Page 1

I/O
Application Note DK9222-1209-0007
Measurement technology
Keywords
Energy measurement
Power factor
Energy analysis
EtherCAT Terminal
Bus Terminal
KL3403
EL3403
Consideration of the energy efficiency of a plant by
means of energy measurement
The measurement of energy consumption variables in the connected circuit is possible using the KL3403 Bus
Terminal and the EL3403 EtherCAT Terminal: the terminals directly output the effective values for voltage,
current and active power and total up the energy consumption internally; further parameters can be
calculated on the basis of the values determined.
Approach
Energy costs belong to the operating costs of a plant and are accounted for as overheads in lump sum shares to all cost
centres, since they cannot be attributed to any particular originator. In order to increase profits by reducing energy costs, the
costs must primarily be attributed to a particular consumer. This could similarly be entire plants or buildings or also individual
segments. If the consumption can be attributed, the optimisation of operating conditions is easier to implement and, in case of
doubt, their benefit also proven. By means of a transparent supply network, savings potentials can be specifically implemented
and the success of individual measures can also be observed in the long term. Furthermore, the financial expenditure for the
production of a certain lot size can be adopted into the cost calculation, since the energy throughput per production lot can be
determined as a result.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
1
Page 2
Application Note DK9222-1209-0007
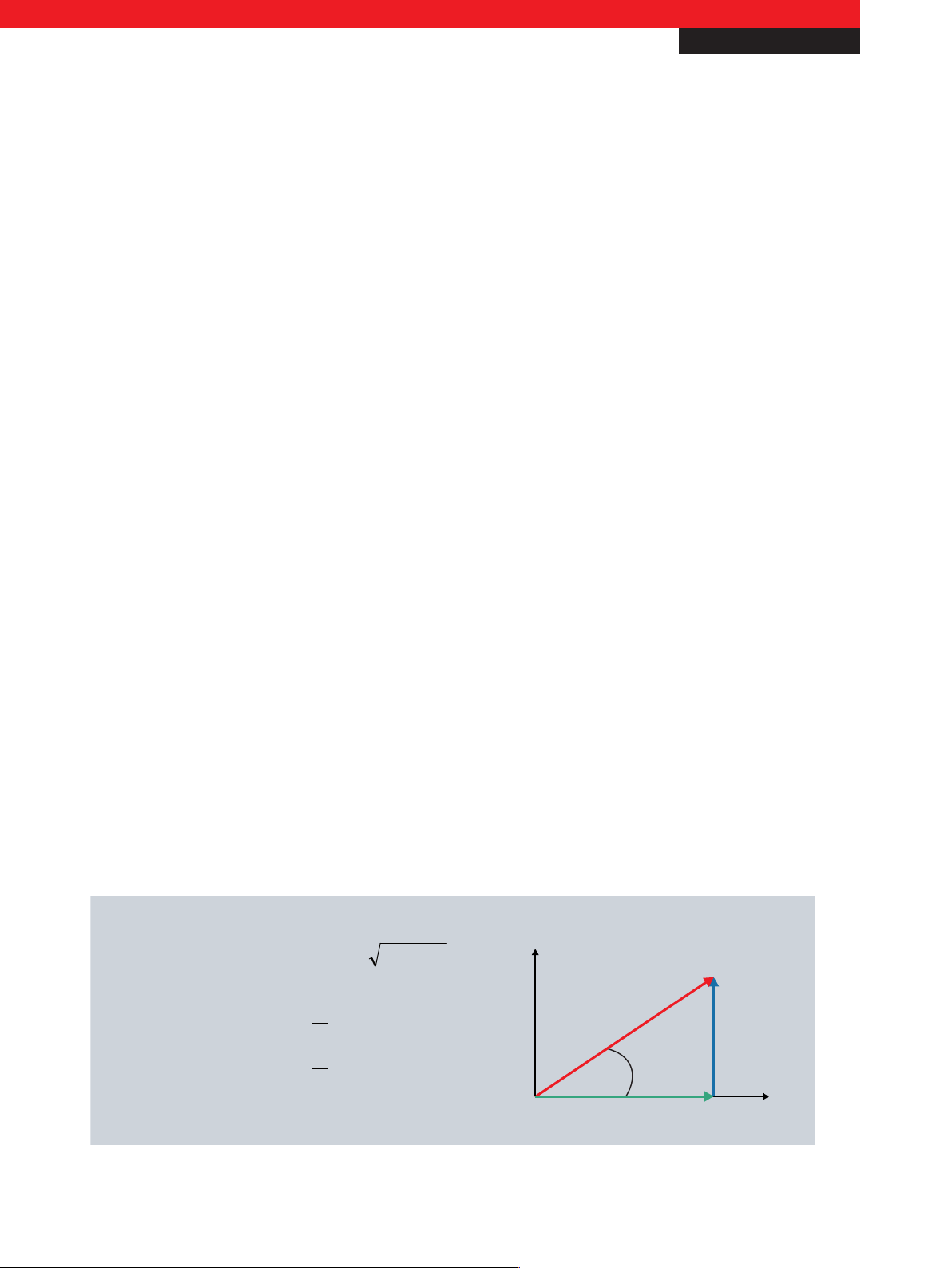
Active power
P
Apparent power
S
Reactive power
Q
Active power factor
cos φ
Reactive power factor
sin φ
Electric work
W
~ Energy consumption
= U * I * cos φ
= U
eff
* I
eff
= P2+Q2
= U * I * sin φ
=
=
= U * I * t
P
S
Q
S
Q
S
P
φ
Measurement technology
As a rule, the following are starting points that need to be addressed in order to reduce energy costs:
– reduction in electricity costs: total active energy obtained, reactive power costs and also costs for peak loads
– stabilisation of manufacturing processes and avoidance of production losses
– identification of ‘energy hogs’
