Page 1

Avaya Solution Interoperability Test Lab
Configuring Avaya 10x0 Series SIP Video Endpoints with
Avaya Aura
TM
Aura
Communication Manager Feature Server Release
TM
Session Manager Release 6.0 and Avaya
6.0 – Issue 1.0
Abstract
These Application Notes describe the configuration of the Avaya 10x0 Series SIP Video
Endpoints with Avaya AuraTM Session Manager and Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager
as a Feature Server.
Avaya AuraTM Session Manager provides SIP proxy/routing functionality, routing SIP
sessions across a TCP/IP network with centralized routing policies and registrations for
SIP endpoints.
Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager operates as a Feature Server for the SIP
endpoints which communicate with Avaya AuraTM Session Manager over SIP trunks.
These Application Notes provide information for the setup, configuration, and verification of
the call flows tested on this solution.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
1 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 2

Table of Contents:
1. Introduction ............................................................................................................. 4
1.1. Equipment and Software Validated......................................................................... 5
2. Configuring Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server ..................... 5
2.1. Verify System Capabilities and Licensing ............................................................... 5
2.1.1. SIP Trunk Capacity Check ................................................................................. 6
2.1.2. AAR/ARS Routing Check ................................................................................... 6
2.1.3. Enable Private Numbering .................................................................................. 7
2.2. Add Node Name of Avaya AuraTM Session Manager ............................................. 7
2.3. Configure Codec Type ............................................................................................ 8
2.4. Configure IP Network Region ................................................................................. 8
2.5. Add SIP Signaling Group ........................................................................................ 9
2.6. Add SIP Trunk Group ........................................................................................... 10
2.7. Administering Numbering Plan ............................................................................. 11
2.8. Configure Stations ................................................................................................ 12
2.9. Configure Off-PBX-Telephone Station-Mapping ................................................... 14
2.10.Save Translations ................................................................................................. 14
3. Configure Avaya Aura™ Session Manager .......................................................... 14
3.1. Administer SIP Domains ....................................................................................... 15
3.2. Define Locations ................................................................................................... 16
3.3. Add Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server ............................... 17
3.3.1. Define a SIP Element for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature
Server ............................................................................................................... 17
3.3.2. Define Element Link for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server
......................................................................................................................... 18
3.3.3. Define Routing Policy for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature
Server ............................................................................................................... 18
3.3.4. Define Applications for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server
......................................................................................................................... 19
3.3.5. Define Application Sequences for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager
Feature Server ................................................................................................. 20
3.3.6. Define Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature as an Administrable
Entity ................................................................................................................ 21
3.3.7. Add SIP Users .................................................................................................. 23
4. Configure Avaya 10x0 Video Endpoint ................................................................. 27
5. Verification Steps .................................................................................................. 34
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
2 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 3

