Page 1

Communication Server 1000
Central Answering Position
Implementation Guide
NN43011-501
.
Page 2

Document status: Standard
Document version: 01.01
Document date: 1 August 2006
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks
All Rights Reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical
data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without
express or implied warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this
document. The information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
Nortel, the Nortel logo and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Sourced in Canada.
Page 3

Revision History
August 2006
Standard 01.01. This document is issued to support Central Answering
Position (CAP) functionality for the IP Phone 2004 and the M3904 digital
telephone.
3
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 4

4 Revision History
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 5

Contents
About this document 7
Subject 7
Applicable systems 7
Intended audience 9
Conventions 9
Related information 9
About the Central Answering Position 11
Contents 11
Introduction 11
Hardware requirements 13
CAP Configuration 15
Contents 15
Introduction 15
Key layouts 15
Configuring CAP using CLI commands 16
Configuring CAP using Telephony Manager 22
5
CAP functionality versus M2250 functionality 11
Key-Based Accessory (KBA) modules 16
Key Expansion Modules (KEM) 16
Telephone properties 23
Key functions 23
Telephone features 24
Logging onto the ACD queue 27
Contents 27
Introduction 27
Logging onto the ACD queue 27
Logging out of the ACD queue 28
Common CAP features 29
Contents 29
Introduction 29
Conference 30
Direct Station Select (BFS) 30
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 6

6 Contents
Directory Number (DN) 31
Display Queue (Disp Queue) 31
Make Busy 32
No Hold Conference (N.H. Conf) 32
Override 32
Park 33
Privacy Release (Priv Rls) 34
Program 34
Transfer 35
Other features 37
Contents 37
Call Forward and Busy Status 37
Feature Operation 37
Feature Requirements 38
Feature Interactions 38
Feature Programming 39
Forced Camp-on/Priority Override 39
Feature Operation 41
Feature Requirements 41
Feature Interactions 42
Feature Programming 42
Procedures
Procedure 1 Accessing telephone properties 23
Procedure 2 Changing key functions 23
Procedure 3 Changing telephone features 24
Procedure 4 System configured in Position ID mode 27
Procedure 5 System configured in Agent ID mode 28
Procedure 6 System configured in Position ID or Agent ID mode 28
Procedure 7 Adding a person to a call 30
Procedure 8 Making a Direct Station Select call 30
Procedure 9 Making an internal call 31
Procedure 10 Displaying CAP information 31
Procedure 11 Making the CAP appear busy 32
Procedure 12 Adding a person to a call 32
Procedure 13 Overriding a busy signal and connecting to a call 33
Procedure 14 Parking a call on the System Park extension 33
Procedure 15 Parking a call on an extension other than the System Park
extension 33
Procedure 16 Retrieving a parked call 34
Procedure 17 Removing privacy from a line 34
Procedure 18 Transferring a call without consultation 35
Procedure 19 Transferring a call with consultation 35
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 7

About this document
This is a global document. Contact your system supplier or your Nortel
Networks representative to verify that the hardware and software described
is supported in your area.
Subject
This guide describes the Central Answering Position (CAP) used with CS
1000/Meridian 1 systems. The information in this guide includes:
•
description of the CAP and a list of required equipment
•
procedures to configure the CAP
•
procedures to log on to the ACD queue
•
description of common CAP features, including procedures on how to
use them
Note on legacy products and releases
This NTP contains information about systems, components, and features
that are compatible with Nortel Communication Server 1000 Release 4.5
software. For more information on legacy products and releases, go to
ww.nortel.com and from the main menu, select Support & Training and
w
then Technical Documentation.
7
Applicable systems
This document applies to the following systems:
•
Communication Server 1000S (CS 1000S)
•
Communication Server 1000M Chassis (CS 1000M Chassis)
•
Communication Server 1000M Cabinet (CS 1000M Cabinet)
•
Communication Server 1000M Half Group (CS 1000M HG)
•
Communication Server 1000M Single Group (CS 1000M SG)
•
Communication Server 1000M Multi Group (CS 1000M MG)
•
Communication Server 1000E (CS 1000E)
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 8
8 About this document
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet
•
Meridian 1 PBX 51C
•
Meridian 1 PBX 61C
•
Meridian 1 PBX 81
•
Meridian 1 PBX 81C
Note: When upgrading software, memory upgrades may be required on
the Signaling Server, the Call Server, or both.
System migration
When particular Meridian 1 systems are upgraded to run CS 1000 Release
4.5 and configured to include a Signaling Server, they become CS 1000M
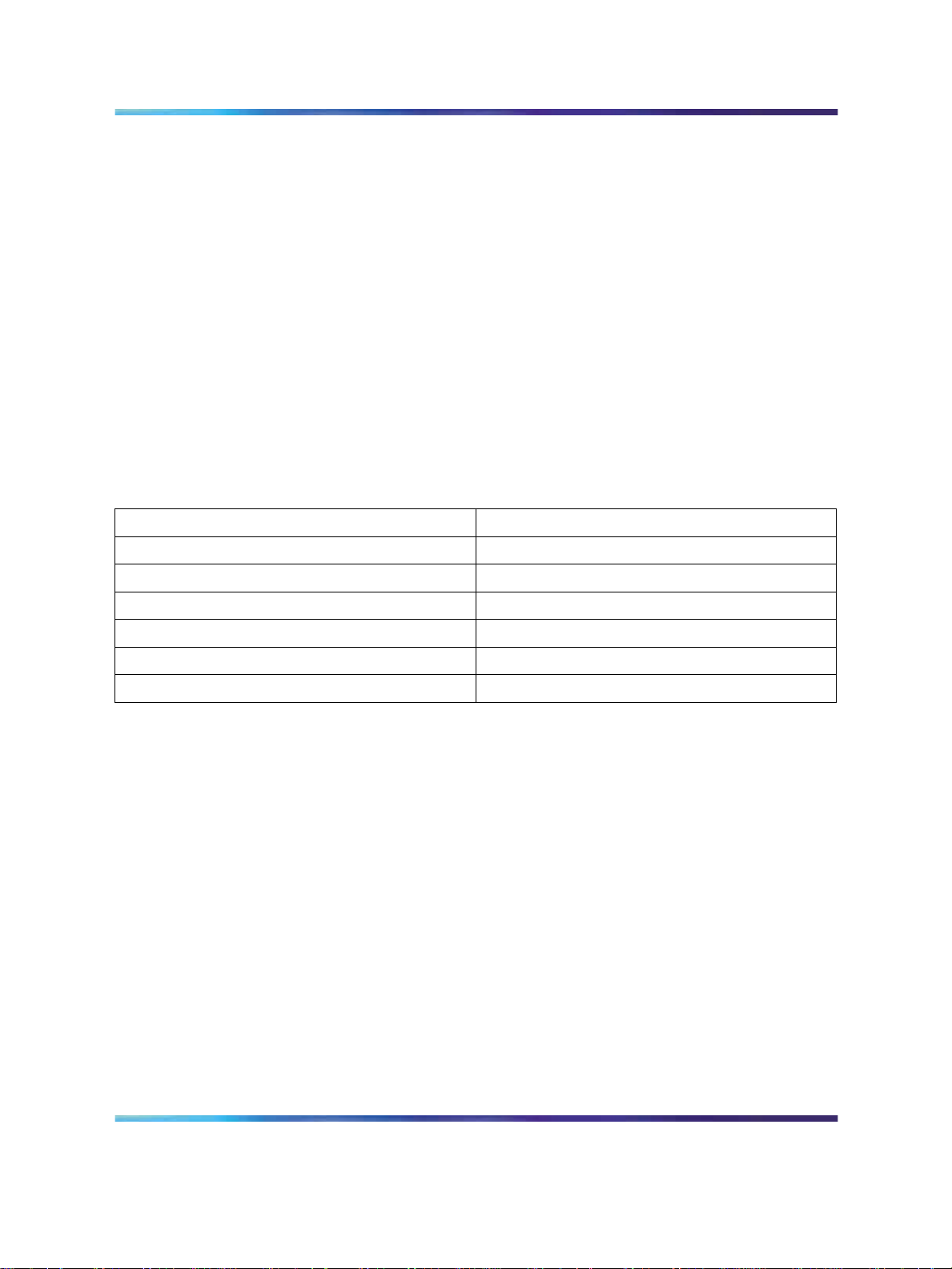
systems. "Meridian 1 systems to CS 1000M systems" (page 8) lists each
Meridian 1 system that supports an upgrade path to a CS 1000M system.
Meridian 1 systems to CS 1000M systems
This Meridian 1 system...
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis CS 1000M Chassis
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet CS 1000M Cabinet
Meridian 1 PBX 51C CS 1000M Half Group
Meridian 1 PBX 61C CS 1000M Single Group
Meridian 1 PBX 81 CS 1000M Multi Group
Meridian 1 PBX 81C CS 1000M Multi Group
Maps to this CS 1000M system
Note the following:
•
When a CS 1000/Meridian 1 system is upgraded to run CS 1000
Release 4.5 software, that system becomes a Meridian 1 PBX 11C
Chassis.
• When an Option 11C system is upgraded to run CS 1000 Release 4.5
software, that system becomes a Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet.
For more information, see one or more of the following NTPs:
•
Communication Server 1000M and Meridian 1: Small System Upgrade
Procedures (553-3011-258)
•
Communication Server 1000M and Meridian 1: Large System Upgrade
Procedures (553-3021-258)
•
Communication Server 1000S: Upgrade Procedures (553-3031-258)
•
Communication Server 1000E: Upgrade Procedures (553-3041-258)
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 9

