AVER AL128 Datasheet

AL128 Data Sheets

Contents
AL128
1.0 Features ________________________ 3
2.0 Applications _____________________ 4
3.0 General Description _______________ 4
4.0 Pinout Diagram __________________ 5
5.0 Pin Definition and Description ______ 6
6.0 Functional Description ___________ 12
6.1 Input Interface ___________________ 12
6.1.1 24-bit RGB_______________________ 13
6.1.2 VAFC___________________________ 13
6.1.3 Feature Connector _________________ 14
6.1.4 Sampling (Pixel) Clock _____________ 14
6.2 Hardware and Software Control Modes
___________________________________ 15
6.3 Video Timing ____________________ 15
6.4 Supported Resolutions_____________ 17
6.5 Flicker Filter_____________________ 18
6.6 Overscan/Underscan Control _______ 18
9.0 Board Design and Layout
Considerations ______________________40
9.1 Grounding_______________________ 40
9.2 Power Planes _____________________ 40
9.3 Power Supply Decoupling __________ 40
9.4 Digital Signal and Clock Interconnect 40
9.5 Analog Signal Interconnect _________ 41
9.6 Component Placement _____________ 41
10.0 Mechanical Drawing _____________42
11.0 Power Consumption______________44
6.7 Pan and Position Control___________ 18
6.8 Zoom Feature ____________________ 18
6.9 Frame Buffer Management _________ 19
6.10 Digital Video Encoder ____________ 19
6.11 Push Button Interface/OSD________ 19
6.12 Memory Control Timing __________ 20
6.13 I2C Programming________________ 23
7.0 Electrical Characteristics__________ 26
7.1 Recommended Operating Conditions_ 26
7.2 Characteristics ___________________ 26
8.0 AL128 Register Definition_________ 27
8.1 Index of the Control Registers_______ 27
8.2 Control Register Description________ 28
8.3 AL128 Plug & Play Hardware Table _ 38
April 2, 1999 2
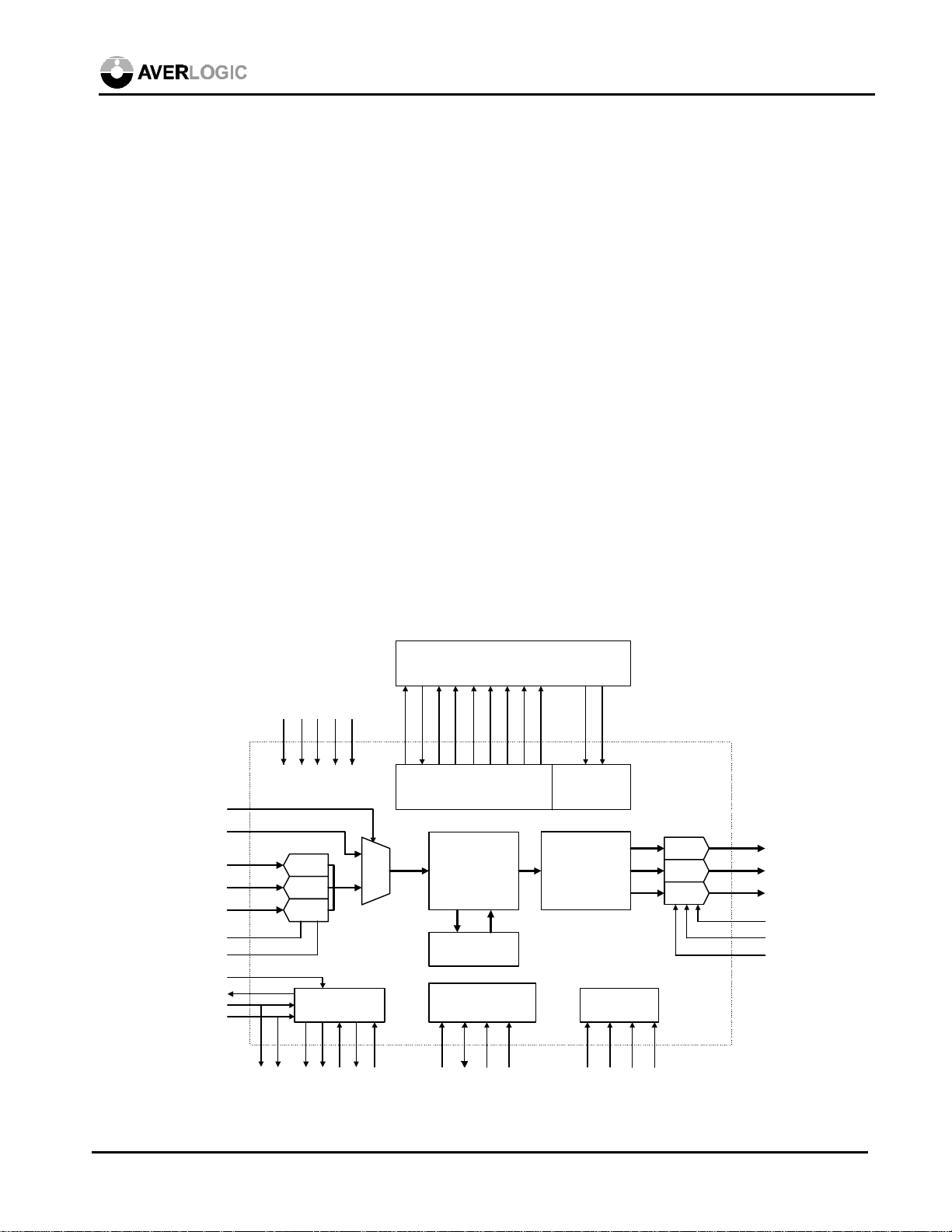
AL128 Plug and Play VGA to NTSC/PAL Converter
GHSOUT
GVSOUT
SELECT
I
1.0 Features
• Convert non-interlaced VGA or Macintosh
video into interlaced TV format (NTSC/PAL)
• Analog RGB output for SCART interface
• Highly integrated design with built-in
NTSC/PAL encoder, ADC, DAC and SRAM
• Broadcast TV quality
• High clarity 5-line anti-flicker filter
• 8 levels of sharpness control
• Plug and play with no need for software or
micro-controller
• Supports up to full 1024x768 VGA resolution
• Automatically supports scan rate from 50 Hz
up to 100 Hz
• Linear vertical and horizontal overscan/
underscan control
AL128
• Zoom and freeze controls
• Four-touch-button interface with on-screen-
menu (on TV) to control all key functions
• Horizontal and vertical position centering
control
• Optional digital 24-bit RGB/VAFC interface
for best quality
• Power down feature controlled by software or
hardware
• Full programmability via I2C interface
• Picture panning control
• Brightness control
• Built-in color bar
• Simultaneous display on PC and TV monitors
• Single 5-volt support
• Thin, small LQFP package for PCMCIA or
notebooks. 28x28 PQFP available upon request
ADEN
Digital R, G, B
VRT
VRB
GCLK
GHSDIV
GHSYNC
GVSYNC
Field Memory
RGB
PAL
/RESET/RESET
R
G
B
/PWRDN
8-bit
ADC
8-bit
ADC
8-bit
ADC
Generating
TVCLK
INTYPE
Timing
XIN1
XOUT1
MUX
XIN2
XOUT2
MD
MQ
Management
MWENL
MWRST
MWENH
Memory
Unit
Digital
Video
Processor
Video
Memory
I2C
2 C
Interface
SCL
SDA
MREN
MRRST
2
CADDR
2
MWCLK
C
I
MRCLK
Memory
Configuration
Digital
Encoder
MEMTYPE
MEMCONF
Setup
TV
Push Button
Interface
MENU
INC
DEC
9-bit
DAC
9-bit
DAC
9-bit
DAC
ACMP / R
AY / G
AC / B
RSET
VREF
COMP
AL128-01
April 2, 1999 3

2.0 Applications
PC ready multimedia TV
TV output for laptop, network, entertainment PC
Net browser/set-top box
Internet TV
VGA add-on card with TV output
VGA to TV converter box
3.0 General Description
AL128
The AL128 PC to TV scan converter chip
accepts graphic data up to 1024x768
resolution from PC and Macintosh graphics
controllers and converts it into broadcastquality NTSC or PAL TV signals. In addition
to analog RGB, 24-bit digital RGB data can
be input to maintain the best video quality and
avoid noise problems. This new chip is pin-topin compatible with the AverLogic AL100 but
provides analog RGB output for SCART
implementation.
