Page 1

Installing and maintaining Avaya B189
Conference IP Phone
Release 1.0
16-604293
Issue 1
January 2014
Page 2

©
2013 Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to ensure that the
information in this document is complete and accurate at the time of
printing, Avaya assumes no liability for any errors. Avaya reserves the
right to make changes and corrections to the information in this
document without the obligation to notify any person or organization of
such changes.
Note
Using a cell, mobile, or GSM phone, or a two-way radio in close
proximity to an Avaya IP telephone might cause interference.
Documentation disclaimer
“Documentation” means information published by Avaya in varying
mediums which may include product information, operating instructions
and performance specifications that Avaya may generally make
available to users of its products and Hosted Services. Documentation
does not include marketing materials. Avaya shall not be responsible
for any modifications, additions, or deletions to the original published
version of documentation unless such modifications, additions, or
deletions were performed by Avaya. End User agrees to indemnify and
hold harmless Avaya, Avaya's agents, servants and employees against
all claims, lawsuits, demands and judgments arising out of, or in
connection with, subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to
this documentation, to the extent made by End User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked
websites referenced within this site or documentation provided by
Avaya. Avaya is not responsible for the accuracy of any information,
statement or content provided on these sites and does not necessarily
endorse the products, services, or information described or offered
within them. Avaya does not guarantee that these links will work all the
time and has no control over the availability of the linked pages.
Warranty
Avaya provides a limited warranty on Avaya hardware and software.
Refer to your sales agreement to establish the terms of the limited
warranty. In addition, Avaya’s standard warranty language, as well as
information regarding support for this product while under warranty is
available to Avaya customers and other parties through the Avaya
Support website:
designated by Avaya. Please note that if you acquired the product(s)
from an authorized Avaya Channel Partner outside of the United States
and Canada, the warranty is provided to you by said Avaya Channel
Partner and not by Avaya.
Licenses
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS AVAILABLE ON THE AVAYA
WEBSITE,
SUCH SUCCESSOR SITE AS DESIGNATED BY AVAYA, ARE
APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO DOWNLOADS, USES AND/OR
INSTALLS AVAYA SOFTWARE, PURCHASED FROM AVAYA INC.,
ANY AVAYA AFFILIATE, OR AN AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER (AS
APPLICABLE) UNDER A COMMERCIAL AGREEMENT WITH AVAYA
OR AN AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER. UNLESS OTHERWISE
AGREED TO BY AVAYA IN WRITING, AVAYA DOES NOT EXTEND
THIS LICENSE IF THE SOFTWARE WAS OBTAINED FROM
ANYONE OTHER THAN AVAYA, AN AVAYA AFFILIATE OR AN
AVAYA CHANNEL PARTNER; AVAYA RESERVES THE RIGHT TO
TAKE LEGAL ACTION AGAINST YOU AND ANYONE ELSE USING
OR SELLING THE SOFTWARE WITHOUT A LICENSE. BY
INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, OR
AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU, ON BEHALF OF
YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR WHOM YOU ARE INSTALLING,
DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE (HEREINAFTER
REFERRED TO INTERCHANGEABLY AS “YOU” AND “END USER”),
http://support.avaya.com or such successor site as
HTTP://SUPPORT.AVAYA.COM/LICENSEINFO OR
AGREE TO THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS AND CREATE A
BINDING CONTRACT BETWEEN YOU AND AVAYA INC. OR THE
APPLICABLE AVAYA AFFILIATE (“AVAYA”).
Avaya grants you a license within the scope of the license types
described below, with the exception of Heritage Nortel Software, for
which the scope of the license is detailed below. Where the order
documentation does not expressly identify a license type, the
applicable license will be a Designated System License. The applicable
number of licenses and units of capacity for which the license is granted
will be one (1), unless a different number of licenses or units of capacity
is specified in the documentation or other materials available to you.
“Software” means Avaya’s computer programs in object code, provided
by Avaya or an Avaya Channel Partner, whether as stand-alone
products, pre-installed , or remotely accessed on hardware products,
and any upgrades, updates, bug fixes, or modified versions thereto.
“Designated Processor” means a single stand-alone computing device.
“Server” means a Designated Processor that hosts a software
application to be accessed by multiple users. “Instance” means a single
copy of the Software executing at a particular time: (i) on one physical
machine; or (ii) on one deployed software virtual machine (“VM”) or
similar deployment.
License types
Designated System(s) License (DS). End User may install and use
each copy or an Instance of the Software only on a number of
Designated Processors up to the number indicated in the order. Avaya
may require the Designated Processor(s) to be identified in the order
by type, serial number, feature key, Instance, location or other specific
designation, or to be provided by End User to Avaya through electronic
means established by Avaya specifically for this purpose.
Shrinkwrap License (SR). You may install and use the Software in
accordance with the terms and conditions of the applicable license
agreements, such as “shrinkwrap” or “clickthrough” license
accompanying or applicable to the Software (“Shrinkwrap License”).
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, no use should be made of
materials on this site, the Documentation, Software, Hosted Service,
or hardware provided by Avaya. All content on this site, the
documentation, Hosted Service, and the Product provided by Avaya
including the selection, arrangement and design of the content is
owned either by Avaya or its licensors and is protected by copyright
and other intellectual property laws including the sui generis rights
relating to the protection of databases. You may not modify, copy,
reproduce, republish, upload, post, transmit or distribute in any way any
content, in whole or in part, including any code and software unless
expressly authorized by Avaya. Unauthorized reproduction,
transmission, dissemination, storage, and or use without the express
written consent of Avaya can be a criminal, as well as a civil offense
under the applicable law.
Third Party Components
“Third Party Components” mean certain software programs or portions
thereof included in the Software or Hosted Service may contain
software (including open source software) distributed under third party
agreements (“Third Party Components”), which contain terms
regarding the rights to use certain portions of the Software (“Third Party
Terms”). As required, information regarding distributed Linux OS
source code (for those Products that have distributed Linux OS source
code) and identifying the copyright holders of the Third Party
Components and the Third Party Terms that apply is available in the
Documentation or on Avaya’s website at:
Copyright or such successor site as designated by Avaya. You agree
to the Third Party Terms for any such Third Party Components
Preventing Toll Fraud
“Toll Fraud” is the unauthorized use of your telecommunications
system by an unauthorized party (for example, a person who is not a
corporate employee, agent, subcontractor, or is not working on your
http://support.avaya.com/
2 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 3

company's behalf). Be aware that there can be a risk of Toll Fraud
associated with your system and that, if Toll Fraud occurs, it can result
in substantial additional charges for your telecommunications services.
Avaya Toll Fraud intervention
If you suspect that you are being victimized by Toll Fraud and you need
technical assistance or support, call Technical Service Center Toll
Fraud Intervention Hotline at +1-800-643-2353 for the United States
and Canada. For additional support telephone numbers, see the Avaya
Support website:
designated by Avaya. Suspected security vulnerabilities with Avaya
products should be reported to Avaya by sending mail to:
securityalerts@avaya.com.
Trademarks
The trademarks, logos and service marks (“Marks”) displayed in this
site, the Documentation, Hosted Service(s), and Product(s) provided
by Avaya are the registered or unregistered Marks of Avaya, its
affiliates, or other third parties. Users are not permitted to use such
Marks without prior written consent from Avaya or such third party
which may own the Mark. Nothing contained in this site, the
Documentation, Hosted Service(s) and Product(s) should be construed
as granting, by implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license or right
in and to the Marks without the express written permission of Avaya or
the applicable third party.
Avaya is a registered trademark of Avaya Inc.
All non-Avaya trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and
other countries.
Downloading Documentation
For the most current versions of Documentation, see the Avaya
Support website:
designated by Avaya.
Contact Avaya Support
See the Avaya Support website: http://support.avaya.com for Product
or Hosted Service notices and articles, or to report a problem with your
Avaya Product or Hosted Service. For a list of support telephone
numbers and contact addresses, go to the Avaya Support website:
http://support.avaya.com (or such successor site as designated by
Avaya), scroll to the bottom of the page, and select Contact Avaya
Support.
VCCI-Class B statement:
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the VCCI Council.
If this is used near a radio or television receiver in a domestic
environment, it may cause radio interference. Install and use the
equipment according to the instruction manual.
http://support.avaya.com or such successor site as
http://support.avaya.com, or such successor site as
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 3
Page 4

4 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 5

Contents
Chapter 1: About this guide...............................................................................................
Intended audience....................................................................................................................................
Documentation..........................................................................................................................................
Support......................................................................................................................................................
Chapter 2: Overview...........................................................................................................
Overview...................................................................................................................................................
Connection layout.....................................................................................................................................
Chapter 3: Installing the deskphone.................................................................................
Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone...........................................................................................................
Updating phone software for installation...................................................................................................
Creating the pre-installation checklist.......................................................................................................
Plugging in Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone........................................................................................
Plugging in and resetting the deskphone using the Dynamic Addressing Process..................................
Phone initialization....................................................................................................................................
Understanding the plug in and reset process...........................................................................................
Understanding unnamed registration........................................................................................................
Chapter 4: Maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phones...........................................
About software distribution packages.......................................................................................................
Downloading software packages..............................................................................................................
Contents of the settings file.......................................................................................................................
Downloading text language files...............................................................................................................
Applying settings to logical groups............................................................................................................
Chapter 5: Using local Administrative Menu procedures...............................................
About Administration Menu procedures....................................................................................................
Entering the Administration Menu.............................................................................................................
Entering and validating IPv4 addresses....................................................................................................
Local administrative menu........................................................................................................................
Setting the operational mode to 802.1X....................................................................................................
Using the preinstallation checklist.............................................................................................................
Changing IP address information..............................................................................................................
Enabling and disabling the debug mode...................................................................................................
Clearing the phone settings......................................................................................................................
Changing the group identifier....................................................................................................................
Changing Ethernet interface control.........................................................................................................
Logging off from the phone.......................................................................................................................
Resetting system values...........................................................................................................................
Restarting the phone.................................................................................................................................
Changing SSON settings..........................................................................................................................
Performing a self-test................................................................................................................................
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting...............................................................................................
Resolving error conditions.........................................................................................................................
Failure to hear DTMF tones......................................................................................................................
Correcting a power interruption.................................................................................................................
Using the VIEW procedure for troubleshooting.........................................................................................
7
7
7
7
9
9
9
11
11
11
11
13
14
15
17
20
21
21
22
23
24
24
25
25
26
26
27
28
28
29
31
32
33
33
34
35
36
36
37
39
39
40
40
40
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 5
Page 6

