Page 1

Avaya Communication Manager
Call Center Software
Basic Call Management System (BCMS)
Operations
07-300061
Issue 5.0
May 2005
Page 2

© 2004 Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Notice
While reasonable efforts were made to ensure that the information in this
document was complete and accurate at the time of printing, Avaya Inc.
can assume no liability for any errors. Changes and corrections to the
information in this document may be incorporated in future releases.
Documentation disclaimer
Avaya Inc. is not responsible for any modifications, additions, or deletions
to the original published version of this documentation unless such
modifications, additions, or deletions were performed by Avaya.
Customer and/or End User agree to indemnify and hold harmless Avaya,
Avaya's agents, servants and employees against all claims, lawsuits,
demands and judgments arising out of, or in connection with, subsequent
modifications, additions or deletions to this documentation to the extent
made by the Customer or End User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya Inc. is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked
Web sites and does not necessarily endorse the products, services, or
information described or offered within them. We cannot guarantee that
these links will work all of the time and we have no control over the
availability of the linked pages.
Warr ant y
Avaya Inc. provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to your
sales agreement to establish the terms of the limited warranty. In
addition, Avaya’s standard warranty language, as well as information
regarding support for this product, while under warranty, is available
through the following Web site:
http://www.avaya.com/support
Preventing toll fraud
"Toll fraud" is the unauthorized use of your telecommunications system
by an unauthorized party (for example, anyone who is not a corporate
employee, agent, subcontractor, or person working on your company's
behalf). Be aware that there may be a risk of toll fraud associated with
your system and that, if toll fraud occurs, it can result in substantial
additional charges for your telecommunications services.
Avaya fraud intervention
If you suspect that you are being victimized by toll fraud and you need
technical assistance or support, call Technical Service Center Toll Fraud
Intervention Hotline at +1-800-643-2353 for the United States and
Canada. For additional support telephone numbers, see the Avaya Web
site:
http://www.avaya.com/support
Providing telecommunications security
Telecommunications security (of voice, data, and video communications)
is the prevention of any type of intrusion to (that is, either unauthorized or
malicious access to or use of) your company's telecommunications
equipment by some party.
Your company's "telecommunications equipment" includes both this
Avaya product and any other voice/data/video equipment that could be
accessed via this Avaya product (that is, "networked equipment").
An "outside party" is anyone who is not a corporate employee, agent,
subcontractor, or person working on your company's behalf. Whereas, a
"malicious party" is anyone (including someone who may be otherwise
authorized) who accesses your telecommunications equipment with
either malicious or mischievous intent.
Such intrusions may be either to/through synchronous (time-multiplexed
and/or circuit-based) or asynchronous (character-, message-, or
packet-based) equipment or interfaces for reasons of:
• Use (of capabilities special to the accessed equipment)
• Theft (such as, of intellectual property, financial assets, or
toll-facility access)
• Eavesdropping (privacy invasions to humans)
• Mischief (troubling, but apparently innocuous, tampering)
• Harm (such as harmful tampering, data loss or alteration,
regardless of motive or intent)
Be aware that there may be a risk of unauthorized intrusions associated
with your system and/or its networked equipment. Also realize that, if
such an intrusion should occur, it could result in a variety of losses to your
company (including, but not limited to, human and data privacy,
intellectual property, material assets, financial resources, labor costs, and
legal costs).
Your responsibility for your company's telecommunications
security
The final responsibility for securing both this system and its networked
equipment rests with you, an Avaya customer's system administrator,
your telecommunications peers, and your managers. Base the fulfillment
of your responsibility on acquired knowledge and resources from a
variety of sources, including, but not limited to:
• Installation documents
• System administration documents
• Security documents
• Hardware-/software-based security tools
• Shared information between you and your peers
• Telecommunications security experts
To prevent intrusions to your telecommunications equipment, you and
your peers should carefully program and configure:
• Your Avaya-provided telecommunications systems and their
interfaces
• Your Avaya-provided software applications, as well as their
underlying hardware/software platforms and interfaces
• Any other equipment networked to your Avaya products.
Trademarks
Avaya is a trademark of Avaya Inc.
All non-Avaya trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Document ordering information:
Avaya Publications Center
Voi ce: +1-207-866-6701
Fax: +1-207-626-7269
Write: Globalware Solutions
Web: http://www.avaya.com/support
E-mail: totalware@gwsmail.com
Order: Document No. 07-300061, Issue 5.0
For the most current versions of documentation, go to the Avaya support
Web site:
http://www.avaya.com/support
COMPAS
This document is also available from the COMPAS database. The
COMPAS ID for this document is 107011.
Avaya support
Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report problems or
to ask questions about your contact center. The support telephone
number is 1-800-242-2121 in the United States. For additional support
telephone numbers, see the Avaya Web site:
http://www.avaya.com/support
1-800-457-1764 (Toll-free, U.S. and Canada only)
1-800-457-1764 (Toll-free, U.S. and Canada only)
200 Ward Hill Avenue
Haverhill, MA 01835 USA
Attention: Avaya Account Manager
May 2005
Page 3

Avaya Communication Manager
Call Center Software
Basic Call Management System (BCMS) Operations
Contents
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Purpose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Intended users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Conventions and terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Reasons for reissue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Related documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Change description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Software documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Administration documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Hardware documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Call Center documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Avaya CMS upgrade documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Base load upgrades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Platform upgrades and data migration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Avaya Call Management System Upgrade Express (CUE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Documentation Web sites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
BCMS description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Printing and storing reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Acceptable Service Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Percent within service level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Acceptable Service Level administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
System capacities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Interactions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
VuStats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
System access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Logging in and logging off. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Constraints for accessing BCMS data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
BCMS login ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Logging in . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Logging off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
How to change the BCMS password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Issue 5.0 May 2005 3
Page 4

Contents
Generating reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Displaying and printing real-time reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Displaying real-time reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Printing real-time reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Displaying historical reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Printing historical reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Scheduling historical reports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Report reference. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Report commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Real-time reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Split status report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Sample report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
System status report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Sample report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
VDN status report. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Sample report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Historical reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Types of BCMS historical reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Agent report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Sample reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Agent summary report. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Sample reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Split report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Sample reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Split summary report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Sample reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
4 BCMS Operations
Page 5

Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Trunk group report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Sample reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Trunk group summary report. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Sample reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
VDN report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Sample reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Header definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
VDN summary report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Sample reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Header definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Contents
System printer and Report Scheduler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
System printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
System printer administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
System printer data link operation and maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Report Scheduler. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Print intervals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Adding a report to Report Scheduler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Printing reports on the system printer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Listing scheduled reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Changing scheduled reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Removing scheduled reports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Using reports for ACD planning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Planning/engineering objectives. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
System status report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Split status report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
VDN status report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Trunk group report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Agent report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Split report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
VDN report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Engineering ACD applications with report data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
About interpolation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Agent engineering/optimizing guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Agent engineering examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Average service time engineering tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Issue 5.0 May 2005 5
Page 6

Contents
Trunk Engineering Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Appendix A: BCMS/CMS report heading comparison . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Summary of differences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Report heading comparison tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
6 BCMS Operations
Page 7

Preface
This section includes the following topics:
● Purpose on page 7
● Intended users on page 8
● Overview on page 8
● Conventions and terminology on page 9
● Reasons for reissue on page 9
● Related documentation on page 10
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to provide a comprehensive description of the Basic Call
Management System (BCMS) feature, which is available with Avaya Communication
Manager Call Center Software and Enterprise Communications Server (ECS) products.
This document also describes the Report Scheduler feature, which is often used with
BCMS.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 7
Page 8

Preface
Intended users
This document is written for BCMS administrators.This document might be useful for
system administrators, Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) split supervisors, ACD
administrators, and ACD agents.
Overview
This document includes the following topics:
● BCMS description on page 15
Provides a brief overview of the BCMS feature and lists the types of BCMS reports.
● System access on page 21
Provides procedures on how to log in and log off BCMS. This section also provides the
procedures for changing the BCMS password.
● Generating reports on page 25
Describes the procedures for displaying, printing, and scheduling BCMS reports.
● Report reference on page 41
Provides a detailed description of each type of BCMS report.
● System printer and Report Scheduler on page 91
Describes the optional Report Scheduler feature. This section also includes a
description of Report Scheduler commands and a display of the reports.
● Using reports for ACD planning on page 101
Describes desirable objectives and how the BCMS reports can be used to plan,
engineer, and optimize ACD splits and trunk groups.
8 BCMS Operations
Page 9

Conventions and terminology
If you see any of the following safety labels in this document, take careful note of the
information presented.
!
CAUTION:
CAUTION: Caution statements call attention to situations that can result in harm to
software, loss of data, or an interruption in service.
!
WARNING:
WARNING: Warning statements call attention to situations that can result in harm to
hardware or equipment.
Conventions and terminology
!
DANGER
DANGER: Danger statements call attention to situations that can result in harm to
:
personnel.
!
SECURITY ALERT:
SECURITY ALERT: Security alert statements call attention to situations that can increase the
potential for unauthorized use of a telecommunications system.
Reasons for reissue
● This document was updated to include information for the R12 release of the Avaya Call
Management System software
● A general update and correction of a variety of small problems, such as typographical
errors, was done.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 9
Page 10

Preface
Related documentation
You might find the following Avaya CMS documentation useful. This section includes the
following topics:
● Change description on page 10
● Software documents on page 10
● Administration documents on page 11
● Hardware documents on page 11
● Call Center documents on page 11
● Avaya CMS upgrade documents on page 12
● Documentation Web sites on page 13
Change description
For information about the changes made in Avaya CMS R13, see:
● Avaya Call Center 3.0 and Call Management System (CMS) Release 13 Change
Description, 07-300304
Software documents
For more information about Avaya CMS software, see:
● Avaya Call Management System Release 13 Software Installation, Maintenance, and
Troubleshooting Guide, 07-300340
● Avaya CMS Open Database Connectivity Version 4.2, 585-780-701
● Avaya Call Management System Release 13 LAN Backup User Guide, 07-300338
● Avaya Call Management System Release 13 External Call History Interface, 07-300332
● Avaya CMS Custom Reports, 585-215-822
● Avaya CMS Forecast User Guide, 585-215-825
● Avaya Visual Vectors Release 13 Installation and Getting Started, 07-300353
● Avaya Visual Vectors Release 13 User Guide, 07-300354
● Avaya Call Management System (CMS) Supervisor Release 13 Report Designer,
07-300335
10 BCMS Operations
Page 11

Administration documents
For more information about Avaya CMS administration, see:
● Avaya Call Management System Release 13 Administration, 07-300331
● Avaya Call Management System (CMS) Release 13 Database Items and Calculations,
07-300330
● Avaya Call Management System Supervisor Release 13 Reports, 07-300334
● Avaya Call Management System (CMS) Supervisor Release 13 Installation and Getting
Started, 07-300333
● Avaya Call Management System High Availability User Guide, 07-300066
● Avaya Call Management System High Availability Connectivity, Upgrade and
Administration, 07-300065
Hardware documents
Related documentation
For more information about Avaya CMS hardware, see:
● Avaya Call Management System Sun Fire V880/V890 Computer Hardware Installation,
Maintenance, and Troubleshooting, 585-215-116
● Avaya Call Management System Sun Blade 100/150 Workstation Hardware Installation,
Maintenance, and Troubleshooting, 585-310-783
● Avaya Call Management System Terminals, Printers, and Modems, 585-215-874
Call Center documents
For more information about Avaya Call Center documents, see:
● Avaya Communication Manager Call Center Software Basic Call Management System
(BCMS) Operations, 07-300061
● Avaya Call Management System Switch Connections, Administration, and
Troubleshooting, 585-215-876
● Avaya Communication Manager Call Center Software Call Vectoring and Expert Agent
Selection (EAS) Guide, 07-300303
● Avaya Communication Manager Call Center Software Automatic Call Distribution (ACD)
Guide, 07-300301
● Avaya Business Advocate User Guide, 07-300336
Issue 5.0 May 2005 11
Page 12

Preface
Avaya CMS upgrade documents
There are several upgrade paths supported with Avaya CMS. There is a document
designed to support each upgrade.
This section includes the following topics:
● Base load upgrades on page 12
● Platform upgrades and data migration on page 12
● Avaya Call Management System Upgrade Express (CUE) on page 12
Base load upgrades
Use a base load upgrade when upgrading CMS to the latest load of the same version (for
example, r13ak.g to r13al.k). A specific set of instructions is written for the upgrade. The
instructions are shipped to the customer site with the CMS software CD-ROM as part of a
Product Correction Notice (PCN).
For more information about base load upgrades, see:
● Avaya Call Management System Release 13 Base Load Upgrade
Platform upgrades and data migration
Use a platform upgrade when upgrading to a new hardware platform (for example,
upgrading from a SPARCserver 5 to a Sun Blade 150). The new hardware platform is
shipped from the Avaya factory with the latest CMS load. Therefore, as part of the upgrade
you will have the latest CMS load (for example, R3V9 to R13).
For more information about platform upgrades and data migration, see:
● Avaya Call Management System Release 13 Platform Upgrade and Data Migration,
07-300339
Avaya Call Management System Upgrade Express (CUE)
Use CUE when CMS is being upgraded from an earlier version (for example, R3V9) to the
latest version (for example, R13).
A specific set of upgrade instructions is written for the upgrade. These instructions are
included on the CUE software CD-ROM that is shipped to the customer site with the CUE
kit.
For information about customer requirements for CUE upgrades, see:
● Avaya Call Management System Release 13 CMS Upgrade Express (CUE) Customer
Requirements, 700356744
12 BCMS Operations
Page 13

For information about CUE upgrade procedures, see:
● Avaya Call Management System Release 13 Sun Blade 100/150 Workstation Mirrored
and Nonmirrored Systems CMS Upgrade Express (CUE), 07-300481
● Avaya Call Management System Release 13 Sun Fire V880/V890 Computer CMS
Upgrade Express (CUE), 07-300344
Documentation Web sites
For Avaya product documentation, go to http://www.avayadocs.com. Additional information
about new software or hardware updates will be contained in future issues of this book.
New issues of this book will be placed on the Web site when available.
Use the following Web sites to view related support documentation:
● Information about Avaya products and service
Related documentation
http://www.avaya.com
● Sun hardware documentation
http://docs.sun.com
● Informix documentation
http://www.informix.com
● Tivoli Storage Manager documentation
http://www.tivoli.com
Issue 5.0 May 2005 13
Page 14

Preface
14 BCMS Operations
Page 15

BCMS description
BCMS helps you monitor the operations of your ACD application. BCMS collects data
related to the calls on the switch and organizes the data into reports that help you manage
ACD facilities and personnel. The BCMS reports allow you to manage the hourly and/or
daily operations of the ACD by:
● Monitoring trunk group usage
● Monitoring the calling volume for each split
● Monitoring VDNs
● Monitoring the work load of each agent
● Comparing agent performance.
These reports can be displayed on a video display terminal in real time, printed
immediately, scheduled to print at a later time, or scheduled to print periodically at times
you specify.
Note:
Note: All references to splits in this book also apply to skills as used with the
Expert Agent Selection (EAS) feature. See Interactions
information.
on page 20 for more
This section includes the following topics:
● Reports on page 16
● Printing and storing reports on page 17
● Acceptable Service Level on page 18
● System capacities on page 19
● Interactions on page 20
Issue 5.0 May 2005 15
Page 16

BCMS description
Reports
The BCMS feature provides the following reports:
● Real-time reports that present data on:
● Historical reports that present historical information and can be printed immediately or
scheduled for subsequent printing. These reports present data on:
- All splits, on a system basis, that are administered for internal measurement or for
both internal and external measurement
- Individual splits and the agents staffing them that have been administered for
internal measurement or for both internal and external measurement
- VDNs that are administered for internal measurement or for both internal and
external measurement.
- Individual agents or a group of agents, based on the time of day
- Individual agents or a group of agents, based on the day of the week
- Individual splits or a group of splits, based on the time of day
- Individual splits or a group of splits, based on the day of the week
- Individual trunk groups or a group of trunk groups, based on the time of day
- Individual trunk groups or a group of trunk groups, based on the day of the week
- Individual Vector Directory Numbers (VDNs) based on the time of day
- Individual VDNs based on the day of the week
Note:
Note: Agents can be measured by their physical extension (that is, the extension
number they use), or by their Login IDs when either EAS or BCMS/VuStats
Login IDs is optioned.
Report reference
on page 41 describes each BCMS report in detail while Using reports for
ACD planning on page 101 describes how to plan and maintain an ACD based on the
information provided by these reports.
16 BCMS Operations
Page 17

Printing and storing reports
The BCMS reports may be displayed on an administration terminal or printed on its
associated printer. The reports can also be scheduled to print at a later time using the
Report Scheduler.
As an option, a personal computer (PC) or host computer may be used to store the reports
and provide additional data manipulation capabilities.
Note:
Note: The BCMS software resides completely on the switch and does not include
any special software or unique communications protocol for the PC/host
computer application. Although Avaya does propose the use of a PC to
collect, store, and print the reports, Avaya does not recommend an
applications software package for the PC. Since Avaya does not install,
administer, or control the PC application, Avaya does not guarantee correct
operation of this arrangement.
Customers using a PC to collect report data will need the following report output
information for each report:
Printing and storing reports
1. Begin with one-half page of line feeds.
2. Print a four-line banner containing the following information:
● Print job ID
● Command
● Time of day
● User
3. Provide a form feed.
4. Begin report data using 80 characters per line. Use spaces where there are no data,
and a newline character at the end of each line.
5. Provide a form feed after each page of data. The page length is defined in system
parameters.
6. Provide a form feed when the report has finished printing.
BCMS data is stored in volatile switch memory; it cannot be saved to or retrieved from
tape. The switch preserves historical data if a Reset System 1, Reset System 2, or Reset
System Interchange (in a duplicated system) occurs. Real-time data is preserved if a Reset
System 1 or Reset System Interchange occurs.
The switch loses all data (historical and real-time) during software upgrades.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 17
Page 18

