Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation Manual

Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0
Installation—Devices
NN40170-304
Document status: Standard
Document issue: 03.02
Document date: October 2010
Product release: BCM 6.0
Job function: Installation
Type: Technical Publication
Language type: English

Copyright © 2010 Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Notices
While reasonable efforts have been made to ensure that the information in this document is complete and accurate at the time of
printing, Avaya assumes no liability for any errors. Avaya reserves the right to make changes and corrections to the information
in this document without the obligation to notify any person or organization of such changes.
Documentation disclaimer
Avaya shall not be responsible for any modifications, additions, or deletions to the original published version of this
documentation unless such modifications, additions, or deletions were performed by Avaya. End User agree to indemnify and
hold harmless Avaya, Avaya’s agents, servants and employees against all claims, lawsuits, demands and judgments arising out
of, or in connection with, subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to this documentation, to the extent made by End
User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked Web sites referenced within this site or documentation(s)
provided by Avaya. Avaya is not responsible for the accuracy of any information, statement or content provided on these sites
and does not necessarily endorse the products, services, or information described or offered within them. Avaya does not
guarantee that these links will work all the time and has no control over the availability of the linked pages.
War ranty
Avaya provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to your sales agreement to establish the terms of the limited warranty.
In addition, Avaya’s standard warranty language, as well as information regarding support for this product, while under warranty,
is available to Avaya customers and other parties through the Avaya Support Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support
Please note that if you acquired the product from an authorized reseller, the warranty is provided to you by said reseller and not
by Avaya.
Licenses
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS AVAILABLE ON THE AVAYA WEBSITE, HTTP://SUPPORT.AVAYA.COM/
LICENSEINFO/ ARE APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO DOWNLOADS, USES AND/OR INSTALLS AVAYA
SOFTWARE, PURCHASED FROM AVAYA INC., ANY AVAYA AFFILIATE, OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER
(AS APPLICABLE) UNDER A COMMERCIAL AGREEMENT WITH AVAYA OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER.
UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED TO BY AVAYA IN WRITING, AVAYA DOES NOT EXTEND THIS LICENSE IF THE
SOFTWARE WAS OBTAINED FROM ANYONE OTHER THAN AVAYA, AN AVAYA AFFILIATE OR AN AVAYA
AUTHORIZED RESELLER, AND AVAYA RESERVES THE RIGHT TO TAKE LEGAL ACTION AGAINST YOU AND
ANYONE ELSE USING OR SELLING THE SOFTWARE WITHOUT A LICENSE. BY INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING
OR USING THE SOFTWARE, OR AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU, ON BEHALF OF YOURSELF AND THE
ENTITY FOR WHOM YOU ARE INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE (HEREINAFTER
REFERRED TO INTERCHANGEABLY AS "YOU" AND "END USER"), AGREE TO THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS
AND CREATE A BINDING CONTRACT BETWEEN YOU AND AVAYA INC. OR THE APPLICABLE AVAYA AFFILIATE
("AVAYA").
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, no use should be made of the Documentation(s) and Product(s) provided by Avaya. All
content in this documentation(s) and the product(s) provided by Avaya including the selection, arrangement and design of the
content is owned either by Avaya or its licensors and is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws including the
sui generis rights relating to the protection of databases. You may not modify, copy, reproduce, republish, upload, post, trans
or distribute in any way any content, in whole or in part, including any code and software. Unauthorized reproduction,
transmission, dissemination, storage, and or use without the express written consent of Avaya can be a criminal, as well as a civil
offense under the applicable law.
Third Party Components
Certain software programs or portions thereof included in the Product may contain software distributed under third party
agreements ("Third Party Components"), which may contain terms that expand or limit rights to use certain portions of the
Product ("Third Party Terms"). Information regarding distributed Linux OS source code (for those Products that have distributed
the Linux OS source code), and identifying the copyright holders of the Third Party Components and the Third Party Terms that
apply to them is available on the Avaya Support Web site: http://support.avaya.com/Copyright.
Trademarks
The trademarks, logos and service marks ("Marks") displayed in this site, the documentation(s) and product(s) provided by
Avaya are the registered or unregistered Marks of Avaya, its affiliates, or other third parties. Users are not permitted to use such
Marks without prior written consent from Avaya or such third party which may own the Mark. Nothing contained in this site, the
documentation(s) and product(s) should be construed as granting, by implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license or right in
and to the Marks without the express written permission of Avaya or the applicable third party. Avaya is a registered trademark
of Avaya Inc. All non-Avaya trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Downloading documents
For the most current versions of documentation, see the Avaya Support. Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support
Contact Avaya Support
Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report problems or to ask questions about your product. The support
telephone number is 1-800-242-2121 in the United States. For additional support telephone numbers, see the Avaya Web site:
http://www.avaya.com/support
mit

Contents
New in this release 7
Features 7
Introduction 9
Overview of key hardware elements and devices 11
BCM450 main and expansion units 12
BCM50 main and expansion units 12
Media bay module types 12
Avaya BCM 6.0 features 13
Avaya BCM 6.0 applications 13
Digital devices 13
Central Answering Position 14
Wireless devices 14
WLAN handsets 221X 15
Avaya 6120 and 6140 WLAN Handsets 15
IP devices 15
Analog devices 22
Analog station media bay module 22
Analog terminal adapter 23
Device compatibility and installation requirements 25
Release compatibility 25
Navigation 13
Corded display sets and options 13
Cordless sets and options 14
Key indicator module 14
BST Doorphone 14
Avaya 4000 Series DECT Handsets 15
Digital mobility phones 15
Navigation 15
IP phone registration 16
IP phone configuration 17
Registering the telephone to the system 17
Configuring telephone settings 18
Troubleshooting IP telephones 20
Avaya 1100 Series IP Deskphones 20
Avaya 1100 Series Expansion Module 20
Avaya 1200 Series IP Deskphones 20
Avaya 1200 Series Expansion Module 21
Avaya 2000 Series IP Deskphones 21
IP Key Expansion Module 21
Avaya 2050 IP Softphone 22
Avaya 2033 IP Conference Phone 22
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 3

