
BiPAC 6404VGP R3
VoIP/802.11g Broadband
Firewall Router
User Manual
Version release: 5.53.s6.b1
Last Revised: Date 03-09-2010

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction...................................................................................................................1
Introduction to your Router ..........................................................................................................1
Features ............................................................................................................................... 1
Chapter 2: Installing the Router..........................................................................................................4
Important note for using this router..............................................................................................4
Package Contents ....................................................................................................................... 4
Device Description....................................................................................................................... 5
Cabling ........................................................................................................................................7
Chapter 3: Basic Installation...............................................................................................................8
Connecting Your Router
Network Configuration ...............................................................................................................10
Factory Default Settings ............................................................................................................ 18
Information from your ISP..........................................................................................................19
Configuring with your Web Browser...........................................................................................20
Chapter 4: Configuration .................................................................................................................. 21
Status ........................................................................................................................................ 22
EWAN Status .....................................................................................................................22
ARP Table........................................................................................................................... 23
DHCP Table........................................................................................................................ 24
Routing Table
NAT Sessions..................................................................................................................... 26
UPnP Portmap....................................................................................................................26
VoIP Status.........................................................................................................................27
VoIP Call Log......................................................................................................................27
Event Log ........................................................................................................................... 28
Error Log ............................................................................................................................ 29
Diagnostic........................................................................................................................... 29
Quick Start
Configuration ............................................................................................................................. 35
LAN - Local Area Network .................................................................................................. 36
WAN - Wide Area Network.................................................................................................. 56
System ............................................................................................................................... 60
Firewall and Access Control ............................................................................................... 66
VoIP - Voice over Internet Protocol .....................................................................................81
QoS - Quality of Service ..................................................................................................... 97
Virtual Server (known as Port Forwarding).......................................................................106
Wake on LAN .................................................................................................................... 113
Time Schedule.................................................................................................................. 114
Advanced ......................................................................................................................... 117
Logout......................................................................................................................................123
Chapter 5: Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................ 124
Appendix: Product Support & Contact............................................................................................125
.................................................................................................................................30
...............................................................................................................9
.....................................................................................................................25

Chapter 1: Introduction
Introduction to your Router
Welcome to the VoIP/802.11g Broadband Firewall Router. The router is an “all-in-one” VoIP
Broadband router, combining a Broadband router, Ethernet network switch and 2 ports for Voice
over IP functionalities, providing everything you need to get the machines on your network
connected to the Internet over your DSL/Cable broadband connection. With features such as a
Quick-Start wizard and DHCP Server, you can be online in no time at all and with a minimum of
fuss and configuration, catering for first-time users to the guru requiring advanced features and
control over their Internet connection and network.
Features
Voice over IP compliance with SIP standard
The router supports cost-effective, toll-quality voice calls over the Internet. It complies with the most
popular industrial standard, SIP protocol, to ensure the interoperability with SIP devices and major
VoIP Gateways. The VoIP router supports call waiting, silence suppression, voice activity detection
(VAD), comfort noise generation (CNG), line echo cancellation, caller ID (Bell 202, V3) and so on.
802.11g Wireless AP with WPA Support (Wireless Router only)
With integrated 802.11g Wireless Access Point in the router, the device offers a quick and easy
access among wired network, wireless network and broadband connection with single device
simplicity, and as a result, mobility to the users. In addition to 54 Mbps 802.11g data rate, it also
interoperates backward with existing 802.11b equipment. The Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA-PSK
and WPA2-PSK) and Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) supported features enhance the security
level of data protection and access control via Wireless LAN.
Fast Ethernet Switch
A 4-port 10/100Mbps fast Ethernet switch is built in with automatic switching between MDI and
MDI-X for 10Base-T and 100Base-TX ports. An Ethernet straight or crossover cable can be used
directly for auto detection.
EWAN
The router offers a WAN port to be used to connect to Cable Modems, VDSL and fibre optic lines.
This alternative, yet faster method to connect to the internet will provide users more flexibility to get
online.
Quick Installation Wizard
It supports a WEB GUI page to install this device quickly. With this wizard, end users can enter the
information easily which they get from their ISP, then surf the Internet immediately.
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) and UPnP NAT Traversal
This protocol is used to enable simple and robust connectivity among stand-alone devices and PCs
from many different vendors. It makes network simple and affordable for users. UPnP architecture
leverages TCP/IP and the Web to enable seamless proximity networking in addition to control and
data transfer among networked devices. With this feature enabled, users can now connect to Net
meeting or MSN Messenger seamlessly.
1

Network Address Translation (NAT)
Allows multi-users to access outside resources such as the Internet simultaneously with one IP
address/one Internet access account. Many application layer gateway (ALG) are supported such
as web browser, ICQ, FTP, Telnet, E-mail, News, Net2phone, Ping, NetMeeting, IP phone and
others.
SOHO Firewall Security with DoS and SPI
Along with the built-in NAT natural firewall feature, the router also provides advanced hacker
pattern-filtering protection. It can automatically detect and block Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
The router is built with Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) to determine if a data packet is allowed
through the firewall to the private LAN.
Domain Name System (DNS) Relay
It provides an easy way to map the domain name (a friendly name for users such as
www.yahoo.com) and IP address. When a local machine sets its DNS server with this router’s IP
address, every DNS conversion request packet from the PC to this router will be forwarded to the
real DNS in the outside network.
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS)
The Dynamic DNS service allows you to alias a dynamic IP address to a static hostname. This
dynamic IP address is the WAN IP address. For example, to use the service, you must first apply
for an account from a DDNS service like http://www.dyndns.org/. More than 5 DDNS servers are
supported.
Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS gives you full control over which types of outgoing data traffic should be given priority by the
router, ensuring important data like gaming packets, customer information, or management
information move through the router ay lightning speed, even under heavy load. The QoS features
are configurable by source IP address, destination IP address, protocol, and port. You can throttle
the speed at which different types of outgoing data pass through the router, to ensure P2P users
don’t saturate upload bandwidth, or office browsing doesn’t bring client web serving to a halt. In
addition, or alternatively, you can simply change the priority of different types of upload data and let
the router sort out the actual speeds.
Virtual Server (“port forwarding”)
Users can specify some services to be visible from outside users. The router can detect incoming
service requests and forward either a single port or a range of ports to the specific local computer to
handle it. For example, a user can assign a PC in the LAN acting as a WEB server inside and
expose it to the outside network. Outside users can browse inside web servers directly while it is
protected by NAT. A DMZ host setting is also provided to a local computer exposed to the outside
network, Internet.
Rich Packet Filtering
Not only filters the packet based on IP address, but also based on Port numbers. It will filter packets
from and to the Internet, and also provides a higher level of security control.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Client and Server
In the WAN site, the DHCP client can get an IP address from the Internet Service Provider (ISP)
automatically. In the LAN site, the DHCP server can allocate a range of client IP addresses and
2

distribute them including IP address, subnet mask as well as DNS IP address to local computers. It
provides an easy way to manage the local IP network.
Static and RIP1/2 Routing
It has routing capability and supports easy static routing table or RIP1/2 routing protocol.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
It is an easy way to remotely manage the router via SNMP.
Web based GUI
It supports web based GUI for configuration and management. It is user-friendly and comes with
on-line help. It also supports remote management capability for remote users to configure and
manage this product.
Firmware Upgradeable
Device can be upgraded to the latest firmware through the WEB based GUI.
Rich Management Interfaces
It supports flexible management interfaces with local console port, LAN port, and WAN port. Users
can use terminal applications through the console port to configure and manage the device, or
Telnet, WEB GUI, and SNMP through LAN or WAN ports to configure and manage the device.
3

Chapter 2: Installing the Router
Important note for using this router
Package Contents
VoIP/802.11g Broadband Firewall Router
CD-ROM containing the online manual
Ethernet (CAT-5) Cable
RJ-45 to RS-232 Console kit
Power adapter
A detachable antenna
Quick Start Guide
4
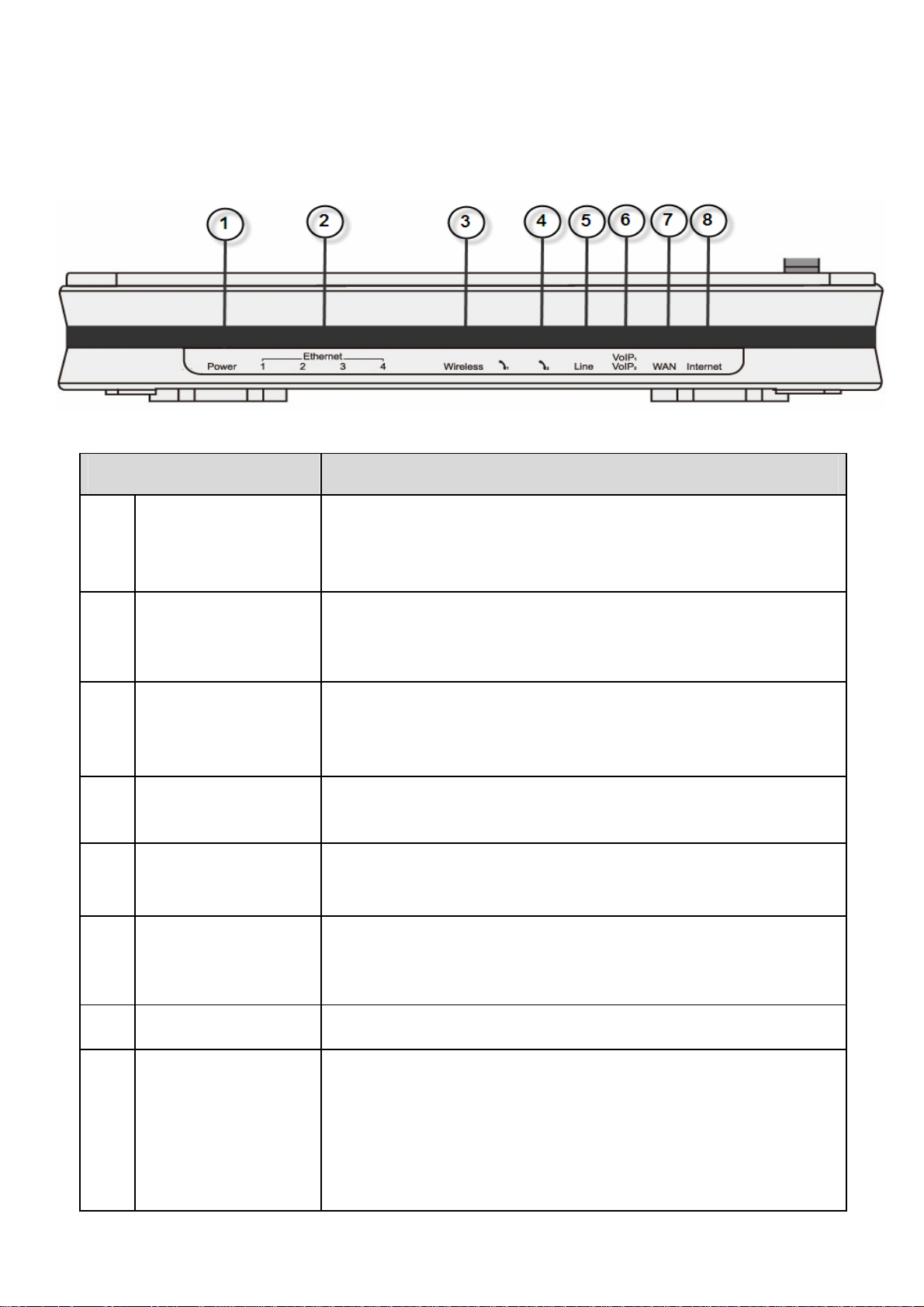
Device Description
The Front LEDs
LED Meaning
1 Power
2 Ethernet Port
3 Wireless
Lit orange when power is ON.
