Beverage Air BRT-68 Service Manual

SERVICE &
INSTALLATION
MANUAL
ICE CREAM
DIPPING
CABINETS
R-404A Refrigerant
1/2003 51-1468-01
CARRIER COMMERCIAL REFRIGERATION, INC.
Providing BEVERAGE-AIR • FRIGIDAIRE • KELVINATOR • UNIVERSAL NOLIN Products/Services
If additional information is necessary, call the factory.
Our toll free number is 1-800-684-1199.Technical
assistance engineers are willing to assist you in any way
possible. Office hours are from 8:00a.m. to 5:30 p.m.,
Eastern Standard Time.
Important information is contained in this manual which should
be retained in a convenient location for future reference.
MODEL DESIGNATION INFORMATION
115V, 60HZ
PART # MODEL # DATA PLATE
52-1961-35 BRT-68 BRT68
52-2077-02 BRT68P BRT68
52-2077-04 BRT68W BRT68
52-1961-36 BRT90 BRT90
52-2077-03 BRT90P BRT90
52-2077-05 BRT90W BRT90
EXPORT 220V, 50HZ
PART # MODEL # DATA PLATE
52-1961-31 EBRT-68 EBRT68
52-1961-41 EBRT68P EBRT68
52-1961-32 EBRT90 EBRT90
52-1961-42 EBRT90P EBRT90
EXPORT 220V, 60HZ
PART # MODEL # DATA PLATE
52-1961-33 KBRT-68 KBRT68
52-1961-34 KBRT90 KBRT90
Manual effective for models produced January, 2003. Starting ser ial number 6527372.
SECTION I
Introduction

blank
Dipping Cabinets - Introduction
These Dipping Cabinets are designed to merchandise ice
cream or yogurt-type products.Dipping cabinets are
produced in three sizes: 8,12,and 16 facings of ice cream
containers.The cabinet systems contain CFC free refr igerant,
metered into the system by a capillary tube.The evaporator
is a cold wall which has the refrigerant lines strapped to the
inner liner of the cabinet.The condenser is a bare tube
mounted on a pullout machinery compartment tray for ease
of servicing. All electrical controls are easily accessible for
repair.The temperature within the cabinet is controlled
thermostatically, allowing for maintenance of correct dipping
temperatures.
Mechanical equipment may require repair at times.This
manual presents information that is helpful in maintaining,
diagnosing,and repairing these cabinets .
The high level of quality built into these units will allow for
many years of trouble-free operation.
INTRODUCTION 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
4TABLE OF CONTENTS
Due to Frigidaire’s policy of continuous quality improvement, specifications are subject to change without notice.
INTRODUCTION
Introduction ........................................................................ 3
Table of Contents ................................................................4
Cabinet Specifications / Dimensional Data: BRT-68 ............ 5
Cabinet Specifications / Dimensional Data: BRT-90 ............ 6
Handling & Installation ...................................................... 7
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
General Information - Refrigeration Systems.................... 11
BRT-68 Electrical & Refrigeration Information .................. 13
BRT-90 Electrical & Refrigeration Information .................. 14
EBRT-68 & KBRT-68 Electrical &Refrigeration Info ........ 15
EBRT-90 & KBRT-90 Electrical &Refrigeration Info ........ 16
BRT-68 & BRT-90 Wiring Diagram .................................. 17
EBRT/KBRT-68 & 90 Wiring Diagram .............................. 18
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Pre-Service Check List ...................................................... 21
General Maintenance Information .................................... 22
Compressor Installation / Diagnostics .............................. 24
Cleaning & Maintenance .................................................. 26
Cleaning the Lid ................................................................ 27
Lid Seal Replacement ...................................................... 28
Lid Gasket Replacement .................................................. 29
Lid Pivot Bushing Assembly Replacement ...................... 30
Center & End Pivot Rod Replacement .............................. 31
Fluorescent Lamp Holder/Light Starter Socket Replac. .... 32
Fluorescent Bulb & Starter Replacement .......................... 33
Thermostat Replacement .................................................. 34
Master Power Supply Switch / Light Switch Removal ...... 35
Condenser Fan Motor Replacement .................................. 36
Ballast Replacement ........................................................ 37
Metering Device / Heat Exchanger Replacement .............. 38
Cabinet Troubleshooting Guide ........................................ 39
Compressor Troubleshooting Guide ................................ 42
Fluorescent Lamp Troubleshooting Guide ........................ 45
PARTS LISTS
Cabinet Parts .................................................................. 48
Lamp Assembly Parts ...................................................... 50
Condensing Unit Parts ...................................................... 52
Electrical Parts .................................................................. 54
Lid Parts .......................................................................... 56
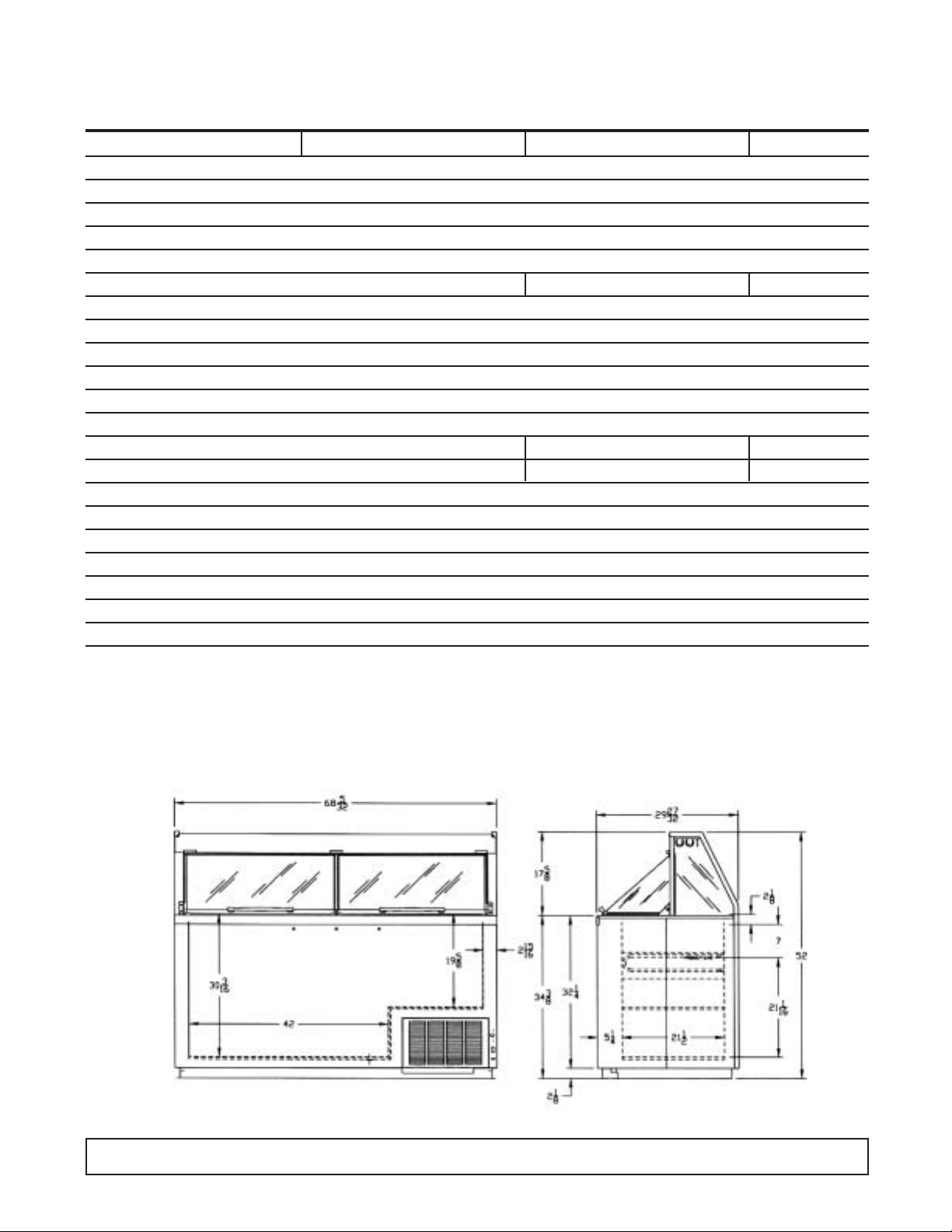
INTRODUCTION 5
CABINET SPECIFICATIONS
BRT68 EBRT68 KBRT68
Temp. Range +10°F to -8°F
Capacity 19.1 Cu. Ft.
