Page 1

DECT Messenger Fundamentals
Avaya Communication Server 1000
NN43120-120, 04.02
7.5
March 2012
Page 2
©
2012 Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to ensure that the
information in this document is complete and accurate at the time of
printing, Avaya assumes no liability for any errors. Avaya reserves the
right to make changes and corrections to the information in this
document without the obligation to notify any person or organization of
such changes.
Documentation disclaimer
“Documentation” means information published by Avaya in varying
mediums which may include product information, operating instructions
and performance specifications that Avaya generally makes available
to users of its products. Documentation does not include marketing
materials. Avaya shall not be responsible for any modifications,
additions, or deletions to the original published version of
documentation unless such modifications, additions, or deletions were
performed by Avaya. End User agrees to indemnify and hold harmless
Avaya, Avaya's agents, servants and employees against all claims,
lawsuits, demands and judgments arising out of, or in connection with,
subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to this documentation,
to the extent made by End User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked Web
sites referenced within this site or documentation provided by Avaya.
Avaya is not responsible for the accuracy of any information, statement
or content provided on these sites and does not necessarily endorse
the products, services, or information described or offered within them.
Avaya does not guarantee that these links will work all the time and has
no control over the availability of the linked pages.
Warranty
Avaya provides a limited warranty on its Hardware and Software
(“Product(s)”). Refer to your sales agreement to establish the terms of
the limited warranty. In addition, Avaya’s standard warranty language,
as well as information regarding support for this Product while under
warranty is available to Avaya customers and other parties through the
Avaya Support Web site:
you acquired the Product(s) from an authorized Avaya reseller outside
of the United States and Canada, the warranty is provided to you by
said Avaya reseller and not by Avaya.
Licenses
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS AVAILABLE ON THE AVAYA
WEBSITE,
APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO DOWNLOADS, USES AND/OR
INSTALLS AVAYA SOFTWARE, PURCHASED FROM AVAYA INC.,
ANY AVAYA AFFILIATE, OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER
(AS APPLICABLE) UNDER A COMMERCIAL AGREEMENT WITH
AVAYA OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER. UNLESS
OTHERWISE AGREED TO BY AVAYA IN WRITING, AVAYA DOES
NOT EXTEND THIS LICENSE IF THE SOFTWARE WAS OBTAINED
FROM ANYONE OTHER THAN A V A Y A, AN A V A Y A AFFILIA TE OR AN
AVAYA AUTHORIZED RESELLER; AVAYA RESERVES THE RIGHT
TO TAKE LEGAL ACTION AGAINST YOU AND ANYONE ELSE
USING OR SELLING THE SOFTWARE WITHOUT A LICENSE. BY
INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, OR
AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU, ON BEHALF OF
YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR WHOM YOU ARE INSTALLING,
DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE (HEREINAFTER
REFERRED TO INTERCHANGEABL Y AS “YOU” AND “END USER”),
AGREE TO THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS AND CREATE A
BINDING CONTRACT BETWEEN YOU AND AVAYA INC. OR THE
APPLICABLE AVAYA AFFILIATE (“AVAYA”).
HTTP://SUPPORT.AVAYA.COM/LICENSEINFO/ ARE
http://support.avaya.com. Please note that if
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, no use should be made of
materials on this site, the Documentation, Software, or Hardware
provided by Avaya. All content on this site, the documentation and the
Product provided by Avaya including the selection, arrangement and
design of the content is owned either by Avaya or its licensors and is
protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws including the
sui generis rights relating to the protection of databases. You may not
modify, copy, reproduce, republish, upload, post, transmit or distribute
in any way any content, in whole or in part, including any code and
software unless expressly authorized by Avaya. Unauthorized
reproduction, transmission, dissemination, storage, and or use without
the express written consent of Avaya can be a criminal, as well as a
civil offense under the applicable law.
Third-party components
Certain software programs or portions thereof included in the Product
may contain software distributed under third party agreements (“Third
Party Components”), which may contain terms that expand or limit
rights to use certain portions of the Product (“Third Party Terms”).
Information regarding distributed Linux OS source code (for those
Products that have distributed the Linux OS source code), and
identifying the copyright holders of the Third Party Components and the
Third Party Terms that apply to them is available on the A vaya Support
Web site:
Preventing Toll Fraud
“T oll fraud” is the unauthorized use of your telecommunications system
by an unauthorized party (for example, a person who is not a corporate
employee, agent, subcontractor, or is not working on your company's
behalf). Be aware that there can be a risk of Toll Fraud associated with
your system and that, if Toll Fraud occurs, it can result in substantial
additional charges for your telecommunications services.
Avaya Toll Fraud Intervention
If you suspect that you are being victimized by T oll Fraud and you need
technical assistance or support, call Technical Service Center Toll
Fraud Intervention Hotline at +1-800-643-2353 for the United States
and Canada. For additional support telephone numbers, see the Avaya
Support Web site:
vulnerabilities with Avaya products should be reported to Avaya by
sending mail to: securityalerts@avaya.com.
Trademarks
The trademarks, logos and service marks (“Marks”) displayed in this
site, the Documentation and Product(s) provided by Avaya are the
registered or unregistered Marks of Avaya, its affiliates, or other third
parties. Users are not permitted to use such Marks without prior written
consent from Avaya or such third party which may own the Mark.
Nothing contained in this site, the Documentation and Product(s)
should be construed as granting, by implication, estoppel, or otherwise,
any license or right in and to the Marks without the express written
permission of Avaya or the applicable third party.
Avaya is a registered trademark of Avaya Inc.
All non-Avaya trademarks are the property of their respective owners,
and “Linux” is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Downloading Documentation
For the most current versions of Documentation, see the Avaya
Support Web site:
Contact Avaya Support
Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report problems
or to ask questions about your Product. The support telephone number
is 1-800-242-2121 in the United States. For additional support
telephone numbers, see the Avaya W eb site: http://support.avaya.com.
http://support.avaya.com/Copyright.
http://support.avaya.com. Suspected security
http://support.avaya.com.
2 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: New in this release...........................................................................................
Features....................................................................................................................................................
Revision history.........................................................................................................................................
Chapter 2: Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide...............................................
Preface......................................................................................................................................................
Avaya DECT Messenger overview...........................................................................................................
What is Avaya DECT Messenger.....................................................................................................
Modules overview.............................................................................................................................
eCONFIG basic concepts.................................................................................................................
DECT Messenger concepts.............................................................................................................
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG........................................................................................
Starting the eCONFIG......................................................................................................................
eCONFIG main window....................................................................................................................
Managing devices............................................................................................................................
Managing groups..............................................................................................................................
Managing group members...............................................................................................................
Managing users................................................................................................................................
Adding a DECT device to the Messenger system....................................................................................
Chapter 3: DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual..............................................
Preface......................................................................................................................................................
About the manual.............................................................................................................................
Guidelines for maintenance and administration of a server or specialized computer......................
DECT Messenger overview......................................................................................................................
Avaya DECT Messenger functional description...............................................................................
Modules overview.............................................................................................................................
Linking modules...............................................................................................................................
DECT Messenger in a WAN or MAN network...........................................................................................
Licensing...................................................................................................................................................
CSTA connection (link) license.........................................................................................................
SOPHO CTI module License Manager licenses..............................................................................
Detailed module descriptions....................................................................................................................
eKERNEL.........................................................................................................................................
eDMSAPI..........................................................................................................................................
eIO....................................................................................................................................................
eSMTP.............................................................................................................................................
eSMTP_Server.................................................................................................................................
eAPI..................................................................................................................................................
eWEB...............................................................................................................................................
eCONFIG.........................................................................................................................................
eGRID..............................................................................................................................................
eTM..................................................................................................................................................
eLOG................................................................................................................................................
eCAP................................................................................................................................................
eESPA..............................................................................................................................................
7
7
7
9
9
10
10
12
14
16
19
19
20
22
31
37
42
48
53
53
54
54
56
56
58
61
64
65
65
68
69
69
70
70
70
71
71
72
73
73
73
74
74
74
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 3
Page 4

eLOCATION.....................................................................................................................................
eSMS................................................................................................................................................
eSNMP.............................................................................................................................................
eFR...................................................................................................................................................
Web administrator............................................................................................................................
What is required to run DECT Messenger................................................................................................
Hardware Requirements..................................................................................................................
Software Requirements....................................................................................................................
DMC Configuration...........................................................................................................................
DATABASES in DECT Messenger............................................................................................................
Supported Database types...............................................................................................................
How to set up the Databases...........................................................................................................
Installing and getting started.....................................................................................................................
Stopping IIS WEB Services..............................................................................................................
Installing DECT Messenger..............................................................................................................
Getting Started.................................................................................................................................
Using eCONFIG........................................................................................................................................
Using eCONFIG (Local) on the DECT Messenger Server PC.........................................................
Using eCONFIG (Remote) on remote PC (client) in the Network....................................................
Using eTM.................................................................................................................................................
eDMSAPI Inbound....................................................................................................................................
Incoming Alarm (IA) from DMC........................................................................................................
Incoming Alarm (IA) from IP DECT..................................................................................................
Incoming Confirmation (IC)..............................................................................................................
Parameters required to set an alarm................................................................................................
SET/RESET structure......................................................................................................................
eLOCATION..............................................................................................................................................
How it works.....................................................................................................................................
eLOCATION Module in eCONFIG....................................................................................................
Connecting National Instruments modules...............................................................................................
General.............................................................................................................................................
Hardware Installation........................................................................................................................
Software Installation.........................................................................................................................
Understanding Security features...............................................................................................................
Session Guarding.............................................................................................................................
Watchdog.........................................................................................................................................
Using eBackup..........................................................................................................................................
Setting up e-mail integration (eSMTP_Server/eSMTP)............................................................................
General.............................................................................................................................................
Using eSMTP Server................................................................................................................................
How eSMTP Works..........................................................................................................................
Installing IIS......................................................................................................................................
Configuring eSMTP_Server in eConfig............................................................................................
Configuring IIS for DECT Messenger...............................................................................................
Using eSMTP............................................................................................................................................
Sending SMS messages...........................................................................................................................
eSMTP.............................................................................................................................................
74
74
75
75
75
76
76
77
77
80
80
81
81
81
82
83
90
90
92
93
94
94
95
96
96
103
107
108
109
110
110
113
114
119
119
119
126
130
130
131
131
134
134
135
138
139
139
4 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Page 5

eASYNC...........................................................................................................................................
V.24 - RS232 connections (eCAP, eESPA)...............................................................................................
eCAP................................................................................................................................................
eESPA..............................................................................................................................................
Using Import/Export menu........................................................................................................................
eLOG.........................................................................................................................................................
OUTrqs.csv file.................................................................................................................................
How to use the Files.........................................................................................................................
Checking diagnostics................................................................................................................................
General.............................................................................................................................................
Logging.............................................................................................................................................
Module Window................................................................................................................................
eKERNEL Window...........................................................................................................................
Simulation Options in a Module........................................................................................................
eKERNEL Service Options...............................................................................................................
Index.....................................................................................................................................
139
142
143
143
144
145
150
155
155
155
156
158
163
164
164
165
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 5
Page 6

6 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Page 7

Chapter 1: New in this release
Features
There are no new features introduced with this release.
Revision history
March 2012 Standard 04.02. This document is up-issued
to support Avaya Communication Server
1000 Release 7.5, and contains additional
changes relating to updates in Release 4.1
of the Messenger software.
November 2010 Standard 04.01. This document is up-issued
to support Avaya Communication Server
1000 Release 7.5.
June 2010 Standard 03.01. This document is up-issued
to support Avaya Communication Server
1000 Release 7.0.
May 2009 Standard 02.01. This document is up-issued
to support Communication Server 1000
Release 6.0.
October 2008 Standard 01.06 This document is up-issued
to support Communication Server 1000
Release 5.5, and contains additional
changes relating to updates in Release 4 of
the Messenger software.
September 2008 Standard 01.02. This document is up-issued
to support Communication Server 1000
Release 5.5, and contains changes relating
to updates to the Messenger software.
May 2008 Standard 01.01 This document is issued to
support Communication Server 1000
Release 5.5. Some of the information in this
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 7
Page 8

New in this release
new document was previously in DECT
Fundamentals, NN43120-114.
8 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 9
Chapter 2: Avaya DECT Messenger
Administrator Guide
This chapter contains information on the following topics:
• Avaya DECT Messenger overview on page 10
- What is Avaya DECT Messenger on page 10
Modules overview on page 12
-
- eCONFIG basic concepts on page 14
- DECT Messenger concepts on page 16
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG on page 19 eCONFIG Section
•
- Starting the eCONFIG on page 19
eCONFIG main window on page 20
-
- Managing devices on page 22
Managing groups on page 31
-
- Managing group members on page 37
- Managing users on page 42
Adding a DECT device to the Messenger system on page 48
•
Preface
This chapter contains an overview of Avaya DECT Messenger in general, and information for
users of the eCONFIG module specifically . It contains important information on the underlying
structure of the eCONFIG module, and on creating, deleting, and making changes to Users,
Devices, and Groups.
This chapter does not cover all of the menus and associated menu items that are available in
the eCONFIG module. Menus and associated menu items that are not covered require detailed
technical background knowledge.
For information about the other menu parameters in the eCONFIG module, or information for
any of the other modules in Avaya DECT Messenger, refer to Avaya DECT Messenger
Installation and Commissioning, NN43120-301.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 9
Page 10

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
Avaya DECT Messenger overview
DECT Messenger provides a software tool, the eCONFIG, for making changes to the
configuration. The eCONFIG is on either the same PC as the DECT Messenger software, or
on another PC in the TCP/IP network. After you run eCONFIG on another PC, the number of
items you can change is limited.
What is Avaya DECT Messenger
DECT Messenger is a software platform that allows message generation, message routing,
and message protocol conversion. Figure 1: Avaya DECT Messenger on page 10 shows the
inputs and outputs of DECT Messenger.
Figure 1: Avaya DECT Messenger
Message input
The following input can generate messages in DECT Messenger:
• ESPA 4.4.4 pager protocol: DECT Messenger can receive pager messages from ESPA
4.4.4-compatible pager equipment.
• RS232/V.24 serial input: many protocols are supported as input for generating a
predefined message or a user defined message.
• DECT handset with E2 (Low Rate Messaging Services [LMRS]) messaging.
• E-mail to the DECT Messenger server PC: send a message from e-mail to a telephone
set or SMS to cell phone or any other output on DECT Messenger.
• Switches (push button, toggle): message alerts generated by alarm contacts, door
contacts, fire contacts, and so on.
10 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 11

• Analogue voltage/current levels: this form of message generation is used to guard
industrial equipment. For example, equipment output messages can indicate pressure,
temperature, and so on.
• Web interface from which you generate messages manually.
• Programs you write that communicate (using TCP/IP socket) with DECT Messenger:
DECT Messenger provides a port on TCP/IP that is open to receive input data from this
type of unique program.
Message output
DECT Messenger supports the following output:
• DECT E2 messages (up to 160 characters)
Although DECT Messenger supports up to 160 characters, the DECT equipment or the
handset can limit this number to 128, or even 48, characters. If the handset supports only
48 characters, the message is broken into sections and sent in parts to the handset.
• Messages sent to Ergoline or DECT extensions during ringing and after a call is connected
Avaya DECT Messenger overview
Each device type can specify message length. Messages that are too long to be displayed
are broken into sections suitable for the display devices.
• SMS messages to cell phones
DECT Messenger can send SMS messages to cell phones. A modem or a box that
behaves like an actual cell phone with a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card can be
the interface to the cell phone provider.
This option is mainly used as an alternative device. You can forward the message to a
cell phone if a message to a DECT handset is not acknowledged.
• E-mail messages
DECT Messenger can send e-mail using Simple Mail T ransfer Protocol (SMTP) to any e-
mail server.
• Digital output to control relays or similar equipment
In the event of an alarm, use the relay contacts to control equipment such as lamps, door-
contacts or hooters. Contacts are used as alternative devices (overflow) in case a
message is not confirmed.
• ESPA 4.4.4 pager protocol
DECT Messenger can send messages to paging equipment using the ESPA 4.4.4
protocol.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 11
Page 12