Lit green when the system is ready.
Lit red means system is fail. Restart the device or contact
Billion for support.
Lit when one of LAN ports is connected to an Ethernet device.
Lit green when the speed of transmission hits 100Mbps;
Lit orange when the speed of transmission hits 10Mbps.
Blink when data is being Transmitted / Received.
Lit green when the wireless connection is established.
Flash when sending/receiving data.
Flash once per second while Wi-Fi protected setup is in
progress.
Phone 1x - 2x
4
(RJ-11 connector)
Line(Router with
LINE
5
port only)
VoIP 1x - 2x
6
(RJ-11 connector)
7 WAN
8 Internet
Lit green when phone is off hook.
Lit green when the inbound and outbound calls are
transmitted through PSTN.
After SIP registration is OK, the LED will lit green whenever
phone 1is off hook but will lit orange for phone 2.
Note: Orange light also means when both Phone 1 and 2
are registered OK at the same time.
Lit green/orange when connected to an modem or Cable
modem's Ethernet port well.
Lit green when IP connected.
Flashes green when IP connected and IP traffic is passing
through the device.
Lit red when device attempted to become IP connected and
failed.
Lit off when device in bridged mode or when connection WAN
is absent.
5
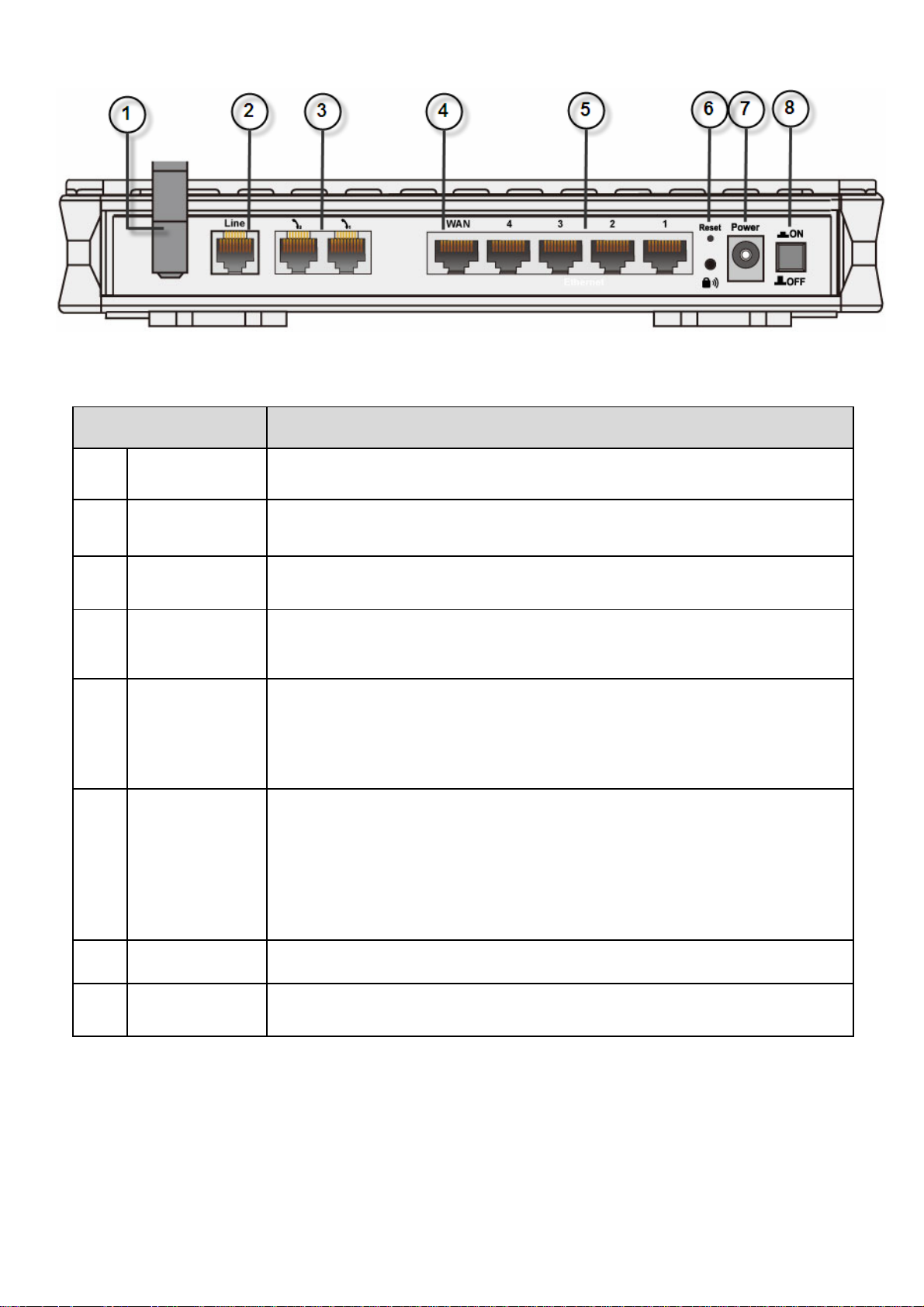
The Rear Ports
Port Meaning
1 Antenna Connect the detachable antenna to this port.
2 Line Connect this port to the telephone jack on the wall with RJ-11cable.
3. Phone 1X-2X Connect this port to an analog phone set with RJ-11 cable.
4 WAN
WAN 10/100M Ethernet port (with auto crossover support); connect
xDSL / Cable modem here.
Connect a UTP Ethernet cable (Cat-5 or Cat-5e) to one of the LAN
ports when connecting to a PC or an office/home network of 10Mbps
5 Ethernet
or 100Mbps.
Caution: Port 4 can be either a LAN or Console port at a time
but not both.
To be sure the device is being turned on press RESET button for:
1-3 seconds: quick reset the device.
6 seconds and above, power off, power on the device: restore to
6 RESET
factory default settings. (Cannot login to the router or forgot your
Username/Password. Press the button for more than 6 seconds).
Caution: After pressing the RESET button for more than
6 seconds, to be sure you power cycle the device again.
7 Power Connect it with the supplied power adapter.
8 Power Switch Power ON/OFF switch.
6

Cabling
The most common problem associated with Ethernet is bad cabling. Make sure that all connected
devices are turned on. On the top of the product is a bank of LEDs, as a first check, verifies that the
relevant LAN Link and WAN Link LEDs are lit. If they are not, verify that you are using the proper
cables.
7

Chapter 3: Basic Installation
The router can be configured through your web browser. A web browser is included as a standard
application in the following operating systems: Linux, Mac OS, Windows 7/98/NT/2000/XP/Me/Vista,
etc. The product provides an easy and user-friendly interface for configuration.
Please check your PC network components. The TCP/IP protocol stack and Ethernet network
adapter must be installed. If not, please refer to your Windows-related or other operating system
manuals.
There are ways to connect the router, either through an external repeater hub or connect directly to
your PCs. However, make sure that your PCs have an Ethernet interface installed properly prior to
connecting the router device. You ought to configure your PCs to obtain an IP address through a
DHCP server or a fixed IP address that must be in the same subnet as the router. The default IP
address of the router is 192.168.1.254 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 (i.e. any attached PC
must be in the same subnet, and have an IP address in the range of 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.253).
The best and easiest way is to configure the PC to get an IP address automatically from the router
using DHCP. If you encounter any problem accessing the router web interface it is advisable to
uninstall your firewall program on your PCs, as they can cause problems accessing the IP address
of the router. Users should make their own decisions on what is best to protect their network.
Please follow the following steps to configure your PC network environment.
8
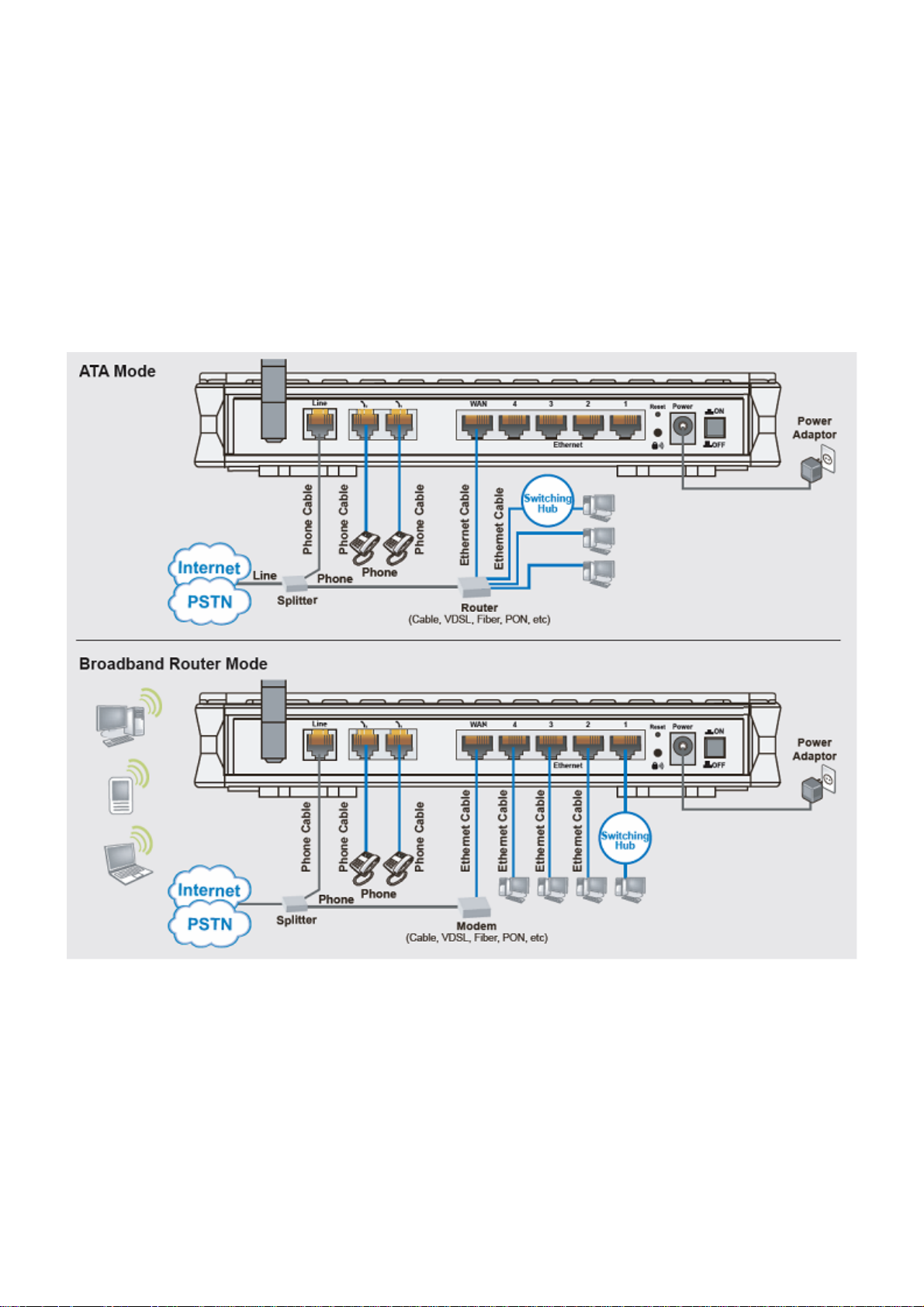
Connecting Your Router
1. (a) ATA Mode: Connect the ATA to a WAN (Connect to modem/router).
