Page 1

Configuring SDLC Services
Router Software Version 10.0
Site Manager Software Version 4.0
Part No. 112921 Rev. A
January 1996
Page 2

4401 Great America Parkway 8 Federal Street
Santa Clara, CA 95054 Billerica, MA 01821
Copyright © 1988–1996 Bay Networks, Inc.
All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. January 1996.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Bay Networks, Inc.
The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement and may only be used in accordance with the
terms of that license. A summary of the Software License is included in this document.
Restricted Rights Legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013.
Notice for All Other Executive Agencies
Notwithstanding any other license agreement that may pertain to, or accompany the delivery of, this computer software, the
rights of the United States Government regarding its use, reproduction, and disclosure are as set forth in the Commercial
Computer Software-Restricted Rights clause at FAR 52.227-19.
Trademarks of Bay Networks, Inc.
ACE, AFN, BCN, BLN, BN, CN, FRE, LN, Optivity, SynOptics, SynOptics Communications, Wellfleet and the Wellfleet
logo are registered trademarks and AN, ANH, ASN, BaySIS, BayStack, BCNX, BLNX, BNX, EZ Internetwork, EZ LAN,
FN, PathMan, PhonePlus, PPX, Quick2Config, RouterMan, SPEX, Bay Networks, Bay Networks Press, the Bay Networks
logo and the SynOptics logo are trademarks of Bay Networks, Inc.
Third-Party T rademarks
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, Bay Networks, Inc. reserves the right to
make changes to the products described in this document without notice.
Bay Networks, Inc. does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or circuit
layout(s) described herein.
Portions of the code in this software product are Copyright © 1988, Regents of the University of California. All rights
reserved. Redistribution and use in source and binary forms of such portions are permitted, provided that the abov e copyright
notice and this paragraph are duplicated in all such forms and that any documentation, advertising materials, and other
materials related to such distribution and use acknowledge that such portions of the software were developed by the
University of California, Berkeley. The name of the Univ ersity may not be used to endorse or promote products deri v ed from
such portions of the software without specific prior written permission.
SUCH PORTIONS OF THE SOFTWARE ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
In addition, the program and information contained herein are licensed only pursuant to a license agreement that contains
restrictions on use and disclosure (that may incorporate by reference certain limitations and notices imposed by third parties).
Page 3

Bay Networks Software License
Note:
This is Bay Networks basic license document. In the absence of a
software license agreement specifying varying terms, this license — or the
license included with the particular product — shall govern licensee’s use of
Bay Networks software.
This Software License shall govern the licensing of all software provided to licensee by Bay Networks (“Software”).
Bay Networks will provide licensee with Software in machine-readable form and related documentation
(“Documentation”). The Software provided under this license is proprietary to Bay Networks and to third parties from
whom Bay Networks has acquired license rights. Bay Networks will not grant any Software license whatsoev er, either
explicitly or implicitly, except by acceptance of an order for either Software or for a Bay Networks product
(“Equipment”) that is packaged with Software. Each such license is subject to the following restrictions:
1. Upon delivery of the Software, Bay Networks grants to licensee a personal, nontransferable, none xclusiv e license
to use the Software with the Equipment with which or for which it was originally acquired, including use at any
of licensee’s facilities to which the Equipment may be transferred, for the useful life of the Equipment unless
earlier terminated by default or cancellation. Use of the Software shall be limited to such Equipment and to such
facility. Software which is licensed for use on hardware not offered by Bay Networks is not subject to restricted
use on any Equipment, however, unless otherwise specified on the Documentation, each licensed copy of such
Software may only be installed on one hardware item at any time.
2. Licensee may use the Software with backup Equipment only if the Equipment with which or for which it was
acquired is inoperative.
3. Licensee may make a single copy of the Software (but not firmware) for safekeeping (archives) or backup
purposes.
4. Licensee may modify Software (but not firmware), or combine it with other software, subject to the provision
that those portions of the resulting software which incorporate Software are subject to the restrictions of this
license. Licensee shall not make the resulting software available for use by any third party.
5. Neither title nor ownership to Software passes to licensee.
6. Licensee shall not provide, or otherwise make available, any Software, in whole or in part, in any form, to any
third party. Third parties do not include consultants, subcontractors, or agents of licensee who have licensee’s
permission to use the Software at licensee’s facility, and who have agreed in writing to use the Software only in
accordance with the restrictions of this license.
7. Third-party owners from whom Bay Networks has acquired license rights to software that is incorporated into
Bay Networks products shall have the right to enforce the provisions of this license against licensee.
8. Licensee shall not remove or obscure any copyright, patent, trademark, trade secret, or similar intellectual
property or restricted rights notice within or affixed to any Software and shall reproduce and affix such notice on
any backup copy of Software or copies of software resulting from modification or combination performed by
licensee as permitted by this license.
4401 Great America Parkway, Santa Clara, CA 95054
8 Federal Street, Billerica, MA 01821
Bay Networks, Inc.
Page 4

Bay Networks Software License
9. Licensee shall not reverse assemble, reverse compile, or in any way reverse engineer the Software. [Note: For
licensees in the European Community, the Softw are Directi ve dated 14 May 1991 (as may be amended from time
to time) shall apply for interoperability purposes. Licensee must notify Bay Networks in writing of any such
intended examination of the Software and Bay Networks may provide review and assistance.]
10. Notwithstanding any foregoing terms to the contrary, if licensee licenses the Bay Networks product “Site
Manager,” licensee may duplicate and install the Site Manager product as specified in the Documentation. This
right is granted solely as necessary for use of Site Manager on hardware installed with licensee’s network.
11. This license will automatically terminate upon improper handling of Software, such as by disclosure, or Bay
Networks may terminate this license by written notice to licensee if licensee fails to comply with any of the
material provisions of this license and fails to cure such failure within thirty (30) days after the receipt of written
notice from Bay Networks. Upon termination of this license, licensee shall discontinue all use of the Software
and return the Software and Documentation, including all copies, to Bay Networks.
12. Licensee’s obligations under this license shall survive expiration or termination of this license.
(continued)
4401 Great America Parkway, Santa Clara, CA 95054
8 Federal Street, Billerica, MA 01821
Bay Networks, Inc.
Page 5

Contents
About This Guide
Audience ...........................................................................................................................xi
Before You Begin .............................................................................................................. xi
Bay Networks Customer Support .....................................................................................xii
CompuServe ..............................................................................................................xii
InfoFACTS ................................................................................................................. xiii
World Wide Web ........................................................................................................xiii
How to Get Help ..............................................................................................................xiv
Conventions .....................................................................................................................xiv
Ordering Bay Networks Publications ............................................................................... xv
Acronyms ......................................................................................................................... xv
Chapter 1
Synchronous Data Link Control Overview
SDLC Networking ...........................................................................................................1-1
SDLC Features ...............................................................................................................1-2
Link Station Roles ....................................................................................................1-2
Transmission Capabilities .........................................................................................1-2
Physical Connections ...............................................................................................1-3
Frame Format ...........................................................................................................1-3
Using APPN Services with SDLC ...................................................................................1-4
Using DLSw Services with SDLC ...................................................................................1-4
For More Information about SDLC ..................................................................................1-4
Chapter 2
SDLC Implementation Notes
Link Stations ...................................................................................................................2-1
Synchronous Line Parameters .......................................................................................2-1
SDLC Timers ..................................................................................................................2-2
Configurable Window Size ..............................................................................................2-2
v
Page 6

