Page 1

CallPilot
Message Networking
Part No. P0606015 04
23 March 2004
Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 2

2
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up
and Operation Guide
Copyright © 2003 Nortel Networks
All rights reserved. 2003.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The information
in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks NA Inc.
The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in accordance with the
terms of that license.
Trademarks
NORTEL NETWORKS is a trademark of Nortel Networks.
Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
P0606015 04
Page 3
Contents
Chapter 1
About CallPilot Message Networking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Requirements for setting up Message Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
About Message Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Digital and AMIS networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
About Digital Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
How Digital Networking works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
About AMIS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
How AMIS works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Ways of sending network messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Site-Based Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Network Delivery Mailboxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Direct Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Assigning Message Networking to subscribers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
How to get help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3
Chapter 2
Setting up Digital Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Setting the Digital Networking properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Configuring your system network properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Configuring your system if you do not use DNS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Configuring Business Communications Manager to use IP addresses . . . . . . . . 16
Configuring CallPilot 100/150 to use domain names or IP addresses . . . . . . . . . 19
Configuring DNS on CallPilot 100/150 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Creating and installing hosts files on CallPilot 100/150 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Changing your local CallPilot Host name or IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Chapter 3
Setting up AMIS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Setting up AMIS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
AMIS networking properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
About Call Blocking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Call Blocking periods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Example of Call Blocking periods for one day . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Setting up Call Blocking times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
About Dialing Translation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
How the Dialing Translation Table works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Phone number Translation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Examples of Dialing Translation Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Setting the Dialing Translation properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 4

4 Contents
Building a Dialing Translation Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Reviewing entries in the Dialing Translation Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Changing an entry in the Dialing Translation Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Deleting a Dialing Translation Table entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Testing network message capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Sending a test network message . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Chapter 4
Creating network sites. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Setting the general networking properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Creating a network site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Changing the properties of a network site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Recording a site name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Deleting a site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Disabling Network Messaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Enabling Broadcast and Group List Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Before you test network message capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
For your local and destination sites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
For your local sites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
For your destination sites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Loopback mailbox numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Disabling Network Receive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Disabling Network Delivery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Disabling Network Reply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Disabling Network Messaging through a Class of Service setting . . . . . . . . . 52
Enabling Broadcast Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Enabling Network Group Lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Chapter 5
Network Delivery Mailboxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
About Network Delivery Mailboxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
About creating Network Delivery Mailboxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Creating a Network Site mailbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Creating a Network AMIS mailbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Changing Network Delivery Mailbox parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Deleting a Network Delivery Mailbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Chapter 6
Troubleshooting Non Delivery Notification messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Non Delivery Notification messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
P0606015 04
Page 5

Contents 5
Chapter 7
Message Networking programming record. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 6

6 Contents
P0606015 04
Page 7

Chapter 1
About CallPilot Message Networking
This guide leads a System Administrator through setting up Message Networking and is an
ongoing reference aid. Use this guide if you have a Business Communications Manager or
CallPilot 100/150 system.
Requirements for setting up Message Networking
To use Message Networking you need to know:
• how to use the telephones on your system. If you use Nortel Networks Business Series
Terminals refer to the CallPilot Reference Guide, the CallPilot Manager Set Up and
Operation Guide or the CallPilot Quick Reference Cards.
• if you use Business Communications Manager, which mailbox interface you use.
See the CallPilot Reference Guide for information on how to check which interface you use.
• how to start CallPilot Manager and use the CallPilot Manager interface.
For information see “Starting CallPilot Manager” and “About the CallPilot Manager
interface” in Chapter 2 of the CallPilot Manager Set Up and Operation Guide
7
• if you use Business Communications Manager, how to start Unified Manager and use the
Unified Manager interface.
Refer to the Business Communications Manager Programming Operations Guide.
• specific addressing information about CallPilot and other voice messaging sites on your
network. We recommend that you work with the Network Administrator when you set up
Message Networking.
About Message Networking
Message Networking links your voicemail system with voicemail systems at different locations.
Message Networking uses Digital Networking and Audio Message Interchange Specification
(AMIS) to let subscribers exchange messages with subscribers at other locations.
You must apply the Message Networking Software Authorization Code before your system can
receive or send network messages. Contact your vendor to purchase or trial a software
authorization code for Message Networking.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 8
8 Chapter 1 About CallPilot Message Networking
Digital and AMIS networking
Message Networking uses two types of networking:
Digital Networking
• transfers messages using an internet or intranet connection using Voice Profile for Internet
Mail (VPIM) to support interconnection to equipment from Nortel Networks and other
vendors
AMIS
• supports an analog transfer protocol that does not require any formal data networking
arrangements
About Digital Networking
Digital Networking links CallPilot and other voicemail systems at different locations. Digital
Networking lets users at different sites exchange voice and fax messages on a network connected
by Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). Digital Networking uses Simple
Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to exchange the messages.
Fax messages can be sent and received only on Business Communications Manager systems that
have the Fax option installed. Fax is not available on CallPilot 100/150.
Note: Any voice message that you use send over the Internet using Digital Networking
can be subject to interception by unauthorized parties.
How Digital Networking works
Digital Networking provides voice and fax messaging to mailboxes at different sites on a network.
Each CallPilot site on the network must have Digital Networking installed to send, receive or reply
to network messages.
Network voice messaging occurs between mailboxes at different sites. For example, a message
recorded at an office in Miami, Florida can be transferred directly to the appropriate mailbox at
Vancouver, British Columbia.
Each site on a network is assigned a unique Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). The FQDN
distinguishes a site from every other site on the network. An FQDN is the full name of the site,
including all subdomain and domain names, separated by periods. For example,
arabians.horse.com is an FQDN.
If you use Digital Networking and you do not use DNS to resolve domain names, you can
configure your system and client computers to use an IP address only. How to do this is explained
in Chapter 2.
P0606015 04
Page 9

Chapter 1 About CallPilot Message Networking 9
About AMIS
Audio Messaging Interchange Specification (AMIS) provides voice messaging to mailboxes at
different sites on a communication network. A network is a collection of offices, locations or sites
connected by telecommunication links. Each site on the network must have AMIS to send, receive
and reply to network messages. Direct AMIS addressing lets local subscribers send a voice
message to any subscriber inside or outside the company who has an AMIS voicemail address.
AMIS networking uses ordinary telephone lines to exchange voice messages. An AMIS address
consists of a telephone number and a mailbox number.
Note: AMIS calls can incur long distance charges.
How AMIS works
AMIS provides voice messaging to mailboxes at different sites on a network. A network is a
collection of offices, locations or sites connected by telecommunication links. Each site on the
network must have AMIS installed and enabled to send, receive or reply to network messages.
Network voice messaging occurs between mailboxes at different sites. For example, a message
recorded at an office in Cleveland, Ohio can be transferred directly to the appropriate mailbox at
an office in Toronto, Ontario.
Note: For AMIS to function, you must create a Dialing Translation Table and set the
Dialing Translation Parameters. For more information about Dialing Translation, refer to
“About Dialing Translation” on page 29.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 10
10 Chapter 1 About CallPilot Message Networking
Ways of sending network messages
With Message Networking subscribers can send network messages to any supported site on the
network. Sites must have Network Receive enabled to receive network messages.
Subscribers can send network messages using:
• Site-Based Addressing
• Network Delivery Mailboxes
• Direct Addressing
Note: For how to send messages using Site-Based Addressing, Network Delivery
Mailboxes or Direct Addressing refer to the CallPilot Message Networking User Guide.
Site-Based Addressing
Use site-based addressing to set up a formal network of sites. Site-Based Addressing lets callers
send a message to other locations. Local subscribers can send messages to subscribers at a remote
site using an address that is the same as the recipient’s phone number. Your site-based addressing
can match your organization’s telephone network addressing.
Network Delivery Mailboxes
Network Delivery mailboxes let local subscribers send a voice message to another subscriber
using what appears to be a local mailbox. Each Network Delivery Mailbox has a local mailbox
number and the destination site subscriber’s name appears in the local company directory.
When callers send a message to Network Delivery Mailboxes, they record a message and select
the Network Delivery Mailbox number. CallPilot sends the message to the specified network
address and mailbox.
For example, you can set up mailbox 5656 as a Network Delivery Mailbox. You add the Network
Delivery Mailbox to your CallPilot system and specify the site prefix and destination mailbox 450
at the destination site. Each time a CallPilot subscriber accesses mailbox 5656 at your site,
CallPilot knows it is a message intended for mailbox 450 at another location and automatically
delivers it.
Network Delivery Mailboxes can also appear in the Company Directory, although only a
subscriber can select a Network Delivery Mailbox. Callers who are not subscribers on your
CallPilot system cannot access Network Delivery Mailboxes.
Direct Addressing
With Direct Addressing subscribers can send a voice message to a mailbox at a different location
on a network. To use Direct Addressing you must know the destination site’s phone number and
the mailbox number of the person you want to send a message to. Direct Addressing is available
for AMIS only.
P0606015 04
Page 11

Chapter 1 About CallPilot Message Networking 11
Assigning Message Networking to subscribers
You assign Message Networking to subscribers through the mailbox Class of Service. Any
subscriber with an initialized mailbox can use Message Networking. For information on Class of
Service values see the CallPilot Manager Set Up and Operation Guide.
How to get help
USA and Canada
Authorized Distributors - Technical Support
Telephone:
1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835)
If you already have a PIN Code, you can enter Express Routing Code (ERC) 196#.
If you do not yet have a PIN Code, or for general questions and first line support, you can enter
ERC 338#.
Website:
http://www.nortelnetworks.com/support
Presales Support (CSAN)
Telephone:
1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835)
Use Express Routing Code (ERC) 1063#
EMEA (Europe, Middle East, Africa)
Technical Support
Telephone:
00800 800 89009
Fax:
44-191-555-7980
email:
emeahelp@nortelnetworks.com
CALA (Caribbean & Latin America)
Technical Support
Telephone:
1-954-858-7777
email:
csrmgmt@nortelnetworks.com
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 12

12 Chapter 1 About CallPilot Message Networking
APAC (Asia Pacific)
Technical Support
Telephone:
+61 388664627
Fax:
+61 388664644
email:
asia_support@nortelnetworks.com
P0606015 04
Page 13

