Page 1

INSTRUCTION
10MHz DDS SWEEP/FUNCTION GENERATOR
MANUAL
Model 4017B
0
Page 2

Table of Contents
1. Introduction to the Model 4017B 2
1.1. Description ...................................................................................................................................................................................2
1.2.
Feature Summary
2.
Front panel
2.1. Brief description. Using the controls. ..........................................................................................................................................2
2.2.
.........................................................................................................................................................................................2
Buttons and knobs. LED functionality description.
3. Operating the Model 4017B........................................................................................................................................... 6
3.1. Parameter’s setting....................................................................................................................................................................6
3.1.1. Frequency setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode). ..........................................................................................................6
3.1.2. Level setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode)...................................................................................................................8
3.1.3. Offset setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode)..................................................................................................................8
3.1.4. Duty cycle setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode). .........................................................................................................9
3.1.5. CMOS level setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode). ......................................................................................................9
3.1.6. Sweep time setting (only for INTERNAL SWEEP mode). ................................................................................................9
3.1.7. Sweep width setting (only for INTERNAL SWEEP mode). ............................................................................................10
3.1.8.
3.2. Mode description......................................................................................................................................................................10
3.2.1 EXTERNAL VCG (External Voltage Control Generator...........................................................................................10
3.2.2 INTERNAL SWEEP........................................................................................................................................................12
3.2.3 FREQCOUNTER (Frequency Counter mode).............................................................................................................13
3.2.4 Saving the default loaded mode at power-up ................................................................................................................14
3.2.5 Setting parameters examples...........................................................................................................................................14
3.3 Remote operation.....................................................................................................................................................................25
3.3.1 Brief command description ................................................................................................................................................25
3.3.2 Commands description .......................................................................................................................................................25
3.3.3 Remote program examples..............................................................................................................................................34
Gate setting (only for FREQCOUNTER mode).
3.2.1.1 Selecting EXTERNAL VCG mode.............................................................................................................................12
3.2.1.2 Selecting output waveform..........................................................................................................................................12
3.2.1.3 Selecting the frequency ...............................................................................................................................................12
3.2.1.4 Selecting the level........................................................................................................................................................13
3.2.1.5 Selecting the offset ......................................................................................................................................................13
3.2.1.6 Selecting the duty cycle...............................................................................................................................................13
3.2.1.7 Selecting output TTL/CMOS level .............................................................................................................................13 .
3.2.2.1 Selecting INTERNAL SWEEP mode .........................................................................................................................12
3.2.2.2 Selecting output waveform..........................................................................................................................................12
3.2.2.3 Selecting the frequency ...............................................................................................................................................12
3.2.2.4 Selecting the level........................................................................................................................................................13
3.2.2.5 Selecting the offset ......................................................................................................................................................13
3.2.2.6 Selecting the duty cycle...............................................................................................................................................13
3.2.2.7 Selecting output TTL/CMOS level .............................................................................................................................13
3.2.2.8 Selecting sweep width .................................................................................................................................................13
3.2.2.9 Selecting sweep time ...................................................................................................................................................13
3.2.2.10
3.2.3.1 Selecting FREQCOUNTER mode ..............................................................................................................................14
3.2.3.2 Selecting gate period ...................................................................................................................................................14
3.2.5.1 Example of setting parameters in EXTERNAL VCG mode ......................................................................................14
3.2.5.2 Example of setting parameters in INTERNAL SWEEP mode ..................................................................................16
3.2.5.3 Example of setting gate period in FREQCOUNTER mode .......................................................................................19
3.2.5.4 Example of saving the default mode at power-up ......................................................................................................19
3.2.5.5 Waveform examples ....................................................................................................................................................20
3.3.2.1 General rules................................................................................................................................................................25
3.3.2.2 Commands description ................................................................................................................................................26
3.3.3.1 Example of setting parameters in EXTERNAL VCG mode using REMOTE control mode ....................................34
3.3.3.2 Example of setting parameters in INTERNAL SWEEP mode using REMOTE control mode ................................35
3.3.3.3
Selecting type of sweeping ....................................................................................................................... 13
Example of setting parameters in FREQCOUNTER mode using REMOTE control mode
4 Specifications ............................................................................................................................................................... 37
5 Service Information.................................................................................................................................................... 38
........................................................................................................................................................ 2
........................................................................................................ 3
................................................................................................. 10
................................. 36
1
Page 3

1. Introduction to the 4017B.
1.1 Description
The B&K Precision Model 4017B Sweep/Function Generator is the newest 40XX family member. The 4017B enhances the
performance achieved by its successful predecessor, BK Precision Model 4017A Sweep/Function Generator. These performances are
achieved by using direct digital waveform synthesis (DDS) techniques for generating high accuracy and precision frequencies. A high
performance Digital Signal Processor (DSP) controls every aspect of the DDS system, and is used for precise generation and processing
of waveforms. The 4017B has a vast number of applications in both analog and digital electronics, in the engineering, manufacturing,
servicing, educational and hobbyist fields. This versatile signal source is capable of generating waveform (such as sine, triangle and
square), pulse generation (through variable symmetry) and frequency sweep. Additionally, the instrument provides a built-in frequency
counter.
The core of the function generator is a DSP, which is used to generate precision sine, square or triangle waveforms over 0.01Hz to
10MHz range. This encompasses subaudible, audio, ultrasonic and RF applications. The symmetry of the waveforms can be changed
between 0% to 100% in 1% step, converting the instrument to a pulse generator capable of generating rectangular waves or pulses, ramp
or sawtooth waves and slued sine waves. An external voltage may be used to control operating frequency that can be changed using a
ratio between 1:1 and 1:100. Frequency sweep can be adjusted by changing the rate and the time sweep, and also the manner in which
frequency is changed, linear or logarithmic.
The B&K Precision Model 4017B has 3 jacks: 2 for output and 1 input. The OUTPUT jack is the main signal output. The TTL/CMOS
jack is a TTL/CMOS compatible square wave output. The VCG/SWEEP jack is an input used for controlling the operating frequency
and input to frequency counter.
The 4017B is capable of supplying an output level of 20.0V
the OUTPUT jack. The output impedance is 50 ohms; therefore the 50 ohm loaded output level is 10.0V
capability of ±5.0 V
worked on. The offset level can be adjusted with a resolution of 1mV.
The 4017B is capable of generating a TTL/CMOS compatible square wave on TTL/CMOS jack. The output level can be up to 14.0
V
(unloaded).
pp
On the VCG/SWEEP input jack, DC levels can be applied between 0V to 10.0V in order to change the output operating frequency with
a ratio between 1:1 and 1:100. This jack is also used as a frequency counter input, for frequencies between 5Hz and 100MHz.
The front panel of the Model 4017B includes LCD display, buttons, “intelligent” knobs and an LED in order to operate the unit quick
and easy. The “intelligent” knobs are one of the main features of this new model, which reduces the number of controls needed for
changing the value of a parameter. The LCD display is a large 2-line 16 columns back lighted display.
The unit also features an EIA-RS232 connector on the rear of the unit. This permits the user to remote control the 4017B using ASCII
characters. No special hardware or protocols are needed; any dumb terminal or computer serial port can be used. The baud rate is fixed
to 9600 BPS.
. The output level can be adjusted with a resolution of 1mV and 10mV, depending on the level range being
pp
with an offset voltage of ± 10.0V
pp
(unloaded) on the main signal output,
pp
, with an offset voltage
pp
1.2 Feature Summary
2. Front panel.
2.1 Brief description.
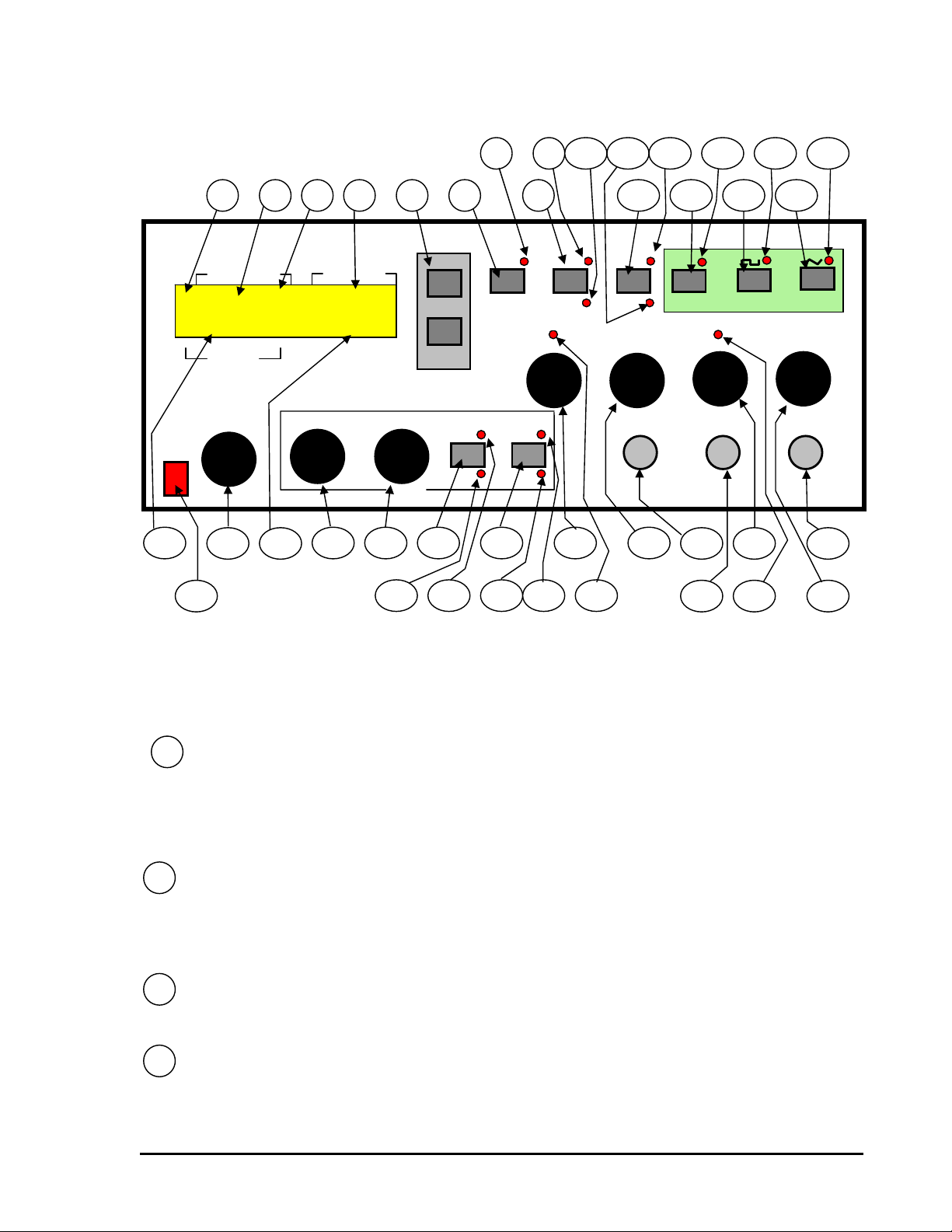
Located on the Front Panel is the LCD display, controls, power switch, connection jacks and LED (see the figure 2 for details).
The LCD display is a backlit, 2-row 16-columns LCD display.
There are two kinds of controls: buttons and knobs.
All buttons are implemented as 1-parameter single function control, except the range buttons that have a second function. Pressing the
range buttons (UP and DOWN buttons) twice at the same time will save the current working state as the default loaded state at powerup. Pressing any other buttons at the same time will have no effect upon the current working state. There are 2 kinds of buttons: one
category has no LED’s, the other category has LED’s. Pressing one of the buttons from the first category will change the values on the
LCD display.
The knobs are implemented as 3-parameter single function control, with “intelligent” control. The parameters defining an knob are:
value, rotation’s direction, and rotation’s speed. The value identifies the parameter being changed. The rotation’s direction, clockwise or
counter clockwise, determines whether the value of the parameter is increment or decrement respectively, by an amount of 1. The speed
of rotation sets the position in the parameter’s digits of the digit being modified. The “intelligent knob” implementation allows a very
simple and intuitive way of changing parameter values and reducing the number of controls used.
2
Page 4
®
p
Ω
2.2 Buttons and knobs. LED functional description.
7
1
4 3 2
POWER
FREQUENCY
22.222KHz 100k
1.01 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
FREQUENCY
UP
DOWN
ut
Range
WIDTHTIME
SWEEP
INT
EXT
-20dB
LIN
LOG
20
23
21
24 25 26
29
22
27 28
30 31
waveform frequency or the frequency measured sampling COUNTER IN input. The second line is used to display other parameters of
the generated waveform, depending on the mode being worked: level, offset introduced, TTL/CMOS level, duty cycle when in
EXTERNAL VCG mode, and additional parameters, time and width sweep when in INTERNAL SWEEP mode. In
FREQCOUNTER mode on the second line, the gate used in sampling COUNTER IN input is displayed.
depending on the working mode. If in EXTERNAL VCG or INTERNAL SWEEP, the value represents the generated waveform
frequency on the main output source, OUTPUT jack, and it is a 5-digit resolution value. If in FREQCOUNTER mode, the value
represents the frequency of the signal sampled on COUNTER IN input, and can be a 9-digit resolution value.
Frequency unit value. This field will display the multiplying factor used for displaying frequency value. It changes when the
user modifies the range using “UP” and “DOWN” buttons.
Frequency range. This field will display the range in which the frequency value displayed in frequency field can be changed.
It changes when user modifies the range using “UP” and “DOWN” buttons.
LCD Display. This is a 2 line X 16 columns LCD-large type display. The first line will always display the generated
1
2
Frequency field. This field is used for displaying parameter frequency. The value displayed has a different meaning
3
4
9
85 6
COUNTER
VCG
SWEEP
32
10
33
12 13
11
CMOS
TTL
COUNTER IN
34
14
TTL CMOS VCG SWEEP
35
36
15
16
WAVEFORM
37
38
17 19
18
OUTPUT LEVELDUTY CYCLE CMOS LEVEL DC OFFSET
OUTPUT
50
39
40
3
Page 5