5.1. Verify Avaya Aura
TM
Session Manager Configuration ........................................... 34
5.1.1. Verify Avaya AuraTM Session Manager is Operational ..................................... 34
5.1.2. Verify SIP Link Status ....................................................................................... 36
5.1.3. Verify Registrations of SIP Endpoints ............................................................... 37
5.2. Verify Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server Configuration ...... 39
5.3. Call Scenarios Verified ......................................................................................... 42
6. Acronyms .............................................................................................................. 43
7. Conclusion ............................................................................................................ 43
8. Additional References ........................................................................................... 43
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
3 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 4
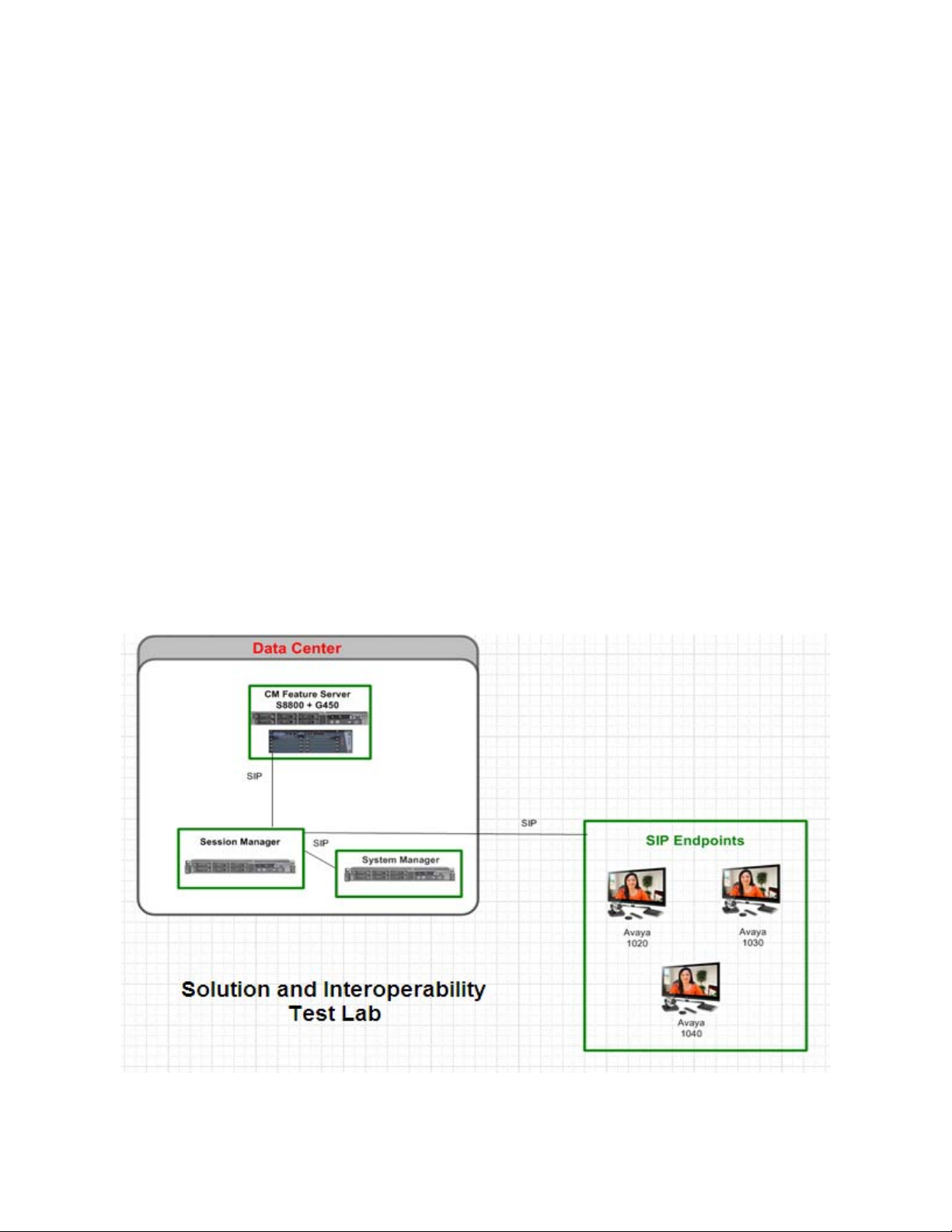
1. Introduction
These Application Notes present a sample configuration for a network that uses Avaya Aura™
Session Manager to support registration of Avaya 10x0 (1010, 1020, 1030, 1040, and 1050) SIP
Video endpoints and enables connectivity to Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager Feature
Server 6.0 using SIP trunks.
As shown in Figure 1, Avaya Aura™ Session Manager is managed by Avaya Aura™ System
Manager. Avaya 10x0 Video Endpoints configured as SIP endpoints utilize the Avaya Aura™
Session Manager User Registration feature and require Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager
operating as a Feature Server. Communication Manager Feature Server only supports IP
Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)-SIP users that are registered to Avaya Aura™ Session Manager.
The Communication Manager Feature Server is connected to Session Manager via an IMSenabled SIP signaling group and associated SIP trunk group.
For the sample configuration, Avaya Aura™ Session Manager runs on an Avaya S8510 Server.
Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager 6.0 Feature Server runs on a S8800 server with an
Avaya 450 Gateway. The results in these Application Notes should be applicable to other Avaya
servers and media gateways that support Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager 6.0.
These Application Notes will focus on the configuration of the Communication Manager Feature
Server and Session Manager. Detailed administration of Communication Manager Evolution
Server will not be described (see the appropriate documentation listed in Section 8).
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Figure 1 – Sample Configuration
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
4 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 5
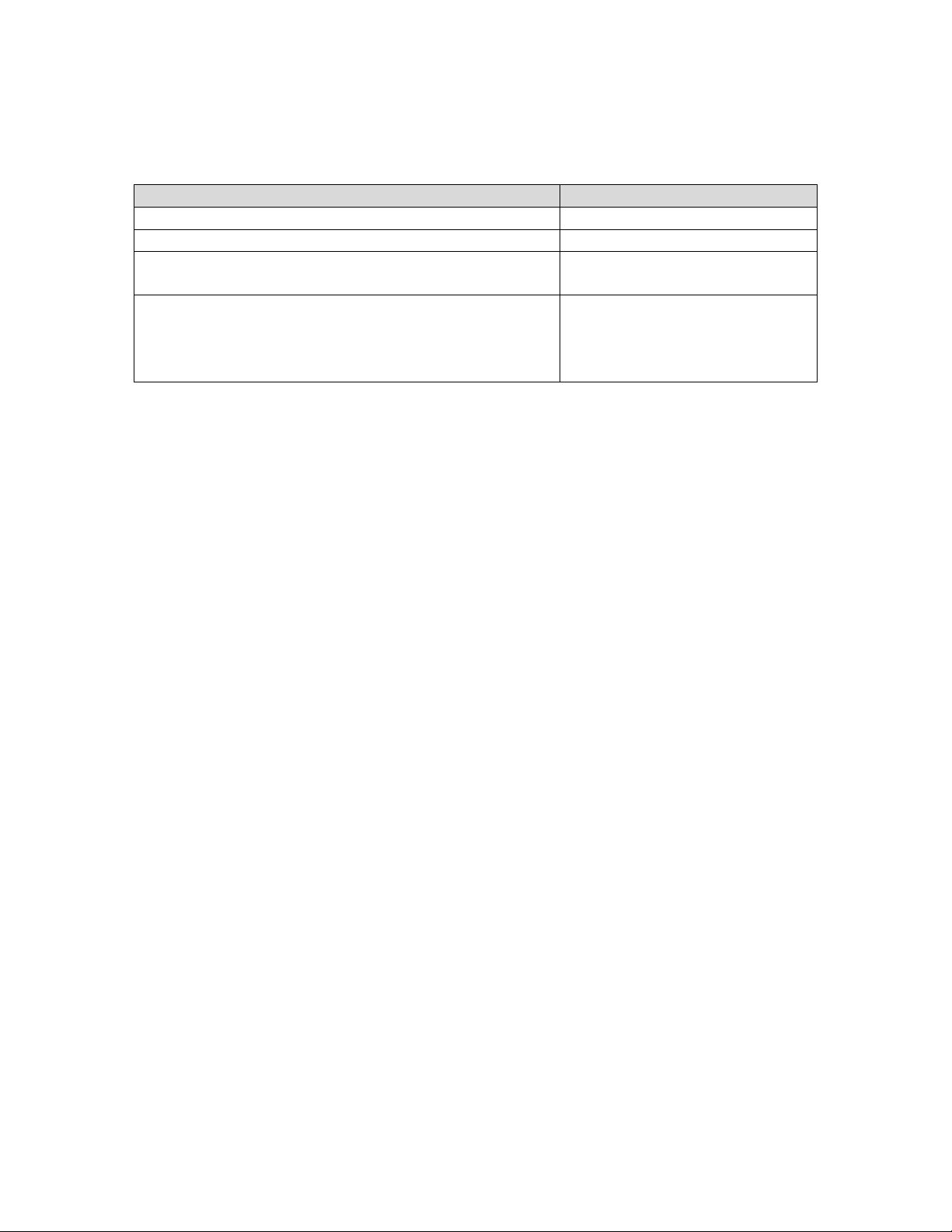
1.1. Equipment and Software Validated
The following equipment and software were used for the sample configuration.
Equipment Software
Avaya AuraTM Session Manager Release 6.0.0.0.600020
Avaya AuraTM System Manager Release 6.0 Load: 6.0.0.0.11
Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager
• Avaya S8800 Server Feature Server
Avaya IP Telephones10x0 Video Endpoints (SIP):
• 1020
• 1030
• 1040
Release R016x.00.0.345.0-2350
FW: AV_PP1_4.7.0 (19)2.0
FW:3.0 AV_EX2_4.7.0 (19)
FW:1.5 AV_TM2_4.7.0 (19)
2. Configuring Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager
Feature Server
This section describes the administration of Communication Manager Feature Server using a
System Access Terminal (SAT). Alternatively, some of the station administration could be
performed using the Communication System Management application on System Manager.
These instructions assume the G450 Media Gateway is already configured on the
Communication Manager Feature Server. Some administration screens have been abbreviated for
clarity.
Verify System Capabilities and Communication Manager Licensing
Administer IP node names
Administer codec type
Administer IP network region
Administer SIP signaling group
Administer SIP trunk group
Administer numbering plan
Administer station endpoints
Administer off-pbx-telephone station-mapping
Save translations
After completing these steps, the “save translation” command should be performed
.
2.1. Verify System Capabilities and Licensing
This section describes the procedures to verify the correct system capabilities and licensing have
been configured. If there is insufficient capacity or a required feature is not available, contact an
authorized Avaya sales representative to make the appropriate changes.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
5 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 6