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
Modules overview
DECT Messenger consists of separate modules. There are three main groups of modules:
• Core—core components of the software, including security and maintenance tools.
• Input/Output modules—used for sending or receiving messages to or from supported
devices.
• Add-Ons—optional expansion modules adapted for specific customer needs.
• Web Administrator—a web application that enables web-based access to a limited set of
functions.
The following sections provide an overview of the modules. Detailed module descriptions are
provided in Avaya DECT Messenger Installation and Commissioning, NN43120-301.
Core modules
The following core modules are available:
• eKERNEL
The eKERNEL is the core software in the system and must always be present. eKERNEL
is between the incoming and the outgoing modules and must always be running. The
system does not operate if eKERNEL is absent or nonfunctional.
• eCONFIG/eGRID
The eCONFIG module is used to set up and configure the system, messages, and
message flows. The eCONFIG is a user-friendly variant of the eGRID.
• eGUARDIAN
The eGUARDIAN is a integrated into eKERNEL and is used in conjunction with an input
module that receives data at regular intervals. The eGUARDIAN module checks the data
input at regular intervals. If the input is not received within a specified time period, the
eGUARDIAN module sends a message indicating that an input is down.
• eBACKUP
The eBACKUP module takes care of making a backup of the configuration database at
regular intervals. -
• eTM
The eTM (T ask Manager) is a background module that automatically starts up other DECT
Messenger modules in case they are down. Most of the core modules are typically
deployed on the server PC. Exceptions are eCONFIG, which can optionally be deployed
and used from a client PC (with limited configuration capabilities) and eTM, which is
recommended to run on every DECT Messenger PC, client or server.
12 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 13
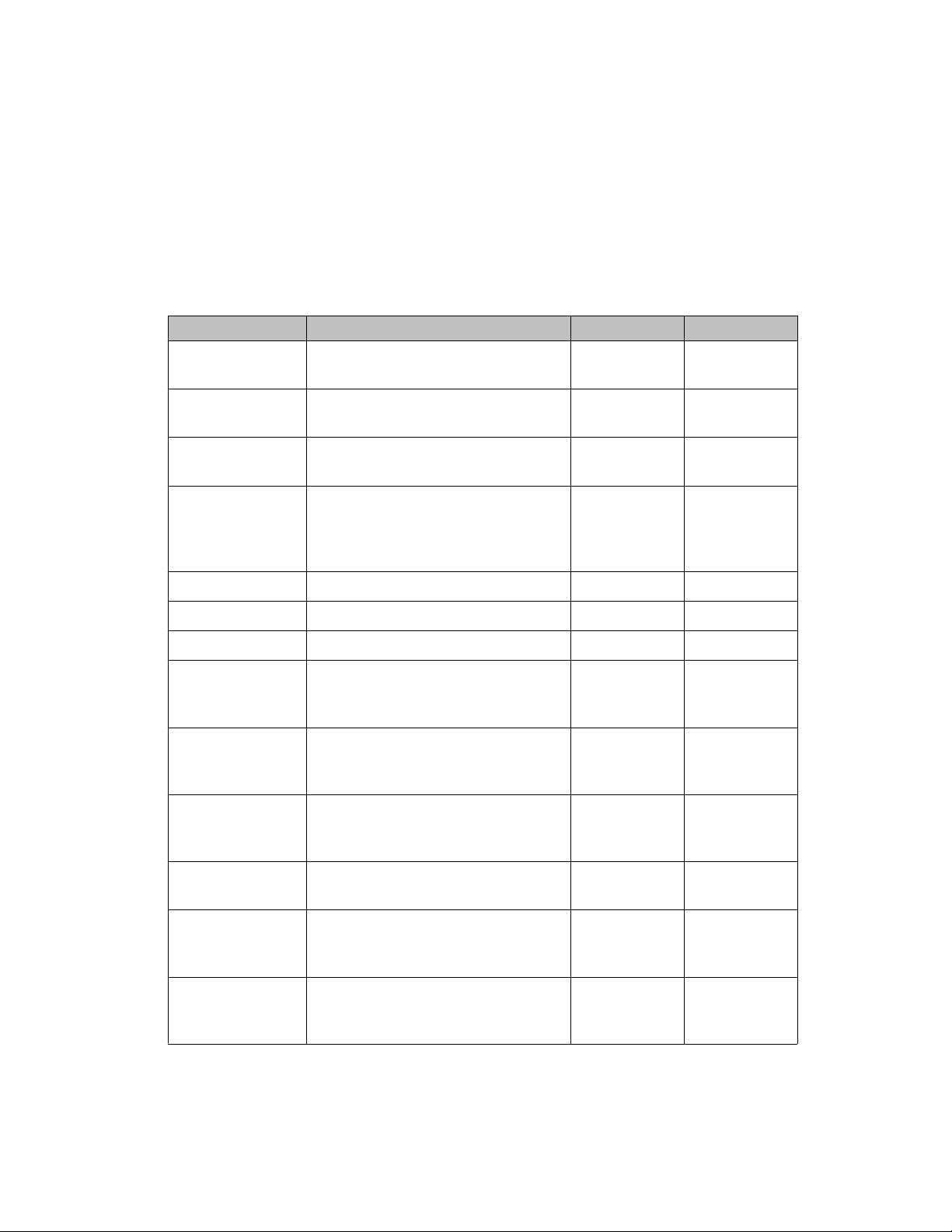
Incoming and outgoing modules
There is a wide range of incoming and outgoing modules available. They all communicate with
the eKERNEL module. Each module has a specific incoming or outgoing function. This means
that the incoming modules can receive messages and outgoing modules can send messages.
provides an overview of the modules.
Table 1: Incoming and outgoing Modules
Module Name Function Incoming Outgoing
Avaya DECT Messenger overview
eCAP V.24/RS232 interface and protocol
converter.
eESPA Input/Output module for the
connection to pager interfaces.
eAPI Input device for custom-made
programs.
eIO Digital and analogue inputs and
digital outputs (contacts and
switches).
eWEB Web interface. Yes eSMTP-server Receiving e-mail messages. Yes eSMTP (client) Sending e-mail messages. - Yes
eDMSAPI Sending and receiving E2-DECT
messages using the CSTA interface.
eASYNC Asynchronous modem interface to
cell phone SMS provider, or to wide
area paging system.
Yes -
Yes Yes
Yes -
Yes, analogue
levels and
digital levels
(contacts)
Yes, receiving
E2-DECT
messages
- Yes
Yes, switches
Yes, sending
E2-DECT
messages
eLOCATION Location detection after a call is made
from a DECT handset or when LRMS
(E2) is sent from DECT handset.
eVBVoice Interactive Voice Responds used to
various message types
eSNMP Receive an SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c
trap from an SNMP sending process
or equipment
eSMS Send SMS message to a mobile
phone. Inbound SMS can be used to
confirm alarm
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 13
In addition to
the eCSTA
module.
Yes Yes
Yes
Yes (to
confirm)
Yes
Page 14
Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
Add-on modules
The add-ons are input/output modules tailored to specific customer needs. They are not
covered by the standard product documentation.
• Web Administrator
The Web Administrator is a web-based user interface that offers access to certain
configuration functions, sending messages to users and groups, reporting functions, and
so on.
• Logging
The eKERNEL has built-in logging functionality for technical purposes known as eLOG.
The log files are located in the following directory: [INSTALLDIR]\Logs where
[INST ALLDIR] is the installation directory . The default installation directory is: C:\Program
Files\Avaya\Avaya DECT Messenger\.
eCONFIG basic concepts
The system configuration is stored in a database. You use the eCONFIG module to make
changes to the configuration. This section explains how the eCONFIG module uses the
database.
You can use the eCONFIG on the local DECT Messenger server PC. You can also install the
eCONFIG on a remote PC to do remote configuration maintenance. Database handling is
different for local and remote situations.
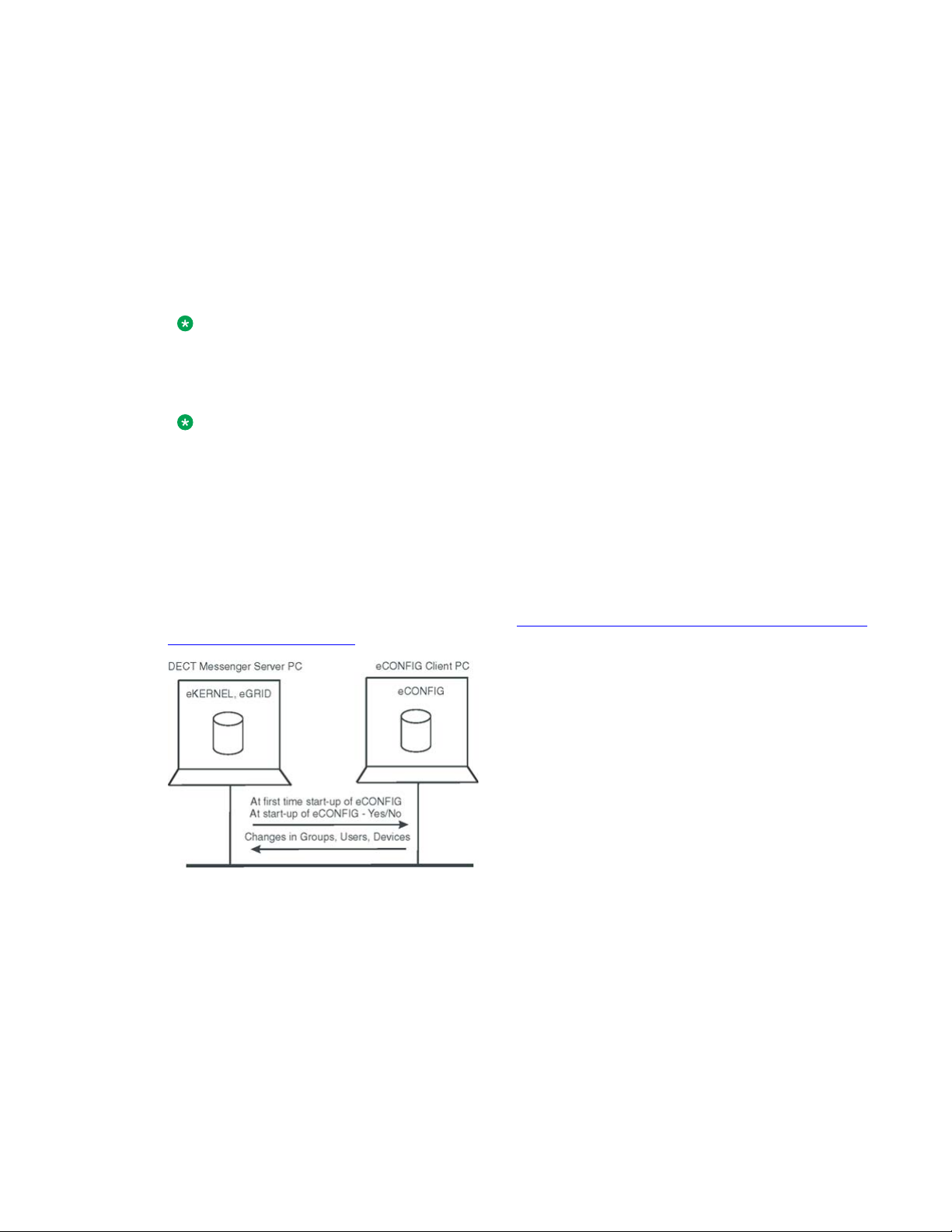
eCONFIG (local) on the DECT Messenger server PC
After the eCONFIG is installed on the DECT Messenger server PC, the database is handled
as shown in eCONFIG (local) on the server PC.
Figure 2: Database handling after eCONFIG is on local PC
After you open the eCONFIG for the first time, the eCONFIG makes a copy of the operational
configuration database in DECT Messenger . This copy is stored locally on the server PC where
14 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 15
Avaya DECT Messenger overview
eCONFIG is running. If you make configuration changes using the eCONFIG, these changes
are stored in the local working copy of the database in the eCONFIG. To make these changes
active, you must close down all the DECT Messenger modules and then close the eCONFIG
using the File > Exit menu. The operational database is deleted automatically, and the
database from the eCONFIG is saved into the DECT Messenger directory and becomes the
new operational database. After you restart the modules that you closed down, the new
configuration becomes active.
After you make changes in Users, Groups, or Devices, the changes are saved in the eCONFIG
database, as well as in the operational database, and so are immediately activated.
Note:
While making configuration changes with eCONFIG, ensure that no one else is making
changes in the operational database. If there are other pending changes, an error may occur
after you shut down the eCONFIG and attempt to apply the configuration changes.
Note:
If there are monitored devices in the active configuration, and one of these devices initiates
a follow-me, the diversion information is stored in the active database. Therefore, you cannot
restore the eCONFIG database, and all the changes that you make are lost (except for the
changes in Users, Groups, and Devices).
eCONFIG (remote) on remote PC (client) in the network
After the eCONFIG is installed on a remote PC (not the DECT Messenger server PC) in the
network, the database is handled as shown in
installed on a remote PC on page 15.
Figure 3: Database handling after eCONFIG is installed on a remote PC
After you open the eCONFIG for the first time at the remote PC, a copy is made of the
configuration database of DECT Messenger. This copy is stored on the remote PC where the
eCONFIG is running. You cannot make system configuration changes in this database, but
you can make changes in Users, Groups, and Devices.
After you make changes in Users, Groups, or Devices, these changes are stored in the
eCONFIG database on your PC. The changes are also immediately stored in the operational
database on the DECT Messenger (server) PC and are, therefore, immediately active.
Figure 3: Database handling after eCONFIG is
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 15
Page 16
Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
Note:
If there is more than one eCONFIG active at the same time, on different PCs, the individual
eCONFIG databases are not updated/synchronized after a user makes a change in one
eCONFIG. Only the database in the eCONFIG module where the change is made is
updated, together with the operational database. Changes made in Groups using the eWEB
interface are not written into the databases of the eCONFIG modules — these changes are
only written into the operational database.
Note:
The database is never saved to the server PC when you work on a remote PC.
Restarting eCONFIG
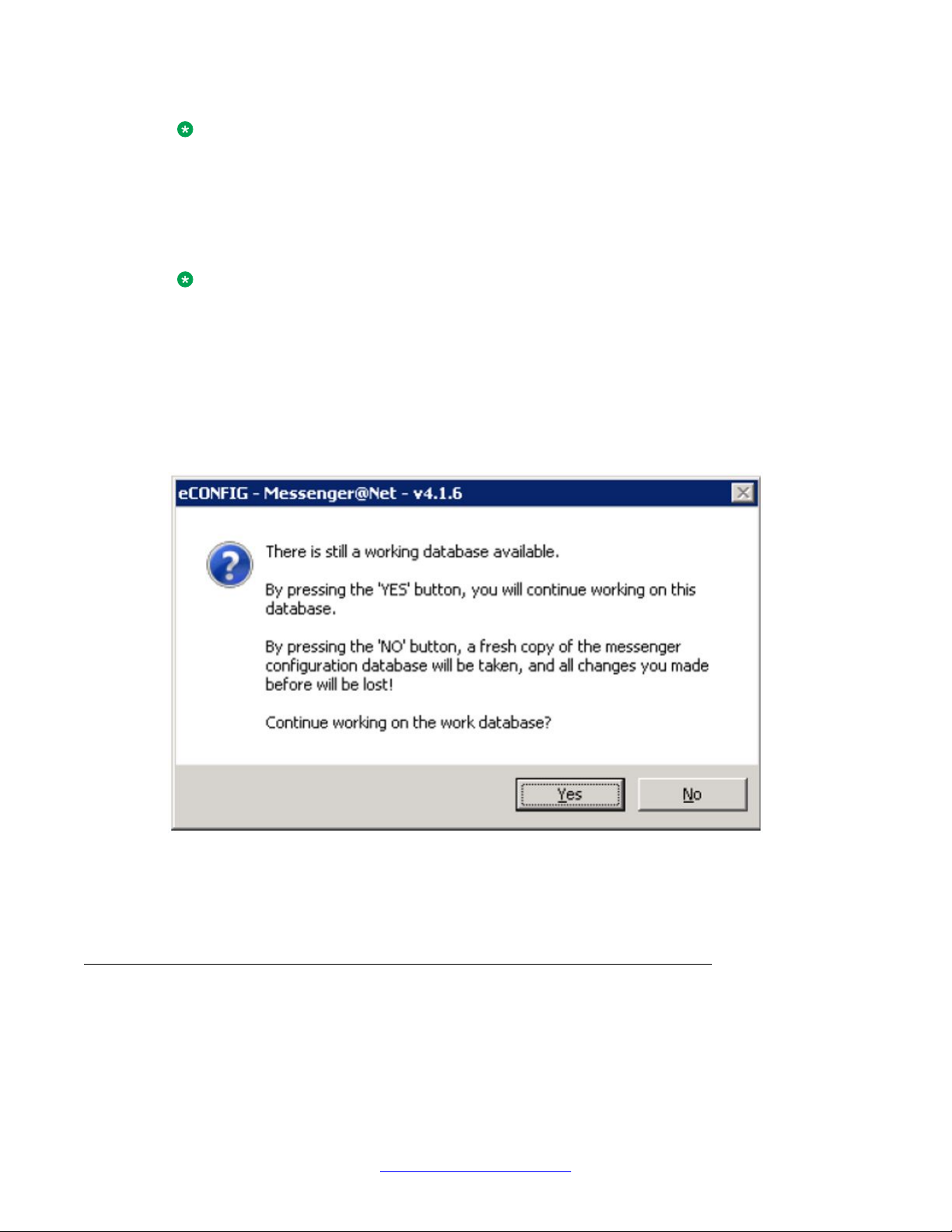
When you start eCONFIG, the program may find a working database in the local maintenance
directory . If so, eCONFIG asks you whether you want to continue with this database or retrieve
a fresh copy from the operational database.
Figure 4: Message box asking which database to use
Avaya recommends choosing No to make a fresh copy of the operational database and ensure
that there is no database inconsistency.
DECT Messenger concepts
DECT Messenger receives alarms (messages) from input modules. Understanding how these
incoming alarms are processed is an important step towards understanding the eCONFIG
menu structure.
16 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 17
Avaya DECT Messenger overview
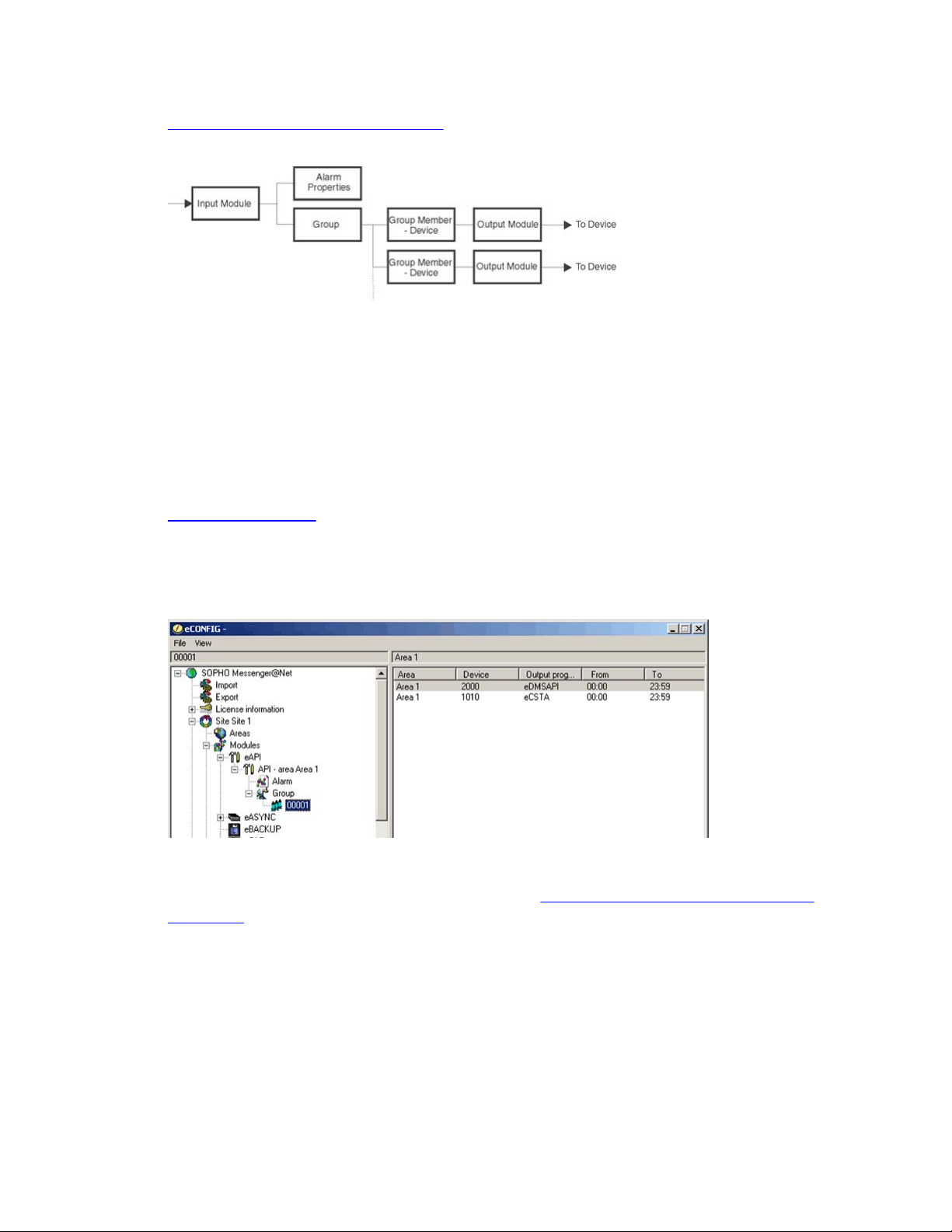
Figure 5: Alarm processing structure on page 17 shows the relation among the modules and
how messages are processed.
Figure 5: Alarm processing structure
Alarms originate at an input program (input module). An incoming alarm carries an alarm
identifier and a group identifier. The alarm identifier must match an identifier in the Alarm
Properties functional block, which specifies how the alarm is processed (priority , time intervals,
and so on). The group identifier determines the final destination. The incoming group identifier
must match a group identifier in the Groups functional block, which contains one or more output
destinations (that is, the group members). The group members are the devices assigned to a
Group.
Figure 6: eCONFIG on page 17 shows the main window of eCONFIG with an example of an
input module (the application programming interface [eAPI]). The eAPI input module is found
in eCONFIG in the Modules > eAPI menu. Select the instance of the module as it appears on
your screen (in this example, the menu selection is Modules > eAPI > API - area Area 1).
Each input module displays different properties.
Figure 6: eCONFIG
The following explanations relate to the blocks in Maintaining DECT Messenger using
eCONFIG on page 19:
• Input Module
The Alarm carries two dif ferent identifiers from the input module to the actual Kernel: the
alarm identifier and the group identifier. The identifier provides the message for the output
device.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 17
Page 18