Intended audience
This document is intended for individuals responsible for configuring the
Central Answering Position on an IP Phone 2004 or M3904 digital telephone.
Conventions
Terminology
In this document, the following systems are referred to generically as
“system”:
•
Communication Server 1000M (CS 1000M)
•
Meridian 1
The following systems are referred to generically as “Small System”:
•
Communication Server 1000M Chassis (CS 1000M Chassis)
•
Communication Server 1000M Cabinet (CS 1000M Cabinet)
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet
Related information 9
The following systems are referred to generically as “Chassis system”:
•
Communication Server 1000M Chassis (CS 1000M Chassis)
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis
The following systems are referred to generically as “Cabinet system”:
•
Communication Server 1000M Cabinet (CS 1000M Cabinet)
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet
Related information
This section lists information sources that relate to this document.
NTPs
The following NTPs are referenced in this document:
•
Telephones and Consoles (553-3001-367)
•
IP Phones (553-3001-368)
•
Software Input/Output (553-3001-311)
•
Communication Server 1000M and Meridian 1: Small System
Installation and Configuration (553-3011-210)
•
Communication Server 1000M and Meridian 1: Large System
Installation and Configuration (553-3021-210)
•
Communication Server 1000: IP Line (553-3001-365)
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 10

10 About this document
Online
To access Nortel documentation online, go to www.nortel.com and from the
main menu on the home page, select Support & Training and then Technical
Documentation.
CD ROM
To obtain Nortel documentation on CD-ROM, contact your Nortel customer
representative.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 11

