Page 1

KL6051
Data transfer terminal with serial RS422 terminal
Configuration Instructions
Version 2.1
2006-10-24
Page 2

Contents
Contents
1. Foreword 3
Notes on the documentation 3
Safety Instructions 4
2. Technical data 5
3. Description of functions 6
4. Terminal configuration 6
5. Register description 8
General register description 8
Terminal-specific register description 10
Register communication KL6051 10
6. Data transfer, function 13
7. Annex 14
Mapping in the bus coupler 14
Table of the register 16
Support and Service 17
Beckhoff Headquarters 17
2 KL6051
Page 3

Foreword
Foreword
Notes on the documentation
This description is only intended for the use of trained specialists in control and automation engineering
who are familiar with the applicable national standards. It is essential that the following notes and explanations are followed when installing and commissioning these components.
Liability Conditions
The responsible staff must ensure that the application or use of the products described satisfy all the requirements for safety, including all the relevant laws, regulations, guidelines and standards.
The documentation has been prepared with care. The products described are, however, constantly under
development. For that reason the documentation is not in every case checked for consistency with performance data, standards or other characteristics. None of the statements of this manual represents a
guarantee (Garantie) in the meaning of § 443 BGB of the German Civil Code or a statement about the
contractually expected fitness for a particular purpose in the meaning of § 434 par. 1 sentence 1 BGB. In
the event that it contains technical or editorial errors, we retain the right to make alterations at any time
and without warning. No claims for the modification of products that have already been supplied may be
made on the basis of the data, diagrams and descriptions in this documentation.
Delivery conditions
In addition, the general delivery conditions of the company Beckhoff Automation GmbH apply.
Copyright
©
This documentation is copyrighted. Any reproduction or third party use of this publication, whether in
whole or in part, without the written permission of Beckhoff Automation GmbH, is forbidden.
KL6051 3
Page 4
Foreword
i
Safety Instructions
State at Delivery
All the components are supplied in particular hardware and software configurations appropriate for the
application. Modifications to hardware or software configurations other than those described in the documentation are not permitted, and nullify the liability of Beckhoff Automation GmbH.
Description of safety symbols
The following safety symbols are used in this documentation. They are intended to alert the reader to the
associated safety instructions..
This symbol is intended to highlight risks for the life or health of personnel.
Danger
This symbol is intended to highlight risks for equipment, materials or the environ-
Attention
Note
ment.
This symbol indicates information that contributes to better understanding.
4 KL6051
Page 5
Technical data
Technical data
Technical data KL6051
Data transfer channels
Data transfer rate
Bit transfer
Line impedance
Data transfer link
Power supply
Current consumption from K-Bus
Electrical isolation
Bit width in the process image
Configuration
Weight approx..
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Relative humidity
Vibration/shock resistance
EMC resistance Burst / ESD
Installation position
Type of protection
TxD and RxD, full duplex
62500 Baud (8N1)
with differential signal
120 Ω
approx. 1000 m twisted pair
via the K-Bus
65 mA typ.
500 Vrms (K-Bus / signal voltage)
I/O: 4 x 8 bits user data, 1 x 8 bits control/status (up to 5 x 8 bits user
data possible)
no address setting or configuration settings
60 g
0°C ... +55°C
-25°C ... +85°C
95%, no condensation
conforms to IEC 68-2-6 / IEC 68-2-27
conforms to EN 50082 (ESD, Burst) / EN 50081
any
IP20
KL6051 5
Page 6