2.1.1. SIP Trunk Capacity Check
Issue the display system-parameters customer-options command to verify that an adequate
number of SIP trunk members are licensed for the system as shown below:
display system-parameters customer-options Page 2 of 11
OPTIONAL FEATURES
IP PORT CAPACITIES USED
Maximum Administered H.323 Trunks: 12000 0
Maximum Concurrently Registered IP Stations: 18000 0
Maximum Administered Remote Office Trunks: 12000 0
Maximum Concurrently Registered Remote Office Stations: 18000 0
Maximum Concurrently Registered IP eCons: 414 0
Max Concur Registered Unauthenticated H.323 Stations: 100 0
Maximum Video Capable Stations: 18000 0
Maximum Video Capable IP Softphones: 18000 0
Maximum Administered SIP Trunks: 24000 128
Maximum Administered Ad-hoc Video Conferencing Ports: 24000 50
Maximum Number of DS1 Boards with Echo Cancellation: 522 0
Maximum TN2501 VAL Boards: 128 0
Maximum Media Gateway VAL Sources: 250 0
Maximum TN2602 Boards with 80 VoIP Channels: 128 0
Maximum TN2602 Boards with 320 VoIP Channels: 128 0
Maximum Number of Expanded Meet-me Conference Ports: 300 0
(NOTE: You must logoff & login to effect the permission changes.)
2.1.2. AAR/ARS Routing Check
Verify that ARS is enabled (on page 3 of system-parameters customer options)
display system-parameters customer-options Page 3 of 11
OPTIONAL FEATURES
A/D Grp/Sys List Dialing Start at 01? n CAS Main? n
Answer Supervision by Call Classifier? n Change COR by FAC? n
ARS? y Computer Telephony Adjunct Links? y
ARS/AAR Partitioning? y Cvg Of Calls Redirected Off-net? y
ARS/AAR Dialing without FAC? y DCS (Basic)? y
ASAI Link Core Capabilities? y DCS Call Coverage?
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
6 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 7

2.1.3. Enable Private Numbering
Use the “change system-parameters customer-options” command to verify that Private
Networking is enabled as shown below:
display system-parameters customer-options Page 5 of 11
OPTIONAL FEATURES
Multinational Locations? y Station and Trunk MSP? y
Multiple Level Precedence & Preemption? n Station as Virtual Extension? y
Multiple Locations? y
System Management Data Transfer? n
Personal Station Access (PSA)? y Tenant Partitioning? n
PNC Duplication? n Terminal Trans. Init. (TTI)? y
Port Network Support? n Time of Day Routing? n
Posted Messages? n TN2501 VAL Maximum Capacity? y
Uniform Dialing Plan? y
Private Networking? y Usage Allocation Enhancements? y
Processor and System MSP? y
Processor Ethernet? y Wideband Switching? n
Wireless? y
2.2. Add Node Name of Avaya AuraTM Session Manager
Using the change node-names ip command, add the node-name and IP for the Session
Manager’s software asset, if not previously added.
change node-names ip Page 1 of 2
IP NODE NAMES
Name IP Address
default 0.0.0.0
procr 135.9.88.72
procr6 ::
silasm4 135.9.88.62
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
7 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 8

2.3. Configure Codec Type
Issue the change ip-codec-set n command where “n” is the next available number. Enter the
following values:
Enter “G.711MU” and “G.729” as supported types of Audio Codecs
Silence Suppression: Retain the default value “n”.
Frames Per Pkt: Enter “2”.
Packet Size (ms): Enter “20”.
Media Encryption: Enter the value based on the system requirement. For the sample
configuration “none” was used.
change ip-codec-set 1 Page 1 of 2
IP Codec Set
Codec Set: 1
Audio Silence Frames Packet
Codec Suppression Per Pkt Size(ms)
1: G.711MU n 2 20
2: G.729 n 2 20
3:
Media Encryption
1: none
2.4. Configure IP Network Region
Using the change ip-network-region 1 command, set the Authoritative Domain. For the
sample configuration “dr.avaya.com” was used. Verify the Intra-region IP-IP Direct Audio,
and Inter-region IP-IP Direct Audio fields are set to yes.
change ip-network-region 1 Page 1 of 19
IP NETWORK REGION
Region: 1
Location: 1 Authoritative Domain: dr.avaya.com
Name: CMFS-Video
MEDIA PARAMETERS Intra-region IP-IP Direct Audio: yes
Codec Set: 1 Inter-region IP-IP Direct Audio: yes
UDP Port Min: 2048 IP Audio Hairpinning? n
UDP Port Max: 16585
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
8 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 9