Capacity (3 Gal. Tubs) 20
Facings (3 Gal. Tubs) 12
Storage (3 Gal. Tubs) 8
Compressor Size 1/3 Hp. 3/4 Hp. 3/4 Hp.
Shipping Weight (App.) 644 lbs.
Condenser Type Bare Tube
Evaporator Type Cold Wall - Refrigerated Cross Bars
Refrigerant R-404A
Refrigerant Control Capillary Tube
Defrost System Manual
Rated Amps 8.0 4.1 4.1
Electrical Specs. 115V, 60 Hz., 1 Ph. 220V, 50 Hz., 1Ph 220V, 60 Hz., 1 Ph.
Power Cord No. 16AWG
NSF Listing NSF1
Canopy Construction S.S. Top with Glass Ends Straight or Curved Front Glass
Lids (Plexiglass) 2 Lids
Interior Finish White Baked Enamel on Galvanized Steel
Exterior Finish White Baked Enamel
Lighting Two 40 Watt Bulbs
DIMENSIONAL DATA
REAR VIEW END VIEW
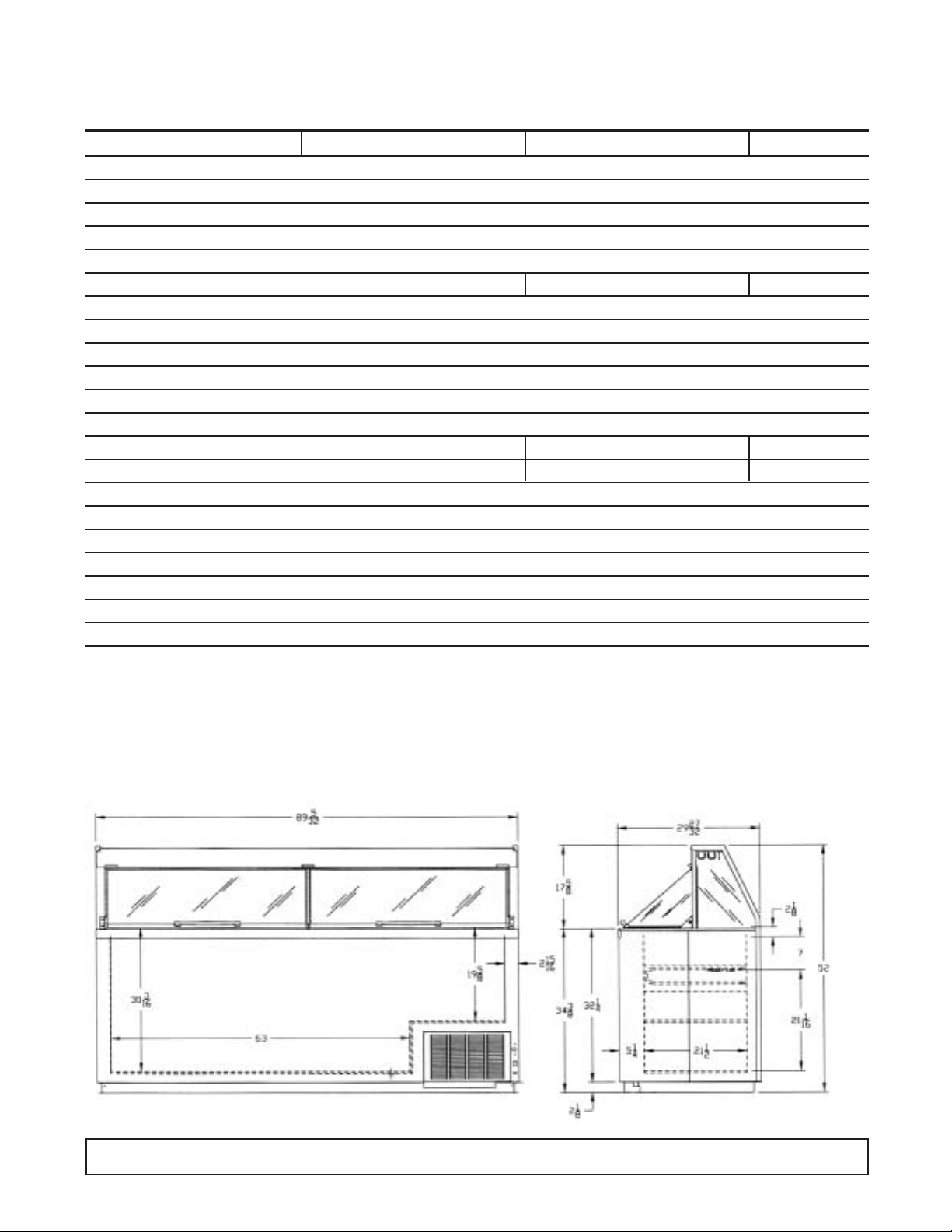
6 INTRODUCTION
CABINET SPECIFICATIONS
BRT90 EBRT90 KBRT90
Temp. Range +10°F to -8°F
Capacity 24.4 Cu. Ft.
