Page 1

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Fixed Dome Network Camera
User’s Manual
Page 2
About this Document
This manual is intended for administrators and users of the AXIS 209FD/FD-R
Network Camera, and is applicable for software release 4.47 and later. It
includes instructions for using and managing the camera on your network.
Previous experience of networking will be of use when using this product.
Some knowledge of UNIX or Linux-based systems may also be beneficial, for
developing shell scripts and applications. Later versions of this document will
be posted to the Axis Website, as required. See also the product’s online help,
available via the Web-based interface.
Safety Notices Used In This Manual
Caution! - Indicates a potential hazard that can damage the product.
Important! - Indicates a hazard that can seriously impair operation.
Do not proceed beyond any of the above notices until you have fully
understood the implications.
Intellectual Property Rights
Axis AB has intellectual property rights relating to technology embodied in
the product described in this document. In particular, and without limitation,
these intellectual property rights may include one or more of the patents listed
at http://www.axis.com/patent.htm and one or more additional patents or
pending patent applications in the US and other countries.
This product contains licen
“About” in the product’s user interface for more information.
This product contains source code copyright
terms of Apple Public Source License 2.0 (see
http://www.opensource.apple.com/apsl/).
The source code is available from:
http://devel
oper.apple.com/darwin/projects/bonjour/
Legal Considerations
Video and audio surveillance can be prohibited by laws that vary from country
to country. Check the laws in your local region before using this product for
surveillance purposes.
This product includes one (1) MPEG-4 decoder license. To purchase further
licenses, contact your reseller.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful in
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures: re-orient or relocate the receiving antenna. Increase the
separation between the equipment and receiver. Connect the equipment to an
outlet on a different circuit to the receiver. Consult your dealer or an
experienced radio/TV technician for help. Shielded (STP) network cables must
be used with this unit to ensure compliance with EMC standards.
USA - This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B computing device pursuant to Subpart B of Part 15 of FCC rules,
which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference
when operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the user at his/her
own expense will be required to take whatever measures may be required to
correct the interference.
Canada - This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Europe - This equipment is not connected to immunity related functions
in motor vehicles. It fulfills the requirements of the EM
account the automotive environment. This digital equipment fulfills the
requirements for radiated emission according to limit B of EN55022, and the
requirements for immunity according to EN55024 residential, commercial, and
light industry.
Japan - This is a class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary
Control Council for Interference from Information Technology Equipment
(VCCI). If this is used near a radio or television receiver in a domestic
environment, it may cause radio interference. Install and use the equipment
AXIS COMMUNICATIONS
<Product Name> Quick User’s Guide
according to the instruction manual.
Australia - This electronic device meets the requirements of the Radio
communications (Electromagnetic Compatibility) Standard AS/NZS CISPR22.
Equipment Modifications
This equipment must be installed and used in strict accordance with the
instructions given in the user documentation. This equipment contains no
user-serviceable components. Unauthorized equipment changes or
modifications will invalidate all applicable regulatory certifications and
approvals.
Liability
Every care has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Please inform
your local Axis office of any inaccuracies or omissions. Axis Communications
AB cannot be held responsible for any technical or typographical errors and
reserves the right to make changes to the product and manuals without prior
notice. Axis Communications AB makes no warranty of any kind with regard
to the material contained within this document, including, but not limited to,
the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose.
Axis Communications AB shall not be liable nor responsible for incidental or
sed third-party software. See the menu item
Apple Computer, Inc., under the
terference to radio or television
C directive taking into
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance or use
of this material.
Trademark Acknowledgments
Apple, Boa, Bonjour, Ethernet, Internet Explorer, Linux, Microsoft, Mozilla,
Netscape Navigator, OS/2, Real, QuickTime, UNIX, Windows, WWW are
registered trademarks of the respective holders. Java and all Java-based
trademarks and logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun
Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and other countries. Axis
Communications AB is independent of Sun Microsystems Inc.
TM
is a certification mark of the UPnPTM Implementers Corporation.
UPnP
Support
Should you require any technical assistance, please contact your Axis reseller.
If your questions cannot be answered immediately, your reseller will forward
your queries through the appropriate channels to ensure a rapid response. If
you are connected to the Internet, you can:
• download user documentation and firm
• find answers to resolved problems in the FAQ database. Search by product,
category, or phrases
• report problems to Axis support by logging in to your private support area
• visit Axis Support at www.axis.com/techsup/
ware updates
WEEE Directive
The European Union has enacted a Directive 2002/96/EC on Waste
Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE Directive). This directive
is applicable in the European Union member states.
The WEEE marking on this prod
indicates that the product must not be disposed of together with
household waste. To prevent possible harm to human health and/or the
environment, the product must be disposed of in an approved and
environmentally safe recycling process. For further information on how to
dispose of this product correctly, contact the product supplier, or the local
authority responsible for waste disposal in your area.
Business users should contact the product supplier
dispose of this product correctly. This product should not be mixed with other
commercial waste.
AXIS 209FD User’s Manual Rev 4.0
September 2008
Part No: 32983
Copyright© Axis Communications AB, 2007 - 2008
uct (see right) or its documentation
for information on how to
Page 3

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Contents
Product overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Key features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Accessing the Camera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Access from a browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
AXIS Media Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Setting the root password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Accessing the camera from the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
The Live View page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Video Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
How to stream MPEG-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
MPEG-4 clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Motion JPEG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Configuring the camera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Accessing the Setup link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Video & Image . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Image . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Overlay/Mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Advanced . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Live View Config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
HTML Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
External Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Sequence Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Event Config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Event Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Event Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Camera Tampering (AXIS 209 FD-R/FD-R M12) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Motion Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
System Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Date & Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
LED Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Advanced
Resetting to the factory default settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Unit connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
General performance considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Bandwidth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Glossary of Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
3
Page 4

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Product overview
Description
The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 Fixed Dome Network Camera is a high-performance, progressive-scan
camera with a discreet compact casing that effectively protects against tampering.
4
The AXIS 209FD is ideally suited for office and business locatio
209FD-R/FD-R M12 allows it to be used in humid environments such as professional in-vehicle
surveillance.
Multi-window motion detection and simultaneous Motion
on image quality and bandwidth efficiency. The frame rate can be up to 30 fps in VGA.
Multi-level password protection, IP-address
over Ethernet reduces cabling requirements and enables centralized power back up. Supported by the
industry's largest base of surveillance applications, the AXIS 209FD is the perfect solution for securing
shops, hotel receptions and corridors, while the AXIS 209FD-R/FD-R M12 is the perfect solution for
securing buses, trains, trams, and other types of transportation vehicles.
filtering and HTTPS encryption ensure network security. Power
ns, whereas the product casing of the AXIS
JPEG and MPEG-4 allow for optimization both
Key features
• Discreet and compact design, effectively protecting against tampering/vandalisation
• The product casing for the AXIS 209FD-R/FD-R M12
environments such as mass transit vehicles.
• Superior image quality with progressive scan and 30 frames per
• Simultaneous Motion JPEG and MPEG-4 for optimized quality and bandwidth
• Power over Ethernet for reduced cabling and
• Multi-window motion detection with alarm image buffering
consolidated power
is ruggedized so it can be used in humid
second in VGA
Page 5
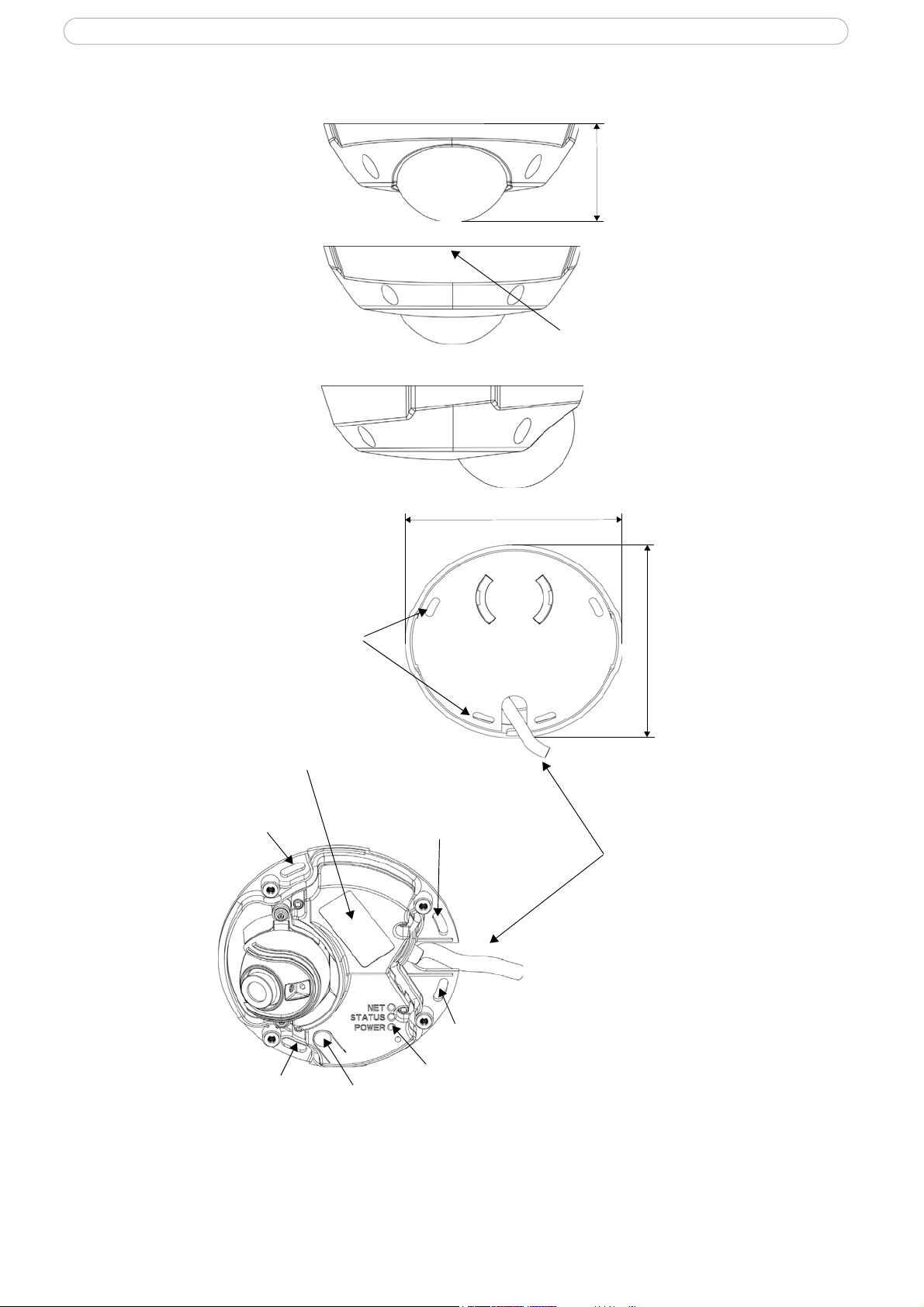
Overview
Dimensions
Diameter 1 = 102mm (4.02”), Diameter 2 = 100mm (3.94”)
Height = 39mm (1.54”)
Weight = 0.18 kg (0.40lb)
Front view
Rear view
Side view
Position of rear cable
exit (optional)
Base plate
Network cable with
connector
Screw holes
∅102mm
∅100mm
39mm
Indicator LEDs
Screw hole
Screw hole
Screw hole
Product ID & Serial
number (S/N) label
Screw hole
Control button
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
5
Page 6

