Page 1

Avaya
Reference Guide
AVAYA C460
MULTILAYER MODULAR SWITCH
SOFTWARE VERSION 2.0
May 2003
Page 2

avaya.com
© 2003 Avaya Inc. All rights reserved. All trademarks identified by the ® or TM are registered trademarks
or trademarks, respectively, of Avaya Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners
Document no. 555-500-200
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Using the CLI ................................................................................................................. 1
CLI Architecture.................................................................................................... 1
Conventions Used................................................................................................. 2
CLI Help ................................................................................................................. 2
Command Line Prompt........................................................................................ 2
Navigation, Cursor Movement and Shortcuts.................................................. 4
Command Syntax..................................................................................................4
Command Abbreviations ............................................................................4
Universal Commands........................................................................................... 5
Retstatus command ......................................................................................5
Tree command ..............................................................................................5
terminal width ..............................................................................................6
terminal length ..............................................................................................6
clear screen ....................................................................................................7
Avaya C460 Sessions ............................................................................................ 8
Security Levels....................................................................................................... 9
Entering the Supervisor Level ....................................................................9
Entering the CLI .........................................................................................10
Entering the Technician Level ..................................................................10
Getting Help.........................................................................................................10
Command Syntax................................................................................................10
Command Abbreviations ..........................................................................10
Router Configuration Contexts......................................................................... 11
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands ..................................................................................... 13
access list ......................................................................................................13
area ...............................................................................................................13
arp .................................................................................................................14
arp timeout .................................................................................................. 14
banner login ................................................................................................15
banner login line .........................................................................................15
banner post-login .......................................................................................15
banner post-login line ................................................................................16
clear arp-cache ............................................................................................ 16
clear cam ...................................................................................................... 17
clear dot1x config .......................................................................................17
clear dynamic vlans ...................................................................................17
clear event-log ............................................................................................. 18
Avaya C460 Reference Guide i
Page 4

Contents
clear fragment .............................................................................................18
clear interface ..............................................................................................19
clear ip route ................................................................................................19
clear ip route (Layer 3) ...............................................................................19
clear ip traffic ...............................................................................................20
clear log ........................................................................................................20
clear port mirror ..........................................................................................20
clear port static-vlan ...................................................................................21
clear radius authentication server ............................................................21
clear rmon2 statistics ..................................................................................22
clear screen ..................................................................................................22
clear snmp trap ...........................................................................................22
clear system-log ..........................................................................................23
clear timezone .............................................................................................23
clear vlan ......................................................................................................24
clear vlan (Layer 3) ....................................................................................24
configure ......................................................................................................25
copy l2-config tftp .......................................................................................25
copy running-config startup-config .........................................................25
copy startup-config tftp .............................................................................26
copy tftp EW_archive .................................................................................27
copy tftp l2-config .......................................................................................27
copy tftp startup-config .............................................................................28
copy tftp SW_imageA ................................................................................28
copy tftp SW_imageB .................................................................................29
default-metric ..............................................................................................30
default-metric (OSPF) ................................................................................30
default-metric (RIP) ....................................................................................31
disable interface ..........................................................................................31
enable interface ...........................................................................................32
enable vlan commands ..............................................................................32
erase startup-config ....................................................................................33
fragment chain ............................................................................................33
fragment size ...............................................................................................33
fragment timeout ........................................................................................34
get time .........................................................................................................34
hostname ......................................................................................................34
hostname (Layer 3) .....................................................................................35
interface ........................................................................................................36
ip access-default-action ..............................................................................37
ip access-group ............................................................................................37
ip access-list .................................................................................................38
ip access-list-cookie ....................................................................................39
ip access-list-copy .......................................................................................39
ii Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 5

Contents
ip access-list-dscp name ............................................................................40
ip access-list-dscp operation .....................................................................40
ip access-list-dscp precedence ..................................................................41
ip access-list-dscp trust .............................................................................. 42
ip access-list-name ......................................................................................42
ip access-list-owner ....................................................................................43
ip address ....................................................................................................43
ip admin-state .............................................................................................44
ip bootp-dhcp network ..............................................................................44
ip bootp-dhcp relay ....................................................................................45
ip bootp-dhcp server ..................................................................................46
ip broadcast-address .................................................................................. 46
ip default-gateway .....................................................................................47
ip directed-broadcast ................................................................................. 47
ip icmp-errors ............................................................................................. 48
ip max-arp-entries ......................................................................................48
ip max-route-entries ...................................................................................49
ip netbios-rebroadcast ...............................................................................49
ip netmask-format ...................................................................................... 50
ip ospf authentication-key ........................................................................51
ip ospf cost ...................................................................................................51
ip ospf dead-interval ..................................................................................52
ip ospf hello-interval ..................................................................................52
ip ospf priority ............................................................................................53
ip ospf router-id .......................................................................................... 53
ip proxy-arp ................................................................................................ 54
ip redirects ...................................................................................................54
ip rip authentication key ...........................................................................54
ip rip authentication mode .......................................................................55
ip rip default-route-mode .........................................................................56
ip rip poison-reverse .................................................................................. 56
ip rip rip-version ........................................................................................57
ip rip send-receive-mode ..........................................................................57
ip rip split-horizon .....................................................................................58
ip route .........................................................................................................59
ip routing .....................................................................................................59
ip routing-mode ..........................................................................................60
ip simulate ................................................................................................... 61
ip vlan/ip vlan name ................................................................................. 61
ip vrrp ..........................................................................................................62
ip vrrp address ............................................................................................62
ip vrrp auth-key ..........................................................................................63
ip vrrp override addr owner .....................................................................63
ip vrrp preempt ..........................................................................................64
Avaya C460 Reference Guide iii
Page 6

Contents
ip vrrp primary ...........................................................................................64
ip vrrp priority ............................................................................................65
ip vrrp timer ................................................................................................66
line .................................................................................................................66
network (RIP) ..............................................................................................67
network (OSPF) ...........................................................................................67
no rmon alarm .............................................................................................68
no rmon event .............................................................................................68
no rmon history ..........................................................................................69
no username ................................................................................................69
nvram initialize ...........................................................................................69
passive-interface .........................................................................................70
ping ...............................................................................................................71
ping (Layer 3) ..............................................................................................71
redistribute (OSPF) .....................................................................................72
redistribute (RIP) ........................................................................................72
reset ...............................................................................................................73
rmon alarm ..................................................................................................75
rmon event ...................................................................................................76
rmon history ................................................................................................76
rmon2 protocol-dir .....................................................................................77
rmon2 protocol-dist ....................................................................................77
router ospf ....................................................................................................78
router rip ......................................................................................................78
router vrrp ...................................................................................................79
session ..........................................................................................................79
set allowed managers .................................................................................80
set allowed managers ip ............................................................................80
set arp-aging-interval .................................................................................81
set arp-tx-interval .......................................................................................81
set boot bank ................................................................................................82
set broadcast storm control .......................................................................82
set broadcast storm control threshold .....................................................83
set device-mode ..........................................................................................83
set device-mode (Layer 3) .........................................................................84
set dot1x max-req ........................................................................................84
set dot1x quiet-period ................................................................................84
set dot1x re-authperiod ..............................................................................85
set dot1x server-timeout ............................................................................85
set dot1x supp-timeout ..............................................................................85
set dot1x system-auth-control disable .....................................................86
set dot1x system-auth-control enable ......................................................86
set dot1x tx-period ......................................................................................87
set icmp-redirect .........................................................................................87
iv Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 7

Contents
set inband vlan ............................................................................................88
set intelligent-multicast .............................................................................88
set intelligent-multicast client port pruning time ..................................88
set intelligent-multicast group-filtering delay time .............................. 89
set intelligent-multicast router port pruning time ................................89
set interface inband ....................................................................................90
set interface outband .................................................................................. 90
set interface ppp ......................................................................................... 91
set interface ppp enable/disable/off/reset ............................................ 91
set ip route ...................................................................................................92
set license .....................................................................................................94
set logout .....................................................................................................94
set mac-aging ..............................................................................................95
set mac-aging-time .....................................................................................95
set outband duplex .....................................................................................96
set outband negotiation ............................................................................. 96
set outband speed .......................................................................................97
set policy type .............................................................................................97
set port auto-negotiation-flowcontrol-advertisement ..........................99
set port channel ...........................................................................................99
set port classification ................................................................................ 100
set port disable ..........................................................................................101
set port dot1x initialize ............................................................................101
set port dot1x max-req .............................................................................102
set port dot1x port-control ......................................................................102
set port dot1x quiet-period .....................................................................103
set port dot1x re-authenticate .................................................................103
set port dot1x re-authentication .............................................................103
set port dot1x re-authperiod ...................................................................104
set port dot1x server-timeout ................................................................. 104
set port dot1x supp-timeout ...................................................................105
set port dot1x tx-period ...........................................................................105
set port duplex .......................................................................................... 106
set port edge admin state ........................................................................106
set port enable ...........................................................................................107
set port flowcontrol .................................................................................. 109
set port level ..............................................................................................110
set port mirror ...........................................................................................110
set port name .............................................................................................111
set port negotiation ..................................................................................111
set port point-to-point admin status ......................................................112
set port powerinline .................................................................................113
set port powerinline priority ..................................................................113
set port redundancy .................................................................................114
Avaya C460 Reference Guide v
Page 8

Contents
set port redundancy on/off ....................................................................115
set port redundancy-intervals .................................................................115
set port spantree ........................................................................................116
set port spantree cost ................................................................................117
set port spantree force-protocol-migration ...........................................117
set port spantree priority .........................................................................118
set port speed ............................................................................................118
set port static-vlan ....................................................................................119
set port trap ...............................................................................................119
set port vlan ...............................................................................................120
set port vlan-binding-mode ....................................................................121
set power redundancy .............................................................................121
set powerinline budget ............................................................................122
set ppp authentication incoming ............................................................122
set ppp baud-rate ......................................................................................123
set ppp chap-secret ...................................................................................123
set ppp incoming timeout .......................................................................123
qset radius authentication enable/disable ............................................124
set radius authentication retry-number ................................................124
set radius authentication retry-time .......................................................125
set radius authentication secret ..............................................................125
set radius authentication server .............................................................125
set radius authentication udp-port ........................................................126
set slot power admin ................................................................................126
set slot power priority ..............................................................................127
set snmp community ................................................................................128
set snmp retries .........................................................................................128
set snmp timeout ......................................................................................129
set snmp trap .............................................................................................129
set snmp trap auth ....................................................................................130
set spantree default-path-cost .................................................................131
set spantree enable/disable ....................................................................131
set spantree forward-delay ......................................................................132
set spantree hello-time .............................................................................132
set spantree max-age ................................................................................132
set spantree priority .................................................................................133
set spantree tx-hold-count .......................................................................133
set spantree version ..................................................................................134
set system contact .....................................................................................134
set system location ....................................................................................135
set system name ........................................................................................135
set time client .............................................................................................136
set time protocol .......................................................................................136
set time server ...........................................................................................137
vi Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 9

