Page 1

BiPAC 7301VGP
VoIP/ 802.11g
ADSL2+ Firewall Router
User Manual
Version Release 2.04
Page 2

TTaabbllee ooff CCoonntteennttss
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................. 3
I
NTRODUCTION TO YOUR ROUTER
F
EATURES
.................................................................................................................................................. 3
............................................................................................................. 3
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ROUTER ......................................................................................... 6
I
MPORTANT NOTE FOR USING THIS ROUTER
P
ACKAGE CONTENTS
T
HE FRONT
T
HE REAR PORTS
C
ABLING
LEDS...................................................................................................................................... 7
.................................................................................................................................................. 10
................................................................................................................................. 6
....................................................................................................................................... 8
................................................................................................ 6
CHAPTER 3: BASIC INSTALLATION.................................................................................................11
C
ONNECTING YOUR ROUTER
F
ACTORY DEFAULT SETTINGS
.................................................................................................................... 12
.................................................................................................................. 17
Web Interface (Username and Password) .......................................................................................... 17
LAN Device IP Settings ...................................................................................................................... 17
ISP setting in WAN site....................................................................................................................... 17
DHCP server ...................................................................................................................................... 17
LAN and WAN Port Addresses............................................................................................................ 17
I
NFORMATION FROM YOUR
C
ONFIGURING WITH YOUR WEB BROWSER
ISP ................................................................................................................ 18
.............................................................................................. 19
CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURATION......................................................................................................... 20
S
TATUS
.................................................................................................................................................... 21
ARP Table ........................................................................................................................................... 21
Wireless Association Table (Wireless Router only)............................................................................. 21
Routing Table...................................................................................................................................... 21
DHCP Table........................................................................................................................................ 23
Email Status........................................................................................................................................ 24
VoIP Status.......................................................................................................................................... 24
Event Log............................................................................................................................................ 24
Error Log............................................................................................................................................ 25
NAT Sessions ...................................................................................................................................... 25
Diagnostic........................................................................................................................................... 25
UPnP Portmap ................................................................................................................................... 26
Q
UICK START
C
ONFIGURATION
........................................................................................................................................... 27
...................................................................................................................................... 29
LAN (Local Area Network) ................................................................................................................. 29
Bridge Interface .............................................................................................................................. 29
Ethernet........................................................................................................................................... 30
Ethernet Client Filter ...................................................................................................................... 31
Wireless (Wireless Router only)..................................................................................................... 33
Wireless Security (Wireless Router only) ...................................................................................... 35
Wireless Client (MAC Address) Filter (Wireless Router only)...................................................... 37
Port Setting ..................................................................................................................................... 38
DHCP Server .................................................................................................................................. 39
WAN (Wide Area Network) ................................................................................................................. 40
ISP .................................................................................................................................................. 40
DNS ................................................................................................................................................ 50
ADSL.............................................................................................................................................. 51
Table of Contents i
Page 3

System ................................................................................................................................................. 52
Time Zone....................................................................................................................................... 52
Remote Access................................................................................................................................ 52
Firmware Upgrade.......................................................................................................................... 54
Backup / Restore............................................................................................................................. 54
Restart Router................................................................................................................................. 56
User Management........................................................................................................................... 57
Firewall and Access Control .............................................................................................................. 58
General Settings.............................................................................................................................. 59
Packet Filter.................................................................................................................................... 60
Intrusion Detection ......................................................................................................................... 67
URL Filter....................................................................................................................................... 69
Firewall Log ................................................................................................................................... 72
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) ................................................................................................... 73
Wizard............................................................................................................................................. 74
General Settings.............................................................................................................................. 76
Phone Ports..................................................................................................................................... 78
PSTN Dial Plan .............................................................................................................................. 80
VoIP Dial Plan ................................................................................................................................ 83
Ring & Tone ................................................................................................................................... 86
Special dial codes ........................................................................................................................... 87
QoS (Quality of Service)..................................................................................................................... 88
Prioritization ................................................................................................................................... 88
Outbound IP Throttling (LAN to WAN)......................................................................................... 90
Inbound IP Throttling (WAN to LAN) ........................................................................................... 91
Virtual Server (“Port Forwarding”) .................................................................................................. 96
Add Virtual Server.......................................................................................................................... 97
Edit DMZ Host ............................................................................................................................... 98
Edit DMZ Host ............................................................................................................................... 99
Edit One-to-One NAT (Network Address Translation) ................................................................ 100
Time Schedule................................................................................................................................... 102
Configuration of Time Schedule .................................................................................................. 104
Advanced .......................................................................................................................................... 105
Static Route................................................................................................................................... 105
Dynamic DNS .............................................................................................................................. 106
Check Email ................................................................................................................................. 107
Device Management..................................................................................................................... 108
IGMP .............................................................................................................................................112
VLAN Bridge ................................................................................................................................112
S
AVE CONFIGURATION TO FLASH
L
OGOUT
..................................................................................................................................................116
............................................................................................................116
CHAPTER 5: TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................................117
P
ROBLEMS STARTING UP THE ROUTER
P
ROBLEMS WITH THE
P
ROBLEMS WITH THE
WAN I
LAN I
NTERFACE
NTERFACE
.....................................................................................................117
..................................................................................................117
...................................................................................................118
APPENDIX A: PRODUCT SUPPORT AND CONTACT INFORMATION.....................................119
Table of Contents iii
Page 4

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Chapter 1: Introduction
Introduction to your Router
Welcome to the VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router. The router is an “all-in-one” VoIP ADSL router,
combining an ADSL modem, ADSL router, Ethernet network switch and 1 port for Voice over IP
functionalities, providing everything you need to get the machines on your network connected to the
Internet over your ADSL broadband connection. With features such as an ADSL Quick-Start wizard and
DHCP Server, you can be online in no time at all and with a minimum of fuss and configuration, catering
for first-time users to the guru requiring advanced features and control over their Internet connection and
network.
Features
Voice over IP compliance with SIP standard
The router supports cost-effective, toll-quality voice calls over the Internet. It complies with the
most popular industrial standard, SIP protocol, to ensure the interoperability with SIP devices and
major VoIP Gateways. The VoIP ADSL router supports call waiting, silence suppression, voice
activity detection (VAD), comfort noise generation (CNG), line echo cancellation, caller ID (Bell
202, V3) and so on.
Lifeline Support
The router integrates RJ-11 FXO port for inbound and outbound calls transmitted through PSTN.
Users can receive phone calls from PSTN while enjoying VoIP call service at the same time. In
addition, the device automatically fallbacks to lifeline POTS to enable making normal phone calls
when there is power outage, or when the Internet connection is down.
Express Internet Access
The router complies with ADSL worldwide standards. It supports downstream rate up to 12/24
Mbps with ADSL2/2+, 8Mbps with ADSL. Users enjoy not only high-speed ADSL services but also
broadband multimedia applications such as interactive gaming, video streaming and real-time
audio much easier and faster than ever. It is compliant with Multi-Mode standard (ANSI T1.413,
Issue 2; G.dmt (ITU G.992.1); G.lite (ITU G.992.2); G.hs (ITU G994.1); G.dmt.bis (ITU G.992.3);
G.dmt.bisplus (ITU G.992.5)).
802.11g Wireless AP with WPA Support
With integrated 802.11g Wireless Access Point in the router, the device offers a quick and easy
access among wired network, wireless network and broadband connection (ADSL) with single
device simplicity, and as a result, mobility to the users. In addition to 54 Mbps 802.11g data rate, it
also interoperates backward with existing 802.11b equipment. The Wireless Protected Access
(WPA) and Wireless Encryption Protocol (WEP) supported features enhance the security level of
data protection and access control via Wireless LAN.
Fast Ethernet Switch
A 4-port 10/100Mbps fast Ethernet switch is built in with automatic switching between MDI and
MDI-X for 10Base-T and 100Base-TX ports. An Ethernet straight or crossover cable can be used
directly for auto detection.
Multi-Protocol to Establish A Connection
Supports PPPoA (RFC 2364 - PPP over ATM Adaptation Layer 5), RFC 1483 encapsulation over
ATM (bridged or routed), PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516), and IPoA (RFC1577) to establish a
connection with the ISP. The product also supports VC-based and LLC-based multiplexing.
3
Chapter 1: Introduction
Page 5
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Quick Installation Wizard
Supports a WEB GUI page to install this device quickly. With this wizard, end users can enter the
information easily which they get from their ISP, then surf the Internet immediately.
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) and UPnP NAT Traversal
This protocol is used to enable simple and robust connectivity among stand-alone devices and
PCs from many different vendors. It makes network simple and affordable for users. UPnP
architecture leverages TCP/IP and the Web to enable seamless proximity networking in addition to
control and data transfer among networked devices. With this feature enabled, users can now
connect to Net meeting or MSN Messenger seamlessly.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Allows multi-users to access outside resources such as the Internet simultaneously with one IP
address/one Internet access account. Many application layer gateway (ALG) are supported such
as web browser, ICQ, FTP, Telnet, E-mail, News, Net2phone, Ping, NetMeeting, IP phone and
others.
SOHO Firewall Security with DoS and SPI
Along with the built-in NAT natural firewall feature, the router also provides advanced hacker
pattern-filtering protection. It can automatically detect and block Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
The router is built with Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) to determine if a data packet is allowed
through the firewall to the private LAN.
Domain Name System (DNS) relay
Provides an easy way to map the domain name (a friendly name for users such as
www.yahoo.com) and IP address. When a local machine sets its DNS server with this router’s IP
address, every DNS conversion request packet from the PC to this router will be forwarded to the
real DNS in the outside network.
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS)
The Dynamic DNS service allows you to alias a dynamic IP address to a static hostname. This
dynamic IP address is the WAN IP address. For example, to use the service, you must first apply
for an account from a DDNS service like http://www.dyndns.org/. More than 5 DDNS servers are
supported.
Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS gives you full control over which types of outgoing data traffic should be given priority by the
router, ensuring important data like gaming packets, customer information, or management
information move through the router ay lightning speed, even under heavy load. The QoS features
are configurable by source IP address, destination IP address, protocol, and port. You can throttle
the speed at which different types of outgoing data pass through the router, to ensure P2P users
don’t saturate upload bandwidth, or office browsing doesn’t bring client web serving to a halt. In
addition, or alternatively, you can simply change the priority of different types of upload data and let
the router sort out the actual speeds.
Virtual Server (“port forwarding”)
Users can specify some services to be visible from outside users. The router can detect incoming
service requests and forward either a single port or a range of ports to the specific local computer
to handle it. For example, a user can assign a PC in the LAN acting as a WEB server inside and
expose it to the outside network. Outside users can browse inside web servers directly while it is
protected by NAT. A DMZ host setting is also provided to a local computer exposed to the outside
network, Internet.
Rich Packet Filtering
Not only filters the packet based on IP address, but also based on Port numbers. It will filter
packets from and to the Internet, and also provides a higher level of security control.
4
Chapter 1: Introduction
Page 6

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client and server
In the WAN site, the DHCP client can get an IP address from the Internet Service Provider (ISP)
automatically. In the LAN site, the DHCP server can allocate a range of client IP addresses and
distribute them including IP address, subnet mask as well as DNS IP address to local computers. It
provides an easy way to manage the local IP network.
Static and RIP1/2 Routing
Supports an easy static routing table or RIP1/2 routing protocol to support routing capability.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
It is an easy way to remotely manage the router via SNMP.
Web based GUI
Supports web based GUI for configuration and management. It is user-friendly and comes with online help. It also supports remote management capability for remote users to configure and
manage this product.
Firmware Upgradeable
Device can be upgraded to the latest firmware through the WEB based GUI.
Rich management interfaces
Supports flexible management interfaces with local console port, LAN port, and WAN port. Users
can use terminal applications through the console port to configure and manage the device, or
Telnet, WEB GUI, and SNMP through LAN or WAN ports to configure and manage the device.
5
Chapter 1: Introduction
Page 7
Warning
Attention
Chapter 2: Installing the Router
Important note for using this router
Package Contents
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Do not use this router in high humidity or high temperatures.
Do not use the same power source for this router as other
equipment.
Do not open or repair the case yourself. If this router is too hot,
turn off the power immediately and have it repaired at a qualified
service center.
Avoid using this product and all accessories outdoors.
Place this router on a stable surface.
Only use the power adapter that comes with the package. Using
a different voltage rating power adaptor may damage this router.
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Chapter 2: Installing the router
CD-ROM containing the online manual
RJ-11 ADSL/ telephone Cable
Ethernet (CAT-5 LAN) Cable
Console tool
Power adapter
A detachable antenna
Quick Start Guide
6
Page 8
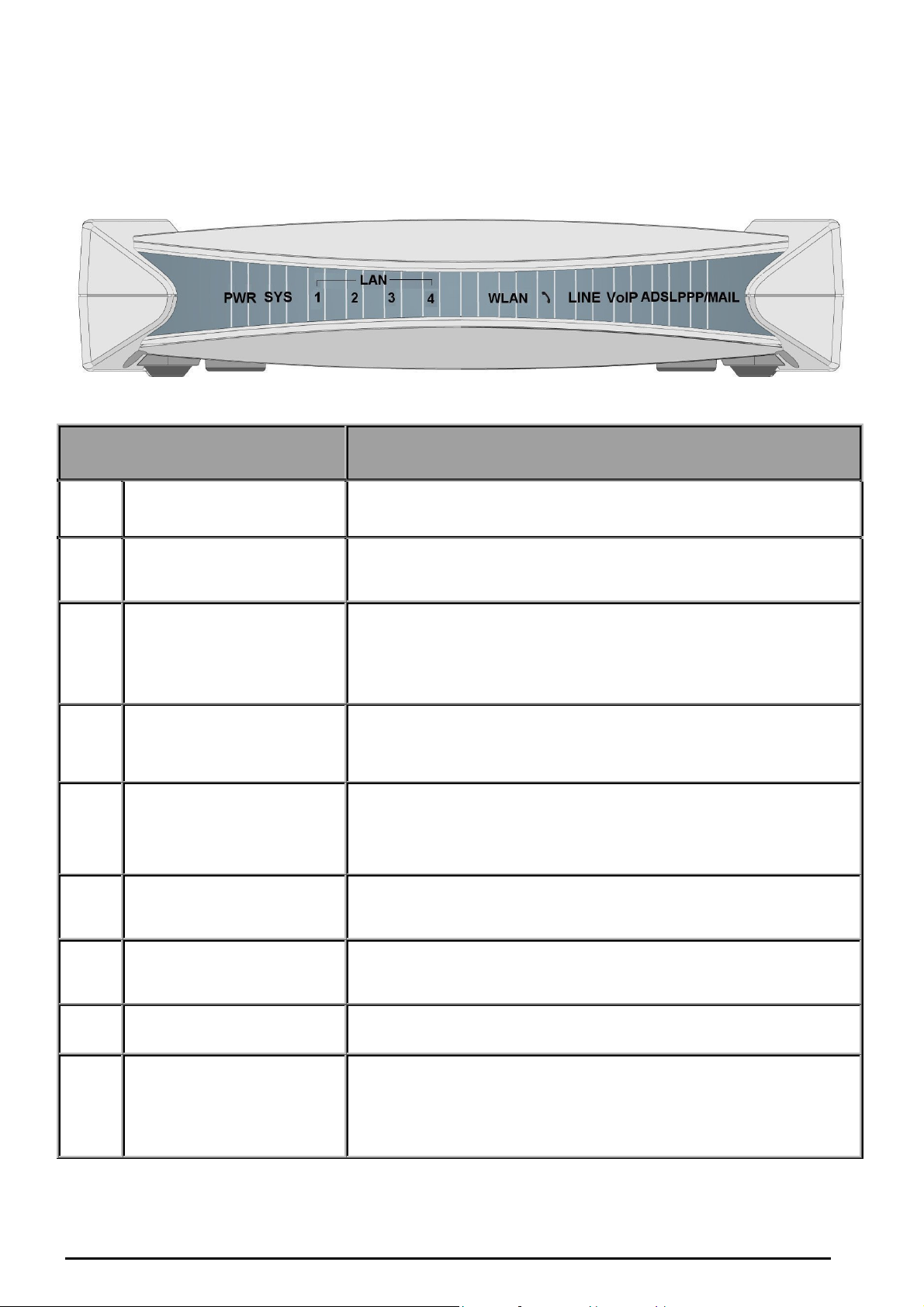
The Front LEDs
LED Meaning
1 PWR Lit when power is ON.
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
2 SYS Lit when the system is ready.
Lit when connected to an Ethernet device.
Green for 100Mbps; Orange for 10Mbps.
Blinking when data is Transmitted / Received.
3 – 6
LAN Port
1X — 4X
(RJ-45 connector)
Lit green when the wireless connection is established.
8 WLAN
Flashes when sending/receiving data.
Phone
9
(RJ-11 connector)
10 LINE
11
VoIP
12 ADSL
Lit green when the phone is off-hook.
Lit when the inbound and outbound calls transmitted
through PSTN.
Lit when SIP registration is OK.
Lit when successfully connected to an ADSL DSLAM
(“linesync”).
Lit steady when there is a PPPoA / PPPoE connection.
13 PPP / MAIL
Lit and flashed periodically when there is email in the Inbox.
7
Chapter 2: Installing the router
Page 9
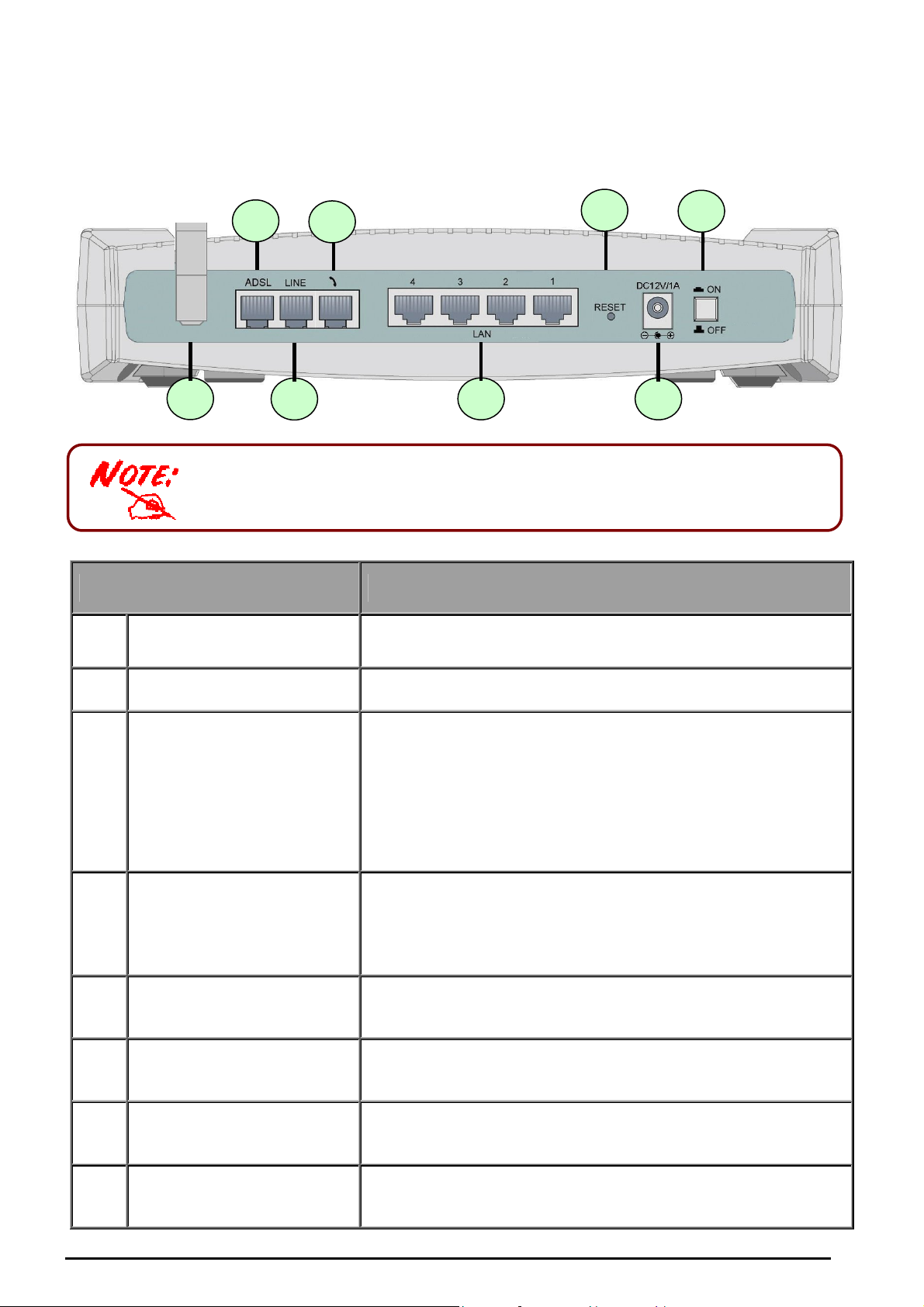
1
2
3
5 6
4 8
7
The Rear Ports
The Ethernet Port # 4 can be connected to the computer and console. You need
a special console tool which is included in this package to connect the LAN
cable of Port 4 when connecting to a PC’s RS-232 port (9-pin serial port).
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Power Switch
1
Power
2
3 RESET
LAN
4
1X — 4X
(RJ-45 connector)
Phone
5
(RJ-11 connector)
Port Meaning
Power ON/OFF switch
Connect the supplied power adapter to this jack.
After the device is powered on, press it to reset the
device or restore to factory default settings.
0-3 seconds: reset the device
6 seconds above: restore to factory default settings (this
is used when you can not login to the router, e.g. forgot
the password)
Connect a UTP Ethernet cable (Cat-5 or Cat-5e) to one of
the four LAN ports when connecting to a PC or an
office/home network of 10Mbps or 100Mbps.
Connect RJ-11 cable to this port when connecting to an
analog phone set.
LINE
6
ADSL
7
Antenna
8
Chapter 2: Installing the router
Connect RJ-11 cable to this port when connecting to the
telephone wall jack.
Connect the supplied RJ-11 (“telephone”) cable to this
port when connecting to the ADSL/telephone network.
Connect the detachable antenna to this port.
8
Page 10

