Page 1
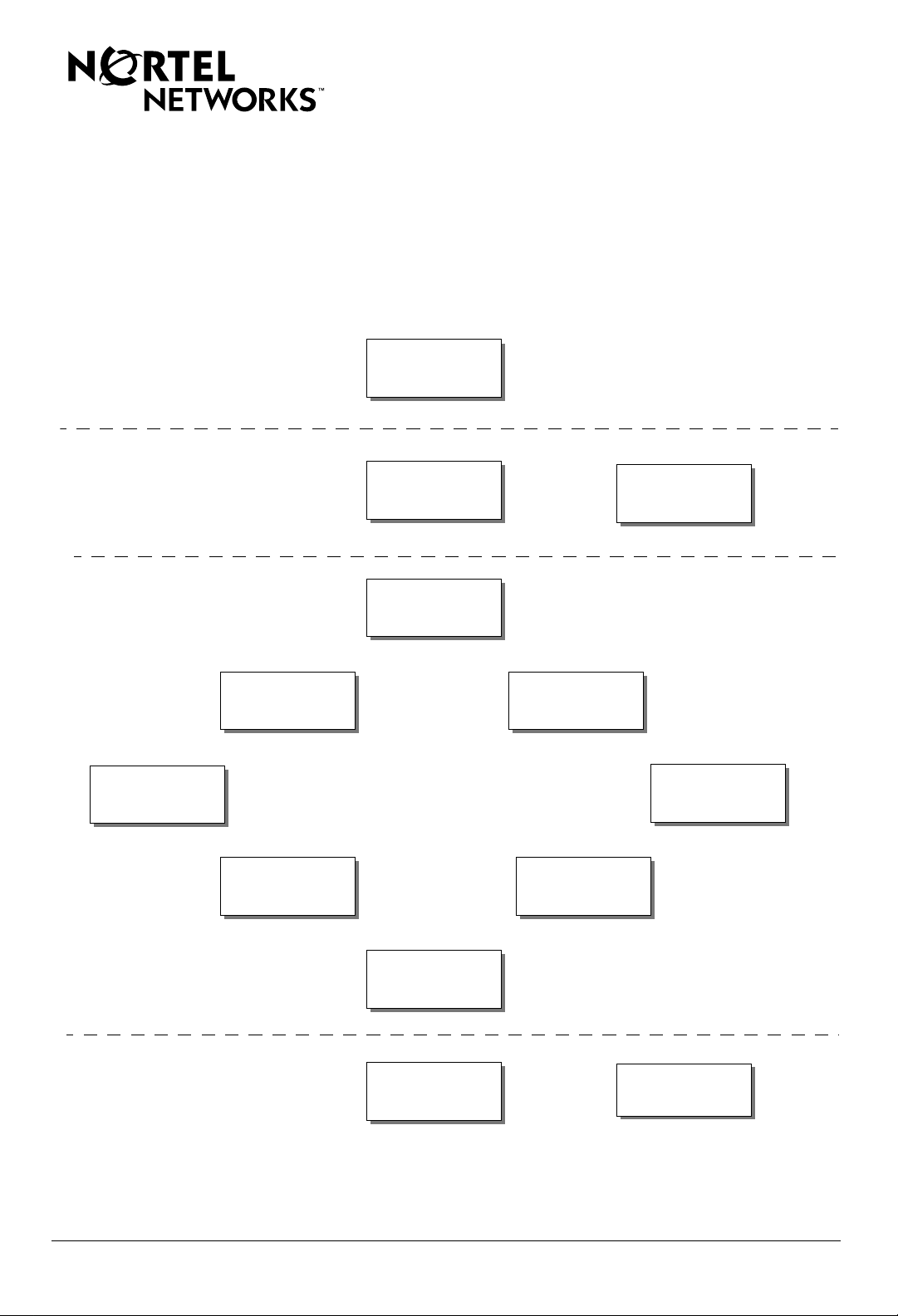
Documentation Roadmap
for Configuring BayRS
Routers and Protocols
What do
services so you can customize and manage your network. This roadmap provides an overview of the
documentation set followed by a brief description of each manual and a link to it.
To navigate around the roadmap, click on any box. To open a specific manual, click on the name of the
manual (shown in italics).
Locating BayRS
Documentation
Installing
Configuring
you
want your
router
to be? Whatever it is, Nortel Networks offers dozens of protocols and
Hard copy, CD, and
Web documents
Release notes
Configurat i on tools
Installation guides
Line services
Managing and
Troubleshooting
WAN protocols
IP protocols
IBM protocols
Managing routers
Security
LAN protocol s
ATM protocols
Troubleshooting
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 1
Page 2
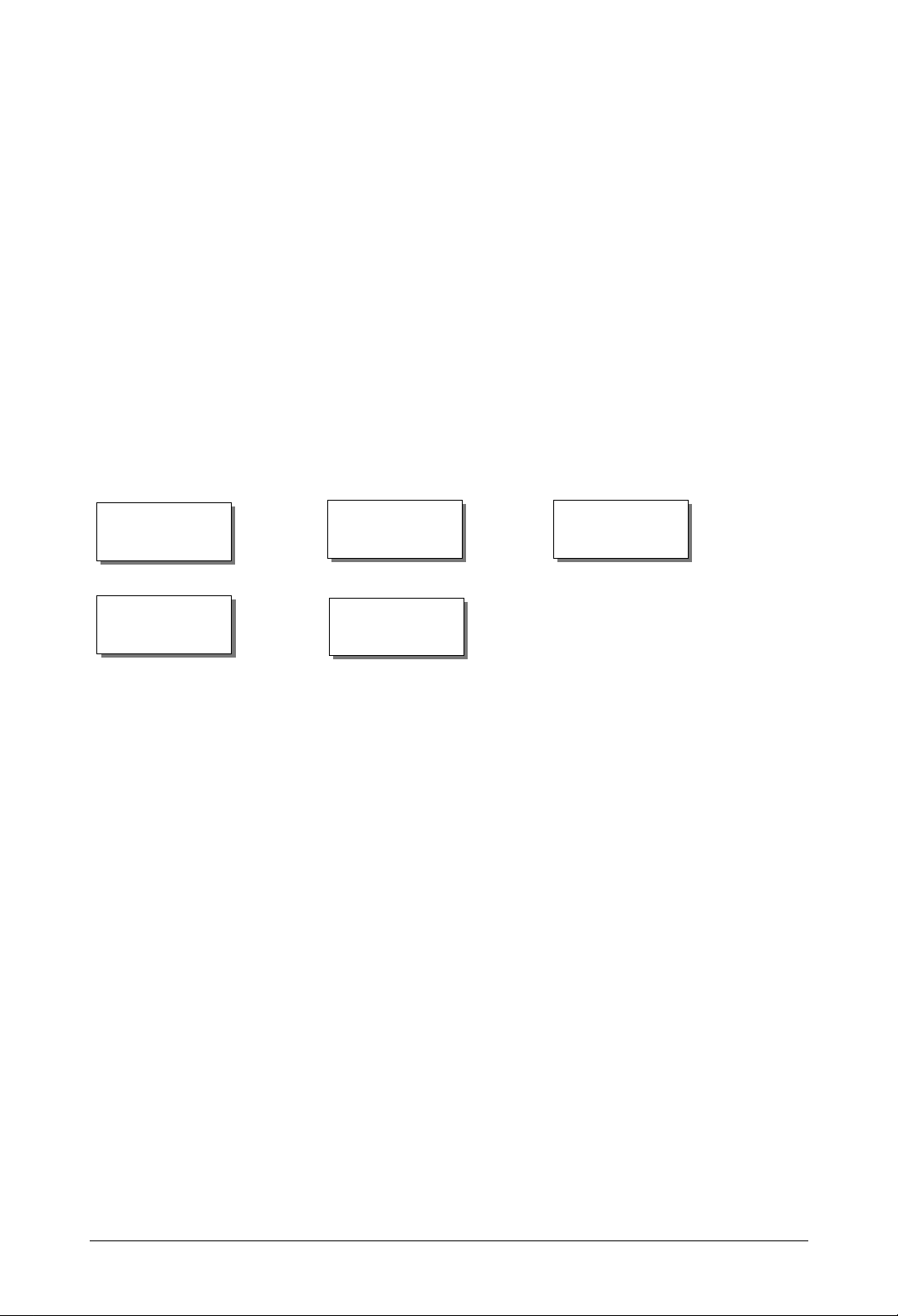
Where to locate BayRS documentation
Your router comes with several hard-copy documents including the installation guide, release
notes, known anomalies, fixed anomalies, and the document change notice (DCN). Other
documents for configuring and managing your router come on a CD called the Online Library.
This CD comes with a manual that describes how to install the online library and provides an
overvie w of the li brary’s features. You can view the library on a PC, UNIX, or Macintosh pl atform.
All manuals (except the known anomalies document) are also available on the Web at
http://www.nortelnetworks.com/documentation.
Back to Roadmap
Release notes
Read the following release no tes for the late st hardware and software info rmation:
Notes for BayRS and
the BCC
Known Anoma li e s
Notes for Site
Manager
Fixed Anomalies
Document Change
Notice
Release Notes for Ba yRS
These release notes provide information about the latest version of BayRS. They include
information about ne w fe atures, up grading your softwa re, general guidelines, BCC gui delines , and
operating limitations. The release notes also include information about supported protocols,
standards, and flash memory cards.
Back to Roadmap
Release Notes for Site Manager
These release notes provide information about the latest version of Site Manager. They include
information about compatibility with BayRS, system requirements, and general guidelines.
Back to Roadmap
BayRS Document Change Notice
The document change notice (DCN) contains additions and corrections to BayRS manuals since
BayRS Version 15.1. The DCN is organized by manual title and release number.
Back to Roadmap
2 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 3