Capacity (3 Gal. Tubs) 28
Facings (3 Gal. Tubs) 16
Storage (3 Gal. Tubs) 12
Compressor Size 1/3 Hp. 3/4 Hp. 3/4 Hp.
Shipping Weight (App.) 754 lbs.
Condenser Type Bare Tube
Evaporator Type Cold Wall - Refrigerated Cross Bars
Refrigerant R-404A
Refrigerant Control Capillary Tube
Defrost System Manual
Rated Amps 8.0 4.1 4.1
Electrical Specs. 115V, 60 Hz., 1 Ph. 220V, 50 Hz., 1Ph 220V, 60 Hz., 1 Ph.
Power Cord No. 16AWG
NSF Listing NSF1
Canopy Construction S.S. Top with Glass Ends Straight or Curved Front Glass
Lids (Plexiglass) 2 Lids
Interior Finish White Baked Enamel on Galvanized Steel
Exterior Finish White Baked Enamel
Lighting Two 40 Watt Bulbs
DIMENSIONAL DATA
REAR VIEW END VIEW
HANDLING & INSTALLATION-Illuminated Dipping Cabinets
INTRODUCTION 7
FREIGHT DAMAGES AND SHOR TAGES
IMPORTANT
The cabinet was inspected and packaged at the
factory, and should have arrived in excellent
condition. The transportation company or other
parties involved in the shipment are responsible for
loss and/or “damage.” Always make an inspection
before and after uncrating, pref erab ly at the point of
unloading by the transportation company.
INSPECTING FOR DAMAGES
Note:
Always use care when removing shipping tape,
blocks, pads, hardware or other material. Contact
your dealer or distributor if technical assistance
is required.
Check the cartons or containers. If these are damaged
in any way, open them and inspect the contents in the
driver’s presence. If damage is detected, do the
following:
1. Have the driver note the nature and extent of the
damage on the freight bill.
2. Notify the transportation company’s office to request
an inspection. Carrier claim policies usually require
inspections to be made within 15 days of delivery.
3. If damage is noticed, file a claim with the
transportation company.
FILING A CLAIM
File a claim for loss at once with the transportation
company for:
A. A cash adjustment B. Repairs C. Replacement
When filing your claim, retain all packaging materials
and receipts.
HANDLING THE CABINET
Note:
The refrigeration system of the cabinet is designed
to operate with the cabinet located on a flat surface.
Do not tilt the cabinet more than 30° to any side. If
the cabinet must be tilted on an angle for handling or
moving purposes, allow it to sit in an upright position
20 to 30 minutes prior to operating.
CHOOSE A LOCATION
This model cabinet should be situated to allow proper air
circulation. The cabinet must be installed on sturdy, level
floor and positioned so that it can be plugged into a
properly grounded three-prong electrical wall outlet. The
electrical outlet should not be controlled by a wall switch
which might be turned off accidentally.
UNCRATING THE CABINET
The cabinet should be moved as close as possible to
the operating location before removing the skid. Be
sure to follow the steps in the “INSPECTING FOR
DAMAGES” instructions.
INSTALLING THE CABINET
Whenever possible leave the crate skid on the cabinet
until it is moved close to the final position. When it is
necessary to move the cabinet through a doorway, it
may be necessary to remove the crate skid.
Run the cabinet down to storage temperature before
adding product.
CAUTION
A. Do not locate cabinet where sunlight or drafts from
fans, air conditioners or open doors can affect product
temperature.
B. Run cabinet before building in or attaching panels or
accessories.
C. Employee side access panel must be kept clear for
adjustments and service.
D. Cabinet must be installed on the finished floor to
assure rear raceway cover and condensing unit
(employee side) can be pulled or removed for service.
DO NOT seal in with cover molding or caulking in the
area where condensing unit pulls out.
E. Do not use extension cords to power this equipment.
Run any necessary electrical, water supply and drain
lines before setting the cabinet in position. Shim under
the cabinet as necessary to level it. N.S.F. approval
requires sealing the cabinet to the floor. This can be
done by applying a bead of mastic sealer between the
cabinet bottom flange and the floor.
Should several cabinets be set up in a row, space is
provided in the rear toe space for routing electrical and
plumbing lines.Access to this space requires removing
screws and the metal cover which runs the length of the
cabinet.
Rivnuts are provided on the operator's side for
mounting dipperwell and other accessories.
CABINET START-UP
Once the cabinet has been located in its permanent
location and the proper power and grounding have
been provided, the following items must be checked or
completed:
A. Cut and remove the compressor hold-down band (if
applicable) so the compressor “floats” freely.

B. Check for traces of oil on the compressor pan which
could mean a broken or leaking refrigeration line.
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCE SHOULD THE
COMPRESSOR BE STARTED WHEN OIL IS
PRESENT UNTIL INSPECTED BY A SERVICE
TECHNICIAN.
C. INSPECT THE FACTORY WIRING FOR TERMINALS
THAT MIGHT HAVE VIBRATED LOOSE IN
SHIPPING. TIGHTEN ALL SCREW TYPE
TERMINALS.
D. Check the refrigeration lines to see that they are
“free” and no damage was done during shipping.
E. Check fan blade for free operation.
F. Turn on the main po wer s witch.Once the compressor
starts, the voltage should be checked at the
compressor terminals to determine if there is proper
voltage to the compressor. The voltage should not
exceed the 10% above or below the rated
compressor voltage.
EXAMPLE: If the voltage reads 115 volts with no load
and it drops below 103 volts when the compressor
starts, it may indicate that the supply wiring is too small
or that the wire run is too long.
G. Listen for any unusual noise such as lines vibrating,
etc. Correct the problem by tightening screws,
slightly bending tubing, etc.
H.The temperature control thermostat which is located
in the rear post is factory set for average conditions.
A customer adjustment requires a coin or
screwdriver to turn the slotted shaft.A numbered dial
makes it easy to keep track of adjustments. #1 is
warmest setting and #7 is coldest setting. An “OFF”
position is provided for your convenience in
defrosting the cabinet.
I. Allow the cabinet to pull down and cycle prior to
loading with product (Approx. 24 hours).
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
This appliance is equipped with a three-prong
(grounding) plug for your protection against shock
hazards.The appliance should be plugged directly into
a properly grounded three-prong receptacle.
Where a two-prong wall receptacle is encountered, it
must be replaced with a properly grounded three-prong
receptacle in accordance with the National Electrical
Code and local codes and ordinances. The work must
be done by a licensed electrician.