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
9
Chapter 2: Installing the router
Page 11

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Cabling
One of the most common causes of problems is bad cabling or ADSL line(s). Make sure that all
connected devices are turned on. On the front of the product is a bank of LEDs. Verify that the LAN Link
and ADSL line LEDs are lit. If they are not, verify that you are using the proper cables.
Ensure that all other devices connected to the same telephone line as your router (e.g. telephones, fax
machines, analogue modems) have a line filter connected between them and the wall socket (unless
you are using a Central Splitter or Central Filter installed by a qualified and licensed electrician), and
ensure that all line filters are correctly installed and the right way around. Missing line filters or line filters
installed the wrong way around can cause problems with your ADSL connection, including causing
frequent disconnections.
10
Chapter 2: Installing the router
Page 12

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
The router can be configured with your web browser. A web browser is included as a standard
application in the following operating systems: Linux, Mac OS, Windows 98/NT/2000/XP/Me, etc. The
product provides a very easy and user-friendly interface for configuration.
PCs must have an Ethernet interface installed properly and be connected to the router either directly or
through an external repeater hub, and have TCP/IP installed and configured to obtain an IP address
through a DHCP server or a fixed IP address that must be in the same subnet as the router. The default
IP address of the router is 192.168.1.254 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 (i.e. any attached PC
must be in the same subnet, and have an IP address in the range of 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.253). The
best and easiest way is to configure the PC to get an IP address automatically from the router using
DHCP. If you encounter any problems accessing the router’s web interface it may also be advisable to
uninstall any kind of software firewall on your PCs, as they can cause problems accessing the
192.168.1.254 IP address of the router. Users should make their own decisions on how to best protect
their network.
Please follow the steps below for your PC’s network environment installation. First of all, please check
your PC’s network components. The TCP/IP protocol stack and Ethernet network adapter must be
installed. If not, please refer to your Windows-related or other operating system
Any TCP/IP capable workstation can be used to communicate with or through the
router. To configure other types of workstations, please consult the manufacturer’s
documentation.
manuals.
11
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
Page 13
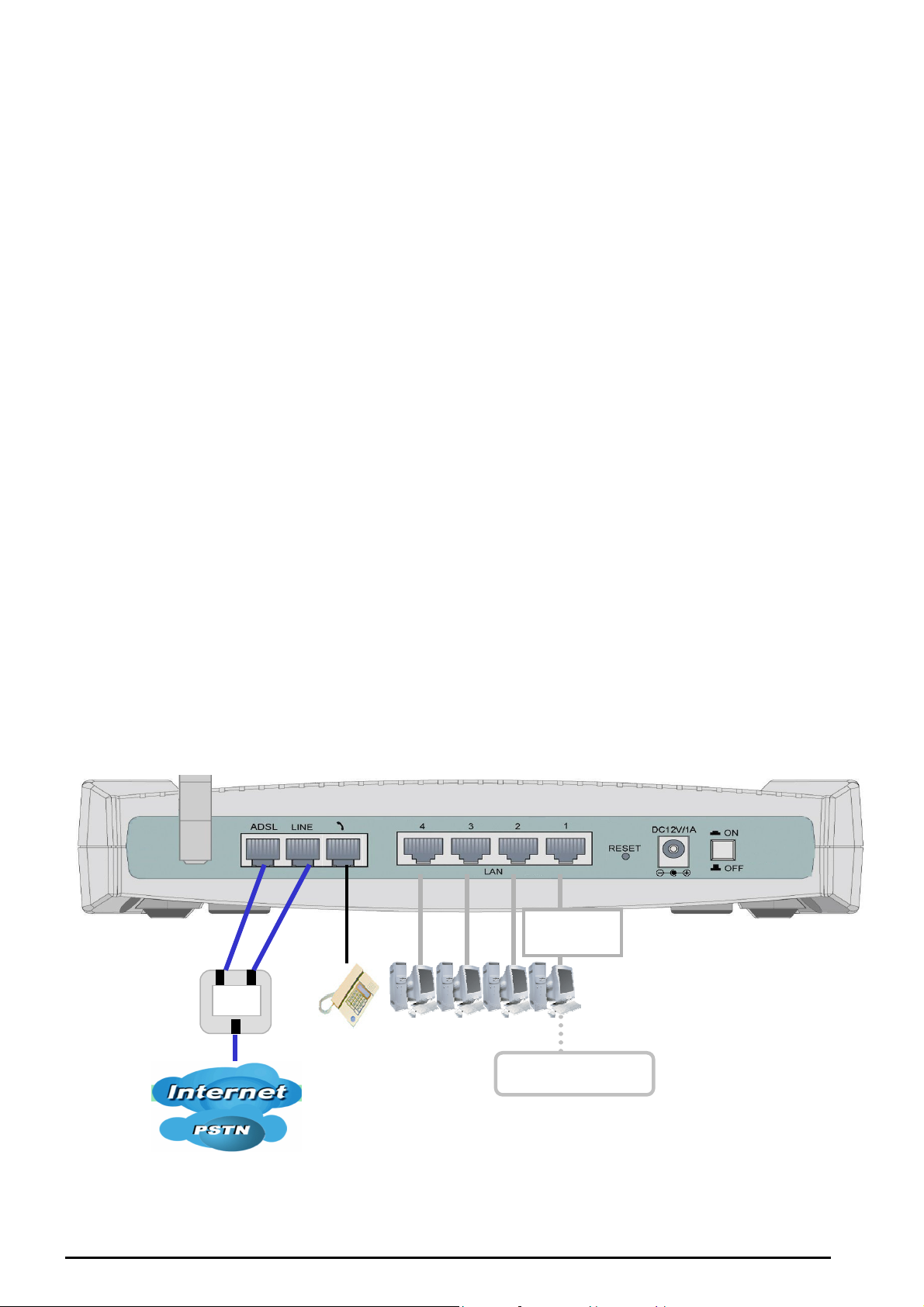
Connect more
computers
Analog Phone
ADSL
Splitter
ADSL
Phone
Line
Switching/
HUB
Connecting your router
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
1. Connect this router to a LAN (Local Area Network) and the ADSL/telephone (ADSL) network.
2. Power on the device.
3. Make sure the PWR and SYS LEDs are lit steadily and that the LAN LED is lit.
4. Connect an RJ11 cable to VoIP port when connecting to an analog phone set.
5. Connect RJ-11 cable to LINE Port when connecting to the telephone wall jack.
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
12
Page 14
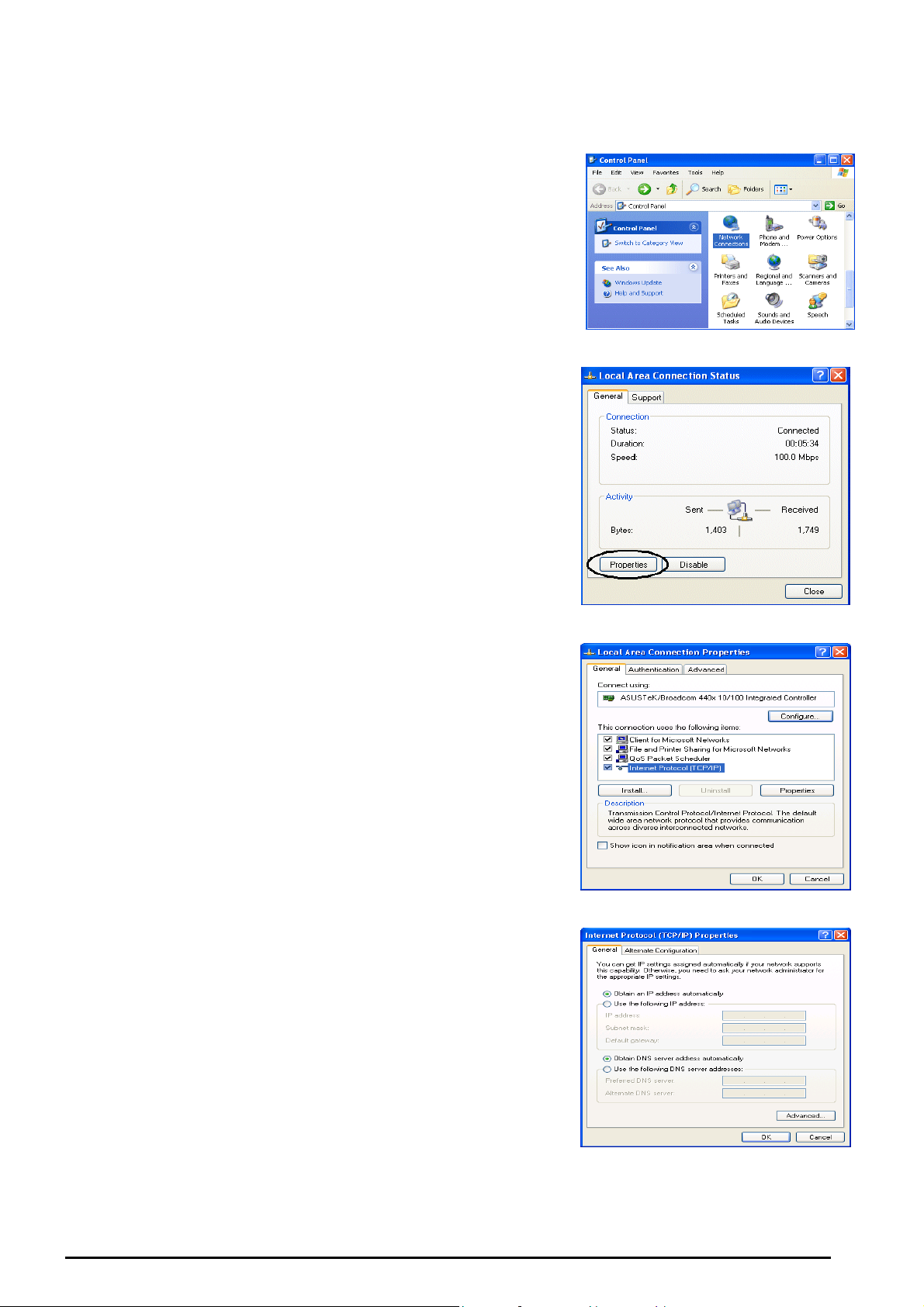
Configuring PCs in Windows in Window XP
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
1. Go to Start / Control Panel (in Classic View). In the Control
Panel, double-click Network Connections.
2. Double-click Local Area Connection. (See Figure 3.1)
3. In the LAN Area Connection Status window, click
Properties. (See Figure 3.2)
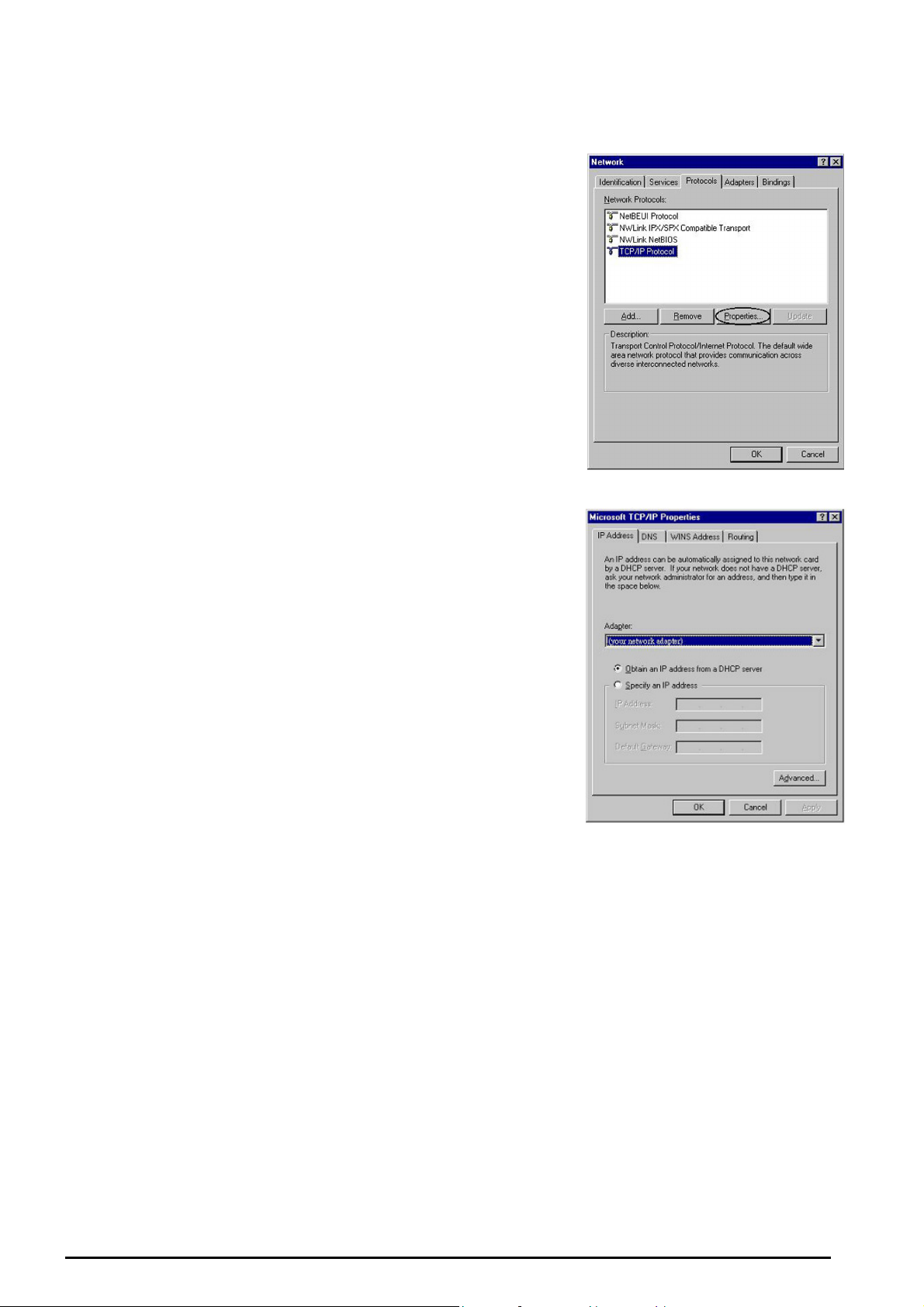
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
(See Figure 3.3)
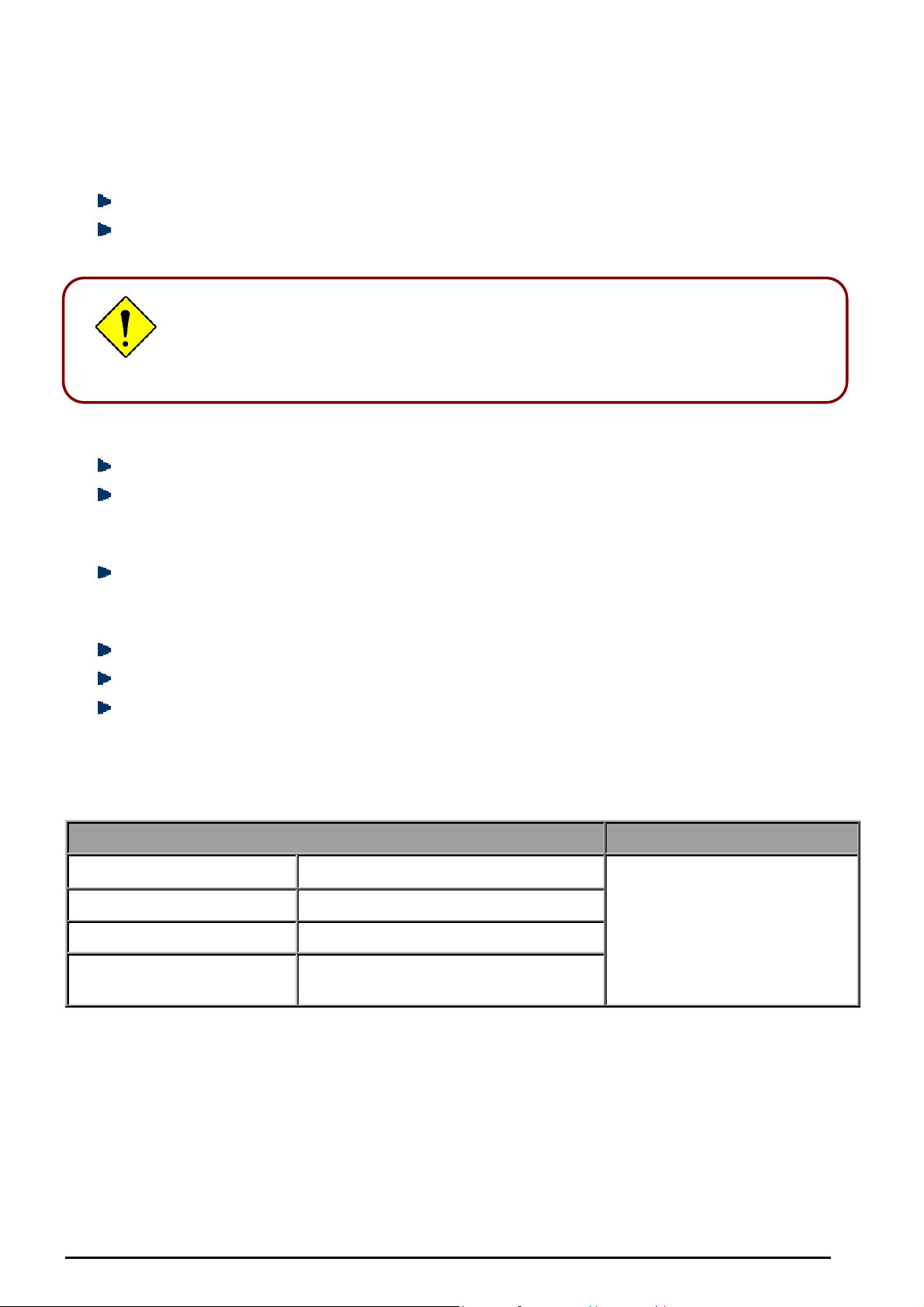
5. Select the Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain
DNS server address automatically radio buttons. (See
Figure 3.4)
6. Click OK to finish the configuration.
Figure 3.1: LAN Area Connection
Figure 3.2: LAN Connection Status
Figure 3.3: TCP / IP
Figure 3.4: IP Address & DNS
Configuration
13
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
Page 15
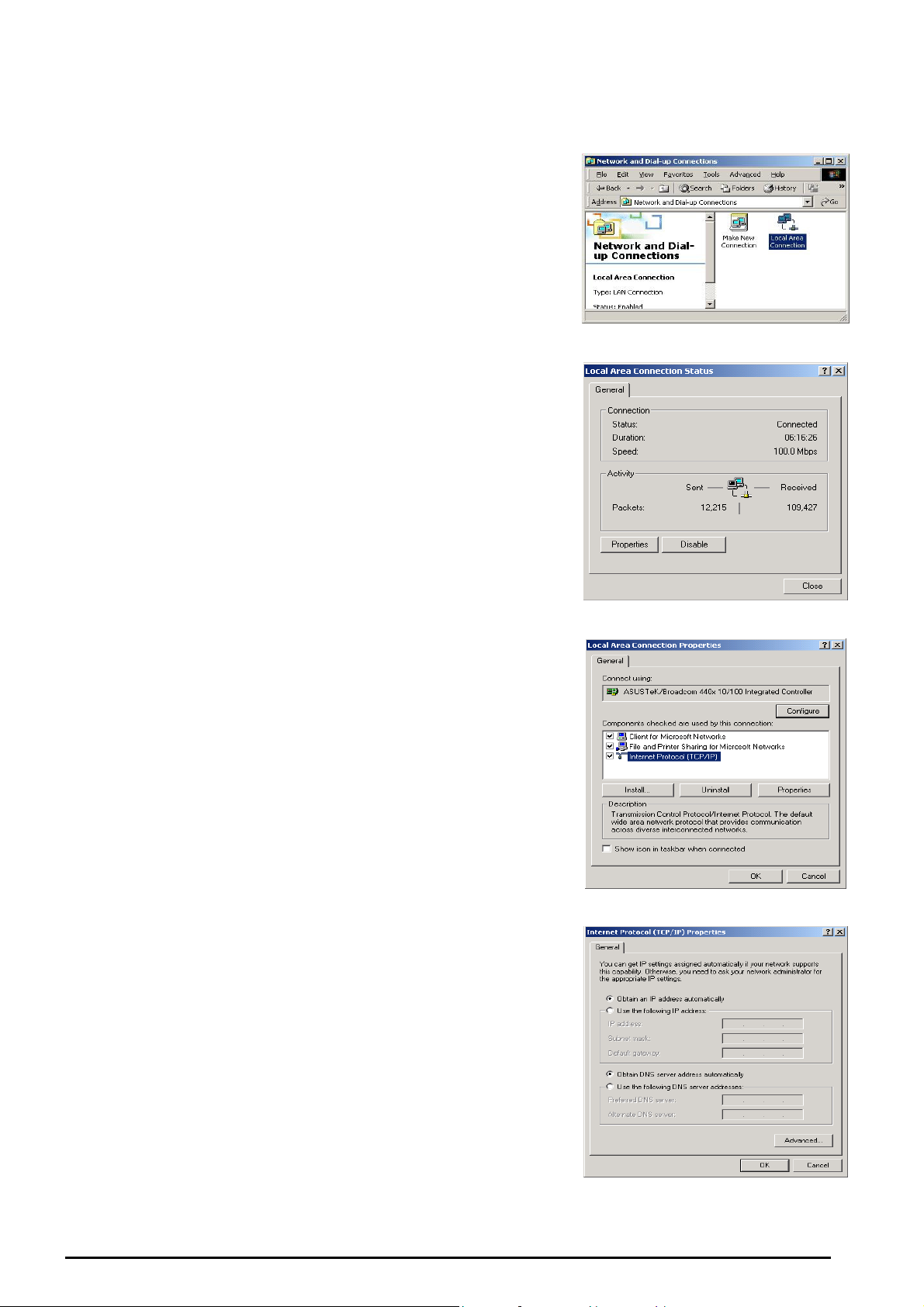
Configuring PCs in Windows 2000
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
1.
Go to Start / Settings / Control Panel. In the Control Panel,
double-click Network and Dial-up Connections.
2.
Double-click Local Area (“LAN”) Connection. (See Figure
3.5)
3.
In the LAN Area Connection Status window, click
Properties. (See Figure 3.6)
4.
Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
(See Figure 3.7)
5.
Select the Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain
DNS server address automatically radio buttons. (See
Figure 3.8)
6.
Click OK to finish the configuration.
Figure 3.5: LAN Area Connection
Figure 3.6: LAN Connection Status
Figure 3.7: TCP / IP
Figure 3.8: IP Address & DNS
Configuration
14
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
Page 16
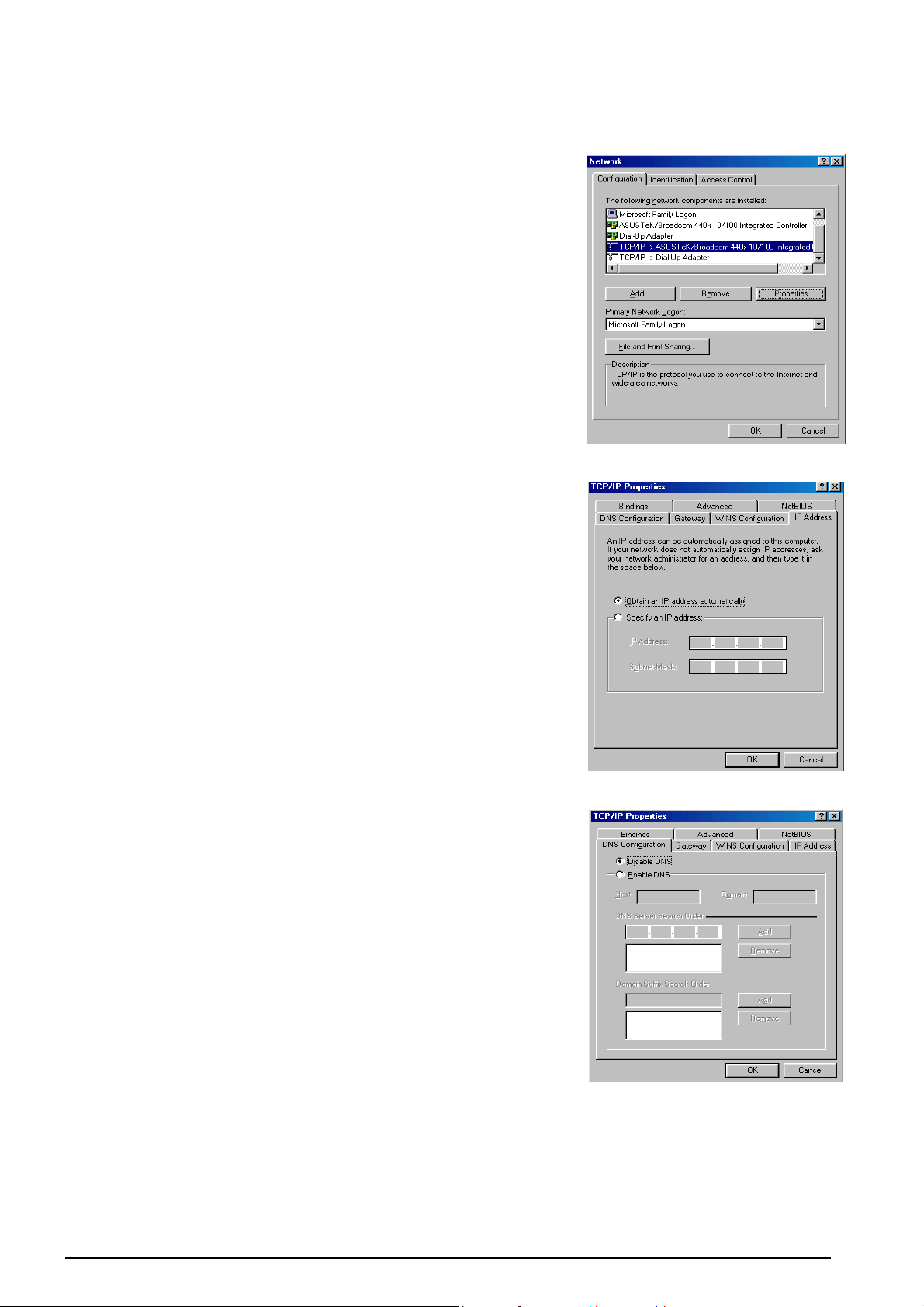
Configuring PC in Windows 95/98/ME
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
1. Go to Start / Settings / Control Panel. In the Control Panel,
double-click Network and choose the Configuration tab.
2. Select TCP / IP -> NE2000 Compatible, or the name of any
Network Interface Card (NIC) in your PC. (See Figure 3.9)
3. Click Properties.
4. Select the IP Address tab. In this page, click the Obtain an