BayRS, BCC, and Site Manager Known Anomalies
This hard-copy document lists the known anomalies (also referred to as bugs, change requests, or
CRs) that were found in the latest version of BayRS, the BCC, and Site Manager.
Back to Roadmap
BayRS, BCC, and Site Manager Fixed Anomalies
This hard-copy document lists the fixed anomalies (also referred to as bugs, change requests, or
CRs) that were fixed in the latest version of BayRS, the BCC, and Site Manager.
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 3
Page 4
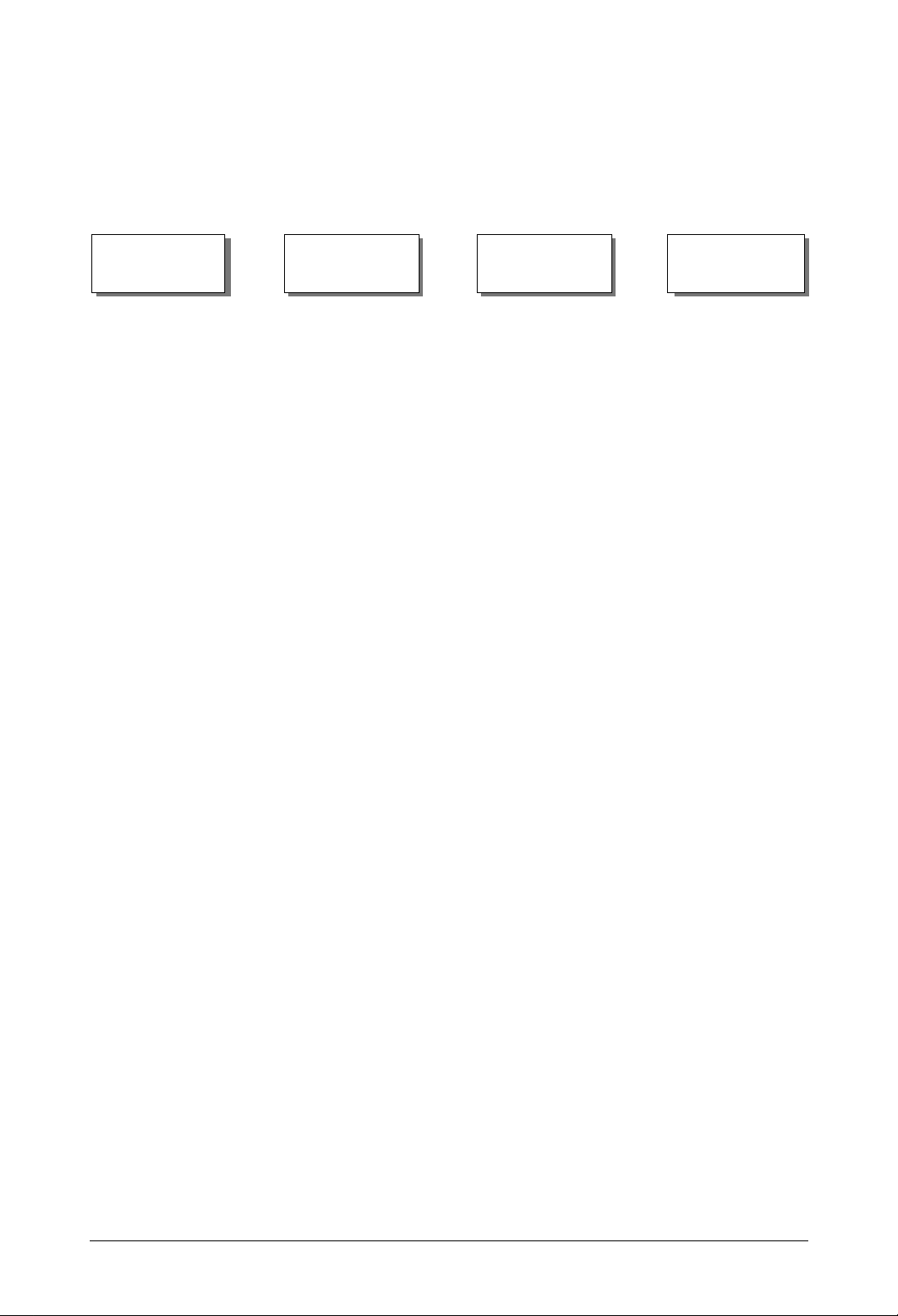
Installation
Refer to the appropriate installation guide to install your router and then read Quick-Starting
Routers to connect it to a network.
Hardware
Installation Guides
Quick-Starting
Routers
ASN Routers ARN Remote Access
Hardware Installation Guides
The following manuals describes how to install, configure, and maintain BayRS routers.
For information about a specific platform, click on the appropriate title.
• Installing and Maintaining BN Platforms
• Installing and Maintaining ASN Routers and BNX Platforms
• Installing and Operating ARN Routers
• Installing and Operating the Passport 5430 Multiservice Access Switch
• Installing and Operating the Passport 2430 Multiservice Access Switch
• Cable Guide—This guide lists the specific cables for your Nortel Networks router. If you need
to meet special r equir ements, this guide a lso pr o vid es the pinout info rmatio n an d refe rence s to
the industry specifications and standards so that you can build your own cables.
Back to Roadmap
Quick-Starting Routers
This manual describes how to boot your router locally and configure its initial interface to an IP
network. When you complete the quick-start installation procedure, the router will route IP traffic
on your network. This manua l also describes ho w to inst all Site Manager and provides an o vervi ew
of BayRS security featu res.
Back to Roadmap
Connecting ASN Routers to a Network
This manual describ es ho w to boot an Access St ack Node (ASN) router o v er a netw ork i nterfac e to
connect it to a network.
Back to Roadmap
Configuring Remote Access for AN and Passport ARN Routers
This manual describes how to connect Access Node (AN), Access Node Hub (ANH), and
Advanced Remote Node (ARN) routers to corporate backbone networks.
Back to Roadmap
4 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 5

