Page 1

Application Guide
For Technical Service Call Your Local Bio-Rad Office
or in the U.S. Call 1-800-4BIORAD (1-800-424-6723)
Catalog Number
161-0993
Ready Gel
®
Precast Gels
Page 2

Table of Contents
Section 1 General Information.............................................................................................. 1
1.1 Introduction.......................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Ready Gel System Specifications......................................................................................................... 2
1.3 Ready Gel Comb Configurations.......................................................................................................... 2
Section 2 Setup and Basic Operation................................................................................... 3
2.1 Setting Up and Running Ready Gel Precast Gels................................................................................. 3
Section 3 SDS-PAGE.............................................................................................................7
3.1 Introduction.......................................................................................................................................... 7
3.2 Ready Gel Tris-HCl Gel Composition.................................................................................................... 8
3.3 Ready Gel Tris-HCl Gel Selection Guide............................................................................................... 8
3.4 SDS-PAGE Buffers............................................................................................................................... 9
3.5 Sample Preparation.............................................................................................................................. 9
3.6 Running Conditions.............................................................................................................................. 9
Section 4 Native PAGE..........................................................................................................10
4.1 Introduction..........................................................................................................................................10
4.2 Ready Gel Tris-HCl Gel Composition....................................................................................................10
4.3 Ready Gel Tris-HCl Gel Selection Guide ..............................................................................................11
4.4 Native PAGE Buffers.............................................................................................................................11
4.5 Sample Preparation.............................................................................................................................12
4.6 Running Conditions ............................................................................................................................ 12
Page 3

Section 5 Peptide Analysis.................................................................................................. 11
5.1 Introduction......................................................................................................................................... 11
5.2 Ready Gel Tris-Tricine/Peptide Gel Composition..................................................................................11
5.3 Ready Gel Tris-Tricine/Peptide Gel Selection Guide............................................................................. 11
5.4 Tris-Tricine/Peptide Buffers.................................................................................................................. 12
5.5 Sample Preparation.............................................................................................................................12
5.6 Running Conditions............................................................................................................................ 12
Section 6 Isoelectric Focusing............................................................................................ 13
6.1 Introduction......................................................................................................................................... 13
6.2 Ready Gel IEF Gel Composition ......................................................................................................... 13
6.3 Ready Gel IEF Gel Selection Guide......................................................................................................13
6.4 IEF Buffers...........................................................................................................................................14
6.5 Sample Preparation.............................................................................................................................14
6.6 Running Conditions............................................................................................................................. 14
Section 7 Protease Analysis by Zymogram PAGE................................................................15
7.1 Introduction..........................................................................................................................................15
7.2 Ready Gel Zymogram Gel Composition...............................................................................................15
7.3 Ready Gel Zymogram Gel Selection Guide..........................................................................................15
7.4 Zymogram Gel Buffers.........................................................................................................................16
7.5 Sample Preparation.............................................................................................................................16
7.6 Running Conditions............................................................................................................................. 16
Page 4

Section 8 Nondenaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE...................................................................... 17
8.1 Introduction......................................................................................................................................... 17
8.2 Ready Gel TBE Gel Composition.........................................................................................................17
8.3 Ready Gel TBE Gel Selection Guide....................................................................................................17
8.4 Nondenaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE Buffers.......................................................................................... 18
8.5 Sample Preparation.............................................................................................................................18
8.6 Running Conditions............................................................................................................................. 18
Section 9 Denaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE............................................................................19
9.1 Introduction......................................................................................................................................... 19
9.2 Ready Gel TBE-Urea Gel Composition................................................................................................ 19
9.3 Ready Gel TBE-Urea Gel Selection Guide........................................................................................... 19
9.4 TBE-Urea Buffers................................................................................................................................ 20
9.5 Sample Preparation............................................................................................................................ 20
9.6 Running Conditions............................................................................................................................ 20
Section 10 Detection.......................................................................................................... 21
10.1 SDS-PAGE and Native PAGE Detection...................................................................................... 21–22
10.2 Peptide Gel Staining......................................................................................................................... 23
10.3 IEF Gel Staining................................................................................................................................ 24
10.4 Zymogram Gel Staining.................................................................................................................... 25
10.5 TBE Gel Staining.............................................................................................................................. 26
10.6 TBE-Urea Gel Staining...................................................................................................................... 26
Page 5

Section 11 Stock and Staining Solutions.......................................................................27–31
11.1 Stock Solutions................................................................................................................................. 27
11.2 Protein Staining Solutions............................................................................................................ 28–29
11.3 Peptide Staining Solutions................................................................................................................ 29
11.4 Zymogram Staining Solutions ...........................................................................................................30
11.5 Nucleic Acid Staining Solutions ........................................................................................................ 31
Section 12 Troubleshooting........................................................................................... 32–33
Section 13 Ordering Information......................................................................................... 34
13.1 Ready Gel Precast Gels ....................................................................................................................34
13.2 Ready Gel Accessories......................................................................................................................35
13.3 Buffers...............................................................................................................................................36
13.4 Detection Reagents........................................................................................................................... 37
13.5 Blotting Membranes.......................................................................................................................... 38
13.6 Protein and DNA Standards.............................................................................................................. 38
13.7 Equipment.........................................................................................................................................38
Page 6

Section 1
General Information
1.1 Introduction
Ready Gel
®
precast gels greatly simplify polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. They are specifically for use with
the Mini-PROTEAN Systems (Mini-PROTEAN Tetra, Mini-PROTEAN-III and Mini-PROTEAN Dodeca Cells).
Stringent production and quality control criteria, and the use of the highest quality reagents, ensure reproducible electrophoretic analysis with minimum effort. Every gel is checked during production for defects, and
each lot of gels is further tested by electrophoresis to verify quality.
Ready Gel precast gels come ready to use with preformed sample wells and a stacking gel when necessary.
Each Ready Gel Cassette is 8 x 10 cm (H x W) and 4.0 mm thick. Gel dimension is 6.8 x 8.6 cm (HxW) and
1.0 mm thick. Each gel is individually packaged in a leakproof pouch with an absorbent pad containing gel
buffer and 0.02% Sodium Azide.
Ready Gel precast gels are available for use in Tris-glycine (Tris-HCl and zymogram gels), Tris-Tricine, TBE,
TBE-urea, and IEF buffer systems. The Tris-HCl gels can be used for SDS-PAGE and non-SDS gel electrophoresis. The Tris-Tricine/peptide gels are optimized for peptide electrophoresis. The TBE gels are for use in
nucleic acid electrophoresis and can be used for native protein electrophoresis. TBE-urea gels provide
denaturing conditions for nucleic acids. Resolution of different size ranges of proteins or nucleic acids can
be obtained by choosing the correct gel.
1
Page 7

