Page 1
Business Communication Manager 50
Call Server 2000
> Solution Reference Design Guide
For BCM50 to CS2K VoIP
Enterprise Solution Engineering
Document Date: November 4th, 2005
Document Version: 2.0
Page 2

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Copyright © 2005 Nortel Networks
All rights reserved. November 2005
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements,
configurations, technical data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be
accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied warranty. Users must take
full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks Inc.
The software described in this document is furnished under a lice nse agreement and may be
used only in accordance with the terms of that license.
Trademarks
Nortel, the Nortel logo, the Globemark, Unified Networks, PASSPORT and BayStack are
trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Adobe and Acrobat Reader are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporate.
All other Trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 1
Page 3

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Abstract
The proliferation of VoIP technologies and the subsequent interconnect of Nortel’s Enterprise and
Carrier networks, requires the dissemination of detailed concepts and configuration information.
This document describes the setup of a converged Carrier / Enterprise service consisting of PBX
hosted subscribers that can leverage the wealth of services offered by the IP Telco Network.
Target Audience
This document is intended for an informed audience of Nortel Networks Sales Engineers,
Deployment Primes, Installation personnel, and especially Customers.
Acknowledgements
This Configuration Guide is the product of numerous individuals and teams who have
demonstrated the very best in teamwork, innovation, and integrity. The authors wish to extend
their personal appreciation for their talented effort.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 2
Page 4

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.
INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................... 5
1.1
1.2
1.3
BCM50
A
U
TO
CS2K I
NTERCONNECTION
VAILABILITY AND ORDERING
SE CASE
...................................................................................................................................... 6
........................................................................................... 5
...................................................................................................... 6
2. CS2K SETUP.......................................................................................................................................7
2.1
S
OFTWARE OPTIONALITY CONTROL
2.2
T
RUNKING
2.2.1 TABLE: CLLI............................................................................................................................ 7
2.2.2 TABLE: TRKGRP..................................................................................................................... 8
2.2.3 TABLE TRKSGRP.................................................................................................................... 8
2.2.4 TABLE TRKMEM..................................................................................................................... 8
2.3
C
ALL PROCESSING (CALLP) TRANSLATIONS
2.3.1 TABLE XLAPLAN..................................................................................................................... 9
2.3.2 TABLE OFRT ........................................................................................................................... 9
2.3.3 TABLE HNPACONT................................................................................................................. 9
2.3.4 TABLE LTDEF......................................................................................................................... 9
2.3.5 TABLE LTDATA..................................................................................................................... 10
2.3.6 TABLE LTCALLS ...................................................................................................................10
2.3.7 TABLE LTMAP....................................................................................................................... 10
2.4
P
ACKETIZATION
2.5
ETSI PRI T
2.5.1 Problem Identification............................................................................................................ 11
2.5.2 Workaround............................................................................................................................ 12
3. BCM50................................................................................................................................................ 15
3.1
C
AVEATS
3.1.1 Centrex IP Call Manager (CICM) SN07 Testing ................................................................... 15
3.1.2 Called Party Number Display (CPND).................................................................................. 15
3.1.3 T.38 FAX................................................................................................................................. 16
3.2
K
EY CODES
3.3
IP N
3.4
IP T
3.5
T
ELEPHONES & LINES
3.6
D
IALING PLAN
3.7
H.323........................................................................................................................................... 23
..................................................................................................................................... 7
........................................................................................................................... 10
RUNKS & OVERLAP SIGNALING
..................................................................................................................................... 15
.................................................................................................................................. 16
ETWORKING
ELEPHONY RESOURCES
.......................................................................................................................... 17
......................................................................................................... 18
.................................................................................................................. 20
............................................................................................................................. 20
(SOC) ................................................................................... 7
................................................................................. 8
................................................................................. 11
4. GWC................................................................................................................................................... 26
4.1
A
DDING
GWC
IN
CMT................................................................................................................ 26
4.2
A
SSOCIATING
4.3
R
ESERVING
4.4
C
ONFIGURING VOICE NETWORK SETTINGS
5. APPENDIX A: DMS READ FILES................................................................................................. 32
5.1.1 Translation Verification (Traver)........................................................................................... 32
6. APPENDIX B: DMS CLLIREF....................................................................................................... 37
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 3
H323 G
H323 C
ATEWAY TO
ARRIERS ON
GWC
H323 G
IN
CMT....................................................................... 27
ATEWAY IN
................................................................................. 30
CMT.......................................................... 29
Page 5