5
Range buttons. Pressing those buttons will change the frequency range. Pressing the UP and DOWN buttons means that
frequency range will change up and down, respectively. If reaching the upper or lower range by pressing the UP or DOWN buttons, it
will pass to the lower range or upper range, respectively. Changing the range will affect the frequency field, frequency unit value and
frequency range.
By pressing these two buttons together twice, the current mode and parameters will be saved as the default power-up working state.
-20 dB button. Pressing this button will engage/disengage 20dB attenuation in the signal on OUTPUT jack. Pressing this
6
button will change the level field. A light at - 20dB LED indicates engaging the attenuator. No light at –20dB LED indicates
disengaging the attenuator.
7
– 20 dB LED. LED associated with the – 20 dB button has a solid light when the attenuator is active, and no light when
attenuator is disabled.
8
COUNTER/VCG SWEEP button. Pressing this button will engage/disengage FREQCOUNTER mode. Engaging
FREQCOUNTER mode will change the content of LCD display and will also be indicated by a lighted COUNTER LED only.
Disengaging FREQCOUNTER mode will change the content of the LCD display and will also be indicated by a lighted VCG
SWEEP LED only.
9
COUNTER LED. LED is associated with COUNTER/VCG SWEEP button that lights when FREQCOUNTER mode is
active.
10
VCG SWEEP LED. LED is associated with COUNTER/VCG SWEEP button and lights when EXTERNAL VCG or
INTERNAL SWEEP mode is active, and it is associated with a lighted EXT LED or INT LED respectively.
11
TTL/CMOS button. Pressing this button will enable/disable the use of CMOS LEVEL knob. If enabled, the CMOS LED is
lighted and the output level on TTL/CMOS output jack can be changed. If disabled, the TTL LED is lighted and there will be a fixed
level on TTL/CMOS output jack.
12
TTL LED. LED is associated with TTL/CMOS button, and lights when there is an output of a fixed TTL style signal on
TTL/CMOS output jack.
13
CMOS LED. LED is associated with TTL/CMOS button and lights when there is an output of a variable CMOS style signal
on TTL/CMOS output jack.
14
SINE WAVE SELECT button. Pressing this button will enable outputting of a sine style waveform on main output,
OUTPUT jack, and will be indicated by a lighted SINE WAVE LED.
15
SINE WAVE SELECT LED. LED associated with
style signal on OUTPUT jack.
16
SQUARE WAVE SELECT button. Pressing this button will enable outputting of a square style waveform on main output,
OUTPUT jack, and it will be indicated by a lighted SQUARE WAVE SELECT LED.
17
SQUARE WAVE SELECT LED. LED associated with SQUARE WAVE SELECT button, it lights when unit outputs a
square wave style signal on OUTPUT jack.
SINE WAVE SELECT button, it lights when unit outputs a sine wave
4
Page 6

18
TRIANGLE WAVE SELECT button. Pressing this button will enable outputting of a triangle style waveform on main
output, OUTPUT jack, and it will be indicated by a lighted TRIANGLE WAVE SELECT LED.
19
TRIANGLE WAVE SELECT LED. LED associated with TRIANGLE WAVE SELECT button, it lights when unit
outputs a triangle wave style signal on OUTPUT jack.
20
OTHER PARAMETERS field. This field is used for showing other parameters’ values of the output signal on the OUTPUT
jack such as level, offset, duty cycle, sweep time, sweep width or the CMOS output level on TTL/CMOS jack. As long as the value of
a parameter during a 7-second period is not changed, the unit will automatically show the output level on the OUTPUT jack.
21
OTHER PARAMETERS identifiers. This field is associated with OTHER PARAMETERS field and will show a message
relevant to the nature of the parameter value shown in OTHER PARAMETERS field. As long as the value of a parameter during a 7-
second period is not changed, the unit will automatically display the message identifying the output level parameter.
22
POWER switch. Turns power on and off.
23
FREQUENCY knob. This knob controls the changing of the frequency within the current frequency range. The value is
displayed in frequency field. The changes are applied upon the start frequency in EXTERNAL VCG and INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
(See chapter x for a detailed explanation).
This knob has no meaning in FREQCOUNTER mode.
24
SWEEP TIME knob. This knob controls the changing of the time value set for sweeping the range between start frequency
and stop frequency. This knob has no meaning except INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
25
SWEEP WIDTH knob. This knob controls the changing of the ratio used for calculation of the width of frequency range,
swept in INTERNAL SWEEP mode. This knob has no meaning except in INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
26
SWEEP INT/EXT button. Pressing this button will change the working mode between EXTERNAL VCG and
INTERNAL SWEEP. The new mode will be indicated by the lighting of the corresponding LED, INT LED or EXT LED.
27
EXT LED. LED is associated to SWEEP INT/EXT button and lights when EXTERNAL VCG mode is active.
28
INT LED. LED is associated to SWEEP INT/EXT button and lights when INTERNAL SWEEP mode is active.
29
SWEEP LIN/LOG button. Pressing this button will change the way the frequency range in INTERNAL SWEEP mode will
sweep between linear mode and logarithm mode. The lighting of the corresponding LED, LIN LED or LOG LED will indicate the
working sweep mode. Button is valid only in INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
30
LOG LED. LED is associated to SWEEP LIN/LOG button and lights when logarithm sweep mode is engaged.
31
LIN LED. LED is associated to SWEEP LIN/LOG button and lights when linear sweep mode is engaged.
32
DUTY CYCLE knob . This knob controls the changing of the duty cycle of the output waveform on OUTPUT jack. It has
meaning only for EXTERNAL VCG and INTERNAL SWEEP.
5
Page 7

33
DUTY CYCLE LED. LED is associated with DUTY CYCLE knob and lights when the waveform is asymmetric.
34
CMOS LEVEL knob. This knob controls the changing of the CMOS level on the output of TTL/CMOS jack. This knob has
meaning only for EXTERNAL VCG and INTERNAL SWEEP. It is only active if TTL/CMOS button enables it. The CMOS LED
must be lit.
35
VCG SWEEP/COUNTER IN jack. Input jack is used to control the output frequency in EXTERNAL VCG mode or as
frequency count input in FREQCOUNTER mode.
36
TTL/CMOS jack. Output jack is used for supplying a fixed TTL style signal or variable CMOS style signal, depending of
the TTL/CMOS button, whose frequency is the same as the signal’s frequency on the main output, OUTPUT jack.
37
DC OFFSET knob. This knob controls the offset level added to the signal outputted on the OUTPUT jack. It has an LED
associated, DC OFFSET LED, which lights when the offset added is not zero. This knob has meaning only in EXTERNAL VCG and
INTERNAL SWEEP.
38
DC OFFSET LED. LED associated with DC OFFSET knob, lights when the value of offset added to the signal on the
OUTPUT jack is not zero.
39
OUTPUT LEVEL knob. This knob controls the output level on main output, OUTPUT jack. This knob has meaning only in
EXTERNAL VCG and INTERNAL SWEEP.
40
OUTPUT jack. The main output jack, used to supply the desired waveform, defined by frequency, level, offset, duty cycle
for EXTENAL VCG mode and moreover time and width sweep for INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
3. Operating the Model 4017B.
There are 2 modes of controlling the unit and 3 modes of operating the unit. One of the control modes uses the front panel; the other
mode is by remote, using the RS232 interface. Each mode of control excludes the other. When you are using the front panel you cannot
control the unit by remote. Engaging remote mode, using special command, deactivates the use of front panel controls. Disengaging the
remote control by using a special command enables the use of front panel button.
The 3 modes of operating are EXTERNAL VCG (external voltage control generator), INTERNAL SWEEP and FREQCOUNTER
(frequency counter).
Section 3.1. - Mode description will describe the setting of operating modes using front panel controls. Section 3.2.-Remote operation,
will have a complete description of the remote control mode.
3.1.
Parameter’s setting
3.1.1. Frequency setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode).
The f
requency setting depends on the mode being worked. On EXTERNAL VCG mode, output frequency depends on the value set by
turning the FREQUENCY knob and the DC value applied to VCG/SWEEP input jack. On INTERNAL SWEEP mode, since
frequency is sweeping a range, the value set by turning the FREQUENCY knob represents the start frequency of the range being swept.
For all modes (except FREQCOUNTER mode), frequency is displayed on the first line, using a 5-digit field and a decimal point,
whose position depends on the selected range. The unit is displayed after the frequency value field. The frequency range used is always
displayed on the right of the first line.
6
Page 8