Installation error and status messages.....................................................................................................
Operational errors and status messages..................................................................................................
LLDP Troubleshooting..............................................................................................................................
Proposed Solution............................................................................................................................
LLDP setup and troubleshooting steps.....................................................................................................
Proposed solution for DHCP configured deskphones......................................................................
Proposed solution for script-configured deskphones.......................................................................
Proposed solution for LLDP-configured deskphones.......................................................................
Secure Shell Support................................................................................................................................
Index.....................................................................................................................................
43
47
50
51
51
52
52
53
53
55
6 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Page 7
Chapter 1: About this guide
Intended audience
This guide is for personnel who install the Avaya B189 Conference IP Phones, Local Area
Network (LAN), and the related server system.
Documentation
Using
16-604295 Using Avaya B189
Administering
16-604294 Administering Avaya
Support
Visit the Avaya Support website at http://support.avaya.com for the most up-to-date
documentation, product notices, and knowledge articles. You can also search for release
notes, downloads, and resolutions to issues. Use the online service request system to create
a service request. Chat with live agents to get answers to questions, or request an agent to
connect you to a support team if an issue requires additional expertise.
Document
number
Title Use this document to: Audience
Conference IP Phone
B189 Conference IP
Phone
Refer to procedures for using
Avaya B189 Conference IP
Phone.
Refer to administrative tasks
that you can perform for Avaya
B189 Conference IP Phone.
End users
End users and
administrators
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 7
Page 8

About this guide
8 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 9

Chapter 2: Overview
Overview
Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone is a multiline H.323 IP deskphone that you can use to make
calls and hold conferences with HD quality voice.
The features of the deskphone include a 5-inch touch screen, mute, and volume control
buttons, one On-hook/Off-hook button, and a Phone button. You can navigate the menu only
through the touch screen. Bi-color LEDs provide visual indication of an incoming call, call in
progress, call on hold, and a muted microphone. As the LEDs are visible from all angles, the
deskphone visually alerts the users. You can attach additional microphones to the conference
phone to cover a wide area.
Connection layout
The following table lists the connections that are available on the conference phone.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 9
Page 10
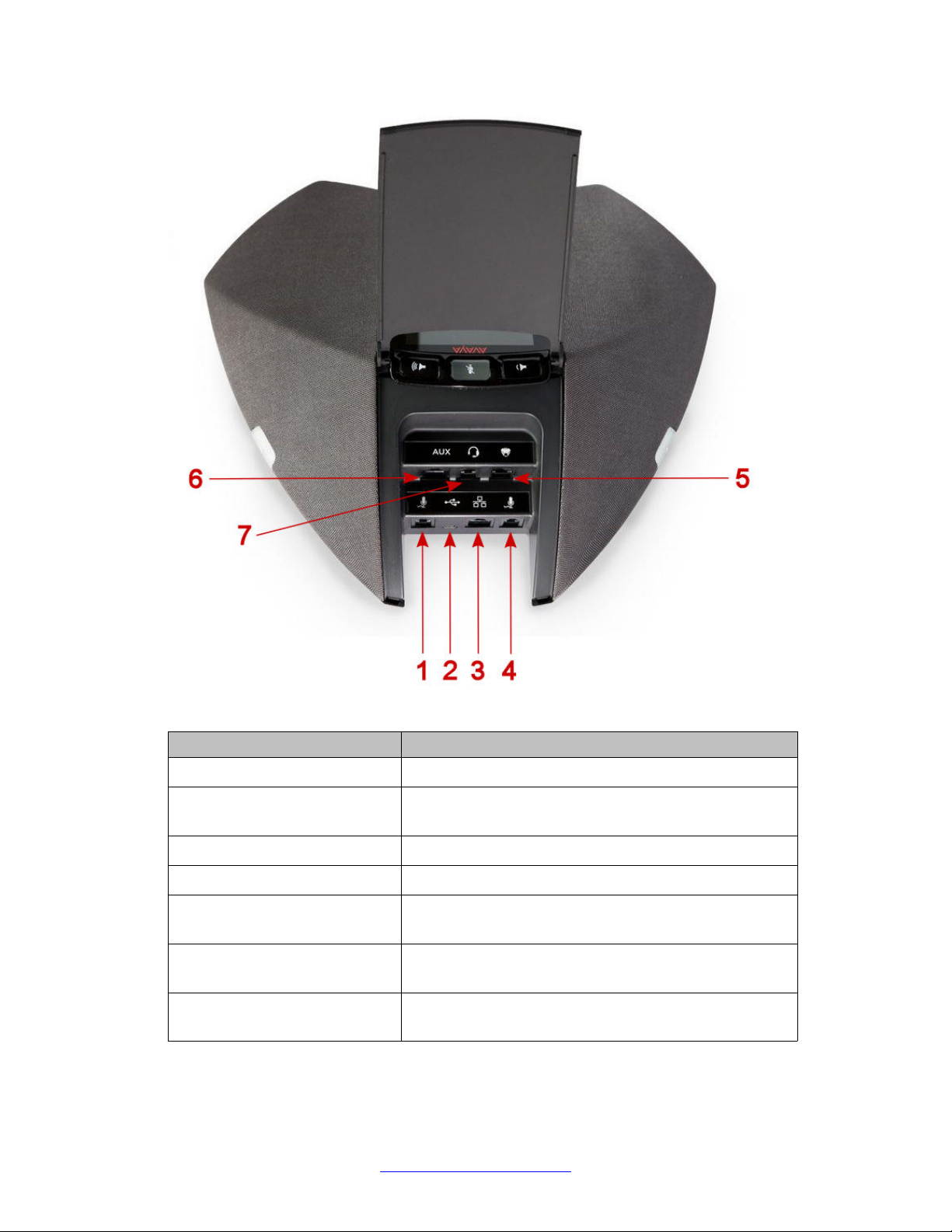
Overview
Figure 1: Connection layout on Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone
Callout number
Description
1 Left side expansion microphone port
2 USB Connection
Note: This connection is reserved for future use.
3 RJ 45 Network connection socket
4 Right side expansion microphone port
5 Daisy chain connection socket
Note: This connection is reserved for future use.
6 Auxiliary connection port
Note: This connection is reserved for future use.
7 Headset connection port
This connection is reserved for future use.
10 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 11
Chapter 3: Installing the deskphone
Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone
The Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone product line uses Internet Protocol (IP) technology with
Ethernet interfaces.
Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone supports DHCP and HTTP/HTTPS over IPv4/UDP including
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) and Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP).
Both the protocols enhance deskphone administration and servicing.
These deskphones use DHCP to get dynamic IP Addresses and HTTP or HTTPS to download
new software versions or customized settings.
Updating phone software for installation
About this task
A phone that is shipped from the factory might not contain the most up-to-date software for
registration and operation. When you first plug in the phone, a software download from an
HTTP server might be initiated. The software download provides the phone upgraded
functionality.
For subsequent downloads of software upgrades, the media server provides the capability for
a remote restart of the IP phone. When you restart the phone, the phone automatically restarts
and performs a download if new software is available. For more information, see
software distribution packages on page 21 and Downloading software packages on
page 22.
Creating the pre-installation checklist
Before plugging in an Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone, verify the following requirements. If
you fail to meet the requirements, the phone might not funtion properly and can negatively
impact the network. Print copies of this checklist for each server and deskphone.
About
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 11
Page 12
Installing the deskphone
1. The LAN uses Ethernet Category 5e cable to run the IPv4 version of Internet
2.
3. Verify that you have installed the following circuit packs on the switch:
4. Verify that you have configured the Avaya call server correctly.
Requirements for your network:
Protocol.
Your call server must haveAvaya Aura®Communication Manager Release 5.2.1,
6.0, or later installed.
• TN2602 or TN2302IP Media Processor circuit pack. Avaya recommends that
sites with a TN2302 IP Media Processor circuit pack must install a TN2602 circuit
pack to benefit from increased capacity.
• TN799C or D Control-LAN (C-LAN) circuit pack.
Important:
Release 6.0 or later requires TN799C V3 or greater C-LAN circuit pack(s). For
more information, see the Communication Manager Software and Firmware
Compatibility Matrix on the
For more information, see Administering Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone, 16–
604294, and Communication Manager documentation on the Avaya Support
website.
Avaya Support website.
5. Verify that you have administered the DHCP server and application correctly.
See Administering Avaya B189 Conference IP Deskphone, 16–604294.
6. Verify that you have administered the HTTP/HTTPS server and application
correctly.
See Administering Avaya B189 Conference IP Deskphone, 16–604294.
7. Verify that you have loaded the upgrade script and application files from the Avaya
Support website correctly on the HTTP/HTTPS server.
8. If applicable, administer the DNS server as described in Administering Avaya B189
Conference IP Phone, 16–604294.
Note:
All server applications mentioned in items 5 -9 can co-reside on the same hardware, subject
to the specific restrictions of each individual application. For more information about
administering other network equipment, administering applications, for example, firewalls,
and information about topics like port utilization, see Administering Avaya B189 Conference
IP Phone.
Requirements for each deskphone:
10. Verify that you have an extension number and an Communication Manager
security code (password) for each applicable IP deskphone. If your call server and
the phone settings file support unnamed registration, you do not need an
extension or password. However, without an extension or password, the phone
12 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 13