BCMS description
Acceptable Service Level
Before using BCMS, you should understand the concept of Acceptable Service Level and
set the acceptable service level field on various screens.
Acceptable Service Level is the desired time for an agent to answer a call for a given VDN
or hunt group. Timing for a call begins when the call encounters a VDN or enters a hunt
group queue. If the number of seconds to answer the call is equal to or less than the
administered acceptable service level for the VDN or hunt group, the call is recorded as
acceptable.
This section includes the following topics:
● Percent within service level on page 18
● Acceptable Service Level administration on page 19
Percent within service level
A service level can be administered for each hunt group or VDN if the BCMS/VuStats
Service Level customer option has been enabled and if the hunt group or VDN is
measured by BCMS.
To calculate the percentage of calls within the acceptable service level, BCMS divides the
number of acceptable calls by the calls offered.
For hunt groups, BCMS calculates the Percent Within Service Level as follows:
% IN SERV LEVL
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------=
accepted * 100
ACDcalls + abandons + outflows + dequeued
where:
● accepted - Is the number of calls answered for which the queue time was less than or
equal to the administered service level for the split.
● dequeued - Is the number of calls that encountered the split queue, but were NOT
answered, abandoned, or outflowed. This occurs with multiple split queuing.
For VDNs, BCMS calculates the Percent Within Service Level as follows:
% IN SERV LEVL
accepted * 100
----------------------------------------=
calls offered
where:
● accepted - Is the number of answered calls (num ans) for which the time to answer was
less than or equal to the administered service level for the VDN. num ans here refers to
the data item on the screen.
18 BCMS Operations
Page 19
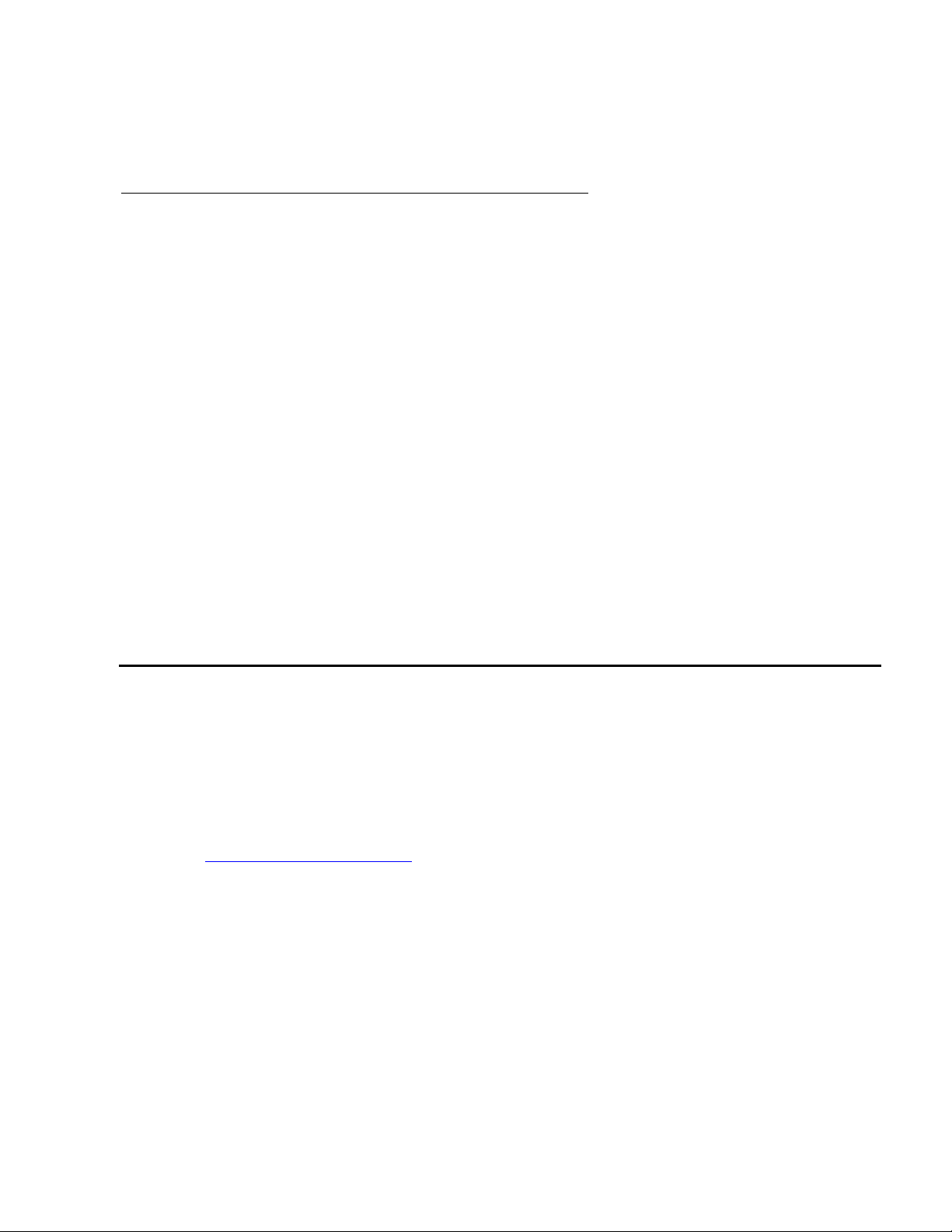
● calls offered - Is the total number of completed calls that accessed the VDN during the
current interval.
Acceptable Service Level administration
The Acceptable Service Level is administered on the System-Parameters
Customer-Options, VDN, and Hunt Group screens. On the System-Parameters
Customer-Options screen (changeable using a superuser ID), verify that the field BCMS/
VuStats Service Level is set to y.
On the Hunt Group screen, set the Acceptable Service Level field to a number
between 0 and 9999 seconds. Set the Measured field to either internal or both.
On the Vector Directory Number screen, set the Acceptable Service Level field to a
number between 0 and 9999 seconds. Set the Measured field to either internal or
both.
The column % IN SERV LEVL on a report will be blank if:
● The BCMS/VuStats Service Level field on the Customer Options screen is set to n
System capacities
● No service level is defined for the split or VDN (it cannot be set if BCMS Service Level is
set to n)
● No call ended in the interval
System capacities
Because system capacity limits change often, this information is now being maintained in a
document for each switch release. For switch releases up to R9, consult the System
Description document. For switch releases R10 and later, see the Capacity Tables
document. All of these documents can be accessed from the Avaya documentation Web
site:
http://www.avayadocs.com/
Issue 5.0 May 2005 19
Page 20
BCMS description
Interactions
This section includes the following topics:
● CMS on page 20
● VuStats on page 20
CMS
From the administration perspective, the ACD parameters associated with trunk groups,
hunt groups, and VDNs are any of the following:
● Not measured
● Internally measured by BCMS
● Externally measured by CMS
VuStats
● Measured both internally by BCMS and externally by CMS.
Note that using BCMS in conjunction with CMS increases the maximum number of agents
and trunk groups that can be measured for a particular ACD application. In other words,
the capacities for BCMS are additive to those of CMS.
Note:
Note: If both BCMS and CMS are used simultaneously, switch performance may
be degraded.
VuStats enables agents and supervisors with telephone displays to view data about
agents, splits, and VDNs. Much of this information is the same as that provided by BCMS.
20 BCMS Operations
Page 21

System access
This section includes the following topics:
● Logging in and logging off on page 21
● How to change the BCMS password on page 24
Logging in and logging off
A BCMS terminal is treated by the system as a remote management terminal. You can
access BCMS reports either from a local system management terminal, on a dial-up basis,
or by using the Avaya Site Administration terminal emulator tool.
This section includes the following topics:
● Constraints for accessing BCMS data on page 21
● BCMS login ID on page 22
● Logging in on page 22
● Logging off on page 23
Constraints for accessing BCMS data
When dial-up access is used, the following constraints affect the number of terminals that
can access BCMS data simultaneously:
● The number of dial-up (Netcon) channels
● The number of Terminal User IDs (TUIs). A TUI is a switch resource used by:
- The Technical Service Center (TSC) when logged in
- The management terminal when powered up
- A remote management terminal when logged in
- A BCMS terminal when logged in
Issue 5.0 May 2005 21
Page 22

System access
- The system printer while printing
- A journal/log printer when administered
When the switch is configured with more than one management terminal, typically one
terminal is dedicated to administration and/or maintenance tasks while the others are used
for ACD/BCMS features.
BCMS login ID
The switch provides several different categories of login IDs. The login ID identifies the
user and that user’s permitted capabilities to the system. You must create a login ID for
each supervisor or user that you want to view BCMS reports. A BCMS login ID can allow
you to display, print, and schedule BCMS reports.
Logging in
There are many ways to log in to BCMS: from a local terminal, from a remote terminal, or
using the Avaya Site Administration tool. The remote terminal requires a data module for
dialing up the system and Avaya Site Administration can use a modem or a LAN
connection.
To log into BCMS:
1. If remote, dial in to the switch. If local, turn on the terminal and press BREAK if a login
prompt is not displayed.
The terminal displays a login prompt.
2. Enter your login ID and press RETURN.
The screen displays the password prompt.
3. Enter your password and press RETURN. The system verifies that the login ID and
password you entered are valid. If you entered an invalid login ID or password, the
system displays a message and requires you to log in again.
22 BCMS Operations
Page 23
Logging in and logging off
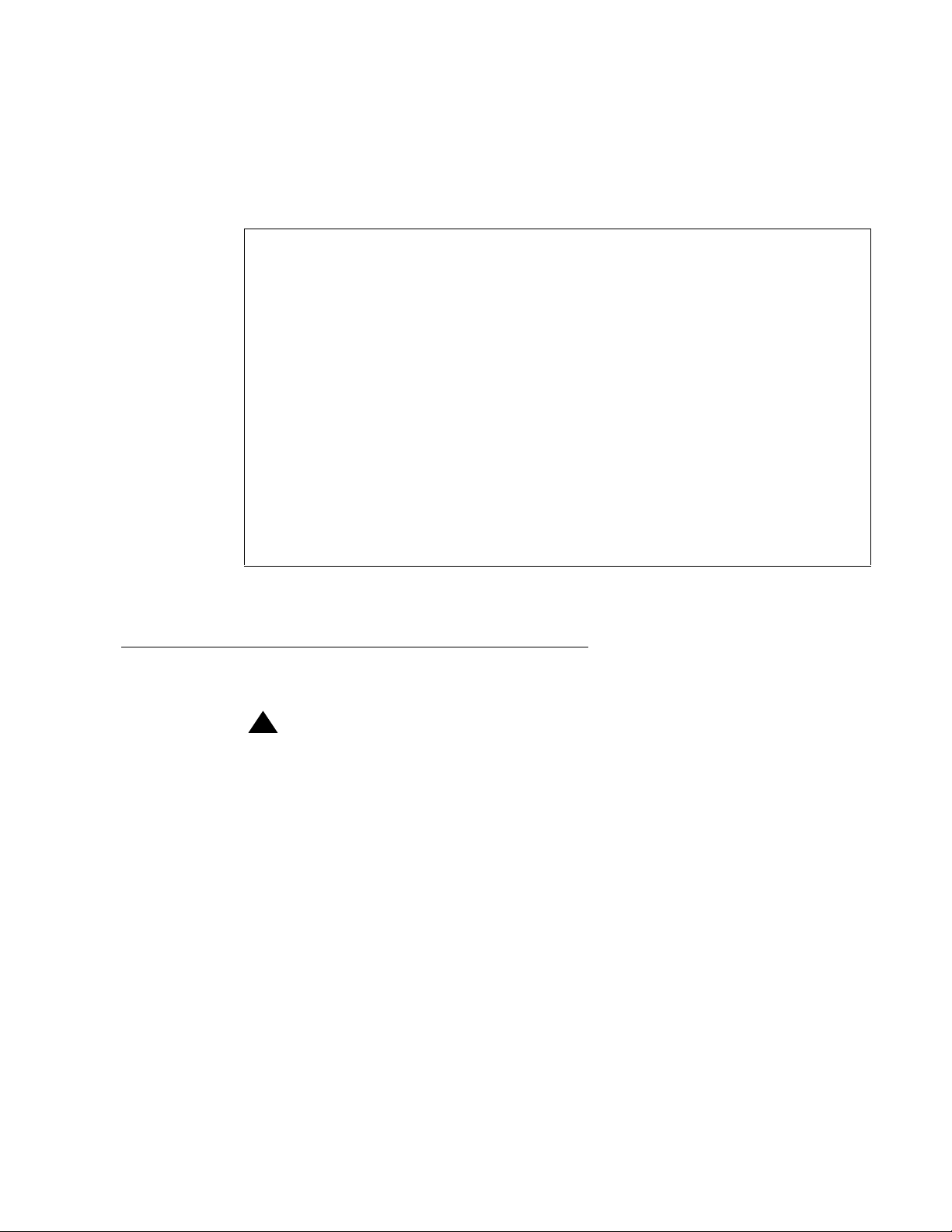
4. Enter the appropriate terminal type. In most cases, use the default terminal type that
the system displays.
After you enter the appropriate terminal type, the system displays the command
screen.
This system is restricted to authorized users
for legitimate business purposes. Unauthorized
access is a criminal violation of the law.
Copyright (c) 1992 - 2001 Avaya Inc.
Unpublished & Not for Publication
All Rights Reserved
The system is now ready for you to enter a command to generate a BCMS report.
Logging off
SECURITY ALERT: Whenever you are not using BCMS, log off the system.
To log off the system, perform the following steps:
1. Enter:
logoff
The system displays a message questioning if you want to log off.
2. Enter: y
You are logged off from the system.
Command:
!
SECURITY ALERT:
Issue 5.0 May 2005 23
Page 24
System access
How to change the BCMS password
Any user can change the password for their own login ID. Only users with special
privileges, such as the system administrator, can change the password for other users.
!
SECURITY ALERT:
SECURITY ALERT: To protect access to the system, the password should be changed at regular
intervals, each time a new person takes over a login ID, and if an
unauthorized person has discovered the password. Once a password is
assigned or changed, do not give the password to anyone and keep any
written passwords in a locked place.
To change a password:
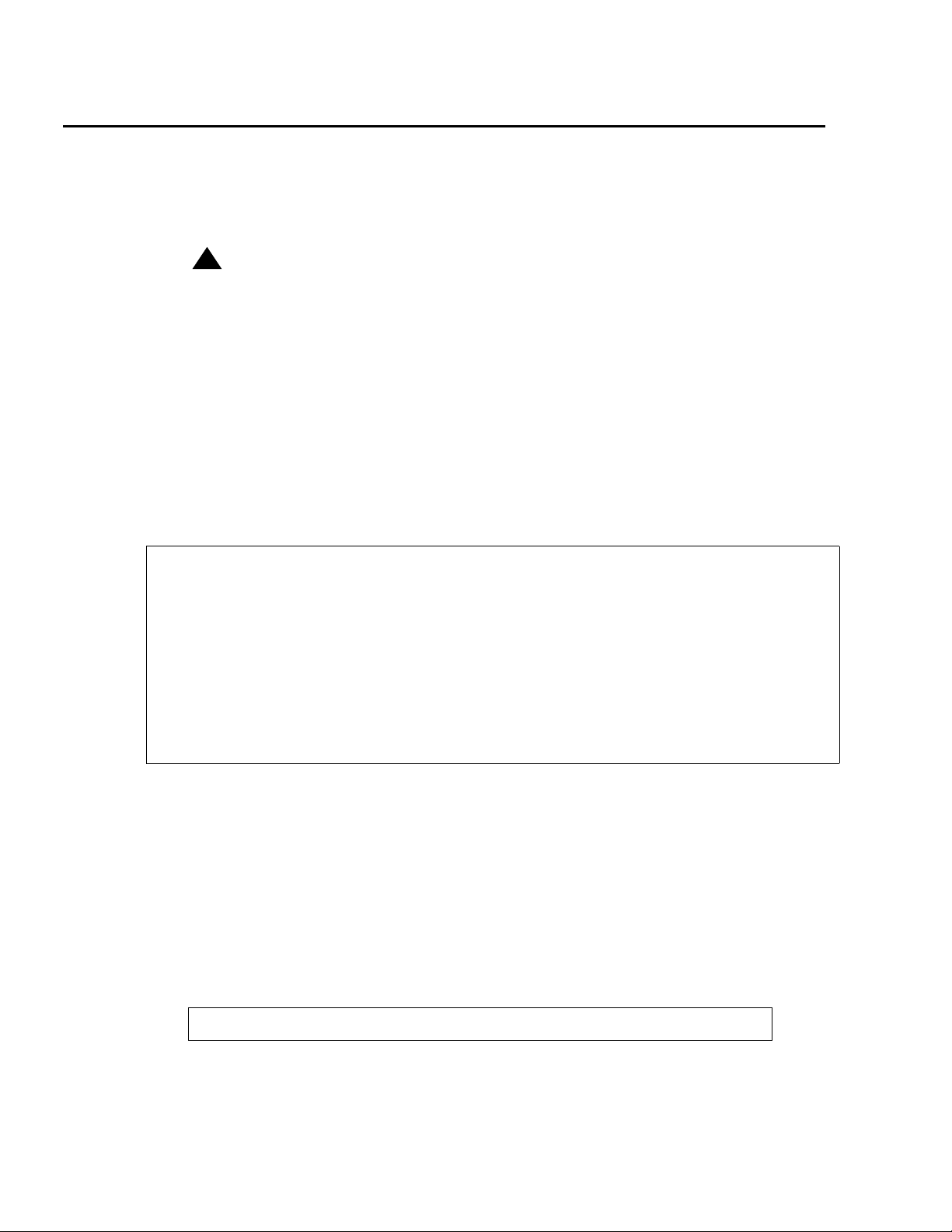
1. At the command prompt, enter:
change password <login name>
The system displays the Password Administration screen. The cursor is positioned on
the Password of Login Making Change field.
change password bcms Page 1 of 1
PASSWORD ADMINISTRATION
Password of Login Making Change:
LOGIN BEING CHANGED
Login Name: bcms
LOGIN'S PASSWORD INFORMATION
Login's Password:
Reenter Login's Password:
2. Enter your password and press RETURN.
The cursor is positioned on the Login’s Password field.
3. Enter your new password and press RETURN.
Valid passwords contain a minimum of four characters either alphabetic or numeric.
The cursor is positioned on the Reenter Login’s Password field.
4. Re-enter your new password and press ENTER.
The system displays the following message:
command completed successfully
24 BCMS Operations
Page 25