Configuration tools
Three configuration tools support BayRS: the BCC, Site Manager, and the Technician Interface.
Nortel Networks recommends using either the BCC or Site Manager. In most cases, you can use
either tool to configure your router.
The T ec hnician Int erfa ce is for e xperi enced netw ork admin istrators . Nortel Networks r ecommends
using the Technician Interface for troubleshooting only because it provides limited support for
configuring protocol parameters. It also does not verify configuration files or check them for
consistency before allowing you to save them.
Click on any configuration tool for a more detailed description:
BCC Site Manager Technician Interface
Bay Command Console (BCC)
This section describes the two BCC manuals: a user guide and a quick reference.
Using the Bay Command Console (BCC)
The BCC is the Nortel Network command-line interface for configuring routers. This manual
explains how to use BCC commands and provides a tutorial that guides you through the initial
configuration of a Nortel Networks router. You can use the BCC to perform tasks such as creating
or deleting IP interfaces on the router.
Back to Configuration Tools
Back to Roadmap
BCC Quick Reference
This quick reference provides experienced users with a sample configuration, a table of the most
commonly used BCC commands, and helpful shortcuts and tips.
Back to Configuration Tools
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 5
Page 6

Site Manager
Configuring and Managing Routers with Sit e Manager
Site Manager is a graphical user interface (GUI) for configuring routers. This manual describes
how to create configuration files, customize software images, manage configuration files, and
monitor router performance.
You can use Site Manager on a PC or a UNIX workstation and integrate it with many popular
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) applications, such as the Hewlett-Packard
OpenView Network Node Manager.
Back to Configuration Tools
Back to Roadmap
Technician Interface
The three ma nuals in this s ection document the Technician Interface, which resid es in the router ’s
operating system kernel. The Technician Interface automatically loads when you boot the router.
You can establish a session through the router’s console port, through a local ASCII terminal, or a
dial-up connection.
Using Technician Interface Software
The Technician Interface is a command-line interface for configuring routers. This manual
explains how to use the Technician Interface to in stall a router, maintain or diagnose router
operation, and monitor and configure certain basic router functions.
Back to Configuration Tools
Back to Roadmap
Using Technician Interface Scripts
Technician Interface scripts enable you to view and use information stored in the management
information base (MIB). This manual describes how to use the script commands (
enable/disable
and
) to display statis tical and configuration information about router ser vic es, and
show/monitor
to enable or disable those services.
Back to Configuration Tools
Back to Roadmap
Writing Technician Interface Scripts
Technician Interface scripts enable network administrators to read and execute Technician
Interface commands from a remote workstation and transfer the files to the router via TFTP or
XMODEM. This manual describes how to write your own Technician Interface scripts, which are
very similar to U NIX shell scripts.
Back to Configuration Tools
Back to Roadmap
6 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 7
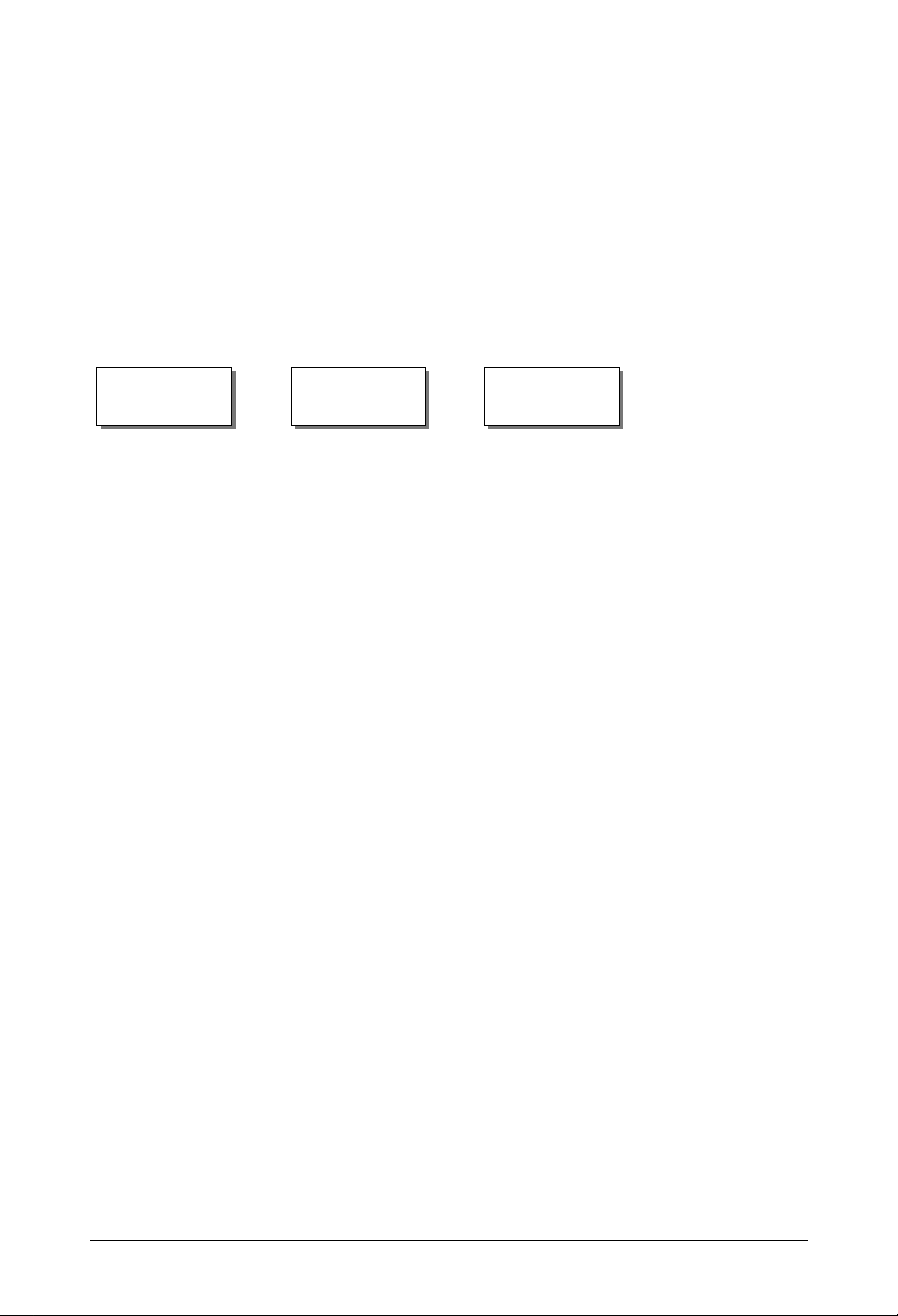
Security
Depending on your security needs, you can configure your router with one or more of the
following security services and protocols.
• IPsec protects data while it travels over public networks.
• L2TP protects data by creating a virtual private network (VPN).
• RADIUS protects data by authorizing remote users before giving them access to a network.
Click on any of the following security services for a more detailed desc ription:
IPsec L2TP RADIUS
Configuring IPsec Services
The IP Security (IPsec) standards were developed to ensure secure, private communications for the
remote access, extranet, and intranet virtual private networks (VPNs) used in enterprise
communications. This manual describes how to configure IPsec services on a Nortel Networks
router.
Back to Security
Back to Roadmap
Configuring L2TP Services
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) provides remote users, such as telecommuters, mobile
professionals, and personnel in remote branch offices, with dial-in access to a corporate network.
L2TP enables users to create a virtual private network (VPN) over a public network, such as the
Internet, but offers the security and exclusivity of a private network. This manual describes how to
configure L2TP services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to Security
Back to Roadmap
Configuring RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) centralizes security and controls the
billing of services. RADIUS authentication identifies remote users before you give them access
to a central network site. RADIUS accounting collects data during a remote user’s dial-in session
so that you can determine billing charges. This manual describes how to configure RADIUS
services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to Security
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 7
Page 8