About the Central Answering Position
Contents
This section contains information on the following topics:
"Introduction" (page 11)
"Hardware requirements" (page 13)
Introduction
The Central Answering Position (CAP) is an alternative to the Nortel M2250
attendant console. It operates as an Automatic Call Distribution (ACD)
agent on a IP Phone 2004 or an M3904 Digital telephone. A CAP can
provide many of the call-handling features required by an attendant such as
transferring, parking, and placing calls. Optional IP Phone Key Expansion
modules and M3900 Key-Based Accessory modules can be added to the
appropriate CAP telephone for additional lines and features, as well as to
provide Direct Station Select and Busy Lamp Field functionality.
11
CAP functionality versus M2250 functionality
Although the CAP is an attendant position, it is an ACD agent and does not
operate the same as the M2250 Attendant Console.
Note: The CAP telephone cannot be viewed as having the same
capabilities as an M2250 attendant console. It is an IP Phone 2004
or M3904 digital telephone with optional key expansion or key-based
accessory modules and can only deliver telephone-level features, not
console-specific functionality. As a result of this limitation, the CAP
telephone does not have access to attendant features such as Network
Attendant Services (NAS).
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 12
12 About the Central Answering Position
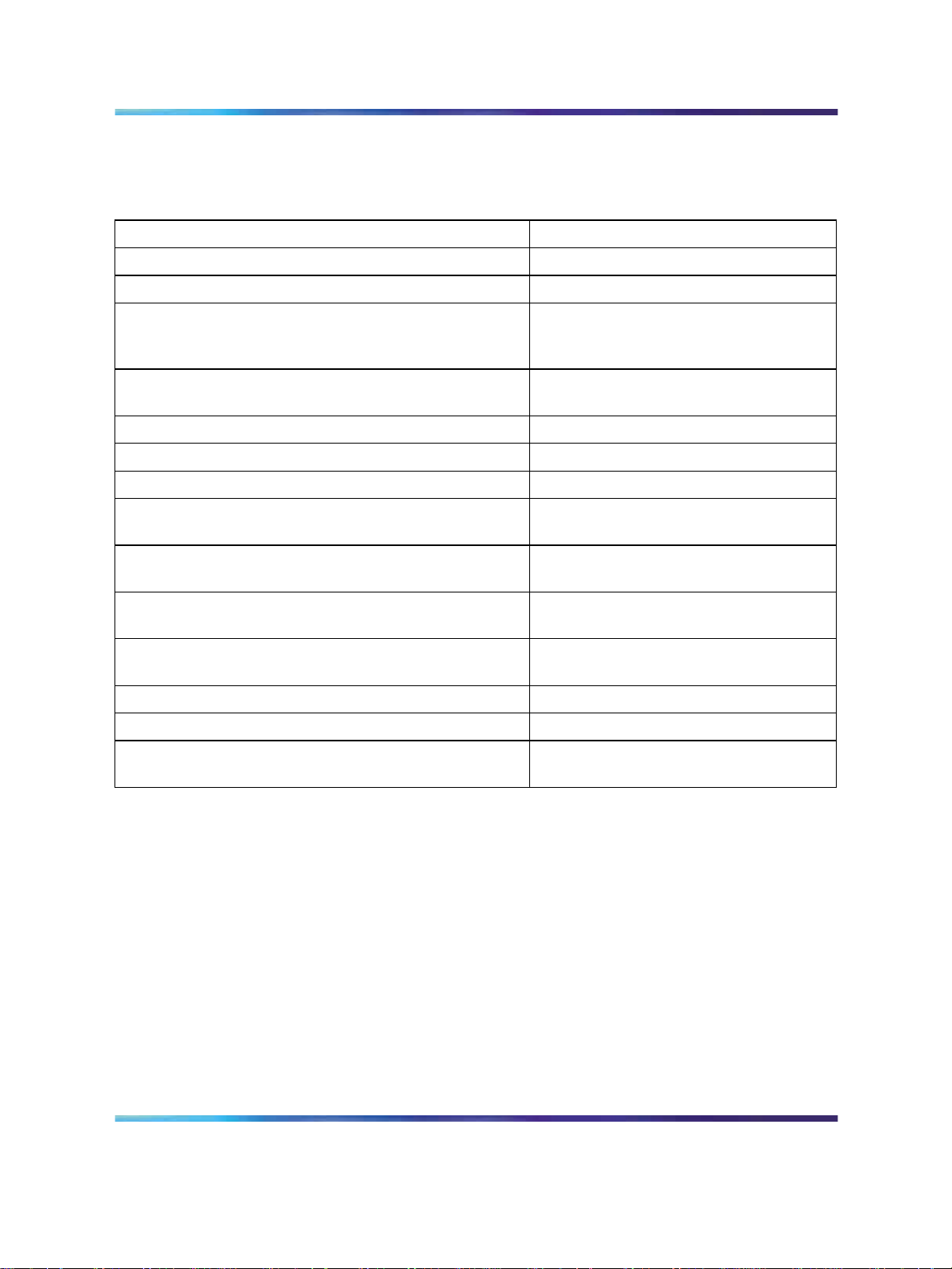
"CAP features versus M2250 features" (page 12) compares common CAP
features to similar M2250 attendant console features:
CAP features versus M2250 features
Central Answering Position (CAP) M2250 Attendant Console
Override. Busy Verify
Not Ready. Position Busy
Make Set Busy (Night Service is entered when the last
Central Answering Position logs out of the ACD queue
by depressing the Make Set Busy key).
A Night Service key can also be defined for an ACD
DN so equipped.
Transfer/No Hold Conference. Release (to extend)
Transfer. Exclude Source/Destination
Conference/No Hold Conference. Conference
In Calls Key (Key 0) - Incoming calls only. (1 or more
DN keys can be assigned for outgoing calls).
Call Forward and Busy Status (BFS) and Add-on
modules.
Keys configured as BFS keys enable you to connect to
an extension by pressing a single key.
ACD position configured as supervisor and provisioned
with an ACD agent observe key.
Overflow/Interflow. Attendant Overflow Position
ACD Recorded Announcement. Attendant RAN
ACD position configured as supervisor and provisioned
with a Display Calls Waiting key.
Night Service
Loop Key 0
Busy Lamp Field
Direct Station Select
Supervisor Console
Call Waiting Indicator
Attendant Console features not available with CAP
The following is a list of Attendant Console features that are not available
with a CAP telephone:
•
The CAP does not have the capability to provision feature keys that
function like incoming call indicators
•
The following attendant features have no equivalent on the CAP:
— Trunk Group Busy
— Incoming Call Indicators
— Attendant Administration Function Keys
— Multiple Loop Keys (for incoming/outgoing calls)
— Signal Source/Destination
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 13

Consider the above information when deciding between the functionality of
a CAP or a M2250 console.
Hardware requirements
The following equipment is required for a CAP:
•
IP Phone 2004 or M3904 digital telephone
•
Optional Key expansion module for a IP Phone 2004
•
Optional Key-Based Accessory module for a M3904 digital telephone
Hardware requirements 13
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 14

14 About the Central Answering Position
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 15

CAP Configuration
Contents
This section contains information on the following topics:
"Introduction" (page 15)
"Key layouts" (page 15)
"Configuring CAP using CLI commands" (page 16)
"Configuring CAP using Telephony Manager" (page 22)
Introduction
This section assumes that the IP Phone 2004 or M3904 digital telephone
is installed and ready to be configured as a CAP. Use one of the following
methods to configure the telephone as a CAP:
•
CLI commands
15
•
Telephony Manager (TM)
Key layouts
Each CAP telephone is preconfigured with certain features that make it
easy to respond to and transfer calls. For information on preprogrammed
data, see Communication Server 1000M and Meridian 1: Small System
Installation and Configuration (553-3011-210).
CAP features are not limited to those preconfigured; some features can
be changed to meet specific needs. In addition to several fixed-feature
keys, each CAP telephone comes with programmable soft keys that can be
configured using the overlays described later in this section.
See Telephones and Consoles (553-3001-367) for a complete list of
preconfigured features for the M3904 digital telephone.
See IP Phones (553-3001-368) for a complete list of preconfigured features
for the IP Phone 2004.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 16

16 CAP Configuration
Key-Based Accessory (KBA) modules
The Key-Based Accessory module (KBA) provides 22 additional line/feature
keys for the M3904 digital telephone. You can add up to two KBAs for a
total of 44 line/feature keys.
See Telephones and Consoles (553-3001-367) for information on the
installation and configuration of M3904 digital telephones and Key-Based
Accessory modules, or consult the installation guide that comes with your
product.
Key Expansion Modules (KEM)
The Nortel IP Phone Key Expansion Module (KEM) is a hardware
component that connects to IP Phone 2004 and provides additional line
appearances and feature keys. Up to two IP Phone KEMs can be connected
to an IP Phone 2004 for a total of 48 line/feature keys.
Note 1: Key Expansion Modules are supported only with RLS 4.0 or
later.
Note 2: The IP Phone 2004 can also have up to 48 additional
line/feature keys using the Shift key functionality and one IP Phone
KEM. With two IP Phone KEMs connected, the Shift key functionality
does not affect the IP Phone KEMs because the maximum number of
line/feature keys is already available.
These keys act as Direct Station Select (DSS) keys and Busy Lamp Field
arrays. Each of these keys is programmed with the Terminal Number (TN)
of the telephone to which it corresponds.
You can use these keys to visually access the status of a telephone, or
to contact and extend calls to telephones. The status of a telephone is
indicated by the key lamp in the following ways:
Idle — The key lamp is off.
Busy — The key lamp is steadily lit.
Forwarding — The key lamp is flashing.
See IP Phones (553-3001-368) for information on the installation and
configuration of Key Expansion Modules, or consult the installation guide
that comes with your product.
Configuring CAP using CLI commands
Use the system CLI to access the following overlays in the order they are
listed:
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 17