Chapter 2
Setting up Digital Networking
Setting the Digital Networking properties
Setting up Network properties involves entering your site’s:
• SMTP proxy name, if applicable
•local prefix
• Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or IP address
SMTP proxy name
Before you can use Digital Networking, you must find out from the Network Administrator
whether the network has an SMTP proxy. SMTP proxies restrict access to a company’s internal
network from the internet. A proxy provides network security and prevents unauthorized access.
If your network has a direct connection to the internet or intranet, it does not have an SMTP proxy
and you do not have to enter an SMTP proxy name. If your network has an SMTP proxy, you must
enter the domain name of the SMTP proxy of your site. Contact your Network Administrator for
more information.
13
The FQDN of the SMTP proxy can be a maximum of 128 alphanumeric characters. The domain
name cannot have any spaces or punctuation except for characters such as periods, dashes or
underscores that are part of the name.
Local prefix
Before your site can receive messages from other sites, you must enter a local prefix for your site.
The local prefix is the sequence of digits that must be prefixed to local mailbox numbers to make
them unique across your network. The prefix is usually the same at your site prefix in the network
numbering plan.
The local prefix is a number from one to nine digits. This prefix can be the same as your site’s area
code and three-digit exchange prefix. For example, if customers dial 403-246-xxxx to reach your
site, 403246 can be your local prefix.
You must give your local prefix number to the Network Administrator and System Administrator
at each digital site. If you change it, give them your new prefix. They can update your local prefix
in their Site Tables.
FQDN
The FQDN is the domain name used for referring to your site, and is added to all outgoing
messages. For example, NortelNetworks.com is a domain name.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 14
14 Chapter 2 Setting up Digital Networking
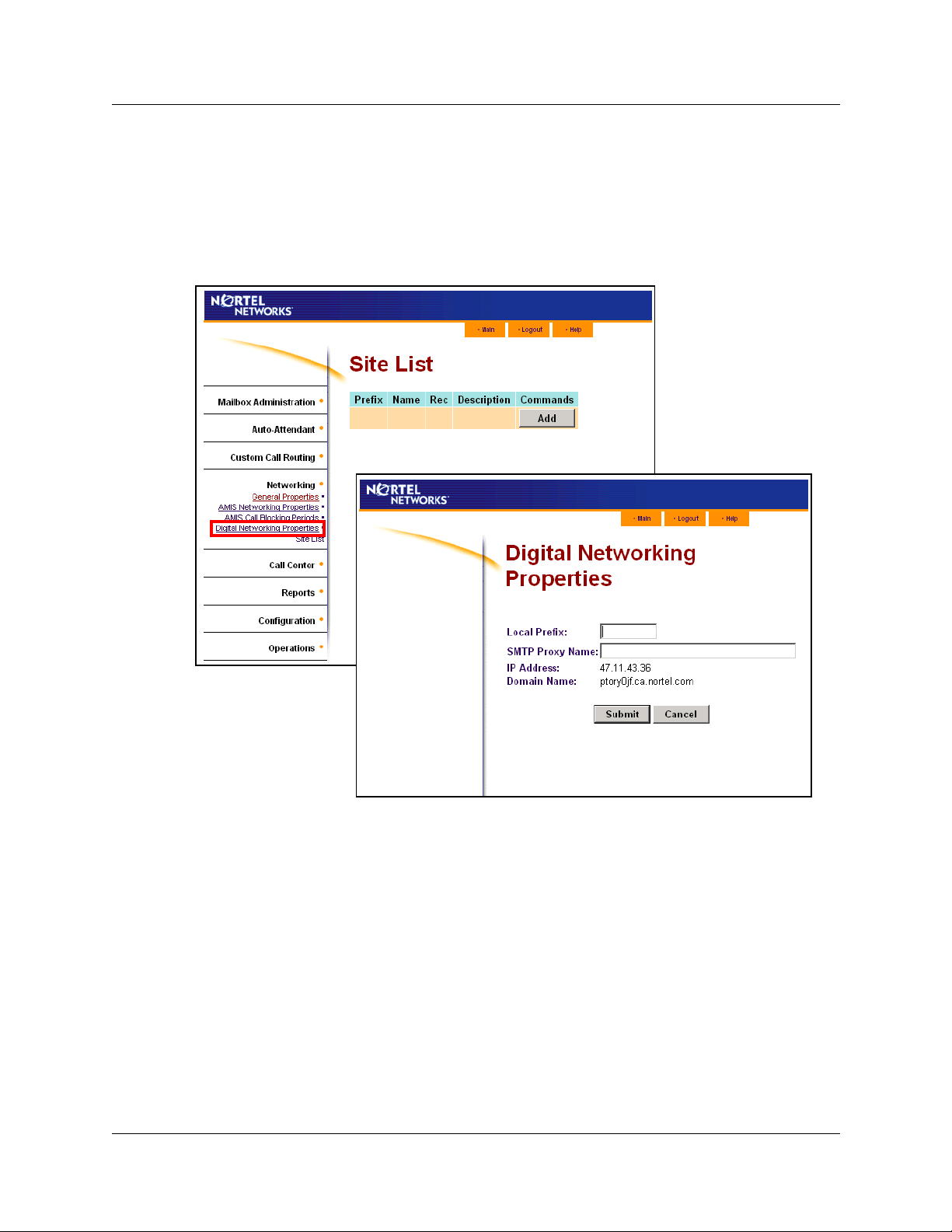
To set the Digital Networking properties
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Networking heading.
3 Click the Digital Networking Properties link.
The Digital Networking Properties page appears.
4 In the Local Prefix box type the local prefix.
5 In the SMTP Proxy Name box type the SMTP Proxy Name.
6 The IP Address and Domain Name are read-only. If you use a DNS your system displays the
domain name. If you do not use a DNS the IP address is displayed.
7 Click the Submit button.
P0606015 04
Page 15
Chapter 2 Setting up Digital Networking 15
Configuring your system network properties
Configuring your system network properties involves setting up message networking according to
whether you use a DNS server, host names or IP addresses.
Note: We recommend that you use a DNS server. If you use a Business Communications
Manager system and all of the digital sites in your network use DNS, go to
network sites” on page 43.
If you use a CallPilot system and all of the digital sites in your network use DNS, go to
“Configuring DNS on CallPilot 100/150” on page 20, and then go to “Creating network
sites” on page 43.
When you send a digital networking message, the internet uses the Domain Name System (DNS)
to translate domain names into IP addresses. Domain names, such as www.example.com, are
alphabetic, so they are easy for subscribers to remember. However, the internet is based on IP
addresses, which are numbers such as 198.105.232.4. Every time you use a domain name, a DNS
server translates the name into the corresponding IP address. For example, the domain name
www.example.com can translate to 198.105.232.4.
“Creating
If you do not use domain names, the internet uses IP addresses. If you use IP addresses your
system does your name mapping for you. Some businesses do not use DNS servers, for example, if
they have a private network.
Configuring your system if you do not use DNS
Digital networking requires consistent name mapping throughout the network of digital sites. The
best way to provide name mapping is by using a DNS server. If you do not use a DNS server you
can use either a hosts file or IP addresses.
If your network contains only Business Communications Manager or CallPilot 100/150 systems
you can use IP addresses and do not have to use hosts files.
If your network contains sites other than Business Communications Manager or CallPilot 100/150
digital sites, you must use hosts files if you do not use a DNS server.
If you use Business Communications Manager as a gateway to an internet service provider and
DNS servers cannot provide name resolution for the Business Communications Manager or other
digital sites, you must use hosts files to provide consistent name mapping throughout the network.
You must do your system network configuration before you can add network sites. You can test
your system’s name mapping with ping and nslookup commands. On CallPilot 100/150 you can
test your system’s name mapping by adding a network site.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 16

16 Chapter 2 Setting up Digital Networking
If DNS is not available you must do one of the following:
• If your digital network contains sites with sites other than Business Communications Manager
and CallPilot 100/150, you must use a hosts file to provide consistent name mapping
throughout the VPIM network. If you use CallPilot 100/150, refer to
hosts files on CallPilot 100/150” on page 21.
Note: You can use a hosts file in combination with DNS in situations where DNS
is not available in all branch locations.
• If your digital network contains, and will only contain, Business Communications Manager or
CallPilot 100/150 sites, you can use IP addresses to create network sites. Refer to
“Configuring Business Communications Manager to use IP addresses” on page 16 or
“Configuring CallPilot 100/150 to use domain names or IP addresses” on page 19 to create
network sites using IP addresses.
Note: The DNS servers must provide constant name mapping throughout the network.
Host files can be used to augment DNS if necessary. An instance where both hosts files
and DNS may be required is when a Business Communications Manager is used as a
gateway between a private network and an ISP.
“Creating and installing
Configuring Business Communications Manager to use IP addresses
1 Ensure no DNS servers are currently configured. Refer to “Ensuring no DNS servers are
configured on your Business Communications Manager” on page 17.
2 Enter the hosts name on the Business Communications Manager system. Refer to “Entering a
Host Name on the Business Communications Manager system” on page 18.
3 Configure computers running Message Networking with the IP address of the Business
Communications Manager system.
P0606015 04
Page 17
Chapter 2 Setting up Digital Networking 17
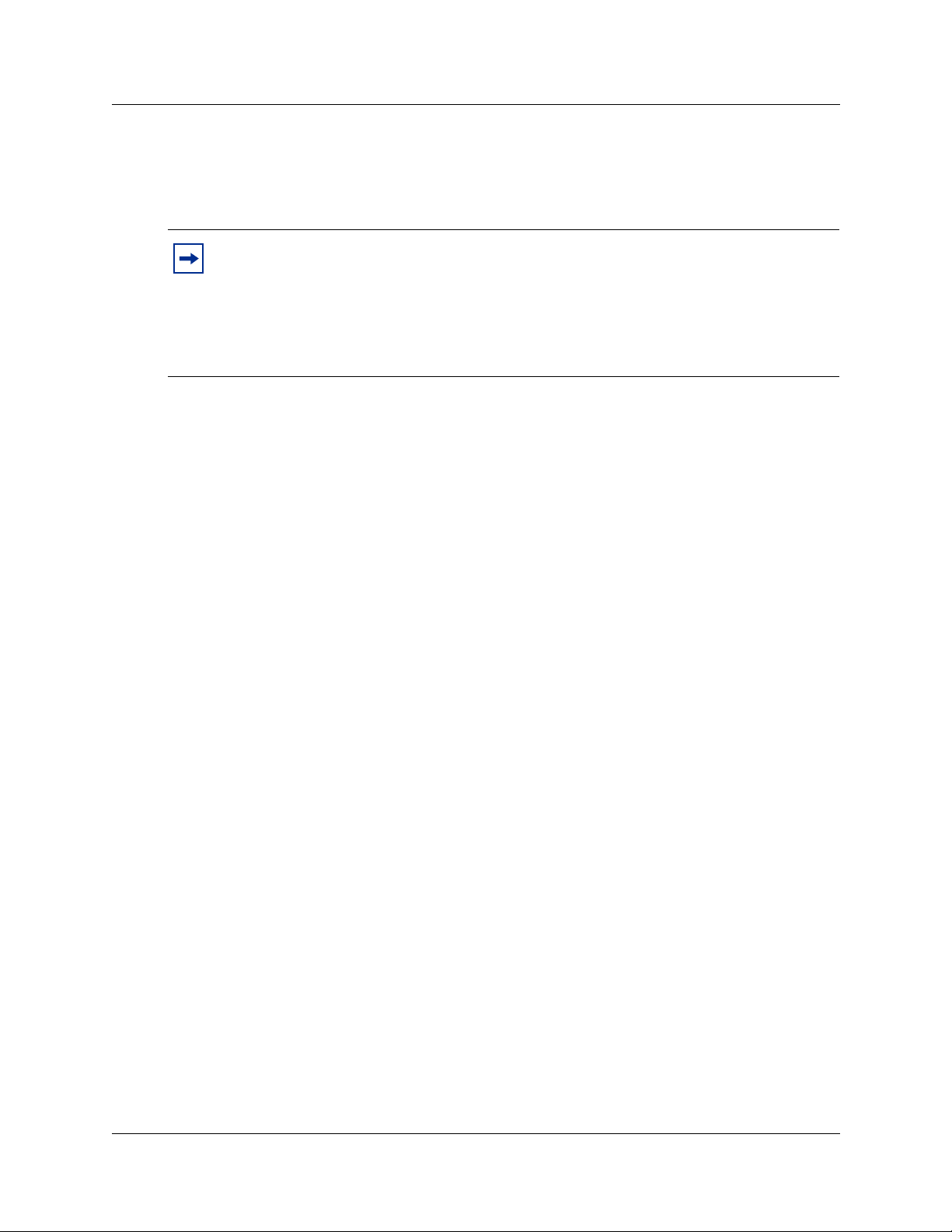
Ensuring no DNS servers are configured on your Business
Communications Manager
1 Start Unified Manager.
2 Click the Services key.
3 Click the DNS heading.
4 Ensure that the Primary (& Sec.) Server IP Addr box is empty.
If it is not, delete the entry and press the Enter key on your keyboard to save your changes.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 18
18 Chapter 2 Setting up Digital Networking
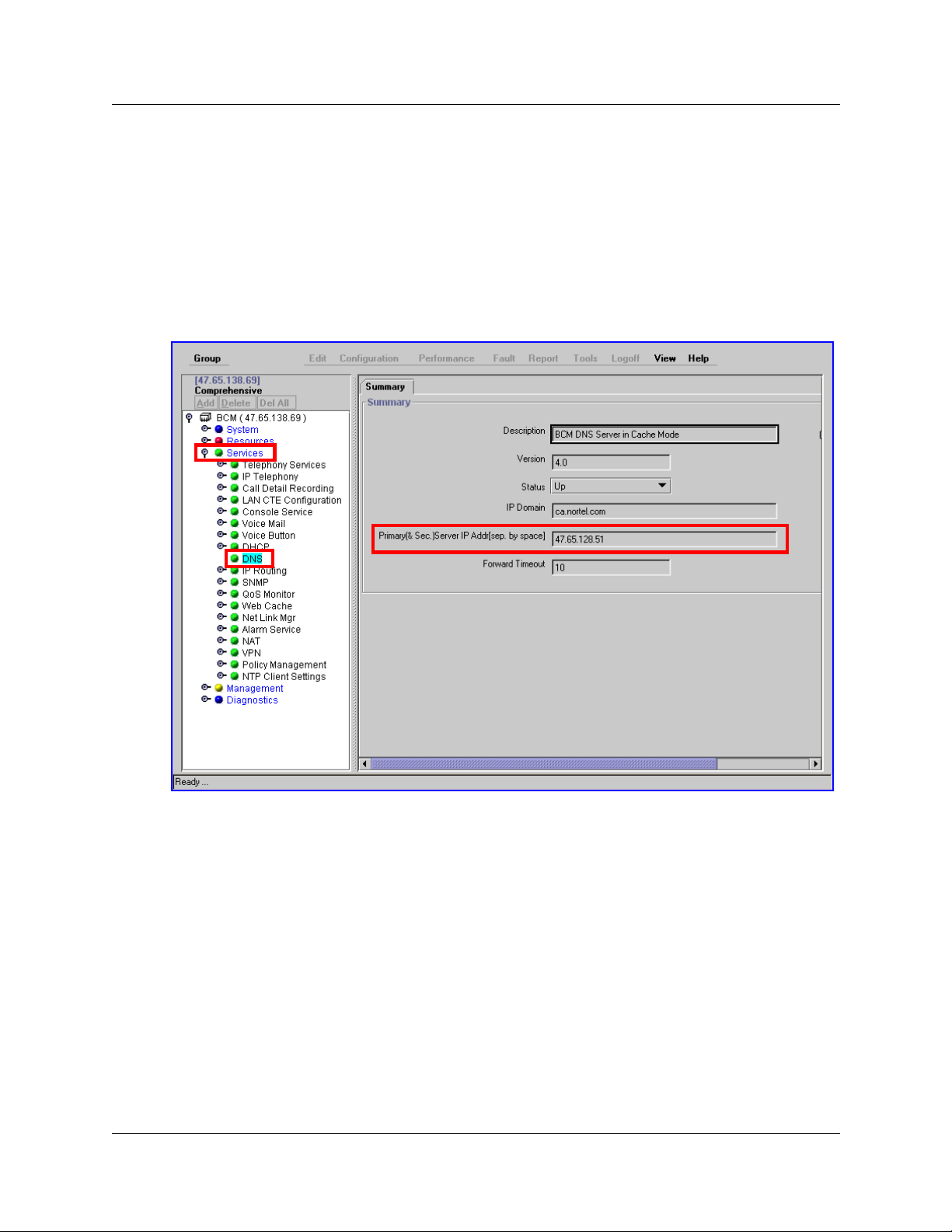
Entering a Host Name on the Business Communications
Manager system
The host name is the system text name for the host site. It can be up to 128 characters long.
1 Start Unified Manager.
2 Click the System heading.
3 In the System Name box enter a host name.
A system name can be any name (for example, myCompany).
4 Press the Enter key on your keyboard to save your new system name.
5 You must now configure computers running Message Networking with the IP address of the
Business Communications Manager system. Refer to the system documentation for type of
message networking you use.
P0606015 04
Page 19