IP address automatically radio button. (See Figure 3.10)
5. Then select the DNS Configuration tab. (See Figure 3.11)
6. Select the Disable DNS radio button and click OK to finish
the configuration.
Figure 3.9: TCP / IP
Figure 3.10: IP Address
Figure 3.11: DNS Configuration
15
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
Page 17
Configuring PC in Windows NT4.0
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
1.
Go to Start / Settings / Control Panel. In the Control
Panel, double-click Network and choose the Protocols tab.
2.
Select TCP/IP Protocol and click Properties. (See Figure
3.12)
3.
Select the Obtain an IP address from a DHCP server radio
button and click OK. (See Figure 3.13)
Figure 3.12: TCP / IP
Figure 3.13: IP Address
16
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
Page 18
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Factory Default Settings
Before configuring your, you need to know the following default settings.
Web Interface (Username and Password)
Username: admin
Password: admin
The default username and password are “admin” and “admin” respectively.
LAN Device IP Settings
IP Address: 192.168.1.254
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
If you ever forget the password to log in, you may press the RESET button up to
6 seconds to restore the factory default settings.
ISP setting in WAN site
PPPoE
DHCP server
DHCP server is enabled.
Start IP Address: 192.168.1.100
IP pool counts: 100
LAN and WAN Port Addresses
The parameters of LAN and WAN ports are pre-set in the factory. The default values are shown below.
LAN Port WAN Port
IP address
Subnet Mask
DHCP server function
IP addresses for
distribution to PCs
192.168.1.254
255.255.255.0
Enabled
100 IP addresses continuing from
192.168.1.100 through 192.168.1.199
The PPPoE function is enabled
to automatically get the WAN
port configuration from the ISP,
but you have to set the
username and password first.
17
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
Page 19
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Information from your ISP
Before configuring this device, you have to check with your ISP (Internet Service Provider) what kind of
service is provided such as PPPoE, PPPoA, RFC1483, or IPoA.
Gather the information as illustrated in the following table and keep it for reference.
PPPoE VPI/VCI, VC-based/LLC-based multiplexing, Username, Password, Service
Name, and Domain Name System (DNS) IP address (it can be automatically
assigned by your ISP when you connect or be set manually).
PPPoA VPI/VCI, VC-based/LLC-based multiplexing, Username, Password, and
Domain Name System (DNS) IP address (it can be automatically assigned by
your ISP when you connect or be set manually).
RFC1483 Bridged VPI/VCI, VC-based/LLC-based multiplexing to use Bridged Mode.
RFC1483 Routed VPI/VCI, VC-based/LLC-based multiplexing, IP address, Subnet mask,
Gateway address, and Domain Name System (DNS) IP address (it is fixed IP
address).
IPoA VPI/VCI, VC-based/LLC-based multiplexing, IP address, Subnet mask,
Gateway address, and Domain Name System (DNS) IP address (it is fixed IP
address).
18
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
Page 20
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Configuring with your Web Browser
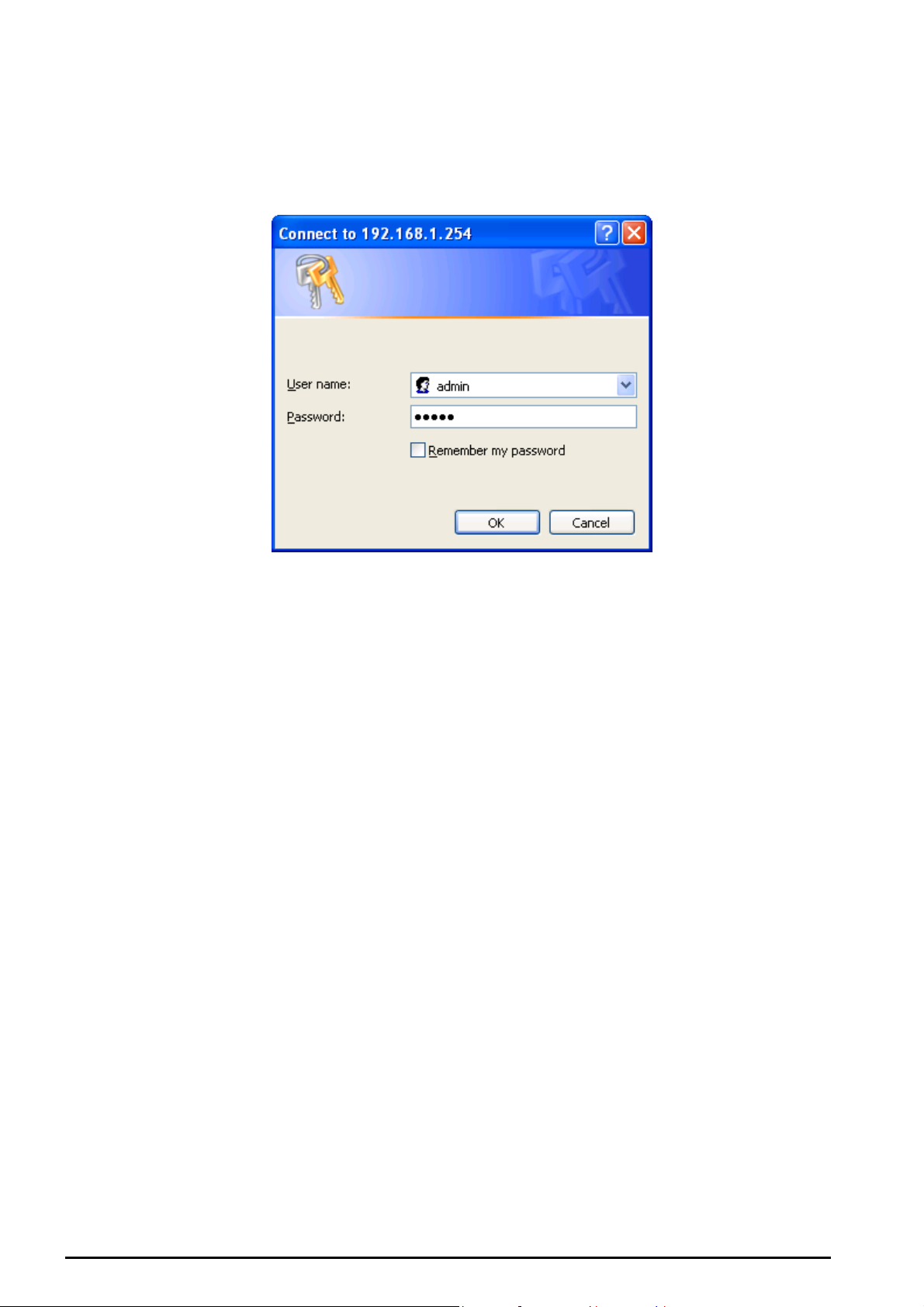
Open your web browser, enter the IP address of your router, which by default is 192.168.1.254, and click
“Go”, a user name and password window prompt will appear. The default username and password
are “admin” and “admin”. (See Figure 3.14)
Figure 3.14: User name & Password Prompt Widonw
Congratulation! You are now successfully logon to the VoIP ADSL2+ Router!
19
Chapter 3: Basic Installation
Page 21
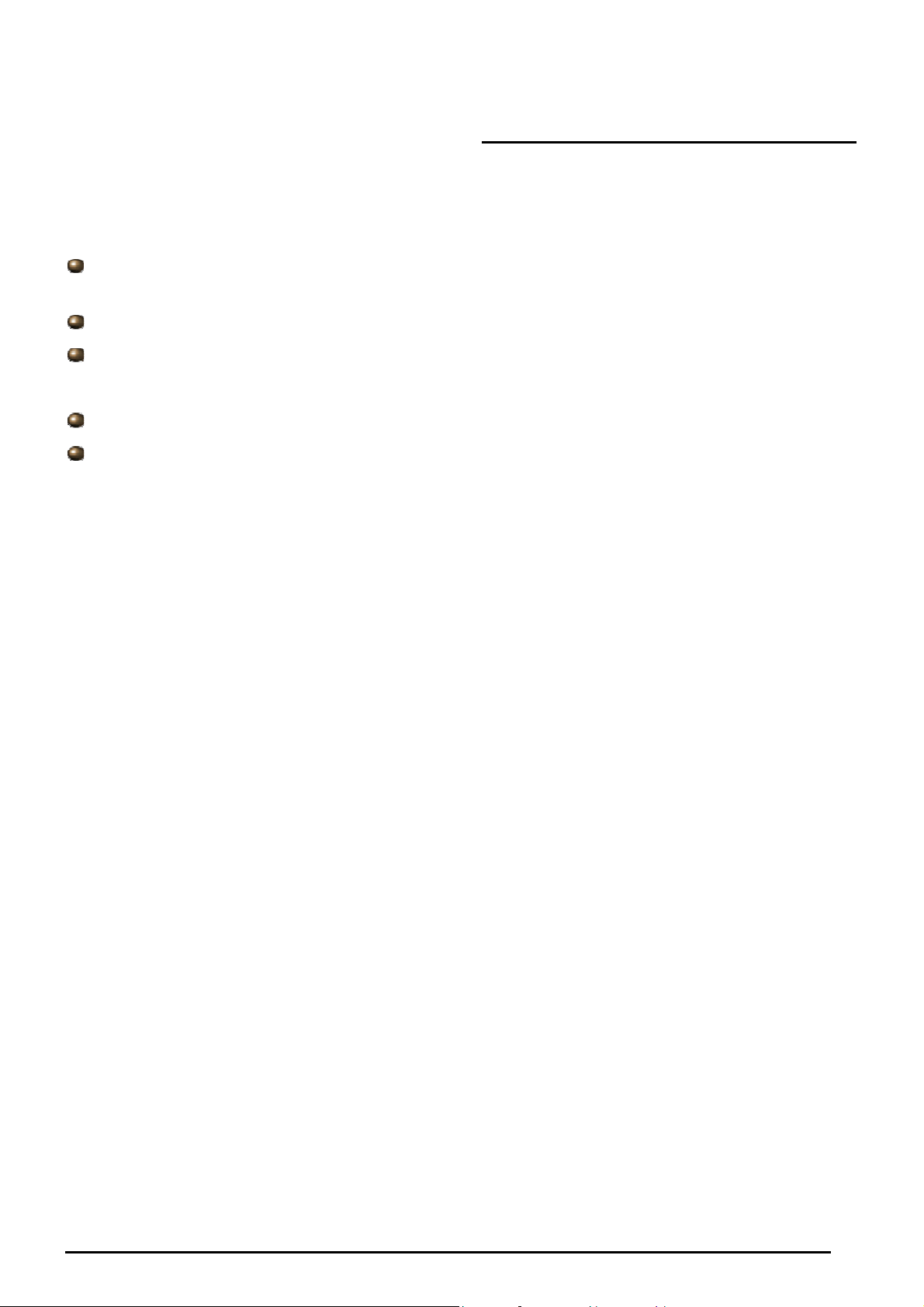
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Chapter 4: Configuration
At the configuration homepage, the left navigation pane where bookmarks are provided links you directly
to the desired setup page, including:
Status (ARP Table, Wireless Association Table(wireless router only), Routing Table, DHCP Table,
Email Status, VoIP Status, Event Log, Error Log, NAT Sessions, Diagnostic and UPnP Portmap)
Quick Start
Configuration
(LAN, WAN, System, Firewall, VoIP, QoS, Virtual Server, Time Schedule and Advanced)
Save Config to FLASH
Language (provides user interface in English and French languages)
Please see the relevant sections of this manual for detailed instructions on how to configure the VoIP
ADSL Router.
20
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 22
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Status
ARP Table
This section displays the router’s ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Table, which shows the mapping of
Internet (IP) addresses to Ethernet (MAC) addresses. This is useful as a quick way of determining the
MAC address of the network interface of your PCs to use with the router’s Firewall – MAC Address
Filter function. See the Firewall section of this manual for more information on this feature.
IP Address: A list of IP addresses of devices on your LAN (Local Area Network).
MAC Address: The MAC (Media Access Control) addresses for each device on your LAN.
Interface: The interface name (on the router) that this IP Address connects to.
Static: Static status of the ARP table entry:
“no” for dynamically-generated ARP table entries
“yes” for static ARP table entries added by the user
Wireless Association Table (Wireless Router only)
IP Address: It is IP address of wireless client that joins this network.
MAC: The MAC address of wireless client.
Routing Table
21
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 23