– lowering of maintenance costs
– extension of the service lives of electronic and electrical equipment
– cost centre allocation
Both the EL3403 EtherCAT Terminal and the KL3403 Bus Terminal provide the hardware for the analysis and localisation of
I/O
energy consumption. In addition to the important data from a three-phase supply network, they also record any energy peaks
occurring over a selectable time period and total up the energy consumption internally, so that different modes of operation or
shifted peak usage times can be judged even after just one production cycle. In addition to a general consideration of energy
efficiency, the quantity of energy used for the production of a particular lot size can be determined in order to adapt the price
per unit accordingly or to optimise manufacturing costs.
Function of the KL3403 Bus Terminal
The KL3403 Bus Terminal enables analysis via the fieldbus of the energy consumption of the connected plant or building
segment or, quite specifically, the key energy data of individual consumers. The voltages of the three phases and neutral can be
measured by directly wiring the individual cables to the terminal. In order to measure current, the current of the three phases
L1, L2 and L3 is fed in via simple current transformers. The measured current and voltage values are output as effective values.
From the effective values for voltage (U) and current (I), the KL3403 calculates the effective power (P), the energy consumption
(W) and the power factor (cos φ) for each phase. The apparent power (S) and the phase shift angle (φ) can be derived from
these values.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Fig. 1: Calculation of the important energy consumption variables
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
2
Page 3

Application Note DK9222-1209-0007
u i
t
a)
u
1
t
b)
t
c)
u
1
u
1
Measurement
interval 2T
i
i
i
u
t
ϕ
i
t
P
S
P
Measurement technology
I/O
Fig. 2: Left: typical current-voltage curve, right: types of current that can be measured
The following types of current can be measured with the KL3403: current and voltage curve for phase control (a), pulse
duration control (b) and burst firing control (c); the measurement interval is set analogous to the control interval.