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
You can set or change the properties of an input module.
• Alarm Properties
The alarm identifier is used to determine how the alarm is processed. Specifications are
in the All Alarms menu (for more information, see
page 20). Examples of the alarm properties are Priority, Repeat Interval Time, and so
on.
Note:
There are alarm identifiers predefined in the system configuration. Therefore, it is not
necessary to define all alarm identifiers. For information on available alarm properties,
see DECT Messenger Installation and Commissioning, NN43120-301.
• Group
The group identifier that originates at the input module determines the group to which the
alarm must be sent. In Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG on page 19, the
group identifier is 00001. The group identifier can be a group name or any string of
characters.
• Group Member -- Device
eCONFIG main window on
The group is composed of group members, and each group member is an actual device
(for example, an Ergoline, a DECT handset, or an e-mail address). The output device can
be a member of more than one group. For example, a DECT handset with extension
number 2000 can be assigned to more than one group as a group member. In
Figure 6:
eCONFIG on page 17, Group 00001 has two devices (2000 and 1010). Device 2000 uses
the output program eDMSAPI, which means that Device 2000 is a DECT handset using
E2 messaging.
• Output Module - Output Program
An output device makes use of an output module, also referred to as an output program.
You can specify settings in the output module to process the output alarm.
Refer to the following sections for instructions on creating, deleting, and changing parameters
for Groups, Users, and Devices:
•
Managing devices on page 22
• Managing groups on page 31
• Managing group members on page 37
• Managing users on page 42
18 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 19

Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
This chapter explains the eCONFIG user interface and available functionality.
Starting the eCONFIG on page 19
•
Starting the eCONFIG
The procedures below describe the steps necessary to start the eCONFIG module.
Before starting eCONFIG:
1. Ensure that DECT Messenger is correctly installed and already preconfigured by a
technician.
2. Ensure that the Kernel software is installed and running.
If you are on a remote PC (not the server PC), ensure that the main server is booted.
If you are using the server PC, an icon appears in the Windows task bar to indicate
that the eKERNEL is running.
If other modules are also running, an icon is displayed for each (for example, the
eDMSAPI).
To launch the eCONFIG configuration utility:
1. Use the shortcut available in the Start Menu:
Start > Programs > Avaya DECT Messenger > eCONFIG
2. Enter your login information.
Log in with the username and password provided by your system manager. If you
are the system manager, and you have not changed any usernames and passwords
yet, log in with the default login. The default login is admin (username), admin
(password).
3. Select the database.
Note:
The eCONFIG asks you which database you want to use. Ensure that you read
the information on database handling in eCONFIG basic concepts on page 14
before proceeding.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 19
Page 20
Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
You have two options for database selection:
• Click YES: the eCONFIG uses the database that is still available in the
eCONFIG module from a previous session. This database can be an old
database.
• Click NO: the eCONFIG makes a fresh copy of the operational database from
the DECT Messenger server . Avaya recommends that you choose this option.
It ensures that you have a copy of the actual operational database. If you work
on a remote PC, you must select this option to avoid conflicts with changes
made from other locations by other users.
4. The eCONFIG main window opens.
Detailed information is provided in
eCONFIG main window
The main eCONFIG window is shown in eCONFIG main window.
eCONFIG main window on page 20.
Figure 7: eCONFIG main window
Note:
The contents of the eCONFIG window are different for each user or for each system
configuration. eCONFIG main window shows all the menu items that are possible.
20 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 21

Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
The following menu items are available:
• Import/Export menu: provides the option to import configuration data into tables in the
configuration database, or to export configuration data from the configuration database
tables. The file type is .csv.
Note:
Do not use the Import/Export menu items if you do not have detailed configuration
database knowledge. If you make mistakes, it can corrupt your system.
• License information: provides information about the current licenses that are active in your
DECT Messenger. You cannot make license changes from this menu.
• Site Site 1: indicates the location of the eKERNEL (core) software. There is typically only
one eKERNEL in a system, so there is only one site displayed. (In exceptional cases,
there can be more than one site, but only one eKERNEL (that is, one site) can be active
at any given instant.
• Areas: indicates the subdivisions in a site. Areas are used only if you have a connection
from your DECT Messenger to more than one DECT Mobility Card (DMC) with DECT.
For each connection from your DECT Messenger to a DMC system or an IP DECT
system, you must specify a different area. Use a number to identify the area. The area
number is used in the various modules in DECT Messenger. Note that in almost all
installations you have only one area.
• Modules: provides an overview of all the modules in the Messenger.
Note:
The list of modules can differ for each user . The list of modules is displayed only if you
have view/edit rights.
Note:
The All TCP Clients menu item is not a module. All TCP Clients provides information
about the module TCP/IP connections. You cannot make any configuration changes
from this menu.
• All Alarms: provides a list of all alarm specifications available in Messenger.
Note:
The alarm specification is linked to an input module. Therefore, to create a new alarm
specification, you must use the Module menu. From the All Alarms menu, you can make
changes only to existing alarm specifications.
• All Users: defines all users. Note that there are two separate groups of users: eCONFIG
users and eWEB users. If you have sufficient rights, you can change user settings and
add new users from this menu.
• Groups and devices: use this menu to make changes in group and device characteristics.
Y ou cannot create new groups here because a group is always uniquely linked to an input
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 21
Page 22

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
module. You can, however, create new devices here because a device does not have a
unique relationship with only one group.
• Holiday: use this menu to specify the public holidays. This information is used for the
group members. You enable the specified holidays in the properties for each group
member.
Note:
If you are using the eCONFIG on a remote PC, you cannot make changes to property
settings. You can change only Users, Groups, and Devices.
Managing devices
The following sections provide information that explain the following DECT Messenger tasks:
• creating a new device
• changing the parameters of an existing device
• editing device parameters
The following are examples of device types in DECT Messenger:
• DNR in the DMC
• Directory Number (DN) in SIP DECT
• e-mail address
• cell phone number (for SMS)
• relay contacts
You must know the properties of each device type relative to the equipment that hosts it (that
is, device properties in the DMC, in the Mail Server, and so on).
Note:
Task procedures are explained in the following sections. T o carry out these procedures, you
must have sufficient user rights to access all the menus that are used in these procedures.
If you do not have sufficient rights, you cannot see the menu options described, or you see
them but cannot make changes.
Creating a new device
Complete the following steps to create a new device.
Creating a new device
1. Access the eCONFIG Groups and Devices menu.
• Open eCONFIG.
22 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 23
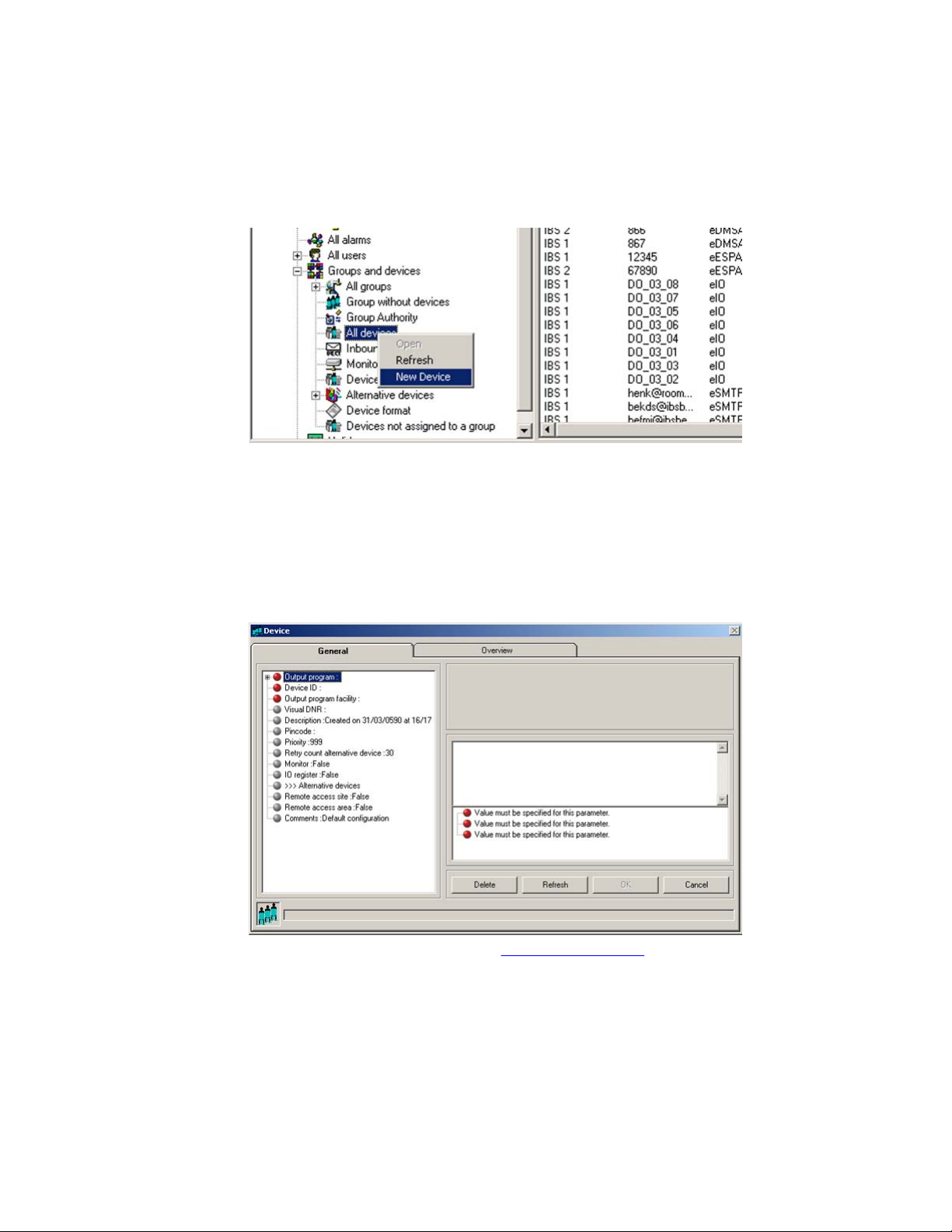
• Expand the Groups and Devices menu by clicking the + to the left of it.
2. Add a new device.
• Right-click the All Devices parameter.
• Select New Device as shown in the following example:
3. Set parameters for the new device.
Note the following when setting parameters:
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
• A red bullet before an item indicates that the item is mandatory.
• Some items contain default parameter values.
• Avaya recommends that you use the Browse option, when present, to define
a location, rather than typing an entry.
The parameters are described in Device parameters on page 25.
4. Confirm your choices.
Click OK and follow the instructions on screen.
5. Assign the new device to a group (optional).
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 23
Page 24
Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
Select All Groups from the Groups and Devices menu, or Group from the input
module menu of your choice.
Changing device parameters
Complete the following steps to change device parameters.
Changing device parameters
1. Access the eCONFIG Groups and Devices menu.
• Open eCONFIG.
• Expand the Groups and Devices menu by clicking the + to the left of it.
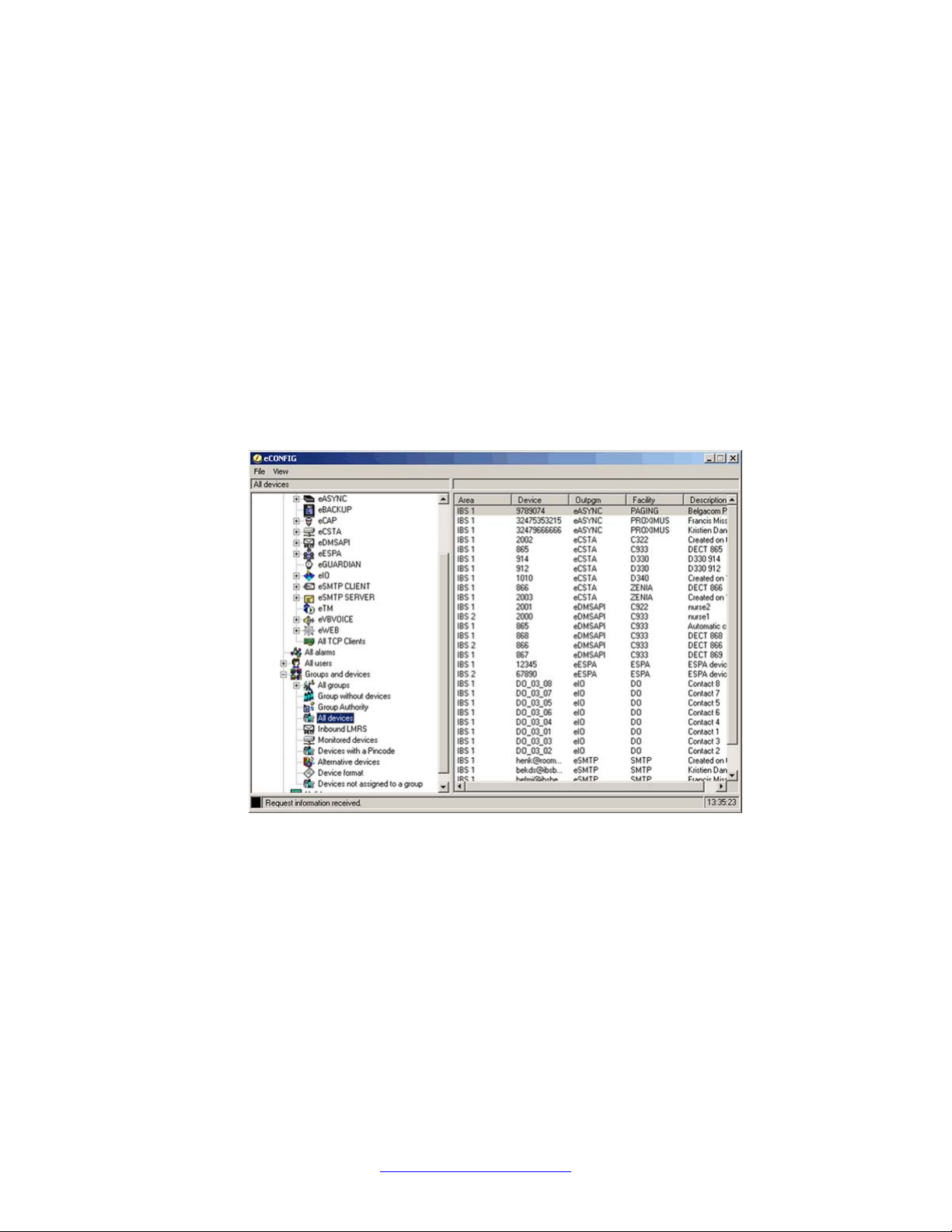
2. Open the All Devices information window.
Left-click the All Devices parameter. The following window appears:
3. Select the device of your choice.
• In the right panel, browse in the list of devices in DECT Messenger.
• Double-click the device that you want to edit. The Properties window of the
device opens:
24 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 25
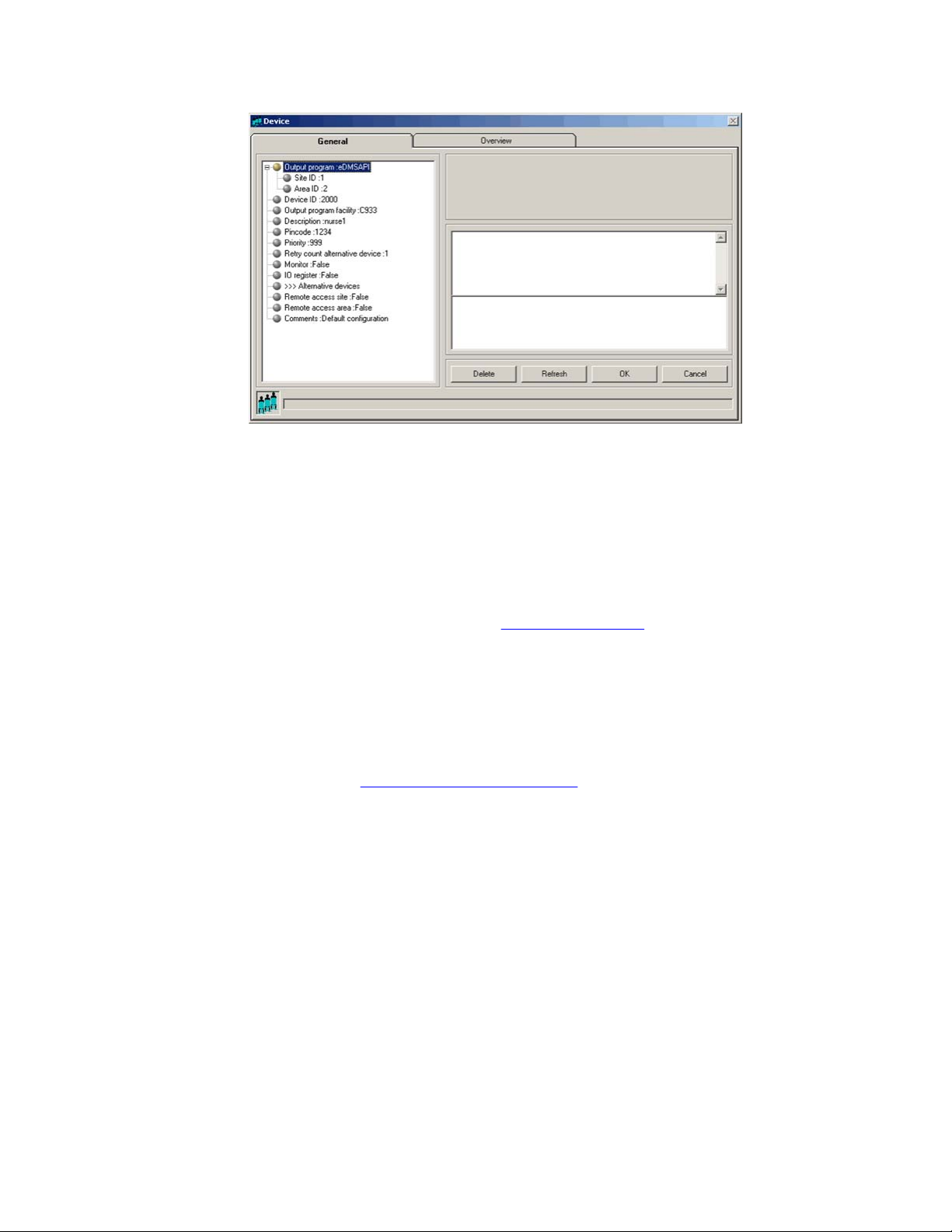
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
4. Change the parameters.
Click the name of the property you want to change. If you edit the parameters, note
the following:
The parameters are described in
5. Confirm your choices.
Click OK and follow the instructions on the screen, if applicable.
Deleting a device
To delete a device, follow
button. DECT Messenger asks you to confirm the action. After you confirm the action, the
device is deleted immediately.
Device parameters
As in previous sections, you can specify the following parameters for a device:
• Output Program
• You cannot change the Output Program, the Site ID, the Area ID, or the
Device ID.
• Avaya recommends that you use the Browse option, when present, to define
a location, rather than typing an entry.
Device parameters on page 25.
Changing device parameters on page 24; at Step 4, click the Delete
This field specifies the output program that processes a request. A device can be defined
in more than one module. The indicated application threads the message using the
capabilities of the infrastructure. The eDMSAPI can, for example, send E2 messages
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 25
Page 26
Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
(non-voice-call to extensions such as DECT C4050 and C4060). The supported output
programs are currently:
- eASYNC for sending SMS to PROXIMUS, or KPN and PAGING to BELGACOM.
- eDMSAPI for sending E2 messages to DECT handsets that support E2 (LRMS).
- eESPA for sending messages to an ESPA 4.4.4 interface (pager equipment).
- eIO for enabling/disabling discrete output contacts.
- eSMTP for sending e-mail to an e-mail provider.
- eSMS for sending SMS messages to GSM phones.
Note:
The output program is associated with a Site ID (which is typically 1) and an Area ID.
If there is more than one entry of the same output program, each one can have a
different area. Select the correct area.
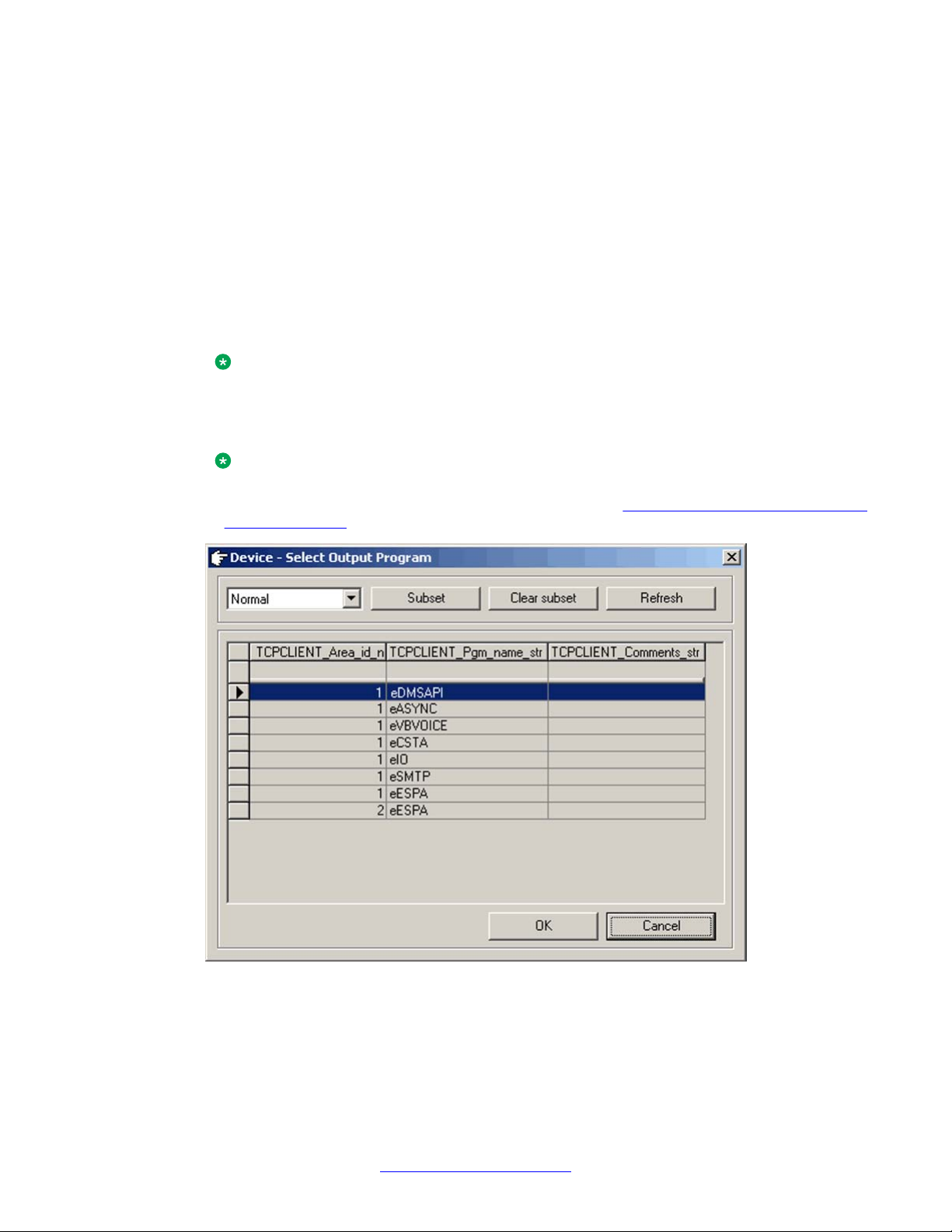
Note:
Selecting the output program is only possible when you create a new device. Always
use the Browse button to select the output program. Figure 8: Select Output Program
browser window on page 26 shows the browser window.
Figure 8: Select Output Program browser window
• Device ID
The device ID is the actual identifier of the device in the output equipment.
26 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 27
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
Device ID consists of <board-id> and <index> delimited with #. For example, 04#01.
Table 2: Variable definitions
Variable Definition
<board-id> A fixed length value, in the range of 01 to 32, which
indicates the DMC card ID in a PBX.
<index> A variable length value, in the range of 00 to 509, which
indicates the index of a DECT handset subscribed to a
DMC card.
The <board-id> value is calculated differently against a system type as follows:
- For a small system, such as Option 11C, the <board-id> of a DMC card placed in
the Main Cabinet/Chassis is the same as the card slot number where the DMC card
is installed (in the range of 01 to 10). DMC card numbering in Expansion Cabinets/
Chassis continues sequentially in the range 11 to 20.
The following table illustrates Device ID numbering for a small system.
Table 3: Device ID numbering for a small system
Cabinet/Chassis Card slot <board id> Device ID
Main Cabinet or
Main Chassis +
Chassis Expander
Expansion
Cabinet or
Expansion
Chassis 1 +
Expander
1 1 01#xxx
2 2 02#xxx
… … …
9 9 09#xxx
10 10 10#xxx
1 11 11#xxx
2 12 12#xxx
… … …
9 19 19#xxx
10 20 20#xxx
- For a large system, such as Avaya Communication Server 1000E, <board-id> falls
in the range of 01 to 32, and is calculated with the formula: <board-id> = 16 *
<shelf_number> + <card_slot_number> + 1
The following table illustrates Device ID numbering for a large system.
Table 4: Device ID numbering for a large system
Shelf Card slot <board id> Device ID
0 0 1 01#xxx
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 27
Page 28
Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
Shelf Card slot <board id> Device ID
0 1 2 02#xxx
… … … …
0 14 15 15#xxx
0 15 16 16#xxx
1 0 17 17#xxx
1 1 18 18#xxx
… … … …
1 14 31 31#xxx
1 15 32 32#xxx
The following table shows examples of valid device IDs.
Table 5: Example device IDs
DMC Card installed in Device ID
2nd slot on Main Cabinet on Avaya CS1000 M, handset is
subscribed with index 01
7th slot of shelf 0 on CS 1000E, handset is subscribed with
index 123
14th slot of shelf 1 on CS 1000E, handset is subscribed with
index 03
02#01
08#123
31#03
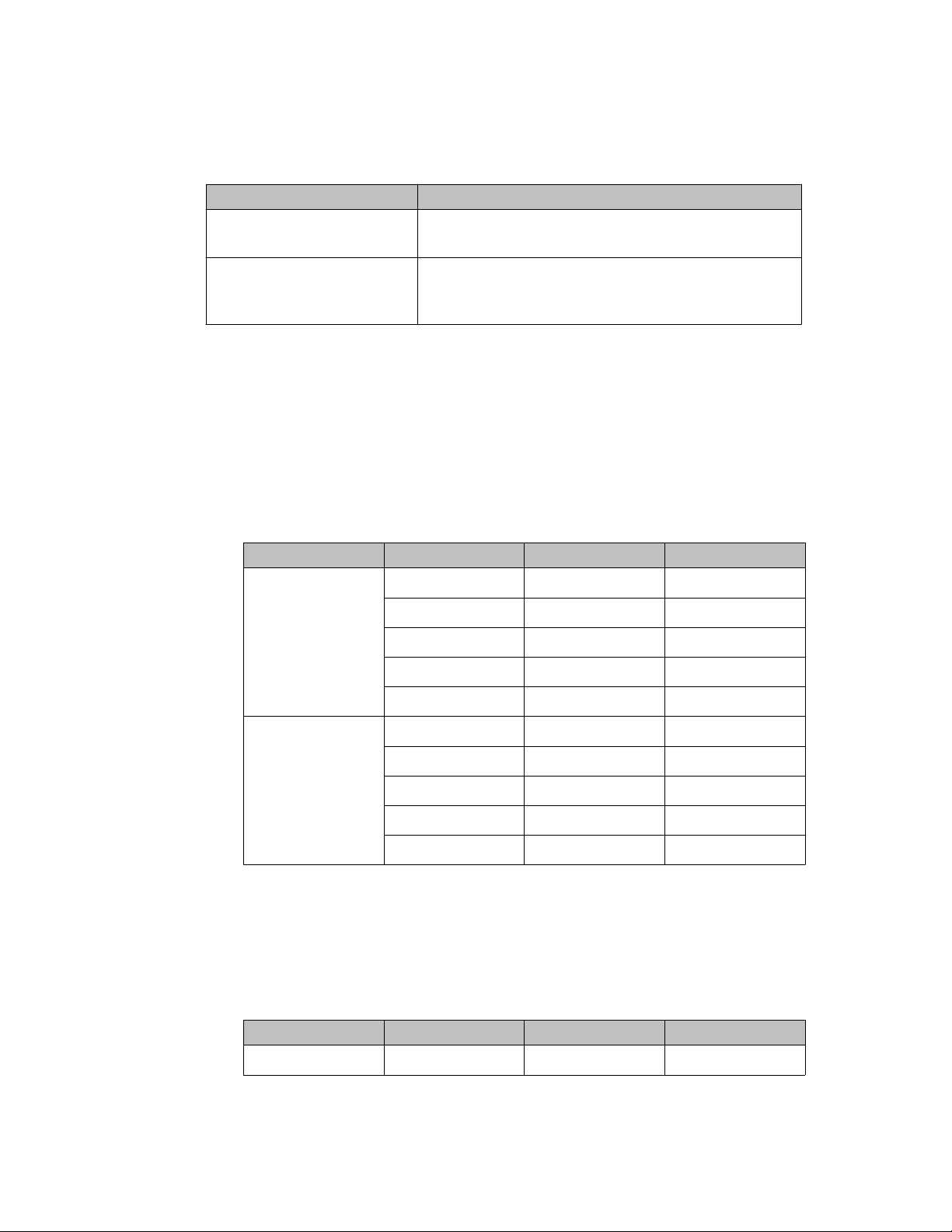
• Output program facility
The indicated application threads the message using the capabilities of the output device.
The display of extensions can differ in character length, and so on. Therefore, DECT
Messenger must know to which device type the message is being sent (for example,
C4050 or 4060 for eDMSAPI).
Use the Browse button to select the correct output program facility .
Figure 9: Device Select
Facility on page 29 shows the selection window for the eDMSAPI.
28 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 29
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
Figure 9: Device Select Facility
• Description
The Description field is used to enter a description of the device. The description is used
to show information about the devices in the web interface (for example, DECT: John
Peterson).
• Pincode
The pincode is used to confirm messages using the eDMSAPI (IC). Confirmation means
that an active alarm on the device is reset from the same or another extension. To reset
the alarm using eDMSAPI (IC), the CLI of the calling extension must be entered here as
the pincode.
• Priority
Reserved for future use.
• Retry count alternative device
Retry count alternative device defines how many times the application tries to deliver
the message before switching to an alternative device (if one is defined in the list of
Alternative Devices in the Groups and Devices menu). The default value is 30.
Therefore, if an alarm has a silence interval (defined in the alarm properties) of 120
seconds, the alarm is removed for this device after one hour (and set for the alternative
device, if defined).
A value of 0 indicates that the application never tries to send the message to an alternative
device, and that the alarm is sent to the device every silence interval until the alarm is
reset by the input program, for example (a reset). A value of 1 indicates that after one
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 29
Page 30