2.5. Add SIP Signaling Group
Issue the add signaling-group n command, where “n” is an available signaling group number,
for one of the SIP trunks to the Session Manager, and fill in the indicated fields. In the sample
configuration, trunk group “1” and signaling group “1” were used to connect to Avaya Aura™
Session Manager. Default values can be used for the remaining fields.
Group Type: “sip”
Transport Method: ”tcp”
IMS Enabled?: “y”
IP Video?: “y”
Peer Detection Enabled?: “y”
Peer Server: Use default value. Note: default value is replaced with
“SM” after SIP trunk to Session Manager is established
Near-end Node Name: procr from Section 2.2
Far-end Node Name: Session Manager node name from Section 2.2
Near-end Listen Port: “5060”
Far-end Listen Port: “5060”
Far-end Domain: Authoritative Domain from Section 2.4
Enable Layer 3 Test: “y”
Direct IP-IP Early Media?: “y”
display signaling-group 1 Page 1 of 1
SIGNALING GROUP
Group Number: 1 Group Type: sip
Transport Method: tcp
IMS Enabled? y
IP Video? y Priority Video? y
Peer Detection Enabled? y Peer Server: SM
Near-end Node Name: procr Far-end Node Name: silasm4
Near-end Listen Port: 5060 Far-end Listen Port: 5060
Far-end Network Region: 1
Far-end Domain: dr.avaya.com
Bypass If IP Threshold Exceeded? n
Incoming Dialog Loopbacks: eliminate RFC 3389 Comfort Noise? n
DTMF over IP: rtp-payload Direct IP-IP Audio Connections? y
Session Establishment Timer(min): 3 IP Audio Hairpinning? n
Enable Layer 3 Test? y Direct IP-IP Early Media? y
H.323 Station Outgoing Direct Media? n Alternate Route Timer(sec): 6
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
9 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 10

2.6. Add SIP Trunk Group
Add the corresponding trunk group controlled by this signaling group via the add trunk-group
n command, where “n” is an available trunk group number and fill in the indicated fields.
Group Type: “sip”
Group Name: A descriptive name.
TAC: An available trunk access code.
Service Type: “tie”
Signaling Group: The number of the signaling group added in Section 2.5
Number of Members: The number of SIP trunks to be allocated to calls
routed to Session Manager (must be within the limits
of the total number of trunks configured in Section 2.1.1).
add trunk-group 1 Page 1 of 21
TRUNK GROUP
Group Number: 1 Group Type: sip CDR Reports: y
Group Name: SIP Video TG to silasm4 COR: 1 TN: 1 TAC: #001
Direction: two-way Outgoing Display? y
Dial Access? n Night Service:
Queue Length: 0
Service Type: tie Auth Code? n
Signaling Group: 1
Number of Members: 64
Once the add command is completed, trunk members will be automatically generated based on
the value in the Number of Members field.
On Page 2, set the Preferred Minimum Session Refresh Interval to 1200. Note: to avoid extra
SIP messages, all SIP trunks connected to Session Manager should be configured with a
minimum value of 1200.
add trunk-group 1 Page 2 of 21
Group Type: sip
TRUNK PARAMETERS
Unicode Name: auto
Redirect On OPTIM Failure: 5000
SCCAN? n Digital Loss Group: 18
Preferred Minimum Session Refresh Interval(sec): 1200
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
10 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 11

On Page 3, set Numbering Format to be “private”. Use default values for all other fields.
add trunk-group 1 Page 3 of 21
TRUNK FEATURES
ACA Assignment? n Measured: none
Maintenance Tests? y
Numbering Format: private
UUI Treatment: service-provider
Replace Restricted Numbers? n
Replace Unavailable Numbers? n
2.7. Administering Numbering Plan
SIP Users registered to Session Manager needs to be added to either the private or public
numbering table on the Communication Manager Feature Server. For the sample configuration,
private numbering was used and all extension numbers were unique within the private network.
However, in many customer networks, it may not be possible to define unique extension
numbers for all users within the private network. For these types of networks, additional
administration may be required as described in References [3] and [8] in Section 8.
To enable SIP endpoints to dial extensions defined in the Communication Manager Feature
Server, use the “change private-numbering x” command, where x is the number used to
identify the private number plan. For the sample configuration, extension numbers starting with
5-XXXX are used on the Communication Manager Feature Server.
Ext Len: Enter the extension length allowed by the dial plan
Ext Code: Enter leading digit (s) from extension number
Trunk Grp: Enter the SIP Trunk Group number for the SIP trunk
between the Feature Server and Session Manager
Private Prefix: Leave blank unless an enterprise canonical numbering
scheme is defined in Session Manager. If so, enter the
appropriate prefix.
change private-numbering 1 Page 1 of 2
NUMBERING - PRIVATE FORMAT
Ext Ext Trk Private Total
Len Code Grp(s) Prefix Len
5 5 1 5 Total Administered: 1
Maximum Entries: 540
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
11 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 12

2.8. Configure Stations
The method is the same for administering all of the Avaya 1000 series video endpoints with the
exception of the 1040 and 1050’s. The only difference is that the 1040 can be administered to
have up to 3 call appearances and the 1050 can have up to 7 call appearances for conferencing
via their internal MCU’s. The 1010, 1020, and 1030 have to be administered with only one callappearance since they are a single-line endpoint with no conferencing or transferring capabilities.
For each SIP user to be defined in Session Manager, add a corresponding station on the
Communication Manager Feature Server. Note: instead of manually defining each station using
the Communication Manager SAT interface, the preferred option is to automatically generate the
SIP station when adding a new SIP user. See Section 3.3.6 for more information on adding SIP
users.
The phone number defined for the station will be the number the SIP user enters to register to
Session Manager. Use the “add station x” command where x is a valid extension number
defined in the system. In this example extension 55002 is an Avaya 1020 video endpoint. On
page 1 of the change station form:
Phone Type: Set to 9630SIP
Name: Display name for user
Security Code: Number used when user logs into station. Note: this code
should match the “Shared Communication Profile
Password” field defined when adding this user in Session
Manager. See Section 3.3.6.
IP Video? Enable endpoint for video
add station 55002 Page 1 of 6
STATION
Extension: 55002 Lock Messages? n BCC: 0
Type: 9630SIP Security Code: 123456 TN: 1
Port: S00006 Coverage Path 1: 1 COR: 1
Name: SIL Video Lab - 1020 Coverage Path 2: COS: 1
Hunt-to Station:
STATION OPTIONS
Time of Day Lock Table:
Loss Group: 19
Message Lamp Ext: 55002
Display Language: english Button Modules: 0
Survivable COR: internal
Survivable Trunk Dest? y IP SoftPhone? n
IP Video? y
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
12 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 13
Note: It is important to assign only one call-appearance for the 1010, 1020, and 1030’s.
add station 55002 Page 4 of 6
STATION
SITE DATA
Room: Headset? n
Jack: Speaker? n
Cable: Mounting: d
Floor: Cord Length: 0
Building: Set Color:
ABBREVIATED DIALING
List1: List2: List3:
BUTTON ASSIGNMENTS
1: call-appr 5:
2: 6:
3: 7:
4: 8:
On page 6, set:
SIP Trunk option: Enter SIP Trunk Group defined in Section 2.6
change station 55002 Page 6 of 6
STATION
SIP FEATURE OPTIONS
Type of 3PCC Enabled: None
SIP Trunk: 1
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
13 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 14

