Page 1
Operating/Safety Instructions
Consignes de fonctionnement/sécurité
Instrucciones de funcionamiento
y seguridad
53514
53518
IMPORTANT: IMPORTANT : IMPORTANTE:
Read Before Using Lire avant usage Leer antes de usar
Consumer Information
Renseignement des consommateurs
Información para el consumidor
Toll Free Number: Appel gratuit : Número de teléfono gratuito:
1-877-BOSCH99 (1-877-267-2499) http://www.boschtools.com
For English Parlez-vous français? ¿Habla español?
See page 2 Voir page 14 Ver página 26
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 1
Page 2
-2-
Read and understand all instructions. Failure to follow all instructions
listed below, may result in electric shock, fire and/or serious personal injury.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Work Area
Keep your work area clean and well lit.
Cluttered benches and dark areas invite
accidents.
Do not operate power tools in explosive
atmospheres, such as in the presence of
flammable liquids, gases, or dust. Power
tools create sparks which may ignite the
dust or fumes.
Keep by-standers, children, and visitors
away while operating a power tool.
Distractions can cause you to lose control.
Electrical Safety
Do not abuse the cord. Never use the
cord to carry the tool. Keep cord away
from heat, oil, sharp edges, or moving
parts. Replace damaged cords
immediately. Damaged cords may create a
fire.
A battery operated tool with integral
batteries or a separate battery pack must
be recharged only with the specified
charger for the battery. A charger that may
be suitable for one type of battery may
create a risk of fire when used with another
battery.
Use battery operated tool only with
specifically designated battery pack. Use
of any other batteries may create a risk of
fire.
Personal Safety
Stay alert, watch what you are doing, and
use common sense when operating a
power tool. Do not use tool while tired or
under the influence of drugs, alcohol, or
medication. A moment of inattention while
operating power tools may result in serious
personal injury.
Dress properly. Do not wear loose
clothing or jewelry. Contain long hair.
Keep your hair, clothing, and gloves away
from moving parts. Loose clothes, jewelry,
or long hair can be caught in moving parts.
Avoid accidental starting. Be sure switch
is in the locked or off position before
inserting battery pack. Carrying tools with
your finger on the switch or inserting the
battery pack into a tool with the switch on
invites accidents.
Remove adjusting keys or wrenches
before turning the tool on. A wrench or a
key that is left attached to a rotating part of
the tool may result in personal injury.
Do not overreach. Keep proper footing
and balance at all times. Proper footing
and balance enable better control of the tool
in unexpected situations.
Use safety equipment. Always wear eye
protection. Dust mask, non-skid safety
shoes, hard hat, or hearing protection must
be used for appropriate conditions.
Tool Use and Care
Use clamps or other practical way to
secure and support the workpiece to a
stable platform. Holding the work by hand
or against your body is unstable and may
lead to loss of control.
Do not force tool. Use the correct tool for
your application. The correct tool will do
the job better and safer at the rate for which
it is designed.
Do not use tool if switch does not turn it
on or off. A tool that cannot be controlled
with the switch is dangerous and must be
repaired.
Disconnect battery pack from tool or
place the switch in the locked or off
position before making any adjustments,
changing accessories, or storing the tool.
Such preventive safety measures reduce the
risk of starting the tool accidentally.
Store idle tools out of reach of children
and other untrained persons. Tools are
dangerous in the hands of untrained users.
When battery pack is not in use, keep it
away from other metal objects like: paper
!
WARNING
General Safety Rules
For All Battery Operated Tools
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 2
Page 3
-3-
Safety Rules for Cordless Planers
Secure the material being planed. Never
hold it in your hand or across legs. Small
workpiece must be adequately secured so
that the rotating planer blades will not pick it
up during forward motion of the planer.
Unstable support can cause the blades to
bind causing loss of control and injury.
Always start the plane before blade is in
contact with the workpiece and allow the
blade to come to full speed. Tool can
vibrate or chatter if blade speed is too slow
at beginning of cut and possibly kickback.
Check the workpiece for nails, if there are
nails, either remove or set them well
below intended finished surface. If the
planer blades strike objects like nails it may
cause the tool to kickback and serious
personal injury may result.
Disconnect battery pack from tool or
place the switch in the locked or off
position before making any assembly,
adjustments or changing accessories.
Such preventive safety measures reduce the
risk of starting the tool accidentally.
After changing blades, rotate the blade
cylinder (cutter drum) to make sure
blades are not hitting any part of the
blade head housing and the blade locking
screws are tight. Spinning blades could
strike tool housing and damage tool as well
as possible injury.
Always hold the tool firmly with both
hands for maximum control.
Never pull the plane backward over the
workpiece. Loss of control may occur.
Do not put fingers or any objects into the
chip ejector or clean out chips while tool
is running. Contact with blade drum will
cause injury.
Disconnect battery pack from tool if it
becomes necessary to remove chips. The
blades are hidden from view and you may
be cut if blade is contacted.
Never place the plane down until the
blade is completely at rest. Surface
contact with coasting blade drum may
cause the plane to walk out of control.
Some dust created by
power sanding, sawing,
grinding, drilling, and other construction
activities contains chemicals known to
cause cancer, birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Some examples of
these chemicals are:
• Lead from lead-based paints,
• Crystalline silica from bricks and cement
and other masonry products, and
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically-
treated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies,
depending on how often you do this type of
work. To reduce your exposure to these
chemicals: work in a well ventilated area,
and work with approved safety equipment,
such as those dust masks that are specially
designed to filter out microscopic particles.
clips, coins, keys, nails, screws, or other
small metal objects that can make a
connection from one terminal to another.
Shorting the battery terminals together may
cause sparks, burns, or a fire.
Maintain tools with care. Keep cutting
tools sharp and clean. Properly maintained
tools with sharp cutting edge are less likely
to bind and are easier to control.
Check for misalignment or binding of
moving parts, breakage of parts, and any
other condition that may affect the tool's
operation. If damaged, have the tool
serviced before using. Many accidents are
caused by poorly maintained tools.
Use only accessories that are recom-
mended by the manufacturer for your
model. Accessories that may be suitable for
one tool may create a risk of injury when
used on another tool.
Service
Tool service must be performed only by
qualified repair personnel. Service or
maintenance performed by unqualified
personnel may result in a risk of injury.
When servicing a tool, use only identical
replacement parts. Follow instructions in
the Maintenance section of this manual.
Use of unauthorized parts or failure to follow
Maintenance Instructions may create a risk
of shock or injury.
!
WARNING
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 3
Page 4
Before using battery charger, read all
instructions and cautionary markings on
(1) battery charger, (2) battery pack, and
(3) product using battery.
Use only the charger which accompanied
your product or direct replacement as
listed in the catalog or this manual. Do not
substitute any other charger. Use only Bosch
approved chargers with your product. See
Functional Description and Specifications.
Do not disassemble charger or operate
the charger if it has received a sharp blow,
been dropped or otherwise damaged in
any way. Replace damaged cord or plugs
immediately. Incorrect reassembly or
damage may result in electric shock or fire.
Do not recharge battery in damp or wet
environment. Do not expose charger to
rain or snow. If battery case is cracked or
otherwise damaged, do not insert into
charger. Battery short or fire may result.
Charge only Bosch approved rechargeable
batteries. See Functional Description and
Specifications. Other types of batteries may
burst causing personal injury and damage.
Charge battery pack in temperatures
above +40 degrees F (4 degrees C) and
below +105 degrees F (41 degrees C).
Store tool and battery pack in locations
where temperatures will not exceed 120
degrees F (49 degrees C). This is important
to prevent serious damage to the battery
cells.
Battery leakage may occur under extreme
usage or temperature conditions. Avoid
contact with skin and eyes. The battery
liquid is caustic and could cause chemical
burns to tissues. If liquid comes in contact
with skin, wash quickly with soap and water,
then with lemon juice or vinegar. If the liquid
contacts your eyes, flush them with water for
a minimum of 10 minutes and seek medical
attention.
Place charger on flat non-flammable
surfaces and away from flammable
materials when re-charging battery pack.
The charger and battery pack heat during
charging. Carpeting and other heat
insulating surfaces block proper air
circulation which may cause overheating of
the charger and battery pack. If smoke or
melting of the case are observed unplug the
charger immediately and do not use the
battery pack or charger.
Use of an attachment not recommended or sold by Bosch may result in a
risk of fire, electric shock or injury to
persons.
-4-
Battery/Charger
Battery Care
When batteries are not in
tool or charger, keep
them away from metal objects. For
example, to protect terminals from shorting
DO NOT place batteries in a tool box or
pocket with nails, screws, keys, etc. Fire or
injury may result.
To prevent fire or injury
when batteries are not in
tool or charger, always place protective
cap onto end of battery pack. Protective
cap, guards against terminal shorting.
DO NOT PUT BATTERIES INTO FIRE OR
EXPOSE TO HIGH HEAT. They may
explode.
!
WARNING
!
WARNING
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 4
Page 5