Contents
set timezone ..............................................................................................137
set trunk .....................................................................................................138
set vlan .......................................................................................................138
set vlan (Layer 3) ......................................................................................139
set web aux-files-url .................................................................................139
set welcome message ...............................................................................140
show access lists .......................................................................................140
show allowed managers status ..............................................................141
show allowed managers table ................................................................142
show arp-aging-interval ..........................................................................143
show arp-tx-interval ................................................................................143
show banner login ....................................................................................143
show banner post-login ........................................................................... 144
show boot bank .........................................................................................144
show broadcast storm control ................................................................144
show cam ...................................................................................................145
show cam mac ...........................................................................................147
show cam vlan ..........................................................................................147
show chassis-identity ...............................................................................148
show copy status ......................................................................................148
show cpu load ...........................................................................................149
show cs .......................................................................................................149
show device-mode ...................................................................................150
show dot1x ................................................................................................150
show dot1x statistics ................................................................................150
show dynamic vlans ................................................................................151
show environment fans ...........................................................................151
show environment power .......................................................................152
show erase status ......................................................................................153
show event-log ..........................................................................................153
show event-log (Layer 3) .........................................................................153
show fragment ..........................................................................................153
show icmp-redirect ..................................................................................154
show image version .................................................................................154
show intelligent-multicast .......................................................................154
show interface ...........................................................................................155
show ip access-group ...............................................................................155
show ip access-list-dscp ..........................................................................156
show ip access-lists ..................................................................................156
show ip access-list-summary ..................................................................157
show ip arp ................................................................................................157
show ip icmp .............................................................................................158
show ip interface ......................................................................................159
show ip interface brief ............................................................................. 160
Avaya C460 Reference Guide vii
Page 10

Contents
show ip ospf ..............................................................................................160
show ip ospf database ..............................................................................161
show ip ospf interface ..............................................................................161
show ip ospf neighbor .............................................................................162
show ip protocols ......................................................................................162
show ip reverse-arp ..................................................................................163
show ip route .............................................................................................163
show ip route (Layer 3) ............................................................................163
show ip route best-match ........................................................................164
show ip route static ..................................................................................164
show ip route summary ...........................................................................165
show ip traffic ............................................................................................165
show ip unicast cache ...............................................................................167
show ip unicast cache networks .............................................................168
show ip unicast cache networks detailed ..............................................169
show ip unicast cache nextHop ..............................................................169
show ip unicast cache summary .............................................................170
show ip vrrp ..............................................................................................170
show ip vrrp detail ...................................................................................171
show l2-config ...........................................................................................173
show license ...............................................................................................183
show logout ...............................................................................................183
show mac-aging ........................................................................................183
show mac-aging-time ...............................................................................184
show module .............................................................................................185
show outband ............................................................................................186
show policy type .......................................................................................186
show port ...................................................................................................187
show port auto-negotiation-flowcontrol-advertisement ....................188
show port channel ....................................................................................188
show port classification ...........................................................................190
show port dot1x ........................................................................................191
show port dot1x statistics ........................................................................193
show port edge state ................................................................................194
show port flowcontrol ..............................................................................194
show port mirror ......................................................................................195
show port point-to-point status ..............................................................196
show port redundancy .............................................................................197
show port trap ...........................................................................................197
show port vlan-binding-mode ................................................................198
show powerinline .....................................................................................198
show powerinline budget ........................................................................199
show ppp authentication .........................................................................200
show ppp baud-rate .................................................................................200
viii Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 11

Contents
show ppp configuration .......................................................................... 201
show ppp incoming timeout ..................................................................201
show ppp session .....................................................................................201
show radius authentication ....................................................................202
show rmon alarm .....................................................................................202
show rmon event ......................................................................................203
show rmon history ...................................................................................204
show rmon statistics ................................................................................204
show rmon2 dscp-stats ............................................................................205
show rmon2 protocol-dir ........................................................................206
show rmon2 protocol-dist ....................................................................... 206
show rmon2 state ..................................................................................... 208
show running-config ................................................................................209
show secure current .................................................................................210
show snmp ................................................................................................211
show snmp retries ....................................................................................212
show snmp timeout .................................................................................212
show spantree ...........................................................................................212
show spv ....................................................................................................214
show startup-config .................................................................................216
show system ..............................................................................................217
show system-log ....................................................................................... 217
show system-log (Layer 3) ......................................................................219
show tftp download software status .....................................................219
show tftp upload status ...........................................................................219
show time ..................................................................................................220
show time parameters ............................................................................. 220
show timezone ..........................................................................................221
show trunk ................................................................................................221
show username .........................................................................................222
show vlan ..................................................................................................222
show vlan (Layer 3) .................................................................................. 223
show web aux-files-url ............................................................................223
sync spv .....................................................................................................224
tech .............................................................................................................224
terminal length ..........................................................................................225
terminal width .......................................................................................... 225
timers basic ................................................................................................ 225
timers ospf .................................................................................................227
traceroute ...................................................................................................228
tree ..............................................................................................................228
username ................................................................................................... 229
validate-group ..........................................................................................230
validate policy-list ....................................................................................231
Avaya C460 Reference Guide ix
Page 12

Contents
Layer 2 CLI Commands............................................................................................ 233
Layer 3 CLI Commands............................................................................................ 237
Glossary....................................................................................................................... 241
x Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 13

Chapter 1
Using the CLI
This chapter describes the Avaya C460 CLI architecture and conventions, and
provides instructions for accessing the Avaya C460 for configuration purposes.
The configuration procedure involves establishing a Telnet session or a serial
connection and then using the Avaya C460’s internal CLI. For details on
establishing a connection, see the User’s Guide that accompanies the switch.
The CLI is command-line driven and does not have any menus. To activate a
configuration option, you must type the desired command at the prompt and press
Enter.
You can also configure your Avaya C460 using the C460 Manager with its graphical
user interface. For details, see the "Device Manager" chapter in the User’s Guide that
accompanies the switch and the Avaya MSNM C460 Device Manager User’s Guide
on the Documentation and Utilities CD.
CLI Architecture
The C460 supports both Layer 2 switching and Layer 3 switching.
The C460 CLI includes two CLI entities to support this functionality.
• The Switch CLI entity is used to manage Layer 2 switching.
• The Router CLI entity is used to manage Layer 3 switching.
To switch between the entities, use the session command. For details, see
"Avaya C460 Sessions" below.
Configuration of the password commands and community commands in one
entity is automatically attributed to the other entity in the switch.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 1
Page 14

Chapter 1 Using the CLI
Conventions Used
• Mandatory keywords are in the computer bold font.
• Information displayed on screen is displayed in computer font.
• Variables that you supply are in pointed brackets <>.
• Optional keywords are in square brackets [].
• Alternative but mandatory keywords are grouped in braces {} and separated by
a vertical bar |.
• Lists of parameters from which you should choose are enclosed in square
brackets [ ] and separated by a vertical bar |.
• If you enter an alphanumeric string of two words or more, enclose the string in
inverted commas.
CLI Help
• To display all commands available in a context type a question mark.
• To display all commands starting with a certain string, type the first few letters
followed by a question mark.
• To get help containing all commands parameters with their legal values as well
as its syntax and an example:
— type a question mark at the end of command or at the stage where it is
unique, or
— type "help" followed by the command
• Use the Tab key to complete an unambiguous command.
Command Line Prompt
Four factors affect the command line prompt:
• Host name of the CLI entity - the host name is used as the prefix of the
command prompt.
• Module Number - counting from the top and used as part of the prefix. In this
document the Module number in the prompt is generic and is represented by
“N”.
• Security level - used as the suffix of the prompt (Refer to "Security Levels" on
page 9.)
• Application context - used as body of the prompt, this part is not mandatory.
Example:
Host name of the router is London
Router is module number three
Application context is OSPF
2 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 15

Chapter 1 Using the CLI
The command line prompt looks as follows:
London-1(configure router:ospf)#
The command prompt is not hierarchical in structure. If you wish to use several
commands, each beginning with the same keyword, you must retype all parts of the
command each time. For example, if after you want to set the system contact and the
system name you must type both set system contact and
set system name. However, you can use command abbreviations.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 3
Page 16
Chapter 1 Using the CLI
Navigation, Cursor Movement and Shortcuts
The CLI contains a simple text editor with these functions:
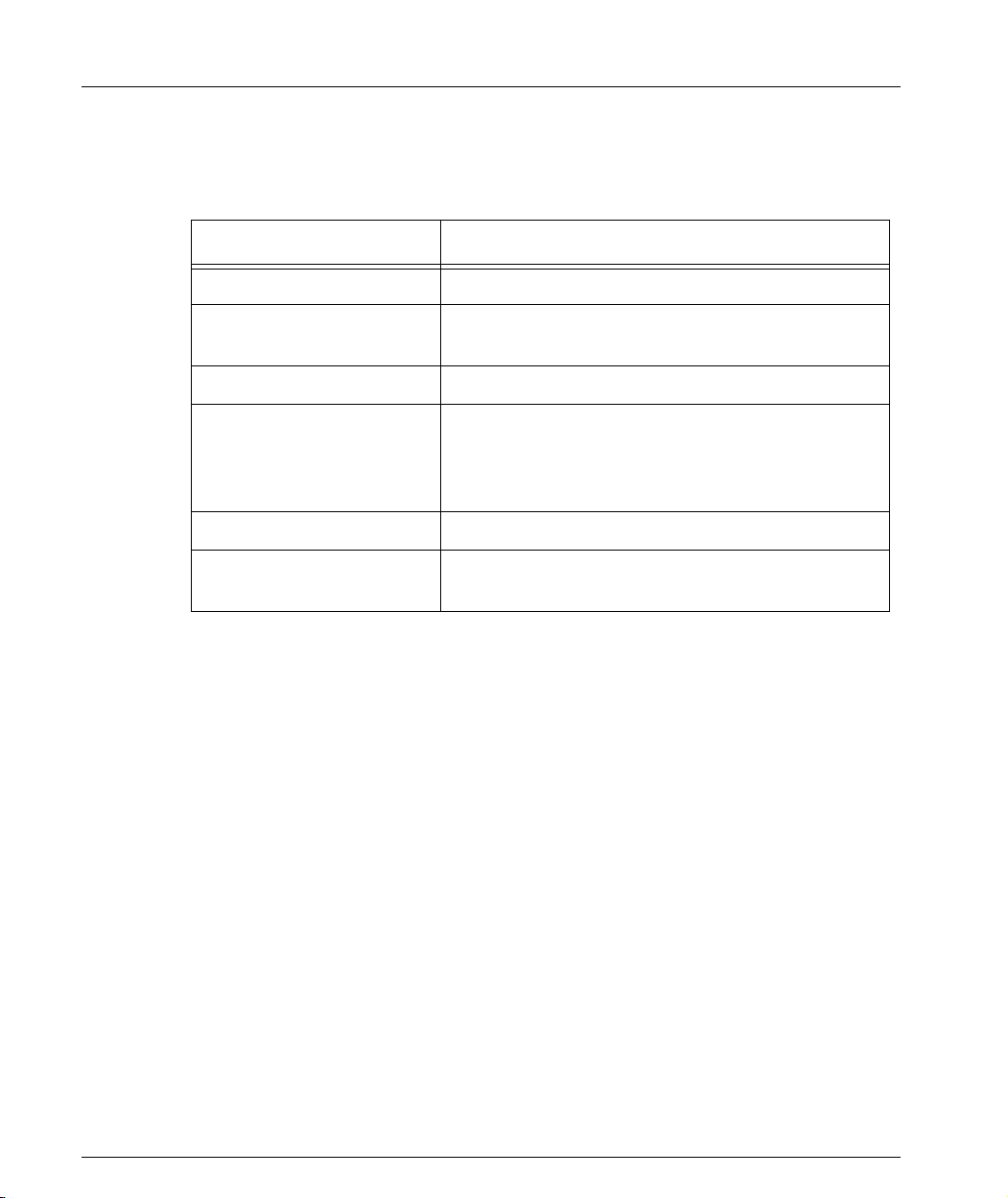
Table 1.1 Navigation, Cursor Movement and Shortcuts
Keyboard Functions
Backspace Deletes the previous character
Up arrow/Down arrow Scrolls back and forward through the command
history buffer
Left arrow/Right arrow Moves the cursor left or right
Tab Completes the abbreviated command. Type the
minimum number of characters unique to the
command. An exception is the Reset System
command which you must type in full.
Enter Executes a single-line command
“ “ If you type a name with quotation marks, the
marks are ignored.
Command Syntax
Commands are not case-sensitive. That is, uppercase and lowercase characters may
be interchanged freely.
Command Abbreviations
All commands and parameters in the CLI can be truncated to an abbreviation of any
length, as long as the abbreviation is not ambiguous. For example, version can
be abbreviated ver.
For ambiguous commands, type the beginning letters on the command line and
then use the Tab key to toggle through all the possible commands beginning with
these letters.
4 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 17