LAN pr otocols
Nortel Networks supports the following LAN protocols. Click on any of the following for a
description:
AppleTalk Bridging DECnet IPX
OSI VINES XNS
Configuring AppleTalk Services
This manual describes how to configure AppleTalk services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to LAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring Bridging Services
This manual includes information about the following topics: transparent bridges, source routing
bridges, NetBIOS, translation bridges, native mode LANs, and spanning trees. This manual
describes how to configure bridging services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to LAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring DECnet Services
This manual describes how to configure DECnet services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to LAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring IPX Services
This manual describes how to configure Internetwork Packet Exchange (I PX) s erv ices on a Nortel
Networks router.
Back to LAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring OSI Services
This manual descri bes how to configure Open Systems Inter connection (OSI) serv ice s on a Nortel
Networks router.
Back to LAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
8 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 9

Configuring VINES Services
This manual describes how to configure Virtual Networking System (VINES) serv ices on a Nort el
Networks router.
Back to LAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring XNS Services
The Nortel Networks implementation of the Xerox Networking System (XNS) protocol is based
on the Xerox System Integration Standard specification (Xerox Corporation, December 1981),
commonly refer red to as The Gra y Book. This man ual descr ibes ho w to co nfigur e XNS servic es on
a Nortel Networks router.
Back to LAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 9
Page 10

ATM protocols
Nortel Networks supports several ATM services. To configure an ATM network, start with ATM
Services and then go to the other manuals for the protocols that you want to add. Click on any of
the following for a description:
ATM Services
MPOA and NHRP
ATM DXI
TDM
ATM Half Bridge
VRRP
Configuring ATM Services
Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) relays traffic across a Broadband Integrated Services Digital
Network (B-ISDN). ATM provides a cost-effective way of transmitting voice, video, and data
across a WAN network. ATM can also emulate a LAN network and allow virtual communication
between traditional LAN devices. This manual describes how to configure ATM services on a
Nortel Networks router.
Back to ATM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring ATM DXI Services
ATM Data Exchange Interface (DXI) enables you to access an ATM network over a synchronous
connection. Synchro nous interfaces use l in k modul es that work with a Fast Routing Engi ne (FRE)
to form an Intelligent Link Interface (ILI) pair. This ILI pair must use ATM DXI as a WAN
protocol to connect to an ATM data service unit/channel service unit (DSU/CSU). The DSU/CSU
then converts these packets to uniform 53-byte cells for transmission over the ATM network. This
manual describes how to configure ATM DXI services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to ATM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring ATM Half-Bridge Services
The ATM Half Bridge (AHB) protocol operates on BLN and BCN routers that connect remote
hosts to an IP routed network via a digital subscriber line (DSL). AHB converts bridged frames
containing IP packets to unencapsulated routed frames and performs the reverse function for
packets returning from the opposite direction. AHB meets the requirements of public network
providers who want to develop an end-to-end solution using DSL to provide high-speed Internet
and remote LAN access to ISPs and corporate networks. This manual describes how to configure
AHB services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to ATM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
10 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 11

Configuring MPOA and NHRP Services
Multi-Protocol over ATM (MPOA) maps routed and bridged traffic flows to ATM SVCs. This
technique creates network shortcuts between source and destination clients. This is generally
referred to as cut-through or zero-hop routing.
Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) provides address resolution services by mapping IP
addresses to ATM addresses. This manual describes how to configure MPOA and NHRP services
on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to ATM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring TDM Services
Time di visio n multiple xing (TDM) transmi ts signals f rom multiple channel s ov er a single pat h. For
example, a transmitting device can interleave three incoming signals into one outgoing signal.
Then the receiving device divides the single stream back into its original signals. The transmitting
device allocates bandwidth to each channel on the basis of time slots, which ensures that each
device gets its required share of the available bandwidth. This manual describes how to configure
TDM services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to ATM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring VRRP Services
The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) allows you to configure redundant routers to
protect a network from the irrecoverable failure of one or more IP interfaces. One VRRP router
acts as the master virtual router for an IP address, while other VRRP routers act as backup virtual
routers. VRRP eliminates any single point of failure within your network. VRRP runs over IP, but
you can also configure VRRP on an ATM network configured with Multi-Protocol over ATM
(MPOA). This manual describes how to configure VRRP services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to ATM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 11
Page 12

IBM protocols
Nortel Networks supports several IBM protocols and services. Click on any of the following for a
description:
APPN BSC Transport DLSw LLC
LNM SDLC
Configuring APPN Services
Advanced Pee r-to-Pee r Networ king (APPN) e xtends IBM ’s Systems Network Archit ecture (SN A).
Nortel Networks routers can serve as APPN nodes in an IBM SNA network (with or without the
presence of an IBM mainframe computer). The Nortel Networks APPN implementation complies
with Version 2 of the IBM APPN Network Node specification, with advanced optional APPN
function sets. This manual des cribe s ho w to conf igu re APPN servic es on a Nortel Networ ks rout er.
Back to IBM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring BSC Transport Services
Binary Synchronous Communic ation (BSC) pro vides transp ort services that enable yo u to transmit
data over a multiprotocol network. BSC typically operates over low-speed lines up to 19.2 Kb/s.
BSC is character-or ient ed, assumes 8-bit chara cters , and most ofte n uses the EBCDIC code set for
data transmission. This manual describes how to configure BSC transport services on a Nortel
Networks router.
Back to IBM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
12 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 13

