Page 1

Configuring Data Compression Services
BayRS Version 13.10
Site Manager Software Version 7.10
Part No. 117352-D Rev. 00
November 1998
Page 2

4401 Great America Pa rkw ay 8 Federal S treet
Santa Clara, CA 95054 Billerica, MA 01821
Copyright © 1998 Bay Networks, Inc.
All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. November 1998.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data,
and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or
implied warranty. Users must t ak e full re spo nsibility fo r th e ir app lica tio ns o f any products specif i ed in th is d ocum ent .
The information in this document is proprietary to Bay Networks, Inc.
The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement and may only be used in accordance
with the terms of that license. A summary of the Software License is included in this document.
Trademarks
AN, BN, FRE, and Bay Networks are registered trademarks and Advanced Remote Node, ARN, ASN, BayRS,
BayStack, System 5000, and the Bay Networks logo are trademarks of Bay Networks, Inc.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are t he property of their respective owners.
Restricted Rights Legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer So ftware clause at DFARS 252.227-7013.
Notwithstanding any other license agreement that may pertain to, or accompany the delivery of, this computer
software, the rights of the United States Government regarding its use, reproduction, and disclosure are as set forth in
the Commercial Computer Software-Restricted Rights cl ause at FAR 52.227-19.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, Bay Networks, Inc. reserves the
right to make changes to the pr oducts described in this document without notice.
Bay Networks, Inc. does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or
circuit layout(s) described herein.
Portions of the code in this software product may be Copyright © 1988, Regents of the University of California. All
rights reserved. Redistribution and use in source and binary forms of such portions are permitted, provided that the
above copyright notice and this paragraph are duplicated in all such forms and that any documentation, advertising
materials, and other materials related to such distribution and use acknowledge that su ch portions of the software were
developed by the University of California, Berkeley. The name of the University may not be used to endorse or
promote products derived from such portions of the software without specific prior written permission.
SUCH PORTIONS OF THE SOFTWARE ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
In addition, the program and information contained herein are licensed only pursuant to a license agreement that
contains restricti ons on use and disclosure (that may incorporate by reference certai n limitations and no tices imposed
by third parties).
ii
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 3

Bay Networks, Inc. Software License Agreement
NOTICE: Please carefully read this license agre ement before copying or using the accompanying software or
installing the hardware unit with pre-enabled software (each of which is referred to as “Software” in this Agreement).
BY COPYING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, YOU ACCEPT ALL OF THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF
THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT. THE TERMS EXPRESSED IN THIS AGREEMENT ARE THE ONLY TERMS
UNDER WHICH BAY NETWORKS WILL PERMIT YOU TO USE THE SOFTWARE. If you do not accept these
terms and conditions, retu rn the product, unused and in the origina l shipping container, within 30 days of purchase to
obtain a credit for the full purchase price.
1. License Grant. Bay Networks, Inc. (“Bay Networks”) grants the end user of the Software (“Licensee”) a personal,
nonexclusive, nontransferable license: a) to use the Software either on a single computer or, if applicable, on a single
authorized device identified by host ID, for which it was originally acquired; b) to copy the Software solely for backup
purposes in support of authorized use of the Software; and c) to use and copy the associated user manual solely i n
support of authorized use of the Software by Licensee. This license applies to the Software only and does not extend
to Bay Networks Agent software or other Bay Networks software products. Bay Networks Agent software or other
Bay Networks software products are licensed for use under the terms of the applicable Bay Networks, Inc. Software
License Agreement that accomp anies such software and upon payment by the end user of the applicable license fees
for such software.
2. Restrictions on use; reservation of rights. The Software and user manuals are protected under copyright laws.
Bay Networks and/or it s licensors retain all title and ownership in both the Software and user manuals, including any
revisions made by Bay Networks or i ts licensors. The copyr ight notice must be reproduced and included with any
copy of any portion of the Software or user manuals. Licensee may not modify, translate, decompile, disassemble, use
for any competitiv e analysis, re v erse engineer , distrib ute, or create deriv ati ve works from the Softwa re or user manuals
or any copy, in whole or in part. Except as expressly provided i n t hi s Agreement, Licensee may not copy or tr ansfer
the Software or user manuals, in whole or in part. The Soft ware and user manuals embody Bay Networks’ and its
licensors’ confidential and proprietary intellectual property. Licensee shall not sublicense, assign, or otherwise
disclose to any third party the Software, or any information about the operation, design, performance, or
implementation of the Software and user manuals that is confidential to Bay Networks and its licensors; however,
Licensee may grant permission to its consultants, subcontractors, a nd agents to use the Softw are at Licensee’s facility,
provided they have agreed to use the Software only in accordance with the terms of this license.
3. Limited warranty. Bay Networks warrants each item of Software, as delivered by Bay Networks and properly
installed and operated on Bay Networks hardware or other eq uipment it is originally licensed for, to function
substantially as described in its accompanying user m anual during its warranty period , which begins on the date
Software is first shipped to Licensee. If an y item of S oftware f ails to so function d uring its w arranty period, as the sole
remedy Bay Networks will at its discretion provide a suitable fix, patch, or workaround for the problem that may be
included in a future Software release. Bay Network s fur ther w arra nts to Licen see that the medi a on which the
Software is provided will be free from defec ts in materials and wo rkman ship under no rmal use for a peri od of 90 da ys
from the date Software is first shipped to Licensee. Bay Networks will replace defective media at no charge if it is
returned to Bay Netw orks during the warran ty perio d alon g with proof of the date of shipment . This war ranty do es not
apply if the media has been dam aged as a resul t of acci dent, misuse , or ab use. The Licen see assumes all re sponsibilit y
for selection of the Software to achieve Licensee’s intended results and for the installation, use, and results obtained
from the Software. Bay Networks does not warrant a) that the functions contained in the software will meet the
Licensee’ s requireme nts, b) that the Software will operate in the hardware or software combinations that th e Licen see
may select, c) that the operation of the Softw a re will be uninterru pte d or error free, or d) that all defec ts in the
operation of the Software will be corrected. Bay Networks is not obligated to remedy any Software defect that cannot
be reproduced with the latest Software release. These warranties do not apply to the So ftw are if i t has been (i) altered,
except by Bay Netwo rks or in a ccordance with its instru ction s; (ii) used in con junc tion with another v en dor’s product,
resulting in the defect; or (iii) damaged by improper environment, abuse, misuse, accident, or negligence. THE
FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND LIMITATIONS ARE EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL
OTHER WARRANTIES EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT L IMITATION ANY WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Licensee is responsible for the security of
117352-D Rev. 00 iii
Page 4

its own data and information and for maintaining adequate procedures apart from the Software to reconstruct lost or
altered files, data, or programs.
4. Limitation of liability. IN NO EVENT WILL BAY NETWORKS OR ITS LICENSORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY
COST OF SUBSTITUTE PROCUREMENT; SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES; OR ANY DAMAGES RESULTING FROM INACCURATE OR LOST DATA OR LOSS OF USE OR
PROFITS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF THE SOFTWARE, EVEN
IF BAY NETWORKS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT
SHALL THE LIABILITY OF BAY NETWORKS RELATING TO THE SOFTWARE OR THIS AGREEMENT
EXCEED THE PRICE PAID TO BAY NETWORKS FOR THE SOFTWARE LICENSE.
5. Government Licensees. This provision applies to all Software and documentation acquired directly or indirectly
by or on behalf of the United States Government. The Software and documentation are commercial products, licensed
on the open market at market prices, and were developed entirely at private expense and without the use of any U.S.
Government funds. The license to the U.S. Government is granted only with restricted rights, and use, duplication, or
disclosure by the U.S. Government is subject to the restrictions set forth in subparagraph (c)(1) of the Commercial
Computer Software––Restricte d Rig hts cla u se o f FAR 52.227-19 and the lim itatio ns se t o ut in this license for civilian
agencies, and subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause of DFAR S
252.227-7013, for agencies of t he Department of Defense or their successors, whichever is applicable.
6. Use of Software in the European Community. This provision applies to all Software acquired for use within the
European Community. If Licensee uses the Software within a country in the European Community, the Software
Directive enacted by the Council of European Commun ities Directive dated 14 May, 1991, will apply to the
examination of the Software to facilitate interoperability. Licensee agrees to notify Bay Networks of any such
intended examination of the Software and may procure support and assistance from Bay Networks.
7. Term and termination. This license is effecti ve until terminated; however, all of the restrictions with respect to
Bay Networks’ copyright in the Software and user manuals will cease being effective at the date of expiration of the
Bay Networks copyright; those restrictions relating to use and disclosure of Bay Networks’ confidential information
shall continue in effect. Licensee may terminate this license at any time. The license will automatically terminate if
Licensee fails to comply with any of the terms and conditions of the license. Upon termination for any reason,
Licensee will immediately destroy or return to Bay Networks the Software, user manuals, and all copies. Bay
Networks is not liable to Licensee for damages in any form solely by reason of the termination of this license.
8. Export and Re-export. Licensee agrees not to export, directly or indirectly, the Software or related technical data
or information without first obtaining any required export licenses or other governmental approvals. Without limiting
the foregoing, Licensee, on behalf of itself and its subsidiaries and affiliates, agrees that it will not, without first
obtaining all export licenses and approvals required by the U.S. Government: (i) export, re-exp ort, transfer, or divert
any such Software or technical data, or any direct product thereof, to any country to which such exports or re-exports
are restricte d or em b argoed under United States export control laws and regulatio ns , or to any national or resident of
such restricted or embargoed countries; or (ii) provide the Software or related technical data or information to any
military end user or for any military end use, including the design, development, or production of any ch emical,
nuclear, or biological weapons.
9. General. If any provision of this Agreement is held to be invalid or unenf orceable by a court of competent
jurisdiction, the remainder of the provisions of this Agreement shall remain in full force and effect. This Agreement
will be governed by the laws of the state of California.
Should you have any questions concerning this Agreement, contact Bay Networks, Inc., 4401 Great America Parkway,
P.O. Box 58185, Santa Clara, California 95054-8 185.
LICENSEE ACKNOWLEDGES THAT LICENSEE HAS READ THIS AGREEMENT, UNDERSTANDS IT, AND
AGREES TO BE BOUND BY ITS TERMS AND CONDITIONS. LICENSEE FURTHER AGREES THAT THIS
AGREEMENT IS THE ENTIRE AND EXCLUSIVE AGREEMENT BETWEEN BAY NETWORKS AND
LICENSEE, WHICH SUPERSEDES ALL PRIOR ORAL AND WRITTEN AGREEMENTS AND
COMMUNICATIONS BETWEEN THE PARTIES PERTAINING TO THE SUBJECT MATTER OF THIS
AGREEMENT. NO DIFFERENT OR ADDITIONAL TERMS WILL BE ENFORCEABLE AGAINST BAY
NETWORKS UNLESS BAY NETWORKS GIVES ITS EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT, INCLUDING AN
EXPRESS WAIVER OF THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT.
iv 117352-D Rev. 00
Page 5

Contents
Preface
Before You Begin .............................................................................................................xiii
Text Conventions .............................................................................................................xiv
Acronyms ........................... .......................... .......................... ......................... ................. xv
Bay Networks Technical Publications ..............................................................................xvi
How to Get Help .............................................................................................................xvii
Chapter 1
Starting Compres sion
Summary of Bay Networks Data Compression Features ...............................................1-2
Software-Based Data Compression .........................................................................1-2
Hardware-Based Data Compression for the BN Platform ........................................1-3
Previous Hardware-Based Data Compression .........................................................1-4
Preparing a Configuration File for Data Compression ....................................................1-4
Configuring Software Compression ................................................................................1-5
Enabling Compression for PPP ................................................................................1-6
Enabling Compression for Frame Relay ...................................................................1-6
Enabling Compression for X.25 ................................................................................1-8
Configuring Hardware Compression ..............................................................................1-9
Configuring Compression for a BN (FRE-2-060E Processor) ..................................1-9
Configuring Compression for a BN (Octal Synchronous Link Module) ..................1-10
Configuring Compression for an ASN ....................................................................1-11
For More Information ....................................................................................................1-12
Chapter 2
Data Compression Overview
Bay Networks Compression Services ............................................................................2-2
Data Compression Architecture ......................................................................................2-3
LZ-77 Algorithm .......................................................................................................2-3
Hi/fn LZS Algorithm ..................................................................................................2-4
117352-D Rev. 00
v
Page 6