1.2 Mini-format gel System Specifications
Gel material Polyacrylamide
Gel dimensions 8.6 x 6.8 cm (W x L)
Gel thickness 1.0 mm
Resolving gel height 5.5 cm
Cassette dimensions 10 x 8.0 cm (W x L)
Cassette material Back (long): acrylic; front (short): glass
Comb material Polycarbonate
Total running buffer volume 700 ml for 2 gels, 1,000 ml for L. gels (Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell)
Storage conditions Store flat at 4ºC; DO NOT FREEZE
1.3 Ready Gel Comb Configurations
Comb Load Volume
9-well 30 µl
10-well 30 µl
10-well 50 µl
12-well 20 µl
15-well 15 µl
IPG 7 cm ReadyStrip
™
IPG strip
Prep 450 µl with one 15 µl reference well
2
Page 8

Section 2
Setup and Basic Operation Using Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell
2.1 Setting Up and Running Ready Gel Precast Gels
1. Each Ready Gel should be used immediately after it is removed from the storage pouch.
2. Remove the comb and gently rinse the wells with deionized water or running buffer.
3. Use the key knife or a razor blade to cut the tape at the bottom of the gel along the black “cut here” line.
It is helpful to cut all the way to the edge of the cassette where the pull tab begins.
4. Pull the tape tab along the cut line, up from the cassette and at an angle towards the comb end of the
gel.
Required materials:
• Clean and dry Mini-PROTEAN®Tetra cell tank
• Electrophoresis module (Electrode Assembly Module only for 1 or 2 gels; for 3 or 4 gels also use the
Companion Running Module)
• Running buffer (700 ml for 2 gels; 1000 ml for 4 gels)
• Ready Gel®precast gels or hand-cast gels
• PowerPac™Basic power supply
1. Assembly
3
Page 9

Note: When running 2 gels only, use the Electrode Assembly (the one with the banana plugs), Not the
Companion Running Module (the one without the banana plugs). When running 4 gels, both the Electrode
Assembly and the Companion Running Module must be used, for a total of 4 gels (2 gels per assembly).
a. Set the clamping frame to the open position on a clean flat surface (see Figure 4a)
b. Place the first gel sandwich or gel cassette (with the short plate facing inward) onto the gel supports;
gel supports are molded into the bottom of the clamping frame assembly; there are two supports in
each side of the assembly. Note that the gel will now rest at a 30° angle, tilting away from the center
of the clamping frame. Please use caution when placing the first gel, making sure that
the clamping frame remains balanced and does not tip over. Now, place the second gel on
the other side of the clamping frame, again by resting the gel onto the supports. At this point there
will be two gels resting at an angle, one on either side of the clamping frame, tilting away from the
center of the frame (see Figure 4b).
Note: It is critical that gel cassettes are placed into the clamping frame with the short plate facing inward.
Also, the clamping frame requires 2 gels to create a functioning assembly, If an odd number of gels (1 or
3) is being run, you must use the buffer dam (see Figure 4b).
c. Using one hand, gently pull both gels towards each other, making sure that they rest firmly and
squarely against the green gaskets that are built into the clamping frame; make certain that the short
plates sit just below the notch at the top of the green gasket.
d. While gently squeezing the gel sandwiches or cassettes against the green gaskets with one hand
(keeping constant pressure and both gels firmly held in place), slide the green arms of the clamping
frame over the gels, locking them into place. Alternatively, you may choose to pick-up the entire
assembly with both hands, making sure that the gels do not shift, and simultaneously sliding both
arms of the clamping frame into place (see Figure 4c).
4
Page 10
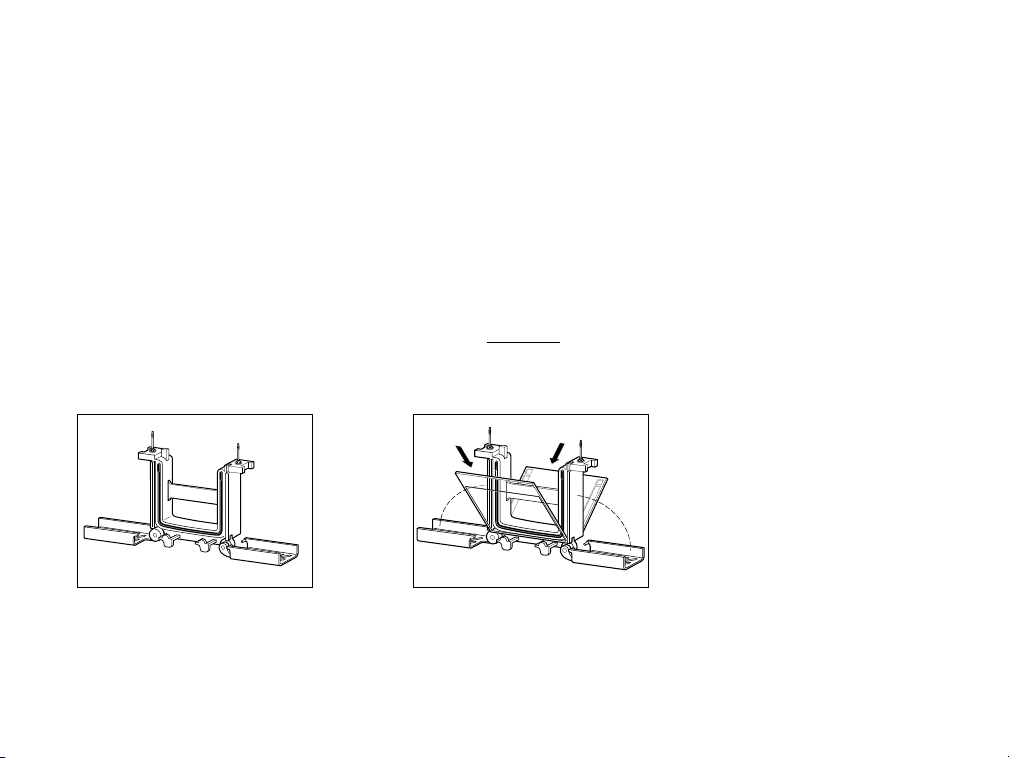
The arms of the clamping frame push the short plates of each gel cassette up against the notch in
the green gasket, creating a leak-proof seal (check again to make certain that the short plates sit just
below the notch at the top of the green gasket). At this point, the sample wells can be washed-out
with running buffer, and sample can be loaded (Figure 4d).
Note: If running more than 2 gels, repeat steps 1a–d with the Companion Running Module.
Important Note: Do not attempt to lock the green arms of the clamping frame, without first ensuring
that the gel cassettes are perfectly aligned and stabilized against the notches on the green gaskets of the
module. To prevent the gels from shifting during the locking step, firmly and evenly grip them in place
against the core of the module with one hand.
CAUTION: When running 1 or 2 gels only, DO NOT
place the Companion Running Module
in the tank. Doing so will cause excessive heat generation and prevent
electrophoretic separation.
5
4a
4b
Page 11