Universal Commands
Universal commands are commands that can be issued anywhere in the hierarchical
tree.
Retstatus command
Use the retstatus command to show whether the last CLI command you
performed was successful. It displays the return status of the previous command.
The syntax for this command is: retstatus
Example::
C460-1# set port negotiation 2/4 disable
Link negotiation protocol disabled on port 2/4.
C460-1# retstatus
Succeeded
Tree command
The tree command displays the commands that are available at your current
location in the CLI hierarchy.
The syntax for this command is: tree
Output Example:
Chapter 1 Using the CLI
Example:
C460-1# tree
terminal
width
length
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 5
Page 18

Chapter 1 Using the CLI
terminal width
Use the terminal width command to set the terminal width of the terminal
display.
The syntax for this command is:
terminal width [<character>]
character none - Displays the current width in
Example:
C460-1> terminal width 80
terminal width: 80
terminal length
Use the terminal length command to set the length of the terminal display.
characters.
number - Set the new
screen width in
characters
The syntax for this command is:
terminal length [<screen-length>]
screen-length none - Displays the current length in lines.
number - Set the new screen length in lines.
Example:
C460-1> terminal length 25
6 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 19

clear screen
Chapter 1 Using the CLI
Use the clear screen command to clear the current terminal display.
The syntax for this command is:
clear screen
Example:
C460-1> clear screen
Welcome to C460
SW version 1.0.0
C460-1>
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 7
Page 20

Chapter 1 Using the CLI
Avaya C460 Sessions
You can use sessions to switch between C460 Supervisor modules or to switch
between Layer 2 and Layer 3 commands in the C460 CLI.
To switch between C460 modules use the command:
session [<mod_num>] <mode>.
The <mod_num> is the number of the module in the chassis, counting from the top
down. The <mode> can be either switch or router. When Module Number is not
specified, the command switches between the modes in the local module. Use
switch mode to configure layer 2 commands. Use router mode to configure routing
commands.
Example:
To configure router parameters in the module that you are currently logged into,
type the following command:
session router.
L When you use the session command the security level stays the same.
8 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 21

Security Levels
There are four security access levels (modes) – User, Privileged, Configure and
Supervisor.
• The User mode is a general access level used to show system parameter values.
• The Privileged mode is used by site personnel to access switch configuration
options.
• The Configure mode is used by site personnel for Layer 3 configuration.
• The Supervisor mode is used to define user names, passwords, and access levels
of up to 10 local users.
A login name and password are always required to access the CLI and the
commands. The login names and passwords, and security levels are established
using the username command.
Switching between the entities, does not effect the security level since security levels
are established specifically for each user. For example, if the operator with a
privileged security level in the Switch entity switches to the Router entity the
privileged security level is retained.
Entering the Supervisor Level
The Supervisor level is the level in which you first enter Cajun Campus CLI and
establish user names for up to 10 local users. When you enter the Supervisor level,
you are asked for a Login name. Type root as the Login name and the default
password root (in lowercase letters):
Chapter 1 Using the CLI
Welcome to C460
SW version 1.0.0
Login: root
Password:****
Password accepted.
C460-1(super)#
Defining new users
Define new users and access levels using the username command in Supervisor
Level.
Exiting the Supervisor Level
To exit the Supervisor level, type the command exit.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 9
Page 22

Chapter 1 Using the CLI
Entering the CLI
To enter the CLI, enter your username and password. Your access level is indicated
in the prompt as follows:
The User level prompt is shown below:
C460-1>
The Privileged level prompt is shown below:
C460-1#
The Configure level prompt for Layer 3 configuration is shown below:
C460(configure)#
The Supervisor level prompt is shown below:
C460(super)#
Entering the Technician Level
This level is can only be accessed from the Privileged and Supervisor levels not from
the User level.
L This feature is for use by Avaya Technical Support only.
Getting Help
On-line help may be obtained at any time by typing a question mark (?), or the
word help on the command line or by pressing the F1 key. To obtain help for a
specific command, type the command followed by a space and a question mark.
Example:
C460-1> show ?
C460-1> help show
Command Syntax
Commands are not case-sensitive. That is, uppercase and lowercase characters may
be interchanged freely.
Command Abbreviations
All commands and parameters in the CLI can be truncated to an abbreviation of any
length, as long as the abbreviation is not ambiguous. For example, version can
be abbreviated ver.
For ambiguous commands, type the beginning letters on the command line and
then use the TAB key to toggle through all the possible commands beginning with
these letters.
10 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 23

Router Configuration Contexts
You can either use the general C460 commands available from the
Router(configure)# prompt or you can enter one of two router configuration
context modes:
• Router interface context:
This allows you to define parameters individually for each interface. To enter
this context, type interface <interface_name>
The prompt changes to Router>(config-if:<interface_name>)#
• Router protocol context:
This allows you to define parameters for a specific routing protocol (RIP, OSPF,
and VRRP). To enter this context, type router <protocol_name>
The prompt changes to Router>(configure router:protocol_name)#
To exit these context modes, type the command exit.
Chapter 1 Using the CLI
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 11
Page 24

Chapter 1 Using the CLI
12 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 25

Chapter 2
Avaya C460 CLI Commands
This chapter describes all the C460 CLI commands and parameters in alphabetical
order.
access list
See “ip access-list”
area
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Router-OSPF mode.
Type router ospf at the command prompt to enter Router -OSPF mode if
necessary.
Use the area command to configure the area ID of the router.
Use the no area command to delete the area ID of the router (set it to 0) and
remove the stub definition.
The default area is 0.0.0.0.
L You cannot define a stub area when OSPF is redistributing other protocols or
when the Area ID is 0.0.0.0.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] area <area id> [<stub>]
area id IP address
stub Stub
Example:
Router-1 (configure router:ospf) # area 192.168.49.1
Router-1 (configure router:ospf) # area 192.168.49.1 stub
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 13
Page 26

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
arp
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the arp command to add a permanent entry to the Address Resolution Protocol
(ARP) cache.
Use the no arp command to remove an entry, either static entry or dynamically
learned.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] arp <ip-address> <mac-address>
ip-address IP address, in dotted decimal format, of the station
mac-address MAC address of the local data link
Example:
To add a permanent entry for station 192.168.7.8 to the ARP cache:
C460-1(configure)# arp 192.168.7.8 00:40:0d:8c:2a:01
Example:
To remove an entry to the ARP cache for the station 192.168.13.76:
C460-1(configure)# no arp 192.168.13.76
arp timeout
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the arp timeout command to set the amount of time that an entry remains in
the ARP cache.
Use the no arp timeout command to restore the default value, 14,400.
14 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 27

banner login
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
The syntax for this command is:
[no] arp timeout <seconds>
seconds The amount of time, in seconds, that an entry remains
in the arp cache.
Example:
To set the arp timeout to one hour:
C460-1(configure)# arp timeout 3600
To restore the default arp timeout:
C460-1(configure)# no arp timeout
Use the banner login command to enter the login banner configuration mode.
Use the no banner login command to set the login banner to the default value.
L Delete the current banner using the no banner login command before
creating a new banner, .
The syntax for this command is:
[no] banner login
Example:
C460-1(super)# banner login
C460-1(super)#
banner login line
See “line”
banner post-login
Use the banner post-login command to enter the post-login configuration
mode.
Use the no banner post-login command to set the post-login banner to the
default value.
L Before creating a new banner, delete the current banner using the no banner
post-login command.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 15
Page 28
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
The syntax for this command is:
[no] banner post-login
Example:
C460-1(super)# banner post-login
C460-1(super)#
banner post-login line
See “line”
clear arp-cache
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the clear arp-cache command to delete dynamic entries from the ARP
cache and the IP route cache.
The syntax for this command is:
clear arp cache[<vlan>|<ip addr>[<mask>]]
vlan VLAN string (up to 16 characters
ip addr IP address
mask IP mask
Example:
C460-1(configure)# clear arp-cache
Flushing all arp entries
Flushed 100 ARP entries
Done!
16 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 29
clear cam
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear cam command to delete all entries from the CAM table.
The syntax for this command is:
clear cam
Example:
C460-1# clear cam
CAM table cleared.
clear dot1x config
User level: privileged, supervisor.
Use the clear dot1x config command to disable dot1x on all ports and return
values to the default settings..
The syntax for this command is:
clear dot1x config
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
C460-1(super)# clear dot1x config
Original Configuration was Restored
clear dynamic vlans
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear dynamic vlans command to clear dynamically learned VLANs.
Only the VLANs learned by the switch from incoming traffic are cleared using this
command.
The syntax for this command is:
clear dynamic vlans
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 17
Page 30

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
C460-1# clear dynamic vlans
This command will delete all the vlans that were
dynamically learned by the device - do you want to continue
(Y/N)? y
Dynamic vlans were deleted from device tables
clear event-log
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear event-log command to delete the log file of a Supervisor module.
The syntax for this command is:
clear event-log [<module_number>]
clear fragment
spv_num
Number of Supervisor Module (1 to 2)
(Optional)
Example:
C460-1# clear event-log
*** Clearing the reset file ***
- do you want to continue (Y/N)? y
C460-1#
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear fragment command to restore fragment action database defaults
and free all waiting fragments.
The syntax for this command is:
clear fragment
Example:
Router-1# clear fragment
Done!
18 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 31

clear interface
clear ip route
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear interface command to clear the inband or outband interface
from the NVRAM.
The syntax for this command is:
clear interface [outband | inband]
outband Clears the outband interface
inband Disables the inband interface
Example:
C460-1# clear interface outband
Interface outband Cleared.
You must reset the device in order for the change to take
effect.
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear ip route command to delete IP routing table entries.
The syntax for this command is:
clear ip route <destination> <mask>
destination
mask
IP address of the network, or specific host to be added
IP address of the router
Example:
C460-1# clear ip route 134.12.3.0 255.255.255.0
Route deleted.
clear ip route (Layer 3)
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 19
Page 32