Chapter 2 Setting up Digital Networking 19
Configuring CallPilot 100/150 to use domain names or IP addresses
If you do not have a DNS you can configure your CallPilot host to recognize the domain names of
other CallPilot sites on your system. For example, a bank can create domain names for each branch
that has a CallPilot site on their system, with the names “Downtown”, “South Side” and “West
End”, so that an employees who wants to send a message to another branch can just use its domain
name, and does not have to know the IP addresses of the branch.
To configure CallPilot 100/150 to use IP addresses
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Configuration heading.
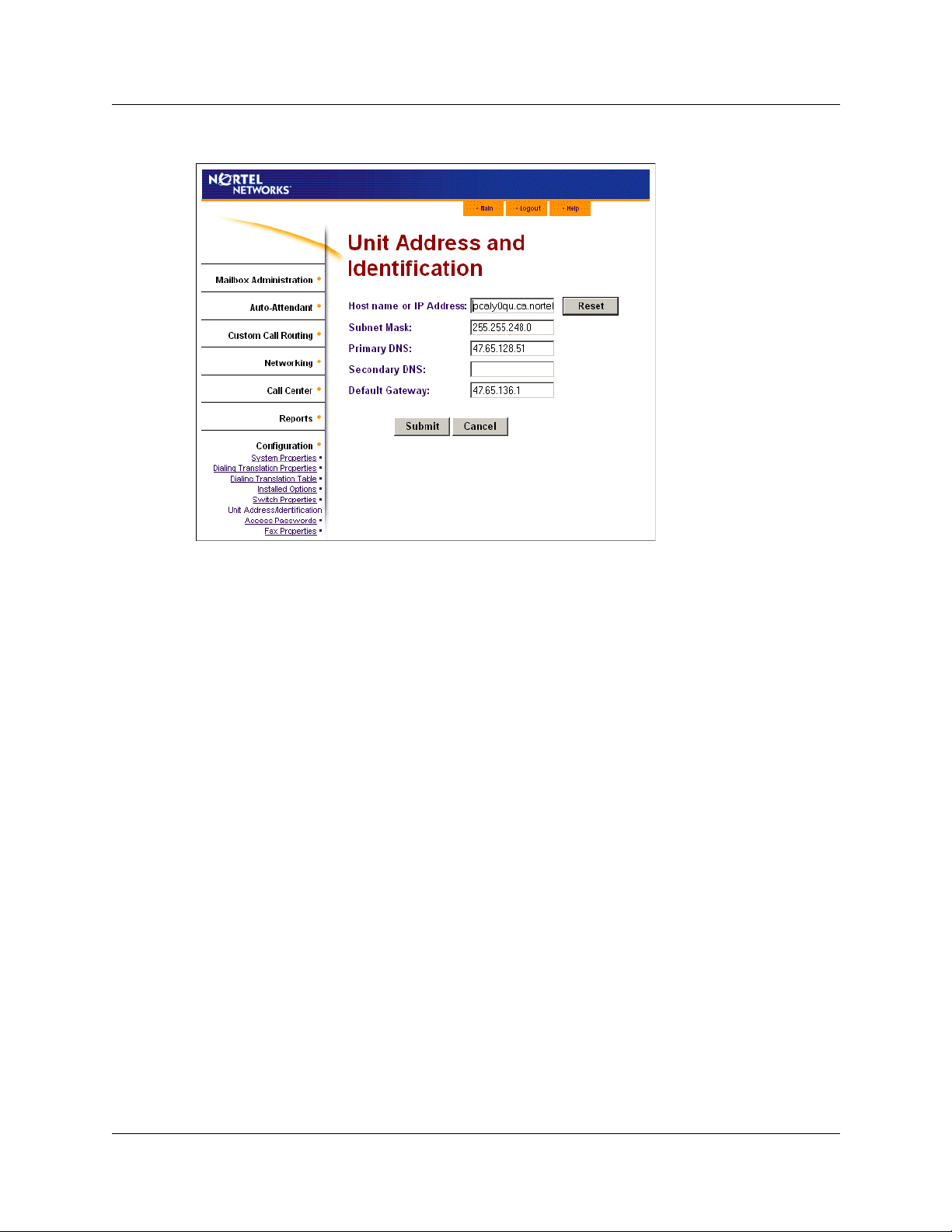
3 Click the Unit Address/Identification link.
The Unit Address and Identification page appears.
4 In the Host name or IP Address box enter your IP address.
5 Leave the Primary DNS and Secondary DNS boxes empty.
6 Click the Submit button.
7 You must reboot CallPilot for the new settings to take effect.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 20

20 Chapter 2 Setting up Digital Networking
Configuring DNS on CallPilot 100/150
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Configuration heading.
3 Click the Unit Address/Identification link.
The Unit Address and Identification page appears.
4 In the Host name or IP Address box enter your CallPilot’s Host name.
It must be a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN.)
Warning: The FQDN must be in the same subnet that is specified by the Subnet
Mask and the Default Gateway IP address. If you enter an FQDN that is not in the
same subnet, you can cause the CallPilot to continuously reboot. To correct this
problem, use the serial interface to change the IP address of the CallPilot. For more
information, refer to “Changing the IP address using a serial cable” in the CallPilot
Installation and Maintenance Guide.
5 In the Primary DNS box enter the IP address of the external DNS server.
6 In the Secondary DNS box enter the IP address of secondary DNS server if you use one.
7 Click the Submit button.
8 You must reboot CallPilot for the new settings to take effect.
P0606015 04
Page 21
Chapter 2 Setting up Digital Networking 21
Creating and installing hosts files on CallPilot 100/150
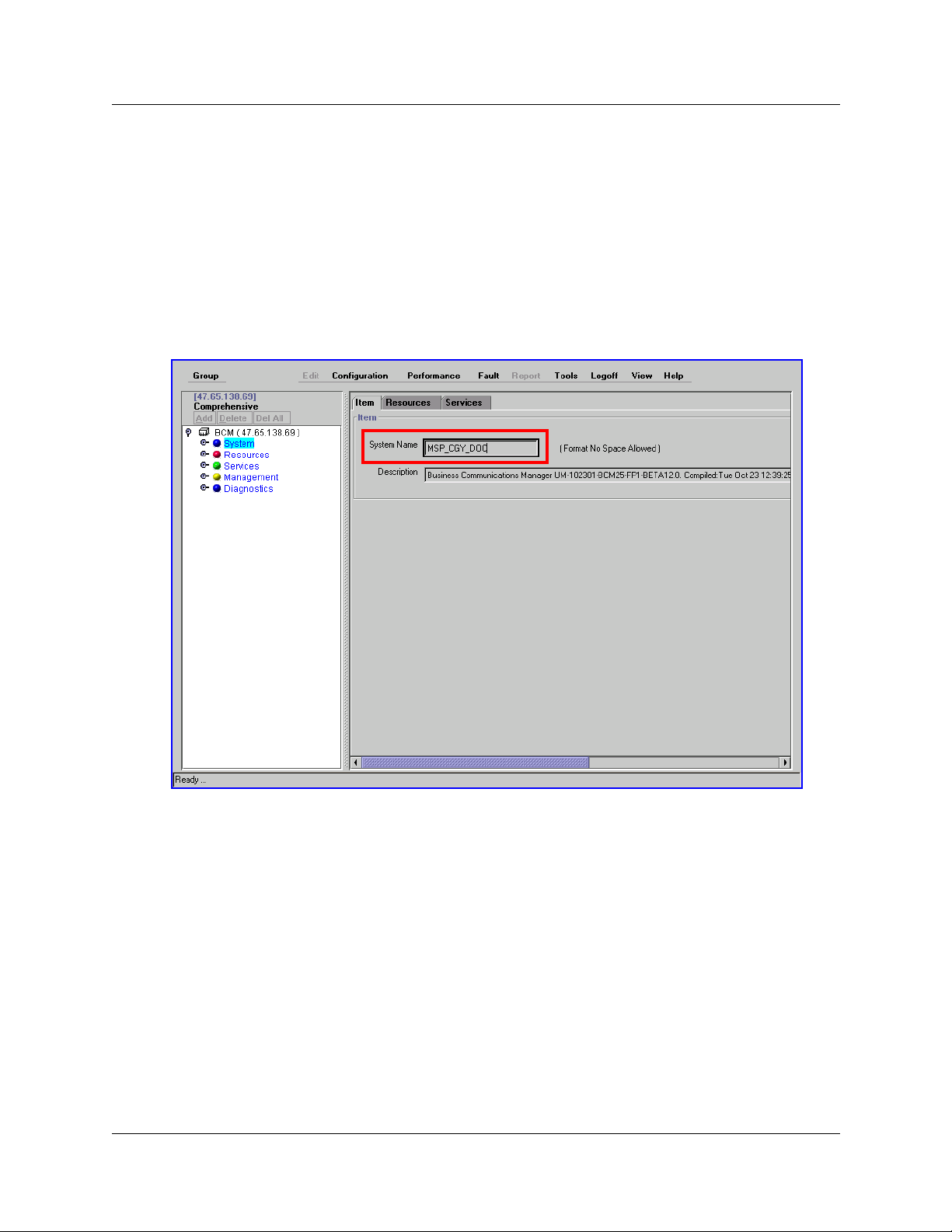
1 In a text editor such as Notepad, create a hosts file that contains the IP address and the hosts
name/FQDN of your CallPilot and the other CallPilot sites on your system. Make sure that the
name of your local CallPilot system comes first in the list. List the addresses in the form IP
address followed by the name/FQDN of the units, and type a line break by pressing the
ENTER key after the last entry in the hosts file. Type a single space between the IP address
and the hosts name. For example:
204.171.64.2 headoffice.callpilot.com
IP address of
CallPilot host
single space
FQDN of
CallPilot host
2 Name the file HOSTS and save it as a text file with no extension, for example, save the file as
“HOSTS” and not “HOSTS.txt”. This is an example of a hosts file. The first entry is the main
CallPilot unit. The other entries are branches.
3 FTP the HOSTS file to your CallPilot’s 7.0/ST directory.
Caution: You must FTP the file using the ASCII format, NOT binary.
If you use binary the hosts file will not work.
4 Start CallPilot Manager.
5 Click the Configuration heading.
6 Click the Unit Address/Identification link.
The Unit Address and Identification page appears.
7 In the Host name or IP Address box enter your CallPilot’s host name.
Your host name must be a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN.)
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 22
22 Chapter 2 Setting up Digital Networking
8 In the Primary DNS box enter your CallPilot’s IP address.
9 Click the Submit button.
10 You must reboot CallPilot for the new settings to take effect.
Changing your local CallPilot Host name or IP address
1 Make the change to the host name or IP address first.
2 Create a hosts file, making sure that the new host name is the first entry in the hosts file.
3 FTP the hosts file to your CallPilot’s 7.0/ST directory. You must FTP the file using the ASCII
format, NOT binary. If you use binary the hosts file will not work.
4 Reboot CallPilot for the new settings to take effect.
P0606015 04
Page 23

