 27
Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 19
"""" Application.DefaultFilePath
Sets or returns the default path specification used by the
application for opening document files.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or
"""" Application.Dialogs
Returns the Dialogs
dialog boxes of the application.
Access Read-only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or
"""" Application.Documents
Returns the Documents
documents.
Access Read-only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or
"""" Application.EnableEvents
Enables or disables Automation events notification (Default:
False) (see Appendix).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or
String.
collection that represents all the built-in
Dialogs.
collection that represents all the open
Documents.
Boolean.
"""" Application.FullName
Returns the file specification for the application, including path.
(Ex : c:\drawdir\scribble).
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or
String.
Page 28

Chapter 2 -- 20
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Application.Height
Returns or sets the height of the main window of the application
(in pixel unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Application.Left
Returns or sets the distance between the left edge of the main
window of the application and the left edge of the screen (in
pixel unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Application.Locked
Locks the User Interface if True.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Application.Name
Returns the name of the application (for example, ”Microsoft
Word”). Default property.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
.
.
.
.
"""" Application.Options
Represents application and general document options. Many of
the properties for the Options object correspond to items in the
Options dialog box (Tools menu). Use the Options property to
return the Options object.
The following example sets two application options:
With Options
.LoadPrinterSetup = True
.MeasureSystem = lppxInch
End With
Page 29

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 21
Access Read-only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Options
"""" Application.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
"""" Application.Path
Returns the path of the Application ( with « \ » character).
Access Read-only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Application.PrinterSystem
Returns the PrinterSystem
the system.
Access Read-only.
Type VT_DISPATCH o r PrinterSystem
"""" Application.RecentFiles
object that represents all printers in
.
.
.
Returns the RecentFiles
recent files used (File menu in UI).
Access Read-only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or RecentFiles
"""" Application.Top
Returns or sets the distance between the top edge of the main
window of the application and the top edge of the screen (in
pixel unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
collection that represents the list of last
.
.
Page 30

Chapter 2 -- 22
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Application.UserControl
True if the application was created by the user.
False if the application was created in programming (with the
CreateObject or GetObject method in Visual Basic).
Note
If the application is visible to the user, this property will always
return True.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Application.Version
Returns the software version number.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Application.Visible
True if the application is visible. (Default: False, if application
was launched with CreateObject).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Application.Width
Returns or sets the width of the main window of the application
(in pixel unit).
.
.
.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
.
Page 31

Reference Guide
Object Methods
Chapter 2 -- 23
"""" Application.ErrorMessage
VTS_BSTR or String
Returns the string message error associated with the error code
parameter.
Return value: Message associated.
Parameters:
intErrorCode Required VT_I2 or Integer
"""" Application.GetLastError
VTS_I2 or Integer
Returns the last error code generated.
Return value: Error code (see Error code table below).
Parameters:None.
No error 0
Can’t open data file 1200
Can’t open query file 1201
Can’t open descriptor file 1202
Can’t open label file 1203
Can’t open POC file 1204
Can’t open log file 1205
ErrorMessage( intErrorCode )
. Error code to process.
GetLastError()
Printer not found 1300
Driver not found 1301
Incorrect Datasource enum value 1400
Incorrect Rotation enum value 1401
Incorrect HRAlign enum value 1402
Incorrect HRPosition enum value 1403
Incorrect HR check digit enum value 1404
Incorrect Anchor point enum value 1405
Incorrect counter base enum value 1406
Incorrect Label object enum value 1407
Incorrect view size enum value 1408
Incorrect view mode enum value 1409
Incorrect MeasureSystem enum value 1410
Incorrect dialog type enum value 1411
Page 32

Chapter 2 -- 24
Programmer’s Guide
Incorrect language enum value 1412
Incorrect symbology enum value 1413
Incorrect built in document property enum
value
Incorrect view orientation enum value 1415
Incorrect form prompt mode enum value 1416
Object not found 1500
Can’t create object 1501
Variable not found 1502
Can’t create variable 1503
Invalid font object 1504
Invalid variable object 1505
Name of item already used 1506
Database not connected 1600
Database connection failed 1601
Number must be positive 2000
Data type must be a boolean 2001
Invalid path 2002
File already exists 2003
Can’t prompt dialog box (no active document) 2100
1414
Not sufficient access rights to perform this
operation
Figure 3 Error code table
3000
Page 33

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 25
"""" Application.ShowHelp
VTS_NONE ShowHelp(strHelpFile, longHelpContext)
This method activates a help file.
Parameters:
strHelpFile Optional VT_BSTR or String
file to open (.HLP or .CHM). If not specified, associated help file
is opened.
. Specifies the help
longHelpContext Optional VT_I4 or Long
to jump to. If not specified, general index is prompted.
"""" Application.Move
VTS_NONE Move( longposLeft, longposTop)
Moves the application window to the specified position (posLeft,
posTop), in pixel unit.
Parameters:
longposLeft RequiredVT_I4orLong
between the left edge of the main window of the application and
the left edge of the screen(in pixel unit).
longPosTop RequiredVT_I4orLong
between the top edge of the main window of the application and
the top edge of the screen (in pixel unit).
"""" Application.Resize
VTS_NONE Resize( longWidth, longHeight)
Resizes the application window (Width, Height), in pixel unit.
Parameters:
longWidth RequiredVT_I4orLong
main window of the application (in pixel unit).
longHeight RequiredVT_I4orLong
main window of the application (in pixel unit).
. Specifies the id context
. Sets the distance
. Sets the distance
. Sets the width of the
. Sets the height of the
"""" Application.Quit
VTS_NONE Quit()
Quits the current application. No effect if the application has
been launched manually. First executes a Document.CloseAll
(True) then releases the application.
Page 34

Chapter 2 -- 26
PrinterSystem Object
Properties Methods
(None) Families
Models
Printers
Ports
Add
Remove
Rename
Object Methods
"""" PrinterSystem.Families
Programmer’s Guide
VTS_DISPATCH or Strings
Retrieves printer families list.
"""" PrinterSystem.Models
VTS_DISPATCH or Strings
Retrieves models associated with a family.
Parameters:
strFamilyName Optional VT_BSTR or String
Family for which the models list is needed. If none, it returns the
full models list.
"""" PrinterSystem.Printers
VTS_DISPATCH or Strings
Retrieves installed printers as string pairs < Printer, Port >.
Parameters:
intKindOfPrinters OptionalVT_I2orInteger
Printers
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxInternalPrinters= 1
lppxWindowsPrinters= 2
lppxAllPrinters= 3
.(default lppxInternalPrinters).
Families ()
Models ( strFamilyName)
.Itspecifiesthe
Printers ( intKindOfPrinters)
or enumKindOf-
Page 35