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Routing Table
Valid: It indicates a successful routing status.
Destination: The IP address of the destination network.
Netmask: The destination netmask address.
Gateway/Interface: The IP address of the gateway or existing interface that this route will use.
Cost: The number of hops counted as the cost of the route.
RIP Routing Table
Destination: The IP address of the destination network.
Netmask: The destination netmask address.
Gateway: The IP address of the gateway that this route will use.
Cost: The number of hops counted as the cost of the route.
22
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 24

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
DHCP Table
Leased: The DHCP assigned IP addresses information.
IP Address: A list of IP addresses of devices on your LAN (Local Area Network).
Expired: The expired IP addresses information.
Permanent: The fixed host mapping information
Leased Table
IP Address: The IP address that assigned to client.
MAC Address: The MAC address of client.
Client Host Name: The Host Name (Computer Name) of client.
Expiry: The current lease time of client.
Expired Table
Please refer the Leased Table.
Permanent Table
Name: The name you assigned to the Permanent configuration.
IP Address: The fixed IP address for the specify client.
MAC Address: The MAC Address that you want to assign the fixed IP address
Maximum Lease Time: The maximum lease time interval you allow to clients
23
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 25
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Email Status
Details and status for the Email Account you have configured the router to check. Please see the
Advanced section of this manual for details on this function.
VoIP Status
Details and status for the VoIP Account you have configured the router to check. Please see the Phone
Configuration section of this manual for details on this function.
Event Log
This page displays the router’s Event Log entries. Major events are logged to this window, such as when
the router’s ADSL connection is disconnected, as well as Firewall events when you have enabled
Intrusion or Blocking Logging in the Configuration – Firewall section of the interface. Please see the
Firewall section of this manual for more details on how to enable Firewall logging.
24
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 26
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Error Log
Any errors encountered by the router (e.g. invalid names given to entries) are logged to this window.
NAT Sessions
This section lists all current NAT sessions between interface of types external (WAN) and internal (LAN).
Diagnostic
It tests the connection to computer(s) which is connected to LAN ports and also the WAN
Internet connection. If PING www.google.com is shown FAIL and the rest is PASS, you ought
to check your PC’s DNS settings is set correctly.
25
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 27

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
UPnP Portmap
The section lists all port-mapping established using UPnP (Universal Plug and Play). Please see the
Advanced section of this manual for more details on UPnP and the router’s UPnP configuration options.
26
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 28

Quick Start
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
For detailed instructions on configuring your WAN settings, please see the WAN section of this manual.
Usually, the only details you will need for the Quick Start wizard to get you online are your login (often in
the form of username@ispname), your password and the encapsulation type. In addition, you have the
option to provide specific DNS as your desire, or check the Enable box to get the DNS automatically
from your ISP.
Your ISP will be able to supply all the details you need, alternatively, if you have deleted the current
WAN Connection in the WAN – ISP section of the interface, you can use the router’s PVC Scan feature
to attempt to determine the Encapsulation types offered by your ISP.
Click Start to begin scanning for encapsulation types offered by your ISP. If the scan is successful you
will then be presented with a list of supported options:
27
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 29

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Select the desired option from the list and click Apply to return to the Quick Start interface to continue
configuring your ISP connection. Please note that the contents of this list will vary, depending on what is
supported by your ISP.
28
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 30
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Configuration
When you click this item, you get following sub-items to configure the ADSL router.
LAN, WAN, System, Firewall, VoIP, QoS, Virtual Server, Time Schedule and Advanced
These functions are described below in the following sections.
LAN (Local Area Network)
There are seven items within the LAN section: Bridge Interface, Ethernet, Ethernet Client Filter,
Wireless, Wireless Security, Wireless Client Filter, Port Setting and DHCP Server.
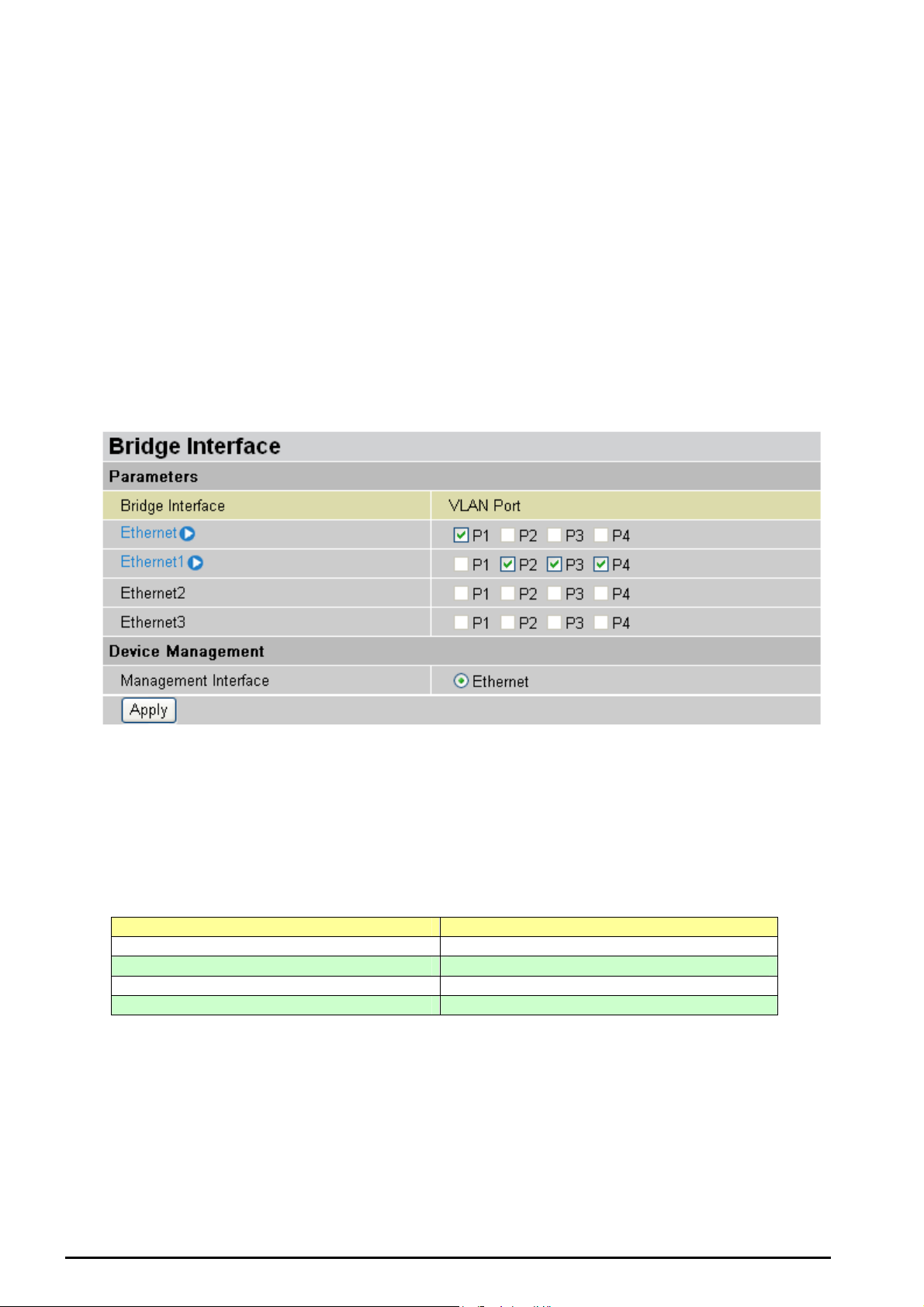
Bridge Interface
You can setup member ports for each VLAN group under Bridge Interface section. From the
example, two VLAN groups need to be created.
Ethernet: P1 (Port 1)
Ethernet1: P2, P3 and P4 (Port 2, 3, 4) Please uncheck P2, P3, P4 from Ethernet VLAN port first.
Note: You should setup each VLAN group with caution. Each Bridge Interface is arranged in
this order.
Bridge Interface VLAN Port (Always starts with)
Ethernet P1 / P2 / P3 / P4
Ethernet1 P2 / P3 / P4
Ethernet2 P3 / P4
Ethernet3 P4
Management Interface: To specify which VLAN group has possibility to do device
management, like doing web management.
Note: NAT/NAPT can be applied to management interface only.
29
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 31