Chapter 3
Enabling SDLC Services
Enabling SDLC on an Interface ......................................................................................3-1
SDLC Line Parameter Descriptions ................................................................................3-3
Chapter 4
Editing SDLC Parameters
Using the Parameter Descriptions ..................................................................................4-1
Accessing SDLC Parameters .........................................................................................4-2
Editing SDLC Global Parameters ...................................................................................4-3
Editing SDLC Interface Parameters ................................................................................4-4
SDLC Interface Parameter Descriptions ..................................................................4-6
Deleting an SDLC Interface ..........................................................................................4-14
Adding an SDLC Link Station .......................................................................................4-15
Editing SDLC Link Station Parameters .........................................................................4-17
SDLC Link Station Parameter Descriptions ...........................................................4-18
Deleting SDLC from the Router ....................................................................................4-27
Appendix A
SDLC Default Parameter Settings
Index
vi
Page 7

Figures
Figure 1-1. SDLC Frame Format ................................................................................1-3
Figure 3-1. SDLC Line Parameters Window ..............................................................3-2
Figure 3-2. Select Protocols Window .........................................................................3-2
Figure 4-1. Configuration Manager Window ...............................................................4-2
Figure 4-2. Edit SDLC Global Parameters Window ....................................................4-3
Figure 4-3. SDLC Interface Configuration Window ....................................................4-5
Figure 4-4. SDLC Link Station Configuration Window ..............................................4-15
Figure 4-5. Link Station Configuration Window ........................................................4-16
vii
Page 8

Page 9

Tables
Table A-1. SDLC Line Parameters ........................................................................... A-1
Table A-2. SDLC Interface Parameters .................................................................... A-2
Table A-3. SDLC Link Station Parameters ............................................................... A-3
ix
Page 10

Page 11

Audience
About This Guide
If you configure and manage Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC) services for
Bay Networks routers, refer to this guide for
• An overview of the SDLC protocol and its client protocols (Chapter 1)
• Implementation notes that may affect how you configure SDLC services
(Chapter 2)
• Instructions on enabling SDLC services on the router (Chapter 3)
• Instructions on editing SDLC parameters (Chapter 4)
For information and instructions on starting up and managing Bay Networks
router configurations, refer to
Configuring Routers
.
Written for system and network managers, this guide describes the Bay Networks
implementation of SDLC for networks containing Bay Networks routers. You
should be familiar with the IBM networking concepts associated with the Systems
Network Architecture (SNA) and SDLC.
Before Y ou Begin
Before using this guide, you must complete the following procedures:
• Open a configuration file.
• Specify the router hardware, if this is a local-mode configuration file.
• Select the link- or net-module connector on which you are enabling SDLC.
Refer to
Configuring Routers
for instructions.
xi
Page 12

Configuring SDLC Services
Bay Networks Customer Support
Bay Networks provides live telephone technical support to our distributors,
resellers, and service-contracted customers from two U.S. and three international
support centers. If you have purchased your Bay Networks product from a
distributor or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff of that
distributor or reseller for assistance with installation, configuration,
troubleshooting, or integration issues.
Customers also have the option of purchasing direct support from Bay Networks
through a variety of service programs. The programs include priority access
telephone support, on-site engineering assistance, software subscription, hardware
replacement, and other programs designed to protect your investment.
To purchase any of these support programs, including PhonePlus™ for 24-hour
telephone technical support, call 1-800-2LANWAN. Outside the U.S. and
Canada, call (408) 764-1000. You can also receive information on support
programs from your local Bay Networks field sales office, or purchase Bay
Networks support directly from your reseller. Bay Networks provides several
methods of receiving support and information on a nonpriority basis through the
following automated systems.
CompuServe
xii
Bay Networks maintains an active forum on CompuServ e. All you need to join us
online is a computer, a modem, and a CompuServe account. We also recommend
using the CompuServe Information Manager software, available from
CompuServe.
The Bay Networks forum contains libraries of technical and product documents
designed to help you manage and troubleshoot your Bay Networks products.
Software agents and patches are available, and the message boards are monitored
by technical staff and can be a source for problem solving and shared experiences.
Customers and resellers holding Bay Networks service contracts can visit the
special libraries to acquire advanced levels of support documentation and
software.
Page 13

InfoFACTS
About This Guide
To open an account and receive a local dial-up number, call CompuServe at
1-800-524-3388 and ask for Representative No. 591.
• In the United Kingdom, call Freephone 0800-289378.
• In Germany, call 0130-37-32.
• In Europe (except for the United Kingdom and Germany), call
(44) 272-760681.
• Outside the U.S., Canada, and Europe, call (614) 529-1349 and ask for
Representative No. 591, or consult your listings for an office near you.
Once you are online, you can reach our forum by typing the command GO
BAYNETWORKS at any ! prompt.
InfoFACTS is the Bay Networks free 24-hour fax-on-demand service. This
automated system contains libraries of technical and product documents designed
to help you manage and troubleshoot your Bay Networks products. The system
can return a fax copy to the caller or to a third party within minutes of being
accessed.
W orld Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW) is a global information system for file distribution
and online document viewing via the Internet. Y ou need a direct connection to the
Internet and a Web Browser (such as Mosaic or Netscape).
Bay Networks maintains a WWW Home Page that you can access at http://
www.baynetworks.com. One of the menu items on the Home Page is the
Customer Support Web Server, which offers technical documents, software
agents, and an E-mail capability for communicating with our technical support
engineers.
xiii
Page 14

Configuring SDLC Services
How to Get Help
For additional information or advice, contact the Bay Networks Technical
Response Center in your area:
United States 1-800-2LAN-WAN
Valbonne, France (33) 92-966-968
Sydney, Australia (61) 2-903-5800
Tokyo, Japan (81) 3-328-005
Conventions
This section describes the conventions used in this guide.
arrow character (
➔
) Separates menu and option names in instructions.
➔
Example: Protocols
AppleTalk identifies the
AppleTalk option in the Protocols menu.
bold text
Indicates text that you need to enter and command
dinfo
names in text. Example: Use the
command.
brackets ([ ]) Indicate optional elements. You can choose none, one,
or all of the options.
italic text
Indicates variable values in command syntax
descriptions, new terms, file and directory names, and
book titles.
quotation marks (“ ”) Indicate the title of a chapter or section within a book.
screen text
Indicates data that appears on the screen. Example:
Bay Networks Trap Monitor Filters
Set
vertical line (|) Indicates that you enter only one of the parts of the
command. The vertical line separates choices. Do not
type the vertical line when entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is
show at routes
show at routes
nets
|
, you enter either
show at nets
or
, but not both.
xiv
Page 15

Ordering Bay Networks Publications
To purchase additional copies of this document or other Bay Networks
publications, order by part number from Bay Networks Press™ at the following
numbers. You may also request a free catalog of Bay Networks Press product
publications.
Phone: 1-800-845-9523
FAX - U.S./Canada: 1-800-582-8000
FAX - International: 1-916-939-1010
Acronyms
AN Access Node
APPC Advanced Peer-to-Peer Communications
APPN Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking
ASN Access Stack Node
CP Control Point
DLSw Data Link Switching
FEP front-end processor
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
LAN local area network
LLC logical link control
MAC Media Access Control
NetBIOS Network Basic Input-Output System
NRZ non-return to zero
NRZI non-return to zero inverted
PDU protocol data unit
PU physical unit
RFC Request for Comments
SAP service access point
SDLC Synchronous Data Link Control
SNA Systems Network Architecture (IBM)
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
XID exchange identification
About This Guide
xv
Page 16