Integration of the KL3403 Bus Terminal
Internal pre-processing of the KL3403 provides rms values in the process image, without requiring high computing capacity
on the controller. The terminal outputs the measurement data in a 3 x 3-byte block, i.e. three bytes for each phase. Two bytes
per phase are pure process data, while one byte transmits the different status bits. The measured total energy performance is
written to the terminal’s internal non-volatile memory in a 15-minute cycle, so that these data are also available after a loss of
power. The recorded measurement values are transmitted to the controller via an arbitrary fieldbus (integration of the terminal
via bus coupler) and are available to the higher-level control system (BDE, ERP or the like) for continuous energy monitoring. In
order to achieve fast, cost-optimised and reliable communication of the energy data, the terminal can be integrated in existing
network architectures via different bus couplers.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
3
Page 4

Application Note DK9222-1209-0007
M
3~
230 V AC, 50 Hz
L1
L2
L3
N
PE
Etherne t TCP/IP
Fipio
Drive
Y-axis
Measurement technology
I/O
Fig. 3: Integration in any fieldbus environment as Bus Terminal or EtherCAT Terminal
Differences between EL3403 and KL3403
In principle, the EL3403 EtherCAT Terminal has the same range of functions as the KL3403 Bus Terminal, but is optimised for
measurements in the 50/60 Hz mains network. Significant differences are briefly listed here; further information and specific
details on the respective terminals can be taken from the documentation at www.beckhoff.com. EtherCAT Terminals are
integrated via EtherCAT Couplers, Bus Terminals via Bus Couplers.
Unlike the KL3403, the value for reactive power is also calculated internally in the EL3403. The energy consumption is totalled
up per sign, since different tariffs often apply to drawing out and feeding in.
As opposed to the KL3403, the EL3403 offers a considerably higher measurement value resolution. The standard version of the
KL3403 achieves a measurement value resolution of 1 mA, whereas the EL3403 enables a resolution of down to 1 µA. Both
values have a tolerance of 0.5 % FS (see documentation for details and further terminal variants). The EL3403 uses EtherCAT
as the transmission medium with a high data transmission rate, with which it is possible to read out all essential measurement
values in parallel if need be.
The EL3403’s measurement range for frequency measurements is narrower, but considerably more accurate. However, the
KL3403 can also be used for DC measurements. The measurement cycle is also optimised to the 50/60 Hz mains network in the
case of the EL3403: the measurement range automatically snaps to one period of the mains frequency. A multiple of the period
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
4
Page 5

I/O
– 3-phase power measurement terminal www.beckhoff.com/KL3403
– 3-phase power measurement EtherCAT Terminal www.beckhoff.com/EL3403
– Bus Terminal www.beckhoff.com/BusTerminal
– EtherCAT Terminal www.beckhoff.com/EtherCAT-Terminal
– Documentations www.beckhoff.com/documentations
Application Note DK9222-1209-0007
Measurement technology
can also be selected.
Further details on technology and configuration can be taken from the documentation. Program examples for the use of the
KL3403 in combination with other controllers are available on request.
This publication contains statements about the suitability of our products for certain areas of application. These statements are based on typical features of our products. The examples shown in this publication are for demonstration purposes only. The information provided herein should not be regarded as specific operation characteristics. It is incumbent on the
customer to check and decide whether a product is suit-able for use in a particular application. We do not give any warranty that the source code which is made available with this
publication is complete or accurate. This publication may be changed at any time with-out prior notice. No liability is assumed for errors and/or omissions. Our products are described
in detail in our data sheets and documentations. Product-specific warnings and cautions must be observed. For the latest version of our data sheets and documentations please visit
our website (www.beckhoff.com).
© Beckhoff Automation GmbH, December 2009
The reproduction, distribution and utilisation of this document as well as the communication of its contents to others without express authorisation is prohibited. Offenders will be
held liable for the payment of damages. All rights reserved in the event of the grant of a patent, utility model or design.
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
5
 Loading...
Loading...