"LD 16 - Defining and modifying trunk routes" (page 17)
"LD 14 - Defining and modifying trunks" (page 17)
"LD 23 - Configuring ACD as the night number" (page 18)
"LD 15 - Configuring customer options" (page 20)
"LD 11 - Configuring CAP" (page 21)
Note: The followingis a summary of the steps to follow when configuring
the CAP from a CLI. Refer to Software Input/Output: Administration
(553-3001-311) for a complete listing of prompts and responses for
the overlays.
Default selections for each prompt are shown in parentheses.
To configure RAN trunk routes, respond as follows for prompts in LD 16:
LD 16 - Defining and modifying trunk routes
Configuring CAP using CLI commands 17
Prompt Response
REQ Request
CHG Change existing data block
END Exit overlay program
OUT Remove data block
NEW Add new data block to the system
TYPE bbb bbb = trunk type (COT, TIE, DID, etc.)
DMOD
1-127
Comment
Default Model number for this route (Small Systems, CS 1000S, MG
1000B, and MG 1000T)
To configure RAN trunks, respond to prompts as follows in LD 14:
Note: LD 14 is also used to assign incoming trunks with a Priority (with
CLS=APY)
LD 14 - Defining and modifying trunks
Prompt Response
REQ Request.
CHG Change existing data block.
Comment
END Exit overlay program.
MOV Movedata block from one TN to another. Not valid for Small System
and CS 1000S Models. MOV cannot be used to move a Phantom
TN. MOV command cannot be used to move trunk data blocks.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 18

18 CAP Configuration
Prompt Response
Comment
NEW x Add new data block to the system. Follow NEW with a value of 1-255
to create that number of consecutive trunks. You are not allowed to
create more than one Phantom TN at a time. When a value different
than 1 is entered for the creation of a Phantom TN, it is simply ignored
and only one TN is created.
OUT x Remove data block. Follow OUT with a value of 1-255 to remove
that number of consecutive trunks.
TYPE
aaa <m>
aaa = the trunk type (COT, TIE, DID, etc.) "m" is optional. Enter "m"
if you are using a model trunk.
MODL
1-127
Model number for Small System.
Model number for CS 1000S.
TN l s c u Terminal Number. If you enter a value for "m" this prompt does not
appear.
CDEN *D Density. If you enter a value for "m" this prompt does not appear.
TOTN l s c u To Terminal Number. If you enter a value for "m" this prompt does
not appear.
The CAP queue (ACD queue) is configured using LD 23. Respond to the
prompts as follows:
LD 23 - Configuring ACD as the night number
Prompt Response
Comment
REQ NEW Add new data to the system.
TYPE ACD Automatic Call Distribution data block. Requires Basic Automatic Call
Distribution (BACD) package 40.
CUST
ACDN
xx
xxxx
Customer number associated with this data block as defined in LD 15.
ACD Directory Number. Up to 4 digits, up to 7 digits with Directory
Number Expansion (DNXP) package 150.
MWC NO Message Waiting Center
ACPQ (NO), YES Answer Call Priority Queue. International Supplementary Features
(SUPP) package 131 must be installed. Answered calls are (are not)
given priority when re-entered in queue.
AST (NO), YES Associated Set. The Associate Set assignments are performed in LD
10 and LD 11 for each ACD telephone. Associated set (only used
with Meridian Link).
DSAC (NO), YES ACD DN is not an IS/Data Service Access Code. ACD DN is an
IS/Data Service Access Code. Prompted when MWC = NOServer
IS/data service access code (only used with Meridian Link).
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 19

Configuring CAP using CLI commands 19
Prompt Response
MAXP
1-120
Comment
Maximum Number of Agent Positions. The value of the MAXP can
be increased to the allowed maximum or decreased to the current
number agents.
SDNB (NO), YES Secondary DN Blocking. Block calls to the Secondary DN while busy
on ACD call. Block (or not) calls to the Secondary DN.
BSCW (NO), YES Block Calls to the Secondary DN on Walkaway. The caller to the
source DN hears busy tone. Block (or not) calls to the secondary DN
on walkaway.
ISAP (NO), YES Integrated Services Application Protocol (ACD messages sent across
the ISDN/AP link). Set to YES for Meridian Mail applications. ACD
messages sent (not sent) across the ISDN/AP link.
RGAI (NO), YES Ring Again for Internal calls. When internal caller dials a queue with
no available agents, fast ringback is provided. If RGAI = YES, the
caller can activate Ring Again to be presented to the next available
agent. Enter YES for Data Service Access Code (DSAC). RGAI must
= YES for DSAC.Ring again for internal calls.
FRRT
0-511
First RAN Route number for ACD. The route and at least one trunk
must exist before defining FRRT. Enter X to remove.
FRT
0-2044
First RAN Time (the time in seconds allowed before unanswered
incoming ACD calls are connected to the first RAN). Prompted if
FRRT is defined. If a value is not entered FRT defaults to blank and
there is no connection to the RAN.
SRRT
0-511
Second RAN Route number for ACD. The route and at least one
trunk must exist before defining SRRT. Enter X to remove. Second
RAN route number for ACD.
SRT
0-2044
Second RAN Time. Time in seconds before second RAN is
connected to ACD calls. Prompted if SRRT is defined. There is no
default for SRT.
NRRT
0-511
Night RAN Route number assigned as night announcement for ACD
calls. If NRRT and NCFW are both defined, then NRRT course first.
The route and at least one trunk must exist before defining NRRT.
Enter X to remove.
FROA (NO), YES First RAN On Arrival (the 1st RAN to be given to incoming calls
immediately; FRT time ignored). If FROA = NO, the call is forced
to wait FRT time. Recorded Announcement is given only if an idle
agent is not found.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 20

20 CAP Configuration
Prompt Response
NCFW
x...x
Comment
Night Call Forward DN for ACD calls (up to 23 digits) and Operator
Revert DN for Meridian Mail (IMS, IVMS). NCFW is tracked on reports
as interflow. NCFW can be up to 31 digits. Precede NCFW entry with
X to delete. Typing four asterisks (****) at the NCFW prompt does
not let the user exit.
FORC (NO), YES Force. Calls are forced to arrive in answered state. When FORC =
YES, the call arrives on Key 0 (in-calls key) in an answered state.
Headsets are recommended for this option.
Use LD 15 to do the following:
•
Define and modify the attendant extension number
• Define the night number and time
•
If necessary, define a second night number and time
•
Define customer options
In LD 15, respond to the prompts as follows:
LD 15 - Configuring customer options
Prompt Response
Comment
REQ: CHG Change existing data block.
TYPE: NIT Night Service
CUST
NIT1
0-99
x...x
Customer Number
Enter the ACD DN programmed in LD 23.
TIM1 hh mm Hour and Minute for First Night Service DN. Enter the hour and
minute for First Night Service DN, where: hh = 0-23, mm = 0-59.
Enter X to remove the time. If no time is entered here, the system
assumes a 24-hour clock.
...
REQ: CHG Change existing data block.
TYPE MPO_DAT
Multi-Party Options
A
CUST
0-99
Customer Number
FMOP (NO), YES Flexible Misoperation options are (are not) required.
- RGNA STD Ring No Answer treatment. Standard Operation (STD) is default.
- AOCS
xxx yyy
All Other Cases. Where: xxx is for internal calls and yyy or ATN
is for external calls.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 21