IMPORTANT
Do not, under any circumstance, cut or remove the
round grounding plug from the appliance plug.
WARNING
Consult a licensed electrician if you have any doubt
about the grounding of your wall receptacle. Only a
licensed electrician can determine the polarization of
your wall receptacle. Only a properly installed threepronged wall receptacle assures the proper
polarization with the appliance plug.
IMPORTANT USAGE INSTRUCTIONS
Dipping Cabinet
The cabinet must be located in an area free from air
drafts created by open doors, air conditioning ducts,
and fans. The cabinet should not be located in the
direct sunlight.
The rear grill must be clear of any obstructions so the
intake and exhausting of air f or the condensing unit can
move freely.
Dipping cabinets are designed for use in an air
conditioned store. This cabinet is designed for
merchandising, not hardening of the product.
High humidity can cause fogging of the lid and front glass.
High temperatures, installation of warm product and
heavy usage can cause the product to soften. This
condition will be more noticeable at the top of the cans.
The corners of the cabinets are the coldest areas.
These areas should be used for product that is more
difficult to keep firm.
Frost and ice act as insulators.The need for defrosting
will depend on usage and product firmness.
If the frost is scraped daily with a plastic scraper,
intervals between complete defrosting may be
extended.
Thermostat adjustments should be made one
increment warmer or colder allowing 24 hours between
adjustments to allow the product to stabilize.
8 INTRODUCTION
SECTION II
Pr inciples of
Operation

blank
GENERAL INFORMATION - REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 11
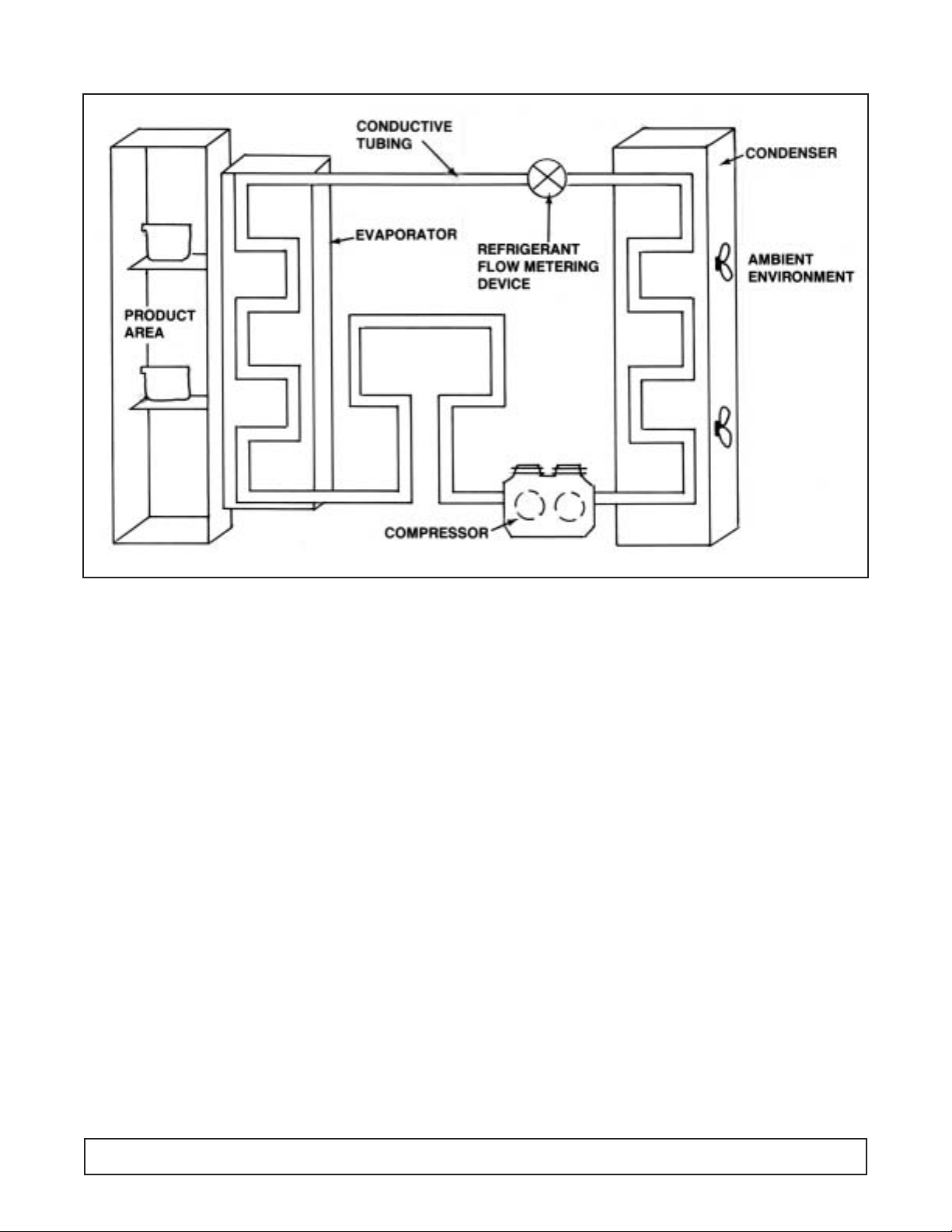
FIGURE 1
Basic refrigeration is based upon the Second Law of
Thermodynamics … “Heat will always flow from a warm
object to and be absorbed by an object of substance of
colder temperature.”
The purpose of a mechanical refrigeration system is to
provide for efficient and continuous cooling.
In order for this to take place, the system must provide
a means to transfer heat from the products being
refrigerated to an area that will not affect the product
(See Figure 1).
This is accomplished through the circulation of
refrigerant contained in conductive tubing, past the area
where the products are stored.
The refrigerant absorbs the heat from the product area
and transports it to where the heat can be dissipated
into the air outside the cabinet. Four essential
components are needed in a simple refrigeration
system:
An Evaporator
A Compressor
A Condenser
and a Refrigerant Flow Metering Device
The purpose of the evaporator is to draw the heat from
the product or storage area. As low temperature, low
pressure liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator, it
begins to boil or vaporize as it absorbs the heat of the
product and cabinet interior.
The vaporized refrigerant is drawn through the
evaporator by the compressor , in addition to causing the
necessary flow of refrigerant within the circuit.
The compressor also increases the pressure of the
vaporized refrigerant flowing from the compressor to the
condenser.
The increased pressure causes the temperature of the
refrigerant to rise above the ambient temperature of the
room.
This condition allows the heat in this vaporized high
pressure refrigerant to be released into the room’s
ambient environment.