Compression Control Protocol (CCP) ......................................................................2-4
Bay Networks WAN Compression Protocol (WCP) ..................................................2-4
PPP Hi/fn LZS Compression Protocol ......................................................................2-5
Data Compression Performance ....................................................................................2-5
Hardware Compression ..................................................................................................2-5
Hardware Compression for the BN ..........................................................................2-6
Hardware Compression for the ASN ........................................................................2-6
Hardware Compression Contexts for WCP ..............................................................2-6
Hardware Compression Contexts for Hi/fn LZS .......................................................2-7
How Data Compression Works .......................................................................................2-8
CCP Negotiations ...................................................................................................2-10
WCP Negotiations ..................................................................................................2-10
Data Transmission ..................................................................................................2-11
Compression Features for Specific Protocols ...............................................................2-11
PPP Services .............................................. ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .2-11
PPP Multiline ........................... ....... ...... ....................................... ...... ....... ...... .2-11
PPP Multilink .................................. ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ....................2-12
PPP Bandwidth-on-Demand .............................. ....... ...... ...... ...........................2-13
PPP Dial-on-Demand ..................... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ....................2-13
PPP Dial Backup .................................. ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .2 -13
Frame Relay Services ............................................................................................2-14
Frame Relay Hybrid Access ............................................................................2-14
Frame Relay Dial-on-Demand .........................................................................2-14
Frame Relay Dial Backup ................................................................................2-14
X.25 Services .........................................................................................................2-15
X.25 PDN and DDN Services ..........................................................................2-15
Adjusting X.25 Max Window Size ....................................................................2-16
Chapter 3
Customizing Data Compression
Allocating Compression Memory for WCP .....................................................................3-2
Maximizing the Compression Ratio ..........................................................................3-2
Maximizing Throughput ............................................................................................3-3
8 KB History Size ...............................................................................................3-4
32 KB History Size .............................................................................................3-4
History Size with Hardware Compression .........................................................3-4
vi
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 7

Modifying the History Size .................................................................................3-6
Preventing Data Loss for PPP and Frame Relay .....................................................3-7
Customizing Hardware Compression .............................................................................3-9
Selecting Software or Hardware Compression ........................................................3-9
Selecting a Fallback Compression Mode ...............................................................3-11
Changing the Compression Control Protocol ...............................................................3-13
Disabling and Reenabling Compression ................... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ....................3-14
Disabling and Reenabling WCP on a Line .................................. ....... ...... ....... ...... .3-1 4
Disabling and Reenabling WCP on a Circuit ............ ....................................... ...... .3-14
Disabling Hi/fn LZS ........................ ....... ...... ....... ...... ....................................... ...... .3-15
Deleting Data Compression from a Router ...................................................................3-16
Appendix A
Site Manager Parameters
WCP Line Interface Parameters .................................................................................... A-2
WCP Circuit Interface Parameters ................................................................................. A-8
Hi/fn LZS Interface Parameters ................................................................................... A-11
PPP Interface Parameters for Compression ................................................................ A-14
Appendix B
Show Commands for Hardware Compression
show hwcomp all ..................................................................................................... B-2
show hwcomp state ................................................................................................. B-3
show hwcomp stats ................................................................................................. B-3
show hwcomp errors ............................................................................................... B-5
show hwcomp chip .................................................................................................. B-6
show wcp hwcomp all ............................................................................................. B-7
show wcp hwcomp state ......................................................................................... B-8
show wcp hwcomp stats ......................................................................................... B-9
show wcp hwcomp errors ...................................................................................... B-10
show hifn hwcomp all ............................................................................................ B-11
show hifn hwcomp state ........................................................................................ B-12
show hifn hwcomp stats ........................................................................................ B-13
show hifn hwcomp errors ...................................................................................... B-14
show hardware daughter_card .............................................................................. B-14
117352-D Rev. 00
vii
Page 8

Appendix C
Monitoring Software Compression
Using the BCC show Commands
show wcp lines ..............................................................................................................C-2
show wcp circuits ........................................................................................................... C-2
show wcp vcs ................................................................................................................C-3
show wcp stats all ..........................................................................................................C-4
show wcp stats error1 .................................................................................................... C-4
show wcp stats error2 .................................................................................................... C-5
show hifn circuits ...........................................................................................................C-6
show hifn stats ............................................................................................................... C-6
show hifn stats error ......................................................................................................C-7
Index
viii
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 9

Figures
Figure 2-1. CCP and WCP Initialization on a PPP Link .............................................2-9
Figure A-1. WCP Line Interfaces List Window ........................................................... A-2
Figure A-2. WCP Circuit Interfaces List Window ....................................................... A-8
Figure A-3. Hi/fn LZS Interface List Window ............................................................ A-11
117352-D Rev. 00
ix
Page 10

Page 11

Tables
Table 1-1. Link Modules Supported by FRE-2-060E Processor with Advanced
Compression Coprocessor Daughterb oard 1 - 3
Table 2-1. Data Compression Algori thm s and Pr oto cols ................................. ...... ...2-3
Table 3-1. Memory Allocation for Software Compression History ............................3-4
Table 3-2. Hardware Compression: 8 KB Contexts ..................................................3-5
Table 3-3. Hardware Compression: 32 KB Contexts ................................................3-5
Table 3-4. Default Compression Type Dependencies ...............................................3-9
117352-D Rev. 00
xi
Page 12

Page 13

Preface
Data compression
reducing the amouont of bandwidth needed to tr ansport LAN protocols over a
wide area. Bay Networ ks® routers and routi ng softw are suppor t data compr ession
over frame relay, X.25, and PPP (dial-up or leased lines). This guide describes
what you do to start and customize data compression on a Bay Networks router.
This guide describes how to use Site Manager to configur e da ta compre ss ion on a
router.
If you are responsible for configuring data compression, you need to read this
guide.
If you want to Go to
Start compression. Chapter 1
Learn about data compression services. Chapter 2
Change default settings for compression parameters. Chapter 3
Obtain information about Site Manager parameters (this is the same
information you obtain using Site Manager online Help).
Before You Begin
is a routing feature that elimin at es re dunda ncy in data streams,
Appendix A
117352-D Rev. 00
Before using this guide, you must complete the following procedures. For a new
router:
• Install the router (refer to the installation guide that came with your router).
• Connect the router to the network and create a configuration file (refer to
Quick-Starti ng Router s, Configuring BaySt ac k Remo te Access
ASN Routers to a Network)
.
, or
Connecting
xiii
Page 14

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Make sure that you are running the latest version of Bay Networks BayRS™ and
Site Manager software. For information about upgrading BayRS and Site
Manager, see the upgrading guide for your version of BayRS.
Text Conventions
This guide uses the following text conventions:
angle brackets (< >) Indicate that you choose the text to enter based on the
description inside the brackets. Do not type the
brackets when entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is:
ping <
ip_address
ping 192.32.10.12
, you enter:
>
bold text
italic text
screen text
Indicates command names and options and text that
you need to enter.
Example: Enter
Example: Use the
show ip {alerts | routes}.
command.
dinfo
Indicates file and directory names, new terms, book
titles, and variables in command syntax descriptions.
Where a variable is two or more words, the words are
connected by an underscore.
Example: If the command syntax is:
show at <
valid_route
valid_route
is one variable and you substitute one value
>
for it.
Indicates system output, for example, prompts and
system messages.
Example:
Set Bay Networks Trap Monitor Filters
xiv
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 15

Preface
separator ( > ) Shows menu paths.
Example: Protocols > I P ide nti fies the IP option on the
Protocols menu.
Acronyms
vertical line (
) Separates choices for command keywords and
|
arguments. Enter only one of the choices. Do not type
the vertical line when entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is:
show ip {alerts | routes}
show ip alerts
or
show ip routes
, you enter either:
This guide uses the following acronyms:
ACK acknowledgement
CCP Compression Control Protocol
CPC continuous packet com pression
DDN Defense Data Network
DLCI data link connection identifier
DTR data terminal ready
IETF Internet Engineering Task Force
, but not both.
117352-D Rev. 00
ILCCP Individual Link Compression Control Protocol
ILI intelligent link interface
ISDN Integrated Servic es Digital Network
ISDN BRI ISDN Basic Rate interface
ISDN PRI ISDN Primary Rate Interface
LAPB Link Access Procedure-Balanced
LCP Link Control Protocol
MCE1 multichannel E1
MCT1 multichannel T1
MIB management information base
xv
Page 16

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
NCP Network Control protocol
PDN Public Data Network
PPC packet-by-packet compression
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol
PVC permanent virtual circuit
RFC Request for Comments
VC virtual circuit
WAN wide area network
WCP WAN Compression Protocol
Bay Networks Technical Publications
You can now print Bay Networks technical manuals and release notes free,
directly from the Internet. Go to
Bay Networks product for which you need documentation. Then locate the
specific category and model or version for your hardware or software product.
Using Adobe Acrobat Re ader, you can open the manuals and r eleas e note s, sea rch
for the sections you need, and print them on most standard printers. You can
download Acrobat Reader free from the Adobe Systems Web site,
www.adobe.com
.
support.baynetw orks.com/l ibra ry/tp ubs/
. Find the
xvi
You can purchase Bay Networks documentation sets, CDs, and selected technical
publications through the Bay Networks Collateral Catalog. The catalog is located
on the World Wide Web at
into sections arranged alphabetically:
• The “CD ROMs” section lists available CDs.
• The “Guides/Books” section lists books on technical topics.
• The “Technical Manuals” section lists available printed documentation sets.
Make a note of the part numbers and prices of the items that you want to order.
Use the “Marketing Collateral Catalog description” link to place an order and to
print the order form.
support.baynetworks.com/catalog.html
and is divided
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 17

How to Get Help
For product assi stance, support contracts, information about educational services,
and the telephone numbers of our gl obal supp ort offices, go to the following URL :
http://www.baynetworks.com/corpor ate/ conta cts/
In the United States and Canada, you can dial 800-2LANWAN for assistance.
Preface
117352-D Rev. 00
xvii
Page 18

Page 19

Chapter 1
Starting Compression
The quickest way to begin using data compression on your network is to enab le it
with the default configuration that Bay Networks software supplies. This chapter
briefly introduces Bay Networks data compression and includes the procedures
for configuring compression with the default configuration values.
This chapter contains the following information:
Topic Page
117352-D Rev. 00
Summary of Bay Networks Data Compression Features
Preparing a Configuration File for Data Compression 1-4
Configuring Software Compression 1-5
Configuring Hardware Compression 1-9
For More Information 1-12
1-2
1-1
Page 20

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Summary of Bay Networks Data Compression Features
You can configure both software- a nd hardware-based compression on a circuit or
line basis. Features specific to software and hardware compression follow.
Software-Based Data Compression
Bay Networks offers two software compression protocols:
• WAN Compression Protocol (WCP) -- for Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP),
frame relay, and X.25 links
• Hi/fn LZS -- for PPP links only
The Hi/fn™ LZS® compression option is not included with your initial
Note:
purchase of BayRS. Bay Networks Hi/fn LZS compression software
incorporates LZS (licensed from Hi/fn) and therefore must be purchased
separately. To run Hi/fn LZS compression on a PPP link between a Bay
Networks router and a no n-Ba y Netwo rks rout er, you must obtain a license for
the Hi/fn LZS compression software, which is delivered on a separate CD.
1-2
These two protocols use different Lev-Zimpel algorithms to implement
compression and provide differen t levels of interoperability between Bay
Networks routers and routers made by other vendors.
If both ends of the connection are Bay Networks routers, use WCP as the
compression protocol. If the connection is a PPP link and only one end of the
connection is a Bay Networks router, use Hi/fn LZS.
Software-based data compression works over WAN links. Specifically, WCP
works with PPP, frame relay, and X.25 links; Hi/fn LZS works only with PPP
links. Both WCP and Hi/fn LZS work with PPP multilink. WCP also works with
PPP multiline.
Software compression includes the following features:
• Support for all Bay Networks platforms: BayStack
Access Stack Node (ASN
Backbone Node (BN
™
), Advanced Remote Node™ (ARN™),
®
), and System 5000
™
™
Access Node (AN®),
• Compression for a Bay Networks Fast Routing Engine (FRE®) module at
4 x 128 KB/s compressed throughput, full duplex; or 512 KB/s aggregate
compressed throughput
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 21