(b) Broadband Router Mode: Connect the Router to a LAN (Local Area Network)
and WAN (Connect to Cable or modem).
2. Power on the device.
3. Make sure the Power LED lit steadily and that the LAN LED is lit.
4. Connect your router to the telephone jack on the wall with RJ-11 cable.
9
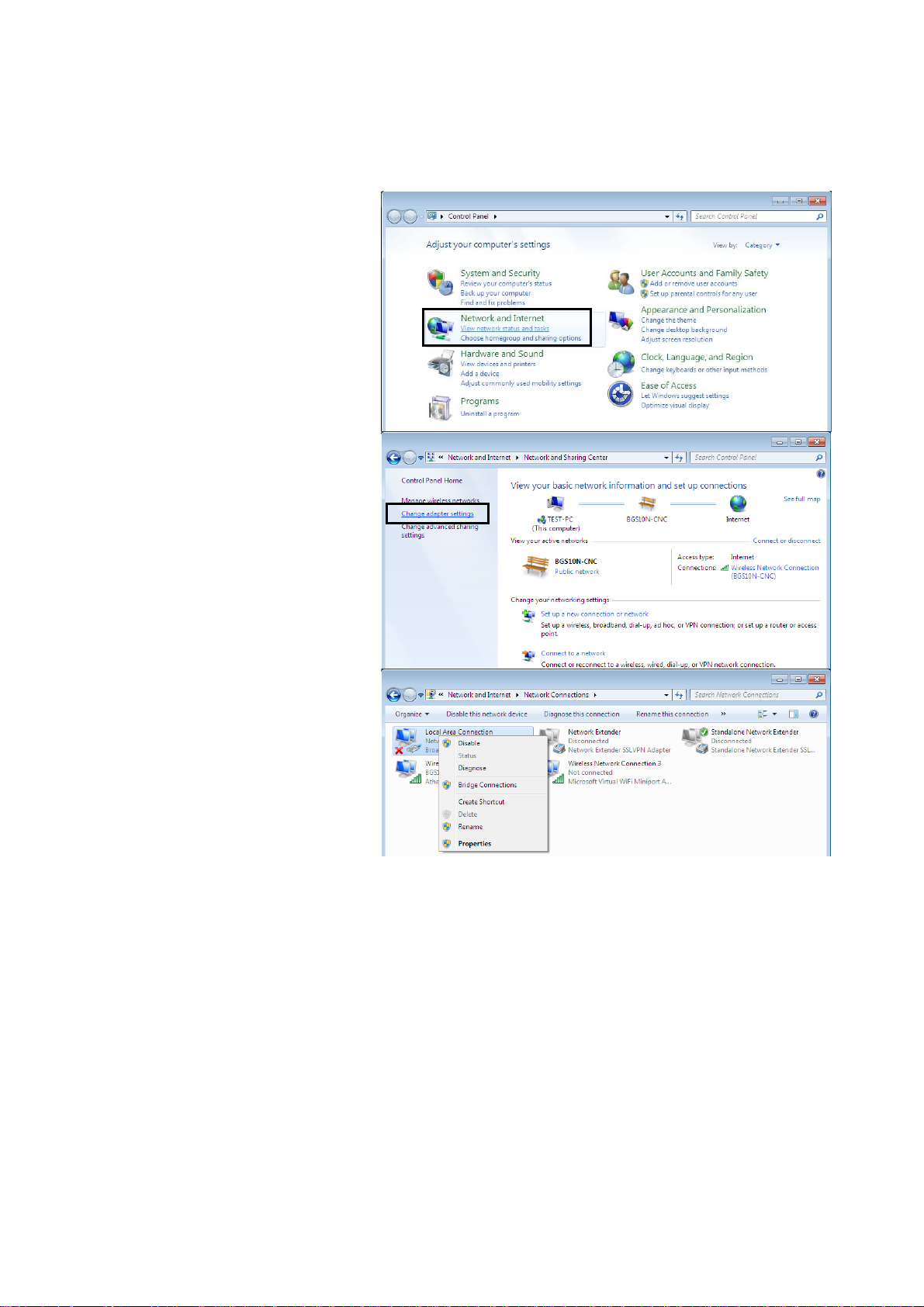
Network Configuration
Configuring PC in Windows 7
1. Go to Start. Click on Control
Panel.
2. Then click on Network and
Internet.
3. When the Network and
Sharing Center window pops
up, select and click on Change
adapter settings on the left
window panel.
4. Select the Local Area
Connection, and right click the
icon to select Properties.
10
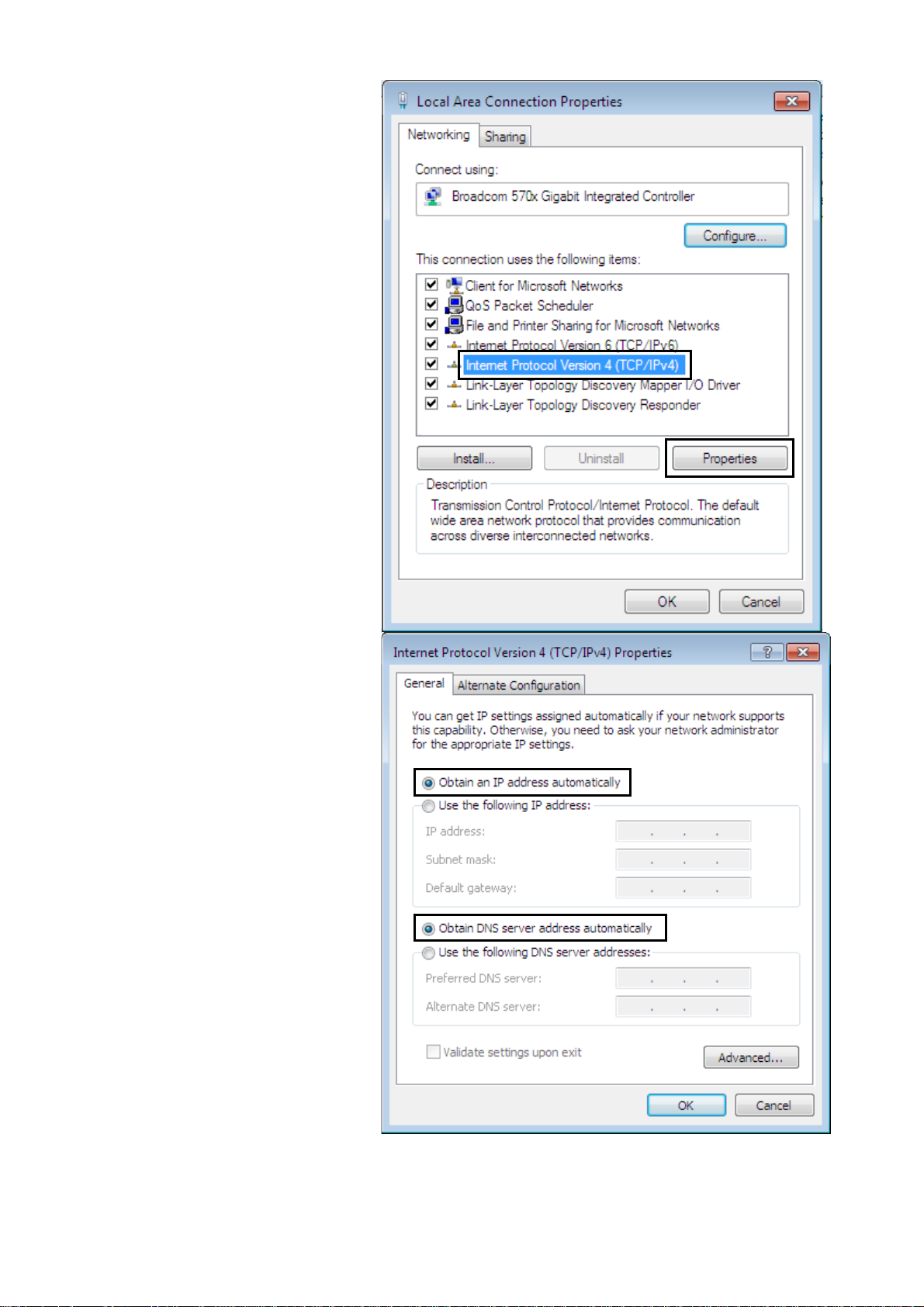
5. Select Internet Protocol
Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) then click
Properties.
6. In the TCP/IPv4 properties
window, select the Obtain an IP
address automatically and
Obtain DNS Server address
automatically radio buttons.
Then click OK to exit the setting.
7. Click OK again in the Local
Area Connection Properties
window to apply the new
configuration.
11
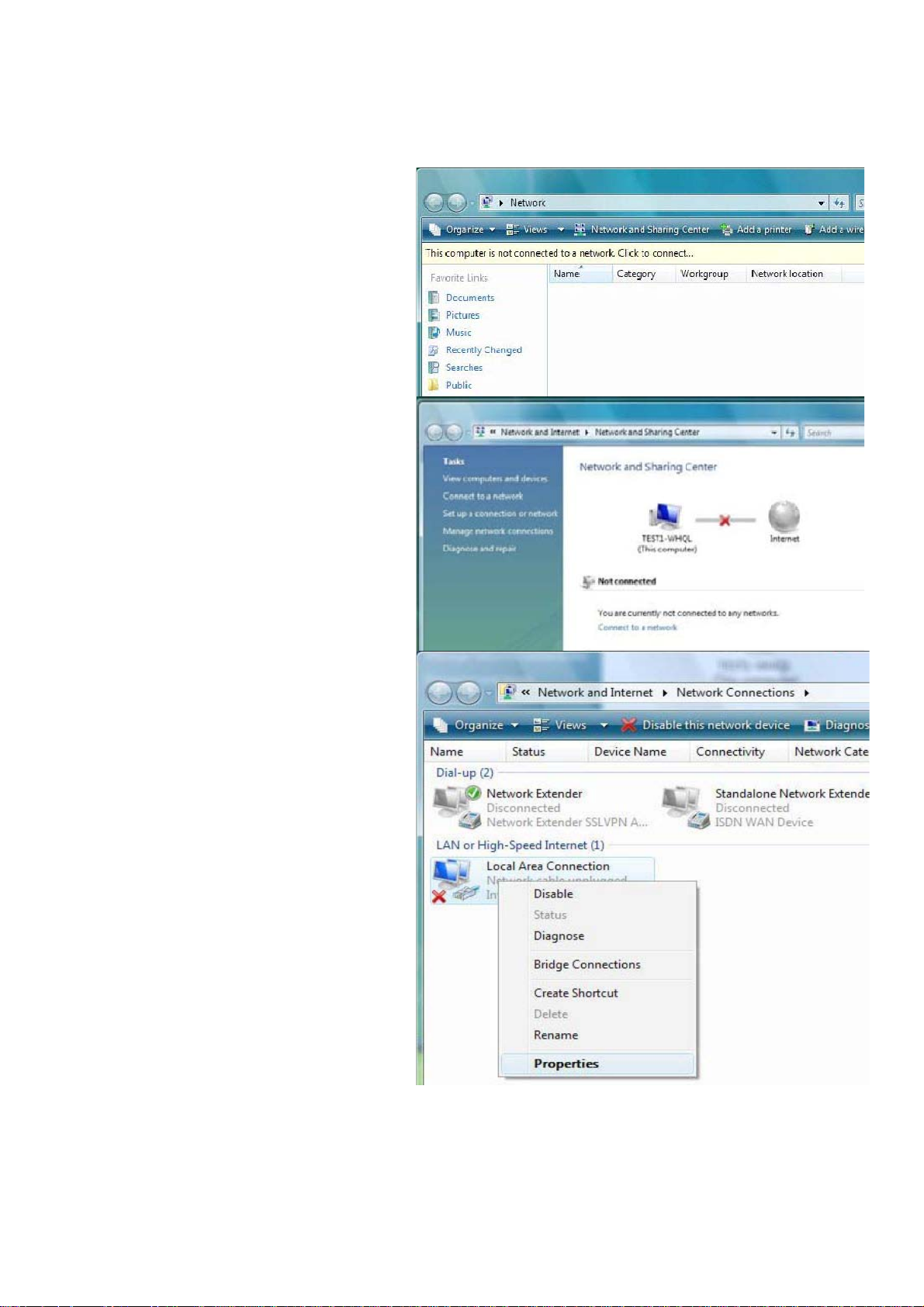
Configuring PC in Windows Vista
1. Go to Start. Click on Network.
2. Then click on Network and Sharing
Center at the top bar.