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
List of Figures
Figure 1: Succession Network Reference Architecture................................................................... 5
Figure 2: Detailed Network Diagram ............................................................................................... 6
Figure 3: H.225 Setup Packet Trace............................................................................................. 11
Figure 4: BCM50 Key Codes......................................................................................................... 16
Figure 5: BCM50 IP Addressing.................................................................................................... 17
Figure 6: BCM50 DHCP, General Settings ................................................................................... 18
Figure 7: BCM50 Telephony Resources, IP Terminal Global Settings......................................... 19
Figure 8: BCM50 Telephony Resources, IP Terminal Details....................................................... 19
Figure 9: BCM50 Lines, Target Lines............................................................................................ 20
Figure 10: BCM50 Telephony, Active Sets ................................................................................... 20
Figure 11: BCM50 Dialing Plan, Public Network........................................................................... 21
Figure 12: BCM50 Dialing Plan, Private Networks........................................................................ 21
Figure 13: BCM50 Dial Plan - Routing, Routes............................................................................. 22
Figure 14: BCM50 Dial Plan - Routing, Destination Codes........................................................... 22
Figure 15: BCM50 Dialing Plan - Line Pools................................................................................. 23
Figure 16: BCM50 Port Ranges ....................................................................................................24
Figure 17: BCM50 Telephony Resources – IP Trunks, Local Gateway........................................ 24
Figure 18: BCM50 Telephony Resources, Media Parameters...................................................... 25
Figure 19: GWC – Add GWC ........................................................................................................26
Figure 20: GWC – Provisioning..................................................................................................... 27
Figure 21: GWC – Associate Media Gateway............................................................................... 28
Figure 22: GWC – Provisioning Gateway...................................................................................... 29
Figure 23: GWC – Add Carrier...................................................................................................... 29
Figure 24 GWC – Carriers............................................................................................................. 30
Figure 25: GWC Packet Level Main Screen.................................................................................. 31
Figure 26: Packetization Rate Selection ....................................................................................... 31
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 4
Page 6
Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
1. Introduction
The coupling of Nortel’ Succession Solution with the Business Communication Manager (BCM)
has proven to be a significant step forward in the convergence of Enterprise and Carrier
Networks.
It is fully anticipated that the addition of CS2K Gatekeeper functionality will result in a new specter
of service offerings, and interconnect scenarios, to the Enterprise. This guide details the setup of
a field deployable solution.
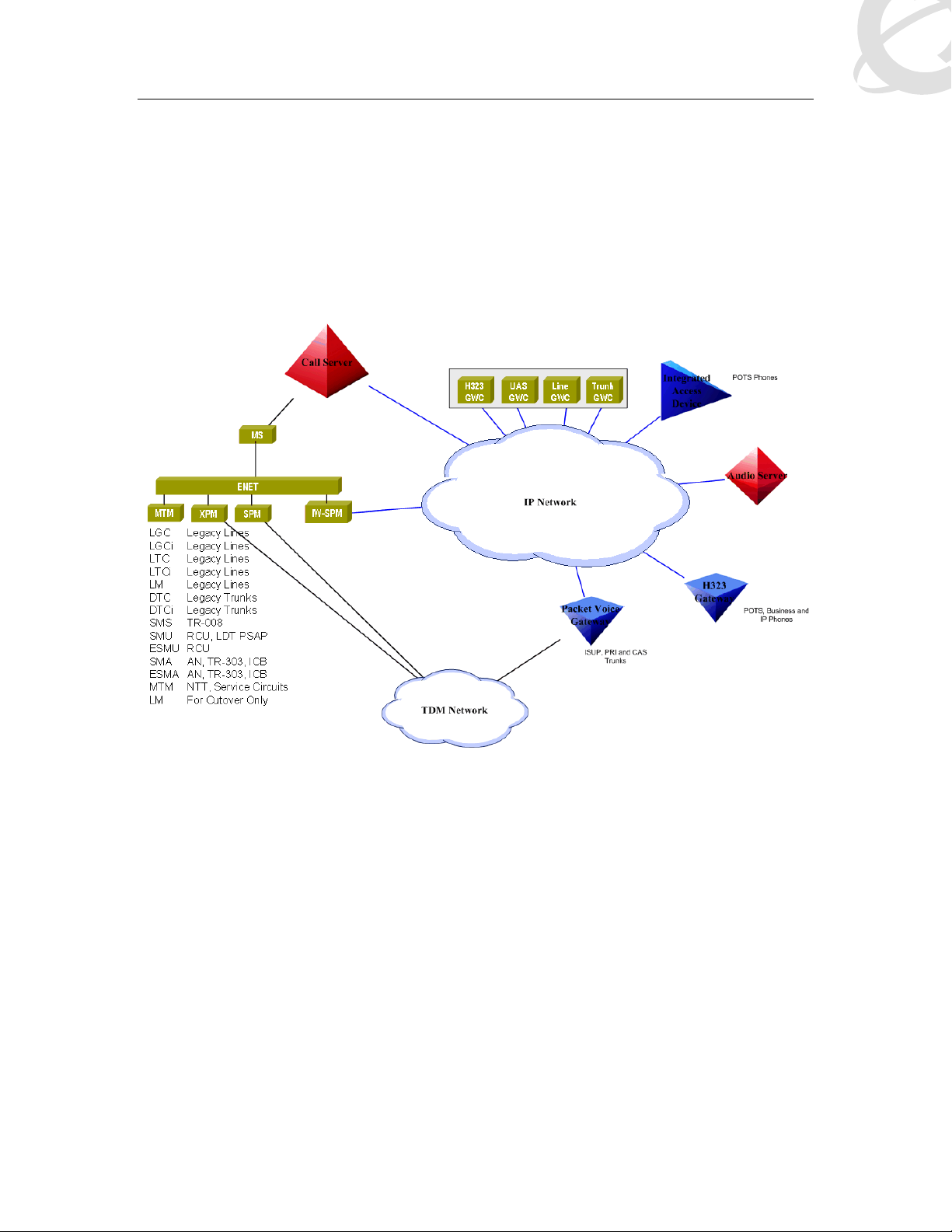
Figure 1: Succession Network Reference Architecture
1.1 BCM50 to CS2K Interconnection
The nuts and bolts of the architecture are the workings of the IP domain that binds the BCM to
the CS2K (see Figure 2: Detailed Network Diagram). This new coupling of the traditional Carrier
and Enterprise environments will require that SEs and Partners have a basic understanding of the
components within this hybrid topology.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 5
Page 7
Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
CS2K
MS
ENET
LTC
LCME
Set C
TDM
Phone
613-234-4025
10.102.40.8
Interwork
SPM
GWC
(Gatekeeper)
10.102.40.60
10.102.40.13
BCM_M50
10.102.40.108
613-235-4353
IP
10.102.40.110
613-236-4353
BCM2_M50
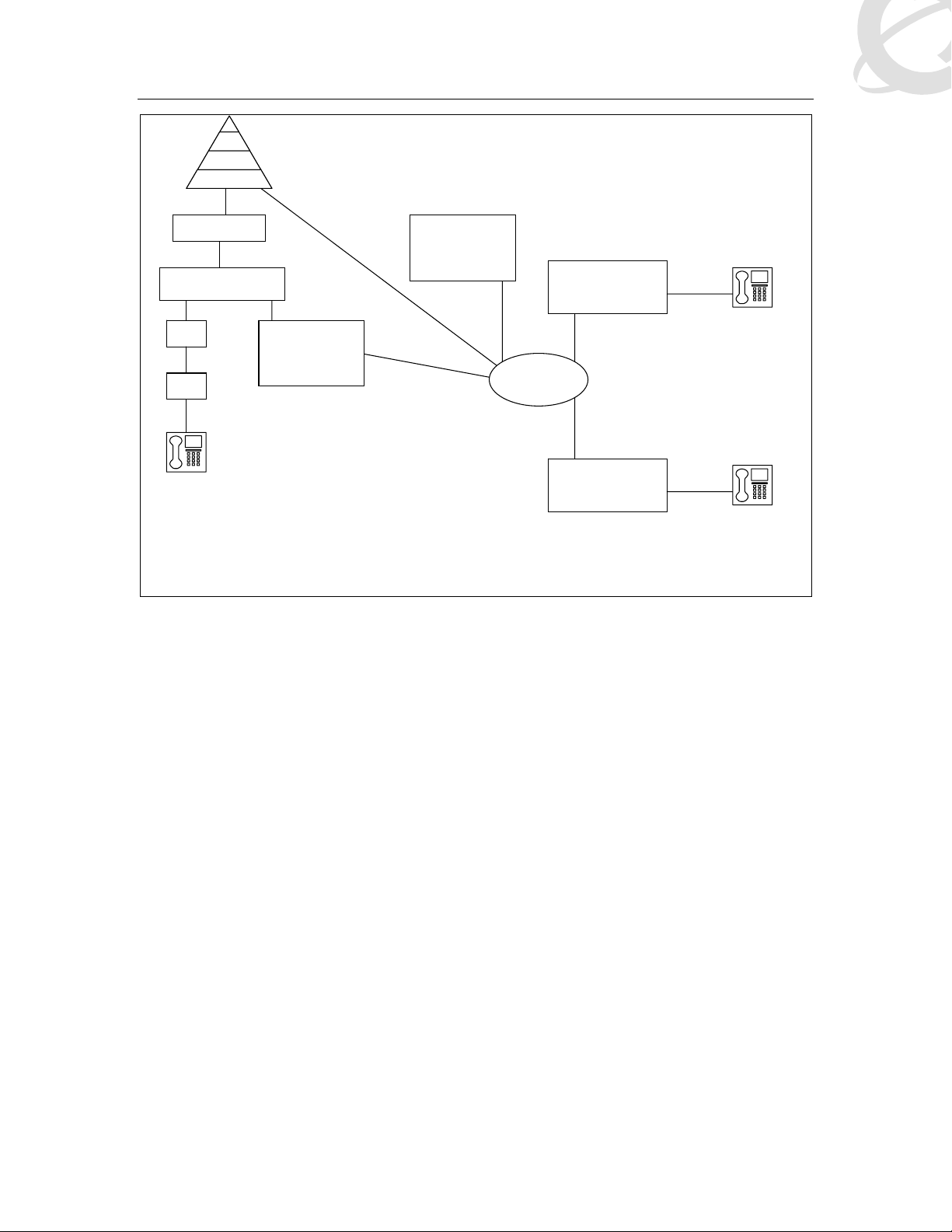
Figure 2: Detailed Network Diagram
Set A
i2004
10.102.40.109
Extension 353
Target Line 126
Set B
i2004
10.102.40.112
Extension 353
Target Line 127
From the Enterprise, Succession’s CS2K will appear as a Gatekeeper in the IP space; and as
such will require minimum programming to interoperate correctly. However, the challenge for SEs
will rest with the design, implementation, and understanding of the carrier portion of the network.
The CS2K will view the BCM as a call processing destination, defined in terms of Directory
Numbers (DN), virtual trunks, and gateway endpoints. Detailed examples of these entities are
available in the following chapters of this document
.
1.2 Availability and Ordering
This solution applies to the following Generally Available (GA) software streams:
• BCM50 Release 1
•
SN07, ISN07, SN08, and ISN08
1.3 Use Case
Within this document, a simple office-code translation plan will be used as a reference framework.
From
Figure 2: Detailed Network Diagram
550; a VoIP Trunk access code of 9 will be used on the BCMs. From the above diagram, here are
a few examples of dialing sequences:
• A (BCM_M50) calls B (BCM2_M50) via the CS2K, A dials: 9-550-236-4353
• B (BCM2_M50) call A (BCM_M50) via the CS2K, B dials: 9-550-235-4353
• A calls C (CS2K analogue line), A dials: 9-234-4025
•
C calls B (BCM2_M50), C dials: 550-235-4353
, the BCM50s are accessed via an area code of
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 6
Page 8