Do not attempt to disassemble the battery or
remove any component projecting from
the battery terminals. Fire or injury may
result. Prior to disposal, protect exposed
terminals with heavy insulating tape to
prevent shorting.
NICKEL-CADMIUM BATTERIES
If equipped with a nickel-cadmium battery,
the battery must be collected, recycled or
disposed of in an environmentally sound
manner.
“The EPA certified RBRC
Battery Recycling Seal on the
nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd)
battery indicates S-B Power
Tool Company is voluntarily
participating in an industry
program to collect and recycle these
batteries at the end of their useful life, when
taken out of service in the United States or
Canada. The RBRC program provides a
convenient alterative to placing used Ni-Cd
batteries into the trash or the municipal
waste stream, which may be illegal in your
area.
Please call 1-800-8-BATTERY for information
on Ni-Cd battery recycling and disposal
bans/restrictions in your area, or return your
batteries to a Skil/Bosch/Dremel Service
Center for recycling. S-B Power Tool
Company’s involvement in this program is
part of our commitment to preserving our
environment and conserving our natural
resources.”
NICKEL-METAL HYDRIDE BATTERIES
If equipped with a nickel-metal hydride
battery, the battery can be disposed of in a
municipal solid waste stream.
-5-
!
WARNING
Battery Disposal
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 5
Page 6
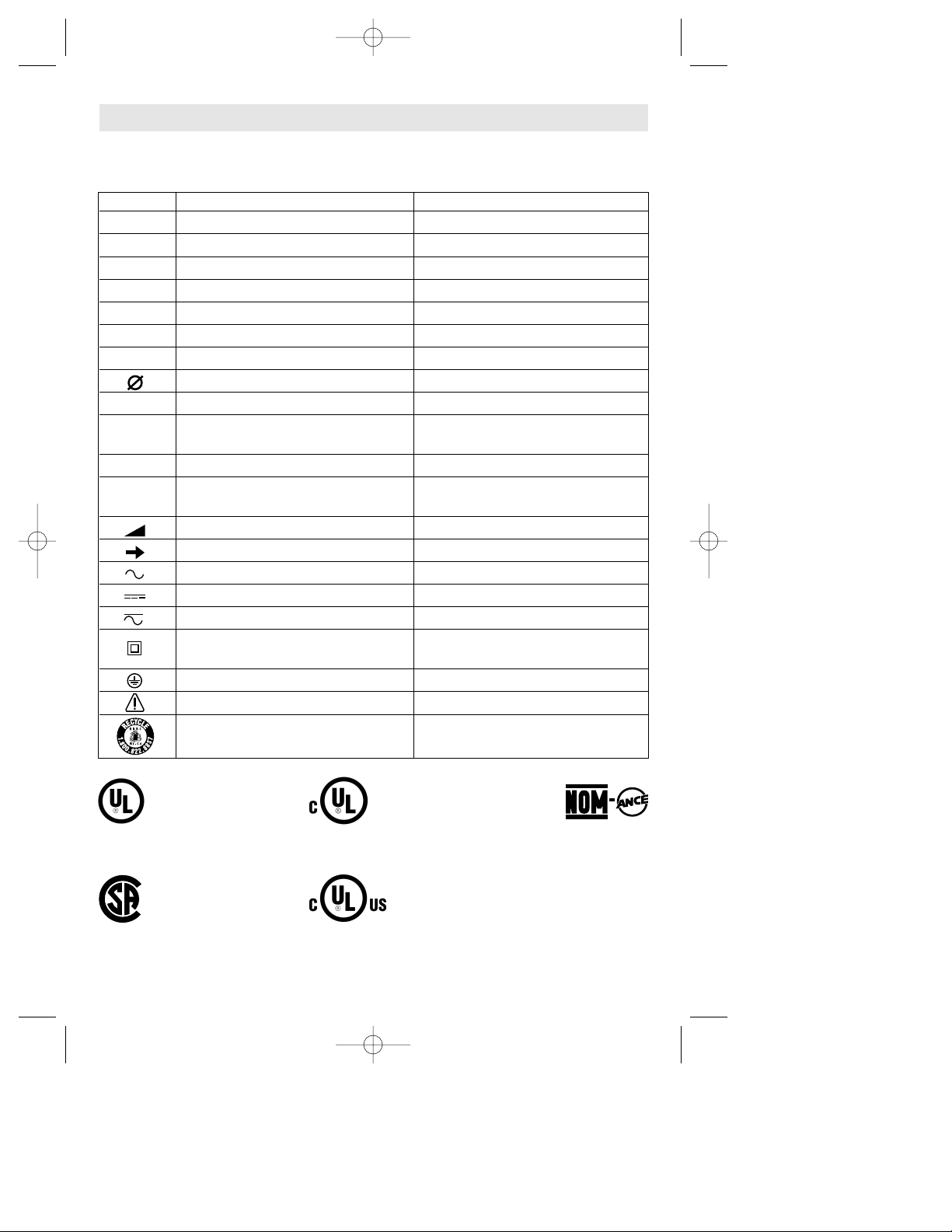
-6-
IMPORTANT: Some of the following symbols may be used on your tool. Please study them
and learn their meaning. Proper interpretation of these symbols will allow you to operate the
tool better and safer.
Symbol Name Designation/Explanation
V Volts Voltage (potential)
A Amperes Current
Hz Hertz Frequency (cycles per second)
W Watt Power
kg Kilograms Weight
min Minutes Time
s Seconds Time
Diameter Size of drill bits, grinding wheels, etc.
n
0
No load speed Rotational speed, at no load
.../min Revolutions or reciprocation per minute Revolutions, strokes, surface speed,
orbits etc. per minute
0 Off position Zero speed, zero torque...
1, 2, 3, ... Selector settings Speed, torque or position settings.
I, II, III, Higher number means greater speed
Infinitely variable selector with off Speed is increasing from 0 setting
Arrow Action in the direction of arrow
Alternating current Type or a characteristic of current
Direct current Type or a characteristic of current
Alternating or direct current Type or a characteristic of current
Class II construction Designates Double Insulated
Construction tools.
Earthing terminal Grounding terminal
Warning symbol Alerts user to warning messages
Ni-Cad RBRC seal Designates Ni-Cad battery recycling
program
Symbols
0
This symbol designates
that this tool is listed by
Underwriters Laboratories.
This symbol designates
that this tool is listed by
the Canadian Standards
Association.
This symbol designates
that this tool is listed to
Canadian Standards by
Underwriters Laboratories.
This symbol
designates
that
this tool
complies
to NOM
Mexican
Standards.
This symbol designates
that this tool is listed by
Underwriters Laboratories,
and listed to Canadian
Standards by Underwriters
Laboratories.
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 6
Page 7
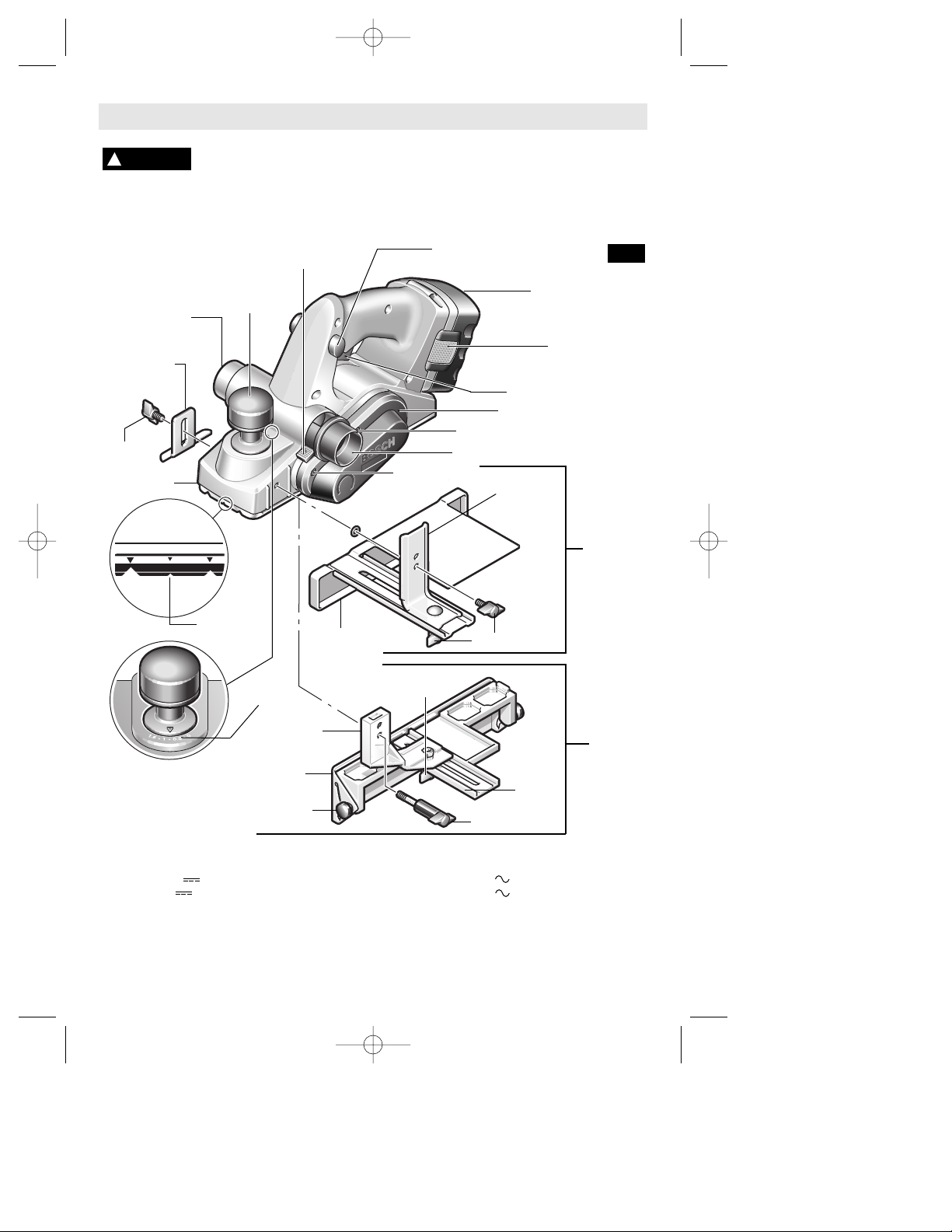
-7-
Functional Description and Specifications
Disconnect battery pack from tool or place the switch in the locked or
off position before making any assembly, adjustments or changing
accessories. Such preventive safety measures reduce the risk of starting the tool
accidentally.
!
WARNING
Cordless Planers
WING
KNOB
RABBETING
DEPTH STOP
(OPTIONAL)
DEPTH
ADJUSTMENT
KNOB
CHIP EXHAUST
PORT
CHIP EXHAUST PORT
DEPTH
SCALE
PORT SELECTOR
LEVER
TRIGGER SWITCH
“LOCK-OFF”
BUTTON
FRONT SHOE
PIVOT
FENCE
ROUND
KNOB
GUIDE
BRACKET
WING KNOB
WING KNOB
FENCE
SCREW
DRIVE BELT COVER
CHAMFER
V-GROOVE
GUIDE
BRACKET
WIDTH
SCALE
DELUXE
ANGLE
FENCE
(OPTIONAL)
WING
KNOB
STANDARD
PARALLEL
WIDTH
GUIDE
FENCE
FIG. 1
THE CUTTING DEPTH
CHOICES ARE
APPROXIMATELY
1/16", 3/64", 1mm (•),
1/32", 1/64", & 1/128" (•)
BATTERY
RELEASE TABS
BATTERY PACK
SCREW
Maximum Capacities
Planing depth 0 - 1/16" (0 - 1.6mm)
Rabbeting depth 0 - 5/16" (0 - 8mm)
Cutting width 3-1/4" (82mm)
BC006 charger requires 12 V DC input
NOTE: ONLY USE CHARGERS LISTED ABOVE
Model Voltage No load Charge Charger Voltage Battery
number rating speed time number rating pack
53514 14.4 V n0 13,000/min 1 hr. BC001-6 & BC016 120 V 60 Hz BAT040 & BAT038
53518 18 V n0 13,000/min 1 hr. BC003, 4, 6, & BC016 120 V 60 Hz BAT026 & BAT025
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 7
Page 8
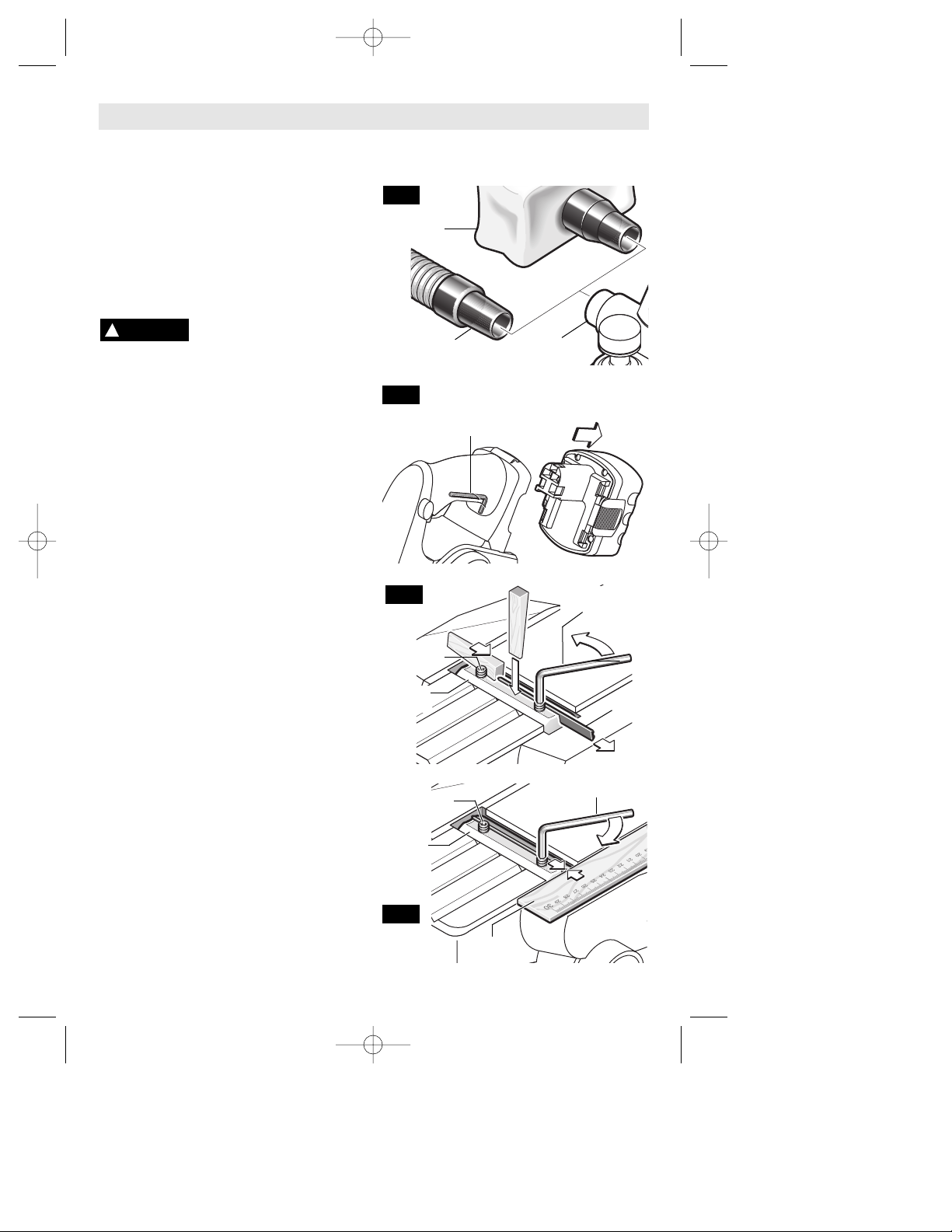
CHIP EXTRACTION
The planer comes with two chip exhaust
ports, which may be used with a chip bag or
a shop vacuum and vacuum connector (Fig.2)
to keep your work environment cleaner. The
chip bag or vacuum connector may be
attached to either end of the exhaust port.
Moving the port selector lever to position 1
(towards front of tool) discharges chips to the
left, while position 2 (towards rear of tool)
discharges chips to the right (Fig. 1)
PLANER BLADES
The planer blades are
sharp and fragile and must
be handled carefully to avoid injury to the
user or damage to the blades.
The planer blades have two cutting edges,
and may be reversed when one of the cutting
edges becomes dull or chipped.
Do not attempt to sharpen or use
resharpened used blades of any kind. Use
only blades designated for use with this
model, because other blades will cause
vibration, decrease perfomance and may not
clamp securely in blade holder.
BLADE WRENCH & STORAGE AREA
Your tool is equipped with a blade wrench
that is conveniently located in the handle
base where it is always handy and unlikely to
get lost or misplaced (Fig. 3).
REVERSING OR REPLACING BLADES
To reverse or replace the blade, loosen the
clamping screws with blade wrench. With the
screws loosened, slide the blade lengthwise
out of the cutter drum, taking care to keep
your fingers away from the sharp edges of the
blade (Fig. 4).
A piece of wood may be used for this
purpose. If the blade is gummed and difficult
to remove, you may clean the blade with
mineral spirits, lacquer thinner or alcohol.
Clean all surfaces before reinstalling the new
blade, as this will ensure an accurate blade
setting and proper tool performance.
BLADE ALIGNMENT
To ensure an even cut, it is important that the
blade is adjusted so that it aligns with the
outside edge of the front and rear shoes.
This alignment can be done as follows: place
a straight edge or a piece of wood along the
outside surface of the front shoe and rear
shoe, then slide the planer blade to just
contact the straight edge or wood (Fig.5).
Make sure the blade sits correctly in the
holder groove of the cutter drum.
You may then tighten the clamping screws
which secure the blade and your planer is
ready for use.
-8-
Assembly
FIG. 2
FIG. 4
FIG. 3
FIG. 5
CHIP BAG
(OPTIONAL)
EXHAUST
PORTS
VACUUM
CONNECTOR
BLADE
CLAMPING
SCREW
CUTTER
DRUM
CLAMPING
SCREW
BLADE WRENCH
2.5 MM BLADE
WRENCH
CUTTER
DRUM
STRAIGHT
EDGE
!
WARNING
BLADE WRENCH &
STORAGE AREA
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 8
Page 9
-9-
Operating Instructions
TRIGGER "ON/OFF" SWITCH
Hold the tool with both
hands while starting the
tool, since torque from the motor can
cause the tool to twist.
To turn tool "ON", depress the "Lock-OFF"
button and squeeze the trigger switch. To
turn the tool "OFF", release the trigger
switch which is spring loaded and will return
to "OFF" position automatically.
To increase switch life, do not turn switch on
and off while tool and drum are held against
a workpiece.
BRAKE
When the trigger is released it activates the
electrical brake to stop the blade quickly. This
feature is especially useful when making
repetitive cuts.
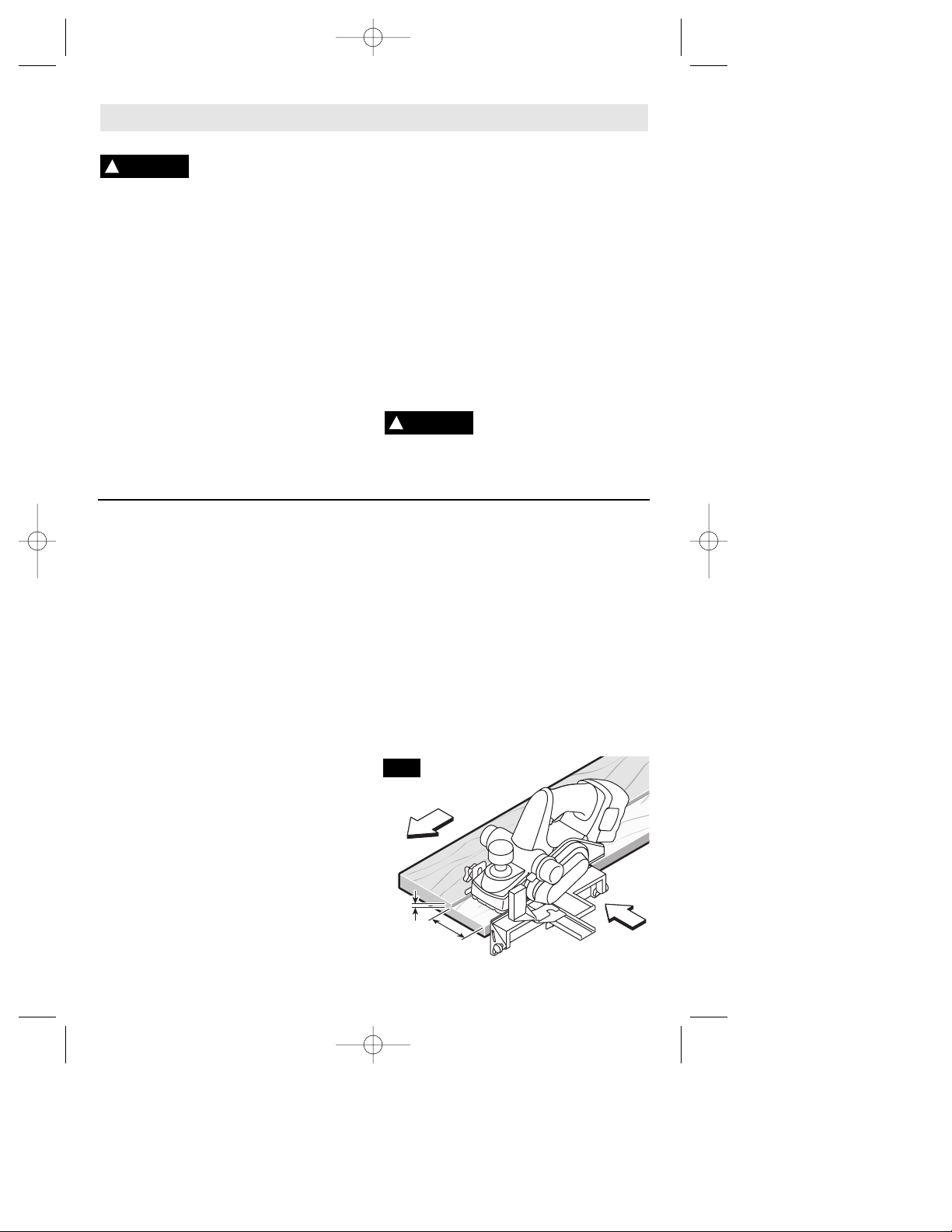
PLANING ACTION
Check that the workpiece is held in place
securely on your work surface, and standing
comfortably, hold the planer firmly with both
hands. With the planer fully adjusted, place
the front shoe on the workpiece, (be certain
that the cutter drum is not in contact with
the work) and start the planer as described
earlier. With pressure on the front shoe, and
the fence against the side of the work (to
control the width or angle,) feed the planer
steadily until the rear shoe fully engages the
workpiece. Now gradually transfer pressure
to the rear shoe, and continue planing to the
end of the cut. Feed the planer at a uniform
and reasonable rate, which does not put
excessive strain on the motor or blades, (do
not pull the planer back over the surface
already cut.) Use progressive cuts until you
are near the desired depth, and then readjust to a light cut for the final pass to
obtain a good surface finish.
The motor may stall if
improperly used or
overloaded. Reduce the pressure (feed
rate) or depth of cut to prevent possible
damage to the tool if the motor labors.
!
CAUTION
ADJUSTING DEPTH OF CUT
Proper cutting depth should be determined
according to the hardness, gumminess or
moisture content of the material being cut,
as well as the feed rate, and is largely a
matter of experience. Start with a light cut
and increase the depth setting if the plane
moves freely through the workpiece with no
excessive load on the motor. Do not change
depth of cut while planing.
The cutting depth is determined by the
difference in height between the adjustable
front shoe, and the fixed rear shoe of the
planer. As the front shoe is adjusted, it
retracts and exposes the blade, which can
then remove the desired amount from the
workpiece. The cutting depth is graduated
from 0 to 1/16 of an inch, and the "0"
indicates the blade is fully retracted.
Adjusting depth of cut: Rotate depth
adjustment knob until the indicator engages
the detent which indicates the desired
cutting depth on the depth scale (Fig. 1).
The planer may be set to cut any depth from
0 to 1/16 of an inch.
STANDARD PARALLEL WIDTH
GUIDE FENCE
The width guide fence can be used to cut
various desired widths (Fig. 1).
Installing the guide fence: Place the wing
knob through the appropriate hole in the
guide bracket and screw into the housing.
Securely tighten wing knob.
Setting the cutting width: Loosen wing knob
and slide the fence along the guide bracket
to the desired position. Securely tighten
wing knob. Be certain that the flat washer
(supplied) is fitted between the bottom of the
guide fence and wing knob or the guide
fence is likely to slip.
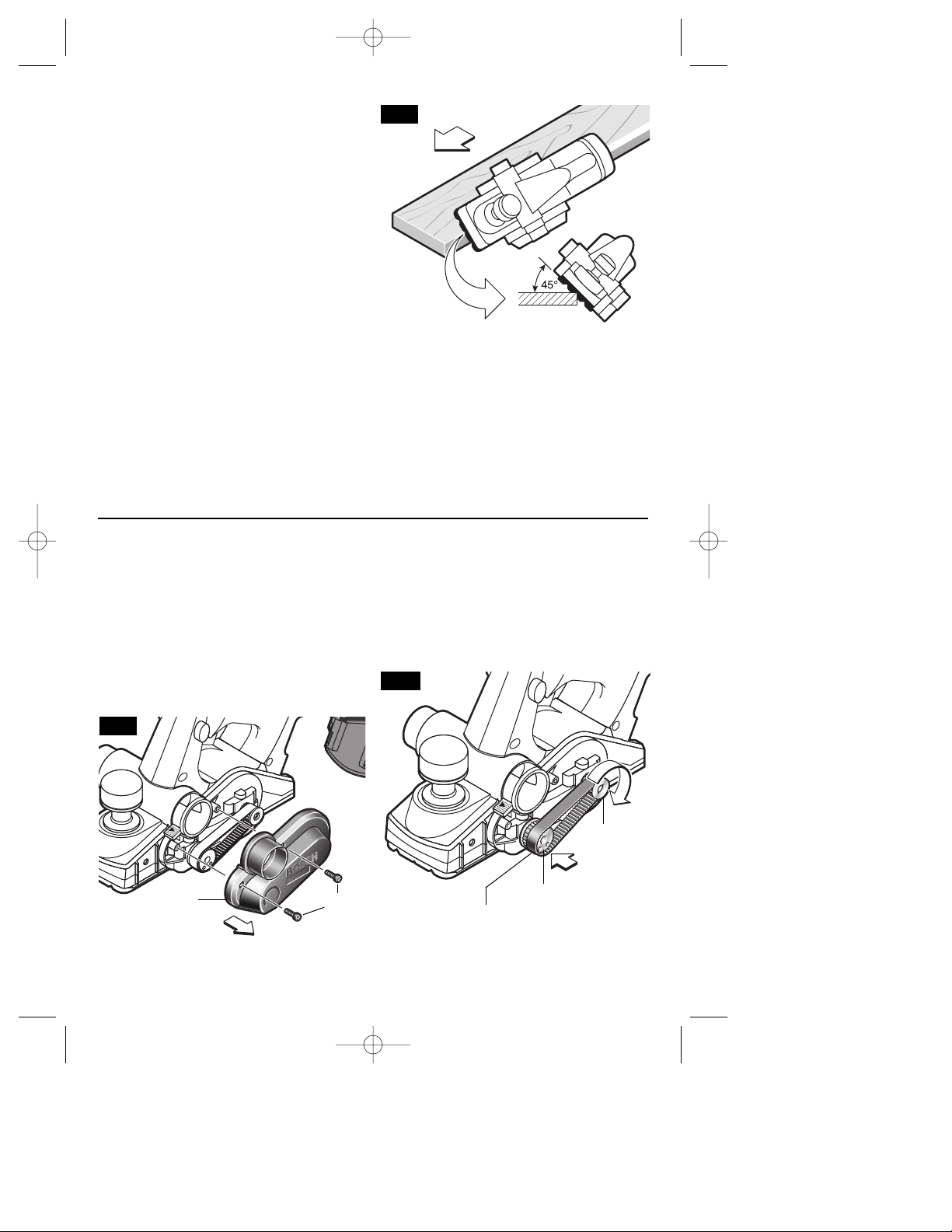
DELUXE ANGLE FENCE
The optional deluxe angle fence (Fig. 6) can
be used to cut various desired widths, with
the additional capability of guiding the
!
WARNING
82 mm
max
8 mm
max
FIG. 6
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 9
Page 10
-10-
planer on any angle up to 45 degrees, to
allow edge chamfering (Fig. 7).
Installing the angle fence: Place the wing
knob through the appropriate hole in the
guide bracket and screw into the housing.
Securely tighten wing knob (Fig. 1).
Setting the cutting width: Loosen wing knob
and using the width scale, slide the fence
along the guide bracket to the desired
position. Securely tighten wing knob (Fig. 1).
Setting the cutting angle: Loosen round
knobs and pivot the fence to the desired
position. Securely tighten round knobs (Fig. 1).
Note that the adjustable front shoe contains
a chamfer V-groove, which will follow the
corner of a workpiece to allow easier
handling when using the deluxe angle/width
fence (Fig. 7).
RABBETING DEPTH STOP
The optional rabbeting depth stop accessory
(Fig. 1) allows the user to set any rabbeting
depth from 0 to 5/16 inch. For best results, it
is important that the blade be properly
aligned (See "BLADE ALIGNMENT"). The
width of the rabbet is controlled by the width
fence. The maximum cutting width is 3-1/4",
and the final depth is achieved by repetitive
cutting until the rabbeting depth guide
contacts the workpiece. The maximum
rabbeting depth is 5/16"
Setting the rabbet depth: Loosen wing knob
and using the depth scale on the rabbeting
depth stop, set the desired rabbet depth.
Securely tighten wing knob.
FIG. 7
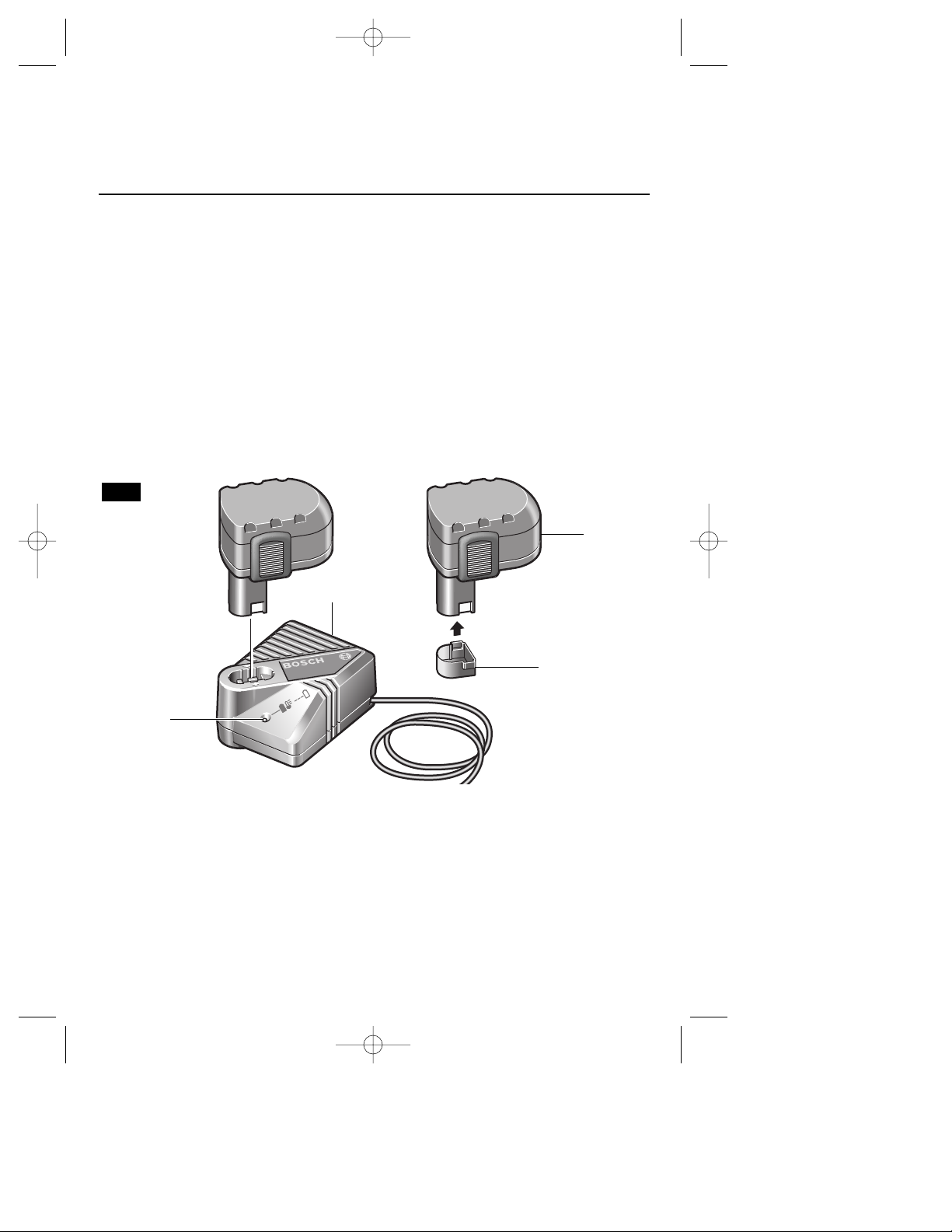
DRIVE BELT
The drive belt is a normal maintenance part
and should be inspected periodically for
wear. If the drive belt shows signs of drying
out, cracking or tearing, it should be
replaced. If the drive belt will not track
properly or comes off the pulleys, it should
be replaced.
Installing new drive belt: Loosen screws and
remove the drive belt cover (Fig. 8). Cut and
remove the worn drive belt. Before installing
the new drive belt, clean both pulleys
thoroughly. First place the new drive belt
onto the drive pulley then rotate clockwise
while pushing the belt onto the driven pulley.
Reinstall the drive belt cover and securely
tighten screws (Fig. 9).
FIG. 9
DRIVE
PULLEY
DRIVEN
PULLEY
DRIVE
BELT
DRIVE
BELT
COVER
SCREW
FIG. 8
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 10
Page 11
-11-
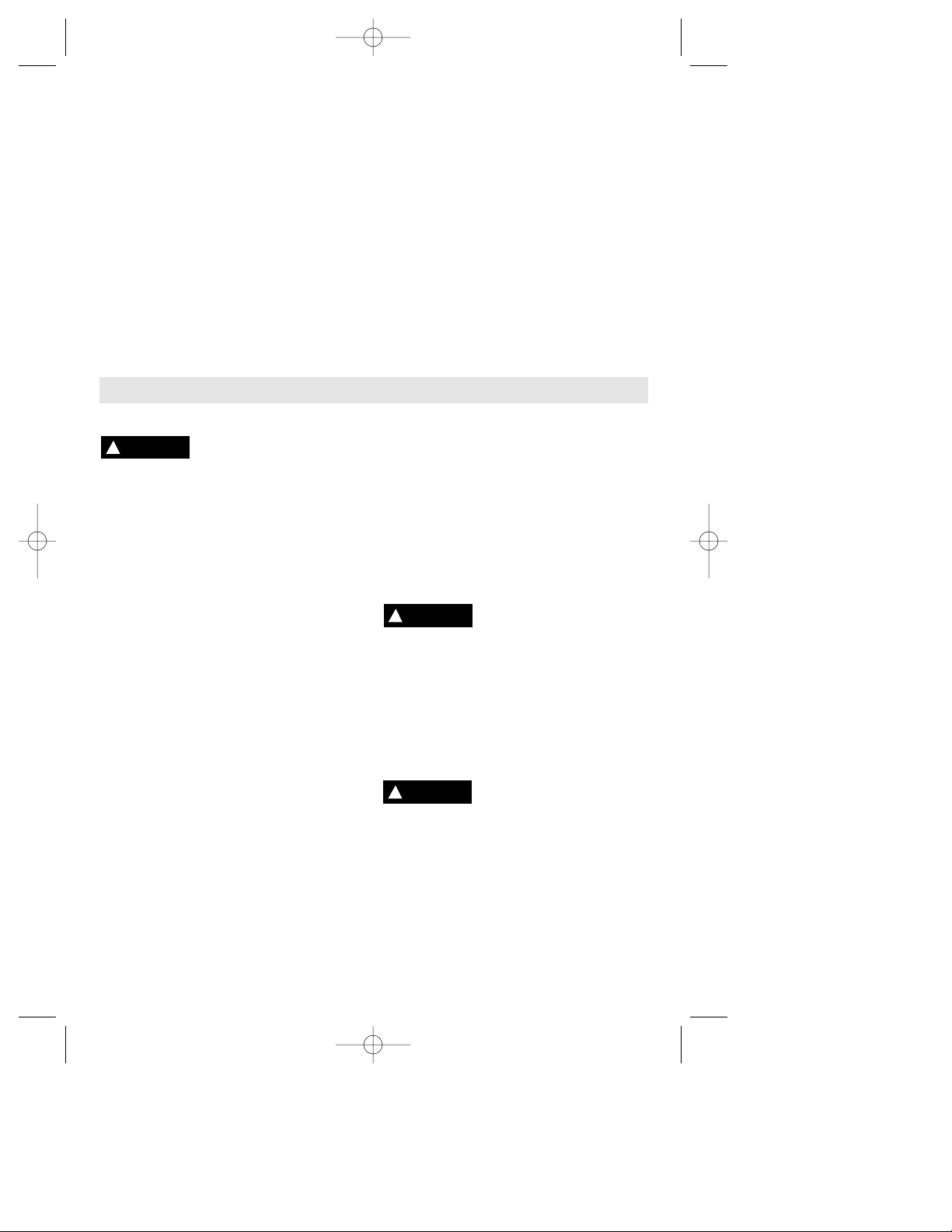
Release battery pack from tool by pressing
on both sides of the battery release tabs and
pull downwards. Before inserting battery
pack, remove protective cap from battery
pack. To insert battery, align battery and
slide battery pack into tool until it locks into
position. Do not force.
RELEASING AND INSERTING BATTERY PACK
CHARGING BATTERY PACK (1 HOUR CHARGER)
Plug charger cord into your standard power
outlet. Before inserting battery pack, remove
protective cap, then insert battery pack into
charger (Fig. 10).
The charger’s green indicator will begin to
“BLINK”. This indicates that the battery is
receiving a fast charge. Fast-charging will
automatically stop when the battery pack is
fully charged.
When the indicator light stops “BLINKING”
(and becomes a steady green light) fast
charging is complete.
When you begin the charging process of the
battery pack, a steady green light could also
mean the battery pack is too hot or too cold.
The purpose of the light is to indicate that the
battery pack is fast-charging. It does not
indicate the exact point of full charge. The
light will stop blinking in less time if the
battery pack was not completely
discharged.
When the battery pack is fully charged,
unplug the charger (unless you're charging
another battery pack) and slip the battery
pack back into the tool handle.
To prevent fire or injury when batteries are
not in tool or charger, always place
protective cap onto end of battery pack.
INDICATOR
LIGHT
CHARGER
BATTERY
PACK
PROTECTIVE
CAP
1. The battery pack accepts only about 80%
of its maximum capacity with its first few
charge cycles. However, after the first few
charge cycles, the battery will charge to full
capacity.
2. The charger was designed to fast charge
the battery only when the battery
temperature is between 40˚F (4˚C) and 105˚F
(41˚C).
3. A substantial drop in operating time per
charge may mean that the battery pack is
nearing the end of its life and should be
replaced.
IMPORTANT CHARGING NOTES
FIG. 10
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 11
Page 12
Maintenance
Service
NO USER SERVICEABLE
PARTS INSIDE. Preventive
maintenance performed by unauthorized
personnel may result in misplacing of
internal wires and components which
could cause serious hazard. We recom-
mend that all tool service be performed by a
Bosch Factory Service Center or Authorized
Bosch Service Station. SERVICEMEN:
Disconnect tool and/or charger from power
source before servicing.
BATTERIES
Be alert for battery packs that are nearing
their end of life. Battery packs typically last
from 500 to 1000 charges. If you notice
decreased tool performance or significantly
shorter running time between charges then it
is time to replace the battery pack. Failure
to do so can cause the tool to operate
improperly or damage the charger.
Long term battery storage should be in
the discharged state. Battery packs last
longer and re-charge better when they are
stored discharged. Remember to fully recharge battery packs before using after
prolonged storage.
TOOL LUBRICATION
Your Bosch tool has been properly lubricated
and is ready for use. It is recommended that
tools with gears be regreased with a special
gear lubricant yearly.
D.C. MOTORS
The motor in your tool has been engineered
for many hours of dependable service. To
maintain peak efficiency of the motor, we
recommend it be examined every six
months. Only a genuine Bosch replacement
motor specially designed for your tool should
be used.
Cleaning
To avoid accidents, always
disconnect the tool and/or
charger from the power supply before
cleaning. The tool may be cleaned most
effectively with compressed dry air. Always
wear safety goggles when cleaning tools
with compressed air.
Ventilation openings and switch levers must
be kept clean and free of foreign matter. Do
not attempt to clean by inserting pointed
objects through opening.
Certain cleaning agents
and solvents damage
plastic parts. Some of these are: gasoline,
carbon tetrachloride, chlorinated cleaning
solvents, ammonia and household
detergents that contain ammonia.
!
WARNING
!
WARNING
!
CAUTION
-12-
4. If you anticipate long periods (i.e. a month
or more) of non-use of your tool, it is best to
run your tool down until it is fully discharged
before storing your battery pack. After a long
period of storage, the capacity at first
recharge will be lower. Normal capacity will be
restored in two or three charge/discharge
cycles. Remember to unplug charger during
storage period.
5. If battery does not charge properly:
a. Check for voltage at outlet by
plugging in some other electrical device.
b. Check to see if outlet is connected to
a light switch which turns power “off” when
lights are turned off.
c. Check battery pack terminals for dirt.
Clean with cotton swab and alcohol if
necessary.
d. If you still do not get proper charging,
take or send tool, battery pack and charger
to your local Bosch Service Center. See
“Tools, Electric” in the Yellow Pages for
names and addresses.
Note: Use of chargers or battery packs not
sold by Bosch may void the warranty.
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 12
Page 13