3. When the Network and Sharing
Center window pops up, select and
click on Manage network
connections on the left window
column.
4. Select the Local Area Connection,
and right click the icon to select
Properties.
12
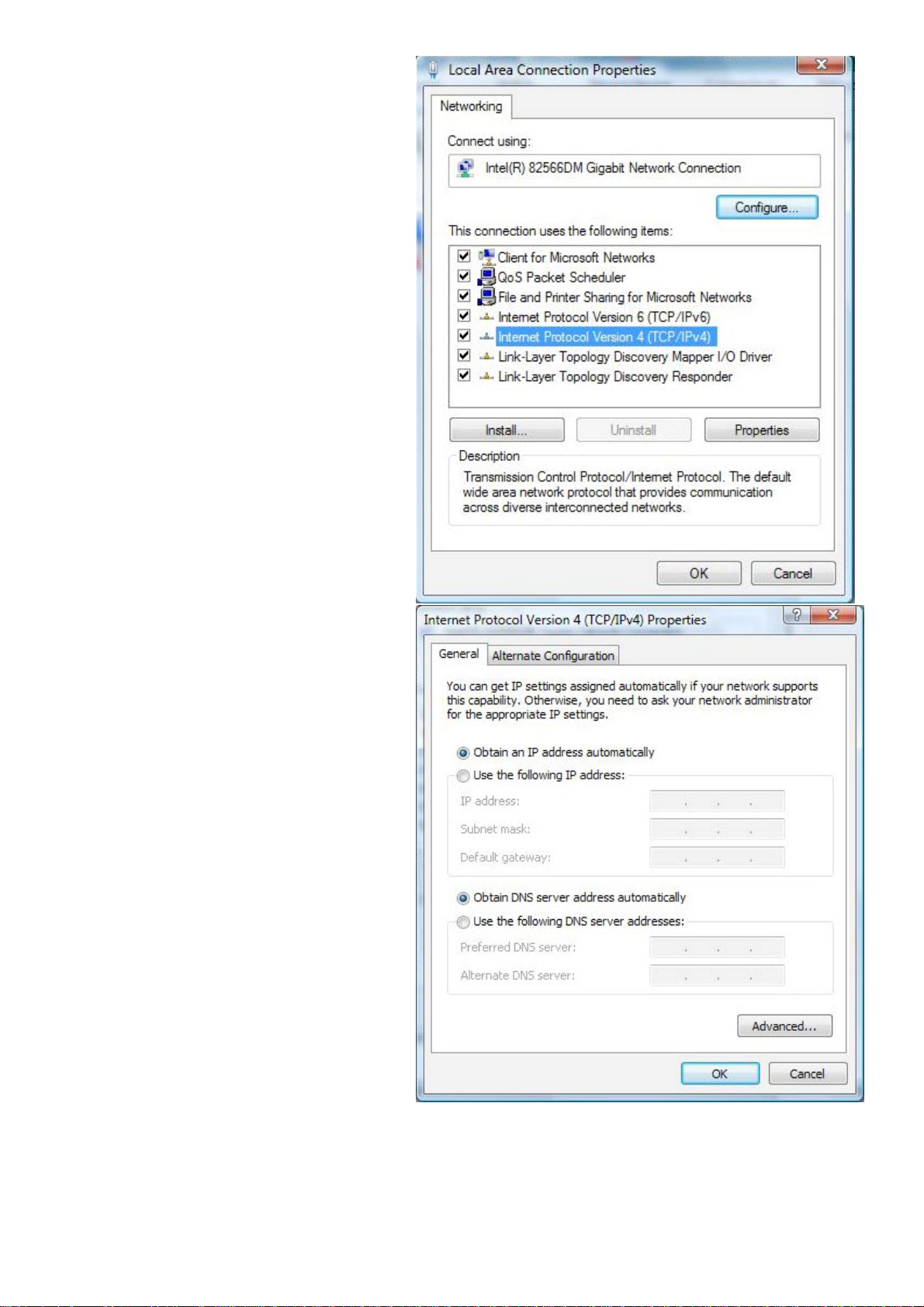
5. Select Internet Protocol Version4
(TCP/IPv4) then click Properties.
6. In the TCP/IPv4 properties window,
select the Obtain an IP address
automatically and Obtain DNS
Server address automatically
radio buttons. Then click OK to exit
the setting.
7. Click OK again in the Local Area
Connection Properties window to
apply the new configuration.
13
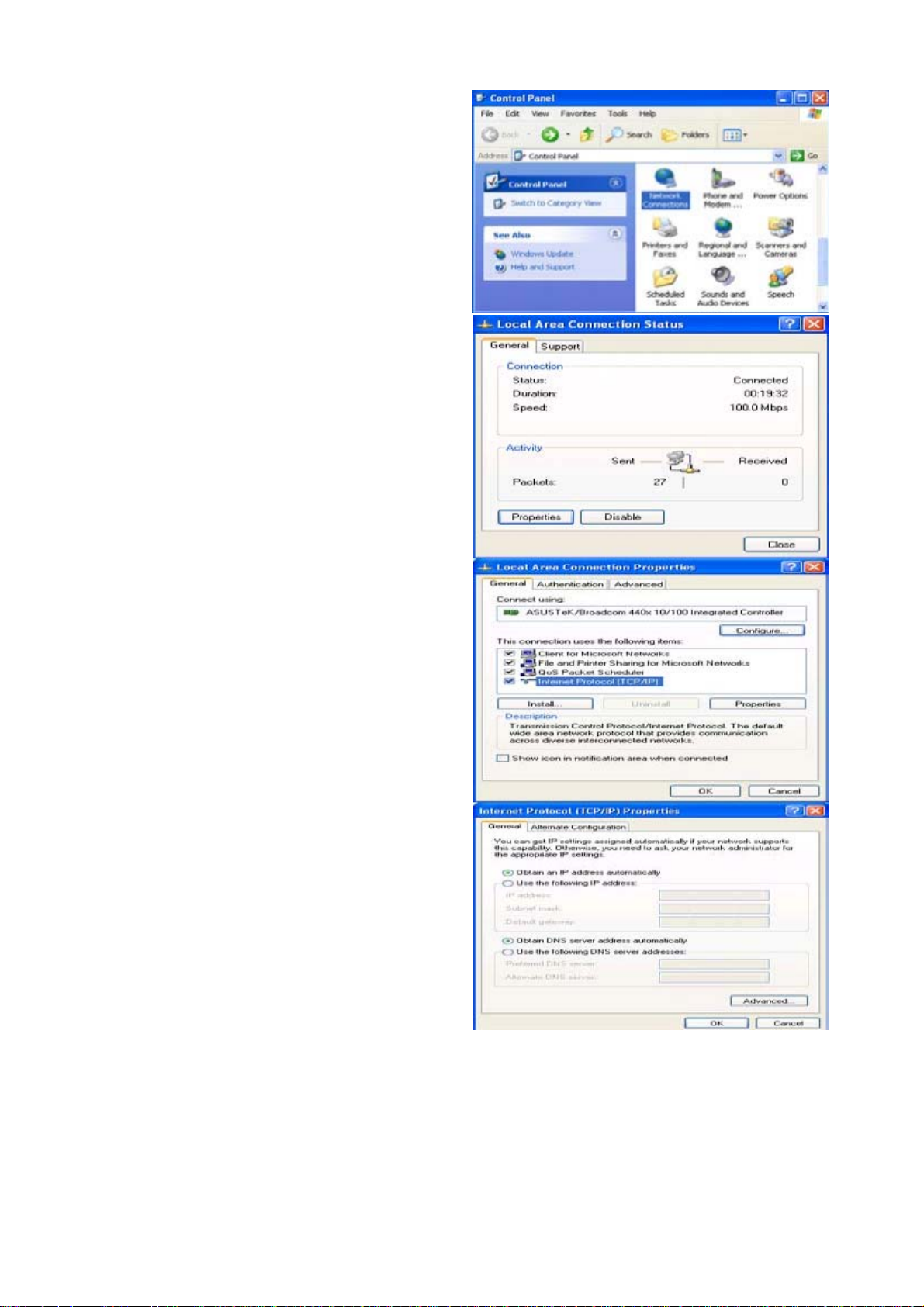
Configuring PC in Windows XP
1. Go to Start > Control Panel (in
Classic View). In the Control Panel,
double-click on Network Connections
2. Double-click Local Area Connection.
3. In the Local Area Connection Status
window, click Properties.
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and
click Properties.
5. Select the Obtain an IP address
automatically and the Obtain DNS
server address automatically radio
buttons.
6. Click OK to finish the configuration.
14
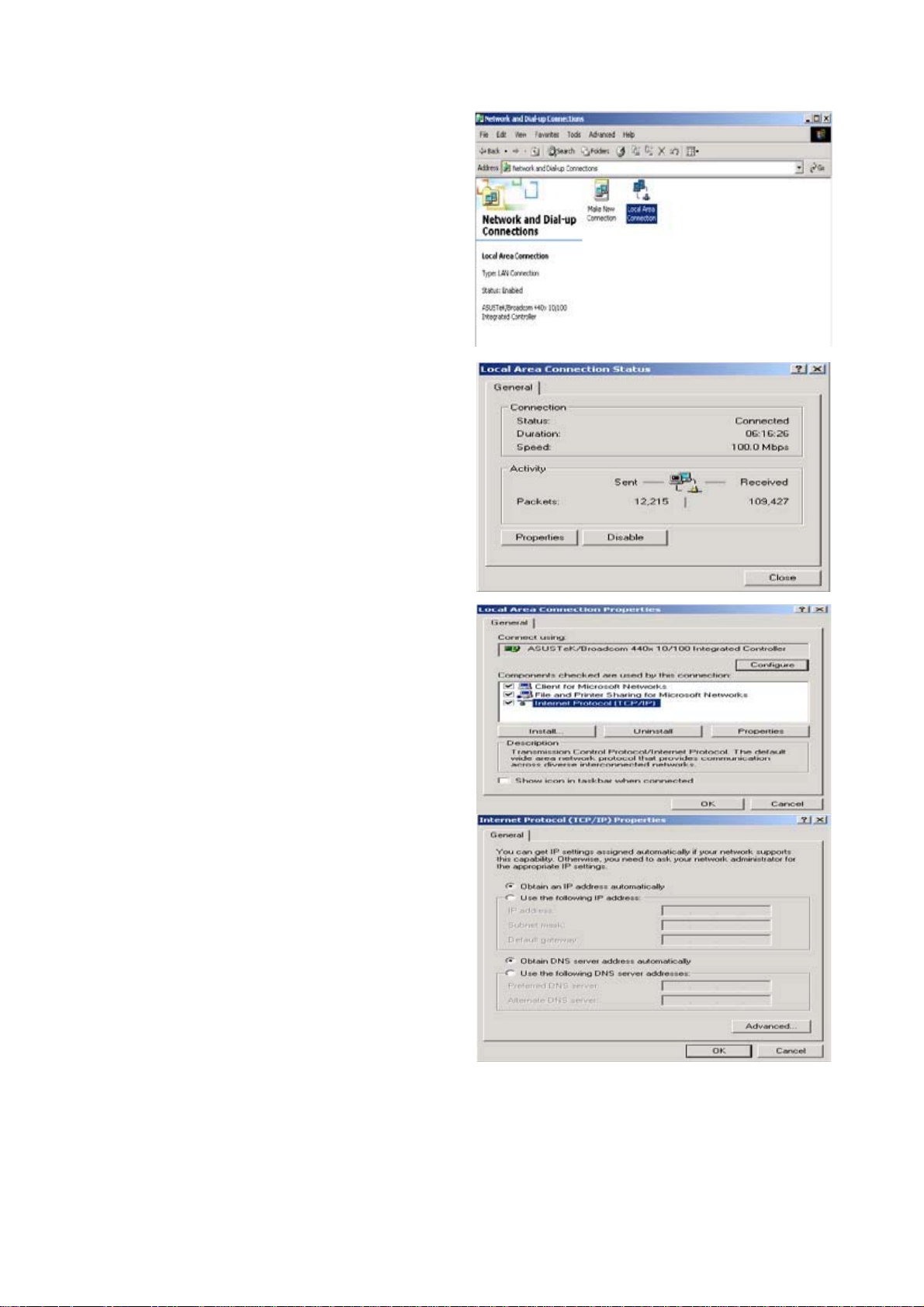
Configuring PC in Windows 2000
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel.