Description of functions
Offset Terminal1 = 0
Offset Terminal2 Channel1 = 1
Offset Terminal2 Channel2 = 2
Offset Terminal3 Channel1 = 1
User information data allocation
To the bus terminal
Features
Beckhoff Lightbus
coupler BK2000
Description of functions
The KL6051 serial interface terminal enables an exchange of data between
different field bus systems. Regardless of the higher-level field bus system,
data can be exchanged in full duplex mode. Up to 40 inputs and 40 outputs
are transmitted between the field bus systems and, in addition, the status
byte contains information about the quality and the status of data transfer.
The terminal is supplied with a 200 ms RCV timeout, i.e. the inputs of the
higher-level controller are set to zero if the terminal does not receive any
valid data via the serial interface from the second station within 200 ms. In
the default setting, 32 bits are bidirectionally available for data exchange.
Coupling of two field bus systems
Exchange of up to 40 bits bidirectionally
Status byte for data channel status message
Safeguarded data transfer by longitudinal parity, vertical parity, log
Transmission medium: RS422 full duplex
Maximum transmission distance: 1000 m
Simple software interface for control by the emulation of up to 40 bits
Parallel I/O
Data transfer time exchange time < 5 ms
Terminal configuration
The terminal can be configured and parametrized via the internal register
structure.
Each terminal channel is mapped in the bus coupler. The data of the terminal is mapped differently in the memory of the bus coupler depending on
the type of the bus coupler and on the set mapping configuration (eg Motorola / Intel format, word alignment.
For parametrization of a terminal, the control / status byte must also be
mapped.
When using the Beckhoff Lightbus coupler BK2000, the control / status
byte is always mapped in additon to the data bytes. It is always in the low
byte at the offset address of the terminal channel. In the case of the
KL6051 there will be 6 bytes data (5 bytes user data and 1 byte control/status) exchanged with the control system.
6 KL6051
Beckhoff Lightbus
bus coupler
BK2000
The terminal is
mapped in the
bus coupler
0
K-Bus
Data H
D4
D1
C/S
Data LData H
C/S
Data L
C/S
D3
D2
D0
C/S
LH
depending on mapping
KL6051
Page 7

To the bus terminal
Offset Terminal1 = 0
Offset Terminal2 Channel1 = 1
Offset Terminal2 Channel2 = 1
Offset Terminal3 Channel1 = 1
The control/status byte must be
To the bus terminal
i
Terminal configuration
Profibus coupler BK3000
Interbus coupler BK4000
When using the Profibus coupler BK3000, how the KL6051 is to map itself
in the bus coupler is set in the master configuration software. The figure
shows the mapping for 6 bytes of input data and 6 bytes of output data.
Profibus bus coupler
The control/status byte must be
inserted for parametrization
BK3000
The terminal is
mapped in the
bus coupler
Data L
Data H
C/S
D3
D4
D2
D0
D1
0
C/S
Offset Terminal2 Channel1 = 1
The conrol/staus byte and D2
can be inserted (KL6051)
Offset Terminal1 = 0
K-Bus
By default, the Interbus coupler BK4000 maps the KL6051 with 4 bytes of
input data and 4 bytes of output data. Parametrization via the field bus is
not possible. The KS2000 software is needed to redefine the terminal’s
parameters.
Other bus couplers and
further information
Note
Parametrization with the
KS2000 software
Interbus bus coupler
BK4000
The terminal is
mapped in the
bus coupler
Data H
Data L
Data H
Data L
Data H
D2
D3
D0
0
D1
inserted for parametrization
(KS2000)
KL6051
K-Bus
You will find further information of the mapping configuration of bus couplers in the annex of the respective bus coupler manual under the heading
of "Configuration of Masters".
The annex contains an overview of possible mapping configurations depending on the parameters that can be set.
Parametrization operations can be carried out independently of the field
bus system using the Beckhoff KS2000 configuration software via the serial configuration interface in the bus coupler.
KL6051 7
Page 8