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Control button - Press this button to install using the AXIS Internet Dynamic DNS Service, or to restore the
factory default settings, as described in Resetting to the factory default settings, on p
age 31.
LED Indicators
LED Color Description
Network Green Steady for connection to 100 Mbit/s network. Fla
Amber Steady for connection to 10 Mbit/s netw
Unlit No connection.
Status Green Shows steady green for normal operation.
e Status LED can be configured to be unlit during normal operation, or to flash
Note: Th
only when the camera is accessed. See the online help files for more information. Go to
Setup > System Options > LED settings
Amber Steady during startup, reset to factory default
Red Slow flash for failed upgrade.
Power Green Normal operation.
Amber Flashes green/amber during firmware upgrade.
shes for network activity.
ork. Flashes for network activity.
or when restoring settings.
6
Page 7
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Accessing the Camera
The network camera must be installed first before you can access it. To install the camera please see the
installation guide supplied with the product.
7
The camera can be used with most operating
systems and browsers. The recommended browser is Microsoft
Internet Explorer with Windows, Safari with Macintosh and Mozilla with other operating systems.
Notes:
• To view streaming video in Microsoft Internet Explorer, set your browser to allow ActiveX controls and allow the AXIS Media
Control (“AXIS Media Control” (page -7)) to be installed on your computer.
• QuickTimeTM and Real PlayerTM are also supported for viewing streaming MPEG-4 video and audio.
• If your computer restricts the use of additional software components, it is also possible to use the Firefox browser, which does not
require extra components.
• The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 includes one (1) decoder license for viewing MPEG-4 video streams. This is automatically
installed with AMC. The administrator can disable the installation of the MPEG-4 decoder, to prevent unlicensed copies from
being installed. Further licenses are available from your Axis dealer.
Access from a browser
1. Start a browser (Internet Explorer, Firefox)
2. Enter the IP address or host name of the camera in the
Location/Address field of your browser.
To access the camera from a Macintosh computer (Mac OSX),
select the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 from the drop-down list.
3. If this is the first time the camera is accessed, see Setting the root password, on page 8. Otherwise
enter
your user name and password, as set by the administrator.
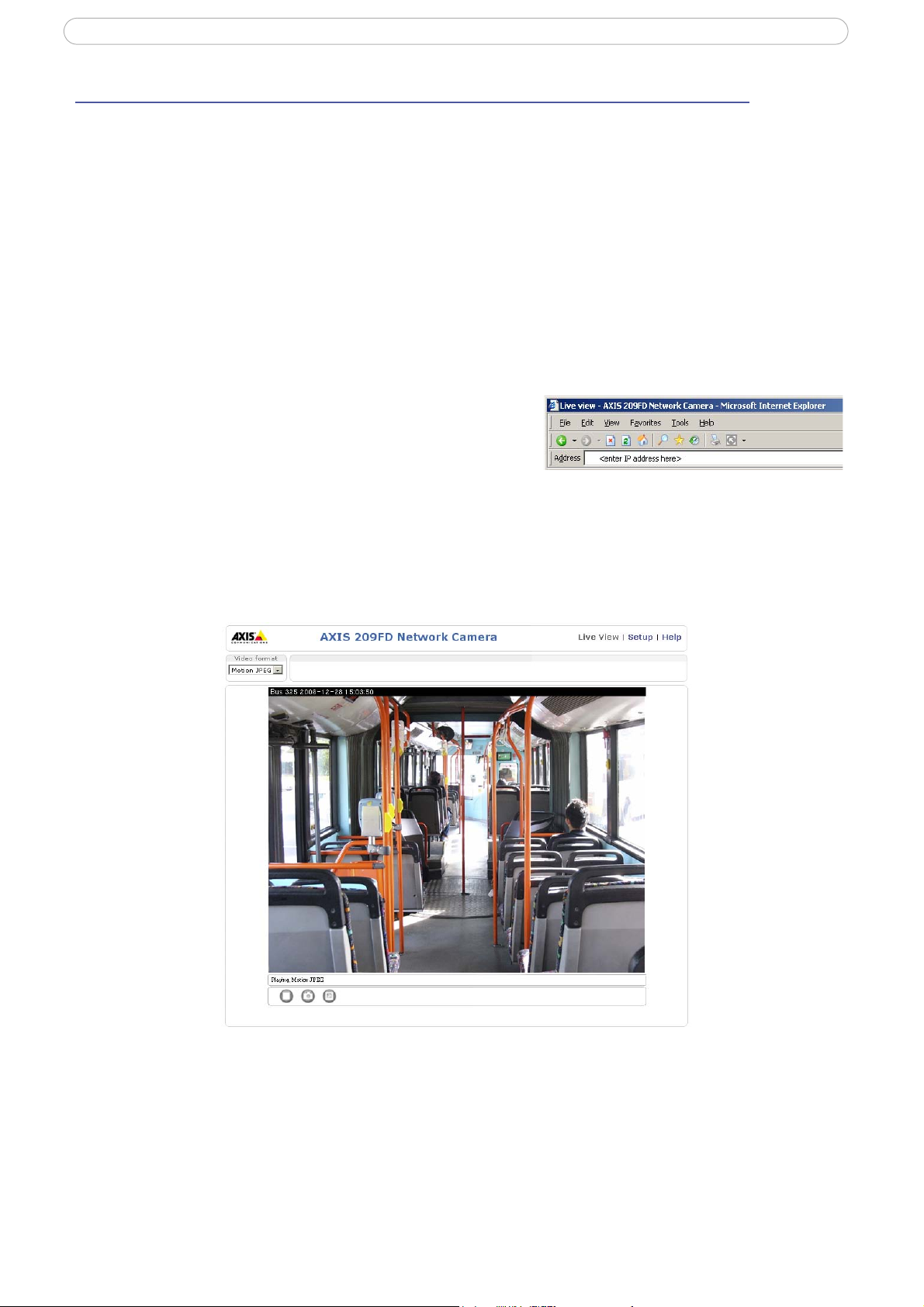
4. The camera’s Live View page is now displayed in your browser.
simply click on the Bonjour tab and
Note:
The layout of the Live View page may have been customized to specific requirements. Consequently, some of the examples and
functions featured here may differ from those displayed on your own Live View page.
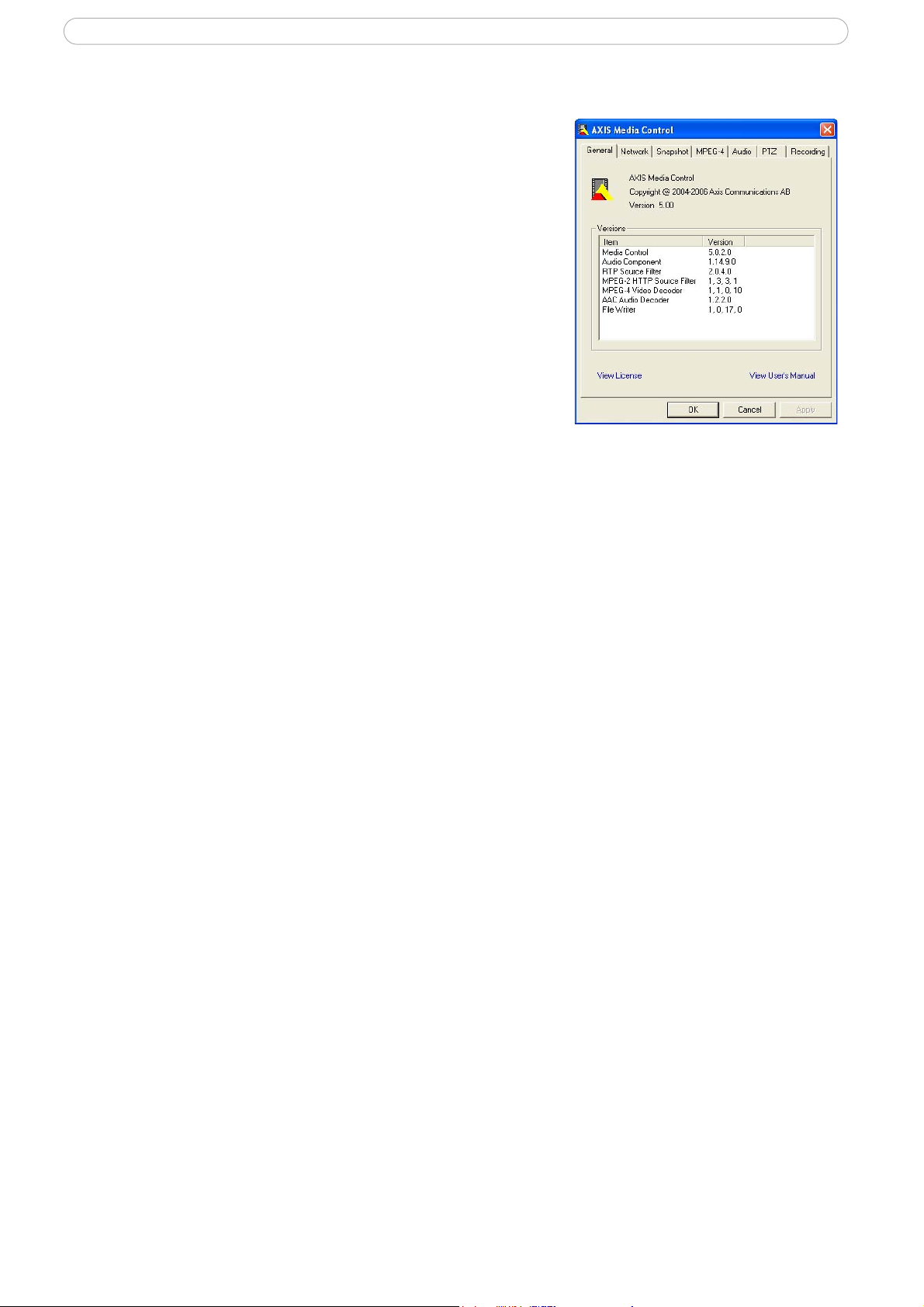
AXIS Media Control
The AXIS Media Control (AMC) is installed automatically the first time the camera is accessed
from Microsoft Internet Explorer. The AMC control panel is used to configure various video settings, and can be opened by right-clicking on the video image in the Live View web page. Please
see the readme file included in the tool for more information.
Page 8
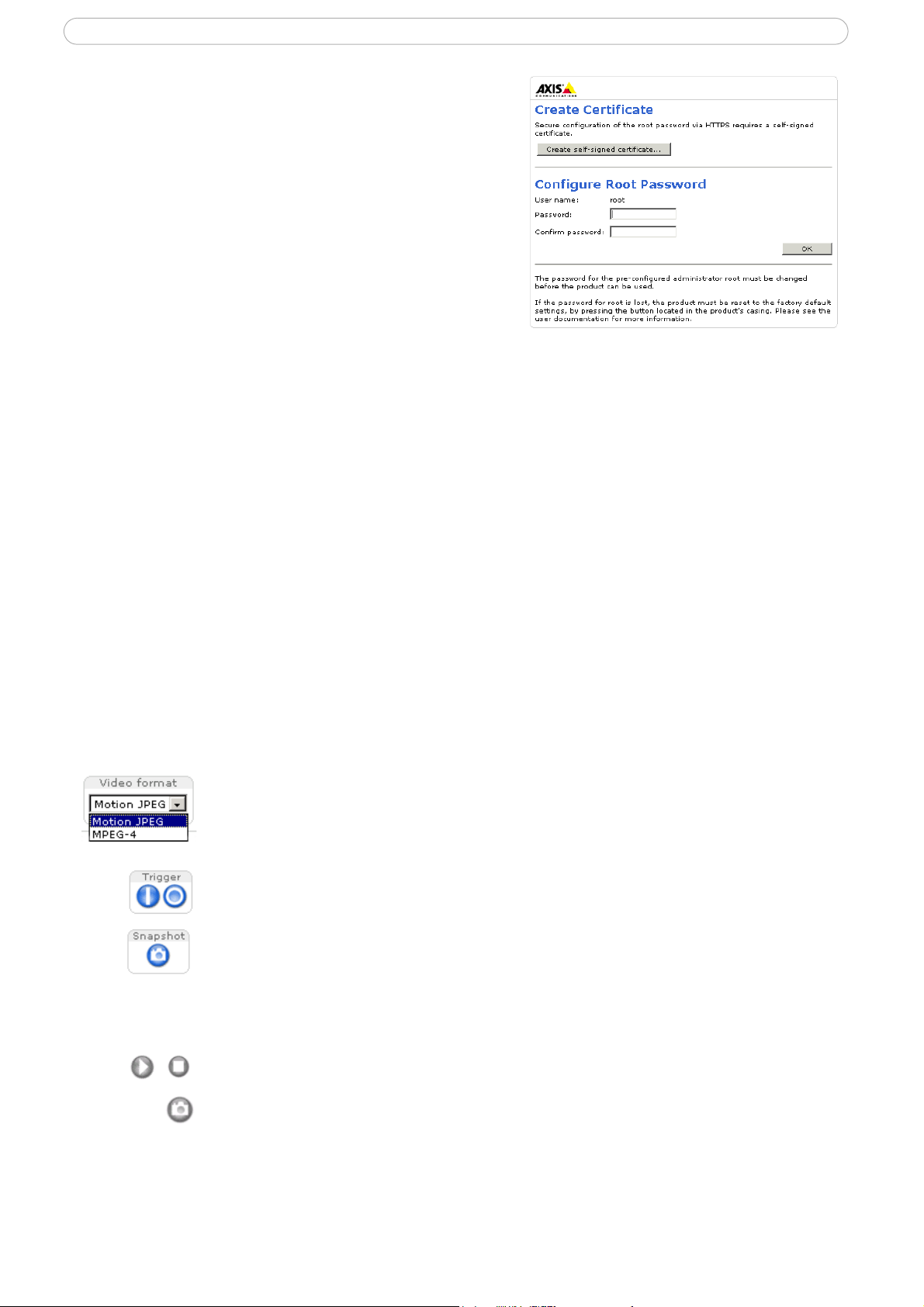
Setting the root password
1. When accessing the camera for the first time, the
‘Configure Root Password’ dialog appears.
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
8
Note:
Before you enter your password at this point, you can secure configuration of the root password via HTTPS by creating a self-signed certificate. To do so, click the Create self-signed certificate... button in the
Create Certificate window, and then proceed as follows.
2. Enter a password and then re-enter, to confirm the
spelling. Click OK.
3. The ‘Enter Network Password’ dialog appears. Enter
the User name: root
Note:
The default administrator user name root is permanent and cannot be
deleted or altered.
4. Enter the password as set in step 2 above, and click OK. If the password is lost, the camera must be
reset to the factory default settings. See Resetting to the factory default settings, on page 31.
5. If required, click Yes to install the AXIS Media Control (AMC). You will need administrator rights
on the computer to do this.
Accessing the camera from the Internet
Once installed, the camera is accessible on your local network (LAN). To access the camera from the Internet
you must configure your broadband router to allow incoming data traffic to the camera. To do this, enable
the NAT-traversal feature, which will attempt to automatically configure the router to allow access to the
camera. This is enabled from Setup > System Options > Network > TCP/IP Advanced.
For more information, please see NAT tr
Internet Dynamic DNS Service at www.axiscam.net or, for
aversal (port mapping) for IPv4, on page 28. See also the AXIS
Technical notes on this and other topics, visit the
Axis Support Web at www.axis.com/techsup
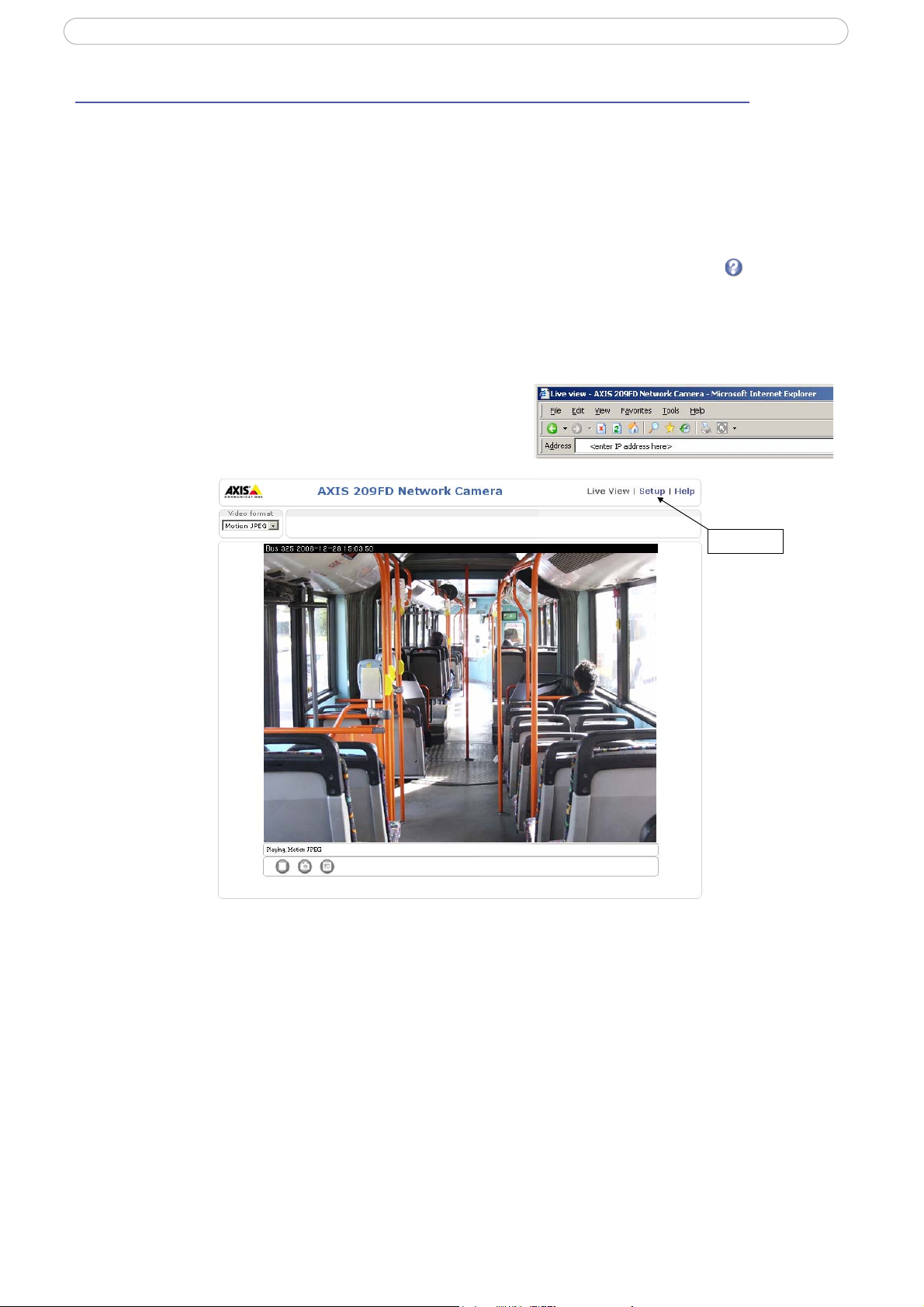
The Live View page
Depending on whether or not the Live View page has been customized, the buttons described below may or
may not be visible.
The Video format drop-d
temporarily changed.
The manual Trigger button can trigger an event
configured from Setup > Live View Config > Layout.
The Snapsh
ot button saves a snapshot of the video image currently being displayed.
Right-click on the video image to save it in JPEG format on your computer. This button
is primarily intended for use when the AMC viewer toolbar is not available.
The AMC (AXIS Medi
a Control) viewer toolbar is available in Microsoft Internet Explorer only. It
displays the following buttons:
The Play/Stop button starts and
own list allows the video format on the Live View page to be
directly from the Live View page. This is
stops the live video stream.
The Snapshot
button saves a snapshot of the video image currently being displayed. The
Snapshot function and the target directory for saving snapshots can be configured from
the AMC Control Applet in the Windows Control Panel (Internet Explorer only).
Page 9