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 27
"""" PrinterSystem.Ports
Note
VTS_DISPATCH or Strings
Retrieves all installed ports on the system.
"""" PrinterSystem.Add
VTS_BSTR or String
boolDirectAccess)
Installs a new printer and returns the full name assigned to it.
Parameters:
strPrinterName Required VT_BSTR or String
to install (got with Printers.InternalPrinters).
strPortName Required VT_BSTR or String
associated with the printer.
boolDirectAccess Optional VT_BOOL or Boolean
FALSE). Is the port used with direct access or not.
Only models can be installed with this method.
"""" PrinterSystem.Remove
VTS_NONE Remove (strPrinterPortName).
Ports ().
Add (strPrinterName, strPortName,
.PrinterName
.PortName
(default value
Note
Removes an installed printer.
Parameters:
strPrinterPortName Required VT_BSTR o r String.
an installed printer (got with PrinterSystem.Printers(lppxInternalPrinters) method).
Only models can be removed.
If an active document uses this printer, the operation fails.
Full name of
Page 36

Chapter 2 -- 28
Programmer’s Guide
"""" PrinterSystem.Rename
VTS_NONE Rename (strPrinterName, strNewPrinterName).
Renames a model.
Parameters:
strPrinterName Required VT_BSTR or String
installed printer to rename.
.Nameof the
Note
strNewPrinterName Required VT_BSTR or String
name to assign.
Only models can be renamed.
.New
Page 37

Reference Guide
Options Object
Properties Methods
Application (None)
CreateBackup
DefaultDescriberPath
DefaultSharedVarPath
DefaultImagePath
DefaultPrintOutFilePath
DefaultQueryPath
DefaultUserSettingsPath
EuroConversionRate
Language
LoadPrinterSetup
LoadPrinter
MeasureSystem
OpenMergeDatabase
Parent
OpenReadOnly
SharedFileAccessTimeout
TrayNotification
Chapter 2 -- 29
Object Properties
"""" Options.Application
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
object that represents the
object.
Page 38

Chapter 2 -- 30
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Options.CreateBackup
ReturnsorsetstheCreateBackup
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Options.DefaultDescriberPath
Returns or sets the DefaultDescriberPath
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Options.DefaultSharedVarPath
Returns or sets the DefaultSharedVarPath
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Options.DefaultImagePath
Returns or sets the DefaultImagePath
Access Read/Write.
option. (Default: True).
.
.
.
option.
option.
option.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Options.DefaultPrintOutFilePath
Returns or sets the DefaultPrintOutPath
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Options.DefaultQueryPath
Returns or sets the DefaultQueryPath
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
.
.
.
option.
option.
Page 39

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 31
"""" Options. DefaultUserSettingsPath
Returns or sets the DefaultUserSettingsPath
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Options. EuroConversionRate
ReturnsorsetstheEuroConversionRate
6.55957).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_R4orSingle
"""" Options.Language
Returns or sets the Language
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxEnglish = 1
lppxFrench = 2
lppxGerman = 3
lppxItalian = 4
lppxSpanish = 5
lppxDanish = 6
lppxSwedish = 7
lppxJapanese = 8
lppxHungarian = 9
lppxDutch = 10
lppxCzech = 11
lppxNorwegian = 12
lppxFinnish = 13
lppxPortuguese = 14
lppxSimplifiedChinese = 15
lppxTraditionalChinese = 16
lppxKorean = 17
.
option. (Default
.
option.
or enumLanguage type.
option.
Note
Depending on the product, not all languages are available.
Page 40

Chapter 2 -- 32
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Options.LoadPrinter
Note
Returns or sets the LoadPrinter
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Options.LoadPrinterSetup
Returns or sets the LoadPrinterSetup
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Options.MeasureSystem
ReturnsorsetstheMeasureSystem
meter
).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I2orInteger
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxMillimeter = 0
lppxInch = 1
Using lppxMillimeter unit means that values entered are in
Millimeter per cent.
Using lppxInch unit means that values entered are in Inch per
thousand.
option. (Default : False).
.
option. (Default : True).
.
option. (Default : lppxMilli-
or enumMeasureSystem type.
"""" Options.OpenMergeDatabase
Returns or sets the OpenMergeDatabase
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
.
option. (Default: False)
Page 41

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 33
"""" Options.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
"""" Options.OpenReadOnly
ReturnsorsetstheOpenReadOnly
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Options. SharedFileAccessTimeout
Returns or sets the SharedFileAccessTimeout
10000 ms)
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Options.TrayNotification
Enables or disables notification of printing in System Tray Bar.
(Default: True)
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
.
option. (Default : False)
.
option. (Default:
.
Page 42

Chapter 2 -- 34
Dialogs Collection
Properties Methods
Application Item (Default)
Count
Parent
Object Properties
"""" Dialogs.Application
Programmer’s Guide
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" Dialogs.Count
Returns the number of items in the specified collection.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_I2orInteger
"""" Dialogs.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
object that represents the
object.
.
Page 43

Reference Guide
Object Methods
Chapter 2 -- 35
"""" Dialogs.Item
Note
Note
VTS_DISPATCH or Dialog
Returns a member of a collection, by position.
If the value provided as Index does not match any existing
member of the collection, no object is returned.
Parameters:
intIndex Required VT_I2 or Integer
index number of a member of the collection.
The index must be a numeric expression (a number from 1 to
the value of the collection’s Count property), or a constant.
If the value provided as Index doesn’t match any existing
member of the collection, an error occurs.
The Item method is the default method for collections. Therefore, the following two lines of code are equivalent.
Object.Dialogs(1)
Object.Dialogs.Item(1)
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxPrinterSelectDialog= 1
lppxOptionsDialog= 2
lppxFormDialog= 3
lppxPrinterSetupDialog= 4
lppxPageSetupDialog= 5
lppxDocumentPropertiesDialog= 6
Item( intIndex ).
or enumDialogType.The
Page 44

