Page 1

TwinCAT
Application Note DK9322-0810-0036
TwinCAT, Building Automation
Keywords
M-Bus
Master
counter
consumption measurement
Building Automation
energy measurement
EN 1434
EN 13757
flow measurement
calorimetry
IEC 870
EN 1434-3
M-Bus connection for energy and consumption meters
via TwinCAT
This application example from the ‘Building Automation Sub-bus Systems’ series describes the basic
principles of M-Bus, the KL6781 M-Bus master terminal and the functionality and of the TwinCAT PLC
library M-Bus from Beckhoff. The M-Bus is predominately used in buildings and properties with a large
number of end users. Through serial data transmission a KL6781 M-Bus master can read up to 40 energy and
consumption meters.
1. The M-Bus
The M-Bus (meter bus) is a fieldbus for logging, analyzing, optimizing and controlling energy and process data. It is as used as
a standardized system for reading energy and consumption meters or other end devices or actuators. Signals are transferred
serially from the connected slaves (measuring devices) to a master via a reverse polarity protected two-wire line. Depending
on the application the data are stored or prepared for further processing. The field devices can be supplied with power via the
bus cable. M-Bus is a typical single-master bus, in which the master requests and picks up the data from the slaves. With a
primary address space of 250 addresses, up to 250 slaves can be connected to a master. Via modem interfaces, large distances
can be covered in order to bring together modular extensions or complex systems. The M-Bus system is predominately used
by operating companies supplying a large number of end users (e.g. industrial and technology parks, trade shows, building
management systems, etc.).
Meanwhile the M-Bus has become established as a separate standard in EN 13757. This standard describes the M-Bus for
application via a two-wire bus (part 2) and for radio transmission (part 4). However, standardization at the protocol level is
incomplete. The data telegram features a freely available segment which manufacturers can use for transferring various (non-
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
1
Page 2