Configuring CAP using CLI commands 21
Prompt Response
- RCY1 1 - (6) - 15 Number of Cycles of Re-ringing before forwarding to attendant or
- RCY2 1 - (4) - 15 Number of Cycles of Ringing before forwarding to transferring station.
Comment
disconnecting. Applies only if RGNA = DAR or AAR.
Valid only for the RGNA option.
In LD 15, the customer data block and ATDN (Attendant Directory Number)
default to 0. When 0 is dialed by a station user, the nonexistent console is
seen by the system as being in Night Service. Therefore, all dial 0 calls are
directed to the night number, which is the ACD directory number of the CAP.
All calls redirected to the CAP that are subsequently transferred to a station
can be redirected to Call Pilot or recalled to the CAP ACD queue. The
software associated with this produces prompts in LD 15, which determine
whether or not a call is recalled to the CAP queue or redirected to a forward
no answer destination, such as Call Pilot.
Note: The IP Phone 2004 has four soft-labeled, predefined soft keys
that can provide up to 10 features. Because they are predefined, the
user cannot change the key number assignment. Use LD 11 to program
keys 16 to 26 on the IP Phone 2004.
In LD 11, respond to the prompts as follows:
LD 11 - Configuring CAP
Prompt Response
REQ CHG Change existing data block.
TYPE
...
CLS (AGN) ACD Agent
...
KBA (0)-2 Key-Based Accessory module for M3904 (if applicable).
KEM (0)-2 Key Expansion Module for IP Phone 2004 (if applicable).
...
3904
I2004 IP Phone 2004
SPV ACD Supervisor
TDD Tandem Digit Display
SWA Station-to-Station Call Waiting Allowed. A Call Waiting key or CWT
Comment
M3904 digital telephone
must be defined. Must have CLS=HTD because hunting takes
precedence.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 22

22 CAP Configuration
Prompt Response
KEY xx ACD
yyyy (cccc
or D) zzz
xx MSB Make Set Busy key. On the M3905 key numbers 8-11 are reserved
xx DWC
yyyy
xx TRN Call Transfer key. On the M3904 and M3905, key 17 is reserved for
xx AO6 Six-Party Conference key. On the M3904 and M3905, key number
Comment
Automatic Call Distribution key xxxx=key number; yyyy=ACD DN or
Message Center DN; cccc=CLID table entry of (0)-N, where N=the
value entered at the SIZE prompt in LD 15 minus 1; D=the character
D (when the character D is entered, the system searches the DN
keys, from key 0, up to find a DN key with CLID table entry. The
CLID associated with the found DN key will be used); zzz=agent’s
position ID.
for AAG, AMG, ASP, DWC, MSB and NRD.
ACD Supervisor Display Waiting Calls key. Where: yyyy=ACD DN.
Up to 4 digits, up to 7 digits with Directory Number Expansion (DNXP)
package 150. A maximum of eight DWC keys can be assigned per
queue on eight supervisors. Agent sets can only have 1 SWC key
for their own queue. ACD agent telephones can support the display
waiting calls key. Must have CLS=SPV and ADD or DDS. The key
can be used with supervisors and agents. On the M3905 key numbers
8-11 are reserved for AAG, AMG, ASP, DWC, MSB and NRD.
TRN or NUL. basic-24 On the IP Phone 2004 key 17 is reserved
for TRN or NUL.
18 is reserved for AO3, AO6, or NUL. On the IP Phone 2004 key
number 18 is reserved for AO3, AO6, or NUL.
xx NHC No Hold Conference key
xx PRK Call Park. The Transfer (TRN), or Six-Party Conference (A06) key
plus a Dial Access code can be used instead of the Park key. On the
M3904 and M3905, key 21 is reserved for PRK or NUL. On the IP
Phone 2004 key 21 is reserved for PRK or NUL.
xx BFS aa
bb
Busy-Forward Status. Where: TN=Terminal Number to be screened.
A Key cannot be assigned to a BRI set. Note: It is possible to
configure the TN of the same set against only the BFS key if the
Class of Service is BFEA.
Configuring CAP using Telephony Manager
You can use Telephony Manager (TM) Desktop Services to view and modify
the configuration of your telephone through a web browser. The web
display includes a graphical view of the telephone and shows the configured
features.
Note: Your network administrator determines the features and privileges
you can use in TM Desktop Services. If you are not sure of your access
privileges, contact your network administrator for more information.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 23

You can use the Features page to modify telephone features not assigned
to keys. Features are related to individual prompts in LD 10 or 11, with one
or more configurable parameters.
Where applicable, a drop-down list containing all possible values for the
feature is provided. If no drop-down list is provided, type the value into
the field.
Telephone properties
Procedure 1 Accessing telephone properties
Step Action
Configuring CAP using Telephony Manager 23
1
2
Log on to a TM session.
On the Desktop Services main menu, choose a Telephone DN
from the Telephones list.
The General page appears, showing information about the telephone
you selected.
Note: The telephones are identified by prime directory number
(DN). To create this list, the Web server scans all the employee
databases, one per system, on the server. If you have
telephones on different systems that are served by different
Optivity Telephony Manager (OTM) servers, you must log in to
the different servers to access these telephones. Contact your
network administrator to obtain a URL, user login name, and
password for each of these OTM servers.
3
From the General page you can make configuration changes to your
telephone by selecting the Keys or Features buttons. Each of these
functions is described below.
—End—
Key functions
Procedure 2 Changing key functions
Step Action
1
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
From the General page, click the Keys button. The Keys page
appears.
Communication Server 1000
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 24

24 CAP Configuration
Note: The M3904 digital telephone has two layers of keys. You
can access the second layer of keys by clicking the Shift button
on the telephone image.
2
If an M3900 Key-Based Accessory or an IP Phone Key Expansion
Module is installed, click Next to view the next list of available keys.
3
Select a key by clicking on it. The properties for the key are
displayed.
4
Click Change to modify the properties for the selected key. The
Key Change Wizard appears.
5
Follow the Wizard instructions to change the properties of the
selected key.
6
After you change the keys and click the Submit button, the Confirm
Changes dialog box appears.
7
Verify the information and click Confirm. If no errors exist, a change
confirmation page appears.
Telephone features
Procedure 3 Changing telephone features
—End—
Step Action
1
From the General page, click the Features button.
The Features page appears.
2
From the list of features displayed, change the Value field for the
feature you want to modify. Some fields have drop-down menus from
where you can make a selection.
3
When you finish, click Submit to make the changes or Reset to
clear the fields and undo your changes.
4
After you change the features and click the Submit button, the
Confirm Changes dialog box appears.
5
Verify the information and click Confirm. If there are no errors, a
change confirmation page appears.
—End—
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 25

Configuring CAP using Telephony Manager 25
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 26