Page 17

Chapter 1
Synchronous Data Link Control Overview
This chapter describes the following Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC)
features and services:
• SDLC networking
— Link stations
— Transmission capabilities
— Physical connections
— Frame format
• Using APPN and DLSw services with SDLC
Read this chapter if you are configuring Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking
(APPN) or Data Link Switching (DLSw) networks. SDLC parameter settings can
influence APPN and DLSw performance.
SDLC Networking
SDLC is the synchronous, bit-oriented link control protocol in the IBM System
Network Architecture (SN A). SDLC’ s connection-oriented protocol operates with
the Data Link Switching (DLSw) protocol and the Advanced Peer-to-Peer
Networking (APPN) architecture.
SDLC supports point-to-point and multipoint topologies. In point-to-point
topologies, one SDLC device is connected to the SDLC port. In multipoint
topologies, several SDLC devices are connected to the SDLC port via a modemsharing device.
1-1
Page 18

Configuring SDLC Services
SDLC Features
You can configure most of the following features using the SDLC parameters
described in Chapter 4.
Link Station Roles
A link station is a logical connection between adjacent nodes, where one node is a
primary link station and the other node is a secondary link station. Only one link
station on an SDLC line can be the primary station; all other stations on the line
must be secondary.
SDLC supports primary, secondary, and negotiable link stations.
A primary link station does the following:
• Controls a data link
• Issues commands
• Initiates error-recovery procedures
A secondary link station receives commands and responds to primary link station
polls.
In DLSw configurations, a Bay Networks router must be configured as a primary
or a secondary link station. When configured as a primary SDLC link station, the
router communicates with downstream PU 2.0 and PU 2.1 nodes. When
configured as a secondary SDLC link station, the router communicates with PU 4,
PU 5, and PU 2.1 devices.
In APPN configurations (PU 2.1 devices only), a Bay Networks router supports
negotiable link stations, where the two link stations exchange XIDs to negotiate
which one will be primary and which secondary.
Transmission Capabilities
SDLC supports full- and half-duplex transmissions over leased lines. With fullduplex, data transmissions can occur in both directions (between primary and
secondary link stations) at the same time. With half-duplex, transmissions can
occur in only one direction at a time.
1-2
Page 19
Physical Connections
SDLC supports communication with attached SNA/SDLC devices using V.24
(RS-232), V.35, and X.21 (nonswitched) connections. SDLC supports line speeds
up to 64 Kb/s, depending on the physical connection. For example, V.24 interfaces
can operate at speeds up to 19.2 Kb/s, while V.35 interfaces can operate at speeds
up to 64 Kb/s.
Frame Format
SDLC sends and receives three types of frames:
•
Supervisory frames
retransmission when an error occurs or when frames arrive out of sequence.
•
Information frames
•
Unnumbered frames
Figure 1-1 illustrates the format of SDLC frames.
Synchronous Data Link Control Overview
transmit ready or busy status, control polling, and request
transmit data.
control initialization and status reporting.
Flag Address Field Control Field
Figure 1-1. SDLC Frame Format
Information
Field
Frame
Checking
Field
Flag
Each frame begins with a one-byte flag that alerts the receiver to the frame’s
presence.
The Address field can be one or tw o bytes long. This field identifies the secondary
link station that is communicating with the primary link station. In a poll, the
Address field identifies the station being polled. In a response, this field identifies
the transmitting secondary station.
The Control field is one byte long and identifies the function of the frame. This
field defines the frame format (supervisory, information, or unnumbered).
The optional Information field is a variable-length field (the length must be a
multiple of eight bits).
1-3
Page 20

Configuring SDLC Services
A two-byte Frame-checking field lets the receiving station check the received
frame for errors.
A one-byte flag ends the frame.
Using APPN Services with SDLC
You can configure any SDLC interface for APPN services. APPN nodes can
communicate with adjacent nodes using SDLC links over point-to-point and
multipoint configurations. For information on the APPN node types and how to
configure APPN, see
Configuring APPN Services
Using DLSw Services with SDLC
You can configure any SDLC interface for DLSw services. For information on
DLSw, see
Configuring DLSw Services
For More Information about SDLC
For more information about SDLC and IBM SNA, refer to the following IBM
publications:
.
.
1-4
•
IBM Synchronous Data Link Control: Concepts
•
IBM System Network Architecture: Technical Overview
•
IBM System Network Architecture: Concepts and Products
•
Systems Network Architecture APPN Architecture Reference
•
APPN Architecture and Product Implementations Tutorial
• Data Link Switching: Switch-to-Switch Protocol RFC 1434
(GA27-3093)
(GC30-30723)
(GC30-3072)
(SC30-3422-3)
(GG24-3669)
Page 21

Keep the following implementation notes in mind when you configure SDLC
services.
Link Stations
With DLSw, you can configure SDLC as a primary or secondary link station only.
With APPN, you can configure primary, secondary, and negotiable link stations.
You set up SDLC link stations as follows:
• For primary link stations, you must configure the adjacent link station’s
Chapter 2
SDLC Implementation Notes
parameters.
• For secondary link stations, you must configure the station’s own link station
parameters.
• F or negotiable link stations, you must configure the station’s own link station
parameters, as well as the parameters for a potential adjacent link station.
Refer to Chapter 4 for information on configuring SDLC link stations.
Synchronous Line Parameters
When you add SDLC to a synchronous line, Site Manager opens the SDLC Line
Parameters window, which allows you to edit the following parameters:
• Clock Source
• Internal Clock Speed
• Sync Line Coding
• Cable Type
2-1
Page 22

Configuring SDLC Services
• RTS Enable
Chapter 3 describes how to complete the SDLC Line Parameters windo w. To vie w
or change synchronous line parameters that do not appear in the SDLC Line
Parameters window, edit the line parameters of the desired circuit. For
information on editing other synchronous line parameters, refer to
Line Services
Note:
The BOFL (Breath of Life) parameter enables the transmission of
proprietary Breath of Life messages over a point-to-point connection between
the local router and a remote peer. Disable this parameter so that the BOFL
messages do not interfere with SDLC frames.
SDLC Timers
SDLC uses timers to manage traffic over SDLC links. If you configure SDLC on a
link with a slow baud rate, the default values for SDLC timer parameters may not
be adequate for the line. You should edit the timer values whenever you adjust the
speed of the line.
Configuring
.
For example, if you are using a line with a 4800 baud rate, increase the REPLYTO
Timer parameter value in the SDLC Link Station Configuration window (refer to
Figure 4-4) to 60 tenths of a second. Edit the REPLYTO Timer value whenever
you adjust baud rate with the Internal Clock Speed parameter or the external
modem baud rate.
Configurable Window Size
In SDLC, a window controls the number of frames that a link station can send
before it receives an acknowledgment. The size of the window depends on the
modulo in use in your network’s implementation of SDLC. Modulo 8 operation
allows a maximum window size of 7. Modulo 128 operation allows a maximum
window size of 127.
For example, with a window size of 7, a link station can transmit frames 0 through
6 before requiring acknowledgment from the receiving station. The sending
station will not send more frames until it receives an acknowledgment.
You edit this window size with the MAXOUT parameter, described in Chapter 4.
2-2
Page 23

Chapter 3
Enabling SDLC Services
This chapter describes how to enable SDLC services. It assumes you have read
Configuring Routers
1. Opened a configuration file.
2. Specified router hardware if this is a local-mode configuration file.
3. Selected the link- or net-module connector on which you are enabling SDLC,
or configured a WAN circuit if this connector requires one.
When you enable SDLC services, you are required to specify only a few
parameters. The Configuration Manager supplies default values for the rest. If you
want to edit these parameters, refer to Chapter 4.
and that you have completed the following steps:
Enabling SDLC on an Interface
To enable SDLC on an interface:
1.
Select SDLC in the WAN Protocols window.
The Configuration Manager displays the SDLC Line Parameters window
(Figure 3-1).
3-1
Page 24

Configuring SDLC Services
Figure 3-1. SDLC Line Parameters Window
3-2
2.
Configure the parameters.
Refer to the parameter descriptions in this chapter to configure the
synchronous line parameters.
3.
Click on OK.
The Select Protocols window appears (Figure 3-2).
Figure 3-2. Select Protocols Window
Page 25