-13-
Accessories
If an extension cord is
necessary, a cord with
adequate size conductors that is capable
of carrying the current necessary for your
tool must be used. This will prevent
excessive voltage drop, loss of power or
overheating. Grounded tools must use 3wire extension cords that have 3-prong
plugs and receptacles
.
NOTE: The smaller the gauge number, the
heavier the cord.
RECOMMENDED SIZES OF EXTENSION CORDS
120 VOLT ALTERNATING CURRENT TOOLS
!
WARNING
Tool’s
Ampere
Rating
Cord Size in A.W.G.
Wire Sizes in mm
2
3-6
6-8
8-10
10-12
12-16
18 16 16 14 .75 .75 1.5 2.5
18 16 14 12 .75 1.0 2.5 4.0
18 16 14 12 .75 1.0 2.5 4.0
16 16 14 12 1.0 2.5 4.0 —
14 12 — — — — — —
25 50 100 150 15 30 60 120
Cord Length in Feet Cord Length in Meters
* Standard parallel width guide fence
** Deluxe angle fence
** Rabbeting depth stop
* Blade wrench 2.5mm
* Carbide reversible blades (2)
* Vacuum connector
** Vacuum hose
** Chip bag
(*= standard equipment)
(**= optional accessories)
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 13
Page 14