There are 5 frequency ranges available, which allows the user to set desired frequency between 0.00Hz and 10.000MHz. Pressing UP
and DOWN buttons will change the range. Within every range the frequency can be changed with a 5-digit resolution using
FREQUENCY knob.
The table below shows the frequency limits for every range, measuring unit and how it displays the frequency range:
Range Lower Value Upper Value Unit Displayed frequency range
1 0.00 999.99 Hz 1k
2 1.0000 9.9999 KHz 10k
3 10.000 99.999 KHz 100k
4 100.00 999.99 KHz 1M
5 1.0000 10.000 MHz 10M
On the TTL/CMOS output jack there is a CMOS or TTL style signal, depending on the selection of TTL/CMOS button, with the
same frequency as the signal outputted on OUTPUT jack (see section 3.1.z. for details).
Table 1: Frequency ranges
Frequency setting in EXTERNAL VCG mode.
Whether or not a DC level is applied on the VCG/SWEEP input jack, turning the FREQUENCY knob will force the unit to display the
frequency value outputted on the LCD display if 0 volts is applied on VCG/SWEEP input jack (but only on the period that the knob is
being turned). To have certain results, 0 volts must be applied on the VCG/SWEEP input jack.
Use UP and DOWN buttons to select the appropriate range then turn the FREQUENCY knob till you reach the desired frequency (see
Table1 for range’s details).
Applying a DC value between 0 V and +10V will cause a frequency decrease, on a ratio between 1:1 and 1:100. Applying 0 V DC value
will have no effect on the output frequency but applying a + 10.0V will decrease the output frequency 100 times.
For certain output frequencies, apply fixed DC levels on VCG/SWEEP jack.
Varying the positive DC level on VCG/SWEEP jack will cause the output frequency to sweep. The output frequency will follow the
changes in DC level.
ATTENTION: If the DC level applied on VCG/SWEEP jack causes the output frequency to decrease under the range limit, then
output frequency will not be limited to the lowest frequency allowed in that range. It will be displayed using the
current range displaying rules.
INTERNAL SWEEP mode frequency setting.
The value displayed on the frequency value field on the LCD display represents the instant output frequency and is updated on the LCD
display every 0.1s.
Use UP and DOWN buttons to select the appropriate range of the sweep start frequency. The FREQUENCY knob is used to select the
sweep start frequency within a range (see Table1 for range’s details).
The sweep is always done from the start frequency down to stop frequency. The start frequency is always greater then the stop
frequency. The stop frequency can reach a maximum of 1:100 of start frequency (see subchapter 3.1.x for learning how to set the stop
frequency). The unit reaches the stop frequency after a time, which can be set between 0.01s and 30.00s, with 0.01s resolution (see
subchapter 3.1.y for learning how to set the time sweep).
Turning the FREQUENCY knob will force the unit to display the sweep start frequency. Each time the sweep start frequency is
modified, either by pressing the UP or DOWN button or turning the FREQUENCY knob, the sweep will be reinitialized and the unit
will start outputting from the start frequency again.
INTERNAL SWEEP mode frequency setting.
7
Page 9
The value displayed on the frequency value field on the LCD display represents the instant output frequency and is updated on the LCD
display every 0.1s.
Use the UP and DOWN buttons to select the appropriate range of the sweep start frequency. The FREQUENCY knob is used to select
the sweep start frequency within a range (see Table1 for range’s details).
The sweep is always done from the start frequency down to stop frequency, thus start frequency is always greater then the stop
frequency. The stop frequency can reach a maximum of 1:100 of start frequency (see subchapter 3.1.x for learning how to set the stop
frequency). The unit reaches the stop frequency after a time, which can be set between 0.01s and 30.00s, with 0.01s resolution (see
subchapter 3.1.y for learning how to set the time sweep).
Turning the FREQUENCY knob will force unit to display the sweep start frequency. Each time the sweep start frequency is modified,
either by pressing the UP or DOWN button or turning the FREQUENCY knob, the sweep will reinitialized and unit will start
outputting again from the start frequency.
ATTENTION:
instant frequencies will be displayed using the current range displaying rules.
If stop frequency is under the current lower range limit, the frequency sweep will not stop at the range limit; the
3.1.2. Level setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode).
This section describes the setting of the signal level at the main output jack, OUTPUT jack.
Level can be set between 10mV
engaging/disengaging the –20dB attenuate on the signal path (see Table2 for details). The –20dB LED associated with the button will
light when the –20dB attenuate is engaged. Turning the OUTPUT LEVEL knob will change the level value within the current range.
and 10.0V
p-p
(on 50Ω load), using 2 ranges. Pressing –20dB button will change the level range by
p-p
Range Lowest value Highest value Unit Resolution -20dB LED
1 10 1000 MV 1 Lighted
2 1.01 10.00 V 0.01 No light
Level is displayed on the second line of the LCD display, using a 4-digit value field, followed by the unit. The decimal point is used
only for the upper range. On the right of the second line, the word “Output” will be displayed to identify that the level parameter has
changed. Since the second line is used for displaying other parameters when they are modified, the unit will display the output level
again automatically 7 seconds after the last parameter modification,
Note: The level displayed on the LCD is considered a LOADED value which is the level that will appear across a 50Ω load connected
to the OUTPUT jack. If you are connecting the output to a high impedance load, the output voltage will be twice what is
entered.
Table2: Level ranges
3.1.3. Offset setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode).
This section describes the setting of the DC level added to the signal at the main output, OUTPUT jack.
Offset can be set between – 5.000 V and + 5.000 V (on 50Ω load), by turning the DC OFFSET knob and using 0.001V resolution (see
Table 3). The DC Offset LED associated to DC OFFSET knob will be lighted when the DC level added to the signal is not zero.
Offset is displayed on the second line of the LCD display using a sign digit and a 4-digit value field, followed by the measuring unit. On
the right of the second line the word “Offset will be displayed” to identify that the offset parameter has changed. Automatically, 7
seconds after the last change of the offset value, the unit will display the output level.
Note:
Range Lowest value Highest value Unit Resolution
1 - 5.000 + 5.000 V 0.001
1. The offset voltage specified is a 50Ω LOADED value. This is the voltage that will appear across a 50Ω load
connected to the OUTPUT jack. If the output is being connected to a high impedance load, the output voltage will
be twice what is entered.
2. Care must be taken when specifying an output offset voltage and level such that the output does not clip. The loaded
output cannot swing higher than + 5.000 V or lower than – 5.000 V. Therefore:
Table 3: Offset range
8
Page 10
3.1.4. Duty cycle setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode).
This section describes the duty cycle setting of the signal outputted at the main output, OUTPUT jack.
Duty cycle can be set between 0% - 100%, by turning the DUTY CYCLE knob, using 1% resolution (see Table 4). The DUTY
CYCLE LED associated to DUTY CYCLE knob will be lighted when set duty cycle differs 50%, thus the signal on main output is
asymmetric.
Duty cycle is displayed on the second line of the LCD display, using a 3-digit value field, followed by the measuring unit. On the right
of the second line, the words “Duty Cycle” will be displayed to identify that the duty cycle parameter is shown. Automatically, 7
seconds after the last change of the duty cycle value, the unit will display the output level.
3.1.5. CMOS level setting (except FREQCOUNTER mode).
This section describes the level setting of the TTL/CMOS style signal outputted at the TTL/CMOS output jack.
Output level at the TTL/CMOS jack can be fixed or adjustable, depending on the TTL/CMOS button. The button enables/disables the
use of CMOS LEVEL knob.
If CMOS LEVEL knob is disabled, it will output a fixed level TTL style signal at 4.5V (unloaded). The TTL LED will be lit. The fixed
TTL level is displayed on the second line of the LCD display using a 2-digit value field followed by the measuring unit. The words
“TTL OUT” will be displayed on the right of the second line to identify that the TTL level is shown. The unit will display the output
level automatically 7 seconds after the last turning of CMOS LEVEL knob,
If CMOS LEVEL knob is enabled, the CMOS output level can be set between 4.0V and 14.0V (unloaded) by turning it using 0.1V
resolution (see Table 5). The CMOS LED will be lighted. The CMOS level is displayed on the second line of the LCD display using a
3-digit value field followed by the measuring unit. the words “CMOS OUT” will be displayed on the right of the second line to identify
that the CMOS level is shown. The unit will automatically display the output level 7 seconds after the last turning of CMOS LEVEL
knob.
Signal
Pressing this button will enable/disable the use of CMOS LEVEL knob. If enabled, the CMOS LED is lighted and the output level on
TTL/CMOS output jack can be changed. If disabled, the TTL LED is lighted and there is a fixed level on TTL/CMOS output jack.
| offset voltage | + ½ * V
Range Lowest value Highest value Unit Resolution
1 0 100 % 1
< 5.0 V
p-p
Table 4: Duty cycle range
Lowest value Highest value Unit Resolution LED lighted
TTL 4.5 4.5 V - TTL LED
CMOS 4.0 14.0 V 0.1 CMOS LED
Table 5: CMOS level range
3.1.6. Sweep time setting (only for INTERNAL SWEEP mode).
This section describes the sweep time setting of the signal outputted on OUTPUT jack when INTERNAL SWEEP mode is active
(INT LED and LIN/LOG LED are lighted).
Sweep time parameter represents the time needed by the unit to perform a frequency sweep between two frequencies, a start frequency
and a stop frequency. Sweep time can be set between 0.01 s and 30.00 s by turning the SWEEP TIME knob using a 0.01s resolution
(see Table 6).
Range Lowest value Highest value Unit Resolution
1 0.01 30.00 s 0.01
9
Page 11