Starting Compression
• Compression for a BayStack AN platform at 2 x 64 KB/s compressed
throughput, full duplex; or 128 KB/s aggregate compressed throughput
• Compression on all intelligent link interface (ILI) modules that support serial
and ISDN BRI ports
• Compression on MCT1 and MCE1 lines
Hardware-Based Data Compression for the BN Platform
The FRE-2-060E processor module with advanced compression coprocessor
daughterboard, available with BayRS Version 12.20 for the BN router platform,
extends hardware-based data compression services to the link modules listed in
Table 1-1
Table 1-1. Link Modules Supported by FRE-2-060E Processor with Advanced
Compression Coprocessor Daughterboard
Link Modules Bay Networks Part Number
Octal Sync 5008
Oct Sync, HWComp32 AG2104037
Oct Sync, HWComp128 AG2104038
Dual Port Multi Channel T1 5945
Single Port Multi Channel T1 5944
Dual Port Multi Channel E1 77007
Single Port Multi Channel E1 77009
75 ohm Dual Por t MCE1-II AG2111004
75 ohm Single Port MCE1-II AG2111003
120 ohm Dual Por t MCE1-II AG2111002
120 ohm Single Port MCE1-II AG2111001
DB15 Quad MCT1 AG2111007
Ethernet Sync Advanced Filter 5431
.
117352-D Rev. 00
1-3
Page 22
Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
The type of data compression you configure depends on the upper layer protocol
you want to run over the link, as follows:
• To run frame relay, use WCP.
• To run PPP, use WCP if you are connecting Bay Networks routers.
Use Hi/fn LZS if you are connecting routers of different vendors.
Previous Hardware-Based Data Compression
You can continue to use hardware-based data compression services provided by
releases earlier than BayRS Version 12.20, which were based on:
• Optional daughterboards for PPP and frame relay networks that use the octal
synchronous link module for the BN, using FRE-2 processors only.
If a FRE-2-060E is present in the same slot as an octal synchronous
Note:
hardware compressio n daught erboar d, the FRE-2-060 E will be used inste ad of
the octal synchronous daughterboard.
• Optional net modules for PPP and frame relay networks that use the ASN.
Hardware compressi on can compr ess dat a transmit ted over WANs attached to
the following net modules: dual and quad synchronous, MCE1/ISDN PRI,
MCT1/ISDN, dual synchronous with ISDN BRI, and Quad BRI.
Preparing a Configuration File for Data Compression
To configure data c ompressi on, us e the Bay Netw orks Site Manage r con f i guration
1-4
tool. For information about working with configuration files, see
Managing Ro uters with Site Manager, as appropriate
Before starting data compression, you must create and save a configuration file
with at least one unconfigured WAN interface, such as a synchronous or MCT1
port.
.
Configuring and
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 23
Configuring Software Compression
Software compres sion w orks o n all rout er platf orms and al l seri al inte rface s. After
you open a configuration file , you can enable compression using Site Manager.
To use Site Manager to configure this interface for compression for PPP, frame
relay, or X.25, first complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
Starting Compression
1. In the main Site Manager window, choose
Tools.
2. Choose
3. Choose
Dynamic
4. Select the file. The Configuration Manager window
Configuration Manager
Local File, Remote File
, or
Cache
.
. The Configuration Manager menu opens.
,
The Tools menu opens.
Site Manager prompts you for the
configuration file you want to open.
opens, displaying the router modules.
From the Configuration Manager window, proceed to the following sections to
configure a WAN protocol and compression.
• Enabling Compression for PPP
on page 1-6
• Enabling Compression for Frame Relay on page 1-6
• Enabling Compression for X.25 on page 1-8
117352-D Rev. 00
1-5
Page 24
Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Enabling Compression for PPP
To co nfigure software c ompression on a PPP interface , complete the following
tasks:
You do this System responds
Site Manager Procedure
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
click on the link or net module connector
for which you are enabling data
compression.
2. Accept the default circuit name or rename
the circuit, then click on OK.
3. Choose
4. Click on OK. The Select Protocols window opens.
5. Enable data compression for PPP by
choosing one of the fo ll o w in g:
• Choose
Bay Networks router.
• Otherwise, choose
6. Click on OK. You return to the Configuration Manager
as the WAN proto co l. Site Manager enable s the protocol.
PPP
if connecting to anothe r
WCP
Hi/fn LZS
.
Enabling Compression for Frame Relay
To configure software compression on a frame relay interface, complete the
following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
The Add Circuit window opens.
The WAN Protocols window opens.
Site Manager enables compression on
this interface.
window.
1-6
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
click on the link or net module connector
for which you are enabling data
compression.
2. Accept the default circuit name or rename
the circuit, then click on OK.
3. Choose
protocol.
Frame Relay
as the WAN
The Add Circuit window opens.
The WAN Protocols window opens.
Site Manager enables the protocol.
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 25
Starting Compression
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
4. Click on OK. The Select Protocols window opens.
5. Enable data comp ression for frame relay
by choosing
6. Click on OK. You return to the Configuration Manager
WCP
.
(continued)
Site Manager enables compression on
this interface.
window.
117352-D Rev. 00
1-7
Page 26
Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Enabling Compression for X.25
To en able WCP on an X.25 interface , you must first add an X.25 service record,
then enable compr ession fo r the X.25 i nterf ace. See
information about X.25 service records.
To en able compress ion on an X.25 interface, com plete the foll owing tasks:
You do this System responds
Site Manager Procedure
Configuring X.25 Ser vices
for
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
click on the link or net module connector
for which you are enabling data
compression.
2. Accept the default circuit name or rename
the circuit, then click on OK.
3. Choose
4. Enter the required information, then click
on OK.*
5. Click on
6. Enter the required information then click
on OK.
7. Choose
8. Choose
9. Choose
10. Set the
to
Enable
Do this for each X.25 interface that you
configure.
11. Click on
* Site M anager requires that you configure certain packet and service parameters.
Configuring X.25 Services
See
† At the time you enable compression, you can also enable other protocols.
and click on OK. The X.25 Pa cket Configuration window
X.25
. The X.25 Service Record window opens.
Add
*
Protocols
Add/Delete
WCP
Enable Compression
.
Done
. The Protocols menu opens.
. The Select Protocols window opens.
. Site Manager enables compression on
parameter
. You return to the Configuration Manager
for information about these parameters.
The Add Circuit window opens.
The WAN Protocols window opens.
opens.
The X.25 Service Configuration window
opens.
You return to the X.25 Service
Configuration window.
this interface and then returns you to the
X.25 Service Conf iguration wi ndow.†
Site Manager enables compression for
this interface.
window.
1-8
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 27
Starting Compression
Configuring Hardware Compression
To us e hardware comp ression for th e BN router, you must have eith er an octal
synchronous link module w ith a hardware compression daughterboard or the
FRE-2-060E processor module with advanced compression coprocessor
daughterboard. For the ASN router, you must have a hardware compression net
module.
You can use hardware compression with PPP and frame relay.
Configuring Compression for a BN (FRE-2-060E Processor)
To configure hardware compression for a BN that has a FRE-2-060E processor
module with advanced compression coprocessor daughterboard,
following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
complete the
117352-D Rev. 00
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
click on the slot in which the FRE-2-060E
processor module with advanced
compression coprocessor is installed and
choose the link m odule for which you want
to enable data compression.
2. Click on OK. You return to the Configuration Manager
3. Choose a port. The Add Circuit window opens.
4. Accept the default circuit name or enter a
new name, then click on OK.
5. Choose one of these WAN protocols:
• PPP
•
Frame Relay
6. Click on OK. The Select Protocols window opens.
Site Manager selects the module.
window. The link module is added to the
slot.
The WAN Protocols window opens.
Site Manager selects the protocol.
(continued)
1-9
Page 28
Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
7. Enable data compression as follows:
• For frame relay, choose
• For PPP, choose
another Bay Networks router.
Otherwise, choose
8. Click on OK. You return to the Configuration Manager
WCP
Hi/fn LZS
.
WCP
if connecting to
.
(continued)
Site Manager enables compression on
this interface.
window.
Configuring Compression for a BN (Octal Synchronous Link Module)
To configure hardware compression for a BN that has an octal synchronous link
module with a hardware compression daughterboard,
tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
click on an empty slot and choose one of
the following octal synchronous link
modules with a hardware compression
daughterboard:
• AG2104037
• AG2104038*
2. Click on OK. You return to the Configuration Manager
3. Choose a port. The Add Circuit window opens.
4. Accept the default circuit name or enter a
new name, then click on OK.
5. Choose one of these WAN protocols:
• PPP
•
Frame Relay
6. Click on OK. The Select Protocols window opens.
Site Manager selects the module.
window. The link module is added to the
slot.
The WAN Protocols window opens.
Site Manager selects the protocol.
complete the following
(continued)
1-10
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 29
Starting Compression
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
7. Choose
8. Click on OK. You return to the Configuration Manager
* If you have a hardware compression link module on a BN, you can use hardware compression on
any WAN port on a slot. Hardware compression on the BN does not work across slots.
. Site Manager enables compression on
WCP
Configuring Compression for an ASN
To configure hardware compression for the ASN, complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
click on an empty slot and choose one of
the following net modules for hardware
compression:
• AF2104007
•
AF2104012
2. Click on OK. You return to the Configuration Manager
3. Click on the slot that contains the
hardware compression module and
choose a WAN net module.
4. Click on OK. You return to the Configuration Manager
5. Choose a port. The Add Circuit window opens.
6. Accept the default circuit name or enter a
new name, then click on OK.
7. Choose one of these WAN protocols:
• PPP
•
Frame Relay
*
(continued)
this interface.
window.
Site Manager selects the net module.
window. The net module is added to the
slot.
Site Manager selects the WAN net
module.
window. The WAN net module is placed
over the compression module.
The WAN Protocols window opens.
Site Manager selects the protocol.
(continued)
117352-D Rev. 00
1-11
Page 30
Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
You do this System responds
8. Click on OK. The Select Protocols window opens.
9. Choose
10. Click on OK. You return to the Configuration Manager
* If y ou ha ve a hardw are compression net module on an ASN, you can use hardware compression on
any WAN port on that single router or s lot. Hardware compression on the ASN does not work
across slots; that is, it does not provide compression for any other ASNs in the stack.
. Site Manager enables compression on
WCP
For More Information
For detailed inf ormation abou t Bay Networks data compression, see Chapter 2,
“Data Compression Overview
For information and recommendatio ns about using nondef ault v alues to cus tomize
compression, see Chapter 3
Site Manager Procedure
(continued)
this interface.
window.
.”
, “Customizing Data Compression.”
1-12
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 31

Chapter 2
Data Compression Overview
Bay Networks data compression services enable you to reduce line costs and
improve response times over wide area networks. In addition, they eliminate
redundancies in data streams. When you use compression on a network,
bandwidth efficiency improves so you can transmit more data.
This chapter contains the following information:
Topic Page
117352-D Rev. 00
Bay Networks Compression Services
Data Compression Architecture 2-3
Data Compression Performance 2-5
Hardware Compr ession 2-5
How Data Compression Works 2-8
Compression Features for Specif ic Protocols 2-11
2-2
2-1
Page 32

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Bay Networks Compression Services
Bay Networks compression services include:
• Software-based compression for PPP, frame relay, and X.25 networks for all
router platforms and all serial interfaces.
PPP compression works on multiline, multilink, on the ISDN BRI and PRI
modules, and on lines that use Raise DTR or V.25bis modem interfaces with
dial services. Frame relay compression works on multiline and dial backup
lines.
• Hardware-based compression for PPP and frame relay networks for BN
routers using one of the following modules:
-- Octal synchronous link module using FRE-2 processors
-- FRE-2-060E processor module with the advanced compression
coprocessor daughterboard to which you can connect a broad range of
Bay Networks link modules (see “Hardware-Based Data Compression for
the BN Platform” on page 1-3 for the list of supported link modules).
Hardware compression on the BN supports all PPP and frame relay services
that WCP software compressio n suppor ts.
2-2
• Hardware-based compression for PPP and frame relay networks for the ASN
router.
A compression net mo d ule compresses data transmitted o v er a WAN network
by dual and quad synchronous, MCE1/ISDN PRI, MCT1/ISDN, dual
synchronous with ISDN BRI, and Quad BRI net modules. Hardware
compression on the ASN supports all PPP services that WCP software
compression supports.
Bay Networks WCP software- and hardware-based compression interoperate fully
because they use the same algorithm.
Hi/fn LZS hardware compress ion is su pporte d by the FRE-2- 060E proc essor with
the advanced compression coprocessor daughterboard for the BN when
connecting to a router from another vendor that is also running the Hi/fn LZS
algorithm.
To use software data compression effectively, you must decide how to allocate
memory for this task. The goal is to compress data as much as possible and to
transmit the data as quickly as possible without taxing the resources of the router.
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 33

Data Compression Architecture
WCP and Hi/fn LZS use different compression algorithms and protocols. The
compression protocol that you choose depends on whether you are
communicating with routers from Bay Networks or other vendors.
Data Compression Overview
Table 2-1
lists the algorithms and protocols that Bay Networks uses to provide
data compression services for WCP and Hi/fn LZS.
Table 2-1. Data Compression Algorithms and Protocols
WCP Hi/fn LZS
LZ-77 algorithm Hi/fn LZS algorithm
Compression Control Protocol (RFC 1962) Compression Control Protocol (RFC 1962)
Bay Networks proprietary WAN
Compression Protocol (WCP)
References the PPP Hi/fn LZS
Compression Protocol (RFC 1974) as a
guideline
You must ensure that routers at both ends of the connection are using the same
compression protocol.
• If both ends of the connection are Bay Networks routers, configure both
routers to use WCP as the compression protocol.
• If the connection is a PPP link and only one end of the connection is a Bay
Networks router, configure both router s to use Hi/fn LZS.
If you want the router to negotiate which protocol is used, set the Compression
Protocol parameter to Any (see page A-15
for the parameter description).
LZ-77 Algorithm
Bay Networks WCP data c ompress ion softw are is based on a L empel-Zi v (LZ-77)
algorithm. The algorit hm uses a sliding history buffer that stores the data that the
network link has processed most recently. The compressor compares new data
strings with data it has already processed and stored in the buffer. When the
compressor detects data strings that match data it has already processed, it
replaces those strings with offset and length tokens that are shorte r than the
original strings, thus compressing the data.
117352-D Rev. 00
2-3
Page 34