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
attempt, the application clears the message for this device and send the message to the
alternative device, if defined.
Note:
In this second case (value=1), the switch to the alternative device is immediate (that
is, there is no silence interval between the two calls). Therefore, you must ensure that
there are no loop conditions defined in the list of alternative devices.
A value of 2 indicates that the alternative device is contacted after the second attempt.
• IO Register
This parameter is only applicable for devices that are assigned to output program
eDMSAPI.
All devices with this value set to True are monitored by the eDMSAPI to see if an E2
message is sent. After a device sends an E2 message, the message always goes to
DECT Messenger directly (and not to the destination number). Messages sent to DECT
Messenger are processed by DECT Messenger in the same way that messages from
other input devices are processed. There must be a correct specification in the eDMSAPI
inbound configuration that points to a group and an alarm. The message is sent to the
group members in the group that is assigned to the inbound configuration in the
eDMSAPI.
• Alternative devices
Use this parameter to assign one or more alternative devices to a device. After you click
this item, a panel at the right side of the window displays the list of possible alternative
devices. Select New from the menu to add an alternative device. Select Edit to make
changes in the list of alternative devices already assigned to this device.
• Remote access site
The Remote access site parameter is only applicable when you have more than one
site, and you are using the web interface. A web server (eWEB) and a device are each
assigned to only one site; if both are assigned to the same site, you can see the device
from the web interface. Devices assigned to sites other than that to which the web server
is assigned are only visible if the Remote access site parameter is set to True.
• Remote access area
The Remote access area parameter is only applicable when you have more than one
area, and you are using the web interface. A web server (eWEB) and a device are each
assigned to only one area; if both are assigned to the same area, you can see the device
from the web interface. Devices assigned to areas other than that to which the web server
is assigned are only visible if the Remote access area parameter is set to True.
• Comments
This field is informational only, and can contain remarks from the administrator.
30 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 31

Managing groups
Creating a new group
Complete the following steps to create a new group.
Creating a new group
1. Open eCONFIG.
2. Access the pop-up menu of the input module for which you want to create the new
group.
• Select the input module for which you want to create a new group from the
Modules menu.
Note:
A group is always associated with an input module. You cannot create a new
group in the Groups and Devices menu.
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
• Expand the input module for which you want to create a new group. The
instances (eAPI - area Area 1 in this example) of the input module are
displayed.
• Expand the instance. The submenu items Alarm and Group are displayed.
• Expand Group to view all the groups for this instance of the input module.
• Right-click the Group parameter. A pop-up menu opens.
3. Create the new group and set the parameters.
• Select New Group from the Group pop-up menu.
• Enter values for the group parameters.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 31
Page 32

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
After you enter the parameters, note the following:
• A red bullet before an item indicates that the parameter is mandatory.
• Some items contain default parameter values.
• Avaya recommends that you use the Browse option, when present, to define
a location, rather than typing an entry.
Note:
The group name that you enter must match the group name entered for the input
module. If the input module is an eAPI, eCAP , or eESP A, the group name matches
that in the external system. Therefore, you must know the external system that
delivers the group name.
Note:
The input module provides not only a group name, but also an alarm. Ensure that
the alarm from the input module corresponds to an alarm in the alarms list. Ask
a system specialist if you are uncertain about this.
The parameters are described in more detail in
4. Confirm your choices.
Click OK and follow the instructions on the screen, if applicable.
Changing group parameters
Complete the following steps to change group parameters.
Group parameters on page 34.
Changing group parameters
1. Open eCONFIG.
2. Select the input module for which you want to change the group parameters.
32 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 33

Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
Select the input module for which you want to change group parameters from the
Modules menu.
Note:
A group is always associated with an input module. However, to change group
parameters, you can also select a group from the Groups and Devices menu.
3. Open the group.
• Expand the input module for which you want to create a new group. The
instances (eAPI - area IBS 1 in this example) of the input module are
displayed.
• Expand the instance. The submenu items Alarm and Group are displayed.
• Expand the Group item to view all the groups for this instance of the input
module.
• Right-click the Group parameter. A pop-up menu opens.
Note:
This illustration shows the eAPI input module.
• Select Open. The Group Properties/Parameters window opens.
4. Change group parameters.
The parameters are described in section
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 33
Group parameters on page 34.
Page 34

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
5. Confirm your choices.
Click OK and follow the instructions on the screen, if applicable.
Deleting a group
To delete a group, follow Changing group parameters on page 32; at Step 4, click the Delete
button. DECT Messenger asks you to confirm the action. After you confirm the action, the group
is deleted immediately.
Group parameters
You can specify the following group parameters for a device:
• Group ID
The Group ID field defines a unique identifier for a group. The field is a unique key in the
database that is created automatically after you create a new group. The ID consists of
an input program identifier and the group name that you (initially) assigned to the group.
This group ID has an internal (that is, in the database) link to the group members.
• Group name
The Group name field shows the group indicator that is typically received from the
external alarm system through the input program (or generated by the input program itself
if the external alarm system does not provide a group name). In many environments,
alarm systems are capable of sending destination information in the alarm string. For
instance, destination information can be referred to with terms such as paging number,
group, or destination. In most cases, the group names are determined by third-party
vendors and cannot be changed.
34 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 35

Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
Note:
You can use the same group name for more than one input program. You can use the
same group name because the DECT Messenger software adds the input program ID
to the group name, which makes the group ID unique. This group ID is created
automatically after you create the group. However, you can change the group name
later. The Group ID remains the same.
• Description
Administrators can easily recognize the group (for example, Intensive Care) by reading
the descriptive text in the Description field.
• Comments
The Comments field contains additional information. For example, "Warning: minimum
three DECT extensions required".
• Input program
The Input program parameter provides information about the input program. Y ou cannot
change this parameter. After you create a new group for an input program, these
parameters are assigned automatically.
• Group members
Use the Group members parameter to assign group members to the group (assign
devices to the group from the list of devices). After assigned, these devices become group
members. If the device (for example, an extension) that you want to assign is not in the
list, create that device first according to the procedures
Creating a new device on page
22.
Use the Group members menu to open the window shown in Figure 10: Group members
window on page 36.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 35
Page 36

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
Figure 10: Group members window
The section Changing group member parameters on page 40 provides information on
assigning new members, editing members, and deleting members.
• Group authority
The Group authority field defines which users are granted access to the group to make
changes using the eWEB interface, or to use the eCONFIG. If you specify ALL, all users
have access to this particular group, and you do not need to enter all individual users. As
a result, however, you have no granular authority definition, because all users are granted
access. Note that eWEB allows only maintenance of the groups that are assigned to input
programs of the same site as the eWEB. For example, an eWEB instance of site 1 allows
only maintenance of groups of site 1.
Use the Group authority menu to open the window shown in
Figure 11: Group
authority on page 37.
36 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 37

Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
Figure 11: Group authority
Click the New button to give a new user the authority to make changes in the group. Click
the Edit button to edit a user authority.
Warning:
If you want to delete a user from this group, do not click Delete in the window shown
in Figure 11: Group authority on page 37, because that deletes the entire group.
Instead, click Edit. A window specifically for that user opens. Click Delete in this
window to remove the user from the group.
Managing group members
A group has group members. These are devices to which an alarm for that group is sent. You
can assign new members to a group, and you can delete members from a group. These
procedures are described in the following sections:
Assigning a new member to a group on page 37
•
Changing group member parameters on page 40
•
• Removing a group member on page 40
Member parameters on page 41
•
Assigning a new member to a group
Complete the following steps to assign a new member to a group.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 37
Page 38