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
2. CS2K Setup
It should be clearly understood by the reader that the design and implementation of translations is
customer specific. What is contained herein is one way of accomplishing the objective; there are
other methods which are equally effective.
To simplify the vulgarization of the concepts within, a North American ISDN PRI context was
selected. This does not limit this solution to that signaling context; it does work with other PRI
variants.
2.1 Software Optionality Control (SOC)
It is critical that the CS2K have the H.323 Gatekeeper functionality activated. For further
information on the SOC, please consult NTP 297-8991-901 (www.nortel.com); customers may
purchase software activation codes from authorized Nortel Sales Representatives.
For the H.323 Gatekeeper, please ensure that CS2B0004 is enabled. Firstly, you need to unlock
the SOC by assigning a limit; this will also set the right to use flag:
• assign limit 100 <license key #1> to CS2B0004
Secondly, activation is accomplished by setting the state. This requires a second license key:
• assign state on <license key #2> to CS2B0004
When completed, the CS2B004 option should appear as follows:
>soc
SOC:
OPTION NAME RTU STATE USAGE LIMIT UNITS LAST_CHG
CS2B0004 H323 Gatekeeper Y ON 8 100 1VC 05/01/20
2.2 Trunking
The CS2K needs to have unique addressable connection paths on which it may route calls to
each BCM. These are referred to as trunk members within a group. They are defined in the
following order through the tables.
2.2.1 TABLE: CLLI
The Common Language Location Identifier, or CLLI, is the route of the trunk group datafill. In this
example, the CLLI BCM_M50 is associated to an administrator.
CLLI ADNUM TRKGRSIZ ADMININF
---------------------------BCM_M50 411 50 PIERRE_FOURNIER
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 7
Page 9

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
2.2.2 TABLE: TRKGRP
The trunk group is characterized with PRA to indicate that it will appear to call processing as
ISDN PRI signaling and ISDN translations.
GRPKEY GRPTYP TRAFSNO PADGRP NCCLS GRPINFO
-----------------------------------------BCM_M50 PRA 0 NPDGP NCRT MIDL N (ISDN 550) $ $
2.2.3 TABLE TRKSGRP
Detailed signaling setup (DS1, Q.931) and physical location (GWC card & port) are defined here.
SGRPKEY CARDCODE SGRPVAR SGRPVAR
-------------------------------BCM_M50 0 DS1SIG ISDN 20 20 87Q931 2 N STAND NETWORK PT_PT USER N
UNEQ 160 N DEFAULT GWC 9 114 1 64K HDLC $ $
2.2.4 TABLE TRKMEM
CLLI EXTRKNM SGRP MEMVAR
-----------------------BCM_M50 1 0 GWC 9 114 2
BCM_M50 2 0 GWC 9 114 3
BCM_M50 3 0 GWC 9 114 4
BCM_M50 4 0 GWC 9 114 5
2.3 Call Processing (CallP) Translations
Designing CallP translations requires training and experience. The text of this section
provides enough information to permit qualified personnel to complete the task. It is not a
replacement for adequate training; please do not attempt unless properly qualified to do
so.
The trunk group has been defined as an ISDN PRI, so the next step is to define a set of
rudimentary translations to be able to route the calls to and from the BCM. For this,
• a “type” of translation is defined in XLAPLAN
• an office route in table OFRT
• association between the dialed digits and the office routes in HNPACONT and its sub
tables
• and finally, the ISDN specifics in “LT” family (ISDN Logical Terminal) of tables
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 8
Page 10

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
2.3.1 TABLE XLAPLAN
XLAPIDX SCRNCL HSTS PRTNM ZEROMPOS RESINF OPTIONS ADMINI NF
---------------------------------------------------------BCM_PRI_TRAF NSCR 550 PRI_TRAF NONE N $ PRI_TRAFFIC
2.3.2 TABLE OFRT
RTE RTELIST OPTIONS
------------------550 (N D BCM_M50 0 N N) $ $
2.3.3 TABLE HNPACONT
STS SNPA NORTREFS NOAMBIGC RTEREF HNPACODE ATTRIB RTEMAP
OPTIONS
---------------------------------------------------------------613 Y 1023 0 (237) (1) (0) (0) $
2.3.3.1 SUB RTEREF
RTE RTELIST
----------55 (T OFRT 550) $
RET
613 Y 1023 0 (237) (1) (0) (0) $
2.3.3.2 SUB HNPACODE
FROMDIGS TODIGS CDRRTMT
----------------------235 235 LRTE 55
RET
613 Y 1023 0 (237) (1) (0) (0) $
2.3.4 TABLE LTDEF
Is the Logical Terminal (LT) definition table; it defines logical terminals and access
privileges. It also specifies an LTID and access privileges for the PRI trunk group.
LTKEY LTAP CLASSREF
-------------------
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 9
Page 11

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
ISDN 550 B PRA 47 NTNAPRI V1 NIL (NOPMD ) $
2.3.5 TABLE LTDATA
The logical terminal data table stores service-related data associated with the logical
terminal identifier (LTID), field LTDKEY, which is the key to this table.
LTDKEY LTDRSLT
-------------ISDN 550 SERV SERV Y Y ALWAYS ALWAYS (PRI_IP_PROT H323) $
2.3.6 TABLE LTCALLS
Logical terminal calls table. It specifies the types of calls that can route over each PRI
trunk group. This table defines the first translations for each trunk group and call type.
LTID XLARTSEL OPTIONS
--------------------ISDN 550 PUB XLALEC 0 BCM_PRI_TRAF NLCA_NILLA_0 $
2.3.7 TABLE LTMAP
The logical terminal map table associates the logical terminal identifier (LTID) to a trunk
group (identified by CLLI).
LTKEY MAPPING OPTION
-------------------ISDN 550 CLLI BCM_M50 (TEI 0) $
2.4 Packetization
Succession CS2K Solution supports both 10 and 20 millisecond (ms) rates; what is critical is that
all components bet set to the same value. Care must be taken to ensure that the IW-SPM and the
GWC are set to the same rate as the CS2K and the BCM.
The IW-SPM, required for interwork with locally hosted legacy lines, is set as follows for 20 ms:
TABLE MNIPPARM
TOP
MNKEY DFCODEC PRFCODEC PKTRATE INGRESS EGRESS JITMIN JITMAX JITTARG
ECAN
VOICE CMFNOISE T38 RFC2833 RTCP TONESET LOGINT CRCERROR USIZEPKT
OSIZEPKT
FRAGMENT JABBER DROPEVNT BRDCAST JITTER LATENCY VPKTLOST MINLOG
OMPARMS
------------------------------------------------------------------------IWSPM G711ULAW G729 20 0 0 0 100 0 DISABLE OFF DISABLE DISABLE DISABLE N
NORTHAMERICA 5 20 10 20 10 20 10 20 10 20 10 20 10 20 10 20 10 20 10 20 10
1000 50 1000 1000
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 10
Page 12