-14-
Consignes générales de sécurité
pour tous les outils à pile
Vous devez lire et comprendre toutes les instructions. Lenon-respect, même partiel,
des instructions ci-après entraîne un risque de choc életrique, d'incendie et/ou de
blessures graves.
CONSERVEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS
AVERTISSEMENT
!
Aire de travail
Veillez à ce que l'aire de travail soit propre et bien
éclairée. Le désordre et le manque de lumière
favorisent les accidents.
N'utilisez pas d'outils électriques dans une
atmosphère explosive, par exemple enprésence de
liquides, de gaz ou de poussières inflammables. Les
outils électriques créent des étincelles qui pourraient
enflammer les poussières ou les vapeurs.
Tenez à distance les curieux, les enfants et les
visiteurs pendant que vous travaillezavec un outil
électrique. Ils pourraient vous distraire et vous faire
faire une fausse manoeuvre.
Sécurité électrique
N'abusez pas du cordon. Ne transportez jamais
l'outil par le cordon. Tenez le cordon à l'écart de la
chaleur, de l'huile, des arêtes vives ou des pièces
mobiles. Remplacez les cordons endommagés
immédiatement. Les cordons endommagés peuvent
provoquer un incendie.
Un outil à pile avec piles incorporées ou bloc-pile
distinct doit être rechargé uniquement avec le
chargeur indiqué pour la pile. Un chargeur qui peut
être adéquat pour un type de pile peut créer un risque
d'incendie lorsqu'il est utilisé avec une autre pile.
Utiliser un outil à pile uniquement avec le bloc-pile
désigné spécifiquement. L'emploi de toute autre pile
peut créer un risque d'incendie.
Sécurité des personnes
Restez alerte, concentrez-vous sur votre travail et
faites preuve de jugement. N'utilisez pas un outil
électrique si vous êtes fatigué ou sous l'influence de
drogues, d'alcool ou de médicaments. Un instant
d'inattention suffit pour entraîner des blessures graves.
Habillez-vous convenablement. Ne portez ni
vêtements flottants ni bijoux. Confinez les cheveux
longs. N'approchez jamais les cheveux, les
vêtements ou les gants des pièces en mouvement.
Des vêtements flottants, des bijoux ou des cheveux
longs risquent d'être happés par des pièces en
mouvement. Gardez les poignées sèches, propres et
exemptes d'huile et de graisse.
Évitez la mise en marche accidentelle. Assurez-vous
que l'interrupteur est en position de blocage ou
d'arrêt avant d'insérer le bloc-pile. Il est dangereux
de transporter l'outil avec le doigt sur l'interrupteur ou
d'insérer le bloc-pile dans un outil alors que
l'interrupteur est en position de marche.
Enlevez les clés de réglage ou de serrage avant de
démarrer l'outil. Une clé laissée dans une pièce
tournante de l'outil peut provoquer des blessures.
Ne vous penchez pas trop en avant. Maintenez un bon
appui et restez en équilibre entout temps. Un bonne
stabilité vous permet de mieux réagir à une situation
inattendue.
Utilisez des accessoires de sécurité. Portez toujours
des lunettes ou une visière. Selon les conditions,
portez aussi un masque antipoussière, des bottes de
sécurité antidérapantes, un casque protecteur et/ou un
appareil antibruit.
Utilisation et entretien des outils
Immobilisez le matériau sur une surface stable au
moyen de brides ou de toute autre façon adéquate. Le
fait de tenir la pièce avec la main ou contre votre corps
offre une stabilité insuffisante et peut amener un
dérapage de l'outil.
Ne forcez pas l'outil. Utilisez l'outil approprié à la
tâche. L'outil correct fonctionne mieux et de façon plus
sécuritaire. Respectez aussi la vitesse de travail qui lui
est propre.
N'utilisez pas l'outil si l'interrupteur ne le met pas
en marche ou à l'arrêt. Un outil qui ne peut être
contrôlé par l'interrupteur est dangereux et doit être
réparé.
Débranchez le bloc-pile de l'outil ou mettez
l'interrupteur en position de blocage ou d'arrêt avant
d'effectuer tout réglage, de changer les accessoires
ou de remiser l'outil. Ces mesures de sécurité
préventives réduisent le risque d'une mise en marche
accidentelle de l'outil.
Rangez les outils hors de la portée des enfants et
d'autres personnes inexpérimentées. Les outils sont
dangereux dans les mains d'utilisateurs novices.
Lorsque le bloc-pile n'est pas en usage, tenez-le à
l'écart d'autres objets métalliques tels que
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 14
Page 15

-15-
Fixez la pièce à raboter. Ne la tenez jamais à la
main et ne la posez jamais sur vos genoux. Les
petites pièces doivent être correctement bridées pour
les empêcher d’être happées par la rotation des fers
du rabot quand on pousse celui-ci vers l’avant. Si le
support est instable, les fers risquent de coincer et de
causer une perte de contrôle et des blessures.
Démarrez toujours le rabot et laissez-le monter en
régime avant de mettre le fer en contact avec la
pièce. L’outil risque de vibrer ou de sursauter si la
vitesse du fer est trop faible quand on commence le
rabotage et il risque de reculer brutalement.
Vérifiez que la pièce est exempte de clous. S’il y a
des clous, enlevez-les ou chassez-les bien en
dessous de la dimension souhaitée pour la surface
terminée. Si les fers du rabot rencontrent des objets
tels que des clous, l’outil risque de reculer
brutalement et de causer des blessures corporelles
graves.
Débranchez le bloc-pile de l'outil ou placez
l'interrupteur à la position de blocage ou d'arrêt
avant d'effectuer tout assemblage ou réglage ou de
changer les accessoires. Ces mesures de sécurité
préventives réduisent le risque d'une mise en marche
accidentelle de l'outil.
Après avoir changé les fers, faites tourner le
cylindre porte-fers (tambour) pour vérifier que les
fers ne touchent aucune partie du carter et que les
vis de blocage des fers sont serrées. Les fers en
rotation risquent de heurter le carter de l’outil et
d’abîmer celui-ci. Ils risquent aussi de causer des
blessures.
Tenez toujours l’outil fermement à deux mains pour
mieux le maîtriser.
Ne tirez jamais le rabot vers l’arrière sur la surface
de la pièce. Vous risquez d’en perdre le contrôle.
Ne mettez pas les doigts ou tout autre objet dans la
buse d’évacuation des copeaux. Ne dégagez jamais
les copeaux avec l’outil en marche. Vous vous
blesseriez si vous touchiez le tambour porte-fers.
Débranchez le bloc-pile de l'outil s’il devenait
nécessaire de dégager les copeaux. Les fers sont
cachés et ils risquent de vous couper si vous les
touchez.
Ne posez jamais le rabot avant que le fer soit à
l’arrêt complet. Si le fer touchait une surface lorsque
le tambour est en roue libre, vous risqueriez de
perdre le contrôle de votre rabot.
Les travaux à la machine
tel que ponçage, sciage,
meulage, perçage et autres travaux du bâtiment
peuvent créer des poussières contenant des produits
chimiques qui sont des causes reconnues de cancer,
de malformation congénitale ou d’autres problèmes
reproductifs. Ces produits chimiques sont, par
exemple :
• Le plomb provenant des peintures à base de plomb,
• Les cristaux de silices provenant des briques et du
ciment et d’autres produits de maçonnerie, et
• L’arsenic et le chrome provenant des bois traités
chimiquement
Le niveau de risque dû à cette exposition varie avec la
fréquence de ces types de travaux. Pour réduire
l’exposition à ces produits chimiques, il faut travailler
dans un lieu bien ventilé et porter un équipement de
sécurité approprié tel que certains masques à poussière
conçus spécialement pour filtrer les particules
microscopiques.
Consignes de sécurité pour les rabots sans fil
trombones, pièces de monnaie, clés, clous, vis ou
autres petits objets métalliques susceptibles
d'établir une connexion d'une borne à une autre. Le
court-circuitage des bornes de batterie ensemble peut
causer des étincelles, des brûlures ou un incendie.
Prenez soin de bien entretenir les outils. Les outils de
coupe doivent être toujours bien affûtés et propres.
Des outils bien entretenus, dont les arêtes sont bien
tranchantes, sont moins susceptibles de coincer et plus
faciles à diriger.
Soyez attentif à tout désalignement ou coincement
des pièces en mouvement, à tout bris ou à toute autre
condition préjudiciable au bon fonctionnement de
l'outil. Si vous constatez qu'un outil est endommagé,
faites-le réparer avant de vous en servir. De
nombreux accidents sont causés par des outils en
mauvais état.
N'utilisez que des accessoires que le fabricant
recommande pour votre modèle d'outil. Certains
accessoires peuvent convenir à un outil, mais être
dangereux avec un autre.
Réparation
La réparation des outils électriques doit être confiée à
un réparateur qualifié. L'entretien ou la réparation d'un
outil électrique par un amateur peut avoir des
conséquences graves.
Pour la réparation d'un outil, n'employez que des
pièces de rechange d'origine. Suivez les directives
données à la section « Réparation » de ce manuel.
L'emploi de pièces non autorisées ou le non-respect des
instructions d'entretien peut créer un risque de choc
électrique ou de blessures.
AVERTISSEMENT
!
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 15
Page 16

Avant d'utiliser le chargeur de pile, lisez toutes les
consignes et tous les marquages d'avertissement
sur (1) le chargeur de pile, (2) le bloc-pile et (3) le
produit utilisant la pile.
N'utilisez que le chargeur qui accompagnait votre
produit ou remplacement direct, comme indiqué
dans le catalogue ou ce manuel. Ne substituez aucun
autre chargeur. N’utiliser que les chargeurs approuvés
par Bosch avec votre produit. Voir Description
fonctionnelle et Spécifications.
Ne désassemblez pas le chargeur et ne l'utilisez pas
s'il a reçu un choc violent, s'il est tombé ou s'il a
été endommagé par ailleurs. Remplacez
immédiatement les cordons ou les fiches abîmés.
Un remontage incorrect ou des dommages peuvent
provoquer un incendie ou des secousses électriques.
Ne rechargez pas la pile dans un environnement
mouillé ou humide. N'exposez pas le chargeur à la
pluie ou la neige. Si le boîtier de la pile est fissuré
ou endommagé par ailleurs, ne l'insérez pas dans le
chargeur. Il pourrait y avoir un incendie ou un court-
circuit de pile.
Ne charger que des piles rechargeables approuvées
par Bosch. Voir Description fonctionnelle et
Spécifications. Les autres types de piles peuvent
éclater causant ainsi des blessures et des dommages.
Chargez le bloc-pile à des températures de plus de 4
degrés C (+40°F) et de moins de 41 degrés C
(+105°F). Rangez l'outil et le bloc-pile à des
endroits dont la température ne dépasse pas 49
degrés C (+120°F). Ceci est important pour prévenir
des dommages considérables aux éléments des piles.
Il peut y avoir une fuite de pile dans des conditions
extrêmes d'utilisation ou de température. Évitez tout
contact avec la peau et les yeux. Le liquide de pile
est caustique et pourrait causer des brûlures
chimiques aux tissus. Si le liquide vient en contact
avec la peau, lavez rapidement à l'eau savonneuse,
puis au jus de citron ou au vinaigre. Si le liquide vient
en contact avec les yeux, rincez-les à l'eau pendant au
moins 10 minutes et sollicitez des soins médicaux.
Posez le chargeur sur une surface plate
inflammable et à distance de matériaux
inflammables lorsqu’on recharge un bloc-piles. Le
chargeur et le bloc-piles s’échauffent pendant la
charge. Le coussinet de mousse souple et autres
surfaces isolantes empêchent la circulation normale
de l’air, ce qui peut provoquer une surchauffe du
chargeur et du bloc-piles. S’il y a dégagement de
fumée ou si le boîtier fond, débranchez le chargeur
immédiatement et n’utilisez ni le chargeur, ni le blocpiles.
L'utilisation d'un accessoire non recommandé ni
vendu par Bosch peut causer des risques d'incendie,
de chocs électriques ou de lésions corporelles.
-16-
Chargeur de pile
Lorsque les piles ne sont
pas dans l’outil ou le
chargeur, gardez-les à l’écart d’objets métalliques.
Ainsi, pour éviter un court-circuitage des bornes, NE
PLACEZ PAS les piles dans la boîte à outils ou dans la
poche avec des clous, des vis, des clés, etc. Ceci peut
provoquer un incendie ou des blessures.
Afin d’éviter tout risque
d’incendie ou de blessure
lorsque les piles ne sont pas dans l’outil ou dans le
chargeur, placez toujours un capuchon de sécurité sur
l’extrémité du bloc-piles. Le capuchon de protection
protège contre les courts circuits aux bornes.
NE METTEZ PAS LES PILES AU FEU ET NE LES
EXPOSEZ PAS À UNE CHALEUR ÉLEVÉE. Elles peuvent
exploser.
Entretien des piles
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 16
Page 17

-17-
Ne tentez pas de
désassembler le bloc-piles
ou d’enlever tout composant faisant saillie des
bornes de piles, ce qui peut provoquer un incendie ou
des blessures. Avant la mise au rebut, protégez les
bornes exposées à l’aide d’un ruban isolant épais pour
prévenir le court-circuitage.
PILES NICKEL-CADMIUM
Si le produit est équipé d'une pile nickel-cadmium, la
pile doit être ramassée, recyclée ou mise au rebut
d'une manière qui ne soit pas nocive pour
l'environnement.
“Le sceau RBRC de recyclage des
piles, homologué par l’EPA
(Agence pour la protection de
l’environnement des États-Unis),
qui se trouve sur les piles au nickelcadmium (Ni-Cd) indique que S-B
Power Tool Company participe
volontairement à un programme industriel de
ramassage et de recyclage de ces piles au terme de
leur vie utile, pourvu qu’elles soient mises hors
service aux États-Unis ou au Canada. Le programme
du RBRC offre une alternative pratique à la mise des
piles au Ni-Cd usées au rebut ou au ramassage
d’ordures municipal, ce qui pourrait être interdit dans
votre région.
Veuillez appeler le 1-800-8-BATTERY pour obtenir de
plus amples renseignements sur le recyclage des piles
au Ni-Cd et sur les restrictions ou interdictions de
mise au rebut qui s’appliquent à votre région ou
renvoyez vos piles à un Centre de Service
Skil/Bosch/Dremel pour recyclage. La participation de
S-B Power Tool Company à ce programme s'insère
dans le contexte de notre engagement à préserver
notre environnement et à conserver nos ressources
naturelles.”
PILES NICKEL-HYDRURE DE MÉTAL
Si le produit est équipé d'une pile nickel-hydrure de
métal, la pile peut être mise au rebut dans un flux de
déchets solides municipaux.
AVERTISSEMENT
!
Mise au rebut des piles
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 17
Page 18

-18-
Symboles
Important : Certains des symboles suivants peuvent être utilisés sur votre outil. Veuillez les étudier et apprendre
leur signification. Une interprétation appropriée de ces symboles vous permettra d'utiliser l'outil de façon plus
efficace et plus sûre.
Symbole Nom Désignation/Explication
V Volts Tension (potentielle)
A Ampères Courant
Hz Hertz Fréquence (cycles par seconde)
W Watt Puissance
kg Kilogrammes Poids
min Minutes Temps
s Secondes Temps
Diamètre Taille des mèches de perceuse, meules,
etc.
n
0
Vitesse à vide Vitesse de rotation, à vide
.../min Tours ou mouvement alternatif par Tours, coups, vitesse en surface, orbites,
minute etc., par minute,
0 Position d'arrêt Vitesse zéro, couple zéro ...
1, 2, 3, ... Réglages du sélecteur Réglages de vitesse, de couple ou de
l, ll, lll, ... position. Un nombre plus élevé signifie
une vitesse plus grande.
Sélecteur variable à l'infini avec arrêt La vitesse augmente depuis le réglage 0
Flèche Action dans la direction de la flèche
Courant alternatif Type ou caractéristique du courant
Courant continu Type ou caractéristique du courant
Courant alternatif Type ou caractéristique du courant
ou continu
Construction classe II Désigne des outils construits avec double
isolation
Borne de terre borne de mise à la terre
Symbole d'avertissement Alerte l'utilisateur aux messages
d'avertissement.
Sceau Ni-Cad RBRCmc Désigne le programme de recyclage des piles
Ni-Cad.
0
Ce symbole signifie que cet
outil est approuvé par
Underwriters Laboratories.
Ce symbole signifie que cet
outil est approuvé par
l'Association canadienne de
normalisation.
Ce symbole signifie que
cet outil est approuvé
conformément aux normes
canadiennes par Underwriters
Laboratories.
Ce symbole
signifie que
cet outil se
conforme aux
normes
mexicaines
NOM.
Ce symbole signifie que cet outil
est approuvé par Underwriters
Laboratories et qu’il a été
homologué selon les normes
canadiennes par Underwriters
Laboratories.
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 18
Page 19