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Click the View Full Screen button to make the video image fill the entire screen area. No
other windows will be visible. Press Esc (Escape) on the computer keyboard to exit full
screen.
Click the Record button to
MPEG-4).
start an MPEG-4 recording (only available when viewing
9
Page 10
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Video Streams
The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 provides several different image and video stream formats. The type to
use depends on your requirements and on the properties of your network.
10
The Live View page provides access to MPEG-4 and Motion
JPEG video streams, as well as to single JPEG
images. Other applications and clients can also access these video streams/images directly, without going
via the Live View page.
How to stream MPEG-4
This video compression standard makes good use of bandwidth, and can provide DVD-quality video streams
at less than 1 Mbit/s. Note that the image settings of the MPEG-4 stream are the same for all clients.
Deciding on the combination of protocols and
on the properties of your network. The options available in AMC (see page 11) are:
Unicast RTP This unicast method (RTP over UDP)
should be your first consideration for live
unicast video, especially when it is
important to always have an up-to-date
video stream, even if some images are
dropped.
RTP over RTSP This unicast method (RTP tunneled over
RTSP) is useful
configure firewalls to allow RTSP traffic.
RTP over RTSP over HTTP This unicast method can be used to
traverse
monly configured to allow the HTTP protocol, thus allowing RTP to be tunneled.
as it is relatively simple to
firewalls. Firewalls are com-
methods to use depends on your viewing requirements, and
Unicasting is used for video-on-demand bro
traffic on the network until a client connects and requests the stream.
Note that there is a maximum of 10
adcasting, so that there is no video
simultaneous unicast connections.
Multicast RTP This method (RTP over UDP) should be used for live multicast video. The
AMC will negotiate with the camera to determine ex
images are dropped.
Multicasting provides the most efficient use
multicast broadcast cannot however, pass a network router unless the router is configured to allow this. It is thus not possible
to multicast over the Internet, for example.
Note also that all multicast viewers count
of bandwidth when there are large numbers of clients viewing simultaneously. A
as one unicast viewer in the maximum total of 10 simultaneous connections.
actly which transport protocol to use in the order listed
video stream is always up-to-date, even if some
above. This order can be changed and the options disabled, to suit any specific requirements.
Important!
MPEG-4 is licensed technology. The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 includes
one viewing client
license. Installing additional unlicensed copies of the viewing client is prohibited. To purchase additional licenses, contact your Axis reseller.
Page 11
MPEG-4 clients
AXIS Media Control (AMC)
The recommended method of accessing live video (MPEG-4 and
Motion
AXIS Media Control (AMC) in Microsoft Internet Explorer in
Windows.
The AMC control panel can be used to configure various video and
a
udio settings. Please see the readme file included in the tool for
more information.
The AMC control panel is automatically installed on first use, after
which i
Open the AMC Control Panel from:
• Windows Control Panel (from the Start menu)
• Alternatively, right-click the video image in Internet
QuickTime™ & Real Player™
JPEG) from the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 is to use the
t can be configured.
Explorer
and click Settings in the menu.
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
11
To access the video stream from e.g. QuickT
ime™ or Real Player™ the following path can be used:
rtsp://<ip>/mpeg4/media.amp
Notes:
• The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 supports QuickTime 6.5.1 (or later) and Real Player 10.5 (or later)
• QuickTime adds latency to the video and audio stream (up to 3 seconds)
• It may be possible to use other players to view the MPEG-4 stream using the paths above, although this is not guaranteed by Axis
• <ip> = IP address
Motion JPEG
This format uses standard JPEG still images for the video stream. These images are then displayed and
updated at a rate sufficient to create a stream that shows constantly updated motion.
The Motion JPEG stream uses considerable amounts of bandwidth, but provides excellent image quality an
access to every individual image contained in the stream. The recommended method of accessing Motion
JPEG live video from the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 is to use the AXIS Media Control (AMC) in
Microsoft Internet Explorer in Windows.
Note also that multiple clients accessing Motion
Alternative methods of accessing the video stream
Video/images from the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 can
• Motion JPEG server push (if supported
HTTP connection to the browser and sends data as and when required, for as long as required.
• Still JPEG images in a browser. Enter e.g. the path: http://<ip>/axis-cgi/jpg/image.cgi?resol
tion=320x240
• Windows Media Player. This requires AMC and the MPEG-4 viewing clien
can be used are listed below in the order of preference.
• Unicast via RTP: axrtpu://<ip>/mpeg4/media.amp
• Unicast via RTSP: axrtsp://<ip>/mpeg4/media.amp
• Unicast via RTSP, tunneled via HTTP: axrtsphttp://<ip>/mpeg4/media.amp
• Unicast via RTSP, tunneled via HTTPS: axrtsphttps://<ip>/mpeg4/media.amp
• Multicast: axrtpm://<ip>/mpeg4/media.amp
Note:
<ip> = IP address
JPEG streams can use different image settings.
also be accessed in the following ways:
by the client, example, Firefox). This option maintains an open
u-
t to be installed. The paths that
d
Page 12
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Setup link
Configuring the camera
This section describes how to configure the camera, and is intended for product Administrators, who have
unrestricted access to all the configuration menus; and Operators, who have access to the settings for Video
& Image, Audio, Live View Config and Event Configuration.
12
The camera is configured from the Setup lin
Specifications, on page
The descriptions below show examples of the features
details of each setting, please refer to the online help available from the setup tools. Click to access the
online help.
37).
k from a browser. (For supported browsers, see Technical
available in the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12. For
Accessing the Setup link
Follow the instructions below to access the Setup link from a browser.
1. Start your browser and enter the IP
name of the camera in the location/address field.
2. The Live View page is now displayed. Click Setup to
view more menu options.
address or host
Page 13
Video & Image
Text, date and
time overlay
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
13
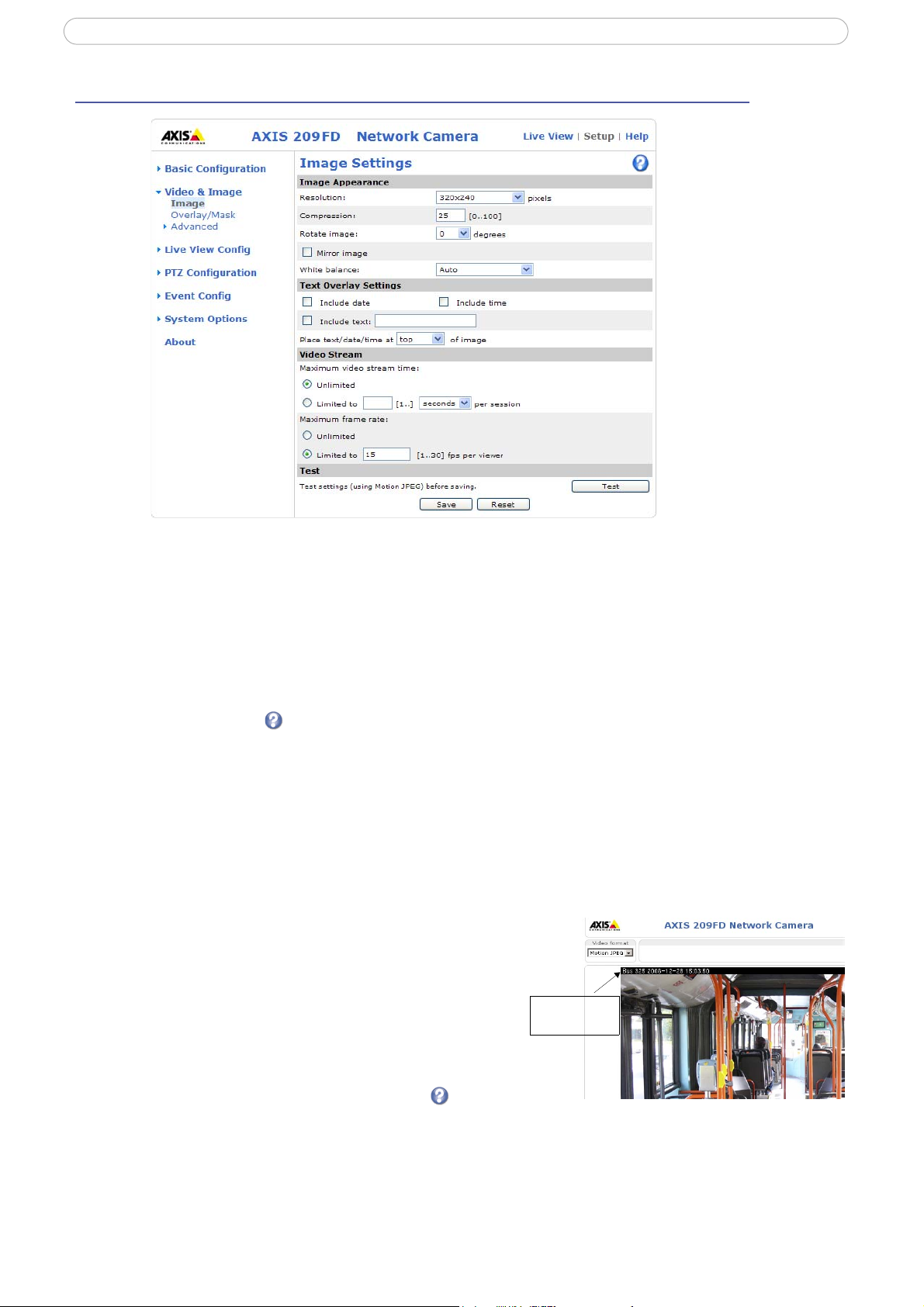
Image
Use these settings to change the image as required. The image can be rotated, the image resolution and
compression be adjusted, and the white balance be changed. The image can also be mirrored to change the
perspective.
The configuration of the video image will affect the camera’s
used and on the available bandwidth. Setting higher resolution and lower compression improves video
image quality, but increases the amount of bandwidth required.
Please see the online help for further information on these settings.
Mirroring
Mirroring is the horizontal flipping of an image, that
affect performance.
Mirroring is a useful function when you need a direct
phones. A person looks into the camera and a direct view of the face is displayed. The mirror settings should
be defined before we define the parameters for privacy masks and motion detection.
gives you another image perspective. This does not
view of the image - for example, in ATMs and door
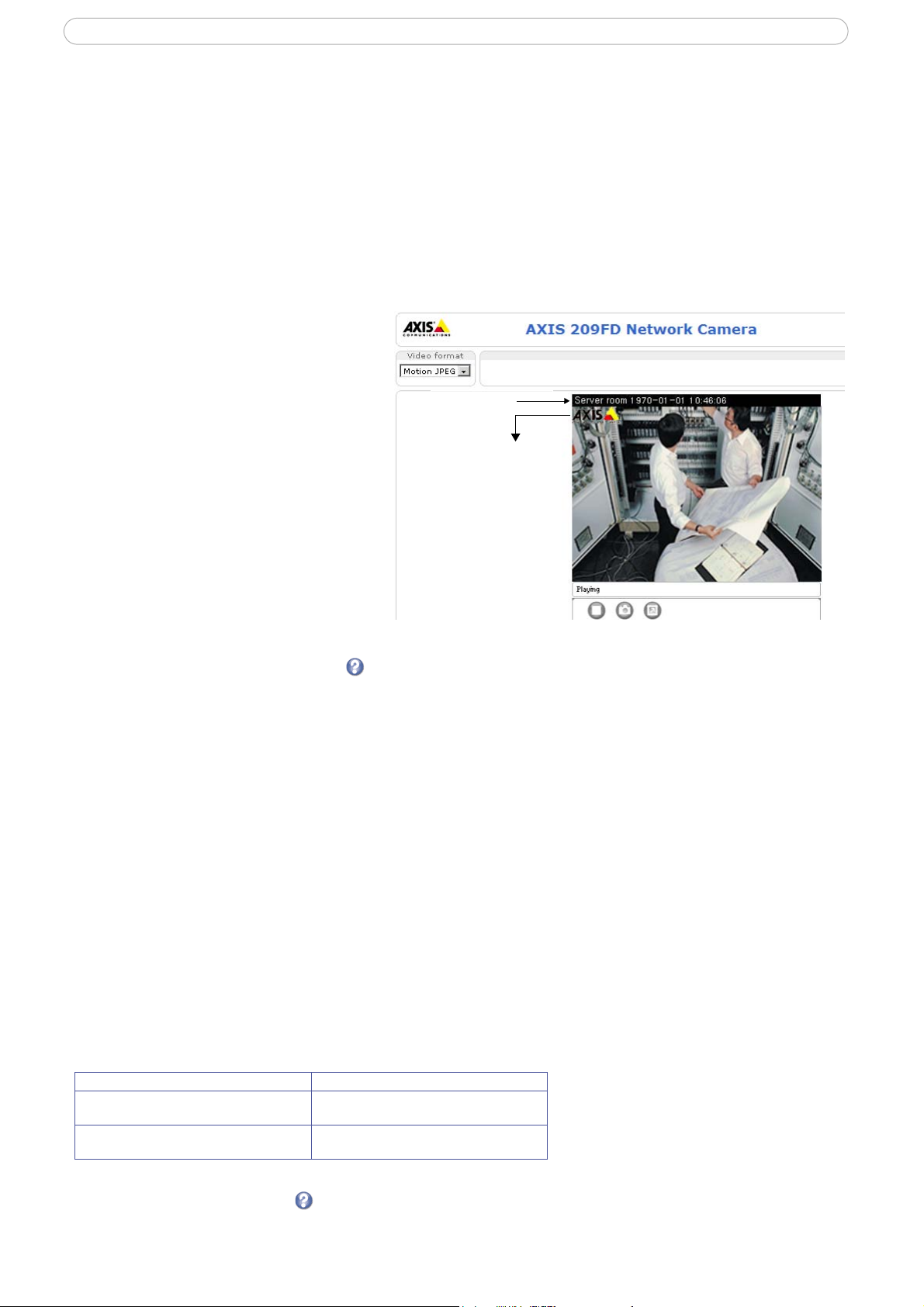
Text Overlay Settings
The date, time, and user defined text can be included on one
line, either on the top or bottom of the video image.
overall performance, depending on how it is
It is also possible to set how the text and text background are
displayed.
and the text background can also be set to black, white,
semi-transparent, or transparent.
Please see the online help for further information .
You can set the text to be either black or white,
Page 14
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Text, date and
time overlays
Overlay image
Video Stream
Define the maximum video stream time per session in seconds, minutes or hours. When the set time has
expired, a new stream can be started by refreshing the page in the browser. For unlimited video stream time,
select the Unlimited radio button option. Note that the maximum video stream time does not apply to
clients connecting via multicast.
14
The fram
e rate allowed to each viewer can also be limited to avoid bandwidth problems on the network. To
allow the highest available frame rate, select the Unlimited radio button option.
For a preview of the image click Test.
When satisfied with the settings, click Save. Note that the preview
image will be in JPEG format, even though the settings are valid both for Motion JPEG and MPEG-4.
Overlay/Mask
Overlay/Mask Settings
When using an image overlay, select
from the following options:
ploaded image as overlay - usually
• U
used to provide extra information in
the video image.
• Configurable a
- up to three black areas are used to
conceal parts of the video image.
The difference between an overlay and a
privacy mask
cannot be bypassed by accessing the
video stream with the help of the AXIS
HTTP API, whereas an overlay can. After you choose one of these options further options are displayed for
the selected type. See the online help for further information.
reas as privacy masks
is that a privacy mask
Upload and use an overlay/mask
To upload an overlay image/privacy mask to the camera:
1. Select the type of overlay to use in Overlay/Mask Type.
In the Upload own image field, click the Browse button and locate the image file on your
2.
computer or server.
3. Click the Upload button and follow the on-screen instructions.
To use an already uploaded image:
1. Select an uploaded image from the Use image drop-down list.
2.
Place the image at the required location by entering the x and y coordinates (0,0 being the upper
left corner).
3. Click Save.
Overlay image requirements
Image Formats Image Size
• Windows 24-bit BMP (full color) The height and width of the overlay image in
• Windows 4-bit BMP (16 colors) The height and width of the overlay image in
must be divisible by 4.
pixels
must be divisible by 16.
pixels
There are a number of limitations when using overlay images, such as the size and positioning of images.
Please refer to the online help for more information.
Page 15