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Please see 4.4
Configuring Voice Network Settings
for information on the GWC packetization
setup.
2.5 ETSI PRI Trunks & Overlap Signaling
There are two types of signaling associated with ISDN PRI: ENBLOC and OVERLAP. Both
pertain to the method in which digits are forwarded, first refers to the method when all digits are
sent at one time and the latter where they are forwarded in multiple messages. Unused in North
America, overlap is quite common in the remainder of the world.
There are a few key points that should be highlighted to ensure simple operation of a BCM
connected to an overlap aware network:
• In general BCMs, who do not support overlap signaling, can interoperate with PRI
overlap signaling provided all digits are contained within the H.323 setup message.
• Future CS2K releases intend to incorporate PRI variant checking to ensure that H.323
trunk groups destined to BCMs will not support overlap signaling.
2.5.1 Problem Identification
The BCM will reject H.225 setup messages that contain the “canOverlapSend” flag set to “True”,
see highlight box inError! Reference source not found.
Figure 3: H.225 Setup Packet Trace
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 11
Page 13

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
2.5.2 Workaround
Setting the Q.931 “sending complete” flag will allow the BCM to ignore the canOverlapSend value
and accept the incoming H.225 setup message. The CS2K’s call processing translations can do
this on a per trunk basis; this is accomplished in table PXCODE.
2.5.2.1 Identifying the Correct Entry in Table PXCODE
A quick way to identify the target tuple is to execute a traver. You will need 2 pieces of
information: a valid DN on the CS2K, and the trunk access code for the BCM. For this example,
we are using DN 820-2524 with a trunk access code of 323. Note that the destination digits used,
i.e. 1234567, are simply padding.
The relevant data is highlighted in yellow:
traver l 8202524 3231234567 b
TABLE IBNLINES
LG 00 0 00 31 0 DT STN IBN 8202524 CSLINES 0 0 115 $
TABLE DNATTRS
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE DNGRPS
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE IBNFEAT
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE CUSTSTN
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE OFCVAR
AIN_OFFICE_TRIGGRP NIL
INAP Origination Attempt TDP: no subscribed trigger.
INAP Info Collected TDP: no subscribed trigger.
TABLE NCOS
CSLINES 0 0 0 DFLT $
TABLE CUSTHEAD: CUSTGRP, PRELIMXLA, CUSTXLA, FEATXLA, VACTRMT, AND DIGCOL
CSLINES NXLA K4PSTN CSFETXLA 0 CSACCDIG
TABLE DIGCOL
CSACCDIG 3 COL L 7
TABLE IBNXLA: XLANAME K4PSTN
TUPLE NOT FOUND
Default from table XLANAME:
K4PSTN
(NET N N 0 N CSDIG N Y DOD N K4PSTN CS_NPRT CS_NIL NONE $) $ F
TABLE DIGCOL
CSDIG 3 COL L 7
TABLE LINEATTR
K4PSTN IBN NONE NT 0 0 NILSFC 0 PX K4PSTN NIL 00 CS_NPRT CS_NIL $
LCABILL OFF - BILLING DONE ON BASIS OF CALLTYPE
TABLE XLAPLAN
CS_NPRT NSCR 115 NPRT NONE N $ $
TABLE RATEAREA
CS_NIL NLCA NIL NILLATA $
TABLE PXHEAD
K4PSTN DFLT CONT ( MM 7 7) ( XLT PX K4PSTN)$ DFOP ( CLASS INTL) ( AMAXLAID PSTN)$
NOCON STD
THE DIGITS USED TO INDEX THE NEXT TABLE ARE: 3231234567
TABLE PXCODE
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 12
Page 14

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
K4PSTN 323 323 RTE ( PF 3) ( MM 5 18) ( DEST 115)$
TABLE: PXRTE
KEY: K4PSTN 115
. S OTT5BCM
EXIT TABLE PXRTE
TABLE AMAXLAID
PSTN DFLT (FLEXCTYP GENERIC 900 OVRDALL )$
INAP Info Analyzed TDP: no subscribed trigger.
INAP Route Select Failure TDP: no subscribed trigger.
+++ TRAVER: SUCCESSFUL CALL TRACE +++
DIGIT TRANSLATION ROUTES
1 OTT5BCM N CDN E164 IN 1234567 NIL_NSF BC SPEECH
TREATMENT ROUTES. TREATMENT IS: GNCT
1 BUSYANN
+++ TRAVER: SUCCESSFUL CALL TRACE +++
From this we see that the PXCODE entry is K4PSTN 323 323, and that the current minimum
digits is 5 with a maximum of 18. We will need to reset these values to 7 and 7; as we are using 7
digit dialing to the BCM.
2.5.2.2 Table PXCODE
The following is a session capture of the required change; it is self explanatory.
>TABLE PXCODE; pos K4PSTN 323 323
JOURNAL FILE UNAVAILABLE - DMOS NOT ALLOWED
TABLE: PXCODE
K4PSTN 323 323
RTE (PF 3) (MM 5 18) (DEST 115) $
>cha
JOURNAL FILE UNAVAILABLE - DMOS NOT ALLOWED
ENTER Y TO CONTINUE PROCESSING OR N TO QUIT
>y
XLASEL: RTE
>
OSEL: PF
>
PFDIGS: 3
>
OSEL: MM
>
MIN: 5
>7
MAX: 18
>7
OSEL: DEST
>
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 13
Page 15

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
DEST: 115
>
OSEL:
>$
TUPLE TO BE CHANGED:
K4PSTN 323 323
RTE (PF 3) (MM 7 7) (DEST 115) $
ENTER Y TO CONFIRM, N TO REJECT OR E TO EDIT.
>y
TUPLE CHANGED
JOURNAL FILE INACTIVE
>list
XLANAME FROMD TOD
XLADATA
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- K4PSTN 323 323
RTE (PF 3) (MM 7 7) (DEST 115) $
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 14
Page 16

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
3. BCM50
The BCM50 is programmed via a new application, the Element Manager, available via HTTP
access to the maintenance port. A good number of screen captures of this new Element Manager
have been included in this document in order to familiarize users with both the location and the
format of the programming information.
3.1 Caveats
3.1.1 Centrex IP Call Manager (CICM) SN07 Testing
The specific combination of BCM50 to CICM VoIP lines in the SN08 context was successfully
tested. An SN07 CICM setup was not available at the time of test, and was not explicitly verified.
However, it is expected that there will be no operational differences between the SN08 and SN07
versions.
3.1.2 Called Party Number Display (CPND)
3.1.2.1 Network Name Display
Business Communications Manager displays the name of the calling party, when available, on
both Private and Public ISDN PRI interfaces. The displayed name can include the Receiving
Calling Name, Receiving Redirected Name, and/or Receiving Connected Nam e.
If only a number is available for CLI on an incoming call, you can program a system speed dial in
such a way that a name displays when that number calls in.
The outgoing name display consists of the Business name and the telephone name.
The following table provides a list of the name/number display features and the list of ISDN
interfaces that support each feature.
Interface
Feature NI PRI DMS Custom PRI SL1 (MCDN) NI-BRI ETSI EURO ETSI QSIG
Receiving Calling Name Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported
Receiving Redirected Name Supported Supported Supported Supported
Receiving Connected Name Supported Supported Supported
Sending Calling Party Name Supported Supported Supported Supported
Connected Name Supported Supported Supported Supported
Table 1: CPND Test Results
Note: Network Name Display is an optional feature that is available based on the interface you
subscribe to.
MCDN note: MCDN networks fully support name display features.
3.1.2.2 Receiving and Sending Calling Party Name
Network Name Display allows the name of an incoming PRI/BRI, analog with CLID, or VoIP with
MCDN call to appear on the Business Communications Manager telephone receiving the call.
Calling Party Name with status of Private can appear on the Called Party telephone as Private
name. If the incoming Calling Name is defined by the CO as a private name, then Private name
appears on the answering telephone. If the Calling Party Name is unavailable it can appear on
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 15
Page 17