Plugging in Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone
has limited functionality. For information about unnamed registration, see About
unnamed registration on page 20.
11. Verify that a Category 5e LAN jack is available at each phone site and a Category
5 modular line cable that connects the deskphone to the LAN jack. Cat 5 cables
with an RJ45 plug have a plug size restriction of 36 mm.
12. Verify that each deskphone receives power through a Telephone Power Module
or a POE switch. For PoE Input connection, use only with UL listed I.T.E.
equipment with PoE output. If LAN supplies IEEE-standard power, or Power over
Ethernet, to the deskphone, the phones do not require a power module. PoE must
support Class 3.
Plugging in Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone
Caution:
Use the correct jack when you plug in the phone. You can find the jacks at the rear of the
phone housing. Flip the cover to see the connecting jacks. Icons on the side of the jacks
represent the correct use of each
Procedure
1. Plug one end of the CAT5 cable into the corresponding jack in the phone.
2. Connect the other end of the CAT5 cable to the wall connector as show in the
following figure.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 13
Page 14
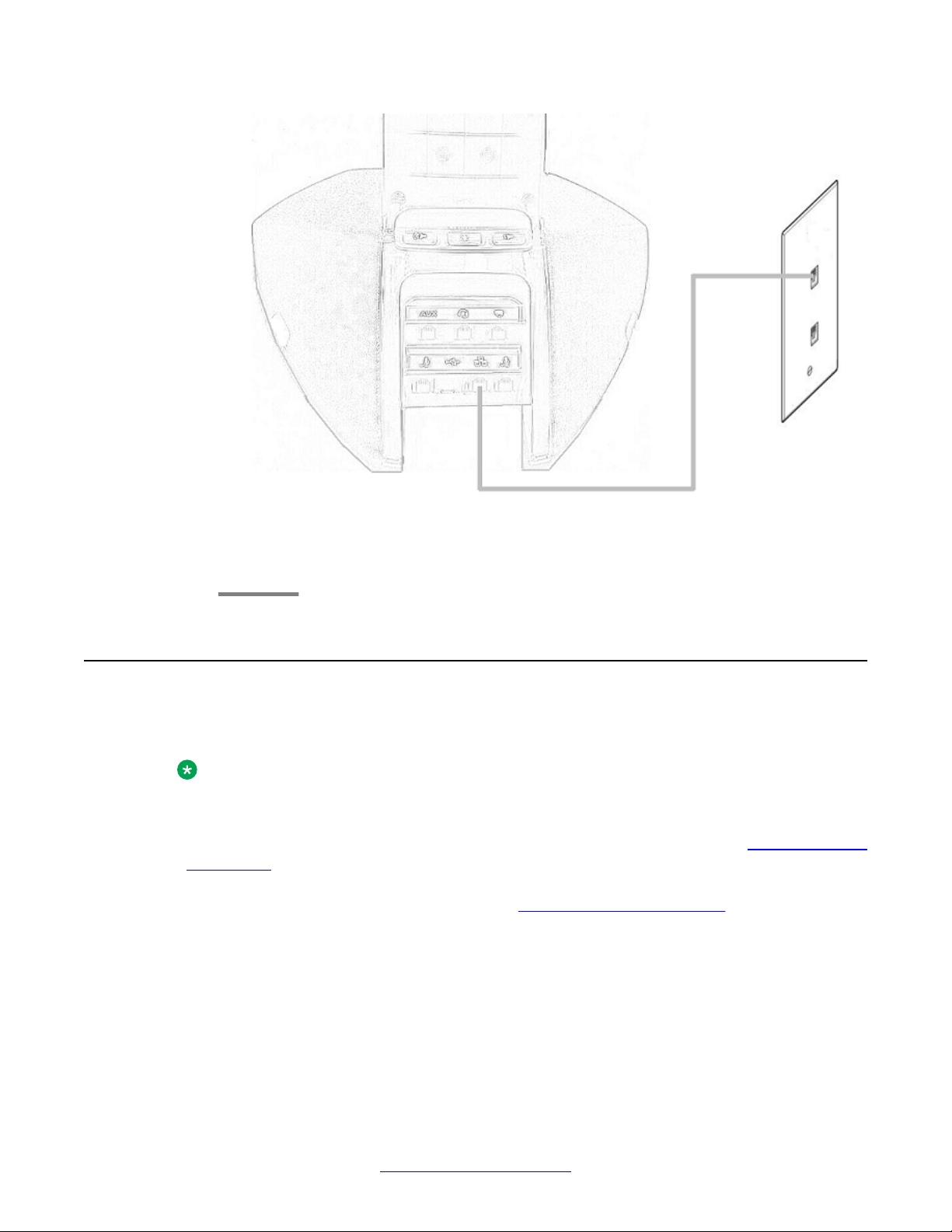
Installing the deskphone
Figure 2: Connecting Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone to a wall LAN connector
The phone powers on.
Plugging in and resetting the deskphone using the Dynamic Addressing Process
Note:
Before you start this process you must have an extension number for the IP deskphone and
the Communication Manager security code (password) for that extension, unless you intend
to use the deskphone with unnamed registration. For more information, see
registration on page 20. Any reference to the HTTP server applies equally to an HTTPS
server. You can run the plug in and reset process successfully using the following
description. If you see error messages, see
As the deskphone initializes, you see messages, some of which are part of DHCP process,
with a power on indication and dynamic feedback. These messages indicate that the phone is
active and not locked. You also receive useful information, about the status of the network, the
server, or the downloading operations, before the dial tone.
Chapter 5: Troubleshooting on page 39.
About unnamed
14 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 15

Phone initialization
This section description describes the software architecture on which the requirements are
based and provides an overview of how you can expect the phone to operate during startup
and software upgrades. This description is not a comprehensive description of all internal tasks
performed during startup.
The system stores the files in five areas of reprogrammable nonvolatile or flash memory in the
phones:
• A boot program area
• Two Kernel/Root File Systems
• One Application File System
• One Temporary Storage area
The phone supports two Kernel or Root File Systems for backup if one file system is corrupted
but activates only one file system when the phone starts or resets. Temporary Storage stores
a new Signed Application or Library Software Package that the current application downloads.
You can then install the package in the active Kernel or Root File System after the next
reset.
Phone initialization
When a phone starts, the boot programs check the Kernel or Root File System that was marked
as the one to be activated. If this file system is not corrupted, the boot program transfers control
to a process in that file system. If that file system is corrupted, the boot program checks the
other Kernel/Root File System.
If that file system is not corrupted, the system:
• Marks that file system as the file system to be activated
• Sets the value of RFSINUSE to the name of the Signed Kernel or Root Software Package
that was used to install that file system
• Transfers control to a process in the file system
If both Kernel/Root File Systems are corrupted, the phone becomes nonfunctional and you
must return the phone for repairs.
A process in the active Kernel/Root File System first checks whether a Signed Application or
a Library Software Package is stored in Temporary Storage. If yes, the process installs the
Application Software Package or the Library Software Package. The system installs both if
either software package has a different file name than the currently installed version and
replaces the existing corresponding files in the Application File System. The process then
deletes the copy of the Signed Application or Library Software Package stored in Temporary
Storage. If the process does not find a Signed Application or Library Software Package in
Temporary Storage, the process checks the integrity of the application files. If the files are
corrupted, the process installs files from the Backup Package and replaces the corrupted
application files in the Application File System. Each time an Application Software Package or
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 15
Page 16

Installing the deskphone
a Library Software Package is installed, the system sets the value of the persistent parameter
APPINUSE to the file name of the Signed Application or Library Software Package from which
the package was installed. If the application files are not corrupted, or after the Backup
Package has been installed, the system transfers control to the application installed in the
Application File System. Note that the processes in the Kernel/Root File System do not connect
to the network or download files.
The application then connects to the network, obtains any necessary IP address information,
and download files. The file download begins with the upgrade and settings configuration files,
and including Signed Software Packages and other separately downloaded files such as
Language Files and Certificate Files. When the phone downloads a Signed Software Package
which can contain either Kernel and Root Software Packages or Application and Library
Software Packages, it is initially stored in volatile memory (RAM). The system installs the other
downloaded files such as Language Files and Certificate Files directly in the Application File
System.
When either type of Signed Software Package is downloaded, the Signing Authority Certificate
is extracted from the package and is validated using a copy of the Avaya Product Root
Certificate Authority Certificate that is contained in the existing application software files. If the
Signing Authority Certificate is invalid, the package is deleted. If the Signing Authority
Certificate is valid, the Hardware Version File in the package is validated using the
corresponding Signature File in the package and the Signing Authority Certificate. If the
signature is invalid, the package is deleted. If the signature is valid, the Hardware Version File
is used to validate whether the package is valid for the model and hardware version of the
phone. If the package is invalid, the package is deleted. If the package is valid, the signature
of the software package is validated using the corresponding Signature Files in the package
and the Signing Authority Certificate. If either signature is invalid, the package is deleted.
If the signatures are valid and the signed software package is a Signed Application/Library
Software Package, the package is stored in Temporary Storage. If the Backup Flag is set in
the Hardware Version File, a copy of the Signed Application / Library Software Package is also
stored as the Backup Package, replacing the previous Backup Package.
If the signatures are valid and the Signed Software Package is a Signed Kernel or a Root
Software Package, the system installs the Kernel Software Package or the Root File System
Software Package or both, if either has a different file name than the currently installed version.
The system replaces the existing corresponding files in the Kernel/Root File System that was
not active during startup. A Root File System Software Package might also install new boot
programs in the boot program area. The system then marks the Kernel or the Root File System
as the one to be activated after the next power-up or reset. The system then sets the value of
the persistent parameter RFSINUSE to the file name of the Signed Kernel/Root Software
Package that was installed.
If a new Signed Kernel or Root Software Package was installed, the phone activates the new
Kernel or Root File System that will install the new Signed Application or Library Software
Package stored in Temporary Storage. If a new Signed Kernel or Root Software Package was
not installed, the phone application registers with a call server.
16 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 17

Understanding the plug in and reset process
Understanding the plug in and reset process
Plug the phone into the Ethernet wall jack. The phone receives power from the port and
performs the following processes:
Note:
Do not unplug the phone during the download process. Wait for the download process to
complete. If the application was downloaded earlier, the whole process takes approximately
1 to 2 minutes after the phone is plugged in. For software upgrades, including the boot file
and application file download, the process might take 5 to 10 minutes. The duration depends
on factors such as LAN loading and the number of phones being installed.
1. The system checks the system initialization value for the language file in use
(NVLANGFILE) for a non-null value, in which case the text strings in that language
file are used for text display. Otherwise, the display shows English text strings.
2. The boot programs check the Kernel or the Root File System that has previously
been marked as the one to be activated to ensure that it has not become corrupted.
If the Kernel or the Root File System is not corrupted, the system transfers control
to a process in that file system. If that file system is corrupted, the boot program
checks the other Kernel/Root File System. If that file system is not corrupted, the
file system is marked as the one to be activated. The system then sets the value of
RFSINUSE to the name of the Signed Kernel or Root Software Package that was
used to install that file system, and the control is transferred to the Signed Kernel
or Root Software Package. If both Kernel and Root File Systems are corrupted, the
system halts the processing. The software checks whether a Signed Application or
Library Software Package has been previously downloaded. If the system finds the
Application Software Package or the Library Software Package the Application
Software Package or the Library Software Package is installed. If either the
Application Software Package or the Library Software Package has a different file
name than the currently installed version, the system replaces the existing
corresponding files in the Application File System. The system then deletes the
downloaded Signed Application or Library Software Package. If a new Signed
Application or Library Software Package is not found, the integrity of the application
files is checked. If the files are corrupted, the system installs the files from the
Backup Package, replacing the corrupted files in the Application File System. Each
time an Application Software Package or a Library Software Package is installed,
the system sets the value of the persistent parameter APPINUSE to the file name
of the Application Software Package that was installed. If the application files are
not corrupted, or after the Backup Package has been installed, control is transferred
to the application installed in the Application File System. While the system loads
the application files into volatile memory and transfers control is transferred to the
application files, the bottom text line shows the value of the APPINUSE
parameter.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 17
Page 18