Advanced
Camera
This page contains settings for fine-tuning the video image.
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
15
Lighting Conditions
To compensate for the lighting Conditions, the Color level, Brightness, Sharpness, and the exposure
control can be adjusted.
Low Light Behavior
Exposure priority defines the balance between image quality and the frame rate. Higher image quality may
reduce frame rate and increase motion blur. A prioritized frame rate may instead increase image noise.
Depending on requirements, use this to prioritize the image quality or the frame rate.
Please refer to the online help for more information .
MPEG-4
These are the tools for adjusting the MPEG-4 settings and controlling the video bit rate.
Page 16

GOV Settings
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
16
The GOV structure describes the composition of the MPEG-4 video stream. Se
value saves considerably on bandwidth. The Cyclic refresh parameter gives a smoother bit rate and can be
useful if bandwidth is limited.
Bit Rate Control
Limiting the maximum bit rate is a good way of control
stream. Leaving the Maximum bit rate as unlimited will provide consistently good image quality, but at the
expense of increased bandwidth usage whenever there is more activity in the image. Limiting the bit rate to
a defined value will prevent excessive bandwidth usage, but images will be lost when the limit is exceeded.
Note that a maximum bit rate can be used for both
The bit rate type can be set as Variable Bit
rate according to the images' complexity, thus using a lot of bandwidth for a lot of activity in the image
and less for lower activity in the monitored area.
CBR allows you to set a fixed Target bit rate that
which will not change whatever happens in the image.
As the bit rate would usually need to increase
frame rate and image quality will be affected negatively. To go some of the way towards compensating for
this, it is possible to prioritize either the frame rate or the image quality whenever the bit rate would need to
be increased. Not setting a priority means the frame rate and image quality will be affected more or less
equally.
Rate (VBR) or Constant Bit Rate (CBR). VBR will adjust the bit
for increased image activity, but in this case cannot, the
ling the bandwidth used by the MPEG-4 video
variable and constant bit rates.
will consume a predictable amount of bandwidth, and
tting the GOV-length to a high
Page 17

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Live View Config
Layout
The settings on this page allow you to decide the layout of the Live View page. You can include action
buttons, decide the default video format, and the default viewer among other things.
17
Default Video Format
Select the default video format to use on the Live View page. Checking the Show video format selection
box option displays a drop-down list on the Live View page allowing you to temporarily change the format.
When using MPEG-4 as the video format
It is also possible to view Motion JPEG when MPEG-4 is chosen as default and vice versa.
Note:
, the default viewer is AXIS Media Control with Internet Explorer.
Default Viewer
From the drop-down lists, select the default method for viewing video images for your browser. The camera
will attempt to show the video images in the selected video format and viewer. If this is not possible, the
camera will override the settings and select the best available combination.
Browser Viewer Description
AMC Recommended viewer in Windows Internet Explorer (MPEG-4 /Motion JPEG).
QuickTime MPEG-4 only.
Windows
Internet Explorer
Other browsers
Java applet A slower imaging alternative to AMC. Requires one
• JVM (J2SE) 1.4.2 or higher
•
JRE (J2SE) 5.0 or higher
Still image Displays still images only. Hit the Refresh butt
Server Push Recommended viewer for other browsers (Motion JPEG).
QuickTime MPEG-4 only.
Java applet A slower imaging alternative to Server
Still image Displays still images only. Hit the Refresh butt
Push (Motion JPEG only).
of the following installed on the client:
on in your browser to view a new image.
on in your browser to view a new image.
Viewer Settings
Show viewer toolbar - Check this box to display the AXIS Media Control (AMC) or the QuickTime viewer
toolbar under the video image in your browser.
Enable MPEG-4 decoder installation - The
included with AMC. This is used to prevent installation of unlicensed copies. Further decoder licenses can be
purchased from your Axis dealer.
Enable recording button - This displays the button for starting
View page.
administrator can disable the installation of the MPEG-4 decoder
MPEG-4 recordings directly from the Live
Page 18

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Action Buttons
The Show manual trigger button option lets you manually trigger and stop an event from the Live View
page. See Event Config, on p
age 20.
18
Enabling the display of the Sn
clicking the button. This button is mainly intended for use with browsers other than Internet Explorer, or
when otherwise not using AXIS Media Control (AMC) to view the video stream. AMC (an ActiveX control)
for Internet Explorer provides its own snapshot button.
apshot button allows users to save a snapshot from the video stream by
User Defined Links
Enter a descriptive name for the link and enter the URL in the field provided. The link appears on the Live
View page.
User defined CGI links can be used to issue HTTP
Select the option Show custom link 1.
Enter a descriptive name, for example, CAM1.
Enter the cgi link:
http://192.168.0.125/axis-cgi/com/startevent.cgi?camera=1&co
Select the option Show custom link 2.
Enter a descriptive name, for
Enter the cgi link:
http://192.168.0.125/axis-cgi/com/startevent.cgi?camera=1&co
example, CAM1 Stop Event.
API requests. For example:
ntinuouspantiltmove=30,-30
ntinuouspantiltmove=0,0
For more information on the VAPIX® API, see the Developer pages
www.axis.com/developer.
at the Axis web site
HTML Examples
You can add live video from the AXIS 209FD to your own web site. The camera can transmit a Motion
JPEG stream to up to 20 simultaneous connections, although an administrator can restrict this to fewer. If
MPEG-4 is set as video format, multicasting is used and the audio and video stream is available for an
unlimited number of viewers connected to the parts of the network where multicast is enabled. Please note
that a separate MPEG-4 license is required for each viewer.
Select the preferred Video format from the drop down
using AMC, and MPEG-4 using QuickTime.
The Motion JPEG selection has additional settings for
configure the video stream to suit your web page.
Click Update once satisfied.
The camera generates the required source code for your
own web page code.
list. The available options are Motion JPEG, MPEG-4
Image type, Image size and other Optional settings to
configuration. Copy this code and paste it into your
External Video
An external video source is a source originating from some other Axis device on the network. The images
from these sources can be displayed just as if they were produced by the AXIS 209FD.
The External Video Source List shows all
information displayed is the source’s name and the path to the video stream. Up to 20 external video
sources can be configured.
Working with External Video Sources:
of the external video sources currently configured. The
Page 19

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
To add a new video source, click the Add button. This opens the External Video Source Setup dialog; Here
you can make all the necessary settings.
19
To modify an existing video source, select
To delete an external video source, select
it and click the Modify button.
it and click the Remove button.
Sequence Mode
Sequence Mode is a configuration that automatically displays the view from multiple, previously defined
preset positions (see the online help) and external video sources (see above).
This is useful for security personnel viewin
or at random, through the selected preset positions and video sources.
To set up a sequence mode, simply select the desired preset positions and/or v
number of seconds or minutes to display each one for. Each position or video source can be displayed for
up to 59 minutes.
g a surveillance system that constantly rotates, in the listed order
ideo sources and enter the
Page 20

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Event Config
Pre-defined parameters, known as an Event or Event Type can trigger certain actions in the camera. A
common event type is an alarm that causes the camera to upload images. Many event types use an Event
Server, to receive uploaded images.
An event that is triggered by a signal, such as a door switch, motion detection, or system event, is called a
ggered event, see page 20.
tri
20
A scheduled event ru
An Action
refers to what happens when the event occurs.
This section describes how to configur
ns at pre-programmed times.
e the camera to perform certain actions when events occur.
Event Servers
Event Servers are used to receive uploaded image files and/or notification messages. To set up Event server
connections in your camera, go to Setup > Event Configuration > Event Servers and enter the required
information for the required server type.
Server type Purpose Information required
• Receives uploaded images • Descriptive name of your choice
FTP Server
HTTP Server
TCP Server
For details on each setting, please
• Receives notification messages
• Receives uploaded images
• Receives notification messages • Descriptive name of your choice
see the online help available from each web page.
When the setup is complete, the connection can be tested by clicking the Test
takes approximately 10 seconds).
• Network address (IP address or host name)
• User Name and Password (for FTP server)
• Upload path e.g. images/
• Descriptive name of your choice
• URL (IP address or host name)
• User Name and Password (for HTTP server)
• Network address (IP address or host name)
• Port number
button (the connection test
Event Types
An Event Type describes how and when the camera will perform certain actions.
Example::
event that uses motion detection has been configured to act
on this, the camera can e.g. record and save images to an FTP
server, and/or send a notification e-mail to a pre-configured
e-mail address with a pre-configured message. Images can be
sent as e-mail attachments.
Triggered Events
A triggered event can b
If somebody passes in front of the camera and an
e activated by:
• a manual trigger from an action button in the web interface, or by a trigger sent via the VAPIX® API
• detected movement in a configured
motion detection window
• on restart (boot) after e.g. power loss
• a temperature alarm
• a camera tampering alarm (AXIS 209
FD-R/FD-R M12)
Page 21

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
How to set up a triggered event
This example describes how to set up the camera to upload images when there is movement in the image:
21
1. Click A
dd triggered on the Event types page.
2. Enter a descriptive name for the event, such as Movement.
3. Set the priority - High, Normal or Low (see the online help).
4. Set the Respond to Trigger... parameters. Define when the event will be active; for
example, only after office hours.
5. Select the trigger alternative from the Triggered by... drop-down list - Motion detection. Select
the required window and choose if the alarm should be triggered when motion starts or stops.
6. Set the When Triggered... parameters, that is define what the camera will do if there is an alarm for example, upload images to an FTP server or send an e-mail notification.
7. Click OK to save the Event in the Event Types list.
Please see the online help for descriptions of each available op
Up to 10 event types can be configured in the camera, and up to three of these can be configured to upload images. Files names
Note:
can be formatted according to specific requirements. See File Naming & Date/Time Formats online help.
tion.
Pre-trigger and Post-trigger buffers
This function helps to check what happen
ed immediately before and/or after a trigger, for example 30
seconds before and/or after the event. Check the Upload images box option under Event Types > Add
Triggered... > When Triggered... to view the options. All uploaded images are JPEG images.
Include pre-trigger buffer - refers
to images stored internally in the server from the time immediately
preceding the trigger. Check the box to enable the pre-trigger buffer, enter the desired length of time, and
specify the required image frequency.
Include post-trigger buffer
Note:
• Pre-trigger and Post-trigger buffers will be lost if the connection to the event server fails.
• The maximum length of the pre-/post-buffer depends on the video image size and selected frame rate.
• If the pre- or post-buffer is too large for the camera’s internal memory, the frame rate will be reduced and
individual images may be missing. If this occurs, an entry will be created in the unit's log file.
contains images from just after the trigger. Configure as for pre-trigger.
Continue image upload (unbuffered) - enables the upload of video images for a fixed length of time.
Specify the length of time for the uploaded recording, in seconds, minutes or hours, or for as long as the
trigger is active. Finally, set the desired image frequency to the maximum (the maximum available) or to a
specified frame rate. The frame rate will be the best possible, but might not be as high as specified,
especially if uploading via a slow connection.
Scheduled Events
A Scheduled event can
be activated at preset times, in a repeating pattern on selected days.
Configuration example:
Click Add scheduled on the Event types page.
1.
2. Enter a descriptive name for the event, such as “Scheduled e-mail upload.”
3. Set the priority (High, Normal or Low).
4. Set the Activation Time parameters (24h clock) - when the event will be active; for example, start
on Sundays at 13.00 with a duration of 12 hours.
5. Set the When Activated... parameters; this defines what the camera will do at the specified time;
for example, send uploaded images to an e-mail address.
6. Click OK to save the Event in the Event Types list.
Please see the online help for descriptions of each available option.
Page 22

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Camera Tampering (AXIS 209 FD-R/FD-R M12)
The camera tampering application, which is currently available only for the AXIS 209 FD-R/FD-R M12,
generates an alarm whenever the camera is repositioned, or when the lens is covered, sprayed or severely
defocused. You must create an event, see How to set up a triggered event, on
an alarm.
page 21, for the camera to send
22
Once you have set up camera tampering correctly, if you significantly change the area in front of the camera, i.e., 90% of the area
Note:
must have been changed, an alarm will be triggered.
For example, if you have set up your Axis camera to monitor a room and you move furniture, pictures, and change the wall paper,
so that you have changed nearly the entire appearance of the room, an alarm will be triggered.
The settings available are:
Minimum duration - This sets the minimum
tampering period, that is an alarm will not be triggered until
this period has lapsed, even if the tampering conditions are otherwise met. This can help prevent false
alarms for known conditions that affect the image.
Alarm for dark images - If the camera len
s is sprayed and the image is darkened, it will not be possible to
distinguish this from other situations where the same effect is seen, that is when the lighting conditions
change. When this is enabled, alarms are generated for all cases where the image turns dark or the lens is
sprayed.
Page 23

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Motion Detection
Motion detection is used to generate an alarm whenever movement occurs (or stops) in the video image. A
total of 10 Include and/or Exclude windows can be configured.
23
• Included window
• Ex
cluded windows define areas within an Include window that should be ignored (areas outside
s target specific areas within the whole video image
Include windows are automatically ignored)
Once configured, the motion detection win
dows will appear in the list of available triggers, for triggering
events. See How to set up a triggered event above.
Using the motion detection feature may decrease the camera’s overall performance.
Note:
Configuring Motion Detection
1. Click Motion Detection in the Event Configuration menu.
2. Click the Configure Included Window radio button and click New.
3. Enter a descriptive name under Window name.
4. Adjust the size (drag the bottom right-hand corner) and position (click on the text at the top and
drag to the desired position).
5. Adjust the Object size, History and Sensitivity profile sliders (see table below for details). Any
detected motion within an active window is then indicated by red peaks in the Activity window
(the active window has a red frame).
6. Click Save.
To exclude parts of the Include window, click the Configure Excluded Windows button
and position the Exclude window as required, within the Include window.
Please see the online help for descriptions of each available option.
Object Size
High level Only very large objects
trigger motion detection
Low level Even very small objects
Default value Low Medium to High Medium to High
ger motion detection
trig
History Sensitivity
An object that appears in the region will trigger
the motion detection for a long period
An object that appears in the region will trigger
motion detection for only a very short period
Ordinary colored objects on ordinary backgrounds will trigger the motion detection
Only very bright objects on a dark background
will trigger motion detection
Page 24

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Tips:
• Avoid triggering on small objects in the video image by setting the object size level to high.
• To reduce the number of triggers if there is a lot of movement during a short period of time, select a high history level.
• To only detect flashing light, low sensitivity can be selected. In other cases, a high sensitivity level is recommended.
24
Page 25