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
the Called Party telephone as Unknown name.
If the call is answered by a Hunt group, the hunt group name appears instead of the telephone
name in forming the connected name.
The Connected Name is a transient display that appears for approximately three seconds. The
Connected Name is sent only if the OLI is programmed (“Configuring line access” on page 405).
You can program both a public and private OLI. The system uses the one appropriate to the type
of call.
3.1.2.3 Network name display interactions
If available, the Calling and Connected Name information passes between trunks with Selective
Line Redirection (SLR). Only Calling Name information passes between trunks in cases where
Direct System Inward Access (DISA) results in tandeming of trunks.
3.1.3 T.38 FAX
T.38 FAX support is enabled via the selection of the BCM profile in the GWC. Supported
functionality and detailed configuration information for the CS2K, GWC, and the BCM can be
found on www.nortel.com
.
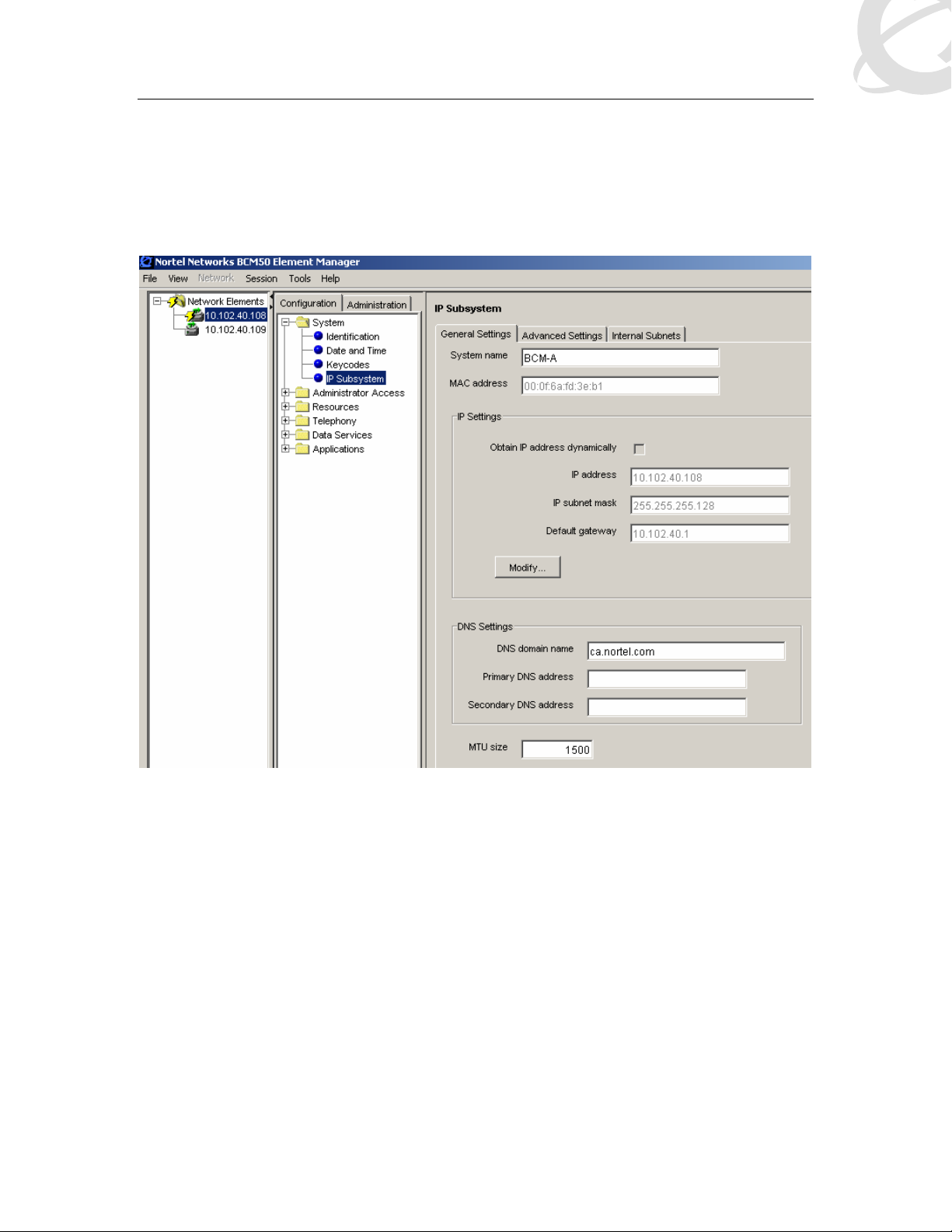
3.2 Key Codes
Ensure that the system has an appropriate number of the following key coded functionality:
• IP Client seats
• VoIP GW Trunks
Figure 4: BCM50 Key Codes
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 16
Page 18
Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
3.3 IP Networking
The BCMs in this example are configured as per Figure 2: Detailed Network Diagram on page 5.
If DHCP is used for the IP Sets, it needs to be activated and a range of IPs need to be setup via
the Address Range Tab (Figure 6: BCM50 DHCP, General Settings).
Note: in order to simplify the setup, BCM50 NAT is not used.
Figure 5: BCM50 IP Addressing
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 17
Page 19

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 6: BCM50 DHCP, General Settings
3.4 IP Telephony Resources
The IP Telephony resources are listed in the Telephony Resources level of the Resources level.
It is at this point where the default CODEC and packetization (payload size) are configured.
In section 2.4
mS sampling rates, and the selected value must be consistently applied to both the IW-SPM and
the GWC. The selected value must also be used in the BCM50.
Note that the IP and Application Sets module must be highlighted (clicked upon) in order to see
the details
Packetization
.
, the reader is reminded that Succession supports both 10 and 20
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 18
Page 20

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 7: BCM50 Telephony Resources, IP Terminal Global Settings
Any active IP sets will be displayed in the IP Terminal.
Figure 8: BCM50 Telephony Resources, IP Terminal Details
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 19
Page 21

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
3.5 Telephones & Lines
Start with the selection of a target line. Program both the Public and Private received digits.
Figure 9: BCM50 Lines, Target Lines
The target line is assigned to the Set at the Active Sets level. In addition the Public and Private
Outgoing Line Identification (OLI) can to be programmed here.
Figure 10: BCM50 Telephony, Active Sets
3.6 Dialing Plan
A few key settings are captured in the following screen shots:
• Public received number length: 7 digits (CS2K pushes 613-234-4353)
•
Public network dialing plan: National
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 20
Page 22

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 11: BCM50 Dialing Plan, Public Network
Note: No changes were made to the Private Network settings. Pictured here are the defaults
used.
Figure 12: BCM50 Dialing Plan, Private Networks
A new route, number 100, was created and assigned to BlocA the VoIP pooled resources. Note
that the external number, digits that can be inserted as a prefix, was intentionally left blank.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 21
Page 23

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 13: BCM50 Dial Plan - Routing, Routes
It was simpler if the access code of 9 was t o be used to access an outgoing line form the BCM50.
Thus, destination code 9 was mapped to route 100, with an absorbed length of all (digit 9 is not
passed to the CS2K).
Figure 14: BCM50 Dial Plan - Routing, Destination Codes
As a final check, the linepool to DN assignment is verified. Here, DN 353 does have access to
.
BlocA
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 22
Page 24