Sweep time parameter is displayed on the second line of the LCD display using a 4-digit value field and a decimal point, followed by
the measuring unit. The words “Sweep Time” will be displayed on the right of the second line to identify that the sweep time parameter
is shown. The unit will automatically display the output level 7 seconds after the last change of the sweep time value.
Table 6: Sweep time range
3.1.7. Sweep width setting (only for INTERNAL SWEEP mode).
This section describes the sweep width setting of the signal outputted on the OUTPUT jack when INTERNAL SWEEP mode is active
(INT LED and LIN/LOG LED are lighted).
Frequency sweep is performed by changing the output frequency within a range. The start frequency is always greater than the stop
frequency. The start frequency setting is performed by turning the FREQUENCY knob. The stop frequency represents a fraction of the
start frequency; the fraction set by turning the SWEEP WIDTH knob. The sweep width value is not directly obtained by turning a
knob; we must calculate it using the formula:
where “value_SWEEP_WIDTH_knob” represents the value set by turning the SWEEP WIDTH knob.
The fraction of the start frequency can be set between 1 and 100 by turning SWEEP WIDTH knob, using 1-unit resolution (see Table
7).
Value Stop frequency Sweep width Resolution Observation
1 Start frequency 0 Lowest value
100 (Start frequency)/100 0.99*(start frequency)
Sweep width parameter is displayed on the second line of the LCD display using a 3-digit value field and a decimal point followed by
the measuring unit. The words “Sweep Width” will be displayed on the right of the second line to identify that the sweep width
parameter is shown. The unit will automatically display the output level 7 seconds after the last change of the sweep width value.
sweep_width = start_frequency * [1 – 1/(value_SWEEP_WIDTH_knob)] [Hz]
1
Table 7:
sweep
width calculation
Highest Value
3.1.8. Gate setting (only for FREQCOUNTER mode).
This section describes the gate period time setting used for measuring the signal frequency applied on COUNTER IN jack.
By pressing the range buttons, UP and DOWN, we can switch gate period time. There are 4 available period times for the gate: 0.01 s,
0.1 s, 1 s, and 10 s.
Gate period time is displayed on the second line of the LCD display. The mode identifier is displayed first, then the word “Counter”,
followed by the value of the gate period time.
3.2. Mode description
3.2.1. EXTERNAL VCG (External Voltage Control Generator).
This mode is used for generating an output waveform whose output frequency depends on the value set using the range buttons, the
FREQUENCY knob, and the external positive DC level applied on VCG SWEEP/COUNTER IN jack. The positive DC value applied
on VCG SWEEP/COUNTER IN jack will cause the output frequency to decrease proportionally, with a ratio between 1:1 and 1:100
(for DC value between 0.0 V and +10.0 V, respectively).
3.2.1.1. Selecting EXTERNAL VCG mode.
EXT LED lighting indicates active EXTERNAL VCG mode.
Otherwise there are 2 modes of selecting EXTERNAL VCG mode using front panel buttons depending on the current working mode
and the current value of SWEEP INT/EXT button.
10
Page 12

If in the INTERNAL SWEEP mode (INT LED lights), pressing the SWEEP INT/EXT button will engage the EXTERNAL VCG
mode. By engaging this mode, the EXT LED lights, and INT LED stops lighting.
If in the FREQCOUNTER mode (COUNTER LED lights), pressing the COUNTER/VCG SWEEP button will engage the mode
selected by the SWEEP INT/EXT button. If the button activates the INTERNAL SWEEP, the case will be the same as described in
the previous paragraph otherwise the button will activate EXTERNAL VCG mode.
3.2.1.2. Selecting output waveform.
Pressing one of the “WAVEFORM” buttons: SINE WAVE SELECT, SQUARE WAVE SELECT or TRIANGLE WAVE
SELECT, will engage one of the desired waveform: sine, square or triangle respectively. The current selected type of waveform will
have their corresponding LED lighted.
The shape of the waveform can be changed by modifying the duty cycle parameter (see example from section 3.2.5.4, where there are
displayed waveforms, with different duty cycle parameters).
3.2.1.3. Selecting the frequ en cy.
The output frequency can be set on the OUTPUT jack between 0.00Hz and 10.000MHz. See section 3.1.1 for details regarding setting
of the frequency value. This will also set the output frequency of the TTL/CMOS style signal outputted on TTL/CMOS jack.
To set certain frequency values it is preferable that the VCG/SWEEP input jack is disconnected from any source signal before pressing
the range buttons or turning the FREQUENCY knob. This way the VCG/SWEEP input jack does not affect the setting of the current
output frequency.
After setting the frequency using front panel controls, the selected output frequency can be modified by applying positive DC levels on
the VCG/SWEEP input jack. The DC levels must be within [0V, 10.0V] range, causing the output frequency to decrease with a ratio of
the original value with the ratio varying between 1:1 and 1:100, respectively.
ATTENTION: Appl
Applying certain positive DC levels on VCG/SWEEP jack will decrease the output frequency; the resulting fixed output frequency
represents a fraction of the original output frequency (see example 1).
Changing the DC level in a ramp style will cause a frequency sweep on the main signal output, the OUTPUT jack (see example from
section 3.2.5.1).
3.2.1.4. Selecting the level.
ying in excess DC levels above +10.0 V on VCG SWEEP input jack can damage the input.
The signal’s output level on OUTPUT jack can be set using the OUTPUT LEVEL knob between 10mV
regardless of the waveform type. See section 3.1.2 for details regarding setting of the level value (see example from section 3.2.5.1).
and 10.0V
p-p
(on 50Ω load),
p-p
The –20dB LED will be lighted if the –20dB attenuation is engaged on the main signal output path.
3.2.1.5. Selecting the offset .
The DC level added to the output signal on OUTPUT jack can be set using the DC OFFSET knob between – 5.000V and + 5.000V (on
50ohm load), regardless of the waveform type. See section 3.1.3 for details regarding setting of the offset value (see example from
section 3.2.5.1).
The DC OFFSET LED lights if the offset value is not 0.
3.2.1.6. Selecting the dut y cycle.
The duty cycle of the output signal on the OUTPUT jack can be set using the DUTY CYCLE knob, between 0% and 100%, regardless
of the waveform type. See section 3.1.4 for details regarding the setting of the offset value (see also examples 1, 2 and 3 on section
3.2.1.8).
11
Page 13

Attention:
The DUTY CYCLE LED lights when output signal is asymmetric.
See section 3.2.5.5 for waveform examples.
The square wave has the true meaning of duty cycle. By turning the DUTY CYCLE knob, the symmetry of the waveform
will change for the sine wave and triangle wave. For sine wave, a distorted wave shape will be obtained and for the
triangle wave, a ramp wave will be obtained.
3.2.1.7. Selecting output TTL/CMOS level.
The TTL/CMOS signal level can be changed using the TTL/CMOS button and CMOS LEVEL knob.
If CMOS output style is enabled, the output level can be set between + 4.0V and +14.0V, unloaded.
See section 3.1.5 for details regarding setting of the CMOS level (see also examples 1 and 2 on section 3.2.1.8).
3.2.2. INTERNAL SWEEP
This mode is used for outputting a signal on the OUTPUT jack that sweeps a frequency range. The output frequency does not depend
on any value applied on the input jack, VCG SWEEP/COUNTER IN.
3.2.2.1. Selecting INTERNAL SWEEP mode .
INT LED lighting indicates active INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
There are 2 modes of selecting INTERNAL SWEEP mode using the front panel buttons depending on the current working mode and
the current value of SWEEP INT/EXT button.
In EXTERNAL VCG mode (EXT LED lights), pressing the SWEEP INT/EXT button will engage the INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
By engaging this mode, the INT LED lights and EXT LED stops lighting.
In FREQCOUNTER mode (COUNTER LED lights), pressing COUNTER/VCG SWEEP button will engage the mode selected by
SWEEP INT/EXT button. If the button activates EXTERNAL VCG, the case is the same as described in the previous paragraph,
otherwise the button will activate the INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
3.2.2.2. Selecting output waveform.
Pressing one of the “WAVEFORM” buttons: SINE WAVE, SELECT, SQUARE WAVE SELECT or TRIANGLE WAVE
SELECT, will engage one of the desired waveform: sine, square or triangle respectively. The current selected type of waveform will
have their corresponding LED lighted.
The shape of the waveform can be changed by modifying the duty cycle parameter (see section 3.2.5.4, where there are displayed
waveforms for different duty cycle parameters).
3.2.2.3. Selecting the frequ en cy.
The sweep start frequency can be set directly on the OUTPUT jack using the range buttons and the FREQUENCY knob. Sweep start
frequency can be set between 0.00Hz and 10.000MHz (see section 3.1.1 for details regarding the setting of the frequency value).
The sweep stop frequency cannot be set directly. The SWEEP WIDTH knob must be turned in order to modify the sweep stop
frequency (see sections 3.1.7 and 3.2.1.9 for details).
Modifying any sweep parameter will restart the sweep with the new loaded parameters from the start frequency. Turning the
FREQUENCY knob will always display the sweep start frequency on LCD display (see section 3.2.5.2 for example of setting sweep
start frequency).
12
Page 14

3.2.2.4. Selecting the level.
The signal’s output level can be set on the OUTPUT jack, using the OUTPUT LEVEL rotary knob, between 10mV
50 Ω load), regardless of the waveform type. See section 3.1.2 for details regarding the setting of the level value (see example from
section 3.2.5.2).
The –20dB LED will be lighted if the –20dB attenuation is engaged on the main signal output path.
and 10.0Vpp (on
pp
3.2.2.5. Selecting the offset .
The DC level added to the output signal on OUTPUT jack can be set by using the DC OFFSET rotary knob between – 5.000V and +
5.000V (on 50 Ω load), regardless of the waveform type. See section 3.1.3 for details regarding the setting of the offset value (see
example from section 3.2.5.2).
The DC OFFSET LED lights if the offset value is not 0.
3.2.2.6. Selecting the dut y cycle.
The duty cycle of the output signal on the OUTPUT jack can be set by using the DUTY CYCLE rotary knob between 0% and 100%,
regardless of the waveform type. See section 3.1.4 for details regarding setting of the offset value (see example from section 3.2.5.2).
Attention
The DUTY CYCLE LED lights when output signal is asymmetric.
See section 3.2.5.5 for waveform examples.
:
The true meaning of duty cycle applies only to the square wave. By turning the DUTY CYCLE knob, the symmetry
of the waveform will be changed for the sine wave and triangle wave. The sine wave will cause distorted wave
shapes and the triangle will cause ramp waves.
3.2.2.7 Selecting output TTL/CMOS level.
You can set the level of the signal outputted on TTL/CMOS jack using the TTL/CMOS button and CMOS LEVEL rotary knob. This
signal’s frequency is the same as the signal’s frequency outputted on OUTPUT jack.
If CMOS output style is enabled, the output level can be set between + 4.0V and +14.0V (unloaded).
See section 3.1.5 for details regarding setting of the CMOS level (see example from section 3.2.5.2).
3.2.2.8 Selecting sweep width
The width of the frequency range sweep can be set by changing the value of a ratio. This ratio represents the ratio applied to sweep start
frequency in order to determine the sweep stop frequency.
To do so turn the SWEEP WIDTH knob until it reaches the desired ratio. This ratio can be changed between 1:1 and 1:100. See section
3.1.7 for details regarding the sweep width setting (see also example from section 3.2.5.2).
3.2.2.9 Selecting sweep t im e
The time of a single complete frequency range sweep can be set by turning the SWEEP TIME knob until the desired time is reached.
The time sweep can be changed between 0.01s and 30.00s. See section 3.1.6 for details regarding the sweep time setting (see also
example from section 3.2.5.2).
3.2.2.10 Selecting type of sweeping
The way the output frequency is modified can be set in a linear or in a logarithmic mode by pressing the LIN/LOG button. This button
has two associated LED’s to indicate which way is active, LIN and LOG LED.
When INTERNAL SWEEP mode is not active, the LIN/LOG button action is disabled and none of the LED associated is lighted.
The way the change in frequency is selected does not affect any sweep parameters.
3.2.3 FREQCOUNTER (Frequency Counter mode)
This mode is used for measuring the signal applied on the VC G SWEEP/COUNTER IN input jack. The applied signal must be from
50mV
up to 10V
p-p
The unit is capable of measuring frequencies from 5 Hz to 100 MHz, using 1 Hz resolution.
.
p-p
Attention:
Applying levels in excess of above +10.0V
on VCG SWEEP/COUNTER IN input jack, can damage the input.
p-p
13
Page 15