TwinCAT
Application Note DK9322-0810-0036
TwinCAT, Building Automation
standardized) data or control characters. Before using new slaves it is therefore important to verify compatibility with the
evaluation unit. All manufacturers of M-Bus meters offer downloadable specifications of the M-Bus protocols for their meters.
2. Typical field devices
The field devices used for M-Bus are typically meters for measuring tasks within a building. Examples of field devices include
heat meters, water meters, hot water meters, electricity meters, pulse meters, switching devices, and heating cost distributors.
A distinction is made between the reading mode. For local reading only one meter is connected, for remote reading several
meters are integrated. The following data transfer options are available, depending on the reading type. The transfer protocol
according to IEC 870 and EN1434-3 is used for all transfer routes.
2.1 Local reading (single meter)
– one optical interface (EN 61107 section 3.2)
– one inductive interface (CEN TC176/WG4)
– one 20 mA current loop, CL (EN 61107 section 3.1)
2.2 Remote reading (several meters)
– one two-wire fieldbus, meter bus (CEN TC176/WG4)
– one 11-bit modem
– radio system (433 or 868 MHz)
3. Master versions
The master can be an independent device or a PC with level converter. It reads the data of the connected field devices at
configurable intervals and stores the meter readings permanently. In conjunction with the KL6781 M-Bus master terminal and
the TwinCAT PLC M-Bus library, all Industrial and Embedded PCs from Beckhoff as well as the BC and BX series Bus Terminal
Controllers can be used as M-Bus master. The Beckhoff Bus Terminal Controllers from the BC and BX series (except for BCxx50)
can also be used as a master, although in this case the limited transfer rates, the limited multi-tasking functionality and the
longer cycle times must be taken into account. In addition, the program memory and, consequently the mapping is limited
depending on the Bus Terminal Controller, so the number of meters that can be read is limited as a result.
Notes regarding the use of devices from the Beckhoff BC/BX series:
M-Bus devices may deliver very large values (that may exceed the DWord value range) and are therefore output in string
format. Conversion to the Real format may result in inaccuracies or even invalid values. Conversion to the LReal format is
therefore preferable. This approach is not available on controllers from the BC/BX series. If the values have to be provided in a
number format, controllers from the BC/BX series are unsuitable if those values exceed the DWord value range.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
2
Page 3
TwinCAT
Slave
Slave
Slave
Slave
Slave
Slave
SlaveSlave
M-Bus
master
Slave
Slave
Slave
Slave
Slave
Slave
Slave
Slave
M-Bus
master
Application Note DK9322-0810-0036
TwinCAT, Building Automation
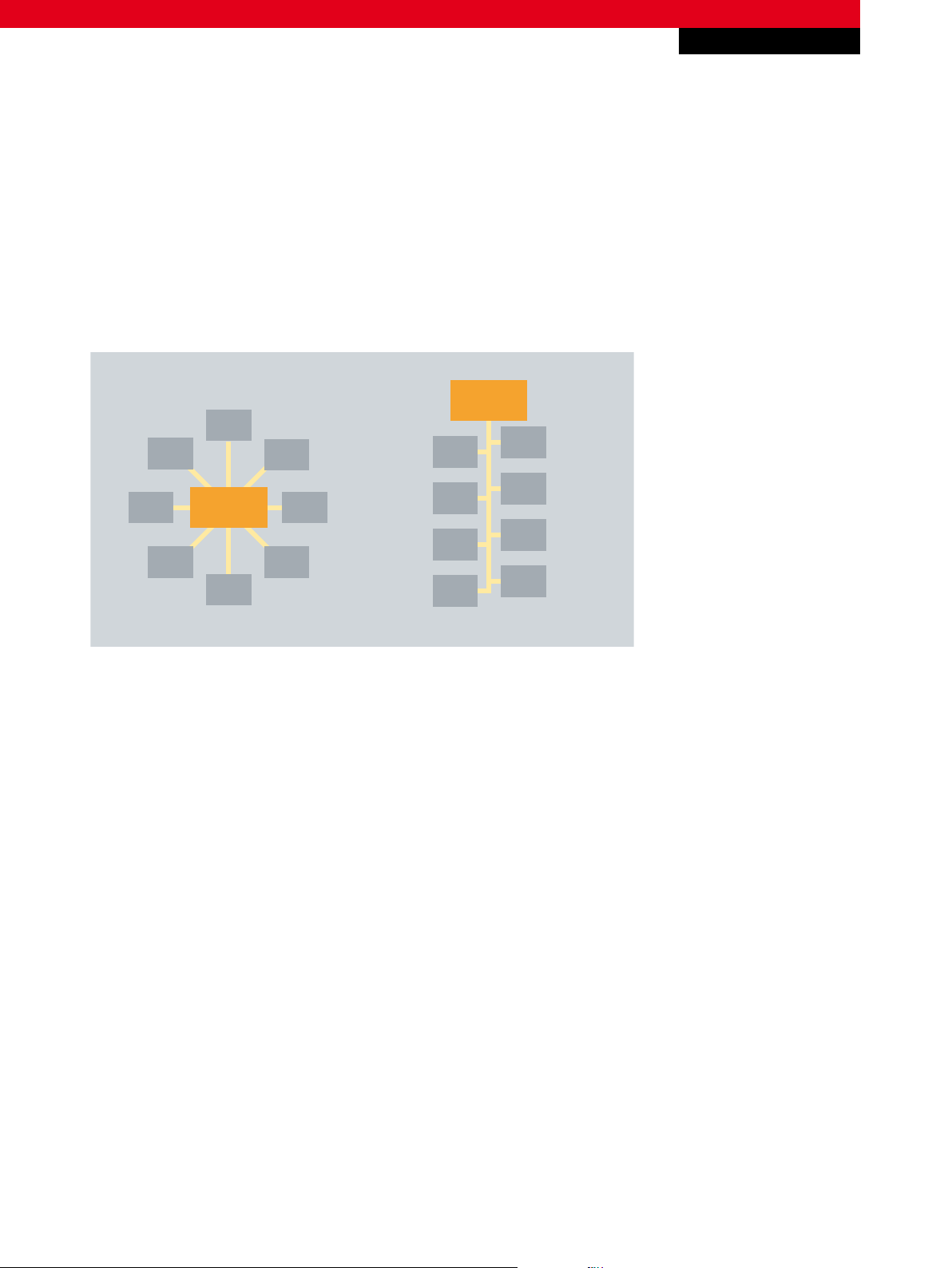
4. Topologies
Devices can be connected to M-Bus in a strand or star topology. The maximum number of meters per segment is 250. Larger
systems can be formed and cascaded with the aid of repeaters.
Fig. 1 Possible M-Bus topologies
One of the factors limiting the size of an M-Bus network is the wire cross-section. Wiring of an existing building is very complex
and expensive, which is why in such applications radio solutions with lower infrastructure costs tend to be used.
When configuring an M-Bus topology it should be noted that the plug connectors of the bus cable are not standardized, which
may result in complications if components from different manufacturers are used.
4.1 Laying system, cross-section and cable lengths
The lower the line resistance, the longer the cable can be. However, as a basic rule the cross-section should not be less than
0.5 mm² (#20 AWG). Transmission errors may occur if the maximum cable length is exceeded or if the cable cross-section is too
small. A normal telephone cable of type J-Y(ST)Y n x 2 x 0.8 mm (#20 AWG standard twisted-pair) can be used.
Figure 2 shows the number of M-Bus devices that can be connected in relation to the cable length of the M-Bus.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
3
Page 4