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
System Options
Security
User access control is enabled by default. An administrator can set up other new users, by giving them user
names and passwords. It is also possible to allow anonymous viewer login, which means that anybody may
access the Live View page, as described below:
25
Users - the user lis
t displays the authorized users and user groups (levels):
Viewer Provides the lowest level of access, which only allows access to the Live View page.
Operator An Operator can view the Live View page, create
settings. Operators have no access to the System Options.
Administrator An administrator has unrestricted access to the Setup
all other users.
and modify events and adjust certain other
Tools and can determine the registration of
To prevent unauthorized use of the product, the AXIS 209FD network camera supports multi-user p
protection, where access can be restricted to a defined number of users only (maximum of 20).
The AXIS 209FD Network Camera supports different
• HTTP Basic Authentication - This
authenticates the user by requesting a user name and a pass-
word. The exchange of network credentials is in simple base64 coding and
• HTTP Digest Authentication - This method also
methods of user authentication. These are:
is not encrypted.
requests a user name and password, but the
exchange of credentials is encrypted, which better secures it against eavesdropping.
User Settings - ch
• Anonymous viewer login
• Maximu
eck the relevant checkboxes to enable:
- allows any viewer direct access to the Live View page.
m number of simultaneous viewers - enter a value here to restrict the number of Motion
JPEG and MPEG-4 viewers accessing the unit. This is useful if you need to save on bandwidth.
Note that within the limit of 20 users,
all multicast viewers count as 1 viewer.
IP Address Filter
assword
Enable IP Address Filtering to allow o
r deny access to the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12. Once enabled, the
IP addresses in the list will be allowed or denied access according to the choice made in the drop-down list
Allow/Deny the following IP addresses.
The administrator can add up to 256 IP address entries to the list (a single
entry can contain multiple IP
addresses). The users from these IP addresses need to be specified in the user list with the appropriate access
rights. This is done from Setup > System Options > Security > Users.
Referrals
To prevent unauthorized clients from including the video
stream from the cameras into external Web pages,
check the Referrals box option and enter the IP address or Host name of the computer that hosts the Web
pages with the included video stream. Several IP addresses/host names can be defined and are separated by
semicolons (;). This option is only applicable to Motion JPEG video streams.
Notes:
•If the referrals feature is enabled and you wish to also allow normal access to the Live View page, the product's
own IP address or host name must be added to the list of allowed referrers.
•Restricting referrers has no effect on an MPEG-4 video stream. To restrict an MPEG-4 stream, IP address filtering must be enabled.
•Restricting referrers is of greatest value when not
the allowed referrers are automatically restricted to those allowed IP addresses.
using IP address filtering. If IP address filtering is used, then
HTTPS
The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 supports encrypted browsing using HTTPS.
Page 26

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
A self-signed certificate can be used until a Certificate Authority-issued certificate has been obtained. Click
the Create self-signed Certificate button to install a self-signed certificate. Although self-signed certificates
are free and offer some protection, true security will only be implemented after the installation of a signed
certificate issued by a certificate authority.
26
A signed certificate can be obtained from an issuing
Certificate Authority by clicking the Create Certificate
Request button. When the signed certificate is returned, click the Install signed certificate button to import
the certificate. The properties of any certificate request currently resident in the camera or installed can also
be viewed by clicking the Properties... button. The HTTPS Connection Policy must also be set in the
drop-down lists to enable HTTPS in the camera. For more information, please refer to the online help.
Date & Time
Current Server Time - Displays the current date and time (24h clock). The time can be displayed in 12h
clock format in the Overlay (see below).
New Server Time
automatically adjust for daylight savings time, select the Automatically adjust for daylight saving time
changes.
From the Time Mode
• Synchronize with computer time - sets the time
• Synchronize with NTP Server - the camera will obtain the time from an NTP server every 60
minutes.
• Set manually - this option allows you to manually set the time and date.
If using a host name for the NTP server, a DNS server must be configured under TCP/IP settings.
Note:
See Basic TCP/IP Settings below.
- Select your time zone from the drop-down list. If you want the server clock to
section, select the preferred method for setting the time:
from the clock on your computer.
Date & Time Format Used in Images - Specify the formats for the date and time (12h or 24h) displayed in
the video streams.
Use the predefined formats or use your own custom
date and time formats. See Advanced File Naming &
Date/Time Formats in the online help for information on how to create your own file formats.
Network
Basic TCP/IP Settings
IP Address Configuration
The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 supports both
enabled simultaneously, and at least one version must always be enabled.
When using IPv4, the IP address for the
camera can be set automatically via DHCP, or a static IP address
can be set manually.
If IPv6 is enabled, the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 will receive an
configuration in the network router.
There are also options for setting up notification of changes in the IP address,
Internet Dynamic System. For more information on setting the IP address, please see the online help.
Notes:
• DHCP is a protocol for automatic IP address assignment on a network. IP address assignment via DHCP may lead to the situation
where the IP address changes and you lose contact with the camera. Configure the options for notification of IP address change
(under Services) to receive notification from the camera when the IP address changes.
• Alternatively, if your DHCP server can update a DNS server, you can access the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 by host name which is
always the same, regardless of the IP address.
IP version 4 and IP version 6. Both versions may be
IP address according to the
and for using the AXIS
Page 27

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Services
Enable ARP/Ping setting of IP address - The IP address can be set using the ARP/Ping method, which
associates the unit's MAC address with an IP address. Check this box to enable the service. Leave disabled to
prevent unintentional resetting of the IP address.
27
Notes:
Options for notification of IP address change - If the IP address for the camera changes, automatically by
DHCP for example, you can choose to be notified of the change. Click Settings... and enter the required
information.
AXIS Internet Dynamic DNS Service - Use
for easy access to your AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 (requires Internet access).
Click Settings...
existing settings (requires access to the Internet). The domain name currently registered at the Axis Internet
Dynamic DNS service for your product can at any time be removed.
For more information, please refer to the
Advanced TCP/IP Settings
DNS Configuration
DNS (Domain Name System) provides the translation
Obtain DNS server address via DHCP - automati
server. Click the View button to see the current settings.
Use the following DNS server address
Domain name
Multiple domains can be separated by semicolons (;). The host name is always the first part of a Fully
Qualified Domain Name, e.g. myserver is the host name in the Fully Qualified Domain Name
myserver.mycompany.com where mycompany.com is the Domain name.
• The ARP/Ping service is automatically disabled 2 minutes after the unit is started, or as soon as an IP address is set.
• Pinging the unit will still be possible when this service is disabled.
the AXIS Internet Dynamic DNS service to assign a host name
to register the camera with the Axis Internet Dynamic DNS service, or to modify the
online help .
of host names to IP addresses on your network.
cally use the DNS server settings provided by the DHCP
- enter the desired DNS server by specifying the following:
- enter the domain(s) to search for the host name used by the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12.
Primary and Secondary DNS servers - en
NTP Configuration
Obtain NTP server address via DHCP - check this radio button to automatically look up and
server settings as provided by DHCP. Click the View button to see the current settings.
Use the following NTP server address - to make manual settings, check this radio button option and enter
the host name
Host Name Configuration
The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 can be accessed using
name is usually the same as the assigned DNS Name.
For more information, please see Secur
Link-Local IPv4 Address
This is enabled by default and assigns the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 an
with UPnP
time - these will not affect each other.
or IP address of the NTP server in the Network address field.
™. The camera can have both a Link-Local IP and a static/DHCP-supplied IP address at the same
ter the IP addresses of the primary and secondary DNS servers.
use the NTP
a host name, instead of an IP address. The host
ity.
additional IP address for use
Page 28

HTTP
LAN (intranet)
WAN (internet)
Broadband
(NAT)
router
ISP
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
28
The default HTTP port number (80) can be changed to
any port within the range 1024-65535. This is useful
for e.g. simple security port mapping.
HTTPS
The HTTPS port to use. The default setting is 443.
NAT traversal (port mapping) for IPv4
A broadband router allows devices on a private network (LAN) to share a si
ngle connection to the Internet.
This is done by forwarding network traffic from the private network to the “outside” i.e. the Internet.
Security on the private network (LAN) is increased since most broadband routers are pre-configured to stop
any attempts to access the private network (LAN) from the public network/Internet.
Use NAT traversal when
your AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 is located on an intranet (LAN) and you wish to
make it available from the other (WAN) side of a NAT router. With NAT traversal properly configured, all
HTTP traffic to an external HTTP port in the NAT router will be forwarded to the camera.
Notes:
• For NAT traversal to work, this must also be supported by the broadband router.
• The broadband router has many different names: “NAT router”, “Network router“, Internet Gateway”, “Broadband sharing device”
or “Home firewall” but the essential purpose of the device is the same.
Enable/Disable - When enabled, the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 will attempt to configure port mapping
in a NAT router on your network, using UPnP™. Note that UPnP™ must be enabled in the camera (see
System Options > Network > UPnP).
Use manually selected NAT router
- Select this option to manually select a NAT router and enter the IP
address for the router in the field provided.
If a router is not manually specified, the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R
M12 will automatically search for NAT
routers on your network. If more than one router is found, the default router will be selected.
Alternative HTTP port
- Select this option to manually define an external HTTP port. Enter the port number
in the field provided. If no port is entered here a port number will automatically be selected when NAT
traversal is enabled.
Notes:
• An alternative HTTP port can be used/be active even if NAT traversal is disabled. This is useful if e.g. your NAT router does not
support UPnP and you need to manually configure port forwarding in the NAT router.
• If you attempt to manually enter a port that is already in use, another available port will automatically be selected.
• When the port is selected automatically it will be displayed in this field. This can be changed by entering a new port number and
clicking Save.
FTP
The FTP server running in the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
enables the upload of e.g. new firmware, user
applications, etc. Check the box to enable the service.
Page 29

RTSP
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
29
The RTSP protocol allows a connecting clie
and enter the RTSP port number to use. The default setting is 554. Note that MPEG-4 video streams will not
be available if this service is not enabled.
Network Traffic
Connection Type - The
automatically selected. If necessary, you can set the connection speed by selecting it from the drop-down
list.
Maximum bandwidth - To minimize the impact on other services runnin
configure the maximum network bandwidth the product will be allowed to use. Specify the maximum
bandwidth (in Mbit/s or kbit/s) allowed, or set to Unlimited.
SOCKS
SOCKS is a networking proxy protocol. The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 can be configured to use a
server to reach networks on the other side of a firewall/proxy server. This functionality is useful if the
camera is located on a local network behind a firewall, but notifications, uploads, alarms, etc., need to be
sent to a destination outside the local network (e.g. to the Internet).
QoS (Quality of service)
Quality of Service (QoS) provide
traffic on a network. Quality can be defined as e.g. a maintained level of bandwidth, low latency, no packet
losses, etc. The main benefits of a QoS-aware network can be summarized as:
default setting is Auto-negotiate, which means that the correct speed is
s the means to guarantee a certain level of a specified resource to selected
nt to start an MPEG-4 stream. Check the box to enable the server
g on your network, it is possible to
SOCKS
• The ability to prioritize traffic and thus allow critical flows to be served before fl
priority.
• Greater reliability in the network, thank
may use, and thus control over bandwidth races between applications.
The QoS in Axis network video products
originating from the product. This makes it possible for network routers and switches to e.g. reserve a fixed
amount of bandwidth for these types of traffic. The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 marks the following types
of traffic:
•video
•event/alarm
• management network traffic.
QoS Settings
For each type of network traffic supported by your
(Differentiated Services Code Point) value. This value is used to mark the traffic’s IP header. When the
marked traffic reaches a network router or switch, the DSCP value in the IP header tells the router or switch
which type of treatment to apply to this type of traffic, for example, how much bandwidth to reserve for it.
Note that DSCP values can be entered in decimal or hex
decimal.
For more information on Quality of Service, please
marks the data packets for various types of network traffic
s to the control of the amount of bandwidth an application
Axis network video product, enter a DSCP
form, but saved values are always shown in
see the Axis support web at www.axis.com/techsup
ows with lesser
SMTP (email)
Enter the host names (or IP addresses) and port numbers for your primary and secondary mail servers in the
fields provided
predefined addresses via SMTP.
If your mail server requires authentication, check the box for Use authentication to log in to this server
d enter the necessary information.
an
, to enable the sending of notifications and image/video email messages from the camera to
Page 30

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
SNMP
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) allows remote management of network devices.
Depending on the level of security required, select the version of SNMP to use. The three levels of security
are:
• SNMP V1 - includes no security.
• SNMP V2c - uses very simple security. The community n
ame can be specified as a password for read or
read/write access to all supported SNMP objects. The community is the group of network devices using
SNMP.
• SNMP V3 - provides encryption and secure passwords.
HTTPS must be enabled.
UPnP™
30
The camera includes support for UPnP
™, which is enabled by default. If also enabled on your computer, the
camera will automatically be detected and a new icon will be added to “My Network Places.”
UPnP must also be enabled on your Windows XP or ME computer. To do this, open the Control Panel from the Start Menu and
Note:
select Add/Remove Programs. Select Add/Remove Windows Components and open the Networking Services section. Click
Details and then select UPnP as the service to add.
RTP
RTP/ MPEG-4. These settings are the port range, IP address, port number (video and audio), and
Time-To-Live value to use for the video stream(s) in multicast MPEG-4 format. Only certain IP addresses
and port numbers should be used for multicast streams. For more information, please see the online help.
Bonjour
The AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12 includes support for Bonjour. When enabled,
the camera is automatically
detected by operating systems and clients that support this.
LED Settings
The Status indicator LED on the camera can be set to flash at a configurable interval (or to not light up at
all) whenever the unit is accessed. For a listing of all LED behavior, see page 6, or the online help. Note that
the LED does not flash when the stream i
s retrieved using MPEG-4 multicast.
Maintenance
• Restart - The camera is restarted without changing any of the settings.
• Restore - The unit is restarted and most current
settings are reset to factory default values. The set-
tings that will not be reset are as follows:
• the boot protocol (DHCP or static)
•
the static IP address
• the default router
•the subnet mask
• Default - The default button should be used
era's settings to the factory default
Upgrade Server -
Backup -
To take a backup of all of the parameters, and any user-defined scripts, click this button. If
See Upgrading the firmware, on page 33.
values (including the IP address)
with caution. Pressing this will return all of the cam-
necessary, it will then be possible to return to the previous settings, if settings are changed and there is
unexpected behavior.
Restore - cli
ck the Browse button to locate the saved backup file (see above) and then click the Restore
button. The settings will be restored to the previous configuration.
Backup and Restore can only be used on the same unit running the same firmware. This feature is not intended for the configu-
Note:
ration of multiple units or for firmware upgrades.
Page 31