Installing the deskphone
3. The system starts and sets the internal clock/calendar is set to 0:00:00 Saturday,
4. The phone activates the Ethernet line interface to allow the start of procedures. The
5. The IP phone sends a request to the DHCP server and invokes the DHCP
January 1, 2000.
activation occurs soon after power-up or a reset.
The phone displays the speed of the Ethernet interface in Mbps, that is, 10, 100, or
1000. The phone then displays the message Program below the speed until the
software determines whether the interface is 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1000 Mbps.
process.
The phone displays one of the following messages:
• DHCP: s secs
where s is the number of seconds that have elapsed after the DHCP process was
started. The phone displays the first message if 802.1Q tagging is off and access
to local programming procedures is not disabled or restricted. For more information,
Chapter 3: Using Local Administrative (Craft) Options . on page 25 The phone
see
displays the second message if 802.1Q tagging is on and access to local
programming procedures is disabled or restricted. If the first and second message
alternate every 2 seconds, 802.1Q tagging is on. When the phone displays both
messages alternately, access to local programming procedures is not disabled or
restricted. Finally, the phone displays the third message if 802.1Q tagging is off and
access to local programming procedures is disabled or restricted.
6. The system determines the DHCP protocol and the applicable parameters that are
enabled.
The DHCP server provides the IP addresses for the following hardware:
• The phone
• The HTTP/HTTPS server
• The TN799C or D Control-LAN (C-LAN) circuit pack on the media server
7. Using the list of gateway IP addresses provided by the DHCP server, the phone
performs a router check. The phone cycles through the gateway IP addresses with
ARPs or pings until it receives a response. When the router is located, the router
processes the received LLDP TLVs. Then the HTTP process starts.
8. While the IP phone connects to the HTTP server, the phone displays one of the
following messages:
HTTP: n ipadd
where n is the number of the IP address obtained from the HTTP server and ipadd
is the IP address.
9. When connected, the phone looks for an upgrade script file.
18 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 19

Understanding the plug in and reset process
10. The HTTP server sends and identifies an upgrade script.
The phone might send the GET message several times. Each time the GET
message is sent, all IP phones display the following message: HTTP: n uri
For HTTP, n is the number of HTTP requests made by the phone and uri is the URI
for the current HTTP request.
11. While the upgrade script file is being downloaded, all IP phones display the following
message: HTTP: n sc etag
where n is the number of the IP address obtained from the HTTP server, sc is the
status code of the HTTP response, and etag is the value of the ETag header.
12. When the phone establishes the validity of the application file received, the phone
displays the following message: File Obtained; please wait...... s secs
where s is the number of seconds that elapse while non-volatile memory is
erased.
13. While the application file is saved in flash memory, all IP phones display the
following message: Saving to flash 1% 1 secs
where the percentage of the file and the number of elapsed seconds increase as
the application file is stored in flash memory.
14. The phone contacts the Avaya Media Server and displays a login screen that
displays the following:
Extension, Password text boxes, and a Login button.
Steps to be performed by user after phone displays login and extension prompts:
1. Enter a new extension and the password.
Note:
Unnamed registration is registering a phone with the call server without entry of
an extension or password. You must set the UNNAMEDSTAT parameter to
enable unnamed registration. phones that are registered unnamed have limited
functionality. For more information, see
About unnamed registration on
page 20.
All IP phones display the following:
Extension
Password
Log In
2. Enter the extension number and password and press Log In.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 19
Page 20

Installing the deskphone
You can see the extension as you enter the extension, but the password is displayed
as stars (*). The system determines whether the extension is in use.
When this process is complete, you can hear a dial tone when you press the Phone
On-hook/Off-hook button. The dial tone indicates that the IP phone is installed
successfully.
Understanding unnamed registration
In an IP phone, when you register with a call server, and receive limited service, without
requiring an extension and password entry, this functionality is called as Unnamed registration.
Unnamed registration is useful in the following environments:
• “Hot-desking” environments where a time gap exists between one user logging out and
another user logging in on the same deskphone.
• Road warrior mode of use where a traveller can run the telephony features and
functionality by taking over the office deskphone extension.
In both examples, the user unregisters the deskphone by logging off or by taking the office
deskphone extension over to another deskphone. Without unnamed registration, the
deskphone in the first example will wait for an extension and password entry and the
deskphone in the second example will continue attempting to register at regular intervals. The
disadvantage of a unregistered deskphone is that no one can use the deskphone, for example,
to report a building emergency like a fire.
In Unnamed registration, the deskphone registers without an extension and password.
Because there is no extension, telephony functionality is limited, specifically:
• The user has only one call appearance, and hence, cannot transfer or conference calls.
• The user has no administered feature buttons, and cannot invoke on-hook dialing.
• The user cannot reach extension-based information, such as the Contacts data of a given
user or Option settings.
• The user is limited to the calling capability administered for PSA (Personal Station Access)
on the call server, for example, access to an emergency number.
• The deskphone cannot receive any outside calls.
Unless otherwise disabled, the deskphone automatically attempts to register unnamed if no
action is taken on the deskphone Extension entry screen within 60 seconds. To disable and
prevent unnamed registration, enter an ID or password. The system ignores unnamed
registration after any dialpad entry.
20 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 21

Chapter 4: Maintaining Avaya B189
Conference IP Phones
About software distribution packages
Important:
For any new software release, download the latest software distribution package and read any
Product Support Notices (PSNs) associated with the new release. Both are available on the
Avaya support site at
The software distribution packages contain the following:
• One or more software files.
• One upgrade file such as B189Hupgrade.txt
www.avaya.com/support.
• All the display text language files. For example, mlf_SB189_v78_korean.txt
• A file named av_prca_pem_2033.txt that contains a copy of the Avaya Product Root
Certificate Authority certificate in PEM format. You can downloaded this file to the phones
based on the value of the TRUSTCERTS parameter.
• A file named release.xml that is used by the Avaya Software Update Manager
application.
Note:
Settings files are not included in the software distribution packages because the files
overwrite the existing file and settings.
Two configuration files are:
• The upgrade file, that notifies the phone to upgrade software. The phone attempts to read
this file after a reset. The upgrade file also contains directions to the settings file.
• The settings file contains the option settings that enable, disable, or otherwise customize
the settings you might need to tailor the Avaya IP phones for your enterprise.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 21
Page 22

Maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phones
Downloading software packages
You can use the upgrade file and the application files included in the Software Distribution
Package that Avaya provides to upgrade the phones. Do not modify the upgrade files. You
must save all the essential files on your file server. When you download a new release onto a
file server that has an existing release:
1. Stop the file server.
2. Administer the required port setting in HTTPPORT or TLSPORT for HTTP or TLS,
respectively if you want to specify a port the phones must use to communicate with
the file server.
3. Back up all the current file server directories as applicable.
4. Copy the 46xxsettings.txt file to a backup location.
5. Remove all the files in the download directory. This ensures that you do not have
an inappropriate binary or configuration file on the server. The only system values
that can be used in the Conditional statement are: BOOTNAME, GROUP,
MACADDR, and MODEL.
6. Download the self-extracting executable file or the corresponding zip file.
7. Extract all the files.
8. Copy the 46xxsettings.txt file back into the download directory.
9. Check the Readme file for release-specific information.
10. Modify the 46xxsettings.txt file as required.
11. Restart the HTTP server.
12. Reset your phones.
You can download the default upgrade file from
the phone uses default settings for customer-definable options.
You might want to open the default file and administer the options to add useful functionality
to your Avaya IP phones. Ensure that the file resides in the same directory as the upgrade file,
and name the file as 46xxsettings.scr or 46xxsetting.txt. The Avaya IP phones can operate
without this file.
http://www.avaya.com/support. With this file,
22 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 23

Contents of the settings file
The settings file can include any of six types of statements, one per line:
• Tags that are lines that begin with a single pound (#) character followed by a single space
character and a text string with no spaces.
• Goto commands, of the form GOTO tag. Goto commands cause the phone to continue
interpreting the settings file at the next line after a #tag statement. If such a statement
does not exist, the rest of the settings file is ignored.
• Conditionals, of the form IF $parameter_name SEQ string GOTO tag. Conditionals
cause the Goto command to be processed if the value of the parameter named
parameter_name exactly matches string. If no such parameter named parameter_name
exists, the entire conditional is ignored. You can use the following parameters in a
conditional statement: GROUP, MACADDR, MODEL and MODEL4.
• SET commands, of the form SET parameter_name value. The system ignores any
invalid values for the associated parameter_name so the default or previously
administered value is retained. All values must be text strings, even if the value itself is
numeric or a dotted decimal IP Address.
Contents of the settings file
• Comments, which are statements with a pound (#) character in the first column.
Note:
Enclose all data in quotation marks for proper interpretation.
• GET commands, of the form GET filename . If the phone downloads the file named as
filename, the phone interprets the file as an additional settings file and does not interpret
additional lines in the original file. If the phone cannot obtain the file, the telephone
continues to interpret the original file.
The Avaya-provided upgrade file includes lines that direct the phone to GET
46xxsettings.txt and 46xxsettings.scr. These lines cause the phone to use HTTP/
HTTPS to attempt to download the file specified in the GET command. If the phone obtains the
file, its contents are interpreted as an additional script file. If the file cannot be obtained, the
phone continues processing the upgrade script file. The phone processes the upgrade script
file so that if there is no 46xxsettings.scr file, the phone looks for a 46xxsettings.txt file. If the
phone obtains the settings file successfully but does not include any setting changes the phone
stops using HTTP. This process happens when you initially download the script file template
from the Avaya support Web site, before you make any changes. When the settings file
contains no setting changes, the phone does not go back to the upgrade script file.
You can customize the settings file and identify non-default option settings, application-specific
parameters, and other settings. You can download a template for this file from the
Support website.
Avaya
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 23
Page 24

Maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phones
For details about specific parameter values, see Chapter 7 in the Administering Avaya B189
Conference IP Phone. Specify settings that are different from default values, although you can
also specify default values.
Downloading text language files
About this task
You must save the language files used for text entry and display purposes in the same location
as the 46xxsettings file or in the HTTP Server directory. The HTTP Server directory is defined
using the SET HTTPDIR HTTP server directory path command.
You can download a new language file version only if the filename differs from the language
file previously downloaded. Alternately, you can remove the old language file using an empty
SET LANGxFILE command in the 46xxsettings file before downloading a language file with the
same filename.
Applying settings to logical groups
You might have different communities of end users with the same phone model but requiring
different administered settings. This section provides examples of the group settings for each
of these situations.
You can separate groups of users is to associate each of them with a number. Use the GROUP
parameter for this purpose. You cannot set GROUP system value in the 46xxsettings file. The
GROUP parameter can only be set on a phone-by-phone basis. To set the GROUP parameter,
first identify which phones are associated with which group, and designate a number for each
group. The number can be any integer from 0 to 999, with 0 as the default. The largest group
is assigned as Group 0.
Then, at each phone that does not have default parameters, instruct the installer or end-user
to invoke the local Administration Menu procedure. For more information, see
Administrative procedures on page 25 and specify which GROUP number to use. After the
GROUP assignments are in place, edit the configuration file to allow each phone of the
appropriate group to download its proper settings.
About local
24 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 25