Application Note DK9322-0810-0036
0
500
(1640)
1000
(3280)
1500
(4921)
2000
(6561)
2500
(8202)
3000
(9842)
3500
(11483)
4000
(13123)
4500
(14763)
total cable length [m] (ft)
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
M-Bus devices
Number of M-Bus devices depending on the cable length
2 x 2 x 0.6 mm² (2 x 2 x #19 AWG)
2 x 2 x 0.8 mm² (2 x 2 x #18 AWG)
3 x 1.5 mm² (3 x #16 AWG)
TwinCAT, Building Automation
TwinCAT
Fig. 2 Number of M-Bus devices
5. Communication
M-Bus is a single-master bus based on serial data transmission. The master queries the meters via the bus by modulating
the supply voltage: A logical 1 corresponds to a signal level of 36 V DC, a logical 0 is represented by 24 V DC. This ensures
that the power supply for the slaves can take place via the bus. The slave responds to the master by modulating its current
consumption: 1.5 mA corresponds to logical 1, logical 0 is detected between 11 and 20 mA. Data transfer rates of 300 to
9,600 baud are possible, in some cases more than 9,600 baud. The maximum possible transfer rate of a meter depends on the
manufacturer. The user must therefore check which baud rate can be used for all connected field devices within a strand. In
delivery state (unparameterized) many slaves are set to 2,400 baud as standard.
Two addressing modes are possible:
With primary addressing the master sends a request for data transmission to the end device 1...250. The addressed slave
responds with a standard dataset, which in the simplest case consists of the meter reading, measured medium, device type,
serial number and manufacturer‘s code.
Secondary addressing can be used to extend the address space of M-Bus. With secondary addressing the master sends a
request for data transmission to all end devices via the special address 253. Individual end devices are addressed via serial
number, manufacturer‘s code and medium. The addressed slave responds with the standard dataset.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
4
Page 5

TwinCAT
M-Bus
Pulse
Pulse meter
FB_MBUS_...
m³
Water
FB_MBUS_...
Water meter
m³
Gas
FB_MBUS_...
Gas meter
kWh
Heat
FB_MBUS_...
Heat meter
kWh
Energy
Electricity meter
FB_MBUS_...
Address 1...40
CX8090
KL6781
Ethernet
The M-Bus library provides function blocks for any meter
type that can be used for reading out consumption data.
Application Note DK9322-0810-0036
TwinCAT, Building Automation
6. Power supply
The power supply of the slaves and the master is manufacturer-dependent. A wide range of options is available, including
230 V AC external, 30 V DC external, 30 V DC integrated, etc. In addition there are battery-powered field devices which do not
require a power supply connection. In this case the operator should be aware that each meter reading reduces the service life
of the battery.
7. TwinCAT PLC M-Bus library
With the TwinCAT PLC M-Bus library TwinCAT supports M-Bus communication. Thus up to 40 slaves can be easily connected to
the I/O-level via the M-Bus master terminal KL6781 without an additional level converter in a suitable topology (star or strand).
Devices from different manufacturers can be operated on the same bus. The M-Bus library only evaluates data with variable
data structure that are identified by a leading low byte. The TwinCAT PLC M-Bus library also supports secondary addressing,
which is possible with M-Bus for extending the address space. The TwinCAT PLC M-Bus library is free of charge and already
included in the installation package of TwinCAT.
Fig. 3 Connection of M-Bus devices via Bus Terminal KL6781 and programming with TwinCAT PLC library M-Bus
7.1 Benefits for the user
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
5
Page 6