In the Control Panel, double-click on
Network and Dial-up Connections.
2. Double-click Local Area Connection.
3. In the Local Area Connection Status
window click Properties.
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and
click Properties.
5. Select the Obtain an IP address
automatically and the Obtain DNS
server address automatically radio
buttons.
6. Click OK to finish the configuration.
15
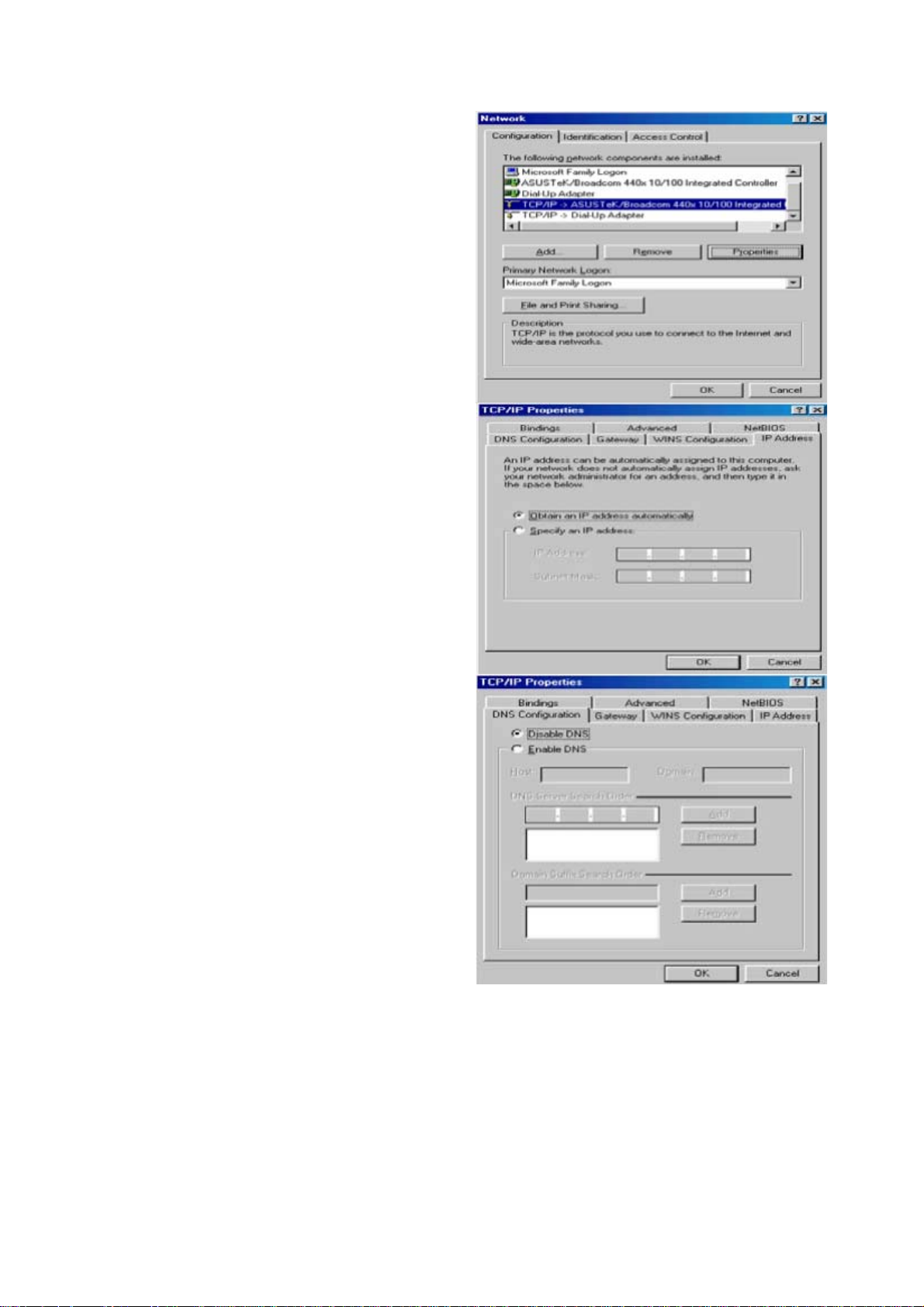
Configuring PC in Windows 95/98/Me
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel.
In the Control Panel, double-click on
Network and choose the Configuration
tab.
2. Select TCP/IP > NE2000 Compatible,
or the name of your Network Interface
Card (NIC) in your PC.
3. Select the Obtain an IP address
automatically radio button.
4. Then select the DNS Configuration.
5. Select the Disable DNS radio button
and click OK to finish the configuration.
16
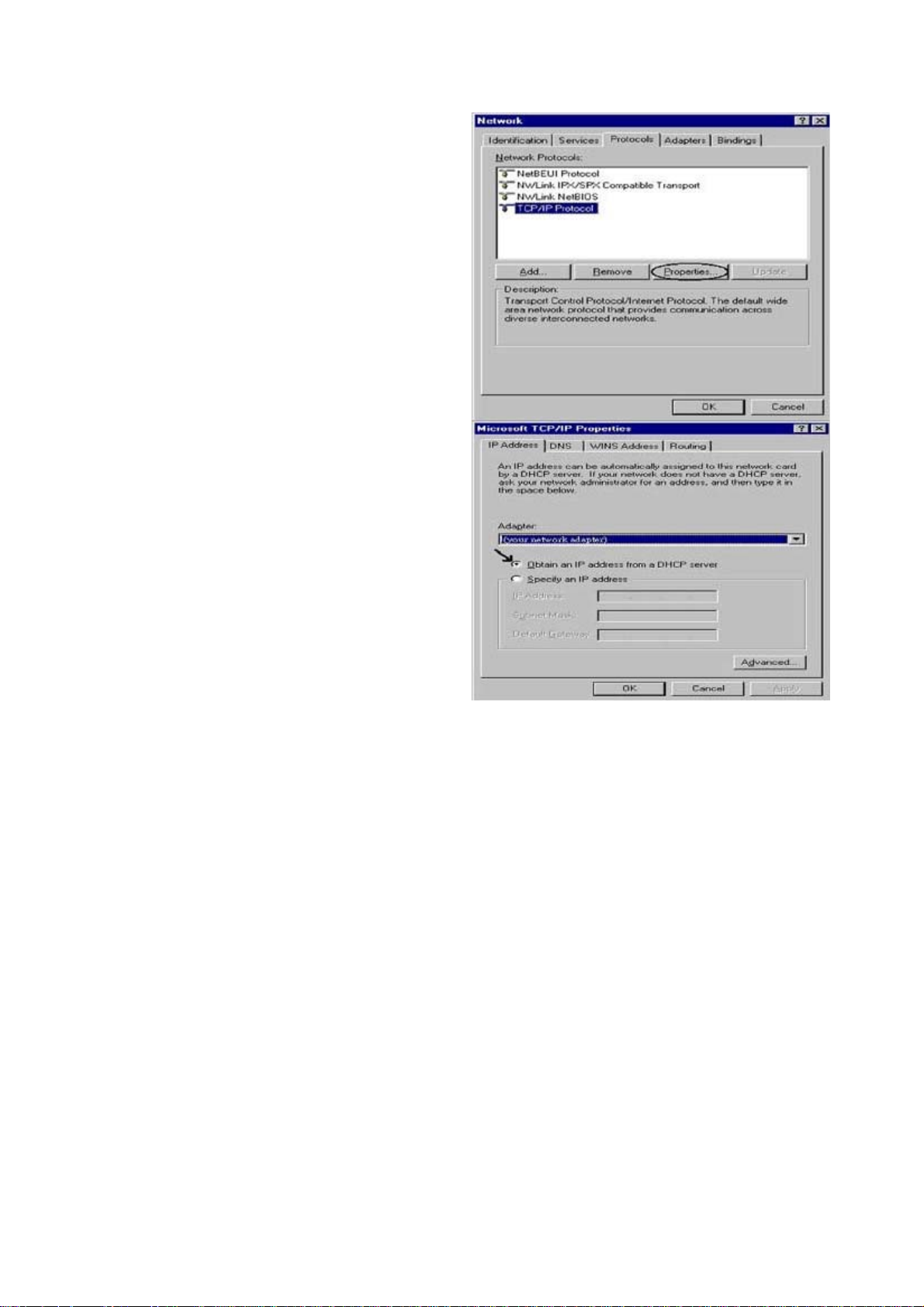
Configuring PC in Windows NT4.0
1. Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel.
In the Control Panel, double-click on
Network and choose the Protocols tab.
2. Select TCP/IP Protocol and click
Properties.
3. Select the Obtain an IP address from
a DHCP server radio button and click
OK.
17

Factory Default Settings
Before configuring your router, you need to know the following default settings.
Web Interface (Username and Password)
Username: admin
Password: admin
The default username and password are “admin” and “admin” respectively.
Device LAN IP settings
IP Address: 192.168.1.254
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
ISP setting in WAN site
PPPoE
DHCP server
DHCP server is enabled.