Chapter 5: Using local Administrative Menu
procedures
About Administration Menu procedures
During or after you successfully install an IP phone, a system message might instruct you to
administer one of the manual procedures described in this chapter. These local administrative
procedures are also referred to as Administration Menu procedures.
Local Administrative Options has one form that provides access to all the capabilities and
functions described in this chapter.
Note:
You can modify the settings file to set parameters for any IP phones that download their
upgrade script and application files from the same HTTP server. For more information, see
Administering Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone.
Caution:
Only trained installers or technicians should perform local administrative procedures.
Perform these procedures only if instructed to do so by the system or LAN administrator.
Static administration of these options causes upgrades to work differently with static
administration of these options than by dynamic administration. Values assigned to options
in static administration do not change with upgrade scripts. These values remain stored in
the phone until one of the following happens:
• You download a new boot file
• You reset the IP phone. See
Use these option-setting procedures only with static addressing and, as always, only if
instructed by the system or LAN administrator. Do not use these option-setting
procedures if you are using DHCP. DHCP is the Dynamic Addressing Process, as
indicated in
page 14.
Powering-up and resetting the phone (Dynamic Addressing Process) on
Resetting system values on page 35.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 25
Page 26

Using local Administrative Menu procedures
Entering the Administration Menu
Procedure
1. On the phone, tap Settings.
The phone displays the Settings screen and the options that are available.
2. Tap Administration Menu.
The deskphone displays the Administration Login screen.
3. In the Password text box, enter the password.
4. Tap Log In.
The phone displays the Administration Procedures screen and the options that
are available.
Entering and validating IPv4 addresses
The dial pad uses numeric-only entry when an IPv4 address or the subnet mask is entered.
On a touch screen use a single tap. Use an asterisk to place a period within the address being
entered.
When you press star (*) on the dial pad with the cursor in one of the three fields towards the
left of the display, the following happens:
• If you enter a valid value a period displays. The space after the field displays a period.
• The cursor moves to the next space.
When you press star (*) with the cursor in one of the three fields to the right side of the display,
the system beeps to inidicate an error and the cursor remains in the field to the right. Pressing
the “*” button while the cursor is in the last (right most) field results in an error beep and the
cursor being left where it is. If you enter all three dots that separate the fields and if the value
of each field is valid, the IPv4 address or subnet mask is complete.
The value of a given field might be invalid when you:
• Enter a digit that makes the value of the first field of an IPv4 address exceed 223.
• Enter a digit that makes the value of the last three fields of an IPv4 address exceed
255.
• Enter a digit that makes the value of any field of a subnet mask exceed 255.
26 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 27

Local administrative menu
Using the administrative procedures, you can customize the IP deskphone installation for your
specific operating environment. This section provides a description of each local administrative
option covered in this guide, with references to the pages on which the option appears.
Local administrative menu
Craft
Procedure
value (in
English)
8021X Set 802.1X operational mode Setting The 802.1X Operational Mode on
ADDR Address information
CLEAR Clear all values to factory
DEBUG Enable/disable Debug Mode Disabling/enabling debug mode.
GROUP Set the Group Identifier Changing The group identifier on
INT Interface Control Changing Ethernet interface control on
LOGOUT Log off the deskphone Loging off The deskphone on
RESET
VALUES
Craft Procedure Purpose See
page 28.
Using The pre-installation checklist on
programming
defaults
Reset system initialization
values to defaults
page 28 and Changing IP address
information on page 29.
Clearing the deskphone settings on
page 32.
page 33.
page 33.
page 34.
Resetting system values on page 35.
RESTART
PHONE
SSON Set the Site-Specific Option
TEST Initiate a self-test Performing a self-test on page 37.
VIEW View current parameter values
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 27
Restart the deskphone Restarting The deskphone on
page 36.
Changing SSON settings on page 36.
Number
Using The VIEW craft procedure for
and file names
troubleshooting on page 40.
Page 28

Using local Administrative Menu procedures
Setting the operational mode to 802.1X
About this task
Use the following procedure to set or change the operational mode.
Procedure
1. When you select 802.1X from the Administrative Menu screen, the deskphone
displays the following:
802.1 Supplicant
Pass-thru
The options that are displayed depend on the following parameters as set in the
settings file:
• Disabled if DOT1XSTAT = 0
• Unicast-only if DOT1XSTAT = 1
• Unicast/multicast if DOT1XSTAT = 2
and the Pass-thru line is a text string associated with the current system value
of DOT1X where:
• Enabled mode if DOT1X = 0
• Enabled w/Logoff if DOT1X = 1
• Disabled if DOT1X = 2
2. Tap the line you want to change.
A green tick mark is set next to the option that you have selected.
3. To change the setting, tap the option again.
4. Tap Save to store the new setting and redisplay the Administrative Menu
screen.
Using the preinstallation checklist
Before performing static programming of address information, verify that the call system meets
all the requirements listed in the Requirements to verify for your network section of the Creating
the pre-installation checklist on page 11. You can skip item 4., as it refers to the DHCP server.
In addition, you must have the values for the following parameters. To prevent data entry errors
28 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 29

that have a negative impact on your network, obtain and print copies of the following
parameters for each subnet:
• The IP Address of the call server.
• The IP Address of the gateway or the router.
• The IP netmask.
• The IP Address of the HTTP server.
Changing IP address information
About this task
To assign IP addresses to IP phones, use the automatic method described in Powering-up
and resetting the phone (Dynamic Addressing Process) on page 14. There might be times,
however, when manual assignment of IP addresses is required.
Changing IP address information
Caution:
Static addressing is necessary when a DHCP server is unavailable. But static addressing
has room for text entry errors. So Avaya recommends that you install a DHCP server and
do not use static addressing.
Use the following procedure to invoke manual address information programming.
Procedure
1. Tap and select ADDR from the Administration Menu screen. The next screen
displays the following fields with the prompt Select address to change.
Static addressing
field
IP Address nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn phone IP address (IPADD)
Call Server nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn or
Router IP address nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn Router in use; gateway/
Subnet Mask nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn IP network mask
Field value Description
Call Server in use; media
hhhh:hhhh::hhhh:hhhh:hh
hh
server IP address
router IP address
(NETMASK)
HTTP Server nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn or
hhhh:hhhh::hhhh:hhhh:hh
hh
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 29
IP address of HTTP File
Server in use
Page 30

Using local Administrative Menu procedures
Static addressing
field
HTTPS Server nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn or
802.1Q L2Q text string
VLAN ID dddd NVL2QVLAN
Static VLAN Test ddd VLANTEST
Field value Description
IP address of HTTPS
hhhh:hhhh::hhhh:hhhh:hh
hh
As defined by the selected
L2Q text string
(TLS) File Server in use
L2Q setting text
description
where:
• nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn is the current IP address in IPv4 format associated with the
specific address information on the left side, which could be either a value
previously set by a technician, or the original value of NVIPADD if no previous
change was made,
• L2Q text string is the text string associated with the current system value of
L2Q where Auto = an L2Q value of 0, On = an L2Q value of 1, and Off = an
L2Q value of 2, and
• dddd is the current value of NVL2QVLAN and ddd is the current value of
NVVLANTEST, respectively.
2. Scroll to and tap the line for the address you want to change.
3. Select one of the following as appropriate to the item you selected:
Task Steps
To change any of the
IP address values
such as Phone, Call
Server, Router, Mask,
and File Server
To change the 802.1Q
value
Use the key pad on the screen to enter the new IP
address. IP addresses have three sets of three digits
followed by a period. Tapping star (*) following entry of
three digits causes a period to be placed in the next
position, and the cursor to advance one position to the
right. For example, to enter the IP address
111.222.333.444 in IPv4 format, tap the number 1 on the
key pad three times, then tap *, tap the number 2 on the
key pad three times, then tap *, tap the number 3 on the
key pad three times then tap *, then tap the number 4 on
the key pad three times.
Proceed to the next step.
Tap 802.1Q. On the 802.1Q screen, scroll and tap the
indicated options of Auto, On, or Off. The indicated
options are the text strings corresponding to the L2Q
values defined as Auto if L2Q=0, On if L2Q=1, and Off if
L2Q= 2 .
30 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 31

Enabling and disabling the debug mode
To change the VLAN
ID value
To change the
VLANTEST value
Use the key pad on the screen to enter the new static
VLAN ID of from 0 to 4094, inclusive. Proceed to the next
step.
Use the key pad on the screen to enter the new value of
the DHCPOFFER wait period of from 0 to 999.
4. Tap Save to store the new setting and redisplay the Administration Menu screen or
Cancel to return to theAdministration Menu screen without saving the value
entered.
Once the new values are stored, the phone resets automatically.
Enabling and disabling the debug mode
Before you begin
If the default password is used, the setting associated with the serial port cannot be
changed.
About this task
You can use the debug mode to send all your debug data in a file, nnn_report.gz where you
replace nnn by the deskphone extension as specified by the user during registration.
Procedure
1. Access the Administration Procedures.
2. On the Administration Procedures screen, tap Debug.
The Debug procedures screen displays the following options:
Setting Status
Log Mode Off
Serial Port Off
Log to file Off
Phone Report
Note:
The Phone Report is always
available. If the URI is not present,
the report is stored on the phone
SSH Off
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 31
Page 32

Using local Administrative Menu procedures
3. Tap an option to turn it off or on. To generate a phone report, tap Phone Report
and then tap Create on the Phone Report screen that the phone displays.
The report is generated and saved in the nnn_report.gz debug file in the backup
folder specified by BRURI.
4. If you have made any changes to the settings, tap Save to save the settings.
Clearing the phone settings
About this task
Sometimes, you might want to remove all administered values, user-specified data, and option
settings and return a phone to its factory settings. You might have to remove all administered
values when you give a phone to a new, dedicated user and when the LOGOFF option is not
sufficient. For example, a new user is assigned the same extension, but requires different
permissions than the previous user.
The CLEAR option erases all administered data—static programming, HTTP and HTTPS
server programming, and user settings including Contact button labels and locally programmed
Feature button labels, and restores all such data to default values. Using the CLEAR option
does not affect the software load itself. If you upgrade the phone, the phone retains the latest
software. After you clear a phone of the settings, you can administer the phone normally.
Caution:
This procedure erases all administered data without any possibility of recovering the data.
Neither the boot code nor the application code is affected by this procedure.
Use the following procedure to clear the phone of the administrative, user-assigned, and
options values.
Procedure
1. Tap CLEAR from the Administration Menu screen. The phone displays the Press
Clear again to confirm. message.
2. Tap Clear to clear all values to use initial default values.
Tap Cancel. If you do not want to clear all values and to terminate the procedure
and retain the current values.
The phone displays the following text:
Clearing values...
The phone is reset to the default factory settings.
32 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 33

• All system values and system initialization values.
• 802.1X identity and password.
• User options, parameter settings, identifiers, and password.
After clearing the values, the phone resets.
Changing the group identifier
About this task
Use the following procedure to set or change the group identifier.
Note:
Perform this procedure only if the LAN Administrator instructs you to do so. For more
information about groups, see
Applying settings to logical groups on page 24.
Changing the group identifier
Procedure
1. Select Group from the Administration Procedures screen.
The screen displays the Group text box.
2. In the Group text box, enter a valid Group value from 0 to 999.
3. Tap Save to store the new setting. The deskphone displays the Administration Menu
screen.
Changing Ethernet interface control
About this task
Use the following procedure to set or change the interface control value.
Procedure
1. When you select INT from the Administration Procedures screen, the phone
displays the following options:
The options that are displayed are the text strings associated with the current
PHY1STAT on the Ethernet line.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 33
Page 34