Chapter 3
Setting up AMIS
Setting up AMIS
AMIS provides your site with network voice messaging features. This chapter describes how to set
up and test AMIS on your Business Communications Manager or CallPilot 100/150 system.
Note: Make sure that your Company Greetings are 15 seconds or longer. For how to
record Company Greetings refer to the CallPilot Manager Set Up and Operation Guide.
AMIS networking properties
AMIS networking properties are:
23
International Access code
Country code
Area code
Telephone number
Outdial route
Enable Loopback mailbox
This code identifies the country where your site is. This code allows
international calling capability. In Canada and the United States, the
International Access code is 011. This number can have a maximum of four
digits.
This code is assigned to the country where your site is located. In Canada
and the United States, the Country code is 1. This code can have a
maximum of four digits. This information is used to generate the return
address of your location.
This code is assigned to your calling area. For example, the area code for
Kansas City is 816 and the area code for Calgary is 403. Each province,
state, and, sometimes city has a specific area code. This number can have
a maximum of six digits. This information is used to generate the return
address of your location.
The system telephone number at your site is the number assigned to the
Auto Attendant. This number can have a maximum of 16 digits. This
information is used to generate the return address of your location.
The numbers your site uses to access Line, Pool or Route codes. The
Outdial route is the Line or Pool number that AMIS uses to make an
outgoing call or the Route code used to call a specific site.
You use a Loopback Mailbox to test if two sites are communicating. When
a Loopback mailbox receives a message, it sends it back to the originating
mailbox. Before you can test network message capability, you must enable
the Loopback Mailbox.
The Loopback mailbox is not enabled by default. Enable the Loopback
mailbox while you set up and test your network. Disable the Loopback
mailbox after you know that it is working.
System name
Sender name
You can record a system name. When you include the system name, the
recorded system name is added to all messages sent from your site. The
system name plays as part of the recorded message.
The sender’s recorded name can be attached to each message sent from
your site. The sender’s name plays as part of the recorded message. The
normal default setting is disabled.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 24
24 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
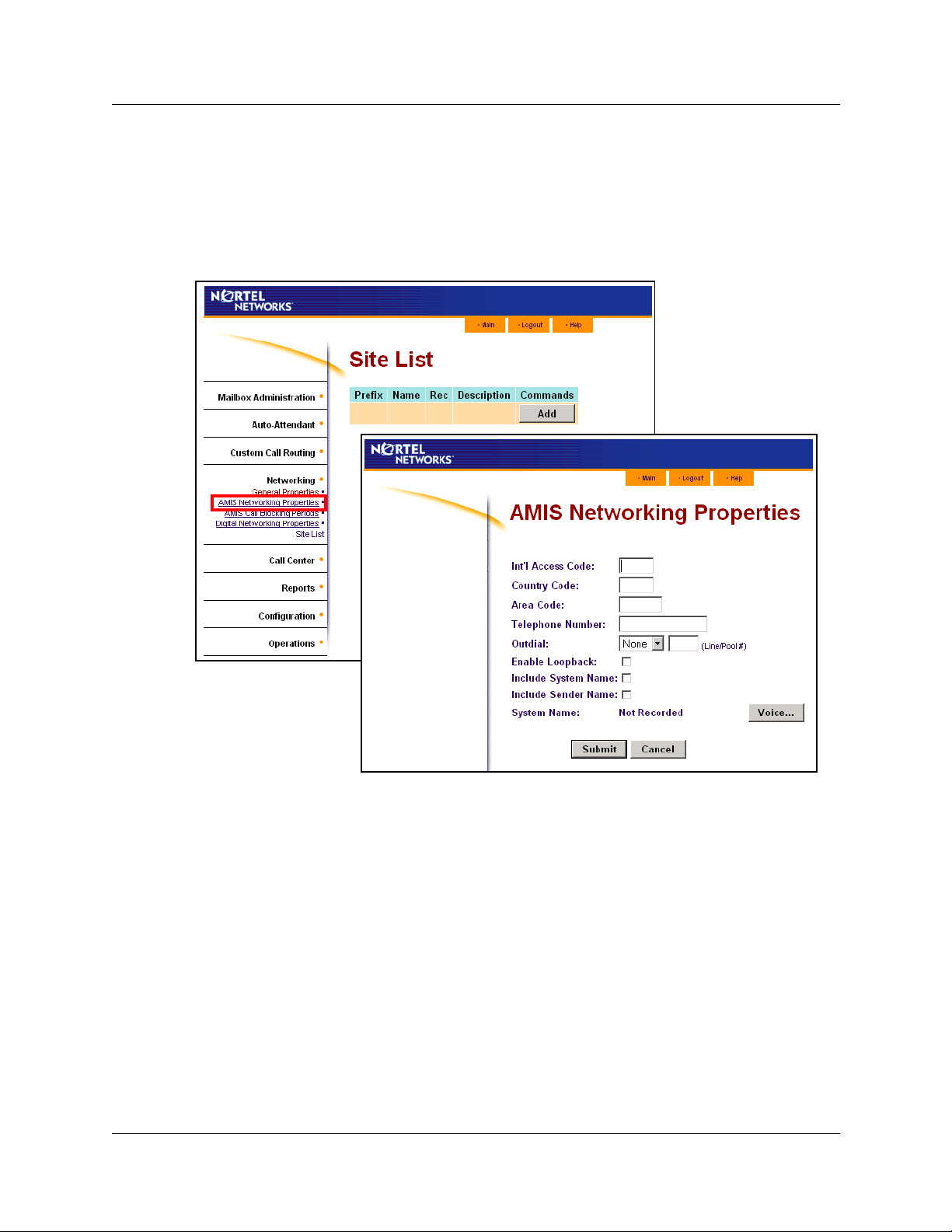
To set up AMIS networking properties
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Networking heading.
3 Click the AMIS Networking Properties link.
The AMIS Networking Properties page appears.
4 In the Int’l Access Code box type the International Access code.
The code can have up to four digits. The International Access code for North America is 011.
5 In the Country Code box type the Country code.
The code can have up to four digits. The Country code for North America is 1.
6 In the Area Code box type the area code for your city, state or province.
The area code can have up to six digits.
7 In the Telephone Number box type the system phone number of your site.
This number can have up to 16 digits.
8 From the Outdial list box select an Outdial route:
select Line to select a specific outgoing line and type the line number in the Line/Pool # box
or
select Pool for CallPilot to select a line within a line pool and type the pool number in the
Line/Pool # box
or
P0606015 04
Page 25

Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS 25
select Route to outdial using routing codes.
For more information about routing codes refer to the Business Communications Manager
Programming Operations Guide if you use Business Communications, or your Norstar system
documentation if you use CallPilot 100/150.
9 Select the Enable Loopback check box if you want to enable the Loopback mailbox.
10 Select the Include System Name check box to include the system name in outgoing
messages.
11 Select the Include Sender Name check box to include the sender name in outgoing messages.
12 Click the Voice button to record a system name.
The System Spoken Name appears.
13 In the Connect to box, type the extension number or telephone number you are using to record
the greeting or prompt.
For a local extension, just type the extension number. For a telephone number that is not a
local extension, type the sequence of digits that dial the telephone number from the voicemail
system. For example, you might need to dial 9, the area code, and then the telephone number.
14 Click the Dial button.
The telephone rings.
15 Pick up the handset. Do not use Handsfree. Click the Record button. After the tone, record the
system name.
16 After you finish recording, click the Stop button.
17 To listen to the recording, click the Play button, or to save the recording, click the Save
button.
18 Click the Close button and replace your telephone handset.
The System Spoken Name window closes.
19 On the AMIS Networking Properties page, click the Submit button.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 26

26 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
About Call Blocking
After you create AMIS sites you can set up call blocking. Call Blocking establishes times when
AMIS Network Delivery Messages are prohibited. You can limit non-urgent calls during peak
periods or when long distance rates are highest. You can establish Call Blocking for every day of
the week.
Note: If you want Call Blocking to continue past midnight, you must create two Call
Blocking periods. The first Call Blocking period ends at midnight and the second Call
Blocking period begins at midnight of the next day.
Decide the maximum amount of time a non-urgent AMIS message must wait before being
delivered during a typical business day. Ensure that no call blocking period exceeds this limit.
Call Blocking periods
There are four Call Blocking periods per day. For example, you can establish a period on Monday
from 08:00 to 11:00 a.m., and from noon until 4:00 p.m. The available time for network calls to
occur is before 08:00 a.m., between 11:00 a.m. and 12:00 p.m., and any time after 4:00 p.m. The
following table shows an example of the Call Blocking periods for Monday.
Example of Call Blocking periods for one day
Day Period Call Blocking time from Call Blocking time to
Monday 1 08:00 a.m. 11:00 a.m.
Monday 2 12:00 p.m. 4:00 p.m.
Monday 3 : :
Monday 4 : :
In the table Example of Call Blocking periods for one day, the hours available for network
messaging are before 08:00 a.m., between 11:00 a.m. and noon and after 4:00 p.m.
Note: Call Blocking applies to outgoing messages. Incoming messages are received at
any time. Call Blocking does not apply to urgent messages.
P0606015 04
Page 27

Setting up Call Blocking times
Set AMIS call blocking periods to block AMIS delivery calls when long-distance rates are
expensive or private networks are congested. If network congestion is a concern, set call blocking
for the peak traffic times.
To set up AMIS Call Blocking times
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Networking heading.
3 Click the AMIS Call Blocking Periods link.
The AMIS Call Blocking Periods page appears.
Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS 27
4 Select the day you want to set up call blocking times for.
5 In the From box type the time call blocking begins and select AM or PM.
Any single-digit hour or minute must be preceded by a zero. For example, type 8:00 as 08:00.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 28

28 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
6 In the To box type the time of day call blocking ends and select AM or PM.
Any single-digit hour or minute must be preceded by a zero. For example, type 8:00 as 08:00.
7 You can select the Same As Previous Day check box if you want to use the previous day's
settings for the call blocking period.
8 Click the Submit button.
Note: If there is an overlap in the call blocking periods established for the same day,
AMIS determines the time band from the earliest and latest times of the overlapping
time bands and treats the times as one call blocking period.
P0606015 04
Page 29

About Dialing Translation
There are situations when CallPilot generates an outbound call. For example, if a mailbox owner
replies to a Calling Line Identification (CLID) message. In this situation, CallPilot generates a
phone number to be dialed by the central office (CO).
Another example is when Network Reply or the Loopback mailbox is used. In these cases, the
phone number that is replied to is taken from information transmitted with the original message.
In both situations several changes must occur before the number is dialed through the local
telephone network. You must set up the Dialing Translation properties and create the Dialing
Translation Table to determine these changes.
How the Dialing Translation Table works
A phone number is derived from information attached to an incoming Caller ID message. The
number is then searched for in the Dialing Translation Table. If the leading digits of the telephone
number match a Dialing Translation Table Input value, the Output value is substituted for the
Input value. This change results in a telephone number that can be dialed on the local network.
Changing the number usually involves removing an area code or inserting an access code, based
on the dialing rules of the local network. For example, if a local number is prefixed with the long
distance code 1, it is removed by the Dialing Translation Table.
Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS 29
The Dialing Translation process is immediate so calls do not take any longer to dial. Some
telephone numbers do not need to be changed before dialing. CallPilot can function without a
Dialing Translation Table except that the Reply feature cannot be used.
Phone number Translation
The Dialing Translation Table must define each possible case where a change is needed to allow
the number to be dialed on the local network.
The Dialing Translation Table changes Network extensions into numbers that can be dialed on the
local network. The Network extension form of a phone number is the usual form in which the
number appears. For example, the phone number 403-555-5050, in its Network extension form,
must be translated into a number that can be dialed on the local telephone network. The Dialing
Translation Table follows the rules required to make the call.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 30