p
p
3.2.3.1 Selecting FREQCOUNTER mod e
COUNTER LED lighting indicates active FREQCOUNTER mode.
Engage in FREQCOUNTER mode by pressing the COUNTER / VCG SWEEP button. The COUNTER LED will be lighted and the
word “Counter” will be displayed on the second line of the LCD.
3.2.3.2 Selecting gate.
One of the four available gate periods can be set by using the UP and DOWN range keys. These different gate periods allow different
counting precision.
See section 3.1.8 for details regarding gate period setting (see also example from section 3.2.5.3).
3.2.4 Saving the default loaded mode at power-up
The current working mode and its parameters can be saved on a non-volatile location. This is loaded at power-up, with the unit
resuming work from this point. If the unit will be used for a certain application that requires little changes in the mode’s working
parameters, the workload will be eased by speeding the setting of the parameters.
By pressing the range buttons UP an d DOWN twice at the same time, you can save the current working mode and its parameters.
By pressing the buttons once, the LCD display will change, and a message will appear: “Press again for saving config.” indicating the
action necessary for saving active configuration. Pressing the buttons once again at the same time will save the active mode and a new
message will be displayed: “Configuration saved”. Pressing any other button, combinations of buttons or turning knobs will exit the
saving and the unit will display the previous content (i.e. before saving).again on the LCD
After a successful saving, the message “Configuration saved” will remain displayed for 3 seconds. Afterward, the unit will
automatically display the previous content (i.e. before saving) on the LCD again.
Note: During the whole process the unit will work normally. There are no breaks or pauses in the unit function.
See example from section 3.2.5.3 of saving a working configuration, and how the LCD display must look like in the case of a successful
saving.
3.2.5 Setting parameters examples.
Initial state
Suppose the unit is powered up, and the LCD displays look like
Figure 2. The unit is in EXTERNAL VCG mode, symmetric
triangle style waveform outputted, no signal at VCG/SWEEP input
jack, output frequency set to 2.2222KHz, output level 1.01V, DC
offset 0V, TTL style signal outputted on TTL /CMOS jack.
Suppose only the following LED is lighted: EXT LED, VCG
SWEEP LED, TTL LED, TRIANGLE WAVE SELECT LED
(see Figure 1).
3.2.5.1 Example of sett ing parameters in EXTERNAL VCG mode.
To output a sine wave signal, symmetry 65%, frequency 878KHz, level 6V
+ 8.0 V (unloaded).
Step 1
Press the UP button twice to reach the frequency range which is the desired
frequency (see table1). The LCD display should look like Figure 3. The output
frequency is now 222.22 KHz.
14
, DC offset -1.023 V, the CMOS output level must be set to
p-p
FREQUENCY
2.2222KHz 10K
1.01 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 2: LCD example of using
second frequency range
FREQUENCY
ut
222.22KHz 1M
1.01 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 3: LCD example of using
fourth frequency range
ut
Page 16

p
yCy
p
Step 2
Turn the FREQUENCY knob till you reach the desired frequency, 878.00 KHz.
The LCD display should look like Figure 4. The output frequency is now 878 KHz.
Step 3
Press the SINE WAVE SELECT button. The unit must output a symmetrical sine wave type signal on the OUTPUT jack. The SINE
WAVE SELECT LED will light; the TRIANGLE WAVE SELECT LED will not light.
Step 4
Turn the DUTY CYCLE knob clock wise until the displayed duty cycle reaches
65%. The LCD display should look like Figure 5. The output signal on the
OUTPUT jack should be asymmetric (an example of an asymmetric sine wave is
given in section 3.2.4.3).
The DUTY CYCLE LED must be lighted.
FREQUENCY
878.00KHz 1M
1.01 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 4: LCD example of using
fourth frequency range
FREQUENCY
ut
878.00KHz 1M
65% Dut
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 5: LCD example of displaying duty
cycle parameter
cle
Step 5
Turn the OUTPUT knob clockwise until the displayed output level reaches + 6.0V.
The LCD display should look like Figure 6.
Step 6
Turn the DC OFFSET knob counter clockwise until the displayed output offset
reaches – 1.023V. The LCD display should look like Figure 7.
The DC OFFSET LED must be lighted.
Step 7
Press the TTL/CMOS button. The CMOS LE D will light; the TTL LED will not
light. Turn the CMOS LEVEL knob clockwise until the CMOS level reaches 8.0V.
The LCD display should look like Figure 8.
15
FREQUENCY
878.00KHz 1M
6.00 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 6: LCD example of
displaying level
FREQUENCY
ut
878.00KHz 1M
- 1.023 V Offset
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 7: LCD example of displaying
offset parameter
FREQUENCY
878.00KHz 1M
8.0 V CMOS OUT
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 8: LCD example of displaying
CMOS output level
Page 17

Step 8 (automatic step performed)
p
p
p
p
The unit will display the output level parameter as shown in Figure 6, 7 seconds after the last change on the second line of LCD display.
External voltage control generator.
The current output frequency should be changed to 878 KHz by controlling the DC level applied to VCG/SWEEP input jack. Apply a
DC level between + 5.0 V and + 10.0 V. The output frequency must sweep a range between 17.56 KHz and 8.78 KHz.
Illustrated below shows what will happen at the limits of the DC level range applied to the VCG/SWEEP jack.
Step 9
Apply a + 5.0 V DC level at the VCG/SWEEP jack. The output frequency will be
17.56 KHz, and the LCD display should look like Figure 9 at the start of the
frequency sweep.
FREQUENCY
17.56KHz 1M
6.00 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 9: LCD example of displaying
frequency when applying a DC level
ut
Step 10
Change the DC level until it reaches + 10.0V. The output frequency will reach 8.78
KHz, and the LCD display should look like Figure 10 at the end of the frequency
sweep.
3.2.5.2 Example of setting parameters in INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
To output a square wave signal whose frequency sweeps a 6MHz range in 21.33s, set the sweep frequency to start at 8.000MHz,
symmetry 40%, level 500mV
Step 1
Press the UP button 3 times to reach the desired frequency range (see Table1). The
LCD display should look like Figure 11. The output frequency will now be 2.2222
MHz.
Step 2
Turn the FREQUENCY knob clockwise until you reach the desired frequency,
8.000MHz. The LCD display should look like Figure 12. The output frequency is
now 8.0 MHz.
, DC offset + 2.10V. Set a CMOS output level to + 4.0 V (unloaded).
p-p
16
FREQUENCY
8.78KHz 1M
6.00 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 10: LCD example of displaying
frequency when applying a DC level
FREQUENCY
2.2222MHz 10M
1.01 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 11: LCD example of using
fifth frequency range
FREQUENCY
8.0000MHz 10M
1.01 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 12: LCD example of using
fifth frequency range
ut
ut
ut
Page 18

yCy
p
p
Step 3
Press the SQUARE WAVE SELECT button. The unit must output a symmetrical square wave type signal on the OUTPUT jack. As
an effect of pressing the button, the SQUARE WAVE SELECT LED lights and the TRIANGLE WAVE SELECT LED is not
lighted.
Step 4
Turn the DUTY CYCLE knob counter clock wise until the displayed duty cycle
reaches 40%. The LCD display should look like Figure 13. The output signal on
OUTPUT jack should be asymmetric (an example of an asymmetric square wave is
given in section 3.2.5.3).
The DUTY CYCLE LED must be lighted.
FREQUENCY
8.0000MHz 10M
40% Dut
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 13: LCD example of displaying
duty cycle parameter
cle
FREQUENCY
Step 5
Press the –20dB button. This will engage the – 20dB attenuation on the main signal
path. The signal level must decrease with –20dB, the output level will reach a level
of 101mV
The –20dB LED must be lighted.
(on 50ohm load). The LCD display should look like Figure 14.
p-p
8.0000MHz 10M
101mV Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 14: LCD example of using
-20dB attenuation
ut
FREQUENCY
Step6
Turn the OUTPUT knob clock wise until the displayed output level reaches 500mV.
The LCD display should look like Figure 15.
Output level is now 500mV
(on 50ohm load).
p-p
Step 7
8.0000MHz 10M
500mV Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 15: LCD example of using
-20dB attenuation
ut
Turn the DC OFFSET knob clock wise until the displayed offset level reaches +
2.100 V. The LCD display should look like Figure 16.
The DC OFFSET LED must be lighted.
There will be an asymmetric square wave signal of 500mV
the OUTPUT jack positioned at +2.100 V
above the zero level.
p-p
(on 50ohm load), on
p-p
FREQUENCY
8.0000MHz 10M
+ 2.100 V Offset
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 16: LCD example of displaying
offset parameter
17
Page 19

p
p
p
p
Step 8
Press the TTL/CMOS button. The CMOS LE D will light and the TTL LED will
not light. Turn the CMOS LEVEL knob counter clockwise until CMOS level
reaches 4.0V. The LCD display should look like Figure 17.
Step 9
Press the SWEEP INT/EXT button. Switch the current mode to INTERNAL SWEEP when the INT LED lights.
Calculating the frequency sweep parameters.
The frequency stop frequency must be 2MHz to get a 6 MHz frequency range sweep. Using the formula given in section 3.1.7, the
fraction parameter set by turning SWEEP WIDTH knob must be 4 because the stop frequency represents a fraction of the start
frequency; the fraction set by turning the SWEEP WIDTH rotary knob,
Step 10
Turn SWEEP WIDTH knob counter clockwise until the displayed sweep width
parameter reaches 4. The LCD display should look like Figure 18.
FREQUENCY
8.0000MHz 10M
4.0 V CMOS OUT
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 17: LCD example of displaying
CMOS output level
FREQUENCY
8.0000MHz 10M
4 Swee
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 18: LCD example of displaying sweep
width parameter
Width
Step 11
Turn SWEEP TIME knob clock wise until the displayed sweep time parameter
reaches 21.33s. The LCD display should look like Figure 19.
All the sweep parameters should be set and the asymmetric square wave signal at the OUTPUT jack should be sweeping a 6 MHz
frequency range on 21.33s. There should be a CMOS type signal on the TTL/CMOS output jack whose frequency follows the main
output signal frequency.
Step 12 (automatic step performed)
After setting all the parameters at the limits of the frequency range sweep, the LCD display must look like Figure 20, when internal
sweep starts, and Figure 21, when internal sweep stops.
FREQUENCY
FREQUENCY
8.0000MHz 10M
21.33s Swee
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 19: LCD example of displaying sweep
time parameter
FREQUENCY
Time
2.0000MHz 10M
8.0000MHz 10M
500mV Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 20: LCD example of sweep
start frequency
ut
500mV Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 21: LCD example of sweep
stop frequency
18
ut
Page 20