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Hi/fn LZS Algorithm
Hi/fn is a wholly owned subsidiary of Stac, Inc. Bay Networks Hi/fn LZS
compression software incorporates LZS from Hi/fn.
Bay Networks Hi/fn LZS compression software is based on the Hi/f n LZS
algorithm to transport compressed packets across a PPP link. Hi/fn LZS
implements an error detection mechanism, which means that it can detect whether
packets are lost during tr ansmission . Hi/fn LZS doe s not retr ansmit pac kets i f the y
are lost.
The Hi/fn LZS compression algorithm searches incoming data for redundant data
strings and replaces these strings in the outgoing data with encoded tokens of
shorter length. Hi/fn LZS creates the encoded tokens from information in a table
that the Hi/fn LZS algorithm builds. This table consists of string matches, which
point to previous incoming data. As the table is built and tokens are created,
subsequent data is compressed based on previous data.
Compression Control Protocol (CCP)
Bay Networks uses RFC 1962, the Compression Control Protocol (CCP), to
enable or disable compression across a PPP link and determine what kind of
compression is used. CCP also includes a history reset request and
acknowledgment ca pability, which Hi/fn LZS uses but WCP does not. WCP uses
its own negotiation mechanism.
Bay Networks WAN Compression Protocol (WCP)
Bay Networks proprietary WAN Compression Protocol (WCP) is an IETF draft
standard. WCP enables compression for frame relay and for X.25, and transports
compressed packets f or PPP, frame relay, and X.25. WCP negotiates compre ssion
mode, history size, and buffer size. For PPP and frame relay, WCP also
retransmits packets in the event of packet loss and protects against inadvertent
data expansion (LAPB retransmits packets for X.25).
WCP is most effective for sites that have WAN connections operating at relatively
low speeds su ch as 56/ 64 KB, where you w an t to ach ie v e da ta compre ssion a t lo w
cost and with minimal memory requirements. WCP supports connections up to
512 KB/s on the FRE-040. For networks operating at faster speeds, you should
use hardware compression.
2-4
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 35

PPP Hi/fn LZS Compression Protocol
PPP uses CCP to negotiate how the router uses the Hi/fn LZS Compression
Protocol (RFC 1974). Specifically, CCP negotiates the different compression
modes that RFC 1974 supports. Bay Networks negotiates only mode 3 and the
number of compression histories, of which we support only one history.
RFC 1974 is specif i ed only as an er ror de te ction protoc ol; u nli ke WCP, it does not
contain a transmit history. Instead, it relies on upper layer protocols to retransmit
data when errors occur.
For more information about compression protocol modes, refer to RFC 1974.
Data Compression Performance
The goals in using data compre ssion are t o achie v e a high compres sion rati o while
maximizing throughput.
compared to the size of the same data after it is compressed.
the amount of data that goes across the network in a specific amount of time. The
amount of throughput can indicate the efficiency and speed of the network.
Compression ratio
Data Compression Overview
is the size of uncompressed data
Throughput
refers to
The compression ratio varies according to the effectiveness of the compression
algorithm, but also according to the characteristics of the data you are
transmitting. Data that includes many redundant strings compresses at a high
ratio.
Throughput varies according to the num ber of devices in the network through
which the data must travel. Throughput is also affected by the compression and
decompression process.
Hardware Compression
Bay Networks hardware-based compression works with frame relay and PPP
networks. It best serves sites that support T1 or E1 lines, which often concentrate
many lower-speed remote connections. The hardware compression facility
operates at high speeds and also supports high-density WAN connections. Use
hardware compression when you want to achieve high compression ratios and
throughput, and also want to conserve router memory for other functions.
117352-D Rev. 00
2-5
Page 36

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Hardware Compression for the BN
The BN supports the following compression daughterboards:
• AG2104037 - Octal Sync with a 32-contexts hardware compression
daughterboard
• AG2104038 - Octal Sync with a 128-contexts hardware compression
daughterboard
• Advanced compression coprocessor daughterboard with 128 or 256 contexts
installed on the FRE-2-060E processor module
Hardware Compression for the ASN
The hardware compression net modules for the ASN can compress data
transmitted over WAN networks attached to dual and quad synchronous,
MCE1/ISDN PRI, MCT1/ISDN, dual synchronous with ISDN BRI, and
Quad BRI net modules. One compress ion net module in a single ASN can pro vide
hardware compression for all the net modules on that router. It does not provide
compression for any other ASN in the stack.
The compression net module is a vailable in both a 32-contexts and a 128-co nte xts
version.
The ASN supports the following compression net modules:
• AF2104007 - 32-contexts hardware compression net module
• AF2104012 - 128-contexts hardware compression net module
Hardware Compression Contexts for WCP
2-6
A
context
circuit (VC). Compression hardware maps a context to specific regions of
compression and decompression memory.
• A 32-contexts compression da ughterboard or net module can run comp ression
refers to compression and decompression for a single virtual
simultaneously over 31 continuous packet compression (CPC) contexts, each
using an 8 KB history size, with one shared 8 KB packet-by-packet
compression (PPC) context.
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 37

Data Compression Overview
• A 128-contexts compression daughterboard or net module can run
compression simultaneously over 127 CPC contexts, each using an 8 KB
history size, with one shared 8 KB PPC context.
• A 256-contexts advanced compression coprocessor daughterboard installed
on a FRE-2-060E processor module can r un compress ion simult aneously ov er
255 CPC contexts, each using an 8 KB history size, with one shared
8 KB PPC context.
The 32-contexts, 128- conte xt s, and 256-c ontexts daughterboards and net modules
differ in their amount of memory.
• The 32-contexts daughterboard and net module have 512 KB compression/
256 KB decompression.
• The 128-contexts daughter boards and net module have 2 MB compression/
1 MB decompression.
• The 256-contexts advanced compression coprocessor daughterboard has
4 MB compression/2 MB decompression.
You should plan your netw or k to us e hardw are c ompressi on on th e VCs
Note:
most important to you within the limits of your equipment. If you configure
more VCs for hardware compression than your daughterboard or net module
can support, you cannot control which VCs will use hardware compression.
By default, all VCs that exce ed the hardware context limit use software
compression.
For information about customizing CPC and PPC, see Chapter 3
Data Compression.”
Hardware Compression Contexts for Hi/fn LZS
Hi/fn LZS supports a 2 KB history size and CPC contexts only. Hi/fn LZS does
not support PPC contexts.
117352-D Rev. 00
, “Customizing
2-7
Page 38

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
How Data Compression Works
To transmit compressed data, the router must complete one or both of the
following:
• CCP negotiations (for PPP connections using WCP or Hi/fn LZS)
• WCP negotiations (for PPP, frame relay, and X.25 connections using WCP)
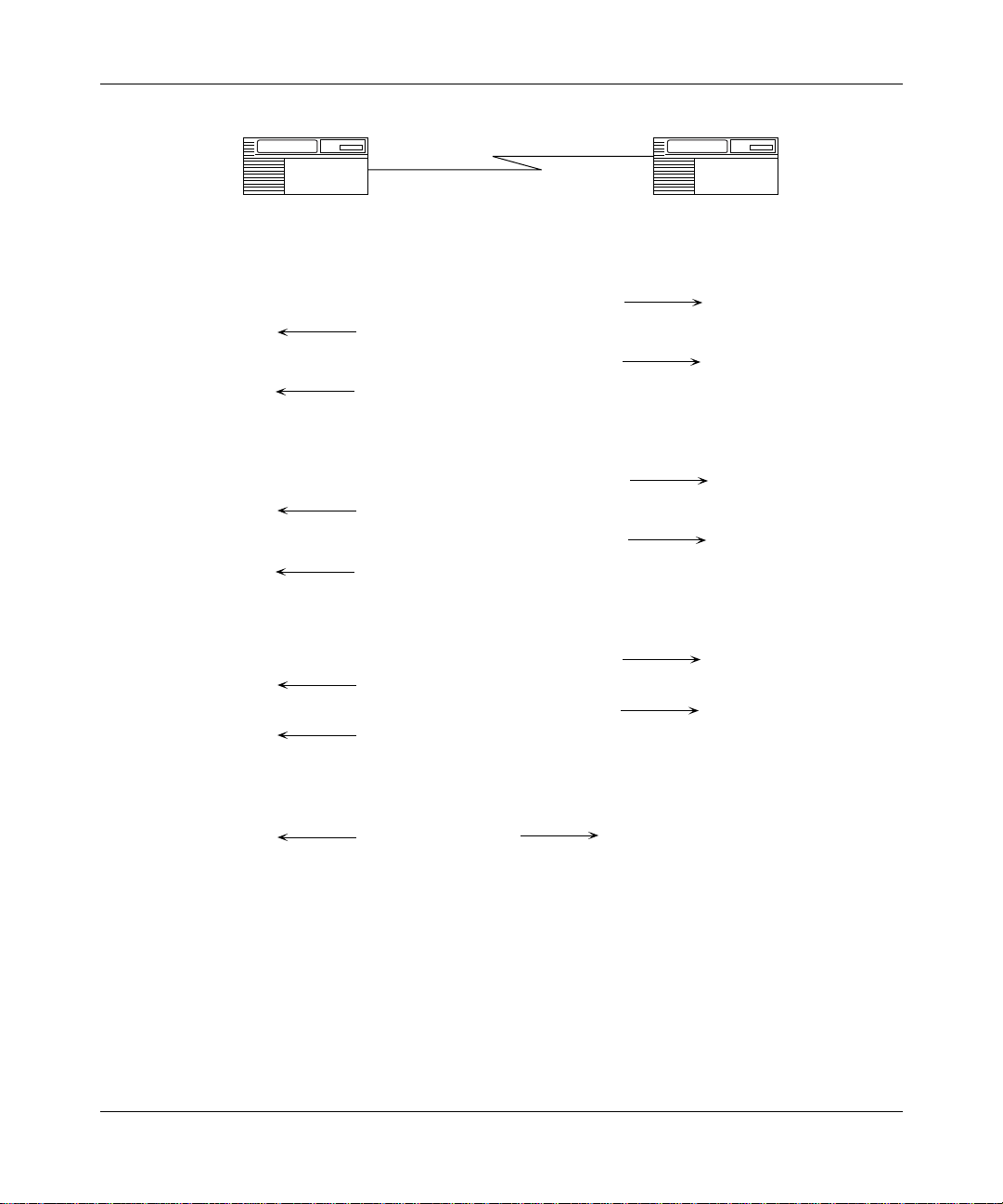
The following sections describe how these negotiations work. As you read these
sections, see Figure 2-1
link.
If compression is across a frame relay or X.25 link, the router negotiates only
WCP; CCP does not apply.
, which illustrates CCP and WCP initialization on a PPP
2-8
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 39
Data Compression Overview
Router A Router B
1. PPP interface on network; LCP negotiations complete; begin CCP negotiations:
Send initialization-request
Send initialization-request
Send initialization-ACK
Send initialization-ACK
2. CCP negotiations complete; begin WCP negotiations, including compression mode,
history size, and buffer size:
Send initialization-request
Send initialization-request
Send initialization-ACK
Send initialization-ACK
117352-D Rev. 00
3. WCP negotiations complete; begin NCP negotiations:
Send configure-request
Send configure-request
Send configure-ACK
Send configure-ACK
4. NCP open; begin transmitting data:
Send data
DC0001A
Figure 2-1. CCP and WCP Initialization on a PPP Link
2-9
Page 40

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
CCP Negotiations
CCP allows the two ends of a PPP connection to negotiate whether to use data
compression and, if so, w hich algorithm to use. Both WCP and Hi/fn LZS use
CCP to negotiate compression.
If one side of a link requests an algorithm that the other side does not
Note:
support, traffic over the link continues, but in uncompressed form.
In Figure 2-1
configuration and network control protocol negotiations that the Link Control
Protocol (LCP) uses to establish a link.
For Hi/fn LZS, CCP also provides the following:
• History reset request messages
• Request acknowledgment messages
These messages help to synchronize the receipt and transmission of the
compression and decompression history after a packet is lost. WCP does not use
these messages.
For an explanation of LCP negotiations, see
WCP Negotiations
WCP allows two ends of a PPP, frame relay, or X.25 connection to negotiate
compression.
Frame relay and X.25 use WCP to ne gotiate whether to use data compression and
which algorithm to use. (PPP uses CCP and WCP to negotiate this information.)
As with PPP, if one side of a link requests an algorithm that the other side does not
support, traf fic c ontinues, b ut in uncompre ssed form. All th ree WAN protocols use
WCP to negotiate options such as compression mode, hi st ory s iz e, and buffer size.
, negotiations begin when PPP establishes a link. CCP uses the same
Configuring PPP Services.
2-10
Each side of a link running dat a compres sion has a compress or, a decompressor, a
compression history, and a retransmission buffer. You can edit WCP parameters
for compression mode, history size, and buffer size to optimize compression
performance on your network (see “Allocating Compression Memory for WCP
on page 3-2
).
117352-D Rev. 00
”
Page 41

Data Compression Overview
Data Transmission
For PPP links using WCP, Network Control Protocol (NCP) negotiations and
WCP negotiations occur simultaneously. When PPP, NCP, and WCP negotiations
are complete, data transmission using compression begins.
For PPP links usin g Hi/fn LZS , data tr ansmis sion usi ng compre ssion begins when
CCP and NCP negotiations are complete.
For frame relay an d X.25 lin ks, dat a tran smissi on using compress io n be gins whe n
WCP negotiations are complete.
Compression Features for Specific Protocols
Bay Networks data compression services vary in some details according to the
WAN protocols that you configure. Read the following sections to learn about
how Bay Networks implements data compression for PPP, frame relay, and X.25
services.
PPP Services
You can use software or hardware data compression on all PPP circui ts , including
multiline and multilink, bandwidth-on-demand, dial-on-demand, and dial backup
lines. When you use compre ssion on a ba ndwidth-on- demand, dial-on -demand, or
dial backup circ uit, WCP au tomati cally con fi gures or delet es compress ion as li nes
are added to or removed from the circuit.
PPP Multiline
Multiline
data paths. A
or dial-up physical line, or it can be a virtual circuit connection. Multiline
provides both increased fault tolerance and greater bandwidth between two sites.
For more information about Bay Networks multiline, see
Services.
117352-D Rev. 00
enables you to configur e a single circ uit consisti ng of one or more WAN
data path
is a logical point-to-point channel; it can be a permanent
Configuring WAN Line
2-11
Page 42