4.
Select either DLSw or APPN to run on the SDLC circuit.
Site Manager then displays the appropriate windows from which you enable
APPN or DLSw. For information on enabling APPN and DLSw, refer to
Configuring APPN Services
and
SDLC Line Parameter Descriptions
Use the following parameter descriptions to configure the SDLC line parameters
(Figure 3-1).
Parameter: Clock Source
Default: Internal
Options: External | Internal
Function: Specifies the origin of the synchronous timing signals. If you set this
parameter to Internal, this router supplies the required timing signals. If
you set this parameter to External, an external network device supplies the
required timing signals. If you are using a modem, or if the adjacent link
station is providing the clock source, set this parameter to External.
Enabling SDLC Services
Configuring DLSw Services.
Instructions: Set this parameter to either Internal or External, as appropriate for your
network.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.5.1.13
3-3
Page 26

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Internal Clock Speed
Default: 64 KB
Options: 1200 B | 2400 B | 4800 B | 7200 B | 9600 B | 19200 B | 32000 B |
38400 B | 56 KB | 64 KB | 125 KB | 230 KB | 420 KB | 625 KB |
833 KB | 1.25 MB | 2.5 MB | 5 MB
Function: Sets the clock speed of an internally supplied clock when the Clock
Source parameter is set to Internal.
Instructions: Click on Values and set the clock speed for the internal clock to the
desired data transmission rate across the synchronous line. If you are
using the Quad Sync module, be sure to set the same clock speed on all
ports.
You cannot edit the Internal Clock Speed parameter when the Clock
Source parameter is set to External.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.5.1.14
Parameter: Sync Line Coding
Default: NRZ
Options: NRZ | NRZI | NRZI Mark
Function: Specifies the line coding of the physical synchronous line. You must
change the value to match the line coding of a device at the other end of
the line.
This parameter is relevant only for the AN and ASN routers, and routers
containing the Octal Sync link module.
NRZ — Indicates Non-Return to Zero coding
NRZI — Indicates Non-Return to Zero Inverted coding
NRZI Mark — Indicates Non-Return to Zero Inverted Mark coding
Instructions: Select the appropriate value for synchronous line coding.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.5.1.88
3-4
Page 27

Enabling SDLC Services
Parameter: Cable Type
Default: Null
Options: Null | RS232 | RS422 | V35 | X21
Function: Specifies the cable interface type of the device.
Instructions: Click on Values and select the installed cable interface type.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.5.1.83
Parameter: RTS Enable
Default: Disable
Options: Enable | Disable
Function: Controls the toggling of the Request to Send (RTS) signal on the
interface. For manual dial modems (2-wire), set this parameter to Enable.
For leased modems (4-wire), set this parameter to Disable.
Instructions: Click on Values and select Enable or Disable.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.5.1.16
3-5
Page 28

Page 29

Chapter 4
Editing SDLC Parameters
Use the Configuration Manager to access, configure, and edit
• SDLC global parameters
• SDLC interface parameters
• SDLC link station parameters
To edit SDLC parameters, you need to configure one SDLC interface. If you have
not yet configured an SDLC interface, refer to Chapter 3.
You may want to customize parameters for DLSw or APPN as well, since they use
SDLC services on the router. For information on DLSw, refer to Configuring
DLSw Services. For information on APPN, refer to Configuring APPN Services.
Using the Parameter Descriptions
For each SDLC parameter, this chapter provides the following information:
• Default setting (parameter value that the system software sets; APPN and
DLSw configurations may affect some SDLC default settings during
operation)
• All valid options
• Function
• Instructions for setting the parameter value
• Management Information Base (MIB) object ID
4-1
Page 30

Configuring SDLC Services
The Technician Interface lets you modify parameters by issuing set and commit
commands with the MIB object ID. This process is equivalent to modifying
parameters using Site Manager. For more information about using the Technician
Interface to access the MIB, refer to Using Technician Interface Software.
Caution: The Technician Interface does not verify that the value you enter for
a parameter is valid. Entering an invalid value can corrupt your
configuration.
Accessing SDLC Parameters
T o access and edit SDLC parameters, begin at the Configuration Manager windo w
and select Protocols➔SDLC to display the SDLC options submenu (Figure 4-1).
4-2
Figure 4-1. Configuration Manager Window
Page 31

Editing SDLC Global Parameters
SDLC has only one configurable parameter (Enable) visible at the global level. To
change the setting of the global parameter, begin at the Configuration Manager
window and proceed as follows:
1. Select Protocols➔SDLC➔Global.
The Edit SDLC Global Parameters window appears (Figure 4-2).
Editing SDLC Parameters
Figure 4-2. Edit SDLC Global Parameters Window
Change the setting of the Enable parameter, if necessary.
2.
(Refer to the description of the parameter that follows this procedure.)
3. Click on OK to save your changes and exit the window.
4-3
Page 32

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Enable
Default: Enable
Options: Enable | Disable
Function: Enables or disables the system software mechanisms that use the SDLC
interface on a synchronous circuit.
The system software also performs the following actions when you
choose a setting:
Disable — Switches every SDLC interface enabled on the router to the
disabled (inactive) state.
Enable — Reinitializes every SDLC interface on the router based on
• The current setting of the associated interface Enable parameter
• The current state of the associated circuit
Instructions: Select Disable to switch ev ery SDLC interface e xisting on the node to the
inactive state.
Select Enable only when an existing SDLC interface is in the disabled
state. You can choose Enable to globally reinitialize all SDLC interfaces
configured on the node. Then, each interface maintains the most recent
setting of its own interface Enable parameter.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.1.2
Editing SDLC Interface Parameters
To access and edit the SDLC interface parameters, begin at the Configuration
Manager window (refer to Figure 4-1) and proceed as follows:
1. Select Protocols➔SDLC➔Interfaces.
The SDLC Interface Configuration window appears (Figure 4-3).
4-4
Page 33

Editing SDLC Parameters
Figure 4-3. SDLC Interface Configuration Window
Select the interface you want to customize.
2.
The parameter values for that interface appear in the parameter value
windows. (Click on Values to display the valid range of values for any
parameter.)
3. Edit the parameters you want to change.
Refer to the parameter descriptions in the next section.
4. Click on Apply to save your changes.
Repeat Steps 2 through 4 for each interface you want to edit.
5. Click on Done to exit the SDLC Interface Configuration window.
4-5
Page 34

Configuring SDLC Services
SDLC Interface Parameter Descriptions
Use the following parameter descriptions to edit SDLC interface parameters.
Parameter: Enable
Default: Enable
Options: Enable | Disable
Function: Enables or disables the SDLC interface added previously to this WAN
physical circuit.
Instructions: Select Enable if you disabled this SDLC interface previously and now
want to re-enable the interface on its associated WAN physical circuit.
Select Disable if you want to disable this SDLC interface on its associated
WAN physical circuit.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.2
Parameter: Port Name
Default: None
Options: Any valid port name
Function: Defines the port name you want to assign to this SDLC interface.
Instructions: Enter the name of the port you want to assign to this SDLC interface. You
can use any combination of alphanumeric characters. We recommend you
use the same name assigned to the circuit on which you added SDLC, for
example, S51.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.4
4-6
Page 35