Configuring DLSw Services
Data link switching (DLSw) provides the following services:
• Transports connection-oriented SNA and NetBIOS data across a network
• Prevents sessions from timing out due to slow network response time
• Reroutes traffic around failed links
• Improves response time by reducing network overhead
• Interconnects multiple locations without requiring a network manager to reconfigure existing
bridges
This manual describes how to configure DLSw services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to IBM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring LLC Services
Logical Link Control (LLC) e nabl es SNA devices and NetBIOS PCs to establish ses sio ns through
a LAN topology. LLC also adds higher-layer sequencing and error control in bridged LAN
environments. The Nortel Networks implementation of the LLC protocol consists of LLC class 1
(LLC1), a connectionless del iv ery servic e, and LLC class 2 (LLC2), a connect ion-oriented se rvice.
Most protocols use LLC1, but LAN Network Manager (LNM) servers, data link switching
(DLSw) services, and Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking (APPN) require LLC2. This manual
describes how to configure LLC services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to IBM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring LNM Services
LAN Network Manager (LNM) manages multisegment 802.5/token ring networks. Network
administrators can use LNM to monitor a single LAN or a group of LANs. LNM can also
communicate with the IBM NetView host-based network management product. This enables a
NetVie w administrator to access certain operating capabilities of the LNM. This manual describes
how to configure LNM services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to IBM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring SDLC Services
Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC) is the synchronous, bit-oriented link control protocol in
the IBM Systems Network Architecture (SNA). SDLC is not a peer-to-peer protocol like frame
relay; SDLC networks consist of a primary station that controls all communication and one or
more secondary stations. For example, a mainframe in Los Angeles may support a multidrop line
with controllers connected to drops in offices in Boston, New York, and Washington. This manual
describes how to configure SDLC services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to IBM Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 13
Page 14

IP protocols
Nortel Networks supports several IP services. To configure an IP network, start with the IP, ARP,
RARP, RIP, and OSPF manual and then go to the other manuals for the protocols that you want to
add. Click on any of the following for a description:
IP, ARP, RARP, RIP,
and OSPF
DVMRP, IGMP,
MOSPF, PIM, and
RSVP
VRRP
BGP and EGP GRE, NAT, RIPSO,
DNS, FTP, TFTP,
Te lnet, NTP, TC P,
NetBIOS, and IP
accounting
BCC IP show
Commands
DiffServ and COPS
IPv6 and RIPv6
and BFE
Polled
Asynchronous Over
TCP/IP (AOT)
Configuring IP, ARP, RARP, RIP, and OSPF Services
IP routers need both an IP address and a physical address to transmit data. The Internet Protocol
(IP) assigns the IP address, and the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) determines the physical
address by binding a n IP addr ess t o a med ia ac cess c ontrol (M AC) address. You can al so configure
a Nortel Networks router as a Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) server. A RARP
server supplies clients on the same physical or logical LAN with IP addresses.
The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance-vector protocol, which means that RIP
computes distance based on the number of hops (or routers) from the source network to the target
network. For RIP, the “best” path to a destination is the shortest path (the path with the fewest
hops). Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a link state protocol, which means that OSPF
periodically tes ts the status of th e physi cal conne ction t o each of its ne ighborin g router s, b ut al lo ws
you to configure the cost metrics. This manual describes how to configure IP services on a Nortel
Networks router.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
14 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 15

Configuring IP Exterior Gateway Protocols (BGP and EGP)
Exterior gate ways are routers at the edge of au tonomous systems. To exchange r outing i nformatio n
with each other and to route packets between domains, these gateways use the Border Gateway
Protocol (BGP) and the Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP). BGP routers exchange complete
routing information only wh en the y estab lish the peer conn ection. Th ereafte r , BGP peers e xchange
routing information in the form of routing updates. EGP routers periodically exchange complete
routing information, not just updates. This manual describes how to configure BGP and EGP
services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring Differentiated Services
Differentiated services enable you to designate a specific level of performance on a packet-bypacket basis. For example, if you have applications that require high performance and reliable
service, such as voice and video over IP, you can use differentiated services to give preferential
treatment t o this data over other traffic.
Differentiated service networks may also have a bandwidth broker, which is a server that
dynamically installs filters. In these networks, the router uses the Common Open Policy Service
(COPS) protocol to communicate with the bandwidth broker. COPS is a quality-of-service (QoS)
policy exchange protocol for communicating network QoS policy information between the
bandwidth broker and its clients. This manual describes how to configure differentiated services
and COPS on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring GRE, NAT, RIPSO, and BFE Services
Some traffic requires special handling before it can be transported across an IP network. To meet
these special needs, Nortel Networks offers the following services:
• Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) creates tunnels to transport non-IP traffic over IP
networks.
• Network Address Translation (NAT) assigns a global IP address that maps to several
unregistered loc al addresse s. Companies tha t do not hav e enough glob ally unique IP addr esses
for each host on its network use this protocol to access the Internet. NAT can also translate
unregistered addresses into registered addresses so those addresses can access the Internet.
• Revised IP Security Option (RIPSO) enables routers to use Department of Defense security
labels in tra ffic that they transmit or receive on an IP network.
• Blacker front-end (BFE) i s a cl assi f ied encryp tion d e v ice used by h osts to communi cate across
unsecured wide area networks. BFE devices are typically found in government networks.
This manual describes how to configure GRE, NAT, RIPSO, and BFE services on a Nortel
Networks router.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 15
Page 16

