Page 1
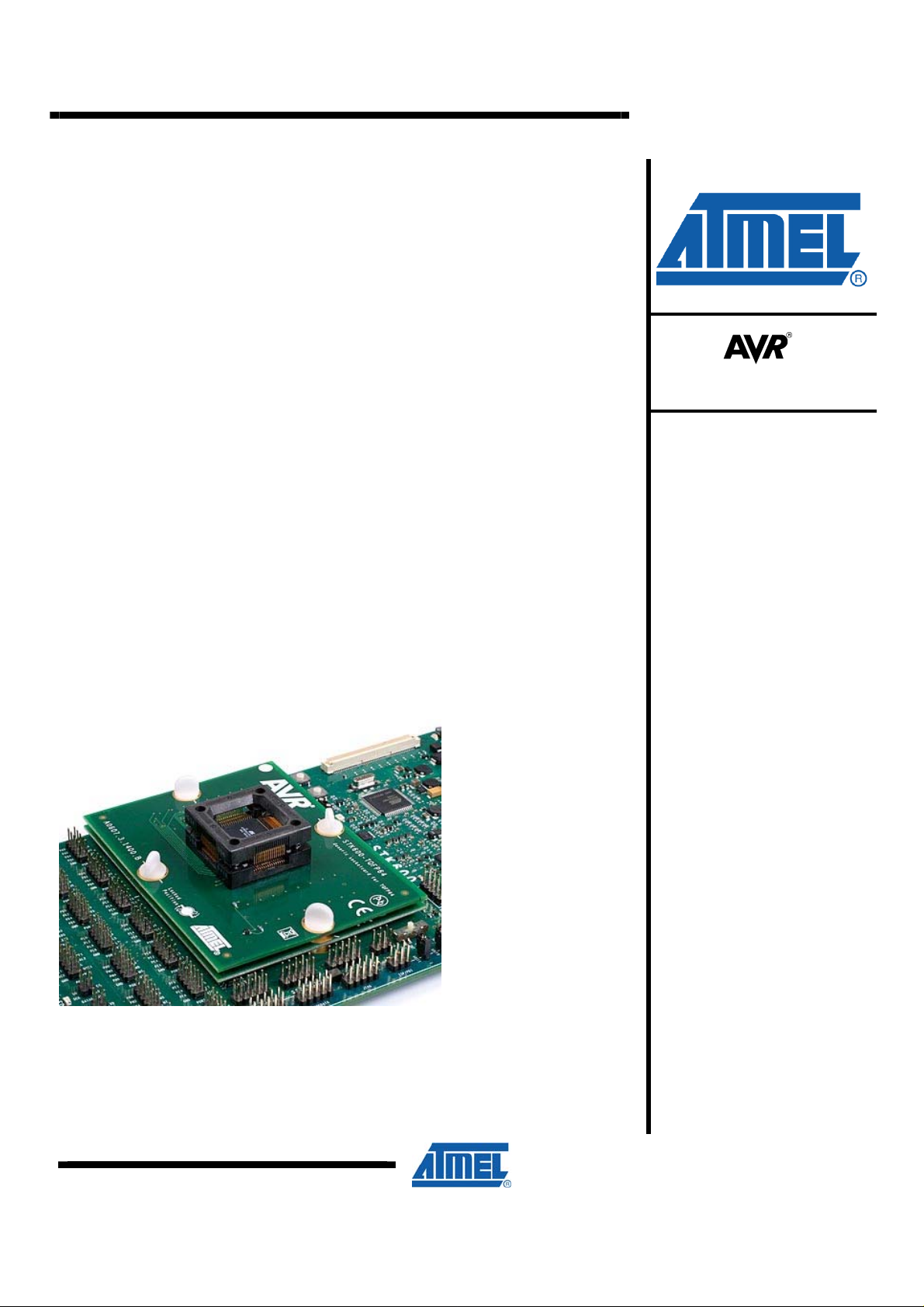
AVR600: STK600 Expansion, routing and socket
boards
1 Introduction
This application note describes the process of developing new routing, socket and
expansion cards for the STK
creating such cards.