3.2.5.3 Example of setting gate period in FREQCOUN TER mode.
g
To measure the frequency of an input signal on VCG SWEEP/COUNTER IN jack, use 2 gate periods, 0.1s and 10s.
Suppose the frequency of the input signal is 63,877,099Hz, the level is under 10V
Step1
p-p
.
FREQUENCY
Press the COUNTER IN/VCG SWEEP button. The FREQCOUNTER mode will
be engaged and the COUNTER LED will light. The rest of the LED indicating
working mode, VCG SWEEP LED, INT LED and EXT LED will not light.
Using a 0.01 s gate period will be the fastest period available. At high frequencies
values, there will be the highest counter error.
The content of the LCD display changes and it must look like Figure 22
63877102 Hz
Counter 0.01 s
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 22: LCD example of displaying measured
frequency using 0.01 s gate period
FREQUENCY
time
63877100 Hz
Counter 0.1 s
Figure 23: LCD example of displaying measured
frequency using 0.01 s gate period
Step 2
Pressing the UP button once will change the gate period to 0.1s. The
gate period will decrease to 0.1s and the count will be more accurate.
The content of the LCD display will change and it must look like
Figure 23.
Step 3
Pressing the UP button twice will change the gate period to 10s. The gate period will
decrease to 10 s and the count will be the most accurate available.
The content of the LCD display will changes and it must look like Figure 24.
Figure24: LCD example of displaying measured
3.2.5.4 Example of saving the active mode
frequency using 0.01 s gate period
This example will show the saving of the current configuration. See Figure 1 (beginning of section 3.2.), to see how the
LCD display will look like before starting the saving.
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
time
FREQUENCY
63877009 Hz
Counter 10 s
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
time
FREQUENCY
Step 1
Press both the range buttons, UP and DOWN at the same time. The LCD display
content will change, and it must look like Figure 25.
The unit is expecting the user to press the range buttons again at the same time.
19
Press again for
savin
Figure25: LCD example of displaying the
initialization of saving current configuration
config.
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Page 21

p
Step 2 (the successful case)
FREQUENCY
Press both the range buttons, UP and DOWN again at the same time. The current
configuration will be saved and the LCD display content will change, and it must
look like Figure 26, for 3 seconds.
Configuration
saved
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 26: LCD example of displaying the success of
saving current configuration
Step 2’ (automatic step performed)
FREQUENCY
There are 2 ways to get this situation.
The first way is to have a successful saving.
nd
is to press the other button, combinations of buttons or turning knobs. The
The 2
saving of configuration is abandoned.
Either way, the LCD display must look like figure 27.
2.2222KHz 10K
1.01 V Out
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 27: LCD example of displaying after a
configuration saving
3.2.5.5 Waveform examples
This section will have examples of the outputted waveforms: sine, square, triangle for different duty cycle values.
ut
Attention: The true meaning of duty cycle applies only for the square wave. By turning the DUTY CYCLE knob, the
symmetry of the waveform can change for sine wave and triangle wave. Therefore distorted wave shapes will
be obtained for the sine wave and ramp waves will be obtained for the triangle.
Sine wave type signals
Example of asymmetric sine wave, duty cycle set to 0%.
20
Page 22

Example of asymmetric sine wave, duty cycle set to 20%.
Example of symmetric sine wave, duty cycle set to 50%.
Example of asymmetric sine wave, duty cycle set to 68%.
Example of asymmetric sine wave, duty cycle set to 80%.
21
Page 23

Example of asymmetric sine wave, duty cycle set to 100%.
Example of square wave type signals
Example of asymmetric square wave (pulse wave), duty cycle set to 0%.
Example of asymmetric square wave (pulse wave), duty cycle set to 25%.
Example of symmetric square wave, duty cycle set to 50%.
22
Page 24

Example of asymmetric square wave (pulse), duty cycle set to 70%.
Example of asymmetric square wave (pulse), duty cycle set to 95%.
Example of triangle (ramp) wave type signals
Example of ramp wave (asymmetric triangle), duty cycle set to 0%.
Example of ramp wave (asymmetric triangle), duty cycle set to 20%.
23
Page 25

Example of symmetric triangle, duty cycle set to 50%.
Example of ramp wave (asymmetric triangle), duty cycle set to 70%.
Example of ramp wave (asymmetric triangle), duty cycle set to100%.
24
Page 26

3.3 REMOTE mode
This is not an operating mode; it is another method of controlling the Model 4017B, through the RS232 interface. By using the
REMOTE mode, every aspect of the unit can be controlled using a terminal without having to turn or press the front panel buttons.
When REMOTE mode is active, the front panel controls will be disabled, and the terminal will have the full control.
REMOTE mode is implemented through RS232 interface by using 9600 BPS fixed communication speed, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit and no
parity.
REMOTE mode engaged will be indicated by displaying the word “Remote” on the second line of the LCD display and by the sending
of a message to the remote terminal through interface.
REMOTE mode disengaged will be indicated by returning the LCD display to the displaying mode without the word “Remote” on the
second line of display. A message will be sent to the terminal through interface and the front panel controls will be enabled.
3.3.1 Brief command description.
Commands type:
• Type I: Commands for engaging/disengaging REMOTE mode.
• Type II: Commands for determining information regarding the unit.
• Type III: Commands for setting mode and parameters.
• Type IV: Commands for loading/saving the default mode loaded at power-up.
• Type V: Commands for aborting/forcing command execution.
For every command, the unit returns a specific message regarding the type in case of success. Failing to process a command will return
specific error messages to the terminal. For full description of the commands see section 3.3.2.
The type I command is used for engaging and disengaging the REMOTE mode. Without giving the command for engaging remote
mode, the unit will not accept commands of III and IV type. These commands will also enable/disable the front panel controls.
The type II command is used for finding information regarding the unit, i.e.: model, software version, hardware version, serial number,
and whether or not unit is connected. These commands can be sent without REMOTE mode being active.
The type III command is used for a complete setting of the operating mode and its associated parameters. The implemented commands
can emulate every front panel control. These commands are processed only if unit is in REMOTE mode.
The type IV command is used for saving/loading the current configuration, saved configuration on/from a non-volatile location,
configuration loaded at power-up. These commands are processed only if unit is in REMOTE mode.
The type V command is used for aborting the current command execution or to force evaluation of the value sent to the unit in the case
of type III command. These commands are processed even if unit is not in REMOTE mode.
3.3.2 Commands description
3.3.2.1 General rules
All commands are implemented using hex ASCII characters “0” to “9” and “A” to “F”. Sending other characters will abort processing,
the characters received will be discarded and a specific error message will be sent to the terminal.
Characters within a command can be sent with a maximum 4-second timeout. Failing to send a character within this time will abort the
process, the characters received will be discarded and a specific error message will be sent to the terminal.
There are commands that do not transfer a parameter’s values and commands that send a parameter’s values through interface. There
are rules when you transfer values. You can send a value using a combination of a maximum 10 ASCII characters. After 10 characters
are received or are exceeding the 4-second timeout, the unit will start processing the value.
The processing can be forced by issuing the character “!”.
25
Page 27

General syntax:
XXXX[[z]yyyyyyyyyy]
These are the notations used in the syntax expression:
XXXX Represents the main command body implemented using the hex ASCII characters “A” to “F”, “0” to
[z] Parameter used only for type III command and represents the sign digit. Use it only when you have to
[yyyyyyyyyy] Parameter used only for type III command and its value represents a maximum 10-digit value.
“9”. Main command body can be up to 4–digit length. Commands are not case sensitive.
send a sign number (i.e. offset value).
Restrictions:
• Values can be sent using ASCII characters “0” to “9”, “.”,”K”, “M”. There cannot be any other characters in the 10-digit value.
• There cannot be two “.”, two “M” or two “K” in the same 10-digit value.
• Use the sign digit, “+” or “-” only for values that can be negative.
• There cannot be two sign digits or the unit will abort processing the value, the characters will be discarded and a specific error
message will be sent to the terminal.
Note: Any command can be aborted at any sending stage, by issuing character “X”. This will abort the current command processing,
previous received characters will be discarded and a specific message will be sent to the terminal.
3.3.2.2 Commands description.
Type I command: commands used to enable/disable the REMOTE mode.
RERE command
Syntax: RERE
Parameters: None
Description: Enables REMOTE mode. On the second line of the LCD display, the “Remote”
Example: RERE
Message returned to terminal: “Remote mode engaged”
message will be displayed instead of the”Output” message. The parameters can be
modified only through the RS-232 interface and the front panel will be disabled.
RDRD command
Syntax: RDRD
Parameters: None
Description: Disables REMOTE mode. On the second line of the LCD display, the “Output”
Example: RDRD
Message returned to terminal: “Remote mode off”.
message will be displayed instead of the “Remote” message. The parameters can be
modified only through the front panel.
26
Page 28