Start IP Address: 192.168.1.100
IP pool counts: 100
LAN and WAN Port Addresses
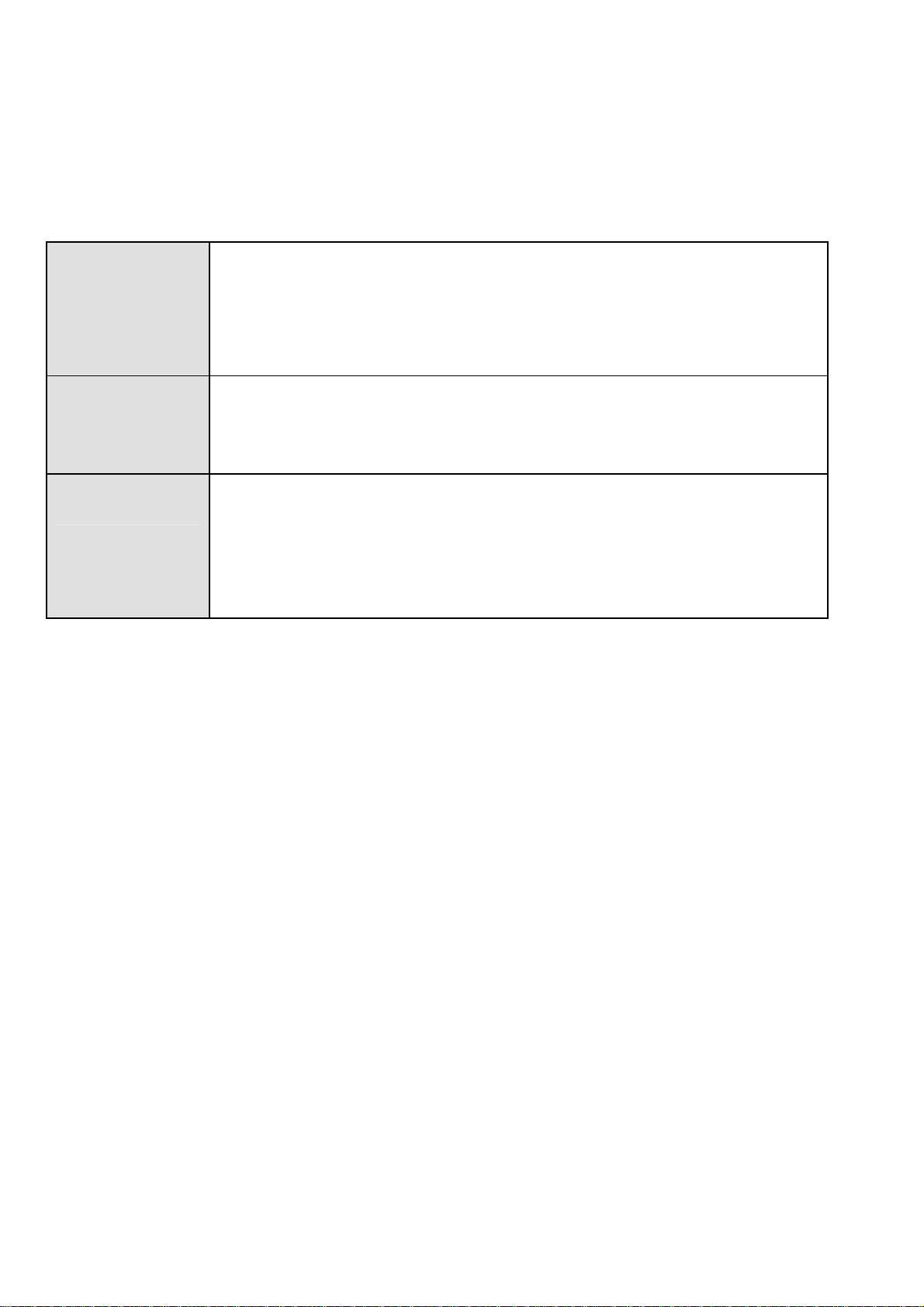
The parameters of LAN and WAN ports are pre-set in the factory. The default values are shown in
the table.
LAN Port WAN Port
IP address
Subnet Mask
DHCP server function
192.168.1.254
255.255.255.0
Enabled in ports 1, 2, 3 and
The PPPoE function is
enabled to automatically get
the WAN port configuration
from the ISP.
4
IP addresses for distribution
to PCs
100 IP addresses continuing
from 192.168.1.100 through
192.168.1.199
18
Information from your ISP
Before configuring this device, you have to check with your ISP (Internet Service Provider) to find
out what kind of service is provided such as DHCP (Obtain an IP Address Automatically, Static IP
(Fixed IP Address) or PPPoE.
Gather the information as illustrated in the following table and keep it for reference.
DHCP (Obtain
an IP Address
Automatically)
Static IP(Fixed
IP Address)
Configure this WAN Interface to use DHCP client protocol to get an IP
address from your ISP automatically. Your ISP provides an IP address to
the router dynamically when logging in.
Configure this WAN interface with a specific IP address. This IP address
should be provided by your ISP.
PPPoE PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) is known as a dial-up DSL or cable service. It
is designed to integrate the broadband services into the current widely
deployed, easy-to-use, and low-cost dial-up-access networking
infrastructure.
19
Configuring with your Web Browser
Open your web browser, enter the IP address of your router, which by default is 192.168.1.254,
and click “Go”, a user name and password window prompt will appear. The default username and
password are “admin” and “admin” respectively. (See Figure 3.14)
Figure 3.14: User name & Password Prompt Window
Congratulations! You are now successfully logging onto the VoIP / 802.11g Broadband
Router!
20

Chapter 4: Configuration
At the configuration homepage, the left navigation column provides you the link to each configuration
page. The category of each configuration page is listed as below.
Status
EWAN Status
ARP Table
DHCP Table
Routing Table
NAT Sessions
UPnP Portmap
VoIP Status
VoIP Call Log
Event Log
Error Log
Diagnostic
Quick Start
Configuration
LAN
WAN
System
Firewall
VoIP
QoS
Virtual Server
Wake on LAN
Time
Schedule
Advanced
Language (provides user interface in English and French languages)
21
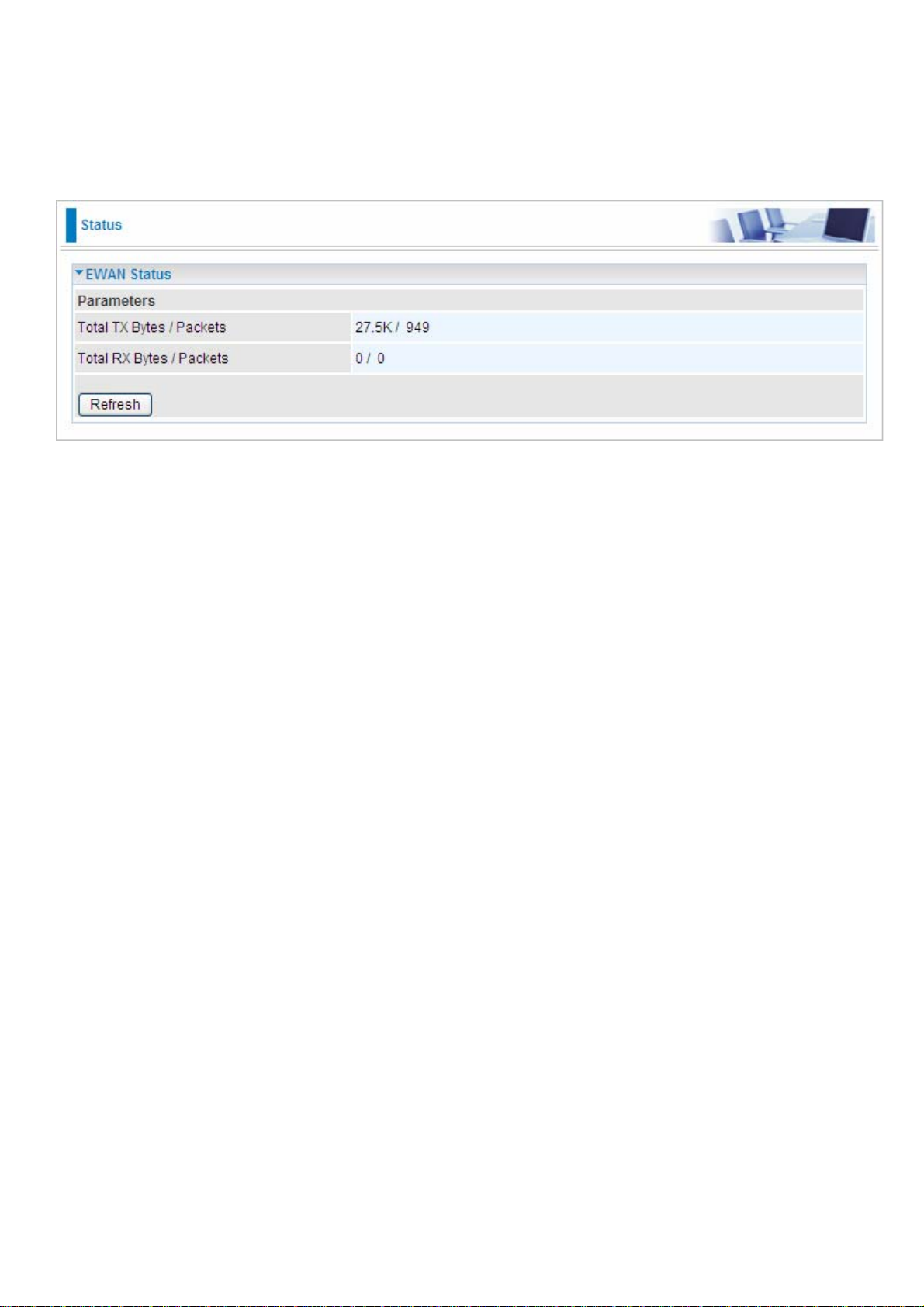
Status
EWAN Status
The router offers a WAN port to be used to connect to Cable Modems and fiber optic lines. This
alternative, yet faster method to connect to the internet will provide users more flexibility to get online.
Total TX Bytes / Packets: The statistics of total data transmission in bytes / packets since system
ready.
Total RX Bytes / Packets: The statistics of total data received in bytes / packets since system ready.
22
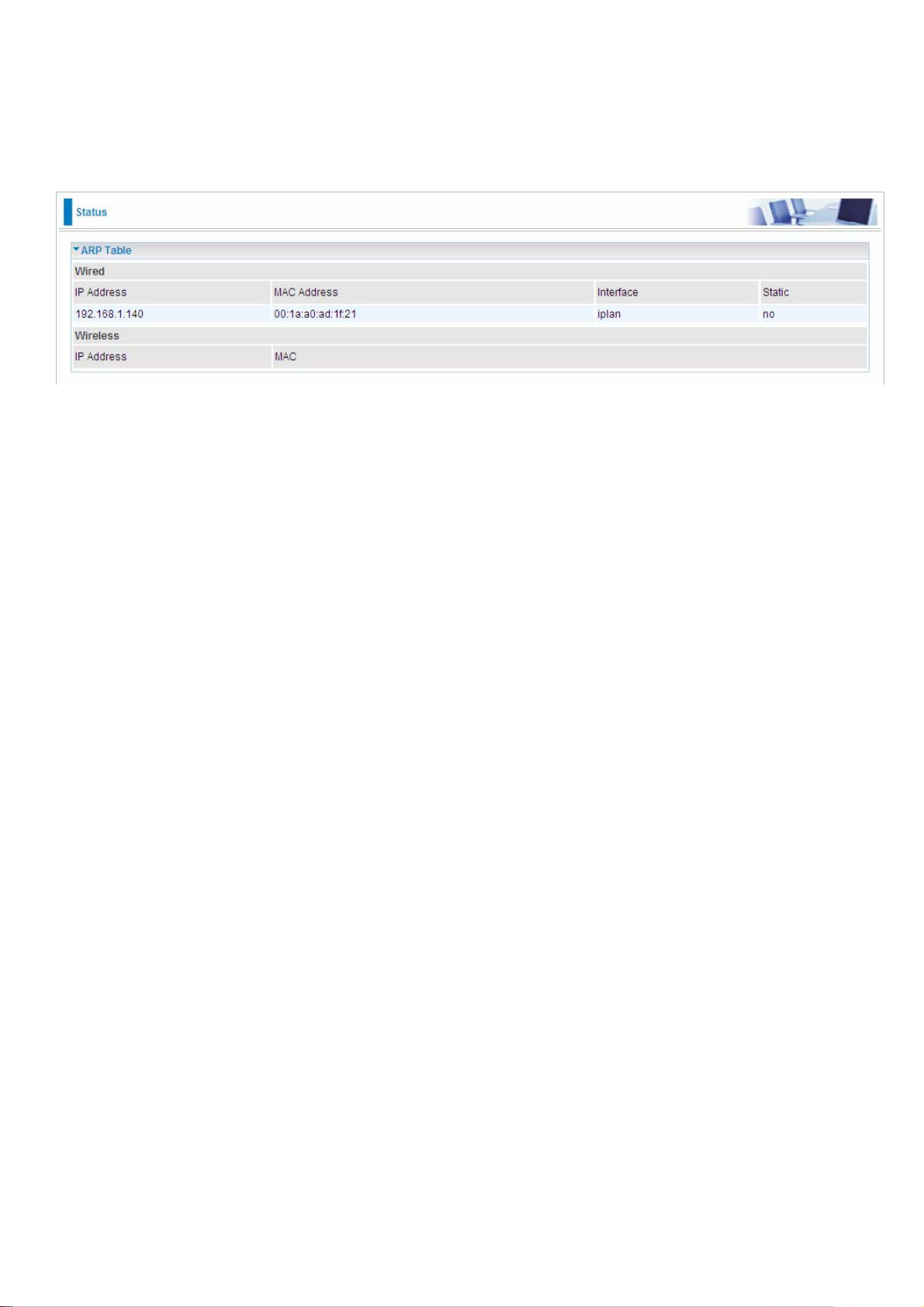
ARP Table
This section displays the router ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Table which shows the mapping
of Internet (IP) addresses to Ethernet (MAC) addresses. This is a quick way of determining the MAC
address of the network interface of your PCs that use the Firewall – MAC Address Filter function.