Fig. 4. Assembling the Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell Electrophoresis Module.
6
4c
4d
4e
Page 12

Section 3
SDS-PAGE
3.1 Introduction
Ready Gel Tris-HCl gels provide a versatile system for the separation of proteins by molecular weight (SDS-PAGE
conditions) or charge to mass ratio (native conditions). (See section 4 for native PAGE applications and
protocols.) This is possible because Ready Gel Tris-HCl gels are made without SDS, allowing the sample
buffer and running buffer to determine the separation mechanism. Historically, SDS-PAGE systems contained
SDS in both the gel and the running buffer. Reproducible SDS-PAGE separations are performed in gels
lacking SDS provided the sample buffer and running buffers contain sufficient SDS to saturate the proteins
during electrophoresis. The recommended concentration of SDS is 2% in sample buffer and 0.1% in running
buffers.
SDS-PAGE uses discontinuous chloride and glycine ion fronts to form moving boundaries that stack and
then separate SDS-coated polypeptides by molecular weight. Protein samples are prepared in a reducing
denaturing sample buffer containing either 2-mercaptoethanol or dithiothreitol as the reducing reagent, and
heat and SDS are used to denature the proteins. 2-Mercaptoethanol and dithiothreitol eliminate protein
secondary structure by reducing disulfide bonds. SDS minimizes charge variability among proteins, giving
them the same charge to mass ratio and forcing them into rod-like shapes. This effectively eliminates the
effects of protein conformation and native charge density on the electrophoretic migration distance. Molecular
weight determinations are obtained by plotting the logarithm of protein molecular mass vs. the relative
mobility (Rf= distance migrated by protein/distance migrated by dye front).
7
Page 13

3.2 Ready Gel Tris-HCl Gel Composition
Gel buffer 0.375 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.8
Cross-linker 2.6% C
Stacking gel 4% T, 2.6% C
Storage buffer 0.375 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.8
Shelf life 12 weeks
3.3 Ready Gel Tris-HCl Gel Selection Guide
Tris-HCl gels are available in a wide selection of single percentages and gradients for the separation of
proteins by SDS-PAGE.
Tris-HCl Gels Optimal Separation Tris-HCl Gradient Gels Optimal Separation
5% 100–250 kD 4–15% 20–250 kD
7.5% 40–200 kD 4–20% 10–200 kD
10% 30–150 kD 8–16% 20–120 kD
12% 20–120 kD 10–20% 10–100 kD
15% 10–100 kD
18% 10–50 kD
8
Page 14

3.4 SDS-PAGE Buffers
Running Buffer 1X Working Concentration 10x Stock
25 mM Tris Tris base 15.0 g
192 mM glycine Glycine 72.0 g
0.1% SDS SDS 5.0 g
to 500 ml with deionized water
Note: running buffer should be
~ pH 8.3. Do not adjust the pH.
Sample Buffer 2X Working Concentration
2X Stock
62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 0.5 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 1.0 ml
2% SDS 10% (w/v) SDS 1.6 ml
25% glycerol Glycerol 2.0 ml
0.01% Bromophenol Blue 1.0% Bromophenol Blue 0.08 ml
5% 2-mercaptoethanol 2-Mercaptoethanol 0.4 ml
or 350 mM DTT (added fresh) Deionized water 2.92
ml
8.0 ml
3.5 Sample Preparation
Determine the appropriate protein concentration of your sample based on the detection method and load
volume used. (See section 10.1 for approximate stain sensitivities.) Dilute 1 part sample with 1 part sample
buffer (see section 3.4) and heat at 95ºC for 5 min.
3.6 Running Conditions
Power conditions 200 V constant
Starting current: 50 mA/gel
Final current: 30 mA/gel
Run time 35 min
9
Page 15

Section 4
Native PAGE
4.1 Introduction
Ready Gel Tris-HCl gels are made without SDS, allowing separation of protein in their native conformation.
The nonreducing and nondenaturing environment of native PAGE allows the detection of biological activity
and can improve antibody detection. Native PAGE can also be used to resolve multiple protein bands where
molecular mass separation by SDS-PAGE would reveal only one.
Native PAGE uses the same discontinuous chloride and glycine ion fronts as SDS-PAGE to form moving
boundaries that stack and then separate polypeptides by charge to mass ratio. Proteins are prepared in a
nonreducing nondenaturing sample buffer, which maintains the proteins’ secondary structure and native
charge density. Native PAGE is not suitable for accurate molecular weight determination due to the variability
of charge to mass ratio among different proteins.
4.2 Ready Gel Tris-HCl Gel Composition
Gel buffer 0.375 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.8
Cross-linker 2.6% C
Stacking gel 4% T, 2.6% C
Storage buffer 0.375 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.8, NaN
3
Shelf life 12 weeks from the date of manufacture
10
Page 16

4.3 Ready Gel Tris-HCl Gel Selection
Native PAGE separates by charge to mass ratio, making individual protein migration protein dependent.
Optimal Tris-HCl gel percentages will have to be determined experimentally.
4.4 Native PAGE Buffers
Running Buffer Working Concentration 10x Stock
25 mM Tris Tris base 15.0 g
192 mM glycine Glycine 72.0 g
to 500 ml with deionized water 87.0 g
Note: running buffer should be
~ pH 8.3. Do not adjust the pH.
Sample Buffer 2X Working Concentration
2X Stock
62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 0.5 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 1.0 ml
25% glycerol Glycerol 2.0 ml
1% Bromophenol Blue 1% Bromophenol Blue 1.0 ml
Deionized water 4.92 ml
8.0 ml
11
Page 17

4.5 Sample Preparation
Determine the desired protein concentration and load volume of your sample based on the detection
method used. (See section 10.1 for approximate stain sensitivities). Sample preparation for native PAGE
applications requires special consideration. In the absence of SDS, the net charge of a polypeptide will be
determined by the pH of the sample buffer. Only polypeptides with a net negative charge will migrate into a
native PAGE Tris-HCl gel. Most polypeptides have an acidic or slightly basic pl (~3–8). These proteins can be
separated using a standard protocol by diluting 1 part sample with 1 part native sample buffer (see section
4.4; DO NOT HEAT SAMPLES).
Strongly basic peptides (pl >9) will have a net positive charge in a native PAGE Tris-HCl gel. In order for
polypeptides with a net positive charge to migrate into a native PAGE Tris-HCl gel, the polarity of the
electrodes must be changed by reversing the color-coded jacks when connecting to the power supply.
4.6 Running Conditions
Power conditions 200 V constant
Starting current: 50 mA/gel
Final current: 30 mA/gel
Run time 35 min
12
Page 18