Editing SDLC Parameters
Parameter: Link Station Role
Default: PRIMARY
Options: PRIMARY | SECONDARY | NEGOTIABLE
Function: Defines the link station role. With DLSw, you can configure only primary
and secondary SDLC link stations. With APPN, you can configure
primary, secondary, and negotiable link stations.
Instructions: Enter PRIMAR Y or SECOND ARY if you want to assign a specific role to
the link station. Enter NEGOTIABLE if you want the link station to
exchange XIDs with another negotiable link station to determine which
will be primary and which will be secondary.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.27
Parameter: Link Station Address
Default: 2
Range: 1 to 254
Function: Specifies the address of the port if the link station role is secondary or
negotiable.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 254.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.29
Parameter: Support Negotiable Connection
Default: FALSE
Options: TRUE | FALSE
Function: Specifies whether this SDLC link station supports negotiable connections.
Instructions: Enter TRUE if the SDLC link station supports negotiable connections;
otherwise, enter FALSE.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.33
4-7
Page 36

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Max Frame Retransmit Count
Default: 5
Range: 1 to 7
Function: Specifies the maximum number of times to retransmit a frame or group of
frames.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 7.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.23
Parameter: Non-productive Timer
Default: 2000 milliseconds
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Specifies the time allowed for receipt of a valid frame from the primary
link station. This parameter operates with the Non-productive Retry Limit
parameter.
SDLC primarily uses this timer to produce an outage when a secondary
station produces continuous frames without setting the F-bit (Final bit).
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.12
Parameter: Non-productive Retry Limit
Default: 15
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Used with the Non-productive Timer parameter to provide the overall
time before SDLC sends an outage message to the device.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535, where 1 causes SDLC to generate an
outage after the first Non-productive Timer expires, and 65535 specifies
an unlimited retry count.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.13
4-8
Page 37

Editing SDLC Parameters
Parameter: Idle Line Timer
Default: 6000 milliseconds
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Specifies the time used to determine whether a line is completely inactive.
This parameter operates with the Idle Line Retry Limit parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535. Enter the maximum value, 65535, if you
never want to terminate sessions on the line, even if it is completely
inactive. If you enter a smaller value, the timer expires when no activity
occurs on the line for the specified number of milliseconds.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.10
Parameter: Idle Line Retry Limit
Default: 20
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Specifies the number of times to run the Idle Line Timer before failure.
This parameter operates with the Idle Line Timer parameter to pro vide the
overall idle timeout period.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535, where 1 causes SDLC to generate an
outage after the first Idle Line Timer expires, and 65535 specifies an
unlimited retry count.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.11
Parameter: Port Write T imer
Default: 3000 milliseconds
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Specifies the maximum amount of time allowed to transmit a complete
frame. This parameter operates with the Port Write Retry Limit
parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535 milliseconds.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.14
4-9
Page 38

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Port Write Retry Limit
Default: 10
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Used with the Port Write Timer parameter to provide the overall time
allowed to transmit a complete frame before SDLC sends an outage
message to the device.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535, where 1 causes SDLC to generate an
outage after the first Port Write Timer expires, and 65535 specifies an
unlimited retry count.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.15
Parameter: Link Connection Timer
Default: 3000 milliseconds
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Used with the Link Connection Retry Limit parameter to provide the time
interval after which SDLC fails to activate a port because it has not
received a Data Set Ready (DSR) response.
This feature is for switched lines only and is not currently implemented.
Instructions: Accept the default. This parameter is reserved for future enhancements.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.16
Parameter: Link Connection Retry Limit
Default: 10
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Specifies the number of times the link has been tested for a connection
before it fails the pending activate port request. The maximum value for
this parameter specifies an infinite number of times. This parameter
operates with the Link Connection Timer parameter.
Instructions: Accept the default. This parameter is reserved for future enhancements.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.17
4-10
Page 39

Editing SDLC Parameters
Parameter: Primary Full Duplex
Default: FALSE
Options: TRUE | FALSE
Function: Specifies whether the primary SDLC link station supports full-duplex
data transmission.
Instructions: Enter TRUE if the primary SDLC station supports full-duplex data
transmission. Enter FALSE if the primary station supports half-duplex
transmission.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.18
Parameter: Secondary Full Duplex
Default: FALSE
Options: TRUE | FALSE
Function: Specifies whether the secondary SDLC link station supports full-duplex
data transmission.
Instructions: Enter TRUE if the secondary SDLC station supports full-duplex data
transmission. Enter FALSE if the secondary station supports half-duplex
transmission.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.19
Parameter: Enable Reject Frame
Default: TRUE
Options: TRUE | FALSE
Function: Specifies whether SDLC can send a reject (REJ) command upon
receiving an out-of-sequence Information frame. If the REJ command is
not used, SDLC requests retransmission of frames through Receiver
Ready (RR), Receiver Not Ready (RNR), or Information frames. Use of
the REJ command is useful only with full-duplex transmission.
Instructions: Enter TRUE to use REJ commands for out-of-sequence Information
frames; otherwise, enter FALSE.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.20
4-11
Page 40

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Max XID Size
Default: 256
Range: 2 to 256
Function: Specifies the maximum XID size that will be sent or recei ved on this link.
Instructions: Enter a value from 2 to 256.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.22
Parameter: Max Frame Size
Default: PDU2057
Options: PDU265 | PDU521 | PDU1033 | PDU2057
Function: Specifies the maximum frame size SDLC supports. This value includes
the Transmission Header (TH) and Request Header (RH).
Instructions: Enter a frame size that is equal to or larger than the lar gest frame size that
will be received.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.24
Parameter: Total Link Station Limit
Default: 16
Range: 1 to 254
Function: Specifies the total link station activation limit.
Instructions: Enter the total number of link stations (from 1 to 254) that you want to
reserve for inbound and outbound activation on this port.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.30
4-12
Page 41

Editing SDLC Parameters
Parameter: Inbound Link Station Limit
Default: 8
Range: 1 to 254
Function: Specifies the inbound link station activation limit.
Instructions: Enter the number of link stations (from 1 to 254) that you want to reserve
for inbound activation on this port.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.31
Parameter: Outbound Link Station Limit
Default: 8
Range: 1 to 254
Function: Specifies the outbound link station activation limit.
Instructions: Enter the number of link stations (from 1 to 254) that you want to reserve
for outbound activation on this port.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.32
Parameter: Receive Buffer Pool Size
Default: 7
Range: 1 to 255
Function: Sets the receive b uffer pool size, that is, the number of b uf fers you want to
preallocate for receiving frames from the line.
Instructions: Enter the number of buffers you want for the receive b uffer pool. You can
enter a value from 1 to 255; however, we recommend that you accept the
default, because increasing the receive buffer pool size uses up more
memory.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.34
4-13
Page 42

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Initial Flow Control Credit
Default: 7
Range: 1 to 50
Function: Regulates the flow of data from the SDLC device to the SDLC interface.
Instructions: Accept the default. This parameter is reserved for future enhancements.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.9
Parameter: Enable Stats Collection
Default: TRUE
Options: TRUE | FALSE
Function: Turns statistics collection on or off for this port.
Instructions: Enter TRUE to enable statistics collection; otherwise, enter FALSE.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.2.1.35
Deleting an SDLC Interface
4-14
To delete an SDLC interface from its associated physical circuit:
1. In the SDLC Interface Configuration window (refer to Figure 4-3), select
the SDLC interface you want to delete.
2. Click on Delete.
The system deletes the SDLC entry you selected, and the entry disappears
from the list of SDLC interfaces in the SDLC Interface Configuration
window.
To simultaneously delete all SDLC interfaces from the node, follow the steps in
the section “Deleting SDLC from the Router.”
Page 43

Adding an SDLC Link Station
To add an SDLC link station:
1. In the SDLC Interface Configuration window (refer to Figure 4-3), select
Link Station.
The SDLC Link Station Configuration window appears (Figure 4-4).
Editing SDLC Parameters
Figure 4-4. SDLC Link Station Configuration Window
Click on Add.
2.
A window prompts you for the address of the link station (Figure 4-5).
4-15
Page 44