See the Firewall section of this manual for more information on this feature.
IP Address: Shows a list of IP addresses of devices on your LAN (Local Area Network).
MAC Address: Shows the MAC (Media Access Control) addresses of each device on your LAN.
Interface: Shows the interface name (on the router) that this IP Address connects to.
Static: Static status of the ARP table entry:
“no” for dynamically-generated ARP table entries.
“yes” for static ARP table entries added by the user.
23
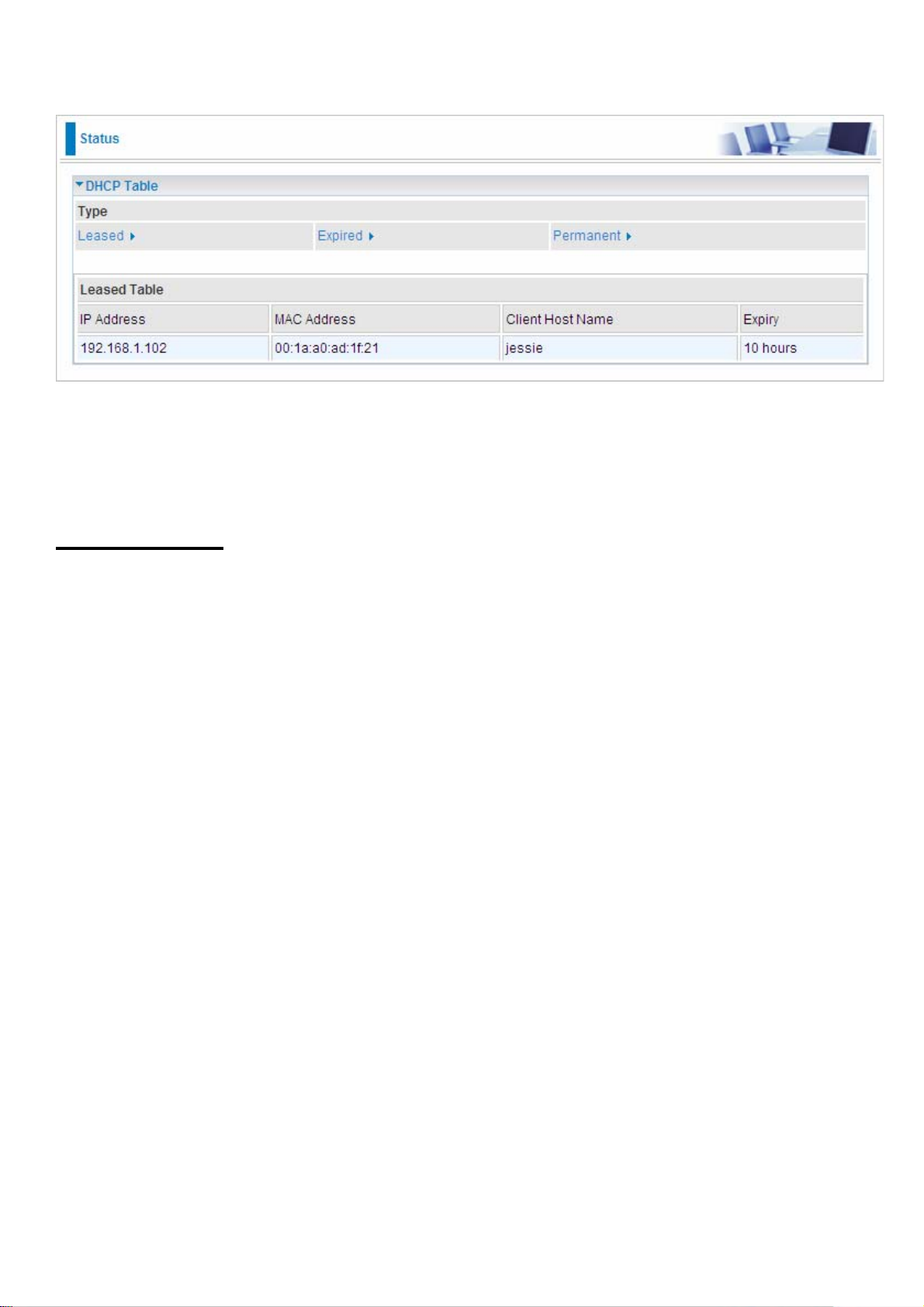
DHCP Table
Leased: Shows the information of the DHCP assigned IP addresses.
Expired: Shows the information of all expired IP addresses.
Permanent: Shows the fixed host mapping information.
Leased Table
IP Address: Shows the IP address that is assigned to each client.
MAC Address: Shows the MAC address of each client.
Client Host Name: Shows the Host Name (Computer Name) of the client.
Expiry: Shows the current lease time of each client.
24
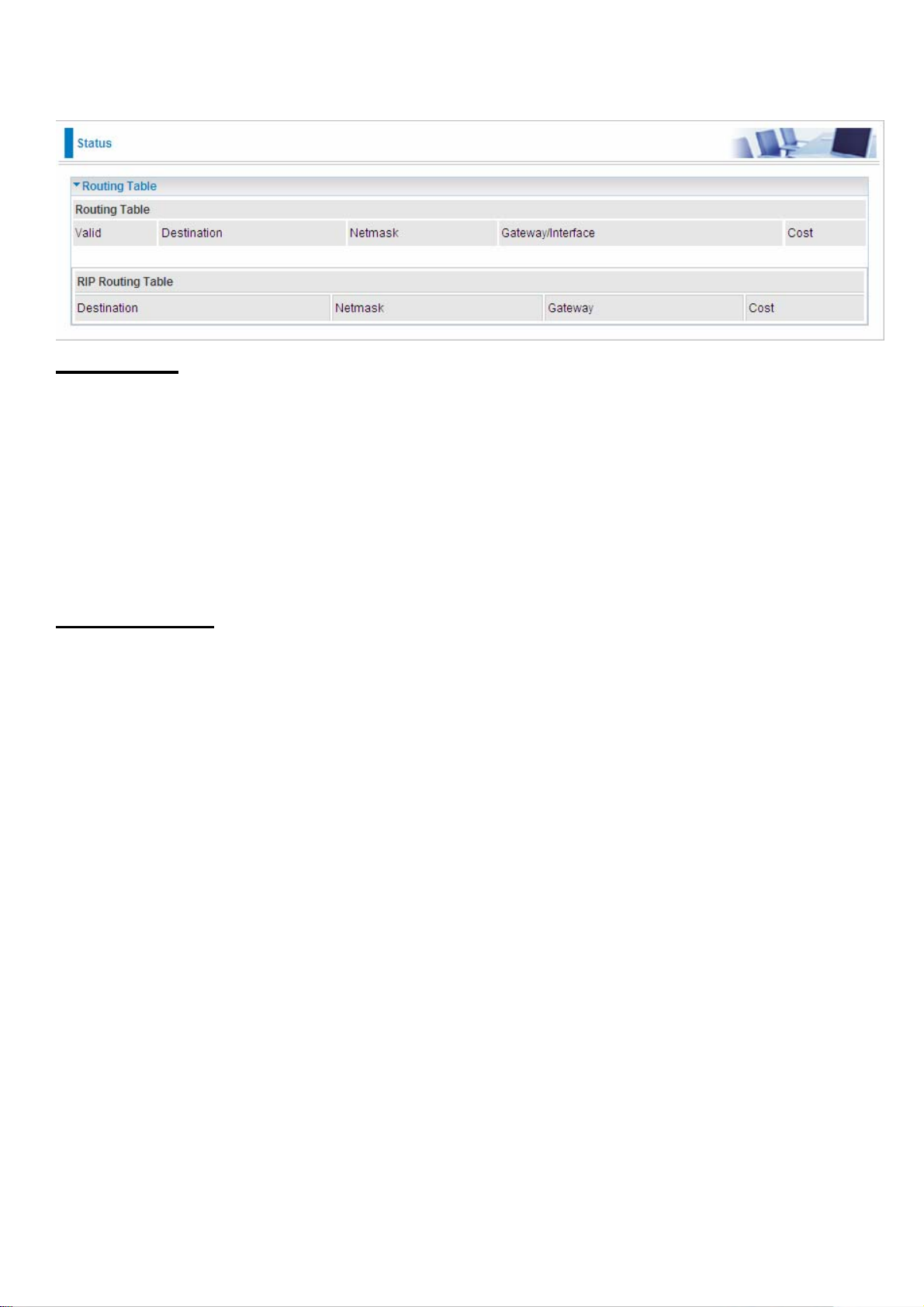
Routing Table
Routing Table
Valid: A check mark indicates a successful routing status.
Destination: Shows the IP address of the destination network.
Netmask: Shows the destination Netmask address.
Gateway/Interface: Shows the IP address of the gateway or the existing interface that this route
will use.
Cost: The number of hops counted as the cost of the route.
RIP Routing Table
Destination: Shows the IP address of the destination network.
Netmask: Shows the destination Netmask address.
Gateway: Shows the IP address of the gateway that this route will use.
Cost: The number of hops counted as the cost of the route.