Register description
Register description
Process variables R0 - R7: Registers in the terminal’s internal RAM:
The complex terminals can be adjusted to different operating modes or
functionalities. The " general description of register " describes the contents of the registers, which are identical for all complex terminals.
The terminal-specific registers are explained in the section following to it.
The access to the internal registers of the terminal is described in the sec-
tion " register communication ".
General register description
Complex terminals that possess a processor are capable of bidirectionally
ex-changing data with the higher-level control system. Below, these terminals are referred to as intelligent bus terminals. They include the analog
inputs (0-10V, -10-10V, 0-20mA, 4-20mA), the analog outputs (0-10V, -1010V, 0-20mA, 4-20mA), serial interface terminals (RS485, RS232, TTY,
data transfer terminals), counter terminals, encoder interfaces, SSI interfaces, PWM terminals and all other parametrizable terminals.
Internally, all intelligent terminals possess a data structure that is identical
in terms of it's essential characteristics. This data area is organized in
words and embraces 64 memory locations. The essential data and parameters of the terminal can be read and adjusted by way of the structure.
Function calls with corresponding parameters are also possible. Each logical channel of an intelligent terminal has such a structure (therefore, 4channel analog terminals have 4 register sets.
This structure is broken down into the following areas:
(You will find a list of all registers at the end of this documentation).
Area Address
Process variables
Type registers
Manufacturer parameters
User parameters
Extended user area
The process variables can be used in additional to the actual process
image and their functions are specific to the terminal.
R0 - R5: These registers have a function that depends on the terminal
type.
R6: Diagnostic register
The diagnostic register may contain additional diagnostic information. In
the case of serial interface terminals, for example, parity errors that have
occurred during data transfer are indicated.
R7: Command register
High-Byte_Write = function parameter
Low-Byte _Write = function number
High-Byte _Read = function result
Low-Byte_ Read = function number
0-7
8-15
16-30
31-47
48-63
8 KL6051
Page 9

Register description
Type registers R8 - R15 Registers in the terminal’s internal ROM der Klemme
The type and system parameters are programmed permanently by the
manufacturer and can only be read by the user but cannot be modified.
R8: Terminal type:
The terminal type in register R8 is needed to identify the terminal.
R9: Software version X.y
The software version can be read as an ASCII character string.
R10: Data length
R10 contains the number of multiplexed shift registers and their length in
bits.
The bus coupler sees this structure.
R11: Signal channels
In comparison with R10, the number of logically existing channels is located here. For example, one physically existing shift register may consist of
several signal channels.
R12: Minimum data length
The respective byte contains the minimum data length of a channel to be
transferred. If the MSB is set, then the control/status byte is not necessarily
needed for the function of the terminal and, with appropriate configuration
of the coupler, is not transferred to the control system.
R13: Data type register
Data type register
0x00
0x01
0x02
0x03
0x04
0x05
0x06
0x07
0x08
0x11
0x12
0x13
0x14
0x15
0x16
Terminal without valid data type
Byte array
1 byte n bytes structure
Word array
1 byte n words structure
Double word array
1 byte n double words structure
1 byte 1 double word structure
1 byte 1 double word structure
Byte-array with a variable logical channel length
1 byte n bytes structure with a variable logical channel
length (eg 60xx)
Word-array with a variable logical channel length
1 byte n words structure with a variable logical channel
length
Double word array with a variable logical channel length
1 byte n double words structure with a variable logical
channel length
R14: not used
R15: Alignment bits (RAM)
The analog terminal is set to a byte limit in the terminal bus with the alignment bits.
Manufacturer parameters R16 - R30 is the area of the "Manufacturer parameters" (SEEROM)
The manufacturer parameters are specific to each terminal type. They are
programmed by the manufacturer but can also be modified from the control
system. The manufacturer parameters are stored permanently in a serial
EEPROM and are therefore not destroyed by power failures.
These registers can only be modified after setting a code word in R31.
KL6051 9
Page 10