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 15: BCM50 Dialing Plan - Line Pools
3.7 H.323
Key points for this part of the setup are:
• RTP and UDP Ports Ranges were left to the default settings
• Verify that the call signaling port is set to 1720 and the RAS to 1719. The RAS setting
must match the GWC value (see Figure 21: GWC – Associate Media Gateway)
1
This follows the common convention for Call Signaling and RAS port settings. Note that for BCM 3.x on the
BCM200/400/1000, port 1719 is used for the internal gatekeeper associated with support for Symbol NetVision phones
and cannot be used for CS2K RAS. See Nortel technical configuration ITAS TIP 317 GL, January 2005, for additional
details on selecting an appropriate RAS port for BCM 3.x systems.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 23
1
Page 25

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 16: BCM50 Port Ranges
The details of the CS2K are added at the Telephony Resource, IP Trunks level:
• H.323 Call signaling: Gatekeeper Routed
• Primary Gatekeeper IP: the GWC’s IP
• Alias Name: must match value in GWC (Figure 21: GWC – Associate Media Gateway)
• Gateway Protocol: none
Figure 17: BCM50 Telephony Resources – IP Trunks, Local Gateway
Click on the Media Parameters tab, and verify/set the values for
• Preferred CODEC list: ensure G.711 and G.729 are included
• Set the default sample sizes to either 10 or 20 mS and remember to set matching values
on IW-SPM and GWC.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 24
Page 26

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 18: BCM50 Telephony Resources, Media Parameters
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 25
Page 27

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
4. GWC
The Gateway Controller (GWC) is managed via the CS2K Management Tool (CMT): Sun
workstation hosted Nortel OAM application. The following setup will be executed by the hosting
Telco and not in the domain of the Enterprise.
The configuration steps are self-explanatory; additional comments have been added to highlight
key input.
For further information, please refer to NN10205-511 version 05.02 Gateway Controller
Configuration Management located on http://nortel.com/helmsman online repository for Packet
Trunking - IP SN07 Standard (PTIP07).
4.1 Adding GWC in CMT
Follow pages 99-106 of the NTP NN10205-511. This section lists all the required information to
add a GWC in CMT.
Figure 19: GWC – Add GWC
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 26
Page 28

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 20: GWC – Provisioning
4.2 Associating H323 Gateway to GWC in CMT
Following the procedures documented in pages 147-156 of the NT P NN10205-511, a H323
Gateway is associated to a GWC in the following manner:
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 27
Page 29

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 21: GWC – Associate Media Gateway
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 28
Page 30
Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 22: GWC – Provisioning Gateway
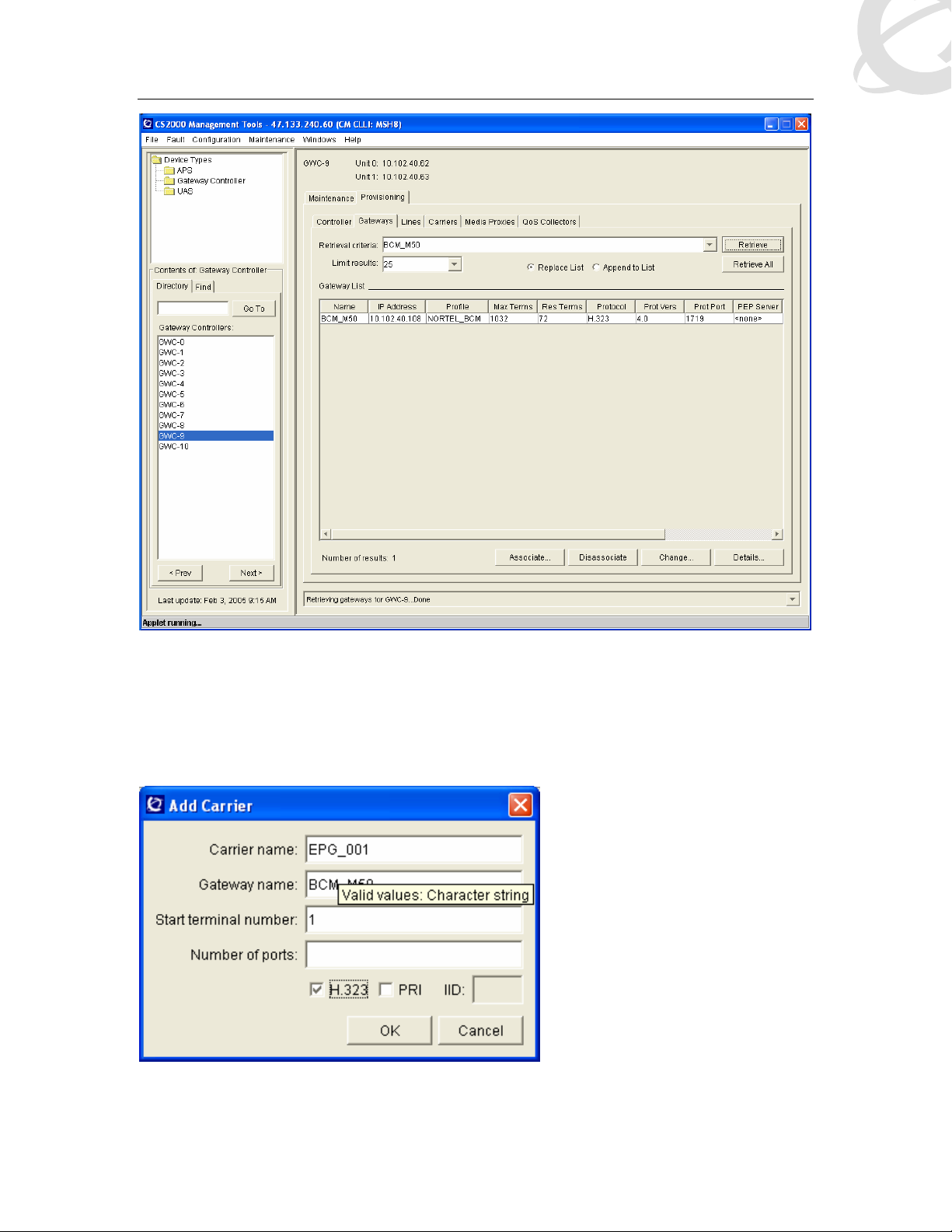
4.3 Reserving H323 Carriers on H323 Gateway in CMT
Once the Gateway is associated to the GWC, the next step is to set up the H.323 carriers. Refer
to pages 169-191 of the NTP NN10205-511
Figure 23: GWC – Add Carrier
.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 29
Page 31
Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
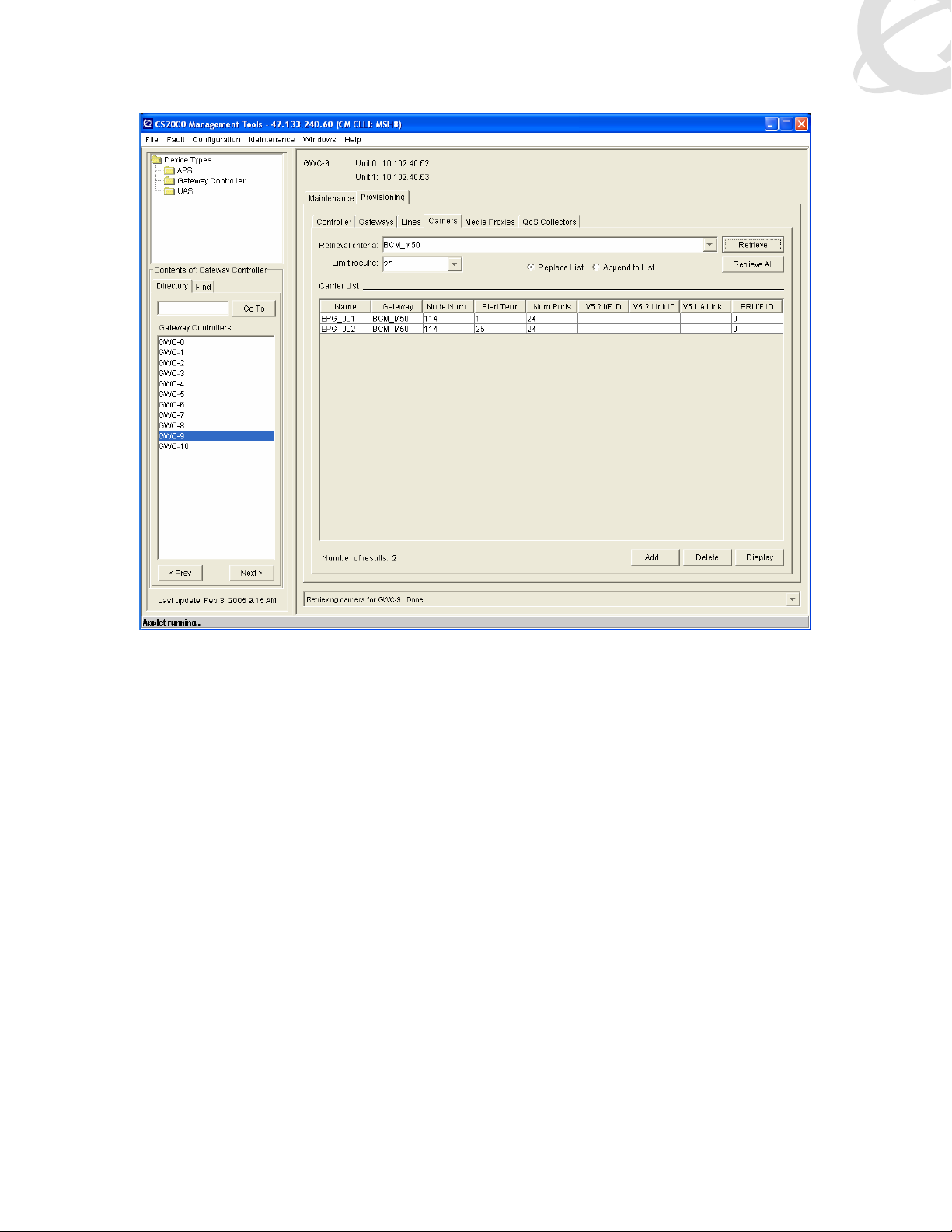
Figure 24 GWC – Carriers
4.4 Configuring Voice Network Settings
The final step in configuring the GWC is to ensure that sampling rate is correctly configured.
Succession’s CS2K supports 10 or 20 millisecond (mS) sampling; the IW-SPM the GWC and the
BCM50 need to be set to the same value.
Details on the IW-SPM setup can be found in 1 ; the GWC details follow pages 20-27 of the NTP
NN10205-511.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 30
Page 32