-19-
Description fonctionnelle et spécifications
Débranchez le bloc-pile de l'outil ou placez l'interrupteur à la position de blocage
ou d'arrêt avant d'effectuer tout assemblage ou réglage ou de changer les
accessoires. Ces mesures de sécurité préventives réduisent le risque d'une mise en marche accidentelle de
l'outil.
AVERTISSEMENT
!
Numéro Tension Régime Temps Numéro Tension Bloc
de chargeur nominale à vide de charge de chargeur nominale piles
53514 14.4 V n0 13,000/min 1 hr. BC001-6 & BC016 120 V 60 Hz BAT040 et BAT038
53518 18 V n0 13,000/min 1 hr. BC003, 4, 6, & BC016 120 V 60 Hz BAT026 et BAT025
Capacidades máximas
Profundidad de acepillad 0 - 1/16" (0 - 1,6 mm)
Profundidad de rebajado 0 - 5/16" (0 - 8 mm)
Anchura de corte 3-1/4" (82 mm)
Le chargeur BC006 nécessite une puissance d’alimentation
de 12 V CC.
NOTE : N’UTILISER QUE LES CHARGEURS
REPERTORIES CI-DESSUS
Rabot sans fil
BOUTON À
AILETTES
BUTÉE DE
PROFONDEUR
POUR FEUILLURE
(EN OPTION)
BOUTON DE
RÉGLAGE DE
PROFONDEUR
RACCORD
D’ÉVACUATION DES
COPEAUX
RACCORD D’ÉVACUATION DES COPEAUX
ÉCHELLE DE
PROFONDEUR
LEVIER DE SÉLECTION
DU RACCORD
INTERRUPTEUR À GÂCHETTE
BOUTON DE VERROUILLAGE
SUR ARRÊT
SEMELLE AVANT
GUIDE
INCLINABLE
BOUTON
ROND
SUPPORT
DE GUIDE
BOUTON À AILETTES
BOUTON À AILETTES
GUIDE
VIS
CAPOT DE COURROIE
GORGE EN VÉ
POUR
CHANFREINER
SUPPORT
DE GUIDE
ÉCHELLE
DES
LARGEURS
GUIDE
INCLINABLE
DE LUXE
(EN OPTION)
BOUTON À
AILETTES
GUIDE DE
LARGEUR
PARALLÈLE
STANDARD
FIG. 1
LES CHOIX DE PROFONDEUR
DE COUPE SONT ENVIRON :
1/16 po, 3/64 po, 1mm (•),
1/32 po, 1/64 po, & 1/128 po (•)
TOUCHES DE
DÉVERROUILLAGE
DES PILES
BLOC-PILES
VIS
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 19
Page 20

-20-
Assemblage
ÉVACUATION DES COPEAUX
Le rabot est muni de deux raccords d’évacuation de
copeaux sur lesquels on peut brancher soit un sac à
copeaux soit un aspirateur d’atelier avec un raccord
d’aspiration (Fig. 2) pour améliorer la propreté de
votre environnement de travail. Le sac à copeaux ou
le raccord d’aspiration peut être branché sur l’un ou
l’autre des raccords d’évacuation.
Quand le levier de sélection du raccord est en position
1, (vers l’avant de l’outil), les copeaux sont évacués à
gauche. En position 2 (vers l’arrière de l’outil), les
copeaux sont évacués à droite (Fig. 1).
FERS DE RABOT
Les fers de rabot sont
coupants et fragiles. Ils
doivent être manipulés avec soin pour éviter de se
blesser ou de les abîmer.
Les fers ont deux bords tranchants et ils peuvent être
retournés quand un des tranchants est émoussé ou
ébréché.
N'essayez pas d’affûter les fers ou d’utiliser des fers
ré-affûtés quels qu’ils soient. N’utilisez que des fers
conçus pour ce modèle. Toute autre fer risque de
causer des vibrations, de réduire la performance de la
machine ou d’être mal serrée dans le fer-lame.
CLÉ À FER ET
CASE DE RANGEMENT
Votre outil est pourvu d’une clé à fer qui est située
commodément dans la base de la poignée où elle est
toujours à la portée de la main et peu susceptible
d’être perdue ou égarée (Fig. 3).
RETOURNEMENT OU REMPLACEMENT DES FERS
Pour retourner ou remplacer le fer, desserrer les vis
de blocage à l’aide de la clé à fers. Une fois les vis
desserrées, faites glisser le fer dans le sens axial pour
le sortir du tambour en faisant bien attention
d’éloigner les doigts des bords tranchants du fer (Fig. 4).
Vous pouvez utiliser un morceau de bois pour cette
opération. Si le fer est encrassé et difficile à enlever,
vous pouvez le nettoyer avec du solvant, du diluant à
vernis ou de l’alcool.
Nettoyez toutes les surfaces avant de monter le fer
neuf. Cela assurera qu’il est positionné précisément et
permettra à l’outil de fonctionner correctement.
ALIGNEMENT DU FER
Pour que le rabotage soit régulier, le fer doit être à ras
des bords extérieurs des semelles avant et arrière.
Pour effectuer l’alignement, placez un règle ou un
morceau de bois le long de l’extérieur des semelles
avant et arrière, et ensuite enfoncez la lame jusqu’à ce
qu’elle touche tout juste le règle ou le morceau de
bois (Fig. 5).
Assurez-vous que le fer est bien en place dans la fente
du tambour.
Vous pouvez maintenant serrer les vis de blocage qui
tiennent le fer en place. Votre rabot est alors prêt à
l’emploi.
AVERTISSEMENT
!
FIG. 2
FIG. 4
FIG. 3
FIG. 5
SAC À COPEAUX
(EN OPTION)
RACCORDS
D’ÉVACUATION
RACCORD
D’ASPIRATION
FER
VIS DE
BLOCAGE
TAMBOUR
VIS DE
BLOCAGE
CLÉ À FER
CLÉ À FER DE
2,5 MM
TAMBOUR
RÈGLE
CLÉ À FER ET
CASE DE RANGEMENT
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 20
Page 21

-21-
Consignes de fonctionnement
INTERRUPTEUR MARCHE/ARRÊT
À GÂCHETTE
Tenez l’outil à deux mains
quand vous le démarrez
car le couple du moteur risque de le faire pivoter.
Pour mettre l’outil en marche, enfoncez le bouton de
verrouillage sur arrêt et appuyez sur l’interrupteur à
gâchette. Pour arrêter l’outil, lâchez la gâchette. Elle
est rappelée par ressort et reviendra automatiquement
à la position arrêt.
Pour allonger la durée de vie de l’interrupteur, ne
démarrez pas l’outil ou ne l’arrêtez pas quand celui-ci
ou le tambour est appuyé contre la pièce à raboter.
FREIN
Quand on relâche la gâchette, le frein est actionné et
arrête rapidement la lame. Cette caractéristique est des
plus utiles lors de sciages à répétition.
RABOTAGE
Vérifiez que la pièce est bien fixée sur votre surface de
travail. Placez-vous debout dans une position
confortable et saisissez le rabot fermement avec les
deux mains. Avec le rabot bien réglé, posez la semelle
avant sur la pièce (en s’assurant que la tambour ne
touche pas la pièce) et démarrez le rabot comme
décrit précédemment. Tout en maintenant la pression
sur la semelle avant et avec le guide contre le côté de
la pièce (pour obtenir la largeur ou l’angle de coupe
désiré), faire avancer le rabot régulièrement jusqu’à
ce que la semelle arrière repose complètement sur la
pièce. Transférez alors graduellement la pression vers
la semelle arrière et continuez à raboter jusqu’à la fin
de la passe. Faites avancer le rabot à une vitesse
régulière et raisonnable pour ne pas placer de
contraintes excessives sur le moteur ou les fers, (ne
faites pas avancer le rabot en la mauvaise direction).
Faites des passes progressives jusqu’à ce que vous
soyez près de la profondeur finale. Réglez alors le
rabot pour une profondeur de coupe faible qui vous
permettra d’obtenir un meilleur fini lors de la dernière
passe.
Il se peut que le moteur
cale en cas d’usage
incorrect ou de surcharge. Réduire la pression
(vitesse d’avance) ou la profondeur de coupe pour
éviter d’abîmer l’outil quand le moteur peine.
AVERTISSEMENT
!
MISE EN GARDE
!
RÉGLAGE DE LA PROFONDEUR DE COUPE
La profondeur de coupe correcte dépend de la dureté
du matériau, de son aspect gommeux et de son taux
d’humidité aussi bien que de la vitesse d’avance Sa
détermination requiert de l’expérience. Commencez
avec une profondeur faible et augmentez-la si le rabot
se déplace facilement sur la pièce sans sollicitation
excessive du moteur. Ne changez pas la profondeur
de coupe pendant le rabotage.
La profondeur de coupe est déterminée par la
différence de hauteur entre la semelle avant réglable
et la semelle arrière fixe. Quand on règle la semelle
avant, elle se rétracte et fait apparaître le fer, qui peut
alors raboter la profondeur désirée sur la pièce. La
profondeur de coupe est graduée de 0 à 1/16 po, avec
‘0’ indiquant que le fer est complètement rentré.
Réglage de la profondeur de coupe : Faites tourner le
bouton de réglage de la profondeur jusqu’à ce que
l’index s’enclenche dans le cran, ce qui indique la
profondeur de coupe désirée sur le cadran de
profondeur (Fig. 1).
Le rabot peut être réglé pour n’importe quelle
profondeur de coupe entre 0 et 1/16 po.
GUIDE DE LARGEUR PARALLÈLE STANDARD
Le guide de largeur peut être utilisé pour raboter des
largeurs variées (Fig. 1).
Montage du guide : Enfilez le bouton à ailettes dans le
trou du support de guide approprié et vissez-le dans
le carter. Serrez fermement le bouton à ailette.
Réglage de la largeur de rabotage : Desserrez le
bouton à ailettes et faites coulisser le guide le long de
son support pour le mettre à la position souhaitée.
Serrez fermement le bouton à ailettes. Assurez-vous
que la rondelle plate (fournie) est installée
correctement entre le dessous du guide et le bouton à
ailettes, sinon, il est probable que le guide se
déréglera.
GUIDE INCLINABLE DE LUXE
Le guide inclinable de luxe en option (Fig. 6) peut être
utilisé pour raboter à des largeurs variées et aussi
pour raboter des chanfreins à tout angle inférieur ou
égal à 45 degrés (Fig. 7).
Montage du guide inclinable : Enfilez le bouton à
ailettes par le trou approprié du support de guide et
82 mm
max
8 mm
max
FIG. 6
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 21
Page 22

-22-
vissez-le dans le carter. Serrez fermement le bouton à
ailettes (Fig. 1).
Réglage de la largeur de coupe : Desserrer le bouton
à ailettes et, en vous aidant de l’échelle des largeurs,
faites coulisser le guide le long de son support pour le
mettre à la position souhaitée. Serrez fermement le
bouton à ailettes (Fig. 1).
Réglage de l’angle : Desserrer les boutons ronds et
faites pivoter le guide à la position désirée. Serrez
fermement les boutons ronds (Fig. 1).
Remarquez que la semelle avant réglable est munie
d’une rainure en vé pour chanfreins qui permet de
suivre l’arête de la pièce pour faciliter le rabotage
quand vous utilisez le guide inclinable de luxe (Fig. 7).
BUTÉE DE PROFONDEUR POUR FEUILLURES
La butée de profondeur pour feuillures, vendue en
option, (Fig. 1) vous permet de régler le rabot pour
réaliser des feuillures de profondeur quelconque entre
0 et 5/16 po. Pour obtenir de bons résultats, il faut
que le fer soit aligné correctement (voir ALIGNEMENT
DU FER). La largeur de la feuillure se règle avec le
guide de largeur. Sa largeur maximale est de 3 – 1/4
po. La profondeur finale s’obtient en faisant des
passes successives jusqu’à ce que la butée de
profondeur pour feuillures touche la surface de la
pièce. La profondeur maximale de la feuillure est de
5/16 po.
Réglage de la profondeur de la feuillure : Desserrez le
bouton à ailettes et, en vous aidant de l’échelle de
profondeur sur la butée de profondeur pour feuillures,
réglez à la profondeur désirée. Serrez fermement le
bouton à ailettes.
COURROIE DE TRANSMISSION
La courroie de transmission est une pièce d’usure
normale. Contrôlez son usure périodiquement. Si elle
apparaît se dessécher, se fissurer ou se déchirer, il
faut la remplacer. Si elle ne reste pas en ligne ou
glisse des poulies, il faut également la remplacer.
Montage d’une courroie neuve : desserrer les vis et
enlever le capot de courroie (Fig. 8). Coupez et
enlevez la courroie usée. Avant de monter la courroie
neuve, nettoyez à fond les deux poulies. Commencez
par placer la courroie neuve sur la poulie menante,
ensuite tournez la courroie en sens horaire tout en la
poussant sur la poulie menée. Remontez le capot de
courroie et serrer les vis fermement (Fig. 9).
FIG. 9
POULIE
MENANTE
POULIE
MENÉE
COURROIE DE
TRANSMISSION
CAPOT DE
COURROIE
VIS
FIG. 8
FIG. 7
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 22
Page 23

-23-
Enlevez le bloc-piles de l’outil en pinçant les deux
côtés à la hauteur des touches de déverrouillage et en
le tirant vers le bas. Avant d’introduire le bloc-piles,
retirez le capuchon de protection de celui-ci. Pour
remettre le bloc dans l’outil, glissez-le dans l’ouverture
jusqu’à ce qu’il se verrouille en place. Ne forcez pas
outre mesure.
DÉPOSE ET REPOSE DU BLOC-PILES
CHARGE DU BLOC-PILE (CHARGEUR DE 1 HEURE)
Branchez le cordon du chargeur dans votre prise de
courant standard. Avant d’introduire le bloc-piles,
retirez le capuchon de protection et introduisez le blocpiles dans le chargeur (Fig. 10).
Le témoin vert du chargeur commencera à
CLIGNOTER, ce qui indique que la pile reçoit une
charge rapide. La charge rapide s'arrêtera
automatiquement lorsque le bloc-pile est à pleine
charge.
Le témoin CESSE DE CLIGNOTER (et s'allume en vert
continu) au terme de la charge rapide.
Lorsque vous commencez le processus de charge du
bloc-pile, un témoin vert continu pourrait également
signifier que le bloc-pile est trop chaud ou trop froid.
Le témoin a pour but d'indiquer que le bloc-pile est en
charge rapide. Il n'indique pas le point exact de pleine
charge. Le témoin cessera de clignoter en moins de
temp si le bloc-pile n'était pas entièrement déchargé.
Lorsque le bloc-pile est entièrement chargé,
débranchez le chargeur (à moins que vous ne chargiez
un autre bloc-pile) et réinsérez le bloc-pile dans la
poignée de l'outil.
Afin d’éviter tout risque d’incendie ou de blessure
lorsque les piles ne sont pas dans l’outil ou dans le
chargeur, placez toujours un capuchon de sécurité sur
l’extrémité du bloc-piles. Le capuchon de protection
protège contre les courts circuits aux bornes.
TÉMON
LUMINEUX
CHARGEUR
BLOC-PILES
CAPUCHON DE
PROTECTION
REMARQUES IMPORTANTES CONCERNANT LA CHARGE
1. Lors des premiers cycles de charge, le bloc-piles
neuf n’absorbe que 80 % de sa capacité maximale.
Par la suite, cependant, les piles se chargeront à
pleine capacité.
2. De même, le chargeur n’est destiné qu’à la charge
rapide des bloc-piles dont la température se situe
entre 4°C (40°F) et 41°C (105°F).
3. Une diminution marquée de la réserve énergétique
entre les charges peut signaler l’épuisement du blocpiles et le besoin d’un remplacement.
4. Si vous prévoyez de longues périodes (à savoir, un
mois ou plus) de non-utilisation de votre outil, il est
préférable d'utiliser votre outil jusqu'à ce que sa pile
soit entièrement déchargée avant de remiser votre
bloc-pile. Après une longue période de remisage, la
FIG. 10
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 23
Page 24

Maintenance
Entretien
IL N’EXISTE À
L’INTÉRIEUR AUCUNE
PIÈCE SUSCEPTIBLE D’ÊTRE ENTRETENUE PAR
L’UTILISATEUR. L’entretien préventif exécuté par
des personnes non autorisés peut entraîner un
positionnement erroné des composants et des fils
internes, ce qui peut présenter de graves dangers.
Nous recommandons de confier toute intervention
d’entretien sur l’outil à un centre de service-usine Bosch
ou à un centre de service après-vente Bosch agréé.
TECHNICIENS : Débranchez l’outil et/ou le chargeur de
la source de courant avant d’entretenir.
PILES
Faire attention aux blocs-piles qui approchent la fin
de leur vie. Les blocs-pile peuvent en général être
rechargés entre 500 et 1 000 fois. Si vous remarquez
une diminution dans les performances de votre outil ou
une durée de fonctionnement réduite de manière
significative entre charges, il est temps de remplacer le
bloc-piles. S’il n’est pas remplacé, il se peut qu’il
endommage le chargeur ou que l’outil fonctionne
incorrectement.
Les piles doivent être déchargées avant de les
entreposer pour une longue durée. Les blocs-piles
durent plus longtemps et se rechargent mieux quand ils
sont rangés déchargés. Rappelez-vous qu’il faut
complètement recharger les blocs-piles avant toute
utilisation survenant après un stockage prolongé.
GRAISSAGE DE L’OUTIL
Votre outil Bosch a été graissé de manière appropriée et
il est prêt à l’usage. Il est recommandé de regraisser les
outils avec engrenages à l’aide d’un lubrifiant spécial
d’engrenages chaque année.
MOTEURS C.C.
Le moteur de votre outil a été conçu pour de
nombreuses heures d’utilisation fiable. Pour maintenir
l’efficacité maximale du moteur, nous recommandons
de l’examiner tous les six mois. Seul un moteur de
remplacement Bosch authentique, conçu spécialement
pour votre outil, doit être utilisé.
Nettoyage
Pour éviter les accidents,
débranchez toujours l’outil
et/ou le chargeur de la source de courant avant de
nettoyer. La façon la plus efficace de nettoyer l’outil est
à l’aide d’air sec comprimé. Portez toujours des
lunettes de sécurité en nettoyant les outils à l’air
comprimé.
Les prises d’air et les leviers de commutation doivent
être gardés propres et exempts de corps étrangers. Ne
tentez pas de nettoyer en insérant des objets pointus à
travers l’ouverture.
Certains produits de
nettoyage et dissolvants
dont la gazoline, le tétrachlorure de carbone, les
nettoyeurs chlorés, l’ammoniaque et les détergents
ménagers contenant de l’ammoniaque peuvent
abîmer les pièces en plastique.
AVERTISSEMENT
!
AVERTISSEMENT
!
MISE EN GARDE
!
capacité sera réduite à la première recharge. La
capacité normale sera rétablie en deux ou trois cycles
de charge/décharge. N'oubliez pas de débrancher le
chargeur durant la période de remisage.
5. Si le bloc-piles ne se charge pas normale-ment :
a. Vérifiez la présence de courant à la prise en y
branchant un autre appareil électrique.
b. Vérifiez si la prise n’est pas raccordée con-
jointement à un interrupteur qui servirait à éteindre les
lumières.
c. Vérifiez la propreté des bornes du bloc-piles.
Nettoyez-les au besoin avec un bâtonnet imbibé
d’alcool.
d. Si vous n’arrivez toujours pas à obtenir la charge
satisfaisante, confiez l’outil, le bloc-piles et le
chargeur à votre centre d’entretien Bosch habituel.
Voir les noms et adresses des centres d’entretien
sous la rubrique « Outils électriques» dans les pages
jaunes de l’annuaire de téléphone.
Remarque : L’usage de chargeurs ou de blocs-piles
autres que ceux vendus par Bosch peut annuler la
garantie.
-24-
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 24
Page 25