Section 5
Peptide Analysis
5.1 Introduction
Ready Gel Tris-Tricine/peptide gels are optimized for separating peptides and proteins <10 kD. Superior
resolution of peptides is achieved by moving the peptide-SDS complexes more slowly through the gel. This
allows the faster moving SDS micelles, which normally interfere with peptide separations, to completely
separate from the peptides, allowing distinct peptide bands to resolve.
5.2 Ready Gel Tris-Tricine/Peptide Gel Composition
Gel buffer 1.0 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.45
Cross-linker 2.6% C
Stacking gel 4% T, 2.6% C
Storage buffer 1.0 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.45, NaN
3
Shelf life 12 weeks from the date of manufacture
5.3 Ready Gel Tris-Tricine/Peptide Gel Selection Guide
Tris-Tricine/peptide gels are available in either a single percentage gel or a linear gradient gel.
Peptide Gel Optimal Separation
16.5% 15–30 kD
10–20% 1–40 kD
13
Page 19

5.4 Tris-Tricine/Peptide Buffers
Running buffer Working Concentration 10x Stock
100 mM Tris Tris base 60.55 g
100 mM Tricine Tricine 89.60 g
0.1% SDS SDS 5.0 g
to 500 ml with deionized water
Note: Tricine running buffer should be
~ pH 8.25. Do not adjust the pH.
Sample Buffer Working Concentration
2X Stock
200 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 1.0 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 2.0 ml
2% SDS 10% SDS 2.0 ml
40% glycerol Glycerol 4.0 ml
0.04% Coomassie Blue G-250 0.5% Coomassie Blue G-250 0.8 ml
2% 2-mercaptoethanol 2-Mercaptoethanol 0.2 ml
or 350 mM DTT (Added fresh) Deionized water 1.0 ml
10.0 ml
5.5 Sample Preparation
Determine the appropriate protein concentration of your sample based on the detection method and load
volume used. (See section 10.2 for approximate stain sensitivities.) Dilute 1 part sample with 1 part sample
buffer and heat at 95ºC for 5 min.
5.6 Running Conditions
Power Conditions 100 V constant
Starting current: 30–35 mA/gel
Final current: 15–20 mA/gel
Run Time 100 min
14
Page 20

Section 6
Isoelectric Focusing
6.1 Introduction
Ready Gel IEF gels are cast with Bio-Rad’s Bio-Lyte
®
ampholytes, amphoteric molecules that set up a pH
gradient across the gels. Proteins migrate in IEF gels to their neutral isoelectric point (pI), where the protein
has zero net charge. Ready Gel IEF gels contain no denaturing agents, so all focusing is performed under
native conditions.
6.2 Ready Gel IEF Gel Composition
Gel buffer 2% ampholyte, pH 3–10, 5–8
Cross-linker 3.0% C
Stacking gel None
Storage buffer Deionized water, NaN
3
Shelf life 26 weeks from the date of manufacture
6.3 Ready Gel IEF Gel Selection Guide
Ready Gel IEF gels are available in narrow and broad pH ranges.
IEF gel pH Range
5–8 5–8
3–10 4–8.5
15
Page 21

6.4 IEF Buffers
Running buffer 1x Cathode Buffer 5x Cathode Buffer
20 mM lysine (free base) Lysine (free base) 14.50 g
20 mM arginine (free base) Arginine (free base) 17.42 g
to 1 L with deionized water
1x Anode Buffer
10x Anode Buffer
7mM% phosphoric acid Phosphoric acid 4.2 ml
to 1 L with deionized water
Sample Buffer 50% glycerol
6.5 Sample Preparation
Determine the appropriate protein concentration of your sample based on the detection method and load
volume used. (See section 10.3 for approximate stain sensitivities.) Dilute 1 part sample with 1 part sample
buffer.
6.6 Running Conditions
Power conditions Stepwise
100 V constant 60 min
250 V constant 60 min
500 V constant 30 min
Starting current: 5–15 mA/gel
Final current: 5–15 mA/gel
Run time 150 min
16
Page 22

Section 7
Protease Analysis by Zymogram PAGE
7.1 Introduction
Ready Gel zymogram gels are used to test for proteolytic activity when performing protein characterizations.
Gels are cast with gelatin or casein, which act as substrates for proteases that are separated on the gel.
Proteases are detected by renaturing the enzyme followed by a development period in which the protease
breaks down the substrate. Zymogram gels are stained with Coomassie Blue R-250, which stains the
substrate while leaving clear areas around active proteases.
7.2 Ready Gel Zymogram Gel Composition
Gel buffer 0.375 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.6
Cross-linker 2.6% C
Stacking gel 4% T, 2.6% C
Storage buffer 0.375 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.6, 0.2% NaN
3
Shelf life 12 weeks from the date of manufacture
7.3 Ready Gel Zymogram Gel Selection Guide
Ready Gel zymogram gels are available with either gelatin or casein as substrate and should be selected
based on their substrate and separation range.
Zymogram Gel Optimal Separation
10% zymogram gel with gelatin 30–150 kD
12% zymogram gel with casein 20–120 kD
17
Page 23

7.4 Zymogram Buffers
Running buffer Working Concentration 10x Stock
25 mM Tris Tris base 15.0 g
192 mM glycine Glycine 72.0 g
0.1% SDS SDS 5.0 g
to 500 ml with deionized water
Note: running buffer should be
~pH 8.3. Do not adjust the pH.
Sample Buffer Working Concentration
2X Stock
62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 0.5 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 1.25 ml
4% SDS 10% SDS 4.0 ml
25% glycerol Glycerol 2.5 ml
0.01% Bromophenol Blue 1% Bromophenol Blue 0.1 ml
Deionized water 2.15 ml
10 ml
7.5 Sample Preparation
Determine the appropriate protein concentration of your sample based on the detection method and load
volume used. (See section 10.4 for approximate stain sensitivities.) Dilute 1 part sample buffer with 1 part
Zymogram sample buffer. Dry samples can be dissolved directly in sample buffer. Do not heat.
7.6 Running Conditions
Power conditions 100 V constant
Starting current: 10–15 mA/gel
Final current: 6 mA/gel
Run time 90 min
18
Page 24