An integrated high-quality anti-flicker filter
(SmartFilter ) removes the unpleasant
flicker caused by the interlaced display of high
contrast graphics while maintaining the
original clarity and sharpness of informative
data such as natural pictures and text.
With 512Kbytes of memory, plug-and-play is
achieved by automatically detecting the scan
rate and resolution of the incoming graphic
signals without the use of software. With less
memory than other solutions on the market,
high resolution data is processed and stored by
using a complex and proprietary buffer
management system. No compromise is made
at all with video quality by using either
compression or sub-sampling algorithms.
The major functions of the AL128 can be
accessed using four push buttons combined
with the on-screen-menu feature, eliminating
the cost of a micro-controller and complex
control panel. The superior quality scaling
algorithm, which reduces the jagged-edge
artifacts from line dropping, can smoothly fit
graphics of 640x480 (up to 100 Hz) and
1024x768 (up to 75Hz) resolutions into the
visible region of the NTSC or PAL screen.
Both horizontal and vertical sizes can be
linearly adjusted. Additional features include
eight levels of flicker control using 5-line
filter, zoom control and picture freeze.
This highly integrated mix-signal chip,
packaged in 24mm x 24mm 160-pin LQFP
(low quad flat package), is powered by a
single 5-volt power supply. Power-down is
achieved by using either hardware or software
control.
The enhanced features and superior quality
make the AL128 very suitable for PC video to
TV conversion in PC ready multimedia TV’s,
scan converter boxes, VGA add-on cards,
Web TVs, or network / laptop PCs.
April 2, 1999 4
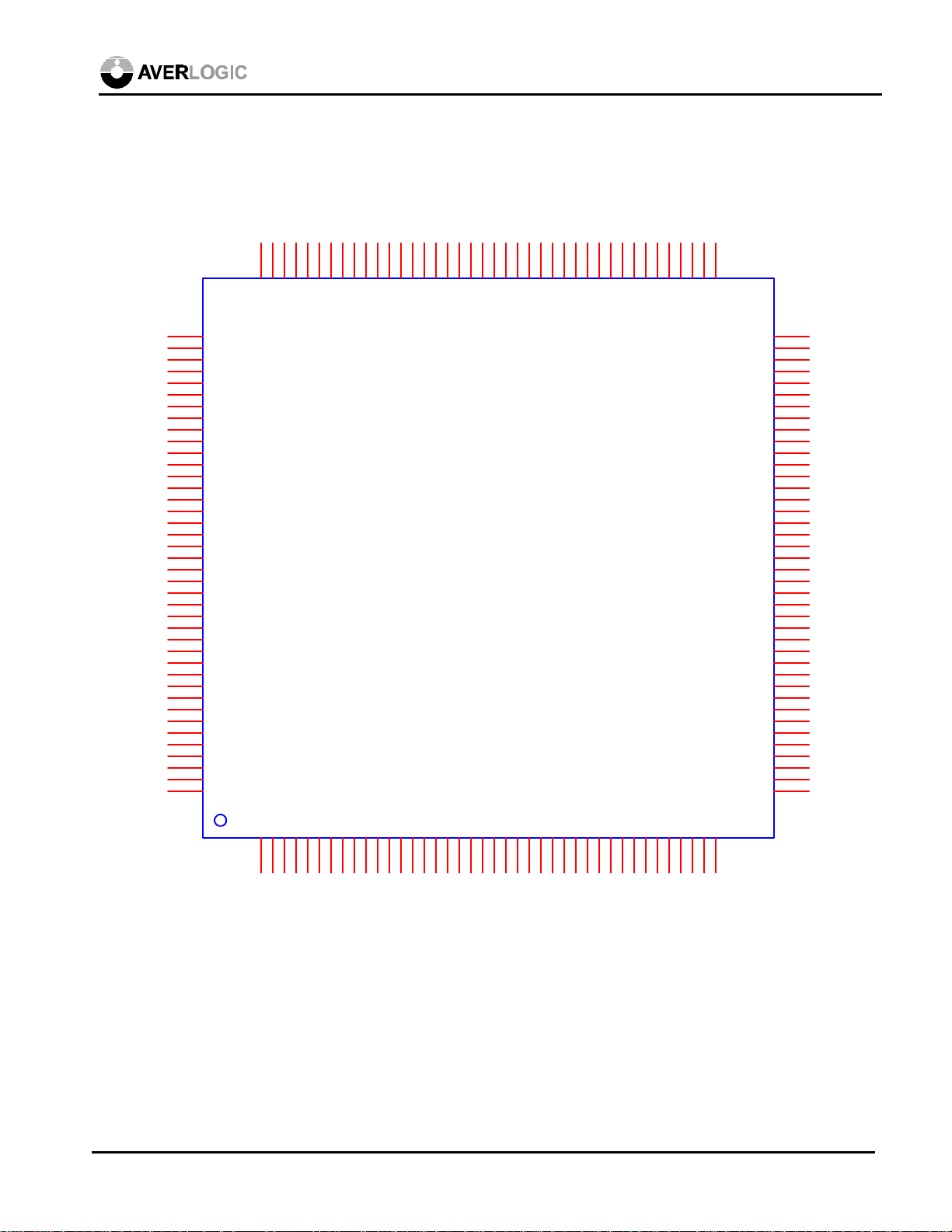
4.0 Pinout Diagram
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
108
107
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
AL128
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
BLUE5
BLUE4
VDD
BLUE3
BLUE2
BLUE1
BLUE0