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Support
The Support Overview page provides valuable information on troubleshooting and contact information,
should you require technical assistance.
31
System Overview - is a quick look over the camera’s status and
includes the camera’s Firmware version, IP address, Security, Optional Network Services, Event Settings,
Image settings and Recent log items. Many of the captions are also links to the proper Setup page to
conveniently make adjustments in the camera’s settings.
Logs & Reports - When contacting Axis support, please be sure to provide a valid
query.
settings. Information that can be found here
Server Report with your
Advanced
Scripting is an advanced function that provides the means for customizing and using scripts.
Caution!
The scripting function is a very powerful
contact with the unit. If a script does cause problems, reset the unit to its factory default settings (in which
case, a previously saved backup file will be useful for returning the unit to its latest configuration).
Axis strongly recommends that you do not use th
consequences. Axis support provides no assistance for customized scripts.
For more information, please visit the Developer pages
Plain Config
All parameters can be set and modified from this page. Help is available via the links on the standard setup
pages.
- this function is for the advanced user with previous experience of configuring Axis cameras.
tool. Improper use may cause unexpected behavior or even loss of
is function unless you fully understand its
at www.axis.com/developer
About
Third Party Software Licenses - Click View licenses for a list of the licensed software used in the
AXIS 209FD/FD-R Network Camera.
Resetting to the factory default settings
To reset the camera to the original factory default settings, go to the System Options > Maintenance web
page (as described in Maintenance, on page 30) or use the Control button, which is found inside
cover (see Overview, on page 5) as described below:
Using the Control Button
To reset the camera to the factory default settings using the Control Button:
1. Remove the camera’s cover.
Disconnect the network to remove power.
2.
3. Press and hold the Control button while reconnecting the cable.
4. Keep the Control button pressed until the Status Indicator color changes to amber (this may take
up to 15 seconds).
5. Release the Control button.
6. When the Status Indicator changes to Green (which may take up to 1 minute), the process is
complete and the camera has been reset. The unit will now have the default IP address
192.168.0.90
the camera
Unit connectors
(AXIS 216FD) network connector. Female RJ-45 Ethernet connector for 10BaseT/100BaseTX. Supports
Power over Ethernet. Using shielded cables is recommended.
Page 32

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
(AXIS 209FD-R) network connector. Female RJ-45 Industrial connector. Compatible with Woodhead
RJ-Lnxx IP67 connectors Supports Power over Ethernet. Using shielded cables is recommended
(AXIS 209FD-R M12) network connector. Male M12 D-code Ethernet connector. Supports Power over
Ethernet. Using shielded cables is recommended.
32
Page 33

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Troubleshooting
Checking the firmware
Firmware is software that determines the functionality of the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12. One of your
first actions when troubleshooting a problem should be to check the currently installed firmware version.
The latest version may contain a correction that fixes your particular problem. The current firmware version
in your camera can be seen on the page Setup > Basic Configuration.
Upgrading the firmware
When you upgrade the firmware with a file from the Axis Web site, your camera will receive the latest
available functionality. Always read the upgrade instructions and release notes available with each new
release, before updating the firmware.
33
Note:
Notes:
Pre-configured and customized settings will be saved when the firmware is upgraded (providing the same features are available
in the new firmware) although this is not guaranteed by Axis Communications. Always read the instructions and release notes
provided with each new release, before upgrading the firmware.
1. Save the firmware file to your computer.
The latest version of the firmware is
available free of charge from the Axis Web
site at www.axis.com/techsup
2. Go to Setup > System Options >
Maintenance in the camera’s Web pages.
3. In the Upgrade Server section, browse to
the desired firmware file on your computer.
Click Upgrade.
•After starting the upgrade process, always wait
at least 5-10 minutes before restarting the camera, even if you suspect the upgrade has failed.
•Your dealer reserves the right to charge for any repair attributable to faulty upgrading by the user.
•The AXIS Camera Management software tool can be used for multiple upgrades. Please see the Axis Web site at
www.axis.com for more information.
Emergency recovery procedure
If the power/network connection to the camera is lost during the upgrade, the process will fail and the unit
will become unresponsive. A flashing red Status LED indicates a failed upgrade. To recover the unit, follow
the steps below. The serial number is found on the label inside the camera cover.
1. UNIX/Linux - From the command line, type the following:
arp -s <IP address of camera> <Serial number> temp
ping -s 408 <IP address of camera>
Windows - From a command/DOS prompt, type the following:
arp -s <IP address of camera> <Serial number>
ping -l 408 -t <IP address of camera>
2. If the unit does not reply within a few seconds, restart it and wait for a reply. Press CTRL+C to stop
Ping.
3. Open a browser and type in the camera’s IP address. In the page that appears, use the Browse
button to select the upgrade file to use, e.g. axis209fdr.bin. Then click the Load button to restart
the upgrade process.
Page 34

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
4. After the upgrade has completed (1-10 minutes), the unit will automatically restart and show a
steady green on the Power and Status LEDs and flashing green or amber on the Network LED.
5. Referring to the installation guide, reinstall the camera.
6. Windows - If you are using a DHCP server, type the following from a command/DOS prompt:
arp -d <IP address of camera>
If the emergency recovery procedure does not get the camera up and running again, please contact Axis
support at www.axis.com/techsup/
Axis Support
If you contact Axis support, please help us to help you solve your problems, by providing the server report,
the log file and a detailed description of the problem.
34
Server Report - go
information about the server and its software, as well as a list of the current parameters.
The Log
unit since the last system restart and can be a useful diagnostic tool when troubleshooting.
file is available from Setup > System Options > Logs & Reports. The Log file records events in the
to Setup > System Options > Support Overview. The server report contains important
Page 35

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Symptoms, Possible Causes and Remedial Actions
Problems setting the IP address
When using ARP/Ping Try the installation again. The IP address must be set within two minutes after power has been applied to the cam-
era. Ensure the Ping length is set to 408. See the Installation Guide.
The camera is located on a different
subnet
The IP address is being used by
another device
Possible IP address conflict with
another device on the same subnet
The camera cannot be accessed from a browser
The IP address has been changed by
DHCP
Other networking problems Test the network cable by connecting it to another network device, then Ping that device from your workstation.
Camera is accessible locally, but not externally
Broadband router configuration To configure your broadband router to allow incoming data traffic to the camera: Enable the NAT-traversal fea-
Firewall protection Check the Internet firewall with your system administrator.
Default routers required Check if you need to configure the default router settings.
Problems with the MPEG-4 format
No MPEG-4 displayed in the
client
No multicast MPEG-4 displayed in
the client
Multicast MPEG-4 only accessible by
local clients
Poor rendering of MPEG-4 images Color depth set incorrectly on clients. Set to 16-bit or 32-bit color.
Color saturation is different in
MPEG-4 and Motion JPEG
Lower frame rate than expected Reduce number of applications running on the client computer.
Why do I not get 30 frames per second? See the section General performance considerations, on page 39.
Lost or poor images in pre-trigger
buffer (MPEG-4 video stream)
Image degeneration Decrease the GOV length, see the online help for more information.
The Status and Network indicator LEDs are flashing red rapidly
Hardware failure Contact your Axis dealer.
If the IP address intended for the camera and the IP address of your computer are located on different subnets, you
will not be able to set the IP address. Contact your network administrator to obtain an appropriate IP address.
Disconnect the camera from the network. Run the Ping command. (In a Command/DOS window, type ping and the
IP address of the unit).
If you receive: Reply from <IP address>: bytes = 32; time = 10 ms..... - this means that the IP address may
already be in use by another device on your network. You must obtain a new IP address and reinstall the unit.
If you see: Request timed out - this means that the IP address is available for use with your camera. In this case,
check all cabling and reinstall the unit.
The static IP address in the camera is used before the DHCP server sets a a dynamic address. This means that if the
same default static IP address is also used by another device, there may be problems accessing the camera. To
avoid this, set the static IP address to 0.0.0.0.
1) Move the camera to an isolated network or to one with no DHCP or BOOTP server. Set the IP address again,
using the AXIS IP Utility (see the Installation Guide) or the ARP/Ping commands.
2) Access the unit and disable DHCP in the TCP/IP settings. Return the unit to the main network. The unit now has
a fixed IP address that will not change.
3) As an alternative to 2), if a dynamic IP address via DHCP or BOOTP is required, select the required service and
then configure IP address change notification from the network settings. Return the unit to the main network. The
unit will now have a dynamic IP address, but will notify you if the address changes.
See the instructions above.
ture, which will attempt to automatically configure the router to allow access to the camera.
This is enabled from Setup > System Options > Network > TCP/IP Advanced.
Note that if your router does not support NAT traversal, it is recommended that port forwarding is configured
manually instead. To do this, set a static IP address for the camera, and set the router to allow HTTP traffic to the
camera’s IP address and HTTP port. Note that the default HTTP port (80) may already be used by the router itself
(for remote administration), so changing the HTTP port for the camera (to e.g. 8000) is recommended.
Check that the correct network interface is selected in the AMC control panel applet (network tab).
Check that the relevant MPEG-4 connection methods are enabled in the AMC control panel applet (network tab).
In the AMC control applet, select the MPEG-4 tab and click the button Set to default MPEG-4 decoder.
Check with your network administrator that the multicast addresses used by the
camera are valid for your network.
Check with your network administrator to see if there is a firewall preventing viewing.
Check if your router supports multicasting, or if the router settings between the client and the server need to be
configured. The TTL (Time To Live) value may need to be increased.
If text overlays are blurred, or if there are other rendering problems, you may need to enable Advanced Video Rendering from the MPEG-4 tab in the AMC control panel applet.
Ensure that your graphics card is using the latest device driver. The latest drivers can usually be downloaded from
the manufacturer's web site.
Modify the settings for your graphics adapter. Please see the adapter's documentation for more information.
Limit the number of simultaneous viewers. This is done in System Options > Security > Users.
Check with the system administrator that there is enough bandwidth available. See also the online help.
Check in the AMC control panel applet (MPEG-4 tab) that video processing is not set to Decode only I frames.
Lower the image resolution.
Make sure that Cyclic refresh under Setup > Video & Image > Advanced > MPEG-4
is disabled.
35
The Status indicator LED is flashing red and the camera is inaccessible
Page 36

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
36
A firmware upgrade has been interrupted or the firmware has otherwise
been damaged
No images displayed on web page
Problem with AMC.
(Internet Explorer only)
Installation of additional ActiveX
component restricted or prohibited
Video/Image problems, general
Image too dark or too light Check the video image settings. See the online help on Video and Image Settings.
Missing images in uploads This can occur when trying to use a larger image buffer than is actually available. Try lowering the frame rate or
Slow image update Configuring, e.g. pre-buffers, motion detection, high-resolution images, high frame rates, etc, will reduce the per-
Poor performance Poor performance may be caused by e.g. heavy network traffic, multiple users accessing the unit, low performance
Poor quality snapshot images
Screen incorrectly configured on your
workstation
Browser freezes
Netscape 7.x or Mozilla 1.4 (or later)
can sometimes freeze on a slow computer
Motion Detection triggers unexpectedly
Changes in luminance Motion detection is based upon changes in luminance in the image. This means that if there are sudden changes in
See the Emergency Recovery Procedure above.
To enable the updating of video images in Microsoft Internet Explorer, set your browser to allow ActiveX controls.
Also, make sure that AXIS Media Control (AMC) component is installed on your workstation.
Configure your camera to use a Java applet for updating the video images under
Live View Config > Layout > Default Viewer for Internet Explorer. See the online help for more information.
the upload period.
formance of the camera.
clients, use of features such as motion detection or event handling.
In Display Properties, configure your screen to show at least 65000 colors, i.e. at least 16-bit. Using only 16 or 256
colors will produce dithering artifacts in the image.
Lower the image resolution.
the lighting, motion detection may be triggered mistakenly. Lower the sensitivity setting to avoid problems with
luminance.
For further assistance, please contact your reseller or see the support pages on the Axis Website at
www.axis.com/techsup
Page 37

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Technical Specifications
Item Specification
Models AXIS 209FD: VGA
AXIS 209FD-R: VGA, with a rugged and IP67-rated RJ-45 connector
AXIS 209FD-R M12: VGA, with a rugged and IP67-rated M12 connector
Image sensor 1/4” Micron Progressive Scan RG B VGA CMOS
Lens • 3.0mm, F2.0, fixed iris
• F
ocus range: 0.5m to infinity
Angle of view • 66° horizontal
Camera angle
adjustment
Illumination 1.5-10000 lux, F2.0
Video compression • Motion JPEG
Resolutions • 9 resolutions from 640x480 to 160x120 via API, 6 selections via configuration web page
Frame rate Up to 30 fps at all resolutions (Motion JPEG or MPEG-4)
Video streaming • Simultaneous Motion JPEG and MPEG-4
Image settings • Compression levels: 100
Shutter time 1/10000 s to 1/4 s
Security • Multiple user access levels with password protection
Users • 20 simultaneous users
Alarm and event
managem
Connectors • (AXIS 209FD) Female RJ-45 for Ethernet 10BaseT/100BaseTX
Casing • Polycarbonate base and polycarbonate transparent cover
ent
• Tilt: 0-90°
• Pan:
±10°
• Rotation: ±10°
• MPEG-4 Part 2 (ISO/IEC 14
• Profiles: SP and ASP
• Controllable frame rat
• Constant and variable bit rate (MPEG-4)
• Rotation: 0º, 180º
• Configurable color level, brightness, sharpness, white balance, exposure control
• Overlay capabilities: time, date, text, image or privacy mask
• Mirroring
• IP address filtering
• HTTPS encryption
• Digest authentication
• Unlimi
• Image upload over FTP, email and HTTP
• Notification over TCP, email and HTTP
• 9 MB of pre- and post alarm buffer (approx 5 min of 320x240 resolution video at 4 fps)
(AXIS 209FD)
• Events triggered by video motion detection, or
(AXIS 209FD-R/AXIS 209FD-R M12)
• Events triggered by video motion detection, tampering alarm, or according to a schedule
• (AXIS 209FD-R) Rugged, female RJ-45 connector.
• (AXIS 209FD-R M12) Rugged, male M12 D-code connector.
• Tamper-proof mounting
ted number of users using multicast (MPEG-4)
496-2) with motion estimation
e and bandwidth
according to a schedule
37
(AXIS 209FD-R)
• IP66
Processors and
memory
Power Power over Ethernet IEEE 802.3af, Class 1
Operating conditions (AXIS 209FD)
• CPU, video processing and compression: ARTPEC-A
• RAM: 32 MB
• Flash memory: 8 MB
• Temperature: 0 - 50 ºC (32-122 ºF)
• Humidity 20 - 80% RH (non-condensing)
(AXIS 209FD-R)
• Temperature: -20 – 50 ºC (-4 –122 ºF)
• Humidity 20
- 80% RH (non-condensing)
Page 38

Item Specification
Installation,
management and
maintenance
Video access from
Web browser
Minimum web
browsin
g
requirements
System integration
support
Supported protocols IPv4/v6, HTTP, HTTPS, SSL/TLS*, TCP, IC
Accessories (included) • Installation Guide, CD with installation tool, recording
• AXIS Camera Management tool on CD and web-based configuration
• Configuration of backup and restore
• Firmware upgrades over HTTP or FTP, firmware available at www.axis.com
• Camera live view
• Video recording to file (ASF)
• Pentium III CPU 500 MHz or higher or equivalent AMD
• 128 MB RAM
• DirectX 9 compatible graphics board, Direct Draw
• Windows XP, 2000, Internet Explorer 6.x or later
For other operating systems and browsers, see www.axis.com/techsup
• Open API for application integration, including VAPIX(R) fr
event trigger data in video stream
• Quality of Service (QoS) Layer 3, DiffServ Model
• Embedded Linux operating system
* Available at www.axis.com
MP, QoS, SNMPv1/v2c/v3 (MIB-II), RTSP, RTP, UDP, IGMP, RTCP, SMTP, FTP,
DHCP, UPnP, Bonjour, ARP, DNS, DynDNS, SOCKS, NTP
More information on protocol usa
* This product includes software developed by the Open SSL Project for
(www.openssl.org)
decoder, decoder software for Windows
• Key for tamper-proof screws
ge available at www.axis.com
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
om Axis Communications*, AXIS Media Control SDK*,
use in the Open SSL Tool kit
software and User’s Manual, licenses for 1 encoder and 1
38
(AXIS 209FD-R/AXIS 209FD-R M12)
• 1 Silica gel bag
(AXIS 209FD, AXIS 209FD-R)
• AXIS PoE Midspan 1-port (single packs only)
Video management
are
softw
(not included)
Accessories
(not included)
Approvals • EN 55022 Class B
Dimensions (HxWxD)
& weight
AXIS Camera Station - Video management software for viewing, recording and archiving up to 25 cameras
See www.axis.com/partner/adp_partners.htm for more software applications via partners
• Multi-user decoder license pack
(AXIS 209FD-R)
• Woodhead connector
• EN 61000-
• EN 61000-3-3
• EN 55024
• FCC Part 15, Subpart B, Class B
• ICES-003 Class B
• VCCI Class B
• C-tick AS/NZS CISPR 22
• MIC, Class B
• EN 60950-1
(AXIS 209FD-R)
• CE: Automotive environment
• EN 55025
• EN 50155:
• ISO16750-3: Vibration
• IP66
• 39 x 102 x 100 mm (1.5” x 4.0” x 3.9”)
eight: 0.18kg (0.40lb)
• W
3-2
Vibrations, mechanical shock and temperature
Page 39