As heat is released, the vaporized refrigerant returns to
a liquid state.
If there is a large amount of heat to be released, this
heat transfer is increased by using a fan to ensure a
constant flow of cooler ambient air through the
condenser coil.
The cooled liquid refrigerant leaves the condenser
under high pressure and travels to the refrigerant flow
metering device.
This device regulates the flow of refrigerant into the
evaporator.
By restricting this flow, the liquid refrigerant mo ves to the
evaporator under low pressure.(See FIGURE 1)
This lower pressure is necessary for the refrigerant to
have the capability to vaporize and absorb heat.
The cycle will continue until the desired temperature
within the product area is reached.
At this point, the compressor shuts off and the
refrigerant cycle is interrupted until further cooling is
required.
This simple refrigeration system is known as a single
stage system. It is the most common refrigeration
system and is used for applications where the product
area temperatures do not exceed -20° Fahrenheit.
The single stage system is used on product dipping
cabinets.
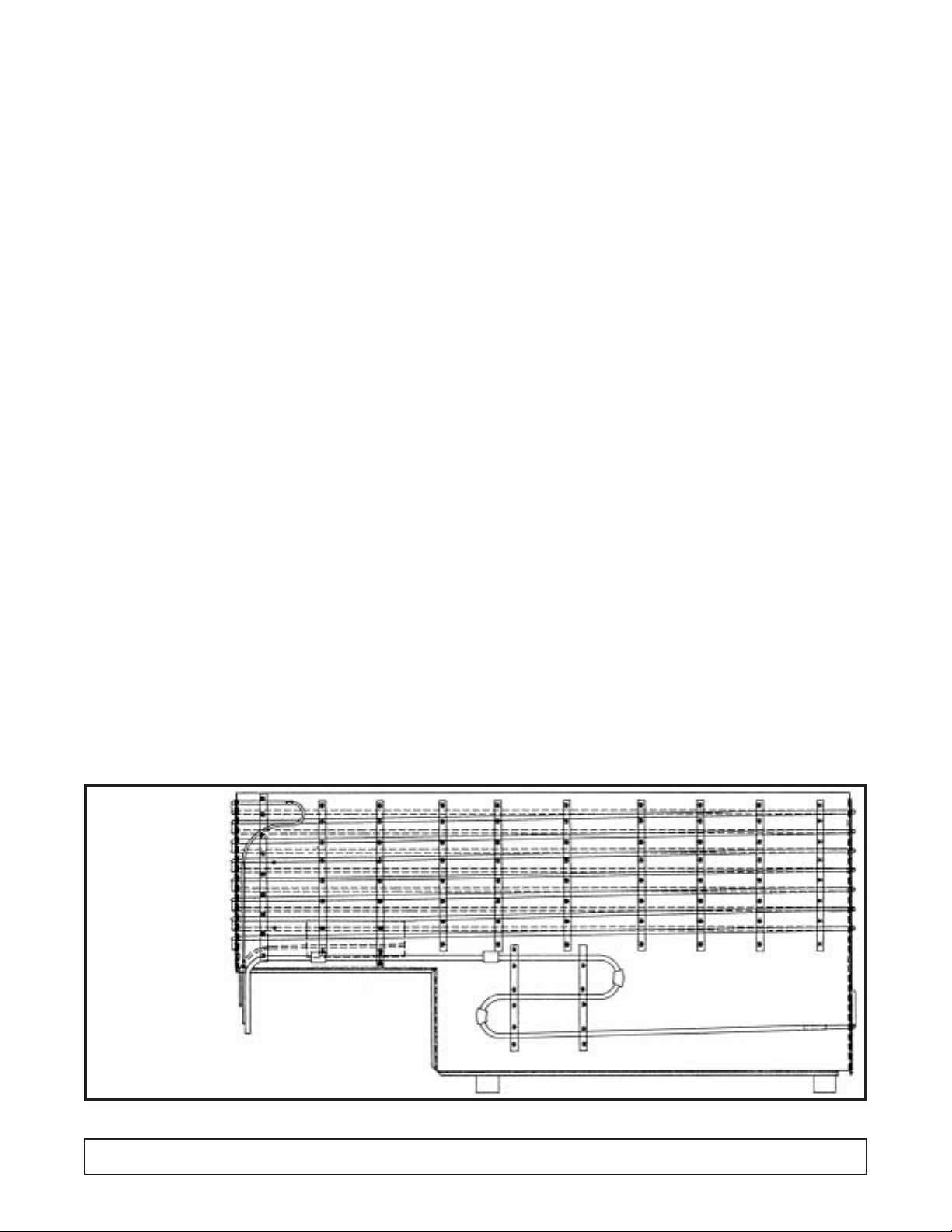
Product dipping cabinets utilize a cold wall evaporator.
(See FIGURE 2).
Here the refrigerant lines actually contact the product
area’s inner wall. Heat is transferred through the wall
and into the refrigerant.
To understand how the refrigerant system creates cold
temperatures, it is important to understand how the
temperatures of the area into which the heat will be
dissipated affect the system’s performance.
Simply stated, a refrigerant system’s ability to cool a
product area is dependent upon the unit’s ambient
environment.
For example, a single stage system dissipating heat
throught its condenser into a 60°F ambient environment
is capable of cooling a cabinet’s interior to a lower
temperatue than an identical system operaing in an
80°F ambient environment.
To understand the complete heat transfer and extraction
process in systems, let’s discuss the function of the
major system components.
There are three components in each system used for
transferring heat. They are the Evaporator, the
Compressor, and the Condenser.
Heat is transferred through the refrigerant lines by the
compressor. This heated refrigerant arrives at the
condenser for dissipation.
The heat transfers to the e vapor ator because it is colder .
The heat then moves through the compressor and
leaves the cabinet at the condenser, where it transfers
or dissipates into the cooler room air.
This heat transfer continues until the system has
absorbed all the heat it is capable of removing, and has
pulled down to the coldest temperature possible, or it
has reached its thermostatic set point and shuts off.
On product dipping cabinets, the copper evaporator
lines are strapped to the inner tank walls to form a cold
wall evaporator.
This is foamed into place with two inches of urethane
instulation to form a rigid bond between the outer shell
and inner liner, which is another metal barrier used for
strength and insulation separation.
The direction of the refrigerant flow is from the top to the
bottom.
The cold wall evaporator is not serviceable within the
walls of the cabinet because of the foam construction.