ADGND
AB
ADVDD
ADVDD
AG
ADGND
VRT
VRB
ADGND
AR
ADVDD
VDD
GHSYNC
GVSYNC
GND
GCLK
VDD
GHSOUT
GHSDIV
GVSOUT
/PWRDN
/RESET
VDD
TVCLK
CLKTYPE
XOUT2
XIN2
GND
INTYPE1
INTYPE0
XOUT1
XIN1
GND
GND
BLUE6
BLUE7
RGBOUT
PAL
INC
GREEN0
GREEN1
GREEN2
DEC
SELECT
MENU
VDD
GREEN3
GREEN4
ADEN
VDD
TEST1
GREEN5
GREEN6
GREEN7
I2CADDR
SDA
I2C
GND
SCL
RED0
RED1
GND
TEST2
RED2
RED3
RED4
RED5
RED6
RED7
AL128
GND
TEST3
TEST4
TEST5
TEST6
TEST7
VDD
MQ0
TEST8
TEST9
MQ1
MQ2
VDD
TEST10
MQ3
MQ4
GND
GVSOUT2
TEST11
MQ5
MQ6
MQ7
TVVSYNC
TVHSYNC
GHSOUT2
GND
VDD
MD0
MD1
MD2
TVCSYNC
DAVDD
VREF
TEST12
MD3
MD4
GND
DAGND
AC/BOUT
MD5
MD6
MWENL
MWENH
MEMCONF0
MEMCONF1
MWCLK
MEMTYPE
MWRST
MRRST
MRCLK
DAVDD
DAVDD
DAGND
DAGND
AY/GOUT
MD7
VDD
GND
VDD
GND
MREN
MQ8
MQ9
MQ10
MQ11
VDD
MQ12
MQ13
MQ14
MQ15
GND
MD8
MD9
MD10
MD11
GND
MD12
MD13
MD14
MD15
VDD
COMP
RSET
ACMP/
ROUT
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
April 2, 1999 5
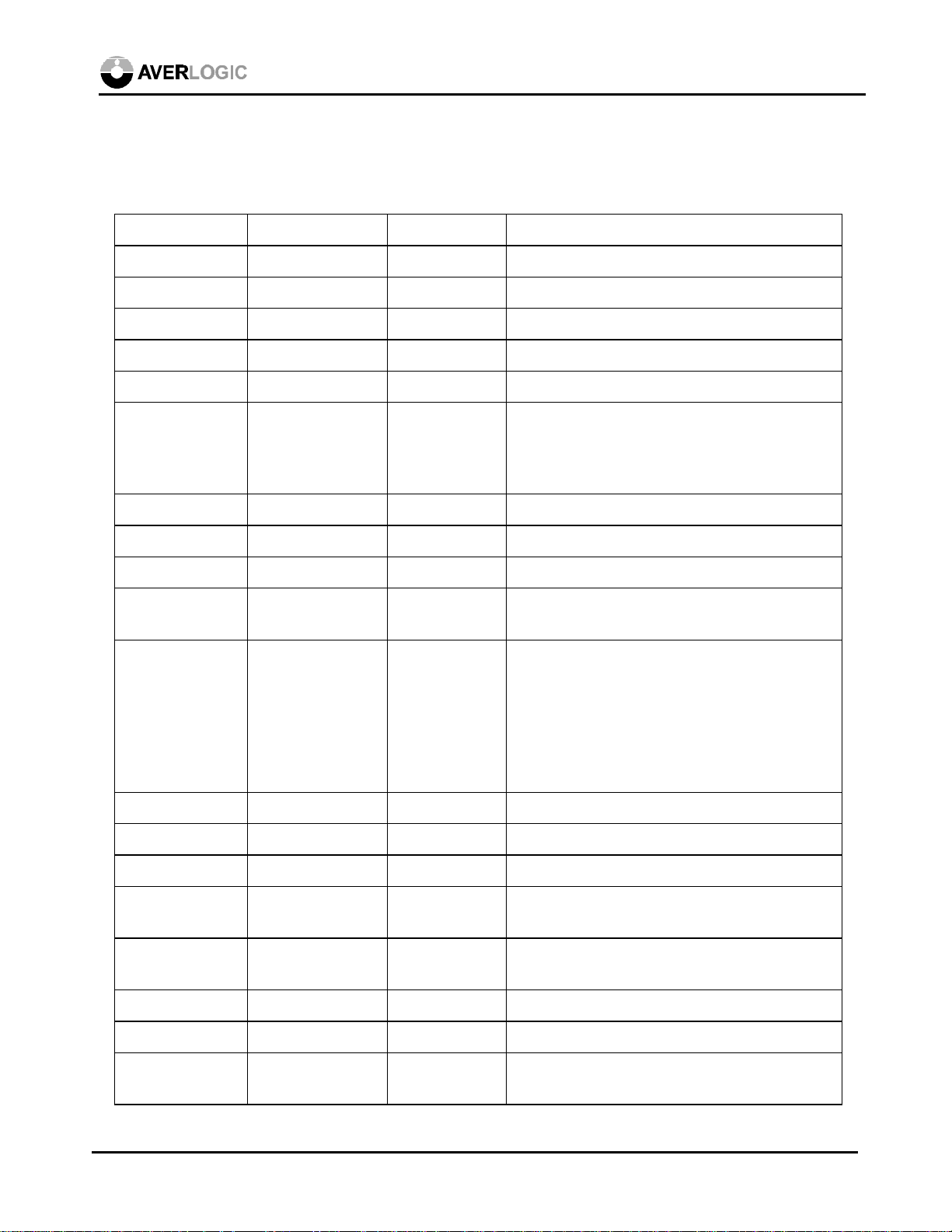
5.0 Pin Definition and Description
Total pin count: 160 pins
Symbol Type Pin Description
/PWRDN in (CMOSd) 148 Power down enable (active low)
/RESET in (CMOSd) 149 Reset (active low)
AB in (0.7 V) 129 Analog Blue
AC/BOUT out (1/0.7 V p-p) 37 Analog chroma output or analog blue output
ACMP/ROUT out (1/0.7 V p-p) 41 Analog composite output or analog red output
ADEN in (CMOSd) 7 Internal ADC enable
0, internal ADC disable
1, internal ADC enable
AG in (0.7 V) 132 Analog Green
AL128
AR in (0.7 V) 137 Analog Red
AY/GOUT out (1/0.7 V p-p) 39 Analog luma output or analog green output
BLUE<7:0> in (CMOSd) 119-122, 124-
127
CLKTYPE in (CMOSd) 152 Clock Frequency
COMP in (0.1uF) 43 DAC Compensation pin, 0.1uF pull-up
DEC in (CMOSsd) 4 Decrement button
GCLK in (CMOS) 143 Graphic pixel clock
GHSDIV out (CMOS) 146 Graphic pixel clock divide by M signal for
GHSOUT out (TTL) 145 Graphic hsync output buffered from external
Graphic Blue input data
0 - 28.63636 MHz for NTSC,
35.46895 MHz for PAL
1 - 14.31818 MHz for NTSC,
17.734475 MHz for PAL
external PLL circuits.