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
Assigning a new member to a group
1. Open eCONFIG.
Ensure that the member that you want to assign to the group is already in DECT
Messenger as a device. (A group member is a device that is assigned to a group.)
If the member does not exist as a device, see
2. Access the Group Properties window.
Use one of the following methods to access the Group Properties window:
• Select Input Module from the Modules menu.
• Expand the input module for which you want to create a new group.
• Expand the module instance. The submenu items Alarm and Group display.
• Expand the Group item.
• Right-click the Group parameter. A pop-up menu displays.
• Select Open. The Group Properties/Parameters window opens.
or
Creating a new device on page 22.
• Expand the Groups and Devices menu in the eCONFIG main window.
• Expand the All groups menu. All the groups are displayed.
• Open the group properties window by either double-clicking the group that you
want to edit, or right-clicking on the group and selecting Open.
3. Open the Group members window.
Click the >>>Group members item.
38 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 39

Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
A list of group members displays (the example shows only one group member:
device 1010).
4. Add a new member.
• Click New. The following window opens.
• Click the Device ID menu item.
• Use the Browse button to select the device that you want to add as a member
to the group.
Note:
After you select a device, the area and output program are defined automatically
for the member.
For more information on the parameters, see
Member parameters on page 41.
5. Confirm your choices.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 39
Page 40

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
Click OK and follow the instructions on the screen, if applicable.
Changing group member parameters
Complete the following steps to change the parameters for a group member.
Changing group member parameters
1. Open the Group members window.
Follow Steps 1, 2, and 3 in
2. Select the group member to edit.
In the right panel of the window is a list of one or more group members that are
assigned to the group. Select the group member that you want to edit, and click
Edit.
3. Change the parameters.
A window, similar to the one in Step 4 of
page 37, opens, however all parameters are entered.
• Click the item you want to change.
Note:
Y ou can change all parameters except the group ID and the parameters for device
ID.
4. Confirm your choices.
Click OK and follow the instructions on the screen, if applicable.
Removing a group member
Complete the following steps to remove a member from a group.
Assigning a new member to a group on page 37.
Assigning a new member to a group on
Removing a group member
1. Open the Group members window.
Follow Steps 1, 2, and 3 in
2. Select the group member to remove.
In the right panel of the window is a list of one or more group members that are
assigned to the group. Select the group member that you want to edit, and click
Edit.
3. Remove the member from the group.
40 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Assigning a new member to a group on page 37.
Page 41

A window, similar to the one in Step 4 of Assigning a new member to a group on
page 37, opens, however all parameters are entered.
• Remove the member by clicking the Delete button.
4. Confirm your choices.
Click OK and follow the instructions on the screen, if applicable.
Member parameters
Member parameters are parameters that are added to a device for a specific group. These
parameters are only applicable for the combination of a device and a group, and can be
different after the same device is assigned to another group.
The following parameters can be specified for a group member:
• Group ID
The Group ID field defines a unique identifier for a group. The field is a unique key in the
database that is created automatically after you create a new group. You cannot change
the Group ID at this parameter.
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
• Device ID
Use the Device ID parameter to assign each device as a member of a group. Always use
the Browse button that is active after you click this menu item.
The parameters display after you select each device, because these are linked to the
device that you select.
• From:
The From: value contains a value in format xx:xx, where a valid hour and time must be
specified. Valid range is 00:00 to 23:59. Incorrect values give unpredictable results. The
value denotes the start of the time interval during which the defined device is active as a
member of the group. For example, a value of 00:00 indicates that the group member is
active at midnight. V alue 12:00 specifies that the group member starts at noon. The time
interval ends in the time specified in the To: value.
• To:
The To: value contains a value in format xx:xx, where a valid hour and time must be
specified. Valid range is 00:00 to 23:59. Incorrect values give unpredictable results. The
value denotes the end of the time interval during which the defined device is active as a
member of the group. For example, a value of 23:59 indicates that the group member
becomes inactive at midnight. A value of 12:00 specifies that the group member stops its
activity at noon. The time interval begins at the time specified in the From: value (see the
previous bullet). The From: value can be larger than the To: value. In this case, the active
time can start at 21:00 and end at 06:00 (night-shift). Also note that a member can be
active from both 08:00–12:00 and 13:15–17:30. To define two time intervals for the same
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 41
Page 42

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
device, you must define it as two group members (same device): one active from 08:00–
12:00, and the other active from 13:15–17:30.
• Monday . . . . Saturday
This value is a Boolean value: True or False. After set to True, the member is active on
that day.
• Holiday
This value is a Boolean value: True or False. After set to True, the member is to be present
on holidays. The holidays are defined in the Holiday parameter of the eCONFIG menu.
• Activate Timestamp
The Activate Timestamp value specifies the time after the member record is activated.
The timestamp is formatted as follows: YYYYMMDDHHMMSS (for example:
20010101000000). The Activate Timestamp and Deactivate Timestamp is used to
define a time interval during which records are active. This functionality is typically used
in environments where there is extensive up-front planning of staff resources, flexible
schedules, holiday periods, and so on.
• Deactivate Timestamp
The Deactivate Timestamp value specifies the time after the member record is
deactivated. The timestamp is formatted as follows: YYYYMMDDHHMMSS (for example:
20010101000000). The Activate Timestamp and Deactivate Timestamp is used to
define a time interval during which records are active. You can use this functionality to
anticipate future changes in availability of staff, and is typically used in environments
where there is extensive up-front planning of staff resources, flexible schedules, holiday
periods, and so on.
• Comments
The Comments field contains additional information for administrative purposes.
Note:
If a group member is not active because of the member settings, overflow to alternative
devices is not activated.
Managing users
DECT Messenger makes a distinction between the users for eWEB and users for eCONFIG.
The mechanisms for handling these users are exactly the same. The only difference is that the
eWEB users are applicable for Login and Authority levels in eWEB, and eCONFIG users are
applicable for Login and Authority levels in eCONFIG.
42 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 43

Creating a new user
The following procedure describes how to create a new user.
Create a new user
1. Open eCONFIG.
2. Expand the All Users menu.
Note:
Two submenu items are listed: eWEB and eCONFIG. eWEB contains the users
for eWEB, while eCONFIG contains the users for eCONFIG. These are separate
from each other, however the approach and authority mechanism is the same,
so the steps in this section apply to both.
3. Access the pop-up menu.
In the All users menu, right-click either eCONFIG or eWEB.
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
4. Create a new user.
Depending on the option you chose in step 3, select one of the following:
• New eConfig User
• New eWEB User
5. Enter the parameters for the new user.
Select each item in the left panel and enter parameters.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 43
Page 44

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
The parameters are explained in User parameters on page 45.
6. Confirm your choices.
Click OK and follow the instructions on the screen, if applicable.
Changing user properties
The following procedure describes how to change the properties for user.
Changing user properties
1. Open the Group Members window.
2. Expand the All Users menu.
Two menu items are available: eWEB and eCONFIG. eWEB contains the users for
eWEB and eCONFIG contains the users for eCONFIG. These are separate from
each other, however the approach and authority mechanism is the same, so the
steps in this section apply to both.
3. Select the menu item that contains the user you want to edit.
Select either eCONFIG or eWEB, depending on where the user resides. A list of
users opens in the right panel.
4. Open the Properties window for the user you want to edit.
Double-click the user for which you want to change the properties.
5. Change the parameters.
Change the parameters by clicking the item and changing the field contents.
44 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 45
Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
The parameters are explained in User parameters on page 45.
6. Confirm your choices.
Click OK and follow the instructions on the screen, if applicable.
Deleting a user
The following procedure describes how to delete a user.
Deleting a user
1. Open the User Properties window.
2. Delete the user.
3. Confirm your choices.
User parameters
The following parameter descriptions are applicable for the parameters for both eWEB and
eCONFIG users.
• User ID
Follow Steps 1, 2, 3, and 4 of the procedure in
44.
Click the Delete button.
Click OK and follow the instructions on the screen, if applicable.
Changing user properties on page
This is the username that must be entered in the login dialog box. Maximum length is ten
characters. Avaya recommends that you create a user profile for each user who has
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 45
Page 46

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
access to the eWEB interface. Sharing user profiles can result in unauthenticated users,
which generates alarms.
• Password
This field contains a password with a maximum length of ten characters. Users can
change their own password using the eWEB interface. You can create new users with
default passwords (for example, the same as the user identifier), and request that the
users change their password at first usage.
Note:
Passwords are stored without encryption in the DECT Messenger structure. Therefore,
hackers can retrieve authentication information from the system. Also, table information
can be made available through eWEB (depending on your configuration). Because the
security mechanism is limited, Avaya recommends that you not use any passwords
that are used on other systems that contain secured information. Using identical
passwords across both secured and less-secured environments leads to severe
security exposure. Inform all users of this issue.
• Security level
Y ou can use the security level parameter to define a number in the range of 00–99. The
higher the number, the more authority a user is given. The value 99 is the highest level
which gives full access to all menu items, and allows read and edit. This value can be
assigned to top-level administrators. The value 00 is the lowest possible value. Avaya
recommends that you limit the number of initially assigned values to 2 or 3 levels, and
handle increments by 10. Good start values are 20 for low-end users, 40 for mid-range
users, and 60 for administrators. As you become familiar with user patterns, a more
granular level of security can be defined for users.
Note:
The level is related to the values specified in the table of contents of the eWEB module
where a read and edit threshold level is assigned to each individual menu. For example,
a user with level 20 can execute all the functions with level 00 up to 20.
Note:
In the eCONFIG, the level thresholds for the menus are fixed. For all menus, the read
level threshold is 10, and the edit level threshold is 30.
• Description
This is a text description of the user, and is for administrative purposes only. The real
name of the user is often stored in this field.
• Language
You must enter a four-digit code representing the language for the eWEB module. For
the eCONFIG you must fill in a two-character representation for the language (for
example, EN represents English). If you make a mistake, only menu icons are displayed,
and not the menu items.
- Language field for eWEB user
46 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 47

Maintaining DECT Messenger using eCONFIG
The language field contains a four-digit identifier that represents the language used
for eWEB and eGRID access. The codes are those used in an iSeries 400, and are
in the range of 29xx. Currently supported values in eWEB are the following:
• 2909: Belgian English
• 2963: Belgium Dutch
• 2966: Belgium French
Check the commercial documentation to determine if other languages are available.
If other languages are available, the codes are as follows:
• 2922: Portuguese
• 2923: Dutch Netherlands
• 2924: English
• 2925: Finnish
• 2926: Danish
• 2928: French
• 2929: German
• 2931: Spanish
• 2932: Italian
• 2933: Norwegian
• 2937: Swedish
• 2980: Brazilian Portuguese
- Language field for eCONFIG user
The language identifier for the eCONFIG consists of a two-character identifier. For
example, EN represents English, NL represents Dutch, and so on. Check with the
commercial department to determine which languages are available.
• e-mail address
The e-mail address field contains the e-mail address of the user. After the user sends
an e-mail using the web interface (Send SMTP Message menu), this e-mail address is
used in the From: field (that is, the originator address).
• All object authority
The user can maintain all groups in DECT Messenger with the All object authority
parameter. Remember that a user can be assigned to a group. After assigned to a group,
the user (when logged in) can make changes in the group configuration of the groups to
which this user is assigned. However, if the All object authority option is set to True, the
user is allowed to maintain and make changes in all groups in DECT Messenger. This
gives the user administrator privileges for all groups.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 47
Page 48

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
In most cases, the False value is used so that the user does not have all object
authority.
• Security administrator
The Security administrator value is set to either True or False. Set the option to True
to allow the user to maintain the user settings of other users (that is, to give the user
Administrator rights for all other users, including the right to change passwords, and so
on).
There is a difference in implementation between the eWEB and the eCONFIG:
- Security administrator rights in eWEB
After a user with security administrator rights logs in to the web interface, that user has
access to view the eWEB_USER_AUTH table in which the user passwords are visible in
ASCII text. The user can also change the passwords for all users using the Change
Password option.
- Security administrator rights in eCONFIG
Users with security administrator rights in the eCONFIG see a list of all users in the All
users > eConfig user menu. These users can change settings and passwords for all
users, delete users, and create new users.
Users with no security administrator rights see only their name in the All users > eConfig
user menu, and can change only their password (and no other settings).
• Comments
The Comments field contains additional information for administrative purposes.
Adding a DECT device to the Messenger system
Use the following steps to add the basic configuration for a DECT handset.
Adding a DECT device to the Messenger system
1. Configure a device format.
Ensure that you have a Device Format for this type of DECT handset. For
information about configuring device formats, refer to Avaya DECT Messenger
Installation and Commissioning, NN43120-301.
Browse to Groups and Devices > Device Format. If your DECT Handset is
configured under Device Format on the eConfig module, your DECT handset type
is shown beside the eDMSAPI output program.
2. Add new Device.
Within Groups and Devices, right click All Devices, and choose New Device.
48 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 49

3. Configure the new device.
Make the following configuration changes:
• Select eDMSAPI as the Output program.
Adding a DECT device to the Messenger system
• For Device ID, enter either: Board_Number#Index_Number if you are
configuring traditional DECT handsets OR a DN if you are configuring SIP
DECT handsets. Example: For a DMC Card in Slot 4 of an Option 1 1c Cabinet,
and a DECT handset subscribed to index 2, the Device ID is 04#02.
For more information about Device ID, see
• Configure the Output Program Facility according to the type of DECT handset
you have. Example: C4050
• Visual DNR The Directory Number (DN) of the DECT handset. Example: 2947
• Description Add a description of the handset. This can be the name of the
handset owner. Example: Emmett Lee This description is displayed on the
eWeb 'Send DMS-API Message' Extension box.
• Set IO Register to True
4. Check alarms.
• In eCONFIG, open the menu Modules, and expand the eDMSAPI module by
clicking the + beside it. Under the eDMSAPI module, the instances of the input
module (For example, eDMSAPI - area One) are listed. Expand this instance.
The items Alarm and Group appear. Click Alarm.
• Ensure that you have at least two Alarms, as follows:
- E2_MSG_N
Device parameters on page 25
- E2_MSG_U
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 49
Page 50

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
5. Add a group.
• In eCONFIG, open the menu Modules, and expand the eDMSAPI module by
clicking the + beside it. Under the eDMSAPI module, the instances of the input
module (For example, eDMSAPI - area One) are listed.
• Expand this instance. The items Alarm and Group appear.
• Right-click Group, and select New Group in the pop-up menu.
6. Configure the new group.
Make the following configuration changes:
• Populate the Group_Name. If you are adding a single DECT handset, use the
DN of this handset as the group name.
• Populate the Description
• Group Members. Click New. Browse under Device_ID for the device you
created in Step 2.
• Group Authority. Click New. Under User_ID browse for *ALL
7. Open the Inbound data call handling menu.
• In eConfig, open the menu Modules, and expand the eDMSAPI module by
clicking the + beside it. Under the eDMSAPI module, the instances of the input
module (For example, eDMSAPI - area One) are listed.
• Right-click the instance of the eDMSAPI module (For example, eDMSAPI area One), and click Open in the pop-up menu.
• Scroll to the bottom of the menu and expand Inbound data-call handling.
• 3 choices are displayed:
- Inbound
- Inbound Event
- Inbound Result
50 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 51

Adding a DECT device to the Messenger system
8. Configure Inbound data call handling.
Make the following configuration changes for Inbound:
• Click New
• Called Device: Enter the DN of the DECT handset
• Called type: *IA
Make the following configuration changes for Inbound Event:
• Click New
• Called device: Enter the DN of the DECT handset
• Calling Device: *ALL
• Alarm ID for normal messages: Browse and select the alarm E2_MSG_N
• Alarm ID for urgent messages: Browse and select the alarm E2_MSG_U
Make the following configuration changes for Inbound Result:
• Click New
• Called device: Enter the DN of the DECT handset
• Calling Device: *ALL
• Group name: Browse and select the Group you created in Step 4
• Message: [msg] [Calling number]
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 51
Page 52

Avaya DECT Messenger Administrator Guide
52 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 53

Chapter 3: DECT Messenger Customer
Engineer Manual
This chapter contains information on the following topics:
• DECT Messenger overview on page 56
• Modules overview on page 58
DECT Messenger in a WAN or MAN network on page 64
•
• Licensing on page 65
• Detailed module descriptions on page 69
What is required to run DECT Messenger on page 76
•
• DATABASES in DECT Messenger on page 80
Installing and getting started on page 81
•
• Using eCONFIG on page 90
• Using eTM on page 93
eDMSAPI Inbound on page 94
•
• Connecting National Instruments modules on page 110
Understanding Security features on page 119
•
• Using eBackup on page 126
Setting up e-mail integration (eSMTP_Server/eSMTP) on page 130
•
• Using eSMTP Server on page 131
Using eSMTP on page 138
•
• Sending SMS messages on page 139
• V.24 - RS232 connections (eCAP, eESPA) on page 142
Using Import/Export menu on page 144
•
• Checking diagnostics on page 155
Preface
This chapter is for Avaya DECT Messenger version 4.0, and is designed to be used in
conjunction with the information found in other chapters. This chapter describes the steps
necessary to configure and begin using the system. It describes how various modules work,
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 53
Page 54

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
but does not go into detail. For detailed descriptions of modules and how they work, consult
Avaya DECT Messenger Installation and Commissioning, NN43120-301.
The process for installing DECT Messenger is described in Avaya DECT Messenger
Installation and Commissioning, NN43120-301.
Note:
No legal rights can be obtained from the information in this manual.
About the manual
This chapter is the Customer Engineer Manual for DECT Messenger , and is intended to assist
the engineer in understanding the structure of DECT Messenger.
The modules and related database tables are described in detail in the publication Avaya DECT
Messenger Installation and Commissioning, NN43120-301.
Guidelines for maintenance and administration of a server or specialized computer
The following are general rules for administering and maintaining a server or other specialized
computer:
1. Keep operating system and application software up-to-date.
Servers are a critical part of business infrastructure. The operating system and
application software must be current to ensure stable, secure operation. An
automated or semiautomated process for upgrades and patches can be used,
however upgrades and patches can have unpredictable interactions with running
services. Contact Avaya for detailed information concerning the possible impact of
specific updates or fixes.
2. Do not run unnecessary services or applications.
To reduce risk, do not run any non-essential service or application. Problems with
such services or applications include the potential for unwanted interactions
between them (for example, ports that are used by other applications), insufficient
server capacity , and security issues that are introduced by those applications. If you
must run a combination of applications, contact Avaya for more information.
Check the manufacturer's features for other products, and determine whether those
features require resources that DECT Messenger requires.
3. Back up your data.
All computers eventually fail (hardware or software), and after servers fail, the data
stored on them is often lost. Keeping current backups of the system, and data stored
54 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 55

on it, is essential for every production system (servers, specialized machines, and
so on). The backup procedure depends on many factors, such as the following:
• volume of data
• rate of data change
• recovery procedure
• time for backup and recovery
• response of the applications
There are many issues to consider for your backup process:
• Automatic backups can fail
• Certain other applications must be aware when the backup process is taking
place, to avoid conflicts and so on.
Create a backup policy that is built on the existing IT infrastructure. Refer to the
specifications (requirements) for the products involved for detailed information.
4. Keep a record of account maintenance and authorized users.
Preface
Keep a current list of the accounts that have access to the server and the account
privileges. If unauthorized users have access to the server, the entire server activity
can be compromised. Consequently, the business can be compromised (for
example, after confidential information is accessed).
5. Use specialized software for servers.
Consider installing specialized software to provide anti-virus protection,
maintenance tools, and firewall protection.
Firewall policies can be implemented in the entire network based on enterprise
firewalls. Where these are not available, a desktop solution is acceptable. Avaya
applications can use a range of ports and access types. Contact Avaya for
information about ports and access. Anti-virus and firewall software must be
included in the list of applications that require periodic updates.
Popular maintenance tools include ScanDisk and Defrag. After an unpredictable
event, scanning the disk can be performed automatically or manually. Database
applications are very sensitive to this fragmentation, leading to potential
performance bottlenecks or application errors, so Avaya recommends scheduling
regular defragmentation during off-peak hours.
6. Provide physical security for the system.
A power failure is one of the most common problems in a server environment, and
also one of the most dangerous, because power failures can cause data loss after
the system shuts down without closing data files and applications. An
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) filters the current and, in the event of a general
power failure, provides the system with enough power that the applications can
close properly.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 55
Page 56