30 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
Examples of Dialing Translation Tables
The following tables are examples of Dialing Translation Tables and how they work. Every
Dialing Translation Table entry consists of an Input value column and an Output value column.
The values in the Input column represent the leading digits of the Network extensions which, if
matched, are replaced by the corresponding value in the Output column. The * after a value
signifies any digits in the telephone number that remain to be dialed. CallPilot automatically adds
the * after every Input and Output value.
A telephone number either matches or does not match a specific Input value.
A Dialing Translation Table from a site in metropolitan Toronto
INPUT OUTPUT Explanation
011* 011* The Table does not attempt to translate international telephone numbers.
416* * The Table removes the 416 area code and dials all calls as 7 digits.
905206*
90527*
etc.
(135 more
entries)
905* 1905* All other 905 numbers not listed in the Input column above are long distance
* 1* Any numbers that start with digits other than 011, 416 and 905 are long
905206*
90527*
etc.
(135 more
entries)
These telephone exchanges can be dialed as local (no long distance charges)
10 digit calls from the 416 area.
numbers and must be dialed as 11 digit long distance numbers.
distance, and have 1 added as a prefix.
A Dialing Translation Table from a site in Mountainview, California
INPUT OUTPUT Explanation
P0606015 04
The Dialing Translation Table is empty. The local network in
Mountainview supports 10 digit national dialing with recognized long
distance charging.
In situations like the Mountainview example, there is no need to build a
Dialing Translation Table.
Page 31

Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS 31
A Dialing Translation Table from a site with area code 206 near a border with area code 360
INPUT OUTPUT Explanation
011* 011* The Table does not attempt to translate international telephone numbers.
20644*
206626*
etc.
(40 more
entries)
206* 1206* All other 206 numbers require 11 digit long distance dialing.
360224*
360227*
360472*
360* 1360* ... but all other 360 numbers are 11 digit long distance numbers.
* 1* All numbers starting with other than 011, 206 and 360 are long distance and
44*
626*
etc.
(40 more
entries)
360224*
360227*
360472*
Due to the site location, some calls can be dialed as local 7 digit numbers.
These 360 numbers can be dialed as 10 digit local numbers...
have 1 added as a prefix.
Network Access
Dialing Table Translation results in a number that can be dialed on the local network. The final
step is to prefix any digits required to reach the local network from your Business
Communications Manager 3.5 or CallPilot 100/150 system. For systems that are behind a PBX or
PABX, typically in North America · must be prefixed to the telephone number. For systems
attached to Central Office (CO) lines no digits need to be prefixed.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 32

32 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
Setting the Dialing Translation properties
After you set up the AMIS properties, you must set up the Dialing Translation properties and
create the Dialing Translation Table. For AMIS to function, you must enter values for the long
distance access code, the area code and the access code, and enable reply translation.
To set the Dialing Translation properties
1 Start Call Pilot Manager.
2 Click the Configuration heading.
3 Click the Dialing Translation Properties link.
The Dialing Translation Properties page appears.
P0606015 04
Page 33

4 Set the Dialing Translation properties:
Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS 33
Long Distance Access Code
Area Code
Access Code
Enable Reply Translation
5 Click the Submit button.
This prefix is removed from any numbers that do not require it to make
the call. This simplifies creating the Dialing Translation Table. For
North America, set the long distance access code to 1. The default for
this property is none. The length of this property is a maximum of two
digits.
The system prefixes an area code to a phone number if the caller who
entered the number did not enter an area code. If the addressing
information attached to a message is missing an area code, the area
code is prefixed to the number. The system considers the area code
missing if the number has fewer than 10 digits. The default for this
property is none. The maximum length of this property is 6 digits.
After Dialing Translation, this number prefixes all numbers, to access
the local telephone network. The access code is required if CallPilot is
installed behind a PBX. In North America, the access code is usually
9. If CallPilot is connected directly to CO lines, set the Access Code to
none. The default for this property is none. The maximum length of
this property is 16 digits.
If you use AMIS, you must enable Reply Translation. The default for
this property is not enabled.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 34

34 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
Building a Dialing Translation Table
To build a Dialing Translation Table, you must enter an Input value and an Output value for each
entry. The Input value is the number that the system looks up in the Dialing Translation Table. If
the corresponding entry matches, the system substitutes the Output value for the Input value. The
resulting number is ready to dial on the local network. Refer to
Tables” on page 30 for examples of Dialing Translation Tables.
To build a Dialing Translation Table
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Configuration heading.
3 Click the Dialing Translation Table link.
The Dialing Translation Table page appears.
4 Click the Add button.
The Dialing Translation Setup page appears.
“Examples of Dialing Translation
5 In the Input Value box type the input value.
6 In the Output Value box type the output value.
7 Click the Submit button.
P0606015 04
Page 35

Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS 35
Reviewing entries in the Dialing Translation Table
You can review the entries in the Dialing Translation Table at any time.
To review Dialing Translation Table entries
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Configuration heading.
3 Click the Dialing Translation Table link.
The Dialing Translation Table page appears.
4 After you review the Dialing Translation Table entries, click the Main button.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 36

36 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
Changing an entry in the Dialing Translation Table
After you build a Dialing Translation Table, you can change the Input and Output values of an
entry at any time.
To change an entry in the Dialing Translation Table
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Configuration heading.
3 Click the Dialing Translation Table.
The Dialing Translation Table page appears.
4 Click the Change link for the value you want to change.
The Dialing Translation Setup page appears.
5 In the new value in the Input Value or the Output Value box.
6 Click the Submit button.
P0606015 04
Page 37

Deleting a Dialing Translation Table entry
To delete an entry in the Dialing Translation Table
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Configuration heading.
3 Click the Dialing Translation Table link.
The Dialing Translation Table page appears.
Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS 37
4 Click the Delete link for the Dialing Translation entry you want to delete.
A message appears that asks you to confirm the deletion.
5 Click the OK button.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 38

38 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
Testing network message capability
Use the AMIS Loopback Mailbox to test your network message capability. The Loopback
Mailbox is a test mailbox that lets you determine whether AMIS messages are being sent over the
network. Each site in a network has a Loopback Mailbox.
To test AMIS using the Loopback Mailbox, record a message and send it to the Loopback Mailbox
of another site in the network. The Loopback Mailbox sends the message back to the mailbox you
use at your location. This lets you see if your site’s network identification number is properly set
up and if your site can receive messages from other sites in the network.
Before you test network message capability
For your local and destination sites
1 Check that you have Network Delivery, Network Reply and Network Receive enabled in your
General Networking settings. For more information refer to
properties” on page 43.
2 Check that there is no Call Blocking during the time that you want to test the Loopback
Mailbox. For more information refer to
“Setting up Call Blocking times” on page 27.
“Setting the general networking
For your local sites
Check that the mailbox you use to send the network message from has a Class of Service that has
networking enabled. For more information refer to the CallPilot Manager Set Up and Operation
Guide.
For your destination sites
Make sure that in the destination site’s AMIS Network Properties that Loopback is enabled. For
more information refer to
Note: The Loopback Mailbox is created automatically when AMIS is installed. If the
mailbox number length is 2 digits, the Loopback Mailbox number is 13. If the mailbox
number length is 4 digits, the Loopback Mailbox number is 1003. If the Group List
leading digit is 1, then the leading digit of the Loopback Mailbox is 2 instead of 1. The
following table shows you how to determine your Loopback Mailbox number.
“To set up AMIS networking properties” on page 24.
P0606015 04
Page 39

Loopback mailbox numbers
Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS 39
If the mailbox extension
length is:
2 digits
3 digits 103 203
4 digits 1003 2003
5 digits 10003 20003
6 digits 100003 200003
7 digits 1000003 2000003
The Loopback
mailbox number is:
13 23
If the Group List leading digit is 1,
the Loopback mailbox number is:
You cannot open the Loopback mailbox or perform any mailbox functions from it.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 40

40 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
Sending a test network message
To test network message capability you must send a message from your site to the Loopback
mailbox at a site on the AMIS network. When the Loopback mailbox at the destination site
receives the message, it automatically returns the message to the mailbox used at the originating
site. If you use the System Administrator's Mailbox, the test message you record is left as a
message in your System Administrator Mailbox. If you receive the message, it indicates Network
Messaging is operating properly. If you do not receive the message or if a protocol error occurs,
refer to
Use the procedure that corresponds to your mailbox interface. For information on determining
which mailbox interface you use, see the CallPilot Reference Guide.
To send a test network message using the AMIS Loopback mailbox Norstar Voice Mail
“Troubleshooting Non Delivery Notification messages” on page 65.
1 Press ≤·°⁄.
Follow the voice prompts or the display button options to open
your mailbox.
0 new 0 saved
PLAY REC ADMIN
Record message:
RETRY PAUSE OK
Accept rec?
RETRY PLA Y O K
Mbox:
DIR QU IT
Address Type?
NETW AMIS
Dest Ph:
RETRY OK
<phone #>
ADD OK
Dest mb:
RETRY OK
AMIS msg:
OP TS CC O T HR
Network msg:
VIEW SEND
2 Press REC or ‹.
After the tone, record a message.
3 Press OK or £ to end the recording.
4 Press OK or £ to accept the recording.
5 Press ££.
6 Press AMIS.
7 Enter the system phone number of the destination site
and press OK or £.
8 Press OK or £.
9 Enter the Loopback mailbox number and press OK or £.
10 Press OTHR or £.
11 Press SEND.
P0606015 04
12 Press ® to end the programming session.
Page 41

Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS 41
To send a test network message using the AMIS Loopback mailbox CallPilot
1 Press ≤·°⁄.
Follow the voice prompts or the display button options to open
your mailbox.
No messages
COMP MBO X EXIT
To:
NAME SP EC C NC L
Dest ph:
RETRY OK
<phone #>
ADD OK
Dest mb:
RETRY OK
To:
NAME SPEC DON E
Empty
REC
Recording...
REREC OK
Rec stopped
PLAY DE L SEND
2 Press COMP or ‡fi.
3 Press SPEC or ⁄·.
4 Enter the system phone number of the destination site
and press OK or £.
5 Press OK or £.
6 Enter the Loopback mailbox number and press OK or £.
7 Press DONE or £.
8 Press REC or fi.
9 Record your message and then press OK or £.
10 Press SEND or ‡·.
11 Press ® to end this programming session.
To determine if Network Messaging is working, open your mailbox. The message you record
returns as a message to your mailbox. If the message does not appear in your mailbox after five
minutes:
• ensure that the Network Delivery option is enabled.
• ensure that the Call Blocking periods at your site and at the receiving site allow Network
Messaging during the time you attempt to test the system. Call Blocking prevents calls being
sent during a specific time period.
• consider whether the test message is delayed by the period of the Retry interval. The Retry
interval is a Class of Service feature. For more information on Class of Service, refer to the
CallPilot Manager Set Up and Operation Guide.
• consider whether the test message is subject to line availability at your site or at the receiving
site.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 42

42 Chapter 3 Setting up AMIS
P0606015 04
Page 43

Chapter 4
Creating network sites
The procedures in this chapter are for Digital and AMIS networking. If you use digital networking
you must have configured name mapping by DNS or hosts files on your system before you can add
network sites. See
your system’s name mapping with ping and nslookup commands. On CallPilot 100/150 you can
test your system’s name mapping by adding a network site.
Setting the general networking properties
The general networking properties control how your site interacts with other networking sites.
When you install Message Networking all of the properties are enabled except for Network
Broadcast Messaging and Network Group List Messaging.
To set the general networking properties
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
“Setting up Digital Networking” on page 13 for more information. You can test
43
2 Click the Networking heading.
3 Click General Properties link.
The General Networking Properties page appears.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 44

44 Chapter 4 Creating network sites
General Networking properties
Enable Network Receive
Enable Network Delivery
Enable Network Reply
Enable Network Broadcast
Enable Network Group List
Number of Network Retries
Network Delay
Lets your site receive messages from other sites on the network. The
default setting is enabled.
Lets your site send messages to other sites on the network. The
default setting is enabled.
Lets your site reply to messages sent from other sites on the network.
The default setting is enabled.
Lets you send Broadcast Messages to Network Delivery Mailboxes at
your site. The default setting is disabled.
Lets you add Network Mailboxes to a Group List. The default setting is
disabled. When you send a message to a Group List all of the network
delivery mailboxes on the Group List receive it.
1-9, default 3. Sets the maximum number of times the system
attempts to send a network message before abandoning it and
sending a Non Delivery Notification.
1-60 minutes, default 10. Sets the period between delivery attempts of
the same network message.
4 Click the Submit button.
P0606015 04
Page 45