Using local Administrative Menu procedures
• Auto when PHY1STAT = 1
• 10 Mbps half when PHY1STAT = 2
• 10 Mbps full when PHY1STAT = 3
• 100 Mbps half when PHY1STAT = 4
• 100 Mbps full when PHY1STAT = 5
• 1000 Mbps full when PHY1STAT = 6
2. To change the setting, scroll up or down as required and tap the new setting.
3. Tap Save to store the new settings and redisplay the Administration Procedures
screen.
Logging off from the phone
About this task
Use the following procedure to log off from a phone.
Caution:
Once you are logged off from a phone, you might need a password and extension to log
back in.
Procedure
1. When you select LOGOUT from the Administration Menu procedures screen, the
phone displays the following text:
Press Log Out again to confirm.
2. Press or tap Log Out to log off from the phone.
Press or tap Cancel to return to the Administration Menu procedures screen without
logging off the phone.
34 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 35

Resetting system values
About this task
Note:
When updating Administration procedures from a touch screen deskphone, touching the
line you want to change or the applicable softkey produces the same result as selecting a
line and pressing the applicable softkey on a non-touch screen IP deskphone.
Use the following procedure to reset all system initialization values to the application software
default values.
Caution:
This procedure erases all static information, without any possibility of recovering the data.
Procedure
Resetting system values
1. Select RESET VALUES from the Administration Procedures screen. The
deskphone displays the following text:
Press Reset to confirm.
2. Press Cancel to return to the Administration Procedures screen without resetting
the deskphone.
Press Reset to start the deskphone reset.
The deskphone resets from the beginning of registration, which might take a few
minutes. The deskphone resets:
• All system values and system initialization values except AUTH and NVAUTH
to default values.
• The 802.1X ID and Password to their default values.
• Call server values to their defaults.
• Any entries in the Redial buffer.
• Do not affect user-specified data and settings like Contacts data or the
deskphone login and password. To remove this type of data, see
deskphone settings on page 32.
Clearing the
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 35
Page 36

Using local Administrative Menu procedures
Restarting the phone
About this task
Use the following procedure to restart the phone.
Procedure
1. Select RESTART PHONE from the Administration Procedures screen. The phone
displays the following text:
Press Restart to confirm.
2. Tap Cancel to return to the Administration Procedures screen without restarting the
phone.
Press Restart to proceed with the registration steps. For more information, see
Powering-up and resetting the phone (Dynamic Addressing Process) on page 14.
A restart does not affect user-specified data and settings like Contacts data or the
phone login and password.
The completion of the restart procedure depends on the status of the boot and
application files.
Changing SSON settings
About this task
Caution:
Do not perform this procedure if you are using static addressing. Perform this procedure
only if you are using DHCP and the LAN administrator instructs you to do this.
Note:
When updating Administration Procedures from a touch screen phone, touching the line you
want to change or the applicable softkey produces the same result as selecting a line and
pressing the applicable softkey on a non-touch screen IP phone.
Use the following procedure to set the Site-Specific Option Number (SSON).
36 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 37

Procedure
1. Select SSON from the Administration Procedures screen.
The phone displays the current SSON value with a numeric keypad on the
screen.
2. To change the setting, use the Key pad on the screen to enter a valid SSON value
between 128 and 255.
3. Tap Save to store the new setting and redisplay the Administration Procedures
screen.
Performing a self-test
About this task
Performing a self-test
Note:
Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone stores two software code images in reprogrammable
non-volatile memory. The primary image, called the “big app” must be running to perform a
self-test. The backup image, called the “little app” does not support the self-test.
Use the following procedure to perform self-testing:
Procedure
1. Tap or select TEST from the Administration Procedures screen. The phone displays
the following text:
Press Test to confirm.
2. Tap or press Test to start phone testing.
Tap or press Cancel to return to the Administration Procedures screen without
testing the phone.
The test performs the following actions:
The screen glows red, green and blue color consecutively and plays the standard
ring tone with each color change.
The Mute microphone LED glows red, blue, and green alternately.
After approximately 5 seconds, the top phone screen displays either Self-test
passed or Self-test failed.
3. Press or tap Back to return to the Administration Menu screen.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 37
Page 38

Using local Administrative Menu procedures
38 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 39

Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
Resolving error conditions
About this task
Installers can troubleshoot problems before seeking assistance from the system or LAN
administrator in four areas:
Procedure
1. Check both the power and Ethernet wiring for the following conditions:
• Check whether all components are plugged in correctly.
• Check LAN connectivity in both directions to all servers - DHCP, HTTP, and
HTTPS.
• If the deskphone is powered from the LAN, ensure that the LAN is properly
administered and is compliant with IEEE 802.3af.
2. If you use static addressing:
• Use the VIEW option to find the names of the files being used and verify that
these filenames match those on the HTTP/HTTPS server. For more
information, see
page 40. Check the Avaya Support site at www.support.avaya.com to verify
whether the correct files are being used.
• Use the ADDR option to verify IP addresses. For more information, see
Changing IP address information on page 29.
3. If the deskphone is not communicating with the system, DHCP, HTTP, or Avaya
Media Server, make a note of the last message displayed. For more information,
see
Installation error and status messages on page 43 and Operational errors
and status messages on page 47.
Consult the system administrator. Sometimes, you can correct problems relating to
Communication Manager and HTTP communications by setting the HTTPPORT
value to 81.
Using the VIEW craft procedure for troubleshooting on
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 39
Page 40

Troubleshooting
Failure to hear DTMF tones
As H.323 telephones do not send DTMF tones to non-H.323 telephones, the user need not
perform troubleshooting for failure to hear DTMF tones from a B189 phone. The TN2302AP
board does not pass in-band DTMF tones.
Correcting a power interruption
If power to a B189 Conference phone is interrupted while the phone is saving the application
file, the HTTP/HTTPS application can stop responding. If this occurs, restart the phone.
Using the VIEW procedure for troubleshooting
About this task
Use the following procedure to verify the current values of system parameters and file
versions.
Note:
You can use the ADDR option to view IP addresses if needed. For more information on using
the ADDR option, see
have been entered incorrectly. Verify whether you were provided with correct IP
addresses.
Procedure
1. Select VIEW from the Administration Menu Screen.
The phone displays the following options: IP Parameters, Quality of Service, and
Miscellaneous.
2. Tap the category that you want to see.
The information for that category is displayed.
Changing IP address information on page 29. The IP addresses might
40 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 41

Table 1: IP Parameter Values
Name System Value Format
Using the VIEW procedure for troubleshooting
IP address
(Phone)
Call Server nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn IP address of the call server
Router IP
address
Subnet Mask nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn Up to 15 ASCII characters,
HTTP server nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn IP address of last HTTP
HTTPS server nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn IP address of last HTTPS
802.1Q cccc Text string corresponding to
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn Phone IP address, IPADD
value.
currently in use, otherwise
0.0.0.0.
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn Up to 15 ASCII characters,
the IP address of the router in
use.
NETMASK value.
server used successfully
during initialization or
0.0.0.0. if no file server was
used successfully.
server used successfully
during initialization or
0.0.0.0. if no file server was
used successfully.
the L2Q value.
VLAN ID cccc Up to 4 ASCII characters.
Value is L2QVLAN text Auto
if 802.1Q tagging is 0 or On if
802.1Q tagging is 1. If
802.1Q tagging is off (2), this
line is not displayed.
Static VLAN Test ccc Up to 3 ASCII characters.
Value is VLANTEST value if
802.1Q tagging is 0 or 1. If
802.1Q tagging is off (2), this
line is not displayed.
Table 2: Quality of Service Parameters
Parameter System value Format
L2 Audio n L2QAUD,layer 2 audio
priority value.
L2 Signaling n L2QSIG,layer 2 signaling
priority value.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 41
Page 42

Troubleshooting
Parameter System value Format
L3 Audio nn DSCPAUD,
Differentiated Services
Code Point for audio.
L3 Signaling nn DSCPSIG, Differentiated
Services Code Point for
signaling.
Table 3: Miscellaneous Parameters
Parameter System value Format
Model B189Dccc Up to 8 ASCII characters,
MODEL serial number.
Phone SN cccccccccccccccccc Telephone Serial
Number, up to 18 ASCII
characters.
Group nnn Up to three ASCII
numeric characters:
GROUP value.
Protocol: cccccccc Up to eight ASCII
characters, currently only
H.323
Application File filename.ext Four to 32 ASCII
characters as primary
application.
Ethernet Port cccccccc Ethernet Two to eight ASCII
characters, either 1000
Mbps, 100 Mbps, 10
Mbps, or No.
Kernel/RFS file bootcodename One to 32 ASCII
characters (backup
image name).
Backup App File filename.ext Four to 32 ASCII
characters (backup
application).
3. Scroll across the screen to the entry you want to view.
4. Press Back at any time to return to the Administration Procedures screen.
42 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 43

Installation error and status messages
Avaya B189 Conference IP Phones display messages in the currently selected language or in
the language specified by the LANGSYS parameter value, if the phone is logged off. If English
is not the selected language, the phone displays messages in English only when the message
are associated with local procedures, for example, MUTE VIEW.
The phone displays most of the messages for only about 30 seconds, and then the phone is
reset. The most common exception is Extension in Use, display more than 30 seconds and
which remains until you perform any further action on the phone.
Table 4: Possible error and status messages during installation of B189 phones
Message Cause/Resolution
802.1X Failure
CAUSE: Incorrect credentials provided for authentication or
credentials not provided at all.
RESOLUTION: Follow the display prompts and reenter the 802.1X ID
and password.
Installation error and status messages
IPv4 or IPv6
address
Conflict
Authentication
Error
Bad FileSv
address
Bad Router?
Call Error
CAUSE: The phone has detected an IP address conflict.
RESOLUTION: Verify administration settings to identify duplicate IP
addresses.
CAUSE: The call server does not recognize the extension entered.
RESOLUTION: Confirm the extension is correct and is correctly
administered on the switch. Then try registration again, and enter the
extension accurately.
CAUSE: The HTTP/HTTPS server IP address in the IP phone’s
memory is all zeroes.
RESOLUTION: Depending on the specific requirements of your
network, this may not be an error. If appropriate, either administer the
DHCP server with the proper address of the HTTP/HTTPS server, or
administer the phone locally using the ADDR option. For details on
the ADDR option, see
page 25.
CAUSE: The phone cannot find a router based on the information in
the DHCP file for GIPADD.
RESOLUTION: Use static addressing to specify a router address, or
change administration on DHCP.
For deails, seeAdministering Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone.
CAUSE: The user was on a call when the connection to the
gatekeeper went down due to a network outage or a gatekeeper
problem. The phone attempted to automatically register with the same
or another gatekeeper, but the responding gatekeeper had no record
of the call.
Using Local Administrative (Craft) Options on
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 43
Page 44