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
Also consider location and environment (air conditioning, ventilation, and so on) for
the equipment.
7. Avoid renaming computers.
Avoid changing the name of a computer . This type of change can have far-reaching
implications, sometimes necessitating the reinstallation of applications.
DECT Messenger overview
This section contains the following topics:
Avaya DECT Messenger functional description on page 56
•
• Modules overview on page 58
• Linking modules on page 61
Avaya DECT Messenger functional description
DECT Messenger is a software platform that allows message generation, message routing,
and message protocol conversion. DECT Messenger can be used as alarm equipment,
because messages can be configured to indicate an alarm situation. In fact, in the terminology
of DECT Messenger, a message is also called an alarm.
Figure 12: Input and Output on page 56 shows the various inputs and outputs of DECT
Messenger.
Figure 12: Input and Output
56 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 57

Message input
The following input can generate messages in DECT Messenger:
• ESPA 4.4.4 pager protocol: DECT Messenger can receive pager messages from ESPA
4.4.4-compatible pager equipment.
• RS232/V.24 serial input: many protocols are supported as input for generating a
predefined message or a free message.
• DECT handset with E2 (Low Rate Messaging Services [LMRS]) messaging.
• E-mail the DECT Messenger server PC: send a message by e-mail to a telephone set,
SMS to cell phone or any other output on DECT Messenger.
• Switches (push buttons, toggles): message alerts generated by alarm contacts, door
contacts, fire contacts, and so on.
• Analogue voltage/current levels: this form of message generation is used to guard
industrial equipment. For example, equipment output messages can be pressure
indication, temperature, and so on.
DECT Messenger overview
• Web interface from which you generate messages manually.
• Programs you write that communicate (using TCP/IP socket) with DECT Messenger:
DECT Messenger provides a port on TCP/IP that is open to receive input data from this
type of unique program.
• Calling a specific telephone number. In this case the extension number that is dialled in
combination with the originator telephone number (CLI) is used to generate a predefined
message.
• An SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c trap can generate a message.
Message output
DECT Messenger supports the following output:
• DECT E2 messages (up to 160 characters)
Although DECT Messenger supports up to 160 characters, the DECT equipment or the
handset can limit this to 128, or even 48 characters. If the handset supports only 48
characters, the message is broken into sections and sent in parts to the handset.
• Messages sent to Ergoline or DECT extensions during ringing and after a call is
connected.
The first part of the message is sent as an alert phase. The remaining part (if there is
more) is sent in call connect status.
Message length can be specified for each device type. Messages that are too long to be
displayed are broken into sections suitable for the display devices.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 57
Page 58

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
• SMS messages to cell phones
DECT Messenger can send SMS messages to cell phones. The interface to the cell phone
provider can be a modem, or a box that behaves like an actual cell phone with SIM
card.
This option is mainly used as an alternative device. If a message to a DECT handset is
not acknowledged, the message can be forwarded to a cell phone.
• E-mail messages
DECT Messenger can send e-mail, using SMTP, to any e-mail server.
• Digital output to control relays or similar equipment
In the event of an alarm, the relay contacts can be used to control equipment such as
lamps, door-contacts, or hooters. Contacts are used as alternative devices (overflow) in
case a message is not confirmed.
• ESPA 4.4.4 pager protocol
DECT Messenger can send messages to paging equipment using the ESPA 4.4.4
protocol.
• Windows pop-up message.
The capabilities of the Windows operating system can be used to send a popup message,
similar to the NET SEND command.
Modules overview
DECT Messenger consists of separate modules. There are four main groups of modules:
• Core software modules
• Configuration modules
• Input and output modules
• Security modules
The following sections provide an overview of the modules. Detailed module descriptions are
provided in corresponding chapters.
Core software modules
There is one core software module:
• eKERNEL
58 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 59

The eKERNEL is the core software in the system and must always be present. eKERNEL
is between the incoming and the outgoing modules and must always be running. The system
does not operate if eKERNEL is absent or non-functional.
Configuration modules
There are two configuration modules:
• eGRID
The eGRID module is used to make inquiries and to edit the configuration database. The
configuration database (an MS Access database) stores all the configuration data.
• eCONFIG
The eCONFIG module is used to set up and configure the system, messages, and
message flows. The eCONFIG is a user-friendly variant of the eGRID, and can be used
either on the DECT Messenger PC, or on a remote PC.
Incoming and outgoing modules
DECT Messenger overview
There is a wide range of incoming and outgoing modules available. They all communicate with
the eKERNEL module. Each module has a specific incoming or outgoing function. This means
that the incoming modules can receive messages and outgoing modules can send
messages.
Table 6: Incoming and outgoing modules on page 59 provides an overview of the modules.
Table 6: Incoming and outgoing modules
Module Name Function Incoming Outgoing
eCAP V.24/RS232 interface and protocol
converter.
eESPA Input/Output module for ESPA 444
protocol.
eAPI Input on eKERNEL for locally made
programs. A Visual Basic source is
available, which can be used as basis
to make your own input application.
eIO Digital and analogue inputs and digital
outputs (contacts and switches).
Yes -
Yes Yes
Yes -
Yes, analogue
levels and
digital levels
(contacts)
Yes, switches
eWEB Web interface Yes eSMTP-server Receiving e-mail messages. Yes -
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 59
Page 60

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
Module Name Function Incoming Outgoing
eSMTP (client) Sending e-mail messages - Yes
eDMSAPI Sending and receiving LRMS (E2)
DECT messages using the CSTA
interface.
eASYNC Asynchronous modem interface to
cell phone SMS provider, or to wide
area paging system.
eLOCATION Always in combination with eCST A or
eDMSAPI; after location alarm is
triggered, the location of the DECT
handset is detected. This information
is available in the message that is
generated.
eVBVOICE Interactive Voice Responds used to
various message types. Only
available through Professional
Services!
eSNMP Receive an SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c
trap from an SNMP sending process
or equipment.
eSMS Send SMS message to a mobile
phone. Inbound SMS can be used to
confirm alarm.
Yes, receiving
LRMS (E2)
DECT
messages
- Yes
Yes No
Yes Yes
Yes No
Yes No
Yes, sending
LRMS (E2)
DECT
messages
Security modules
The security modules are used (in addition to an operating system) to provide extra security.
Security provided is based on the module type. The following gives a brief overview of the
available security modules:
• eBACKUP
The eBACKUP module creates a backup of the configuration database at regular
intervals.
• eGUARDIAN
The eGUARDIAN module is used in conjunction with an input module that receives data
at regular intervals. The eGUARDIAN module checks the data input at regular intervals.
If the input is not received within a specified time period, the eGUARDIAN module sends
a message indicating that an input is down.
• eWATCHDOG
The eWATCHDOG is a software module that works with the Watchdog card. The
eWA TCHDOG sends a code to a V.24 interface (COM port) on the DECT Messenger PC.
60 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 61

This COM port is connected to a Watchdog card that expects the code within certain time
intervals. If the code is not received within the time interval, the Watchdog card assumes
that the system is down and restarts the PC or activates a alarm indication.
• eTM
The eTM is the Task Manager, which ensures that the DECT Messenger modules remain
active. If a module fails, the eTM reboots the module automatically . Y ou can specify which
modules are monitored by the eTM. The eTM can be installed on the DECT Messenger
PC where the eKERNEL is located, and on other PCs if there are DECT Messenger
modules also running on other PCs. The eTM is always used in conjunction with the
eCONFIG module.
Logging module
The eKERNEL has a built-in logging function that provides technical logging data. For a more
user-friendly logging function, the eLOG module is also available.
• eLOG
DECT Messenger overview
The eLOG module generates log files. These files contain information about processing
individual alarms/messages. The eLOG module is part of the eKERNEL.
Linking modules
All the modules are software modules (e-modules such as eCAP). The core module is the
eKERNEL. All other modules are input/output modules or security modules that communicate
with the eKERNEL module. Modules do not communicate with each other, except through
eKERNEL. The communication between a module and the eKERNEL passes through a TCP/
IP socket. (A socket consists of an IP address and a port number.) The modules can be
anywhere in a TCP/IP network. Figure 13: Example of logical representation of module
links on page 62 shows logical links between the modules. Figure 14: Example of module
links (practical) on page 62 shows a practical example of module linking.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 61
Page 62

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
Figure 13: Example of logical representation of module links
Figure 14: Example of module links (practical)
In Figure 13: Example of logical representation of module links on page 62, four DECT
Messenger modules are shown (eCAP, eKERNEL, eIO, and eDMSAPI). These modules are
grouped around the eKERNEL. Each input/output module (eCAP, eIO, eDMSAPI)
communicates with the eKERNEL through a socket. The default port numbers are shown in
Figure 13: Example of logical representation of module links on page 62. The IP addresses
are the same if the modules are all on the same PC, but the IP addresses are different if the
modules are on more than one PC. After a module starts, it contacts the eKERNEL and
62 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 63

DECT Messenger overview
exchanges data. During this data exchange, the module indicates the IP address (PC) on which
the module is found.
The illustrations show an example with a site and two areas defined. These concepts are
defined as follows:
• Site
The site is the place where the eKERNEL resides. A site has a fixed relationship with only
one eKERNEL. If you have more than one site, you have more than one eKERNEL. Also,
you can have only one eKERNEL for each PC. This results in a fixed relationship among
site, eKernel, and IP address (PC).
Although you can have more than one site in a network with PCs, only one site can be
active at a time. With only one site active at a time, you can set up a second eKERNEL
(that is, a second site) offline. After the configuration is set, you can shut down the first
site, and start the second one.
Table 7: Example of the site definition table on page 63 shows an example of the site
definition table on the DECT Messenger PC, which shows the link between a site and the
IP address of the computer where the eKERNEL for that site resides.
Table 7: Example of the site definition table
Site IP address
1 192.168.1.99
2 192.168.1.34
• Area
An area is a subdivision in a site. An area refers to a connection from an eDMSAPI module
to a PBX. For each PBX you must create an area. The eDMSAPI modules can exist on
the PC where the eKERNEL is running, and also on another PC.
Referring to
Figure 13: Example of logical representation of module links on page 62 and
Figure 14: Example of module links (practical) on page 62, the site and area structure is
shown in Table 8: Site and Area structure on page 63.
Table 8: Site and Area structure
Site Area Module To DMC
1 1 eDMSAPI 1
1 2 eDMSAPI 2
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 63
Page 64

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
You can use this modular structure to do the following:
• install modules on different computers in the TCP/IP network
• set up a standby eKERNEL on a second site
• connect more than one DMC to DECT Messenger
DECT Messenger in a WAN or MAN network
DECT Messenger can be used in a multiunit MAN (IMP network), or in a multinode WAN
(DPNSS network). If DECT Messenger is installed in a multiunit DMC network (MAN), you can
send LRMS (E2) messages to DECT handsets in units other than those in which DECT
Messenger is connected. The IMP links support LRMS (E2) messaging, but this generates a
heavy load on the interunit links. Therefore, Avaya recommends that you avoid sending LRMS
(E2) messages over interunit links. If you must send LRMS (E2) messages to handsets in a
unit other than the one having the DECT Messenger connection, Avaya recommends that you
make a direct DECT Messenger connection to those other units, as well.
Messenger in a multiunit or multinode environment on page 64 shows a configuration in
which DECT Messenger has connections to more than one DMC. The connection between
the units can be either an interunit (IMP) link (MAN) or a DPNSS connection (WAN), because
there is no messaging passing through the links between the units.
Figure 15: DECT
Figure 15: DECT Messenger in a multiunit or multinode environment
Figure 15: DECT Messenger in a multiunit or multinode environment on page 64 shows a
multiunit or multinode network. DECT Messenger must be able to send messages to DECT
handsets in Unit X/Node X and Unit Z/Node Z. On the DECT Messenger computer (Area 1),
the eKERNEL is running with other modules and an eDMSAPI to send messages to Unit X/
Node X. The second computer (Area 2) provides messaging to Unit Z/Node Z. DECT
Messenger contains a table that provides data about the location of the DECT handsets. If
64 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 65

there is a message for a DECT handset in Unit Z/Node Z, the message is transferred first to
the Area 2 computer, and then to Unit Z/Node Z.
Licensing
Licensing is done by means of the following mechanisms.
• CSTA Connection licenses in the ISPBX. See CSTA connection (link) license on
page 65.
• DECT Messenger License Manager. See Figure 16: DECT Messenger License
Manager on page 66.
• DECT Messenger CTI Licenses (for each DECT system). See SOPHO CTI module
License Manager licenses on page 68.
CSTA connection (link) license
Licensing
Each application connected to the DMC through CSTA is licensed through one or more
application license and seat license. For Avaya DECT Messenger 4.0, the number of
application licenses depends on the configuration.
For each DECT Messenger link to a DMC, one application license is needed for the DMS
(DMSAPI).
DMS is needed for sending and receiving LRMS (E2) messages using the CSTA link.
In addition to the application license, you must have seat licenses. For DMS, the total number
of seat licenses is the sum of the following items:
• total number of simultaneous outgoing messages coming from the eKERNEL
• total number of simultaneous outgoing messages coming from the web interface
• total number of DECT handsets that can send LRMS messages to DECT Messenger
Note:
Messages sent to DECT Messenger can be incoming messages to other devices or
incoming confirmation.
At startup, DECT Messenger immediately reserves the licenses needed, although there is no
call yet. If the number of seat licenses in the DMC is less than the number of seat licenses
specified in DECT Messenger, DECT Messenger cannot reserve the licenses and, therefore,
cannot make a call.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 65
Page 66

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
DECT Messenger License Manager licenses
The DECT Messenger License Manager is the Avaya License Manager . This license manager
uses a dongle (using either a parallel connection or USB) and a license file.
Figure 16: DECT Messenger License Manager on page 66 shows the License Manager.
Figure 16: DECT Messenger License Manager
Note:
Figure 16: DECT Messenger License Manager on page 66 also shows the CTI application
as a licensed application. You require this CTI application license only if a connection exists
to the DECT system.
The following licenses are available through the License Manager:
• Application module licenses
These licenses allow you to use a limited set of functionality licenses. Check the
commercial documentation for the list of modules allowed with these licenses.
The following licenses are available:
- Basic Package
- Full Package
- Professional Package (PS)
66 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 67

Licensing
Note:
The application module license is shown under the equipment licenses in the License
Manager.
• Equipment licenses
Use equipment licenses to add extra equipment to DECT Messenger . Equipment can be
an I/O module, a V.24 connection to an external system, a V.24 connection to ESPA
equipment, or connection to a DECT system for location detection.
Equipment for which you can acquire licenses is as follows:
- DECT Messenger eI/O
- DECT Messenger eCAP
- DECT Messenger ESPA444
- DECT Messenger eLOCATION
- eSMS (with SMS_service)
- eSNMP
• Functionality licenses
These licenses allow you to implement certain functionality . The functionality licenses are
submitted to the PC application module licenses. If the PC application licenses do not
allow you to use a specific functionality, you cannot select this functionality in the
functionality list.
Items that appear in the functionality list are as follows:
- DECT Messenger eGuardian
- DECT Messenger eWatchdog
- DECT Messenger eBackup
- DECT Messenger eCONFIG
- DECT Messenger eDMSAPI
- DECT Messenger eASync
- DECT Messenger eWEB
- DECT Messenger eWEB Adv
- DECT Messenger eSMTP Client
- DECT Messenger eSMTP Server
- DECT Messenger eAPI
- DECT Messenger eLog
- DECT Messenger eBVOICE
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 67
Page 68

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
SOPHO CTI module License Manager licenses
You must have SOPHO CTI module application licenses to connect to the DECT system.
Figure 17: SOPHO CTI Module License Manager
For each connection to a DECT system, you require a CTI application license.
The number of CTI message channel licenses you require is the sum of the following items:
• total number of simultaneous outgoing LRMS messages coming from the eKERNEL.
• total number of simultaneous outgoing LRMS messages coming from the web
interface.
• total number of DECT handsets that can send LRMS messages to DECT Messenger.
At startup, DECT Messenger immediately reserves the licenses needed, although there is no
call yet. If the number of CTI licenses (application and seat licenses) is less than the number
of licenses that are specified in DECT Messenger, DECT Messenger cannot reserve the
licenses and, therefore, cannot make a call.
68 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 69

Detailed module descriptions
This section provides detailed information for the following modules:
eKERNEL on page 69
•
• eDMSAPI on page 70
• eIO on page 70
eSMTP on page 70
•
• eSMTP_Server on page 71
eAPI on page 71
•
• eWEB on page 72
• eGRID on page 73
eTM on page 73
•
• eLOG on page 74
Detailed module descriptions
eKERNEL
The eKERNEL module is the main module of the DECT Messenger application.
Depending on the incoming alarm message, a message is sent to a specific group of devices.
The kernel ensures that all necessary devices receive the message. After a confirmation is
required, the eKERNEL sends the message repeatedly until a confirmation is received. A
maximum of 30 modules can communicate with the eKERNEL module.
The configuration is done with either the eCONFIG or the eGrid module.
It is possible to use one eKERNEL for multiple units in a DMC multiunit network (MAN), multiple
units in a DMC DPNSS network (WAN), and/or to one or more Mobile DECT systems. (For
more information on using DECT Messenger in a multiunit environment, see
page 70.)
• eCAP on page 74
• eESPA on page 74
eLOCATION on page 74
•
• eSMS on page 74
eSNMP on page 75
•
• eFR on page 75
Web administrator on page 75
•
eDMSAPI on
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 69
Page 70