Contents
Release compatibility navigation 25
ISDN basics 25
Services and features for ISDN BRI and PRI 27
ISDN hardware 32
ISDN standards compatibility 35
Plan your Integrated Services Digital Network 35
Order ISDN PRI 36
Order ISDN BRI 36
Supported ISDN protocols 37
MBM trunk requirements 37
MBM station requirements 38
IP phones and IP telephony 41
IP phone Basics 41
IP telephones and VoIP trunks 42
IP telephones 42
Voice over IP trunks 42
IP telephony networking 43
Meridian 1 Internet Telephony Path 45
Telephone interoperability 45
Network gatekeepers 45
Public Switched Telephone Network 47
Key IP telephony concepts 47
Codecs 47
Jitter buffer 48
Quality of service routing 49
Telephone relocation 49
Digital telephone relocation 49
Digital telephone relocation recommendations 49
IP telephones relocation 50
Media bay module configuration 51
Configuring resources for the MBM on BCM450 51
Configuring resources for the MBM on BCM50 53
IP phone registration 55
Enabling registration in Business Element Manager 55
Automatically assign directory names 56
Registering IP phones in the system 56
Accessing the local configuration menu on an Avaya 2001, 2002 or 2004 IP Deskphones 57
Accessing the local configuration menu on an Avaya 2033 IP Deskphone 57
Accessing the local configuration menu on an Avaya 2007 IP Deskphone 58
Accessing configuration menu on an Avaya 1120E or 1140E IP Deskphones 58
Accessing configuration menu on an Avaya 1210, 1220, or 1230 IP Deskphones 59
Deregistering IP telephones 59
Avaya 1100 Series IP Deskphones configuration 61
Opening the network configuration menu 64
4 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

Contents
Setting 802.1x authentication 64
Setting DHCP 65
Setting the IP address 65
Setting the gateway 66
Setting S1 IP 66
Setting S1 port 66
Setting S1 action 67
Setting S1 retry 67
Setting S1 private key 68
Setting S2 IP 68
Setting S2 port 69
Setting S2 action 69
Setting S2 retry 70
Setting S2 private key 70
Setting VLAN 71
Setting the VLAN filter 71
Setting the PC port 72
Setting data VLAN 72
Setting PC_Port Untag All 73
Setting the duplex mode 73
Setting Gratuitous ARP 74
Setting External Application Server 74
Setting the XAS port 75
Upgrading the IP phone firmware 75
Telephone relocation 77
Digital telephone relocation 77
Keeping an IP telephone active 77
IP telephone relocation without changing the DN 78
IP telephone relocation with a changed DN 78
Media encryption on IP phones 79
Configuring SRTP media encryption on a Phase II Avaya 2001, 2002, and 2004 IP
Deskphones 79
Configuring SRTP media encryption on an Avaya 2007 IP Deskphone 80
Configuring SRTP media encryption on an Avaya 1110, 1120E, and 1140E IP Deskphones 80
Configuring SRTP media encryption on an Avaya 1210, 1220, and 1230 IP Deskphones 81
Device Compatibility 83
IP Phones reference 87
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 5

Contents
6 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

New in this release
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms
running Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 (Avaya BCM 6.0).
The following sections detail what’s new in Avaya Business Communications Manager
Installation — Devices (NN40170-500) for Release 6.0.
Features
See the following sections for information about feature changes:
• The Device compatibility and installation requirements section includes information
about the new functionality to have a maximum of five Business Names for CLID.
• The Avaya 1100 Series IP Deskphones configuration section includes procedures
for downloading the license and configuration files for an Avaya 1100 Series IP
Deskphones through a Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection. This enables you
to use your IP Phone remotely. This feature also supports secure call recording.
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 7

New in this release
8 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

Introduction
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms
running Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 (Avaya BCM 6.0).
This document contains conceptual, task-based, and reference information about
analog, digital, IP, and Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) devices on a Avaya
BCM 6.0 system.
The information in this guide explains how to
• install and configure components
• register and relocate telephones and devices
• enable media encryption
Use Business Element Manager, Startup Profile, and Telset Administration to configure
Avaya BCM 6.0 parameters.
Navigation
• Overview of key hardware elements and devices (page 11)
• Device compatibility and installation requirements (page 25)
• IP phones and IP telephony (page 41)
• Media bay module configuration (page 51)
• IP phone registration (page 55)
• Avaya 1100 Series IP Deskphones configuration (page 61)
• Telephone relocation (page 77)
• Media encryption on IP phones (page 79)
• Device Compatibility (page 83)
• IP Phones reference (page 87)
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 9

Introduction
10 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

Overview of key hardware elements and devices
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms
running Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 (Avaya BCM 6.0).
The Avaya BCM 6.0 system provides private network and telephony management
capability to small and medium-sized businesses.
The Avaya BCM 6.0 system
• integrates voice and data capabilities, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) gateway
functions, and Quality of Service (QoS) data-routing features into a single telephony
system
• enables you to create and provide telephony applications for use in a business
environment
This section describes the telephony devices Avaya BCM 6.0 supports.
Navigation
• BCM450 main and expansion units (page 12)
• BCM50 main and expansion units (page 12)
• Media bay module types (page 12)
• Avaya BCM 6.0 features (page 13)
• Avaya BCM 6.0 applications (page 13)
• Digital devices (page 13)
• Wireless devices (page 14)
• IP devices (page 15)
• Analog devices (page 22)
• Analog terminal adapter (page 23)
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 11

Overview of key hardware elements and devices
BCM450 main and expansion units
Attention: The expansion unit mentioned in this section does not apply to BCM50.
BCM450 includes the following key elements:
• BCM450 main unit. You can install up to four media bay modules in the main unit.
• BCM450 expansion cabinet. You can install up to six media bay modules in the
expansion cabinet.
BCM50 main and expansion units
Attention: The expansion unit mentioned in this section does not apply to BCM450.
BCM50 includes the following key elements:
• BCM50 main unit. BCM50a and BCM50ba units include integrated ADSL routers.
BCM50e and BCM50be units include integrated ethernet routers. BCM50b,
BCM50ba, and BCM50be include two integrated BRI ports that replace the four
analog lines on the RJ-21 telephony connector.
• BCM50 expansion unit. You can install up to 2 BCM50 expansion units. You can
install one media bay module (MBM) into each expansion unit.
Media bay module types
BCM 6.0 supports the following MBMs:
•4 x 16
• ADID4
• ADID8
• ASM8, ASM8+
•BRIM
• CTM4, CTM8
•DSM16, DSM32
• DSM16+, DSM32+
•DTM
• FEM. This type is not supported on BCM50.
•GASM
•GATM4, GATM8
• G4 x 16
• G8 x 16
12 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