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Use the clear ip route command to delete all the dynamic routing entries from the
Routing Table.
The syntax for this command is:
clear ip route * | <ip-addr> [<ip-mask>]
ip-addr IP address
ip-mask IP mask address
Example:
C460-1(configure)# clear ip route 192.168.49.1
255.255.255.0
clear ip traffic
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear ip traffic command to clear the ip traffic statistics counters.
The syntax for this command is:
clear ip traffic
Example:
Router-1# clear ip traffic
clear log
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear log command to
clear port mirror
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear port mirror command to cancel port mirroring.
The syntax for this command is:
clear port mirror <source module>/<source port>/<dest module>/
<dest port>
source module Source module number
20 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 33

source port Source port number
dest module Destination module number
dest port Destination port number
Example:
C460-1# clear port mirror 9/2/10/4
this command will delete the port mirror entry
- do you want to continue (Y/N)? y
Mirroring packets from port 9/2 to port 10/4 is cleared
clear port static-vlan
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear port static-vlan command to delete VLANs statically
configured on a port.
The syntax for this command is:
clear port static-vlan [module/port range][vlan num]
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
module/port range Port range
vlan num The VLAN to unbind from the port
Example:
C460-1# clear port static-vlan 3/10 5
VLAN 5 is unbound from port 3/10
clear radius authentication server
User level: read-write, admin.
Removes a primary or secondary RADIUS authentication server.
The syntax for this command is:
clear radius authentication server[{primary|secondary}]
primary Remove primary RADIUS server
secondary Remove secondary RADIUS server
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 21
Page 34

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
C460-1(super)# clear radius authentication server secondary
clear rmon2 statistics
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear rmon2 statistics command to delete rmon2 (AnyLayer SMON)
statistics.
The syntax for this command is:
clear rmon2 statistics
Example:
Router-1# clear rmon2 statistics
Done!
clear screen
User level: read-only, read-write, admin.
Use the clear screen command to clear the screen.
The syntax for this command is:
clear screen
clear snmp trap
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear snmp trap command to clear an entry from the SNMP trap
receiver table.
The syntax for this command is:
clear snmp trap {<rcvr_addr>|all}
rcvr_addr IP address or IP alias of the trap receiver (the SNMP management
station) to clear
all Keyword that specifies every entry in the SNMP trap receiver
table
22 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 35

Example:
clear system-log
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear system-log command to delete the log file of a Supervisor
Module.
The syntax for this command is:
clear system-log [<module_number>]
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
C460-1# clear snmp trap 192.168.173.42
SNMP trap deleted.
clear timezone
spv_num
Number of Supervisor Module (1 to 2)
(Optional)
Example:
C460-1# clear system-log
*** Clearing the reset file ***
- do you want to continue (Y/N)? y
C460-1#
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear timezone command to reset the time zone to its default value UTC
(Coordinated Universal Time)
The syntax for this command is:
clear timezone
Example:
C460-1# clear timezone
Timezone name and offset cleared.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 23
Page 36

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
clear vlan
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the clear vlan command to delete an existing VLAN and return ports from
this VLAN to the default VLAN #1. When you clear a VLAN, all ports assigned to
that VLAN are assigned to the default VLAN #1.
The syntax for this command is:
clear vlan <vlan-id>[name <vlan_name>]
vlan_id VLAN number
vlan_name VLAN name
If you wish to enter a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
Example:
C460-1# clear vlan 100
This command will assign all ports on vlan 100 to their
default in the entire management domain - do you want to
continue (Y/N)? y
VLAN 100 deletion successful
clear vlan (Layer 3)
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the clear vlan command to delete a Router layer 2 interface.
The syntax for this command is:
clear vlan [<ifIndex>] | [name <ifname>]
ifIndex Interface Index
ifname Interface name (used in layer 3 protocols)
Example:
C460-1(configure)# clear vlan 2 name vlan2
24 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 37

If you wish to define a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
configure
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the configure command to enter configure mode.
The syntax for this command is:
configure
Example:
C460-1(super)# configure
C460-1(configure)#
copy l2-config tftp
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the copy l2-config tftp command to upload the Layer 2 parameters from
the current NVRAM running configuration to a file via TFTP.
L To use this command, you need to have an active tftp server and to create a file
L If Avaya MultiService Network Manager is running, you do not require an
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
into which to download the data.
additional TFTP server.
The syntax for this command is:
copy l2-config tftp <filename> <ip>
filename file name (including full path)
ip IP address of the host
Example:
C460-1# copy l2-config tftp c:\C460\config 149.49.152.36
copy running-config startup-config
User level: privileged, supervisor.
Use the copy running-config startup-config command to copy the active
policy configuration to the startup configuration file in the NVRAM.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 25
Page 38

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
The syntax for this command is:
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
C460-1# copy running-config startup-config
1 copy running-config tftp
User level: privileged, supervisor.
Use the copy running-config tftp command to upload the policy
configuration to a TFTP server.
The syntax for this command is:
copy running-config tftp <filename> <ip>
filename Destination file name in the tftp server (full path).
ip The ip address of the tftp server.
Example (for Windows):
C460-1# copy running-config tftp c:\c460\startup.cfg
149.49.100.41
Example: (for Unix):
C460-1# copy running-config tftp /folder/c460/startup.cfg
149.49.100.41
copy startup-config tftp
User level: privileged, supervisor.
Use the copy startup-config tftp command to download a policy
configuration from a TFTP server.
The syntax for this command is:
copy startup-config tftp <filename> <ip>
filename Destination file name in the tftp server (full path).
ip The ip address of the tftp server.
26 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 39

Example (for Windows):
Router-1# copy startup-config tftp c:\c460\startup.cfg
149.49.100.41
Example: (for Unix):
C460-1# copy startup-config tftp /folder/c460/startup.cfg
149.49.100.41
copy tftp EW_archive
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the copy tftp EW-archive command to download the C460 Manager
application into the switch via TFTP.
L To use this command, you need to have an active TFTP server and to create a
file into which to download the data.
L If Avaya MultiService Network Manager is running, you do not require an
additional TFTP server..
The syntax for this command is:
copy tftp EW_archive <filename> <ip>
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
filename C460 Manager image file name (full path)
ip The IP address of the host
Example:
C460-1# copy tftp EW-archive c:\C460\switch1.cfg
192.168.49.10
copy tftp l2-config
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the copy tftp l2-config command to update the Layer 2 parameters in the
current NVRAM running configuration from a file via TFTP.
L To use this command, you need to have an active tftp server and to create a file
into which to download the data.
L If Avaya MultiService Network Manager is running, you do not require an
additional TFTP server.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 27
Page 40

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
The syntax for this command is:
copy tftp l2-config <filename> <ip>
filename file name (including full path)
ip IP address of the host
Example:
C460-1# copy tftp l2-config c:\C460\backup 149.49.152.36
Beginning download operation ...
This operation may take a few minutes...
Please refrain from any other operation during this time.
*********************************************************************
* If you are currently running the C460 Device Manager application, *
* it is recommended to exit from it before performing configuration *
* download operations. *
*********************************************************************
copy tftp startup-config
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the copy tftp startup-config command to copy the C460 configuration
from the saved TFTP file to the Startup Configuration NVRAM.
The syntax for this command is:
copy tftp startup-config <filename> <ip>
filename file name (full path)
ip The ip address of the host
Example:
Router-1> copy tftp startup-config c:\C460\router1.cfg
192.168.49.10
copy tftp SW_imageA
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the copy tftp SW_imageA command to update the software image in Bank
A of all the Supervisor Modules installed in the switch.
L To use this command, you need to have an active tftp server and to create a file
into which to download the data.
L If Avaya MultiService Network Manager is running, you do not require an
28 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 41

additional TFTP server.
copy tftp SW_imageA <filename> <ip>
filename file name (including full path)
ip IP address of the host
Example:
C460-1# copy tftp SW_imageA c:\imgA.bin 149.49.36.200
Beginning download operation ...
This operation may take a few minutes...
Please refrain from any other operation during this time.
*********************************************************************
* If you are currently running the C460 Device Manager application, *
* it is recommended to exit from it before performing configuration *
* download operations. *
*********************************************************************
copy tftp SW_imageB
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the copy tftp SW_imageB command to updates the software image in Bank
B of all the Supervisor Modules installed in the switch. To use this command, you
need to have an active TFTP server, and to create a file into which to download the
data. If MSNM is running, an additional tftp server is not required.
copy tftp SW_imageB <filename> <ip>
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
filename file name (including full path)
ip IP address of the host
Example:
C460-1# copy tftp SW_imageB c:\imgB.bin 149.49.36.200
Beginning download operation ...
This operation may take a few minutes...
Please refrain from any other operation during this time.
*********************************************************************
* If you are currently running the C460 Device Manager application, *
* it is recommended to exit from it before performing configuration *
* download operations. *
*********************************************************************
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 29
Page 42

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
default-metric
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
Use the default metric command to set the interface RIP route metric.
Use the no default metric command to restore the default value.
The default metric is 1.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] default-metric <rip interface metric>
rip interface metric The interface RIP route metric value. The range is 1 to 15.
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # default metric 10
Done!
default-metric (OSPF)
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in the OSPF context
Type router ospf at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
Use the default metric command to set the interface OSPF route metric.
Use the no default metric command to restore the default value.
The default metric is 1.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] default-metric <number>
number The interface RIP route metric value. The range is 1 to 15.
Example:
Router-1 (configure router:ospf) # default metric 10
Done!
30 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 43

default-metric (RIP)
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in the RIP context
Use the default metric command to set the interface RIP route metric.
Use the no default metric command to restore the default value.
The default metric is 1.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] default-metric <number>
number The interface RIP route metric value. The range is 1 to 15.
Example:
Router-1 (configure router:rip) # default metric 10
Done!
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Type router rip at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
disable interface
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the disable interface command to disables the inband or outband
interface.
The syntax for this command is:
disable interface [outband | inband]
outband Disables the outband interface
inband Disables the inband interface
Example:
C460-1# disable interface outband
You must reset the device in order for the change to take
effect.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 31
Page 44