Generating reports
This chapter describes the procedures for displaying and printing real-time reports and for
displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports. Before attempting to print these
reports, make sure that a system printer is connected and administered.
This section includes the following topics:
● Displaying and printing real-time reports on page 25
● Displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports on page 28
Displaying and printing real-time reports
The monitor command is used to display and print real-time status reports. These reports
display data accrued since the last interval boundary. Data is based on hourly or
half-hourly intervals as administered in the BCMS/VuStats Measurement Interval
field on the Feature-Related System Parameters screen.
There are three monitor commands, one to display or print each real-time report:
monitor bcms split
monitor bcms system
monitor bcms vdn
Whenever a status report is displayed on the management terminal, it updates
automatically approximately every 30 seconds. You can immediately update the on-screen
status report by pressing UPDATE. To cancel the monitor command and return to the
command prompt, press CANCEL. If the status report consists of more than one page,
press NEXTPAGE to display any subsequent pages and PREVPAGE to display any
previous pages.
If you incorrectly enter the command, or if the qualifier is not applicable or is not measured,
an error message displays on the message line located on the bottom of the screen. If you
require more information about the error message, press HELP.
Complete the steps in the following topics to display or print real-time reports.
This section includes the following topics:
Issue 5.0 May 2005 25
Page 26
Generating reports
● Displaying real-time reports on page 26
● Printing real-time reports on page 26
Displaying real-time reports
To display a real-time report, complete the following steps:
1. Type the monitor command that will display the report you want to view. See
Commands for displaying real-time reports
2. Press RETURN. The report displays on your screen.
3. Press NEXTPAGE to display subsequent pages and PREVPAGE to display previous
pages.
4. To immediately update the report data, press UPDATE.
5. To exit the report, press CANCEL.
on page 26.
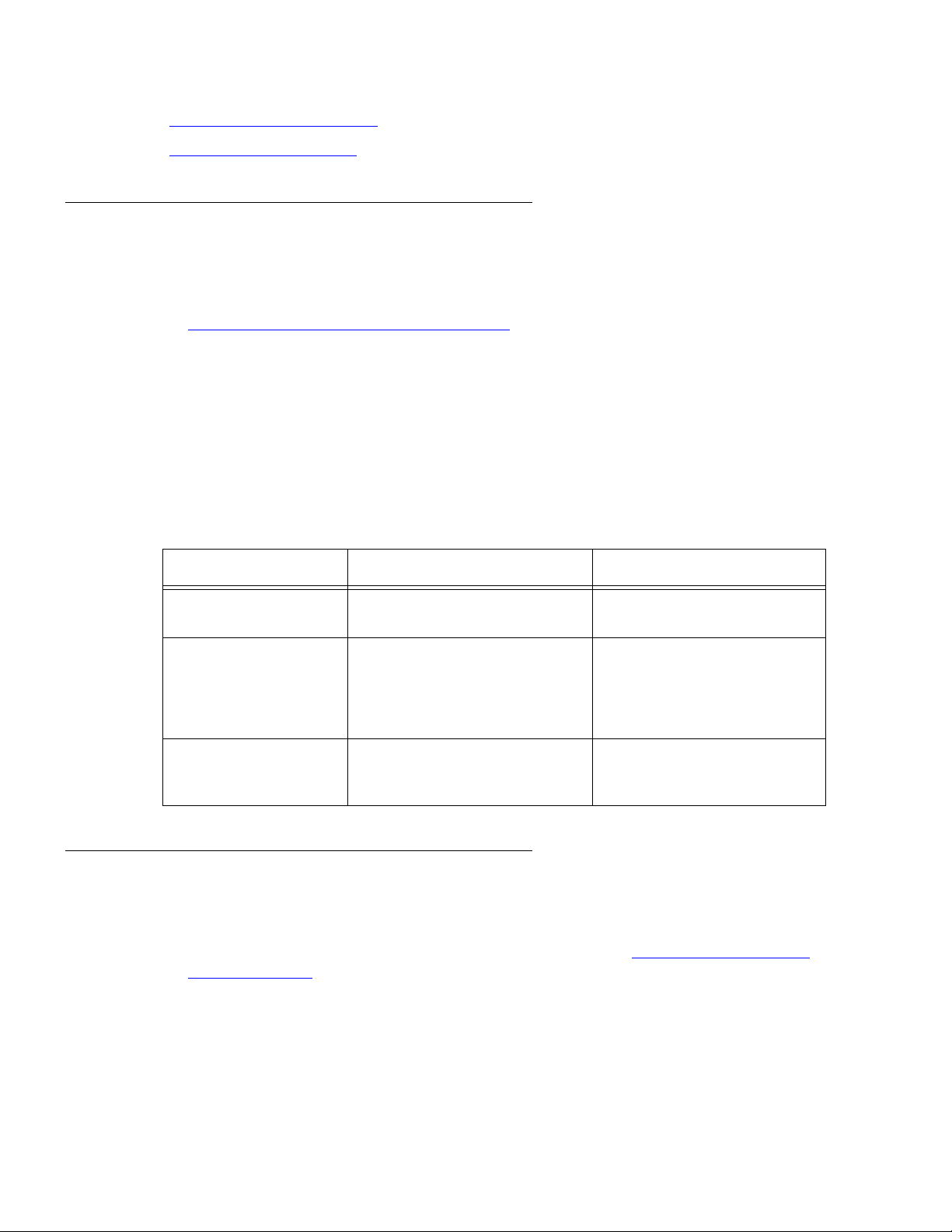
Commands for displaying real-time reports
To view the Enter Where
Split status report monitor bcms split ## ## is an administered split
System status report monitor bcms system ## ## is an administered split
VDN status report monitor bcms vdn ## ## is an administered VDN
Printing real-time reports
To print a real-time report, complete the following steps:
1. Type the monitor command that will print the report. See Commands for printing
real-time reports.
measured by BCMS.
or range of splits measured
by BCMS. ## is optional. If
not included, the report
shows all splits.
extension measured by
BCMS.
2. Press RETURN. The report prints on the printer that is attached to your terminal.
26 BCMS Operations
Page 27
Displaying and printing real-time reports
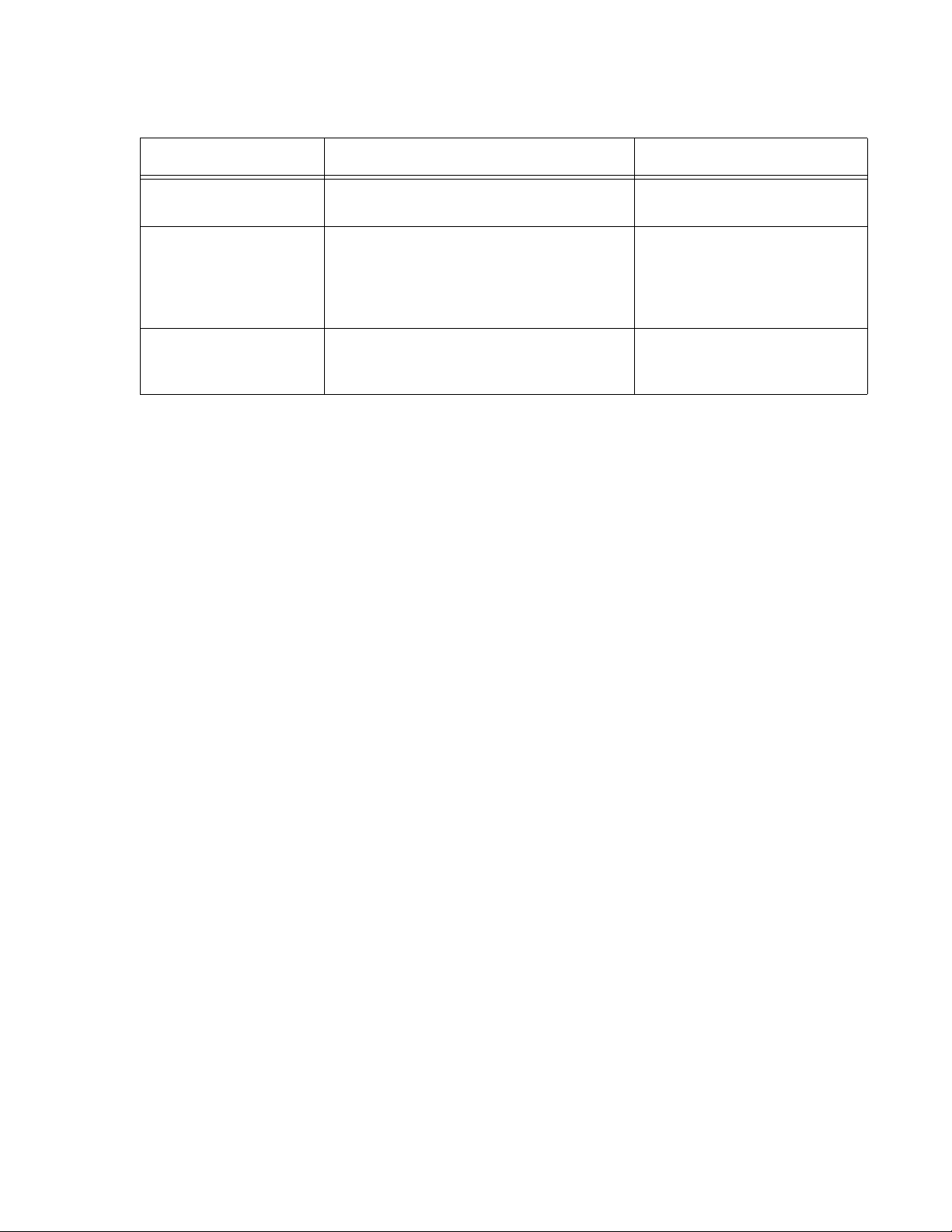
Commands for printing real-time reports
To view the Enter Where
Split status report monitor bcms split ## print ## is an administered split
measured by BCMS.
System status report monitor bcms system ## print ## is an administered split
or range of splits measured
by BCMS. ## is optional. If
not included, the report
shows all splits.
VDN status report monitor bcms vdn ## print ## is an administered VDN
extension measured by
BCMS.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 27
Page 28

Generating reports
Displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports
The list commands are used to display historical information for agents, splits, trunk
groups, and VDNs. There are eight secondary list commands:
list bcms agent
list bcms summary agent
list bcms split
list bcms summary split
list bcms trunk
list bcms summary trunk
list bcms vdn
list bcms summary vdn
With these commands, you can specify:
● Whether you want data that is collected during a specified range of dates or during a
specified period of time. Data collected during a specified period of time is based on
hourly or half-hourly intervals as administered in the BCMS/VuStats Measurement
Interval field on the Feature-Related System Parameters screen.
!
CAUTION:
CAUTION: The switch stores time interval data in a time database that holds a
maximum of 25 intervals. Data for the 26th interval overwrites the first
interval in the time database (and so on). Therefore, if the half-hour option is
selected, care should be exercised to ensure that time interval reports are
run while the data for the desired interval is still available in the time
database. For example, if you select the half-hour option, print the report
twice daily to ensure that you do not lose information.
● The times or days for which you want to see data.
● That the system immediately display the report on your terminal.
● That the system print the report. If you include print at the end of the command, the
system will immediately print the report to the printer attached to the management
terminal. If you include schedule at the end of the command, the system will allow you
to schedule the report to print to the system printer immediately (immediate), at a later
time (deferred), or routinely at specified times (scheduled).
Use the steps in the following topics to display, print, or schedule historical reports.
28 BCMS Operations
Page 29
This section includes the following topics:
● Displaying historical reports on page 29
● Printing historical reports on page 32
● Scheduling historical reports on page 35
Displaying historical reports
To display an historical report, complete the following steps:
1. Type the list command that will display the report you want to view. See Commands
for displaying historical reports on page 29.
2. Press RETURN. The report displays on your screen.
3. Press NEXTPAGE to display subsequent pages and PREVPAGE to display previous
pages if appropriate.
Displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports
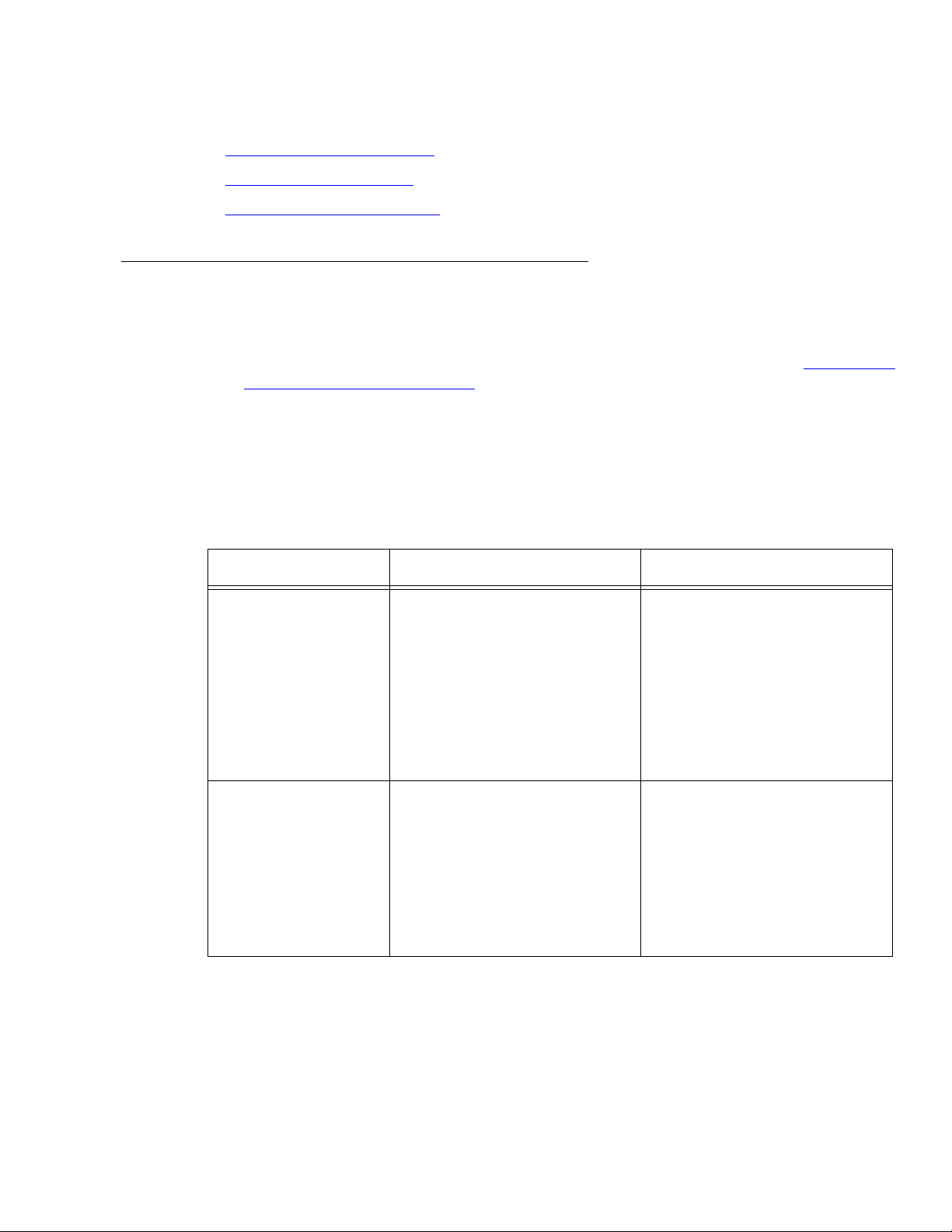
Commands for displaying historical reports
To view the Enter Where
Agent report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms agent ## time
staffed xx:xx xx:xx
## is a valid agent extension
or login ID measured by
BCMS.
staffed lists data only for the
intervals that the agent has
staffed time.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
Agent report (daily) list bcms agent ## day
staffed xx/xx xx/xx
## is a valid agent extension
or login ID measured by
BCMS.
staffed lists data only for the
days that the agent has staffed
time.
The first xx/xx is the start
day. The second xx/xx is the
stop day.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 29
Page 30
Generating reports
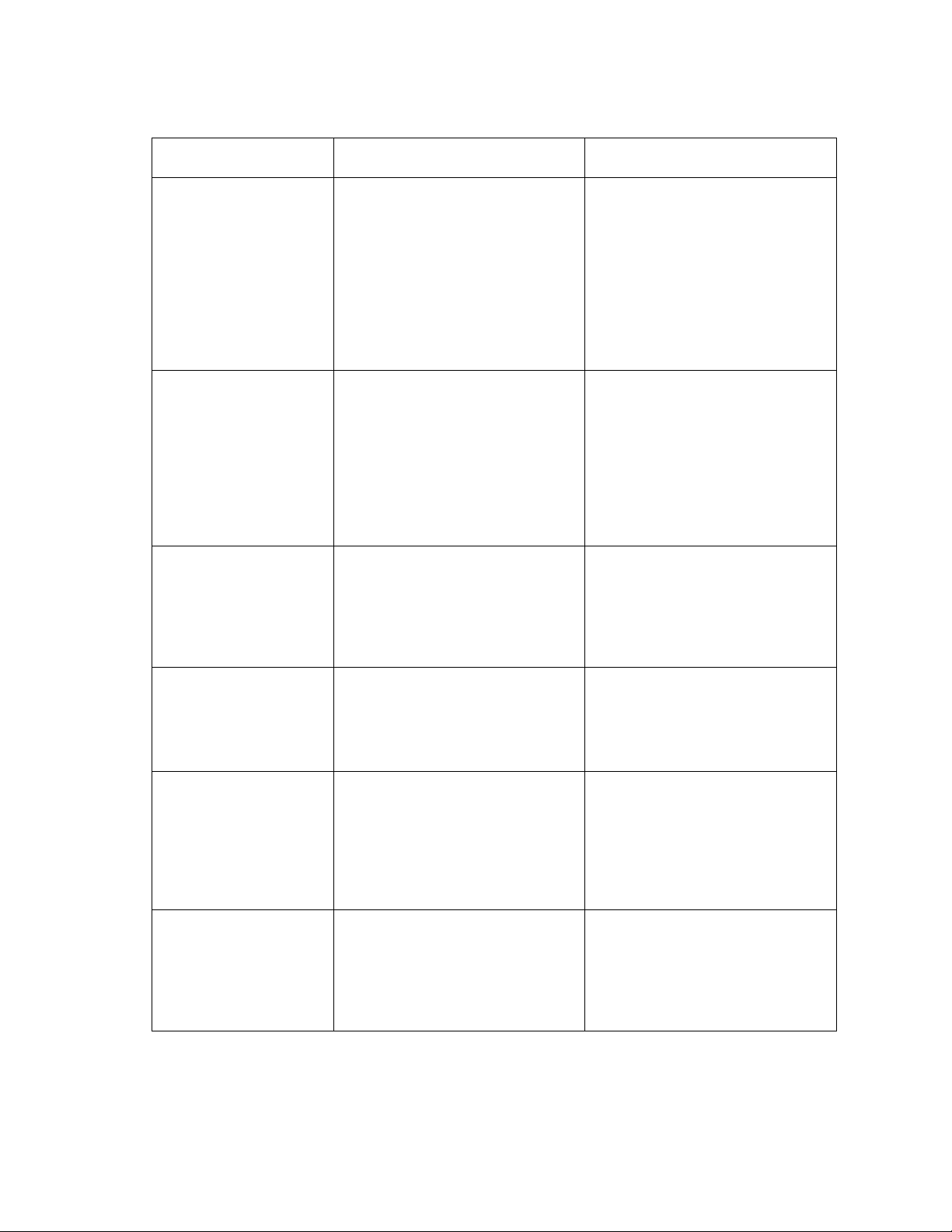
Commands for displaying historical reports (continued)
To view the Enter Where
Agent summary
report (hourly/
half-hourly)
Agent summary
report (daily)
Split report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms summary
agent ## time staffed
xx:xx xx:xx
list bcms summary
agent ## day staffed
xx/xx xx/xx
list bcms split ## time
xx:xx xx:xx
## is a valid agent extension
or login ID or range of
extensions/ login IDs
measured by BCMS.
staffed lists data only for
agents with staffed time.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is a valid agent extension
or login ID or range of
extensions/ login IDs
measured by BCMS.
staffed lists data only for
agents with staffed time.
The first xx/xx is the start
day. The second xx/xx is the
stop day.
## is an administered split
measured by BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
Split report (daily) list bcms split ## day
xx/xx xx/xx
Split summary report
(hourly/half-hourly)
list bcms summary
split ## time xx:xx
xx:xx
Split summary report
(daily)
list bcms summary
split ## day xx/xx xx/
xx
## is an administered split
measured by BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start
day. The second xx/xx is the
stop day.
## is an administered split or
range of splits measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is an administered split or
range of splits measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start
day. The second xx/xx is the
stop day.
30 BCMS Operations
Page 31

Displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports
Commands for displaying historical reports (continued)
To view the Enter Where
Trunk group report
(hourly/half-hourly)
Trunk group report
(daily)
Trunk group
summary report
(hourly/half-hourly)
Trunk group
summary report
(daily)
list bcms trunk ## time
xx:xx xx:xx
list bcms trunk ## day
xx/xx xx/xx
list bcms summary
trunk ## time xx:xx
xx:xx
list bcms summary
trunk ## day xx/xx xx/
xx
## is a trunk group measured
by BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is a trunk group measured
by BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start
day. The second xx/xx is the
stop day.
## is a trunk group or range of
trunk groups measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is a trunk group or range of
trunk groups measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start
day. The second xx/xx is the
stop day.
VDN report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms vdn ## time
xx:xx xx:xx
VDN report (daily) list bcms vdn ## day
xx/xx xx/xx
## is an administered VDN
extension measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is an administered VDN
extension measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start
day. The second xx/xx is the
stop day.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 31
Page 32

Generating reports
Commands for displaying historical reports (continued)
To view the Enter Where
VDN summary report
(hourly/half-hourly)
VDN summary report
(daily)
list bcms summary vdn
## time xx:xx xx:xx
list bcms summary vdn
## day xx/xx xx/xx
Printing historical reports
If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, see Scheduling historical
reports on page 35.
To print an historical report, complete the following steps:
## is an administered VDN
extension or range of
extensions measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is an administered VDN
extension or range of
extensions measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start
day. The second xx/xx is the
stop day.
4. Type the list command for the report that you want to print. See Commands for printing
historical reports on page 33.
32 BCMS Operations
Page 33

Displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports
5. Press RETURN. The report prints on the printer that is attached to your terminal.
Commands for printing historical reports
To print the Enter Where
Agent report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms agent ## time
staffed xx:xx xx:xx
print
Agent report (daily) list bcms agent ## day
staffed xx/xx xx/xx
print
Agent summary
report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms summary agent
## time staffed xx:xx
xx:xx print
## is a valid agent extension or
login ID measured by BCMS.
staffed prints data only for
the intervals that the agent has
staffed time.
The first xx:xx is the start time.
The second xx:xx is the stop
time. Both use a 24-hour clock.
## is a valid agent extension or
login ID measured by BCMS.
staffed prints data only for
the days that the agent has
staffed time.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is a valid agent extension or
login ID or range of extensions/
login IDs measured by BCMS.
staffed prints data only for
agents with staffed time.
The first xx:xx is the start time.
The second xx:xx is the stop
time. Both use a 24-hour clock.
Agent summary
report (daily)
Split report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms summary agent
## day staffed xx/xx
xx/xx print
list bcms split ## time
xx:xx xx:xx print
## is a valid agent extension or
login ID or range of extensions/
login IDs measured by BCMS.
staffed prints data only for
agents with staffed time.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is an administered split
measured by BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start time.
The second xx:xx is the stop
time. Both use a 24-hour clock.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 33
Page 34

Generating reports
Commands for printing historical reports (continued)
To print the Enter Where
Split report (daily) list bcms split ## day
xx/xx xx/xx print
Split summary report
(hourly/half-hourly)
list bcms summary split
## time xx:xx xx:xx
print
Split summary report
(daily)
list bcms summary split
## day xx/xx xx/xx
print
Trunk group report
(hourly/half-hourly)
list bcms trunk ## time
xx:xx xx:xx print
## is an administered split
measured by BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is an administered split or
range of splits measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start time.
The second xx:xx is the stop
time. Both use a 24-hour clock.
## is an administered split or
range of splits measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is a trunk group measured
by BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start time.
The second xx:xx is the stop
time. Both use a 24-hour clock.
Trunk group report
(daily)
Trunk group
summary report
(hourly/half-hourly)
Trunk group
summary report
(daily)
list bcms trunk ## day
xx/xx xx/xx print
list bcms summary trunk
## time xx:xx xx:xx
print
list bcms summary trunk
## day xx/xx xx/xx
print
## is a trunk group measured
by BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is a trunk group or range of
trunk groups measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start time.
The second xx:xx is the stop
time. Both use a 24-hour clock.
## is a trunk group or range of
trunk groups measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
34 BCMS Operations
Page 35

Displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports
Commands for printing historical reports (continued)
To print the Enter Where
VDN report (hourly/
half-hourly)
VDN report (daily) list bcms vdn ## day
VDN summary
report (hourly/
half-hourly)
VDN summary
report (daily)
list bcms vdn ## time
xx:xx xx:xx print
xx/xx xx/xx print
list bcms summary vdn
## time xx:xx xx:xx
print
list bcms summary vdn
## day xx/xx xx/xx
print
## is an administered VDN
extension measured by BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start time.
The second xx:xx is the stop
time. Both use a 24-hour clock.
## is an administered VDN
extension measured by BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is an administered VDN
extension or range of
extensions measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start time.
The second xx:xx is the stop
time. Both use a 24-hour clock.
## is an administered VDN
extension or range of
extensions measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
Scheduling historical reports
The Report Scheduler allows you to schedule the day or days for the system to print the
report. If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, you can use the
Report Scheduler feature to print the report immediately to the system printer. For more
detailed information about the Report Scheduler, see System printer and Report
Scheduler on page 91.
To schedule an historical report, complete the following steps:
1. Type the list command that will schedule the report. See Commands for scheduling
historical reports on page 37.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 35
Page 36

Generating reports
2. Press RETURN.
list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Print Interval: immediate
Note: If you do not have a printer directly connected to your terminal, you can
3. Enter schedule and press RETURN.
The Report Scheduler screen displays on your screen. The cursor is located in the
Print Interval field.
REPORT SCHEDULER
Note:
immediately print the report to the system printer by pressing ENTER.
The Print Time field displays beneath the Print Interval field, and fields for
each day of the week display at the bottom of the screen. The cursor is located in the
Print Time field.
list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Page 1
REPORT SCHEDULER
Date: 11:00 pm MON APR 23, 1990
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list bcms agent ## time xx:xx xx:xx
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: xx:xx
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
4. Enter the time you want the report printed and press RETURN.
The cursor moves to the Sun field.
5. Enter y for the days you want the report printed. Press RETURN to move the cursor to
the next field.
36 BCMS Operations
Page 37

Displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports
6. When you are finished, press ENTER.
The report has been scheduled, and the system presents the enter command: prompt.
!
CAUTION:
CAUTION:
Note:
Note: The commands for scheduling historical reports also can be used to defer
printing of a report to a later time. See Report Scheduler
on page 94 for
more information.
Commands for scheduling historical reports
To Print the Type Where
Agent report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms agent ## time
staffed xx:xx xx:xx
schedule
Agent report (daily) list bcms agent ## day
staffed xx/xx xx/xx
schedule
Agent summary
report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms summary agent
## time staffed xx:xx
xx:xx schedule
## is a valid agent extension or
login ID measured by BCMS.
staffed prints data only for
the intervals that the agent has
staffed time.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is a valid agent extension or
login ID measured by BCMS.
staffed prints data only for
the days that the agent has
staffed time.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is a valid agent extension or
login ID or range of extensions/
login IDs measured by BCMS.
staffed prints data only for
agents with staffed time.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 37
Page 38

Generating reports
Commands for scheduling historical reports (continued)
To Print the Type Where
Agent summary
report (daily)
list bcms summary agent
## day staffed xx/xx
xx/xx schedule
Split report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms split ## time
xx:xx xx:xx schedule
Split report (daily) list bcms split ## day
xx/xx xx/xx schedule
Split summary report
(hourly/half-hourly)
list bcms summary split
## time xx:xx xx:xx
schedule
## is a valid agent extension or
login ID or range of extensions/
login IDs measured by BCMS.
staffed prints data only for
agents with staffed time.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is an administered split
measured by BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is an administered split
measured by BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is an administered split or
range of splits measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
Split summary report
(daily)
Trunk group report
(hourly/half-hourly)
Trunk group report
(daily)
38 BCMS Operations
list bcms summary split
## day xx/xx xx/xx
schedule
list bcms trunk ## time
xx:xx xx:xx schedule
list bcms trunk ## day
xx/xx xx/xx schedule
## is an administered split or
range of splits measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is a trunk group measured
by BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is a trunk group measured
by BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
Page 39

Displaying, printing, and scheduling historical reports
Commands for scheduling historical reports (continued)
To Print the Type Where
Trunk group
summary report
(hourly/half-hourly)
Trunk group
summary report
(daily)
VDN report (hourly/
half-hourly)
list bcms summary trunk
## time xx:xx xx:xx
schedule
list bcms summary trunk
## day xx/xx xx/xx
schedule
list bcms vdn ## time
xx:xx xx:xx schedule
VDN report (daily) list bcms vdn ## day
xx/xx xx/xx schedule
## is a trunk group or range of
trunk groups measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is a trunk group or range of
trunk groups measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
## is an administered VDN
extension measured by BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is an administered VDN
extension measured by BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
VDN summary report
(hourly/half-hourly)
VDN summary report
(daily)
list bcms summary vdn
## time xx:xx xx:xx
schedule
list bcms summary vdn
## day xx/xx xx/xx
schedule
## is an administered VDN
extension or range of
extensions measured by
BCMS.
The first xx:xx is the start
time. The second xx:xx is the
stop time. Both use a 24-hour
clock.
## is an administered VDN
extension or range of
extensions measured by
BCMS.
The first xx/xx is the start day.
The second xx/xx is the stop
day.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 39
Page 40

Generating reports
40 BCMS Operations
Page 41

Report reference
This section includes a quick reference to the commands that you can use to display, print,
and schedule BCMS reports. See Generating reports
instructions for displaying, printing, and scheduling reports.
The remainder of this chapter describes each report in detail, providing a brief description
of each report, sample reports, and a description of the information contained in each
report.
Note:
Note: Most BCMS measurement data is collected at the end of a call, whereas
hunt group measurements count calls as soon as they begin. Therefore,
calls spanning a time interval boundary will be counted differently by the
two. If comparing the measurements from BCMS with those from the hunt
groups, there may be slight differences. However, both hunt group and
BCMS measurements should indicate the same trends.
This section includes the following topics:
● Report commands on page 41
on page 25 for more detailed
● Real-time reports on page 43
● Historical reports on page 54
Report commands
The following table is a quick reference to the commands that you can use to display, print,
and schedule BCMS reports.
.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 41
Page 42

Report reference
Report commands table
Action Object Qualifiers
monitor bcms split split number [print]
bcms system [split number] [print]
bcms vdn extension [print]
3
list bcms agent extension|loginID
[time] [staffed] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
extension|loginID [day] [staffed] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
bcms summary agent extension|loginID [time] [staffed] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
extension|loginID [day] [staffed] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
bcms split split number [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
split number [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
bcms summary split split number [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
split number [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
bcms trunk group number [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
group number [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
1 2
bcms summary trunk group number [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
group number [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
bcms vdn extension [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
extension [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
bcms summary vdn extension [time] [start time] [stop time] [print|schedule]
extension [day] [start day] [stop day] [print|schedule]
1. Items depicted within brackets, such as [print], are optional. Items separated by a “pipe” symbol, such as
“extension|loginID” indicate that you must select one or the other.
2. Whenever the command line qualifier [schedule] is initially executed, the system defaults the report for immediate
printing (unless a day/time of day is scheduled) and generates a Job ID. The Job ID is required by the Report
Scheduler feature for updating and deleting the schedule of reports
3. If BCMS/VuStats Login IDs is enabled on the System-Parameters Customer-Options screen, you must enter an agent
login ID or a range of login IDs in place of the physical extension or range of extensions.
42 BCMS Operations
Page 43

Real-time reports
BCMS provides three real-time reports:
● BCMS split status
● BCMS system status
● BCMS VDN status
The BCMS split status report provides the current (real-time) status and cumulative
measurement data for those agents assigned to the split you specify. The BCMS system
status report provides current (real-time) status information for either all BCMS splits or
selected splits. The BCMS VDN status report provides the current (real-time) status and
cumulative measurement data for VDNs monitored by BCMS.
This section includes the following topics:
● Split status report on page 43
● System status report on page 47
Real-time reports
● VDN status report on page 50
Split status report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 43
● Description on page 43
● Sample report on page 44
● Header definitions on page 44
Command
monitor bcms split (split number) [print]
Description
The BCMS split status report provides the current (real-time) status and cumulative
measurement data for those agents assigned to the split you specify. This report displays
data accrued since the last interval boundary. For example, if the interval is set for hourly,
and you issue the command to display the BCMS Split Status report at 11:10 a.m., the
report displays the data accrued since 11:00 a.m. Although this report is updated
Issue 5.0 May 2005 43
Page 44

Report reference
approximately every 30 seconds, you can immediately update the information on the
screen by pressing UPDATE. At the beginning of the next interval, the report resets.
Sample report
monitor bcms split 30 Page 1 of 1
BCMS SPLIT (AGENT) STATUS
Split: 30 Date: 14:25 FRI OCT 26 2001
Split Name: HNT-61
Calls Waiting: 5 Acceptable Service Level: 20
Oldest Call: 1:39 % Within Service Level:
Staffed: 7 Avail: 1 ACD: 1 ACW: 2 AUX: 2 Extn Calls: 2 Other: 1
ACD EXT IN EXT OUT
AGENT NAME LOGIN ID EXT STATE TIME CALLS CALLS CALLS
Agent 1 32191 12345 Avail 12:00 0 0 0
Agent 2 32192 12346 ACD 12:04 1 0 0
Agent 3 32193 12347 ACW 12:12 3 0 0
Agent 4 32194 12348 AUX 11:30 0 0 0
Agent 5 32195 12349 Ext In 12:08 1 2 0
Agent 6 32196 12350 Ext Out 12:10 0 0 1
Agent 7 32197 12351 Other 11:58 0 0 0
$ 32198 12352 INIT 00:00 0 0 0
Header definitions
Split status report
Header Definition
Split The split number specified with the command line.
Split Name The administered name of the split. This name usually describes the
Calls Waiting The number of calls currently queued and calls ringing at an agent
purpose or service of the split (for example, sales, service, or help line). If
no name exists, BCMS displays the split extension (for example,
EXT 65222).
The split name is limited to a maximum of 11 characters. If you enter
more than 11 characters, the additional characters are not printed on the
system printer.
telephone. If any of the calls in the queue are Direct Agent calls, an
asterisk displays before the value in this field.
44 BCMS Operations
Page 45

Real-time reports
Split status report (continued)
Header Definition
Oldest Call The number of minutes and seconds that the oldest call in queue has
been waiting to be answered. This includes calls ringing at an agent
telephone.
Acceptable
Service Level
% Within
Service Level
The desired time for an agent to answer a call for a given hunt group or
VDN. Timing for a call begins when the call enters the hunt group queue.
The percentage of calls answered within the administered service level.
This field is blank if no calls have been recorded for this time interval or if
there is no Acceptable Service Level administered on the Hunt Group
screen.
Staffed The number of agents currently logged into the split. Staffed equals
available agents, agents on ACD calls and agents in ACW, AUX, and
Other.
Avail The number of agents in this split currently available to receive an ACD
call. In order to be counted as being available, agents must be in either
Auto-In (AI) or Manual-In (MI) work mode. If the agent is on another split
call or is performing After Call Work for another split, the agent is not
considered available and is not recorded here. If a call is ringing at the
agent telephone or a call is on hold, the agent is not considered available
unless Multiple Call Handling is active and the agent selects AI/MI with a
call on hold.
ACD The number of agents who are currently on an ACD call for this split. This
value also includes Direct Agent calls and those agents who are currently
on ACD calls that flowed in from another split.
ACW The number of agents in this split who are currently in ACW mode for this
split. If an agent is in ACW mode for another split, the agent is included in
the Other state count for this split. ACW includes agents who are on
extension-in and extension-out calls while in ACW.
AUX The number of agents in this split who are currently in the AUX work
mode for this split. If an agent is answering a call from another split or is
in ACW work mode for another split, that agent is not considered in AUX
work mode for this split and is not included in this number. The agent is
included in the Other state count. AUX includes agents who are on
extension-in and extension-out calls while in AUX, Auto-In, and
Manual-In.
Extn Calls The number of agents in this split who are currently on non-ACD calls.
These non-ACD calls may be either incoming (direct to the extension) or
outgoing (direct from the extension). Those agents receiving or making
extension calls while available, or while in the ACW or AUX work modes
are recorded as being on extension calls.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 45
Page 46

Report reference
Split status report (continued)
Other The number of agents in this split who:
Header Definition
● Are on a call from another split
● Are in ACW work mode for another split
● Have placed a call on HOLD and made no other state selections
● Have a call ringing at their telephones
● Are dialing a number (to place a call or activate a feature)
All of the agents in the Other state are unavailable for ACD calls.
AGENT
NAME
The name of the agent. Generally, this is the first or last name of the
agent. However, if no name is administered on the telephone display, this
field is left blank. When the field is blank, the data can be identified by the
extension.
LOGIN ID The BCMS login IDs (taken from the BCMS/VuStats Login ID screen or
EAS Login screen) for which you requested the report. This column is
empty if BCMS login IDs are not optioned.
EXT The extension number for the agent.
STATE The current work state for the agent. Possible work states are Avail,
ACD, ACW, AUX, Extn, and Other. Unstaffed agents do not display on
the report. When the system time is changed, agents are in the INIT
state. Each agent remains in the INIT state until that agent takes a call or
pushes a work mode button.
TIME The 24-hour clock time at which the agent entered this work state.
ACD CALLS The number of ACD calls that the agent has completed since the
beginning of the current interval. This value includes any calls that flowed
in from other splits. (Calls in process are not counted until they are
completed.)
EXT IN
CALLS
The number of non-ACD calls that the agent has received (incoming)
since the beginning of the current interval. (Calls in process are not
counted until they are completed.) The maximum value is 255.
If an extension-in call is active for less than the time set for the Abandon
Call Timer, the call will not be counted in this field. The duration of such
calls is counted as AUX/OTHER time.
EXT OUT
CALLS
46 BCMS Operations
The number of non-ACD calls that the agent has made (outgoing) since
the beginning of the current interval. (Calls in process are not counted
until they are completed.) The maximum value is 255.
Page 47

System status report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 47
● Description on page 47
● Sample report on page 48
● Header definitions on page 48
Command
monitor bcms system [split number] [print]
Description
The BCMS system status report provides current (real-time) status information for either all
BCMS splits or selected BCMS splits. This report displays data accrued since the last
interval boundary. For example, if the interval is set to hour, and you issue the command to
display the BCMS system status report at 11:10 a.m., the report displays the data accrued
since 11:00 a.m. Although this report is updated approximately every 30 seconds, you can
immediately update the information on the screen by pressing UPDATE. This report is
reset at the beginning of the time interval (for example, hour or half-hour).
Real-time reports
When analyzing this report, keep the following things in mind:
● All averages are for completed calls only.
● A completed call may span more than one time interval. ACD calls that are in process
(have not terminated) are counted in the time interval in which they terminate. For
example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval, but terminates in
the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval, the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00
time interval.
● Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has been exceeded.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 47
Page 48

Report reference
Sample report
monitor bcms system
SPLIT NAME WAIT CALL ANS AGENT CALLS TIME CALLS TIME CALL LEVL
Service 3 1:03 :45 0 3 :30 20 2:30 1:25 85
EXT 4000 5 :33 :15 0 11 :45 36 1:32 :35 91
Header definitions
System status report
Header Definition
BCMS SYSTEM STATUS
Date: 12:53 MON MAY 15, 1995
AVG AVG AVG AVG % IN
CALLS OLDEST SPEED AVAIL ABAND ABAND ACD TALK AFTER SERV
SPLIT NAME The name of the split (for example, sales, service, or help line). If no
name exists, the split extension (for example, EXT 12345) is displayed.
CALLS WAIT The number of calls in the split queue that are currently waiting to be
answered and calls ringing at an agent telephone. If any of the calls in
the queue are Direct Agent calls, an asterisk displays before this field.
OLDEST
CALL
The number of minutes and seconds the oldest call in queue has been
waiting to be answered. This includes calls ringing at an agent
telephone.
48 BCMS Operations
Page 49

System status report (continued)
Header Definition
Real-time reports
AVG SPEED
ANS
The average amount of time it takes before the calls are answered by
agents. This value includes time waiting in the queue and time ringing at
the agent telephone. The calculation is:
Sum of Each Completed Call's Time In Queue + Time Ringing
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Number of ACD Calls Answered
Keep the following things in mind:
● Calls that flow in from other splits do not include time in queue from
the other splits in this calculation. Also, the AVG SPEED ANS does
not include time spent listening to a forced first announcement.
● A completed call may span more than one time period. ACD calls
that are in process (have not terminated) are counted in the time
period in which they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins in
the 10:00 to 11:00 time period, but terminates in the 11:00 to 12:00
time period, the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00
time period.
● Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has
been exceeded.
AVAIL AGENT The number of agents in this split who are currently available to receive
an ACD call directed to this split.
ABAND
CALLS
The total number of ACD callers that have hung up while waiting to be
answered. This includes those calls that have abandoned while in
queue or while ringing. Calls that are not queued (for example, because
the queue is full, the caller receives a forced first announcement and
abandons during the announcement, or because no agents are staffed)
are not counted as abandoned for the hunt group.
AVG ABAND
TIME
The average time before an ACD call abandons. This does not include
any time spent in another split queue before intraflowing to this split.
The calculation is:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Abandon Time
Total Number of Abandoned Calls
This value does not include time spent listening to a forced first
announcement or calls that abandon while listening to a forced first
announcement.
ACD CALLS The number of ACD calls completed during the current interval. This
number also includes those calls that flow in from other splits.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 49
Page 50