26 CAP Configuration
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 27

Logging onto the ACD queue
Contents
This section contains information on the following topics:
"Introduction" (page 27)
"Logging onto the ACD queue" (page 27)
"Logging out of the ACD queue" (page 28)
Introduction
Two procedures are available for logging onto the ACD queue. The method
you use to log on depends on whether your system is configured in Position
ID mode or Agent ID mode. The following procedures describe how to log
on and out of the ACD queue for each type of system configuration.
Logging onto the ACD queue
27
Procedure 4
System configured in Position ID mode
Step Action
1
2
3
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Verify the CAP is in the Make Set Busy state. The Make Set Busy
lamp can be on or off.
Pick up the handset and place it on the desk, or, if you are using a
headset, press the headset key.
Press the Make Set Busy key .
You are logged onto the ACD queue.
—End—
Communication Server 1000
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 28

28 Logging onto the ACD queue
Procedure 5
System configured in Agent ID mode
Step Action
1
Verify the CAP is in the Make Set Busy state. The Make Set Busy
lamp can be on or off.
2
3
Press the Make Set Busy key or unplug the headset.
Enter your Agent ID
Note: The length and valid range of numbers in your agent ID
depends on how the ADS feature is programmed in LD 23.
The set is now in Not Ready mode.
4
Press the Not Ready key again.
You are logged onto the ACD queue.
Logging out of the ACD queue
Procedure 6
System configured in Position ID or Agent ID mode
Step Action
—End—
1
If you want to log out of the ACD queue, press the Make Set Busy
key or unplug the headset.
You are now logged out of the ACD queue.
—End—
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 29

Common CAP features
Contents
This section contains information on the following topics:
"Introduction" (page 29)
"Conference" (page 30)
"Direct Station Select (BFS)" (page 30)
"Directory Number (DN)" (page 31)
"Display Queue (Disp Queue)" (page 31)
"Make Busy" (page 32)
"No Hold Conference (N.H. Conf)" (page 32)
29
"Override" (page 32)
"Park" (page 33)
"Privacy Release (Priv Rls)" (page 34)
"Program" (page 34)
"Transfer" (page 35)
Introduction
This section describes each of the commonly configured features on the
CAP and explains how to use them. The feature keys in the key layout
diagram in the previous section correspond to the features listed in this
section. All of the features are listed in alphabetical order.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 30

30 Common CAP features
Conference
This key lets the CAP to create conferences and to join parties together.
The first party is put on hold while the second party is being added.
Procedure 7 Adding a person to a call
Step Action
1
When you answer a call from the ACD queue and you want to add
another person to the call, first press the Conf key.
2
Dial the number of the person to be added to the call or press the
appropriate Direct Station Select key.
The incoming call is put on hold.
You can consult with the person called when they answer.
3
4
Press Conf to link the conference.
You can repeat the process to add more people to the call or press
Rls to disconnect yourself from the call.
5
To talk back and forth with two people, press Hold to place your
second caller on hold, and then press the ACD queue key to connect
with your first caller. To connect to the second caller, press Hold
and then press Conf.
Direct Station Select (BFS)
Keys configured as Busy Forward Status (BFS) enable you to connect to an
extension. The keys on the add-on module work as Direct Station Select
(DSS) keys.
—End—
Note: Before you press a DSS key, you must press an extension (DN)
key first.
Procedure 8 Making a Direct Station Select call
Step Action
1
2
Press the DN key.
Press the DSS extension key.
—End—
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 31

Directory Number (DN)
This key is used for internal calling or, when required, by one of the feature
keys. For example, you use the DN key to retrieve a parked call. If you have
a PBX system, you can use this feature for outgoing public network calls.
Note: To make outgoing calls from the CAP, you must use the DN key.
You cannot use the ACD queue to make outgoing calls because it can
only receive calls.
Procedure 9 Making an internal call
Step Action
Display Queue (Disp Queue) 31
1
2
3
Lift the handset.
Press the DN key.
Dial the extension of the person that you want to call or press the
DSS key.
Display Queue (Disp Queue)
This key shows the number of calls in the queue, the number of staffed
CAPs, and the waiting time of the oldest call in the queue. With this feature,
the telephone does not have to be idle for you to display information.
Note: To use this feature, the CAP must be programmed to have
Supervisor (SPV) Class of Service. This is done using LD 11.
Procedure 10 Displaying CAP information
Step Action
1
Press the Disp Queue key.
—End—
2
To remove information from the display, press the Disp Queue key
again.
—End—
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 32

32 Common CAP features
Make Busy
This key lets the CAP to indicate that it is not staffed or cannot receive
calls. When the CAP is in the Make Busy state, calls are directed to the
programmed night call forward number for the CAP queue.
Procedure 11 Making the CAP appear busy
Step Action
1
Press Make Busy.
The indicator comes on.
2
To cancel the Make Busy feature, press Make Busy again.
The indicator goes off.
No Hold Conference (N.H. Conf)
This key lets you to add people to a conversation. The original party is
not put on hold as others are added.
Procedure 12 Adding a person to a call
Step Action
1
2
If you have answered a call from the ACD queue, press N. H. Conf.
Dial the number of the person to be added to the call or press the
appropriate Direct Station Select key.
—End—
The incoming call is not put on hold. You do not hear the phone
ringing, and you can still talk to the caller.
—End—
Override
This key lets the CAP interrupt an established call. The priority level of the
telephone involved in the call and the level of the CAP determine whether
an override is permitted.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 33

Procedure 13 Overriding a busy signal and connecting to a call
Step Action
Park 33
Park
1
If you have dialed an internal call and received a busy signal, press
Override.
You now join to the call in progress.
—End—
Because you cannot hold multiple calls on the ACD queue, a call can be
parked so you can receive other calls. The parked call can be retrieved by
the CAP or another telephone that has access to Call Park.
Note: To retrieve calls before the call timer expires, note the extension
on which the calls are parked.
Procedure 14 Parking a call on the System Park extension
Step Action
1
2
If you are on a call, press Park twice.
To take the caller off Park, press Rls to release the call.
—End—
Procedure 15 Parking a call on an extension other than the System Park extension
Step Action
1
2
3
4
If you are on a call, press Park.
Dial the extension number on which you want to park the call.
Press Park again.
Press Rls.
—End—
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 34

34 Common CAP features
Procedure 16 Retrieving a parked call
Step Action
1
2
Press the DN key.
Dial the extension on which the call is parked if the call is parked on
an extension other than the system call park number.
Note: Any telephone with access to Call Park can retrieve a
call that is parked.
Privacy Release (Priv Rls)
You can use this key to join or pick up a call that is on a private line. This
added party must have a telephone that shows the private line.
Procedure 17 Removing privacy from a line
Step Action
1
If you are on a call on a private line, press Priv Rls.
Any telephone that has access to this line can now join the
conversation.
—End—
2
To disconnect from the call after someone else has joined the
conversation, press the Rls key.
—End—
Program
You can use this key to change various display features. Data parameters
such as transmission speed, parity, and terminal mode can also be changed
if the CAP is equipped with an optional data adapter.
•
Press Program.
•
Use the volume control bar to scroll through the programmable features,
and press the number associated with the feature you wish to program.
•
Use the volume bar to adjust the feature you select.
The display features that can be programmed using this key are:
— Volume adjustment
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 35