Type II command: commands used for finding information regarding the unit.
IID command
Syntax: IID
Parameters: None
Description: Asks for the unit type connected to the interface.
Example: IID
Message returned to terminal: “BK Precision Model 4017B”
IP command
Syntax: IP
Parameters: None
Description: Asks for the presence of the unit at the terminal. Unit must return a message
Example: IP
Message returned to terminal: “Unit connected”.
indicating the presence.
ISV command
Syntax: ISV
Parameters: None
Description: Asks the unit about the current soft version.
Example: ISV
Message returned to terminal: “Software version: X.Y”, where X represents the base soft version and Y represents
the number of the soft version derived from the base version.
IHV command
Syntax: IHV
Parameters: None
Description: Asks the unit about the current hard version.
Example: IHV
Message returned to terminal: “Hardware version: Z.W”, where Z represents the base hard version and W
represents the number of the hard version derived from the base version.
IN command
27
Page 29

Syntax: IN
Parameters: None
Description: Sends to terminal the unit’s serial number.
Example: IN
Message returned to terminal: “Serial Number: XXX-YYYY-ZZZZ” where XXX-YYYY-ZZZZ
Represents the serial number according to BK Precision codification.
Type III command: commands for setting mode and its parameters
.
CM command
Syntax: CMx
Parameters: x is a 3 possible value digit: 0, 1 or 2.
Description: Sets the unit’s working mode according to the value of the “x” parameter. If x > 2
If the mode is already set, any action is aborted and a specific message is sent to
Example: CM0 – the “EXTERNAL VCG” mode is engaged.
Message returned to terminal: “Mode EXTERNAL VCG engaged” if x = 0
“Mode INTERNAL SWEEP engaged” if x = 1
“Mode FREQCOUNTER engaged” if x = 2
“Mode unavailable” if x > 2
“Mode already set” to enable a mode which is already running.
the unit remains in the working mode and a specific error message is sent to
terminal.
terminal.
CF command
Syntax: CFx [yyyyyyyyyy]
Parameters: x represents a digit, valid for the following values: “I”, “U”, “D”, “S”.
yyyyyyyyyy is a decimal digit value who takes values between 0 and 1000000000,
Description: Case 1
In EXTERNAL VCG and INTERNAL SWEEP mode, this command
If x = S, the start frequency will be set at the value of the “yyyyyyyyy” parameter
If x = U or x = D, the working domain of the “yyyyyyyyy” parameter will be
If x = I the value of the start frequency will be sent to the terminal.
Case 2
In FREQCOUNTER mode this command modifies the gate period used in
If x = U or x = D the gate period will be increased or respectively decreased.
valid only if x = S.
sets/modifies/interrogates the value of the start frequency.
which takes values between 0.00Hz and 10000000.00Hz with a 0.01HZ resolution.
increased or respectively decreased.
measuring frequency or asks about the measured frequency.
28
Page 30

If x = I the measured frequency will be sent to the terminal.
Example: Case 1
CFS4000 – sets the start frequency at 4000 Hz.
Case 2
CFU – increases the gate period used in measuring frequency
Message returned to terminal: Case 1:
“Output frequency: yyyyyyyy,yy Hz” if the command was correctly sent.
“Wrong value sent” if the “yyyyyyyyy” parameter sent was not a valid value.
Case 2:
“Gate period 0.1 s” and “Measured frequency: yyyyyyyyy Hz” if the gate period is
“Measured frequency: yyyyyyyyy Hz” if asked about measured frequency.
changed.
CL command
Syntax: CLx [yyyyy]
Parameters: x represents a digit that has 2 valid values: “I” or “S”.
yyyyy is a decimal digit value between 10 and 10000, valid if x = S.
Description: These commands set/interrogates the output level on the OUTPUT jack. The
If x = S the output level will be set at the value of the “yyyyy”, a level that can take
If x = I the output level at the OUTPUT jack will be sent to terminal.
Example: CLS345 – sets the output level at 345mV.
Message returned to terminal: “Output level: yyyyy mV” if the command was correctly sent
“Wrong value sent” if “yyyyy” parameter sent was not a valid value.
command is available only in EXTERNAL VCG or INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
values between 10mV and 10000mV.
CO command
Syntax: COx [zyyyy]
Parameters: x represents a digit that has 2 valid values: “I” or “S”.
z is a valid digit only if x = S and has 2 valid values: ”+” or “-“.
yyyy is a decimal digit value between 0 and 5000, valid if x = S.
Description: This command sets/interrogates the offset level added at the OUTPUT jack. The
If x = S, the offset level will be set at the value of the “zyyyy” parameter, offset that
If x = I, the offset value at the OUTPUT jack will be sent to the terminal.
Example: COS-4333 – sets the OUTPUT offset level at -4333 mV.
Message returned to terminal: “Offset: zyyyy mV” if the command is sent correctly.
“Wrong value sent” if ”yyyy” parameter sent was not a valid value.
command is available only in EXTERNAL VCG and INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
can take values between –5000 mV and +5000 mV. It is necessary that the sign is
sent first; otherwise the following parameter will be dropped.
29
Page 31

CT command
Syntax: CTx [yyy]
Parameters: x represents a digit that has only 2 valid values: “I” or “S”.
yyy is a decimal digit value between 40 and 140, valid if x =S.
Description: The command sets/interrogates the level on TTL/CMOS output. The command is
If x = S the CMOS output level will take values between 4.0 and 14.0 V.
If x = I the CMOS level value will be sent to terminal
Example: CTS123 – sets the TTL/CMOS output level at 12.3V
Message returned to terminal: “TTL/CMOS output: 12.3 V” if the command is sent correctly.
“Wrong value sent” if “yyy” parameter sent was not a valid value.
available only on EXTERNAL VCG and INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
CD command
Syntax: CDx[yyy]
Parameters: x represents a digit that has only 2 valid values: “I” or “S”.
yyy is a decimal digit value between 0 and 100, valid if x = S.
Description: The command sets/interrogates the duty cycle of the signal output on OUTPUT
If x = S, the duty cycle will take values between 0 and 100%.
If x = I, the duty cycle value will be sent to the terminal.
Example: CDS0 – sets the duty cycle to 0%.
Message returned to terminal: “Duty cycle: yyy %” if the command is sent correctly.
“Wrong value sent” if the “yyy” parameter sent was not a valid value.
jack. The command is available only on EXTERNAL VCG and INTERNAL
SWEEP mode.
CW command
Syntax: CWx[yyy]
Parameters: x represents a digit that has only 2 valid values: “I” or “S”.
yyy is a decimal digit value between 1 and 100, valid if x = S.
Description: The command sets/interrogates the ratio factor used to calculate the STOP frequency
If x = S the value of the ratio will take values between 1 and 100.
If x = I the ratio factor used to calculate the STOP frequency will be sent to
Example: CWS45 – sets the ratio applied to the START frequency at the value of 45.
Message returned to terminal: “Sweep width ratio: yyy %” if the command is sent correctly.
“Wrong value sent” if the “yyy” parameter sent was not a valid value.
“Command not allowed in current mode” if INTERNAL SWEEP mode isn’t the
of the output signal at OUTPUT jack. The command is available only on
INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
terminal.
current working mode.
CS command
Syntax: CSx [yyyy]
Parameters: x represents a digit that has only 2 valid values: “I” or “S”.
30
Page 32

yyyy is a decimal digit value between 1 and 3000, valid if x = S.
Description: The command sets/interrogates the frequency sweep time of the output signal on the
If x = S the sweep time will take values between 0.01 s and 30.00 s. If x = I the
Example: CSS333 – sets the sweep time value at 3.33 s.
Message returned to terminal: “Sweep time: yy.yy s” if the command is sent correctly.
“Wrong value sent” if the “yyy” parameter sent is not a valid value.
“Command not allowed in current mode” if INTERNAL SWEEP mode isn’t the
OUTPUT jack. The command is available only on INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
sweep time will be sent to terminal.
current working mode.
CV command
Syntax: CVx
Parameters: x represents a digit that has only 2 valid values: “0” or “1”.
Description: The command sets the way in which the frequency is modified during a frequency
If x=0, the linear sweep mode is engaged
If x=1, the logarithmic sweep mode is engaged
Example: CV0
Message returned to terminal: “Linear sweep mode engaged” if x=0.
“Logarithm sweep mode engaged” if x=1.
“Unavailable command” if x is not a valid value.
“Command not allowed in current mode” if the INTERNAL SWEEP mode is not
sweep. This command is available only on INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
the current working mode.
CE command
Syntax: CEx
Parameters: x represents a digit who has only 3 valid values: “0”, “1”, “2”.
Description: The command sets the output signal type: sine, triangle or square on the main output,
If x = 0, a sine wave signal is outputted on OUTPUT jack.
If x = 1 a triangle wave is outputted on OUTPUT jack.
If x = 2 a square wave is outputted on OUTPUT jack.
Example: CE0
Message returned to terminal: “Sine function generated” if x = 0.
“Triangle function generated” if x = 1.
“Square function generated” if x = 2.
“Function not implemented” if x digit sent was not a valid value.
OUTPUT jack. The command is available only on EXTERNAL VCG and
INTERNAL SWEEP mode.
31
Page 33

CB command
Syntax: CBx [y]
Parameters: x represents a digit that has only 2 valid values: “I” or “S”.
y represents a decimal digit, valid if x = S.
Description: The command sets/interrogates the mode of displaying the decimals in American or
If x = S and y = 0, the American mode of displaying the decimals using point will be
If x = S and y = 1, the French mode of displaying the decimals using comma will be
Example: CBS0 – the decimals will be displayed according to the American mode.
Message returned to terminal: “LCD point display engaged (American option)” if y = 0.
“LCD comma display engaged (French option)” if y = 1.
“Incorrect command” if any of the digits sent was not valid.
French.
engaged.
engaged.
CG command
Syntax: CGx[y]
Parameters: x represents a digit that has only 2 valid values: “I” or “S”.
y represents a digit that has 2 valid values: “C” or “T”, only if x = “S”.
Description: The command sets/interrogates the output type on TTL/CMOS jack.
If x = “I”, the type of signal outputted on TTL/CMOS jack will be send to the
If x = “S” and y = “C”, a CMOS style signal will be outputted on TTL/CMOS jack.
If x = “S” and y = “T”, a TTL style signal will be outputted on TTL/CMOS jack
Example: CGST
Message returned to terminal: “TTL signal on TTL/CMOS jack” if y = “T”
“CMOS signal on TTL/CMOS jack” if y =”C”
“Incorrect command” if any of the digits sent was not valid.
terminal.
CA command
Syntax: CAx[y]
Parameters: x represents a digit that has only 2 valid values: “I” or “S”.
y represents a digit that has 2 valid values: “E” or “D”, only if x = “S”.
Description: The command sets/interrogates if –20dB attenuation is engaged or disengaged on the
If x = “I”, a message indicating if attenuation is engaged or disengaged at signal
If x = “S” and y = “E”, the – 20dB attenuation will be engaged on OUTPUT jack.
If x = “S” and y = “D”, the – 20dB attenuation will be disengaged on OUTPUT
Example: CASE – will engage the – 20dB attenuation.
main signal output, OUTPUT jack.
output will be send to the terminal.
jack.
32
Page 34