Report reference
System status report (continued)
Header Definition
AVG TALK
TIME
AVG AFTER
CALL
The average duration of ACD calls for each split. This calculation
includes the time each agent spent talking but does not include ring time
at an agent telephone. Split talk time appears less than the VDN talk
time in the reports. This is because AVG TALK/HOLD time by VDN
includes the time spent on hold while the split/agent AVG TALK does
not. Also, VDN talk time does not include talk time for a call that
becomes part of a conference while split/agent talk time does. This
situation will show a greater talk time for the split.
The calculation is:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total ACD Talk Time
Total Number of ACD Calls Answered
The average ACW time for call-related ACW time completed by agents
in this split during this time interval. Call-related ACW is the time that
occurs immediately after an ACD call (that is, when an agent was in
Manual mode and an ACD call ended, or when the agent presses the
ACW button during an ACD call). AVG AFTER CALL does not include
time spent on direct incoming or outgoing calls while in ACW or time that
immediately follows an EXTN call. The calculation is:
Total Call-Related ACW Time
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Number of Call-Related ACW Sessions
The average is for ACW sessions, which may not correspond to the
number of ACD calls, either because some ACD calls did not have ACW
time or because the call was recorded in another interval.
% IN SERV
LEVL
VDN status report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 51
● Description on page 51
The percentage of calls answered within the administered service level
for this split. Calculation is based on the following
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
accepted * 100
ACDcalls + abandons + outflows + dequeued
where:
● accepted is calls answered whose queue time was less than or
equal to the administered service level for the split.
● dequeued is a call that encountered the split queue, but which was
not answered, abandoned, or outflowed. This occurs with multiple
split queuing.
50 BCMS Operations
Page 51

● Sample report on page 51
● Header definitions on page 51
Command
monitor bcms vdn extension [print]
Description
The VDN status report gives real-time status information for internally measured VDNs.
You must specify the extensions of the VDNs you want the system to monitor. You can
specify the extensions in a list or in a range format.
For example, monitor bcms vdn 123456 123467 123530-123539.
Sample report
monitor bcms vdn 12345-12349
Real-time reports
BCMS VECTOR DIRECTORY NUMBER STATUS
Date: 15:30 Mon May 15, 1995
AVG AVG AVG CALLS % IN
CALLS OLDEST ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK/ CONN FLOW BUSY/ SERV
VDN NAME WAIT CALL CALLS ANS CALLS TIME HOLD CALLS OUT DISC LEVL
knives 5 :25 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 91
EXT 12346* 0 :00 0 :00 0 :00 :00 0 0 0 0
Header definitions
VDN status report
Header Definition
Date The current date and time (updated every 30 seconds or when Update is
pressed).
VDN NAME The name of the VDN being reported. If the VDN does not have a name
administered, this field displays EXT ## where ## is the VDN extension.
CALLS WAIT The number of calls that encountered this VDN and have not been
answered, abandoned, outflowed, or forced busy/disc. Includes calls in
queues, in vector processing, and ringing at an agent telephone.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 51
Page 52

Report reference
VDN status report (continued)
Header Definition
OLDEST
CALL
ACD CALLS The number of completed ACD calls answered in a BCMS-measured
AVG SPEED
ANS
The time the oldest call currently waiting has waited in the VDN. Timing
starts when the call enters the VDN.
split. The split may have been reached via the queue-to-main, check
backup, route-to, messaging split, or adjunct routing commands.
Includes Direct Agent calls (EAS only).
The average speed of answer for ACD and connect calls (see CONN
CALLS below) that have completed for this VDN during the current
period. This includes the time in vector processing, in a split queue, and
time ringing. The calculation is:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Answer Time
Total ACD Calls + Total CONNect CALLS
Answer time for a call is recorded when the call ends. For example, if a
call originates in interval x, is answered in interval y, and ends in interval
z, the associated answer and talk times are recorded in interval z.
ABAND
CALLS
AVG ABAND
TIME
The number of calls to this VDN that have abandoned before being
answered during the current period. This includes VDN calls that were
routed to an attendant, telephone, or announcement, and abandoned
before being answered.
The average time abandoned calls waited before abandoning during the
current period. The calculation is:
Total Abandon Time
-----------------------------------------------------------Total Calls Abandoned
AVG TALK /
HOLD
CONN CALLS The number of completed calls that were routed to a telephone,
FLOW OUT The number of calls that were routed to another VDN or to a trunk,
52 BCMS Operations
The average talk time for ACD calls completed by this VDN during the
current period. This does not include ring time, but it does include any
time the caller spent on hold. Split talk time appears less than the VDN
talk time in the reports. This is because AVG TALK/HOLD time by VDN
includes the time spent on hold while the split/agent AVG TALK does not.
Also, VDN talk time does not include talk time for a call that becomes
part of a conference while split/agent talk time does. This situation will
show a greater talk time for the split.
The calculation is:
Total Talk Time
----------------------------------------ACD Calls
attendant, announcement, messaging split, or call pickup and were
answered there.
including successful look-ahead attempts.
Page 53

VDN status report (continued)
Header Definition
Real-time reports
CALLS
BUSY/DISC
% IN SERV
LEVL
The number of calls that were forced busy or forced disconnect during
the current interval. This value includes:
● Calls that encountered a busy or disconnect vector step
● Calls disconnected by a stop vector step
● Calls forwarded to a split with a full queue
● Calls forwarded to a split with no available agents and no queue
This value does not include abandoned calls.
The percent of calls offered that completed and were answered within
the acceptable service level defined on the VDN screen. The calculation
is:
accepted * 100
---------------------------------------calls offered
calls offered is defined as:
acdcalls + flowout calls + abandoned + connect + busy/disc
accepted is the number of ACD and CONNect calls that were answered
within the administered service level. This field is blank if no calls were
recorded for this time interval. This field is also blank if no Acceptable
Service Level has been administered on the VDN screen.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 53
Page 54

Report reference
Historical reports
BCMS provides eight historical reports. These reports give you information for an interval
of time. You can print the reports for a period of time measured in minutes or hours, or a
period of time measured in days.
This section includes the following topics:
● Types of BCMS historical reports on page 54
● Agent report on page 55
● Agent summary report on page 59
● Split report on page 63
● Split summary report on page 68
● Trunk group report on page 74
● Trunk group summary report on page 78
● VDN report on page 82
● VDN summary report on page 86
Types of BCMS historical reports
The types of BCMS historical reports are as follows:
● Agent
● Agent summary
● Split
● Split summary
● Trunk group
● Trunk group summary
● VDN
● VDN summary
54 BCMS Operations
Page 55

Agent report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 55
● Description on page 55
● Sample reports on page 56
● Header definitions on page 57
Command
list bcms agent extension/loginID [time] [staffed] [start time]
[stop time][print/schedule]
list bcms agent extension/loginID [day] [staffed] [start day]
[stop day] [print/schedule]
Description
Historical reports
The BCMS agent report provides traffic information for the specified agent. Depending on
specifics from the command line, the information may be displayed as either a time interval
or a daily summary. If neither time nor day is specified, time is the default. In this case, the
report displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour), including
data from the most recently completed time interval. To get information on the current time
interval, you must use a monitor bcms command.
When analyzing this report, keep the following in mind:
● All averages are for completed calls only.
● A completed call may span more than one time interval. ACD calls that are in process
(have not terminated) are counted in the time interval in which they terminate. For
example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval, but terminates in
the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval, the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00
time interval.
Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has been exceeded.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 55
Page 56

Report reference
Sample reports
Hourly report
list bcms agent 4222 8:00
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Agent: 4222
Agent Name: s-jones
TIME CALLS TIME CALL TIME OTHER CALLS TIME STAFFED TIME
8:00- 9:00 10 1:15 7:30 25:00 10:40 1 4:00 60:00 :20
9:00-10:00 18 1:40 18:00 4:20 :00 2 3:20 60:00 1:00
10:00-11:00 10 1:20 8:20 16:10 :00 0 :00 38:00 :10
----------- ----- ------ ------- ------- ------- ----- ----- -------- -----SUMMARY 38 1:28 33:50 45:30 10:40 3 3:33 158:00 1:30
BCMS AGENT REPORT
AVG TOTAL TOTAL TOTAL AVG TOTAL TOTAL
ACD TALK AFTER AVAIL AUX/ EXTN EXTN TIME HOLD
Daily report
list bcms agent 4222 day 5/13
BCMS AGENT REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Agent: 4222
Agent Name: s-jones
AVG TOTAL TOTAL TOTAL AVG TOTAL TOTAL
ACD TALK AFTER AVAIL AUX/ EXTN EXTN TIME HOLD
DAY CALLS TIME CALL TIME OTHER CALLS TIME STAFFED TIME
5/14/95 200 1:30 100:00 35:00 80:00 10 2:00 540:00 5:00
5/13/95 38 1:28 34:12 45:30 10:40 3 3:33 158:00 1:30
----------- ----- ------ ------- ------- ------- ----- ----- -------- -----SUMMARY 238 1:30 134:12 80:30 90:40 13 2:22 698:00 6:30
56 BCMS Operations
Page 57

Header definitions
Agent report
Header Definition
Agent The extension or login ID of the agent.
Agent Name The name of the agent. If no name is administered, this field displays EXT
TIME/DAY The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Historical reports
## where ## is the agent extension.
Time is always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are
optional. Reports always start at the earliest time interval (either hour or
half-hour). If no start time is given, the oldest time interval is the default. A
stop time requires an associated start time. If no stop time is given, the
last completed time interval (hour or half-hour) is the default. If no start
time or stop time is given, the report displays data accrued for the
previous 24 time intervals. If you specify day in the command and do not
include a start day or stop day, the report displays data accrued for the
previous 6 days and data accrued through the most recently completed
interval (hour or half-hour) for the current day.
ACD CALLS The number of ACD calls answered by this agent for all splits during the
reporting interval. This value includes calls that flowed in from other splits
and Direct Agent calls.
AVG TA L K
TIME
The average duration of ACD calls for all splits the agent was logged into.
This value includes time spent talking but does not include the amount of
time the agent was holding an ACD call or ring time at the agent
telephone. Split talk time appears less than the VDN talk time in the
reports. This is because AVG TALK/HOLD time by VDN includes the time
spent on hold while the split/agent AVG TALK does not. Also, VDN talk
time does not include talk time for a call that becomes part of a
conference while split/agent talk time does. This situation will show a
greater talk time for the split.
The calculation is:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total ACD Talk Time
Total Number of ACD Calls Answered
TOTAL
AFTER CALL
The total amount of time that the agent spent in call-related or
non-call-related ACW work states for all splits during the reporting
interval. This includes time agents spent on extension-in and
extension-out calls while in the ACW work mode. If an agent entered
ACW in one interval, but ended ACW in another interval, the appropriate
amount of ACW time is credited to each of the intervals.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 57
Page 58

Report reference
Agent report (continued)
Header Definition
TOTAL AVAIL
TIME
TOTAL AUX/
OTHER
The sum of the time that the agent was available to receive ACD calls
during the reporting interval. During this time, the agent:
● Was in Auto-In or Manual-In work mode for at least one split
● Was not in ACW in any split
● Was not on any call or placing any call (unless Multiple Call Handling
[MCH] is active)
● Did not have ringing calls
The total time that this agent was unavailable to receive calls in any split
during the reporting interval.
A split totals AUX TIME whenever any agent is logged into the split and:
● Receives an EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
● Makes an EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
● Presses his or her AUX button
Note that if the agent was in Other for all logged-in splits, that time is
reflected here. For example, ringing calls can cause several seconds of
AUX/OTHER time to accrue.
For the agent report, any non-ACD call time is also totaled in the AVG
EXTN TIME column. Two points of contrast are:
● The measurement TOTAL AUX/OTHER is time-interval based, rather
than call-related. For example, assuming that the previously identified
stipulations are met, if the agent is in AUX from 9:55 to 10:05, 5
minutes is recorded in the 9:00 to 10:00 time interval and 5 minutes is
recorded in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
● The measurement AVG EXTN TIME is call related. For example, if an
agent is on a non-ACD call from 9:55 to 10:05, the call and 10 minutes
of EXTN time is recorded in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
Because the agent report includes some call-related items, the sum of all
items for a given hour may not exactly equal 60 minutes.
EXTN CALLS The total number of non-ACD incoming and outgoing calls for this agent
AVG E X T N
TIME
58 BCMS Operations
during the reporting interval. Only those non-ACD calls that are originated
and/or received while the agent is logged into at least one split are
counted.
If an extension-in call is active for less than the time set for the Abandon
Call Timer, the call will not be counted in this field.
The average amount of time that the agent spent on non-ACD calls while
logged into at least one split during the reporting interval. This average
does not include time when the agent was holding the EXTN call. The
calculation is:
Total Ext Time
-------------------------------------------------------------------Total Number of Ext Calls
If an extension-in call is active for less than the time set for the Abandon
Call Timer, the call will not be counted and the duration of the call will be
counted as AUX/OTHER time.
Page 59

Agent report (continued)
Header Definition
Historical reports
TOTAL TIME
STAFFED
The total time that the agent spent logged into at least one split during the
reporting interval. Staff time is clocked for an agent who is in multiple
splits as long as the agent is logged into any split. Concurrent times for
each split are not totaled.
TOTAL
HOLD TIME
The total time that the agent placed ACD calls on hold. This time is the
caller hold time and is independent of the state of the agent. TOTAL
HOLD TIME does not include the hold time for non-ACD calls.
SUMMARY The total of each of the columns that do not contain averages. Columns
that do contain averages are the total time divided by the total number of
calls.
Agent summary report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 59
● Description on page 59
● Sample reports on page 60
● Header definitions on page 61
Command
Description
This report is similar to the BCMS agent report except that this report provides one line of
data for each agent. You can specify one or more agents by entering agent IDs or
extensions. Data for an agent does not appear on the report if there is no data for that
agent. If you specify that you want the report to include more than one time period, and the
data exists for one or more, but not all of the specified times, the system uses the available
data to calculate and display the one-line summary; the system does not identify which
times are not included in the calculations.
list bcms summary agent extension|loginID [time] [staffed]
[start time] [stop time][print/schedule]
list bcms summary agent extension|loginID [day] [staffed]
[start day] [stop day] [print/schedule]
Issue 5.0 May 2005 59
Page 60

Report reference
Sample reports
Hourly summary
list bcms summary agent 4222-4224 4869 time 8:00-12:00
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Time: 8:00-12:00
AGENT NAME CALLS TIME CALL TIME OTHER CALLS TIME STAFFED TIME
s-jones 10 1:15 7:30 25:00 10:40 1 4:00 60:00 :20
t-anderson 18 1:40 18:00 4:20 :00 2 3:20 60:00 1:00
j-jacobsen 10 1:20 8:20 16:10 :00 0 :0 38:00 :10
----------- ----- ------ ------- ------- ------- ----- ----- -------- -----SUMMARY 38 1:28 33:50 45:30 10:40 3 3:33 158:00 1:30
BCMS AGENT SUMMARY REPORT
AVG TOTAL TOTAL TOTAL AVG TOTAL TOTAL
ACD TALK AFTER AVAIL AUX/ EXTN EXTN TIME HOLD
Daily summary
list bcms sum agent 4222-4223 4869 day 5/14
BCMS AGENT SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Day: 5/14
AVG TOTAL TOTAL TOTAL AVG TOTAL TOTAL
ACD TALK AFTER AVAIL AUX/ EXTN EXTN TIME HOLD
AGENT NAME CALLS TIME CALL TIME OTHER CALLS TIME STAFFED TIME
s-jones 10 1:15 7:30 25:00 10:40 1 4:00 60:00 :20
t-anderson 18 1:40 18:00 4:20 :00 2 3:20 60:00 1:00
j-jacobsen 10 1:20 8:20 16:10 :00 0 :0 38:00 :10
----------- ----- ------ ------- ------- ------- ----- ----- -------- -----SUMMARY 38 1:28 33:50 45:30 10:40 3 3:33 158:00 1:30
60 BCMS Operations
Page 61

Header definitions
Agent summary report
Header Definition
Time/Day The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Historical reports
Time is always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are
optional. Reports always start at the earliest time interval (either hour or
half-hour). If no start time is given, the most recent time interval is the
default. A stop time requires an associated start time. If no stop time is
given, only the start interval/day is used. If no start time or stop time is
given, the most current interval/day is used. If you specify day in the
command and do not include a start day or stop day, the report displays
data for the current day accrued through the most recently completed
interval (hour or half-hour).
AGENT
NAME
ACD CALLS The number of ACD calls answered by this agent for all splits during the
AVG TA L K
TIME
The name of the agent. If no name is administered, this field displays
EXT ## where ## is the agent extension.
reporting interval. This value includes calls that flowed in from other
splits and Direct Agent calls.
The average duration of ACD calls for all splits the agent was logged
into. This value includes time spent talking but does not include the
amount of time the agent was holding an ACD call or ring time at the
agent telephone. Split talk time appears less than the VDN talk time in
the reports. This is because AVG TALK/HOLD time by VDN includes the
time spent on hold while the split/agent AVG TALK does not. Also, VDN
talk time does not include talk time for a call that becomes part of a
conference while split/agent talk time does. This situation will show a
greater talk time for the split.
The calculation is:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total ACD Talk Time
Total Number of ACD Calls Answered
TOTAL
AFTER CALL
The total amount of time that the agent spent in call-related or
non-call-related ACW work states for all splits during the reporting
interval. This includes time agents spent on extension-in and
extension-out calls while in the ACW work mode. If an agent entered
ACW in one interval, but ended ACW in another interval, the appropriate
amount of ACW time is credited to each of the intervals.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 61
Page 62

Report reference
Agent summary report (continued)
Header Definition
TO TAL AVAIL
TIME
TOTAL AUX/
OTHER
The sum of the time that the agent was available to receive ACD calls
during the current interval. During this time, the agent:
● Was in Auto-In or Manual-In work mode for at least one split
● Was not in ACW in any split
● Was not on any call or placing any call (unless Multiple Call Handling
[MCH] is active)
● Did not have ringing calls
The total time that each agent was unavailable to receive calls in any
split during the reporting interval.
A split totals AUX TIME whenever any agent is logged into the split and:
● Receives an EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
● Makes an EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
● Presses his or her AUX button
Note that if the agent was in Other for all logged-in splits, that time is
reflected here. For example, ringing calls can cause several seconds of
AUX/OTHER time to accrue.
For the agent report, any non-ACD call time is also totaled in the AVG
EXTN TIME column. Two points of contrast are:
● The measurement TOTAL AUX/OTHER is time-interval based, rather
than call-related. For example, assuming that the previously
identified stipulations are met, if the agent is in AUX from 9:55
to 10:05, 5 minutes is recorded in the 9:00 to 10:00 time interval
and 5 minutes is recorded in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
● The measurement AVG EXTN TIME is call related. For example, if an
agent is on a non-ACD call from 9:55 to 10:05, the call and 10
minutes of EXTN time is recorded in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
Because the agent report includes some call-related items, the sum of
all items for a given hour may not exactly equal 60 minutes.
EXTN CALLS The total number of non-ACD incoming and outgoing calls for this agent
AVG E X TN
TIME
62 BCMS Operations
during the reporting interval. Only those non-ACD calls that are
originated and/or received while the agent is logged into at least one
split are counted.
If an extension-in call is active for less than the time set for the Abandon
Call Timer, the call will not be counted in this field.
The average amount of time that the agent spent on non-ACD calls
while logged into at least one split during the reporting interval. This
average does not include time when the agent was holding the EXTN
call. The calculation is:
Total Ext Time
-------------------------------------------------------------------Total Number of Ext Calls
If an extension-in call is active for less than the time set for the Abandon
Call Timer, the call will not be counted and the duration of the call will be
counted as AUX/OTHER time.
Page 63