Chapter 2 -- 36
Dialog Object
Properties Methods
Application Show
Parent
Type
Object Properties
"""" Dialog.Application
Programmer’s Guide
Returns the Application
of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" Dialog.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
"""" Dialog.Type
Returns the type of the prompted dialog box.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_I2orInteger
object that represents the root object
object.
or enumDialogType type.
Page 45

Reference Guide
Object Methods
Chapter 2 -- 37
"""" Dialog.Show
VTS_I2 or Integer
Prompts the dialog box associated.
Return value 1 if the user has clicked on OK.
If application is not visible, dialog box is prompted at the top
level of all windows.
If there is no document open, the dialog boxes (except Options
dialog box) can’t be displayed because they depend on the
document.
Show().
2 if the user has clicked on Cancel.
Page 46

Chapter 2 -- 38
RecentFiles Collection
Properties Methods
Application Add
Count Item (Default)
Maximum Clear
Parent Remove
Object Properties
"""" RecentFiles.Application
Programmer’s Guide
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" RecentFiles.Count
Returns the number of items in the specified collection.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_I2orIntege
"""" RecentFiles.Maximum
Returns or sets the maximum number of items in the specified
collection (from 0 to 16).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I2orIntege
"""" RecentFiles.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
r.
r.
object that represents the
object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
Page 47

Reference Guide
Object Methods
Chapter 2 -- 39
"""" RecentFiles.Add
Note
VTS_DISPATCH or RecentFile
boolReadOnly).
Adds a document reference to the collection and in the File
menu.
Parameters:
DocumentReference Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
reference must be unique in the collection.
boolReadOnly Optional VT_BOOL or Boolean
document must be opened, it will be opened with ReadOnly
attribute.
"""" RecentFiles.Clear
VTS_NONE Clear.
Resets the collection and clears menu.
"""" RecentFiles.Item
VTS_DISPATCH or RecentFile
Returns a member of a collection, by position (default method).
If the value provided as Index does not match any existing
member of the collection, no object is returned.
Add(DocumentReference,
.This
.If
Item( intIndex ).
Note
Parameters:
Index Required VT_I2 or Integer
member of the collection.
The index must be a numeric expression (a number from 1 to
the value of the collection’s Count property), or a constant.
If the value provided as Index doesn’t match any existing
member of the collection, an error occurs.
The Item method is the default method for collections. Therefore, the following two lines of code are equivalent.
Object.RecentFiles(1)
Object.RecentFiles.Item(1)
. The index number of a
Page 48

Chapter 2 -- 40
Programmer’s Guide
"""" RecentFiles.Remove
VTS_NONE Remove( intIndex ).
Deletes object with intIndex index.
Page 49

Reference Guide
RecentFile Object
Properties Methods
Application Open
Parent
Path
Name
Object Properties
"""" RecentFile.Application
Chapter 2 -- 41
Returns the Application
the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" RecentFile.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
"""" RecentFile.Path
Returns the path associated with the current filename (always
without « \ » character).
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" RecentFile.Name
Returns the name associated with the current filename.
object that represents the root object of
object.
.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
.
Page 50

Chapter 2 -- 42
Object Methods
Programmer’s Guide
"""" RecentFile.Open
VTS_DISPACTCH or Document
Opens the document associated with the current filename.
Open().
Page 51

Reference Guide
Documents Collection
Properties Methods
Application Add
Count CloseAll
DefaultExt Item (Default)
Parent Open
SaveAll
Object Properties
"""" Documents.Count
Returns the number of items in the specified collection.
Access Read-Only.
Chapter 2 -- 43
Type VT_I2orInteger
"""" Documents.Application
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" Documents.DefaultExt
This property returns the default document filename extension
for the application.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Documents.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
.
object that represents the
object.
.
Page 52

Chapter 2 -- 44
Object Methods
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Documents.Add
Note
VTS_DISPATCH or Document
Adds a new Document
Return value: Returns a Document
Parameters:
strDocumentName Optional VT_BSTR or String.
Specifies the name of the new document to add.
If none, system automatically assigns one.
"""" Documents.CloseAll
VTS_NONE CloseAll ( boolSaveChanges ).
Closes all documents.
Parameters:
boolSaveChanges Optional VT_BOOL or Boolean
the save action for all documents. (default: True).
If boolSaveChanges is True and a document has not been
previously saved, the Saves As dialog box is automatically
prompted.
"""" Documents.Item
VTS_DISPATCH or Document
Returns a Document
name.
If the value provided as Index does not match any existing
member of the collection, no object is returned.
to the collection.
of a collection, either by position or by
Add(strDocumentName).
object if succeeded.
.Specifies
Item( varIndex ).
Note
Parameters:
varIndex Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
index number of a member of the collection.
The index can be a numeric expression (a number from 1 to the
value of the collection’s Count property), a constant, or a string.
If the value provided as Index doesn’t match any existing
member of the collection, an error occurs.
The Item method is the default method for collections. Therefore, the following two lines of code are equivalent.
Object.Documents(1)
Object.Documents.Item(1)
.Thenameor
Page 53

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 45
"""" Documents.Open
VTS_DISPATCH or Document
boolReadOnly ).
Opens the specified document and adds it to the Documents
collection.
Return value: Returns a Document
Parameters:
strFileName Required VT_BSTR or String
the document (paths are accepted).
boolReadOnly Optional VT_BOOL or Boolean
the document as read-only. By default, set to False.
"""" Documents.SaveAll
VTS_NONE SaveAll( boolAlwaysPrompt ).
Saves all the documents in the Documents collection.
If a document hasn’t been previously saved, the Save As dialog
box is prompted even if the Prompt parameter is assigned to
False.
Parameters:
boolAlwaysPrompt Optional VT_BOOL or Boolean.
user wants to prompt the save dialog box (default: False).
Open( strFileName,
object.
. The name of
.Truetoopen
True if
Page 54

Chapter 2 -- 46
Programmer’s Guide
Document Object
Properties Methods
Application Close
BuiltInDocumentProperties CopyToClipboard
Database Merge
Format FormFeed
TriggerForm GeneratePOF
FullName Insert
Name (Default) PrintDocument
DocObjects PrintLabel
Parent Save
Printer SaveAs
ReadOnly Activate
Variables CopyImageToFile
ViewMode
ViewOrientation
WindowState
IsModified
Object Properties
"""" Document.Application
Returns the Application
the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" Document. BuiltInDocumentProperties
Returns the DocumentProperties
document properties.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or DocumentProperties
object that represents the root object of
Object.
collection that represents
collection.
Page 55