Configuring SDLC Services
Figure 4-5. Link Station Configuration Window
Enter the link station address.
3.
(Refer to the description of the parameter that follows this procedure.)
4. Click on OK to save your changes and exit the window.
The SDLC Link Station Configuration window reappears (refer to Figure 4-4)
with the new entry added to the list of existing link stations.
4-16
Complete the procedure in the next section, “Editing SDLC Link Station
Parameters,” to define the configuration information for the link station you
just added.
Note: If you are using SDLC with DLSw, you must configure a local device for
each SDLC link station you add. For information on configuring local devices,
refer to Configuring DLSw Services.
Page 45

Parameter: Link Station Address (hex)
Default: None
Options: Any valid hexadecimal link station address from 0x01 to 0xFE
Function: Specifies the address of the link station.
Instructions: Type 0x followed by the link station address.
MIB Object ID: None
Editing SDLC Link Station Parameters
To edit SDLC link station parameters, complete the following steps. If you just
completed the procedure in “Adding an SDLC Link Station,” go to Step 3.
1. In the Configuration Manager window (refer to Figure 4-1), select
Protocols➔SDLC➔Link Stations.
The SDLC Link Station Configuration window appears (refer to Figure 4-4).
2. Select the address of the link station.
3. Edit the link station parameter values.
Editing SDLC Parameters
For information, refer to the parameter descriptions in the next section.
4. Click on Apply to save your changes.
5. Click on Done to exit.
4-17
Page 46

Configuring SDLC Services
SDLC Link Station Parameter Descriptions
Use the following descriptions as guidelines when you configure the parameters in
the SDLC Link Station Configuration window.
Parameter: Enable
Default: Enable
Options: Enable | Disable
Function: Enables or disables the link station on the port.
Instructions: Enter Enable to enable the link station on the port; otherwise, enter
Disable.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.2
Parameter: PU Name
Default: None
Options: Any valid 8-byte ASCII name
Function: Specifies the physical unit (PU) name of the adjacent link station. This
name uniquely identifies the adjacent link station for statistics and Alert
messages.
Instructions: Enter the 8-byte ASCII link station name.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.32
Parameter: Group Address
Default: 0
Range: 0 to 254
Function: Specifies the address of the group to which this link station belongs (for
secondary link stations only).
Instructions: If the link station is not part of a group (as is the case in a point-to-point
topology), accept the default, 0. If the link station is part of a group, enter
its group poll address.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.5
4-18
Page 47

Editing SDLC Parameters
Parameter: MAXDATA
Default: PDU2057
Options: PDU265 | PDU521 | PDU1033 | PDU2057
Function: Specifies the maximum frame size SDLC supports. This value includes
the Transmission Header (TH) and Request Header (RH).
Instructions: Enter a maximum frame size equal to or larger than the lar gest frame size
the station will receive.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.7
Parameter: MAXOUT
Default: 7
Range: 1 to 127
Function: Controls the maximum number of consecutive frames that an SDLC link
station can send without acknowledgment.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 127.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.10
Parameter: MAXIN
Default: 7
Range: 1 to 127
Function: Controls the maximum number of unacknowledged frames that an SDLC
link station can receive.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 127.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.9
4-19
Page 48

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Response Timer
Default: 100 milliseconds
Range: 100 to 64000
Function: Specifies the length of time that SDLC waits before turning the poll bit
around when it has no work to do.
Instructions: Enter a value from 100 to 64000 milliseconds.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.28
Parameter: RNR Timer
Default: 3 minutes
Range: 1 to 90
Function: Controls the length of time that an SDLC link station allows its adjacent
link station to remain in a busy (RNR) state before declaring it
inoperative. This parameter operates with the RNR Retry Limit
parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 90 minutes.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.15
Parameter: RNR Retry Limit
Default: 4
Range: 1 to 64000
Function: Used with the RNR Timer parameter to pro vide the ov erall timeout before
sending an outage message to a device.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 64000, where 1 causes SDLC to generate an
outage after the first RNR Timer expires, and 64000 specifies an infinite
number of retries.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.27
4-20
Page 49

Editing SDLC Parameters
Parameter: REPLYTO Timer
Default: 30 tenths of a second
Range: 1 to 600
Function: Specifies the maximum length of time a primary link station waits for a
response frame (after sending a frame with a poll bit) before trying to poll
another station. This timer starts when a frame without the F-bit is
received, and stops only when a frame with an F-bit is received.
Instructions: Enter a value from one tenth of a second to 600 tenths of a second. You
should set the timeout value to be no less than the result of the following
formula:
(2 + MAXOUT) x (MAXDATA x 8) x 10
÷ line speed in bits/s
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.8
Parameter: REPLYTO Retry Limit
Default: 10
Range: 1 to 64000
Function: Controls the number of times an adjacent secondary link station fails to
respond before the primary link station sends an outage message.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 64000, where 1 causes SDLC to generate an
outage after the first REPLYTO Timer expires, and 64000 specifies an
infinite number of retries.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.26
4-21
Page 50

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Fast Poll Timer
Default: 400 milliseconds
Range: 1 to 64000
Function: Controls the timeout required before reinserting an adjacent secondary
link station into the polling list after the adjacent secondary station has
been removed for no response. This parameter operates with the F ast Poll
Count Limit parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 64000 milliseconds. Although the timer v alue is in
milliseconds, you should specify a value so that the timer runs for
seconds.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.22
Parameter: Fast Poll Count Limit
Default: 16
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Controls the number of times a link station is removed from the polling
list on the normal poll timer before SDLC switches to the Slow Poll
Timer. This parameter operates with the Fast Poll Timer parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535, where 1 causes SDLC to switch to the
Slow Poll Timer after the first Fast Poll Timer expires, and 65535
specifies an infinite number of retries.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.23
Parameter: Slow Poll Timer
Default: 1000 milliseconds
Range: 1 to 64000
Function: Allows polling to continue (using this timer) when the Fast Poll Count
Limit expires. This parameter operates with the Slow Poll Count Limit
parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 64000 milliseconds.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.24
4-22
Page 51

Editing SDLC Parameters
Parameter: Slow Poll Count Limit
Default: 65535
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Controls the number of times a link station is removed from the polling
list before sending an outage message to a device. This parameter
operates with the Slow Poll Timer parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535, where 1 causes SDLC to generate an
outage after the first Slow Poll Timer expires, and 65535 specifies an
infinite number of retries.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.25
4-23
Page 52

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Pre-Activation Contact Frame
Default: XID
Options: XID | DISC | SNRM | SNRME | TEST
Function: Specifies the frame to use for pre-activation polling. Pre-acti v ation sets up
the router connection table so that DLSw connects to the host before
connecting to the SDLC station, or the reverse. The frames include
XID — Exchange Identification
DISC — Disconnect
SNRM — Set Normal Response Mode
SNRME — Set Normal Response Mode Extended
TEST — Test
The XID default setting causes the router to establish a connection with
the host before connecting to the SDLC link station. The line activates
and the router sends the SNRM frame to the SDLC station. Selecting a
value other than XID causes the router to send that value to the SDLC
station before attempting to connect to the host.
Instructions: Click on Values and select one of the parameter settings.
Accept the XID default setting to establish a DLSw connection with the
host. When the connection succeeds, the router sends an SNRM frame to
the SDLC station.
To establish a connection to the SDLC station first, select SNRM. When
the router receives a response from the SDLC station, it then establishes a
DLSw connection with the host. This minimizes the logging of
unavailable or nonresponding SDLC stations.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.30
4-24
Page 53