Creating a network site
Before local subscribers can send messages to another site using Site-Based Addressing, you must
add the site to your network.
To add a site to your network, you must know these parameters:
Chapter 4 Creating network sites 45
Site name
Site prefix
Host name/IP address
(for digital networking sites
only)
Mailbox prefix
(for digital networking sites
only)
The Site Name is a text name for the site that can be up to 16 characters.
This name is shown to local subscribers when they address a message or
review message envelope information. The site name is optional but
recommended.
The Site Prefix is a number one to nine digits long that identifies the site on
the network. This number must be unique. Make the Site Prefix a number
that is easy for users to recogniz
the same as the sequence of digits that local users dial to place a
telephone call to the site. For example, if local users dial 403-123-4567
call someone at the target site, then 403123 is an easily remembered Site
Prefix.
The Site Prefix cannot overlap any other Site Prefix in your Network Site
Table. For example, if you use Site Prefix 403123, it overlaps with prefixes
and 4031234.
40312
If you use a DNS the host name setting appears. The host name is the
FQDN text name for the host site. It can be up to 128 characters long.
If you do not use a DNS the IP address setting appears.
The Mailbox Prefix is the Local Mailbox Prefix of the target site. Message
Networking ensures that all messages sent to the target site are prefixed
with this number. The Mailbox Prefix ensures uniqueness for the receiving
proxy or networking equipment.
The mailbox prefix can be the same as the remote site prefix.
e and remember. The Site Prefix is usually
to
Phone number
(for AMIS sites only)
Outdial route
(for AMIS sites only )
The phone number is the phone number of the destination site. The phone
number can be a maximum of 30 digits.
The numbers your site uses to access Line, Pool or Route codes. The
Outdial route is the Line or Pool number that AMIS uses to make an
outgoing call or the Route code used to call a specific site.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 46

46 Chapter 4 Creating network sites
To create a network site
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Networking heading.
The Site List page appears.
3 Click the Add button.
The Network Site Properties page appears.
4 In the Site Name box type the Site Name.
5 In the Site Prefix box type the Site Prefix.
6 Choose the type of site you are adding.
P0606015 04
If you want to create a Digital Networking site:
•from Site Type select Digital (VPIM)
• if you use a DNS server, in the Host Name box type the FQDN of the site, or if you do
not use a DNS server, in the IP Address box type the IP address of the site
•in the Mailbox Prefix box type the mailbox prefix of the site
•click the Submit button
Page 47

If you want to create an AMIS site:
•from Site Type select AMIS
•in the Phone Number box type the phone number that is answered by the Auto
Attendant at the destination site.
•from the Outdial list box select an Outdial route.
• type the Line or Pool number in the Line/Pool # box if you select Line or Pool as the
Outdial route.
•click the Submit button
Note: You must create a site before you can record a site name for it. To record a site
name, follow the procedure for
“Recording a site name” on page 49.
You can record the parameters of the sites you create in:
• “Network AMIS mailbox table” on page 75
• “AMIS site table” on page 72
Chapter 4 Creating network sites 47
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 48

48 Chapter 4 Creating network sites
Changing the properties of a network site
You can change properties of a site, except for the Site Prefix. To change the Site Prefix you must
delete the site and create a new site with a new Site Prefix and properties.
To change the properties of a network site
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Networking heading.
The Site List page appears.
3 Select the site you want to change and click the Change button.
The Network Site Properties page appears for the site you select.
4 Change the site properties and click the Submit button.
P0606015 04
Page 49

Recording a site name
The recorded site name is a voice recording of the Site Name. This name plays to local users when
they address a message or review message envelope information. If you do not record the site
name, the voice prompt says “Unknown site”.
Note: You must create a site before you can record a site name for the site.
For best results, use a telephone that is attached to the same switch as your voicemail system.
Avoid using wireless telephones.
To record a site name
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Networking heading.
The Site List page appears.
3 Select the site you want to record a name for and click the Change button.
The Network Site Properties page appears for the site you select.
Chapter 4 Creating network sites 49
4 Click the Voice button.
The page you can record from appears. If you use a CallPilot 100/150 system, the Import and
Export options do not appear.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 50

50 Chapter 4 Creating network sites
5 In the Connect to box, type the extension number or telephone number you are using to record
the greeting or prompt. For a local extension, just type the extension number. For a telephone
number that is not a local extension, type the sequence of digits that dials the telephone
number from the voicemail system. For example, you might need to dial 9, the area code, and
then the telephone number.
6 Click the OK button.
7 Click the Dial button.
The telephone rings.
8 Pick up the handset. Do not use Handsfree. Click the Record button. After the tone, record the
site name.
9 After you finish recording, click the Stop button.
10 To listen to the recording, click the Play button
or
to save the recording, click the Save button. Your recording will not be saved if you hang up
the telephone before you click the Save button.
11 Click the Close button and replace your telephone handset.
The next time you play or record, the phone number shown in the Connect to box is dialed. You do
not need to hang up each time. The connection remains for several minutes, even if you close the
window. You can access another greeting or prompt without having to re-answer your telephone.
The connection disconnects after several minutes of inactivity, or if you log off CallPilot Manager.
P0606015 04
Page 51

Deleting a site
You cannot delete a site if it is in use or if Network Delivery Mailboxes use the Site Prefix. You
must delete the Network Delivery Mailboxes that use the Site Prefix before you delete the site.
To delete a site
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Networking heading.
The Site List page appears.
3 Click Delete link for the site you want to delete.
A message appears asking you to confirm the deletion.
Chapter 4 Creating network sites 51
4 Click the OK button.
The Site List page appears with the site deleted.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 52

52 Chapter 4 Creating network sites
Disabling Network Messaging
Part of administering Network Messaging is ensuring that the network operates smoothly. There
can be times when it is necessary to limit network message capabilities. Message Networking lets
you specify whether your site can receive, send or reply to network messages.
Sometimes it is necessary to disable Network Messaging. You can disable Message Networking
system-wide by:
• disabling Network Receive
• disabling Network Delivery
• disabling Network Reply
You can disable Network Messaging for individual mailboxes through the Class of Service.
Disabling Network Receive
Network Receive lets your site receive messages from other sites on the network. If you do not
want your site to receive network messages, disable Network Receive.
Disabling Network Delivery
Network Delivery lets your site send network messages. Sometimes it is necessary to disable this
feature. For example, you may want to stop the sending of network messages when your company
is closed.
If Network Deliver is disabled, a mailbox owner who tries to send a network message will receive
a Non-Delivery Notification message.
Disabling Network Reply
Network Reply lets people at your site reply to network messages left in their mailboxes from
other sites.
Note: You disable these properties in the general networking properties. For
information about the general networking properties refer to
networking properties” on page 43.
“Setting the general
Disabling Network Messaging through a Class of Service setting
You can restrict Network Messaging for individual mailboxes. You do this by changing or editing
the Class of Service for a mailbox.
P0606015 04
Note: For information about changing a mailbox Class of Service, refer to the CallPilot
Manager Set Up and Operation Guide.
Page 53

Chapter 4 Creating network sites 53
Enabling Broadcast and Group List Messages
Network Messaging involves sending messages across the network from one site to another.
Message Networking provides full network messaging capabilities, including Broadcast Messages
and Network Group List Messages.
The Broadcast Message feature lets you record Broadcast Messages and send them to all Network
Delivery Mailboxes.
For information about recording and sending Broadcast Messages, refer to the CallPilot Manager
Set Up and Operation Guide.
Enabling Broadcast Messages
Before you can send Broadcast Messages over the network, you must enable the Broadcast
Message parameter in the general networking parameters. Refer to
networking properties” on page 43 for information on setting the general networking parameters.
Enabling Network Group Lists
“Setting the general
Enabling Group Lists lets you add Network Mailboxes to a Group List. Any messages sent to a
Group List go to all members, including the Network Mailboxes. You enable the Group Lists
parameter in the general networking parameters. Refer to
properties” on page 43 for information on setting the general networking parameters.
For information about creating a Network Delivery Mailbox, refer to “About Network Delivery
Mailboxes” on page 55. For more information about setting up a Group List, refer to the CallPilot
Manager Set Up and Operation Guide.
Note: If you do not enable Group Lists, messages are not sent to the Network
Mailboxes in a Group List.
“Setting the general networking
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 54

54 Chapter 4 Creating network sites
P0606015 04
Page 55

Chapter 5
Network Delivery Mailboxes
About Network Delivery Mailboxes
A Network Delivery Mailbox makes it convenient for local subscribers to send messages to remote
subscribers. The remote subscriber has a local mailbox number and the remote subscriber’s name
appears in the local directory.
A Network Delivery Mailbox connects to a mailbox at a remote site by using a local mailbox
number that you can access from your site. The Network Delivery Mailbox contains all the
information necessary to transfer a message to a mailbox at another location. This information
includes the destination site prefix and the mailbox number at the destination site.
There are two types of Network Delivery Mailboxes:
•Network Site
• Network AMIS
55
The number of subscribers on your network and the type of network messaging you use determine
how many Network Delivery Mailboxes you need. If you use Business Communications Manager,
you can have up to 998 mailboxes on your system. If you use CallPilot 100/150, you can have up
to 300 Subscriber mailboxes on your system. The mailboxes can include any combination of
Subscriber and Guest mailboxes.
Network Delivery Mailboxes simplify network messaging because mailbox owners must
remember only the Network Delivery Mailbox numbers. CallPilot uses the mailbox number to find
the destination site address and the mailbox at the destination site that receives the message.
CallPilot automatically delivers messages sent through the Network Delivery Mailbox.
For example, a bank has a main office with many branches throughout the city. Sometimes the
main office receives messages for people at the branches. The people at the branch offices can
receive their messages through their Network Delivery Mailboxes at the main office.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 56

56 Chapter 5 Network Delivery Mailboxes
About creating Network Delivery Mailboxes
Before you create a Network Delivery mailbox you must:
• know what leading digit you want to assign to all Network Delivery Mailboxes. This is
optional. You can assign the same leading digit to mailboxes to help you to identify the
different types of CallPilot mailboxes. For example, all Subscriber mailboxes can start with 4,
Guest mailboxes with 5, and Network Delivery Mailboxes with 6.
• know the mailbox length of the mailboxes on your system. The Network Delivery Mailbox
length must be the same length as the other mailboxes on the system; if the mailbox length is
three digits, the Network Delivery Mailbox must also be three digits.
• know the destination site prefix and the destination mailbox number.
• add the site for which you are creating the Network Delivery Mailbox. For information on
creating a site refer to
Note: After you create a Network Delivery Mailbox you must initialize it.
Take these precautions if you set up a remote Group List as a target for a Network
Delivery Mailbox:
• Do not send messages to a group list that includes a Network Delivery Mailbox
whose target is the mailbox you sent the message from.
“Creating a network site” on page 45.
• Make sure that you do not have any Group Lists that send messages to each
other through a Network Delivery Mailbox. For example, a Group List that
contains a Network Delivery Mailbox that forwards the message to another
Group List. This Group List also contains a Network Delivery Mailbox, and this
Network Delivery Mailbox forwards the message back to the original Group
List.
If you set up a Group List where either situation happens, a loop occurs where a single
message can generate many copies of the message.
P0606015 04
Page 57

Creating a Network Site mailbox
Use the “Network Site Mailbox table” on page 74 to record the details of the Network Site
mailboxes you create. You can create a Network Site mailbox for an AMIS or VPIM network site.
To create a Network Site mailbox
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Mailbox Administration heading.
3 Click the Add Mailbox link.
The Add Mailbox page appears.
Chapter 5 Network Delivery Mailboxes 57
4 In the Mailbox box type a valid mailbox number.
Use a mailbox number that does not conflict with existing or potential extensions.
Use the same first digit for all Network Site mailboxes so they are easy to identify.
5 From the Mailbox Type list box select Network (Site).
6 Click the Submit button.
The Network (Site) Mailbox page appears.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 58