Section 8
Nondenaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE
8.1 Introduction
Ready Gel TBE gels are ideal for separating small dsDNA fragments, especially PCR products. The uniform
nature of DNA molecules provides samples with near-uniform charge to mass ratio, allowing nondenaturing
nucleic acid PAGE to separate dsDNA by mass using a continuous TBE buffer system.
8.2 Ready Gel TBE Gel Composition
Gel buffer 89 mM Tris, 89 mM boric acid, 2 mM EDTA, pH 8.3
Cross-linker 3.3% C
Stacking gel 4% T, 3.3% C
Storage buffer 89 mM Tris, 89 mM boric acid, 2 mM EDTA, NaN
3
Shelf life 12 weeks from the date of manufacture
8.3 Ready Gel TBE Gel Selection Guide
Ready Gel TBE gels are available in a selection of single percentages and gradients for the separation of
dsDNA.
TBE Gels Optimal Separation TBE Gradient Gels Optimal Separation
5% 200–2,000 bp 4–20% 10–2,000 bp
10% 50–1,500 bp
15% 20–1,000 bp
19
Page 25

8.4 Nondenaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE Buffers
Running Buffer Working Concentration 10x Stock
50 mM Tris Tris base 0.06 g
89 mM boric acid Boric acid 27.5 g
5 mM EDTA 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) 0.1 ml
to 500 ml with deionized water
Note: TBE running buffer should be
~ pH 8.3. Do not adjust the pH.
Sample Buffer 2X Working Concentration
50 nM EDTA Tris Base 0.06 g
25% glycerol 0.5 M EDTA 0.1 ml
0.2% Bromophenol Blue Glycerol 2.5 ml
0.2% Xylene Cyanole FF 1% Bromophenol Blue 2.0 ml
1% Xylene Cyanole FF 2.0 ml
Make up to 10 ml with deionized water
8.5 Sample Preparation
Determine the desired DNA concentration of your sample based on the detection method used. (See
section 10.5 for approximate stain sensitivities.) Dilute 1 part sample with 4 parts sample buffer (see section
8.4).
8.6 Running Conditions
Power conditions 100 V constant
Starting current: 13 mA/gel
Final current: 11 mA/gel
Run time 45–105 min
20
Page 26

Section 9
Denaturing Nucleic Acid PAGE
9.1 Introduction
Ready Gel TBE-urea gels are ideal for separating small ssDNA and RNA fragments. Applications include
oligonucleotide analysis, RNase protection assays, and northern blotting.
9.2 Ready Gel TBE-Urea Gel Composition
Gel buffer 89 mM Tris, 89 mM boric acid, 2 mM EDTA, 7 M urea, pH 8.3
Cross-linker 3.3% C
Stacking gel 4% T, 3.3% C
Storage buffer 89 mM Tris, 89 mM boric acid, 2 mM EDTA, pH 8.3, NaN
3
Shelf life 8 weeks from the date of manufacture
9.3 Ready Gel TBE-Urea Gel Selection Guide
Ready Gel TBE-urea gels are available in a range of single percentage gels.
TBE-Urea Optimal Separation
5% 50–1,000 bases
10% 25–300 bases
15% 10–50 bases
21
Page 27

9.4 TBE-Urea Buffers
Running Buffer Working Concentration 10x Stock
89 mM Tris Tris base 54.0 g
89 mM boric acid Boric acid 27.5
2 mM EDTA 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) 20.0 ml
to 500 ml with deionized water
Sample Buffer Working Concentration
89 mM Tris, 89 mM boric acid, 2 mM EDTA, pH 8.0 10x TBE 1.0 ml
12% Ficoll Ficoll 1.2 g
0.01% Bromophenol Blue Urea 4.2 g
0.02% Xylene Cyanole FF 1% Bromophenol blue 0.1 ml
7 M urea 1% Xylene Cyanole FF 0.2 ml
0.5 M EDTA 0.02 ml
Make up to 10 ml with deionized water
9.5 Sample Preparation
Determine the desired ssDNA or RNA concentration for your sample based on the detection method used.
(See section 10.6 for appropriate stain sensitivities.) Dilute 1 part sample with 1 part TBE-urea sample buffer.
Dry samples can be dissolved directly in sample buffer. Heat to 70–90°C 4 min before loading.
9.6 Running Conditions
Power conditions 200 V constant
Starting current: 15 mA/gel
Final current: 10 mA/gel
Run time 40–70 min
22
Page 28

Section 10
Detection
10.1 SDS-PAGE and Native PAGE Detection
Total Protein Gel Stains
Method Sensitivity Optimal Protein Load Advantages Disadvantages
Coomassie Blue R-250 36–47 ng ~0.5 µg/band Laboratory standard Requires MeOH
Bio-Safe™Coomassie stain 8–28 ng ~0.5 µg/band Nonhazardous, uses More steps than
no MeOH Coomassie Blue R-250
Copper stain 6–12 ng ~0.2 µg/band Fast, reversible stain Negative stain, must
be photographed;
SDS-PAGE only
Zinc stain 6–12 ng ~0.2 µg/band High-contrast, fast, Negative stain, must
reversible stain be photographed;
SDS-PAGE only
Silver Stain™Plus kit 0.6–1.2 ng ~0.01 µg/band Simple, robust, mass Will not stain
spectrometry compatible glycoproteins
Silver stain 0.6–1.2 ng ~0.01 µg/band Stains complex Not mass spectrometry
proteins, i.e., glycoproteins compatible
and lipoproteins
SYPRO Orange protein 4–8 ng ~0.2 µg/band Will not stain nucleic Optimization required
stain acids; mass spectrometry for maximum
compatible sensitivity
SYPRO Ruby protein gel 1–10 ng ~0.2 µg/band Broad dynamic range, Requires imaging
stain simple robust protocol instrument for
maximum sensitivity
Flamingo Fluorescent 0.25–0.5 ng ~0,2 ng/band Broad dynamic range Requires imaging instrument
gel stain mass spec compatible for maximum sensitivity
23
Page 29