Ethernet
Primary IP Address
IP Address: The default IP on this router.
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
SubNetmask: The default subnet mask on this router.
RIP: RIP v1, RIP v2, and RIP v2 Multicast. Check to enable RIP function.
IP Alias
This function supports to create multiple virtual IP interfaces on this router. It helps to connect two or
more local networks to the ISP or remote node. In this case, an internal router is not required.
IP Address: Specify an IP address on this virtual interface.
SubNetmask: Specify a subnet mask on this virtual interface.
Security Interface: Specify the firewall setting on this virtual interface.
Internal: The network is behind NAT. All traffic will do network address translation when
sending out to Internet if NAT is enabled.
External: There is no NAT on this IP interface and connected to the Internet directly. Mostly
it will be used when providing multiple public IP addresses by ISP. In this case, you can use
public IP address in local network which gateway IP address point to the IP address on this
interface.
DMZ: Specify this network to DMZ area. There is no NAT on this interface.
30
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 32

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Ethernet Client Filter
The Ethernet Client Filter supports up to 16 Ethernet network machines that helps you to manage
your network control to accept traffic from specific authorized machines or can restrict unwanted
machine(s) to access your LAN.
There are no pre-define Ethernet MAC address filter rules; you can add the filter rules to meet your
requirements.
Ethernet Client Filter: Default setting is set to Disable.
Allowed: check to authorize specific device accessing your LAN by insert the MAC
Address in the space provided or click . Make sure your PC’s MAC is listed.
Blocked: check to prevent unwanted device accessing your LAN by insert the MAC
Address in the space provided or click . Make sure your PC’s MAC is not listed.
The maximum client is 16. The MAC addresses are 6 bytes long; they are presented only in
hexadecimal characters. The number 0 - 9 and letters a - f are acceptable.
(Note: Follow the MAC Address Format xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx. Semicolon ( : ) must be included.
Candidates: automatically detects devices connected to the router through the Ethernet.
→→→→
Active PC in LAN
31
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 33

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Active PC in LAN displays a list of individual Ethernet device’s IP Address & MAC Address which
connecting to the router.
You can easily by checking the box next to the IP address to be blocked or allowed. Then, Add to
insert to the Ethernet Client Filter table. The maximum Ethernet client is 16.
32
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 34

Wireless
(Wireless Router only)
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Parameters
WLAN Service: Default setting is set to Enable. If you do not have any wireless, both 802.11g and
802.11b, device in your network, select Disable.
Mode: The default setting is 802.11b+g (Mixed mode). If you do not know or have both 11g and
11b devices in your network, then keep the default in mixed mode. From the drop-down manual,
you can select 802.11g if you have only 11g card. If you have only 11b card, then select 802.11b.
ESSID: The ESSID is the unique name of a wireless access point (AP) to be distinguished from
another. For security propose, change the default wlan-ap to a unique ID name to the AP which is
already built-in to the router’s wireless interface. It is case sensitive and must not excess 32
characters. Make sure your wireless clients have exactly the ESSID as the device, in order to get
connected to your network. (Note: It is case sensitive and must not excess 32 characters.)
ESSID Broadcast: It is function in which transmits its ESSID to the air so that when wireless client
searches for a network, router can then be discovered and recognized. Default setting is Enable.
Disable: If you do not want broadcast your ESSID. Any client uses “any” wireless setting
cannot discover the Access Point (AP) of your router.
Enable: Any client that using the “any” setting can discover the Access Point (AP) in
Regulation Domain: There are seven Regulation Domains for you to choose from, including
North America (N.America), Europe, France, etc. The Channel ID will be different based on this
setting.
Channel ID: Select the ID channel that you would like to use.
Connected: Representing in true or false. That it is the connection status between the system
and the build-in wireless card.
AP MAC Address: It is a unique hardware address of the Access Point.
AP Firmware Version: The Access Point firmware version.
33
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 35

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
It is a wireless access point mode that enables wireless link and communication with other access point.
It is easy to be installed simply define peer’s MAC address of the connected AP. WDS takes advantages
of cost saving and flexibility which no extra wireless client device is required to bridge between two
access points and extending an existing wired or wireless infrastructure network to create a larger
network.
In addition, WDS enhances its link connection security in WEP mode, WEP key encryption must be the
same for both access points.
WDS Service: The default setting is Disable. Check Enable radio button to activate this function.
Peer WDS MAC Address: It is the associated AP’s MAC Address. It is important that your peer’s
AP must include your MAC address in order to acknowledge and communicate with each other.
Note: For MAC Address, Semicolon ( : ) must be included.
34
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 36

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Wireless Security
You can disable or enable with WPA or WEP for protecting wireless network.
The default mode of wireless security is disabled.
(Wireless Router only)
WPA Pre-Shared Key
WPA Algorithms: TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) utilizes a stronger encryption method
and incorporates Message Integrity Code (MIC) to provide protection against hackers.
WPA Shared Key: The key for network authentication. The input format is in character style and
key size should be in the range between 8 and 63 characters.
Group Key Renewal: The period of renewal time for changing the security key automatically
between wireless client and Access Point (AP). Default value is 600 seconds.
Idle Timeout: The default idle timeout is 3600 seconds. A Timeout value base on the case of no
data traffic is send or received. If Router detects no traffic in the wireless, it will start timing the
clock and drop the session as it reaches to the defined timeout value. New session will be reestablished after the old session.
35
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 37

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
WEP
WEP Authentication: There are three options to choose, Open System, Shared Key and Both.
The default is set to Open System which does not request a shared key between the AP sender
and the AP client, only supplying a correct SSID and an encryption key if there is any. With Share
Key authentication, the AP client is granted only if it provided correct challenge response to the AP.
WEP Encryption: To prevent unauthorized wireless stations from accessing data transmitted over
the network, the router offers highly secure data encryption, known as WEP. If you require high
security for transmissions, there are two alternatives to select from: WEP 64 and WEP 128. WEP
128 will offer increased security over WEP 64.
Passphrase: This is used to generate WEP keys automatically based upon the input string and a
pre-defined algorithm in WEP64 or WEP128. You can input the same string in both the AP and
Client card settings to generate the same WEP keys. Please note that you do not have to enter
Key (0-3) as below when the Passphrase is enabled.
Default Used WEP Key: Select the encryption key ID; please refer to Key (0-3) below.
Key (0-3): Enter the key to encrypt wireless data. To allow encrypted data transmission, the WEP
Encryption Key values on all wireless stations must be the same as the router. There are four keys
for your selection. The input format is in HEX style, 5 and 13 HEX codes are required for WEP64
and WEP128 respectively, the separator is “-“. For example, using WEP64, 11-22-33-44-55 is a
valid key, whilst 1122334455 is invalid.
36
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 38

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Wireless Client (MAC Address) Filter (Wireless Router only)
The MAC Address supports up to 16 wireless network machines and helps you to manage your
network control to accept traffic from specific authorized machines or to restrict unwanted
machine(s) to access your LAN.
There are no pre-define MAC Address filter rules; you can add the filter rules to meet your
requirements.
Ethernet Client Filter: Default setting is set to Disable.
Allowed: check to authorize specific device accessing your LAN by insert the MAC
Address in the space provided or click . Make sure your PC’s MAC is listed.
Blocked: check to prevent unwanted device accessing the LAN by insert the MAC Address
in the space provided or click . Make sure your PC’s MAC is not listed.
The maximum client is 16. The MAC addresses are 6 bytes long; they are presented only in
hexadecimal characters. The number 0 - 9 and letters a - f are acceptable.
The maximum client is 16. The MAC addresses are 6 bytes long; they are presented only in
hexadecimal characters. The number 0 - 9 and letters a - f are acceptable.
Note: Follow the MAC Address Format xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx. Semicolon ( : ) must be included.
Candidates: it automatically detects devices connected to the router through the Ethernet.
→Associated Wireless Clients
37
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 39

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Associate Wireless Client displays a list of individual wireless device’s MAC Address that currently
connects to the router.
You can easily by checking the box next to the MAC address to be blocked or allowed. Then, Add
to insert to the Wireless Client (MAC Address) Filter table. The maximum Ethernet client is 16.
Port Setting
This section allows you to configure the settings for the router’s Ethernet ports to solve some of the
compatibility problems that may be encountered while connecting to the Internet, as well allowing
users to tweak the performance of their network.
Port # Connection Type: Five options to choose from: Auto, 10M half-duplex, 10M full-duplex,
100M half-duplex or 100M full-duplex. Sometimes, there are Ethernet compatibility problems with
legacy Ethernet devices, and you can configure different types to solve compatibility issues. The
default is Auto, which users should keep unless there are specific problems with PCs not being
able to access your LAN.
IPv4 TOS priority Control (Advanced users): TOS, Type of Services, is the 2nd octet of an IP
packet. Bits 6-7 of this octet are reserved and bit 0-5 are used to specify the priority of the packet.
This feature uses bits 0-5 to classify the packet’s priority. If the packet is high priority, it will flow first and
will not be constrained by the Rate Limit. Therefore, when this feature is enabled, the router’s Ethernet
switch will check the 2nd octet of each IP packet. If the value in the TOS field matches the checked
values in the table (0 to 63), this packet will be treated as high priority.
38
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 40

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
DHCP Server
You can disable or enable the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server or enable the
router’s DHCP relay functions. The DHCP protocol allows your router to dynamically assign IP
addresses to PCs on your network if they are configured to obtain IP addresses automatically.
To disable the router’s DHCP Server, check Disabled and click Next, then click Apply. When the
DHCP Server is disabled you will need to manually assign a fixed IP address to each PCs on your
network, and set the default gateway for each PCs to the IP address of the router (by default this is
192.168.1.254).
To configure the router’s DHCP Server, check DHCP Server and click Next. You can then
configure parameters of the DHCP Server including the IP pool (starting IP address and ending IP
address to be allocated to PCs on your network), lease time for each assigned IP address (the
period of time the IP address assigned will be valid), DNS IP address and the gateway IP address.
These details are sent to the DHCP client (i.e. your PC) when it requests an IP address from the
DHCP server. Click Apply to enable this function. If you check “Use Router as a DNS Server”,
the ADSL Router will perform the domain name lookup, find the IP address from the outside
network automatically and forward it back to the requesting PC in the LAN (your Local Area
Network).
If you check DHCP Relay Agent and click Next, then you will have to enter the IP address of the
DHCP server which will assign an IP address back to the DHCP client in the LAN. Use this
function only if advised to do so by your network administrator or ISP.
Click Apply to enable this function.
39
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 41

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
WAN (Wide Area Network)
WAN refers to your Wide Area Network connection, i.e. your router’s connection to your ISP and the
Internet. There are two items within the WAN section: ISP, DNS and ADSL.
ISP
The factory default is PPPoE. If your ISP uses this access protocol, click Edit to input other
parameters as below. If your ISP does not use PPPoE, you can change the default WAN
connection entry by clicking Change.
A simpler alternative is to select Quick Start from the main menu on the left. Please see the Quick
Start section of the manual for more information.
40
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 42

RFC 1483 Routed Connections
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Description: Your description of this connection.
VPI and VCI: Enter the information provided by your ISP.
ATM Class: The Quality of Service for ATM layer.
NAT: The NAT (Network Address Translation) feature allows multiple users to access the Internet
through a single IP account, sharing the single IP address. If users on your LAN have public IP
addresses and can access the Internet directly, the NAT function can be disabled.
Encapsulation method: Selects the encapsulation format, the default is LLC Bridged. Select the
one provided by your ISP.
DHCP client: Enable or disable the DHCP client, specify if the Router can get an IP address from
the Internet Service Provider (ISP) automatically or not. Please click Obtain an IP address
automatically via DHCP client to enable the DHCP client function or click Specify an IP address
to disable the DHCP client function, and specify the IP address manually. Your ISP specifies the
setting of this item.
RIP: RIP v1, RIP v2, and RIP v2 Multicast. Check to enable RIP function.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The size of the largest datagram (excluding media-specific
headers) that IP will attempt to send through the interface.
TCP MSS Clamp: It is enabled by default. All TCP traffic routed through the interface will be
examined. If a TCP SYN (synchronize/start) segment is sent with a maximum segment size larger
than the interface MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit), the MSS option will be rewritten in order to
allow TCP traffic to pass through the interface without requiring fragmentation.
41
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 43

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
RFC 1483 Bridged Connections
VPI and VCI: Enter the information provided by your ISP.
ATM Class: The Quality of Service for ATM layer.
Encapsulation method: Select the encapsulation format, this is provided by your ISP.
Acceptable Frame Type: Specify what kind of traffic can through this connection, all traffic or only
VLAN tagged.
Filter Type: Specify the type of ethernet filtering performed by the named bridge interface.
All
Ip
Pppoe
Allows all types of ethernet packets through the port.
Allows only IP/ARP types of ethernet packets through the port.
Allows only PPPoE types of ethernet packets through the port.
PVID for Untagged Frames: PVID is known as Port VLAN Identifier. When an untagged packet is
received by input port(s), this packet will be tagged with specified PVID. The valid value range for
PVID is 1~4094.
42
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 44

PPPoA Routed Connections
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Description: User-definable name for the connection.
VPI/VCI: Enter the information provided by your ISP.
ATM Class: The Quality of Service for ATM layer.
NAT: The NAT (Network Address Translation) feature allows multiple users to access the Internet
through a single IP account, sharing a single IP address. If users on your LAN have public IP
addresses and can access the Internet directly, the NAT function can be disabled.
Username: Enter the username provided by your ISP. You can input up to 128 alphanumeric
characters (case sensitive). This will usually be in the format of “username@ispname” instead of
simply “username”.
Password: Enter the password provided by your ISP. You can input up to 128 alphanumeric
characters (case sensitive).
IP Address: Specify an IP address allowed to logon and access the router’s web server. Note: IP
0.0.0.0 indicates all users who are connected to this router are allowed to logon the device and
modify data.
Authentication Protocol Type: Default is Chap (Auto). Your ISP will advise you whether to use
Chap or Pap.
Connection:
Always on: If you want the router to establish a PPPoA session when starting up and to
automatically re-establish the PPPoA session when disconnected by the ISP.
43
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 45

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Connect to Demand: If you want to establish a PPPoA session only when there is a packet
requesting access to the Internet (i.e. when a program on your computer attempts to access
the Internet).
Idle Timeout: Auto-disconnect the broadband firewall gateway when there is no activity on the
line for a predetermined period of time.
Detail: You can define the destination port and packet type (TCP/UDP) without checking by
timer. It allows you to set which outgoing traffic will not trigger and reset the idle timer.
RIP: RIP v1, RIP v2, and RIP v2 Multicast. Check to enable RIP function.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The size of the largest datagram (excluding media-specific
headers) that IP will attempt to send through the interface.
TCP MSS Clamp: It is enabled by default. All TCP traffic routed through the interface will be
examined. If a TCP SYN (synchronize/start) segment is sent with a maximum segment size larger
than the interface MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit), the MSS option will be rewritten in order to
allow TCP traffic to pass through the interface without requiring fragmentation.
44
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 46

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Advanced Options (PPPoA)
LLC Header: Selects encapsulation mode, true for using LLC or false for using VC-Mux.
Create Route: This setting specifies whether a route is added to the system after IPCP (Internet
Protocol Control Protocol) negotiation is completed. If set to enabled, a route will be created which
directs packets to the remote end of the PPP link.
Specific Route: Specifies whether the route created when a PPP link comes up is a specific or
default route. If set to enabled, the route created will only apply to packets for the subnet at the
remote end of the PPP link. The address of this subnet is obtained during IPCP negotiation.
Subnet Mask: sets the subnet mask used for the local IP interface connected to the PPP transport.
If the value 0.0.0.0 is supplied, the netmask will be calculated from the class of the IP address
obtained during IPCP negotiation.
Route Mask: Sets the subnet mask used by the route that is created when a PPP link comes up. If
it is set to 0.0.0.0, the subnet mask is determined by the IP address of the remote end of the link.
The class of the IP address is obtained during IPCP (Internet Protocol Control Protocol)
negotiation.
MRU: Maximum Receive Unit. This is negotiated during the LCP protocol stage.
Discover Primary / Secondary DNS: This setting enables/disables whether the
primary/secondary DNS server address is requested from a remote PPP peer using IPCP. The
default setting for this command is enabled.
Give DNSto Relay: Controls whether the PPP Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) can
request the DNS server IP address for a remote PPP peer. Once IPCP has discovered the DNS
server IP address, it automatically gives the address to the local DNS relay so that a connection
can be established.
Give DNSto Client: Controls whether the PPP Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) can
request a DNS server IP address for a remote PPP peer. Once IPCP has discovered the DNS
server IP address, it automatically gives the address to the local DNS client so that a connection
can be established.
Give DNSto DHCP Server: Similar to the above, but gives the DNS server address to the DHCP
server.
Discover Primary NBNS / Discover Secondary NBNS: This setting enables/disables whether
the primary/secondary NBNS server address is requested from a remote PPP peer using IPCP.
The default setting for this command is disabled.
Discover Subnet Mask: Specifies if the subnet mask given by IPCP negotiation process is to be
used.
Give Subnet Mask To DHCP Server: Enable to change your DHCP Server settings by using the
given information in IPCP negotiation process.
45
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 47

