Page 1

Arc Flash Labels
Arc Flash Safety
What is arc ash and what causes it?
An arc flash is a short circuit through air that flashes from one
exposed live conductor to another conductor or ground. This
electrical fault can create a dangerous release of energy, including
thermal energy, acoustical energy, pressure wave or debris.
There are many ways an arc flash can occur, including:
• Close proximity of a high-amp source to a conductive object
• Dropping a tool or creating a spark
• Breaks or gaps in insulation
• Failing equipment due to use of substandard parts, improper
installation or even normal wear and tear
• Dust, corrosion or other impurities on the surface of the conductor
What impacts the size of an arc ash event?
Common variables that impact the size and energy
of an arc flash include:
• Amperage
• Voltage
• Arc gap
• Closure time
Arc Flash Labels
• Distance from arc
• Three phase vs. single phase
• Confined space
Did You Know?
Anything above 50V that could be worked
on while energized ,resulting in exposure to
electrical hazards, requires an arc flash label.
Examples include, but are not limited to:
• Switchboards
• Panel boards
• Motor control
centers
• Industrial control
panels
• Meter socket
enclosures
380
NFPA 70E Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace
OSHA cites and fines employers for failure to protect employees
from the dangers of arc flash under regulation 29 CFR 1910.333(a).
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) details how to
comply with this regulation through the NFPA 70E standard.
According to the NFPA 70E standard, there are six primary
responsibilities that facilities must meet, including:
1. Training for employees
2. Written safety program in place that is actionable
3. Personal protective equipment (PPE) available for employees
4. Insulated tools
5. Arc flash hazard degree calculations
6. Properly labeled equipment
Most recent updates (2018)
The NFPA 70E gets updated every three years.
Some of the most recent updates include:
• Updated training and retraining requirements
• Revision to arc flash warning label content
• Elimination of the PPE hazard category 0
• Elimination of prohibited approach boundary
• Additional boundary requirements
• Revisions to selecting appropriate PPE
• Minor terminology changes
(such as work shoes now referred to as footwear)
Page 2
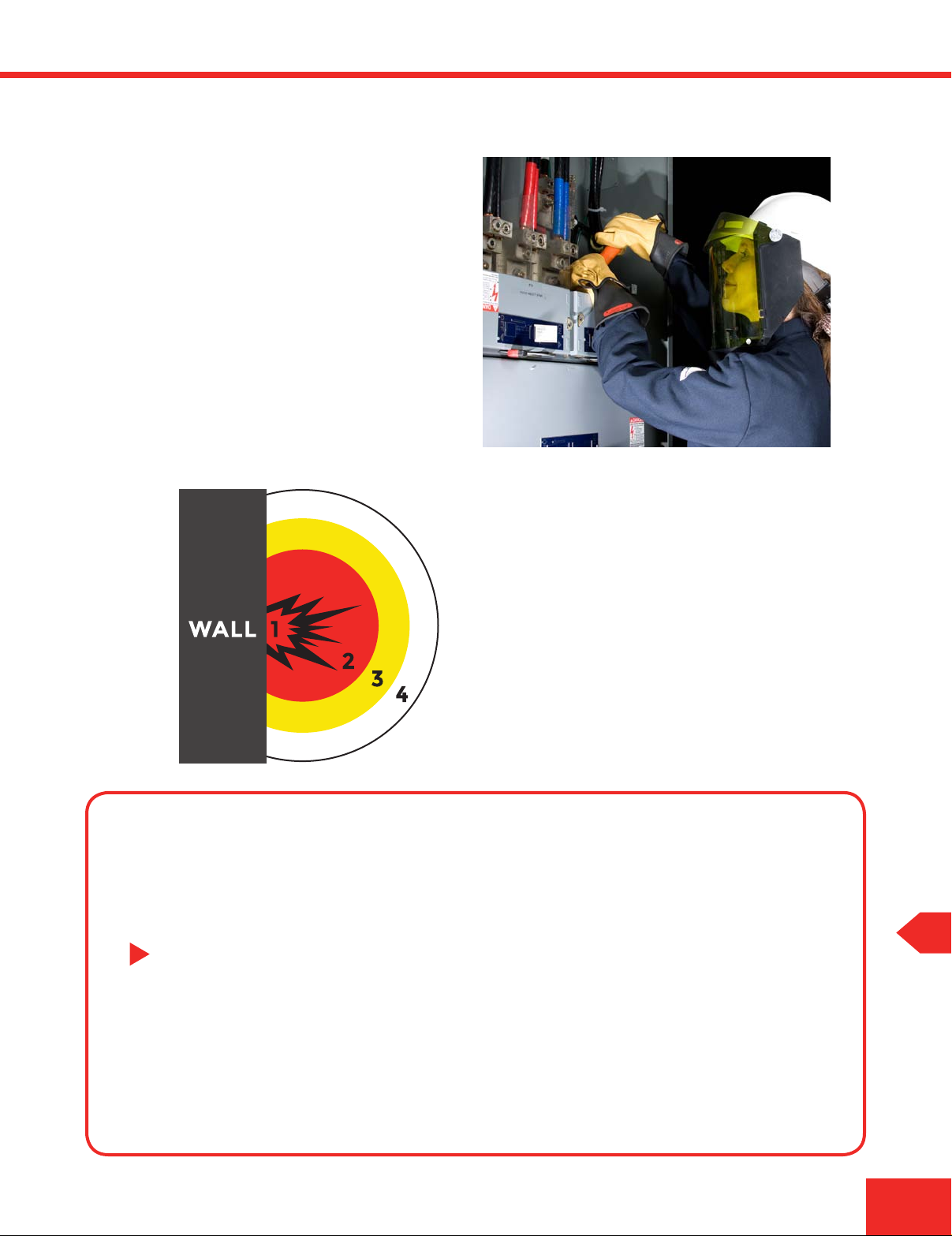
What is an arc ash boundary?
An arc flash boundary is the distance at which an electrical
arc can flash outward and endanger employees working on
electrical equipment.
Additional boundary requirements include:
• Conductive articles of jewelry and clothing: Watchbands,
bracelets, rings, key chains, necklaces, metal frame
glasses, etc. shall not be worn within the restricted
approach boundary
• Working space: Space shall be kept clear and not used
for storage to permit safe operation and maintenance
• Barricades: When the arc flash boundary is greater than
the limited approach boundary, barricades shall not be