VGA HSYNC
GHSOUT2 out (CMOS) 28 No Connection
GHSYNC in (CMOSd) 140 Graphic Hsync
GREEN<7:0> in (CMOSd) 109-112, 114-
117
Graphic Green input data
April 2, 1999 6
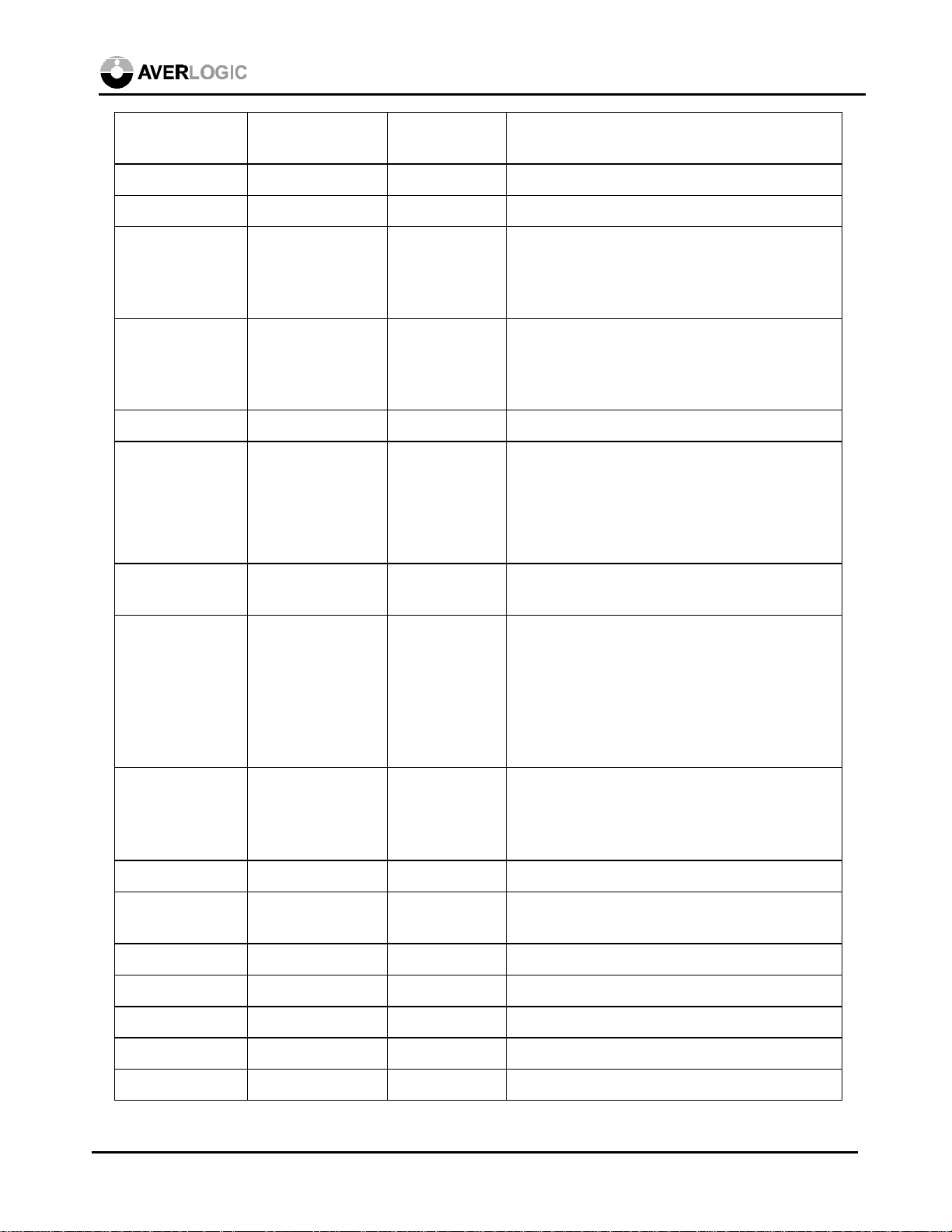
GVSOUT out (TTL) 147 Graphic vsync output buffered from external
VGA VSYNC
GVSOUT2 out (CMOS) 27 Buffered graphic vsync output II.
GVSYNC in (CMOSd) 141 Graphic VSYNC
I2C in (CMOSd) 12 I2C/Vsync programming select
0 - enable VGA sync programming
1 - enable I2C programming
I2CADDR in (CMOSd) 11 I2C sub address
0 - write address = 88, read address = 89
1 - write address = 8C, read address = 8D
INC in (CMOSsd) 3 Increment button
INTYPE<1:0> in (CMOSd) 156,157 Graphic input type
00 - 24-bit RGB 01 - reserved
10 - feature connector
AL128
11 - VAFC
MD<15:0> out (CMOS) 47-50, 52-55,
80-83, 85-88
MEMCONF
in (CMOSd) 75,76 External memory configuration
<1:0>
Memory data to input of external field
memory.
00 – Reserved
01 – One-field memory capture
10 – Two-field memory capture
11 – Reserved
MEMTYPE in (CMOSd) 72 Memory type
0 - OKI MSM518221/222
1 – AverLogic AL422 or NEC µPD42280
MENU in (CMOSsd) 6 Menu button
MQ<15:0> in (CMOSd) 57-60, 62-65,
90-93, 95-98
Memory data from output of external field
memory.