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
enable interface
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the enable interface command to enable the inband and outband
interfaces.
The syntax for this command is:
en[able] interface {outband | inband}
outband Enables the outband interface
inband Enables the inband interface
Example:
C460-1# en interface inband
This command will RESET the device
*** Reset *** - do you want to continue (Y/N)? Y
Attaching network interface lo0... done.
Welcome to C460
SW version 1.0.1
Login:
enable vlan commands
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode.
L Use the enable vlans commands command before configuring VLAN-
oriented parameters, when there is more than one interface on the same VLAN.
The syntax for this command is:
enable vlan commands
Example:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)#enable vlan commands
32 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 45

erase startup-config
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the erase startup-config command to clear the startup configuration.
The syntax for this command is:
erase startup-config
Example:
C460-1# erase startup-config
fragment chain
Use the fragment chain command to set the maximum number of fragments
that can comprise a single IP packet destined to the router.
Use the no fragment chain command to set the fragment chain to the default
value (64).
L The router does not perform reassembly of packets in transit.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] fragment chain <chain-limit>
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
chain-limit The maximum number of fragments that can comprise a single IP
packet, from 2 to 2048. The default is 64.
Example:
C460-1# fragment chain 10
fragment size
Use the fragment size command to set the maximum number of fragmented IP
packets, destined to the router, to reassemble at any given time. Use the no form of
this command to set the fragment size to the default value (100).
L The router does not perform reassembly of packets in transit.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] fragment size
<database-limit>
database-limit The maximum number of packets undergoing re-assembly at
any given time, from 0 to 200. The default is 100.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 33
Page 46

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
Router-1# fragment size 150
fragment timeout
Use the fragment timeout command to set the maximum number of seconds to
reassemble a fragmented IP packet destined to the router. Use the no form of this
command to set the fragment timeout to the default value (10).
L The router does not perform reassembly of packets in transit.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] fragment timeout
timeout The maximum number of seconds to re-assemble an IP packet,
from 5 to 120. The default is 10.
Example:
Router-1# fragment timeout 30
<timeout>
get time
Use the get time command to retrieve the time from the network.
The syntax for this command is:
get time
Example:
C460-1> get time
Time is being acquired from server 0.0.0.0
Time has been acquired from the network.
hostname
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the hostname command to change the Command Line Interface (CLI)
prompt. The current module number always appears at the end of the prompt.
Use the no hostname command to return the CLI prompt to its default.
34 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 47

The syntax for this command is:
[no] hostname [<hostname_string>]
hostname_string • none – displays current hostname
Example:
C460-1# hostname
Session hostname is ‘C460’
C460-1# hostname “gregory”
C460-1(super)#
If you wish to enter a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
hostname (Layer 3)
User level: read-write, admin.
Changes the system prompt used for the router. This command does not change the
system prompt of the switch.
To change the system prompt of the switch, use the host name command in the
Layer 2 tree.
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
• string – the string to be used as the hostname (up to 20
characters).
The syntax for this command is:
[no] hostname [<hostname_string>]
hostname_string The string to be used as the hostname (up to 20 characters).
If you do not enter a string, the current hostname is
displayed.
Example:
Router-1> hostname Marketing
Marketing-1 #
If you wish to define a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 35
Page 48

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
interface
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the interface command to create and enter the Interface Configuration
Mode.
Use the no interface command to delete a specific IP interface.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] interface <interface name>
interface name String (up to 32 characters)
Example:
C460-1(configure)# interface marketing
Done!
Router-1(config-if:marketing)#
If you wish to define a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
36 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 49

ip access-default-action
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the ”read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Use the ip access-default-action command to set the default action for a
specific policy list.
The syntax for this command is:
ip access-default-action <policy-list-number> <defaultaction>
<policy-list-number> integer (100 to 149)
<default-action> default-action-deny|default-action-permit
Example:
C460-1(configure)# access-default-action 101 defaultaction-deny
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
ip access-group
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the ”read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Use the ip access-group command to activate a specific policy list.
Use the no ip access-group command to deactivate the policy list.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip access-group <policy-list-number>[<default-action>]
<priority-list-number> integer (100 to 149)
0 is the default list
<default-action> default-action-deny|default-action-permit
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip access-group 101
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 37
Page 50

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
ip access-list
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the ”read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Use the ip access list command to create a specific policy rule. The access list
contains several of these rules: each rule pertains to the source IP address, the
destination IP address, the protocol, the protocol ports (if relevant), and to the ACK
bit (if relevant).
Use the no ip access list command to delete a specific rule.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip access-list <policy-list-number> <access-list-index>
<action> <protocol> {<source-ip> <source-wildcard> | any |
host <source-ip>}[<operator> <port> [<port]]
{<destination-ip> <destination-wildcard> | any |
host <destination-ip>}[<operator> <port> [<port>]]
[established] [precedence]
<access-list-number> integer (100 to 149)
0 is the default list
<access-list-index> integer (1 to 254)
<command> permit | deny | deny-and-notify | fwd0-7 |
composite op name
<protocol> ip | tcp | udp | integer (1 to 255)
<source-ip> ip network
<source-wildcard> ip network wildcard
<operator> eq | lt | gt | range
<port> integer (1 to 65535)
<destination-ip> ip network
<destination-wildcard> ip network wildcard
<precedence> mandatory | optional]
38 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 51

Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip access-list 101 23 deny ip any
1.2.0.0 0.0.255.255
ip access-list-cookie
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the ”read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Use the ip access-list-cookie command to set the list cookie for a specific
policy list.
The syntax for this command is:
ip access-list-cookie <policy-list-number> <cookie>
<policy-list-number> integer (100 to 149)
<cookie> integer
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip access-list-cookie 101 12345
ip access-list-copy
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the ”read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Use the ip access-list-copy command to copy a configured source policy list
to a destination policy list.
The syntax for this command is:
ip access-list-copy <source-list> <destination-list>
<source-list> integer (100 to 149)
0 is the default list
<destination-list> integer (100 to 149)
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 39
Page 52

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip access-list-copy 100 101
ip access-list-dscp name
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the ”read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Use the ip access-list-dscp name command to set a name for a dscp entry.
The syntax for this command is:
ip access-list-dscp name <policy-list-number> <dscp> <name>
<policy-list-number> integer (100 to 149)
dscp DSCP entry (0 to 63)
<name> entry name
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip access-list-name 101 16 special
If you wish to define a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
ip access-list-dscp operation
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the ”read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Use the ip access-list-dscp operation command to set a DSCP to CoS
mapping.
L The C460 performs the mapping for only those frames than match an ACL rule
with a “permit” action.
The syntax for this command is:
ip access-list-dscp operation <policy-list-number> <dscp>
40 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 53

<action>
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
policylistnumber
dscp Range of dscp. For example:
action • permit: do nothing, let the packet pass:
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip access-list-dscp operation 101 0-63
permit
C460-1(configure)# ip access-list-dscp operation 101 62
fwd5
ip access-list-dscp precedence
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the ”read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Use the ip access-list-dscp precedence command to ?
A valid id number for a policy list currently defined for the module
(100 - 149)
•0 to 63
• <low-dscp>-<high-dscp> <low-dscp>-<low-dscp>: apply the
• deny: drop the packet
• deny-and-notify: drop the packet and send an SNMP trap
• fwd0, fwd1fwd7: Set the frame COS field to 0,7
map to all packets with DSCP from <low-dscp> to <high-dscp>.
The syntax for this command is:
ip access-list-dscp precedence <policy-list-number> <dscp>
<precendence>
policy-listnumber
dscp DSCP entry (0 to 63)
precedence ????
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 41
A valid id number for a policy list currently defined for the
module (100 to 149)
mandatory
optional
Page 54

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip access-list-dscp precedence
C460-1(configure)#
ip access-list-dscp trust
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the ip access-list-dscp trust command to decide which original
frame fields influence the selection of packet priority.
The syntax for this command is:
ip access-list-dscp trust <policy-list-number>
{untrusted|trust-cos |trust-dscp}
policy-listnumber
untrusted Forward the packet with priority 0
trust-cos Forward the packet with its original 802.1p priority (default)
trust-dscp Forward the packet with the maximum priority between 802.1p and
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip access-list-dscp trust 100 trust-dscp
Done!
ip access-list-name
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Use the ip access-list-name command to set a name for a policy list.
The syntax for this command is:
ip access-list-name <policy-list-number> <name>
A valid id number for a policy list currently defined for the module
(100 to 149)
the priority obtained from the DSCP-CoS mapping table
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
<policy-list-number> integer (100 to 149)
42 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 55

<name> list name
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip access-list-name 101 morning
If you wish to define a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
ip access-list-owner
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the ip access-list-owner command to set the owner for a specific policy
list.
The syntax for this command is:
ip access-list-owner <policy-list-number> <owner>
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
<policy-list-number> integer (100 to 149)
<owner> list owner
Example:
Router-1> ip access-list-owner 101 admin
Done!
ip address
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode.
Use the ip address command to assign an IP address and mask to an interface.
The syntax for this command is:
ip address <ip-address> <mask> [<admin-state>]
ip address The IP address assigned to the interface.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 43
Page 56

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
mask Mask for the associated IP subnet
admin-state The administration status – either Up or Down
Example:
To assign the IP address 192.168.22.33 with mask 255.255.255.0 to the interface
“marketing”:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)# ip address 192.168.22.33
255.255.255.0
Done!
ip admin-state
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode.
Use the admin-state command to set the administrative state of an IP interface.
The default state is up.
The syntax for this command is:
ip admin-state <up/down>
up/down Administrative state of the interface:
•up (active)
• down (inactive).
Example:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)# ip admin-state up
ip bootp-dhcp network
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip bootp-dhcp network command to select the network from which
the bootp/dhcp server shall allocate an address. You only need to run this
command is required only when there are multiple interfaces over the VLAN.
Use the no ip bootp-dhcp network command to restore the default value.
44 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 57

The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip bootp-dhcp network <ip-address>
ip-address The IP address of the network.
Example:
To select the network 192.168.169.0 as the network from which an address shall be
allocated for bootp/dhcp requests:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip bootp-dhcp network
192.168.169.0
Done!
ip bootp-dhcp relay
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Use the ip bootp-dhcp command to enable relaying of bootp and dhcp requests
to the bootp/dhcp server.
Use the no ip bootp-dhcp command to disable bootp/dhcp relay.
The default state is disabled.
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip bootp-dhcp relay
Example:
To enable relaying of BOOTP and DHCP requests:
C460-1(configure)# ip bootp-dhcp relay
Done!
To disable relaying of bootp and dhcp requests:
C460-1(configure)# no ip bootp-dhcp relay
Done!
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 45
Page 58

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
ip bootp-dhcp server
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip bootp-dhcp server command to add a bootp/dhcp server to
handle bootp/dhcp requests received by this interface.
Use the no ip bootp-dhcp server command to remove the server. A
maximum of two servers can be added to a single interface.
The syntax for this command is:
ip bootp-dhcp server <ip-address>
ip-address The IP address of the server.
Example:
To add station 192.168.37.46 as a bootp/dhcp server to handle bootp/dhcp requests
arriving at the interface “marketing”:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip bootp-dhcp server
192.168.37.46
Done!
ip broadcast-address
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode.
Use the ip broadcast command to update the interface broadcast address. The
Broadcast address must be filled in with 0s or 1s.
The syntax for this command is:
ip broadcast-address <bc addr>
bc addr The broadcast IP address
Example:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)#ip broadcast address
192.168.255.255
46 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 59

ip default-gateway
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Use the ip default-gateway command to define a default gateway (router).
Use the no ip default gateway command to remove the default gateway.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip default-gateway <ip-address>[<cost>][<preference>]
ip-address The IP address of the router.
cost The path cost. The default is 1
preference Preference, either High or Low. Default is Low.
Example:
To define the router at address 192.168.37.1 as the default gateway:
C460-1(configure)# ip default-gateway 192.168.37.1
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
ip directed-broadcast
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode.
Use the ip directed-broadcast command to enable net-directed broadcast
forwarding.
Use the no ip directed-broadcast command to disables net-directed
broadcasts on an interface.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip directed-broadcast
Example:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)# ip directed broadcast
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 47
Page 60