Register description
i
User parameters
Note
Extended application area R47 - R63
Process variables R1-R5: no function
Type registers R8: terminal type [0x17A3] [R]
10 KL6051
R31 - R47 "Application parameters" area (SEEROM)
The application parameters are specific to each terminal type. They can be
modified by the programmer. The application parameters are stored permanently in a serial EEPROM in the terminal and cannot be destroyed by
power failures. The user area is write protected over a Codeword.
R31: Code word-register in the RAM
The code word 0x1235 must be entered here to enable modification of
parameters in the user area. Write-protection is set if a different value is
entered in this register. When write protection is inactive, the code word is
returned during reading of the register. The register contains the value zero
when write protection is active.
R32: Feature-register
This register defines the operating modes of the terminal. For example, a
user-specific scaling can be activated for the analog I/O’s.
R33 - R47
Registers that depend on the terminal type
These registers have not yet been implemented.
Terminal-specific register description
R6: diagnostic register [R/W]
HB HB Status of station 2 (partner terminal)
LB LB Status of station 1
R7: no function
The terminal type in register R8 is identical with the general terminal designation.
HB,LB = 6051
HB = 0x17
LB = 0xA3
R9: software version X.y [R]
HB = main number X of X.y
LB = sub-number y of X.y
R10: data length [R]
R10 contains the number of multiplexed shift registers in the terminal bus
and their length in bits. The bus coupler sees this structure.
HB = 2 - multiplexed channels
LB = 24-bit shift registers
R11: signal channels [R]
In comparison with R10, this register contains the number of logically existing channels. Thus, for example, one physically existing shift register
may consist of several signal channels or vice versa.
HB = 1
LB = 48
R12: minimum data length (auto configuration) [R]
The respective byte contains the minimum data length to be transferred of
a signal channel. The status byte is omitted if the MSB is set.
HB = 48 ; HB is the number of outputs in the case of auto configuration
LB = 48 ; LB is the number of inputs in the case of auto configuration
Page 11