MRCLK out (CMOS) 68 Memory Read Clock
MREN out (CMOS) 66 Memory Read Enable
MRRST out (CMOS) 69 Memory Read Reset
MWCLK out (CMOS) 73 Memory Write Clock
MWENH out (CMOS) 77 Memory High Byte Write Enable
April 2, 1999 7
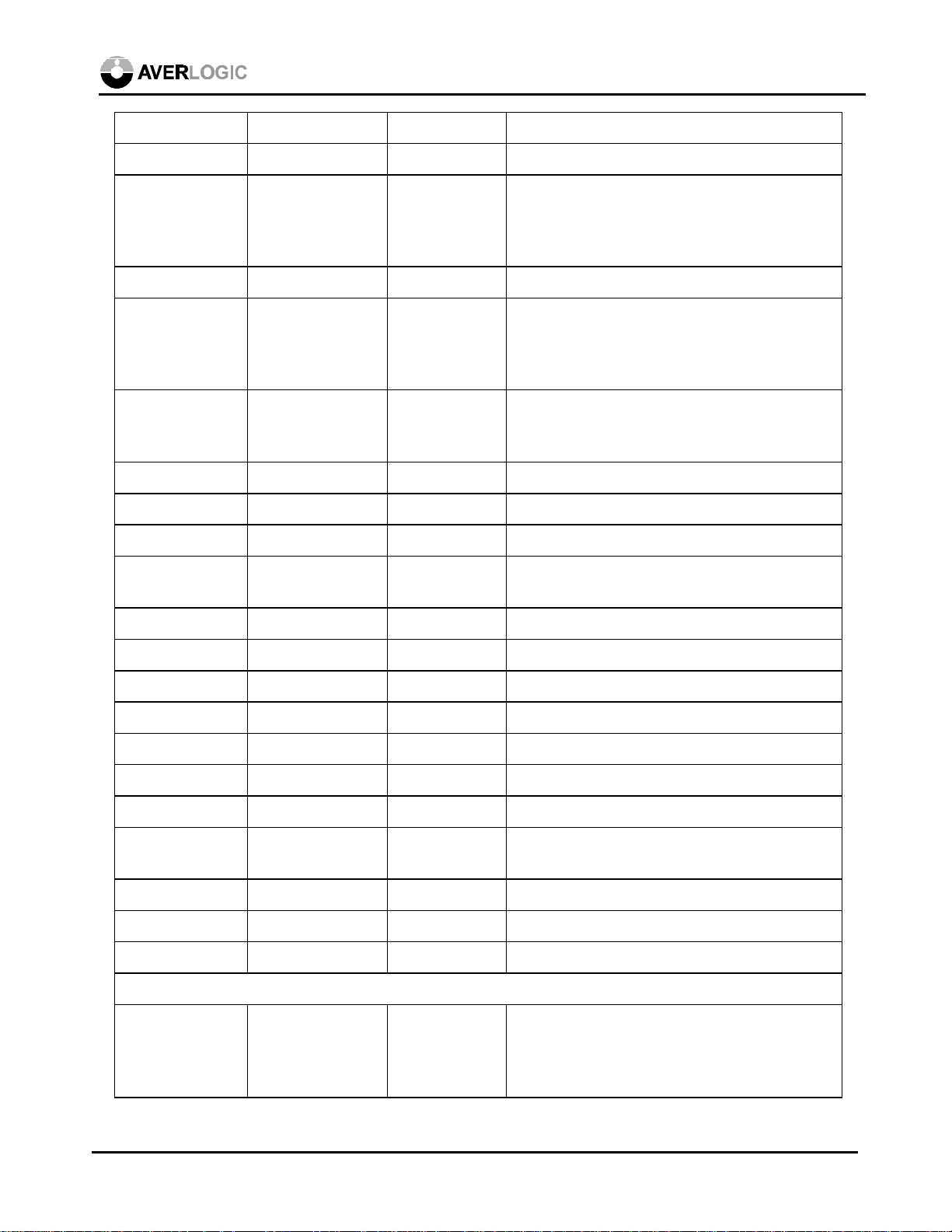
MWENL out (CMOS) 78 Memory Low Byte Write Enable
MWRST out (CMOS) 71 Memory Write Reset
PAL in (CMOSd) 2 NTSC/PAL select
0 - NTSC
1 - PAL
RED<7:0> in (CMOSd) 100-107 Graphic Red input data
RGBOUT in (CMOSd) 1 RGB/YC Composite output select
0 - ACMP, AY, AC
1 - R, G, B
RSET in 42 DAC Full scale current adjust, 82 ohm pull-
down for S-video and Composite output, 140
ohm pull-down for RGB output.
SCL in (CMOSsu) 13 I2C Clock
SDA in/out (CMOSsu) 10 I2C Data
AL128
SELECT in (CMOSsd) 5 Select button
TEST1~12 out (CMOS) 9, 15-18, 20-
Unused pins for factory test purpose only
23, 25,26,33
TVCSYNC out (CMOS) 32 TV composite sync
TVHSYNC out (CMOS) 30 TV horizontal sync
TVVSYNC out (CMOS) 31 TV vertical sync
TVCLK out (CMOS) 151 Clock output for graphic chip clock
VRB in (0 V) 135 ADC Bottom Voltage Reference
VREF in (1.23 V) 35 DAC Voltage Reference Input
VRT in 134 ADC Top Voltage Reference
XIN1/FIN1 in (CMOS) 159 Crystal Input/External Clock Input 1 for
NTSC
XIN2/FIN2 in (CMOS) 154 Crystal Input/External Clock Input 2 for PAL
XOUT1 out (CMOS) 158 Crystal Output 1 for NTSC
XOUT2 out (CMOS) 153 Crystal Output 2 for PAL
Power and Ground
VDD x 13 5V 8, 24, 46, 61,
70, 79, 89, 99,
113, 123, 139,
144, 150
Digital power
April 2, 1999 8

AL128
GND x 14 14, 19, 29, 51,
56, 67, 74, 84,
94, 108, 118,
142, 155, 160
ADVDD x 3 5V 130,131,138 ADC power
ADGND x 3 128,133,136 ADC ground
DAVDD x 3 5V 34,44,45 DAC power
DAGND x 3 36,38,40 DAC ground
Digital ground
Remarks:
CMOSd: CMOS with internal pull-down