-25-
Accessoires
Si un cordon de rallonge
s'avère nécessaire, vous
devez utiliser un cordon avec conducteurs de
dimension adéquate pouvant porter le courant
nécessaire à votre outil. Ceci préviendra une chute
excessive de tension, une perte de courant ou une
surchauffe. Les outils mis à la terre doivent utiliser des
cordons de rallonge trifilaires pourvus de fiches à trois
broches ainsi que des prises à trois broches.
REMARQUE : Plus le calibre est petit, plus le fil est gros.
DIMENSIONS DE RALLONGES RECOMMANDÉES
OUTILS 120 VOLTS COURANT ALTERNATIF
AVERTISSEMENT
!
Intensité
nominale
de l’outil
Longueur en pieds
Longueur en mètres
3-6
6-8
8-10
10-12
12-16
18 16 16 14 .75 .75 1.5 2.5
18 16 14 12 .75 1.0 2.5 4.0
18 16 14 12 .75 1.0 2.5 4.0
16 16 14 12 1.0 2.5 4.0 —
14 12 — — — — — —
25 50 100 150 15 30 60 120
Calibre A.W.G.
Calibre en mm
2
* Guide de largeur parallèle standard
** Guide inclinable de luxe
** Butée de profondeur pour feuillures
* Clé à fer de 2,5 mm
* Fers en carbure réversibles (2)
* Raccord d’aspiration
** Tuyau d’aspiration
** Sac à copeaux
(* = équipement de série)
(** = accessoires optionnels)
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 25
Page 26

-26-
Lea y entienda todas las instrucciones. El incumplimiento de todas las instrucciones
indicadas a continuación puede dar lugar a sacudidas eléctricas, incendios y/o lesiones
personales graves.
CONSERVE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES
ADVERTENCIA
!
Normas generales de seguridad
para todas las herramientas accionadas por baterias
Area de trabajo
Mantenga el área de trabajo limpia y bien iluminada.
Las mesas desordenadas y las áreas oscuras invitan a
que se produzcan accidentes.
No utilice herramientas mecánicas en atmósferas
explosivas, tales como las existentes en presencia de
líquidos, gases o polvos inflamables. Las
herramientas mecánicas generan chispas y éstas
pueden dar lugar a la ignición del polvo o los vapores.
Mantenga a las personas que se encuentren
presentes, a los niños y a los visitantes alejados al
utilizar una herramienta mecánica. Las distracciones
pueden hacer que usted pierda el control.
Seguridad eléctrica
No abuse del cordón. Nunca use el cordón para
llevar la herramienta. Mantenga el cordón alejado
del calor, el aceite, los bordes afilados o las piezas
móviles. Cambie los cordones dañados
inmediatamente. Los cordones dañados pueden
causar un incendio.
Una herramienta accionada por baterías que tenga
baterías integradas o un paquete de baterías
separado se debe recargar solamente con el
cargador especificado para la batería. Un cargador
que puede ser adecuado para un tipo de batería puede
crear un peligro de incendio cuando se usa con otra
batería.
Utilice la herramienta accionada por baterías
solamente con el paquete de baterías designado
específicamente. El uso de cualquier otra batería
puede crear un peligro de incendio.
Seguridad personal
Manténgase alerta, fíjese en lo que está haciendo y
use el sentido común cuando utilice una herramienta
mecánica. No use la herramienta cuando esté
cansado o se encuentre bajo la influencia de drogas,
alcohol o medicamentos. Un momento de distracción
al utilizar herramientas mecánicas puede dar lugar a
lesiones personales graves.
Vístase adecuadamente. No se ponga ropa holgada ni
joyas. Sujétese el pelo. Mantenga el pelo, la ropa y
los guantes alejados de las piezas móviles. La ropa
holgada, las joyas o el pelo largo pueden quedar
atrapados en las piezas móviles. Mantenga los mangos
secos, limpios y libres de aceite y grasa.
Evite el arranque accidental. Asegúrese de que el
interruptor esté en la posición fijada o de apagado
antes de introducir el paquete de baterías. Llevar
herramientas con el dedo en el interruptor o introducir
el paquete de baterías en una herramienta con el
interruptor en la posición de encendido invita a que se
produzcan accidentes.
Quite las llaves de ajuste o de tuerca antes de
encender la herramienta. Una llave de ajuste o de
tuerca que se deje puesta en una pieza giratoria de la
herramienta puede ocasionar lesiones personales.
No intente alcanzar demasiado lejos. Mantenga un
apoyo de los pies y un equilibrio adecuados en todo
momento. El apoyo de los pies y el equilibrio
adecuados permiten un mejor control de la herramienta
en situaciones inesperadas.
Utilice equipo de seguridad. Use siempre protección
de los ojos. Se debe utilizar una máscara antipolvo,
zapatos de seguridad antideslizantes, casco o
protección de los oídos según lo requieran las
condiciones.
Utilización y cuidado de las herramientas
Utilice abrazaderas u otro modo práctico de fijar y
soportar la pieza de trabajo a una plataforma estable.
La sujeción de la pieza de trabajo con la mano o contra
el cuerpo resulta inestable y puede ocasionar pérdida de
control.
No fuerce la herramienta. Use la herramienta
correcta para la aplicación que desea. La herramienta
correcta hará el trabajo mejor y con más seguridad a la
capacidad nominal para la que está diseñada.
No utilice esta herramienta si el interruptor no la
enciende o apaga. Una herramienta que no se puede
controlar con el interruptor es peligrosa y se debe
reparar.
Desconecte el paquete de baterías de la
herramienta o ponga el interruptor en la posición
fijada o de apagado antes de hacer cualquier ajuste,
cambiar accesorios o guardar la herramienta.
Dichas medidas preventivas de seguridad reducen el
riesgo de arrancar la herramienta accidentalmente.
Guarde las herramientas que no esté usando fuera
del alcance de los niños y otras personas no
capacitadas. Las herramientas son peligrosas en las
manos de los usuarios no capacitados.
Cuando no se esté utilizando el paquete de baterías,
manténgalo alejado de otros objetos metálicos
como: sujetapapeles, monedas, llaves, clavos,
tornillos u otros objetos metálicos pequeños que
pueden hacer una conexión de un terminal con otro.
El cortocircuito de los terminales de las baterías puede
causar chispas, quemaduras o un incendio.
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 26
Page 27

-27-
Normas de seguridad para cepillos sin cordón
Fije el material que se vaya a acepillar. Nunca lo
sostenga en la mano ni sobre las piernas. Si la
pieza de trabajo es pequeña, debe fijarse
adecuadamente para que las cuchillas del cepillo
mecánico que giran no la levanten durante el
movimiento del cepillo hacia delante. Un soporte
inestable puede hacer que las cuchillas se atasquen,
causando pérdida de control y lesiones.
Arranque siempre el cepillo mecánico antes de que
la cuchilla entre en contacto con la pieza de trabajo
y deje que la cuchilla alcance toda su velocidad.
La herramienta puede vibrar o chirriar si la velocidad
de la cuchilla es demasiado lenta al comienzo del
corte y es posible que cause retroceso.
Compruebe si la pieza de trabajo tiene clavos. Si
hay clavos, quítelos o clávelos hasta que estén bien
por debajo de la superficie acabada que se desea
obtener. Si las cuchillas del cepillo mecánico
golpean objetos como clavos, pueden hacer que la
herramienta experimente retroceso y el resultado
puede ser lesiones personales graves.
Desconecte el paquete de baterías de la
herramienta o ponga el interruptor en la posición
fijada o de apagado antes de hacer cualquier
ensamblaje, ajustes o cambiar accesorios. Dichas
medidas preventivas de seguridad reducen el riesgo
de arrancar la herramienta accidentalmente.
Después de cambiar las cuchillas, gire el cilindro
de las cuchillas (tambor de corte) para asegurarse
de que las cuchillas no estén golpeando ninguna
parte de la carcasa de la cabeza de las cuchillas y
de que los tornillos de fijación de las cuchillas
estén apretados. Las cuchillas que giran podrían
golpear la carcasa de la herramienta y dañar la
herramienta, así como causar posibles lesiones.
Sujete siempre firmemente la herramienta con las
dos manos para tener un control máximo.
Nunca tire del cepillo mecánico hacia atrás sobre la
pieza de trabajo. Podría producirse pérdida de
control.
No ponga los dedos ni ningún objeto en el eyector
de virutas ni recoja las virutas cortadas mientras la
herramienta esté en marcha. El contacto con el
tambor de las cuchillas causará lesiones.
Desconecte el paquete de baterías de la
herramienta si es necesario quitar las virutas. Las
cuchillas están ocultas de la vista y es posible que
usted se corte si toca alguna de ellas.
Nunca deje el cepillo mecánico hasta que la
cuchilla se haya detenido por completo. El contacto
de la superficie con el tambor de las cuchillas cuando
éste se está moviendo por inercia hasta detenerse
puede hacer que el cepillo mecánico se desplace
fuera de control.
Cierto polvo generado por el
lijado, aserrado, amolado y
taladrado mecánicos, y por otras actividades de
construcción, contiene agentes químicos que se sabe
que causan cáncer, defectos de nacimiento u otros
daños sobre la reproducción. Algunos ejemplos de
estos agentes químicos son:
• Plomo de pinturas a base de plomo,
• Sílice cristalina de ladrillos y cemento y otros
productos de mampostería, y
• Arsénico y cromo de madera tratada químicamente.
Su riesgo por causa de estas exposiciones varía,
dependiendo de con cuánta frecuencia realice este tipo
de trabajo. Para reducir su exposición a estos agentes
químicos: trabaje en un área bien ventilada y trabaje con
equipo de seguridad aprobado, como por ejemplo
máscaras antipolvo que estén diseñadas especialmente
para impedir mediante filtración el paso de partículas
microscópicas.
Mantenga las herramientas con cuidado. Conserve
las herramientas de corte afiladas y limpias. Las
herramientas mantenidas adecuadamente, con bordes
de corte afilados, tienen menos probabilidades de
atascarse y son más fáciles de controlar.
Compruebe la desalineación o el atasco de las piezas
móviles, la ruptura de piezas y cualquier otra
situación que pueda afectar el funcionamiento de las
herramientas. Si la herramienta está dañada, haga
que realicen un servicio de ajustes y reparaciones a
la herramienta antes de usarla. Muchos accidentes
son causados por herramientas mantenidas
deficientemente.
Utilice únicamente accesorios que estén
recomendados por el fabricante de su modelo. Los
accesorios que pueden ser adecuados para una
herramienta pueden volverse peligrosos cuando se
utilizan en otra herramienta.
Servicio
El servicio de ajustes y reparaciones de una
herramienta debe ser realizado únicamente por
personal de reparaciones competente. El servicio o
mantenimiento realizado por personal no competente
podría ocasionar un peligro de que se produzcan
lesiones.
Al realizar servicio de ajustes y reparaciones de una
herramienta, utilice únicamente piezas de repuesto
idénticas. Siga las instrucciones que aparecen en la
sección Mantenimiento de este manual. El uso de
piezas no autorizadas o el incumplimiento de las
instrucciones de Mantenimiento puede ocasionar un
peligro de que se produzcan sacudidas eléctricas o
lesiones.
ADVERTENCIA
!
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 27
Page 28

-28-
Batería/cargador
Antes de utilizar el cargador de baterías, lea todas
las instrucciones e indicaciones de precaución que
se encuentran en (1) el cargador de baterías, (2) el
paquete de baterías y (3) el producto que utiliza
baterías.
Utilice solamente el cargador que acompañaba al el
producto o un reemplazo directo según se indica en
el catálogo o en este manual. No sustituirlo por
ningún otro cargador. Utilice únicamente cargadores
aprobados Bosch con su producto. Consulte
Descripción funcional y especificaciones.
No desarme el cargador ni lo haga funcionar si ha
recibido un golpe brusco, se ha caído o se ha
dañado de cualquier modo. Cambie el cordón o los
enchufes dañados inmediatamente. El reensamblaje
incorrecto o los daños pueden ocasionar sacudidas
eléctricas o incendio.
No recargue la batería en un entorno húmedo o
mojado. No exponga el cargador a lluvia ni nieve.
Si la caja de baterías está agrietada o dañada de
algún otro modo, no la introduzca en el cargador.
Se puede producir un cortocircuito de las baterías o un
incendio.
Cargue solamente baterías recargables aprobadas
Bosch. Consulte Descripción funcional y
especificaciones. Otros tipos de baterías pueden
reventar causando lesiones personales y daños.
Cargue el paquete de baterías a temperaturas
superiores a +40 grados F (4 grados C) e inferiores a
+105 grados F (41 grados C). Guarde la herramienta
y el paquete de baterías en lugares donde las
temperaturas no superen 120 grados F (49 grados
C). Esto es importante para evitar daños graves a los
elementos de la batería.
Se puede producir un escape del líquido de las
baterías bajo condiciones extremas de uso o de
temperatura. Evite el contacto con la piel y los ojos.
El líquido de la batería es cáustico y podría causar
quemaduras químicas en los tejidos. Si el líquido
entra en contacto con la piel, lávela rápidamente con
agua y jabón y luego con jugo de limón o vinagre. Si
el líquido entra en contacto con los ojos, enjuáguelos
con agua durante un mínimo de 10 minutos y obtenga
atención médica.
Ponga el cargador sobre superficies planas
ininflamables y alejado de materiales inflamables
cuando recargue el paquete de baterías. El
cargador y el paquete de baterías se calientan durante
el proceso de carga. Las alfombras y otras
superficies termoaislantes bloquean la circulación
adecuada de aire, lo cual puede causar
sobrecalentamiento del cargador y del paquete de
baterías. Si observa humo o que la carcasa se está
derritiendo, desenchufe inmediatamente el cargador y
no utilice el paquete de baterías ni el cargador.
El uso de un accesorio no recomendado ni vendido
por Bosch puede constituir un peligro de incendio,
sacudidas eléctricas o lesiones a las personas.
Cuando las baterías no están en
la herramienta o en el
cargador, manténgalas alejadas de objetos
metálicos. Por ejemplo, para evitar que las terminales
hagan cortocircuito, NO ponga las baterías en una caja
de herramientas o en un bolsillo con clavos, tornillos,
llaves, etc. Se pueden producir un incendio o lesiones.
Para evitar incendios o
lesiones cuando las baterías no
estén en la herramienta o en el cargador, ponga
siempre la tapa protectora en el extremo del paquete
de baterías. La tapa protectora protege contra el
cortocircuitado de los terminales.
NO ARROJE LAS BATERIAS AL FUEGO NI LAS
EXPONGA AL CALOR INTENSO. Pueden explotar.
ADVERTENCIA
!
Cuidado de las baterías
ADVERTENCIA
!
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 28
Page 29

-29-
Eliminación de las baterías
No intente desarmar la batería
ni quitar ninguno de los componentes que sobresalen de las terminales de la
batería. Se pueden producir lesiones o un incendio.
Antes de tirarla, proteja las terminales que están al
descubierto con cinta adhesiva aislante gruesa para
prevenir cortocircuitos.
BATERIAS DE NIQUEL-CADMIO
Si este producto está equipado con una batería de
níquel-cadmio, dicha batería debe recogerse,
reciclarse o eliminarse de manera segura para el
medio ambiente.
“El sello de reciclaje de baterías
RBRC certificado por la EPA que se
encuentra en la batería de níquelcadmio (Ni-Cd) indica que S-B
Power Tool Company está
participando voluntariamente en un
programa de la industria para recoger y reciclar estas
baterías al final de su vida útil, cuando se retiran de
servicio en los Estados Unidos y Canadá. El programa
RBRC proporciona una alternativa conveniente a tirar
las baterías de Ni-Cd usadas a la basura o a la
corriente municipal de aguas residuales, lo cual quizás
sea ilegal en su área.
Tenga la amabilidad de llamar al 1-800-8-BATTERY
para obtener información acerca de las
prohibiciones/restricciones sobre el reciclaje y la
eliminación de baterías de Ni-Cd en su lugar o
devuelva las baterías a un Centro de servicio
Skil/Bosch/Dremel para reciclarlas. La participación de
S-B Power Tool Company en este programa es parte
de nuestro compromiso hacia preservar nuestro
medio ambiente y conservar nuestros recursos
naturales.”
BATERIAS DE NIQUEL-HIDRURO METALICO
Si este producto está equipado con una batería de
níquel-hidruro metálico, dicha batería debe eliminarse
en un curso de agua municipal para residuos sólidos.
ADVERTENCIA
!
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 29
Page 30