• R2MFC
Attention: All MBMs require the keycode enabled expansion cabinet for use in
BCM50.
Avaya BCM 6.0 features
Avaya BCM 6.0 supports the complete range of IP telephony features offered by existing
Avaya BCM products.
Avaya BCM 6.0 applications
Avaya BCM 6.0 supports many applications provided on the existing Avaya BCM
platform.
Enter the appropriate keycodes to enable the following features (no additional hardware
required):
• Voice Messaging for standard voice mail and auto-attendant features
• Unified Messaging to provide integrated voice mail management between voice mail
and common e-mail applications
Overview of key hardware elements and devices
• Fax Suite to providing support for attached analog fax devices
• Voice networking features
• LAN CTE (computer telephony engine)
• VEWAN
•IP Music
• Contact Center
Digital devices
Avaya BCM 6.0 supports corded display sets, cordless sets, key indicator modules
(KIM), the Business Series Terminal (BST) Doorphone, and the Central Answering
Position.
Navigation
• Corded display sets and options (page 13)
• Cordless sets and options (page 14)
• Key indicator module (page 14)
• BST Doorphone (page 14)
Corded display sets and options
• Avaya 7000 Digital Deskphone (International only): four memory buttons, without
display or indicators.
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 13

Overview of key hardware elements and devices
• Avaya 7100 Digital Deskphone: one-line display, and one memory button without
indicator.
• Avaya 7208 Digital Deskphone: one-line display, and eight memory buttons with
indicators.
• Avaya 7316 Digital Deskphone: two-line display, three display buttons, 16 memory
buttons with indicators, and eight memory buttons without indicators. The Avaya
7316 Digital Deskphone supports separate mute key and a headset key under the
dial pad.
Avaya 7316E Digital Deskphone: two-line display, three display buttons, 16 memory
buttons with indicators, and eight memory buttons without indicators; handsfree, mute,
and headset buttons (under the dial pad).
Cordless sets and options
• Avaya 7406 Digital Mobile Handset cordless telephone system: six memory
buttons with indicators and a two-line display with three display buttons. The Avaya
7406 Digital Mobile Handset provides cordless mobility in a small office
environment. Each base station supports three telephones. Function is based on the
7316 telephone. The base station connects to a digital station media bay module on
the system.
• Avaya 7406E Digital Mobile Handset cordless handset: six memory buttons with
indicators and a three-line display with three display buttons. The Avaya 7406E
Digital Mobile Handset provides cordless mobility in a small office environment.
Each base station supports four handsets. The base station connects to a digital
station media bay module on the system.
Key indicator module
The KIM includes 24 memory buttons with indicators.
BST Doorphone
Use BST Doorphone as an intercom to control access to your building. Press the Call
button on the BST Doorphone to call one or more telephones, or send a distinctive
chime to telephones in an assigned page zone. Place an internal call from any
telephone on the system to the BST Doorphone to set up a two-way voice call. Install a
Door Opening Controller to permit the activation of locks on doors or gates.
Central Answering Position
Central Answering Position (CAP/eCAP) provides additional auto dial positions or
additional line appearances. The CAP consists of a Avaya 7316E Digital Deskphone
telephone and from one to nine KIMs.
Wireless devices
Avaya BCM 6.0 supports Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT)
handsets, digital mobility phones, and WLAN handsets.
14 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

Avaya 4000 Series DECT Handsets
• DECT 413x series handsets: three display soft keys, four-line handset display, and
text messaging.
• DECT 414x series handsets: three display soft keys, four-line handset display,
loudspeaker capability, and text messaging.
Digital mobility phones
• Avaya 7420 DECT Handset: three display soft keys, four-line handset display.
• Avaya 7430 DECT Handset: three display soft keys, and four-line handset display,
text messaging.
• Avaya 7440 DECT Handset: three display soft keys, and four-line handset display,
loudspeaker capability, and text messaging.
WLAN handsets 221X
WLAN handsets use VoIP technology and Push-to-Talk, which enables two-way
communication with another Avaya BCM user.
The handsets communicate with the Avaya BCM system and with the WLAN IP
Telephony Manager 2245. Like wired telephones, the wireless handsets receive calls
directly, receive transferred calls, transfer calls to other extensions, and make outside
and long-distance calls (subject to corporate restrictions). The handsets interoperate
with other IP Line and IP Trunk features and devices, such as IP Peer, and the 20xx IP
Phone and Avaya 2050 IP Softphone series of IP Phones.
Overview of key hardware elements and devices
Avaya 6120 and 6140 WLAN Handsets
The Avaya 6120 and 6140 WLAN Handsets operate with the Avaya BCM and the WLAN
IP Telephony Manager 2245. They are fully functional handsets specifically designed for
the busy office environment. The Avaya 6120 and 6140 WLAN Handset use radio wave
technology to send and receive voice and data transmissions. They operate much like
a cell phone. However, the Handsets use the private communication system installed in
your facility and will not operate outside the area covered by this system.
IP devices
Avaya BCM 6.0 supports IP Phones, IP Phone expansion modules, a softphone, and an
audio conference phone.
Navigation
• IP phone registration (page 16)
• IP phone configuration (page 17)
• Registering the telephone to the system (page 17)
• Configuring telephone settings (page 18)
• Troubleshooting IP telephones (page 20)
• Avaya 1100 Series IP Deskphones (page 20)
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 15

Overview of key hardware elements and devices
• Avaya 1100 Series Expansion Module (page 20)
• Avaya 1200 Series IP Deskphones (page 20)
• Avaya 1200 Series Expansion Module (page 21)
• Avaya 2000 Series IP Deskphones (page 21)
• IP Key Expansion Module (page 21)
• Avaya 2050 IP Softphone (page 22)
• Avaya 2033 IP Conference Phone (page 22)
IP phone registration
Registering IP telephones to the system is a two-stage process.
• Set up the system programming to receive registration under Resources >
Telephony Resources. For more information see, IP phone registration (page 55)
• Configure each telephone.
When the telephone registers, it downloads the information from the system IP
Telephony record to the telephone configuration record. This can include a new
firmware download, which occurs automatically. If new firmware downloads, the
telephone display indicates the event.
Attention: If the telephone displays a prompt that indicates it cannot find the server,
follow the instructions in IP phone registration (page 55) to enter the specific network
path. Troubleshooting IP telephones (page 20) describes other possible prompt
messages.
If you do not automatically register to the system, you can configure the telephone
settings to enable you to access a system on the network. You must perform additional
steps if your IP telephone does not connect to the same LAN to which the system
connects.
After you have entered all the configuration information, the telephone attempts to
connect to the system. The message “Locating Server” appears on the display. If the
connection is successful, the message changes to “Connecting to Server” after 15
seconds. Initialization can take several minutes. Do not disturb the telephone during this
time.
When the telephone connects to the server and is ready to use, the display shows the
time and date, and the six keys at the top of the display become labelled.
If you experience problems with IP telephone registration, see Troubleshooting IP
telephones (page 20).
If the DN record is not configured, as with auto-assigned DNs, you can only place local
calls until other lines assigned in the DN record.
16 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