CMOSsd: CMOS with Schmitt trigger and internal pull-down
CMOSsu: CMOS with Schmitt trigger and internal pull-up
Pin list grouped by functionality
Symbol Pin Number
Graphic Interface
BLUE<7:0> 119-122, 124-127
GREEN<7:0> 109-112, 114-117
RED<7:0> 100-107
GHSYNC 140
GVSYNC 141
GCLK 143
GHSDIV 146
GHSOUT 145
GHSOUT2 28
GVSOUT 147
GVSOUT2 27
Field Memory Interface
MD<15:0> 47-50, 52-55, 80-83, 85-88
MQ<15:0> 57-60, 62-65, 90-93, 95-98
MWENH 77
April 2, 1999 9
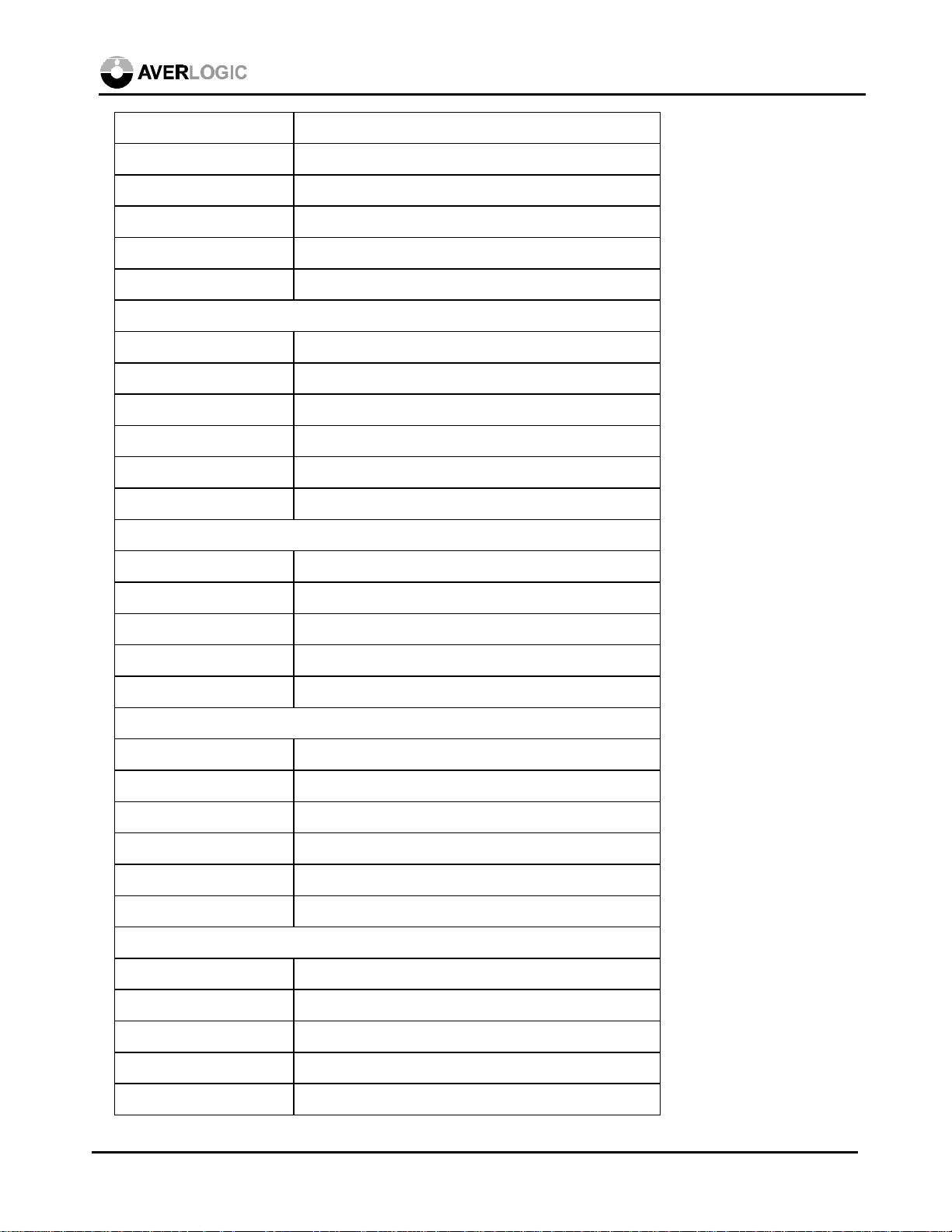
MWENL 78
MWRST 71
MREN 66
MRRST 69
MWCLK 73
MRCLK 68
TV Output
ACMP/ROUT 41
AY/GOUT 39
AC/BOUT 37
TVCSYNC 32
TVHSYNC 30
TVVSYNC 31
AL128
Clocks
XIN1/FIN1 159
XOUT1 158
XIN2/FIN2 154
XOUT2 153
TVCLK 151
User Interface
SCL 13
SDA 10
MENU 6
SELECT 5
INC 3
DEC 4
Mode select Pins
RGBOUT 1
PAL 2
INTYPE<1:0> 156,157
MEMCONF<1:0> 75,76
I2CADDR 11
April 2, 1999 10
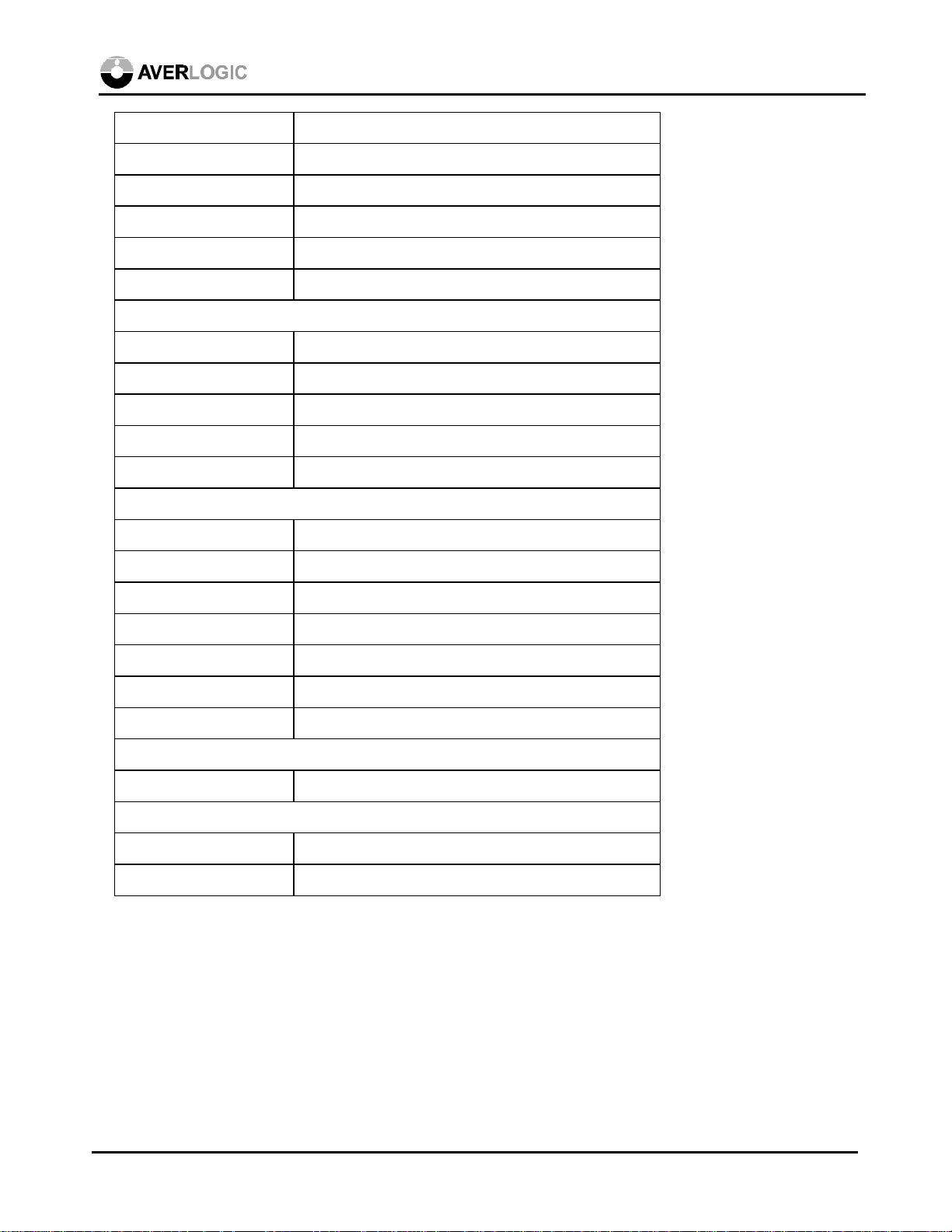
I2C 12
MEMTYPE 72
ADEN 7
CLKTYPE 152
/PWRDN 148
/RESET 149
D/A Converters
COMP 43
VREF 35
RSET 42
DAVDD x 3 34,44,45
DAGND x 3 36,38,40
A/D Converters
AL128
AR 137
AG 132
AB 129
VRT 134
VRB 135
ADVDD x 3 130,131,138
ADGND x 3 128,133,136
Test Pins
TEST1~12 9, 15-18, 20-23, 25, 26, 33
Digital Power
VDD x 13 8,24,46,61,70,79,89,99,113,123,139,144,150
GND x 14 14,19,29,51,56,67,74,84,94,108,118,142,155,160
April 2, 1999 11

AL128
6.0 Functional Description
The AL128 accepts either analog RGB or digital RGB data. The analog RGB data is digitized by
three 50MHz 8-bit video A/D converters and is converted into 24-bit digital RGB data. For graphic
controllers with standard or proprietary digital RGB output such as a high-color feature connector,
VAFC, or flat panel interface, the optional 24-bit digital RGB interface provides a solution for
optimal video quality.