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
General performance considerations
When setting up your system, it is important to consider how various settings and situations will affect
performance. Some factors affect the amount of bandwidth (the bit rate) required, others can affect the
frame rate, and some will affect both. If the load on the CPU reaches its maximum, this will also affect the
frame rate.
The following factors are among the most important to consider:
39
• High image resolutions and/or lower compression l
affected.
• Access by large numbers of Motion JPEG and/or uni
• Simultaneous viewing of different streams (resolution,
Frame rate and bandwidth affected.
• Accessing both Motion JPEG and MPEG-4 video
width affected.
• Heavy usage of event settings affects the c
• Enabled motion detection. Frame rate and
• Heavy network utilization due to poor infrastructure. Bandwidth
• Viewing on poorly performing client PC’s lowers perceived performance. Frame
amera’s CPU load. Frame rate affected.
bandwidth affected.
evels result in larger images. Bandwidth
cast MPEG-4 clients. Bandwidth affected.
compression, etc.) by different clients.
streams simultaneously. Frame rate and band-
affected
rate affected.
Page 40

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
Optimizing your system
To see the bandwidth and frame rate currently required by the video stream, the AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R
M12 provides a tool that can be used to display these values directly in the video image.
40
To do this, special format strings are add
ed as part of a text overlay.
Simply add #r (average frame rate in fps) and/or #b (average
bandwidth in kbps) to the overlay.
For detailed instructions, please
see the online help for Video &
Image > Text Overlay Settings, and the help for File Naming &
Date/Time Formats.
Important!
The figures displayed here are the values as delivered by the camera
limitation) these values might not correspond to those actually received by the client.
•For Motion JPEG, these values will be accurate as long as no frame rate limit has been specified.
. If other restrictions are currently in force, (e.g. bandwidth
Bandwidth
As there are many factors that affect bandwidth, it is very difficult to predict the required amounts. The
settings that affect bandwidth are:
• image resolution
• image compression
•frame rate
• MPEG-4 GOV settings
• bit rate control settings
There are also factors in the monitored scene that will
affect the bandwidth. These are:
• amount of motion
• image complexity
• lighting conditions
For MPEG-4, if there is only limited bandwidth available,
and if this is more important than the image
quality, using a constant bit rate (CBR) is recommended. Use a variable bit rate (VBR) if the image quality
needs to be maintained at a higher level. If supported on the network, consider also using MPEG-4
multicasting, as the bandwidth consumption will be much lower.
Page 41

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
41
Glossary of Terms
ActiveX - A standard that enables software components to interact
with one another in a networked environment, regardless of the
language(s) used to create them. Web browsers may come into
contact with ActiveX controls, ActiveX documents, and ActiveX
scripts. ActiveX controls are often downloaded and installed
automatically as required.
AF (Auto focus) - A system by which the camera lens automatically
ocuses on a selected part of the subject.
f
Angle - The field of view, relative to a standard lens in a 35mm still
amera, expressed in degrees, e.g. 30°. For practical purposes, this is
c
the area that a lens can cover, where the angle of view is determined
by the focal length of the lens. A wide-angle lens has a short focal
length and covers a wider angle of view than standard or telephoto
lenses, which have longer focal lengths.
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) - This protocol is used to
ssociate an IP address to a hardware MAC address. A request is
a
broadcast on the local network to discover the MAC address for an IP
address.
ARTPEC (Axis Real Time Picture Encoder) - This chip is used for
age compression.
im
ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit)
for a specific application, as opposed to a general purpose circuit,
such as a microprocessor.
Aspect ratio - A ratio of width to height in images. A common aspect
ra
tio used for television screens and computer monitors is 4:3.
High-definition television (HDTV) uses an aspect ratio of 9:16.
Autoiris (or DC-Iris) - This special type of iris is electrically
ontrolled by the camera, to automatically regulate the amount of
c
light allowed to enter.
AVI (Audio Video Interleave) - A video format that supports
eous playback of audio and video.
simultan
Bitmap - A bitmap is a data file representing a rectangular grid of
ixels. It defines a display space and color for each pixel (or “bit”) in
p
the display space. This type of image is known as a “raster graphic.”
GIF's and JPEG's are examples of image file types that contain
bitmaps.
Because a bitmap uses this fixed raster method, it cannot easily be
scaled without losing definition. Conversely, a vector graphic image
re
uses geometrical shapes to represent the image, and can thus be
quickly rescaled.
Bit rate - The bit rate (in kbit/s or Mbit/s) is often referred to as
ed, but actually defines the number of bits/time unit and not
spe
distance/time unit.
Bluetooth - Bluetooth is an open standard for wireless transmission
f voice and data between mobile devices (PCs, handheld computers,
o
telephones and printers).
Bonjour - Also known as zero-configuration networking, Bonjour
e
nables devices to automatically discover each other on a network,
without having to enter IP addresses or configure DNS servers.
Bonjour is a trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.
Broadband - In network engineering terms, this describes
mission methods where two or more signals share the same
trans
carrier. In more popular terminology, broadband is taken to mean
high-speed data transmission.
CCD (Charged Coupled Device) - This light-sensitive image device
in many digital cameras is a large integrated circuit that
used
contains hundreds of thousands of photo-sites (pixels) that convert
light energy into electronic signals. Its size is measured diagonally
and can be 1/4”, 1/3”, 1/2” or 2/3”.
CGI (Common Gateway Interface) - A specification for
ommunication between a web server and other (CGI) programs. For
c
example, a HTML page that contains a form might use a CGI program
to process the form data once it is submitted.
CIF (Common Intermediate Format) - CIF refers to the analog video
- A circuit designed
resolutions
also Resolution.
Client/Server - Client/server describes the relationship between two
computer
request from another program, the server, which fulfils the request.
Typically, multiple client programs share the services of a common
server program. A web browser is a client program that requests
services (the sending of web pages or files) from a web server.
CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) - A CMOS is a
wide
positive circuits. Since only one of the circuit types is on at any given
time, CMOS chips require less power than chips using just one type of
transistor. CMOS image sensors also allow processing circuits to be
included on the same chip, an advantage not possible with CCD
sensors, which are also much more expensive to produce.
Codec - In communications engineering, a codec is usually a
code
convert e.g. analog video and audio signals into a digital format for
transmission. The codec also converts received digital signals back
into analog format. A codec uses analog-to-digital conversion and
digital-to-analog conversion in the same chip.
Codec can also mean compression/decompression, in which
generally taken to mean an algorithm or computer program for
reducing the size of large files and programs.
Compression - See Imag
Contrast - Defines the degree of difference between the lightest and
darkest p
DC-Iris - This special type of iris is electrically controlled by the
came
enter.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - DHCP is a protocol
th
at lets network administrators automate and centrally manage the
assignment of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses to network devices in a
network.
DHCP uses the concept of a “lease” or amount of time that a given IP
address will be valid for
depending on how long a user is likely to require the network
connection at a particular location.
DHCP also supports static addresses for e.g. computers running web
ervers, which need a permanent IP address.
s
DNS (Domain Name System) - DNS is used to locate and translate
Inte
domain name is a meaningful and easy-to-remember name for an
Internet address. For example the domain name www.example.com is
much easier to remember than 192.0.34.166. The translation tables
for domain names are contained in Domain name servers.
Domain Server - Domains can also be used by organizations who
wish
Each user within a domain has an account that usually allows them
to log in to and use any computer in the domain, although
restrictions may also apply. The domain server is the server that
authenticates the users on the network.
Duplex - See Fu
Ethernet - Ethernet is the most widely installed local area network
technolog
pair wires. The most commonly installed Ethernet systems are
10BASE-T and 100BASE-T10, which provide transmission speeds up
to 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps respectively.
ETRAX (Ethernet Token Ring AXIS) - Axis' own microprocessor.
Factory default settings - These are the settings that originally
applie
should become necessary to reset a device to its factory default
settings, this will, for many devices, completely reset any settings that
were changed by the user.
Firewall - A firewall works as a barrier between networks, e.g.
etween a Local Area Network and the Internet. The firewall ensures
b
that only authorized users are allowed to access the one network from
352x288 pixels (PAL) and 352x240 pixels (NTSC). See
programs in which one program, the client, makes a service
ly used type of semiconductor that uses both negative and
r/decoder. Codecs are used in integrated circuits or chips that
case it is
e Compression.
arts of an image or video stream.
ra, to automatically regulate the amount of light allowed to
a computer. The lease time can vary,
rnet domain names into IP (Internet Protocol) addresses. A
to centralize the management of their (Windows) computers.
ll-duplex.
y. An Ethernet LAN typically uses special grades of twisted
d for a device when it was first delivered from the factory. If it
Page 42

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
42
the other. A firewall can be software running on a computer, or it can
be a standalone hardware device.
Focal length - Measured in millimeters, the focal length of a camera
ns determines the width of the horizontal field of view, which in
le
turn is measured in degrees.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - An application protocol that uses the
CP/IP protocols. It is used to exchange files between
T
computers/devices on networks.
Frame - A frame is a complete video image. In the 2:1 interlaced
sc
anning format of the RS-170 and CCIR formats, a frame is made up
of two separate fields of 262.5 or 312.5 lines interlaced at 60 or 50 Hz
to form a complete frame, which appears at 30 or 25 Hz. In video
cameras with a progressive scan, each frame is scanned line-by-line
and not interlaced; most are also displayed at 30 and 25 Hz.
Frame rate - The frame rate used to describe the frequency at which
video stream is updated is measured in frames per second (fps). A
a
higher frame rate is advantageous when there is movement in the
video stream, as it maintains image quality throughout.
Full-duplex - Transmission of data in two directions simultaneously.
an audio system this would describe e.g. a telephone systems.
In
Half-duplex also provides bi-directional communication, but only in
one direction at a time, as in a walkie-talkie system. See also Simplex.
Gain - Gain is the amplification factor and the extent to which an
nalog amplifier boosts the strength of a signal. Amplification factors
a
are usually expressed in terms of power. The decibel (dB) is the most
common way of quantifying the gain of an amplifier.
Gateway - A gateway is a point in a network that acts as an entry
oint to another network. In a corporate network for example, a
p
computer server acting as a gateway often also acts as a proxy server
and a firewall server. A gateway is often associated with both a
router, which knows where to direct a given packet of data that
arrives at the gateway, and a switch, which furnishes the actual path
in and out of the gateway for a given packet.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) - GIF is one of the most common
rmats used for images in web pages. There are two versions of
file fo
the format, 87a and 89a. Version 89a supports animations, i.e. a short
sequence of images within a single GIF file. A GIF89a can also be
specified for interlaced presentation.
GOV (Group Of VOPs) - A group of VOP's is the basic unit of an
PEG-4 video stream. The GOV contains different types and numbers
M
of VOP's (I-VOP's, P-VOP's, etc.) as determined by the GOV length
and GOV structure. See also VOP.
GOV length - The GOV length determines the number of images
s) in the GOV structure. See also GOV and VOP.
(VOP'
GOV structure - The GOV structure describes the composition of an
PEG-4 video stream, as regards the type of images (I-VOP's or
M
P-VOP's) included in the stream, and their internal order. See also
GOV and VOP.
Half-duplex - See Full-duplex.
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) - HTML is the set of “markup”
bols or codes inserted in a file intended for display in web
sym
browser. The markup tells the browser how to display the page's
words and images for the user.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) - HTTP is the set of rules for
xchanging files (text, graphic images, sound, video, and other
e
multimedia files) on the web. The HTTP protocol runs on top of the
TCP/IP suite of protocols.
Hub - A (network) hub is used to connect multiple devices to the
twork. The hub transmits all data to all devices connected to it,
ne
whereas a switch will only transmit the data to the device it is
specifically intended for.
IEEE 802.11 - A family of standards for wireless LANs. The 802.11
dard supports 1 or 2 Mbit/s transmission on the 2.4 GHz band.
stan
IEEE 802.11b specifies an 11 Mbit/s data rate on the 2.4 GHz band,
while 802.11a allows up to 54 Mbit/s on the 5 GHz band.
Image compression - Image compression minimizes the file size (in
ytes) of an image. Two of the most common compressed image
b
formats are JPEG and GIF.
Interlacing - Interlaced video is video captured at 50 pictures (known
fields) per second, of which every 2 consecutive fields (at half
as
height) are then combined into 1 frame. Interlacing was developed
many years ago for the analog TV world and is still used widely
today. It provides good results when viewing motion in standard TV
pictures, although there is always some degree of distortion in the
image.
To view interlaced video on e.g. a computer monitor, the video must
e de-interlaced, to produce progressive video, which consists of
first b
complete images, one after the other, at 25 frames per second. See
also Progressive scan.
IP (Internet Protocol) - The Internet Protocol is a method
transmitting
individual and completely independent “packets.” Each computer (or
host) on the Internet has at least one address that uniquely identifies
it from all others, and each data packet contains both the sender's
address and the receiver's address.
The Internet Protocol ensures that the data packets all arrive at the
intende
there is no established connection between the communication
end-points, packets can be sent via different routes and do not need
to arrive at the destination in the correct order.
Once the data packets have arrived at the correct destination, another
protocol
right order. See also TCP.
IP Address - An IP address is simply an address on an IP network
used
allow all the connected computers/devices to find each other and to
pass data back and forth.
To avoid conflicts, each IP address on any given network must be
uniq
change, or it can be assigned dynamically (and automatically) by
DHCP.
An IP address consists of four groups (or quads) of decimal digits
eparated by periods, e.g. 130.5.5.25. Different parts of the address
s
represent different things. Some part will represent the network
number or address, and some other part will represent the local
machine address.
See also IP (Internet Protoc
I-VOP - See VOP.
JPEG (Joint Photographi
file format, JPEG is an image file type commonly used on the web. A
JPEG image is a bitmap, and usually has the file suffix '.jpg' or
“.jpeg.” When creating a JPEG image, it is possible to configure the
level of compression to use. As the lowest compression (i.e. the
highest quality) results in the largest file, there is a trade-off between
image quality and file size.
kbit/s (kilobits per second) - A measure of the bit rate, i.e. the rate at
which
LAN (Local Area Network) - A LAN is a group of computers and
associate
limited geographical area.
Linux - Linux is an open source operating system within the Unix
ily. Because of its robustness and availability, Linux has won
fam
popularity in the open source community and among commercial
application developers.
MAC address (Media Access Control address) - A MAC address is a
uniq
more specifically, its interface with the network. For example, the
network card in a computer has its own MAC address.
Manual iris - This is the opposite to an autoiris, i.e. the camera iris
mus
reach the image sensor.
Mbit/s (Megabits per second) - A measure of the bit rate, i.e. the rate
at
which bits are passing a given point. Commonly used to give the
“speed” of a network. A LAN might run at 10 or 100 Mbit/s. See also
data over a network. Data to be sent is divided into
d address. As IP is a connections protocol, which means that
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) - puts them in the
by a computer/device connected to that network. IP addresses
ue. An IP address can be assigned as fixed, so that it does not
ol).
c Experts Group) - Together with the GIF
bits are passing a given point. See also Bit rate.
d devices that typically share common resources within a
ue identifier associated with a piece of networking equipment, or
t be adjusted manually to regulate the amount of light allowed to
Page 43