R15: alignment bits (RAM)
With the alignment bits, the analog terminal is set to a byte limit in the terminal bus.
HB = LB converted (contains zero in the event of input)
LB = number of bit doublets 0,1,2,3
Manufacturer parameter R16: hardware version [R/W]
HB = main number X of X.y
LB = sub-number y of X.y
User parameters R32 Feature register
[0x0007]
Feature bit nr.
bit 0
bit 1
bit 2
bit 3
bit 15-4
R33: Baud rate
[0x0003] (62.5kHz)
HB = DC
LB = Baud rate = 4MHz / (16 * (LB + 1))
R34: RCV timeout
[0x00014] (200ms)
HB, LB = unsigned integer, 1 digit corresponds to 10ms
When the RCV timeout enable bit is set in R32, this value is valid. If the
terminal does not receive any valid data via the serial interface for X-ms,
the controller's inputs are set to the value ZERO.
R35: TRS timeout
[0x0014] (200ms)
HB, LB = unsigned integer,1 digit corresponds to 10ms
When the TRS timeout enable bit is set in R32, this value is valid. If the
terminal does not receive any valid data via the serial interface for X-ms,
no data is sent via the serial interface. Accordingly, the RCV timeout of the
2rd terminal would take effect.
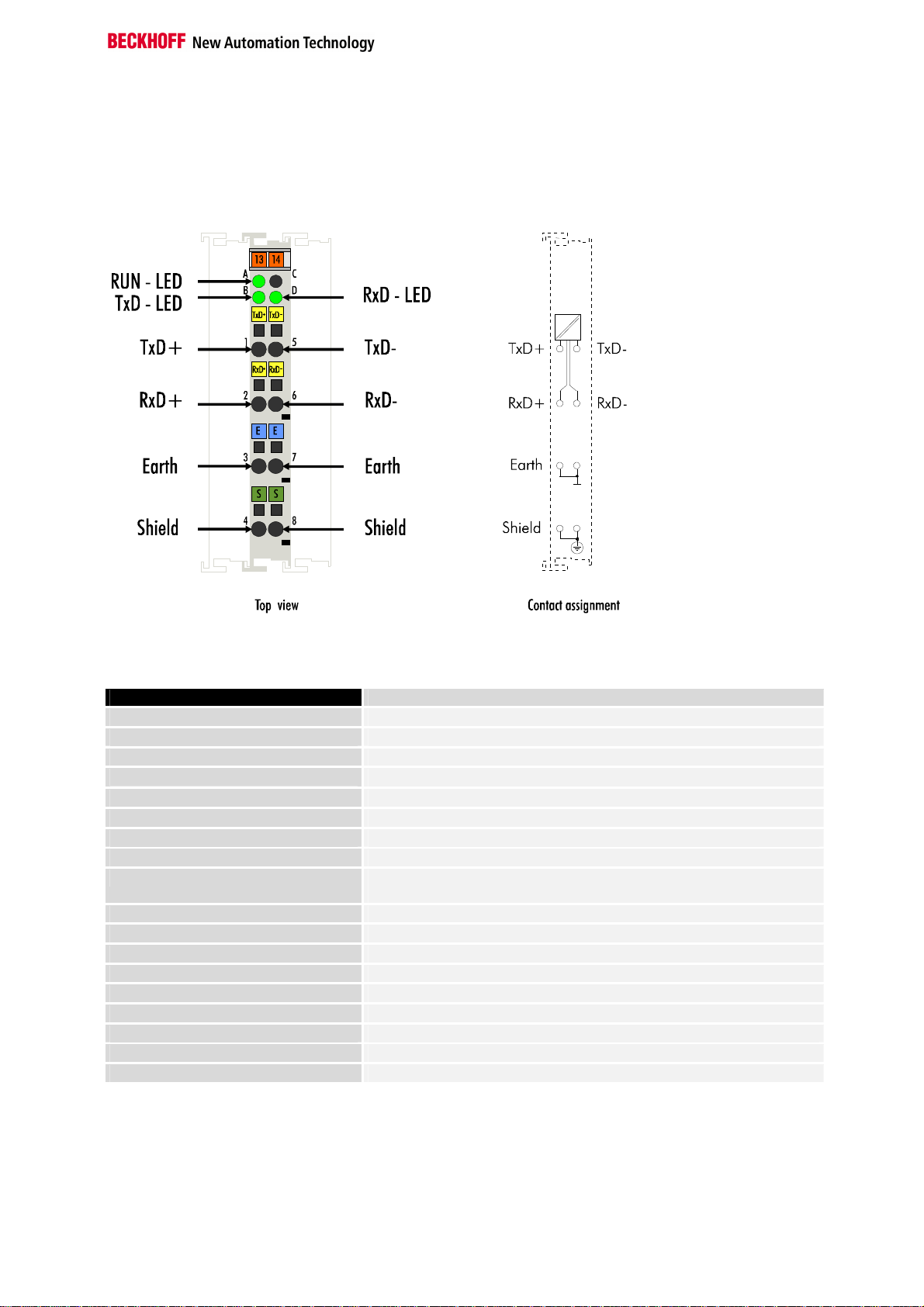
Register communication KL6051
Register access via
process data transfer
Bit 7=1: register mode
When bit 7 of the control byte is set, the first two bytes of the user data are
not used for process data transfer, but are written into or read out of the
terminal’s register.
Bit 6=0: read
Bit 6=1: write
In bit 6 of the control byte, you define whether a register is to be read or
written. When bit 6 is not set, a register is read without modification. The
value can be taken from the input process image.
When bit 6 is set, the user data is written into a register. The operation is
concluded as soon as the status byte in the input process image has supplied an acknowledgement (see examples).
Bits 0 to 5: address
The address of the register to be addressed is entered in bits 0 to 5 of the
control byte.
1 RCV-timeout enable (R334) [1]
1 TRS-timeout enable (R35) [1]
0/1 0: terminal bus communiction via interrupt
0/1 0: data is transferred word-consistently
- not used
Register description
1: terminal bus: poll state [1]
1: data is transferred completely consistently
KL6051 11
Page 12