The 24-bit digital RGB is passed to the digital processing unit of the chip. This DSP unit performs
scan conversion operations and other digital signal processing such as flicker filtering, YUV filtering,
scaling and color space conversion in the digital domain. The processed video data is sent to the
digital TV encoder for converting into broadcast quality composite and S-video signals or original
RGB format, which are in turn converted by three 9-bit D/A converters into analog outputs.
Functions can be controlled by dedicated hardware pins as well as software. The I2C interface
provides full software programmability. The aforementioned hardware and software programmability
also applies to the power-down feature. Alternatively only four push buttons are required to control
the major functions such as sharpness, pan, zoom, brightness, color bar output and position centering
without the use of software or microcontroller.
6.1 Input Interface
RGB data and horizontal and vertical sync signals of the VGA controller are used as inputs. Analog
RGB data or 24-bit digital RGB data are both supported. The analog R, G, B signals are digitized
with three built-in 8-bit A/D converters. The voltage swing of VGA RGB signals is typically 0.7
volts. The VRT and VRB pins set the input voltage references of the A/D converters. When digital
RGB data is used as the input, the internal A/D converters can be disabled by setting pin ADEN low,
which may significantly reduce the power consumption.
Digital inputs for the AL128 can be either 24-bit RGB 888 or 16-bit RGB 565. RGB 565 can in turn
be in VAFC or feature connector format. The INTYPE pins of the AL128 have to be set correctly
to match the different applications.
INTYPE <1:0>
Pin 156, pin 157
0 0 24-bit RGB
0 1 Reserved
1 0 Feature connector (RGB565)
1 1 VAFC (RGB565)
Digital Graphic Input Type
April 2, 1999 12
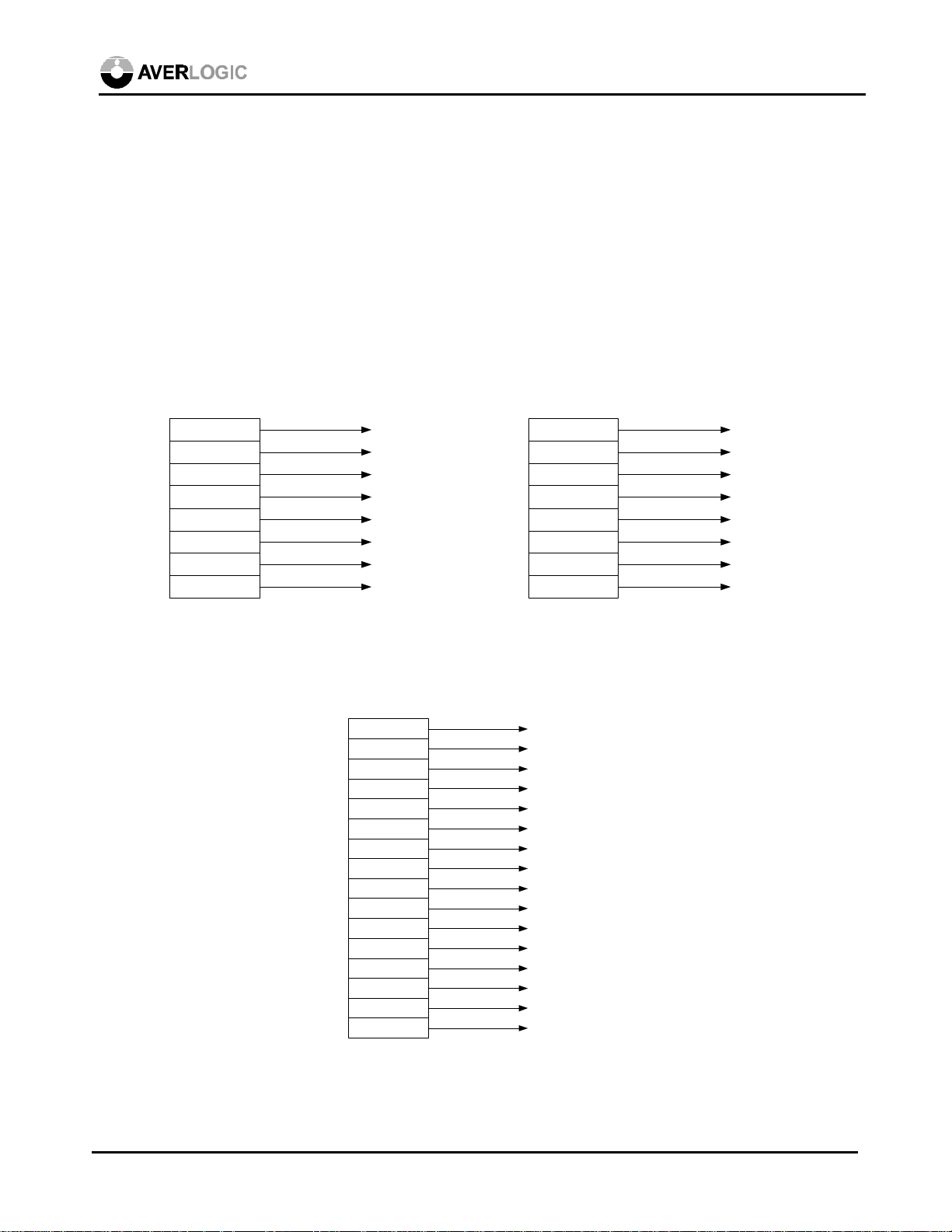
6.1.1 24-bit RGB
The digital 24-bit RGB can be pin-to-pin wired to RED<7:0>, GREEN<7:0> and BLUE<7:0> of
the AL128.