The STK600 starter kit from Atmel has a sandwich design to match a specific part
package and pin out to the generic pin headers. It also features an expansion area
where most part pins are available.
While the variety of IC packages is relatively limited, the number of possible pin
outs increases rapidly with the number of pins. i.e. a 6 pin IC can have 720 (6!)
different pin outs!
The routing / socket card design provides a low cost solution to support upcoming
devices as the socket is the cost driving factor.
STK600 users might also want to create their own routing cards to include
specialized hardware to prototype their design.
Figure 1-1. STK600 router and socket card
®
600. It also describes the physical parameters for
8-bit
Microcontrollers
Application Note
Rev. 8170A-AVR-08/08
Page 2
2 Routing cards
2.1 Connector footprints
The routing cards sit between the generic socket card and the STK600. It has one
pair of electric pads underneath to mate with the STK600 spring loaded connector,
and one pair of pads on top where the socket card connector connects. A part
specific card with the target IC soldered on can be viewed as a routing card without
the top pads.
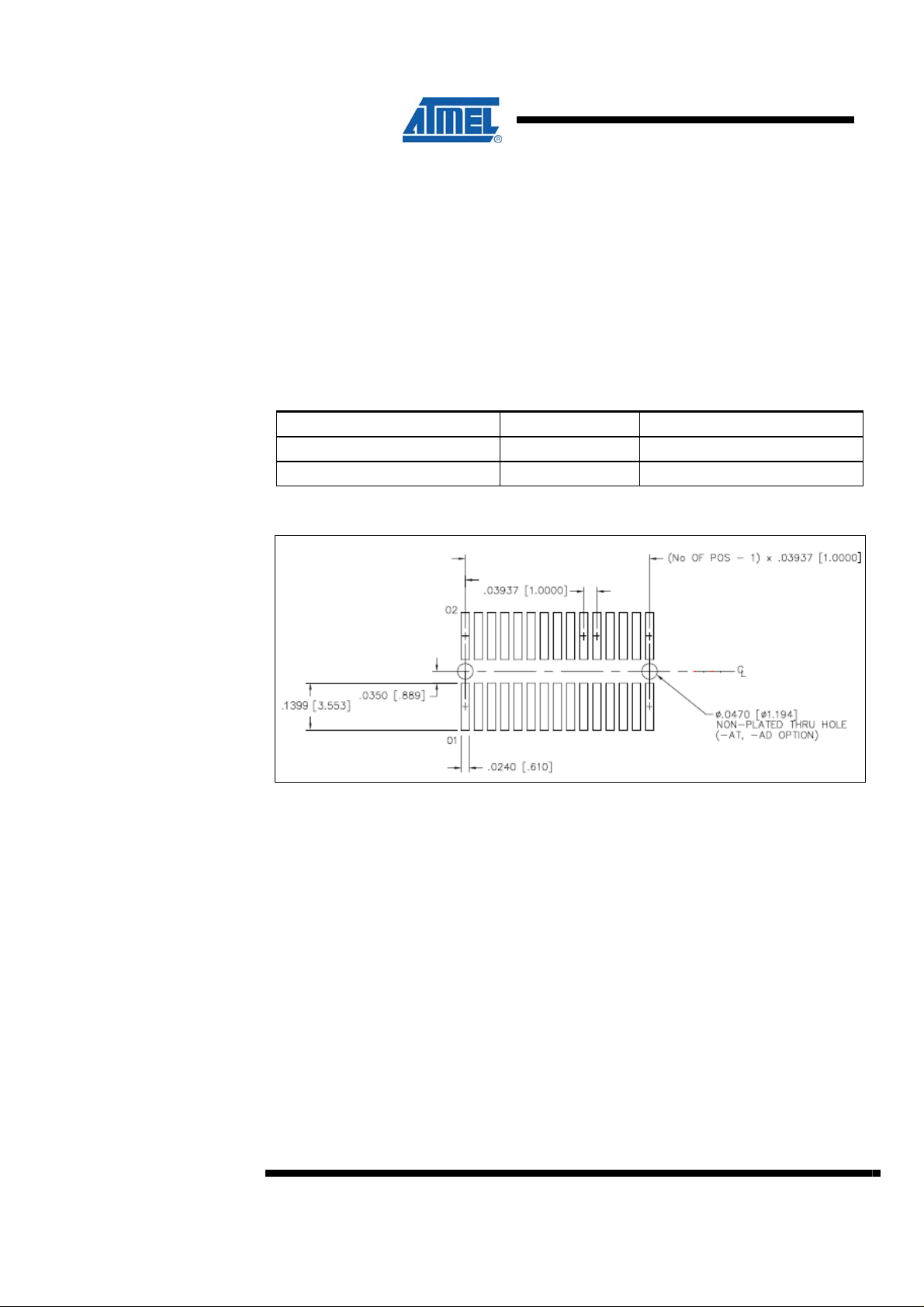
A Routing card should have pads to mate with the following spring loaded connectors:
Table 2-1. Router card connectors
Manufacturer and MPN Quantity Comment
SAMTEC, FSI-140-03-G-D-AD 2 80 pins To socket card (top)
SAMTEC, FSI-150-03-G-D-AD 2 100 pins To STK600 (bottom)
Figure 2-1. PCB land pattern for mating to FSI connectors
2
AVR600
8170A-AVR-08/08
Page 3
2.2 Physical dimensions and component placement
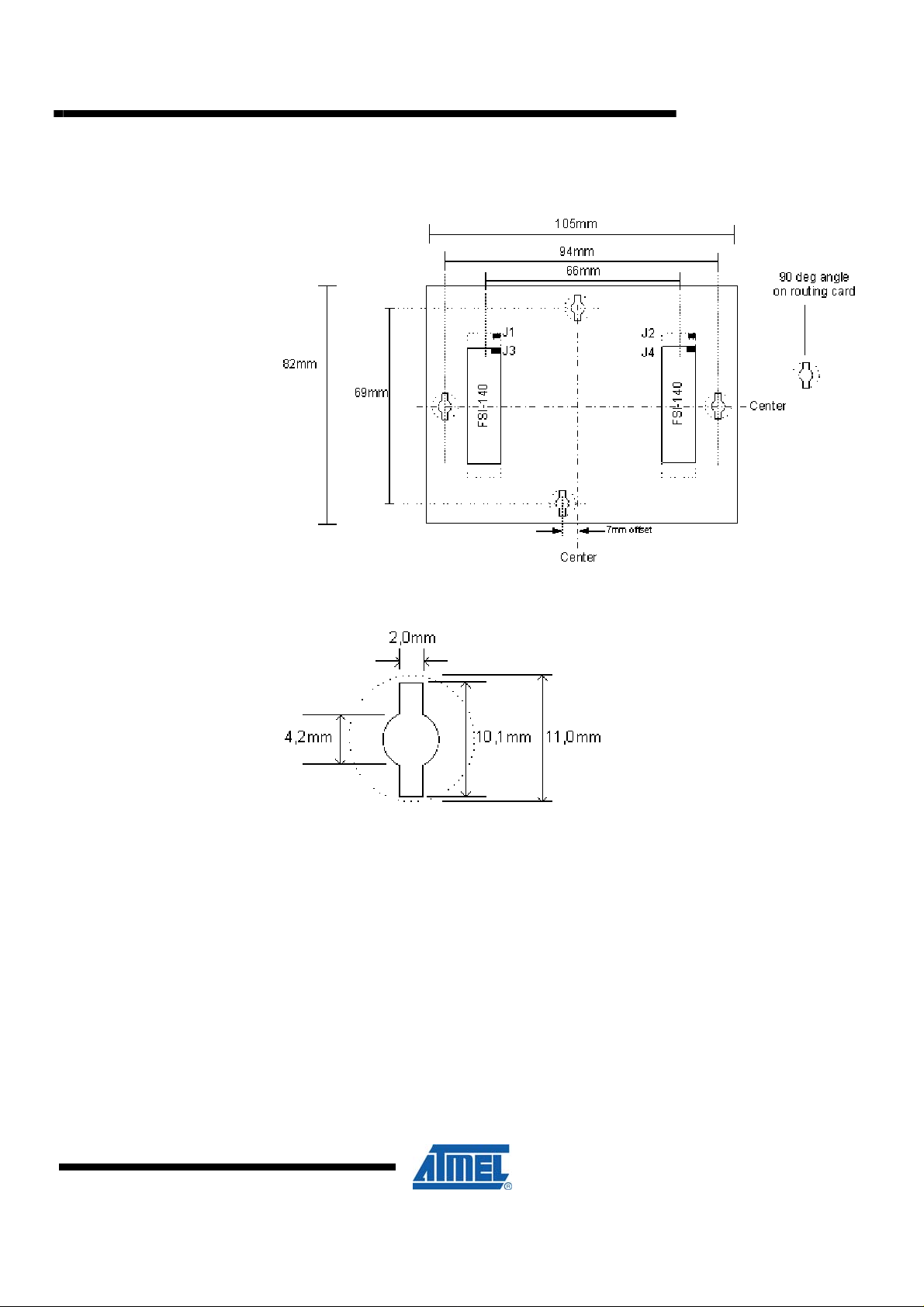
Figure 2-2. Routing card connector pad placement and dimensions
AVR600
Figure 2-3. Clip hole dimensions
The board thickness should be 1.6mm to be compatible with the clips.
Note that components on the main board might conflict with through hole mounted or