Troubleshooting
Message Cause/Resolution
RESOLUTION: Wait for the call to end, and if the phone does not
automatically register, restart the phone.
Connecting...
Contacting
call server...
DHCP: CONFLICT
Discover
aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
CAUSE: The phone is attempting to establish a TCP connection with
the call server. A resource needed to establish the connection might
not be available or the 10 second buffer on switch-related actions
might have expired.
RESOLUTION: Allow the phone to continue attempts to connect to
TCP.
CAUSE: The phone has rebooted successfully and is attempting to
register with the call server.
RESOLUTION: Allow the phone to continue.
CAUSE: At least one of the IP address offered by the DHCP server
conflicts with another address.
RESOLUTION: Review DHCP server administration to identify
duplicate IP address(es).
CAUSE: The phone is attempting to find a DHCP server, and the user
can view the IP addresses.
RESOLUTION: If this message appears for more than a few seconds,
verify with the LAN Administrator that a DHCP server is appropriately
administered on the network. If a DHCP server is not present, you
must interrupt the Discovering process and use static addressing. For
details on configuring a static address, see
Changing IP address
information on page 29. To interrupt the Discovering process, press
the # button, and when you see the 100 Mbs or10 Mbs message,
quickly press the star (*) button.
Discovering... CAUSE: The phone is attempting to find a DHCP server and the user
is not allowed to view IP addresses.
RESOLUTION: If this message appears for more than a few seconds,
verify with the LAN Administrator that a DHCP server is appropriately
administered on the network. If a DHCP server is not available, you
must interrupt the Discovering process and use static addressing. For
information, see
Changing IP address information on page 29. To
interrupt the Discovering process, press the pound (# )button, and
when you see the 1000 Mbps , 100 Mbps or 10 Mbps message,
quickly press the star (*) button.
EEPROM error,
repair
required
Emergency
Option
Extension in
Use
Extension in
use: <NNNN>
CAUSE: Application file was not downloaded or saved correctly.
RESOLUTION: The phone automatically resets and attempts to reinitialize.
CAUSE: Incompatible emergency option.
RESOLUTION: This must not happen. Contact Avaya support.
CAUSE: The call server detects an extension conflict with an existing
set or Softphone.
RESOLUTION: By pressing Continue, you can force the current
phone to register and thereby disconnect the other user. When Login
44 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 45

Message Cause/Resolution
Press continue
to take over
this extension
Login|Continue
is selected instead, the phone re-prompts for entry of a different
extension and password.
Installation error and status messages
Finding
router...
Gatekeeper
Error
Gateway Error
Incompatible
Invalid file
IP address
Error
CAUSE: This phone is proceeding through boot-up.
RESOLUTION: Allow the phone to continue.
CAUSE: The gatekeeper rejects the registration attempt for an
unspecified reason.
RESOLUTION: Review gatekeeper and call server administrations,
including IP network parameters.
CAUSE: DEFINITY Release 8.4 does not have an H.323 station
extension for this phone.
RESOLUTION: On the station administration screen, ensure the DCP
set being aliased for this IP phone has an H.323 station extension
administered, in accordance with switch administration instructions.
CAUSE: This release of the call server does not support the current
version of the IP phone.
RESOLUTION: Upgrade to the current version of Communication
Manager (3.0 or greater) software.
CAUSE: The phone does not have sufficient room to store the
downloaded file.
RESOLUTION: Verify that the proper filename is administered in the
script file, and the correct application file is located in the appropriate
location on the HTTP or HTTPS server.
CAUSE: The gatekeeper reports an invalid IP address.
RESOLUTION: This must not happen. Contact Avaya support.
License Error
Limit Error
NAPT Error
No Ethernet
Packet Error
CAUSE: The call server does not support IP telephony.
RESOLUTION: Contact Avaya to upgrade your license.
CAUSE: The call server has reached its limit of IP stations.
RESOLUTION: Un-register phones that are not in use, or contact
Avaya to upgrade your license.
CAUSE: A device between the phone and the call server is invoking
Network address Port Translation (NAPT), which the B189 phone do
not support.
RESOLUTION: Contact the System Administrator to remove or readminister the device.
CAUSE: When first plugged in, the IP phone is unable to communicate
with the Ethernet.
RESOLUTION: Verify the connection to the Ethernet jack, verify if the
jack is Category 5, verify if power is applied on the LAN to that jack.
CAUSE: Protocol timeout error.
RESOLUTION: Reenter the correct extension and password. If the
condition persists, contact the system administrator.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 45
Page 46

Troubleshooting
Password Error
Message Cause/Resolution
CAUSE: The call server does not recognize the password entered and
displays the Login Error screen.
RESOLUTION: Confirm whether the password is correct, then try
registering again, and enter the password accurately.
Request Error
Restarting...
Subnet
conflict
System busy
CAUSE: The gatekeeper does not accept the registration request sent
by the phone as the request is not formatted properly.
RESOLUTION: The phone will automatically attempt to register with
the next gatekeeper on its list. If the problem persists, reboot the
phone.
CAUSE: The phone is in the initial stage of rebooting.
RESOLUTION: Allow the phone boot process to continue.
CAUSE: The phone is not on the same VLAN subnet as the router.
RESOLUTION: Press star (*) to administer an IP address on the
phone. For information on configuring an IP address, see Changing
IP address information on page 29, or administer network equipment
to administer the phone appropriately.
CAUSE: Most likely, the number of IP endpoints on the call server is
already at maximum capacity. Network resource may not be
unavailable.
RESOLUTION: The phone attempted to access a network resource
such as DHCP server, HTTP server, or the call server and was not
successful. Check the resource being called upon for its availability.
If the resource appears operational and is properly linked to the
network, verify that the addressing is accurate and that a
communication path exists in both directions between the phone and
the resource.
System Error
Undefined
Error
Updating: DO
NOT UNPLUG THE
phone
Waiting for
LLDP
Wrong Set Type
CAUSE: The call server has an unspecified problem.
RESOLUTION: Consult your Avaya Media Server administration and
troubleshooting documentation.
CAUSE: The call server has rejected registration for an unspecified
reason.
RESOLUTION: Consult your Avaya Media Server administration and
troubleshooting documentation.
CAUSE: The phone is updating its software image.
RESOLUTION: The phone update process must be continued.
CAUSE: No File Server or Call Server has been administered, so the
phone is expecting to get the missing data through LLDP.
RESOLUTION: Administer the missing data by one of the following
methods: Statically, dynamically in DHCP, in the 46xxsettings file for
Call Server addresses, or by LLDP. For more information, see LLDP
Troubleshooting on page 50.
CAUSE: The call server does not recognize the set type.
46 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 47

Operational errors and status messages
Message Cause/Resolution
RESOLUTION: Ensure the call server is properly administered to
register a compatible phone for the IP address and extension.
Operational errors and status messages
The following table identifies some of the possible operational problems that might be
encountered after successful Avaya B189 Conference IP phone installation. The user guide
for a specific phone model also contains troubleshooting for users having problems with
specific IP phone applications. Most of the problems reported by phone users are LAN-based,
where Quality of Service, server administration, and other issues can impact end-user
perception of IP phone performance.
Table 5: Operational error conditions for Avaya B189 Conference IP Phones
Condition Cause/Resolution
The phone continually reboots, or reboots
continuously about every 15 minutes.
The phone stops
working in the
middle of a call,
The phone was
working, but does
not work now,
AND no lights are lit
on the phone and the
display is not lit.
AND power to the
phone is normal and
the phone might have
gone through the
restarting sequence.
AND no lights are lit
on the phone and the
display is not lit.
CAUSE: The phone cannot find the HTTP/
HTTPS server and/or call server.
RESOLUTION: Ensure that MCIPADD is
administered either manually or through DHCP
or HTTP, as appropriate. Alternately, this might
be a firmware fault because the MAC address
in memory is corrupted; in this case, you must
return the phone to Avaya for repair.
CAUSE: Loss of power.
RESOLUTION: Check the connections
between the phone, the power supply, and the
power jack. For example, verify whether static
addressing was not used or that any changes
to static addresses were entered correctly.
Follow POE guidelines to troubleshoot POE
related problems.
Loss of path to the Avaya call server, expiry of
DHCP lease, or unavailable DHCP server
when telephone attempts to renegotiate DHCP
lease.
RESOLUTION: As above.
CAUSE: Loss of power.
RESOLUTION: Check the connections
between the phone, the power supply, and the
power jack. Follow POE guidelines to
troubleshoot POE related problems.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 47
Page 48

Troubleshooting
Condition Cause/Resolution
AND power to the
phone is normal, but
there is no dial tone.
The display might
show “System Busy.”
AND the phone was
recently moved.
AND the network was
recently changed to
upgrade or replace
servers, readminister the Avaya
Media Server, add or
change NAT, etc.
CAUSE: Loss of communication with the call
server.
RESOLUTION: Check LAN continuity from the
call server to the phone using ARP or traceroute and from the phone to the call server.
Verify that LAN administration has not
changed for the Gatekeeper, TN 2302AP
boards, or the LAN equipment (routers,
servers, etc.) between the switch and the
phone.
Verify that telephone settings are not changed
locally using VIEW and ADDR information, as
described earlier in this guide. Verify that the
telephone volume is set high. Finally, conduct
a self-test.
CAUSE: Loss of communication with the call
server.
RESOLUTION: As above, but verify whether
the phone is being routed to a different DHCP
server, or even a different call server switch. If
so, the new server or switch might need to be
administered to support the phone.
CAUSE: Loss of communication with the call
server.
RESOLUTION: As above.
The phone works properly, but you cannot
hear incoming DTMF tones.
CAUSE: The TN2302AP board does not pass
in-band DTMF tones.
RESOLUTION: None; the board is operating
as designed.
The phone works properly, but you cannot
hear incoming DTMF tones.
CAUSE: Call server suppresses sidetone
DTMF.
RESOLUTION: After completing call server
administration, enable On-Hook Dialing on the
Change-System-Parameters screen. If the
user has enabled Hands-Free Answer (HFA),
answers a call using the Speaker, switches to
the handset, and presses dialpad buttons, the
phone does not transmit DTMF tones. Disable
HFA to hear DTMF tones.
Hands-Free Answer (HFA) is administered
but the phone did not automatically answer
a call.
CAUSE: HFA only works if the phone is idle.
The phone ignores a second call if a call,
including the ringing tone is in progress.
48 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 49