placed closer than the arc flash boundary
• Insulated tools: Employees shall use insulated tools
when working inside the restricted approach boundary of
exposed energized electrical conductors.
Arc Flash Labels
1. Exposed / energized conductor or circuit part
2. Restricted approach boundary
Distance where there is an increased
likelihood of electric shock
3. Limited approach boundary
Distance where a shock hazard exists
4. Arc ash boundary
Distance from an arc source where the
thermal energy exposure could cause
2nd degree burns on unprotected skin
Arc Flash Risk Assessment
The NFPA 70E 2015 edition requires employers to conduct an arc flash risk assessment to determine the amount
of thermal energy that could be generated from an arc flash incident. The information is then used to define a
flash protection boundary around the potential source, and to determine the level of arc-rated apparel and other
personal protection equipment required when employees cross the boundary while they work on or near explosive
live parts.
At minimum, the safety program needs to be audited at intervals not to exceed three years
and arc ash risk assessments shall be periodically reviewed at intervals not to exceed ve years.
Arc Flash Labels
Who should perform arc ash risk assessments?
Completing a best-in-class arc flash risk assessment in-house requires time, resources and analysis software to
accurately calculate arc flash risk. In addition, simple miscalculations can lead to incorrect incident energy levels
resulting in the improper use of PPE.
Brady’s Arc Flash Risk Assessment Service, performed by a licensed electrical engineer using power system
analysis software, enables you to not only reach compliance, but maintain compliance. Additional services also
include Arc Flash Audits and Arc Flash Safety Training.
381
381
Page 3

Arc Flash Labels
Arc Flash Labeling
Who’s responsible for labeling?
Arc flash labeling is the responsibility of the employer, not the
manufacturer or installer of the equipment.
What needs to be labeled?
Labeling is required for any piece of electrical equipment that is likely
to require examination, adjustment, service or maintenance while
energized, creating the potential for an arc flash incident to occur.
Any modifications or renovations to electrical equipment that
changes data on the label requires an updated arc flash risk
assessment and label.
Where should the label be placed?
Markings must be in a location that is clearly visible to workers before
they may be exposed to any potentially dangerous live parts. Typically,
the label is placed outside the panel or enclosure door.
What needs to appear on the label?
Once an arc flash risk assessment has been conducted, in which the arc flash boundary, the incident energy at the working
Arc Flash Labels
distance and the personal protective equipment required has been determined, Article 130.5 (C) in the 2015 edition of NFPA
70E further dictates that the label must contain these important elements.