FIGURE 2
12 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 13
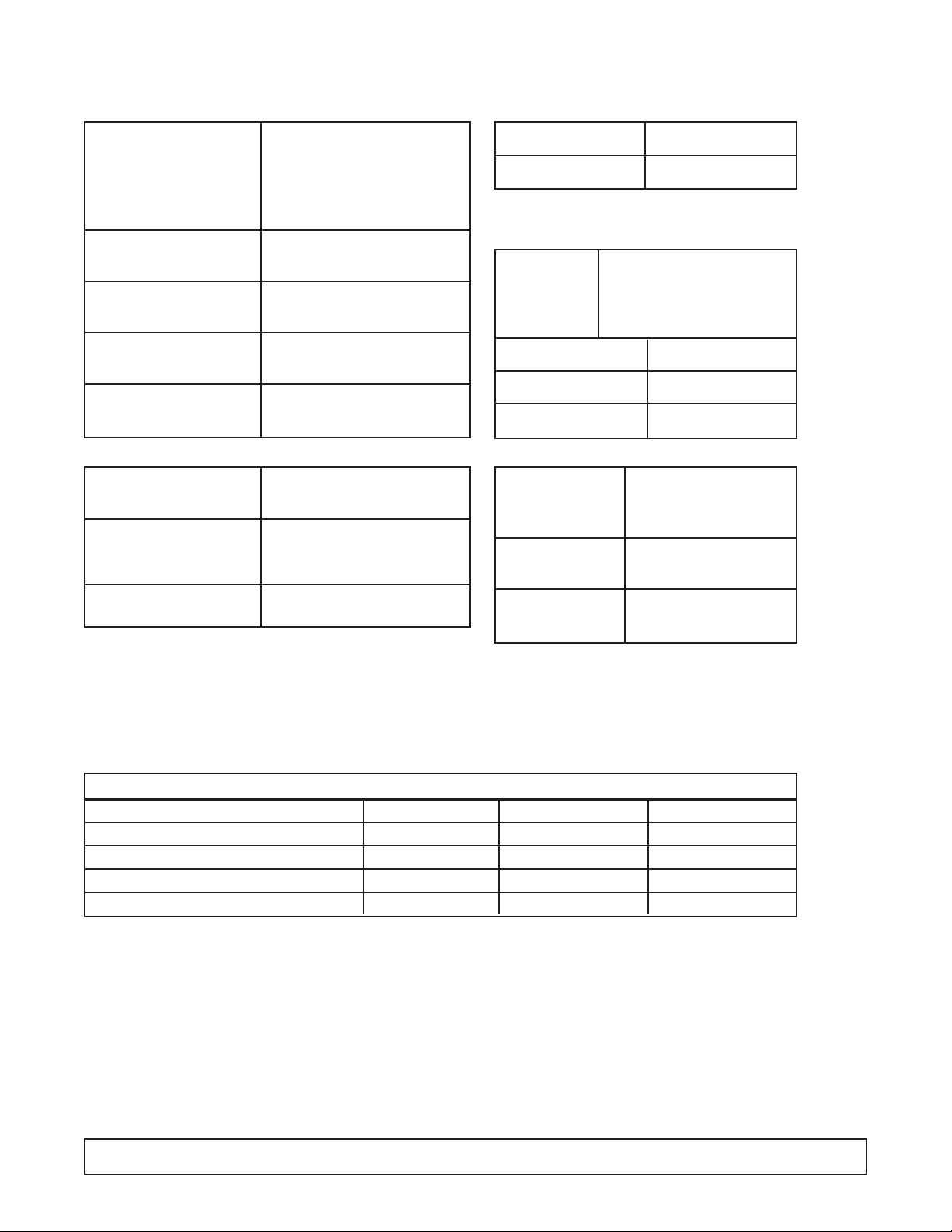
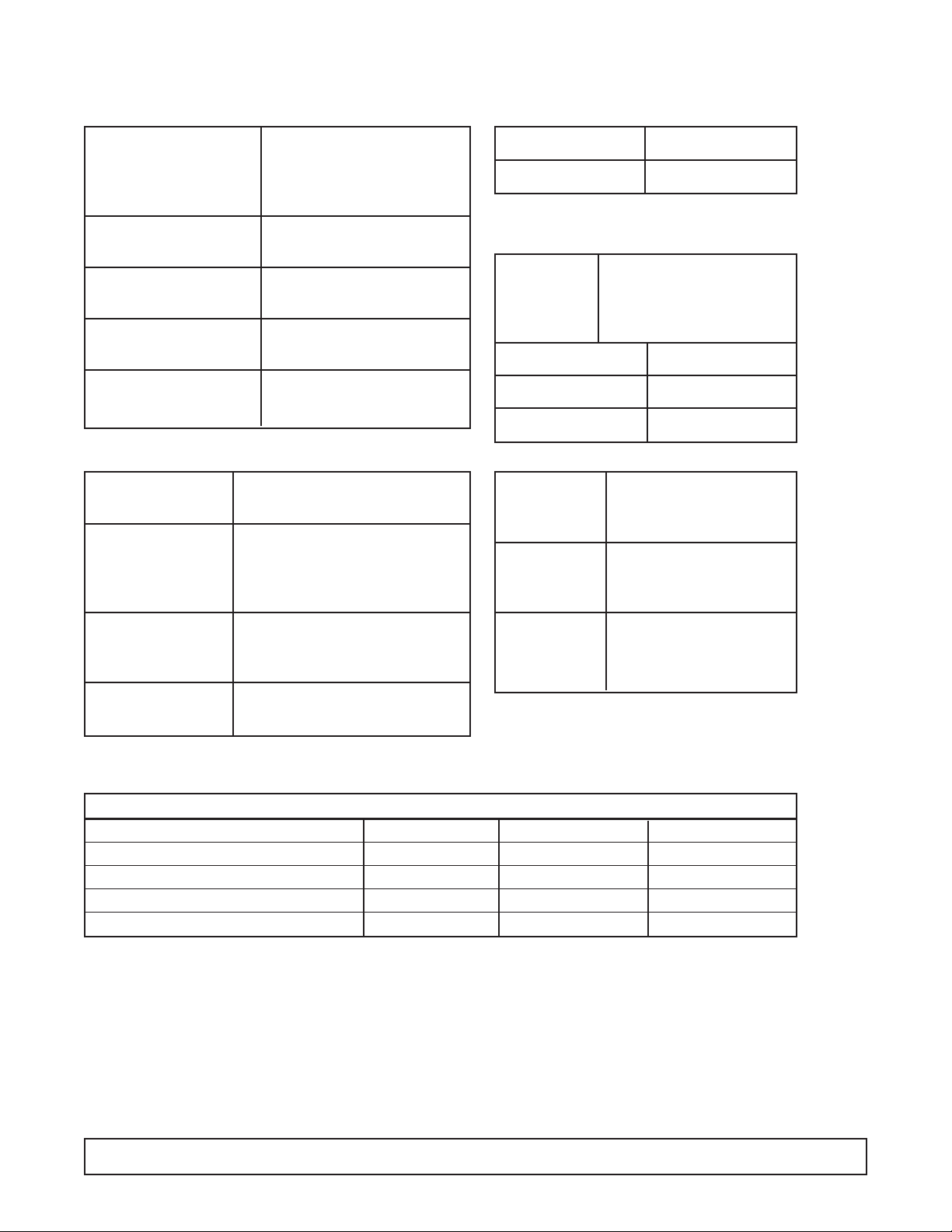
SYSTEM INFORMATION - BRT-68
ELECTRICAL
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig.Charge: R-404A / 25 oz./ 708.75 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Compressor Manufacturer: Americold
Model: HP-127-1
Ph.: 1 Hz.: 60
Volts: 115 Amps: 4.2
Overload Protector Manufacturer: Americold
Start Relay Manufacturer: Americold
Start Capacitor V.: 125 M.F.: 189-227
Run Capacitor VAC: 370 M.F.: 20
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model:5KSM51GG3784
Condenser Diameter: 9.5" # Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:1 29/32"
Power Cord A.W.G.: 16
A.: 15 V.: 125
Light Ballast Manufacturer: G.E.