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 47
"""" Document.Database
Returns the Database
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Database
"""" Document.Format
Returns the Format
document.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Format
"""" Document.TriggerForm
Sets or returns the TriggerForm
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I2 or Integer or enumTriggerForm
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxNever = 1
lppxForEachSerie = 2
lppxForEachLabel = 3
object associated with the document.
object.
object that represents the format of the
object.
in printing situation.
type.
"""" Document.FullName
Returns the file specification for the document, including path.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
Ex : c:\drawdir\scribble.
"""" Document.Name
Returns the document’s name. Default property.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
.
.
Page 56

Chapter 2 -- 48
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Document.IsModified
Tests that the document has been modified since the last save
operation.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
The possible modifications are : creating, deleting and editing
DocObjects; creating and deleting variables...
"""" Document.DocObjects
Returns the DocObjects
objects in the document.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or DocObjects
"""" Document.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
"""" Document.Printer
Returns the Printer
Access Read-Only.
collection that represents all the created
object that represents the associated printer.
.
object.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Printer
"""" Document.ReadOnly
True, if the changes of the current document cannot be saved to
the original document.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
object.
.
Page 57

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 49
"""" Document.Variables
Returns the Variables
Variable
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Variables
"""" Document.ViewMode
Sets or retrieves the current mode of visual display.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I2orInteger
The value can one of the following:
lppxViewModeName = 1
lppxViewModeSize = 2
lppxViewModeValue = 3
lppxViewModeForm = 4
"""" Document.ViewOrientation
Sets or retrieves the orientation of the view of the document.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I2orInteger
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxNoRotation = 0
lppx90DegreeRight = 1
lppxUpSideDown = 2
lppx90DegreeLeft = 3
objects in the document.
collection that represents all the created
collection.
or enumViewMode type.
or enumRotation type.
"""" Document.WindowState
Sets or retrieves the current size of the visual display of the
document.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I2 or Integer or enumWindowState
The value can one of the following:
lppxNormal= 1
lppxMinimized= 2
lppxMaximized= 3
type.
Page 58

Chapter 2 -- 50
Object Methods
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Document.Close
VTS_I2 Close( boolSave ).
Closes document.
Parameters:
boolSave Optional VT_BOOL or Boolean
True, saves document.
"""" Document.CopyToClipboard
VTS_BOOL CopyToClipboard().
Copies an image of the document to the Clipboard.
"""" Document.FormFeed
VTS_I2 FormFeed ().
Ends the process job.
"""" Document.GeneratePOF
VTS_I2 GeneratePOF (strDestinationFileName, strModelFileName ).
.(default false) If
Generates a POF file.
Parameters:
strDestinationFileName Required VT_BSTR or String
the file to print to.
strModelFileName Optional VT_BSTR or String
FullName of Configuration file (.POC) to use.
If none, default POC file is used.
"""" Document.Insert
VTS_I2 Insert ( strDocumentFileName ).
Inserts a document in the current document.
Parameters:
strDocumentFileName Required VT_BSTR or String
the document to insert.
.Nameof
.Nameor
.Nameof
Page 59

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 51
"""" Document. Merge
VTS_I2 Merge (longLabelQuantity, longLabelCopy,
longInterCut, longPageCopy, longLabelNoPrintedFrom,
strFileName).
Note
Merges document with the associated Database
Parameters:
longLabelQuantity RequiredVT_I4orLong
longLabelCopy OptionalVT_I4orLong
longInterCut OptionalVT_I4orLong
longPageCopy OptionalVT_I4orLong
longLabelNoPrintedFrom OptionalVT_I4orLong
strFileName Optional VT_BSTR or String
empty string).
Parameters are described in the User’s Guide.
"""" Document.PrintDocument
VTS_I2 PrintDocument ( longLabelQuantity ).
Prints document and executes an automatic FormFeed.
Parameters:
longLabelQuantity OptionalVT_I4orLong
labels to print (Default : 1).
.
.
(default 1).
(default 1).
(default 1).
(default 1).
. Quantity of
(default
"""" Document.PrintLabel
VTS_I2 PrintLabel (longLabelQuantity, longLabelCopy,
longInterCut, longPageCopy, longLabelNoPrintedFrom,
strFileName).
Prints document.
Page 60

Chapter 2 -- 52
Programmer’s Guide
Parameters:
longLabelQuantity RequiredVT_I4orLong
.
Note
longLabelCopy OptionalVT_I4orLong
longInterCut OptionalVT_I4orLong
longPageCopy OptionalVT_I4orLong
longLabelNoPrintedFrom OptionalVT_I4orLong
strFileName Optional VT_BSTR or String
empty string).
Parameters are described in the User’s Guide.
"""" Document.Save
VTS_I2 Save ().
Saves the document.
If the document has not been saved, a dialog b ox is prompted
automatically.
"""" Document.SaveAs
VTS_I2 SaveAs ( strDocumentFileName ).
Saves the document with a new name.
(default 1).
(default 1).
(default 1).
(default 1).
(default
Parameters:
strDocumentFileName Required VT_BSTR or String
"""" Document.Activate
VTS_NONE Activate ().
Causes the document object to be activated, being the
ActiveDocument
.
.
Page 61

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 53
"""" Document.CopyImageToFile
VTS_BSTR or String
Rotation,Percent, strFilename).
Generates file that contains the Image of the document.
Return value: Returns a string that represents the full name of
the generated Bitmap file.
Parameters:
Colors OptionalVT_I2orInteger
the number of bits-per-pixel. Depending of the generated file,
the values must be : 1, 4, 8, 16, 24, 32.
Extension Optional VT_BSTR or String
Specifies the extension of the file to generate. For a complete
list of extensions, refer to the labeling software documentation.
Rotation OptionalVT_I2orInteger
geometrical degree. The values must be between 0 and 360.
Percent OptionalVT_I2orInteger
factor. The values must be between 1 and 400.
strFileName Optional VT_BSTR or String
specified: name of the generated Bitmap file.
CopyImageToFile(Colors, Extension,
. (Default 8). Specifies
(Default “BMP”).
(Default 0). Rotation in
(Default 100). Scaling
(Default “ “). If
Page 62