TwinCAT
Application Note DK9322-0810-0036
TwinCAT, Building Automation
The function blocks are object-oriented and characterized by a self-contained, more or less complex function. The user
configures the input parameters through which the function block is adapted individually to its task within the associated
system.
Thanks to strongly object-oriented encapsulation of complex system functions within one function block, comprehensive
system programs can be set up with a few function blocks. The blocks are linked to each other via a small number of PLC
variables.
The status of all objects is indicated through a large number of different output variables at the function blocks. This simplifies
the connection of HMI and visualization systems.
For system operators this has the following advantages for system setup and operation:
– faster system program development
– faster parameterization and commissioning of the systems
– guarantee of a very large range of system functions at all times
– improved readability of programs (prerequisite for long-term maintainability and expandability of the systems)
– improved reusability of templates for systems or system components
– faster familiarization of personnel
– simple extension of existing systems
– better program documentation
Notice:
A link to an overview of all meter blocks (meters supported by the TwinCAT PLC M-Bus library) can be found at the end of
this document. Beckhoff can create new meter blocks: To this end, Beckhoff requires a sample device and an M-Bus protocol
description from the device manufacturer.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
6
Page 7

Application Note DK9322-0810-0036
Ethernet (BMS)
switch
CX8090
KL6781
KL6781 M-Bus master Terminal connected to Embedded PC:
– direct connection of M-Bus meters, no level converter required
– remote data acquisition, no access to leased properties required
– seamless integration into Ethernet-based building management
systems via Embedded PC
TwinCAT, Building Automation
TwinCAT
Fig. 4 Direct connection of M-Bus meters without level converter
8. Practical example
A typical area of application for M-Bus-based consumption data acquisition is in decentralized buildings. Individual production
areas within a factory site are equipped with separate acquisition points. A suitable media meter is integrated for each building
element. The data are collected in a control center and managed centrally. This provides the advantage that duplicate data
management is avoided and the data are archived at a central location.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
7
Page 8

Application Note DK9322-0810-0036
Building management
m³
kWh
m³
kWh
m³
kWh
m³
kWh
Ethernet
Consumption data acquisition in distributed buildings
BMS
TwinCAT, Building Automation
TwinCAT
Fig. 5 The building management system is the central switching point for all buildings that are networked with Ethernet.
Each building acts as a separate data acquisition unit: Via the Beckhoff Embedded PC with integrated Ethernet interface the
data can then be made available to a central building management system. This enables the local data to be available directly
in the individual systems as well as centrally. This principle significantly reduces the engineering effort and keeps the data
management transparent.
Another typical practical example is error-free meter reading at short notice when a change of tenants occurs, while
safeguarding the privacy of the tenants. Remote reading enables electronic data acquisition with minimum manpower
requirements (reduction of reading errors) and speedy further processing (compiling of statistics, invoicing, etc.).
– KL6781 M-Bus master terminal www.beckhoff.com/KL6781
– TwinCAT PLC Library M-Bus www.beckhoff.com/english/twincat/twincat_plc_m_bus.htm
– Documentation of M-Bus library at Beckhoff Information System
http://infosys.beckhoff.com/content/1033/tcplclibmbus/html/tcplclibmbus_einleitungvorwort.htm
– Overview of supported M-Bus counter
http://infosys.beckhoff.com/content/1033/tcplclibmbus/html/tckl6781_programmierung.htm
– Building Automation www.beckhoff.com/building
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
8
Page 9

Application Note DK9322-0810-0036
TwinCAT, Building Automation
TwinCAT
This publication contains statements about the suitability of our products for certain areas of application. These statements are based on typical features of our products. The examples shown in this publication are for demonstration purposes only. The information provided herein should not be regarded as specific operation characteristics. It is incumbent on the
customer to check and decide whether a product is suit-able for use in a particular application. We do not give any warranty that the source code which is made available with this
publication is complete or accurate. This publication may be changed at any time with-out prior notice. No liability is assumed for errors and/or omissions. Our products are described
in detail in our data sheets and documentations. Product-specific warnings and cautions must be observed. For the latest version of our data sheets and documentations please visit
our website (www.beckhoff.com).
© Beckhoff Automation GmbH, August 2010
The reproduction, distribution and utilisation of this document as well as the communication of its contents to others without express authorisation is prohibited. Offenders will be
held liable for the payment of damages. All rights reserved in the event of the grant of a patent, utility model or design.
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
9
 Loading...
Loading...