Model: 89G457
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F40T12CW
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 7' of .042
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 120/250 L.R.A.: 100
Warm Cut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 9 / 62 10 / 69 11 / 76
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 198 / 1365 230 / 1586 268 / 1848
Compressor Amps 4.2 4.2 4.3
Total Cabinet Amps 6.1 6.1 6.2
Cavity Temperature 0°F / -17°C 1°F / -17°C 2°F / -16°C
14 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
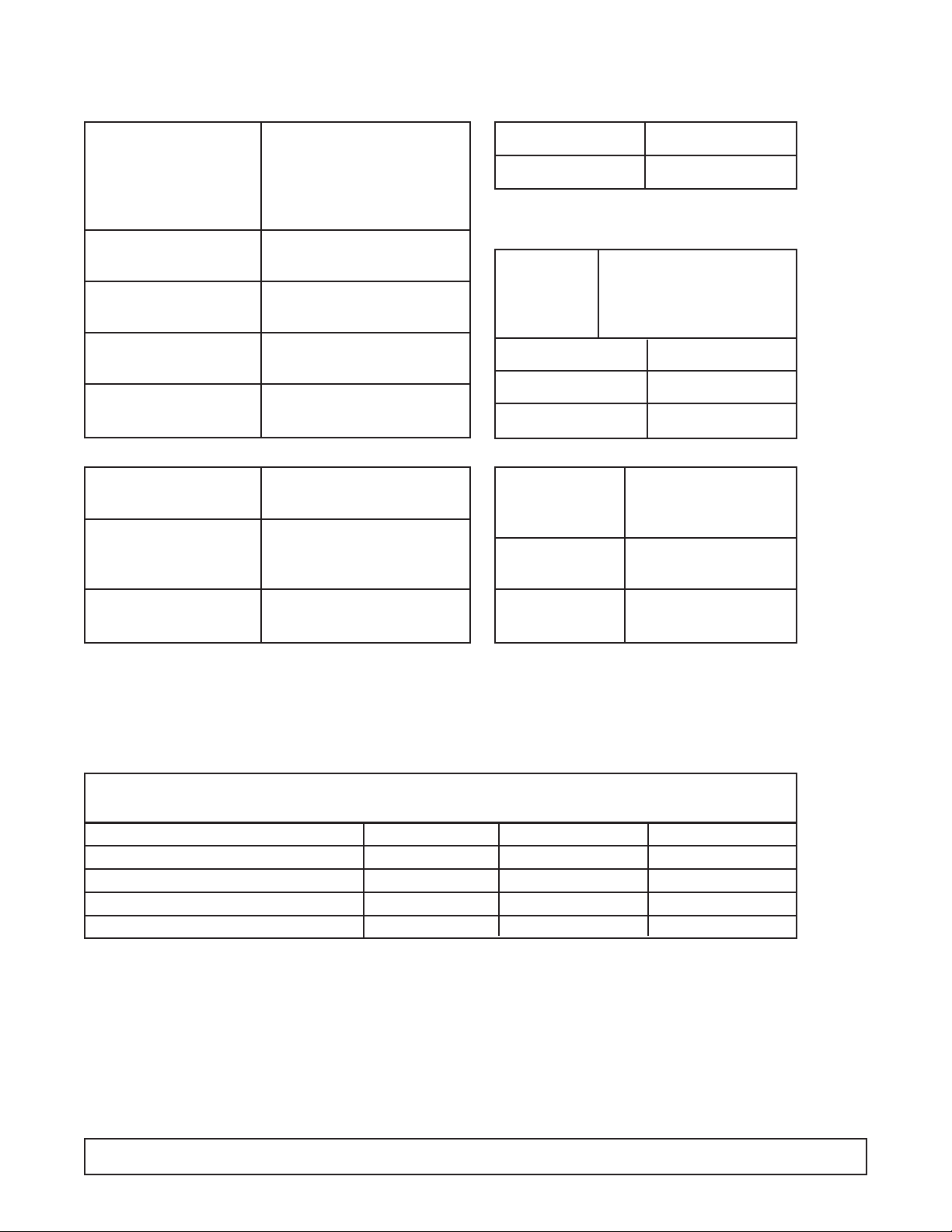
SYSTEM INFORMATION - BRT-90
ELECTRICAL
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig.Charge: R-404A / 27 oz./ 765.45 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Compressor Manufacturer: Americold
Model: HP-127-1
Volts: 115 Amps: 4.2
L.R.A.: — Ph.: 1 Hz.: 60
Overload Protector Americold #1456-3321
Start Relay Americold #1456-3374
Start Capacitor V.: 125 M.F.: 189-227
Run Capacitor V: 370 M.F.: 20
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model:5KSM51GG3784
Condenser Diameter: 9.5" # Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:1 29/32"
Power Cord A.W.G.: 16
A.: 15 V.: 125
Light Ballast Manufacturer: G.E.
Model: 8G3706
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F40T12CW
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 7' of .042
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 120/240 L.R.A.: 100
Warm Cut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CONTROL SETTINGS #4 C.S. #4 C.S. #4 C.S.