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
43
Bit rate.
Monitor - A monitor is very similar to a standard television set, but
cks the electronics to pick up regular television signals.
la
Motion JPEG - Motion JPEG is a simple compression/decompression
te
chnique for networked video. Latency is low and image quality is
guaranteed, regardless of movement or complexity of the image.
Image quality is controlled by adjusting the compression level, which
in turn provides control over the file size, and thereby the bit rate.
High-quality individual images from the Motion JPEG stream are
asily extracted. See also JPEG.
e
Megapixel - See Pi
MPEG (Moving Picture Ex
Experts Group develops standards for digital video and audio
compression. It operates under the auspices of the International
Organization for Standardization (ISO). The MPEG standards are an
evolving series, each designed for a different purpose.
MPEG-2 - MPEG-2 is the designation for a group of audio and video
oding standards, and is typically used to encode audio and video for
c
broadcast signals, including digital satellite and Cable TV. MPEG-2,
with some modifications, is also the coding format used by standard
commercial DVD movies.
MPEG-4 - MPEG-4 is a group of audio and video coding standards
nd related technology. The primary uses for the MPEG-4 standard
a
are web (streaming media) and CD distribution, conversational
(videophone), and broadcast television.
Most of the features included in M
developers to decide whether to implement them or not. This means
that there are probably no complete implementations of the entire
MPEG-4 set of standards. To deal with this, the standard includes the
concept of “profiles” and “levels”, allowing a specific set of
capabilities to be defined in a manner appropriate for a subset of
applications.
Multicast - Bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces
andwidth usage by simultaneously delivering a single stream of
b
information to multiple network recipients.
Multiplexer - A multiplexer is a high-speed switch that provides
full-scree
playback everything that happened on any one camera with no
interference from the other cameras on the system.
Network connectivity - The physical (wired or wireless) and logical
(p
to a network, such as the Internet or a LAN.
NTSC (National Television System Committee) - NTSC is the
te
lines at 60 half-frames/second.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) - This is a designation for
c
sold to other companies under their own names.
PAL (Phase Alternating Line) - PAL is the dominant television
stan
PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) - An early standard for securing
e
HTTPS certificate or certificate request.
Ping - Ping is a basic network program used diagnostically to check
the
particular network address (IP address or host name) is occupied or
not, or if the host at that address is responding normally. Ping can be
run from e.g. the Windows Command prompt or the command line in
Unix.
Pixel - A pixel is one of the many tiny dots that make up a digital
im
the complete image.
PoE (Power over Ethernet) - Power over Ethernet provides power to
a
connection. This is very useful for IP-Surveillance and remote
monitoring applications in places where it may be too impractical or
n images from up to 16 analog cameras. Multiplexers can
rotocol) connection of a computer network or an individual device
levision and video standard in the United States. NTSC delivers 525
ompanies that manufacture equipment which is then marketed and
dard in Europe. PAL delivers 625 lines at 50 half-frames/second.
lectronic mail. The PEM-format is often used for representing an
status of a network host or device. Ping can be used to see if a
age. The color and intensity of each pixel represents a tiny area of
network device via the same cable as used for the network
xel.
perts Group) - The Moving Picture
PEG-4 are left to individual
expensive to power the device from a power outlet.
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) - A protocol that uses a serial
ce for communication between two network devices. For
interfa
example, a PC connected by a phone line to a server.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunnelling Proto
communication rules) that allows corporations to extend their own
corporate network through private “tunnels” over the public Internet.
In this way a corporation can effectively use a WAN (Wide Area
Network) as a large single LAN (Local Area Network). This kind of
interconnection is known as a virtual private network (VPN).
Pre/post alarm images - The images from immediately before and
r an alarm. These images are stored in a buffer for later retrieval.
afte
Progressive scan - Progressive scan, as opposed to interlaced video,
ans the entire picture, line by line every sixteenth of a second. In
sc
other words, captured images are not split into separate fields as in
interlaced scanning.
Computer monitors do not need interlace to show the picture on the
creen, but instead show them progressively, on one line at a time in
s
perfect order, i.e. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 etc., so there is virtually no
“flickering” effect. In a surveillance application, this can be critical
when viewing detail within a moving image, such as a person
running. A high-quality monitor is required to get the best from
progressive scan. See also Interlacing.
Protocol - A special set of rules governing how two entities will
unicate. Protocols are found at many levels of communication,
comm
and there are hardware protocols and software protocols.
Proxy server - In an organization that uses the Internet, a proxy
rver acts as an intermediary between a workstation user and the
se
Internet. This provides security, administrative control, and a caching
service. Any proxy server associated with a gateway server, or part of
a gateway server, effectively separates the organization’s network
from the outside network and the local firewall. It is the firewall
server that protects the network against outside intrusion.
A proxy server receives requests for Internet services (such
page requests) from many users. If the proxy server is also a cache
server, it looks in its local cache of previously downloaded web pages.
If it finds the page, it is returned to the user without forwarding the
request to the Internet. If the page is not in the cache, the proxy
server, acting as a client on behalf of the user, uses one of its own IP
addresses to request the page from another server over the Internet.
When the requested page is returned, the proxy server forwards it to
the user that originally requested it.
P-VOP - See VOP.
Resolution - Image resolution is a measure of how much detail a
igital image can hold: the greater the resolution, the greater the level
d
of detail. Resolution can be specified as the number of pixel-columns
(width) by the number of pixel-rows (height), e.g. 320x240.
Alternatively, the total number of pixels (usually in megapixels) in
image can be used. In analog systems it is also common to use
the
other format designations, such as CIF, QCIF, 4CIF, etc.
RTCP (Real-Time Control Protocol) - RTCP provides support for
real-
time conferencing of groups of any size within an intranet. This
support includes source identification and support for gateways like
audio and video bridges as well as multicast-to-unicast translators.
RTCP offers quality-of-service f
multicast group as well as support for the synchronization of
different media streams.
RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) - RTP is an Internet protocol for
transport of real-time data, e.g. audio and video. It can be used
the
for media-on-demand as well as interactive services such as Internet
telephony.
RTSP (Real Time Stream
and a starting point for negotiating transports such as RTP, multicast
and Unicast, and for negotiating codecs.
RTSP can be considered a “remote control” for controlling the media
tream delivered by a media server. RTSP servers typically use RTP as
s
the protocol for the actual transport of audio/video data.
ing Protocol) - RTSP is a control protocol,
col) - A protocol (set of
as web
eedback from receivers to the
Page 44

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
44
Router - A device that determines the next network point to which a
packet should be forwarded on its way to its final destination. A
router creates and/or maintains a special routing table that stores
information on how best to reach certain destinations. A router is
sometimes included as part of a network switch. See also switch.
Server - In general, a server is a computer program that provides
rvices to other computer programs in the same or other computers.
se
A computer running a server program is also frequently referred to as
a server. In practice, the server may contain any number of server and
client programs. A web server is the computer program that supplies
the requested HTML pages or files to the client (browser).
Sharpness - This is the control of fine detail within a picture. This
feature was origina
filter decoders. This filter took away all high frequency detail in the
black and white region of the picture. The sharpness control
attempted to put some of that detail back in the picture. Sharpness
controls are mostly superfluous in today's high-end TVs. The only
logical requirement for it nowadays is on a VHS machine.
Simplex - In simplex operation, a network cable or communications
hannel can only send information in one direction.
c
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) - SMTP is used for sending
nd receiving e-mail. However, as it is “simple,” it is limited in its
a
ability to queue messages at the receiving end, and is usually used
with one of two other protocols, POP3 or IMAP. These other protocols
allow the user to save messages in a server mailbox and download
them periodically from the server.
SMTP authentication is an extension of SMTP, whereby the client is
quired to log into the mail server before or during the sending of
re
mail. It can be used to allow legitimate users to send email while
denying the service to unauthorized users, such as spammers.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
of the Internet Protocol suite, as defined by the Internet Engineering
Task Force. The protocol can support monitoring of network-attached
devices for any conditions that warrant administrative attention.
Sockets - Sockets are a method for communication between a client
rogram and a server program over a network. A socket is defined as
p
“the endpoint in a connection.” Sockets are created and used with a
set of programming requests or “function calls” sometimes called the
sockets application programming interface (API).
SSL/TSL (Secure Socket Layer/Transport Laye
These two protocols (SSL is succeeded by TSL) are cryptographic
rotocols that provide secure communication on a network. SSL is
p
commonly used over HTTP to form HTTPS, as used e.g. on the
Internet for electronic financial transactions. SSL uses public key
certificates to verify the identity of the server.
Subnet/subnet mask - A subnet is an identifiably separate part of an
rganization's network. Typically, a subnet may represent all the
o
machines at one geographic location, in one building, or on the same
local area network (LAN). Having an organization's network divided
into subnets allows it to be connected to the Internet with a single
shared network address.
The subnet mask is the part of the IP address that tells a network
router how to
to. Using a subnet mask saves the router having to handle the entire
32-bit IP address; it simply looks at the bits selected by the mask.
Switch - A switch is a network device that connects network
gments together, and which selects a path for sending a unit of data
se
to its next destination. In general, a switch is a simpler and faster
mechanism than a router, which requires knowledge about the
network and how to determine the route. Some switches include the
router function. See also Router.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - TCP is used along with the
t Protocol (IP) to transmit data as packets between computers
Interne
over the network. While IP takes care of the actual packet delivery,
TCP keeps track of the individual packets that the communication
(e.g. requested a web page file) is divided into, and, when all packets
have arrived at their destination, it reassembles them to re-form the
complete file.
lly introduced into color TV sets that used notch
- SNMP forms part
r Security)
find the subnet that the data packet should be delivered
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, which means that a
ction is established between the two end-points and is
conne
maintained until the data has been successfully exchanged between
the communicating applications.
Telnet - Telnet is a simple method with which to access another
rk device, e.g. a computer. The HTTP protocol and the FTP
netwo
protocols allow you to request specific files from remote computers,
but do not allow you logon as a user of that computer. With Telnet,
you log on as a regular user with whatever privileges you may have
been granted for specific applications and data residing on that
computer.
TVL (TV Lines) - A method of defining resolutions in analog video.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - UDP is a communications protocol
t offers limited service for exchanging data in a network that uses
tha
the Internet Protocol (IP). UDP is an alternative to the Transmission
Control Protocol (TCP). The advantage of UDP is that it is not required
to deliver all data and may drop network packets when there is e.g.
network congestion. This is suitable for live video, as there is no point
in re-transmitting old information that will not be displayed anyway.
Unicast - Communication between a single sender and a single
ver over a network. A new connection is established for each
recei
new user.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) - An “address” on the network.
USB - (Universal Serial Bus) A plug-and-play interface between a
computer and perip
Varifocal lens - A varifocal lens provides a wide range of focal
lengths, a
provides one.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) - This creates a secure “tunnel”
betwe
“key” will be able to work within the VPN. The VPN network can be
within a company LAN (Local Area Network), but different sites can
also be connected over the Internet in a secure way. One common use
for VPN is for connecting a remote computer to the corporate
network, via e.g. a direct phone line or via the Internet.
VOP (Video Object Plane) - A VOP is an image frame in an MPEG-4
video stream
- An I-VOP is complete image frame.
- A P-VOP codes the differences between images, as long as it is more
eff
be a completely new image.
WAN (Wide-Area-Network) - Similar to a LAN, but on a larger
geogra
W-LAN (Wireless LAN) - A wireless LAN is a wireless local area
netwo
connections for end-users are wireless. The main network structure
usually uses cables.
Web server - A Web server is a program, which allows Web
browsers to
The Web server listens for requests from Web browsers and upon
receiving a request for a file sends it back to the browser.
The primary function of a Web server is to serve pages to other
remote
computer that is permanently connected to the Internet. It also
controls access to the server whilst monitoring and logging server
access statistics.
WEP (Wireless Equivalent Privacy) - A wireless security protocol,
pecified in the IEEE 802.11 standard, which is designed to provide a
s
wireless local area network (WLAN) with a level of security and
privacy comparable to that usually expected of a wired LAN. Security
is at two different levels; 40-bit and 128-bit encryption. The higher
the bit number, the more secure the encryption.
WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) - Part of the Microsoft
Windows NT Se
names and locations with IP addresses, without the user or
administrator having to be involved in each configuration change.
s opposed to a lens with a fixed focal length, which only
en the points within the VPN. Only devices with the correct
icient to do so. Otherwise it codes the whole image, which may also
phical scale.
rk that uses radio waves as its carrier: where the network
computers; consequently, it needs to be installed on a
heral devices, e.g. scanners, printers, etc.
. There are several types of VOP:
retrieve files from computers connected to the Internet.
rver, WINS manages the association of workstation
Page 45

WPA-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access - Pre-Shared Key) - This
wireless encryption method uses a pre-shared key (PSK) for key
management. Keys can usually be entered as manual hex values, as
hexadecimal characters, or as a Passphrase. WPA-PSK provides a
greater degree of security than WEP.
Zoom lens - A zoom lens can be moved (zoomed) to enlarge the view
f an object to show more detail.
o
AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
45
Page 46

AXIS 209FD/FD-R/FD-R M12
46
Index
A
Action Buttons 17
Administrator 12
Alarm 23
AMC Viewer Toolbar 8
ARP/Ping 27
B
Backup 30
Bit Rate 15, 16
Bonjour 7, 30
Buffer Size 21
Buffers 21
C
Camera Tampering 22
Configuration 12
Control Button 6, 31
Live View 8, 12
Live View Config 17
M
Maintenance 30
Manual Trigger Button 18
Motion Detection 23
MPEG-4 Settings 15
N
NAT traversal 8, 28
Network Settings 26
Notification of IP address change 27
NTP Server 26
P
Post-trigger Buffer 21
Pre-trigger Buffer 21
Q
QoS 29
QuickTime 7, 11, 17
D
Date & Time 26
Default Viewer 17
DNS Configuration 27
DNS Server 27
Domain Name 27
E
Emergency Recovery 33
Enable ARP/Ping 27
Event Servers 20
Events 20
F
Factory Default Settings 31
Frame Rate 14
FTP Server 20
G
GOV Settings 16
H
Host Name 27
HTTP Server 20
HTTPS 25
I
Include Windows 23
IP Address Filtering 25
R
Real Player 7, 11
Referrals 25
Restore 30
S
Scheduled Event 21
Security 25
Server Time 26
Services 26
Snapshot Button 18
Snapshot button 8
SNMP 30
Support 31
System Options 25
T
TCP Server 20
TCP/IP Settings 26
Time Mode 26
Troubleshooting 33
U
Upgrade Server 30
UPnP 27, 30
Users 25
V
Video Stream 14
L
LED Settings 30
Lighting Conditions 15
 Loading...
Loading...