• If no one registered the telephone previously, you receive a “New Set” message.
Enter the information as prompted. See Registering the telephone to the system
(page 17).
IP phone configuration
The configuration of the IP phones depends on whether you use Dynamic Host Control
Protocol (DHCP) on the system.
• If you use DHCP service on the system, or you configured the Customer DHCP
server to hand out specific system network details, the IP telephone automatically
attempts to find the server.
After you register the telephone to the system, as described in, Registering the
telephone to the system (page 17)the telephone assumes the parameters it receives
from the system, which are described in Configuring telephone settings (page 18)
• If you did not configure DHCP to provide system information, or if you do not use
DHCP on your network, you must configure your telephone parameters before the
telephone can register to the system. In this case, follow the directions in
Configuring telephone settings (page 18), and then follow the prompts that appear,
as described in Registering the telephone to the system (page 17)
Overview of key hardware elements and devices
• If an external DHCP server does not exist, the DHCP server on the main unit
supplies IP configuration information for all IP devices (PCs and IP Phones). It also
supplies specific connection information to the IP Phones.
Registering the telephone to the system
When you first connect the telephone to the IP connection, you receive one of the
following:
• If the telephone is not yet registered, and when a password is entered in the Terminal
Registration screen, the telephone prompts you for that password.
• If Auto Assign DN is not selected, the telephone prompts you for a DN. For more
information see the Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Configuration –
Devices Guide (NN40170-500).
• If you are prompted for a password, enter the password and press OK.
• If you are prompted for a DN, enter the DN you want assigned to this telephone and
press OK.
When the telephone registers, it downloads the information from the system IP
Telephony record to the telephone configuration record. This can include a new
firmware download, which occurs automatically. If new firmware downloads, the
telephone display indicates the event.
If the telephone displays a prompt that indicates it cannot find the server, follow the
instructions in Configuring telephone settings (page 18)to enter the specific network
path.Troubleshooting IP telephones (page 20) describes other possible prompt
messages.
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 17