IPoA Routed Connections
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Description: User-definable name for the connection.
VPI/VCI: Enter the information provided by your ISP.
ATM Class: The Quality of Service for ATM layer.
NAT: The NAT (Network Address Translation) feature allows multiple users to access the Internet
through a single IP account, sharing a single IP address. If users on your LAN have public IP
addresses and can access the Internet directly, the NAT function can be disabled.
DHCP client: Enable or disable the DHCP client, specifying if the router can obtain an IP address
from the Internet Service Provider (ISP) automatically or not. Please click Obtain an IP address
automatically via DHCP client to enable the DHCP client function or click Specify an IP address
to disable the DHCP client function, and specify the IP address manually. Your ISP specifies the
setting of this item.
RIP: RIP v1, RIP v2, and RIP v2 Multicast. Check to enable RIP function.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The size of the largest datagram (excluding media-specific
headers) that IP will attempt to send through the interface.
TCP MSS Clamp: It is enabled by default. All TCP traffic routed through the interface will be
examined. If a TCP SYN (synchronize/start) segment is sent with a maximum segment size larger
than the interface MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit), the MSS option will be rewritten in order to
allow TCP traffic to pass through the interface without requiring fragmentation.
46
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 48

PPPoE Connections
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Description: A user-definable name for this connection.
VPI/VCI: Enter the information provided by your ISP.
ATM Class: The Quality of Service for ATM layer.
NAT: The NAT (Network Address Translation) feature allows multiple users to access the Internet
through a single ISP account, sharing a single IP address. If users on your LAN have public IP
addresses and can access the Internet directly, the NAT function can be disabled.
Username: Enter the username provided by your ISP. You can input up to 128 alphanumeric
characters (case sensitive). This will usually be in the format of “username@ispname” instead of
simply “username”.
Password: Enter the password provided by your ISP. You can input up to 128 alphanumeric
characters (case sensitive).
Service Name: This item is for identification purposes. If it is required, your ISP will provide you
the information. Maximum input is 20 alphanumeric characters.
IP Address: specify if the Router can get an IP address from the Internet Server Provider (ISP)
automatically or not. Please click Obtain an IP address automatically via DHCP client to enable the
DHCP client function or click Specify an IP address to disable the DHCP client function, and
specify the IP address manually. The setting of this item is specified by your ISP.
Authentication Protocol: Default is Chap (Auto). Your ISP will advise you whether to use Chap
47
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 49

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
or Pap.
Connection:
Always on: If you want the router to establish a PPPoE session when starting up and to
automatically re-establish the PPPoE session when disconnected by the ISP.
Connect to Demand: If you want to establish a PPPoE session only when there is a
packet requesting access to the Internet (i.e. when a program on your computer attempts to
access the Internet).
Idle Timeout: Auto-disconnect the broadband firewall gateway when there is no activity on the line
for a predetermined period of time.
Detail: You can define the destination port and packet type (TCP/UDP) without checking by
timer. It allows you to set which outgoing traffic will not trigger and reset the idle timer.
RIP: RIP v1, RIP v2, and RIP v2 Multicast. Check to enable RIP function.
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit. The size of the largest datagram (excluding media-specific
headers) that IP will attempt to send through the interface.
TCP MSS Clamp: It is enabled by default. All TCP traffic routed through the interface will be
examined. If a TCP SYN (synchronize/start) segment is sent with a maximum segment size larger
than the interface MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit), the MSS option will be rewritten in order to
allow TCP traffic to pass through the interface without requiring fragmentation.
48
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 50

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Advanced Options (PPPoE)
LLC Header: Selects encapsulation mode, true for using LLC or false for using VC-Mux.
Create Route: This setting specifies whether a route is added to the system after IPCP (Internet
Protocol Control Protocol) negotiation is completed. If set to enabled, a route will be created which
directs packets to the remote end of the PPP link.
Specific Route: Specifies whether the route created when a PPP link comes up is a specific or
default route. If set to enabled, the route created will only apply to packets for the subnet at the
remote end of the PPP link. The address of this subnet is obtained during IPCP negotiation.
Subnet Mask: sets the subnet mask used for the local IP interface connected to the PPP transport.
If the value 0.0.0.0 is supplied, the netmask will be calculated from the class of the IP address
obtained during IPCP negotiation.
Route Mask: Sets the subnet mask used by the route that is created when a PPP link comes up. If
it is set to 0.0.0.0, the subnet mask is determined by the IP address of the remote end of the link.
The class of the IP address is obtained during IPCP (Internet Protocol Control Protocol)
negotiation.
MRU: Maximum Receive Unit. This is negotiated during the LCP protocol stage.
Discover Primary / Secondary DNS: This setting enables/disables whether the
primary/secondary DNS server address is requested from a remote PPP peer using IPCP. The
default setting for this command is enabled.
Give DNS to Relay: Controls whether the PPP Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) can
request the DNS server IP address for a remote PPP peer. Once IPCP has discovered the DNS
server IP address, it automatically gives the address to the local DNS relay so that a connection
can be established.
Give DNS to Client: Controls whether the PPP Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) can
request a DNS server IP address for a remote PPP peer. Once IPCP has discovered the DNS
server IP address, it automatically gives the address to the local DNS client so that a connection
can be established.
Give DNS to DHCP Server: Similar to the above, but gives the DNS server address to the DHCP
server.
Discover Primary NBNS / Discover Secondary NBNS: This setting enables/disables whether
the primary/secondary NBNS server address is requested from a remote PPP peer using IPCP.
The default setting for this command is disabled.
Discover Subnet Mask: Specifies if the subnet mask given by IPCP negotiation process is to be
used.
Give Subnet Mask To DHCP Server: Enable to change your DHCP Server settings by using the
given information in IPCP negotiation process.
49
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 51

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
DNS
A Domain Name System (DNS) contains a mapping table for domain name and IP addresses. On
the Internet, every host has a unique and user-friendly name (domain name) such as
www.helloworld.com and an IP address. An IP address is a 32-bit number in the form of
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, for example 192.168.1.254. You can think of an IP address as a telephone
number for devices on the Internet, and the DNS will allow you to find the telephone number for
any particular domain name. As an IP Address is hard to remember, the DNS converts the friendly
name into its equivalent IP Address.
You can obtain a Domain Name System (DNS) IP address automatically if your ISP has provided it
when you logon, check the Enable box. Usually when you choose PPPoE or PPPoA as your WAN
- ISP protocol, the ISP will provide the DNS IP address automatically. You may leave the
configuration field blank.
Alternatively, your ISP may provide you with an IP address of their DNS. If this is the case, you
must enter the DNS IP address manually.
If you choose one of the other three protocols ─ RFC1483 Routed/Bridged and IPoA check with
your ISP, it may provide you with an IP address for their DNS server. You must enter the DNS IP
address if you set the DNS of your PC to the LAN IP address of this router.
50
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 52

ADSL
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Connect Mode: The default setting is Multimode. This mode will automatically detect your ADSL
line code, G.dmt, G.lite, and T1.413. But in some area, multimode cannot detect the ADSL line
code well. If it is the case, please adjust the ADSL line code to G.dmt or T1.413 first. If it still fails,
please try the other values such as ALCTL, ADI, etc.
Activate Line: Aborting (false) your ADSL line and making it active (true) again for taking effect
with setting of Connect Mode.
Coding Gain: Configure the ADSL coding gain from 0 dB to 7dB, or automatic.
Tx Attenuation: Setting ADSL transmission gain, the value is between 0~12.
DSP FirmwareVersion: Current ADSL line code firmware version.
Connected: Display current ADSL line sync status.
Operational Mode: Display current ADSL mode standard (Operational Mode) your Router is using
when ADSL line has sync.
Annex Type: ADSL Annex A, which works over a standard telephone line. Annex B, which works
over an ISDN line.
Upstream: Display current upstream rate of your ADSL line.
Downstream: Display current downstream rate of your ADSL line.
51
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 53

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
System
There are six items within the System section: Time Zone, Remote Access, Firmware Upgrade,
Backup/Restore, Restart and User Management.
Time Zone
The router does not have a real time clock on board; instead, it uses the Simple Network Time
Protocol (SNTP) to get the current time from an SNTP server outside your network. Choose your
local time zone, click Enable and click the Apply button. After a successful connection to the
Internet, the router will retrieve the correct local time from the SNTP server you have specified. If
you prefer to specify an SNTP server other than those in the list, simply enter its IP address as
shown above. Your ISP may provide an SNTP server for you to use.
Daylight Saving is also known as Summer Time Period. Many places in the world adapt it during
summer time to move one hour of daylight from morning to the evening in local standard time.
Check Automatic box to auto set your local time.
Resync Period (in minutes) is the periodic interval the router will wait before it re-synchronizes the
router’s time with that of the specified SNTP server. In order to avoid unnecessarily increasing the
load on your specified SNTP server you should keep the poll interval as high as possible – at the
absolute minimum every few hours or even days.
Remote Access
Chapter 4: Configuration
52
Page 54

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
To temporarily permit remote administration of the router (i.e. from outside your LAN), select a time
period the router will permit remote access for and click Enable. You may change other
configuration options for the web administration interface using Device Management options in
the Advanced section of the GUI.
If you wish to permanently enable remote access, choose a time period of 0 minutes. This setting
cannot be saved into flash when timer set to zero.
53
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 55

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Warning
Firmware Upgrade
Your router’s “firmware” is the software that allows it to operate and provides all its functionality.
Think of your router as a dedicated computer, and the firmware as the software it runs. Over time
this software may be improved and modified, and your router allows you to upgrade the software it
runs to take advantage of these changes.
Clicking on Browse will allow you to select the new firmware image file you have downloaded to
your PC. Once the correct file is selected, click Upgrade to update the firmware in your router.
DO NOT power down the router or interrupt the firmware upgrading while it is
still in process. Improper operation could damage the router.
Backup / Restore
54
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 56

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
These functions allow you to save and backup your router’s current settings to a file on your PC, or
to restore a previously saved backup. This is useful if you wish to experiment with different settings,
knowing that you have a backup handy in the case of any mistakes. It is advisable to backup your
router’s settings before making any significant changes to your router’s configuration.
Press Backup to select where on your local PC to save the settings file. You may also change the
name of the file when saving if you wish to keep multiple backups.
Press Browse to select a file from your PC to restore. You should only restore settings files that
have been generated by the Backup function, and that were created when using the current
version of the router’s firmware. Settings files saved to your PC should not be manually
edited in any way.
After selecting the settings file you wish to use, pressing Restore will load those settings into the
router.
55
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 57

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Restart Router
Click Restart with option Current Settings to reboot your router (and restore your last saved
configuration).
If you wish to restart the router using the factory default settings (for example, after a firmware
upgrade or if you have saved an incorrect configuration), select Factory Default Settings to reset
to factory default settings.
You may also reset your router to factory settings by holding the small Reset pinhole button on the
back of your router in for 10-12 seconds whilst the router is turned on.
56
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 58

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
User Management
In order to prevent unauthorized access to your router’s configuration interface, it requires all users
to login with a password. You can set up multiple user accounts, each with their own password.
You are able to Edit existing users and Create new users who are able to access the device’s
configuration interface. Once you have clicked on Edit, you are shown the following options:
You can change the user’s password, whether their account is active and Valid, as well as add a
comment to each user account. These options are the same when creating a user account, with
the exception that once created you cannot change the username. You cannot delete the default
admin account, however you can delete any other created accounts by clicking Delete when
editing the user.
You are strongly advised to change the password on the default “admin” account when you
receive your router, and any time you reset your configuration to Factory Defaults.
57
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 59

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Firewall and Access Control
Your router includes a full SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) firewall for controlling Internet access from
your LAN, as well as helping to prevent attacks from hackers. In addition to this, when using NAT
(Network Address Translation. Please see the WAN configuration section for more details on NAT) the
router acts as a “natural” Internet firewall, as all PCs on your LAN will use private IP addresses that
cannot be directly accessed from the Internet.
Firewall: Prevents access from outside your network. The router provides three levels of security
support:
NAT natural firewall: This masks LAN users’ IP addresses which are invisible to outside users on the
Internet, making it much more difficult for a hacker to target a machine on your network. This natural
firewall is on when NAT function is enabled.
When using Virtual Servers your PCs will be exposed to the degree
specified in your Virtual Server settings provided the ports specified are
opened in your firewall packet filter settings.
Firewall Security and Policy (General Settings): Inbound direction of Packet Filter rules to prevent
unauthorized computers or applications accessing your local network from the Internet.
Intrusion Detection: Enable Intrusion Detection to detect, prevent and log malicious attacks.
Access Control: Prevents access from PCs on your local network:
Firewall Security and Policy (General Settings): Outbound direction of Packet Filter rules to prevent
unauthorized computers or applications accessing the Internet.
URL Filter: To block PCs on your local network from unwanted websites.
You can find six items under the Firewall section: General Settings, Packet Filter, Intrusion Detection,
URL Filter and Firewall Log.
58
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 60

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
General Settings
You can choose not to enable Firewall, to add all filter rules by yourself, or enable the Firewall
using preset filter rules and modify the port filter rules as required. The Packet Filter is used to filter
packets based-on Applications (Port) or IP addresses.
There are four options when you enable the Firewall, they are:
All blocked/User-defined: no pre-defined port or address filter rules by default, meaning that
all inbound (Internet to LAN) and outbound (LAN to Internet) packets will be blocked. Users
have to add their own filter rules for further access to the Internet.
High/Medium/Low security level: the predefined port filter rules for High, Medium and Low
security are displayed in Port Filters of Packet Filter.
Select either High, Medium or Low security level to enable the Firewall. The only difference
between these three security levels is the preset port filter rules in the Packet Filter. Firewall
functionality is the same for all levels; it is only the list of preset port filters that changes between
each setting. For more detailed on level of preset port filter information, refer to Table 1:
Predefined Port Filter.
If you choose of the preset security levels and then add custom filters, you may temporarily disable
the firewall and recover your custom filter settings by re-selecting the same security level.
The “Block WAN Request” is a stand-alone function and not relate to whether security enable or
disable. Mostly it is for preventing any scan tools from WAN site by hacker.
Any remote user who is attempting to perform this action may result in blocking
all the accesses to configure and manage of the device from the Internet.
59
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 61

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Packet Filter
This function is only available when the Firewall is enabled and one of these four security levels is
chosen (All blocked, High, Medium and Low). The predefined port filter rules in the Packet Filter
must modify accordingly to the level of Firewall, which is selected. See Table1: Predefined Port
Filter for more detailed information.
60
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 62

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Example: Predefined Port Filters Rules
The predefined port filter rules for High, Medium and Low security levels are listed. See Table 1.
(Note: Firewall – All Blocked/User-defined, you must define and create the port filter rules
yourself. No predefined rule is set)
Table 1: Predefined Port Filter
Port Number
Application Protocol
Start End Inbound Outbound Inbound Outbound Inbound Outbound
HTTP(80) TCP(6)
80 80 NO
DNS (53) UDP(17) 53 53 NO
DNS (53) TCP(6)
FTP(21) TCP(6)
Telnet(23) TCP(6)
SMTP(25) TCP(6)
POP3(110) TCP(6)
53 53 NO
21 21 NO NO NO
23 23 NO NO NO
25 25 NO
110 110
NEWS(119)
(Network News
Transfer
Protocol)
TCP(6)
119 119
RealAudio/
RealVideo
UDP(17) 7070 7070
(7070)
Firewall - High Firewall - Medium Firewall – Low
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO NO NO
NO NO
YES YES YES YES
YES
NO
YES
YES YES YES
YES YES YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
PING ICMP(1) N/A N/A
H.323(1720) TCP(6) 1720 1720
T.120(1503) TCP(6) 1503 1503
SSH(22) TCP(6)
22 22 NO NO NO
NTP(123) UDP(17) 123 123
HTTPS(443) TCP(6)
443 443
ICQ (5190) TCP(6) 5190 5190
Inbound: Internet to LAN
Outbound: LAN to Internet.
Chapter 4: Configuration
NO
YES
NO
NO NO NO
NO NO NO
NO
YES
NO
NO NO NO
NO NO NO
YES
NO
YES
YES YES YES
YES YES YES
YES YES YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
YES
NO YES YES
61
Page 63

Packet Filter – Add TCP/UDP Filter
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Rule Name: Users-define description to identify this entry or click to select existing
predefined rules.
Time Schedule: It is self-defined time period. You may specify a time schedule for your
prioritization policy. For setup and detail, refer to Time Schedule section
Source IP Address(es) / Destination IP Address(es): This is the Address-Filter used to allow or
block traffic to/from particular IP address(es). Selecting the Subnet Mask of the IP address range
you wish to allow/block the traffic to or form; set IP address and Subnet Mask to 0.0.0.0 to inactive
the Address-Filter rule.
Tip: To block access to/from a single IP address, enter that IP address as the Host IP Address
and use a Host Subnet Mask of “255.255.255.255”.
Type: It is the packet protocol type used by the application, select either TCP or UDP.
Source Port: This Port or Port Ranges defines the port allowed to be used by the Remote/WAN to
connect to the application. Default is set from range 0 ~ 65535. It is recommended that this option
be configured by an advanced user.
Destination Port: This is the Port or Port Ranges that defines the application.
Inbound / Outbound: Select Allow or Block the access to the Internet (“Outbound”) or from the
Internet (“Inbound”).
Click Apply button to apply your changes.
62
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 64