58 Chapter 5 Network Delivery Mailboxes
7 In the Last Name and First Name boxes type the name of the mailbox.
The mailbox name can be the name of the mailbox at the destination site or another name.
The mailbox name can be 16 characters long. Do not create a name that starts with 1, for
example "1Calgary".
8 Select the Display in Directory check box if you want the name of the mailbox to appear in
the Company Directory.
Note: Network delivery mailboxes are accessible only to:
• local subscribers who use F981 to record a message
• external callers who log on to their mailbox and record a message.
Network delivery mailboxes are not available:
• to subscribers who record a message using F980
• from the Auto Attendant
• from an external caller who is not logged on to a local mailbox.
9 In the Site Prefix box type the Site Prefix.
10 In the Remote Mailbox box type the number of the remote mailbox.
11 Click the Submit button.
12 Click the Mailbox Administration heading.
The Mailbox List page appears.
13 Click the Change link for the Network Site mailbox you created.
The page appears for the mailbox.
14 Click the Voice button to record a mailbox name.
The Mailbox Spoken Name window appears for the mailbox.
P0606015 04
Page 59

Chapter 5 Network Delivery Mailboxes 59
15 In the Connect to box, type the extension number or telephone number you are using to record
the mailbox name.
For a local extension, just type the extension number. For a telephone number that is not a
local extension, type the sequence of digits that dial the telephone number from the voicemail
system. For example, you might need to dial 9, the area code, and then the telephone number.
16 Click the Record button.
The telephone rings.
17 Pick up the handset. Do not use Handsfree. After the tone, record the Network Site mailbox
name.
18 After you finish recording, click the Stop button.
19 To listen to the recording, click the Play button, or to save the recording, click the Save
button.
20 Click the Close button and replace your telephone handset.
21 On the Network Site Mailbox page, click the Submit button.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 60

60 Chapter 5 Network Delivery Mailboxes
Creating a Network AMIS mailbox
Use the “Network AMIS mailbox table” on page 75 to record the details of the Network AMIS
mailboxes you create.
To create a Network AMIS mailbox
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Mailbox Administration heading.
3 Click the Add Mailbox link.
The Add Mailbox page appears.
4 In the Mailbox box, type a valid mailbox number.
Use a mailbox number that does not conflict with existing or potential extensions.
Use the same first digit for all Network AMIS mailboxes so they are easy to identify.
5 From the Mailbox Type list box, select Network (AMIS).
6 Click the Submit button.
The Network (AMIS) Mailbox page appears.
P0606015 04
Page 61

Chapter 5 Network Delivery Mailboxes 61
7 In the Last Name and First Name boxes type the name of the mailbox.
The mailbox name can be the name of the mailbox at the destination site or another name. The
mailbox name can be 16 characters long. Do not create a name that starts with 1, for example
"1Calgary".
8 Select the Display in Directory check box if you want the mailbox to be listed in the
Company Directory.
Note: Network delivery mailboxes are accessible only to:
• local subscribers who use F981 to record a message
• external callers who log on to their mailbox and record a message.
Network delivery mailboxes are not available:
• to subscribers who record a message using F980
• from the Auto Attendant
• from an external caller who is not logged on to a local mailbox.
9 From the Outdial list box select Line, Pool or Route as the outdialing option.
10 If you use a line or pool, enter a number in the Line/Pool# box.
11 In the Remote Phone Number box type the remote phone number.
12 In the Remote Mailbox box type the remote mailbox number.
13 Click the Submit button.
14 Click the Mailbox Administration heading.
The Mailbox List page appears.
15 Click the Change link for the AMIS mailbox.
The Network AMIS page appears for the mailbox.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 62

62 Chapter 5 Network Delivery Mailboxes
16 Click the Voice button to record a mailbox name.
The Mailbox Spoken Name window appears for the mailbox.
17 In the Connect to box, type the extension number or telephone number you are using to record
the mailbox name.
For a local extension, just type the extension number. For a telephone number that is not a
local extension, type the sequence of digits that dial the telephone number from the voicemail
system. For example, you might need to dial 9, the area code, and then the telephone number.
18 Click the Record button.
The telephone rings.
19 Pick up the handset. Do not use Handsfree. After the tone, record the Network Site mailbox
name.
20 After you finish recording, click the Stop button.
21 To listen to the recording, click the Play button, or to save the recording, click the Save
button.
22 Click the Close button and replace your telephone handset.
23 On the Network AMIS Mailbox page, click the Submit button.
P0606015 04
Page 63

Chapter 5 Network Delivery Mailboxes 63
Changing Network Delivery Mailbox parameters
You can change any parameter assigned to a Network Delivery Mailbox except the mailbox
number. If you want to change a mailbox number, you must first delete the mailbox and create a
new Network Delivery Mailbox. For instructions on creating a Network Delivery Mailbox, refer to
“About creating Network Delivery Mailboxes” on page 56. For instructions on deleting a Network
Delivery Mailbox, refer to “Deleting a Network Delivery Mailbox” on page 64.
To change Network Delivery Mailbox parameters
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Mailbox Administration heading.
The Mailbox List page appears.
3 Click the Change link for the Network Delivery Mailbox you want to change.
The page for the mailbox appears.
4 Change the parameters for the mailbox.
5 Click the Submit button.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 64

64 Chapter 5 Network Delivery Mailboxes
Deleting a Network Delivery Mailbox
You can delete a Network Delivery Mailbox at any time. After you delete a Network Delivery
Mailbox, you cannot access it from the Company Directory or deliver network messages to that
particular site.
To delete a Network Delivery Mailbox
1 Start CallPilot Manager.
2 Click the Mailbox Administration heading.
The Mailbox List page appears.
3 Click the Delete link for the Network Delivery Mailbox you want to delete.
A message appears asking you to confirm your deletion.
4 Click the OK button.
P0606015 04
Page 65

Chapter 6
Troubleshooting Non Delivery Notification messages
This chapter describes some problems that can occur while using Message Networking.
If you think there is a problem with the network, contact your Network Administrator.
Non Delivery Notification messages
If a network message cannot be delivered, the sender receives a Non Delivery Notification voice
prompt. This section lists the Digital Networking and AMIS Non Delivery Notification messages,
their meanings and possible solutions.
The destination site is not accepting messages
This error can occur if:
• the destination site has not entered your site in their Network Site list
• the destination site does not have Message Networking enabled
• the destination site is busy receiving other messages
• the destination site has the Network Receive feature disabled
65
The system attempts to resend the message, but is unsuccessful.
Solution:
• Ensure the destination site has entered your site in their Network Site list.
• Ensure the destination site has Message Networking and the Network Receive feature enabled.
• Try resending the message. If you receive the same Non Delivery Notification message,
contact your Network Administrator.
The destination mailbox is not accepting messages
This error can occur if the destination mailbox:
• is not initialized
• is programmed not to accept messages when its owner is away from the office
The system does not attempt to resend the message.
Solution:
• Contact the destination site or the Network Administrator
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 66

66 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Non Delivery Notification messages
A protocol error occurred while delivering the message
For AMIS, this error can occur if:
• a DTMF tone signals the wrong digits
• someone tries to send an AMIS message that is too long. There is a limit of 8 minutes for
AMIS messages. Do not send AMIS messages that are longer than 8 minutes.
• the line disconnects before AMIS sends or receives all the DTMF tones.
A message can still go through even though not all DTMF tones are sent. In these cases, the
protocol error indicates that DTMF signaling was not completed.
Solution:
• Resend the message.
• If this error happens repeatedly, the DTMF setting on your system needs to be adjusted.
Contact your customer service representative.
There is a protocol mismatch with the remote site
This error can occur if:
• the destination site is not a Message Networking site (VPIM)
• the remote site is not a Voice Messaging site (AMIS)
The system does not attempt to resend the message
Solution:
• Ensure the destination site is a Message Networking site.
• Contact your Network Administrator.
Message transfer was interrupted
This error can occur if a system processing error takes place at the destination site during message
processing. The system does not attempt to resend the message.
Solution:
• Contact your Network Administrator.
The domain name of the remote site is not valid
This error can occur if:
• the domain name of the destination site is incorrect
• the domain name is deleted from the Network Site List
• the HOSTS file or Domain Name Server is not configured with the site’s domain name
The system does not attempt to resend the message.
Solution:
• Contact your Network Administrator.
P0606015 04
Page 67

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Non Delivery Notification messages 67
A connection to the remote site could not be established
This error can occur if your site cannot connect to the destination site. The problem is likely a lack
of Internet Protocol (IP) connectivity. The system does not attempt to resend the message.
Solution:
• Contact the destination site or the Network Administrator and verify that the site is on the
network.
The media is not supported at the destination
This error can occur if you send a fax message to a destination site that does not have the Fax
option installed. The Fax option is not available for CallPilot 100/150. The system does not
attempt to resend the message.
Solution:
• Contact the destination site and verify that it has the Fax option installed and enabled
• Contact your Network Administrator
The network is experiencing problems
This error can occur if:
• your site is busy sending other network messages and cannot send your message
• a system error has occurred
The system attempts to resend the message:
• If you receive the same Non Delivery Notification voice prompt, contact your Network
Administrator
The destination site mailbox is full
This error can occur if the destination site’s mailbox is full. The system does not attempt to resend
the message.
Solution:
• Contact your Network Administrator.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 68

68 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Non Delivery Notification messages
The destination site mailbox does not exist
This error can occur if:
• the destination mailbox is deleted
• the System Administrator entered the wrong mailbox number while creating the Network
Delivery Mailbox
• the Network Delivery Mailbox was deleted before the message was sent
• the mailbox number entered for site-based addressing is incorrect
The system does not attempt to resend the message.
Solution:
• Verify the destination site mailbox number.
• Contact your Network Administrator.
The destination site did not answer the call
This error can occur if:
• the destination site disables the Auto Attendant
• the Auto Attendant did not answer the call
• a busy signal was received at the destination site
Solution:
• Ensure the destination site has the Auto Attendant assigned to answer the Central Office (CO)
line designated for network calls. Resend the message. For instructions about assigning the
Auto Attendant to answer lines, refer to the CallPilot Manager Set Up and Operation Guide.
• AMIS cannot deliver a network message if the destination site does not answer the call using
the Auto Attendant.
The destination site could not be reached because an outside line or routing resources
were not available
This error can occur if all retry attempts encounter no lines available or access denied.
This can happen if:
• the line is busy
• the line does not exist
• an unexpected dial tone pause occurs
• if you use a Business Communications Manager or CallPilot 100/150 system, you entered an
incorrect line or pool number
• the outside line selected is not available
• no dial tone is detected on the selected line
• an unexpected dial tone is received
P0606015 04
Page 69

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Non Delivery Notification messages 69
Solution:
• Ensure that the correct line number is assigned and resend the message.
• Assign a different line for outdialing.
• Contact your customer service representative. If this error occurs frequently because of a busy
line, your system’s channel configuration needs to be upgraded.
A data transmission error was detected while attempting to deliver the message
A delay between DTMF tones causes this error. The destination site receives the transmit tone and
perhaps some other digits, but the pause between the tones is too long.
Solution:
• Resend the message.
• Contact your customer service representative if this happens repeatedly.
Timeout occurred while attempting to deliver the message
This error occurs if:
• the destination site is not enabled to answer the lines. Make sure the destination site is set up to
answer the lines.
• the destination site does not receive the first digit in the transmission sequence. A timeout
error occurs if the destination site does not receive a transmission signal within 10 seconds.
• the remote site’s line is not answered by the Auto Attendant and the number of network retries
is exceeded
• the is a long pause in the dialed number, which can be caused by multiple timed pauses, and
the number of network retries is exceeded
• the remote site’s line is busy and the number of network retries is exceeded
Solution:
• Resend the message
• Contact your customer service representative if this happens repeatedly. The DTMF setting on
you system needs to be adjusted.
A Network Delivery Mailbox could not receive your Broadcast Message
This message plays if your site has disabled the Message Delivery Feature, or if the receiving site
has the Network Receive Feature disabled.
The following message could not be delivered to (mailbox owner's name or mailbox
number)
This message plays if a message cannot be received at a site. This can occur if:
• the destination site cannot answer the call
• the destination site does not accept network messages
• the destination site mailbox does not exist
• the destination site mailbox is full
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 70