-30-
Símbolos
Importante: Es posible que algunos de los símbolos siguientes se usen en su herramienta. Por favor,
estúdielos y aprenda su significado. La interpretación adecuada de estos símbolos le permitirá utilizar la
herramienta mejor y con más seguridad.
Símbolo Nombre Designación/explicación
V Volt Tensión (potencial)
A Ampere Corriente
Hz Hertz Frecuencia (ciclos por segundo)
W Watt Potencia
kg Kilogramo Peso
min Minuto Tiempo
s Segundo Tiempo
Diámetro Tamaño de las brocas taladradoras,
muelas, etc.,
n
0
Velocidad sin carga Velocidad rotacional sin carga
.../min Revoluciones o alternación por minuto Revoluciones, golpes, velocidad de
superficie, órbitas, etc., por minuto
0 Posición "off" (apagado) Velocidad cero, par motor cero...
1, 2, 3, ... Graduaciones del selector Graduaciones de velocidad, par motor o
I, II, III, posición. Un número más alto significa
mayor velocidadselector settings
Selector infinitamente variable con La velocidad aumenta desde la
apagado graduación de 0
Flecha Acción en la dirección de la flecha
Corriente alterna Tipo o una característica de corriente
Corriente continua Tipo o una característica de corriente
Corriente alterna o continua Tipo o una característica de corriente
Construcción de clase II Designa las herramientas de construcción
con aislamiento doble.
Terminal de toma de tierra Terminal de conexión a tierra
Símbolo de advertencia Alerta al usuario sobre mensajes de
advertencia
Sello RBRCTM de Ni-Cd Designa el programa de reciclaje de baterías
de Ni-Cd
0
Este símbolo indica que esta
herramienta está catalogada
por Underwriters
Laboratories.
Este símbolo indica que esta
herramienta está catalogada
por la Canadian Standards
Association.
Este símbolo indica que
Underwriters Laboratories ha
catalogado esta herramienta
indicando que cumple las
normas canadienses.
Este símbolo
indica que esta
herramienta
cumple con la
norma mexicana
oficial (NOM).
Este símbolo indica que esta
herramienta está catalogada por
Underwriters Laboratories y que
Underwriters Laboratories la ha
catalogado según las normas
canadienses.
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 30
Page 31

Desconecte el paquete de baterías de la herramienta o ponga el interruptor en la
posición fijada o de apagado antes de hacer cualquier ensamblaje, ajustes o cambiar
accesorios. Dichas medidas preventivas de seguridad reducen el riesgo de arrancar la herramienta
accidentalmente.
-31-
Descripción funcional y especificaciones
ADVERTENCIA
!
Capacidades máximas
Profundidad de acepillad 0 - 1/16" (0 - 1,6 mm)
Profundidad de rebajado 0 - 5/16" (0 - 8 mm)
Anchura de corte 3-1/4" (82 mm)
Cepillo sin cordón
POMO DE
MARIPOSA
TOPE DE
PROFUNDIDAD
DE REBAJADO
(OPCIONAL)
POMO DE AJUSTE
DE PROFUNDIDAD
ORIFICIO DE SALIDA
DE VIRUTAS
ORIFICIO DE SALIDA DE VIRUTAS
ESCALA DE
PROFUNDIDAD
PALANCA DE SELECCIÓN
DE ORIFICIO
INTERRUPTOR GATILLO
BOTÓN DE FIJACIÓN
EN APAGADO
ZAPATA
DELANTERA
TOPE-GUÍA
DE PIVOTE
POMO
REDONDO
SOPORTE
DE GUÍA
POMO DE
MARIPOSA
POMO DE
MARIPOSA
TOPE-GUÍA
TORNILLO
CUBIERTA DE LA CORREA DE
TRANSMISIÓN
RANURA
EN V DE
ACHAFLANAR
SOPORTE
DE GUÍA
ESCALA
DE
ANCHURA
TOPE-GUÍA
ANGULAR DE
LUJO
(OPCIONAL)
POMO DE
MARIPOSA
TOPE-GUÍA DE
ANCHURA
PARALELO
ESTÁNDAR
FIG. 1
LAS OPCIONES DE
PROFUNDIDAD DE CORTE SON
APROXIMADAMENTE
1/16", 3/64", 1 mm (•),
1/32", 1/64" y 1/128" (•)
LENGÜETAS DE
LIBERACIÓN DE LAS
BATERÍAS
PAQUETE DE BATERIAS
TORNILLO
El cargador BC006 requiere alimentación de 12 V CC
NOTA: UTILICE ÚNICAMENTE LOS CARGADORES
INDICADOS ANTERIORMENTE
Número de Tensión Velocidad Tiempo Número de Tensión Paquete
modelo nominal sin carga de carga cargador nominal de baterias
53514 14.4 V n
0
13,000/min 1 hr. BC001-6 & BC016 120 V 60 Hz BAT040 y BAT038
53518 18 V n0 13,000/min 1 hr. BC003, 4, 6, & BC016 120 V 60 Hz BAT026 y BAT025
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 31
Page 32

-32-
Ensamblaje
EXTRACCIÓN DE VIRUTAS
El cepillo mecánico viene con dos orificios de salida
de virutas, que pueden utilizarse con una bolsa para
virutas o con una aspiradora de taller y un conector
de aspiradora (Fig. 2) para mantener más limpio el
entorno de trabajo. La bolsa para virutas o el
conector de aspiradora pueden acoplarse a cualquiera
de los extremos del orificio de salida.
Al mover la palanca selectora de orificio hasta la
posición 1 (hacia la parte delantera de la
herramienta), las virutas se descargan hacia la
izquierda, mientras que al moverla hasta la posición 2
(hacia la parte trasera de la herramienta), las virutas
se descargan hacia la derecha (Fig. 1).
CUCHILLAS DEL CEPILLO MECÁNICO
Las cuchillas del cepillo
mecánico están afiladas y son
frágiles, y deben manejarse con cuidado para evitar
que el usuario sufra lesiones o que las cuchillas se
dañen.
Las cuchillas del cepillo mecánico tienen dos filos y
pueden invertirse cuando uno de los filos se desafile
o astille.
No intente afilar ni utilizar cuchillas usadas reafiladas
de ninguna clase. Utilice únicamente cuchillas
diseñadas para uso con este modelo, porque otras
cuchillas causarán vibración y disminución del
rendimiento, y es posible que no se sujeten
firmemente en el portacuchillas.
LLAVE PARA CUCHILLAS Y AREA PARA GUARDAR
La herramienta está equipada con una llave para
cuchillas que se encuentra convenientemente ubicada
en la base del mango, donde siempre está a mano y
no es probable que se pierda ni que se deje fuera de
su sitio (fig. 3).
INVERSIÓN O CAMBIO DE LAS CUCHILLAS
Para invertir o cambiar la cuchilla, afloje los tornillos
de fijación utilizando la llave para cuchillas. Con los
tornillos aflojados, deslice longitudinalmente el
cuchilla hasta sacarlo del tambor de corte, teniendo
cuidado de mantener los dedos alejados de los filos
afilados de la cuchilla (Fig. 4).
Puede utilizarse un pedazo de madera para este
propósito. Si la cuchilla tiene goma y es difícil
quitarla, puede limpiar la cuchilla con alcoholes
minerales, diluyente de laca o alcohol.
Limpie todas las superficies antes de instalar la
cuchilla nueva, ya que esto garantizará un ajuste
preciso de la cuchilla y un rendimiento adecuado de la
herramienta.
ALINEACIÓN DE LAS CUCHILLAS
Para asegurarse de lograr un corte uniforme, es
importante que la cuchilla se ajuste de manera que
esté alineada con el borde exterior de las zapatas
delantera y trasera. Esta alineación puede realizarse
de la manera siguiente: coloque una regla recta o un
pedazo de madera a lo largo de la superficie exterior
de la zapata delantera y de la zapata trasera, y luego
deslice la cuchilla del cepillo mecánico hasta que
justo haga contacto con la regla recta o el pedazo de
madera (Fig. 5).
Asegúrese de que la cuchilla se asiente correctamente
en la ranura del portacuchilla que está en el tambor de
corte.
Seguidamente, podrá apretar los tornillos de fijación
que sujetan la cuchilla y el cepillo mecánico estará
listo para utilizarse.
ADVERTENCIA
!
FIG. 2
FIG. 4
FIG. 3
FIG. 5
BOLSA PARA
VIRUTAS
(OPCIONAL)
ORIFICIOS
DE SALIDA
CONECTOR DE
ASPIRADORA
CUCHILLA
TORNILLO DE
FIJACIÓN
TAMBOR
DE CORTE
TORNILLO DE
FIJACIÓN
LLAVE PARA
CUCHILLAS
LLAVE DE 2,5
MM PARA
CUCHILLAS
TAMBOR
DE CORTE
REGLA
RECTA
LAVE PARA CUCHILLAS Y AREA
PARA GUARDAR
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 32
Page 33

-33-
Instrucciones de funcionamiento
INTERRUPTOR GATILLO DE ENCENDIDO Y APAGADO
Sostenga la herramienta con
las dos manos mientras la
arranca, ya que el par del motor puede hacer que la
herramienta se tuerza.
Para encender la herramienta, oprima el botón de
"Fijación en apagado" y apriete el interruptor gatillo.
Para apagar la herramienta, suelte el interruptor
gatillo, que está accionado por resorte, y regresará
automáticamente a la posición de apagado.
Para prolongar la duración del interruptor, no lo
ponga en las posiciones de encendido y apagado
mientras la herramienta y el tambor se estén
sosteniendo contra una pieza de trabajo.
FRENO
Cuando se suelta el gatillo, éste activa el freno eléctrico
para detener la hoja rápidamente. Este dispositivo es
especialmente útil cuando se hacen cortes repetitivos.
ACCIÓN DE ACEPILLADO
Compruebe si la pieza de trabajo está sujeta
firmemente en posición correcta sobre la superficie
de trabajo y, ubicándose de manera cómoda,
sostenga firmemente el cepillo mecánico con las dos
manos. Con el cepillo mecánico completamente
ajustado, coloque la zapata delantera sobre la pieza de
trabajo (asegúrese de que el tambor de corte no esté
en contacto con la pieza de trabajo) y arranque el
cepillo mecánico de la manera que se describió
anteriormente. Ejerciendo presión sobre la zapata
delantera y con el tope-guía ubicado contra el lado de
la pieza de trabajo (para controlar la anchura o el
ángulo), haga avanzar firmemente el cepillo mecánico
hasta que la zapata trasera se acople completamente
en la pieza de trabajo. Seguidamente, transfiera
presión gradualmente hacia la zapata trasera y siga
acepillando hasta el final del corte. Haga avanzar el
cepillo mecánico a una velocidad uniforme y
razonable, que no someta a un esfuerzo excesivo ni al
motor ni a las cuchillas (no tire del cepillo mecánico
hacia atrás sobre la superficie que ya haya cortado).
Utilice cortes progresivos hasta que esté cerca de la
profundidad deseada y entonces cambie el ajuste a un
corte más ligero para que con la pasada final se
obtenga un buen acabado de la superficie.
El motor puede detenerse si se
utiliza incorrectamente o se
sobrecarga. Reduzca la presión (la velocidad de
avance) o la profundidad de corte para evitar posibles
daños a la herramienta si el motor funciona con
dificultad.
ADVERTENCIA
!
PRECAUCION
!
AJUSTE DE LA PROFUNDIDAD DE CORTE
La profundidad de corte adecuada debe determinarse
de acuerdo con la dureza, gomosidad o contenido de
humedad del material que se vaya a cortar, así como
con la velocidad de avance, y es principalmente una
cuestión de experiencia. Comience con un corte
ligero y aumente el ajuste de profundidad si el cepillo
mecánico se mueve libremente por la pieza de trabajo
sin carga excesiva en el motor. No cambie la
profundidad de corte mientras esté acepillando.
La profundidad de corte se determina por la diferencia
de altura entre la zapata delantera ajustable y la zapata
trasera fija del cepillo mecánico. A medida que la
zapata delantera se ajusta, se retrae y deja al
descubierto la cuchilla, que puede entonces quitar la
cantidad deseada de material de la pieza de trabajo.
La profundidad de corte está graduada de 0 a 1/16 de
pulgada y el "0" indica que la cuchilla está totalmente
retraída.
Ajuste de la profundidad de corte: Gire el pomo de
ajuste de profundidad hasta que el indicador se
acople con el retén que indica la profundidad de corte
deseada en la escala de profundidad (Fig. 1).
El cepillo mecánico puede ajustarse para cortar a
cualquier profundidad desde 0 hasta 1/16 de pulgada.
TOPE-GUÍA DE ANCHURA PARALELO ESTÁNDAR
El tope-guía de anchura puede utilizarse para cortar
diversas anchuras deseadas (Fig. 1).
Instalación del tope-guía: Coloque el pomo de
mariposa a través del agujero apropiado del soporte
de guía y enrósquelo en la carcasa. Apriete
firmemente el pomo de mariposa.
Ajuste de la anchura de corte: Afloje el pomo de
mariposa y deslice el tope-guía a lo largo del soporte
de guía hasta la posición deseada. Apriete
firmemente el pomo de mariposa. Asegúrese de que
la arandela plana (suministrada) esté ajustada entre la
parte inferior del tope-guía y el pomo de mariposa, o
es posible que el tope-guía resbale.
TOPE-GUÍA ANGULAR DE LUJO
El tope-guía angular de lujo opcional (Fig. 6) puede
utilizarse para cortar diversas anchuras deseadas, con
la capacidad adicional de guiar el cepillo mecánico en
82 mm
max
8 mm
max
FIG. 6
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 33
Page 34

cualquier ángulo hasta 45 grados para permitir el
achaflanado de bordes (Fig. 7).
Instalación del tope-guía angular: Coloque el pomo
de mariposa a través del agujero apropiado del
soporte de guía y enrósquelo en la carcasa. Apriete
firmemente el pomo de mariposa (Fig. 1).
Ajuste de la anchura de corte: Afloje el pomo de
mariposa y, utilizando la escala de anchura, deslice el
tope-guía a lo largo del soporte de guía hasta la
posición deseada. Apriete firmemente el pomo de
mariposa (Fig. 1).
Ajuste del ángulo de corte: Afloje los pomos redondos
y pivote el tope-guía hasta la posición deseada. Apriete
firmemente los pomos redondos (Fig. 1).
Observe que la zapata delantera ajustable contiene
una ranura en V de achaflanar, que seguirá la esquina
de una pieza de trabajo para facilitar el manejo cuando
se utilice el tope-guía angular de lujo/de anchura
(Fig. 7).
TOPE DE PROFUNDIDAD DE REBAJADO
El accesorio de tope de profundidad de rebajado
opcional (Fig. 1) permite al usuario ajustar cualquier
profundidad de rebajado desde 0 hasta 5/16 de
pulgada. Para obtener resultados óptimos, es
importante que la cuchilla esté alineada
adecuadamente (consulte "ALINEACIÓN DE LAS
CUCHILLAS"). La anchura de rebajado se controla
mediante el tope-guía de anchura. La anchura
máxima de corte es de 3-1/4" y la profundidad final se
logra realizando cortes repetitivos hasta que la guía de
profundidad de rebajado entra en contacto con la
pieza de trabajo. La profundidad máxima de rebajado
es de 5/16".
Ajuste de la profundidad de rebajado: Afloje el pomo
de mariposa y, utilizando la escala de profundidad que
está en el tope de profundidad de rebajado, ajuste la
profundidad de rebajado deseada. Apriete firmemente
el pomo de mariposa.
-34-
CORREA DE TRANSMISIÓN
La correa de transmisión es una pieza que requiere
mantenimiento normal y debe inspeccionarse
periódicamente para comprobar si está desgastada.
Si la correa de transmisión muestra señales de estar
secándose, agrietándose o rasgándose, debe
cambiarse. Si la correa de transmisión no describe su
trayectoria adecuadamente o si se sale de las poleas,
debe cambiarse.
Instalación de una correa de transmisión nueva:
Afloje los tornillos y quita la cubierta de la correa de
transmisión (Fig. 8). Corte y quite la correa de
transmisión dañada. Antes de instalar la correa de
transmisión nueva, limpie a fondo las dos poleas.
Coloque primero la correa de transmisión nueva en la
polea motriz y luego haga girar dicha polea en el
sentido de las agujas del reloj a la vez que empuja la
correa sobre la polea impulsada. Vuelva a instalar la
cubierta de la correa de transmisión y apriete
firmemente los tornillos (Fig. 9).
FIG. 7
FIG. 9
POLEA
MOTRIZ
POLEA
IMPULSADA
CORREA DE
TRANSMISIÓN
CUBIERTA DE
LA CORREA DE
TRANSMISIÓN
TORNILLO
FIG. 8
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 34
Page 35