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 9 / 62 10 / 69 12 / 82
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 207 / 1427 234 / 1613 262 / 1806
Compressor Amps 3.8 3.8 3.9
Total Cabinet Amps 6.3 6.3 6.3
Cavity Temperature -0.5°F / -18°C -0.3°F / -17.9°C -1.2°F / -18.4°C
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 15
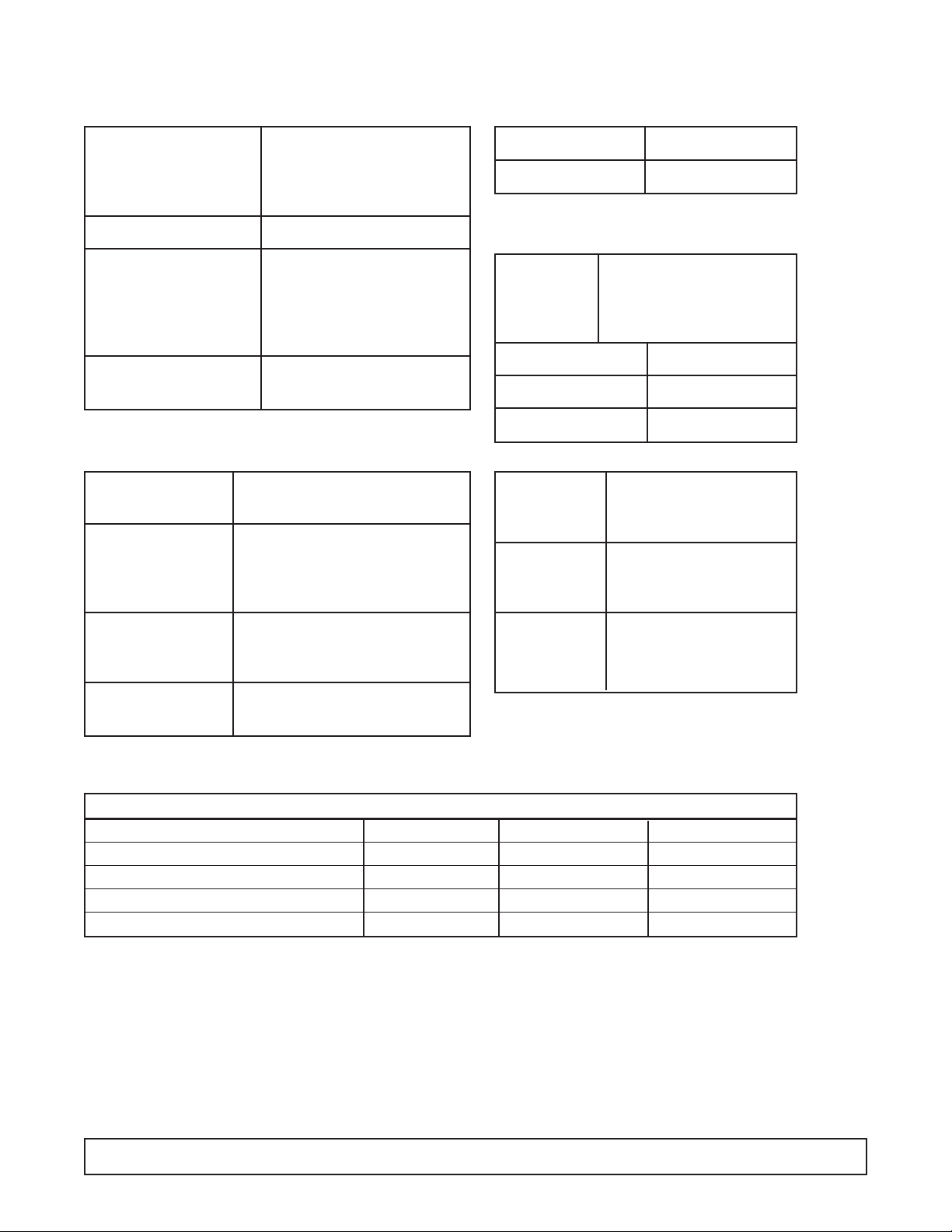
SYSTEM INFORMATION -
EBRT-68
(220V / 50 Hz)
ELECTRICAL KBR T-68 (220V / 60 Hz)
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig.Charge: R-404A / 25 oz./ 708.75 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Compressor Mfg: Copeland (3/4 HP)
Model: KAMB-007E-CAV
Phase: 1 Hz.:50
Overload Protector Model No.: 071-0092-29
Start Relay G.E. 3ARR3CT3E5
Pick up: 340-360
Drop out: 45-115
Model No.: 040-0001-03
Start Capacitor V: 220
M.F.: 145-174
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model: KSM51GG3705
Condenser Diameter: 91⁄2
"# Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades: 1
29
⁄32"
High Pressure Ranco
Switch Preset 400 PSIG Diff 100 PSIG
Power Cord A.W.G.: 16
Amp: 15
Light Ballast Mfg:Vossloh Schwabe
Model: L36.291 (50 Hz)
Robertson: 1-4026 (60 Hz)
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F40T12CW
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 9' of .042
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 125/250 L.R.A.: 100
Warm Cut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CAVITY TEMPERATURE 2°F / -17°C 4°F / -16°C 6°F / -14°C
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 8 / 55 10 / 69 12 / 82
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 188 / 1296 225 / 1551 253 / 1744
Compressor Amps 7.2 7.1 7.1
Total Cabinet Amps 9.5 9.3 9.4
16 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
SYSTEM INFORMATION -
EBRT-90
(220V / 50 Hz)
ELECTRICAL KBR T-90 (220V / 60 Hz)
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig.Charge: R-404A / 27 oz./ 765.45 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Compressor Mfg: Copeland (3/4 HP)
Model: KAMB-007E-CAV
Phase: 1 Hz.:50
Overload Protector Copeland
Model No.: 071-0092-20
Start Relay G.E. 3ARR3CT3E5
Start Capacitor V: 220
M.F.: 145-174
Run Capacitor V: 370
M.F.: 10
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model: KSM51GG370E
115V / 60 Hz. / Ph. 1
Condenser Diameter: 91⁄2
"# Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades: 1
29
⁄32"
High Pressure Ranco
Switch Preset 400 PSIG Diff 100 PSIG
Power Cord A.W.G.: 16
V.: 220 Amp: 15
Light Ballast Mfg:Vossloh Schwabe
Model: L36.291 (50 Hz)
Robertson: 1-4025 (60 Hz)
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F40T12CW
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 9' of .049
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
Model No.: 9540N46
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 125/250 L.R.A.: 100
Warm Cut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CAVITY TEMPERATURE 2°F / -17°C 4°F / -16°C 7°F / -14°C
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 8 / 55 10 / 69 12 / 82
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 228 / 1572 257 / 1772 284 / 1958
Compressor Amps 7.4 7.5 8
Total Cabinet Amps 9.5 9.3 10
 Loading...
Loading...