secondary side mounted components. Areas with such components are highlighted in
the next figure
8170A-AVR-08/08
3
Page 4
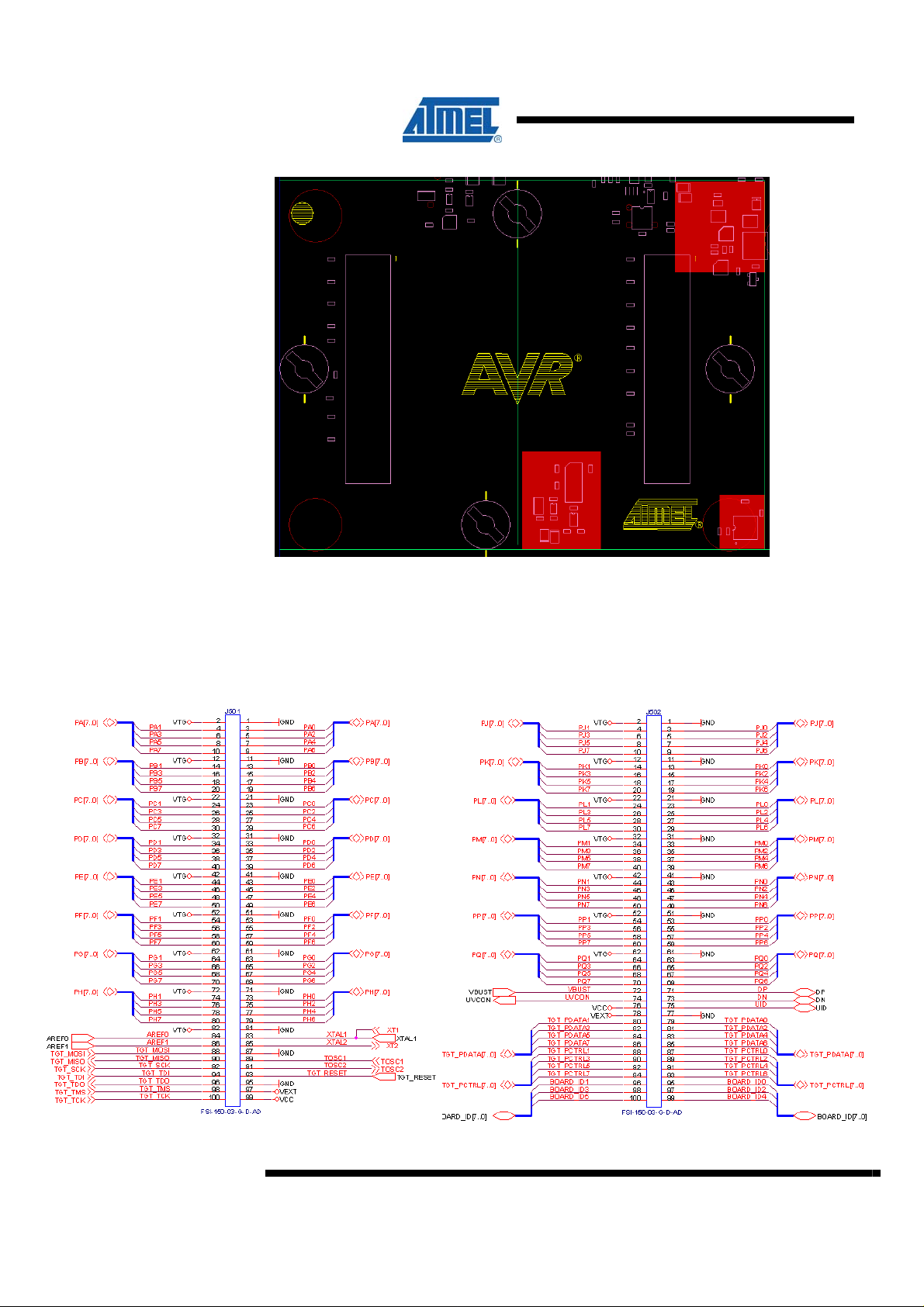
Figure 2-4. Height restricted areas due to main board components
2.3 STK600 socket connectors pinout
The following figure shows the pinout for the STK600 headers. This correspond to the
routing card connectors J1 and J2
Figure 2-5. STK600 Socket connectors pin out
4
AVR600
8170A-AVR-08/08
Page 5

AVR600
Table 2-2. STK600 J201 left, routing card J1 connector pin out
Signal name Pin number Signal name
VTG 2 1 GND
PA1 4 3 PA0
PA3 6 5 PA2
PA5 8 7 PA4
PA7 10 9 PA6