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Packet Filter – Add Raw IP Filter
Rule Name: Users-define description to identify this entry or click to select existing
predefined rules.
Time Schedule: It is self-defined time period. You may specify a time schedule for your
prioritization policy. For setup and detail, refer to Time Schedule section
Protocol Number: Insert the port number, i.e. GRE 47.
Inbound / Outbound: Select Allow or Block the access to the Internet (“Outbound”) or from the
Internet (“Inbound”).
Click Apply button to apply your changes.
63
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 65

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Example: Configuring your firewall to allow for a publicly accessible web server on your LAN
The predefined port filter rule for HTTP (TCP port 80) is the same no matter whether the firewall is set to
a high, medium or low security level. To setup a web server located on the local network when the
firewall is enabled, you have to configure the Port Filters setting for HTTP.
As you can see from the diagram below, when the firewall is enabled with one of the three presets
(Low/Medium/High), inbound HTTP access is not allowed which means remote access through HTTP to
your router is not allowed.
(Note: Inbound indicates accessing from Internet to LAN and Outbound is from LAN to the Internet)
64
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 66

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Configuring Packet Filter:
1. Click Port Filters. You will then be presented with the predefined port filter rules screen (in this
case for the low security level), shown below:
Note: You may click Edit the predefined rule instead of Delete it. This is an example to show to
how you add a filter on your own.
Click Delete
2. Click Delete to delete the existing HTTP rule.
3. Click Add TCP/UDP Filter.
4. Input the Rule Name, Time Schedule, Source/Destination IP, Type, Source/Destination Port,
Inbound and Outbound.
Example:
Application: Cindy_HTTP
Time Schedule: Always On
Source / Destination IP Address(es): 0.0.0.0 (I do not wish to active the address-filter, instead I
use the port-filter)
Type: TCP (Please refer to Table1: Predefined Port Filter)
Source Port: 0-65535
Redirect Port: 80-80 (This is Port defined for HTTP)
Inbound / Outbound: Allow
Click Add TCP/UDP Filter
(I allow all ports to connect with the application))
65
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 67

5. The new port filter rule for HTTP is shown below:
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
7. Configure your Virtual Server (“port forwarding”) settings so that incoming HTTP requests on port 80
will be forwarded to the PC running your web server:
Note: For how to configure the HTTP in Virtual Server, go to Add Virtual Server in Virtual Server
section for more details.
.
66
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 68

Intrusion Detection
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
The router’s Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is used to detect hacker attacks and intrusion
attempts from the Internet. If the IDS function of the firewall is enabled, inbound packets are
filtered and blocked depending on whether they are detected as possible hacker attacks, intrusion
attempts or other connections that the router determines to be suspicious.
Blacklist: If the router detects a possible attack, the source IP or destination IP address will be
added to the Blacklist. Any further attempts using this IP address will be blocked for the time period
specified as the Block Duration. The default setting for this function is false (disabled). Some
attack types are denied immediately without using the Blacklist function, such as Land attack and
Echo/CharGen scan.
Intrusion Detection: If enabled, IDS will block Smurf attack attempts. Default is false.
Block Duration:
Victim Protection Block Duration: This is the duration for blocking Smurf attacks.
Default value is 600 seconds.
Scan Attack Block Duration: This is the duration for blocking hosts that attempt a
possible Scan attack. Scan attack types include X’mas scan, IMAP SYN/FIN scan and
similar attempts. Default value is 86400 seconds.
DoS Attack Block Duration: This is the duration for blocking hosts that attempt a
possible Denial of Service (DoS) attack. Possible DoS attacks this attempts to block
include Ascend Kill and WinNuke. Default value is 1800 seconds.
Max TCP Open Handshaking Count: This is a threshold value to decide whether a SYN Flood
attempt is occurring or not. Default value is 100 TCP SYN per seconds.
Max PING Count: This is a threshold value to decide whether an ICMP Echo Storm is occurring or
not. Default value is 15 ICMP Echo Requests (PING) per second.
67
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 69

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
UDP Echo Port and
No Existing session
Max ICMP Count: This is a threshold to decide whether an ICMP flood is occurring or not. Default
value is 100 ICMP packets per seconds except ICMP Echo Requests (PING).
For SYN Flood, ICMP Echo Storm and ICMP flood, IDS will just warn the user in the Event Log. It
cannot protect against such attacks.
Table 2: Hacker attack types recognized by the IDS
Intrusion Name Detect Parameter Blacklist
Ascend Kill
WinNuke
Smurf
Land attack
Echo/CharGen Scan
Echo Scan
CharGen Scan
X’mas Tree Scan
IMAP
SYN/FIN Scan
SYN/FIN/RST/ACK
Scan
Net Bus Scan
Back Orifice Scan
SYN Flood
ICMP Flood
ICMP Echo
Src IP: Source IP Src Port: Source Port
Dst Port: Destination Port Dst IP: Destination IP
Ascend Kill data Src IP DoS Yes Yes
TCP
Port 135, 137~139,
Flag: URG
ICMP type 8
Des IP is broadcast
SrcIP = DstIP Yes Yes
CharGen Port
UDP Dst Port =
Echo(7)
UDP Dst Port =
CharGen(19)
TCP Flag: X’mas
TCP Flag: SYN/FIN
DstPort: IMAP(143)
SrcPort: 0 or 65535
TCP,
And Scan Hosts
more than five.
TCP
No Existing session
DstPort = Net Bus
12345,12346, 3456
UDP, DstPort =
Orifice Port (31337)
Max TCP Open
Handshaking Count
(Default 100 c/sec)
Max ICMP Count
(Default 100 c/sec)
Max PING Count
(Default 15 c/sec)
Src IP DoS Yes Yes
Dst IP
Yes Yes
Src IP Scan Yes Yes
Src IP Scan Yes Yes
Src IP Scan Yes Yes
Src IP Scan Yes Yes
Src IP Scan Yes Yes
SrcIP Scan Yes Yes
SrcIP Scan Yes Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Type of Block
Duration
Victim
Protection
Drop Packet Show Log
Yes Yes
Chapter 4: Configuration
68
Page 70

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
URL Filter
URL (Uniform Resource Locator – e.g. an address in the form of http://www.abcde.com or
http://www.example.com) filter rules allow you to prevent users on your network from accessing
particular websites by their URL. There are no pre-defined URL filter rules; you can add filter rules
to meet your requirements.
Enable/Disable: To enable or disable URL Filter feature.
Block Mode: A list of the modes that you can choose to check the URL filter rules. The default is
set to Disabled.
Disabled: No action will be performed by the Block Mode.
Always On: Action is enabled. URL filter rules will be monitoring and checking at all hours
of the day.
TimeSlot1 ~ TimeSlot16: It is self-defined time period. You may specify the time period to
check the URL filter rules, i.e. during working hours. For setup and detail, refer to Time
Schedule section.
Keywords Filtering: Allows blocking by specific keywords within a particular URL rather than
having to specify a complete URL (e.g. to block any image called “advertisement.gif”). When
enabled, your specified keywords list will be checked to see if any keywords are present in URLs
accessed to determine if the connection attempt should be blocked. Please note that the URL filter
blocks web browser (HTTP) connection attempts using port 80 only.
For example, if the URL is http://www.abc.com/abcde.html, it will be dropped as the keyword
69
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 71

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
“abcde” occurs in the URL.
Domains Filtering: This function checks the domain name only, not the IP address, in URLs
accessed against your list of domains to block or allow. If it is matched, the URL request will be
sent (Trusted) or dropped (Forbidden). For this function to be activated, both check-boxes must be
checked. The checking procedure is:
1. Check the domain in the URL to determine if it is in the trusted list. If yes, the
connection attempt is sent to the remote web server.
2. If not, check if it is listed in the forbidden list, and if present then the connection attempt
is dropped.
3. If the packet does not match either of the above two items, it is sent to the remote web
server.
4. Please be note that the domain only should be specified, not the full URL. For example
to block traffic to www.sex.com, enter “sex” or “sex.com” instead of “www.sex.com”. In
the example below, the URL request for www.abc.com will be sent to the remote web
server because it is listed in the trusted list, whilst the URL request for www.sex or
www.sex.com will be dropped, because sex.com is in the forbidden list.
Restrict URL Features: This function enhances the restriction to your URL rules.
70
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 72

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Example: Andy wishes to disable all WEB traffic except for ones listed in the trusted domain,
which would prevent Bobby from accessing other web sites.
Andy selects both functions in the Domain Filtering and thinks that it will stop Bobby. But Bobby
knows this function, Domain Filtering, ONLY disables all WEB traffic except for Trusted Domain,
BUT not its IP address. If this is the situation, Block surfing by IP address function can be handy
and helpful to Andy. Now, Andy can prevent Bobby from accessing other sites.
Block Java Applet: This function can block Web content that includes the Java Applet. It is to
prevent someone who wants to damage your system via standard HTTP protocol.
Block surfing by IP address: Preventing someone who uses the IP address as URL for
skipping Domains Filtering function. Activates only and if Domain Filtering enabled.
71
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 73

Firewall Log
Firewall Log display log information of any unexpected action with your firewall settings.
Check the Enable box to activate the logs.
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Log information can be seen in the Status – Event Log after enabling.
72
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 74

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Attention
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)
VoIP enables telephone calls through existing Internet connection instead of going through the PSTN
(Public Switched Telephone Network). It is not only cost-effective, especially for a long distance
telephone charges, but also toll-quality voice calls over the Internet.
After completing VoIP configuration, remember to apply the changes, SAVE
CONFIG and restart to activate your VoIP.
There are six items within the VoIP section: Wizard, General Settings, Phone Port, PSTN Dial Plan,
VoIP Dial Plan and Ring & Tone.
Chapter 4: Configuration
73
Page 75

Wizard
This section provides easy setup for your VoIP service.
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Voice QoS
Setting for Phone Port 1
DSCP:
Marking allows users to classify traffic based on DSCP value and send packets to next Router.
SIP Service Provider:
is done, respective parameters below are automatically displayed.
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP), it is the first 6 bits in the ToS byte. DSCP
This section allows you to select the service provider. When the selection
Select Profile: It allows you to select a desired SIP provider whom is not defined already
in the SIP Service Provider. You may manually setup the SIP accounts by entering SIP
information to User-defined Profile.
Phone Number:
Authentication Username:
Authentication Password:
SIP registrar.
This parameter holds the registration ID of the user within the SIP registrar.
Same as Phone Number.
This parameter holds the password used for authentication within
See below for details.
74
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 76

User-defined Profiles
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Profile Name: A user-defined name is for identifying the Profile.
Registrar Address (or Hostname):
Registrar Port:
from VoIP device.
Expire:
Expire time for the registration message sending.
User Domain/Realm:
Outbound Proxy Address:
is very useful when VoIP device is behind a NAT.
Outbound Proxy Port:
messages.
Phone Number: This parameter holds the registration ID of the user within the SIP registrar.
Authentication Username: Same as Phone Number.
Specify the port of the SIP registrar on which it will listen for register requests
Set different domain name for the SIP proxy server.
Indicate the SIP outbound proxy server IP address. This parameter
Specify the port of the SIP outbound proxy on which it will listen for
Indicate the SIP registrar IP address.
Authentication Password: This parameter holds the password used for authentication within SIP
registrar.
Confirm Password: Re-enter the password for confirmation.
Display Name: This parameter will be appeared on the Caller ID.
75
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 77

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
General Settings
This section reflects and contains basic settings for the VoIP module from selected
provider in the Wizard section. Fail to provide correct information will halt making calls out
to the Internet.
SIP Device Parameters
SIP:
To use SIP as VoIP call signaling protocol.
Default is set to Disable.
Silence Suppression (VAD): Voice Activation Detection prevents transmitting the nature
silence to consume the bandwidth. It is also known as Silence Suppression which is a
software application that ensures the bandwidth is reserved only when voice activity is
activated. Default is set to Enable.
Echo Cancellation: G.168 echo canceller is an ITU-T standard. It is used for isolating the
echo while you are on the phone. This helps you not to hear much of your own voice
reflecting on the phone while you talk. Default is set to Enable.
RTP Port:
endpoints and the different call sessions that may exist within an end-point. (Range from 5100 to
65535, default value is 5100)
Region:
VoIP device must work. When a country is selected, the country parameters are automatically
loaded.
Provide the based value from the media (RTP) ports that are assigned for various
This selection is a drop-down box, which allows user to select the country for which the
Voice QoS, DSCP Marking:
the ToS byte. DSCP Marking allows users to classify traffic based on DSCP value and send
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP), it is the first 6 bits in
76
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 78

packets to next Router.
Setting for Phone Port 1
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Registrar Address (or Hostname):
Registrar Port:
from VoIP device.
Expire:
Expire time for the registration message sending.
User Domain/Realm:
Outbound Proxy Address:
is very useful when VoIP device is behind a NAT.
Outbound Proxy Port:
messages.
Specify the port of the SIP registrar on which it will listen for register requests
Set different domain name for the SIP proxy server.
Indicate the SIP outbound proxy server IP address. This parameter
Specify the port of the SIP outbound proxy on which it will listen for
Indicate the SIP registrar IP address.
How to register to SIP Server
1) In Wizard Section, select your SIP Service Provider and input information in the filed of
Phone Number, Authentication Username and Authentication Password.
2) In Wizard Section, click Apply button to apply the settings.
3) In General Settings, make sure general SIP information are correctly inserted.
4) In General Settings, click Apply button to apply the settings.
5) In General Settings, click Synch Now button to register the account(s) with your SIP
server.
77
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 79

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Phone Ports
This section displays status and allows you to edit the account information of your Phones.
Click Edit to update your phone information.
Login Account Configuration
Phone Number: This parameter holds the registration ID of the user within the SIP registrar.
Authentication Username: Same as Phone Number.
Authentication Password: This parameter holds the password used for authentication within SIP
registrar.
Confirm Password: Re-enter the password for confirmation.
78
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 80

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Display Name: This parameter will be appeared on the Caller ID.
Codec Preference
Codec is known as Coder-Decoder used for data signal conversion. Set the priority of voice
compression; Priority 1 owns the top priority.
G.729: It is used to encoder and decoder voice information into a single packet which reduces the
bandwidth consumption. 8kbps bandwidth is needed.
G.71
1111
µ-LAW: It is a basic non-compressed encoder and decoder technique. µ-LAW uses pulse
code modulation (PCM) encoder and decoder to convert 14-bit linear sample. 64kbps bandwidth
is needed.
G.711A-LAW: It is a basic non-compressed encoder and decoder technique. µ-LAW uses pulse
code modulation (PCM) encoder and decoder to convert 13-bit linear sample. 64kbps bandwidth is
needed.
Non-used: Only available in Priority 2 and 3. It is selected if codec is not to be used.
Note: Codec priority is assigned in the order as G.729 > G.711µ-LAW > G.711A-LAW
Speed Dial
It is for you to store frequently used telephone numbers which you can press number from 0 to 9 and the
pound sign (#) to activate this function. For example, speed dial to phone number lists on 9, just press 9
then #. Your router will automatically call out to number listed on entry 9.
Indicate remote user’s IP address or domain name if this remote user does not register in the SIP server.
If remote user is registered in the SIP server, this field is related to the SIP server’s IP / Domain name.
For examples:
If your friend Tim gives you a SIP URL as sip: 89755@192.246.69.223 then you can fill in as
89755@192.246.69.223.
If your friend Felix gives you a SIP URL as sip: felix@iptel.org then you can fill in as felix@iptel.org.
If your friend Greg gives you an IP address "192.246.56.56" only, then you can fill in as “192.246.56.56”.
In case, some of users may use DDNS, you can fill in with domain name as well.
Volume Control
Volume control helps you to adjust the voice quality of telephone to the best comfortable listening level.
Press “-“, the minus sign, to reduce either microphone or/both speaker’s level of your telephone.
Press “+“, the plus sign, to increase either microphone or/both speaker’s level of your telephone.
79
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 81

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
User dials a wrong SIP number.
Attention
PSTN Dial Plan
This section enables you to configure “VoIP with PSTN switching” on your system. You
can define a range of dial plans to make regular call from VoIP switching to PSTN line.
Prefix numbers is essential key to make a distinguishing between VoIP and Regular phone
call. If actual numbers dialed matches with prefix number defined in this dial plan, the
dialed number will be routed to the PSTN to make a regular call. Otherwise, the number
will be routed to the VoIP networks.
Reminder! In order to utilize this feature, you must have registered and connected to your
SIP Server fist.
Prefix: Specify number(s) for switching to a PSTN call.
Number of Digits: Specify the total number of digits wish to dial out. Maximum digit
number is 15.
Action: Specify a dialing method you wish to make PSTN call(s).
Dial with Prefix: The dialed number with prefix will be sent call through the PSTN.
NOTE: The actual dialed number of valid digits length requires matching in the Number of Digits filed.
Dial without Prefix: The dialed number will be sent call through the PSTN without prefix.
NOTE: The actual dialed number of valid digits length requires matching in the Number of Digits filed.
Dial at Timeout: The dialed number will be sent call through the PSTN with the prefix when
timeout starts. This timeout activates when no more digits are dialed in a specific duration.
NOTE: The actual dialed number of valid digits length MUST NOT exceed in the Number of Digits filed.
Dial at Timeout no Prefix: The dialed number will be sent call through the PSTN without
prefix when timeout starts. This timeout activates when no more digits are dialed in a specific
duration.
NOTE: The actual dialed number of valid digits length MUST NOT exceed in the Number of Digits filed.
Chapter 4: Configuration
The following situation will make phone port 1 and 2 relay to PSTN line
automatically.
- Power down
- Internet Service fail, i.e., lost of WAN IP Address
- SIP service is not accessible. This excludes when:
User manually disables Registration.
User inserts a wrong authentication username or password.
80
Page 82