Total Protein Blot Stains
Method Sensitivity Optimal Protein Load Advantages Disadvantages
SYPRO Ruby protein blot 2–8 ng ~0.2 µg/band Compatible with mass Multiple step protocol; Requires
stain spectrometry, Edman-based imaging instrument for
sequencing, and standard
immunological procedures maximum sensitivity
Colloidal gold stain 1 ng ~0.1 µg/band Sensitive, one step Not compatible with nylon
membranes
Enhanced colloidal 10–100 pg ~0.1 µg/band Increases sensitivity of Multiple steps
gold detection kit colloidal gold stain
AmidoBlack 10B 100–1,000 ng ~5 µg/band Standard membrane Low sensitivity
stain, economical
Immunoblot Detection
Method Sensitivity Optimal Protein Load Advantages Disadvantages
4CN colorimetric (HRP) 500 pg ~0.25 µg/band Fast detection Results may fade
DAB colorimetric (HRP) 500 pg ~0.25 µg/band Fast detection Contains toxic chemicals
Opti-4CN colorimetric (HRP) 100 pg ~0.05 µg/band Color does not fade More expensive than 4CN
Amplified Opti-4CN 10 pg ~0.005 µg/band High sensitivity, low Amplification requires
colorimetric (HRP) background additional steps
BCIP/NBT colorimetric 100 pg ~0.05 µg/band Sensitive, multiple antigen May detect endogenous
(AP) enzyme activity
Amplified alkaline 10 pg ~0.005 µg/band High sensitivity Amplification requires
phosphatase additional steps
Immun-Star
™
10 pg ~0.005 µg/band Long-lasting signal, Requires visualization
chemiluminescent (AP) short and multiple on film or instrumentation
exposures possible
Immun-Star
™
1–3 pg ~0.005 µgband Intensifies signal Requires visualization on
chemiluminescent (hrp) output, very sensitive film or instrumentation
Immun-Star WesternC (HRP) 10 fg ~0.005 µgband long-lasting signal Requires visualzation on
short and multiple on film or instrumentation
exposures possible
24
Page 30

10.2 Peptide Gel Staining
Peptides and small proteins are prone to diffusion and loss during staining. The following protocol uses a
fixation step to prevent sample loss and is suitable for detection of bands as low as 10–20 ng.
Fixative Solution
40% methanol
10% acetic acid
Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 Stain Solution
0.025% Coomassie Blue G-250
10% acetic acid
Destain Solution
10% acetic acid
Place gels in fixative solution and equilibrate for 30 min. Stain gels with Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 stain
solution for 1 hr. Stain should only be used once. Reuse of stain could result in loss of sensitivity. Destain
gels 3 times for 15 min or until the desired background is achieved. Some peptides may not be completely
fixed and may diffuse out of the gels if fixing and staining times are greatly exceeded.
25
Page 31

26
10.3 IEF Gel Staining
Samples on IEF gels can be detected using multiple methods. Use the following table as a guide to select
an appropriate staining method.
Method Sensitivity Optimal Protein Load Advantages Disadvantages
IEF stain 40–50 ng ~0.5 µg/band Simple, no fixation required Requires MeOH
Silver Stain Plus kit 0.6–1.2 ng ~0.01 µg/band Simple, robust, mass Requires TCA
spectrometry compatible fixation
Silver stain 0.6–1.2 ng ~0.01 µg/band Stains complex Requires TCA
proteins, i.e. glycoproteins fixation
and lipoproteins
Page 32

27
10.4 Zymogram Gel Staining
Prior to staining zymogram gels, sample proteases must be first renatured and allowed to break down the
substrate contained in the gel. The following protocol provides basic guidelines for detection. Optimal results
should be determined empirically.
Renaturing Solution
2.5% Triton X-100
Development Solution
50 mM Tris
200 mM NaCl
5 mM CaCl
2
(anhydrous)
0.02% Brij-35
Adjust to pH 7.5
Staining Solution
40% methanol
10% acetic acid
0.5% Coomassie Blue R-250
Destaining Solution
40% methanol
10% acetic acid
Proteins must be renatured first by placing the gels in renaturing solution for 30 min at room temperature.
Incubate gels in development solution at 37ºC for a minimum of 4 hr. Highest sensitivity is typically achieved
with overnight incubation. Optimal results should be determined empirically. Stain gels with Coomassie
Brilliant Blue R-250 staining solution for at least 1 hr at room temperature. Destain until clear bands appear
against the blue background, approximately
Page 33

28
30–60 min.
10.5 TBE Gel Staining
Use the following table as a guide to select an appropriate staining method.
Method Sensitivity Optimal Protein Load Advantages Disadvantages
Ethidium bromide 50 ng ~0.10 µg/band Classic fluorescent DNA stain Carcinogenic
Silver stain 1.0–2.0 ng ~0.5 µg/band More sensitive than Multiple steps
ethidium bromide
10.6 TBE-Urea Gel Staining
Samples on denaturing nucleic acid gels can be detected using multiple methods. Use the following table as
a guide to select an appropriate staining method.
Method Sensitivity Optimal Protein Load Advantages Disadvantages
Ethidium bromide 50 ng ~0.10 µg/band Classic fluorescent DNA stain Carcinogenic
Radiant
®
Red 10 ng ~0.10 µg/band Fast single-step protocol RNA and ssDNA
only
Silver stain 1.0–2.0 ng ~0.5 µg/band More sensitive than Multiple steps
ethidium bromide
Page 34

29
Section 11
Stock and Staining Solutions
11.1 Stock Solutions
0.5 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8
6.06 g Tris base
~60 ml deionized water
Adjust to pH 6.8 with HCl. Make to 100 ml with deionized water and store at 4°C.
10% SDS
Dissolve 1 g SDS in water with gentle stirring and bring to 10 ml with deionized water.
1% Bromophenol Blue
Dissolve 0.1 g of Bromophenol Blue in 10 ml deionized water with gentle stirring.
1% Xylene Cyanole FF
Dissolve 0.1 g of Xylene Cyanole FF in 10 ml deionized water with gentle stirring.
0.5 M EDTA
18.6 g of EDTA
~ 50 ml of deionized water
Adjust to pH 8.0 with 1 N NaOH. Make to 100 ml with deionized water and store at 4°C.
Page 35

30
11.2 Protein Staining Solutions
Coomassie Blue R-250 Staining Solution (0.1%)
Final Concentration
Methanol 400 ml 40%
Acetic acid 100 ml 10%
Coomassie Blue R-250 1.0 g 0.1%
Deionized water 500 ml
Dissolve Coomassie R-250 in methanol/acetic acid. Add deionized water to a final volume of 500 ml.
Coomassie Blue R-250 Destaining Solution
Final Concentration
Methanol 400 ml 40%
Acetic acid 100 ml 10%
Deionized water 500 ml
Silver Staining
See Bio-Rad’s silver stain (catalog #161-0443) or Silver Stain Plus kit (catalog #161-0449) instructions.
IEF Staining Solution
Final Concentration
Isopropyl alcohol 270 ml 27%
Acetic acid 100 ml 10%
Coomassie Blue R-250 0.4 g 0.04%
Crocein Scarlet 0.5 g 0.05%
Deionized water 630 ml
Page 36