Agent summary report (continued)
Header Definition
Historical reports
TOTAL TIME
STAFFED
TOTAL HOLD
TIME
SUMMARY The total of each of the columns that do not contain averages. Columns
Split report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 63
● Description on page 63
● Sample reports on page 64
● Header definitions on page 65
The total time that the agent spent logged into at least one split during
the reporting interval. Staff time is clocked for an agent who is in multiple
splits as long as the agent is logged into any split. Concurrent times for
each split are not totaled.
The total time that the agent placed ACD calls on hold. This time is the
caller hold time and is independent of the state of the agent. TOTAL
HOLD TIME does not include the hold time for non-ACD calls.
that do contain averages are the total time divided by the total number of
calls.
Command
Description
The BCMS split report provides traffic information for the specified split number.
Depending on specifics from the command line, the information may be displayed as either
a time interval or a daily summary. If neither time nor day is specified, time is the default. In
this case, the report displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or
half-hour), including data from the most recently completed time interval. To get
information on the current time interval, you must use a monitor bcms command.
When analyzing this report, keep the following in mind:
● All averages are for completed calls only.
list bcms split (split number) [time] [start time] [stop time]
[print/schedule]
list bcms split (split number) [day] [start day] [stop day]
[print/schedule]
Issue 5.0 May 2005 63
Page 64

Report reference
● A completed call may span more than one time interval. ACD calls that are in process
(have not terminated) are counted in the time interval in which they terminate. For
example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval, but terminates in
the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval, the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00
time interval.
● Asterisks within a field indicate that the maximum for that field has been exceeded.
Sample reports
Hourly report
list bcms split 3 time 8:00-10:00
BCMS SPLIT REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Split: 03
Split Name: services Acceptable Service Level: 17
TIME CALLS ANS CALLS TIME TIME CALL IN OUT OTHER STAFF LEVL
AVG AVG AVG TOTAL TOTAL % IN
ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK AFTER FLOW FLOW AUX/ AVG SERV
8:00- 9:00 32 :25 4 :32 5:15 16:00 3 5 3:30 4.0 80*
9:00-10:00 8 :07 1 :03 3:20 :00 0 0 9:30 2.2 85
----------- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ------- ---- ---- ------ ----- --SUMMARY 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 :26 3 5 13:00 3.1 81
Daily report
list bcms split 3 day 5/14/95
BCMS SPLIT REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Split: 03
Split Name: services Acceptable Service Level: 17
AVG AVG AVG TOTAL TOTAL % IN
ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK AFTER FLOW FLOW AUX/ AVG SERV
DAY CALLS ANS CALLS TIME TIME CALL IN OUT OTHER STAFF LEVL
5/14/95 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 17:20 3 5 13:00 3.1 81
-------- ----- ----- ---- ----- ----- ------- ---- ---- ------- ----- ---
SUMMARY 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 17:20 3 5 13:00 3.1 81
64 BCMS Operations
Page 65

Header definitions
Split report
Header Definition
Split The split number specified with the command line.
Split Name Displays the name that is administered for this split number. If no name
Historical reports
exists, BCMS displays the split extension (for example, EXT 65432).
Acceptable
Service Level
The desired time for an agent to answer a call for a given hunt group.
Timing for a call begins when the call enters the hunt group queue.
TIME/DAY The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Time is always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are
optional. Reports always start at the earliest time interval (either hour or
half-hour). If no start time is given, the oldest time interval is the default. A
stop time requires an associated start time. If no stop time is given, the
last completed time interval (hour or half-hour) is the default. If no start or
stop time is given, the report displays data accrued for the previous 24
time intervals. If you specify day in the command and do not include a
start day or stop day, the report displays data accrued for the previous 6
days and data accrued through the most recently completed interval
(hour or half-hour).
ACD CALLS The number of ACD calls completed for this split during the current
interval. This number also includes calls that flowed in from other splits
and Direct Agent (EAS only) calls.
AVG SPEED
ANS
The average amount of time answered ACD calls (split and Direct Agent)
spent in queue and ringing at an agent telephone before being answered
during the reporting interval. Calls that flowed in do not have queue time
from the previous split included in this average. This calculation is:
Sum of Each Completed Call's Time In Queue + Time Ringing
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Number of ACD Calls Answered
Keep the following in mind:
● This value does not include time listening to a forced first
announcement.
● A completed call may span more than one time period. ACD calls that
are in process (have not terminated) are counted in the time period in
which they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00
to 11:00 time period, but terminates in the 11:00 to 12:00 time period,
the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00 time period.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 65
Page 66

Report reference
Split report (continued)
Header Definition
ABAND
CALLS
AVG ABAND
TIME
AVG TA L K
TIME
The total number of ACD calls that have hung up while waiting to be
answered during this time interval. This value includes those calls that
have abandoned while in queue or while ringing. Calls that are not
queued (because the queue is full, the caller receives a forced first
announcement and abandons during the announcement, or because no
agents are staffed) are not counted as abandoned. Also, calls that
abandon while on hold are not counted as abandoned.
The average time before an ACD call abandons. This value does not
include any time spent in another split queue before flowing into this split.
The calculation is:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Abandon Time
Total Number of Abandoned Calls
This value does not include time listening to a forced first announcement
or calls that abandon while listening to a forced first announcement.
The average amount of time agents are active on ACD calls (split and
direct agent) for each split. This includes time spent talking. The
calculation does not include ring time at an agent telephone or time spent
on hold. Split talk time appears less than the VDN talk time in the reports.
This is because AVG TALK/HOLD time by VDN includes the time spent
on hold while the split/agent AVG TALK does not. Also, VDN talk time
does not include talk time for a call that becomes part of a conference
while split/agent talk time does. This situation will show a greater talk time
for the split.
The calculation is:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total ACD Talk Time
Total Number of ACD Calls Answered
TOTAL
AFTER CALL
FLOW IN The total number of completed calls that this split received as a coverage
The amount of time that the agents in this split spent in call-related or
noncall-related ACW mode during the reporting interval. This value
includes time spent on direct incoming or outgoing calls while in ACW. If
an agent entered ACW in one interval, but left ACW in another interval,
each interval is credited with ACW time.
point (intraflowed) from another BCMS-measured split, or are call
forwarded (interflowed) to this split and completed during the reporting
interval. This total does not include calls that are interflowed from a
remote switch by means of the Look Ahead Interflow feature. FLOW INs
are recorded when a call ends.
66 BCMS Operations
Page 67

Split report (continued)
Header Definition
FLOW OUT The total number of calls queued to this split that were:
● Successfully sent to the split coverage point after queuing for the
specified don’t answer interval. (This does not include calls that went
to coverage based on any other criterion.)
● Forwarded-out via call forwarding.
● Forwarded-out via a route-to extension vector step.
● Answered via the Call Pickup feature.
● Forwarded-out via Look Ahead Interflow.
● First queued to this split and were answered by the second or third
split.
● Redirected back to this split or its coverage path due to Redirect On
No Answer timing.
FLOW OUTs are recorded when a call ends.
Historical reports
FLOW OUT
(continued)
In a multiple split-queuing environment, inflows and outflows become a
bit more complicated. Consider the following scenarios:
● If a multiple queued call is answered in a nonprimary split (that is, a
second or third split), an outflow is recorded in the statistics for the first
split, and an inflow and an answer are recorded in the statistics for the
answering split. For example, suppose there are three splits
numbered 1 through 3. A call comes in for split 1, but all agents in this
split are busy. The call goes into queue for splits 2 and 3. An agent in
split 3 answers the call. In this example, an outflow is recorded in the
statistics for split 1, and an inflow and an answer are recorded in the
statistics for split 3. A dequeued call is counted for split 2.
● If the call is answered in the primary split, no inflows or outflows are
recorded for any split. Splits 2 and 3 record the call as dequeued.
● If a call is queued to three splits (for example, splits 1, 2, and 3, with
split 1 being the primary split), encounters a route-to command that
sends the call to another VDN, that queues to different splits (for
example, splits 4 and 5), an outflow is recorded in the statistics for
split 1. If the call is answered in split 4, an answer is recorded in the
statistics for split 4. However, no inflow is recorded to the statistics for
split 4.
● If the call is answered in split 5, an outflow is recorded for the statistics
for split 4, and both an inflow and an answer are recorded in the
statistics for split 5.
● Similarly, if a multiple queued call routes to another split, an outflow is
recorded to the statistics for the primary split, but no inflow is recorded
to the statistics for the routed-to split.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 67
Page 68

Report reference
Split report (continued)
Header Definition
TOTAL AUX/
OTHER
The total time that logged-in agents in this split were unavailable to
receive calls during the reporting interval. This value includes time spent
on non-ACD calls while in AUX for this split. This value does not include
the time agents spent on another split call or in ACW for another split.
For example, a split totals AUX TIME whenever any agent logs into the
split and:
● Receives an EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
● Makes an EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
● Presses his or her AUX button
Furthermore, the split report measurement AUX TIME is time-interval
based, since it is not directly related to a call. For example, if an agent is
in AUX for any of the previously identified reasons from 9:55 to 10:05, 5
minutes is recorded in the 9:00 to 10:00 time interval and 5 minutes is
recorded in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
AVG STAFF The average number of agents who were logged into this split (staffed)
during the reporting interval.
Total Staff Time
-----------------------------------------Time Interval
% IN SERV
LEVL
The percentage of calls answered within the administered service level.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
accepted * 100
ACDcalls + abandons + outflows + dequeued
where:
● accepted is calls answered when queue time for that call was less than
or equal to the administered service level for the split
● dequeued is a call that encountered the split queue, but that was not
answered, abandoned, or outflowed. This occurs with multiple split
queuing.
An asterisk next to a value in this field indicates that the acceptable
service level changed during the time period.
SUMMARY For those columns that specify averages, the summary is an average for
the entire reporting interval. For the ACD CALLS, ABAND CALLS,
TOTAL AFTER CALL, FLOW IN, FLOW OUT, AUX TIME, and TOTAL
HOLD TIME columns, the summary is the sum of individual time intervals
or specified days.
Split summary report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 69
68 BCMS Operations
Page 69

● Description on page 69
● Sample reports on page 70
● Header definitions on page 71
Command
Description
The BCMS Split Summary report provides traffic measurement information for a specified
group of BCMS splits. Depending on specifics from the command line, the information may
be displayed as either a time interval or a daily summary. If neither time nor day is
specified, time is the default. In this case, the report displays data accrued for the
previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour), including data from the most recently
completed time interval. To get information on the current time interval, you must use a
monitor bcms command.
Historical reports
list bcms summary split (split number) [time] [start time]
[stop time] [print/schedule]
list bcms summary split (split number) [day] [start day]
[stop day] [print/schedule]
This report is similar to the split report except that this report provides one line of data for
each split, which includes all data for the specified times. Data for a split does not appear
on the report if there is no data for that split. If you specify more than one time period, and
data exists for one or more, but not all, of the specified times, the system uses the
available data to calculate and display the one-line summary; the system does not identify
which times are not included in the calculations.
When analyzing this report, keep the following in mind:
● All averages are for completed calls only.
● Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has been exceeded.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 69
Page 70

Report reference
Sample reports
Hourly summary
list bcms summary split 5 3 time 9:00-16:00
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Time: 9:00-16:00
SPLIT NAME CALLS ANS CALLS TIME TIME CALL IN OUT OTHER STAFF LEVL
Sales 32 :25 4 :32 5:15 16:00 3 5 3:30 4.0 75
Service 8 :07 1 :03 3:20 :00 0 0 9:30 2.2 83*
-------- ----- ----- ---- ----- ----- ------- ---- ---- ------- ----- --SUMMARY 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 16:00 3 5 13:00 3.1 76
BCMS SPLIT SUMMARY REPORT
AVG AVG AVG TOTAL TOTAL % IN
ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK AFTER FLOW FLOW AUX/ AVG SERV
Daily summary
list bcms summary split 5 3 day
BCMS SPLIT SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Day: 5/15/95
AVG AVG AVG TOTAL TOTAL % IN
ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK AFTER FLOW FLOW AUX/ AVG SERV
SPLIT NAME CALLS ANS CALLS TIME TIME CALL IN OUT OTHER STAFF LEVL
Sales 32 :25 4 :32 5:15 16:00 3 5 3:30 4.0 75
Service 8 :07 1 :03 3:20 :00 0 0 9:30 2.2 83*
-------- ----- ----- ---- ----- ----- ------- ---- ---- ------- ----- --SUMMARY 40 :21 5 :26 4:52 16:00 3 5 13:00 3.1 76
70 BCMS Operations
Page 71

Header definitions
Split summary report
Header Definition
Time/Day The time or day interval specified in the command line.
SPLIT NAME Displays the name that is administered for this split number. If no name
Historical reports
Time is always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are
optional. Reports always start at the earliest time interval (either hour or
half-hour). If no start time is given, the oldest time interval is the default. A
stop time requires an associated start time. If no stop time is given, the
last completed time interval (hour or half-hour) is the default. If no start or
stop time is given, the report displays data accrued for the previous 24
time intervals. If you specify day in the command and do not include a
start day or stop day, the report displays data accrued for the previous 6
days and data accrued through the most recently completed interval
(hour or half-hour).
exists, BCMS displays the split extension (for example, EXT 65432).
ACD CALLS The number of ACD calls completed for this split during the current
interval. This number includes calls that flowed in from other splits and
Direct Agent calls.
AVG SPEED
ANS
The average amount of time answered ACD calls (split and Direct Agent)
spent in queue and ringing at an agent telephone before being answered
during the reporting interval. Calls that flowed in do not have queue time
from the previous split included in this average. This calculation is:
Sum of Each Completed Call's Time In Queue + Time Ringing
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Number of ACD Calls Answered
Keep the following in mind:
● This value does not include time listening to a forced first
announcement.
● Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has been
exceeded.
ABAND
CALLS
The total number of ACD calls that have hung up while waiting to be
answered during this time interval. This value includes those callers that
hung up while in queue or while ringing. It also includes calls with a talk
time that is less than the value administered for the BCMS/VuStats
Abandon Call Timer. Calls that are not queued (because the queue is full,
the caller receives a forced first announcement and abandons during the
announcement, or no agents are staffed) are not counted as abandoned.
Also, calls that abandon while on hold are not counted as abandoned.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 71
Page 72

Report reference
Split summary report (continued)
Header Definition
AVG ABAND
TIME
AVG TA LK
TIME
TOTAL
AFTER CALL
The average time before an ACD call abandons. This value does not
include any time spent in another split queue before flowing into this split.
The calculation is:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Abandon Time
Total Number of Abandoned Calls
This value does not include time listening to a forced first announcement
or calls that abandon while listening to a forced first announcement.
The average duration of ACD calls (split and direct agent) for each split.
This includes time spent talking. The calculation does not include ring
time at an agent telephone or time spent on hold. Split talk time appears
less than the VDN talk time in the reports. This is because AVG TALK/
HOLD time by VDN includes the time spent on hold while the split/agent
AVG TALK does not. Also, VDN talk time does not include talk time for a
call that becomes part of a conference while split/agent talk time does.
This situation will show a greater talk time for the split.
The calculation is:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total ACD Talk Time
Total Number of ACD Calls Answered
The amount of time that the agents in this split spent in call-related or
noncall-related ACW mode during the reporting interval. This value
includes time spent on direct incoming or outgoing calls while in ACW. If
an agent entered ACW in one interval, but left ACW in another interval,
each interval is credited with ACW time.
FLOW IN The total number of completed calls that this split received as a coverage
point (intraflowed) from another BCMS-measured split, or that are call
forwarded (interflowed) to this split and completed during the reporting
interval. This total does not include calls that are interflowed from a
remote switch by means of the Look Ahead Interflow feature. FLOW INs
are recorded as they occur.
FLOW OUT The total number of calls queued to this split that were:
● Successfully sent to the split coverage point after queuing for the
specified don’t answer interval. (This does not include calls that went to
coverage based on any other criterion.)
● Forwarded-out via call forwarding.
● Forwarded-out via a route-to extension vector step.
● Answered via the Call Pickup feature.
● Forwarded-out via Look Ahead Interflow.
● First queued to this split and were answered by the second or third
split.
● Redirected back to this split or its coverage path due to Redirect On No
Answer timing.
FLOW OUTs are recorded when a call ends.
72 BCMS Operations
Page 73

Split summary report (continued)
Header Definition
Historical reports
FLOW OUT
(continued)
In a multiple split-queuing environment, inflows and outflows become a bit
more complicated. Consider the following scenarios:
● If a multiple queued call is answered in a nonprimary split (that is, a
second or third split), an outflow is recorded in the statistics for the first
split, and an inflow and an answer are recorded in the statistics for the
answering split. For example, suppose there are three splits
numbered 1 through 3. A call comes in for split 1, but all agents in this
split are busy. The call goes into queue for splits 2 and 3. An agent in
split 3 answers the call. In this example, an outflow is recorded in the
statistics for split 1, and an inflow and an answer are recorded in the
statistics for split 3. A dequeued call is counted for split 2.
● If the call is answered in the primary split, no inflows or outflows are
recorded for any split. Splits 2 and 3 record the call as dequeued.
● If a call is queued to three splits (for example, splits 1, 2, and 3, with
split 1 being the primary split), encounters a route-to command that
sends the call to another VDN, that queues to different splits (for
example, splits 4 and 5), an outflow is recorded in the statistics for
split 1. If the call is answered in split 4, an answer is recorded in the
statistics for split 4. However, no inflow is recorded to the statistics for
split 4.
● If the call is answered in split 5, an outflow is recorded for the statistics
for split 4, and both an inflow and an answer are recorded in the
statistics for split 5.
● Similarly, if a multiple queued call routes to another split, an outflow is
recorded to the statistics for the primary split, but no inflow is recorded
to the statistics for the routed-to split.
TOTAL AUX/
OTHER
The total time that logged-in agents in this split were unavailable to
receive calls during the reporting interval. This value includes time spent
on non-ACD calls while in AUX for this split. This value does not include
the time agents spent on another split call or in ACW for another split.
For example, a split totals AUX TIME whenever any agent is logged into
the split and:
● Receives an EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
● Makes an EXTN call while in AUX or AVAIL state
● Presses his or her AUX button
Furthermore, the split report measurement AUX TIME is time-interval
based, since it is not directly related to a call. For example, if an agent is
in AUX for any of the previously identified reasons from 9:55 to 10:05, 5
minutes is recorded in the 9:00 to 10:00 time interval and 5 minutes is
recorded in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval.
AVG STAFF The average number of agents who were logged into this split (staffed)
during the reporting interval.
Total Staff Time
-----------------------------------------Time Interval
Issue 5.0 May 2005 73
Page 74