Transfer
Transfer 35
— Predial recall
— Contrast adjustment
— Call timer enable
— Idle screen format
— Language selection
— Display diagnostics
— Key click
You can use this key to transfer a call to an extension without having to
wait for the desired party to answer.
Procedure 18 Transferring a call without consultation
Step Action
1
2
If you have answered a call from the ACD queue, press Transfer.
Dial the desired number or press the appropriate Direct Station
Select key.
3
Press Transfer while you still hear the phone ringing.
You are no longer connected to the call.
4
If the call is not answered or forwarded by the call forward feature, it
rings back to the CAP telephone (programmable in LD 15).
—End—
Procedure 19 Transferring a call with consultation
Step Action
1
2
If you have answered a call from the ACD queue, press Transfer.
Dial the desired number or press the appropriate Direct Station
Select key.
3
Wait until the call is answered.
The original call is put on hold.
4
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Speak to the person called.
Communication Server 1000
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 36

36 Common CAP features
5
To return to the original caller without extending the call, press the
ACD queue extension key.
6
To disconnect yourself from the call and connect the calling and
called parties, press Transfer again.
—End—
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 37

Other features
Contents
This section contains information on the following topics:
"Call Forward and Busy Status" (page 37)
"Forced Camp-on/Priority Override" (page 39)
Call Forward and Busy Status
The Call Forward and Busy Status (BFS) feature was designed for an
environment where party A forwards their calls to party B, for screening.
Feature Operation
By using a BFS key, party B can:
•
monitor, activate or deactivate the Call Forward feature of party A.
•
override the Call Forward feature of party A, to place a call to party A.
37
•
determine whether party A is busy on a call.
The BFS lamp state of party B indicates whether party A is:
•
forwarded and not busy (lamp in wink state).
•
forwarded and busy (lamp in flash state).
•
not forwarded and not busy (lamp in dark state).
•
not forwarded and busy (lamp in lit state).
If the customer associated with party A has Forward Key Denied Class of
Service (FKD) defined in the customer data, party A’s Call Forward key
becomes inoperative and party B’s BFS key operates as follows when it
is pressed:
•
If party A is forwarded to another station by another BFS key, party A
remains forwarded to that station.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 38

38 Other features
•
If party A has been forwarded to a DN by a remote Flexible Feature
Code, the call forward is overridden, and all new calls are forwarded
to party B.
•
If party A’s calls were forwarded to party B, then party A’s call forward
is canceled.
• If party A’s call forward is not activated, party A’s calls are forwarded to
party B and the CFW lamp on party A’s telephone lights up.
If the customer associated with Party A has Forward Key Allowed Class of
Service (FKA), and party B presses the BFS key, the result is one of the
following:
•
If party A is already forwarded to a station other than B, party A remains
forwarded to that station.
•
If party A’s calls are not forwarded, they are forwarded to party B, and
the CFW lamp on party A’s telephone lights up.
•
If party A’s calls are forwarded to party B, party A’s call forward is
canceled.
Note: If party B presses the BFS key while receiving a dial tone or
special dial tone, the BFS key works as an Auto Dial key to party A.
If a call is placed to party A, and the BFS key on that telephone is pressed,
the call automatically transfers to party B, which is the designated Call
Forward/Busy number. If party B is in Call Forward state, the call rings three
times, then immediately transfers to party C.
If a call originates to party A and the BFS key is not pressed, the call
automatically transfers to party C.
Feature Requirements
Party B must have a Meridian M3904 digital telephone or an IP Phone 2004.
Party A can have a Meridian M3904 digital telephone, an IP Phone 2004, or
an Analog (500/2500 type) telephone, with Call Forward All Calls equipped.
A station can be monitored by a maximum of 16 other stations using the
BFS key.
The same Feature requirements apply as for Call Forward All Calls.
Feature Interactions
None.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 39

Feature Programming
To activate this feature, use the following task list in LD 11 and LD 15.
LD 11 - Configure a BFS key
Forced Camp-on/Priority Override 39
Prompt Response
REQ CHG Change existing data block
TYPE
MODL
TN
...
KEY xx BFS TN Busy Forward Status key
LD 15 - Configure customer for Forward Allowed
Prompt Response
REQ CHG Modify existing data block.
TYPE FTR_DATA Features and options
CUST
3904
I2004 IP Phone 2004
1-127
cu
0-99
Comment
M3904 digital telephone
Model number
Prompted for Small System and CS 1000S Model telephones.
Terminal Number, where c=card and u=unit.
Where: TN=Terminal Number to be screened. A Key cannot be
assigned to a BRI telephone.
Note: It is possible to configure the TN of the same telephone against
the BFS key only if the Class of Service is BFEA.
Comment
Customer number for Large Systems
For CS 1000E
0-31
...
OPT (FKA) Forward Key Allowed
For Small Systems
For CS 1000S
For MG 1000B
For MG 1000T
Forced Camp-on/Priority Override
Forced Camp-on lets a station camp-on to another party involved in an
active call regardless of whether they have an internal or external call on
hold. When used with Priority Override, the capability is called Enhanced
Override.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 40

40 Other features
Forced Camp-on is activated automatically (if Automatic Forced Camp-on,
AFCO,is defined for the customer) or manually using the Enhanced Override
(EOVR) key on Meridian digital telephone telephones or the Enhanced
Override Flexible Feature Code on Analog (500/2500 type) telephones.
Four new station Class Of Service entries are associated with this feature:
•
CPFD/CPFA - Forced camp-on from another telephone denied/allowed.
•
CPTD/CPTA - Forced camp-on to another telephone denied/allowed.
These Class of Service entries are used to identify the ability of a station to
invoke the camp-on feature or to be camped-on by another station.
You can use the Priority Override feature to interrupt an established call and
present another call to the desired party. Before barge-in occurs, a warning
tone is given to all parties involved in the established call. The telephone
performing the override must have a priority level equal to or higher than
both telephones being overridden.
To activate Priority Override, the user of an Analog (500/2500 type)
telephone must invoke a recall and then dial the Override Flexible Feature
Code, while the user of a Meridian digital telephone simply presses the
Override key (OVR). Priority Override can also be activated using the
Enhanced Override Flexible Feature Code or the Enhanced Override key
(EOVR) as described in the preceding paragraph.
Associated with the Priority Override feature are seven priority levels that
can be assigned to Analog (500/2500 type) and Meridian digital telephones.
These levels define the ability of one telephone to override another as
follows:
•
level 0 — This telephone cannot override and cannot be overridden.
•
level 1 — This telephone cannot override but can be overridden.
•
level 2 —This telephone can override level 1 and 2 telephones and can
be overridden by telephones with priorities 2 - 7 (This is the default level).
•
level 3-6 — These telephones are similar to level 2 and can override
telephones of equal or lesser priority level excluding those of level 0, and
can be overridden by telephones of greater or equal priority level.
• level 7 — These telephones can override levels 1 - 7 but can only be
overridden by another telephone of priority 7.
Note: Camp-on is not affected by the override levels.
A Class Of Service (COS) for stations called Override Denied/Allowed
(OVRD/OVRA) defines the ability of a station to use or be overridden by
the Priority Override feature.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 41