Register description
0
63
Terminal´s
Control-/
HHL
L
Control byte in the
register mode
MSB
REG=1 W/R
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
REG = 0 : Process data transfer
REG = 1 : Access to register structure
W/R = 0 : Read register
W/R = 1 : Write register
A5..A0 = Register address
A total of 64 registers can be addressed with the addresses A5....A0.
To the bus coupler
K-Bus
User data
status byte
C/S-bit 7
2 or mors bytes
If control bit 7=0: input/output
If control bit 7=1:
registerconfiguration
A0
Example
If control bit 7=1:
adress in the control bit 0-5
If control bit 6=0: read
If control bit 6=1: write
register set
64 words
Complex bus terminal
The control or status byte occupies the lowest address of a logical channel.
The corresponding register values are located in the following 2 data bytes
(the BK2000 is an exception to the rule: here, an unused data byte is inserted after the control or status byte, thus setting the register value to a word
limit).
Reading register 8 in the BK2000 with a Kl3022 and the end terminal.
If the following bytes are transferred from the controller to the terminal,
Byte0
Control
0x88 0xXX 0xXX 0xXX
the terminal returns the following type designation (0x0BCE corresponds to
the unsigned integer 3022).
Byte0
Status
0x88 0x00 0x0B 0xCE
Byte1
Not used
Byte1
Not used
Byte2
Data OUT, high byte
Byte2
Data IN, high byte
Byte3
Data OUT, low byte
Byte3
Data IN, low byte
12 KL6051
Page 13

A further example
Writing register 31 in the BK2000 with an intelligent terminal and the end
terminal.
If the following bytes (user code word) are transferred from the controller to
the terminal,
Byte0
Control
0xDF 0xXX 0x12 0x35
the user code word is set and the terminal returns the register address with
the bit 7 for register access and the acknowledgement.
Byte0
Status
0x9F 0x00 0x00 0x00
Data transfer, function
Status byte in
the process data mode
8 data bits, 1 start bit, 1 stop bit, even parity
Data containing errors is not transferred to the controller. The processed
data is still valid when the CHK, OVR or PAR date is set. These bits merely
represent the quality of data transfer.
MSB
REG=0
PAR: parity error or invalid data frame
OVR: buffer overflow
CHK: invalid checksum
RCVT2: the partner terminal has an RCD timeout
RCVT1: the terminal is not receiving any data from the partner. The termi-
nal has set the controller inputs to zero.
For use without status information, the data transfer link can be monitored
from the other respective side of the link by means of a bit set by the controller. Data transfer of the KL6051 is checked by a watchdog. Thus, failures of the field buses or of data transfer between the KLK6051 units are
easily recognizable.
Data transfer, function
Byte1
Not used
Byte1
Not used
RCVT1 RCVT2 CHK OVR PAR
Byte2
Data OUT, high byte
Byte2
Data IN, high byte
Byte3
Data OUT, low byte
Byte3
Data IN, low byte
KL6051 13
Page 14

Annex
Mapping in the bus coupler
Default: CANCAL,
CANopen, RS232,
RS485, ControlNet,
DeviceNet
Default: Interbus,
Profibus
Default: Lightbus,
Bus Terminal Controller
(BCxxxx)
Annex
As already described in the chapter terminal configuration, each bus terminal is mapped in the bus coupler. In the standard case, this mapping is
done with the default setting in the bus coupler / bus terminal. This default
setting can be modified with the Beckhoff KS2000 configuration software or
using master configuration software (e.g. ComProfibus or TwinCAT System
Manager). The following tables provide information on how the KL6051
maps itself in the bus coupler depending on the set parameters.
Mapping in the bus coupler
The KL is mapped in the bus coupler depending on the set parameters.
The terminal occupies memory space in the process image of the inputs
and outputs.
I/O Offset High Byte Low Byte
Complete evaluation = 0 3
MOTOROLA format = 0 2
Word alignment = X 1 D3 D2
0 D1 D0
I/O Offset High Byte Low Byte
Complete evaluation = 0 3
MOTOROLA format = 1 2
Word alignment = X 1 D2 D3
0 D0 D1
I/O Offset High Byte Low Byte
Complete evaluation = 1 3
MOTOROLA format = 0 2 D4 D3
Word alignment = 0 1 D2 D1
0 D0 CT/ST
I/O Offset High Byte Low Byte
Complete evaluation = 1 3
MOTOROLA format = 1 2 D3 D4
Word alignment = 0 1 D2 D0
0 D1 CT/ST
I/O Offset High Byte Low Byte
Complete evaluation = 1 3 D4 D3
MOTOROLA format = 0 2 D2
Word alignment = 1 1 D1 D0
0 CT/ST
I/O Offset High Byte Low Byte
Complete evaluation = 1 3 D3 D4
MOTOROLA format = 1 2 D2
Word alignment = 1 1 D0 D1
0 CT/ST
14 KL6051
Page 15