Chapter 2 -- 54
Database Object
Properties Methods
Application Close
AutoVariables MoveFirst
BOF MoveLast
EOF MoveNext
IsOpen MovePrevious
Parent OpenASCII
Name (Default) OpenODBC
DocObjects OpenQuery
Parent Save
Object Properties
"""" Database.Application
Programmer’s Guide
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" Database.AutoVariables
Automatic creation of database variables when database
connects. (Default: True).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
object that represents the
object.
.
Page 63

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 55
"""" Database.BOF
Returns a value that indicates whether the current row position
is before the first row in the current recordset.
Return value:
True The current row position is before the first row.
False The current row position is on or after the first row.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Database.EOF
Returns a value that indicates whether the current row position
is after the last row in the current recordset.
Return value:
True The current row position is after the last row.
False The current row position is on or before the last
row.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Database.IsOpen
Tests if the Database object has been open successfully.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Database.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
.
.
.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
Page 64

Chapter 2 -- 56
Object Methods
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Database.Close
VTS_NONE Close().
Closes an open database.
"""" Database.MoveFirst
VT_BOOL or Boolean
Repositions the current row pointer in the first
recordset and makes that row the current row.
"""" Database.MoveLast
VT_BOOL or Boolean
Repositions the current row pointer in the last
recordset object and makes that row the current row.
"""" Database.MoveNext
VT_BOOL or Boolean
Repositions the current row pointer in the next
current recordset object and makes that row the current row.
"""" Database.MovePrevious
VT_BOOL or Boolean
Repositions the current row pointer in the previous
current recordset object and makes that row the current row.
MoveFirst().
row of the current
MoveLast().
row of the current
MoveNext().
row of the
MovePrevious().
row of the
Page 65

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 57
"""" Database.OpenASCII
VT_BOOL or Boolean
strDescriberFileName ).
Opens ASCII database.
Return value: Returns a boolean that indicates whether the
opening fails or not.
Parameters:
strTextFileName Required VT_BSTR or String
database text file.
strDescriberFileName Required VT_BSTR or string
Describer associated with the text file.
"""" Database.OpenQuery
VT_BOOL or Boolean
Opens a CSQ query file.
Return value: returns a boolean that indicates whether the
opening fails or not.
Parameters:
strQueryFileName Required VT_BSTR or String
which contains the query.
OpenASCII( strTextFileName,
.The
.
OpenQuery( strQueryFileName ).
. The file
"""" Database.OpenODBC
VT_BOOL or Boolean
ion, strQueryString ).
Opens an ODBC database.
Return value: Returns a boolean that indicates whether the
opening fails or not.
Parameters:
strDatasourceConnexion Required VT_BSTR or String
database string connection. For the strDatasourceConnexion
parameter, refer to Microsoft ODBC documentation.
strQueryString Required VT_BSTR or String
query.
OpenODBC( strDatasourceConnex-
.The
.SQL
Page 66

Chapter 2 -- 58
Printer Object
Properties Methods
Application ShowSetup
DeviceCodeNames Send
DeviceFontNames SetParameter
FullName (Default) SwichTo
Name
Parent
WindowsFontNames
WindowsCodeNames
XDPI
YDPI
Object Methods
"""" Printer.ShowSetup
VTS_NONE ShowSetup().
Programmer’s Guide
Prompts the Printer
current printer settings.
"""" Printer.Send
VTS_BOOL Send ( strEscapeSequence ).
Sends an escape sequence to the physical device.
Parameters:
EscapeSequence Required VT_BSTR or String
sequence to send.
Setup dialog box, in order to change the
. Escape
Page 67

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 59
"""" Printer.SetParameter (not yet implemented)
VTS_BOOL or Boolean
varValue).
Changes the current printer settings.
Parameters:
strParameter Required VT_BSTR or String
use.
varValue Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
"""" Printer.SwitchTo ()
VTS_BSTR or String SwitchTo( strPrinterName,
strPortName, boolDirectAccess ).
Changes the current printer.
Return value: Returns the name of the installed printer.
Automatically installs a printer if no printer is already installed.
You don’t need to add a printer through the user interface.
Parameters:
strPrinterName Required VT_BSTR or String
name to switch to.
strPortName Optional VT_BSTR or String
switch to.
SetParameter(strParameter,
. Parameter name to
. Value to set.
.Printer‘s
.Port’sname to
boolDirectAccess Optional VT_BOOL or Boolean
connection of the port direct or not.
Form 1
SwitchTo(« THTPrinter L-1234 », « LPT1: », FALSE).
Result of this instruction is « THTPrinter L-1234,LPT1: ».
Form 2
SwitchTo(« THTPrinter L-1234, ->COM3: »).
Result of this instruction is « Copy of THTPrinter
L-1234, ->COM3: » because printer’s name is unique.
You can either use form 1 or form 2.
Don’t insert spaces between the components in Form 2.
Notice that the names are case sensitive !
. Is the
Page 68

Chapter 2 -- 60
Object Properties
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Printer.Application
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" Printer.DeviceFontNames
Returns the Strings
fonts names.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Strings
"""" Printer.DeviceCodeNames
Returns the Strings
names.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Strings
"""" Printer.FullName
Returns the full name of the pair <Printer, Port>.
collection that represents all the printer
collection that represents all the printer code
object that represents the
object.
collection.
collection.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
.
Page 69

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 61
"""" Printer.Name
Returns the simple name of the current printer.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Printer.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
"""" Printer.XDPI
Returns the horizontal resolution of the printer (in DPI).
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Printer.YDPI
Returns the vertical resolution of the printer (in DPI).
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Printer.WindowsFontNames
.
.
.
Returns the Strings
font names.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Strings
collection that represents all the windows
collection.
Page 70

Chapter 2 -- 62
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Printer.WindowsCodeNames
Returns the Strings
code names.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Strings
collection that represents all the windows
collection.
Page 71

Reference Guide
Format Object
Properties Methods
Application SaveStock
AutoSize
ColumnCount
HorizontalGap
LabelHeight
LabelWidth
MarginLeft
MarginTop
StockName
StockType
PageHeight
PageWidth
Parent
Portrait
Corner
RowCount
VerticalGap
Chapter 2 -- 63
Object Properties
"""" Format.Application
Returns the Application
the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
object that represents the root object of
object.
Page 72