31
IEF Destaining Solution
Final Concentration
Methanol 400 ml 40%
Acetic acid 100 ml 10%
Deionized water 500 ml
11.3 Peptide Staining Solutions
Fixative Solution
Final Concentration
Methanol 400 ml 40%
Acetic acid 100 ml 10%
Deionized water 500 ml
Coomassie Blue G-250 Staining Solution (0.025%)
Final Concentration
Acetic acid 100 ml 10%
Coomassie Blue G-250 0.25 g 0.025%
Deionized water 900 ml
Coomassie Blue G-250 Destaining Solution
Final Concentration
Acetic acid 100 ml 10%
Deionized water 900 ml
Page 37

32
11.4 Zymogram Staining Solutions
Renaturation Buffer
Final Concentration
Triton X-100 25 g 2.5 %
Deionized water 900 ml
to 1 L with deionized water
Development Solution
Final Concentration
Tris base 6.06 g 50 mM
NaCl 11.7 g 200 mM
CaCl
2
(anhydrous) 0.56 g 5 mM
30% Brij-35 0.67 ml 0.02%
Dissolve in 900 ml deionized water, adjust to 7.5 with 6 N HCl, make to 1 L with deionized water.
Staining Solution
Final Concentration
Methanol 400 ml 40%
Acetic acid 100 ml 10%
Coomassie Blue R-250 5 g 0.5%
Deionized water 500 ml
Dissolve Commassie R-250 in Methnaol/acetic acid. Add deionized water to final volume of 500 ml.
Page 38

33
11.5 Nucleic Acid Staining Solutions
Ethidium Bromide Staining
Use Bio-Rad’s ethidium bromide tablets or ethidium bromide solutions (catalog #161-0430 or 161-0443) for nucleic acid staining
solutions.
Silver Staining
See instructions for Bio-Rad’s silver stain, catalog #161-0443, or Silver Stain Plus kit, catalog #161-0449.
Radiant®Red Staining
Use Radiant Red stain, catalog #170-3122, for RNA staining.
Page 39

34
Section 12
Troubleshooting
Improper storage of Ready Gel precast gels can produce numerous artifacts. Gels should be stored flat at
4ºC. Avoid freezing or prolonged storage above 4ºC. If you suspect your gels have been stored improperly,
DO NOT USE THEM.
Problem Possible Cause Solution
Samples do not migrate into gel Tape at the bottom of the cassette Remove tape
not removed
Insufficient buffer in integral buffer chamber Fill buffer chamber with 125 ml
running buffer
Insufficient lower electrode buffer Fill both halves of the lower buffer tank
with sufficient running buffer
Electrical disconnection Check electrodes and connections
Bands “smile” across gel, band pattern Excess heating of gel Check buffer composition
curves upward at both sides of the gel
Completely fill both halves of the lower
buffer tank with sufficient running buffer
Do not exceed recommended running
conditions
Skewed or distorted bands, lateral Excess salt in samples Remove salts from sample by dialysis or
band spreading desalting column prior to sample
preparation
Insufficient sample buffer or wrong formulation Check buffer composition and dilution
instructions
Problem Possible Cause Solution
Vertical streaking Overloaded samples Dilute sample
Page 40

35
Selectively remove predominant protein in
the sample
Sample precipitation Centrifuge samples to remove particulates
prior to sample loading
Gels run too fast, provide poor resolution, Running buffer is too concentrated Check buffer composition
and gel temperature is too high
Artifact bands at ~60–70 kD Possible skin keratin contamination Clean all dishware and wear gloves
while handling and loading gel
Filter all solutions through nitrocellulose
Use 10% iodoacetamide to eliminate
keratin bands
Page 41

36
Section 13
Ordering Information
13.1 Ready Gel Precast Gels
Ready Gel Tris-HCl 10-Well 15-Well Prep Well 10-Well 12-Well 9-Well IPG Comb
Gels 30 µl 15 µl 450 µl 50 µl 20 µl 30 µl 7 cm IPG Strip
5% Tris-HCl 161-1210 161-1211 161-1213 161-1214
7.5% Tris-HCl 161-1100 161-1118 161-1136 161-1154 161-1172
10% Tris-HCl 161-1101 161-1119 161-1137 161-1155 161-1173 161-1191 161-1390
12% Tris-HCl 161-1102 161-1120 161-1138 161-1156 161-1174 161-1391
15% Tris-HCl 161-1103 161-1121 161-1139 161-1157 161-1175
18% Tris-HCl 161-1216 161-1217 161-1219 161-1220
4–15% Tris-HCl 161-1104 161-1122 161-1140 161-1158 161-1176 161-1194 161-1392
4–20% Tris-HCl 161-1105 161-1123 161-1141 161-1159 161-1177 161-1393
8–16% Tris-HCl 161-1222 161-1223 161-1225 161-1226 161-1394
10–20% Tris-HCl 161-1106 161-1124 161-1142 161-1160 161-1178 161-1395
Ready Gel TBE Precast Gels
5%, TBE 161-1109 161-1127 — 161-1163 161-1181
10%, TBE 161-1110 161-1128 — 161-1164 161-1182
15%,TBE 161-1228 161-1229 — 161-1232
4–20%, TBE 161-1234 161-1235 — 161-1237
Ready Gel Tris-Tricine/Peptide Precast Gels
16.5% Tris-Tricine/Peptide 161-1107 161-1125 161-1143 161-1161 161-1179 161-1197
10–20% Tris-Tricine/Peptide 161-1108 161-1126 161-1144 161-1162 161-1180 161-1198
Page 42

37
Ready Gel IEF Precast Gels
IEF pH 3–10 161-1111 161-1129 161-1165
IEF pH 5–8 161-1112
Ready Gel Zymogram Precast Gels
10% Zymogram, gelatin 161-1113 161-1131 — 161-1167 161-1185
12.5% Zymogram, casein 161-1114 — 161-1168
Ready Gel TBE-Urea Precast Gels
5% TBE-Urea 161-1115 161-1133 —
10% TBE-Urea 161-1116 161-1134
15% TBE-Urea 161-1117 161-1135 161-1189
Page 43