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
ip icmp-errors
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the icmp-error command to turn ICMP error messages on.
Use the no icmp-error command to turn ICMP error messages off.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip icmp-errors
Example:
To turn the ICMP error messages on:
C460-1(configure)# ip icmp-errors
Done!
ip max-arp-entries
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the ip max-arp-entries command to set the maximum number of ARP
cache entries allowed in the ARP cache.
Use the no ip max-arp-entries command to restore the default value of 4096.
This command takes effect only after start-up.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip max-arp-entries <value>
value The space available for the IP address table. When you decrease the
number of entries, it may cause the table to be relearned more
frequently. If you do not enter a value, then the current ARP Cache
size is shown.
Example:
To set the maximum number of ARP cache entries to 8000:
C460-1(configure)# ip max-arp-entries 8000
48 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 61

To restore the maximum number of ARP cache entries to its default:
C460-1(configure)# no ip max-arp-entries
ip max-route-entries
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
The ip max-route-entries command exists for compatibility with Avaya™
P580. There is no limitation on the size of the routing table, except for the amount of
available memory.
Use the no ip max-route-entries command to remove the limitation.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip max-route-entries <value>
value number of entries
Example:
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
C460-1(configure)# ip max-route-entries 4000
ip netbios-rebroadcast
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode.
Use the ip netbios-rebroadcast command to set the NETBIOS rebroadcasts
mode on an interface.
Use the no ip netbios-rebroadcast command to disable NETBIOS
rebroadcasts on an interface.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip netbios-rebroadcast <mode>
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 49
Page 62

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
The possible values of mode are:
both Netbios packets received on the interface
rebroadcasted to other interfaces and netbios packets
received on other interfaces are rebroadcasted into
this interface.
disable Netbios packets are not rebroadcasted into or out of
this interface.
Example:
To enable rebroadcasting of netbios packets received by and sent from the interface
“marketing”:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)# ip netbios-rebroadcast both
ip netmask-format
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the ip netmask-format command to specify the format of netmasks in the
show command output.
Use the no ip netmask-format command to restores the default format which is
a dotted decimal.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip netmask-format <mask-format>
The possible mask formats are:
bitcount Addresses are followed by a slash and the total number of bits
in the netmask. For example 17
decimal The network masks are in dotted decimal notation. For
example, 255.255.255.0.
hexadecimal The network masks are in hexadecimal format as indicated by
the leading 0X. For example, 0XFFFFFF00.
50 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 63

Example:
To display netmasks in decimal format:
C460-1(configure)# ip netmask-format bitcount decimal
Done!
ip ospf authentication-key
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip ospf authentication-key command to configure the interface
authentication password.
Use the no ip ospf authentication-key command to remove the OSPF
password.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip ospf authentication-key <key>
key string (up to 8 characters)
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip ospf authenticationkey my_pass
ip ospf cost
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip ospf command to configure interface metric.
Use the no ip ospf cost command to set the cost to its default. The default is 1.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip ospf cost <cost>
cost integer
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 51
Page 64

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip ospf cost 10
Done!
ip ospf dead-interval
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip ospf dead-interval command to configure the interval before
declaring the neighbor as dead.
Use no ospf dead-interval to set the dead-interval to its default value of 40.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip ospf dead-interval <seconds>
seconds Time in seconds (integer value)
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip ospf dead-interval 15
ip ospf hello-interval
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use this command to specify the time interval between hello's the router sends.
Use no ip ospf hello-interval to set the hello-interval to its default.
The default is 10.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip ospf hello-interval <seconds>
seconds integer
52 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 65

ip ospf priority
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip ospf hello-interval 5
Done!
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip ospf priority command to configure interface priority used in DR
election.
Use the no ip ospf priority to set the OSPF priority to its default value.
The default is 1.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip ospf priority <priority>
priority integer
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip ospf priority 17
Done!
ip ospf router-id
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Router-OSPF mode.
Type router ospf at the command prompt to enter Router -OSPF mode if
necessary.
Use the ip ospf router-id command to configure the router identity.
Use the no ip ospf router-id command to return the router identity to its
default (lowest IP interface that exists).
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip ospf router-id <router id>
router id IP address
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 53
Page 66

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
Router-1> ip ospf router-id 192.168.49.1
ip proxy-arp
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode.
Use the ip proxy-arp command to enables proxy ARP on an interface.
Use the no ip proxy-arp command to disable proxy ARP on an interface.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip proxy-arp
Example:
To disable proxy ARP on interface marketing:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)#no ip proxy arp
ip redirects
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip redirects command to enables the sending of redirect messages on
the interface.
Use the no ip redirects command to disable the redirect messages. By default,
sending of redirect messages on the interface is enabled.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip redirects
Example:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)#ip redirects
ip rip authentication key
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
54 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 67

Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip rip authentication key command to set the authentication
string used on the interface.
Use the no ip rip authentication key command to clear the password.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip rip authentication key <password>
password The authentication string for the interface. Up to 16 characters are
Example:
To set the authentication string used on the interface “marketing” to be “hushhush”.
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip rip authentication
key hush-hush
ip rip authentication mode
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip rip authentication command to specify the type of authentication
used in RIP Version 2 packets.
Use the no ip rip authentication command to restore the default value of
none.
The syntax for this command is: [no] ip rip authentication mode
[simple|none]
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
allowed.
simple|none The authentication type used in RIP Version 2 packets:
• simple - clear text authentication.
• none - no authentication.
Example:
To specify simple authentication to be used in RIP Version 2 packets on the interface
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 55
Page 68

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
“marketing”.
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip rip authentication
mode simple
ip rip default-route-mode
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip rip default-route-mode command to enable learning of the
default route received by the RIP protocol. The default state is talk-listen.
The syntax for this command is:
ip rip default-route-mode <mode>
The possible default route modes on an interface are:
talk-listen Set RIP to send and receive default route updates on
the interface.
talk-only Set RIP to send but not receive default route updates
on the interface.
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip rip default-routemode talk listen
Done!
ip rip poison-reverse
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip rip poison-reverse command to enable split-horizon with
poison-reverse on an interface.
Use the no ip poison-reverse command to disable the poison-reverse
mechanism.
The split-horizon technique prevents information about routes from exiting the
router interface through which the information was received. This prevents routing
56 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 69

loops.
Poison reverse updates explicitly indicate that a network or subnet is unreachable
rather than implying they are not reachable. Poison reverse updates are sent to
defeat large routing loops.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip rip poison-reverse
Example:
ip rip rip-version
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Use the ip rip rip-version command to specify the RIP version running on
the interface basis.
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip rip poison-reverse
Done!
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
The syntax for this command is:
ip rip rip-version [1][2]
The possible versions of the RIP packets received and sent on an interface are:
[1] RIP Version 1 packets
[2] RIP Version 2 packets.
Example:
To specify that RIP version 2 should be running on the basis of the interface
“marketing”:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip rip rip-version 2
Done!
ip rip send-receive-mode
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 57
Page 70

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
necessary.
Use the ip rip send-receive command to set the RIP Send and Receive mode
on an interface. The default state is talk-listen.
The syntax for this command is:
ip rip send-receive-mode <mode>[<default route metric>]
mode talk-listen - Set RIP to receive and transmit
default route metric Integer value
Example:
To set the RIP Send and Receive mode on the interface “marketing” to be listen-only:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip rip send-receive-mode
talk listen
Done!
updates on the interface.
talkdefault-listen - Set RIP to receive
updates on the interface and send only a default
route.
ip rip split-horizon
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip rip split-horizon command to enable split-horizon mechanism.
Use the no ip rip split-horizon command to disable the split-horizon.
By default split-horizon is enabled.
The split-horizon technique prevents information about routes from exiting the
router interface through which the information was received. This prevents routing
loops.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip rip split-horizon
58 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 71

ip route
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # no ip rip split-horizon
Done!
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the ip route command to establish a static route.
Use the no ip route command to remove a static route.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip route <ip-address> <mask> <next-hop> [<next-hop>]
[<next-hop>] [<cost>] [<preference>]
ip-address The IP address of the network
mask Mask of the static route
next-hop The next hop address in the network
cost The path cost. The default is 1
preference Preference, either High or Low. Default is Low.
Example:
To define the router 192.168.33.38 as the next hop for the network 192.168.33.0 with
mask 255.255.255.0:
C460-1(configure)# ip route 192.168.33.0 255.255.255.0
10.10.10.10
ip routing
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 59
Page 72

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Use the ip routing command to enable IP routing.
Use the no ip routing command to disable the IP routing process in the device.
By default, IP routing is enabled.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip routing
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip routing
Done!
ip routing-mode
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip routing-mode command to set the IP routing mode of the interface. In
RT-MGMT mode, the interface functions as a routing interface. In
RT_PRIMARY_MGMT mode, the interface function as both a routing interface and
the primary management interface.
The IP address used in MSNM is the primary management interface IP address.
Only one interface can be in RT_PRIMARY_MGMT mode. If no interface is
configured to RT_PRIMARY_MGMT, the IP address used in MSNM is selected
randomly.
The syntax for this command is:
ip routing-mode <mode>
mode RT_MGMT or RT_PRIMARY_MGMT mode
Example:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)#ip routing-mode
RT_PRIMARY_MGMT
60 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 73

ip simulate
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the ip simulate command to check the policy for a simulated packet. The
command contains the addressed list number, and the packet parameters.
The syntax for this command is:
ip simulate <access-list-number> [<priority>] [<dscpvalue>]<source> <destination> [<protocol> [<source port>
<destination port> [<established>]]]
access-list-number integer (100 to 149)
priority fwd0 | fwd1 | ... | fwd7
dspc value dscp0 | dscp1 | ... | dscp63
source source ip address
destination destination ip address
protocol ip | tcp | udp | integer (1 to 255)
source port integer (1 to 65535)
destination port integer (1 to 65535)
established value of TCP established bit
Example:
C460-1(configure)# ip simulate 100 192.67.85.12
193.76.54.25
ip vlan/ip vlan name
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter interface mode.
Use the ip vlan and ip vlan name commands to specify the VLAN on which an
IP interface resides. You can specify either the VLAN ID using the ip vlan
command or the VLAN name using the ip vlan name command.
The no ip vlan or no ip vlan name command to reset the IP interface to the
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 61
Page 74

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
default VLAN.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip vlan <vlan-id>
Example:
To specify VLAN developmental as the VLAN used by interface “products”:
Router-1(config-if:marketing)# ip vlan name development
If you wish to define a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
ip vrrp
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip vrrp command to create a virtual router on the interface.
Use the no ip vrrp command to delete a virtual router.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip vrrp <vr-id>
vr-id Virtual Router ID (1-255)
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip vrrp 1
Done!
ip vrrp address
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip vrrp address command to assign an IP address to the virtual
router.
Use the no ip vrrp address command to remove an IP address from a virtual
router.
62 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 75