Chapter 2 -- 64
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Format. AutoSize
Automatically adjusts the page based on the dimension of the
label, the number of labels, margins, and the amount of space
between labels.
This option is available only for customized page formats.
However, it is always possible to disable the automatic option to
enter the Height and Width values manually.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Format.ColumnCount
Retrieves or sets the number of labels per row (horizontal
count).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Format. HorizontalGap
Retrieves or sets the amount of empty space between the
columns (Horizontal) of labels on a page. (in MeasureSystem
unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Format. VerticalGap
Retrieves or sets the amount of empty space between the rows
(Vertical) of labels on a page (in MeasureSystem
Access Read/Write.
.
.
.
unit).
Type VT_I4orLong
.
Page 73

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 65
"""" Format.LabelHeight
Retrieves or sets the height of the label (in MeasureSystem
unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Format.LabelWidth
Retrieves or sets the width of the label (in MeasureSystem
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Format.MarginLeft
Retrieves or sets the left margin of the page (in MeasureSystem
unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Format.MarginTop
Retrieves or sets the top margin of the page (in MeasureSystem
unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
.
unit).
.
.
.
"""" Format.StockName
Retrieves or sets the name of the format model, if any.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
.
Page 74

Chapter 2 -- 66
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Format.StockType
Retrieves or sets the type of the format type, if any.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Format.PageHeight
Retrieves or sets the height of the page (in MeasureSystem
unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Format.PageWidth
Retrieves or sets the width of the page (in MeasureSystem
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Format.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
"""" Format.Portrait
.
.
.
unit).
Retrieves or sets the orientation of the document.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
.
Page 75

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 67
"""" Format.Corner
Object Methods
Retrieves or sets the radius corner of the document (in
MeasureSystem
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Format.RowCount
Retrieves or sets the number of labels per column (vertical
count).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Format. SaveStock
VTS_NONE Format.SaveStock().
Saves the current stock Name/Type. (In order to reuse it with
others documents)
unit).
.
.
Page 76

Chapter 2 -- 68
DocumentProperties Collection
Properties Methods
Application Item (Default)
Count
Parent
Object Properties
"""" DocumentProperties.Application
Programmer’s Guide
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" DocumentProperties.Count
Returns the number of items in the specified collection.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_I2orInteger
"""" DocumentProperties.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
object that represents the
object.
.
Page 77

Reference Guide
Object Methods
Chapter 2 -- 69
"""" DocumentProperties.Item
Note
Note
VTS_DISPATCH or DocumentProperty
Returns a member of a collection, either by position or by name.
If the value provided as Index does not match any existing
member of the collection, no object is returned.
Parameters:
longIndex Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
index number of a member of the collection.
The index can be a numeric expression (a number from 1 to the
value of the collection’s Count property), a constant, or a string.
If the value provided as Index doesn’t match any existing
member of the collection, an error occurs.
The Item method is the default method for collections. Therefore, the following two lines of code are equivalent.
Object.DocumentProperties(1)
Object. DocumentProperties.Item(1)
An enumerated type enumBuiltInDocumentProperty is enabled:
lppxPropertyManager = 1
lppxPropertyCompany = 2
lppxPropertyCategory = 3
lppxPropertyTitle = 4
lppxPropertySubject = 5
lppxPropertyAuthor = 6
lppxPropertyKeywords = 7
lppxPropertyComments = 8
Item( longIndex ).
.Thenameor
Page 78

Chapter 2 -- 70
DocumentProperty Object
Properties Methods
Application (None)
Name
Parent
Type
Value (Default
Object Properties
"""" DocumentProperty.Application
Programmer’s Guide
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" DocumentProperty.Name
Returns the name of the variable.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" DocumentProperty.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
object that represents the
object.
.
Page 79

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 71
"""" DocumentProperty.Type
Returns the type of the property.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_I2 or Integer or enumProperty
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxPropertyTypeNumber = 1
lppxPropertyTypeBoolean = 2
lppxPropertyTypeDate = 3
lppxPropertyTypeString = 4
lppxPropertyTypeFloat = 5
"""" DocumentProperty.Value
Returns the current value of the DocumentProperty.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_VARIANT or Variant
.
type.
Page 80

Chapter 2 -- 72
DocObjects Collection
Properties Methods
Application Add
Count Item (Default)
Parent Remove
Barcodes
Shapes
OLEObjects
Images
Texts
Object Properties
"""" DocObjects.Application
Programmer’s Guide
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" DocObjects.Count
Returns the number of items in the specified collection.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_I2orInteger
"""" DocObjects.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
object that represents the
object.
.
Page 81

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 73
"""" DocObjects.Barcodes
Returns the Barcodes
Barcode objects
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH o r Barcodes
"""" DocObjects.Shapes
Returns the Shapes
Shape
objects in the document.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Shapes
"""" DocObjects.OLEObjects
Returns the OLEObjects
OLEObject objects
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or OLEObjects
"""" DocObjects.Images
Returns the Images
Image objects
collection that represents all the created
in the document.
collection that represents all the created
collection.
collection that represents all the created
in the document.
collection that represents all the created
in the document.
collection.
collection.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Images
"""" DocObjects.Texts
Returns the Texts
objects
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Texts
in the document.
collection that represents all the created Text
collection.
collection.
Page 82

Chapter 2 -- 74
Object Methods
Programmer’s Guide
"""" DocObjects.Add
Note
VT_DISPATCH or DocObject
strDocObjectName ).
Adds a new DocObject
Return value: Returns a DocObject
Parameters:
longDocObjectType RequiredVT_I4orLong
enumDocObject
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxObjectText = 1
lppxObjectBarCode = 2
lppxObjectImage = 3
lppxObjectLine = 4
lppxObjectRectangle = 5
lppxObjectEllipse = 6
lppxObjectPolygon = 7
lppxObjectOblique = 8
lppxObjectRoundRect = 9
lppxObjectOLEObject = 10
strDocObjectName Optional VT_BSTR or String
name of the object to add.
"""" DocObjects.Item
VTS_DISPATCH or DocObject
Returns a member of a collection, either by position or by name.
If the value provided as Index does not match any existing
member of the collection, no object is returned.
object to the current document.
. The type of object to add.
Add( longDocObjectType,
object.
or
.The
Item( varIndex ).
Note
Parameters:
varIndex Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
index number of a member of the collection.
The index can be a numeric expression (a number from 1 to the
value of the collection’s Count property), a constant, or a string.
If the value provided as Index doesn’t match any existing
member of the collection, an error occurs.
The Item method is the default method for collections. Therefore, the following two lines of code are equivalent.
Object. DocObjects (1)
Object. DocObjects.Item(1)
.Thenameor
Page 83