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
PPP Multilink
Multilink
consists of a
provides capabilities beyond those of multiline circuits. Multilink
of lines between two peers, consisting of up to four links.
bundle
Multilink allows you to:
• Distribute traffic across the lines in the bundle in amounts roughly
proportional to the effective bandwidth of each link.
• Use lines that have different speeds, proportionally distributing traffic over
those lines.
• Balance traffic load and restore packet sequence.
• Use switched lines (such as ISDN B channels) as well as leased lines.
• Monitor traffic volume.
Depending on the version of BayRS, the router handles the operation of PPP
multilink and WCP differently.
For BayRS Version 12.10 and later, by default the router negotiates WCP above
the PPP multilink bundle for new circuits only. Negotiating compression
the bundle
means that data packets are first compr essed and then distributed
above
across the links i n the bundle. The distributi on of traffic occurs once for the entire
bundle, so the balance of traffic across the bundle is more accurate. In addition,
the router uses less memory for compression.
Routers using BayRS Version 12.10 or later with an older configuration file
negotiate WCP below the multilink bundle by default. Negotiating compression
below the bundle
means that data packets are first distributed across the links and
then compressed. Compression is done individually for every li nk. You can
reconfigure the circuit to negotiate WCP above the bundle by changing the CCP
Type parameter to CCP on the routers at both ends of the link.
2-12
If you configure a new multilink circuit on a local router running BayRS Version
12.10 or later, and the remote router is running a version earlier than 12.10, you
must change the CCP Type parameter from the default (CCP) to ILCCP for the
local router and set the PPP Mode to multilink.
For a description of the CCP Type parameter, see page A-14
.
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 43

Data Compression Overview
PPP Bandwidth-on-Demand
Bandwidth-on-demand
allows a secondary dial-up line to augment a primary
leased line when the primary line experiences congestion. Congestion occurs
when traff ic vo lume exceeds line capacity. When congestion abates, th e secondary
line becomes inactive.
If you configure bandwidth-on-demand and WCP, it affects the
bandwidth-on-demand congestion thresholds. These thresholds instruct the router
to activate additional links from a multilink bundle to relieve congestion.
For BayRS Version 12.10 and later, when WCP is negotiated above the multilink
bundle and the router sends or receives data, it calculates the congestion
thresholds based on com pressed data. If WCP is negotiated below the bundle, the
router calculates these thresholds based on uncompressed data.
If a router using BayRS Version 12.10 or later is communicating with a router
using software earlier than Version 12.10, the routers must negotiate WCP below
the bundle, so the thresholds will be based on uncompressed data.
To configure these thresholds, see
Configuring Dial Services
.
PPP Dial-on-Demand
Dial-on-demand
service enables you to establish a circuit only when you want to
transmit and receive data, as opposed to having a leased line, which is always
ava il able. By using a circuit on a demand basis, you can signif ic ant ly redu ce yo ur
line costs.
117352-D Rev. 00
PPP Dial Backup
PPP also allows you to configure
dial backup
service. If a primary PPP line fails
and you enabled dial backup, the router automatically establishes a backup line.
You cannot enable any protocols, including compression, on a backup circuit,
because a backup circuit inherits its protocols from the primary circuit. If the
primary circuit uses com pression, then the backup circuit does also.
For more information about Bay Networks dial services, see
Services
.
Configuring Dial
2-13
Page 44

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Frame Relay Services
You can use software (WCP only) or hardware data compression with frame relay.
You can use compress ion with some vi rtua l circ uits ( VCs), and not wi th othe rs, as
you choose, both for regular frame relay VCs, and for those you configure in
hybrid mode. You can also use compression with dial-o n-demand a nd dial backup
services.
You must enable compression on both sides of a frame relay link. If you enable
data compression on only one side of the link, data transmission occurs, but in
uncompressed form.
Frame Relay Hybrid Access
Hybrid access enables you to combine bridging and routing over a single frame
relay interface.
When you enable data compression for frame relay on a hybrid circuit, both the
bridged and the routed traffic over that circuit are compressed. Note that
compression applies only to the hybrid permanent virtual circuit (PVC), and not to
the other PVCs from the main circuit, unless you also enabled compression for
those interfaces. Conversely, if you enable data compression for other PVCs, but
not on a PVC you configured for hybrid m ode, the hybrid circuit does not use
compression.
2-14
Frame Relay Dial-on-Demand
Frame relay enables you to configure dial-on-demand service.
Dial-on-demand
enables the rout er to ac ti v ate a dial-u p line onl y when t here is data to send or whe n
you config ure t he rout er t o fo rce t he activation of a dia l-up li ne. Us ing fra me rel ay
dial-on-demand ensures t hat you est ablis h connect ions onl y when you need the m,
as opposed to using leased lines, which are active regardless of data activity. This
helps you reduce line costs.
Frame Relay Dial Backup
Frame relay enables you to conf ig ure
dial backup
service. If a primary frame rela y
circuit fails and you enable dial backup, the router automatically establishes a
backup circuit. The backup circuit can be a PPP circuit, a frame relay circuit that
uses direct mode (a service record with only one PVC), or a frame relay circuit
that uses group mode (a service record with two or more PVCs).
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 45

Data Compression Overview
The backup circuit can inherit the primary circuit’s configuration, or it can use its
own. When the fr ame relay primary and backup use the same configuration, they
have a
configuration. The backup circuit uses the same network layer
shared
address as the primary circuit. The data link layer configuration, that is, the
backup PVCs, data link connection identifiers (DLCIs), and filters, can be the
same or differen t from the primary.
If the backup uses a unique configuration, it is a
secondary configuration uses a different network layer address, PVCs, and filters
from the primary.
To use data compression with frame relay dial backup, you must configure
compression on both the primary and the backup circuit. The backup ci rcuit does
not necessarily inherit the PVC configuration from the primary circuit, because
the backup PVCs can have different configurations from the primary.
For more information about Bay Networks dial services, see
Services
X.25 Services
An X.25 network permits as many as 128 VCs to exist on the same ph ysical link at
the same time. You can configure each of these interfaces individually to use data
compression or not.
X.25 PDN and DDN Services
When you use data compression on circuits that you configure for X.25 Public
Data Network (PDN) or Defens e Depa rt ment Network (DDN) services, you must
enable compression on both sides of the link. If you configure compression on
only one side of a PDN or DDN link, the data that travels over that link will be
corrupted.
secondary
configuration. A
Configuring Dial
.
117352-D Rev. 00
You must also remember to enable the X.25 ser vice record compr ession paramet er
for each X.25 interface that you configure. For more informatio n about this
parameter, see
Configuring X.25 Services
.
2-15
Page 46

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Adjusting X.25 Max Window Size
Window size can affect packet throughput across the X.25 network. Se tting the
X.25 Max Window Size parameter too low can cause the router to drop packets
and render data compression ineffective. You should configure this paramet er a t a
higher value than the default setting.
2-16
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 47
Chapter 3
Customizing Data Compression
When you enable data compr ession , de fau lt values are in effect for al l p arameters .
This chapter provides information about customizing Bay Networks compression
to use it most effectively on your network.
This chapter contains the following information:
Topic Page
Allocating Compression Memory for WCP
Customizing Hardware Compression 3-9
Changing the Compression Control Protocol 3-13
Disabling and Reenabling Compression 3-14
Deleting Data Compression from a Router 3-16
3-2
117352-D Rev. 00
3-1
Page 48

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Allocating Compression Memory for WCP
Using WCP across a network involves allocating memory to maximize
compression without ta xing t he reso urces of y our rou ter. To achieve this goal, y ou
can customize compression parameters to:
• Maximize the compression ratio.
• Maximize throughput.
• Prevent data loss.
Maximizing the Compression Ratio
You can compress data in one of two modes:
•
Continuous packet compression (CPC)
maintains compression history across
packets. CPC yields a higher compression ratio than packet-by-packet
compression. In most circumstances, you should select CPC, the default
value, to maximize compr ess ion.
•
Packet-by-packet compression (PPC)
creates a new history for each packet.
PPC yields a lower compression ratio than CPC. Select PPC only for links
that drop a very large number of packets. Be aware that under these
circumstances, implementing data compression may offer little or no
advantage.
If either side of the link specifies PPC, both sides of the link must use PPC.
To specify the compression mode for a line, complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a line from the list.
Protocols
WCP
Lines
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Line Interfaces List window
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
.
(continued )
3-2
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 49
Customizing Data Compression
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
5. Set the
Click on
description on page A-4
6. Click on
Compression Mode
or see the parameter
Help
Done
. You return to the Configuration Manager
parameter.
.
(continued)
window.
To specify the compre ssion mode for a circuit, comple te the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a circuit from the list.
5. Set the
Click on
description on page A-9
6. Click on
Protocols
WCP
Interfaces
Compression Mode
Help
Done
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Circuit Interfaces List window
parameter.
or see the parameter
.
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
.
Maximizing Throughput
Each side of the link has both a compression and decompression history and a
lookup table. The compression and decompression histories maintain a record of
data that has already traveled across the network. The lookup tables maintain
pointers to redundant strings and the offset and length tokens that replace each of
those strings.
You can specify eit her 8 KB or 32 KB of local memory t o maint ain a compress ion
history. When you make this choice, be aware that you are allocating more
memory than the H istory Size parameter value indicate s.
117352-D Rev. 00
3-3
Page 50

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Table 3-1 lists the amount of memory required for 8 KB and 32 KB history sizes.
Table 3-1. Memory Allocation for Software Compression History
Memory Requirements 8 KB History Size 32 KB History Size
Compression history 8 KB 32 KB
Lookup table 16 KB 64 KB
Decompression history 8 KB 32 KB
Total memory required 32 KB 128 KB
If you select different values for history size for the two sides of the link, 8 KB
becomes the history size for both sides of the link.
Hardware compression has similar requirements (see “History Size with
Hardware Compression” on page 3-4).
8 KB History Size
In general, 8 KB histories are appropriate for frame relay and X.25, when you
have large numbers of VCs and need to conserve memory for each of them.
3-4
32 KB History Size
For PPP, with only one circuit per line, you may want t o use a 32 KB his tor y. You
may also want to al locate a 32 KB history size f or link s with speeds higher t han 64
Kb/s to improve throughput. The compressor can find a data pattern match up to
three times faster using a 32 KB history than an 8 KB history.
History Size with Hardware Compression
Hardware compression daughterboards and net modules are available in 32, 128,
and 256 contexts. The numbers 32, 128, and 256 assume a history size of 8 KB
per context, although you can set the history size to either 8 KB or 32 KB. For
example, if y ou set the histo ry si ze to 32 KB, you us e four 8 KB co nte xts, and you
have that many fewer contexts available to run hardware compression on your
network.
Although software compression does not place strict limits on the
Note:
number of contexts you can configure, memory requirements for history size
are the same for both software and hardware compression.
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 51

Customizing Data Compression
Compression daughterboards reserve one 8 KB context for PPC, as opposed to
CPC. There is no limit to the number of VCs that can use th is one PPC context.
The maximum number of VCs for the compression engine is 256.
The compression hardware uses memory in units called
pages,
where a page
equals 32 KB of memory . Each context that uses a 32 KB history use s one page of
memory. Restrictions for CPC contexts using either 8 KB or 32 KB histories are
that the memory used for any one history must be continuous, and that it may not
cross pages. F or 8 KB co ntex ts, thes e restrict ions cr eate fe w c onstrai nts, b ut for 32
KB contexts, they are significant.
Table 3-2
shows the maximum number of 8 KB contexts each daughterboard or
net module can support.
Table 3-2. Hardware Compression: 8 KB Contexts
Maximum 8 KB
Daughterboard or Net Module
32-context 31 0 1
128-context 127 0 1
256-conte xt (advanced
compression c oprocessor
daughterboard)
Table 3-3
shows the maximum number of 32 KB contexts each daughterboard or
CPC Contexts
255 0 1
Available 32 KB
CPC Contexts
Reserved 8 KB
PPC Contexts
net module can support.
117352-D Rev. 00
Table 3-3. Hardware Compression: 32 KB Contexts
Maximum 32 KB
Daughterboard or Net Module
32-context 7 3 1
128-context 31 3 1
256-conte xt (advanced
compression c oprocessor
daughterboard)
CPC Contexts
63 3 1
Available 8 KB
CPC Contexts
Reserved 8 KB
PPC Contexts
3-5
Page 52

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
You can combine 8 KB and 32 KB contexts on one daughterboard or net module.
However, if you bring VCs up and down, memory may fragment. Even when you
have 32 KB or more of compression memory available, if it is on different pages
you will not be able to configure a 32 KB context. To solve this problem, save
your configuration and reset the slot. When you reset the slot, available
compression memory is rearranged to be contiguous.
If you have a v ai lable memory, you can always ad d an 8 KB conte xt, because 8 KB
is the smallest divisible amount of compression memory.
Modifying the History Size
To mod ify the history size for a l ine, complete the following tasks:
You do this System responds
Site Manager Procedure
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a line from the list.
5. Set the
Help
page A-5
6. Click on
Protocols
WCP
Lines
History Size
or see the parameter description on
.
Done
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Line Interfaces List window
parameter. Click on
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
.
3-6
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 53