The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip vrrp <vr-id> address <ip-address>
Example:
To assign address 10.0.1.2 to virtual router 1:
ip vrrp auth-key
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Use the ip vrrp auth-key command to set the virtual router simple password
authentication for the virtual router ID.
Use the no ip vrrp auth-key command to disable simple password
authentication for the virtual router instance.
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
vr-id Virtual Router ID (1-255)
ip-address The IP address to be assigned to the virtual router.
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip vrrp 1 address
10.0.1.2
Done!
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip vrrp <vr-id> auth-key <key-string>
vr-id Virtual Router ID (1-255)
key-string Simple password string.
ip vrrp override addr owner
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip vrrp override addr owner command to accept packets
addressed to the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router, such as ICMP,
SNMP, and TELNET (if it is not the IP address owner).
Use the no ip vrrp override addr owner command to discard these packets.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 63
Page 76

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip vrrp <vr-id> override addr owner
vr-id Virtual Router ID (1-255)
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip vrrp 1 override addr
owner
Done!
ip vrrp preempt
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip vrrp preempt command to configure the router to preempt a lower
priority master for the virtual router ID.
Use the no ip vrrp preempt command to disable preemption for the virtual
router instance.
By default, preemption is enabled.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip vrrp <vr-id> preempt
vr-id Virtual Router ID (1-255)
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip vrrp 1 preempt
Done!
ip vrrp primary
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip vrrp primary command to set the primary address that shall be
used as the source address of VRRP packets for the virtual router ID.
Use the no ip vrrp primary command to return to the default primary address
64 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 77

ip vrrp priority
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
for the virtual router instance.
By default, the primary address is selected automatically by the device.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip vrrp <vr-id> primary <ip-address>
vr-id Virtual Router ID (1-255)
ip-address Primary IP address of the virtual router. This address
should be one of the router addresses on the VLAN.
Example:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip vrrp 1 primary
192.168.66.23
Done!
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip vrrp priority command to set the virtual router priority value
used when selecting a master router.
Use the no ip vrrp priority command to restore the default value.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] ip vrrp <vr-id> priority <pri-value>
vr-id Virtual Router ID (1-255)
pri-value The priority value. The range is 1-254.
Example:
To set the priority value for virtual router 1 to 10:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip vrrp 1 priority 10
Done!
Example:
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 65
Page 78

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
To set the virtual router simple password for virtual router 1 to abcd:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip vrrp 1 auth-key abcd
Done!
ip vrrp timer
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Interface mode.
Type interface [name] at the command prompt to enter Interface mode if
necessary.
Use the ip vrrp timer command to set the virtual router advertisement timer
value (in seconds) for the virtual router ID.
Use no ip vrrp timer command to restore the default value.
The syntax for this command is: [no] ip vrrp <vr-id> timer <value>
vr-id Virtual Router ID (1-255)
value The advertisement transmit time (seconds).
Example:
To set the virtual router advertisement timer value for virtual router 3 to 2:
Router-1(configure-if:marketing) # ip vrrp 3 timer 2
Done!
line
L You can only access this command from the banner or post-login banner
context.
Use the line command to add a line to the banner or post-login banner message.
The syntax for this command is:
line <number> [string]
number Line number in the banner (1 to 24)
string String to be displayed at the given line number (up to 80
characters)
66 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 79

network (RIP)
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
C460-1(super)# line 5 “C460 CLI”
Done!
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in router-RIP mode.
Type router rip at the command prompt to enter router-RIP mode if
necessary.
Use the network command to specify a list of networks on which the RIP is
running.
Use the no network command to remove an entry.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] network <ip-address> [<wildcard-mask>]
ip addr The IP address of the network of directly connected networks
wildcard-mask Wildcard mask address. Exists for compatibility with P550.
Example:
To specify that RIP will be used on all interfaces connected to the network
192.168.37.0:
Router-1 (configure router:rip) # network 192.168.37.0
Done!
network (OSPF)
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Router-OSPF mode.
Type router ospf at the command prompt to enter Router -OSPF mode if
necessary.
Use the network command to enable OSPF in this network.
Use the no network command to disable OSPF in this network.
The default is disabled.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 67
Page 80

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
The syntax for this command is:
network <net addr> [<wildcard-mask> [area <area id>]]
net addr IP address
wildcard-mask Wildcard mask address
area id Area ID. This parameter exists for compatibility with
Example:
Router-1 (configure router:ospf) # network 192.168.0.0
Router-1 (configure router:ospf) # area 192.168.0.0
0.0.255.255 area 0.0.0.0
no rmon alarm
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the no rmon history command to delete an existing RMON alarm entry.
P550.
The syntax for this command is:
no rmon alarm <Alarm Index>
Alarm Index History index defined using rmon alarm command or C460
Manager.
C460-1# no rmon alarm 1026
no rmon event
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the no rmon event command to delete an existing RMON event entry.
The syntax for this command is:
no rmon event <Event Index>
Event Index History index defined using rmon event command or C460
Manager.
C460-1# no rmon event 1054
68 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 81

no rmon history
no username
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the no rmon history command to delete an existing RMON history entry.
The syntax for this command is:
no rmon history <History Index>
History Index User level: read-only, read-write, admin.History
index defined using rmon history command or
RMON management tool
Example:
C460-1# no rmon history 1026
User level: admin.
Use the no username command to remove a local user account.
The syntax for this command is:
no username <name>
name User name
Example:
C460-1(super)# no username john
User account removed.
If you wish to delete a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
L You cannot delete the default user account “root”.
nvram initialize
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the nvram initialize command to reset the configuration parameters to
their factory defaults on the Active and Standby Supervisor modules.
The syntax for this command is:
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 69
Page 82

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
nvram initialize {switch | all}
switch Resets all the switch information (Layer 2 only).
all Resets all parameters including routing parameters in the
switch.
Example:
C460-1# nvram initialize
This command will restore factory defaults, and can
disconnect your telnet session
*** Reset *** - do you want to continue (Y/N)? y
Connection closed by foreign host
L The nvram initialize command does not alter the Active/Standby status of the
Supervisor modules.
passive-interface
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Router-OSPF mode.
Type router ospf at the command prompt to enter Router -OSPF mode if
necessary.
Use the passive interface command to allow interfaces to be flooded into the
OSPF domain as OSPF routes and not external routes.
Use the no passive interface command to disble the flooding.
L An interface becomes passive only if you use the network command to enable
OSPF to run on the interface.
The syntax for this command is:
passive-interface <interface-name/net addr>
interface-name /
Name of interface or IP address.
net addr
Example:
Router-1# passive-interface FastEthernet 1.10
70 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 83

ping
ping (Layer 3)
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
User level: read-only, read-write, admin.
Use the ping command to send ICMP echo request packets to another node on the
network.
The syntax for this command is:
ping [host]
host Host IP address/Internet address of route destination.
If you do not specify a host IP, then the last host IP is used.
Example: to ping the IP number 149.49.48.1:
C460-1> ping 149.49.48.1
149.49.48.1 is alive
User level: user, privileged, supervisor
Use the ping command to send ICMP echo request packets to another node on the
network.
The syntax for this command is:
ping <host> [<interval> [<size> [<timeout> [<source
address>]]]]]
host Host IP address/Internet address of route destination. If missing
then the last host IP is used.
interval Interval between ping commands in seconds (1 to 256)
size Size of packet in bytes (22 to 66500)
timeout Timeout in seconds (1 to 10)
source
IP address of one of the router interfaces
address
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 71
Page 84

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example: to ping the IP number 149.49.48.1 three times:
Router-1> ping 149.49.48.1 3
PING 149.49.48.1: 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 149.49.48.1: icmp_seq=0. time=0. ms
64 bytes from 149.49.48.1: icmp_seq=1. time=0. ms
64 bytes from 149.49.48.1: icmp_seq=2. time=0. ms
----149.49.48.1 PING Statistics---3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 0/0/0
redistribute (OSPF)
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in Router-OSPF mode.
Type router ospf at the command prompt to enter Router -OSPF mode if
necessary.
Use the redistribute command to redistribute routing information from other
protocols into OSPF.
Use the no redistribute command disables redistribution by OSPF.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] redistribute <protocol>
protocol [static | ospf]
Example:
Router-1 (configure router:ospf) # redistribute static
redistribute (RIP)
User level: read-write, admin.
L You can only access this command in router-RIP mode.
Type router rip at the command prompt to enter router-RIP mode if
necessary.
Use the redistribute command to redistribute routing information from other
protocols into RIP.
Use the no redistribute command to disable redistribution by RIP.
72 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 85

reset
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
The default is disabled.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] redistribute <protocol>
protocol Either Static or OSPF
Example:
Router-1 (configure router:rip) # redistribute ospf
Done!
User level: read-only, read-write, admin.
Use the reset command to restart the system or an individual Supervisor module.
The syntax for this command is:
reset [chassis | spvs | 1 | 2]
chassis • Reset the entire chassis, including the Supervisor and I/O
Modules
• Reset the hardware
• Causes disruption to traffic of 10 to 20 seconds
spvs • Reset both the Supervisor modules
• Minimal disruption to the traffic
1 Reset Supervisor module in slot 1
2 Reset Supervisor module in slot 2
L If the Supervisor modules are in Active/Standby configuration, resetting the
active supervisor will cause the standby supervisor to take over and become
active.
L The reset command does not work during configuration saving.
C460-1# reset 1
This command will reset the Active SPV
*** Reset *** - do you want to continue (Y/N)? y
Reseting Active SPV...
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 73
Page 86

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
C460-1(super)# reset chassis
This command will reset the chassis
*** Reset *** - do you want to continue (Y/N)? y
Reseting chassis...
C460-1(super)#
Avaya C460 Boot
Creation date: Jan 6 2003, 18:29:57
Press any key to stop auto-boot...
0
auto-booting...
Bank B is OK.
SW runs from bank B
.....
..........................................................
......................
......................................................
Welcome to C460
SW version 1.0.5
Login:
74 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 87

rmon alarm
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the rmon alarm command to create a new RMON alarm entry.
The syntax for this command is:
rmon alarm <Alarm Number> <variable> <interval> <sampletype>
rising-threshold <rising threshold> <rising event> fallingthreshold <falling threshold> <falling event> <startup alarm>
<owner>
alarm number This is the alarm index number of this entry (it is advisable to
use the same interface number as your alarm index number.)
variable This is the MIB variable which will be sampled by the alarm
entry.
interval The interval between 2 samples.
sample type This can be set to either delta (the difference between 2
samples) or an absolute value.
rising threshold This sets the upper threshold for the alarm entry.
rising event The RMON event entry that will be notified if the upper
threshold is passed.
falling
This sets the lower threshold for the alarm entry.
threshold
falling event The RMON event entry that will be notified if the lower
threshold is passed.
startup alarm The instances in which the alarm will be activated. The
possible parameters are: Rising, Falling, risingOrfalling.
owner Owner name string.
Example:
C460-1# rmon alarm 1026 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.5.1026 60
delta rising-threshold 10000 1054 falling-threshold 10 1054
risingOrFalling gregory
alarm 1026 was created successfully
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 75
Page 88