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
eDMSAPI
The eDMSAPI module is both an input and an output module, which can send and receive
normal and urgent LRMS (E2) messages to and from LRMS DECT handsets such as 4060,
C4050, C4040, industrial handset. The Windows 2000 CSTA service must be running for the
eDMSAPI module to function. The CSTA service supports simultaneous connections to one
or more DMC units for eDMSAPI. If the DECT handsets are in more than one unit, you can
use an eDMSAPI module on one PC, or you can install eDMSAPI modules on other PCs as
well.
The External Application Interface (EAI) – used for LRMS messaging with the web or external
applications – supports normal, urgent and emergency messages. In previous releases the
SNDEMSG was not available.
The EAI also supports LRMS messages up to 160 characters in length when messaging with
SIP DECT. The EAI only supports LRMS messages up to 48 characters in length when
messaging with the DECT Messenger CPU.
eIO
eSMTP
The eIO module is an input and output module that requires specific additional hardware from
National Instruments. If no COM port in the PC is available, a multi-IO board is required. The
additional hardware uses an RS-232 connection. The eIO module connects external hardware
to the Avaya DECT Messenger. Use either digital or analogue input devices for alarm
generation. These devices connect to the National Instruments panel. The panel informs the
eIO module of the presence of DECT Messenger . Switches, motion detectors, or fire detectors
are used as input devices. Voltage or current levels are used as analogue input devices. An
alarm is activated based on the level of the voltage/current. You also use the National
Instruments panel to switch external hardware on or off when the output component of the eIO
module is being used. More information on the National Instruments panel can be found on
the National Instruments web site (www.ni.com).
The eSMTP module is an output module. Use it to send e-mail alarm messages to a specific
e-mail address. To send e-mails, you must enter the IP address of an SMTP-protocol e-mail
server on the network. An e-mail message is sent to one e-mail address only. No option exists
to send the same message to multiple e-mail addresses simultaneously, although you can
send the same message more than once to different e-mail addresses. The subject of the
message is alarm message, and the body is the alarm message. An SMTP mail server is not
included in the eSMTP module because eSMTP behaves as an e-mail client sending e-mail
messages.
70 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 71

eSMTP_Server
The eSMTP_Server is an input module, and is not an SMTP or mail server . This module must
be used in conjunction with the Internet Information Server (IIS). The IIS is a Windows 2000
component that is automatically installed with Windows 2000 Server. In Windows 2000
Professional, the IIS must be separately installed. Alarms are sent based on the e-mail address
entered in the To: field. The alarm message appears in the Subject field of the e-mail. The e-
mail can be empty, because the content is ignored.
E-mail handling procedure in DECT Messenger
After you send an e-mail message to DECT Messenger , the message enters at the SMTP port
of the IIS SMTP Server. The IIS SMTP Server drops the message in a directory on the hard
disk. The eSMTP_Server module checks this directory at regular intervals for newly arrived email messages. If there is an e-mail, eSMTP takes the message from the directory and
analyses it. The e-mail address entered in the To: field of the e-mail is translated into a device
(or group of devices) to which the e-mail must be sent. The Subject: field of the e-mail informs
the devices of the nature of the message. After the message is processed, the eSMTP_Server
sends a confirmation to the address entered in the From: or X-sender field of the message to
inform the user whether the message is accepted or not.
Detailed module descriptions
eAPI
The eAPI module is simply a TCP/IP socket input on the eKERNEL. You can write your own
program to send data to the eKERNEL and generate an alarm with the eAPI. You can write
your program in any programming language, because the eAPI interface is a socket interface.
For more information on the eAPI interface, see Module eAPI in Avaya DECT Messenger
Installation and Commissioning, NN43120-301. Also included in the chapters are examples of
programming code you can use to write your own eAPI program in Visual Basic. A sample
program is also available that ships with the software, called eAPI. The eAPI program is an .exe
file, and is supplied as source code for Visual Basic. If you are familiar with programming in
Visual Basic, you can use the eAPI to create your own interface DECT Messenger.
The eAPI module is often used to develop an application to convert an unsupported protocol
to the DECT Messenger protocol. This requires a detailed specification of the unsupported
protocol, and a test system that uses the unsupported protocol.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 71
Page 72

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
eWEB
The eWeb module can send messages (entered using a web interface) to:
• LRMS (E2)-compatible DECT handsets (C4040, C4050, 4060, Industrial handset, and so
on)
• e-mail using eSMTP (Client)
• Any other output module in DECT Messenger, for example:
- Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) phones using SMS
- Switch on/off an alarm contact
The eWeb server runs on an Apache web server; IIS web server is not supported. To access
the eWEB application, a username and password are required. The eWeb module offers two
interfaces: basic and advanced.
Basic
Using the eWEB Basic module you can send messages directly to a single device only. After
sending messages directly to a single device (LRMS [E2] compatible DECT handsets and email addresses), no control mechanism is available that keeps track of the messages. The
eKERNEL module does not control the messages. For example:
• Person A has a DECT phone with number 1234. Currently this person is not in the office,
and has forwarded their phone to colleague B, with the phone number 1256:
- If a third party uses the web interface Send DMS-API message to send a message to
Person A, the message arrives on the DECT handset of person Al; it is not forwarded
to Person B.
- If a third party sends a Group, Server or User message to a group of which person A
is a part, the message is forwarded to colleague B. (A group can consist of one
member.)
After sending messages to other devices or a group of devices, you can send to a Server,
Group, or User message.
• Using eWEB Server messages, you can send a text message with a maximum length of
8,16 or 32 characters to a group. You cannot see the members of this group. The
eKERNEL handles this message request as an incoming alarm.
• Using eWEB Group messages, you can send predefined and plain-text messages to a
group of devices. The predefined messages can be split into messages for all groups and
group-specific messages. Y ou can see the members of this group. The eKERNEL handles
this message request as an incoming alarm.
• Using eWEB User messages, you can send predefined and free-text messages to a group
of devices. The predefined messages can be split into messages for all users and user-
72 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 73

Advanced
The eWeb Advanced application is an expansion on the eWeb Basic application. Use the
advanced application to perform system management tasks using the web interface, and to
use script messages for emergency situations.
Use these system management tools when you need a quick overview of the configuration of
the system, or to make changes to groups settings or composition. A Script message contains
actions that must be taken in the event of an alarm. The web user can follow the status of this
alarm using the web browser.
eCONFIG
The eCONFIG module is the module most commonly used to make changes in the
configuration. eGRID can be used to make changes in the configuration directly on the
database level, but eCONFIG is a shell over the configuration, providing a more user-friendly
way of making configuration changes. The eCONFIG module can be installed on the local PC
(where the eKERNEL is running), or on a remote PC. If the module is used on the local PC,
almost all parameters in the system can be changed, and new items can be added. If the
module is used on a remote machine, only the Users, Groups, and Device parameters can be
changed, and new users, groups, and devices can be added.
Detailed module descriptions
specific messages. You can see the members of this group. The eKERNEL handles this
message request as an incoming alarm.
eGRID
eTM
The eGRID module is used for configuration purposes only. You can use MS-Access instead
of the eGRID module; however, the most user-friendly way of making changes in the
configuration database is using the eCONFIG module.
The eTM module is the Task Manager in DECT Messenger. eTM is not a scheduler , but serves
as a monitor to ensure that the modules in DECT Messenger are running. If a module stops,
the Task Manager restarts the module within two seconds. If the Task Manager is running,
Windows cannot be shut down.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 73
Page 74

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
eLOG
The eLOG module provides information on how DECT Messenger has processed an incoming
alarm from the input up to the output device. This can be necessary if, for example, no response
is received to indicate whether a recipient received a message or not. The eLOG module does
not have a user interface, and does not provide charts. However, eLOG provides three *.csv
files that contain detailed information about how the alarm was processed.
eCAP
The eCAP Module handles a V.24 interface. Over the V.24 interface, there can be many
protocol variants. A number of protocols are predefined in the eCAP. For the latest list of
supported protocols, refer to Avaya DECT Messenger Installation and Commissioning,
NN43120-301, or check the most recent commercial documentation. You can use the
eCAP_Generic module to set up your own protocol for incoming character strings using the
V.24 interface. If you need a special protocol over the V.24 connection, you can request that
Avaya create this protocol for you; you must provide a detailed protocol specification.
eESPA
The eESPA module supports the ESPA 444 protocol. Incoming and outgoing eESPA also
supports both types of ESPA stations: Controlling station and Polling station.
eLOCATION
You can use the eLOCATION module to determine the approximate location of a DECT
handset after the handset calls a predefined number. The location information relates to the
Radio Cell from which the call originated. The precision of the location depends on the area
covered by the Radio Cell. The smaller the area covered, the greater the precision of the
location.
eSMS
eSMS is a new output module capable of sending SMS messages to mobile GSM Phones. It
uses a GSM terminal instead of an asynchronous modem to connect to the mobile provider.
As a result there are no longer restrictions on mobile provides, which was the case with
aASYNC module. Also eSMS is more scalable as it can transmit messages faster. Finally
eSMS is capable of handling inbound SMS with a specific syntax to confirm alarms based upon
CLIP or pincode.
74 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 75

eSNMP
eFR
Detailed module descriptions
eSNMP is a new input module and can receive SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 traps to set or reset an
alarm. Configuration tables are available to map the parameters from SNMP environment
(address, community , OID, generic, specific…) into the parameters of Messenger environment
(group, message, set/reset…)
eFR is an add-on module for Messenger that implements fault reporting.
eFR performs the following:
• monitors the DISK state and threshold level
• monitors the NETSTAT like connectivity (client/server)
• performs PING to check responsiveness on ICMP level
Notification at begin and end condition is possible through various transport mechanisms, such
as e-mail, SNMP, NET SEND and SMS.
Web administrator
Although eWEB is still supported, a new Web Administrator is available, with a more attractive
user interface and additional functionality, covering maintenance and reporting.
The Web Administrator must be positioned as the maintenance tool of choice for concurrent
daily maintenance by end-user. For more detailed low-level configuration tasks, for example
regarding system restart - the eCONFIG or eGRID remain the confirmation tool of choice.
Web Administrator provides the following functionality.
• Sending messages directly to devices such as the following.
- DECT handset
- Mobile GSM phone
- Windows pop-up message
- E-mail.
• Sending group and user messages
• Sending script messages
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 75
Page 76

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
• Reporting functions
- Inquiry active alarms and ended alarms
- Inquiry active scripts and ended scripts
• Basic maintenance
- Work with group members
- Work with alternative devices
• Advanced maintenance
- Work with groups
- Work with users
- Work with devices
- Work with facilities
• Expert maintenance
- Import Template configuration
Refer to Avaya DECT Messenger Installation and Commissioning, NN43120-301 for more
information.
What is required to run DECT Messenger
Hardware Requirements
The hardware requirements for DECT Messenger are grouped into mandatory requirements
and optional requirements. The optional requirements depend mainly on the number of
modules and users, and the type of modules.
• Mandatory PC Requirements
- Intel® Pentium® 4 processor, 1.8 GHz.
- 256K cache 256MB SDRAM.
- 10/100 MB Network interface card.
- 3.5 Floppy Drive.
- 10 GB free Hard disk space.
76 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 77

- CD-ROM player.
• Optional PC requirements
- Analogue Modem for remote maintenance/support.
- Analogue Modem for dialling to GSM provider to send SMS messages. Only required
if you must send SMS messages to a GSM (cell phone) provider using a dial-in
option.
- Internal Serial Watchdog (type 1120 from Berkshire Products,
www.berkprod.com).
- National Instruments equipment for Digital input, Digital output (contacts), and
analogue input options (for software module eIO). See the chapter dealing with
National Instruments products inAvaya DECT Messenger Installation and
Commissioning, NN43120-301 for more information.
- V.24 multi port card.
Software Requirements
What is required to run DECT Messenger
DECT Messenger works with the following required and optional software:
• Required software
- Windows 2000/XP Professional or Windows 2000/2003 Server.
- If you decide to use MS SQL Server as the database engine, you must have
Windows 2000/2003 Server. Windows 2000/2003/XP Professional is not supported
for SQL Server. (MSDE is supported under Windows 2000/2003/XP Professional.)
- Minimum required Service Package is SP4.
- WINZIP to unzip the DECT Messenger files during installation.
- Virus scanner, because your DECT Messenger is connected to a network.
• Optional software.
- Internet Information Server (IIS) under Windows 2000. This is only required if you
use the eSMTP-Server module for receiving e-mail.
- Apache WEB server under MS Windows. Apache Web server is an optional
component that is included on the CD-ROM, and can be installed during set up of
DECT Messenger.
DMC Configuration
This section describes DMC configuration requirements and options.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 77
Page 78

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
General
DECT Messenger version 4.0 and later require the following firmware on Avaya DECT Mobility
Cards (DMC):
• DMC-4 Firmware: 45100404.dwl firmware
• DMC-8 Firmware: 47000404.dwl firmware
Connection to a DMC
The DECT Messenger Server can be connected to the DMC (DECT system) using a TCP/IP
connection. Verify that your network allows traffic from DECT Messenger to the DMC.
DECT Messenger uses a CTI port to send and receive LRMS messages, requiring one CTI
Messaging Link for each connection to a DECT system. On the DMC card, the default port
number to be used for LRMS Messages is 1025.
To connect to the DECT system you must have the following applications running on your
DECT Messaging Server.
• DECT Messenger eKERNEL
• CSTA_Service (runs in the system tray)
• DECT Messenger eDMSAPI
The CSTA_Service provides the CTI link to the DMC.
Connection to Multiple DECT Systems
To connect to more than one DECT system you must have a CTI link for each DECT system.
Check your license for the number of CTI links available to you.
For each DECT system, you must configure a new eDMSAPI module instance. Each DECT
System must be configured in a different Area, as shown in Figure 18: Connecting to two DECT
systems on page 79.
78 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 79

What is required to run DECT Messenger
Figure 18: Connecting to two DECT systems
Example: Connecting to Two DECT systems.
eKERNEL and eCONFIG are on PC One, as shown in both Figure 18: Connecting to two DECT
systems on page 79 and Example: Connecting to T wo DECT systems. on page 79. Within the
eCONFIG are two eDMSAPI module instances configured for two areas.
• eDMSAPI Area 1 contains the IP addresses for PC 1, and PBX IP address for DECT
System 1.
• eDMSAPI Area 2 contains the IP addresses for PC 2, and PBX IP address for DECT
System 2.
Table 9: Example: Connecting to two DECT systems
PC 1:
License, Dongle, License Manager eDMSAPI module - Area 2
eKERNEL
eCONFIG
CSTA_Service (With at least 2 CTI links)
eDMSAPI module - Area 1
PC 2:
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 79
Page 80

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
DATABASES in DECT Messenger
This section describes the databases used by DECT Messenger.
Supported Database types
DECT Messenger uses two databases:
• Configuration Database
In this database, all configuration data is stored. You can make a copy of this database
as a configuration backup. This database is always an MS Access type, and has file name:
Messenger_CFG.mdb.
• Dynamic Database
The dynamic database contains all data about messages. There are three types of
databases possible:
- MS Access
This is a simple solution that does not require extra database setup actions. The
disadvantage of the MS-Access type of database is that the database slowly grows,
eventually consuming significant resources. After you shut down the eKERNEL, a
database compression function runs to reduce the size of the database.
The database has the file name: Messenger_DATA.mdb.
The DECT Messenger eKERNEL has direct access to the database. The eWEB module
has access to the database through ODBC.
- MSDE
The MSDE (MicroSoft Database Engine) is the database engine that is used in the
MS SQL database. However, no user interface is available, and the maximum
number of concurrent users is five. This is not a problem for DECT Messenger
because you do not need database maintenance on the DECT Messenger database.
To install the database under MSDE, a Batch file is available. The number of
concurrent users is normally less than five.
The DECT Messenger eKERNEL and the eWEB modules have access to the
database through ODBC. You must set up the ODBC link in the ODBC, which is
described in Installing ODBC.
- SQL Server
80 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 81

This is the most extended type of database. SQL Server provides a user interface
to perform Database maintenance. You must install the DECT Messenger database
in MS SQL Server manually.
MS SQL Server is a licensed product. For more information about the license
structure, consult the Microsoft WEB Site. The MS SQL Server also requires MS
Windows 2000/2003 Server.
The DECT Messenger eKERNEL and the eWEB modules have access to the
database through ODBC.
You must set up the ODBC link in the ODBC, which is described in Installing
ODBC.
How to set up the Databases
Installing and getting started
Setting up the databases is described in
you must decide which type of database to use (MS Access or MSDE).
Note:
If you decide to change database type after the installation is completed, in most cases you
can easily switch between the two. However, you cannot change database type from MS
Access/MSDE to SQL Server, if you are running Windows 2000/2003/XP Professional,
because for SQL Server you must have Windows 2000/2003 Server.
Installing and getting started
After installation you must make some changes to have a functioning system. To install the
software, follow the actions in the procedures in the following sections.
Switch the Default WEB access in IIS off to avoid conflicts with the Apache WEB server in
DECT Messenger
Stopping IIS WEB Services
Installing and getting started on page 81. However,
Note:
This section is only applicable if Internet Information Services (IIS) is installed in your
Windows 2000 configuration, and the Apache Server is installed for DECT Messenger WEB
access.
If the Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) is installed in Windows, you must stop the
IIS WEB Services, otherwise IIS conflicts with the Apache Server. Stopping the WEB services
of IIS is described in Stopping WEB Services IIS for DECT Messenger on page 82.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 81
Page 82

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
Stopping WEB Services IIS for DECT Messenger
1. Open the Internet Information Services (IIS) window.
Open IIS by clicking Start on the Windows task bar, and choosing Settings Control
Panel > Administrative Tools > Internet Services Manager.
2. Expand the PC name.
If the PC name is not expanded, click the + sign next to the name to expand the list
and access options for the FTP, WEB, and SMTP services.
3. Stop the Default Web Site.
Right-click Default Web Site to access the pop-up menu. Select Stop in this
menu.
Note:
If the Default Web Site is already stopped, IIS has detected that a conflict on port
80 has occurred with the Apache Web server. Stopping the Default Web Site
prevents this conflict.
4. Verify that the service is stopped.
Ensure that the State column indicates (Stopped) next to Default Web Site.
IIS no longer starts the Web services.
Installing DECT Messenger
The software installation process is described in Avaya DECT Messenger Installation and
Commissioning, NN43120-301.
82 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 83

Installation of DECT Messenger Software
1. Verify that the licenses and Options are set correctly in the DMC.
2. Verify that the CSTA link to the DMC is installed and operational.
3. Verify license availability.
Ensure that you have a DECT Messenger application license available, and that
you have sufficient Seat licenses for DECT Messenger.
Note:
After DECT Messenger starts, the eDMSAPI module reserves the number of
licenses that are specified in the eDMSAPI configuration. If the DMC does not
have sufficient seats for these reservations, the connection to the DMC generates
errors.
4. Follow the Installation instructions.
The installation procedure is described in Avaya DECT Messenger Installation and
Commissioning, NN43120-301.
Installing and getting started
After the installation of DECT Messenger, carry out the next procedure,
Services on page 81.
Getting Started
After installation, you can start DECT Messenger by restarting the PC. Getting Started provides
the procedure to start using the system.
Note:
To load your license file you must first acquire the License file licxxxx.lic and the DECT
Messaging USB Dongle
Getting Started
1. Install the dongle and start the License Manager.
Stopping IIS WEB
• Click Start on the Windows task bar and choose Programs > SOPHO CTI >
Configurators > License Manager:
• The License Manager window appears, and a dialog appears requesting a license
file.
2. Select the license file.
• Browse to the location where your license file is located, and click Open.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 83
Page 84

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
• Close the License Manager.
3. Install a preconfigured database, if you have one.
DECT Messenger already contains a configuration database with data. However
you must adapt the data in the database to your needs.
However, if you have a preconfigured database, specifically made for your system,
you must install that database into the database directory, by carrying out the
following steps:
• Open the following directory using the Windows Explorer: c:\SOPHO
Messenger@net\mdb\.
• If the file messenger_CFG.mdb file exists, rename it with the following name:
previous_messenger_CFG.mdb.
• Copy the preconfigured database into the directory: c:\SOPHO
Messenger@net\mdb.
• Rename the copy with the following name: messenger_CFG.mdb.
4. Configure eGRID tables.
If you are not familiar with eGRID, skip to step 5. If you are familiar with eGRID, edit
the following tables:
• eKERNEL_AREA
• eKERNEL_SITE
• eDMSAPI
• eKERNEL_DEVICE
• eWEB
Use the help information to fill in the tables.
5. Start eCONFIG.
84 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 85