Feature Operation
Several combinations of the Automatic Forced Camp-on and Priority
Override features exist. Each combination provides the station with specific
call scenarios, which are detailed as follows:
•
Setting the Automatic Forced Camp-On (AFCO) prompt to NO in the
customer data, and equipping only an OVR key or OVRD flexible feature
code disallows the use of forced camp-on. The priority override feature
remains operational.
•
Setting the Automatic Forced Camp-On (AFCO) prompt to NO, the
priority level to 0, and the camp-on classes of service to CPFA and
CPTA enables only manual camp-on.
•
Setting the Automatic Forced Camp-On (AFCO) prompt to NO, and
adding an OVR and EOVR key/FFC gives the user the option of using
only priority override (OVR key/FFC) or using manual forced camp-on
that is invoked by the first press of the EOVR key/FFC, followed by
priority override (the second press of the EOVR key/FFC).
•
Setting the Automatic Forced Camp-On (AFCO) prompt to YES and
equipping only the OVR key/FFC automatically applies forced camp-on
where applicable, and allows the use of the OVR key/FFC to implement
priority override.
Forced Camp-on/Priority Override 41
•
Using the EOVR key/FFC with AFCO set to YES simulates the OVR
key/FFC and attempts a priority override, unless Automatic Forced
Camp-on is initially denied. In this case, forced camp-on is attempted
again.
Feature Requirements
The Flexible Feature Code package (FFC) 139 and Multiple-Party Operation
package (MPO) 141 must be equipped.
All stations involved in an established call that is interrupted must have
warning tone allowed Class of Service. Otherwise, both priority override and
forced camp-on features are denied.
Priority Override and Forced Camp-on can operate independently of each
other.
Priority Override and Forced Camp-on cannot be applied to telephones
involved in any of the following:
•
a non-established call
•
a conference call
• an attendant call
•
a Release Link attendant call
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 42

42 Other features
Feature Interactions
•
an attendant call through Centralized Attendant Service or Primary Rate
Access/Integrated Services Digital Network trunk
•
an ACD call
•
a data call
•
a parked call
•
a call-waiting call
•
a held call
•
an operator call back or toll operator barge-in call
•
Make Set Busy active
• Do Not Disturb active
External trunks cannot perform priority override. They can only be
overridden if they are the undesired party of an established call that is
interrupted.
Multiple-Party Operation: When a consultation call is made on a telephone
equipped with Priority Override, a control digit must be dialed from the
telephone to perform a recall and return the call on hold.
Override: Priority Override, when activated, replaces normal override.
Digit Display: After Priority Override is performed on a telephone, its digit
display shows the DN of the overriding telephone.
Feature Programming
To activate this feature, use the following task lists in LD 10, LD 11, LD
14, LD 15, LD 16 and LD 57.
LD 10 - Configure Forward Camp-On/Priority Override on a telephone
Prompt Response
REQ CHG Modify existing data block.
TYPE
MODL
TN
500
500 M 500/2500 Model telephone data block for Small System and CS
1-127
cu
Comment
500/2500 telephone data block
1000S
Model number for small systems
Model number for CS 1000S
This prompt appears for Small System and CS 1000S Model sets.
Terminal Number, where c=card and u=unit.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 43

Forced Camp-on/Priority Override 43
Prompt Response
Comment
...
CLS CPFA Forced Camp-On from another set Allowed
CPTA Forced Camp-On to another set Allowed. CPTA is the default for
VCE TNs.
WTA Warning Tone Allowed
...
PLEV 0-(2)-7 Priority Level, prompted with Priority Override/Forced Camp-On
(POVR) package 186 or Enhanced DPNSS1 Services (DPNSS_ES)
package 288.
2 = set can override sets of level 1 and 2, and can be overridden
by sets of level 2-7.
Note: Prompted when POVR package is equipped.
LD 11 - Configure Forward Camp-On/ Priority Override on a telephone.
Prompt Response
Comment
REQ CHG Modify existing data block.
TYPE
3904
M3904 digital telephone
I2004 IP Phone 2004
MODL
1-127
Model number for small systems
Model number for CS 1000S
This prompt appears for Small System and CS 1000S Model sets.
TN
cu
Terminal Number, where c=card and u=unit.
...
CLS CPFA Forced Camp-On from another set Allowed
CPTA Forced Camp-On to another set Allowed. CPTA is the default for
VCE TNs.
WTA Warning Tone Allowed
...
PLEV 0-(2)-7 Priority Level, prompted with Priority Override/Forced Camp-On
(POVR) package 186 or Enhanced DPNSS1 Services (DPNSS_ES)
package 288.
2=set can override sets of level 1 and 2, and can be overridden by
sets of level 2-7.
Note: Prompted when POVR package is equipped.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 44

44 Other features
Prompt Response
Comment
KEY xx OVR Override key
xx EOVR Enhanced Override key
LD 14 - Configure Warning Tone Allowed
Prompt Response
Comment
REQ CHG Modify existing data block
TYPE
aaa
Trunk type
...
CLS WTA Warning Tone Allowed
LD 15 - Configure Multi Party Operations
Prompt Response
Comment
REQ CG Modify existing data block
TYPE MPO Multi Party Operations data block
CUST
0-99
Customer number for Large Systems
For CS 1000E
0-31
For Small Systems
For CS 1000S
For MG 1000B
For MG 1000T
...
AFCO YES Automatic Forced Camp-On. Prompted with Priority Override (POVR)
package 186.
LD 16 - Configure Priority Level in route data
Prompt Response
Comment
REQ CHG Modify existing data block.
TYPE RDB Route Data Block
CUST
DMOD
xx
1-127
Customer number associated with this route as defined in LD 15
Default Model number for this route (Small Systems, CS 1000S, MG
1000B, and MG 1000T)
ROUT
x...x
Route Number, where x...x=
0-511: Large System
For CS 1000E System
0-127: Small System
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 45

Forced Camp-on/Priority Override 45
Prompt Response
Comment
For MG 1000B and MG 1000T
TKTP
xxx
Trunk Type
...
PLEV 0-(2)-7 Priority Level.
Priority Level 2 sets can override sets of Level 1 and 2, and
can be overridden by sets of Level 2-7. Prompted with Priority
Override/Forced Camp-On (POVR) package 186 or Enhanced
DPNSS1 Services (DPNSS_ES) package 288.
LD 57 - Configure Flexible feature codes
Prompt Response
Comment
REQ NEW Add new data to the system.
CHG Modify existing data block.
...
EOVR
xxxx
Enhanced Override (manual Forced Camp-On followed by Priority
Override)
OVRD
xxxx
Override and Priority Override.
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 46

46 Other features
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Communication Server 1000
NN43011-501 01.01 Standard
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Release 4.5 1 August 2006
Page 47

Page 48

Communication Server 1000
Central Answering Position Implementation Guide
Copyright © 2006, Nortel Networks
All Rights Reserved.
Publication: NN43011-501
Document status: Standard
Document version: 01.01
Document date: 1 August 2006
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The information in
this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
Nortel, Nortel (Logo), the Globemark, SL-1, Meridian 1, and Succession are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Sourced in Canada
To provide feedback or to report a problem with this document, go to w
ww.nortel.com/documentfeedback
 Loading...
Loading...