Operational errors and status messages
Condition Cause/Resolution
RESOLUTION: None.
The phone does not use and ignores the
HTTP or HTTPS script file and settings
file.
The HTTP or
HTTPS script file is
ignored or not
used by the
AND the HTTP or
HTTPS server is a
LINUX or UNIX
system.
phone,
CAUSE: The system value AUTH is set to 1
which indicates that HTTPS is required but no
valid address is specified in TLSSRVR.
RESOLUTION: Change AUTH to 0 (zero), or
enter a valid address for TLSSRVR.
CAUSE: The phone expects lines of the script
file to terminate with a <Carriage
Return> <Line Feed>. Some UNIX
applications only terminate lines with <Line
Feed>. Editing the script file with a UNIX-
based editor can strip a<Carriage
Return> from the file. Doing so causes the
entire file to be treated as a comment, and thus
be ignored.
RESOLUTION: Edit the script file with a
®
Windows
—based editor, or another editor
that does not strip out the <Carriage
Return>.
CAUSE: UNIX and LINUX systems use casesensitive addressing and file labels.
RESOLUTION: Verify the file names and path
in the script file are accurately specified.
AND phone
administration
recently changed.
The system ignores some settings in the
settings file while other settings are being
used properly.
Telephone power is interrupted while the
phone is saving the application file and the
HTTP/HTTPS application stops
responding.
The user indicates an application or option
is not available.
CAUSE: The B189Hupgrade.txt file was edited
incorrectly, renamed, etc.
RESOLUTION: Download a clean copy of the
B189Hupgrade.txt file from the Avaya support
web site at http://www.avaya.com/support, and
do not edit or rename the file. Customize or
change only the 46xxsettings file as required.
CAUSE: Improper administration of settings
file.
RESOLUTION: Verify that customized settings
are correctly spelled and formatted.
See Administering Avaya B189 Conference IP
Deskphone, 16–604294.
CAUSE: The HTTP or HTTPS server stops
responding if power is interrupted while a
phone is saving the application file.
RESOLUTION: Restart the phone
CAUSE: The 46xxsettings script file is not
pointed to accurately, or is not properly
administered to allow the application.
RESOLUTION: Verify that the 46xxsettings
script file is properly specified for your system,
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 49
Page 50

Troubleshooting
Condition Cause/Resolution
verify that the file server is UNIX or LINUX, and
verify the extension.
Then verify that all the relevant parameters
indicated in Chapter 7 of the Administering
Avaya B189 Conference IP Deskphone, 16–
604294, are accurately specified in the
46xxsettings file.
User data disappeared when the user
logged out of one phone and logged in to
another phone.
CAUSE: The second phone is unable to gain
access to the backup file.
RESOLUTION: Verify that the first phone
creates a backup file.
Verify whether appropriate administration was
done in accordance with Chapter 7 of the
Administering Avaya B189 Conference IP
Deskphone, 16–604294. Then verify that the
second phone is administered to retrieve data
from the same location as the first phone.
Then verify that all the relevant parameters
indicated in Chapter 7 of the Administering
Avaya B189 Conference IP Deskphone, 16–
604294, are accurately specified in the
46xxsettings file.
Finally, verify that the HTTP and HTTPS server
on which the backup file is located is
operational and accessible from the second
phone.
LLDP Troubleshooting
If the Waiting for LLDP message appears for more than a few seconds, the message generally
indicates a problem with getting a value for the call server IP address. This error can occur
due to incorrect settings in script files or in the way the network is configured.
On booting, the phone must obtain a valid IP address for the call cerver. The phone can obtain
the value, known as MCIPADD, from several sources:
• A static or manually programmed address on the phone.
• The 46xxsettings.txt file MCIPADD setting.
• A DHCP offer using option 242 that includes the MCIPADD setting.
• Link Layer Discovery Protocol or LLDP.
If the phone cannot find MCIPADD through any of these means, it will fail to register with the
Call Server and will display the Waiting for LLDP message several times before rebooting. For
example, if the MCIPADD value was specified in the 46xxssetting file and the network file
50 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 51

server fails, the phone will not be able to read the MCIPADD value or any of the 46xxsettings
file parameters. Therefore, do not use this method of providing MCIPADD.
Proposed Solution
Procedure
1. A more robust way to provide this value is to use DHCP. You can administer the
DHCP server to provide MCIPADD using DHCP Option 242. You can also
administer the TLSSRVR, HTTPSRVR and L2QVLAN parameters using this option.
phones using non-static addressing automatically use the DHCP request method.
Option 242 is the default DHCP offer and may get MCIPADD and other addresses
using this way.
2. The phone displays the Waiting for LLDP message when both the HTTP and
HTTPS Server IP address are not administered. To administer the HTTP and/or
HTTPS server, use the Administration menu ADDR procedure and enter the correct
HTTP and or HTTPS File Server IP address in the File Server field.
LLDP setup and troubleshooting steps
3. An alternative protocol known as LLDP can also supply call server, and file server
with HTTP and HTTPS IP addresses. This IETF standard protocol requires the
network to be equipped and configured to support LLDP. You can provide HTTP
and the HTTPS Server and call server IP addresses with LLDP in the network using
proprietary Transport Layer Values (TLVs) to pass information to the phones.
For more information about LLDP processing, see Administering Avaya B189
Conference IP Deskphone, 16–604294.
LLDP setup and troubleshooting steps
For manually programmed deskphones, use the Administration Menu ADDR procedure to set
the call server to a valid IP address. For information on entering the IP addresses using the
ADDR procedure, see
Note:
If system value STATIC is set to 0 which is the default setting, the DHCP or the 46xxsettings
file might overwrite the static addresses.
Changing IP address information on page 29.
Note:
See Administering Avaya B189 Conference IP Deskphone, 16–604294, for details on how
to set “STATIC” to use manually programmed IP addresses.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 51
Page 52

Troubleshooting
Proposed solution for DHCP configured deskphones
Procedure
1. Using the Administration menu ADDR procedure, set Phone to 0.0.0.0.
2. Verify or set SSON to 242 which is the default value.
3. Administer the DHCP server option 242 to include MCIPADD=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx where
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the call server IP address.
4. Verify that the DHCP server and the deskphone are on the same VLAN.
5. Verify the DHCP server port 67 and or the DHCP client port 68 are not blocked on
the switch.
6. Verify the configuration of the DHCP Relay Agent on the switch or on a separate
PC, for example, MS Windows Server 2000/2003 whether the deskphones and
DHCP Server are placed on different networks or subnets. DHCP broadcast
messages do not, by default, cross the router interface.
Note:
Do not embed spaces in DHCP Option 242 strings. For more information, see
DHCP Server Administration in Chapter 5 of the Administering Avaya B189
Conference IP Deskphone, 16–604294.
Proposed solution for script-configured deskphones
Procedure
1. Edit the 46xxsettings.txt file to contain a valid Call Server IP address with the line
SET MCIPADD xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the Call Server IP
address.
2. Verify that the B189Hupgrade.txt file contains the line GET 46xxsettings.txt
as the last command line of the upgrade file.
3. Verify that the deskphone can reach the HTTP server and whether the HTTP server
is activated.
4. Verify that the B189Hupgrade.txt and 46xxsettings.txt files are placed in the proper
directory of the HTTP server to access these files.
For more information, see Administering Avaya B189 Conference IP Deskphone,
16–604294.
52 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 53

Proposed solution for LLDP-configured deskphones
About this task
For LLDP-configured deskphones, activate the switch the deskphone is connected to for LLDP.
This is currently only possible with Extreme switches. Activating the switch for LLDP enables
the switch to send appropriate IP addresses using Avaya/Extreme Proprietary HTTP and/or
HTTPS Server and/or Call Server TLVs.
Note:
The deskphone obtains the HTTP and or HTTPS Server and Call Server IP addresses from
LLDP only if the addresses were not configured through other means such as DHCP Server,
Script File, or statically.
Note:
Set the switch LLDP repeat timer to less than 30 seconds.
Secure Shell Support
Note:
For more information, see Administering Avaya B189 Conference IP Deskphone, 16–
604294.
Secure Shell Support
Secure Shell (SSH) protocol is a tool that the Avaya Services organization can use to remotely
connect to IP deskphones to monitor, diagnose, or debug deskphone performance. Release
1.0 supports only the SSHv2 version. Because of the sensitive nature of remote access, you
can disable permission with the SSH_ALLOWED parameter. Even if permission is given, the
deskphone has several inbuilt security features.
You can configure the idle or inactivity time that will disable SSH with the SSH_IDLE_TIMEOUT
parameter.
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 53
Page 54

Troubleshooting
54 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
Comments? infodev@avaya.com
Page 55

Index
Numerics
802.1X operational mode, setting the .........................28
A
Administration menu ...................................................25
C
clearing the phone settings ........................................ 32
craft procedure ........................................................... 40
D
debug mode ............................................................... 31
enabling and disabling ......................................... 31
download file content ..................................................21
downloading software upgrades .................................21
Downloading Text Language Files ............................. 24
DTMF Tones .............................................................. 40
dynamic addressing process ......................................14
layout ..........................................................................10
connections ..........................................................10
legal notices ................................................................. 2
LLDP troubleshooting .................................................50
Local administrative procedures .................................27
logoff procedure ......................................................... 34
O
operation errors .......................................................... 47
overview ..................................................................... 11
P
phone ................................................................ 9, 26, 36
entering the administration menu .........................26
overview .................................................................9
restarting ..............................................................36
plugging in .................................................................. 13
power interruption .......................................................40
power-up and reset process .......................................17
Pre-Installation Checklist ............................................11
Pre-Installation Checklist for Static Addressing ..........28
E
Error Conditions ......................................................... 39
error messages .......................................................... 43
G
Group Identifier ...........................................................33
GROUP Parameter .................................................... 24
I
Initialization .................................................................15
intended audience ........................................................7
Interface Control .........................................................33
IP Deskphone .............................................................11
Requirements .......................................................11
L
Language Files for text entry, Downloading ............... 24
R
related documentation ..................................................7
Requirements, for each IP Deskphone ...................... 11
Reset System Values ................................................. 35
resetting the phone .....................................................14
S
Secure Shell Support ................................................. 53
self-test .......................................................................37
settings file, contents ..................................................23
Site-Specific Option Number Setting ..........................36
Software ..................................................................... 11
software upgrades, downloading ................................21
SSON Procedure ........................................................36
Static Addressing ....................................................... 28
Pre-Installation Checklist ..................................... 28
status messages ...................................................43, 47
support ......................................................................... 7
contact ................................................................... 7
System Values, Reset ................................................ 35
Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014 55
Page 56

Error Conditions ................................................... 39
T
troubleshooting LLDP .................................................50
troubleshooting ...........................................................40
DTMF tones ......................................................... 40
power interruption ................................................ 40
Troubleshooting ..........................................................39
U
Unnamed Registration ................................................20
56 Installing and maintaining Avaya B189 Conference IP Phone January 2014
 Loading...
Loading...