Overview of key hardware elements and devices
Configuring telephone settings
If you are not automatically registered to the system, you can configure the telephone
settings to enable you to access a system on the network. You also must perform these
steps if your IP telephone is not connected to the same LAN to which the system is
connected. For more information about accessing the telephone configuration menus
see, IP phone registration (page 55)
If you experience problems with IP telephone registration, refer to the section
Troubleshooting IP telephones (page 20).
If the DN record is not configured yet, as is the case with auto-assigned DNs, you can
only place local calls until other lines are assigned in the DN record.
If the telephone has not been registered before, you receive a New Set message. Enter
the information, as prompted. The following table describes the values for each display
parameter. For more information see, Registering the telephone to the system (page 17)
IP telephone server configurations
Field Value Description
DHCP 0 or 1 Enter 0 if your network does not use a DHCP server to
dispense IP addresses. (Static DHCP)
Enter 1 if your network uses a DHCP server.
If DHCP = 0
SET IP <IP address> The set IP must be a valid and unused IP address on the
network to which the telephone connects.
NETMASK <subnet mask
address>
DEF GW <IP address> Default Gateway on the network (for example, the nearest
Emulation Key
Mapping
0 or 1 0 = Handset
This is the subnet mask. This setting is critical for locating
the system to which you want to connect.
router to the telephone. The router for IP address W.X.Y.Z
is usually at W.X.Y.1).
If there are no routers between the telephone and the
system network adaptor to which it connects, (for
example, a direct HUB connection), enter the Published
IP address of the
If the IP telephone does not connect directly to the
Published IP address network adapter, set the DEF GW
to the IP address of the network adaptor to which the
telephone connects.
1= Handsfree
Default setting is 1 (handsfree)—do not change.
Avaya BCM 6.0 as the DEF GW.
This setting applies to the 2033 model only.
18 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010
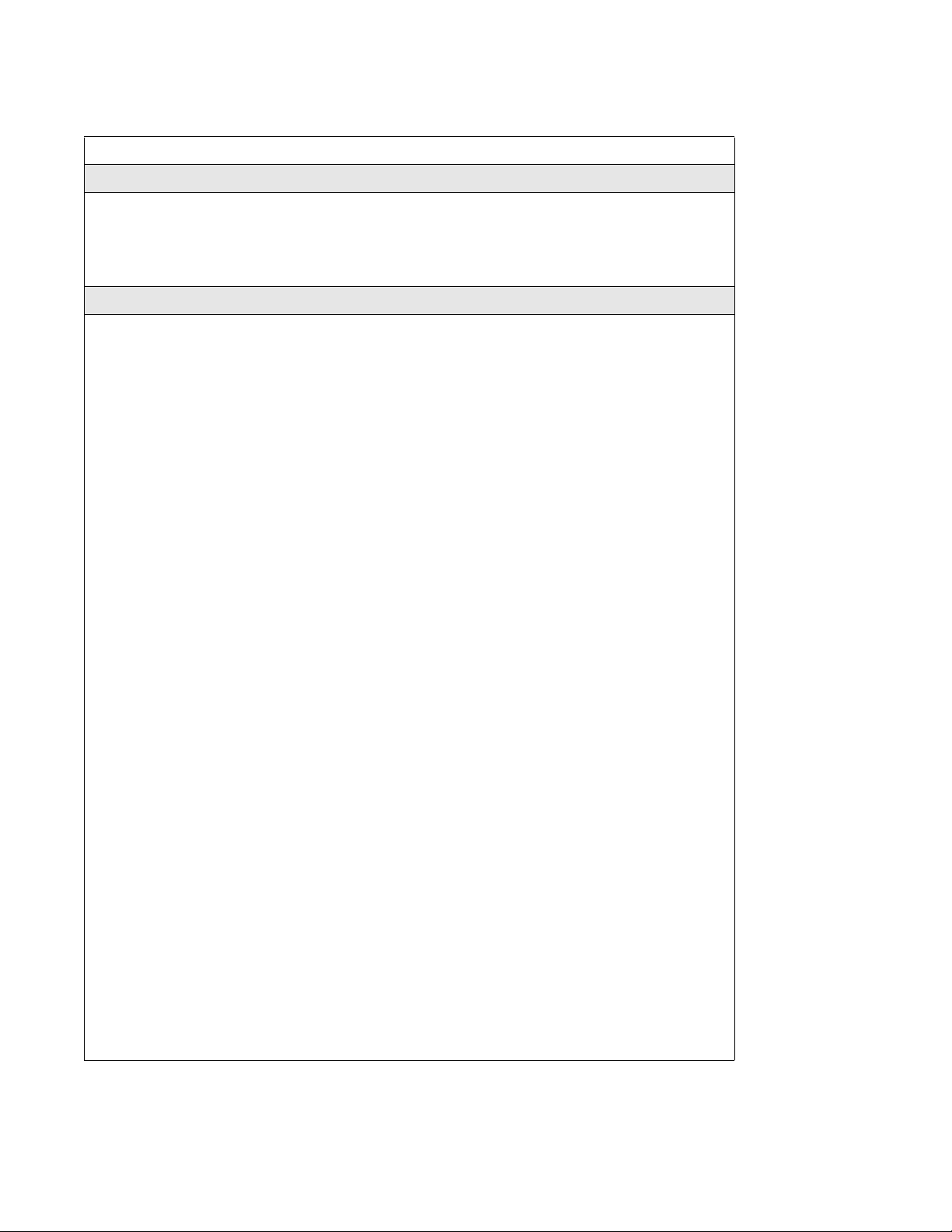
IP telephone server configurations
Field Value Description
If DHCP = 1
Overview of key hardware elements and devices
Manual Cfg?
DHCP:
If DHCP = 0 or Partial
S1 IP <IP address> This is the Published IP address of the first Avaya BCM
S1 PORT Default: *7000 This is the port the telephone uses to access this system.
S1 ACTION Default: 1
S1 RETRY
COUNT
S2 IP <IP address> This is the Published IP address of the second Avaya
S2 PORT Default: *7000 This is the port the telephone uses to access this system.
S2 ACTION Default: 1
S2 RETRY
COUNT
Full = 0
Partial = 1
<digits between
0
and 255>
<digits between
0
If you indicate DHCP for the telephone, but you want to
enter static IP addresses, choose 1 (Partial).
If you choose 0 (Full), the DHCP server assigns IP
addresses that are not static.
system to which you want to register the telephone.
Configure this to the number of times you want the
telephone to retry the connection to the system.
BCM system to which you want to register the telephone.
It can match the S1 setting.
Set this to the number of times you want the telephone to
retry the connection to the system.
and 255>
VLAN 0: No VLAN
1: Manual VLAN
2: Automatically
discover VLAN
using DHCP
Cfg XAS? 0: No (default)
1: Yes
Note 1: Ensure that the firewall filters are set up to allow IP traffic into and out of the system.
Choose 0: NO VLAN if no VLAN exists on the network.
If DHCP does not exist on the network, or if a remote
server supplies DHCP, select number 1 and enter the
VLAN ID (see Note 1).
If you have the system DHCP active on your system,
select 2 if you want DHCP to find the VLAN assignment
automatically.
VLAN is a network routing feature provided by specific
types of switches. To find out if your system uses VLAN,
check with your network administrator. If your system
uses VLAN, the system administrator responsible for the
switch can provide the VLAN IDs for your system (see
Note 1).
If you want to enable connection to a Net6 service
provider server, choose 1. The system prompts you for an
IP address for the server.
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 19

Overview of key hardware elements and devices
Troubleshooting IP telephones
If the system is not properly configured, several messages can appear.
IP telephony display messages
Message Description/Solution
SERVER: NO PORTS LEFT The system has run out of ports. This message remains on the
display until a port becomes available and the telephone is
powered down and then up. To obtain more ports, you can install
additional VoIP keycodes.
INVALID SERVER ADDRESS The S1 is incorrectly configured with the IP address of a system
network adapter other than the published IP address.
IP ADDRESS CONFLICT The telephone detected that a device on the network is currently
using the IP address allocated to the telephone.
REGISTRATION DISABLED The Registration on the system is set to OFF.
SERVER UNREACHABLE.
RESTARTING . . .
NEW SET The telephone has not been connected to the system before, and
Check that you have entered the correct Netmask and gateway
IP addresses. If the settings are correct, contact your system
administrator.
must be registered.
Avaya 1100 Series IP Deskphones
Avaya BCM 6.0 supports Avaya 1100 Series IP Deskphones. The Avaya 1110, 1120E,
and 1140E IP Deskphones. The three phones in the series have a graphical
high-resolution LCD display, backlit, with adjustable contrast.
• Avaya 1110 IP Deskphone has three user-defined feature keys and four soft keys.
• Avaya 1120E IP Deskphone has four user-defined feature keys and four soft
keys.The Avaya 1120 IP Deskphone brings voice and data to the desktop by
connecting directly to a local area network (LAN) though an Ethernet connection.
• Avaya 1140E IP Deskphone has six user defined feature keys and four soft keys
through an Ethernet connection.The Avaya 1140 IP Deskphone brings voice and
data to the desktop by connecting directly to a LAN ISDN devices.
Avaya 1100 Series Expansion Module
Compatible with the Avaya 1120E and 1140E IP Deskphones, the expansion module
includes 18 self-labelling keys. You can connect up to three modules to a phone for a
maximum of 54 additional line or feature keys.
Avaya 1200 Series IP Deskphones
The Avaya 1210, 1220, and 1230 IP Deskphones bring voice and data to the desktop
by connecting directly to a local area network (LAN) through an Ethernet connection.
Programmable button labels appear beside the keys, and soft key labels appear directly
above the keys.
20 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