Customizing Data Compression
To modify the history size for a circuit, complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a circuit from the list.
5. Set the
Help
page A-10
6. Click on
Protocols
WCP
Interfaces
History Size
or see the parameter description on
.
Done
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Circuit Interfaces List window
parameter. Click on
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
Preventing Data Loss for PPP and Frame Relay
Buffer size
You must configure this parameter to protect against data loss if you run PPP or
frame relay . You can use a buffer size of None, Normal, Large, or V ery Large. The
default value is Normal. Configure buffer size based on the following conditions:
• Leng th of time it takes for data to travel over the link
is the amount of memory allocated to store the transmission history.
A Normal buffer size is usually large enough for a coast-to-coast connection
within the United States. You may need a Large or Very Large buffer if your
link is over a satellite connection.
.
117352-D Rev. 00
• Number of dropped packets
For a link with a high number of dr opped pack ets, incr ease the b uf fe r size. F or
a link with a very low number of dropped packets, decrease the buffer size,
even to None, to conserve memory.
3-7
Page 54

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
• Number of resets
For a link with a high number of resets and a low numb er of d rop ped packets,
increase the buffer size. Be aware, however, that a high number of resets may
occur for reasons unrelated to buffer size.
X.25 is a reliable protocol, which means that it has features that check
Note:
for errors and prevent data loss. Bay Networks data compressio n software
ignores the Buffer Size parameter for X.25.
To modify the buffer size, complete the following tasks:
You do this System responds
Site Manager Procedure
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a line from the list.
5. Set the
Help
page A-6
6. Click on
Protocols
WCP
Lines
Buffer Size
or see the parameter description on
.
Done
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Line Interfaces List window
parameter. Click on
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
.
3-8
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 55

Customizing Hardware Compression
The following issues are specific to hardware compression:
Customizing Data Compression
• Selecting software or hardware compression (described on page 3-9
• Selecting a fallback compression mode (described on page 3-11
Selecting Software or Hardware Compression
When you configure a VC for compression, the default compression type varies
(Table 3-4
Table 3-4. Default Compression Type Dependencies
Module Type Default Compression Type
Link module that does not support
hardware compression
Link module that supports hardware
compression
Net module other than hardware
compression net module
Hardware compression net module Hardware
Advanced compression coprocessor
daughterboard
).
Software
Hardware
Software
Hardware
)
)
117352-D Rev. 00
You can use softw are compr essio n with a h ardw are comp ression daughterbo ard or
net module. Bay Networks recommends that you use hardware compression for
connections operating at speeds greater than 512 Kb/s. You should specify
software compressio n for VCs in excess of the number of contexts your hardw a re
compression daughterboard or net module can support.
3-9
Page 56

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
To specify hardware or software compression for a line configured with WCP,
complete the following tasks:
You do this System responds
Site Manager Procedure
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a line from the list.
5. Set the
Help
page A-6.
6. Click on
Protocols
WCP
Lines
Engine Type
or see the parameter description on
Done
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Line Interfaces List window
parameter. Click on
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
.
To specify hardware or software compression for a cir cuit configured with WCP,
complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a circuit from the list.
5. Set the
Help
page A-11
6. Click on
Protocols
WCP
Interfaces
Engine Type
or see the parameter description on
.
Done
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Circuit Interfaces List window
parameter. Click on
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
.
3-10
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 57

Customizing Data Compression
To specify hardware or software compression for an interface configur ed with
Hi/fn LZS compression, complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select an interface from the list.
5. Set the
Help
page A-12.
6. Click on
Protocols
Hi/fn LZS
Interfaces
Engine Type
or see the parameter description on
Done
.
. The Hi/fn LZS menu opens.
. The Hi/fn LZS Interface List window
parameter. Click on
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Selecting a Fallback Compression Mode
The fallback compression mode is the compression mode that you want to use
when no hardware compression contexts are available. You can set a fallback
compression mode for a WCP line interface or for a Hi/fn LZS interface.
When configuring a WCP line interface, the options are as follows:
• Software CPC -- a good choice for lower-speed links, 64 Kb/s or less. It
generally affords a better compression ratio than Hardware PPC.
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
.
117352-D Rev. 00
• Hardware PPC -- a good choice for highe r-spe ed links, greater t han 64 Kb/s. It
provides better throughput than Software CPC.
• None -- a good choice for very high-speed links.
When configuring a Hi/fn LZS circuit interface, the options are as follows:
• Software CPC -- a good choice for lower-speed links, 64 Kb/s or less.
• None -- a good choice for extremely high-speed links, greater than 2.5 Mb/s.
3-11
Page 58

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
To modify the fallback compression mode for a line configured with WCP,
complete the following tasks:
You do this System responds
Site Manager Procedure
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a line from the list.
5. Set the
parameter. Click on
parameter description on page A-7.
6. Click on
Protocols
WCP
Lines
Fallback Compression Mode
Done
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Line Interfaces List window
or see the
Help
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
.
To modify the fallback c ompre ssi on mode for a Hi/fn LZS interface, complete the
following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select an interface from the list.
5. Set the
parameter. Click on
parameter description on page A-13
6. Click on
Protocols
Hi/fn LZS
Interfaces
Fallback Compression Mode
Done
.
. The Hi/fn LZS menu opens.
. The Hi/fn LZS Interface List window
or see the
Help
.
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
.
3-12
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 59

Customizing Data Compression
Changing the Compression Con trol Protocol
The PPP interface p ar amet ers that you can modify for compression are CCP Type
and Compression Protocol. These parameters enable the router to operate with
Bay Networks routers using router software earlier than Version 12.10 and with
non-Bay Networks routers.
Modifying the CCP Type parameter enables a router operating with BayRS
Version 12.10 and later t o be compatib le with router s running pr e vious v ersions of
BayRS that negotiate W CP below the PPP multilink b undle. F or more informat ion
about PPP multilink and how it works with WCP, see “PPP Multilink
page 2-12
Modifying the Compression Protocol parameter lets you specify a particular
protocol to use or instructs the router to negotiate which protocol to use.
You can use Site Manager to modify PPP compression parameters. To change the
compression control protocol, complete the following tasks:
.
Site Manager Procedure
” on
117352-D Rev. 00
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select an interface from the list.
5. Set the
Help
page A-14
6. Set the
parameter. Click on
parameter description on page A-15
7. Click on
Protocols
PPP
Interfaces
CCP Type
or see the parameter description on
.
Compression Protocol
Done
.
. The PPP menu opens.
. The PPP Interface Lists window opens.
parameter. Click on
or see the
Help
.
. You return to the Configuration Manager
The Protocols menu opens.
window.
3-13
Page 60
Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Disabling and Reenabling Compression
You can disable compression on a line or circuit, then reenable it later.
Disabling and Reenabling WCP on a Line
To dis able or reenable WCP on a line, complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a line from the list.
5. Set the
or see the parameter description on
page A-3.
6. Click on
Protocols
WCP
Lines
Enable
Done
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Line Interfaces List window
parameter. Click on
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Help
Disabling and Reenabling WCP on a Circuit
To disable or reenable WCP on a circuit, complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select a circuit from the list.
Protocols
WCP
Interfaces
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Circuit Interfaces List window
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
.
.
(continued)
3-14
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 61

Customizing Data Compression
You do this System responds
5. Set the
or see the parameter description on
page A-9
6. Click on
Disabling Hi/fn LZS
To disable or reenable Hi/fn LZS on an interface, complete the following tasks:
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
4. Select an interface from the list.
5. Set the
or see the parameter description on
page A-12
6. Click on
(continued)
window.
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
window.
Site Manager Procedure
parameter. Click on
Enable
.
Done
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Site Manager Procedure
Protocols
Hi/fn LZS
Interfaces
Enable
.
Done
.
. The Hi/fn LZS menu opens.
. The Hi/fn LZS Interface List window
parameter. Click on
. You return to the Configuration Manager
Help
Help
.
117352-D Rev. 00
3-15
Page 62

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Deleting Data Compression from a Router
To delete compression from all ci rcuits on the router, complete the following
tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
Delete Hi/fn LZS.
4. Click on
Protocols.
or
WCP
Delete WCP
OK.
Hi/fn LZS.
or
The Protocols menu opens.
The WCP or Hi/fn LZS menu opens.
Site Manager prompts you to co nfirm th e
deletion.
You return to the Configuration Manager
window.
Compression is no longer operating on
the router.
3-16
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 63

Appendix A
Site Manager Pa rameters
This appendix contains the Site Manager parameter descriptions for data
compression services. You can display the same information using Site Manager
online Help. This appendix contains the following information:
Topic Page
WCP Line Interface Parameters
WCP Circuit Interface Parameters A-8
Hi/fn LZS Interface Parameters A-11
PPP Interface Parameters for Compression A-14
A-2
For each parameter, this appendix provid es the following information:
• Parameter name
• Configuration Manager menu path
• Default setting
• Valid parameter options
• Parameter function
• Instructions for setting the parameter
• Management information base (MIB) object ID
117352-D Rev. 00
A-1
Page 64

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
The Technician Interface allows you to modify parameters by issuing
commit
commands with the MIB object ID. This process is equivalent to
modifying parameters using Site Manager. For more information about using the
Technician Interface to access the MIB, see
Caution:
The Technician Interface does not verify the validity of your
parameter va lues. Entering an invalid value can corrupt your configuration.
WCP Line Interface Parameters
The WCP Line Interfa ces List windo w (Fig ure A-1) contains all data compression
line parameters.
and
set
Using Technician Interface Software
.
A-2
Figure A-1. WCP Line Interfaces List Window
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 65

Site Manager Parameters
To access the WCP Line Interfaces List window, complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
Protocols
WCP
Lines
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Line Interfaces List window
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
.
The parameter descriptions follow.
Parameter: Enable
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Lines
Default: Enable
Options: Enable
Disabl e
|
Function: Enables or disables data compression on the line.
Instructions: WCP automatically sets this parameter to Enable when you select WCP in the
Select Protocols window. If you want to temporarily disable WCP rather than
delete it from the router, set this parameter to Disable. To reenable WCP , reset it
to Enable.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.1.1.2
117352-D Rev. 00
A-3
Page 66

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Parameter: Compression Mode
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Lines
Default: Continuous Packet
Options: Continuous Packet
Packet by Packet
|
Function: Specifies the compression mode on the line. Continuous packet compression
(CPC) retains compression history across packets and allows a higher
compression ratio than packet-by-packet compression.
Packet-by-packet compression (PPC) resets compression history at the start of
each packet, resulting in a lower compression ratio. Because PPC does not
depend on pre vious packets, you should select this o pti on f or a link that drops a
large number of packets.
Instructions: Select either Continuous Packet or Packet by Packet.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.1.1.5
A-4
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 67

Site Manager Parameters
Parameter: History Size
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Lines
Default: 32K
Options: 32K
8K
|
Function: Specifies the amount of memory allocated to compression history for the line.
Remember that history size has separate compression and decompression
histories and lookup tables on each side of a link.
If the link uses software compression with a history of 8 KB, each end of the
link allocates a total of 32 KB as follows:
• 8 KB for compression
• 16 KB for a lookup table
• 8 KB for decompression
If the link uses a compression history of 32 KB, each end of the link allocates a
total of 128 KB as follows:
• 32 KB for compression
• 64 KB for a lookup table
• 32 KB for decompression
Hardware compression has similar requirements.
Selecting 32K for PPP WCP should not be a problem for the BN, because PPP
allows only one circuit per line. Select 8K or 32K for frame relay and X.25
lines, depending on the resources of your network.
Selecting 32K fo r PPP WCP on t he ASN can cause pr oblems, part icularl y if you
are using a 32-context compression net module.
In general, 8 KB histories are appropriate for WAN links that run at speeds of
64 Kb/s or less, because less throughput is required. Use an 8 KB history size
with frame relay a nd X.25, whic h ha v e la r ge numbe rs of VCs an d may have low
available bandwidth, and with PPP on a 32-context net module.
You may want to alloc at e a 32 KB history size for links with speeds hi ghe r than
64 Kb/s to improve throughput. The compression engine can find a data pattern
match up to three times faster using a 32 KB history.
If you select dif f erent histor y sizes for each si de of a link, th e smalle r of the tw o
becomes the effective history size.
Instructions: S elect either 32K or 8K.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.1.1.6
117352-D Rev. 00
A-5
Page 68