25
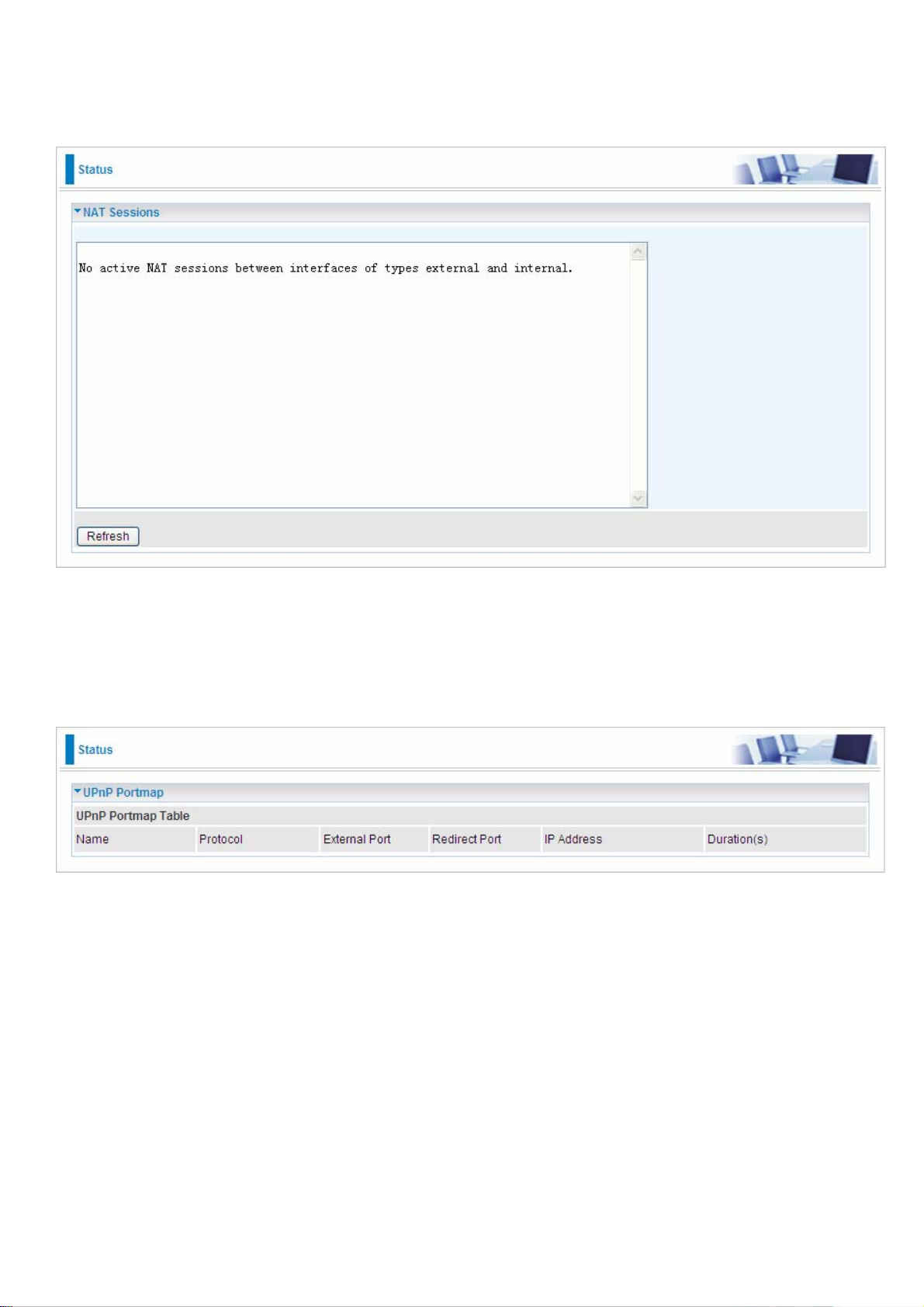
NAT Sessions
This section lists all the current NAT sessions between external (WAN) and internal (LAN) interface.
UPnP Portmap
This section lists all the established port-mapping using UPnP (Universal Plug and Play). See the
Advanced section of this manual for more details on UPnP and the router UPnP configuration
options.
26
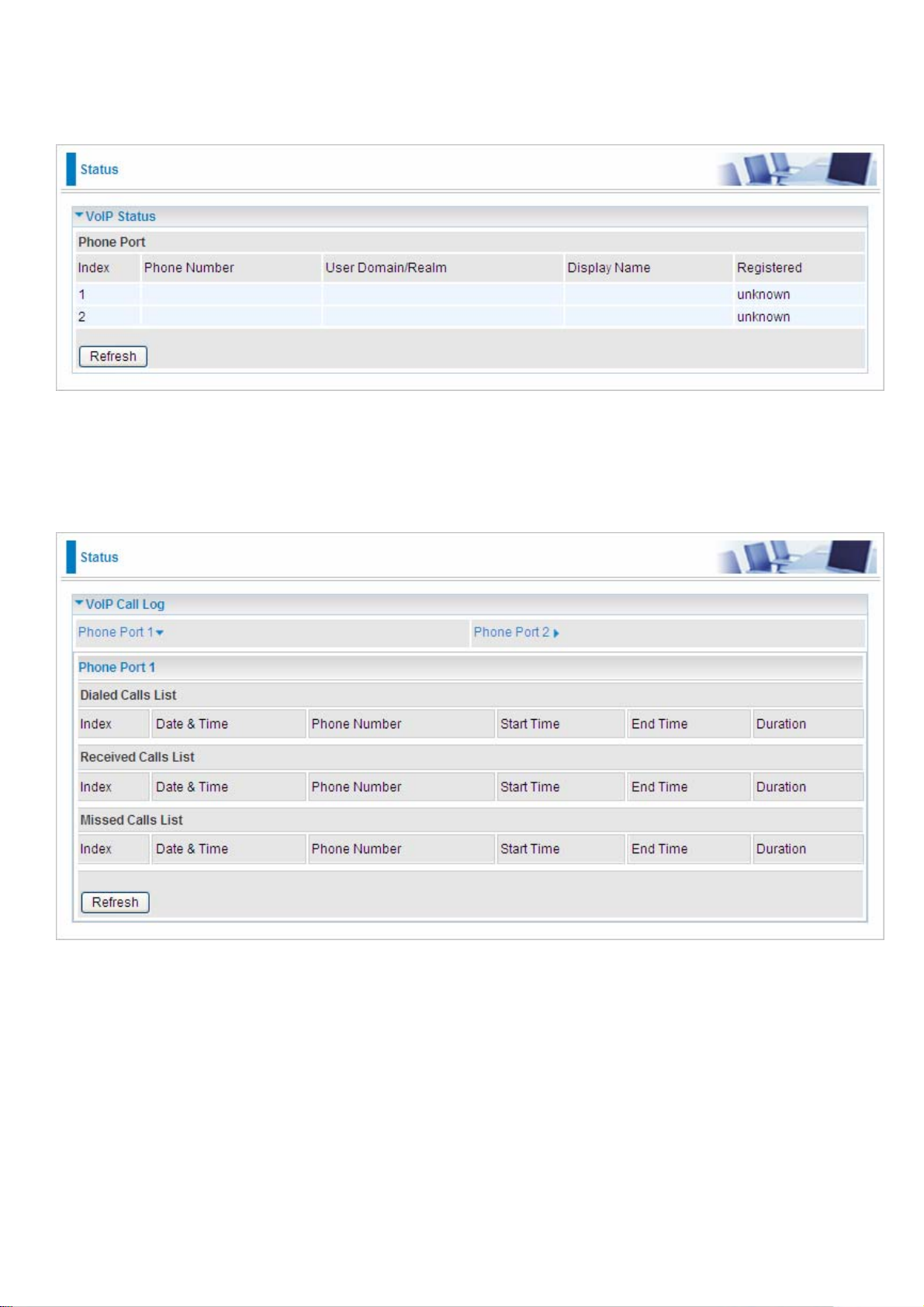
VoIP Status
This table shows the status of the phone ports when VoIP feature has been activated. It displays
information such as domain name, display name & phone number of the VoIP device.
VoIP Call Log
The call log records the data from your VoIP devices such as the date / time of dial out calls, the
duration of the calls, information about the missed calls and also incoming calls.
27
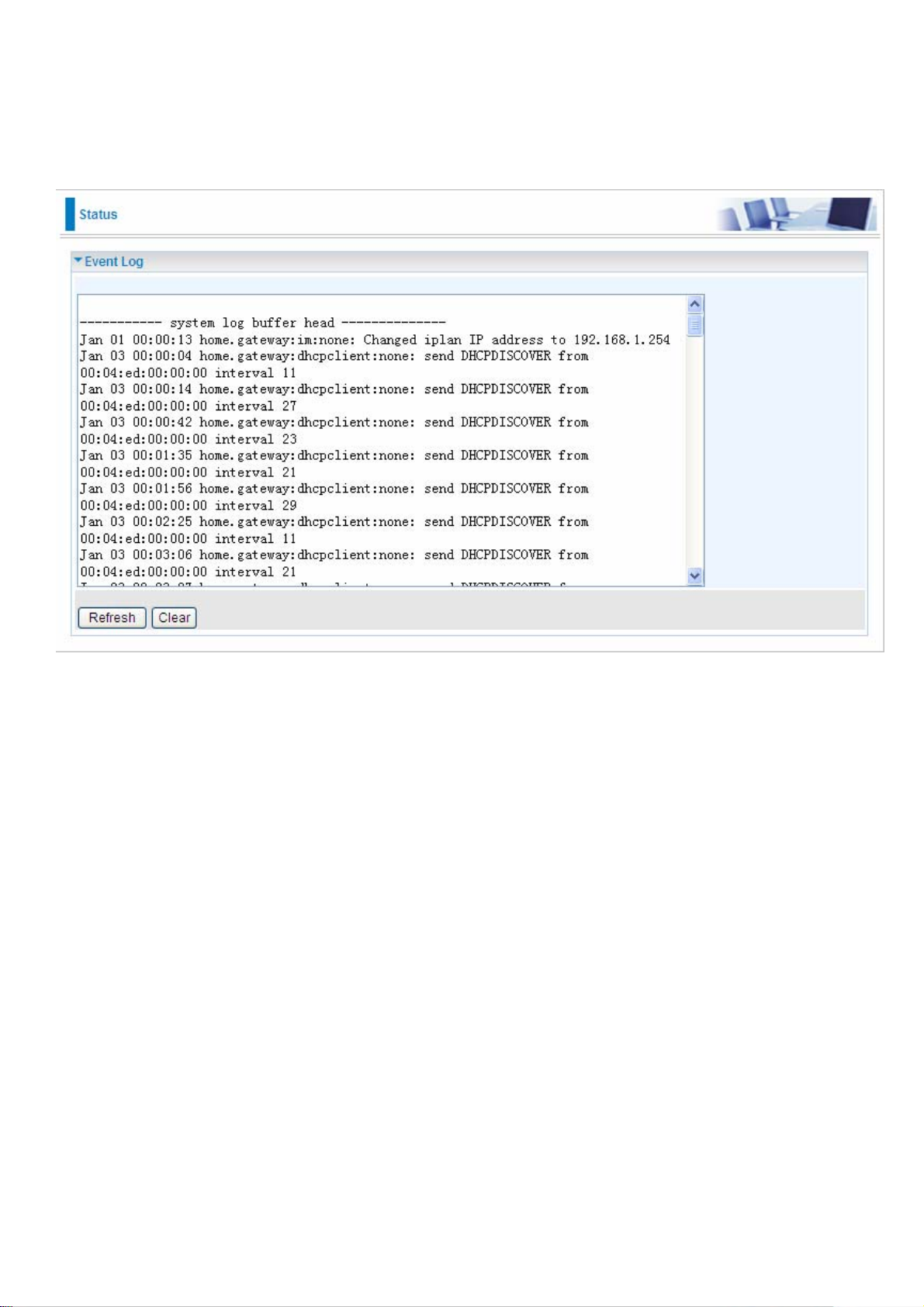
Event Log
This page displays all the event Log entries of the router such as when gets disconnected and
during Firewall triggered events like Intrusion or Blocking Logging. Please see the Firewall
section of this manual for more details on how to enable Firewall logging.
28
 Loading...
Loading...