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
rmon event
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the rmon event command to create an RMON event entry.
The syntax for this command is:
rmon event <Event Number> <type> description <description>
owner <owner>
event number This is the event index number of this entry.
type The type of the event. The possible parameters are:
•trap
•log
•logAndTrap
•none
description A user description of this event
owner Owner name string
Example:
C460-1# rmon event 1054 logAndTrap description "event for
monitoring gregory's computer" owner gregory
event 1054 was created successfully
rmon history
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the rmon history command to create an RMON history entry.
The syntax for this command is:
rmon history <history index> [<module>[</port>]] interval
<interval> buckets <number of buckets> owner <owner name>
history_index This is the history index number of this entry (it is advisable to
use the same interface number as your history index number).
module/port The switch number/the port number.
interval The interval between two samples.
number of
The number of buckets defined.
buckets
76 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 89

owner name The owner name string.
Example:
C460-1# rmon history 1026 1026 3/2 30 buckets 20 owner amir
history 1026 was created successfully
If you wish to define a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
rmon2 protocol-dir
User level: privileged, supervisor.
L If you are at the ”privileged” level, you can only access this command in
Use the rmon2 protocol-dir to add a protocol to the protocol directory.
Use the no rmon protocol-dir command to remove a protocol from the
protocol directory.
The syntax for this command is:
rmon2 protocol-dir UDP|TCP <Port #> [<description> [<owner>]]
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Example:
Router-1# rmon2 protocol-dir UDP 345
Router-1# rmon2 protocol-dir UDP 345 "my description"
Router-1# rmon2 protocol-dir UDP 345 "description" "I am
the owner"
Done!
If you wish to enter a name which includes spaces, you must enclose the entire
name in quotation marks, for example “new york”.
rmon2 protocol-dist
User level: privileged, supervisor.
L If you are at the ”privileged” level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode if necessary.
Use the rmon2 protocol-dist to enable the RMON2 Protocol Distribution
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 77
Page 90

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
application.
Use the no rmon2 protocol-dist command to disable the application.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] rmon2 protocol-dist
Example:
Router-1# rmon2 protocol-dist
Done!
router ospf
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the router ospf command to enable the OSPF protocol on the system.
Use the no router ospf command to disable the OSPF one the system.
The default is disabled.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] router ospf
Example:
Router-1 (super) # router ospf
Done!
router rip
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the router rip command to configure the Routing Information Protocol
(RIP). Use the no router rip command to disable RIP.
The default state is disabled.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] router rip
Example:
78 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 91

router vrrp
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
To enable the RIP protocol:
C460-1(configure)# router rip
Done!
User level: read-write, admin.
L If you are at the “read-write” user level, you can only access this command in
Configure mode.
Type configure at the command prompt to enter configure mode.
Use the command to enable VRRP routing globally.
Use the no router vrrp command to disable VRRP routing.
The syntax for this command is:
[no] router vrrp
Example:
C460-1(configure)# router vrrp
Done!
session
User level: read-only, read-write, admin.
Displays existing sessions or to opens a session with a specific Supervisor Module in
the chassis.
The syntax for this command is:
session [[module_number>] {switch | router}]
module The Supervisor module number (1 to 2).
switch|router
(Optional)
• The entity to which you want to open a
session.
• If you do not specify this parameter, you
will get the default entity of the specific
module:
• switch - Layer 2 entity of the module.
• router - Routing entity
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 79
Page 92

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
C460-1> session router
Router-1 (super) #
L The security level stays the same when you use the session command.
set allowed managers
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set allowed managers command to enables or disable the Allowed
Managers feature.
When this feature is enabled, only those stations whose IP addresses are listed in the
Allowed Managers table can access the device over Telnet, SNMP, or HTTP.
The syntax for this command is:
set allowed managers [enabled|disabled]
Example:
C460-1(super)# set allowed managers enabled
Managers are enabled
set allowed managers ip
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set allowed manager ip command to add or remove an IP address
from the Allowed Managers table. The Allowed Managers table can contain up to
twenty IP addresses.
The syntax for this command is:
set allowed managers ip [add | delete][IP address]
add Add specified IP address to the Allowed Managers
table
delete Deletes specified IP address from the Allowed
Managers table
IP address IP address to be added or remove
80 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 93

Example:
C460-1(super)# set allowed managers ip add 149.49.32.134
Ip was added to the table
set arp-aging-interval
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set arp-aging interval command to set the ARP table aging interval
for gateways’ entries in the agent ARP table.
The MAC value for the default gateway of the agent in the ARP table, is deleted at
the end of every aging interval. The default value is 10 minutes.
The syntax for this command is:
set arp-aging-interval <value>
value The number representing the interval, from 0-10 minutes.
Example:
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
C460-1# set arp-aging-interval 10
ARP table aging interval for gateways was set to 10
minutes.
set arp-tx-interval
User level: read-write, admin.
Sets the keep-alive frames sending interval. Setting the interval to 0 disables the
transmission of the keep-alive frames.
The syntax for this command is:
set arp-tx-interval <inband|outband> <value>
inband|outband • Inband – inband interface
• Outband – outband interface
value The interval in seconds. (0-3600)
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 81
Page 94

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
Example:
C460-1# set arp-tx-interval 15
ARP tx interval was set to 15 seconds.
set boot bank
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set boot bank command to set the system boot bank (for the active
Supervisor Module).
The syntax for this command is:
set boot bank <value>
value • bank-a – set the boot bank to A
• bank-b – set the boot bank to B
Example:
C460-1# set boot bank A
boot bank is A
set broadcast storm control
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set broadcast storm control command to enable or disable
broadcast storm control.
The syntax for this command is:
set broadcast storm control <enable|disable>
enable Enable broadcast storm control
disable Disable broadcast storm control
Example:
C460-1# set broadcast storm enable
Done!
82 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 95

set broadcast storm control threshold
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set broadcast storm control threshold command to set the
broadcast storm control threshold.
The syntax for this command is:
set broadcast storm control threshold <threshold>
threshold In pps (packets per second) from 10 to 144,000 pps
The default value is 500
Example:
C460-1# set broadcast storm control threshold 1000
Done!
set device-mode
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set device-mode command to set the switch mode – Layer 2 or Router
(Layers 2 and 3).
The syntax for this command is:
set device-mode <mode>
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
mode • Router – switch operates at Layers 2 and 3.
• layer2 – switch operates at Layer 2.
Example:
C460-1(super)# set device-mode Router
This command will RESET the switch****
Reset **** do you want to continue (Y/N) ?
Done!
L You need to install the appropriate license before you can set the device mode to
Router.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 83
Page 96

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
set device-mode (Layer 3)
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set device-mode command to change the basic mode of operation of the
C460 switch between Router and Layer 2 modes.
The syntax for this command is:
set device-mode <mode>
mode Router | Layer2
Example:
Router-1> set device-mode Layer2
This command will RESET the device
*** Reset *** - do you want to continue (Y/N)? y
set dot1x max-req
User level: supervisor
Use the set dot1x max-req command to set maximum number of times the port
tries to retransmit requests to the Authenticated Station before the session is
terminated.
The syntax for this command is:
set dot1x max-req <count>
count Number of attempts (1 to 10)
Example:
C460-1(super)# set dot1x max-req 3
set dot1x quiet-period
User level: supervisor
Use the set dot1x quiet-period command to set the minimal time between
authentication attempts.
The syntax for this command is:
set dot1x quiet-period <Seconds>
Seconds Number of seconds – 0 to 65535
84 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 97

Example:
C460-1(super)# set dot1x quiet-period 90
Done!
set dot1x re-authperiod
User level: supervisor
Use the set dot1x re-authperiod command to set the idle time between reauthentication attempts.
The syntax for this command is:
set dot1x re-authperiod <Seconds>
Seconds Idle time in seconds ( 0 to 65535)
Example:
C460-1(super)# set dot1x re-authperiod 90
Done!
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
set dot1x server-timeout
User level: supervisor
Use the set dot1x server-timeout command to set the server retransmission
timeout period for all ports. This is the maximum time that the port will wait for a
reply from the Authentication Server.
The syntax for this command is:
set dot1x server-timeout <Seconds>
Seconds Timeout in seconds (0 to 65535)
Example:
C460-1(super)# set dot1x server-timeout 90
set dot1x supp-timeout
User level: supervisor
Use the set dot1x supp-timeout command to set the maximum time that the
switch will wait for a reply from the Authenticated Station before the session is
terminated.
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 85
Page 98

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
The syntax for this command is:
set dot1x supp-timeout <Seconds>
Seconds Timeout in seconds (0 to 65535)
Example:
C460-1(super)# set dot1x supp-timeout 90
set dot1x system-auth-control disable
User level: supervisor
Use the set dot1x system-auth-control disable command to globally
disable the PBNAC (802.1x) feature.
The syntax for this command is:
set dot1x system-auth-control disable
Example:
C460-1(super)# set dot1x system-auth-control disable
dot1x system-auth-control disabled
set dot1x system-auth-control enable
User level: supervisor
Use the set dot1x system-auth-control enable command to globally
enable the PBNAC (802.1x) feature.
The syntax for this command is:
set dot1x system-auth-control enable
Examples:
• When a RADIUS server is defined:
C460-1(super)# set dot1x system-auth-control enable
dot1x system-auth-control enabled
86 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
Page 99

• When a RADIUS server is not defined:
C460-1(super)# set dot1x system-auth-control enable
*** Warning : Authentication server ( RADIUS ) is disabled/
not-exist and so,
*** no authentication can be made
dot1x system-auth-control enabled
set dot1x tx-period
User level: supervisor
Use the set dot1x tx-period command to set the time interval between
attempts to access the Authenticated Station.
The syntax for this command is:
Example:set dot1x tx-period <Seconds>
Seconds Interval in seconds
C460-1(super)# set dot1x tx-period 90
Done!
Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
set icmp-redirect
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set icmp-redirect CLI command to accept or reject incoming ICMP-redirect
requests.
The syntax for this command is:
set icmp-redirect {accept|reject}
Accept Accept inoming ICMP-redirect requests
Reject Reject incoming ICMP-redirect requests
Example:
C460-1# set icmp-redirect accept
Done!
Avaya C460 Reference Guide 87
Page 100

Chapter 2 Avaya C460 CLI Commands
set inband vlan
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set inband vlan command to set the inband management VLAN.
The syntax for this command is:
set inband vlan <vlan_num>
vlan_num The number of the VLAN.
Example:
C460-1# set inband vlan 1
Management VLAN number set to 1
set intelligent-multicast
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set intelligent-multicast command to enable or disable the IPmulticast filtering application.
The syntax for this command is:
set intelligent-multicast {enable|disable}
Example:
C460-1# set intelligent-multicast enable
Done!
set intelligent-multicast client port pruning time
User level: read-write, admin.
Use the set intelligent-multicast client port pruning time
command to set the aging time for client ports.
The syntax for this command is:
set intelligent-multicast client-port-pruning time <time>
seconds The time in seconds.
88 Avaya C460 Reference Guide
 Loading...
Loading...