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Parameter: Buffer Size
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Lines
Default: Normal
Options: Very Large
Function: Indicates the amount of buffer memory for the transmission history on a line.
Because X.25 has features that check for errors and prevent data loss, data
compression software ignores the Buffer Size parameter for X .25.
Instructions: Set this parameter according to the end-to-end round-trip length of a WCP
connection:
Select Normal for most land-line, coast-to-coast connections.
Select Large or Very Large for connections at a great distance from each other,
such as sate llite conne ctions.
Select None for links that drop a very small number of packets.
Increase the buffer size for a link with a large number of resets.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.1.1.7
Large | Normal | None
|
Parameter: Engine Type
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Lines
Default: Software (unless you conf i gured either an oct al syn chronou s lin k module with a
hardware compression daughterboard or a FRE-2-060E processor module with
an advanced compr es sio n co proc es sor daughterboard for the BN, or a hardware
compression net module for the ASN, in which case the default is Hardware)
Options: Software
Function: Specifies whether compression for this node will be software-based or
hardware-based.
Instructions: S elect Softwa re to use software-based compression, or select Hardware to use
hardware-based co mpression. You can use hardware compres sio n wi th PPP and
frame relay only. You can use software compression with PPP, frame relay, or
X.25.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.1.1.8
A-6
Hardware
|
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 69

Site Manager Parameters
Parameter: Fallback Compression Mode
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Lines
Default: Software CPC
Options: Software CPC
Hardware PPC | None
|
Function: For hardware compression only, specifies the compression mode that you want
to use when no hardware compression contexts are available.
Software CPC is a good choice for lower-speed links, 64 Kb/s or less. It
generally affords a better compression ratio than Hardware PPC.
Hardware PPC is a good choice for higher-speed links, greater than 64 Kb/s. It
provides better throughput than Software CPC.
None is a good choice for very high-speed links.
Instructions: Select Software CPC, Hardware PPC, or None.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.1.1.10
117352-D Rev. 00
A-7
Page 70

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
WCP Circuit Interface Parameters
The WCP Circuit Interfaces L ist window (Figure A-2) contains the data
compression circuit parameters.
A-8
Figure A-2. WCP Circuit Interfaces List Window
To access the WCP Circuit Interfaces List window, complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
Protocols
WCP
Interfaces
.
. The WCP menu opens.
. The WCP Circuit Interfaces List window
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
.
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 71

Site Manager Parameters
The parameter descriptions follow.
Parameter: Enable
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Interfaces
Default: Enable
Options: Enable
Function: Enables or disables data compression on the circuit.
Instructions: WCP automatically sets this parameter to Enable when you select WCP in the
Select Protocols window. If you want to temporarily disable WCP rather than
delete it from the router, set this par ameter to Disable. Reset it to Enable to
reenable WCP.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.2.1.2
Parameter: Compression Mode
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Interfaces
Default: Inherit from Line
Options: Continuous Packet
Function: Specifies the compression mode on the circuit.
Disable
|
Packet by Packet | Inherit from Line
|
Continuous packet compression (CPC) retains compression history across
packets and allows a higher compression ratio than packet-by-packet
compression (PPC).
Packet-by-packet compression (PPC) resets compression history at the start of
each packet, resulting in a lower compression ratio. Because PPC does not
depend on pre vious packets, you should select this o pti on f or a link that drops a
large number of packets.
Inherit from Line allows you to set WCP parameters at the line level and apply
them to circuits. F or PPP, with only one circuit per line, this means th at you can
configure WCP at either the circuit level or the line level.
Instructions: Select Inherit from Line if you want to accept the value in effect for the WCP
Compression Mode line parameter. Otherwise, select either Continuous Packet
or Packet by Packet.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.2.1.4
117352-D Rev. 00
A-9
Page 72

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Parameter: History Size
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Interfaces
Default: Inherit from Line
Options: 32K
8K | Inherit from Line
|
Function: Specifies the amount of memory allocated to compression history for the line.
Remember that history size has separate compression and decompression
histories and l ookup tables on each side of a link. If the l ink uses a compression
history of 8 KB, each end of the link allocates a total of 32 KB as follows:
• 8 KB for compression
• 16 KB for a lookup table
• 8 KB for decompression
If the link uses a compression history of 32 KB, each end of the link allocates a
total of 128 KB as follows:
• 32 KB for compression
• 64 KB for a lookup table
• 32 KB for decompression
Hardware compression has similar requirements.
Selecting 32K for PPP WCP should not be a problem for the BN, because PPP
allows only one circuit per line. Select 8K or 32K for frame relay and X.25
circuits, depending on the resources of your network. Selecting 32K for PPP
WCP on the ASN can cause proble ms, part icul arly i f you are u sing a 32-con te xt
compression net module.
In general, 8 KB histories are appropriate for WAN links that run at speeds of
64 Kb/s or less, because less throughput is required. Use an 8 KB history size
with frame relay a nd X.25, whic h ha v e la r ge numbe rs of VCs an d may have low
availa ble bandwidth, and with PPP on a 32-context net module. You may want
to allocate a 32 KB history size for links with speeds higher than 64 Kb/s to
improve throughput. The compression engine can find a data pattern match up
to three times faster using a 32 KB history. If you select different history sizes
for each side of a link, the smaller of the two becomes the effective history size.
Inherit from Line allows you to set WCP parameters at the line level and apply
them to circu its.
Instructions: Select Inherit from Line if you want to accept the value in effect for the WCP
History Size line parameter. Otherwise, select either 32K or 8K.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.2.1.5
A-10
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 73

Site Manager Parameters
Parameter: Engine Type
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > WCP > Interfaces
Default: Inherit from Line
Options: Software
Function: Specifies whether compression for this node will be software-based or
hardware-based.
Instructions: Select Inherit from Line if you want to accept the value in effect for the WCP
Engine Type line parameter. Otherwise, select Software to use s oftware-bas ed
compression or Hardware to use hardware-based compression.
You can use hardware compression with PPP and fra me re la y onl y. Y ou can use
software compression with PPP, frame relay, or X.25.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.2.1.6
Hardware | Inherit from Line
|
Hi/fn LZS Interface Parameters
The Hi/fn LZS Interface List window (Figure A-3) contains Hi/fn LZS interface
parameters.
117352-D Rev. 00
Figure A-3. Hi/fn LZS Interface List Window
A-11
Page 74

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
To access the Hi/fn LZS Interface List window, complete the following tasks:
You do this System responds
Site Manager Procedure
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
Protocols
Hi/fn LZS
Interfaces
.
. The Hi/fn LZS menu opens.
. The Hi/fn LZS Interface List window
Protocols me nu opens
The
opens.
.
The parameter descriptions follow.
Parameter: Enable
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > Hi/fn LZS > Interfaces
Default: Enable
Options: Enable
Disable
|
Function: Enables or disables Hi/fn LZS compression on this interface.
Instructions: Site Manager automatically sets this parameter to Enable when you select Hi/fn
LZS as the compression protocol. If you want to temporarily disable Hi/fn LZS
rather than delete it from the router, set this parameter to Disable. To reenable
Hi/fn LZS, reset it to Enable.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.5.1.2
Parameter: Engine Type
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > Hi/fn LZS > Interfaces
Default: Software
Options: Software
Hardware
|
Function: Specifies whether data will be compressed by software or hardware.
Instructions: For hardware compres sion, set this parameter to Hardware.
For software comp ression, set this parameter to Software.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.5.1.4
A-12
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 75

Site Manager Parameters
Parameter: Fallback Compression Mode
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > Hi/fn LZS > Interfaces
Default: Software CPC
Options: Software CPC
None
|
Function: When a circuit on this line cannot register for hardware compression due to a
lack of hardware-context memory, this parameter determines whether data will
be compressed by software or remain uncompressed.
Instructions: If you want data to be compressed by software on a circuit that cannot register
for hardware compression, set this parameter to S oftware CPC .
If you want data to remain uncompressed on a circuit that cannot register for
hardware compression, set this parameter to None. None is a good choice for
very high-speed links.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.4.22.5.1.8
117352-D Rev. 00
A-13
Page 76

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
PPP Interface Parameters for Compression
The PPP Interface Lists window contains two parameters for data compression.
(For more inform ation about PPP, see
To access the PPP Interface Lists window, complete the following tasks:
Site Manager Procedure
You do this System responds
Configuring PPP Services
.)
1. In the Configuration Manager window,
choose
2. Choose
3. Choose
Protocols
PPP
Interfaces
.
. The PPP menu opens.
. The PPP Interface Lists window opens.
The Protocols menu opens.
The PPP parameters for compression are as follows.
Parameter: CCP Type
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > PPP > Interfaces
Default: CCP
Options: ILCCP
CCP
|
Function: Specifies the compression control prot ocol that the router uses for this interf ac e.
Instructions: Accept the def ault, CCP, if you select Hi/fn LZS as the c ompression p rotocol, or
if you select WCP as the compression protocol and you set the PPP Mode
parameter to multilink. Using CCP as the compression type means that the
router negotiates compression above the multilink bundle.
Select ILCCP if you are configuring a new circuit and you set the PPP Mode
parameter to multilink, and the remote router is using router software earlier
than Version 12.10. Using ILCCP as the compression ty pe means that t he rou ter
negotiates compression below the multilink bundle.
If you have a router running BayRS Version 12.10 or later using an older
configuration file, the routers negotiate WCP below the multilink bundle by
default. You can change this to CCP for the routers at both ends of the link to
negotiate WCP above the multilink bundle.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.9.2.2.1.71
A-14
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 77

Site Manager Parameters
Parameter: Compression Prot ocol
Path: Configuration Manager > Protocols > PPP > Interfaces
Default: Any
Options: Any
Function: Specifies the compression protocol that the router uses for this interface.
Instructions: Ac cept the default, Any, if you want the router to automatically select the
WCP
|
compression protocol that is compatible with the remote router, as follows:
• If the remote router can use eith er WCP or Hi/ fn LZS, the r outer sel ects WCP,
for example, if both ends of the connection are Bay Networks routers.
• If the remote router does not use WCP, but uses Hi/fn LZS, the router selects
Hi/fn LZS. Conversely, if the remote router does not use Hi/fn LZS, but uses
WCP, the router selects WCP.
• If the remote router does not recognize either WCP or Hi/fn LZS, then CCP
does not complete negotiations and the router will not compress data.
Select WCP as the compression prot ocol if the remote rou ter is a Bay Netw orks
router .
Hi/fn LZS
|
Select Hi/fn LZS as the compression protocol if the remote router is not a Bay
Networks router.
MIB Object ID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.18.3.5.9.2.2.1.72
117352-D Rev. 00
A-15
Page 78

Page 79

Appendix B
Show Commands for Hard ware Compression
This appendix describes how to use the BCC
command to display
show
information about software compression from the management information base
(MIB). The type and amount of data displayed depends on the hardware
compression settings you want to view.
Use the BCC show command to display status and statistical information about
hardware compression.
This appendix includes descriptions of the following
Command Page
show hwcomp all
show hwcomp state
show hwcomp stats
show hwcomp errors
show hwcomp chip
show wcp hwcomp all
show wcp hwcomp state
show wcp hwcomp stats
show wcp hwcomp errors
show hifn hwcomp all
show hifn hwcomp state
show hifn hwcomp stats
show hifn hwcomp errors
show hardware daughter_card
show
commands:
B-2
B-3
B-3
B-5
B-6
B-7
B-8
B-9
B-10
B-11
B-12
B-13
B-14
B-14
117352-D Rev. 00
B-1
Page 80

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
show hwcomp all
The BCC
show hwcomp all
command displays information about active and
unused contexts and statistics about compressed and decompressed packets. This
command com bines statistics for WCP an d Hi/fn.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2-060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression modul e .
State Current operating state of the compression hardware.
Hardware
Compression Module
Type
Compression Module
Chip Type
Active Contexts Number of active contexts by size and type.
Unused Contexts Number of unused contexts by size and type.
Total Compressed
Packets
Total Decompressed
Packets
Total Tx Expanded
Packets
Tot al Rx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Total Compression
Errors
Total Decompression
Errors
Total LCB Errors Number of Longitudinal Check Byte (LCB) errors.
Type of m odule.
Type of chip.
Number of compressed packets.
Number of decompressed packets.
Number of expanded packets transmitted.
Number of uncompressed packets received.
Number of compression errors.
Number of decompression errors.
B-2
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 81

Show Commands for Hardware Compression
Tot al Tx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Total Rx Dropped
Packets
show hwcomp state
The BCC
compression at the instant the command is issued. This command combines
statistics f or WCP and Hi/f n.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
State Current operating state of the compression hardware.
Hardware
Compression Mod
Type
Active Contexts Number of active contexts by size and type.
Unused Contexts Number of unused contexts by size and type.
Number of uncompressed packets transmitted.
Number of dropped packets received.
show hwcomp state
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2-060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression modul e .
Type of m odule.
command displays the status of hardware
show hwcomp stats
The BCC
compression at the instant the command is issued. This command combines
statistics f or WCP and Hi/f n.
117352-D Rev. 00
show hwcomp stats
command displays statistics about hardware
B-3
Page 82

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2-060E with
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2 with Octal Sync
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression modul e .
Total Compressed
Packets
Total DeCompressed
Packets
Total Tx Expanded
Packets
Tot al Rx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Number of compressed packets.
Number of decompressed packets.
Number of expanded packets transmitted.
Number of uncompressed packets received.
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
B-4
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 83

show hwcomp errors
Show Commands for Hardware Compression
The BCC
show hwcomp errors
command displays information about hardware
compression errors. This command combines statistics for WCP and Hi/fn.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2- 060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot a nd module number of the FRE- 2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression m odule.
Total Compression
Errors
Total Decompression
Errors
Total LCB Errors Number of Longitudinal Check Byte (LCB) errors.
Tot al Tx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Total Rx Dropped
Packets
Number of compression errors.
Number of decompression errors.
Number of uncompressed packets transmitted.
Number of dropped packets received.
117352-D Rev. 00
B-5
Page 84