Installing and getting started
If you have already edited the tables using the instructions in step 4, skip to step 7.
If not, start eKERNEL:
• Click Start on the Windows task bar, and choose Programs >... eKERNEL.
• Start the module eCONFIG.
• Log in as user: admin, with password: admin.
6. Enter configuration values.
• In the eCONFIG window, double-click the Site Site1 line. The following window
opens:
• Enter the Administrator name and Administrator e-mail.
• Enter the IP address of the PC where the eKERNEL resides in the field:
eKERNEL IP Address.
• Click OK.
7. Verify the Configuration database path.
Still in the eCONFIG window, you must specify the database locations (the default
database path are usually correct).
• Set the path to the Messenger Configuration database to the following
directory: c:\SOPHO Messenger@net\Mdb\ (unless you have installed to a
directory other than the default). The file name is Messenger_CFG.mdb.
• Verify the path setting for the Configuration database; normally you do not need
to change this.
Note:
The Configuration database type is always MS Access and always points directly
to a file (not using ODBC). The default setting is shown in the following illustration:
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 85
Page 86

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
8. Check the Dynamic database path.
eKERNEL must have a valid path to the dynamic data database (the default
database path are usually correct). Determine which type of database you are using:
MS Access, MSDE, or SQL Server. The settings for MSDE and SQL Server in this
window are the same as the settings in eCONFIG.
• If you are using the MSDE or SQL Server database, ensure that you have set
up the ODBC configuration for the eWEB correctly. Ensure that you have
installed the Messenger_Data database in MSDE (by running a Batch file), or
in SQL Server, using the instructions in Avaya DECT Messenger Installation
and Commissioning, NN43120-301.
• Set the path to the MS Access database: By default this database resides in
the following directory: C:\SOPHO Messenger@net\Mdb\. The file name is
Messenger_DATA.mdb. The following illustration shows the setting for the
default configuration.
• Configure the path for the MSDE or SQL Server database: The path setting for
the MSDE or SQL Server database must point to the ODBC link that you created
after you installed the eWEB module.
86 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 87

Installing and getting started
Note:
The path setting for the MSDE or SQL Server database must be assigned as
System DSN in ODBC.
Before you continue, ensure that you know the username and password for the
database. Normally the User ID (login name) for the database is sa, and the
password is sa. The following illustration shows the eKERNEL settings for the
Messenger_DATA database with User ID sa and password philips (the default
password is sa).
Note:
The Data Source =127.0.0.1 points to the local host. If you do not enter this
information, the eKERNEL automatically assumes that the data source is local.
Therefore, if the ODBC is on the same PC as the eKERNEL, you do not need to
enter the Data source at all, as shown in the following line:
Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Persist Security Info=False;User
ID=sa;Password=philips;Initial Catalog=Messenger_DATA;
9. Set Area.
Double-click the menu Areas. Change the Area name of Area 1. If necessary
remove or change Area 2. This field defines the Area number/name relationship for
administrative purposes.
10. Open the property settings for eDMSAPI.
• Expand the module eDMSAPI, by clicking the + sign in front of it.
• Double-click the instance of the eDMSAPI to open the parameter/property
settings.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 87
Page 88

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
11. Enter configuration information.
Enter the correct values for the IP addresses:
• Area Description - Description field for the DECT system you are connecting
to. Seats Count - Total number of seats you require. (See the Note at the end
of this list)
• Seats count for eKERNEL - Default value = 10
• Seats count for external - Number of seats for eWEB - Default = 3
• External IP address - The IP address of the PC on which the eDMSAPI runs
External Port - Default = 2010
• API Address - IP address of the PC where the CSTA_Service is running API
Port - Default = 59000
• PBX Address: IP address of the DMC on the DECT System you are connecting
to.
• PBX Port - Always 1025 for DMC PBX Type – CS 1000
• PBX License - Always Messenger
• PBX Type - Always Avaya
Note:
Only specify the number of seats you anticipate requiring, (not the total number
of seats allowed by your license), as takes longer for seats to register. Ensure
that you do not exceed the number of seats (CTI Messaging Channels) as
specified in your license Manager. If the number of seats is not sufficient in the
License, you cannot make an LRMS (E2) message call.
12. Add a DECT Device.
88 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 89

13. Configure eWEB module.
• Expand the item Modules > eWEB Module. One instance of the eWEB
module: eWEB - area <x> is shown.
• Double-click the eWEB instance to open the parameters/properties. Click IP
addresses, as shown in
line in the right pane contains the loop back address (127.0.0.1) of the PC. Do
not change this. The second line contains the correct IP addresses.
• Select the second line, and click Edit.
• Enter the IP address of the PC where the Apache server resides in the field:
eWEB_address_str.
• Enter the IP address of the PC where the eKERNEL resides in the field:
eWEB_ekernel_address_str.
• Any data in additional lines is normally not relevant, and can be deleted.
Note:
To delete a line:
- select the line.
Installing and getting started
Figure 19: eWEB Properties on page 90. The first
- click Edit.
- click Delete.
Warning:
Do not select a line and click Delete, because that deletes the entire module.
• Click OK to save the new settings.
14. Verify the operation of DECT Messenger.
• Start the eKERNEL from the shortcut in the Windows Start menu.
• Start the CSTA_Service. This appears in the system tray.
• Start the eDMSAPI module.
• Open your WEB browser, and enter the correct DNS name or the IP address
of the PC where the Apache WEB server resides.
• Log in with the name that you specified in the table eWEB_USER_AUTH. The
web page opens.
• In the left pane, go to Send DMS-API Message. Enter a message, and select
an extension from the list. Note that the information in the list comes from the
table: eKERNEL_DEVICE.
• Click Enter to send the message.
Verify that the message arrives at the extension that you have specified; if the
message arrives, your DMS-API is working correctly.
Now you can set up the other modules as needed.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 89
Page 90

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
Figure 19: eWEB Properties
Using eCONFIG
The eCONFIG Module is the tool most commonly used for making changes in the configuration.
The configuration is stored in a Database. Be cautious when editing the database, because
incorrect or invalid entries can interfere with the operation of DECT Messenger.
You can use the eCONFIG on the local PC that is the DECT Messenger server PC. You can
also install the eCONFIG on a remote PC to perform remote configuration maintenance. The
database is handled is differently for local and remote maintenance.
Using eCONFIG (Local) on the DECT Messenger Server PC
After the eCONFIG is installed on the DECT Messenger server PC the database is handled
as shown in
(Local) on page 91.
Figure 20: Database handling with eCONFIG on the DECT Messenger Server PC
90 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 91

Using eCONFIG
Figure 20: Database handling with eCONFIG on the DECT Messenger Server PC (Local)
After you start the eCONFIG for the first time, a copy is made of the configuration database of
DECT Messenger (Messenger_CFG.MDB). This copy is stored in the eCONFIG directory: C:
\SOPHO Messenger@net eConfig\Mdb with the file name: Messenger_WRK.cfg. After you
make configuration changes using the eCONFIG, these changes are stored in the copy of the
database (Messenger_WRK.cfg) in the eCONFIG directory. To make these changes active,
you must:
Making configuration changes active
1. Close down eTM, eKERNEL, eWEB, and so on.
2. Close eCONFIG using the menu option File > Exit. The operational database is
deleted automatically. The database from the eCONFIG is stored into the DECT
Messenger directory, and renamed to Messenger_CFG.MDB, which is the new
operational database.
3. Restart the modules that you closed down; your new configuration is active.
Note:
After you make changes in the copy of the database in eCONFIG, ensure that nobody else
is making changes in the operational database, as that causes an error if you try to shut
down the eCONFIG and write the database back into the DECT Messenger directory.
Note:
If there are Monitored devices in the active configuration, and one of these devices initiates
a follow-me, the diversion information is stored in the active database. Therefore, you cannot
restore the eCONFIG database, and any changes you have made are lost (except for the
changes in Users, Groups, and Devices, as explained in the following paragraph).
If you make changes in Users, Groups or Devices, these changes are stored in the eCONFIG
database (Messenger_WRK.cfg) and in the operational database (Messenger_CFG.mdb),
and are therefore immediately activated. Saving this information into the operational database
is done by sending an XML string from the eCONFIG to the eKERNEL. The eKERNEL stores
this information into the operational database.
• Starting up the eCONFIG again
After you start the program again, eCONFIG finds a database in its directory . eCONFIG asks
you whether you want to continue with this database or retrieve a fresh copy from the
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 91
Page 92

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
operational database. Avaya recommends that you make a fresh copy of the operational
database, because then you are sure there is no database inconsistency.
Using eCONFIG (Remote) on remote PC (client) in the Network
After the eCONFIG is installed on the DECT Messenger server PC the database is handled
as shown in Figure 21: eCONFIG database handling when used on a remote PC (client
PC) on page 92.
Figure 21: eCONFIG database handling when used on a remote PC (client PC)
After you start the eCONFIG for the first time on the remote PC, a copy is made of the
configuration database of DECT Messenger (Messenger_CFG.MDB). This copy is stored on
the remote PC where the eCONFIG is running, in the eCONFIG directory: C:\SOPHO
Messenger@net\eConfig\Mdb with the file name: Messenger_WRK.cfg. You cannot make
system configuration changes in this database, only changes in:
• Users
• Groups
• Devices
After you make changes in Users, Groups or Devices, these changes are stored in the
eCONFIG database (Messenger_WRK.cfg) and in the operational database
(Messenger_CFG.mdb), and are therefore immediately active. Saving this information into the
operational database is done by sending an XML string from the eCONFIG to the eKERNEL.
The eKERNEL stores this information into the operational database.
Note:
If more than one eCONFIG is active at the same time on different PCs, the individual
eCONFIG databases are not updated or synchronized after changes are made in one
eCONFIG. Only the operational database, and the database in the eCONFIG module where
the change is made, are updated. Changes made in Groups using the eWEB interface are
92 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 93

not written into the databases of the eCONFIG modules. These changes are only written
into the operational database, not into the eCONFIG databases.
• Starting up the eCONFIG again
After you start the program again, eCONFIG finds a database in its directory . eCONFIG asks
you whether you want to continue with this database or retrieve a fresh copy from the
operational database. Avaya recommends that you make a fresh copy of the operational
database, because then you are sure there is no database inconsistency.
Using eTM
The eTM is the Task Manager in DECT Messenger. The eTM opens in the Windows system
tray, and monitors the modules of DECT Messenger. If a module shuts down, eTM restarts
it.
eTM searches for the following key in the system registry to find out which modules to start,
and which PC to start them on:
Using eTM
(HKEY_Current_User/Software/Philips/c:\SOPHO Messenger@net/eTM).
The registry is not filled in automatically. You must edit it manually, with the help of a registry
file, which is generated after you close down the eCONFIG using the File > Exit menu. You
can also create the registry files using eGRID, using the button Generate Registry files for
eTM in the right-top corner of the interface. The registry files are stored in the following
directory:
C:\SOPHO Messenger@net\exe\
An example of the file name is as follows:
eTM - Site 1 - Environment: LOCAL.reg for the local PC, which is the PC where the eKERNEL
is running.
If you have modules running on other PCs, other registry file names are given, which are to
be executed on the PC where the modules are running. For example:
eTM - Site 1 - Environment: 192.168.1.81.reg for the PC with IP address 192.168.1.81.
Note:
On these PCs you must also have eTM running if you want to use the Task Manager.
Note:
An Environment is specified in the name of this registry file. The Environment is the IP
address of a PC where a module is running. On that PC you must install the registry file, if
you want to use the eTM on that PC.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 93
Page 94

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
Environments defined as LOCAL refer to the PC where the eKERNEL is running, whereas
environments that have an IP address refer to the IP address of the PC where the modules
are running.
To add the contents of the registry file into the registry, double-click the *.reg file. To remove
the contents from the registry again, open the registry, go to (HKEY_Current_User/Software/
Philips/), and remove the key of a module from the registry.
eDMSAPI Inbound
The eDMSAPI supports inbound LRMS (Low Rate Message Services) calls from DECT
handsets that support LRMS (E2) messaging.
There are several types of incoming calls, which are briefly explained in the following
subsections.
Incoming Alarm (IA) from DMC
Incoming Alarm is an LRMS (E2) message that is sent from an LRMS DECT extension to an
extension number (DNR) in the DMC. However, the DECT handset from which the LRMS (E2)
message is sent is monitored (IO Registered) by DECT Messenger . The message is delivered
to DECT Messenger , instead of to the intended destination. Therefore, if you send a message
from one DECT handset to another, and the originating handset is IO Registered by DECT
Messenger, this message is not sent to the intended destination directly; DECT Messenger
decides what to do with the message. DECT Messenger treats this incoming message in the
same way as any incoming message, and sends it to the devices specified in a group.
Note:
A message sent from an IO registered DECT handset to another DECT handset always
uses DECT Messenger, with a Group-to-Group Member-to-Device structure.
94 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 95

eDMSAPI Inbound
Figure 22: Incoming alarm (IA) in eDMSAPI
Figure 22: Incoming alarm (IA) in eDMSAPI on page 95 illustrates the handling of an incoming
message (IA) in the eDMSAPI module, as follows:
• DECT extension 2000 sends a message to extension 1200. DECT extension 2000 must
be IO Registered in the Device settings for extension 2000. Therefore, all LRMS (E2)
messages that extension 2000 sends are sent to DECT Messenger.
• DECT Messenger checks the intended destination of the message. If that destination is
in the Inbound configuration in the eDMSAPI module, the message is regarded as a valid
call.
• Based on the combination of the Originator (2000, in this example), and the intended
destination (2500, in this example), the message is transferred to a Group in DECT
Messenger with an appropriate Alarm Identifier. The Group contains Group members
(Devices) to which the message is to be sent.
• If the Group member is extension 2500 (DECT) then the message arrives in the display
of extension 2500.
Incoming Alarm (IA) from IP DECT
Incoming Alarm is an LRMS (E2) message that is sent from an LRMS DECT extension to
another extension number (DNR). In an IP DECT configuration, no direct messaging between
handsets is possible. Instead, the message is available at a TCP/IP port on the IP DECT
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 95
Page 96

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
system. The DECT Messenger system retrieves Incoming Alarms from IP DECT through this
TCP/IP port.
If a DECT handset needs to send messages to DECT Messenger, the extension number of
the handset must be IO monitored (IO Registered) in DECT Messenger. After an incoming
message is received by DECT Messenger from a handset, the message goes to a group that
contains devices. The incoming message is sent to all the devices specified in the Group.
Note:
The IP DECT system does not support sending a message from one DECT handset to
another directly. For sending a message from one DECT handset to another, you always
need a DECT Messenger system.
Incoming Confirmation (IC)
Incoming Confirmation is an LRMS (E2) message that is sent to an extension number (DNR)
in the DMC, and is used to reset an outstanding alarm on a device. The DECT handset from
which the LRMS (E2) message is sent, is monitored (IO Registered) by DECT Messenger . The
CLI of the DECT extension is used as identifier for resetting an outstanding Alarm on a Device.
The PIN code that is specified in the device settings must match this CLI of the DECT
extension. The message that the DECT extension sends is simply ignored.
The extension number to which the message is sent for IC can be a hardware-less Directory
Number (DN) in the DMC.
Note:
A message sent from an IO registered DECT handset to another DECT handset uses DECT
Messenger, with a Group-to-Group Member-to-Device structure.
Parameters required to set an alarm
The structure of DECT Messenger is based on five parameters that are required for generating
an alarm. Those five parameters can come from the input device. The input modules eAPI and
eCAP show that these parameters are required.
page 97 shows the Sending Message option of the eCAP generic, and shows the
parameters.
Figure 23: eCAP Sending Message option on
96 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 97

eDMSAPI Inbound
Figure 23: eCAP Sending Message option
Not all input devices are capable of generating all five input parameters. If parameters are
missing (for example, if a switch is connected to the eIO module), the parameters are taken
from fields in tables.
The following five parameters are needed.
• *SET/*RESET
This is described in
SET/RESET structure on page 103.
• Group
The Group is used to define the destination. The Group contains group members, each
of which is a device.
Note:
This requires that the Group must be defined in DECT Messenger , otherwise an alarm
for a certain group comes in but there is no group specification, which means that the
alarm cannot be delivered.
• Alarm Description
The Alarm Description refers to the eKERNEL_Alarm table, which contains all the
properties that are associated with that specific alarm, such as Priority , ringing time of an
extension, the repeat interval time, and so on.
• Message
This is the actual message that is transferred to the device.
• Remove After: *SENT, *RESET, *CALCULATE
This is described in
Alarm handling is shown in
SET/RESET structure on page 103.
Figure 24: Alarm handling on page 98, which illustrates an input
program that provides the input parameters.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 97
Page 98

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
Figure 24: Alarm handling
Note:
These input parameters can come from external sources (for example, eCAP or eAPI) or
partly from configuration tables.
Detailed explanation of the five parameters
• Group
The input program provides a Group name to which the alarm must be sent. This Group
name must be defined in the eKERNEL_GROUP table. From this eKERNEL_GROUP
table a reference is made to the eKERNEL_MEMBER table. Here, the members in the
group are defined. These members are already the actual devices to which the alarm
must be sent. Therefore, the Group name defines to which devices the alarm is sent; the
Group name is needed to connect the input program with the output devices. In fact, the
tables eKERNEL_GROUP and eKERNEL_MEMBER in the configuration database are
filled in correctly after you use the eCONFIG module for configuration.
Figure 25: Input/output relationships on page 99 shows an example of the relation
between the input program and the output devices, and uses the eIO Module as input
module.
98 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 99

eDMSAPI Inbound
Figure 25: Input/output relationships
Figure 25: Input/output relationships on page 99 shows the settings in the input module
IO, and illustrates the relation between the contacts (push buttons, switches) that are
connected to the module. For example, contact 01 under eIODI_Contact_str has the
Group name Fire1 in the column eIODI_GRP_str. Only eIODI_Group_ is shown in
Figure
25: Input/output relationships on page 99.
Under the eIO Module in the eCONFIG, two menus appear: Alarm and Group. Under the
Group menu, the groups that are specified in the eKERNEL for that input module are
displayed, as shown in
Figure 26: Groups in an input module on page 100.
DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012 99
Page 100

DECT Messenger Customer Engineer Manual
Figure 26: Groups in an input module
A Group name must match a Group name that comes from the input module. In this
example, the Group name (Fire1) must match the Group name that is assigned to the
input contact (01) in
Figure 26: Groups in an input module on page 100. Under the Group
name Fire1, two Members are listed, which are actual output Devices (Device 2000 and
Device DO_02_01).
If a user presses the button connected to Contact 01, the Input Program eIO generates
an Alarm for group Fire1. eIO sends this information to the eKERNEL, where a group is
present with the name Fire1 for the eIO Module. The alarm is passed on to the group
Members: 2000 and DO_02_01.
• Alarm
The Alarm description also comes from the input program, and can be the identifier of the
input program or a character string that is received from an external device (for example,
eCAP, eAPI).
100 DECT Messenger Fundamentals March 2012
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
 Loading...
Loading...