70 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Non Delivery Notification messages
• an outside line is not available
• a protocol error occurs during transmission
• a data transmission error occurs during transmission
• a timeout error occurs during transmission
The destination telephone number does not appear to be a network site
This message occurs if:
• a person answers a ringing line and presses a key when an AMIS message is coming through
on the same line
• an AMIS call is answered by a private answering machine
• an AMIS call is answered by a voicemail prompt, for example a set that is forwarded to
voicemail with F984
• an AMIS call is answered by a Home Transfer node or a Home Mailbox node on a CCR Tree
You receive a protocol error for an AMIS message that is longer than 8 minutes
There is a limit of 8 minutes for AMIS messages. Do not send AMIS messages that are longer than
8 minutes.
Callers do not receive Off-Premise Message Notification and when you try to record a
greeting, prompt or name using CallPilot Manager your telephone does not ring
If you use AMIS networking, make sure that you have more than one outcalling channel set in
CallPilot Manager. For how to set outcalling channels, refer to the CallPilot Manager Set Up and
Operation Guide. If you have one channel set for outcalling, it is possible that while AMIS calls
are in progress, Off-Premise Message Notification does not occur and you cannot use CallPilot
Manager for recording greetings, prompts or names.
P0606015 04
Page 71

Chapter 7
Message Networking programming record
Note: You can photocopy these pages.
General Networking Properties
IP address or Host name Enabled Disabled
Network Receive Enabled Disabled
Network Delivery Enabled Disabled
Network Reply Enabled Disabled
Network Broadcast Enabled Disabled
Network Group List Enabled Disabled
Number of Network Retries (1-9)
71
Network Delay (1-60 minutes)
Digital Networking site table
Use this table to record the properties for the Digital Networking sites you create.
Site name
Site prefix
Host name (FQDN)
Mailbox prefix
Site name recorded Y N
Site name
Site prefix
Host name (FQDN)
Mailbox prefix
Site name recorded Y N
Site name
Site prefix
Host name (FQDN)
Mailbox prefix
Site name recorded Y N
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 72

72 Chapter 7 Message Networking programming record
AMIS site table
Use this table to record the properties for the AMIS sites you create.
Site name
Site prefix
Site name recorded Y N
Destination site phone number
Outdial route Line number
Pool number
Route code
Site name
Site prefix
Site name recorded Y N
Destination site phone number
Outdial route Line number
Pool number
Route code
Site name
Site prefix
Site name recorded Y N
Destination site phone number
Outdial route Line number
Pool number
Route code
Site name
Site prefix
Site name recorded Y N
Destination site phone number
Outdial route Line number
Pool number
Route code
P0606015 04
Page 73

Chapter 7 Message Networking programming record 73
Call Blocking periods table
Use this table to record your Call Blocking periods.
Day Period Call Blocking time from Call Blocking time to
Monday 1 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
2 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
3 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
4 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
Tuesday 1 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
2 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
3 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
4 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
Wednesday 1 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
2 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
3 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
4 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
Thursday 1 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
2 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
3 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
4 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
Friday 1 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
2 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
3 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
4 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
Saturday 1 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
2 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
3 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
4 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
Sunday 1 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
2 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
3 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
4 ____ : ____ ____ : ____
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 74

74 Chapter 7 Message Networking programming record
Network Site Mailbox table
Use this table to record the details of the Network Site Mailboxes you create.
Network Site Mailbox number
Network Site Mailbox name
Include in Directory Y N
Mailbox Name recorded Y N
Destination Site Prefix
Destination Remote Mailbox number
Network Site Mailbox number
Network Site Mailbox name
Include in Directory Y N
Mailbox Name recorded Y N
Destination Site Prefix
Destination Remote Mailbox number
Network Site Mailbox number
Network Site Mailbox name
Include in Directory Y N
Mailbox Name recorded Y N
Destination Site Prefix
Destination Remote Mailbox number
Network Site Mailbox number
Network Site Mailbox name
Include in Directory Y N
Mailbox Name recorded Y N
Destination Site Prefix
Destination Remote Mailbox number
P0606015 04
Page 75

Chapter 7 Message Networking programming record 75
Network AMIS mailbox table
Use this table to record the details of the Network AMIS mailboxes you create.
Network AMIS mailbox number
Network AMIS mailbox name
Include in Directory Y N
Mailbox name recorded Y N
Outdial Line number
Pool number
Route code
Destination site phone number
Network AMIS mailbox number
Network AMIS mailbox name
Include in Directory Y N
Mailbox name recorded Y N
Outdial Line number
Pool number
Route code
Destination site phone number
Network AMIS mailbox number
Network AMIS mailbox name
Include in Directory Y N
Mailbox name recorded Y N
Outdial Line number
Pool number
Route code
Destination site phone number
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 76

76 Chapter 7 Message Networking programming record
P0606015 04
Page 77

Glossary
Administration
AMIS
Area Code
Auto Attendant
Broadcast Message
77
The tasks involved in maintaining CallPilot mailboxes, greetings and set up configuration.
Audio Message Interchange Specification, which enables different voice messaging
systems to interact.
A code assigned to a calling area within an area.
The CallPilot answering service that answers incoming calls with a Company Greeting,
plays a list of options to a caller, and performs call routing functions in response to a
caller's selections.
A message that can be sent only by the System Administrator. This type of message plays
in all initialized Personal Mailboxes.
Call Blocking Periods
Periods of time you establish when network delivery messaging is prohibited.
Channel configuration
The number of channels on your system that you designate for outdialing.
Class of Service
A predetermined number designation that specifies the options for a mailbox.
Company Directory
An internal voice list that contains the names of subscribers with initialized mailboxes
who are in the Company Directory.
Configuring CallPilot Lines
The tasks involved in determining which incoming telephone lines of a business are
answered by CallPilot and which Greeting Table is assigned.
Conventions
The way certain information is described. For example, using underlined text to represent
the second line of the display prompt information.
Country Code
A code for long distance calling assigned to a country.
Designated Operator
The person in a company who is assigned to answer the CallPilot operator request option.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 78

78 Glossary
Direct Addressing
Display
Display Buttons
Display Options
DTMF telephone
The ability to send a message directly to a remote site by specifying the line, pool or route
number, phone number and destination mailbox.
A one or two line screen on a Nortel Networks Business Series Terminal that shows
CallPilot commands and options.
The three buttons on a Nortel Networks Business Series Terminals two line display
telephone. When pressed, these buttons select the specified CallPilot option.
The choices that appear on Nortel Networks Business Series Terminals two line displays.
Callers select display options by pressing the display buttons.
A push button telephone that emits DTMF tones.
Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)
An FQDN is the complete domain name for a specific computer on the Internet. Each site
on a network has a unique FQDN. The FQDN distinguishes a site from every other site on
the network. An FQDN is the full name of the site, including all subdomain and domain
names, separated by periods. For example, pvt.nortel.com is an FQDN.
Group Lists
A collection of mailbox numbers that are assigned a special “Group” number by CallPilot.
When a message is sent to a Group List, mailboxes in the List receive the same message.
Member mailboxes can be located at the same site or at different locations within a
network.
Initialize a mailbox
Preparing a mailbox to receive messages, which includes changing the mailbox default
password and recording a Company Directory name.
International Access Code
A code identifying the digits dialed to access international calling.
Long Distance Access Code
The code used to access direct dial long distance calling services in a country.
P0606015 04
Page 79

Glossary 79
Loopback mailbox
The mailbox you use to test whether a site can transmit and receive network messages.
The Loopback mailbox default number is 103 if the extension length is three digits. Refer
to
“Loopback mailbox numbers” on page 39 for how to determine the Loopback mailbox
number. The length of the Loopback Mailbox number depends on the mailbox number
length.
Mailbox
A storage place for messages on the system.
Network Delivery
The feature that, when enabled, lets a site to send messages to other sites within a network.
Network Delivery Mailboxes
Mailboxes you add that allow access to an assigned mailbox at a destination site within a
network. Network Delivery Mailboxes can be set up with either a Direct Address or a
Site-Based Address.
Network Dialing Parameters
The values that determine how many times the system attempts to contact a destination
site within a network. The dialing parameters also include a retry interval.
Network Messaging
The ability to send, receive and reply to messages sent between remote locations within a
network.
Network Receive feature
The feature that lets a site receive messages from other locations within a network.
Network Reply feature
The feature that lets a site reply to messages sent from other locations within a network.
Outdial route
The parameter that specifies how an outdial call is routed. The outdial route can be a line,
pool number or route code.
Password
A four to eight digit number that is entered on the dialpad. A password is used to open
mailboxes or perform configuration tasks.
Personal mailboxes
Mailboxes that are assigned to subscribers as a place to store messages.
Resetting CallPilot
Returning the CallPilot voice module to its original default settings.
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 80

80 Glossary
Retry interval
Site-based Addressing
Special Mailboxes
Subscriber
System Administrator
System Administrator Mailbox
The amount of time the system waits before making another attempt to contact a
destination site when a failure to connect occurs.
The ability to send a message to a remote site by specifying the destination site’s prefix
and the mailbox number of the person you want to send the message to.
The two mailboxes used by the System Administrator and designated CallPilot operator:
the System Administrator Mailbox and the General Delivery Mailbox.
A mailbox owner.
The person responsible for configuring, updating and maintaining the CallPilot system.
The mailbox used by the System Administrator for sending Broadcast Messages.
This is the System Administrator’s personal mailbox.
Voice prompts
The prerecorded voice messages that are played when accessing the different CallPilot
features and options.
VPIM
Voice Profile for Internet Mail. VPIM is based on existing Internet Mail specifications. It
wraps encoded voice messages in MIME message parts, and uses SMTP to transport them
over TCP/IP networks. The VPIM profile requires that these multi-part messages be
formatted and used according to a specific set of Internet conventions and rules, and its
predictability enables voice mail servers to automatically and correctly handle messages
and their constituent parts.
P0606015 04
Page 81

Index
81
A
AMIS error messages 69
AMIS networking properties
Area code 23
Country code 23
International access code 23
Loopback mailbox 23
Outdial route 23
Sender name 23
System name 23
Telephone number 23
Area code 23
B
Broadcast Message Feature, enabling 53
C
Calling Blocking, setting up 26
Changing 63
Configuring environments without a DNS 15, 16
Country code 23
D
Deleting a Network Site 51
Delivering messages 52
Dialing Table Translation, network access 31
Dialing Translation 29
how it works 29
overview 29
phone number translation 29
table 29
Dialing Translation properties
setting 32
Dialing Translation Table
building 34
changing an entry 36
changing entries 36
deleting entries 37
example 30
reviewing entries 35
Digital Networking
Fax messages 8
Network Group Lists 53
Network Receive 52
Network Reply feature 52
Non Delivery Notification messages 65
overview 8, 9
prerequisites 7
setting properties 43
TCP/IP 8
using 11
Domain Name 8
Domain Name System (DNS), configuring
environments without a DNS
15
E
Error messages 65
F
Fax messages 8
FQDN 8
G
General Networking properties
Network Broadcast 44
Network Delay 44
Network Delivery 44
Network Group List 44
Network Receive 44
Network Reply 44
Number of Network Retries 44
Greeting, recording 49
Group Lists, Network 53
H
Host name 18
Host name/IP address 45
I
International access code 23
Internet, and security 8
IP address 15
L
Loopback
test message 40, 41
Loopback mailbox 23, 38
numbers 39
M
Mailbox, maximum number 55
Message Networking
Network Deliver 52
restricting messages 52
CallPilot Message Networking Set Up and Operation Guide
Page 82

82 Index
N
Network Access 31
Network Broadcast 44
Network Delay 44
Network Deliver, disabling 52
Network Delivery 44
Network Delivery Mailbox 10
adding 57
changing parameters 63
creating 57
deleting 64
maximum number of mailboxes 55
overview 55
parameter summary 57
precautions 56
Network Group List 44, 53
Network Mailbox name 74
Network Mailbox number 74
Network Messaging, disabling 52
Network Receive 44
disabling 52
Network Reply 44
disabling 52
Network Send 52
Network Site
changing 48
deleting 51
Network site parameters
Host name/IP address 45
Outdial route 45
Phone number 45
Site name 45
Site prefix 45
Non Delivery Notification messages 65
Number of Network Retries 44
Remote Group List precautions 56
Remote Mailbox number 74
Reply restrictions 52
S
Sender name 23
Sending network messages 10
Setting General Networking properties 43
Setting the Dialing Translation Parameters 32
Setting up AMIS 23
Setting up outdialing channel configuration 29
Site
changing 48
deleting 51
Site name 45
Site prefix 45
Site-Based Addressing 10
System name 23
System prerequisites 7
T
Telephone number 23
Telephone number Translation 29
Network extension numbers 29
Test network message
sending 40
Testing network message capability 38
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP)
8
V
Voice messages, security of 8
Voice Messaging 7
O
Outdial route 23, 45
P
Phone number 45
Prerequisites 7
Prompt, recording 49
Properties, General Networking 43
R
Receiving messages 52
Recording
greeting 49
prompt 49
P0606015 04
 Loading...
Loading...