-35-
Saque el paquete de baterías de la herramienta
presionando sobre ambos lados de las lengüetas de
liberación de las baterías y tire hacia abajo. Antes de
introducir el paquete de baterías, quite la tapa
protectora de dicho paquete de baterías. Para
introducir la batería, alinee la batería e introduzca el
paquete de baterías en la herramienta hasta que quede
fijo en su posición. No lo fuerce.
LIBERACION E INSERCION DEL PAQUETE DE BATERIAS
Enchufe el cordón del cargador en un tomacorriente
eléctrico estándar. Antes de introducir el paquete de
baterías, quite la tapa protectora y luego introduzca el
paquete de baterías en el cargador (Fig. 10).
El indicador verde del cargador comenzará a
"PARPADEAR". Esto indica que la batería está
recibiendo una carga rápida. La carga rápida se
detendrá automáticamente cuando el paquete de
baterías esté completamente cargado.
Cuando la luz indicadora deje de "PARPADEAR" (y
pase a ser una luz verde constante), la carga rápida se
habrá completado.
Cuando comience el proceso de carga del paquete de
baterías, una luz verde constante también podría
significar que el paquete de baterías está demasiado
caliente o demasiado frío.
El propósito de la luz es indicar que el paquete de
baterías se está cargando rápidamente. No indica el
punto exacto de carga completa. La luz dejará de
parpadear en menos mas tiempo hora si el paquete
de baterías no estaba completamente descargado.
Cuando el paquete de baterías esté completamente
cargado, desenchufe el cargador (a menos que vaya a
cargar otro paquete de baterías) y deslice el paquete
de baterías de vuelta en el interior del mango de la
herramienta.
Para evitar incendios o lesiones cuando las baterías no
estén en la herramienta o en el cargador, ponga
siempre la tapa protectora en el extremo del paquete de
baterías. La tapa protectora protege contra el
cortocircuitado de los terminales.
CARGA DEL PAQUETE DE BATERIAS (CARGADOR DE 1 HORA)
LUZ
INDICADORA
CARGADOR
PAQUETE DE
BATERIAS
TAPA PROTECTORA
NOTAS IMPORTANTES PARA CARGAR
1. El paquete de baterías acepta únicamente alrededor
del 80 por ciento de su capacidad máxima en los
primeros ciclos de carga. Sin embargo, después de
los primeros ciclos de carga, la batería se cargará
hasta su capacidad máxima.
2. El cargador fue diseñado para cargar la batería
rápidamente sólo cuando la temperatura de la batería
está entre 4°C (40°F) y 41°C (105°F).
3. Un descenso considerable en el tiempo de
funcionamiento por carga puede significar que el
paquete de baterías se está acercando al final de su
vida y que debe ser sustituido.
4. Si espera que haya largos períodos (es decir, un
mes o más) en los que no se use la herramienta, lo
mejor es hacerla funcionar hasta que esté
completamente descargada antes de guardar el
FIG. 10
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 35
Page 36

Servicio
NO HAY PIEZAS EN EL INTERIOR
QUE PUEDAN SER AJUSTADAS
O REPARADAS POR EL USUARIO. El mantenimiento
preventivo realizado por personal no autorizado pude
dar lugar a la colocación incorrecta de cables y
componentes internos que podría constituir un peligro
serio. Recomendamos que todo el servicio de las
herramientas sea realizado en un Centro de servicio de
fábrica Bosch o en una Estación de servicio Bosch
autorizada. TECNICOS DE REPARACIONES:
Desconecten la herramienta y/o el cargador de la fuente
de energía antes de realizar servicio de ajustes y
reparaciones.
BATERIAS
Esté alerta a los paquetes de baterías que estén
aproximándose al final de su vida útil. Los paquetes
de baterías duran normalmente de 500 a 1000 cargas.
Si observa una disminución del rendimiento de la
herramienta o un tiempo de funcionamiento
significativamente más corto entre cargas, entonces ha
llegado el momento de cambiar el paquete de baterías.
Si no se hace esto, el resultado puede ser que la
herramienta funcione incorrectamente o que el cargador
se dañe.
Cuando la batería se almacene a largo plazo, debe
estar en estado de descarga. Los paquetes de baterías
duran más y se recargan mejor cuando se almacenan
descargados. Recuerde recargar completamente los
paquetes de baterías antes de utilizarlos después de un
almacenamiento prolongado.
LUBRICACION DE LAS HERRAMIENTAS
Su herramienta Bosch ha sido lubricada adecuadamente
y está lista para la utilización. Se recomienda que las
herramientas con engranajes se vuelvan a engrasar
cada año con un lubricante especial para engranajes.
MOTORES “CORRIENTE DIRECTA”
El motor de la herramienta ha sido diseñado para
muchas horas de servicio fiable. Para mantener un
rendimiento óptimo del motor, recomendamos que éste
sea examinado cada seis meses. Sólo se debe usar un
motor de repuesto Bosch genuino diseñado
especialmente para la herramienta.
Limpieza
Para evitar accidentes,
desconecte siempre la
herramienta y/o el cargador de la fuente de energía
antes de la limpieza. La herramienta se puede limpiar
más eficazmente con aire comprimido seco. Use gafas
de seguridad siempre que limpie herramientas con
aire comprimido.
Las aberturas de ventilación y las palancas de
interruptor deben mantenerse limpias y libres de
materias extrañas. No intente limpiar introduciendo
objetos puntiagudos a través de las aberturas.
Ciertos agentes de limpieza y
disolventes dañan las piezas de
plástico. Algunos de estos son: gasolina, tetracloruro de
carbono, disolventes de limpieza clorados, amoníaco y
detergentes domésticos que contienen amoníaco.
Mantenimiento
ADVERTENCIA
!
ADVERTENCIA
!
PRECAUCION
!
-36-
paquete de baterías. Después de un largo período de
almacenamiento, la capacidad después de la primera
recarga será más baja. La capacidad normal se
restaurará en dos o tres ciclos de carga/descarga.
Recuerde desenchufar el cargador durante el período
de almacenamiento.
5. Si la batería no carga adecuadamente:
a. Compruebe que hay tensión en el tomacorriente
enchufando algún otro dispositivo eléctrico.
b. Compruebe si el tomacorriente está conectado a
un interruptor de luz que corta el suministro de
energía cuando se apagan las luces.
c. Compruebe si hay suciedad en las terminales
del paquete de baterías. Límpielas con un pedazo de
algodón y alcohol si es necesario.
d. Si usted sigue sin obtener una carga adecuada,
lleve o envíe la herramienta, el paquete de baterías y
el cargador al Centro de servicio Bosch local. Busque
bajo “Herramientas eléctricas” en las páginas
amarillas para obtener nombres y direcciones.
Nota: La utilización de cargadores o paquetes de
baterías no vendidos por Bosch puede invalidar la
garantía.
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 36
Page 37

-37-
Accesorios
Si es necesario un cordón de
extensión, se debe usar un
cordón con conductores de tamaño adecuado que sea
capaz de transportar la corriente necesaria para la
herramienta. Esto evitará caídas de tensión excesivas,
pérdida de potencia o recalentamiento. Las herramientas
conectadas a tierra deben usar cordones de extensión
de 3 hilos que tengan enchufes de 3 terminales y
receptáculos para 3 terminales.
NOTA: Cuanto más pequeño es el número de calibre,
más grueso es el cordón.
TAMAÑOS RECOMENDADOS DE CORDONES DE EXTENSION
HERRAMIENTAS DE 120 V CORRIENTE ALTERNA
ADVERTENCIA
!
Capacidad
nominal en
amperios de la
herramienta
Tamaño del cordón en A.W.G.
Tamaños del cable en mm
2
3-6
6-8
8-10
10-12
12-16
18 16 16 14 .75 .75 1.5 2.5
18 16 14 12 .75 1.0 2.5 4.0
18 16 14 12 .75 1.0 2.5 4.0
16 16 14 12 1.0 2.5 4.0 —
14 12 — — — — — —
25 50 100 150 15 30 60 120
Longitud del cordón en pies
Longitud del cordón en metros
* Tope-guía de anchura estándar
**Tope-guía angular de lujo
**Tope de profundidad de rebajado
* Llave de 2.5 mm para cuchillas
* Hojas reversibles de carburo (2)
* Conector de aspiradora
**Manguera de aspiración
**Bolsa para virutas
(* = equipo estándar)
(** = accesorios opcionales)
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 37
Page 38

-38-
Notes:
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 38
Page 39

-39-
Remarques :
Notas:
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 39
Page 40

2 610 917 139 6/02 Printed in U.S.A
LIMITED WARRANTY OF BOSCH PORTABLE AND BENCHTOP POWER TOOLS
S-B Power Tool Company (“Seller”) warrants to the original purchaser only, that all BOSCH portable and benchtop power tools will be free from
defects in material or workmanship for a period of one year from date of purchase. SELLER’S SOLE OBLIGATION AND YOUR EXCLUSIVE REMEDY
under this Limited Warranty and, to the extent permitted by law, any warranty or condition implied by law, shall be the repair or replacement of
parts, without charge, which are defective in material or workmanship and which have not been misused, carelessly handled, or misrepaired by
persons other than Seller or Authorized Service Station. To make a claim under this Limited Warranty, you must return the complete portable or
benchtop power tool product, transportation prepaid, to any BOSCH Factory Service Center or Authorized Service Station. For Authorized BOSCH
Power Tool Service Stations, please refer to your phone directory.
THIS LIMITED WARRANTY DOES NOT APPLY TO ACCESSORY ITEMS SUCH AS CIRCULAR SAW BLADES, DRILL BITS, ROUTER BITS, JIGSAW
BLADES, SANDING BELTS, GRINDING WHEELS AND OTHER RELATED ITEMS.
ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES SHALL BE LIMITED IN DURATION TO ONE YEAR FROM DATE OF PURCHASE. SOME STATES IN THE U.S., SOME
CANADIAN PROVINCES DO NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS ON HOW LONG AN IMPLIED WARRANTY LASTS, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT
APPLY TO YOU.
IN NO EVENT SHALL SELLER BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LIABILITY
FOR LOSS OF PROFITS) ARISING FROM THE SALE OR USE OF THIS PRODUCT. SOME STATES IN THE U.S. AND SOME CANADIAN PROVINCES
DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION OR
EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
THIS LIMITED WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS, AND YOU MAY ALSO HAVE OTHER RIGHTS WHICH VARY FROM STATE TO
STATE IN THE U.S., PROVINCE TO PROVINCE IN CANADA AND FROM COUNTRY TO COUNTRY.
THIS LIMITED WARRANTY APPLIES ONLY TO PORTABLE AND BENCHTOP ELECTRIC TOOLS SOLD WITHIN THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA,
CANADA AND THE COMMONWEALTH OF PUERTO RICO. FOR WARRANTY COVERAGE WITHIN OTHER COUNTRIES, CONTACT YOUR LOCAL
BOSCH DEALER OR IMPORTER.
GARANTIE LIMITÉE DES OUTILS ÉLECTRIQUES PORTATIFS ET D'ÉTABLI BOSCH
S-B Power Tool Company (le « vendeur ») garantit à l'acheteur initial seulement que tous les outils électriques portatifs et d'établi BOSCH seront
exempts de vices de matériaux ou d'exécution pendant une période d'un an depuis la date d'achat. LA SEULE OBLIGATION DU VENDEUR ET LE
SEUL RECOURS DE L’ACHETEUR sous la présente garantie limitée, et en autant que la loi le permette sous toute garantie ou condition implicite qui
en découlerait, sera l’obligation de remplacer ou réparer gratuitement les pièces défectueuses matériellement ou comme fabrication, pourvu que
lesdites défectuosités ne soient pas attribuables à un usage abusif ou à quelque réparation bricolée par quelqu’un d’autre que le vendeur ou le
personnel d’une station-service agréée. Pour présenter une réclamation en vertu de cette garantie limitée, vous devez renvoyer l'outil électrique
portatif ou d'établi complet, port payé, à tout centre de service agréé ou centre de service usine. Veuillez consulter votre annuaire téléphonique
pour les adresses.
LA PRÉSENTE GARANTIE NE S’APPLIQUE PAS AUX ACCESSOIRES TELS QUE LAMES DE SCIES CIRCULAIRES, MÈCHES DE PERCEUSES, FERS
DE TOUPIES, LAMES DE SCIES SAUTEUSES, COURROIES DE PONÇAGE, MEULES ET AUTRES ARTICLES DU GENRE.
TOUTE GARANTIE IMPLICITE SERA LIMITÉE COMME DURÉE À UN AN À COMPTER DE LA DATE D’ACHAT. CERTAINS ÉTATS AMÉRICAINS,
CERTAINES PROVINCES CANADIENNES N’ADMETTANT PAS LE PRINCIPE DE LA LIMITATION DE LA DURÉE DES GARANTIES IMPLICITES, IL
EST POSSIBLE QUE LES LIMITATIONS CI-DESSUS NE S’APPLIQUENT PAS À VOTRE CAS.
EN AUCUN CAS LE VENDEUR NE SAURAIT ÊTRE TENU POUR RESPONSABLE DES INCIDENTS OU DOMMAGES INDIRECTS (INCLUANT, MAIS NE
SE LIMITANT PAS AUX PERTES DE PROFITS) CONSÉCUTIFS À LA VENTE OU L’USAGE DE CE PRODUIT. CERTAINS ÉTATS AMÉRICAINS ET
CERTAINES PROVINCES CANADIENNES N’ADMETTANT PAS LE PRINCIPE DE LA LIMITATION NI L’EXCLUSION DES DOMMAGES INDIRECTS ET
CONSÉQUENTIELS, IL EST POSSIBLE QUE LES LIMITATIONS OU EXCLUSIONS CI-DESSUS NE S’APPLIQUENT PAS À VOTRE CAS.
LA PRÉSENTE GARANTIE VOUS ACCORDE DES DROITS BIEN DÉTERMINÉS, Y COMPRIS POSSIBLEMENT CERTAINS DROITS VARIABLES DANS
LES DIFFÉRENTS ÉTATS AMÉRICAINS, PROVINCES CANADIENNES.
CETTE GARANTIE LIMITÉE NE S'APPLIQUE QU'AUX OUTILS ÉLECTRIQUES PORTATIFS ET D'ÉTABLI VENDUS AUX ÉTATS-UNIS D'AMÉRIQUE,
AU CANADA ET AU COMMONWEALTH DE PORTO RICO.POUR COUVERTURE DE GARANTIE DANS LES AUTRES PAYS, CONTACTEZ VOTRE
IMPORTATEUR OU REVENDEUR BOSCH LOCAL.
© S-B POWER TOOL COMPANY 4300 W. PETERSON AVENUE CHICAGO, IL 60646 USA
EXPORTADO POR: S.B. POWER TOOL COMPANY, CHICAGO, IL 60646, E.U.A.
IMPORTADO POR: ROBERT BOSCH S.A. DE C.V., CALLE ROBERT BOSCH NO. 405, ZONA
INDUSTRIAL TOLUCA, MÉXICO. C.P. 50070 TEL. (72) 792300
GARANTIA LIMITADA PARA HERRAMIENTAS MECANICAS PORTATILES Y PARA TABLERO DE BANCO BOSCH
S-B Power Tool Company ("el Vendedor") garantiza, únicamente al comprador original, que todas las herramientas mecánicas portátiles y para
tablero de banco BOSCH estarán libres de defectos de material o de fabricación durante un período de un año a partir de la fecha de compra. LA
UNICA OBLIGACION DEL VENDEDOR Y EL RECURSO EXCLUSIVO QUE USTED TIENE bajo esta Garantía Limitada y, hasta donde la ley lo permita,
bajo cualquier garantía o condición implícita por ley, consistirá en la reparación o sustitución sin costo de las piezas que presenten defectos de
material o de fabricación y que no hayan sido utilizadas incorrectamente, manejadas descuidadamente o reparadas incorrectamente por personas
que no sean el Vendedor o una Estación de servicio autorizada. Para efectuar una reclamación bajo esta Garantía Limitada, usted debe devolver el
producto, que consiste en la herramienta mecánica portátil o para tablero de banco completa, con el transporte pagado, a cualquier Centro de
servicio de fábrica o Estación de servicio autorizada. Para Estaciones de servicio autorizadas de herramientas mecánicas BOSCH, por favor,
consulte el directorio telefónico.
ESTA GARANTIA LIMITADA NO SE APLICA A ARTICULOS ACCESORIOS TALES COMO HOJAS PARA SIERRAS CIRCULARES, BROCAS PARA
TALADROS, BROCAS PARA FRESADORAS, HOJAS PARA SIERRAS DE VAIVEN, CORREAS PARA LIJAR, RUEDAS DE AMOLAR Y OTROS
ARTICULOS RELACIONADOS.
TODAS LAS GARANTIAS IMPLICITAS TENDRAN UNA DURACION LIMITADA A UN AÑO A PARTIR DE LA FECHA DE COMPRA. ALGUNOS
ESTADOS DE LOS EE.UU., ALGUNAS PROVINCIAS CANADIENSES NO PERMITEN LIMITACIONES EN CUANTO A LA DURACION DE UNA
GARANTIA IMPLICITA, POR LO QUE ES POSIBLE QUE LA LIMITACION ANTERIOR NO SEA APLICABLE EN EL CASO DE USTED.
EL VENDEDOR NO SERA RESPONSABLE EN NINGUN CASO DE NINGUN DAÑO INCIDENTAL O EMERGENTE (INCLUYENDO PERO NO LIMITADO A
RESPONSABILIDAD POR PERDIDA DE BENEFICIOS) QUE SE PRODUZCA COMO CONSECUENCIA DE LA VENTA O UTILIZACION DE ESTE
PRODUCTO. ALGUNOS ESTADOS DE LOS EE.UU. Y ALGUNAS PROVINCIAS CANADIENSES NO PERMITEN LA EXCLUSION O LIMITACION DE
LOS DAÑOS INCIDENTALES O EMERGENTES, POR LO QUE ES POSIBLE QUE LA LIMITACION O EXCLUSION ANTERIOR NO SEA APLICABLE EN
EL CASO DE USTED.
ESTA GARANTIA LIMITADA LE CONFIERE A USTED DERECHOS LEGALES ESPECIFICOS Y ES POSIBLE QUE USTED TAMBIEN TENGA OTROS
DERECHOS QUE VARIAN DE ESTADO A ESTADO EN LOS EE.UU., DE PROVINCIA A PROVINCIA EN CANADA.
ESTA GARANTIA LIMITADA SE APLICA SOLAMENTE A HERRAMIENTAS ELECTRICAS PORTATILES Y PARA TABLERO DE BANCO VENDIDAS EN
LOS ESTADOS UNIDOS DE AMERICA, CANADA Y EL ESTADO LIBRE ASOCIADO DE PUERTO RICO. PARA COBERTURA DE GARANTIA EN OTROS
PAISES, PONGASE EN CONTACTO CON SU DISTRIBUIDOR O IMPORTADOR LOCAL DE BOSCH.
BM 2610917139 6/02 7/10/02 10:50 AM Page 40
 Loading...
Loading...