The keys on either side of the navigation keys are programmable keys. The Avaya 1210
IP Deskphone has two keys, while the Avaya 1220 and 1230 IP Deskphones have six
keys. The system administrator programs these keys.
Avaya 1200 Series Expansion Module
Two expansion module models exist for the Avaya 1200 Series Expansion Module of
phones:
• The Avaya 1200 Series Expansion Module with display.
• The Avaya 1200 Series Expansion Module with paper label.
The Avaya 1200 Series Expansion Module are hardware accessories that connect to
the IP Phone and provide additional line appearances and feature keys.
The expansion modules provide either 12 or 18 additional line or programmable feature
keys for your IP Phone. An IP Phone supports up to seven Avaya 1200 Series
Expansion Module with display or up to two Avaya 1200 Series Expansion Module with
paper labels. An IP phone does not support two different expansion module types on the
same phone.
Overview of key hardware elements and devices
Avaya 2000 Series IP Deskphones
Avaya BCM 6.0 supports:
Avaya 2001 IP Deskphone: connects through an IP link to the Avaya BCM 6.0 system.
The Avaya 2001 IP Deskphone has a single-line text display with a row of display keys
on the second display line. The Avaya 2001 IP Deskphone can be used to call through
any type of Avaya BCM 6.0 line.
Avaya 2002 IP Deskphone: connects through an IP link to the Avaya BCM 6.0 system.
The Avaya 2002 IP Deskphone has a two-line text display with a row of display keys on
the third display line, and four memory keys with indicators. The Avaya 2002 IP
Deskphone can be used to call through any type of Avaya BCM 6.0 line.
Avaya 2004 IP Deskphone: connects through an IP link to the Avaya BCM 6.0 system.
The Avaya 2004 IP Deskphone has a six-line text display with a row of display keys on
the eighth display line, and six memory keys with indicators. The Avaya 2004 IP
Deskphone can be used to call through any type of Avaya BCM 6.0 line.
Avaya 2007 IP Deskphone: connects to a LAN through an Ethernet connection. The
Avaya 2007 IP Deskphone supports call processing features, and can work with an
External Application Server to display web-based and interactive applications on the
large, color LCD touch screen.
IP Key Expansion Module
The IP Key Expansion Module (KEM) can have up to 24 programmable keys (with
labels) for Avaya 2002 and 2004 IP Deskphone models with a maximum of four IP KEMs
for one phone.
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 21