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 75
"""" DocObjects.Remove
VTS_NONE Remove( varIndex ).
Removes a member from the DocObjects
Parameters:
varIndex Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
that specifies the position of a collection member. If numeric
expression: index must be a number from 1 to the value of the
collection’s Count property. If a string expression: index must
correspond to the key argument specified when this member
reffered to was added to the collection.
object.
. An expression
Page 84

Chapter 2 -- 76
DocObject Object
Properties Methods
AnchorPoint Bound
Application Move
BackColor
ForeColor
Height
Left
Locked
Name
Parent
Printable
Rotation
Top
Type
Width
Programmer’s Guide
Object Properties
"""" DocObject.AnchorPoint
Returns or sets the anchor point of the current object.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I2 or Integer or enumAnchorPoint
lppxTopLeft = 1
lppxTopCenter = 2
lppxTopRight = 3
lppxCenterLeft = 4
lppxCenter = 5
lppxCenterRight = 6
lppxBottomLeft = 7
lppxBottomCenter = 8
lppxBottomRight = 9
type.
Page 85

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 77
"""" DocObject.Application
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" DocObject.Height
Returns or sets the height of the object (in MeasureSystem
unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4 or
"""" DocObject.Left
Returns or sets the distance between the left edge of the anchor
point of the object and the left edge of the document (in
MeasureSystem
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" DocObject.Name
Long.
unit).
.
object that represents the
object.
ReturnsorsetsthenameoftheDocObject
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" DocObject.Printable
Sets or not whether the object is printable.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
.
.
.
Page 86

Chapter 2 -- 78
Programmer’s Guide
"""" DocObject.Rotation
Sets or retrieves the rotation of the object.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I2orInteger.
The value can be one of the following: 0, 900, 1800, 2700.
"""" DocObject.Top
Returns or sets the distance between the top edge of the anchor
point of the object and the top edge of the document. (in
MeasureSystem
Access Read/Write.
unit).
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" DocObject.Type
Returns the type of the object (in enumDocObject
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_I2orInteger
"""" DocObject.Width
Returns or sets the width of the object (in enumMeasureSystem
unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
.
type).
.
.
Page 87

Reference Guide
Object Methods
Chapter 2 -- 79
"""" DocObject.Bound
VTS_NONE Bound ( longLeftPosition, longTopPosition ,
longRightPosition , longBottomPosition).
Sets the bounding rectangle of an object.
Parameters:
longLeftPosition RequiredVT_I4orLong
between the left edge of an object and the left edge of the
document (in MeasureSystem
unit).
.Distance
longTopPosition RequiredVT_I4orLong
between the top edge of an object and the top edge of the
document (in MeasureSystem
longRightPosition RequiredVT_I4orLong
between the right edge of an object and the left edge ofthe
document (in MeasureSystem
longBottomPosition RequiredVT_I4orLong
between the bottom edge of an object and the top edge ofthe
document (in MeasureSystem
"""" DocObject.Move
VTS_NONE Move (longLeftPosition, longTopPosition ).
Movesanobjectinitswindow.
Parameters:
longLeftPosition RequiredVT_I4orLong
between the left edge of an object and the left edge of the
document (in MeasureSystem
longTopPosition RequiredVT_I4orLong
between the top edge of an object and the top edge of the
document (in MeasureSystem
unit).
unit).
unit).
unit).
unit).
.Distance
.Distance
.Distance
.Distance
.Distance
Page 88

Chapter 2 -- 80
Images Collection
Properties Methods
Application Add
Count Item (Default)
Parent
Object Properties
"""" Images.Count
Returns the number of items in the specified collection.
Access Read-Only.
Programmer’s Guide
Object Methods
Type VT_I2orInteger
"""" Images.Application
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" Images.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
"""" Images.Add
VTS_DISPATCH or Image
Adds a new Image
Return value: Returns a Image
Parameters:
strImageName Optional VT_BSTR or String
the object to add.
object to the collection.
.
object that represents the
object.
Add(strImageName).
object.
.Thenameof
Page 89

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 81
"""" Images.Item
Note
Note
VTS_DISPATCH or Image
Returns a member of a collection, either by position or by name.
If the value provided as Index does not match any existing
member of the collection, none object returned.
Parameters:
varIndex Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
index number of a member of the collection.
The index can be a numeric expression (a number from 1 to the
value of the collection’s Count property), a constant, or a string.
If the value provided as Index doesn’t match any existing
member of the collection, an error occurs.
The Item method is the default method for collections. The
following two lines of code are equivalent.
Object. Images (1)
Object. Images.Item(1)
"""" Images.Remove
VTS_NONE Remove ( varIndex ).
Removes a member from the collection.
Item( varIndex ).
.Thenameor
Parameters:
varIndex Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
that specifies the position of a member of the collection. If a
numeric expression, index must be a number from 1 to the value
of the collection’s Count property. If a string expression, index
must correspond to the key argument specified when the
member referred to was added to the collection.
. An expression
Page 90

Chapter 2 -- 82
Programmer’s Guide
Image Object
Properties Methods
DocObject object properties DocObject object methods
Brightness
FileName
HorzFlip
VertFlip
Negative
VariableName
VariableObject
Object Properties
"""" Image.Brightness
This adjustment influences the color reduction process. Use this
property to print a color image on a noncolor printer.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I2orInteger
"""" Image.FileName
Retrieves or sets the filename of the image.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Image. VertFlip
Displays the image as if it is reflected in a mirror.
Reflection axis is vertical.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
(between –255 and +255).
.
.
Page 91

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 83
"""" Image. HorzFlip
Displays the image as if it is reflected in a mirror.
Reflection axis is horizontal.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Image.Negative
Prints the image negatively.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Image.VariableName
Retrieves or sets the current variable name associated with the
image.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Image.VariableObject
Retrieves or sets the current Variable
image.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Variable
.
.
.
object associated with the
object.
Page 92