Editing SDLC Parameters
Parameter: Fast Contact Timer
Default: 4000 milliseconds
Range: 1 to 64000
Function: Controls the timeout required before retransmitting an unacknowledged
contact frame (SNRM or XID). For primary SDLC link stations only , this
parameter operates with the Fast Contact Retry Limit parameter and is
also used for special pre-activation polling.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 64000 milliseconds. The value you enter must be
greater than the REPLYTO Timer value described earlier.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.16
Parameter: Fast Contact Retry Limit
Default: 4
Range: 1 to 64000
Function: Controls the number of times to transmit a contact frame (for example,
SNRM) before switching to the Slow Contact Timer. This parameter
operates with the Fast Contact Timer parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 64000, where 1 causes the switch to the Slow
Contact Timer after the first Fast Contact Timer expires. Enter 64000 for
an infinite number of retries.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.17
Parameter: Slow Contact Timer
Default: 4000 milliseconds
Range: 1 to 64000
Function: Allows contact polling to continue (using this timer) when the Fast
Contact Retry Limit expires. This prevents leased (multidrop) links from
being overwhelmed by poll frames for absent stations. This parameter
operates with the Slow Contact Retry Limit parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 64000 milliseconds.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.18
4-25
Page 54

Configuring SDLC Services
Parameter: Slow Contact Retry Limit
Default: 8
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Controls the number of times a contact frame (for example, SNRM) is
transmitted before sending an outage message to the SDLC device. This
parameter operates with the Slow Contact Timer parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535, where 1 causes an outage after the first
Slow Contact Timer expires, and 65535 specifies an unlimited number of
retries.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.19
Parameter: DISC Retransmit Timer
Default: 4000 milliseconds
Range: 1 to 64000
Function: Controls the length of time before retransmitting an unacknowledged
Disconnect (DISC) command. This parameter operates with the DISC
Retransmit Retry Limit parameter for primary SDLC link stations only.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 64000 milliseconds.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.20
Parameter: DISC Retransmit Retry Limit
Default: 4
Range: 1 to 65535
Function: Controls the number of times a Disconnect (DISC) command is
transmitted. This parameter operates with the DISC Retransmit Timer
parameter.
Instructions: Enter a value from 1 to 65535, where 1 causes an outage after the first
DISC Retransmit Timer e xpires, and 65535 specifies an unlimited number
of retries.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.21
4-26
Page 55

Parameter: Poll Bit Set In I-Frame
Default: TRUE
Options: TRUE | FALSE
Function: Specifies whether this link station sends the poll bit on an Information
frame. Certain SDLC implementations do not handle receipt of I-frames
carrying the poll bit.
Instructions: Enter TRUE if this link station can send the poll bit on an Information
frame.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.1.7.5.1.31
Deleting SDLC from the Router
T o delete all SDLC interfaces from the router, begin at the Configuration Manager
window (refer to Figure 4-1) and complete the following steps:
1. Select Protocols➔SDLC➔Delete SDLC.
2. Click on OK in the confirmation window.
Site Manager deletes the SDLC interfaces on the router.
Editing SDLC Parameters
4-27
Page 56

Page 57

Appendix A
SDLC Default Parameter Settings
Tables A-1 through A-3 list the default settings for SDLC parameters. Use the
Configuration Manager to edit any of the Site Manager default settings listed here.
Note that some SDLC parameters assume different defaults in Site Manager,
depending on whether you are configuring APPN or DLSw.
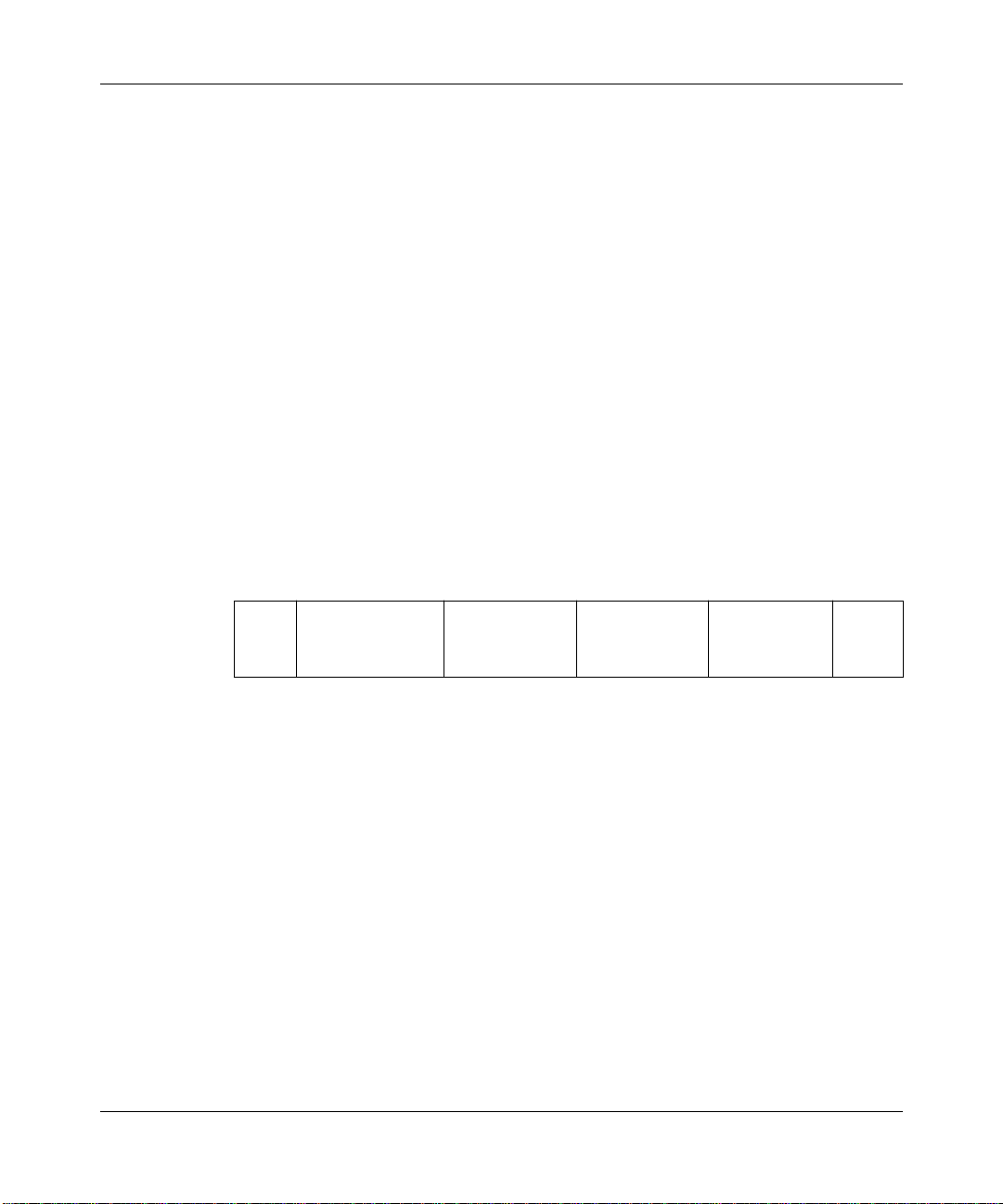
Table A-1. SDLC Line Parameters
Default Setting
Parameter
Clock Source Internal Internal
Internal Clock Speed 19.2 KB 19.2 KB
Sync Line Coding NRZ NRZ
Cable Type RS232 RS232
RTS Enable Disable Disable
with APPN
Default Setting
with DLSw
A-1
Page 58