Incident energy
and corresponding
working distance
Min. arc rating
of clothes
Arc ash
boundary
Site
specic
PPE
Arc Flash and Shock Hazard
Appropriate PPE Required
FLASH PROTECTION SHOCK PROTECTION
Incident Energy at:
Min. Arc Rating:
Arc Flash Boundary:
Glove Class:
PPE:
Shirt and pants or coverall, Nonmelting
(ASTM F1506) or Untreated Fiber) + hard hat
+ safety glasses + hearing protection
18 in.
0.45 cal/cm^
10 in.
Shock Risk When
Cover is Removed
2
Limited Approach
Restricted Ap-
proach
00
Bus Name:
Prot Dev: 100/3 BS-18 LAB PNL
PNL_P-5
480 VAC
42 in.
12 in.
Header
Shock hazard
information
382
Page 4

Arc Flash Labels
Brady Arc Flash Solutions
Arc ash services
Brady understands the importance of electrical safety as a whole
and has licensed engineers who understand not only arc flash
safety, but also the firsthand impact of arc flash risk. We work
with your team to best protect your employees based on your
custom facility and program requirements.
• Arc Flash Risk Assessment
A Brady safety electrical engineer completes your assessment,
provides you with a detailed assessment report, including your
single-line diagram, and installs the correct arc flash labels.
• Arc Flash Audit
Let our electrical engineer perform your arc flash audit and
ensure your assessment is up to date and compliant.
• Arc Flash Safety Training
This custom approach to training incorporates both the NFPA
regulation and your company-specific arc flash requirements
to ensure participating employees can apply their knowledge.
Print your own labels
Create and print customized arc flash labels when
and where you need them with an on-demand label
printer. When you’re working on a project, you can stop
handwriting your labels, and print all the labels you need
in batches. You also avoid the hassle of having to select,
order and wait for pre-printed labels to arrive.
Pre-printed die-cut labels
Pre-printed arc flash labels with the arc flash PPE
category and a list of the required PPE relieve the
employer from having to hand-write this information.
As with the check box labels, a version for both arc
flash and shock hazards is available.
Arc Flash Labels
383
383
Page 5

Arc Flash Labels
Pre-Printed Arc Flash Labels
• Labels come with the hazard category and PPE requirements preprinted
• Write in specifics such as minimum arc rating, protection boundary, etc.
• B-7569 vinyl can be written on with pen or marker
DANGER
Arc Flash & Shock Hazard
Appropriate PPE Required
FLASH PROTECTION
Arc Flash Boundary
Hazard Risk Category
Incident Energy (cal/cm
Corresponding Work Distance
VAC Shock Hazard When:
Minimum Arc Rating of Clothing
Nominal System Voltage
PPE: Arc-rated long sleeve shirt and long pants OR arc-rated coverall
Arc-rated flash suit jacket, pants and hood
Hard hat (with arc-rated hard hat liner AN)
Safety glasses or safety goggles
Equipment ID:
#000000 BRADYID.COM
Catalog # Header Hazard Size Qty
121085 Warning 1 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
121087 Warning 2 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
121091 Warning 3 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
121093 Warning 4 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
121086 Danger 1 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
121088 Danger 2 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
121092 Danger 3 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
121094 Danger 4 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
Write-On Arc Flash Labels
Arc Flash Labels
• Write in specifics such as minimum arc rating, protection boundary, etc.