Configuring IP Multicasting and Multimedia Services
Nortel Networks offers the following multicasting and multimedia services:
• Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) advertises shortest-path routes to
multicasting source networks, that is, any network with hosts that can issue multicast
datagrams.
• Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) allows a host to register its local network with
the local ro uter.
• Multicast OSPF (MOSPF) forwar ds multicast IP traf f ic withi n an OSPF Version 2 autonomou s
system.
• Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) routes multicast traffic between members of multicast
groups that are distributed across various regions of the Internet.
• Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) allows host systems in an IP network to reserve
resources on RSVP-capa ble routers for unicast or multicast dataflows.
This manual describes how to configure multicasting and multimedia services on a Nortel
Networks router.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring IP Utilities
The following IP utilities are application protocols that use IP for message transport:
• DNS • FTP
• NetBIOS over IP • TFTP
• NTP • TCP
• Telnet
This manual describes how to configure these IP utilities on a Nortel Networks router and how to
configure global access policies for Telnet, FTP, TFTP, NTP, SNMP, and HTTP Server. This
manual also describes how to configure IP accounting on frame relay interfaces.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring IPv6 Services
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) uses 128 bits for source and destination addresses. The header
also includes a flow control field that an IPv6 host can use to label packets that require special
handling by IPv6 routers, such as packets that require real-time service. This manual describes
how to configure IPv6 and RIPv6 services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
16 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 17

Configuring Polled AOT Transport Services
Polled Asynchronous over TCP/IP (AOT) transports asynchronous data packets over a TCP/IP
network. Polle d AOT transmissions use TCP timers and ke epali v e sett ings to ensure t hat ther e is an
active TCP connection between two routers before any transmission attempt. Because
asynchronous transmissions are relatively slow (300 bits/s to 9600 bits/s), polling ensures that the
secondary router is available for asynchronous transmission. This manual describes how to
configure polled AOT transport services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring VRRP Services
The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) allows you to configure redundant routers to
protect a network from the irrecoverable failure of one or more IP interfaces. One VRRP router
acts as the master virtual router for an IP address, while other VRRP routers act as backup virtual
routers. VRRP eliminates any single point of failure within your network. VRRP runs over IP, but
you can also configure VRRP on an ATM network configured with Multi-Protocol over ATM
(MPOA). This manual describes how to configure VRRP services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Reference for BCC IP show Commands
This manual explains how to use BCC
commands to display routing, configuration,
show
interface, and statistical data about the following protocols: IP, BGP, DVMRP, GRE, IGMP, NAT,
OSPF, and RIP.
Back to IP Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 17
Page 18

Line services
Ethernet, FDDI, and
token ring
WAN line services
Configuring Ethernet, FDDI, and Token Ring Services
Ethernet, FDDI, and token ring services comprise the physical and data link layer (line) services
for configured LAN circuits. This manual describes how to configure these services on a Nortel
Networks router.
Back to Line Services
Back to Roadmap
Configuring WAN Line Services
WAN line services define the procedures for transferring data accurately and reliably across the
physical layer (data link layer of the OSI model). Procedures include setting the clock speed,
maximum transmission size, retry timer, and priority. When you configure a router, the line
defaults are suitable for most networks. However,
you may want to customize the line services.
This manual describes how to configure WAN line services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to Line Services
Back to Roadmap
18 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 19

WAN protocols
Nortel Networks supports many types of WAN protocols. For a description of a type, click on any
of the following:
Dial protocols Frame relay SMDS X.25PPP
Dial protocols
Nortel Networks supports dial protocols and services. Click on the following for a description:
Dial Services Dial VPN
Configuring Dial Services
Dial services use dia l-up l ines t o connec t remot e users throug h a c entra l switc hed net work to othe r
destinations on the network. Dial-up lines are temporary network connections that a router
activates under the following conditions:
• When the re is data to send across th e network (dial-on-demand).
• When a failed connection needs a backup connection (dial backup).
• When a congested leased line needs an additional connection for more bandwidth
(bandwidth-on-demand).
This manual describes dial-on-demand, dial backup, and bandwidth-on-demand services and how
to configure these dial services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to Dial Protocols
Back to WAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring and Troubleshooting Bay Dial VPN Networks
Bay Dial VP N (virtual private network) provides secure dial-access services over telephone lines
for remote users. Dial VPN offers simple and secure access to virtual private networks and the
Internet through a tunnel, which is a secure, virtual, direct path between two end points. This
manual describes how to configure Dial VPN services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to Dial Protocols
Back to WAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 19
Page 20

Frame relay
Configuring Frame Relay Services
Frame relay is a high-speed, packet-switching WAN protocol that connects geographically
dispersed LANs. Frame relay is a connection-oriented protocol, which means that it relies on
end-to-end paths between devices connected across the network. It implements these connections
using permanent virt ual circuits (PVCs) or switched virt ual circuit s (SVCs). This manual de scribes
how to configure frame relay services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to WAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
PPP
Configuring PPP Services
Point-to-Point Prot ocol (PPP) creates an inte rface between peer rou te rs to al low them to exchange
data. PPP also allows peers to negotiate and determine data link and network layer options. When
negotiations complete successfully, PPP encapsulates the data and transmits it over the link. This
manual describes how to configure PPP services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to WAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
SMDS
Configuring SMDS
Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS) is a public, high-speed, packet-switched network
service that enabl es you to connect local ar ea networ ks across wide ar ea networks. SMDS pro vides
connectionless data transfer across a wide area network without establishing a logical end-to-end
connection.
The use of cell technology makes SMDS well suited for traffic that consumes high bandwidth for
short periods of time. This manual describes how to configure SMDS services on a Nortel
Networks router.
To send information across the network, SMDS divides data into fixed 53-byte cells.
Back to WAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
20 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 21