2.9. Configure Off-PBX-Telephone Station-Mapping
Use the “change off-pbx-telephone station-mapping” command for each extension associated
with SIP users defined in Session Manager. On page 1, enter the SIP Trunk Group defined in
Section 2.6 and use default values for other fields.
change off-pbx-telephone station-mapping 55002 Page 1 of 3
STATIONS WITH OFF-PBX TELEPHONE INTEGRATION
Station Application Dial CC Phone Number Trunk Config Dual
Extension Prefix Selection Set Mode
55002 OPS - 55002 1 1
-
-
On Page 2, enter the following values:
Mapping Mode: “both”
Calls Allowed: “all”
change off-pbx-telephone station-mapping 55002 Page 2 of 3
STATIONS WITH OFF-PBX TELEPHONE INTEGRATION
Station Appl Call Mapping Calls Bridged Location
Extension Name Limit Mode Allowed Calls
55002 OPS 1 both all none
-
2.10. Save Translations
Configuration of Communication Manager Feature Server is complete. Use the “save
translations” command to save these changes
Note: After a change on Communication Manager Feature Server which alters the dial plan,
synchronization between Communication Manager Feature Server and Session Manager needs to
be completed and SIP phones must be re-registered. To request an on demand synchronization,
log into the System Manager console and use the Synchronize CM Data feature under the
Communication System Management menu.
3. Configure Avaya Aura™ Session Manager
This section provides the procedures for configuring the Session Manager and includes the
following items:
Administer SIP domain
Define Logical/Physical Locations that can be occupied by SIP Entities
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
14 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 15

For each SIP entity in the sample configuration:
o Define SIP Entity
o Define Entity Links, which define the SIP trunk parameters used by Avaya
Aura ™ Session Manager when routing calls to/from SIP Entities
o Define Routing Policies, which control call routing between the SIP Entities
o Define Dial Patterns, which govern to which SIP Entity a call is routed
Define the Communication Manager Feature Server as an Managed Element
Adding SIP Endpoints/SIP URE users
Configuration is accomplished by accessing the browser-based GUI of Avaya Aura™ System
Manager, using the URL “http://<ip-address>/SMGR”, where “<ip-address>” is the IP address of
Avaya Aura™ System Manager.
Log in with the appropriate credentials and accept the Copyright Notice.
Expand the Routing Link on the left side of Navigation Menu. Select a specific item such as
Domains.
3.1. Administer SIP Domains
Expand Routing and select Domains.
Click New
In the General Section, under Name add a descriptive name. Under Notes add a brief
description.
Click Commit to save.
The screen below shows the information for the sample configuration.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
15 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 16

3.2. Define Locations
Expand Routing and select Locations. Locations are used to identify logical and/or physical
locations where SIP Entities reside, for purposes of bandwidth management or location-based
routing.
Click New
In the General Section, under Name add a descriptive name.
Under Notes add a brief description.
In the Location Pattern Section, under IP Address Pattern enter pattern used to
logically identify the location Under Notes add a brief description.
Click Commit to save.
The screen below shows the information for Communication Manager Feature Server in the
sample configuration.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
16 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 17

3.3. Add Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server
The following section captures relevant screens for defining Avaya AuraTM Communication
Manager Feature Server applicable for the sample configuration.
3.3.1. Define a SIP Element for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager
Feature Server
The following screen shows addition of Communication Manager Feature Server. The IP
address used is that of the Processor Ethernet (procr) of the Avaya Communication Manager
Feature server.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
17 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 18

3.3.2. Define Element Link for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager
Feature Server
The following screen shows the Element Link defined for the Avaya AuraTM Communication
Manager Feature Server.
3.3.3. Define Routing Policy for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager
Feature Server
Since the SIP users are registered on Session Manager, a routing policy does not need to be
defined for the Communication Manager Feature Server.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
18 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 19

3.3.4. Define Applications for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager
Feature Server
To define the Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server Applications,
Elements -> Session Manager, Application Configuration Applications
o Click New (Not shown)
o Under Name, enter a name for the Application entry
o Under SIP Entity drop-down menu, select the appropriate SIP Entity.
o Under CM System for SIP Entity, this field can be left as the default of Select
CM System.
o Under Description, enter a description if desired.
o Click Commit to save.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
19 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 20

3.3.5. Define Application Sequences for Avaya AuraTM Communication
Manager Feature Server
To define the Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server Application Sequences,
Elements -> Session Manager, Application Configuration Application
Sequences
o Click New (Not shown)
o Under Name, enter a name of the Application Sequence.
o Under Description, enter a description if desired.
o Under Available Applications, select the Application that was created in
Section 3.3.4. The way to select the Application of choice is to click on the
“+” symbol next to the Application desired. This will be added to the
Applications in this Sequence list.
o Click Commit to save.
Second, define an Application Sequence for call application sequencing in the Avaya Aura
Communication Manager Feature Server as shown below:
TM
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
20 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 21

3.3.6. Define Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature as an
Administrable Entity
Before adding SIP users, the Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server must also
be added to System Manager as an administrable entity. This action allows System Manager to
access Communication Manager over its administration interface similar to how other
administration tools such as Avaya Site Administrator access Communication Manager. Using
this administration interface, System Manager will notify the Communication Manager Feature
Server when new SIP users are added.
To define the Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server as an administrable entity,
Elements -> Inventory -> Manage Elements
o Click New (Not shown)
o Under Name, enter an identifier for the Communication Manager Feature
Server.
o Under Type drop-down menu, select CM.
o Under Node, enter the IP address of the administration interface for the Feature
Server as shown below:
Defining the Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server as an administrable
entity (continued):
Manage Elements - Attributes
o Under Login and Password, enter the login and password used for
administration access to the Feature Server.
o Select SSH access.
o Under Port, enter the port number for the administration interface of 5022 as
shown below:
Defining the Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server as an administrable
entity (continued):
Entities – Port
Entities – Access Point
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
21 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 22

TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
22 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 23

3.3.7. Add SIP Users
Add SIP users corresponding to the 96XX SIP stations defined in Section 2.8. Alternatively, use
the option to automatically generate the SIP stations on Communication Manager Feature Server
when adding a new SIP user.
Expand Users
o Select Manage Users
Click New
Step 1: Enter values for the following required attributes for a new SIP user in the General
and Identity sections of the new user form.
Last Name: enter last name of user
First Name: enter first name of user
Login Name: enter extension no.@sip domain
defined in Section 3.1. This field is
primary handle of user.
Authentication Type: select Basic
SMGR Login Password: enter password which will be used to log
into System Manager application
(password). NOTE: This field is only
displayed if adding a new user.
Confirm Password: repeat value entered above. NOTE: This
field is only displayed if adding a new
user.
Shared Communication Profile Password: enter a numeric value which will
be used to logon to SIP phone.
Note: this field must match the
Security Code field on the station
form defined in Section 2.8.
Confirm Password: repeat numeric password
The screen below shows the information when adding a new SIP user to the sample
configuration.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
23 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 24

Step 2: Scroll down to the Communication Profile section and Select New to define a
Communication Profile for the new SIP user. Enter values for the following required
attributes:
Name: enter name of communication profile
Default: enter checkmark to indicate this profile is default profile
Select New to define a Communication Address for the new SIP user. Enter values for the
following required attributes:
Type: select SIP
Handle: enter extension number
Domain: enter SIP domain defined in Section 3.1
Click Add (not shown) to save the Communication Address for the new SIP user.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
24 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 25

The screen below shows the information when adding a new SIP user to the sample
configuration.
Step 3: Assign the Application Sequence defined in Section 3.3.4 to the new SIP user as
part of defining the SIP Communication Profile. The Application Sequence can be used
for both the originating and terminating sequence. Enter values for the following required
attributes of the Station Profile section:
System: select the SIP Entity of the Communication Manager
Feature Server defined in Section 3.3.5 from menu
Use Existing Stations: enter checkmark if station was already defined. Else, station will
automatically be created.
Extension: enter extension number
Template: Select the template (system defined or user defined) you want to
associate with the endpoint. Select the template based on the set
type you want to add.
Security Code: enter numeric value which will be used to logon to SIP phone.
Note: this field must match the value entered for the
Shared Communication Profile Password field
Port: select port number from the list for the selected template
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
25 of 45
Page 26

The screen below shows the information when adding a new SIP user to the sample
configuration.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
26 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 27

4. Configure Avaya 10x0 Video Endpoint
To administer the 10x0 video endpoints log in to the web interface using the IP address of the
video endpoint. You will be redirected to a screen that looks similar to the one below. This is a
sample configuration on how to administer a 10x0 video endpoint.
Step 1: Enter the proper login credentials and press Submit. Most of the Preferences can be
customized to meet your needs. Mentioned below are the absolute necessary items that need to
be administered to get the 10x0 up and running on the network.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
27 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 28

Once logged in select the Preferences tab and then the Network option.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
28 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 29

Select General option and enter values for the following required attributes.
DHCP: enabled/disabled
IP Address: enter IP Address if DHCP is disabled
Subnet Mask: enter Subnet Mask if DHCP is disabled
Default Gateway: enter Default Gateway if DHCP is disabled
Hostname: enter the appropriate Hostname
DNS Servers: enter the appropriate DNS Servers
NTP Server Hostname: enter NTP Server Hostname
Select the Save Changes button to save the administration just added.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
29 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 30

Select the Preferences option and select the Communications option.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
30 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 31

Select the SIP option.
SIP: enabled
SIP Username: enter the SIP Username for the device. NOTE: The SIP
Username should be unique and meaningful to the endpoint.
Authorization Name: enter the SIP Server authorization username. NOTE: The
Authorization Name should be unique and meaningful to the
endpoint.
Authorization Password: enter the SIP Server authorization password
SIP Registration: select the communication path to use when registering with a
SIP Registrar
SIP Proxy: choose ‘Enabled’ to use the SIP proxy
Proxy Hostname: enter the hostname or IP address of the SIP proxy server.
NOTE: This is the Session Manager software asset card IP
address
Proxy IP Port: enter the IP port number of SIP proxy server
SIP Registrar: choose ‘Enabled’ to use the SIP registrar
Registrar Hostname: enter the hostname or IP address of the SIP registrar server
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
31 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 32

Registrar IP Port: enter the IP port number of the SIP registrar server
UDP Signaling Port: enter the UDP port number of the SIP configuration
TCP Signaling: choose ‘Enable’ to use TCP for placing SIP call
TCP signaling Port: enter the TCP port number of the SIP configuration
Select the Save Changes button to save the administration just added.
Select the Preferences option again and select System.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
32 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 33

Select the Identification option. This option will allow the user to display the name and
video/voice numbers on the menu bar.
System Name: enter a descriptive name for the system
Video Number: enter the video number of the system
Voice Number: enter the voice number of the system
Select the Save Changes button to save the administration just added.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
33 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 34

5. Verification Steps
5.1. Verify Avaya Aura
5.1.1. Verify Avaya Aura
TM
Session Manager Configuration
TM
Session Manager is Operational
Verify the overall system status for Session Manager as shown below:
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
34 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 35

Navigate to Elements Session Manager System Status Security Module Status to
view more detailed status information on the status of Security Module for Session Manager.
Verify the Status column displays “Up” as shown below.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
35 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 36

5.1.2. Verify SIP Link Status
Expand the Session Manager menu on the left and click SIP Entity Monitoring. Verify all SIP
Entity Links are operational as shown below:
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
36 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 37

5.1.3. Verify Registrations of SIP Endpoints
Verify SIP users have been created in the Session Manager. In the sample configuration,
Extension 55002 SIP user was created as shown in the highlighted area below:
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
37 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 38

Verify the SIP endpoints have successfully registered with the Session Manager as shown below:
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
38 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 39