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Figure 25: GWC Packet Level Main Screen
Figure 26: Packetization Rate Selection
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 31
Page 33

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
5. Appendix A: DMS Read Files
5.1.1 Translation Verification (Traver)
The traver tool runs through the CS2K translations in the same order as the call processing
software. Thus, by reviewing the attached travered calls, the reader can get a feel for the method
by which the calls to and from the BCM are routed.
5.1.1.1 Debug Note
It is highly recommended that all call debugging be executed while closely observing the DMS
logs; as a successful Traver does not necessarily indicate that calls are completing.
5.1.1.2 CS2K DN to BCM
Line to line call: CS2K DN 234-4025 to BCM2_M50 236-4353.
Traver l 2344025 2364353 b
TABLE IBNLINES
HOST 00 0 00 12 0 DT STN IBN 2344025 EO613 0 0 613 $
TABLE DNATTRS
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE DNGRPS
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE IBNFEAT
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE CUSTSTN
EO613 AIN AIN TIID
TABLE OFCVAR
AIN_OFFICE_TRIGGRP TIID
AIN Orig Attempt TDP: no subscribed trigger.
TABLE NCOS
EO613 0 0 0 EO613 ( XLAS EO613XLA EO613FT NDGT) ( ERWT )$
TABLE CUSTHEAD: CUSTGRP, PRELIMXLA, CUSTXLA, FEATXLA, VACTRMT, AND
DIGCOL
EO613 NXLA EO613XLA EO613FT 0 NDGT
TABLE DIGCOL
NDGT specified: digits collected individually
TABLE IBNXLA: XLANAME EO613XLA
TUPLE NOT FOUND
Default from table XLANAME:
EO613XLA
(NET N N 0 N POTS N N GEN ( LATTR 3 613_OTTPUB_3 EA613_1)
(EA NILC Y 0) $ $)$ 9
TABLE DIGCOL
POTS specified: POTS digit collection
TABLE LINEATTR
3 1FR NONE NT 3 0 NILSFC 0 NIL NIL 00 613_OTTPUB_3 EA613_1 $
LCABILL OFF - BILLING DONE ON BASIS OF CALLTYPE
TABLE XLAPLAN
613_OTTPUB_3 NSCR 613 OTTPUB NONE Y EO613 0 0 $ $
TABLE RATEAREA
EA613_1 NLCA NIL EA613 $
TABLE STDPRTCT
OTTPUB ( 1) ( 0) 4
. SUBTABLE STDPRT
. KEY NOT FOUND
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 32
Page 34

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
. DEFAULT VALUE IS: N NP 0 NA
. SUBTABLE AMAPRT
. KEY NOT FOUND
. DEFAULT VALUE IS: NONE OVRNONE N
TABLE HPCPATTN
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE HNPACONT
613 Y 1023 0 ( 237) ( 1) ( 0) ( 0) 0 $
. SUBTABLE HNPACODE
. 236 236 LRTE 56
. SUBTABLE RTEREF
. 56 T OFRT 551
. . TABLE OFRT
. . 551 N D BCM2_M50 0 N N
. . EXIT TABLE OFRT
. EXIT TABLE RTEREF
EXIT TABLE HNPACONT
LNP Info: Called DN is not resident.
LNP Info: HNPA results are used.
AIN Info Collected TDP: no subscribed trigger.
TABLE FNPA7DIG
EMPTY TABLE: TUPLE NOT FOUND
Checking AIN SDS Trigger Items as SDS is compatible with current call
AIN Info Analyzed TDP: trigger criteria not met.
+++ TRAVER: SUCCESSFUL CALL TRACE +++
DIGIT TRANSLATION ROUTES
1 BCM2_M50 N CDN E164 L 2364353 NIL_NSF BC
SPEECH
TREATMENT ROUTES. TREATMENT IS: GNCT
1 VCA
+++ TRAVER: SUCCESSFUL CALL TRACE +++
5.1.1.3 BCM Trunk to CS2K DN
Incoming to the CS2K from the BCM2_M50’s trunk to the CS2K DN 234-4025.
traver tr BCM2_M50 2344025 b
TABLE TRKGRP
BCM2_M50 PRA 0 NPDGP NCRT MIDL N (ISDN 551) $ $
TABLE LTCALLS
ISDN 551 PUB XLALEC 0 BCM_PRI_TRAF NLCA_NILLA_0 $
TABLE CUSTSTN
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE OFCVAR
AIN_OFFICE_TRIGGRP TIID
TABLE LINEATTR
0 IBN NONE NT 0 0 NILSFC 0 NIL NIL 00 613_NPRT_0 NLCA_NILLA_0 $
LCABILL OFF - BILLING DONE ON BASIS OF CALLTYPE
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 33
Page 35