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
PSTN Dial Plan Examples:
1) Dial with Prefix
If you dial 01223 707070, number 01223707070 will be dialed out via FXO to make a regular
phone call.
2) Dial without Prefix
If you dial 9102, the number 102 will be dialed out via FXO port to make a regular phone call.
3) Dial at Timeout
If you only dial 01223 7070 and no more numbers, after the timeout activates, 012237070 will be
dialed to make a regular call via FXO port.
Even though 0707 (only 4 digits) does not match with number of digits 6 defined in the filed, 7070
is still a valid phone number since it has not exceed 6 digits.
81
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 83

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
4) Dial at Timeout no Prefix
If you only dial 9 7070 and no more numbers, after the timeout activates, 7070 will be dialed
without prefix to make a regular call via FXO port.
Even though 0707 (only 4 digits) does not match with number of digits 6 defined in the filed, 7070
is still a valid phone number since it has not exceed 6 digits
82
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 84

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
VoIP Dial Plan
This section helps you to make a telephony number dialed as making a regular call via
VoIP. You no longer need to memorize a long dial string of number for making a VoIP call.
Parameters
A listed of special dial feature comes handy when you have a miss call or need to transfer a call to a
third party. Details please refer to the section Special dial codes below.
*69 (Return Call): Dial *69 to return the last missed call. It is only available for SIP call(s).
*20 (Do not Disturb ON): Dial *20 to set the No Disturb on. Your phone will not ring if someone
calls.
*80 (Do not Disturb OFF): Dial *80 to set the No Disturb off. Your will be able to hear ring tone
when someone calls.
*90x (Blind Call Transfer): Dial *90 + phone-number to translate a call to a third party. This
feature is enabled by default.
x# Speed Dial (x:2..9): Refer to Phone Port section in the Web GUI. Set up your Speed Dial
phone book first before accessing the Speed Dial feature. It is enabled by default.
## Redial: Press ## to redial the latest number you dialed. This feature is enabled by default.
Note: Refer to Special Dial Code section in this Manual for more details.
Test: Test displays the actual number will be called out to the VoIP service.
Click Apply to apply the settings.
Dial Plan Rules List
Click Add to create and define VoIP dial-plan rule(s).
83
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 85

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Prefix Processing:
Prepend xxx unconditionally: xxx number is appended unconditionally to the front of the
dialing number when making a call.
If Prefix is xxx, delete it: Prefix xxx is removed from the dialing numbers before making a call.
If Prefix is xxx, replace with: Prefix xxx is appended to the front of the dialing numbers when
making a call.
No prefix: No prefix is appended to the front of the dialing numbers. It is set as in default settings.
Main Digit Sequence:
x: Any numeric number between 0 and 9.
. ( period ): Repeat numeric number(s) between 0 and 9.
84
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 86

Here are some Examples for your reference:
Main Digit Sequence Lists: Description
x.
xxx
xxx.
123x.
[x…x]x.
For example: [124]x.
[x-x]x.
For example: [1-3]x.
x[x-x]x.
For example: 9[4-6]8x.
Any digit number between 0 and 9 in variable length.
Maximum length is 16.
Any 3 digit number only between 0 and 9. Total length is 3.
Note: No period is needed (.)
Any number between 0 and 9 with variable length but no
shorter than 3 digits. Maximum length is 16.
Any number (0-9) starting with 123. Maximum length is 16.
Any number (0-9) starting with 1 or 2 or 4. Maximum
length is 16.
Any number (0-9) starting with number 1 to 3. Maximum
length is 16.
Any number (0-9) starting with 9, the second number
between 4-6, and third number 8. Maximum length is 16.
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
85
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 87

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Ring & Tone
This section allows advanced user to change the existing or newly defined parameters for
the various ring tones (dial tone, busy tone, answer tone and etc.)
Country Specific Ring & Tone
Region: Select a country ring-tone, from the drop-down list, where you are located. This VoIP
router provides default parameter of ring tones according to different countries. The ring-tone
parameters are automatically displayed after entering a specific country. If your country is not in
the list, you may manually create ring-tone parameters.
Ring Parameters
Ring Cadence (in ms): Ring cadence is defined by three fields, Frequency: On Time1, Off Time1,
On Time2, Off Time2 and On Time3, Off Time3. Frequency is specified in Hertz. Time is given in
milliseconds.
Tone Parameters
You may need to check with your local telephone service provider for such information. Also, it is
recommended that this option be configured by an advanced user, unless you are instructed to do
so.
Click Apply to apply the settings.
.
86
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 88

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Special dial codes
The following table lists the special dial codes that are built-in to the system:
Option Description
Flash-hook
(Wireless Router with LINE
port only)
*69
## Last number redial
*20
*80 Set do not disturb off
Switch to PSTN line
Note: A quick press of the hook. On some phones a button is provided
which provides Flash-hook functionality. The button is marked "FLASH"
or "RECALL".
Return the last missed call for SIP service only
Note: Entering this on a phone will call the last number which made a
call to the phone. For example A makes a call to B, but hangs up before
B answers. If B enters *69, A will be called.
Set do not disturb on
Note: It is possible to set a Do-Not-Disturb feature on a phone such that
any phone which calls the phone will receive an engaged tone and the
phone called will not ring. For example, B enters *20 and hangs up. A
makes a call to B, and receives the engaged tone and phone B does not
ring.
*74<x><number>#
*90<phone-number>
Set the number for Speed dial code ‘x’, where ‘x’ is a
number between 2 and 9.
Note: Where <x> is a number between 2 and 9, and <number> is the
number to dial. The code needed to dial a speeddial from a phone
connected to a VoIP Router is:
<x>#, where <x> is a number between 2 and 9.
The settings will infect to your setting in Speed Dial on WEB GUI.
Set the number for performing Blind Call Transfer, where
<phone-number> is the number that you wish to transfer the
call to. It’s for SIP service only.
Note: In Blind Call Transfer, you have a call in progress (incoming or
outgoing) and decide you wish to transfer the call to another phone. To
transfer the call, perform the following steps:
1. Hook-flash to get a dial tone.
2. Dial *90<phone-number> (e.g. *907401), there will be a confirmation
tone then hang up. The other end will hear ring back and the called thirdparty phone will ring. When the third-party phone is picked up the two
calls will be connected.
If the third-party phone does not answer then the caller being transferred
can hang up to cancel the connect attempt.
87
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 89

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
You can click
Clear
to delete the existing Application.
QoS (Quality of Service)
QoS function helps you to control your network traffic for each application from LAN (Ethernet and/or
Wireless) to WAN (Internet). It facilitates you to control the different quality and speed of through put for
each application when the system is running with full loading of upstream.
You can find three items under the QoS section: Prioritization and Outbound / Inbound IP Throttling
(bandwidth management).
Prioritization
There are three priority settings to be provided in the Router:
High
Normal (The default is normal priority for all of traffic without setting)
Low
And the balances of utilization for each priority are High (60%), Normal (30%) and Low (10%).
Click Clear
Application: A user-define description to identify this new policy/application.
Time Schedule: Scheduling your prioritization policy.
Priority: The priority given to each policy/application. Its default setting is set to High; you may
adjust this setting to fit your policy/application.
Protocol: The name of supported protocol.
Chapter 4: Configuration
88
Page 90

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Source Port: The source port of packets to be monitored.
Destination Port: The destination port of packets to be monitored.
Source IP Address Range: The source IP address or range of packets to be monitored.
Destination IP address Range: The destination IP address or range of packets to be monitored.
DSCP Marking: Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP), it is the first 6 bits in the ToS byte.
DSCP Marking allows users to classify traffic based on DSCP value and send packets to next
Router. See Table 4. Here is the DSCP Mapping Table:
Table 4: DSCP Mapping Table
DSCP Mapping Table
(Wireless) ADSL Router
Standard DSCP
Disabled None
Best Effort Best Effort (000000)
Premium Express Forwarding (101110)
Gold service (L) Class 1, Gold (001010)
Gold service (M) Class 1, Silver (001100)
Gold service (H) Class 1, Bronze (001110)
Silver service (L) Class 2, Gold (010010)
Silver service (M) Class 2, Silver (010100)
Silver service (H) Class 2, Bronze (010110)
Bronze service (L) Class 3, Gold (011010)
Bronze service (M) Class 3, Silver (011100)
Bronze service (H) Class 3, Bronze (011110)
89
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 91

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
You can click
Clear
to delete the existing Application.
Outbound IP Throttling (LAN to WAN)
IP Throttling allows you to limit the speed of IP traffic. The value entered will limit the speed of the
application that you set to the specified value’s multiple of 32kbps.
Click Clear
Application: A user-define description to identify this new policy/application.
Time Schedule: Scheduling your prioritization policy. Refer to Time Schedule for more
information.
Protocol: The name of supported protocol.
Source Port: The source port of packets to be monitored.
Destination Port: The destination port of packets to be monitored.
Source IP Address Range: The source IP address or range of packets to be monitored.
Destination IP address Range: The destination IP address or range of packets to be monitored.
Outbound Rate Limit: To limit the speed of outbound traffic
Chapter 4: Configuration
90
Page 92

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
You can click
Clear
to delete the existing Application.
Inbound IP Throttling (WAN to LAN)
IP Throttling allows you to limit the speed of IP traffic. The value entered will limit the speed of the
application that you set to the specified value’s multiple of 32kbps.
Application: A user-define description to identify this new policy/application.
Time Schedule: Scheduling your prioritization policy. Refer to Time Schedule for more
information.
Protocol: The name of supported protocol.
Source Port: The source port of packets to be monitored.
Destination Port: The destination port of packets to be monitored.
Source IP Address Range: The source IP address or range of packets to be monitored.
Destination IP address Range: The destination IP address or range of packets to be monitored.
Inbound Rate Limit: To limit the speed of for inbound traffic.
Click Clear
Chapter 4: Configuration
91
Page 93

Example: QoS for your Network
Connection Diagram
VoIP
Normal PCs
VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Restricted
Information and Settings
Upstream: 928 kbps
Downstream: 8 Mbps
VoIP User: 192.168.1.1
Normal Users: 192.168.1.2~192.168.1.5
Restricted User: 192.168.1.100
Throughput
500
kbps
400
300
200
100
0
VoIP/VPN
HIGH
Others
NORMAL
Restricted
LOW
VoIP/VPN
HIGH
Others
NORMAL
Restricted
LOW
92
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 94

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Mission-critical application
The mission-critical application must be sent out smoothly without any dropping. Set priority as high level
for preventing any other applications to saturate the bandwidth.
Voice application
Voice is latency-sensitive application. Most VoIP devices are use SIP protocol and the port number will
be assigned by SIP module automatically. Better to use fixed IP address for catching VoIP packets as
high priority.
Above settings will help to improve quality of your VoIP service when traffic is full loading.
Restricted Application
Some of companies will setup FTP server for customer downloading or home user sharing their files by
using FTP.
With above settings that help to limit utilization of upstream of FTP. Time schedule also help you to only
limit utilization at daytime.
93
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 95

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Advanced setting by using IP throttling
With IP throttling you can specify more detail for allocating bandwidth; even the applications are located
in the same level.
Upstream: 928kbps (29*32kbps)
Mission-critical Application: 192kbps (6*32kbps)
Voice Application: 128kbps (4*32kbps)
Restricted Application: 160kbps (5*32kbps)
Other Applications: 448kbps (14*32kbps)
6+4+14+5=29, 29*32kbps=928kbps
Sometime your customers or friends may upload their files to your FTP server and that will saturate your
downstream bandwidth. The settings below help you to limit bandwidth for the restricted application.
94
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 96

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
95
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 97

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Virtual Server (“Port Forwarding”)
In TCP/IP and UDP networks a port is a 16-bit number used to identify which application program
(usually a server) incoming connections should be delivered to. Some ports have numbers that are preassigned to them by the IANA (the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority), and these are referred to as
“well-known ports”. Servers follow the well-known port assignments so clients can locate them.
If you wish to run a server on your network that can be accessed from the WAN (i.e. from other
machines on the Internet that are outside your local network), or any application that can accept
incoming connections (e.g. Peer-to-peer/P2P software such as instant messaging applications and P2P
file-sharing applications) and are using NAT (Network Address Translation), then you will usually need to
configure your router to forward these incoming connection attempts using specific ports to the PC on
your network running the application. You will also need to use port forwarding if you want to host an
online game server.
The reason for this is that when using NAT, your publicly accessible IP address will be used by and point
to your router, which then needs to deliver all traffic to the private IP addresses used by your PCs.
Please see the WAN configuration section of this manual for more information on NAT.
The device can be configured as a virtual server so that remote users accessing services such as Web
or FTP services via the public (WAN) IP address can be automatically redirected to local servers in the
LAN network. Depending on the requested service (TCP/UDP port number), the device redirects the
external service request to the appropriate server within the LAN network
96
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 98

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Add Virtual Server
Because NAT can act as a “natural” Internet firewall, your router protects your network from being
accessed by outside users when using NAT, as all incoming connection attempts will point to your
router unless you specifically create Virtual Server entries to forward those ports to a PC on your
network.
When your router needs to allow outside users to access internal servers, e.g. a web server, FTP
server, Email server or game server, the router can act as a “virtual server”. You can set up a local
server with a specific port number for the service to use, e.g. web/HTTP (port 80), FTP (port 21),
Telnet (port 23), SMTP (port 25), or POP3 (port 110), When an incoming access request to the
router for a specified port is received, it will be forwarded to the corresponding internal server.
Time Schedule: A self-defined time period to enable your virtual server. You may specify a time
schedule or Always on for the usage of this Virtual Server Entry. For setup and detail, refer to Time
Schedule section
Application: Users-define description to identify this entry or click to select existing
predefined rules.
: 20 predefined rules are available. Click the Radio button to select the rule; Application,
Protocol and External/Redirect Ports will be filled after the selection.
Protocol: It is the supported protocol for the virtual server. In addition to specifying the port
number to be used, you will also need to specify the protocol used. The protocol used is
determined by the particular application. Most applications will use TCP or UDP.
External Port: The Port number on the Remote/WAN side used when accessing the virtual server.
Redirect Port: The Port number used by the Local server in the LAN network.
97
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 99

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Internal IP Address: The private IP in the LAN network, which will be providing the virtual server
application. List all existing PCs connecting to the network. You may assign a PC
with IP address and MAC from this list.
Example:
If you like to remote accessing your Router through the Web/HTTP at all time, you would need to
enable port number 80 (Web/HTTP) and map to Router’s IP Address. Then all incoming HTTP
requests from you (Remote side) will be forwarded to the Router with IP address of 192.168.1.254.
Since port number 80 has already been predefined, next to the Application click Helper. A list of
predefined rules window will pop and select HTTP_Sever.
Application: HTTP_Sever
Time Schedule: Always On
Protocol: tcp
External Port: 80-80
Redirect Port: 80-80
IP Address: 192.168.1.254
Edit: Click it to edit this virtual server application.
Delete: Click it to delete this virtual server application.
Attention
Using port forwarding does have security implications, as outside users will be able to
connect to PCs on your network. For this reason you are advised to use specific
Virtual Server entries just for the ports your application requires, instead of using
DMZ. As doing so will result in all connections from the WAN attempt to access to
your public IP of the DMZ PC specified.
If you have disabled the NAT option in the WAN-ISP section, the Virtual Server
function will hence be invalid.
If the DHCP server option is enabled, you have to be very careful in assigning the IP
addresses of the virtual servers in order to avoid conflicts. The easiest way of
configuring Virtual Servers is to manually assign static IP address to each virtual
server PC, with an address that does not fall into the range of IP addresses that are
to be issued by the DHCP server. You can configure the virtual server IP address
manually, but it must still be in the same subnet as the router.
98
Chapter 4: Configuration
Page 100

VoIP/ 802.11g ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Edit DMZ Host
The DMZ Host is a local computer exposed to the Internet. When setting a particular internal IP
address as the DMZ Host, all incoming packets will be checked by the Firewall and NAT algorithms
then passed to the DMZ host, when a packet received does not use a port number used by any
other Virtual Server entries.
Cautious: This Local computer exposing to the Internet may face varies of security risks.
Disabled: As set in default setting, it disables the DMZ function.
Enabled: It activates your DMZ function.
Internal IP Address: Give a static IP address to the DMZ Host when Enabled radio button is
checked. Be aware that this IP will be exposed to the WAN/Internet.
Listed all existing PCs connecting to the network. You may assign a PC with IP
address and MAC from this list.
Select the Apply button to apply your changes.
99
Chapter 4: Configuration
 Loading...
Loading...