5.2. Verify Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager Feature Server
Configuration
Verify the status of the SIP trunk group by using the “status trunk n” command, where “n” is
the trunk group number administered in Section 2.6. Verify that all trunks are in the “inservice/idle” state as shown below:
status trunk 1
TRUNK GROUP STATUS
Member Port Service State Mtce Connected Ports
Busy
0001/001 T00001 in-service/idle no
0001/002 T00002 in-service/idle no
0001/003 T00003 in-service/idle no
0001/004 T00004 in-service/idle no
0001/005 T00005 in-service/idle no
0001/006 T00006 in-service/idle no
0001/007 T00007 in-service/idle no
0001/008 T00008 in-service/idle no
0001/009 T00009 in-service/idle no
0001/010 T00010 in-service/idle no
Verify the status of the SIP signaling groups by using the “status signaling-group n” command,
where “n” is the signaling group number administered in Section 2.5 Verify the signaling group
is “in-service” as indicated in the Group State field shown below:
status signaling-group 1
STATUS SIGNALING GROUP
Group ID: 1
Group Type: sip
Group State: in-service
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
39 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 40

Use the Communication Manager SAT command, ‘list trace tac #’, where tac # is the trunk
access code defined in Section 2.6 to trace trunk group activity for the SIP trunk between the
Session Manager and the Communication Manager Feature Server as shown below:
list trace tac #001 Page 1
LIST TRACE
time data
10:53:34 TRACE STARTED 08/21/2010 CM Release String cold-00.0.345.0-2350
10:54:29 SIP<INVITE sip:55001@dr.avaya.com;transport=tcp;user=ph
10:54:29 SIP<one SIP/2.0
10:54:29 dial
10:54:29 term trunk-group 1 cid 0xb9
10:54:29 dial
10:54:29 seize trunk-group 1 member 21 cid 0xb9
10:54:29 Calling Number & Name NO-CPNumber NO-CPName
10:54:29 Proceed trunk-group 1 member 21 cid 0xb911:01:07 Setup
10:54:29 SIP>SIP/2.0 180 Ringing
10:54:29 Alert trunk-group 1 member 21 cid 0xb9
10:54:31 active trunk-group 1 member 21 cid 0xb9
10:54:31 G711MU ss:off ps:20
rgn:1 [135.9.88.216]:60656
rgn:1 [135.9.88.174]:60142
10:54:31 G711MU ss:off ps:20
rgn:1 [135.9.88.174]:60142
rgn:1 [135.9.88.216]:60656
10:54:31 SIP>SIP/2.0 200 OK
10:54:31 Video: H264 [135.9.88.216]:60658
10:54:31 Video: H264 [135.9.88.174]:60144
logChl:110 sessId:2 bw:21760 tx/rx:11520
10:54:31 Video: H264 [135.9.88.174]:60144
10:54:31 Video: H264 [135.9.88.216]:60658
logChl:110 sessId:2 bw:21760 tx/rx:11520
10:54:31 SIP<ACK sip:55001@135.9.88.72;transport=tcp SIP/2.0
10:54:37 SIP<BYE sip:55001@135.9.88.72;transport=tcp SIP/2.0
10:54:37 SIP>SIP/2.0 200 OK
10:54:37 idle station 55002 cid 0xb9
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
40 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 41

Use the Communication Manager SAT command, ‘list trace station xxx’, where xxx is the
extension number of the 96XX SIP telephone as shown below:
list trace station 6663000 Page 1
LIST TRACE
time data
10:58:38 TRACE STARTED 08/21/2010 CM Release String cold-00.0.345.0-2350
10:59:07 active station 55002 cid 0xbc
10:59:07 SIP>INVITE sip:55001@dr.avaya.com SIP/2.0
10:59:07 dial
10:59:07 term trunk-group 1 cid 0xbc
10:59:07 dial
10:59:07 seize trunk-group 1 member 23 cid 0xbc
10:59:07 Setup digits 55001
10:59:07 Calling Number & Name 55002 SIL Demo Vide
10:59:07 SIP<SIP/2.0 100 Trying
10:59:07 Proceed trunk-group 1 member 23 cid 0xbc
10:59:07 SIP<INVITE sip:55001@dr.avaya.com SIP/2.0
10:59:07 SIP>SIP/2.0 100 Trying
10:59:07 SIP>SIP/2.0 180 Ringing
10:59:07 SIP<SIP/2.0 180 Ringing
10:59:07 Alert trunk-group 1 member 23 cid 0xbc
10:59:09 SIP>SIP/2.0 200 OK
10:59:09 SIP<SIP/2.0 200 OK
10:59:09 active trunk-group 1 member 23 cid 0xbc
10:59:09 G711MU ss:off ps:20
rgn:1 [135.9.88.216]:60664
rgn:1 [135.9.88.174]:60150
10:59:09 G711MU ss:off ps:20
rgn:1 [135.9.88.174]:60150
rgn:1 [135.9.88.216]:60664
10:59:09 Video: H264 [135.9.88.216]:60666
10:59:09 Video: H264 [135.9.88.174]:60152
logChl:110 sessId:2 bw:21760 tx/rx:11520
10:59:09 Video: H264 [135.9.88.174]:60152
10:59:09 Video: H264 [135.9.88.216]:60666
logChl:110 sessId:2 bw:21760 tx/rx:11520
10:59:09 SIP>ACK sip:55001@135.9.88.72;transport=tcp SIP/2.0
10:59:10 SIP<ACK sip:55001@135.9.88.72;transport=tcp SIP/2.0
11:00:43 SIP>BYE sip:55002@135.9.88.72;transport=tcp SIP/2.0
11:00:43 SIP<BYE sip:55002@135.9.88.72;transport=tcp SIP/2.0
11:00:43 SIP>SIP/2.0 200 OK
11:00:43 idle trunk-group 1 member 23 cid 0xbc
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
41 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 42