X.25 protocols
Nortel Networks supports X.25 protocols and services. Click on the following for a description:
X.25 X.25 Gateway and
LAPB
Configuring X.25 Services
X.25 transports LAN traffic to packet-switching networks, usually over public data networks.
Because public data networks typically use error-prone analog lines, the X.25 protocol provides
extensive error checking, recovery, and packet sequencing. X.25 also allows many different kinds
of equipment to communi cat e across networks at a re la tively low cost. This manual describes how
to configure X.25 services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to X.25 Protocols
Back to WAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Configuring X.25 Gateway Services
X.25 Gateway enables you to send and receive messages between X.25 and TCP/IP networks. It
maps TCP sockets to X.25 virtual circuits (and vice versa) or to Link Access Procedure Balanced
(LAPB) poi nt-to-point c onnection identifiers. The LAPB information field contains the X.25 data
packet. When an X.25 packet reaches the destination router, the LAPB protocol strips away the
LAPB fram e and delivers the pac ket to the network layer for further processing. This m anual
describes how to configure X.25 gateway services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to X.25 Protocols
Back to WAN Protocols
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 21
Page 22

Managing routers
Nortel Networks offers several router management tools. Click on any of the following for a
description:
Data compression SNMP, BootP, and
HTTP Server
DHCP
Interface and Router
Redundancy
Traffic Filters and
Protocol
Prioritization
Configuring Data Compression Services
Data compression eliminates redundancy in data streams and reduces the amount of bandwidth
needed to transport LAN protocols over a wide area network. Nortel Networks supports data
compression over frame relay, X.25, and PPP (dial-up or leased lines). This manua l describes how
to configure data compression services on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to Managing Routers
Back to Roadmap
Managing Routers Using the HTTP Server
HTTP Server is a Web-based router management tool with a graphical user interface. The
HTTP Server is part of the BayRS software and is accessible from any standard Web browser.
Using the HTTP Server software, you can monitor and manage your network’s performance on a
device-by-device basis. For example, you can see where congestion is occurring or where
transmission or reception problems exist. This manual describes how to configure the HTTP
Server on a Nortel Networks router.
Back to Managing Routers
Back to Roadmap
Configuring SNMP, BootP, and DHCP Services
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) communicates management information
between SNMP managers and SNMP agents. These messages enable you to access and manage
objects in a router’s management information base (MIB).
The Bootstrap Protocol (BootP) allows a diskless client to broadcast a request to boot from a
remote server on the same network or on a different physical network. When a suitable server
receives the BOOTREQUEST packet, it transmits the bo ot file to the cli ent vi a a transfer protocol ,
such as Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP).
Dynamic Host Configura tion Prot ocol (DHCP) is an e xt ension of BootP. DHCP allo ws desi gnated
DHCP servers to automatically assign IP addresses and host names to dynamically configured
DHCP clients for a predefined period of time.
This manual describes how to configure SNMP, BootP, and DHCP services on a Nortel Networks
router.
Back to Managing Routers
Back to Roadmap
22 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 23

Configuring Interface and Router Redundancy
Redundancy servi ces enabl e a router to r ecov er fr om either in terf ace or rout er fai lure with minimal
delay.
• Interface redundancy protects your network from failures of individual LAN interfaces by
backing up one interface with another interface on the same router.
• Router redundancy protects a network from the irrecoverable failure of an entire router. You
configure routers to be members of a router redundancy group, which includes a primary
router and one or more secondary routers that take over if th e primary router fails.
This manual describes how to configure interface and router redundancy services on a Nortel
Networks router.
Back to Managing Routers
Back to Roadmap
Configuring Traffic Filters and Protocol Prioritization
Traffic filters manage customer traffic and reduce network congestion. Inbound traffic filters can
restrict access to no des in a netw ork.
Outbound traff ic f il ters ensur e timely deli v ery of c ritical data,
or restrict traffic leaving the network.
Protocol prioritization enables the router to sort traffic into priority queues (high, normal, and low).
Protocol prioritization is an outbound traffic filter mechanism that affects the sequence in which
data leaves an interface; it does not affect traffic as it arrives at the router.
This manual describes how to configure traffic filters and prioritize traffic on a Nortel Networks
router.
Back to Managing Routers
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 23
Page 24

Troubleshooting
Nortel Networks pro vides se v eral trouble shooting tools to isolate and sol ve probl ems. Click on any
of the following for a description:
Troubleshooting
Routers
RMON and RMON2 Event Messages BCC IP show
Commands
Troubleshooting Routers
Nortel Networks routers come with troubleshooting tools that help you diagnose and remedy
router problems. This manual explains how to use those tools to:
• Display event messages.
• Display and change configuration settings and statistics.
ping
• Use the
command.
• Use the packet capture tool.
• Use inbound Telnet to access the Technician Interface.
Back to Troubles hoot in g
Back to Roadmap
Configuring RMON and RMON2
RMON (Remote MONitoring) and RMON2 provide remote troubleshooting and monitoring
within a LAN segment and across an enterprise network.
• RMON provides statistics at the media access control (MAC) layer, allowing you to capture
real-time information across the entire network.
• RMON2 extends the scope of RMON beyond the MAC layer to provide statistics on network
and applicatio n laye r tr af fic (layers 3 thr ough 7 of t he OSI model) . By monit oring higher-layer
protocols, you can obtain an internetwork or enterprise-wide view of network traffic.
This manual describes how to configure RMON and RMON2 services on a Nortel Networks
router.
Back to Troubles hoot in g
Back to Roadmap
Event Messages Database
The event messages database contains a description of all the messages that appear in BayRS
router event logs, except for Debug events. If you monitor the log file and see a message that you
do not understand, use t he event code to query the event dat abase for a description an d a cou rse of
action. Third-party network management software can also use the event code to retrieve
information from the database.
Back to Troubles hoot in g
Back to Roadmap
24 Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00)
Page 25

Reference for BCC IP show Commands
This manual explains how to use BCC
commands to display routing, configuration,
show
interface, and statistical data about the following protocols: IP, BGP, DVMRP, GRE, IGMP, NAT,
OSPF, and RIP.
Back to Troubles hoot in g
Back to Roadmap
Documentation Roadmap (308665-15.2 Rev 00) 25
 Loading...
Loading...