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
TABLE XLAPLAN
BCM_PRI_TRAF NSCR 550 PRI_TRAF NONE N $ PRI_TRAFFIC
TABLE RATEAREA
NLCA_NILLA_0 NLCA NIL NILLATA $
TABLE STDPRTCT
PRI_TRAF ( 0) ( 0) 5
. SUBTABLE STDPRT
WARNING: CHANGES IN TABLE STDPRT MAY ALTER OFFICE
BILLING. CALL TYPE DEFAULT IS NP. PLEASE REFER TO
DOCUMENTATION.
. KEY NOT FOUND
. DEFAULT VALUE IS: N NP 0 NA
. SUBTABLE AMAPRT
. KEY NOT FOUND
. DEFAULT VALUE IS: NONE OVRNONE N
TABLE HPCPATTN
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE HNPACONT
550 Y 700 0 ( 2) ( 1) ( 0) ( 0) 3 $
. SUBTABLE HNPACODE
. 234 234 DN 613 234
TABLE TOFCNAME
613 234 $
TABLE DNINV
613 234 4025 L HOST 00 0 00 12
TABLE DNFEAT
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE DNATTRS
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE DNGRPS
TUPLE NOT FOUND
LNP Info: Called DN is resident.
LNP Info: Called DN has native NPANXX.
LNP Info: HNPA results are used.
AIN Info Collected TDP: no subscribed trigger.
Checking AIN SDS Trigger Items as SDS is compatible with current call
AIN Info Analyzed TDP: trigger criteria not met.
AIN Term Attempt TDP: no subscribed trigger.
+++ TRAVER: SUCCESSFUL CALL TRACE +++
DIGIT TRANSLATION ROUTES
1 LINE 6132344025 ST
TREATMENT ROUTES. TREATMENT IS: GNCT
1 VCA
+++ TRAVER: SUCCESSFUL CALL TRACE +++
5.1.1.4 Inter-BCM Call
The first leg of the call originates as a trunk (BCM2_M50) which is first dialing the office code of
550, then BCM_M50’s DN 235-4353.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 34
Page 36

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
>traver tr bcm2_m50 5502354353 b
TABLE TRKGRP
BCM2_M50 PRA 0 NPDGP NCRT MIDL N (ISDN 551) $ $
TABLE LTCALLS
ISDN 551 PUB XLALEC 0 BCM_PRI_TRAF NLCA_NILLA_0 $
TABLE CUSTSTN
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE OFCVAR
AIN_OFFICE_TRIGGRP TIID
TABLE LINEATTR
0 IBN NONE NT 0 0 NILSFC 0 NIL NIL 00 613_NPRT_0 NLCA_NILLA_0 $
LCABILL OFF - BILLING DONE ON BASIS OF CALLTYPE
TABLE XLAPLAN
BCM_PRI_TRAF NSCR 550 PRI_TRAF NONE N $ PRI_TRAFFIC
TABLE RATEAREA
NLCA_NILLA_0 NLCA NIL NILLATA $
TABLE STDPRTCT
PRI_TRAF ( 0) ( 0) 5
. SUBTABLE STDPRT
WARNING: CHANGES IN TABLE STDPRT MAY ALTER OFFICE
BILLING. CALL TYPE DEFAULT IS NP. PLEASE REFER TO
DOCUMENTATION.
. KEY NOT FOUND
. DEFAULT VALUE IS: N NP 0 NA
. SUBTABLE AMAPRT
. KEY NOT FOUND
. DEFAULT VALUE IS: NONE OVRNONE N
TABLE HPCPATTN
TUPLE NOT FOUND
TABLE HNPACONT
550 Y 700 0 ( 2) ( 1) ( 0) ( 0) 3 $
. SUBTABLE HNPACODE
. 550235 550235 FRTE 550
. SUBTABLE RTEREF
. 550 T OFRT 550
. . TABLE OFRT
. . 550 N D BCM_M50 0 N N
. . EXIT TABLE OFRT
. EXIT TABLE RTEREF
EXIT TABLE HNPACONT
LNP Info: Called DN is not resident.
LNP Info: HNPA results are used.
AIN Info Collected TDP: no subscribed trigger.
Checking AIN SDS Trigger Items as SDS is compatible with current call
AIN Info Analyzed TDP: trigger criteria not met.
+++ TRAVER: SUCCESSFUL CALL TRACE +++
DIGIT TRANSLATION ROUTES
1 BCM_M50 N CDN E164 NA 5502354353 NIL_NSF BC
SPEECH
TREATMENT ROUTES. TREATMENT IS: GNCT
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 35
Page 37

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
1 VCA
+++ TRAVER: SUCCESSFUL CALL TRACE +++
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 36
Page 38

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
6. Appendix B: DMS CLLIREF
The CLLIREF tool scans all CS2K tables for instances of a specific CLLI. The output of the
BCM_M50 CLLIREF is included to ensure that no tables were omitted from this document.
>clliref search BCM_M50
CLLI "BCM_M50" occurs in the following tuples:
Table Key: Sub Tuple
-------- -------> ---------------------------------------------------
----CLLI BCM_M50 411 50 PIERRE_FOURNIER
TRKGRP BCM_M50 PRA 0 NPDGP NCRT MIDL N (ISDN 550) $ $
CLLIMTCE BCM_M50 BCM_M5 5 10 15 NSS 0 0 N N (4)
OFRT 550 (N D BCM_M50 0 N N) $ $
TRKSGRP BCM_M50 0 DS1SIG ISDN 20 20 87Q931 2 N STAND
NETWORK
PT_PT USER N UNEQ 160 N DEFAULT GWC 9 114 1
64K
HDLC $ $
TRKMEM BCM_M50 1 0 GWC 9 114 2
TRKMEM BCM_M50 2 0 GWC 9 114 3
TRKMEM BCM_M50 3 0 GWC 9 114 4
TRKMEM BCM_M50 4 0 GWC 9 114 5
TRKNAME 411 BCM_M50
LTMAP ISDN 550 CLLI BCM_M50 (TEI 0) $
=====================
Total of 11
>clliref search BCM2_M50
CLLI "BCM2_M50" occurs in the following tuples:
Table Key: Sub Tuple
-------- -------> ---------------------------------------------------
----CLLI BCM2_M50 413 50 PIERRE_FOURNIER
TRKGRP BCM2_M50 PRA 0 NPDGP NCRT MIDL N (ISDN 551) $ $
CLLIMTCE BCM2_M50 BCM2_M 5 10 15 NSS 0 0 N N (4)
OFRT 551 (N D BCM2_M50 0 N N) $ $
TRKSGRP BCM2_M50 0 DS1SIG ISDN 20 20 87Q931 2 N STAND
NETWORK
PT_PT USER N UNEQ 160 N DEFAULT GWC 9 114 49
64K
HDLC $ $
TRKMEM BCM2_M50 1 0 GWC 9 114 50
TRKMEM BCM2_M50 2 0 GWC 9 114 51
TRKMEM BCM2_M50 3 0 GWC 9 114 52
TRKMEM BCM2_M50 4 0 GWC 9 114 53
TRKNAME 413 BCM2_M50
LTMAP ISDN 551 CLLI BCM2_M50 (TEI 0) $
=====================
Total of 11
Occurrences of BCM2_M50
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 37
Page 39

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
Contact Us:
For product support and sales information, visit the Nortel Networks website at:
In North America, dial toll-free 1-800-4Nortel, outside North America dial 987-288-3700.
http://www.nortel.com
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 38
Page 40

Technical Configuration Guide for: BCM50 to CS2K V2.0 November, 2005
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Nortel Networks External Distribution 39
 Loading...
Loading...