6.1.2 VAFC
The VAFC format (16-bit, RGB565, in 64k high color) carries red signals in D15~D11, green
signals in D10~D5, and blue signals in D4~D0.
There are two ways to implement VAFC interface. The first way is to set INTYPE as 11 to
accept VAFC format, then input the 16-bit RGB565 (64k high color) to GREEN<7:0> and
BLUE<7:0> of the AL128 as follows:
AL128
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
GREEN 7
GREEN 6
GREEN 5
GREEN 4
GREEN 3
GREEN 2
GREEN 1
GREEN 0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
BLUE 7
BLUE 6
BLUE 5
BLUE 4
BLUE 3
BLUE 2
BLUE 1
BLUE 0
The other way is to keep INTYPE setting as 00 to accept 24-bit RGB888, but connect the inputs
to the higher bits of RED<7:0>, GREEN<7:0> and BLUE<7:0> of the AL128 as follows. The
unused pins can be grounded.
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
RED 7
RED 6
RED 5
RED 4
RED 3
GREEN 7
GREEN 6
GREEN 5
GREEN 4
GREEN 3
GREEN 2
BLUE 7
BLUE 6
BLUE 5
BLUE 4
BLUE 3
April 2, 1999 13
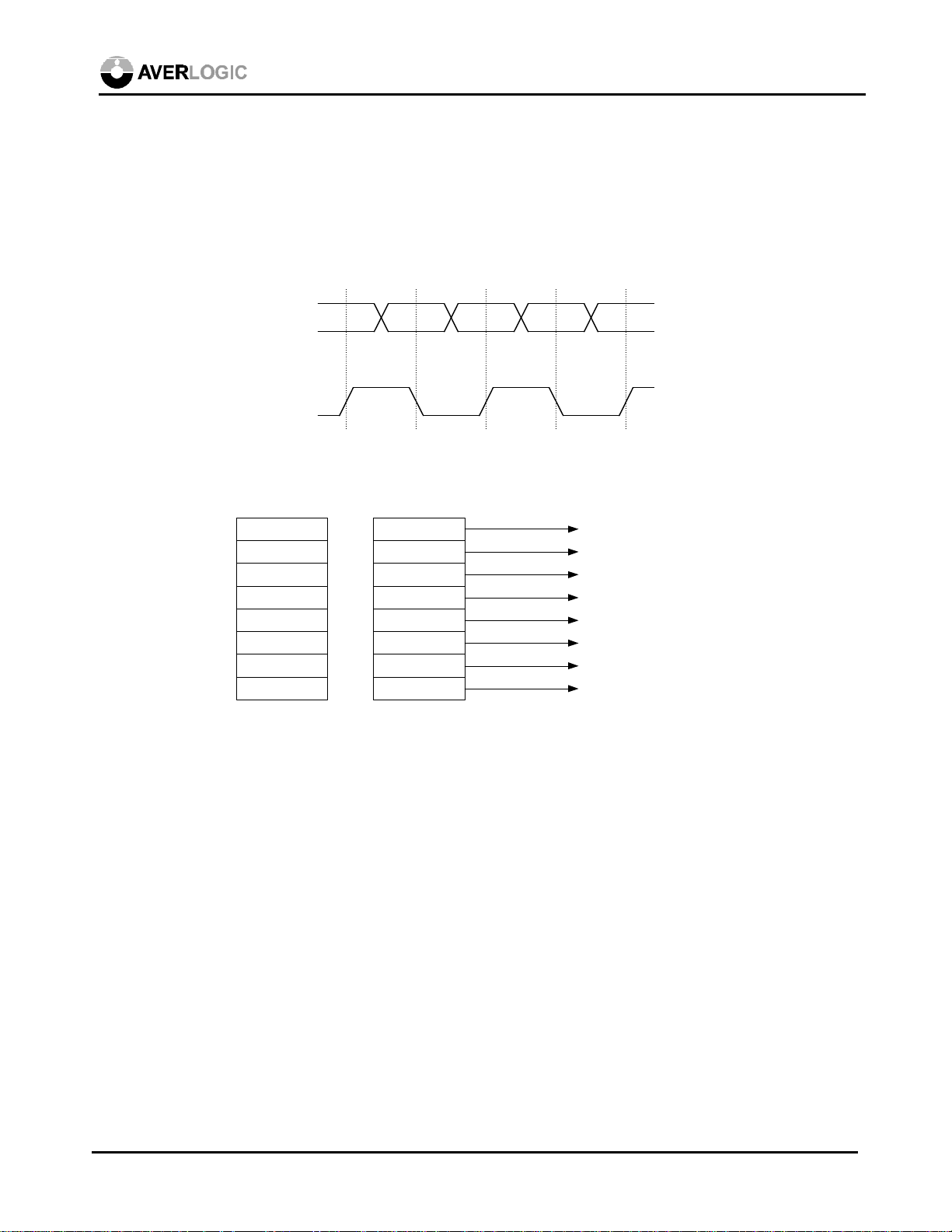
6.1.3 Feature Connector
The definition of the data bits of the feature connector is same as that of the VAFC, i.e.,
D15~D11 represent red signals. D10~D5 green signals, and D4~D0 blue signals. However, since
the feature connector uses 8-bit interface, the two bytes of data must be received within one
pixel/graphic clock (GCLK). The solution is: one byte at the rising edge and one byte at the
falling edge of GCLK as follows:
AL128
DATA
D7~D0 D15~D8 D7~D0 D7~D0D15~D8
GCLK
The eight-bit data is wired to BLUE<7:0> of the AL128 as follows:
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
BLUE 7
BLUE 6
BLUE 5
BLUE 4
BLUE 3
BLUE 2
BLUE 1
BLUE 0
6.1.4 Sampling (Pixel) Clock
The sampling clock for the RGB data can come directly from the graphic pixel clock when this is
available. For external box applications where the graphic pixel clock is not available, the clock
is recovered from the VGA horizontal sync with an external PLL clock chip such as ICS
AV9173. The phase reference signal of the PLL clock chip is generated by the divide-by-M
circuitry of the AL128. The AL128 automatically sets the M divider value, which determines the
sampling frequency for the A/D converter according to the detected resolution of the incoming
graphic data.
April 2, 1999 14
 Loading...
Loading...