Message returned to terminal: “-20dB attenuation engaged on OUTPUT jack” if y = “E”
“-20dB attenuation disengaged on OUTPUT jack” if y =”D”
“Incorrect command” if any of the digits sent was not valid.
Type IV command: Used for saving/loading the current configuration / saved configuration.
SSS command
Syntax: SSS
Parameters: none
Description: Command used to save the current working mode and its parameters as the default
Example: SSS
Message returned to terminal: “Default power-up state saved” if the current working mode and its parameters were
“Unavailable command” if the command sent was incomplete
loaded state at power-up.
successfully saved.
SLS command
Syntax: SLS
Parameters: None
Description: Loads the default loaded state at power-up as the current working state.
Example: SLS
Message returned to terminal: “Default power-up state loaded”
“Unavailable command” if the command sent was incomplete.
Type V command: used for aborting the current command execution or to force evaluation of the value sent to the unit.
Character “X”
Syntax: X
Description: If the character is issued, any command pending for complete reception of characters
Message returned to terminal: “Command aborted by terminal” if the “X” character is issued.
“Incorrect command” if “X” character is issued and the unit was not pending
will be aborted and the received characters are dropped.
previously for full command receiving of sending it.
Character “!”
Syntax: !
Description: Command used to force immediate handling of the parameter value received from
Example: “CFS14.23!” immediately sets the frequency at 14.23 Hz.
Message returned to terminal: If character “!” is issued after receiving a parameter value, the terminal will receive a
“Unavailable command” or “Wrong value sent” are error messages sent to the
the terminal. Command is available only for commands that transfer values to the
unit. When a parameter value has been received, the unit does not wait for a 4 second
timeout in order to start value interpretation.
message regarding the correct settings of the parameter value.
terminal if “!” was issued in other conditions than those specified above.
33
Page 35

3.3.3 Remote program examples
The program examples are the equivalents of the controls used in the example shown in section 3.2.5. Assume the same starting
conditions: EXTERNAL VCG mode, symmetric triangle style waveform outputted, no signal at VCG/SWEEP input jack, output
frequency set to 2.2222KHz, output level 1.01V, DC offset 0V, TTL style signal outputted on TTL/CMOS jack. Suppose only the
following LED are lighted: EXT LED, VCG SWEEP LED, TTL LED, TRIANGLE WAVE SELECT LED (see figure 1).
3.3.3.1 Example of sett ing parameters in EXTERNAL VCG mode using REMOTE control.
Correspondin
Step
1 - RERE
2 1,2 CFS87800000
3 3 CE0
4 4 CDS65
5 5 CLS6000
6 6 COS-1023
7 7 CTS80
8 9 CM1
9 10 CFI
10 - RDRD
After step 9, the LCD Display should look like Figure 28.
g step in
example from
section 3.2.5.1
Issued command Message returned
Remote mode engaged
Output frequency: 878000,00 Hz
Sine function generated
Duty cycle: 65 %
Output level: 6000 mV
Offset: -1.023V
TTL/CMOS output: 8.0 V
Output frequency: 17560,00 Hz
Output frequency: 8780,00 Hz
Remote mode off
FREQUENCY
8.78KHz 1M
6.00 V Remote
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 28: LCD example of displaying
frequency when in REMOTE mode
34
Page 36

3.3.3.2 Example of setting parameters in INTERNAL SWEEP mode using REMOTE control.
Step Corresponding
step in example
from section
3.2.5.2
1 - RERE
2 1,2 CFS800000000
3 3 CE2
4 4 CDS40
5 5,6 CLS500
6 7 COS+2100
7 8 CTS40
8 9 CM1
9 10 CWS4
Issued command Message returned
Remote mode engaged
Output frequency: 8000000,00 Hz
Square function generated
Duty cycle: 40 %
Output level: 500 mV
Offset: +2.100 V
TTL/CMOS output: 4.0 V
Mode INTERNAL SWEEP engaged
Sweep width ratio: 4
10 11 CSS2133
11 - RDRD
After step 10, the LCD display should look like Figure 29.
Sweep time: 21.33 s
Remote mode off
FREQUENCY
8.0000MHz 10M
500mV Remote
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 29: LCD example of sweep start
frequency in REMOTE mode
35
Page 37

3.3.3.3 Example of setting gate period in FREQCOUNTER mode using REMOTE control.
Step Corresponding
step in example
from section
3.2.5.2
Issued command Message returned
1 - RERE
2 1 CM2
3 2 CFU
4 3 CFU
5 3 CFU
6 - CFI
7 - RDRD
Remote mode engaged
Mode FREQCOUNTER engaged
Gate period 0.1 s
Measured frequency: 63877100 Hz
Gate period 1 s
Measured frequency: 63877100 Hz
Gate period 10 s
Measured frequency: 63877099 Hz
Measured frequency: 63877099 Hz
Remote mode off
After step 5, the LCD display should look like Figure 30.
FREQUENCY
63877099 Hz
Remote 10 s
LEVEL
Peak-to-Peak
(into 50Ω)
Figure 30: LCD example of displaying measured
frequency in REMOTE mode
36
Page 38

4. SPECIFICATIONS
REQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS:
Waveforms: Sine, Square, Triangle, ± Pulse, ±
Frequency: 0.01 Hz to 10MHz
ailable ranges: 5
Av
olution: 5 digits
Res
Variable Duty Cycle: 0 to 100% continuously variable, 3-digit
Operating Modes: External VCG, Internal Sweep and
Frequency Stability: output will change less than 0.09%
Ramp
olution
res
Frequency Counter
over
15 minutes after 1-hour warm-up
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS:
Impedance: 50Ω ± 10%
Output Level: 0.1 ÷ 10V
0.2 ÷ 20V
ailable ranges: 2
Av
Resolution: up to 4 digits
Attenuation: -20dB ± 1dB
fset:
DC Of
Preset: ±0.1V typical
Variable: ±10V into open-circuit,
±5V into 50Ω
Resolution: 4 digits
into 50Ω
p-p
into open circuit
p-p
TTL OUTPUT:
Level: 0.8V to 4V
Ri
se Time: ≤20ns
Duty Cycle: 50% typical
CMOS OUTPUT
Max frequency: 10 MHz
ution: 3 digits
Resol
Level: 4V to 14V ±0.5 V
se Time: ≤
Ri
Variabl
e
, Continuously
p-p
VCG (Voltage Controlled Generator) INPUT:
Input Voltage: 0-10 ± 1V causes a 100:1 frequency
Impedance: 10KΩ ±5%
change
SWEEP OPERATION
Mode: LIN/LOG
Width: 100:1, continuously variable, 3-digit
Rate: 0.01 sec to 30 sec, continuously variable, 4
resolution
digits resolution
SINE WAVE
Distortion: 1% typical at 1 kHz
Fl
atness: ±5% (.45 dB)
SQUARE WAVE
Symmetry: 0.1Hz to 100 kHz ≤ 2%
se Time: ≤20ns
Ri
TRIANGLE WAVE
Linearity: ≥ 98% to 100kHz
NOTE: Specifications and information are subject to change without notice. Please visit www.bkprecision.com for the most current
product information.
Sweep Output: 0.1 ÷ 10V
FREQUENCY COUNTER
Accuracy: Time base Accuracy ± 1 count
Time Base Accuracy: ±10PPM (23°C ± 5°C)
Display: 9 digits
INTERFACE:
POWER SOURCE:
RS-232 using a DB-9 female connector,
baud rate set at 9600 BPS
fix
120/230 VAC ±10%, 50/60 Hz, internal
jumper selectable
into 50Ω
p-p
37
Page 39

5. Service Information
Warranty Service: Please return the product in the original packaging with proof of purchase to the address below. Clearly
state in writing the performance problem and return any leads, probes, connectors and accessories that you are using with the
device.
Non-Warranty Service: Return the product in the original packaging to the address below. Clearly state in writing the
performance problem and return any leads, probes, connectors and accessories that you are using with the device. Customers
not on open account must include payment in the form of a money order or credit card. For the most current repair charges
please visit www.bkprecision.com
Return all merchandise to B&K Precision Corp. with pre-paid shipping. The flat-rate repair charge for Non-Warranty Service
does not include return shipping. Return shipping to locations in North American is included for Warranty Service. For
overnight shipments and non-North American shipping fees please contact B&K Precision Corp.
Include with the returned instrument your complete return shipping address, contact name, phone number and
description of problem.
and click on “service/repair”.
B&K Precision Corp.
22820 Savi Ranch Parkway
Yorba Linda, CA 92887
www.bkprecision.com
714-921-9095
Limited Two-Year Warranty
B&K Precision Corp. warrants to the original purchaser that its products and the component parts thereof, will be free from defects in
workmanship and materials for a period of two year from date of purchase.
B&K Precision Corp. will, without charge, repair or replace, at its option, defective product or component parts. Returned product must
be accompanied by proof of the purchase date in the form of a sales receipt.
To obtain warranty coverage in the U.S.A., this product must be registered by completing a warranty registration form on
www.bkprecision.com
Exclusions: This warranty does not apply in the event of misuse or abuse of the product or as a result of unauthorized
alterations or repairs. The warranty is void if the serial number is altered, defaced or removed.
B&K Precision Corp. shall not be liable for any consequential damages, including without limitation damages resulting from loss of
use. Some states do not allow limitations of incidental or consequential damages. So the above limitation or exclusion may not apply to
you.
This warranty gives you specific rights and you may have other rights, which vary from state-to-state.
B&K Precision Corp.
22820 Savi Ranch Parkway
Yorba Linda, CA 92887
www.bkprecision.com
714-921-9095
within fifteen (15) days of purchase.
38
Page 40

Declaration of CE Conformity
according to EEC directives and NF EN 45014 norm
Responsible Party Alternate Manufacturing Site
Manufacturer’s Name: B&K Precision Corporation B&K Taiwan 0574
Manufacture’s Address: 22820 Savi Ranch Pkwy.
Yorba Linda, CA 92887-4610
USA
Declares that the below mentioned product
Product Name: Function Generator
Part Numbers: 4017B
complies with the essential requirements of the following applicable European Directives:
Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC (19.02.73) amended by 93/68/EEC (22.07.93)
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) 89/336/EEC (03.05.88) amended by 92/68/EEC (22.07.93)
and conforms with the following product standards:
Safety EN 61010-1:2001
EMC EN 61326:1997 + A1:1998 + A2:2001
EN 50081-1
EN 50081-2
This Declaration of Conformity applies to above listed products place on the EU market after:
August 4, 2006
Date Victor Tolan
President
Page 41

22820 Savi Ranch Parkway
Yorba Linda, CA 92887
www.bkprecision.com
© 2006 B&K Precision Corp.
Printed in USA
39
 Loading...
Loading...