38
13.2 Buffers
Premixed Running Buffers Premixed Sample Buffers
161-0732 10x Tris/Glycine/SDS, 1 L 161-0737 Laemmli Sample Buffer, 30 ml*
161-0772 10x Tris/Glycine/SDS, 5 L 161-0738 Native Sample Buffer, 30 ml
161-0734 10x Tris/Glycine, 1 L 161-0739 Tricine Sample Buffer, 30 ml
161-0771 10x Tris/Glycine, 5 L 161-0763 IEF Sample Buffer, 30 ml
161-0744 10x Tris/Tricine/SDS, 1 L 161-0764 Zymogram Sample Buffer, 30 ml
161-0761 10x IEF Anode Buffer, 250 ml 161-0767 Nucleic Acid Sample Buffer, 5x, 10 ml
161-0762 10x IEF Cathode Buffer, 250 ml 161-0768 TBE-Urea Sample Buffer, 30 ml
161-0733 10x Tris/Boric Acid/EDTA, 1 L
161-0770 10x Tris/Boric Acid/EDTA, 5 L
* Requires addition of 2-mercaptoethanol or DTT
161-0765 Zymogram Renaturation Buffer, 125 ml
161-0766 Zymogram Development Buffer, 125 ml
Individual Reagents
161-0719 Tris, 1 kg
161-0716 Tris, 500 g
161-0717 Glycine, 250 g
161-0718 Glycine, 1 kg
161-0724 Glycine, 2 kg
161-0301 SDS, 100 g
161-0710 2-Mercaptoethanol, 25 ml
161-0610 Dithiothreitol, 1 g
161-0611 Dithiothreitol, 5 g
161-0404 Bromophenol Blue, 10 g
Page 44

13.3 Detection Reagents
Total Protein Gel Stains Total Protein Blot Stains
161-0436 Coomassie Blue R-250 Stain Solution, 1 L 170-3127 SYPRO Ruby Protein Blot Stain, 200 ml
161-0438 Coomassie Blue R-250 Destain Solution, 1 L 170-6527 Colloidal Gold Total Protein Stain, 500 ml
161-0400 Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250, 10 g 170-6517 Enhanced Colloidal Gold Detection Kit
161-0786 Bio-Safe Coomassie Stain, 1 L 161-0402 Amido Black 10B, 25 g
161-0470 Copper Stain and Destain Kit
161-0440 Zinc Stain and Destain Kit
161-0449 Silver Stain Plus Kit
161-0443 Bio-Rad Silver Stain Kit
170-3120 SYPRO Orange Protein Stain, 500 µl
170-3125 SYPRO Ruby Protein Gel Stain, 1 L
161-0490 Flamingo Fluorescent Gel Stain (10x), 20 ml
161-0491 Flamingo Fluorescent Gel Stain (10x), 100 ml
161-0492 Flamingo Fluorescent Gel Stain (10x), 500 ml
Immunoblot Detection
170-6431 HRP Conjugate Substrate Kit, 4CN
170-6535 HRP Color Development Reagent, DAB
170-8238 Amplified Opti-4CN Kit
170-8235 Opti-4CN Substrate Kit
170-6432 BCIP/NBT AP Conjugate Substrate Kit
170-6412 Amplified Alkaline Phosphatase Kit
170-5012 Immun-Star
™
Substrate Pack
39
Page 45

13.4 Blotting Membranes
162-0232 0.2 µm Nitrocellulose/Filter Paper Sandwich, 8.5 x 13.5 cm, 20 pack
162-0233 0.2 µm Nitrocellulose/Filter Paper Sandwich, 8.5 x 13.5 cm, 50 pack
162-0234 0.45 µm Nitrocellulose/Filter Paper Sandwich, 8.5 x 13.5 cm, 20 pack
162-0235 0.45 µm Nitrocellulose/Filter Paper Sandwich, 8.5 x 13.5 cm, 50 pack
162-0236 Sequi-Blot PVDF/Filter Paper Sandwich, 8.5 x 13.5 cm, 20 pack
162-0237 Sequi-Blot PVDF/Filter Paper Sandwich, 8.5 x 13.5 cm, 50 pack
13.5 Protein and DNA Standards
161-0363 Precision Plus Protein™Unstained Standards (10–250 kD), 1,500 µl, 150 applications
161-0373 Precision All Blue Prestained Standards (10–250 kD), 500 µl, 50 applications
161-0324 Kaleidoscope
™
Prestained Standards, 500 µl, 50 applications
161-0326 Polypeptide SDS-PAGE Standards (1.4–26.6 kD), 200 µl, 400 applications
161-0310 IEF Standards, pI range 4.45–9.6, 250 µl, 500 applications
161-0375 Precision Plus Protein
™
Kalaidoscope Standards 500 µl, 50 applications
161-0370 Precision Plus Protein
™
WesternC Standards, 250 µl, 50 applications
170-8351 20 bp EZ Load
™
Molecular Ruler (20–1,000 bp), 50 µg, 100 applications
170-8352 100 bp EZ Load Molecular Ruler (100–1,000 bp), 25 µg, 100 applications
170-8353 100 bp PCR EZ Load Molecular Ruler (100–3,000 bp), 40 µg, 100 applications
170-8200 AmpliSize
®
Molecular Ruler (50–2,000 bp), 25 µg, 50 applications
165-8004 Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell for Ready Gel Precast gels
13.6 Equipment
165-3302 Mini-PROTEAN 3 Electrophoresis Module
170-3930 Mini Trans-Blot
®
Electrophoresis Transfer Cell
Brij is a trademark of ICI Americas, Inc. Coomassie is a trademark of Imperial Chemical Industries PLC. Ficoll is a trademark of Amersham
Pharmacia Biotech. SYPRO is a trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc. Bio-Rad is licensed to sell SYPRO products for research use only,
under US Patent 5,616,502. Triton is a trademark of Union Carbide.
40
Page 46

Life Science
Group
Web site www.bio-rad.com USA (800) 4BIORAD Australia 02 9914 2800
Austria (01) 877 89 01 Belgium 09-385 55 11 Brazil 55 21 507 6191
Canada (905) 712-2771 China (86-21) 63052255
Czech Republic (420) 2-4141 0532 Denmark 45 44 52-1000
Finland 358 (0)9 804 2200
France 01 47 95 69 65 Germany 089 318 84-177
Hong Kong 852-2789-3300
India (91-124) 6398112/113/114, 6450092/93
Israel 03 951 4127 Italy 39 02 216091 Japan 03-5811-6270
Korea 82-2-3473-4460 Latin America 305-894-5950
Mexico 52 5 534 2552 to 54 The Netherlands 0318-540666
New Zealand 64-9-4152280 Norway 47-23-38-41-30 Poland (48) 22-8126 672
Portugal 351-21-472-7700 Russia 7 095 721 1404 Singapore 65-2729877
South Africa 00 27 11 4428508 Spain 34 91 590 5200
Sweden 46 (0)8-55 51 27 00 Switzerland 061 717-9555 United Kingdom 0800-181134
00-000 0000 Sig 1001Bulletin 0000 US/EG Rev A
Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc.
LIT188 Rev H
Catalog Number
161-0993
 Loading...
Loading...