Report reference
Split summary report (continued)
Header Definition
% IN SERV
The percentage of calls answered within the administered service level.
LEVL
where:
● accepted is calls answered when the queue time for that call was less
● dequeued is a call that encountered the split queue, but that was NOT
An asterisk next to a value in this field indicates that the acceptable
service level changed during the time period.
SUMMARY For those columns that specify averages, the summary is an average for
the entire reporting interval. For the ACD CALLS, ABAND CALLS, TOTAL
AFTER CALL, FLOW IN, FLOW OUT, AUX TIME, and TOTAL HOLD
TIME columns, the summary is the sum of individual time intervals or
specified days.
Trunk group report
This section includes the following topics:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
accepted * 100
ACDcalls + abandons + outflows + dequeued
than or equal to the administered service level for the split
answered, abandoned, or outflowed. This occurs with multiple split
queuing.
● Command on page 74
● Description on page 74
● Sample reports on page 75
● Header definitions on page 76
Command
Description
The BCMS trunk group report gives statistical information for all BCMS measured trunk
groups. The BCMS trunk group report may be used by the ACD administrator and/or
manager to monitor use of the trunk group and to determine the optimal number of trunks
list bcms trunk (group number) [time] [start time] [stop time]
[print/schedule]
list bcms trunk (group number) [day] [start day] [stop day]
[print/schedule]
74 BCMS Operations
Page 75

for the trunk group. Depending on specifics from the command line, the information may be
displayed as either a time interval or a daily summary. If neither time nor day is specified,
time is the default. In this case, the report displays data accrued for the previous 24 time
intervals (hour or half-hour), including data from the most recently completed time interval.
When analyzing this report, keep the following in mind:
● All averages are for completed calls only.
● A completed call may span more than one time interval. ACD calls that are in process
(have not terminated) are counted in the time interval in which they terminate. For
example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00 time interval, but terminates in
the 11:00 to 12:00 time interval, the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00
time interval.
● Asterisks in a field indicate that the maximum for that field has been exceeded.
● A single asterisk at the end of a time or date field indicates that during the interval, trunk
group administration that changed the number of trunks occurred.
Sample reports
Historical reports
Time interval report
list bcms trunk 1 time 8:00 11:00
BCMS TRUNK GROUP REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 12:59 pm THU APR 20, 1995
Group: 1
Group Name: TG 1 Number of Trunks: 11
| INCOMING | OUTGOING |%ALL %TIME
TIME |CALLS ABAND TIME CCS | CALLS COMP TIME CCS|BUSY MAINT
8:00- 9:00* 23 2 2:15 31.02 1 1 1:36 .96 0 0
9:00-10:00 35 2 1:48 35.74 4 4 1:42 4.08 0 0
10:00-11:00 24 1 1:40 22.93 0 0 :00 .00 0 0
----------- ----- ---- ------ -------- ----- ---- ------ ------ --- --SUMMARY 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
Issue 5.0 May 2005 75
Page 76

Report reference
Daily report
list bcms trunk 1 day 4/17
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 12:59 pm THU APR 20, 1995
Group: 1
Group Name: TG 1 Number of Trunks: 11
| INCOMING | OUTGOING |%ALL %TIME
DAY |CALLS ABAND TIME CCS | CALLS COMP TIME CCS|BUSY MAINT
4/17/95* 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
----------- ----- ---- ------ -------- ----- ---- ------ ------ --- -- SUMMARY 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
Header definitions
Trunk group report
BCMS TRUNK GROUP REPORT
Header Definition
Group The trunk group number specified with the command line.
Group Name The name that is administered for this trunk group. If no name is
administered, this field is displayed as blank.
Number of
Trunks
The number of individual trunks in the trunk group at the end of the first
interval being reported.
TIME/DAY The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Time is always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are
optional. Reports always start at the top of the time interval (either hour or
half-hour). If no start time is given, the report displays data accrued for
the previous 24 time intervals. A stop time requires an associated start
time. If no stop time is given, the last completed time interval (hour or
half-hour) is the default. If no start time or stop time is given, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals. If you specify
day in the command and do not include a start day or stop day, the report
displays data accrued for the previous six days and data accrued through
the most recently completed interval (hour or half-hour).
If switch administration causes the number of trunks in a
BCMS-measured trunk group to change during a day or a time interval,
an asterisk displays in the DAY/TIME field.
INCOMING
The total number of incoming calls carried by this trunk group.
CALLS
76 BCMS Operations
Page 77

Trunk group report (continued)
Header Definition
Historical reports
INCOMING
ABAND
INCOMING
TIME
INCOMING
CCS
OUTGOING
CALLS
OUTGOING
COMP
The number of incoming calls that queued to ACD splits, then abandoned
without being answered by a staffed agent within this split during the
reporting interval. This value also includes calls with a talk time that is
less than the value administered for the BCMS/VuStats Abandon Call
Timer. Calls that cannot queue (for example, queue full, or calls that
receive a busy signal from the Central Office because there are no
available trunks) are not included in the INCOMING ABAND number.
Included are calls directly to staffed ACD agents that are unanswered.
The average holding time for incoming calls to this trunk group during the
specified reporting interval. Holding time is defined as the length of time
in minutes and seconds that a facility is used during a call. The
calculation for incoming time is:
Total Holding Time for all Incoming Calls
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Number of Incoming Calls
The total holding time (usage) for incoming calls to the trunk group during
the specified reporting interval. The units are expressed in hundred call
seconds (CCS).
The total number of outgoing calls for this trunk group during the specified
reporting interval.
The total number of outgoing calls that were placed over this trunk group
and answered during the specified reporting interval.
Completion is determined by whichever occurs first:
● return of network answer supervision, or
● a call that lasts longer than the answer supervision time-out parameter.
OUTGOING
TIME
OUTGOING
CCS
The average holding time for outgoing calls during the specified reporting
interval. The calculation is:
Total Holding Time for Outgoing Calls
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Number of Outgoing Calls
The total holding time (usage) for outgoing calls from this trunk group.
The units are expressed in CCS.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 77
Page 78

Report reference
Trunk group report (continued)
% ALL BUSY The percentage of time that all the trunks in this trunk group were busy.
Header Definition
This value includes trunks that are maintenance busy. The calculation is:
Total of all Busy Times
------------------------------------------------------------ X 100()
Time Interval
where Busy Times is expressed in minutes and is the sum of all times
when all trunks were simultaneously busy.
% TIME
MAINT
The percentage of time that one or more trunks have been busied-out for
maintenance. The calculation is:
Total Maintenance Busy Time x 100
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Time Interval x Number of Trunks in Group
where:
● Total Maintenance Busy Time is the sum of Maintenance Busy Time
(in minutes) for all trunks (individually) in this trunk group during this
interval
● Time Interval is expressed in minutes (for example, 30 if using a
half-hour interval, 60 if using a one-hour interval, and 1440 if using a
daily summary)
For reporting purposes, call data is stored during the time interval (hour or
half-hour) that the trunk goes idle, not when the telephone releases. Also,
changing the number of trunks in a trunk group can cause unexpected
results for that interval.
Trunk group summary report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 78
● Description on page 79
● Sample reports on page 79
● Header definitions on page 80
Command
list bcms summary trunk (group number) [time] [start time]
[stop time] [print/schedule]
list bcms summary trunk (group number) [day] [start day]
[stop day] [print/schedule]
78 BCMS Operations
Page 79

Description
The BCMS trunk group summary report provides information about BCMS-measured trunk
groups. You can specify the trunk groups you want included in the report. The BCMS trunk
group report can be used by the ACD administrator and/or manager to monitor use of one
or more trunk groups and to determine the optimal number of trunks for the trunk groups.
Note that this applies only to trunk groups measured by BCMS.
This report is similar to the BCMS trunk group report except that the information for a trunk
group displays on separate lines of the report, with totals of activity for all trunks in the
trunk group for the specified time. You can print the report for a certain time period
specified in either hours or days (up to 7 days).
The report displays only the information that exists and does not identify absent data. If
data does not exist for a specified trunk group, that trunk group does not appear on the
report. Also, if information does not exist for a portion of the specified time period, the
report displays all existing information but does not identify where there is no data.
When analyzing this report, keep the following in mind:
● All averages are for completed calls only.
● Asterisks in a field indicate that the maximum for that field is exceeded.
Historical reports
● A single asterisk at the end of a time or date field indicates that during the interval, trunk
group administration that changed the number of trunks occurred.
Sample reports
Hourly report
list bcms trunk sum 23-25 time 8:00
BCMS TRUNK GROUP SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 12:59 pm THU APR 20, 1995
Time: 8:00-13:00
| INCOMING | OUTGOING |%ALL %TIME
GROUP NAME |CALLS ABAND TIME CCS | CALLS COMP TIME CCS|BUSY MAINT
IN-800 23 2 2:15 31.02 1 1 1:36 0.96 0 0
OUT-WATTS* 35 2 1:48 35.74 4 4 1:42 4.08 0 0
TIE-GROUP 24 1 1:40 22.93 0 0 :00 0.00 0 0
----------- ----- ---- ------ -------- ----- ----- ------ ------ --- --SUMMARY 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
Issue 5.0 May 2005 79
Page 80

Report reference
Daily report
list bcms trunk sum 23 day 5/17/92
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 12:59 pm THU APR 20, 1995
Day: 5/17/95
| INCOMING | OUTGOING |%ALL %TIME
GROUP NAME |CALLS ABAND TIME CCS | CALLS COMP TIME CCS|BUSY MAINT
IN-800* 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
----------- ----- ---- ------ -------- ----- ----- ------ ------ --- --SUMMARY 82 5 1:54 29.89 5 5 1:39 2.52 0 0
Header definitions
Trunk group summary report
BCMS TRUNK GROUP SUMMARY REPORT
Header Definition
Time/Day The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Time is always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are
optional. Reports always start at the top of the time interval (either hour or
half-hour). If no start time is given, the report displays data accrued for
the previous 24 time intervals. A stop time requires an associated start
time. If no stop time is given, the last completed time interval (hour or
half-hour) is the default. If no start time or stop time is given, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals. If you specify
day in the command and do not include a start day or stop day, the report
displays data accrued for the previous six days and data accrued through
the most recently completed interval (hour or half-hour).
If switch administration causes the number of trunks in a
BCMS-measured trunk group to change during a day or a time interval,
an asterisk displays in the DAY/TIME field.
GROUP
NAME
INCOMING
The name that is administered for this trunk group. If no name is
administered, this field is displayed as blank.
The total number of incoming calls carried by this trunk group.
CALLS
INCOMING
ABAND
The number of incoming calls that queued to ACD splits, then abandoned
without being answered by a staffed agent within this split during the
reporting interval. Calls that cannot queue (for example, queue full, or
calls that receive a busy signal from the Central Office because there are
no available trunks) are not included in the INCOMING ABAND number.
Included are calls directly to staffed ACD agents that are unanswered.
80 BCMS Operations
Page 81

Trunk group summary report (continued)
Header Definition
Historical reports
INCOMING
TIME
INCOMING
CCS
OUTGOING
CALLS
OUTGOING
COMP
OUTGOING
TIME
The average holding time for incoming calls to this trunk group during the
specified reporting interval. Holding time is defined as the length of time
in minutes and seconds that a facility is used during a call. The
calculation for incoming time is:
Total Holding Time for all Incoming Calls
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Number of Incoming Calls
The total holding time (usage) for incoming calls to the trunk group during
the specified reporting interval. The units are expressed in hundred call
seconds (CCS).
The total number of outgoing calls for this trunk group during the
specified reporting interval.
The total number of outgoing calls that were placed over this trunk group
and answered during the specified reporting interval.
Completion is determined by whichever occurs first:
● return of network answer supervision, or
● a call that lasts longer than the answer supervision time-out parameter.
The average holding time for outgoing calls during the specified reporting
interval. The calculation is:
Total Holding Time for Outgoing Calls
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Number of Outgoing Calls
OUTGOING
CCS
The total holding time (usage) for outgoing calls from this trunk group.
The units are expressed in CCS.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 81
Page 82

Report reference
Trunk group summary report (continued)
% ALL BUSY The percentage of time that all the trunks in this trunk group were busy.
Header Definition
This value includes trunks that are maintenance busy. The calculation is:
Total of all Busy Times
------------------------------------------------------------ X 100()
Time Interval
where Busy Times is expressed in minutes and is the sum of all times
when all trunks were simultaneously busy.
% TIME
MAINT
VDN report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 82
The percentage of time that one or more trunks have been busied-out for
maintenance purposes. The calculation is:
Total Maintenance Busy Time x 100
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Time Interval x Number of Trunks in Group
where:
● Total Maintenance Busy Time is the sum of Maintenance Busy Time
(in minutes) for all trunks (individually) in this trunk group during this
interval
● Time Interval is expressed in minutes (for example, 30 if using a
half-hour interval, 60 if using a one-hour interval, and 1440 if using a
daily summary)
For reporting purposes, call data is stored during the time interval (hour or
half-hour) that the trunk goes idle, not when the telephone releases. Also,
changing the number of trunks in a trunk group can cause unexpected
results for that interval.
● Description on page 83
● Sample reports on page 83
● Header definition on page 84
Command
list bcms vdn extension [time] [start time] [stop time] [print/
schedule]
list bcms vdn extension [day] [start day] [stop day] [print/
schedule]
82 BCMS Operations
Page 83

Description
The BCMS VDN report provides statistical information for the specified VDN. Depending
on specifics from the command line, the information may be displayed as either a time
interval or a daily summary. If neither time nor day is specified, time is the default. In this
case, the report displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals (hour or half-hour),
including data from the most recently completed interval.
When analyzing this report, keep the following in mind:
● All averages are for completed calls only.
● A completed call may span more than one time period. ACD calls that are in process
(have not terminated) are counted in the time period in which they terminate. For
example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00 time period, but terminates in
the 11:00 to 12:00 time period, the data for this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00 time
period.
● Asterisks indicate that the maximum for the associated field has been exceeded.
Sample reports
Historical reports
Hourly report
list bcms vdn 12345 time 8:00 12:00
BCMS VECTOR DIRECTORY NUMBER REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
VDN: 12345
VDN Name: Ginsu Knives Acceptable Service Level: 17
AVG AVG AVG CALLS % IN
CALLS ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK/ CONN FLOW BUSY/ SERV
TIME OFFERED CALLS ANSW CALLS TIME HOLD CALLS OUT DISC LEVL
08:00-09:00 79 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 85*
----------- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ---- ---- --SUMMARY 79 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 85
Issue 5.0 May 2005 83
Page 84

Report reference
Daily report
list bcms vdn 12345 day 5/14
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
VDN: 12345
VDN Name: Ginsu Knives Acceptable Service Level: 17
DAY OFFERED CALLS ANSW CALLS TIME HOLD CALLS OUT DISC LEVL
5/14/95 79 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 85*
----------- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ---- ---- --SUMMARY 79 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 85
Header definition
BCMS VECTOR DIRECTORY NUMBER REPORT
AVG AVG AVG CALLS % IN
CALLS ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK/ CONN FLOW BUSY/ SERV
VDN report
Header Definition
VDN The VDN specified with the command line.
VDN Name The name that is administered for this VDN. If no name exists, the VDN
extension (for example, EXT 64532) is displayed.
Acceptable
Service Level
The desired time to answer calls to the VDN. Timing for a call begins
when the VDN is encountered.
TIME/DAY The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Time is always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are
optional. Reports always start at the top of the time interval (either hour or
half-hour). If no start time is given, the report displays data accrued for
the previous 24 time intervals. A stop time requires an associated start
time. If no stop time is given, the last completed time interval (hour or
half-hour) is the default. If no start time or stop time is given, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals. If you specify
day in the command and do not include a start day or stop day, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 6 days and data accrued through
the most recently completed interval (hour or half-hour).
CALLS
OFFERED
The total number of completed calls that accessed the VDN during the
current interval. This calculation is:
ACD CALLS + FLOW OUT + CALLS BUSY/DISC + ABAND CALLS
84 BCMS Operations
Page 85

Historical reports
VDN report (continued)
Header Definition
ACD CALLS The total number of calls to the VDN that ended in the specified interval
and were answered by an agent in a BCMS-measured hunt group. ACD
calls include calls that reached the split via the queue-to-main, check
backup, route-to, messaging split, or adjunct routing commands.
AVG SPEED
ANSW
ABAND
CALLS
AVG ABAND
TIME
AVG TA L K/
HOLD
The average speed of answer for answered ACD and CONNect calls that
have ended for this VDN during the current period. This includes time in
vector processing, time in a split queue, and time ringing. This calculation
is:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Answer Time
Total ACD Calls + Total CONNect CALLS
A completed call can span more than one time period. ACD calls that are
in progress (have not terminated) are counted in the time period in which
they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00
time period, but terminates in the 11:00 to 12:00 time period, the data for
this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00 time period.
The total number of calls that have abandoned from the VDN before
being answered or outflowed to another position during the current
interval. This value includes calls that abandoned while in vector
processing or while ringing an agent. It also includes calls with a talk time
that is less than the value administered for the BCMS/VuStats Abandon
Call Timer.
The average time calls spent waiting in this VDN before being abandoned
by the caller during the current interval. The calculation is:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total VDN Abandon Time
Total Number of Abandoned VDN Calls
The average duration of calls (from answer to disconnect) for this VDN
during the current interval. This includes time spent talking and on hold.
The calculation does not include ring time at an agent telephone. Split talk
time appears less than the VDN talk time in the reports. This is because
AVG TALK/HOLD time by VDN includes the time spent on hold while the
split/agent AVG TALK does not. Also, VDN talk time does not include talk
time for a call that becomes part of a conference while split/agent talk
time does. This situation will show a greater talk time for the split.
The calculation is:
CONN
CALLS
Total VDN Talk/Hold Time
--------------------------------------------------------------------NUM ANS
The number of completed calls that were routed to a telephone,
attendant, announcement, messaging split, or call pickup and were
answered there.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 85
Page 86

Report reference
VDN report (continued)
FLOW OUT The total number of completed calls that were routed to another VDN or
Header Definition
to a trunk, including successful lookahead attempts.
FLOW OUT does not include calls that encounter a goto vector
command.
Once a call outflows, the system does not take further measurements on
the call for this VDN. As a result, if an outflowed call later abandons, it is
not recorded in ABAND CALLS for this VDN.
CALLS
BUSY/DISC
% IN SERV
LEVL
The total number of calls that were forced busy or forced disconnect
during the current interval. This value includes:
● Calls that encountered a busy or disconnect vector step
● Calls disconnected by a stop vector step
● Calls forwarded to a split with a full queue
● Calls forwarded to a split with no available agents and no queue
This value does not include abandoned calls.
The percentage of calls that were answered with the administered service
level for this VDN. Calculate as the following:
accepted * 100
---------------------------------------calls offered
where:
● accepted is the number of answered calls when the answer time for
that call was less than or equal to the administered service level for the
VDN.
● calls offered is the total number of completed calls that accessed the
VDN and completed during the current interval.
This field is blank if no calls have been recorded for this time interval. This
field is also blank if no Acceptable Service Level is administered on the
VDN screen.
An asterisk next to a value in this field indicates that the acceptable
service level changed during the time period.
SUMMARY For those columns that specify averages, the summary is an average for
the entire reporting interval. For the TOTAL ATTEMPTS, ACD CALLS,
ABAND CALLS, FLOW OUT, and OTHER CALLS columns, the summary
is the sum of individual time intervals or specified days.
VDN summary report
This section includes the following topics:
● Command on page 87
● Description on page 87
86 BCMS Operations
Page 87