5.3. Call Scenarios Verified
Verification scenarios for the configuration described in these Application Notes included the
following call scenarios:
Calls initiated from the GUI of the respective endpoint
Place a point-to-point video call from a 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered to SM
(CMFS) to another 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered on SM (CMFS). Answer the
call and verify two-way video and two-way talk path for all combinations of calls
between10x0 video endpoints. Verify Call statistics on the endpoint GUI.
Place a point-to-point video call from a 1040 video endpoint registered to SM (CMFS) to
another 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered on SM (CMFS). Answer the call and
verify two-way video and talk path. Place a video conference call from 1040 to a 1020.
Answer the call and verify three-way video and audio conference call. Add a fourth video
endpoint to the call and verity video and audio. Verify Call statistics on the endpoint GUI.
Place a point-to-point audio call from a 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered to SM
(CMFS) to another 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered on SM (CMFS). Answer the
call and verify two-way talk path for all combinations of calls between10X0 video
endpoints. Verify Call statistics on the endpoint GUI.
Place a point-to-point audio call from a 1040 video endpoint registered to SM (CMFS) to
another 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered on SM (CMFS). Answer the call and
verify two-way talk path. Place an audio conference call from 1040 to a 1020/1030/1040.
Answer the call and verify talk path on conference call. Add a fourth video endpoint to the
call and verify talk path. Verify Call statistics on the endpoint GUI.
Calls initiated from the Web interface of the respective endpoint
Place a point-to-point video call from a 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered to SM
(CMFS) to another 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered on SM (CMFS). Answer the
call and verify two-way video and two-way talk path for all combinations of calls
between10x0 video endpoints. Verify Call statistics on the endpoint GUI.
Place a point-to-point video call from a 1040 video endpoint registered to SM (CMFS) to
another 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered on SM (CMFS). Answer the call and
verify two-way video and talk path. Place a video conference call from 1040 to a 1020.
Answer the call and verify three-way video and audio conference call. Add a fourth video
endpoint to the call and verity video and audio. Verify Call statistics on the endpoint GUI.
Place a point-to-point audio call from a 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered to SM
(CMFS) to another 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered on SM (CMFS). Answer the
call and verify two-way talk path for all combinations of calls between10X0 video
endpoints. Verify Call statistics on the endpoint GUI.
Place a point-to-point audio call from a 1040 video endpoint registered to SM (CMFS) to
another 1020/1030/1040 video endpoint registered on SM (CMFS). Answer the call and
verify two-way talk path. Place an audio conference call from 1040 to a 1020/1030/1040.
Answer the call and verify talk path on conference call. Add a fourth video endpoint to the
call and verify talk path. Verify Call statistics on the endpoint GUI.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
42 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 43

6. Acronyms
AAR Automatic Alternative Routing (Routing on Communication
ARS Alternative Routing Service (Routing on Communication
CMFS Communication Manager Feature Server
IMS IP Multimedia Subsystem
IP Internet Protocol
RTP Real Time Protocol
SAT System Access Terminal (Communication Administration
SIL Solution Interoperability Lab
SIP Session Initiation Protocol
SM Avaya AuraTM Session Manager
SMGR System Manager (used to configure Session Manager)
TAC Trunk Access Code (Communication Manager Trunk Access)
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
TLS Transport Layer Security
URE User Relation Element
Manager)
Manager)
Interface)
7. Conclusion
These Application Notes describe how to configure the Avaya AuraTM Session Manager and
Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager operating as a Feature Server to support the Avaya
10x0 Series SIP video endpoints. Interoperability testing included successfully making bidirectional calls between several different types of video endpoints and the use of the
conferencing feature of the internal MCU of the 1040. These successful calls were generated via
the GUI of each respective video endpoint as well as each video endpoints respective Web
interface.
8. Additional References
This section references the product documentation relevant to these Application Notes.
Session Manager
1) Avaya Aura™ Session Manager Overview, Doc ID 03-603323, available at
http://support.avaya.com
2) Installing and Administering Avaya Aura™ Session Manager, Doc ID 03-603324,
available at http://support.avaya.com
3) Avaya Aura™ Session Manager Case Studies, dated January 2, 2010, available at
http://support.avaya.com
4) Maintaining and Troubleshooting Avaya Aura™ Session Manager, Doc ID 03-603325,
available at http://support.avaya.com.
.
.
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
43 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 44

Communication Manager
5) Hardware Description and Reference for Avaya AuraTM Communication Manager
(COMCODE 555-245-207)
http://support.avaya.com/elmodocs2/comm_mgr/r4_0/avayadoc/03_300151_6/245207_6/
245207_6.pdf
6) SIP Support in Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager Running on Avaya S8xxx
Servers, Doc ID 555-245-206, May 2009, available at http://support.avaya.com.
7) Administering Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager, Doc ID 03-300509, May 2009,
available at http://support.avaya.com
.
8) Administering Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager as a Feature Server, Doc ID 03-
603479, November 2009, available at http://support.avaya.com
Avaya 1000 Series Video Endpoints
9) Avaya 1010/1020 Installation Guide, Issue 1, June 2010, available at
http://support.avaya.com
10) Avaya 1010/1020 User Guide, Issue 1, June 2010, available at http://support.avaya.com
11) Avaya 1030 Installation Guide, Issue 1, June 2010, available at http://support.avaya.com
12) Avaya 1040 Installation Guide, Issue 1, June 2010, available at http://support.avaya.com
13) Avaya 1050 Installation Guide, Issue 1, June 2010, available at http://support.avaya.com
14) Avaya Video Communications System Administrator Guide (1050/1040/1030) , Issue 1, June
2010, available at http://support.avaya.com
15)
Avaya Video Communications System User Guide (1050/1040/1030) , Issue 1, June
2010, available at http://support.avaya.com
16)
Avaya Video Camera 100 Installation Guide, Issue 1, June 2010, available at
http://support.avaya.com
17)
Avaya Video Conferencing Manager Deployment Guide, Issue 1, June 2010, available at
http://support.avaya.com
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
44 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
Page 45

©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Avaya and the Avaya Logo are trademarks of Avaya Inc. All trademarks identified by ® and
™ are registered trademarks or trademarks, respectively, of Avaya Inc. All other trademarks
are the property of their respective owners. The information provided in these Application
Notes is subject to change without notice. The configurations, technical data, and
recommendations provided in these Application Notes are believed to be accurate and
dependable, but are presented without express or implied warranty. Users are responsible for
their application of any products specified in these Application Notes.
Please e-mail any questions or comments pertaining to these Application Notes along with the
full title name and filename, located in the lower right corner, directly to the Avaya Solution &
Interoperability Test Lab at interoplabnotes@list.avaya.com
TJM Reviewed:
SPOC 12/01/2010
Solution Interoperability Lab Application Notes
©2010 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
45 of 45
SM6_CMFS6_10x0
 Loading...
Loading...