• B-7569 vinyl can be written on with pen or marker
Catalog # Header Size Qty
121077 Warning 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
121078 Danger 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
SHOCK PROTECTION
Limited Approach Boundary
4
Restricted Approach Boundary
2
40
Prohibited Approach Boundary
)
Class
PPE:
V-rating
Hearing protection (ear canal inserts)
Arc-rated gloves and leather work shoes
Y1234567
*Y1234567*
Arc Flash Hazard
Appropriate PPE Required
Flash Protection Boundary
Hazard Risk Category
Flash Protection Equipment
Arc-rated long sleeve shirt and long pants OR arc-rated coverall
Arc-rated flash suit hood or arc-rated face
shield and arc-rated balaclava
Hard hat and safety glasses or safety goggles
Hearing protection (ear canal inserts)
Leather gloves and leather work shoes
Equipment ID:
2 8
#000000 BRADYID.COM
Incident Energy (cal/cm2)
Y1234567
*Y1234567*
Catalog # Header Hazard Size Qty
121097 Warning 1 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
121099 Warning 2 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
121101 Warning 3 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
121103 Warning 4 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
121098 Danger 1 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
121100 Danger 2 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
121102 Danger 3 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
121104 Danger 4 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
Catalog # Header Size Qty
121079 Warning 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
121080 Danger 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
Arc ash hazard
categories and PPE
requirements
Required Flash
Protection Equipment*
Arc-rated longsleeve shirt and long
pants (or arc-rated coverall)
Hazard
Category
Incident
energy
4 cal/cm
Hazard
Category
Incident
energy
8 cal/cm
Hazard
Category
Incident
energy
25 cal/cm
Hazard
Category
Incident
energy
40 cal/cm
Arc-rated face shield or
arc flash hood
Arc-rated jacket, parka, rainwear or
1
hard hat liner (as needed)
Hard hat
Safety glasses or safety goggles
2
Hearing protection (ear canal inserts)
Leather gloves
Leather footwear (as needed)
Arc-rated longsleeve shirt and long
pants (or arc-rated coverall)
Arc-rated face shield or
arc flash hood
Arc-rated jacket, parka, rainwear or
2
hard hat liner (as needed)
Hard hat
Safety glasses or safety goggles
2
Hearing protection (ear canal inserts)
Leather gloves
Leather footwear
Arc-rated longsleeve shirt and long
pants (or arc-rated coverall)
Arc-rated arc flash
suit jacket and pants
Arc-rated arc flash hood
Arc-rated jacket, parka or rainwear
3
(as needed)
Hard hat and arc-rated hard hat liner
Safety glasses or safety goggles
2
Hearing protection (ear canal inserts)
Leather footwear
Arc-rated gloves
Arc-rated longsleeve shirt and long
pants (or arc-rated coverall)
Arc-rated arc flash
suit jacket and pants
Arc-rated arc flash hood
Arc-rated jacket, parka or rainwear
4
(as needed)
Hard hat and arc-rated hard hat liner
Safety glasses or safety goggles
2
Hearing protection (ear canal inserts)
Leather footwear
Arc-rated gloves
384
Catalog # Header Size Qty
145975 Danger 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
145974 Danger 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
145973 Warning 5 in. x 7 in. 5/pk.
145972 Warning 4 in. x 6 in. 5/pk.
* Arc rating of PPE should correspond
with the Hazard Category and Incident
Energy present.Voltage-rated gloves
and other shock protection may also
be required when working on exposed
energized electrical parts.
Page 6

Poster
• Highlights the common causes of arc
flash and provides safe work practices
and personal protection equipment
requirements
• Laminated on both sides to stand up to
industrial environments
• Full-color printing and eye-catching
graphics for optimum visual impact
• Poster reflects all changes from NFPA
70E-2015 regulation
Catalog # Description Quantity
104571 18 in. x 24 in. poster 1 each
Sign
Label
Sign and Label
• Post signs and labels in the work area
and near electrical equipment to boost
awareness and compliance
• Signs and labels specify the personal
protection equipment required for each
arc flash hazard category
• Sign and label reflects all changes
from NFPA 70E-2015 regulation
• Sign: B-401 rigid plastic with
laminated graphics
Label: B-302 self-sticking polyester
with overlaminate
Catalog # Description Quantity
102523 7 in. x 10 in. sign 1 each
102524 3.5 in. x 5 in. label 5/pack
Arc Flash Labels
Front
Back
Wallet Card
• Ensure compliance and safety by
providing each employee with their
own arc flash wallet card
• Card specifies the personal protection
equipment required for each arc flash
hazard category
• Made of laminated cardstock
• Reflects all changes from
NFPA 70E-2015 regulation
Catalog # Description Quantity
102525 2.1 in. x 3.4 in. card 25/pack
On-Site Arc Flash Training Service
Under the NFPA 70E standard, arc flash training must be
completed every three years.
Brady’s Arc Flash Safety Training is a custom approach to
training that includes:
• Custom training materials with NFPA regulations and your
company-specific arc flash information
• On-site interactive training session
• Attendees receive a workbook and a certificate of completion
Training topics include:
• What is an arc flash and related information, such as
boundaries, labeling, work permits and PPE requirements
• OSHA regulations, responsibilities, training and PPE
• NFPA updates, compliance and PPE tables
• The difference between qualified and unqualified employees
• And more
Arc Flash Labels
385
385
 Loading...
Loading...