Configuring SDLC Services
Table A-2. SDLC Interface Parameters
Default Setting
Parameter
Enable Enable Enable
Port Name APPN port name Circuit name
Link Station Role Negotiable Primary
Link Station Address 4 None
Support Negotiable Connection False False
Max Frame Retransmit Count 5 5
Non-productive Timer 2000 ms 2000 ms
Non-productive Retry Limit 15 15
Idle Line Timer 6000 ms 6000 ms
Idle Line Retry Limit 20 20
Port Write Timer 3000 ms 3000 ms
Port Write Retry Limit 10 10
Link Connection Timer 3000 ms 3000 ms
Link Connection Retry Limit 10 10
with APPN
Default Setting
with DLSw
A-2
Primary Full Duplex False False
Secondary Full Duplex False False
Enable Reject Frame True True
Max XID Size 256 256
Max Frame Size PDU2057 PDU2057
Total Link Station Limit 16 16
Inbound Link Station Limit 8 8
Outbound Link Station Limit 8 8
(continued)
Page 59

SDLC Default Parameter Settings
Table A-2. SDLC Interface Parameters
Default Setting
Parameter
Receive Buffer Pool Size 7 7
Initial Flow Control Credit 7 7
Enable Stats Collection True True
with APPN
(continued)
Default Setting
with DLSw
Table A-3. SDLC Link Station Parameters
Default Setting
Parameter
Enable Enable Enable
PU Name Configured APPN
Group Address 0 None
with APPN
Link Station Name or
NAME portion of the
APPN NETID.NAME
Default Setting
with DLSw
Configured DLSw
Adjacent Link Station
Name
MAXDATA PDU2057 PDU2057
MAXOUT 7 7
MAXIN 7 7
Response Timer 400 ms None
RNR Timer 3 min 3 min
RNR Retry Limit 4 4
REPLYTO Timer 30 tenths of a
second
REPLYTO Retry Limit 10 10
Fast Poll Timer 400 ms 400 ms
Fast Poll Count Limit 16 16
30 tenths of a
second
(continued)
A-3
Page 60

Configuring SDLC Services
Table A-3. SDLC Link Station Parameters
Default Setting
Parameter
Slow Poll Timer 1000 ms 1000 ms
Slow Poll Count Limit 65535 65535
Pre-Activation Contact Frame XID XID
Fast Contact Timer 4000 ms 4000 ms
Fast Contact Retry Limit 4 4
Slow Contact Timer 4000 ms 4000 ms
Slow Contact Retry Limit 8 8
DISC Retransmit Timer 4000 ms 4000 ms
DISC Retransmit Retry Limit 4 4
Poll Bit Set In I-Frame True True
with APPN
(continued)
Default Setting
with DLSw
A-4
Page 61

A
Index
adding SDLC link stations, 4-15
address field in SDLC frames, 1-3
APPN
link station types allowed, 2-1
using with SDLC, 1-4
B
Bay Networks
CompuServe forum, xii
customer support, xii
Home Page on World W ide Web, xiii
InfoFACTS service, xiii
publications, ordering, xv
Technical Response Center, xiv
BOFL parameter, 2-2
C
Cable Type parameter, 3-5
Clock Source parameter, 3-3
CompuServe, Bay Networks forum on, xii
configuring
SDLC link stations, 4-15
connections
physical, 1-3
control field in SDLC frames, 1-3
customer support. See getting help
D
defaults
SDLC parameters, A-1 to A-4
deleting
SDLC from the node, 4-27
SDLC interfaces, 4-14
DISC Retransmit Retry Limit parameter, 4-26
DISC Retransmit Timer parameter, 4-26
DLSw
link station types allowed, 2-1
using with SDLC, 1-4
E
editing
SDLC global parameters, 4-3 to 4-4
SDLC interface parameters, 4-4 to 4-14
SDLC link station parameters, 4-17 to 4-27
Enable parameter, 4-4, 4-6, 4-18
Enable Reject Frame parameter, 4-11
Enable Stats Collection parameter, 4-14
enabling SDLC, 3-1 to 3-5
exchange identification (XID), 1-2, 4-7
F
Fast Contact Retry Limit parameter, 4-25
Fast Contact Timer parameter, 4-25
Fast Poll Count Limit parameter, 4-22
Fast Poll Timer parameter, 4-22
Index-1
Page 62

flag field in SDLC frames, 1-3
formats
SDLC frames, 1-3
frame formats, 1-3
frame-checking field in SDLC frames, 1-3
full-duplex transmission, 1-2
configuring, 4-11
G
getting help
from a Bay Networks Technical Response
Center, xiv
through CompuServe, xii
through InfoFACTS service, xiii
through W orld W ide Web, xiii
Group Address parameter, 4-18
link stations
adding, 4-15
configuration considerations, 2-1
editing, 4-17 to 4-27
types, 1-2
M
Max Frame Retransmit Count parameter, 4-8
Max Frame Size parameter, 4-12
Max XID Size parameter, 4-12
MAXDATA parameter, 4-19
MAXIN parameter, 4-19
MAXOUT parameter, 2-2, 4-19
multipoint topology, 1-1
N
H
half-duplex transmission, 1-2
configuring, 4-11
I
Idle Line Retry Limit parameter, 4-9
Idle Line Timer parameter, 4-9
Inbound Link Station Limit parameter, 4-13
InfoFACTS service, xiii
information field in SDLC frames, 1-3
information frames, 1-3
Initial Flow Control Credit parameter, 4-14
Internal Clock Speed parameter, 3-4
L
Link Connection Retry Limit parameter, 4-10
Link Connection Timer parameter, 4-10
Link Station Address parameter, 4-7, 4-17
Link Station Role parameter, 4-7
negotiable link stations, 1-2
configuring, 2-1, 4-7
Non-productive Retry Limit parameter, 4-8
Non-productive Timer parameter, 4-8
O
Outbound Link Station Limit parameter, 4-13
P
parameters
default settings, A-1 to A-4
SDLC global, 4-3
SDLC interface, 4-4 to 4-14
SDLC line, 3-3 to 3-5
SDLC link station, 4-17 to 4-27
physical connections, 1-3
point-to-point topology, 1-1
Poll Bit Set In I-Frame parameter, 4-27
Port Name parameter, 4-6
Port Write Retry Limit parameter, 4-10
Index-2
Page 63

Port Write Timer parameter, 4-9
Pre-Activation Contact Frame parameter, 4-24
Primary Full Duplex parameter, 4-11
primary link stations, 1-2
configuring, 2-1, 4-7
PU Name parameter, 4-18
R
Receive Buffer Pool Size parameter, 4-13
REPLYTO Retry Limit parameter, 4-21
REPLYTO Timer parameter, 2-2, 4-21
Response Timer parameter, 4-20
RNR Retry Limit parameter, 4-20
RNR Timer parameter, 4-20
RTS Enable parameter, 2-2, 3-5
S
size
window, 2-2
configuring, 4-19
Slow Contact Retry Limit parameter, 4-26
Slow Contact Timer parameter, 4-25
Slow Poll Count Limit parameter, 4-23
Slow Poll Timer parameter, 4-22
supervisory frames, 1-3
Support Negotiable Connection parameter, 4-7
Sync Line Coding parameter, 3-4
synchronous line parameters, 3-3 to 3-5
T
timers, SDLC, 2-2
topologies, 1-1
Total Link Station Limit parameter, 4-12
transmission capabilities, 1-2
SDLC
deleting from router, 4-27
enabling, 3-1 to 3-5, 4-4
interfaces
deleting, 4-14
editing parameters, 4-4
link stations
adding, 4-15
defined, 1-2
editing, 4-17
overview, 1-1 to 1-4
parameters
defaults, A-1 to A-4
editing, 4-1 to 4-27
publications about, 1-4
timers, 2-2
Secondary Full Duplex parameter, 4-11
secondary link stations, 1-2
configuring, 2-1, 4-7
U
unnumbered frames, 1-3
W
window size, 2-2
configuring, 4-19
World Wide Web, Bay Networks Home Page on,
xiii
X
XID (exchange identification), 1-2, 4-7
Index-3
Page 64

 Loading...
Loading...