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
show hwcomp chip
The BCC
show hwcomp chip
command identifies the chip type that is
performing hardware compression.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2- 060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot a nd module number of the FRE- 2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression m odule.
Chip Type Type of chip performing hardware compre ssion services.
B-6
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 85

show wcp hwcomp all
Show Commands for Hardware Compression
The BCC
show wcp hwcomp all
command displays informat ion about active
and unused contexts and statistics about compressed and decompressed packets.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2-060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression modul e .
State Current operating state of the compression hardware.
Hardware
Compression Module
Type
Compression Module
Chip Type
Active Contexts Number of active contexts by size and type.
Unused Contexts Number of unused contexts by size and type.
Total Compressed
Packets
Total Decompressed
Packets
Total Tx Expanded
Packets
Tot al Rx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Total Compression
Errors
Total Decompression
Errors
Total LCB Errors Number of Longitudinal Check Byte (LCB) errors.
Type of m odule.
Type of chip.
Number of compressed packets.
Number of decompressed packets.
Number of expanded packets transmitted.
Number of uncompressed packets received.
Number of compression errors.
Number of decompression errors.
117352-D Rev. 00
B-7
Page 86

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Tot al Tx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Total Rx Dropped
Packets
show wcp hwcomp state
The BCC
compression at the instant the command is issued.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
State Current operating state of the compression hardware.
Hardware
Compression Mod
Type
Active Contexts Number of active contexts by size and type.
Unused Contexts Number of unused contexts by size and type.
show wcp hwcomp state
Number of uncompressed packets transmitted.
Number of dropped packets received.
command displays the status of hardware
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2-060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression modul e .
Type of m odule.
B-8
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 87

show wcp hwcomp stats
Show Commands for Hardware Compression
The BCC
show wcp hwcomp stats
command displays stat istics about hardware
compression at the instant the command is issued.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2-060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression modul e .
Total Compressed
Packets
Total DeCompressed
Packets
Total Tx Expanded
Packets
Tot al Rx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Number of compressed packets.
Number of decompressed packets.
Number of expanded packets transmitted.
Number of uncompressed packets received.
117352-D Rev. 00
B-9
Page 88

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
show wcp hwcomp errors
The BCC
show wcp hwcomp errors
command displays information about
hardware compression errors.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2- 060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot a nd module number of the FRE- 2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression m odule.
Total Compression
Errors
Total Decompression
Errors
Total LCB Errors Number of Longitudinal Check Byte (LCB) errors.
Tot al Tx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Total Rx Dropped
Packets
Number of compression errors.
Number of decompression errors.
Number of uncompressed packets transmitted.
Number of dropped packets received.
B-10
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 89

show hifn hwcomp all
Show Commands for Hardware Compression
The BCC
show hifn hwcomp all
command displays informat ion about acti v e and
unused contexts and statistics about compressed and decompressed packets.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2-060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression modul e .
State Current operating state of the compression hardware.
Hardware
Compression Module
Type
Compression Module
Chip Type
Active Contexts Number of active contexts by size and type.
Unused Contexts Number of unused contexts by size and type.
Total Compressed
Packets
Total Decompressed
Packets
Total Tx Expanded
Packets
Tot al Rx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Total Compression
Errors
Total Decompression
Errors
Type of m odule.
Type of chip.
Number of compressed packets.
Number of decompressed packets.
Number of expanded packets transmitted.
Number of uncompressed packets received.
Number of compression errors.
Number of decompression errors.
117352-D Rev. 00
B-11
Page 90

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
Tot al Tx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Total Rx Dropped
Packets
show hifn hwcomp state
The BCC
compression at the instant the command is issued.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
State Current operating state of the compression hardware.
Hardware
Compression Mod
Type
Active Contexts Number of active contexts by size and type.
Unused Contexts Number of unused contexts by size and type.
show hifn hwcomp state
Number of uncompressed packets transmitted.
Number of dropped packets received.
command displays the status of hardware
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2-060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression modul e .
Type of m odule.
B-12
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 91

show hifn hwcomp stats
Show Commands for Hardware Compression
The BCC
show hifn hwcomp stats
command displays statistics abou t hardware
compression at the instant the command is issued.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2-060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression modul e .
Total Compressed
Packets
Total DeCompressed
Packets
Total Tx Expanded
Packets
Tot al Rx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Number of compressed packets.
Number of decompressed packets.
Number of expanded packets transmitted.
Number of uncompressed packets received.
117352-D Rev. 00
B-13
Page 92

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
show hifn hwcomp errors
The BCC
show hifn hw c om p e r rors
command displays informat ion about
hardware compression errors.
The output contains the following information:
Slot/<Module> For BN routers either:
• The slot and module number of the FRE-2- 060E with
Advanced Compression Coprocessor daughterboard
• The slot a nd module number of the FRE- 2 with Octal Sync
module (with hardware compression daughterboard)
For ASN routers, the slot and module number of the hardware
compression m odule.
Total Compression
Errors
Total Decompression
Errors
Tot al Tx
NonCompressed
Pac ke ts
Total Rx Dropped
Packets
Number of compression errors.
Number of decompression errors.
Number of uncompressed packets transmitted.
Number of dropped packets received.
show hardw are daughter_ca rd
The BCC
hardware that is performing compression services.
The output contains the following information:
Slot Number of the slot in which the FRE-2-060E with Advanced
Card Type Type o f compression hardware.
Revision Version of the advanced compression coprocessor
Serial No. Identification number assigned to the advanced compression
B-14
show hardware daughter_card
Compression Coprocessor daughterboard is located.
daughterboard.
coprocessor daughterboard.
command displays information about
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 93

Appendix C
Monitoring Software Compression
Using the BCC show Commands
This appendix describes how to use the BCC
command to display
show
information about software compression from the management information base
(MIB). The type and amount of data displayed depends on the software
compression settings you want to view.
This appendix includes descriptions of the following
Command Page
show wcp lines
show wcp circuits
show wcp vcs
show wcp stats all
show wcp stats error1
show wcp stats error2
show hifn circuits
show hifn stats
show hifn stats error
show
commands:
C-2
C-2
C-3
C-4
C-4
C-5
C-6
C-6
C-7
117352-D Rev. 00
C-1
Page 94

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
show wcp lines
The
show wcp lines
configured for lines on the router.
The output includes the following information:
Channel Number Number of the channel on which WCP compression is
Slot/<Mod>/
Connector
State State of WCP compression on the line: Enabled or Disabled.
Compression Mode The compression mode operating on the line: continuous packet
History Size The amount of memory allocated to compression history for the
Buffer Size The amount of buffer memory for transmission history on the line
Configured Engine
Type
show wcp circuits
command displays information about WCP compressio n
configured.
The line identified by slot number, modu le type, and connector
number.
compression (CPC), pack et-b y-pac ket compression (PPC), or th e
mode inherited from the line.
line.
The type of compression operating on the line: hardware or
software.
C-2
The
show wcp circuits
command displays information about WCP compression
operating on the circuit.
The output includes the following information:
Circuit Name Circuit name of the interface.
State State of WCP compression on the circuit: Enabled or Disabled.
Compression Mode The compression mode operating on the line: continuous packet
compression (CPC) or packet-by-packet compression (PPC).
History Size The amount of memory allocated to compression history for the
circuit.
Configured Engine
Type
The type of compression operating on the circuit: hardware or
software.
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 95

show wcp vcs
Monitoring Software Compression Using the BCC show Commands
The
show wcp vcs
command displays informat ion about virtual circuits running
WCP compression.
The output includes the following information:
Slot/<Mod>/
Connector
Channel Number Number of the channel on which this virtual circuit is running.
Circuit Name Circuit name of the interface.
Vc Id Identification of the virtual circuit.
Compression State State of the compression software on the virtual circuit:
Decompression State State of the decompressing software on the virtual circuit:
Actual Comp Mode Compression mode operating on the circuit: continuous packet
Actual Hist Size Amount of memory allocated to compression history for the
Actual Engine Type Type of c ompression operating on the circuit: hardware or
Interface identified by slot, module, and connector.
• data (dat a is being compressed)
• disabled (compression software is inoperative)
• disconnected (compression is not connected to the virtual
circuit)
• init (compression software is initializing)
• nak (compression software is returning a negative
acknowledgment)
• data (data is being decompressed)
• disabled (decompression software is inoperative)
• disconnected (decompression is not connected to the virtual
circuit)
• init (decompression software is initializing)
• rexmit (decompression software is ret ransmitting)
• reset (decompression software has been reset)
• connecting (decompression software is connecting to the
virtual circuit)
• disconnecting (deco mpressi on softw are is d isconnecti ng from
the virtual circuit)
compression (CPC) or packet-by-packet compression (PPC).
circuit.
software.
117352-D Rev. 00
C-3
Page 96

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
show wcp stats all
The
show wcp stats all
command displays statistical information about the
performance of WCP compression on the circuit.
The output includes the following information:
Slot/<Mod>/
Connector
Channel Number The number of the channel on which this virtual circuit is running.
Circuit Name Circuit name of the interface.
Vc Id Identification of the virtual circuit.
Compression Ratio Ratio of number of bytes received by the WCP compression
Decompression Ratio Ratio of number of bytes received by the WCP deco mpression
Compressor In Number of packets received by the comp ressor.
Compressor Out Number of packets transmitted from the compressor.
Decompressor In Number of packets received by the decompressor.
Decompressor Out Number of packets transmitted from the decompressor.
CPC pkts Number of CPC packets transmitted (Tx) and received (Rx).
PPC pkts Number of PPC packets transmitted (Tx) and received (Rx)..
The interfac e identified by slot, module, and connector.
software to the number of bytes transmitted by it.
software to the number of bytes transmitted by it.
show wcp stats error1
The
show wcp stats error1
conditions for WCP compression on the connection.
The output includes the following information:
Channel Number The number of the channel on which this virtual circuit is running.
Circuit Name Circuit name of the interface.
Vc Id Identification of the virtual circuit.
Anti-Expanded
Packets (Tx)
Anti-Expanded
Packets (Rx)
C-4
command displays information about error
Number of anti-expanded packets transmitted.
Number of anti-expanded packets received.
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 97

Monitoring Software Compression Using the BCC show Commands
Data Out of Sequence Number of instances registered of the data-out-of-sequence
Rexmit Out of
Sequence
Rexmit Time-Outs Number of timeout messages retransmitted.
Exceeded Ks Number of times that K was exceeded. (WCP maintains a
show wcp stats error2
condition.
Number of times that an acknowledgment was retransmitted out
of sequence.
transmit history of data pac k et s f or a sp ecifie d r ange ca lled “K.” A
packet can be retransmitted if it remains in the range of packets
kept in the transmit history. If a packet is outside the range
specified by K, it cannot b e retransmitt ed.
The
show wcp stats error2
command displays information about error
conditions pertaining to WCP compression on the connection.
The output includes the following information:
Channel Number The number of the channel on which this virtual circuit is running.
Circuit Name Circuit name of the interface.
Vc Id Identification of the virtual circuit.
Reset Packets (Tx) Number of reset packets transmitted.
Reset Packets (Rx) Number of reset packets received.
Re-transmit Request
(Tx)
Re-transmit Request
(Rx)
Re-transmit Naks (Tx) Number of negative acknowledgments transmitted
Re-transmit Naks (Rx) Number of negative acknowledgments received
Number of retransmit request packets transmitted.
Number of retransmit request packets received.
117352-D Rev. 00
C-5
Page 98

Configuring Data Compression Se rvices
show hifn circuits
The
show hifn circui ts
to operate Hi/fn compression.
The output includes the following information:
Circuit Name Circuit name of the interface.
State State of Hi/fn compression on the circuit: Enabled or Disabl ed.
Configured Engine
Type
show hifn stats
The
show hifn sta t s
performance of Hi/Fn compression on the circuit.
The output includes the following information:
Circuit Name Circuit name of the interface.
Compression Ratio Ratio of number of bytes received by the Hi/fn compression
Decompression Ratio Ratio of number of bytes received by the Hi/fn decompression
Compressor In Number of packets received by the comp ressor.
Compressor Out Number of packets transmitted from the compressor.
Decompressor In Number of packets received by the decompressor.
Decompressor Out Number of packets transmitted from the decompressor.
CPC Packets (Tx) Number of CPC packets transmitted.
CPC Packets (Rx) Number of CPC packets received.
command displays information about circuits configured
The type of compression operating on the circuit: hardware or
software.
command displays statistical information about the
software to the number of bytes transmitted by it.
software to the number of bytes transmitted by it.
C-6
117352-D Rev. 00
Page 99

Monitoring Software Compression Using the BCC show Commands
show hifn stats error
The
show hifn stats error
command displays information about error conditions
for Hi/fn compression on the connection.
The output includes the following information:
Circuit Name Circuit name of the interface.
Expanded Pkts (Tx) Number of expanded packets transmitted.
Expanded Pkts (Rx) Number of expanded packets received.
Reset Requests (Tx) Number of reset requests transmitted.
Reset Requests (Rx) Number of reset requests received.
117352-D Rev. 00
C-7
Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...