Chapter 2 -- 84
Barcodes Collection
Properties Methods
Application Add
Count Item (Default)
Parent
Object Properties
"""" Barcodes.Count
Returns the number of items in the specified collection.
Access Read-Only.
Programmer’s Guide
Type VT_I2orInteger
"""" Barcodes.Application
This property returns the Application
root object of the hierarchy.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Application
"""" Barcodes.Parent
Returns the parent object of the specified object.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH.
.
object that represents the
object.
Page 93

Reference Guide
Object Methods
Chapter 2 -- 85
"""" Barcodes.Add
Note
Note
VTS_DISPATCH or Barcode
Adds a new Barcode
Return value: Returns a Barcode
Parameters:
strBarcodeName Optional VT_BSTR or String
name of the object to add.
"""" Barcodes.Item
VTS_DISPATCH or Barcode
Returns a member of a collection, either by position or by name.
If the value provided as Index does not match any existing
member of the collection, no object is returned.
Parameters:
varIndex Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
index number of a member of the collection.
The index can be a numeric expression (a number from 1 to the
value of the collection’s Count property), a constant, or a string.
If the value provided as Index doesn’t match any existing
member of the collection, an error occurs.
The Item method is the default method for collections. The
following two lines of code are equivalent.
Object. Barcodes (1)
Object. Barcodes.Item(1)
object to the collection.
Add( strBarcodeName ).
object.
.The
Item( varIndex ).
.Thenameor
"""" Barcodes.Remove
VTS_NONE Remove ( varIndex ).
Removes a member from the collection.
Parameters:
varIndex Required VT_VARIANT or Variant
that specifies the position of a member of the collection. If a
numeric expression, index must be a number from 1 to the value
of the collection’s Count property. If a string expression, index
must correspond to the key argument specified when the
member referred to was added to the collection.
. An expression
Page 94

Chapter 2 -- 86
Programmer’s Guide
Barcode Object
Properties Methods
DocObject object properties DocObject object methods
BarHeight
CheckMode
Code2D
Device
HRAlignment
HRCheckCharacter
HRFont
HRFreeTextObject
HRDevice
HRGap
HRPosition
NarrowBarWidth
Ratio
Symbology
Value
VariableName
VariableObject
Object Properties
"""" Barcode.BarHeight
Retrieves or sets the bar height of the barcode (in
tem
unit).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
.
MeasureSys-
Page 95

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 87
"""" Barcode.CheckMode
Retrieves or sets the check control of the barcode (in
CheckMode
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLongorenumCheckMode
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxCheckModeNone = 0
lppxCheckMode1Digit = 1
lppxCheckMode2Digit = 2
lppxCheckModeMod11Mod10 = 3
"""" Barcode.Code2D
Retrieves the Code2D
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Code2D
"""" Barcode.Device
Determines if the barcode is graphical or generated by the
printer.
Access Read/Write.
type).
object for 2D barcodes.
object.
enum-
type.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Barcode.HRAlignment
Retrieves or sets the current human readable alignment.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxAlignLeft = 0
lppxAlignCenter = 1
lppxAlignRight = 2
.
or enumAlignment type.
Page 96

Chapter 2 -- 88
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Barcode.HRCheckCharacter
Includes or not the check character control in the human
readable.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Barcode.HRDevice
Determines if the human readable is printer generated or not.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BOOL or Boolean
"""" Barcode.HRFont
Retrieves or sets the font of the human readable.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_FONT or StdFont
"""" Barcode.HRFreeTextObject
Retrieves the Text
readable.
Access Read-Only.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Text
"""" Barcode.HRGap
object representing the text of the human
.
.
object.
object.
Retrieves or sets the gap between the barcode and its human
readable (in MeasureSystem
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
unit).
.
Page 97

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 89
"""" Barcode.HRPosition
Sets or retrieves the position of the human readable.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLongorenumHRPosition
Thevaluecanbeoneofthefollowing:
lppxHRPositionNone = 0
lppxHRPositionBelow = 1
lppxHRPositionAbove = 2
lppxHRPositionFree = 3
"""" Barcode.NarrowBarWidth
Retrieves or sets the narrow bar width of the barcode (in
MeasureSystem
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Barcode.Ratio
Retrieves or sets the ratio of the barcode (between 20 and 35).
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLong
"""" Barcode.Symbology
Retrievesorsetsthesymbologyofbarcode.
unit).
.
.
type.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_I4orLongorenumSymbology
type.
Page 98

Chapter 2 -- 90
Programmer’s Guide
The value can be one of the following (depending on product and
printer):
LppxCode11
lppx25Interleave 50
LppxCode39 51
LppxCode49 52
LppxMaxicode 53
LppxCode16K 54
LppxGermanPostcode 55
LppxEAN8 56
LppxUPCE 57
LppxBC412 58
LppxMicroPDF 59
LppxCode93 65
lppx25Beared 66
LppxCode128 67
LppxEAN128 68
LppxEAN13 69
LppxCode39Full 70
LppxCode128Auto 71
LppxCodablockF 72
lppx25Industrial 73
lppx25Standard 74
LppxCodabar 75
LppxLogmars 76
LppxMsi 77
LppxCodablockA 78
LppxPostnet 79
LppxPlessey 80
LppxCode128SSCC 81
LppxUPCExtended 83
LppxUPCA 85
LppxUPCEXT2 86
LppxUPCEXT5 87
LppxCode25PRDG 88
LppxUPCWEIGHT 89
LppxUPCEPLUS2 97
49
Page 99

Reference Guide
Chapter 2 -- 91
LppxUPCEPLUS5 98
LppxUPCAPLUS2 99
LppxUPCAPLUS5 100
LppxEAN8PLUS2 101
LppxEAN8PLUS5 102
LppxEAN13PLUS2 103
LppxEAN13PLUS5 104
LppxITF 105
lppx25MatrixEuropean 106
lppx25MatrixJapan 107
LppxDatamatrix 120
lppxItf14 121
LppxPdf 122
LppxQrcode 123
LppxRss 124
LppxComposite 125
Note
Depending on the product, not all symbologies are available.
"""" Barcode.Value
Retrievesorsetsthevalueofthebarcode.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
"""" Barcode.VariableName
Retrieves or sets the current variable name associated with the
barcode.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_BSTR or String
.
.
Page 100

Chapter 2 -- 92
Programmer’s Guide
"""" Barcode.VariableObject
Retrieves or sets the current Variable
barcode.
Access Read/Write.
Type VT_DISPATCH or Variable
object associated with the
object.
 Loading...
Loading...