Overview of key hardware elements and devices
Avaya 2050 IP Softphone
The Avaya 2050 IP Softphone provides VoIP services using a telephony server and your
company local area network (LAN). The Avaya 2050 IP Softphone includes one-click
direct dialing from various windows and applications, twelve user defined feature keys,
and four soft keys.
Avaya 2033 IP Conference Phone
The Avaya 2033 IP Conference Phone provides audio conferencing with a keypad that
provides many of the set features of the basic Business Series telephones without
display or memory buttons. The audio conference phone includes three microphones,
and installation instructions.
Analog devices
Avaya BCM 6.0 supports analog telephones (single-line telephones), cordless
telephones, fax machines, answering machines, and modems (with a maximum speed
of 28.8 kbit/s).
You must install an analog station media bay module (ASM8, ASM8+, or GASM) for
analog devices (see Analog station media bay module (page 22)). To connect a
standard analog voice device or data communication device to the Avaya BCM system
through a digital station module, you must install an ATA2 (see Analog terminal adapter
(page 23)).
Analog station media bay module
You can connect a maximum of eight analog telecommunication devices to the analog
station media bay modules (ASM8, ASM8+, and GASM). Analog devices include
standard analog telephones, cordless telephones, fax machines, answering machines,
or modems. The maximum speed for a modem connection is 28.8 kbit/s.
The ASM8 is available in North America only; the ASM8+ and GASM8 are available in
North America, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Poland.
In addition to ASM8 features, the ASM8+ and GASM offer the following features:
• Visual Message Waiting Indicator (VMWI) LED indicates to the end user that a
message is waiting.
• Disconnect supervision (Open Switch Interval [OSI] according to EIA/TIA 464)
indicates to the attached device, in an established communication, that the
connected device must release the call.
22 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010
Overview of key hardware elements and devices
Attention: When disconnect occurs from the central office (CO), the ASM8+ provides
an OSI 850 ms (TIA/EIA 464 section 5.4.10.2.4; minimum is 600 ms) to the off-hook
station of as a disconnect signal. If the station remains on-hook after the disconnect
signal, the ASM8+ disconnects the station equipment from the network without
returning a tone (TIA/EIA 464 section 5.4.10.2.5[1]). After the station equipment goes
on-hook, the ASM8+ station interface restores to on-hook (idle). You must ensure that
the device, application, or interface card connected to an ASM8+ station interface
conform to these on-hook and off-hook conditions.
• Caller ID provides the name, phone number, and other information about the caller
to the end user at the start of the call.
• Firmware downloading capability allows the system to upgrade the ASM8+ and
GASM firmware at customer sites.
• Enhanced ringing capability ASM8+ and GASM provide a ringing voltage of two
REN/65 V rms per port.
• GASM8 is designated as an on-premise station (OPS) port.
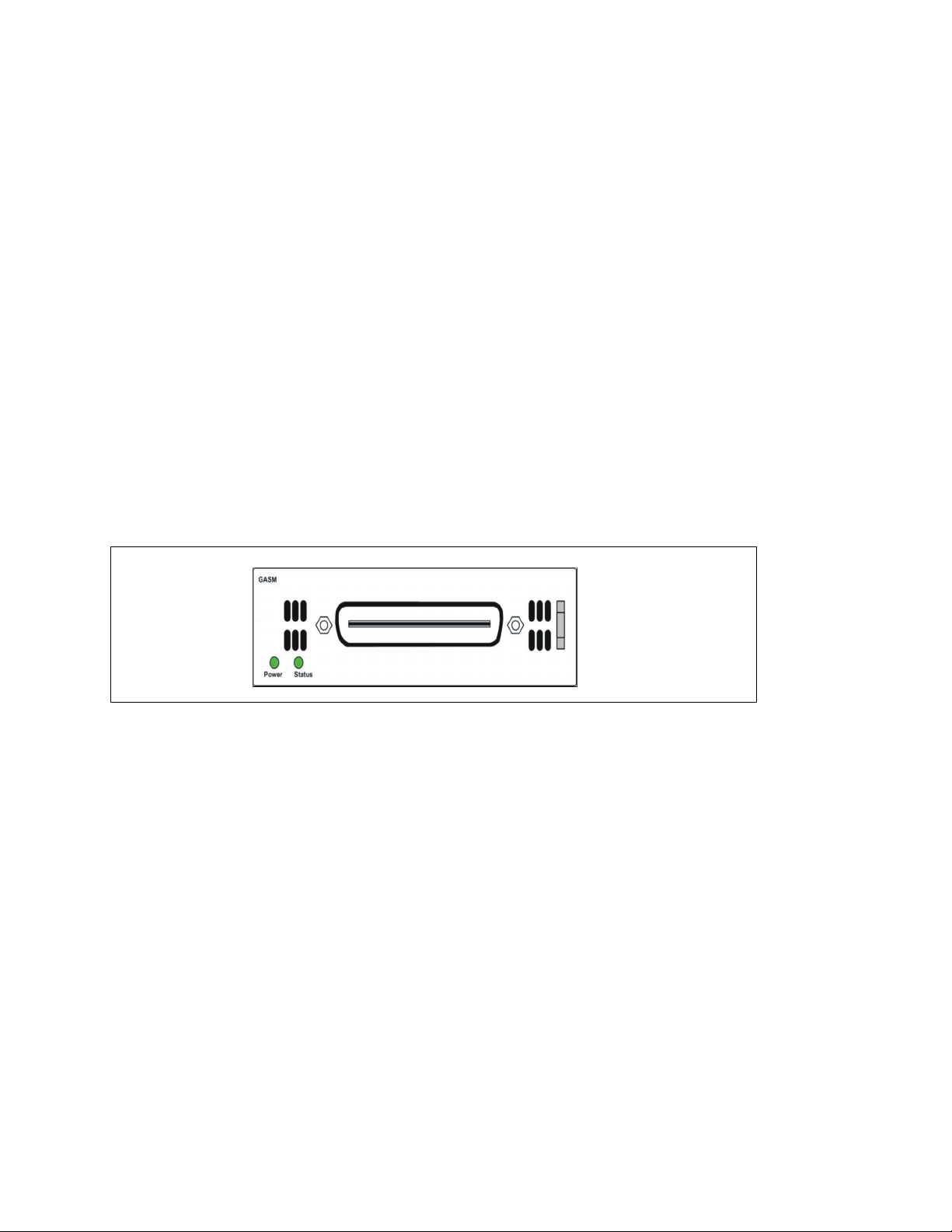
The ASM8, ASM8+, and GASM each have one RJ-21 connector on the faceplate.
GASM faceplate LEDs and connectors
The ringer equivalency number (REN) per port for ASM8 is 1; the REN for ASM8+ and
GASM is 2.
Attention: The termination of the analog interface can consist of any combination of
devices, subject only to the requirement that the sum of the RENs of all the devices
does not exceed the REN of the interface to which the device is connected.
Analog terminal adapter
The analog terminal adapter 2 (ATA2) or ATA connects a standard analog voice device
or data communication device to the Avaya BCM 6.0 system through a digital station
module. Examples of analog voice devices include analog telephones and answering
machines. Examples of analog data communication devices include modems and fax
machines.
The ATA2 provides on-premise service only (protected plan wiring only).
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 23
Overview of key hardware elements and devices
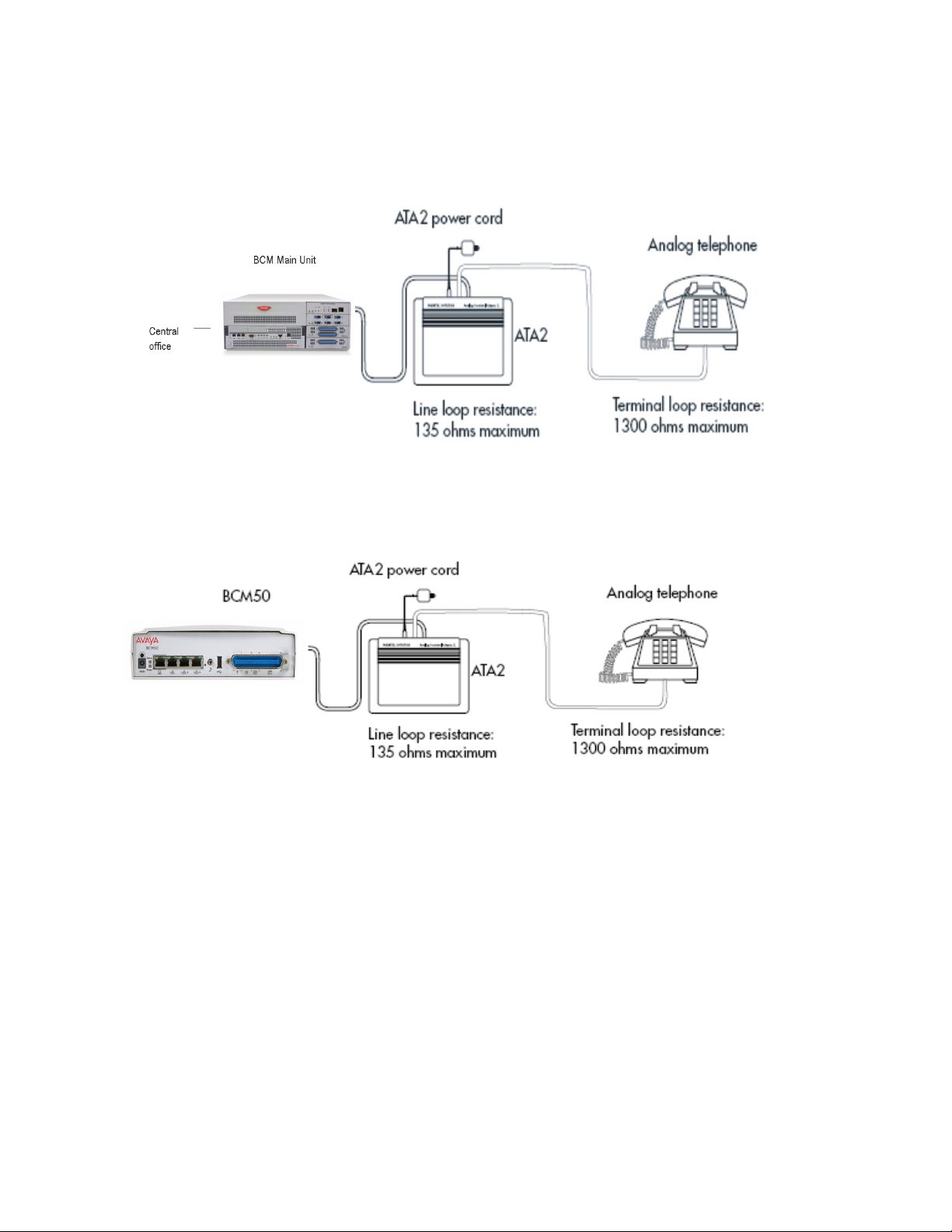
The following figure shows an installation overview for connecting an analog device or
analog data device through an ATA2 to the BCM450 main unit.
Analog device installation overview for BCM450
The following figure shows an installation overview for connecting an analog device or
analog data device through an ATA2 to the BCM50 main unit.
Analog device installation overview for BCM50
24 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