● Sample reports on page 87
● Header definitions on page 88
Command
list bcms summary vdn extension [time] [start time] [stop time]
list bcms summary vdn extension [day] [start day] [stop day]
Description
This report is similar to the VDN report except that it provides one line of data for each
VDN included in the report, and the one line includes all data for the specified times. If no
data exists for a VDN, the VDN does not appear on the report.
Sample reports
Historical reports
[print/schedule]
[print/schedule]
Hourly summary report
list bcms summary vdn 12345, 13443-13448 time 8:00-12:00
BCMS VECTOR DIRECTORY NUMBER SUMMARY REPORT
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Time: 8:00-12:00
AVG AVG AVG CALLS % IN
CALLS ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK/ CONN FLOW BUSY/ SERV
VDN NAME OFFERED CALLS ANSW CALLS TIME HOLD CALLS OUT DISC LEVL
EXT 13443 0 0 :00 0 :00 :00 0 0 0
EXT 13444 0 0 :00 0 :00 :00 0 0 0
EXT 13445 0 0 :00 0 :00 :00 0 0 0
EXT 13446 0 0 :00 0 :00 :00 0 0 0
EXT 13447 0 0 :00 0 :00 :00 0 0 0
EXT 13448 0 0 :00 0 :00 :00 0 0 0
Ginsu Knive 79 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 85*
----------- ----- ----- ----- ---- ----- ----- ----- ---- ---- --SUMMARY 79 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 85
Issue 5.0 May 2005 87
Page 88

Report reference
Daily summary report
list bcms summary vdn 12345 day 5/14
Switch Name: Lab Model Date: 11:05 am MON MAY 15, 1995
Day: 5/14/95
VDN NAME OFFERED CALLS ANSW CALLS TIME HOLD CALLS OUT DISC LEVL
Ginsu Knives 79 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 85*
----------- ----- ----- ----- ---- ----- ----- ----- ---- ---- --SUMMARY 79 50 :39 5 :45 2:30 0 0 24 85
Header definitions
VDN summary report
BCMS VECTOR DIRECTORY NUMBER SUMMARY REPORT
AVG AVG AVG CALLS % IN
CALLS ACD SPEED ABAND ABAND TALK/ CONN FLOW BUSY/ SERV
Header Definition
Time/Day The time or day interval specified in the command line.
Time is always expressed in 24-hour format. Start and stop times are
optional. Reports always start at the top of the time interval (either hour or
half-hour). If no start time is given, the report displays data accrued for
the previous 24 time intervals. A stop time requires an associated start
time. If no stop time is given, the last completed time interval (hour or
half-hour) is the default. If no start time or stop time is given, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 24 time intervals. If you specify
day in the command and do not include a start day or stop day, the report
displays data accrued for the previous 6 days and data accrued through
the most recently completed interval (hour or half-hour).
VDN NAME The name that is administered for this VDN. If no name exists, the VDN
extension (for example, EXT 64532) is displayed.
CALLS
OFFERED
The total number of completed calls that accessed the VDN during the
current interval. This calculation is:
ACD CALLS + FLOW OUT + OTHER CALLS + ABAND CALLS
ACD CALLS The total number of calls to the VDN that ended in the specified interval
and were answered by an agent as a result of a queue-to-main or
check-backup split step.
88 BCMS Operations
Page 89

VDN summary report (continued)
Header Definition
Historical reports
AVG SPEED
ANSW
ABAND
CALLS
AVG ABAND
TIME
AVG TA L K/
HOLD
The average speed of answer for answered ACD and CONNect calls that
have ended for this VDN during the current period. This includes time in
vector processing, time in a split queue, and time ringing. This calculation
is:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Answer Time
Total ACD Calls + Total CONNect CALLS
A completed call can span more than one time period. ACD calls that are
in process (have not terminated) are counted in the time period in which
they terminate. For example, if an ACD call begins in the 10:00 to 11:00
time period, but terminates in the 11:00 to 12:00 time period, the data for
this call is counted in the 11:00 to 12:00 time period.
The total number of calls that have abandoned from the VDN before
being answered or outflowed to another position during the current
interval. This value includes calls that abandoned while in vector
processing or while ringing an agent. Calls that abandoned immediately
after the agent answered are recorded as ACD CALLS.
The average time calls spent waiting in this VDN before being abandoned
by the caller during the current interval. The calculation is:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total VDN Abandon Time
Total Number of Abandoned VDN Calls
The average duration of calls (from answer to disconnect) for this VDN
during the current interval. This includes time spent talking and on hold.
The calculation does not include ring time at an agent telephone. Split talk
time appears less than the VDN talk time in the reports. This is because
AVG TALK/HOLD time by VDN includes the time spent on hold while the
split/agent AVG TALK does not. Also, VDN talk time does not include talk
time for a call that becomes part of a conference while split/agent talk
time does. This situation will show a greater talk time for the split.
The calculation is:
Total VDN Talk/Hold Time
--------------------------------------------------------------------NUM ANS
CONN
CALLS
FLOW OUT The total number of completed calls that were routed to another VDN or
The number of completed calls that were routed to a telephone,
attendant, announcement, messaging split, or call pickup and were
answered there.
to a trunk.
FLOW OUT does not include calls that encounter a goto vector command
or calls that forward to another extension (which are tracked as CONN
CALLS).
Once a call outflows, the system does not take further measurements on
the call for this VDN. As a result, if an outflowed call later abandons, it is
not recorded in ABAND CALLS for this VDN.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 89
Page 90

Report reference
VDN summary report (continued)
Header Definition
CALLS
BUSY/DISC
The total number of calls that were forced busy or forced disconnect
during the current interval. This value includes:
● calls that encountered a busy or disconnect vector step
● calls disconnected by a stop vector step
● calls forwarded to a split with a full queue
● calls forwarded to a split with no available agents and no queue.
This value does not include abandoned calls.
% IN SERV
LEVL
The percentage of calls that were answered with the administered service
level for this VDN. Calculate as the following:
accepted * 100
---------------------------------------calls offered
where:
● accepted is the number of answered calls whose answer time was less
than or equal to the administered service level for the VDN.
● calls offered is the total number of completed calls that accessed the
VDN and completed during the current interval.
An asterisk next to a value in this field indicates that the acceptable
service level changed during the time period.
SUMMARY For those columns that specify averages, the summary is also an
average for the entire reporting interval. For the TOTAL ATTEMPTS, ACD
CALLS, ABAND CALLS, FLOW OUT, and OTHER CALLS columns, the
summary is the sum of individual time intervals or specified days.
90 BCMS Operations
Page 91

System printer and Report Scheduler
The Report Scheduler is enabled on the System-Parameters Features screen. Only an
authorized representative can access and make changes to the System-Parameters
Customer-Options screen. The parameters of the system printer, which are used by the
Report Scheduler feature, are administered on the Feature-Related System Parameters
screen. If the parameters for the system printer are not administered, scheduled reports
cannot be printed. The system administrator may access this screen by entering the
change system-parameters features command. This command and the
requirements for using the Feature-Related System Parameters screen to set up the
Report Scheduler are covered in this section.
This section includes the following topics:
● System printer on page 91
● Report Scheduler on page 94
System printer
The system printer, rather than the printer that is attached directly to the management
terminal, is used to print scheduled reports. Scheduled reports cannot be sent to the
management terminal or to its printer.
Note:
Note: The system printer should not be confused with and does not replace the
printers dedicated to journal, Call Detail Records (CDR), or Property
Management System (PMS). The Report Scheduler is intended to print all
system reports and the output of virtually all list, display, and test
commands.
This section includes the following topics:
● System printer administration on page 92
● System printer data link operation and maintenance on page 93
Issue 5.0 May 2005 91
Page 92

System printer and Report Scheduler
System printer administration
Use the Feature-Related System Parameters screen to administer the hardware
parameters of the system printer. The system administrator may access this screen by
entering the change system-parameters features command.
The following screen shows the system printer parameters. System printer hardware
administration on page 92 describes the printer-related data fields for this screen.
change system-parameters features Page 4 of 12 SPE A
FEATURE-RELATED SYSTEM PARAMETERS
SYSTEM PRINTER PARAMETERS
System Printer Endpoint: 34007 Lines Per Page: 66
EIA Device Bit Rate: 9600
SYSTEM-WIDE PARAMETERS
Switch Name: Aramis
Emergency Numbers - Internal: External: 911
No-License Incoming Call Number:
MALICIOUS CALL TRACE PARAMETERS
Apply MCT Warning Tone? y MCT Voice Recorder Trunk Group:
Delay Sending RELease (seconds)? 0
SEND ALL CALLS OPTIONS
Send All Calls Applies to: extension
Auto Inspect on Send All Calls? n
UNIVERSAL CALL ID
Create Universal Call ID (UCID)? n
UCID Network Node ID:
System printer hardware administration
Field Description
System Printer
Endpoint
Enter one of the following:
● SYS_PRNT if the system printer is connected to the
switch using a terminal server.
● The data module extension number associated with the
system printer.
● eia if the DCE jack is used to interface the printer. The
eia option is not available for G3r systems.
92 BCMS Operations
Page 93

System printer hardware administration (continued)
Field Description
EIA Device Bit Rate Enter 1200, 2400, 4800, or 9600 to match the printer
speed setting. Default is 9600.
Lines Per Page Enter the number of lines per page required for the report.
Valid entries are 24 through 132. Default is 60.
System printer data link operation and maintenance
Operation and maintenance of the system printer data link is significantly different from that
of the CDR and journal printer data links. For example, the CDR and journal printer data
links are maintained in a constant link up state, while the system printer data link is only
brought up once every 15 minutes, provided there are reports to be printed, or when an
immediate report is scheduled.
The system printer data link has three states that identify its operational condition. The
states are:
System printer
● Link up
● Link down
● Maintenance busyout
When the communication path (including software processes, hardware cabling, and
printer) functions properly and data is exchanged successfully, the data link is defined as
being in the link up state. The link down state refers to all times except:
● When reports are being printed
● When maintenance personnel have disabled the link
The maintenance busyout state is the result of executing the busyout sp-link
command from the administration terminal. While the link is in the maintenance busyout
state, the switch software processes are disabled and the link retry operation is disabled.
Monitor the operating status of the system printer and, as necessary, refill the paper bin,
relieve any paper jams, verify that the printer is receiving power, and so forth.
Note:
Note: Only personnel with maintenance permissions can execute the busyout
sp-link command. This is normally only performed via the maintenance
login. Therefore, as necessary, all nonmaintenance personnel should simply
flip the printer power switch to the OFF position to refill the paper bin and
remove jammed paper. Subsequently, the system printer can be restored
on-line by turning the power switch ON.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 93
Page 94

System printer and Report Scheduler
If the system printer link generates either a Warning alarm or a Minor alarm, the problem
should be referred to the proper maintenance personnel.
Report Scheduler
The Report Scheduler may be used with many switch features. Specifically, virtually all
list, display, or test commands may be executed with the schedule qualifier.
Whenever a command containing the schedule option is executed, it results in generating
a Job ID. A maximum of 50 different Job IDs (50 different reports) can be scheduled for
printing. The Report Scheduler feature is used to specify the actual days and time of day
that each report will be printed.
This section includes the following topics:
● Print intervals on page 94
● Adding a report to Report Scheduler on page 94
● Printing reports on the system printer on page 96
● Listing scheduled reports on page 97
● Changing scheduled reports on page 98
● Removing scheduled reports on page 100
Print intervals
For purposes of printing reports, three print intervals are available:
● immediate - If you select this option, the report will be printed immediately.
● scheduled - If you select this option, the date, time, and days parameters for the report
are set administratively. To change them, readministration is required.
● deferred - If you select this option, the report will be generated once for the date, time,
and day specified.
Adding a report to Report Scheduler
To add a report to Report Scheduler, enter a list, test, display, or other command
followed by the schedule option. Whenever a report is initially scheduled, the print
interval of immediate is automatically assigned as the default. Therefore, if immediate
94 BCMS Operations
Page 95

Report Scheduler
printing is not wanted, the print interval must be changed to deferred or scheduled and
a day and print time must be added to Report Scheduler. Report Scheduler field
descriptions describes the data fields for this screen.
list measurements attendant group Page 1 of 1
REPORT SCHEDULER
Job Id: 1 Job Status: none
Command: list measurements attendant group
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: :
Sun: n Mon: n Tue: n Wed: n Thu: n Fri: n Sat: n
Report Scheduler field descriptions
Field Description
Job Id This is a display-only field. Whenever a command is executed with the
qualifier schedule, the system responds by generating a unique Job ID
number. The Job ID assigned by the system is the lowest number within
the range of 1 through 50 that is not in use. Jobs are printed in order
based on the Job ID unless the print job has been rescheduled. The
rescheduled job is moved to the bottom of the print queue.
Job Status This is a display-only field. It identifies the print status of the report. Until
the job is on the Report Scheduler, this field is blank (empty).
Command This is a display-only field. It displays the command being scheduled.
Print Interval This field has three options: immediate, deferred, and scheduled.
The immediate option is initially assigned as a default. Use this option to
print reports immediately.
Use the deferred option to schedule a report for a single printing.
Thereafter, the Job ID is automatically removed from the Report
Scheduler. If you select the deferred option, you must enter the Print
Time and Days of Week.
Use the scheduled option to schedule a regular printing of a report. If
you select the scheduled option, you must enter the Print Time and
Days of Week.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 95
Page 96

System printer and Report Scheduler
Report Scheduler field descriptions (continued)
Field Description
Print Time This field is displayed only when the Print Interval is set to deferred or
scheduled. Within a given hour, reports may be scheduled at 15-minute
intervals (that is, xx:00, xx:15, xx:30, or xx:45).
The system printer requires significant switch processor resources. It is
important that the reports be scheduled for off-peak hours. The reports
should not all be scheduled for the same hour and time interval, but
should be staggered across multiple off-peak time intervals. If, because of
printing volume or other problems, a report is not printed within four hours
of its scheduled time interval, it will not be printed until its next scheduled
time interval. Immediate and deferred jobs would be removed from Report
Scheduler under this scenario and would require that you reschedule
them.
Days of
Week
For each day of the week that the report is to be printed, enter y (yes).
Alternatively, enter n (no) for those days when the report should not be
printed. Selecting an n for all seven days of the week will effectively
disable a report from being printed. Days are defaulted to n.
Printing reports on the system printer
To print a report on the system printer:
1. Execute a command with the schedule qualifier.
The first screen of Report Scheduler is displayed. It indicates that the print interval is
immediate.
2. Either:
● Press ENTER to print the report (immediately) on the system printer, or
● Enter scheduled or deferred. Press ENTER.
Note:
Note: If you are using a PC running the 513 terminal emulation package, your
keyboard will not have an ENTER key. You must map a function key to serve
in this capacity. Pressing RETURN will not achieve the correct results.
When the print interval is changed to scheduled or deferred, the Print Time and
the days of the week fields are displayed.
3. Enter the print time and press ENTER. The cursor is now on the days of the week field.
For those days that you want to print the report, enter a y.
4. Press ENTER to execute the command. The system responds with a prompt for the
next command.
96 BCMS Operations
Page 97

Listing scheduled reports
To display a list of all reports that are on Report Scheduler, enter the list
report-scheduler command. Reports will be printed in the order listed. The following
screen shows an example of the report scheduler. Report Scheduler field descriptions
page 97 describes the headers for this screen.
list report-scheduler
REPORT SCHEDULER
Job Id Days(smtwtfs) Time User Status Type
Command
4 nynnnnn 18:45 bcms printing immediate
list measurements attendant-group time 14:15
2 nynynyn 19:00 bcms waiting scheduled
list measurements call-rate time 07:00
7 nnnnnyn 19:15 bcms waiting deferred
list bcms agent 5000 time 08:00 12:00
23 nnynnnn 19:15 bcms waiting scheduled
list bcms agent 4000 day 09/11 09/15
Report Scheduler
on
Note:
Note: In instances such as those for Job ID 4, if an immediate report is scheduled,
the Days field is completed with one y for the current day and n for the
others.
All fields are display-only. If, after reviewing this report, you determine that change needs
to be made, use the change report-scheduler command to make the changes. See
Changing scheduled reports
on page 98.
Report Scheduler field descriptions
Field Description
Job Id Whenever a command is executed with the schedule qualifier, the
system responds by generating a unique Job ID number. The Job ID
assigned by the system is the lowest number, within the range of 1
through 50, that is not in use.
Days (smtwtfs) On a per-day basis, n indicates that the report will not be printed that
day; y indicates that the report will be printed that day. Selecting n for
all seven days of the week will effectively disable the printing of a
report.
Time The time interval that the report is scheduled to be printed.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 97
Page 98

System printer and Report Scheduler
Report Scheduler field descriptions (continued)
Field Description
User The login ID of the user who scheduled the identified report.
Status This is a display-only field. It identifies the print status of the report.
The four possible states are:
● Waiting - The report is not scheduled for any activity during the
● Print-Next - The report is scheduled to be printed within the
● Printing - The report is currently being printed.
● Printed - The report has been successfully printed during the
Type Indicates the type of print interval that is scheduled for the report
(immediate, scheduled, or deferred).
Command This field displays the complete command line (excluding the
schedule option) that the user entered to produce the identified
report.
current 15-minute time interval.
current 15-minute time interval.
current 15-minute interval.
Changing scheduled reports
Use the change report-scheduler command to change the schedule of a report. To
display this screen, enter the change report-scheduler xx command, where xx
corresponds to the Job ID. The following screen shows an example of the Change
Report-Scheduler screen. Change Report-Scheduler field descriptions
fields for this screen.
change report-scheduler 1 Page 1 of 1
REPORT SCHEDULER
Job Id: 1 Job Status: waiting
Command: list measurements attendant group
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: 12:30
Sun: y Mon: n Tue: y Wed: n Thu: y Fri: n Sat: n
describes the data
98 BCMS Operations
Page 99

Report Scheduler
Note:
Note: When an existing print job is rescheduled, that print job is moved to the
bottom of the print queue, regardless of the Job ID number.
Change Report-Scheduler field descriptions
Field Description
Job Id This is a display-only field. It is the unique identifier for the report. The Job
ID assigned by the system is the lowest number, within the range of 1
through 50, that is not in use.
Job Status This is a display-only field. It identifies the print status of the report. The
four possible states are:
● Waiting - The report is not scheduled for any activity during the current
15-minute time interval.
● Print-Next - The report is scheduled to be printed within the current
15-minute time interval.
● Printing - The report is currently being printed.
● Printed - The report has been successfully printed during the current
15-minute interval.
Command This is a display-only field. It is the command that is to be executed.
Print
Interval
The three possible options are immediate, scheduled, and deferred.
If the print time of a report is changed, so that its scheduled time now falls
inside the current 15-minute time interval (that is, the Job Status field
changes from waiting to print-next), the report will not be printed in
the current interval.
Print Time This field is displayed only when the Print Interval is set to deferred or
scheduled. Within a given hour, reports may be scheduled at 15-minute
intervals (that is, xx:00, xx:15, xx:30, or xx:45).
The system printer requires significant switch processor resources. It is
important that the reports be scheduled for off-peak hours. The reports
should not all be scheduled for the same hour and time interval, but should
be staggered across multiple off-peak time intervals. If, because of printing
volume or other problems, a report is not printed within four hours of its
scheduled time interval, it will not be printed until its next scheduled time
interval. Immediate and deferred jobs would be removed from Report
Scheduler under this scenario and would require that you reschedule
them.
Days of
Week
For each day of the week that the report is to be printed, enter y (yes).
Alternatively, enter n (no) for those days when the report should not be
printed. Selecting an n for all seven days of the week will effectively disable
a report from being printed. Days are defaulted to n.
Issue 5.0 May 2005 99
Page 100

System printer and Report Scheduler
Removing scheduled reports
Use the remove report-scheduler command to remove a report from Report
Scheduler. To display this screen, enter the remove report-scheduler xx command,
where xx corresponds to the Job ID. The following screen shows an example.
remove report-scheduler 1 Page 1 of 1
REPORT SCHEDULER
Job Id: 1 Job Status: waiting
Command: list measurements attendant group
Print Interval: scheduled
Print Time: 12:30
Sun: y Mon: n Tue: y Wed: n Thu: y Fri: n Sat: n
All fields are display-only. Once you have verified that the identified report is the one to be
removed, press ENTER. The system displays the command prompt.
100 BCMS Operations
 Loading...
Loading...