Legend
Complete evaluation: the terminal is mapped with control / status byte.
Motorola format: the Motorola or Intel format can be set.
Word alignment: the terminal is at a word limit in the bus coupler.
CT: Control- Byte (appears in the PI of the outputs).
ST: Status- Byte (appears in the PI of the inputs).
D0 – D4: Data bytes 0 - 4
Annex
KL6051 15
Page 16

Annex
Table of the register
Register set
Address Designation Default R/W Storage medium
R0
Not used 0x0000 R
R1
Not used 0x0000 R
R2
Not used 0x0000 R
R3
Not used 0x0000 R
R4
Not used 0x0000 R
R5
Not used 0x0000 R
R6
Diagnostic register 0x0000 R RAM
R7
Command register not used 0x0000 R
R8
Terminal type 6051 R ROM
R9
Software version number 0x???? R ROM
R10
R11
R12
R13
R14
R15
R16
R17
R18
R19
R20
R21
R22
R23
R24
R25
R26
R27
R28
R29
R30
R31
R32
R33
R34
R35
R36
R37
R38
R39
R40
R41
R42
R43
R44
R45
R46
R47
Multiplexed shift register 0x0218 R ROM
Signal channels 0x0130 R ROM
Minimum data length 0x3030 R ROM
Data structure 0x0000 R ROM
Not used 0x0000 R
Alignment register variable R/W RAM
Hardware version number specific R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Code word register variable R/W RAM
Feature register 0x0007 R/W SEEROM
Baud rate 0x0003 R/W SEEROM
RCV timeout 0x0014 R/W SEEROM
TRS timeout 0x0014 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
Not used 0x0000 R/W SEEROM
16 KL6051
Page 17

Annex
Support and Service
Beckhoff and their partners around the world offer comprehensive support and service, making available
fast and competent assistance with all questions related to Beckhoff products and system solutions.
Beckhoff's branch offices and representatives
Please contact your Beckhoff branch office or representative for local support and service on Beckhoff
products!
The addresses of Beckhoff's branch offices and representatives round the world can be found on her
internet pages: http://www.beckhoff.com
You will also find further documentation for Beckhoff components there.
Beckhoff Headquarters
Beckhoff Automation GmbH
Eiserstr. 5
33415 Verl
Germany
phone: + 49 (0) 5246/963-0
fax: + 49 (0) 5246/963-198
e-mail: info@beckhoff.com
web: www.beckhoff.com
Beckhoff Support
Support offers you comprehensive technical assistance, helping you no only with the application of individual Beckhoff products, but also with other, wide-ranging services:
• support
• design, programming and commissioning of complex automation systems
• and extensive training program for Beckhoff system components
hotline: + 49 (0) 5246/963-157
fax: + 49 (0) 5246/963-9157
e-mail: support@beckhoff.com
Beckhoff Service
The Beckhoff Service Center supports you in all matters of after-sales service:
• on-site service
• repair service
•
spare parts servive
• hotline service
hotline: + 49 (0) 5246/963-460
fax: + 49 (0) 5246/963-479
e-mail: service@beckhoff.com
KL6051 17
 Loading...
Loading...