Device compatibility and installation requirements
The information in this chapter applies to both the BCM50 and the BCM450 platforms
running Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 (Avaya BCM 6.0).
This section provides general information about using Integrated Services Digital
Network (ISDN) lines on your Avaya BCM 6.0 system. You can access detailed
information about ISDN through the internet. Your service provider can also provide you
with specific information to help you understand what suits your requirements.
For more information about ISDN device programming, see Avaya Business
Communications Manager 6.0 Configuration — Telephony (NN40160-502).
Navigation
• Release compatibility (page 25)
• MBM trunk requirements (page 37)
• MBM station requirements (page 38)
Release compatibility
Refer to the following topics for release compatibility information:
Release compatibility navigation
• ISDN basics (page 25)
• Services and features for ISDN BRI and PRI (page 27)
• ISDN hardware (page 32)
• ISDN standards compatibility (page 35)
• Plan your Integrated Services Digital Network (page 35)
• Order ISDN PRI (page 36)
• Order ISDN BRI (page 36)
• Supported ISDN protocols (page 37)
ISDN basics
ISDN technology provides a fast, accurate, and reliable means to send and receive
voice, data, images, text, and other information through the telecom network.
ISDN uses existing analog telephone wires to multiplex data into separate digital
channels, which increases bandwidth.
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 25

Device compatibility and installation requirements
ISDN uses a single transport to carry multiple information types. Where you once
required separate networks for voice, data, images, or video conferencing, it now
combines into one common high-speed transport.
Analog versus ISDN
ISDN offers significantly higher bandwidth and speed than analog transmission because
of its end-to-end digital connectivity on all transmission circuits. Digitalization allows
ISDN lines to provide higher quality signaling than analog POTS lines, and ISDN out-of
band data channel signaling offers faster call set up and tear down.
While an analog line carries only a single transmission at a time, an ISDN line can carry
one or more voice, data, fax, and video transmissions simultaneously.
An analog modem that operates at 14.4 kbyte/s takes 4.5 minutes to transfer a 1MB data
file and a 28.8K modem takes about half that time. If you use one channel of an ISDN
line, the transfer time reduces to 1 minute; if you use two ISDN channels, transfer time
reduces to 30 seconds.
When you transmit data, the connect time for an average ISDN call is three seconds per
call, compared to 21 seconds for the average analog modem call.
Types of ISDN service
Two types of ISDN services (lines) are available: Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary
Rate Interface (PRI). Each line consists of separate channels, known as B and D
channels, that transmit information simultaneously.
• BRI: known as 2B+D because it consists of two B-channels and one D-channel.
• PRI: known as 23B+D (in North America) or 30B+D (in Europe). In North America,
23B+D consists of 23 B-channels and one D channel (T1 carrier). In Europe, 30B+D
consists of 30 B-channels and one D-channel (E1 carrier).
B-channels B-channels are bearer channels used to carry voice or data information at
speeds of 64 kbyte/s. As each ISDN link (BRI or PRI) includes more than one B-channel,
a user can perform more than one transmission at the same time using a single ISDN
link.
D-channels The standard signaling protocol transmits over a dedicated data channel
called the D-channel. The D-channel carries call setup and feature activation
information to the destination and includes speeds of 16 kbyte/s (BRI) and 64 kbyte/s
PRI. Data information consists of control and signal information. For BRI only, data
information also consists of packet switched data, such as credit card verification.
ISDN layers
ISDN layers refer to the standards established to guide the manufacturers of ISDN
equipment, based on the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. The layers
include both physical connections, such as wiring, and logical connections, which are
programmed in computer software.
26 NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010

Device compatibility and installation requirements
When equipment is designed to the ISDN standard for one of the layers, it works with
equipment for the layers above and below it. The following three layers work in ISDN for
Avaya BCM 6.0; to support ISDN service, all three layers must work properly:
• Layer 1: A physical connection that supports fundamental signaling passed between
the ISDN network (your service provider) and the Avaya BCM 6.0 system. When the
LED on a BRI S/T media bay module configured as BRI becomes lit, Layer 1 is
functioning.
• Layer 2: A logical connection between the central office or the far end and the Avaya
BCM 6.0 system. Without Layer 2, call processing is not possible.
• Layer 3: A logical connection between the ISDN network (your service provider) and
the Avaya BCM 6.0 system. For BRI lines, call processing and service profile
identifier (SPID) information exchanges in Layer 3. This controls which central office
services are available to the connection. For example, you can program a network
connection to carry data calls.
Attention: Service profile identifiers (SPIDs) are a part of the BRI National ISDN
standard. SPIDs are not used in the ETSI BRI standard or on PRI.
ISDN bearer capability
Bearer capability describes the transmission standard used by the BRI or PRI line so it
can work within a larger ISDN hardware and software network.
The bearer capability for BRI and PRI is voice/speech, 3.1 kHz audio (fax), and data
(unrestricted 64 kbyte/s, restricted 64 kbyte/s or 56 kbyte/s).
Services and features for ISDN BRI and PRI
As part of an ISDN digital network, your system supports enhanced capabilities and
features, that include:
• fast call set up and tear down
• high-quality voice transmission
• dial-up Internet and local area network (LAN) access
• video transmission
• network name display
• name and number blocking (PRI, BRI, and analog)
• access to public protocols
PRI services and features
The services and features provided over PRI lines include
• Call-by-call service selection (NI protocol)
• Emergency 911 dialing and internal extension number transmission
NN40170-304 Avaya Business Communications Manager 6.0 Installation—Devices October 2010 27
 Loading...
Loading...