VTG 12 11 GND
PB1 14 13 PB0
PB3 16 15 PB2
PB5 18 17 PB4
PB7 20 19 PB6
VTG 22 21 GND
PC1 24 23 PC0
PC3 26 25 PC2
PC5 28 27 PC4
PC7 30 29 PC6
VTG 32 31 GND
PD1 34 33 PD0
PD3 36 35 PD2
PD5 38 37 PD4
PD7 40 39 PD6
VTG 42 41 GND
PE1 44 43 PE0
PE3 46 45 PE2
PE5 48 47 PE4
PE7 50 49 PE6
VTG 52 51 GND
PF1 54 53 PF0
PF3 56 55 PF2
PF5 58 57 PF4
PF7 60 59 PF6
VTG 62 61 GND
PG1 64 63 PG0
PG3 66 65 PG2
PG5 68 67 PG4
PG7 70 69 PG6
VTG 72 71 GND
PH1 74 73 PH0
PH3 76 75 PH2
8170A-AVR-08/08
5
Page 6
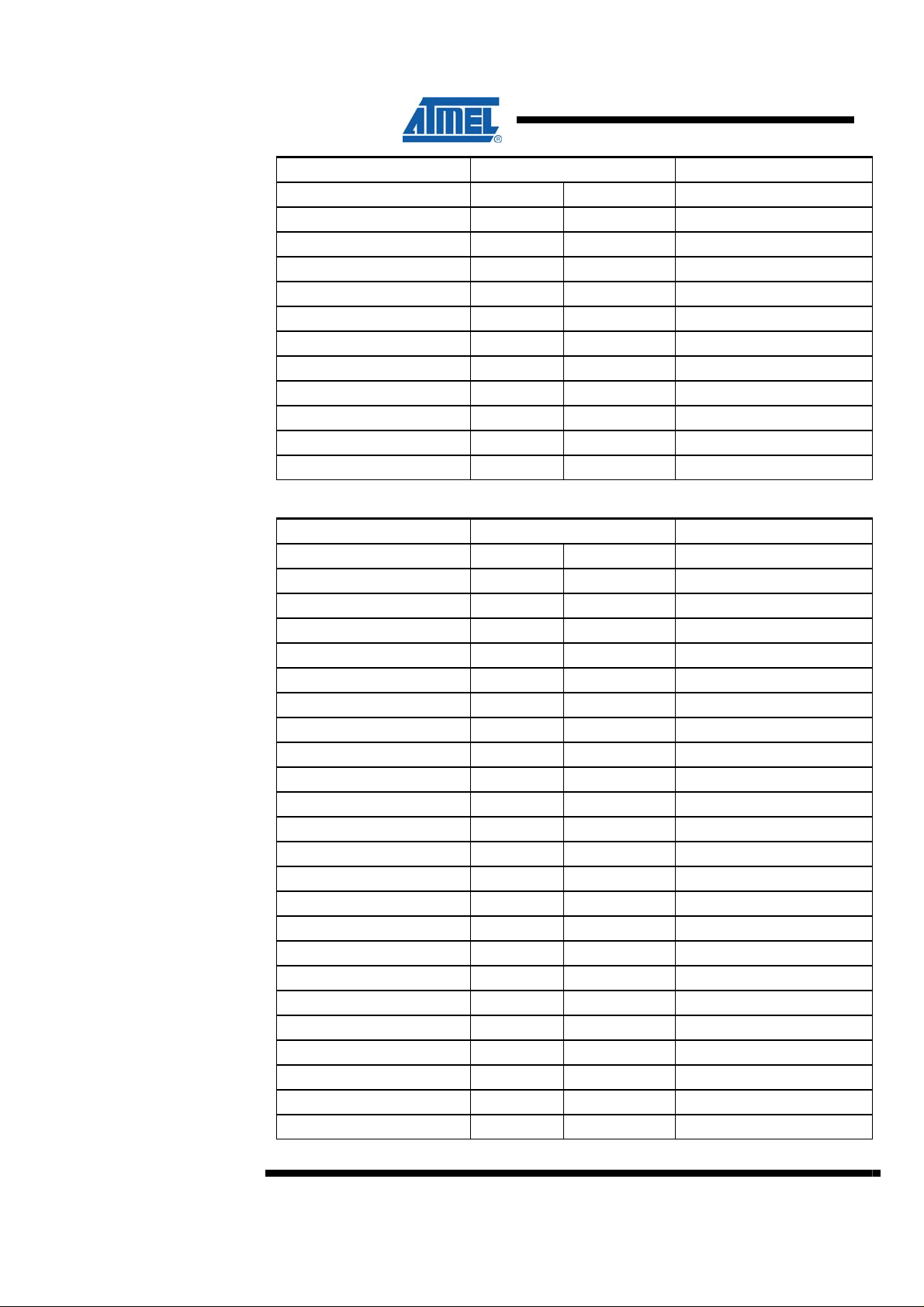
Signal name Pin number Signal name
PH5 78 77 PH4
PH7 80 79 PH6
VTG 82 81 GND
AREF0 84 83 XTAL1
AREF1 86 85 XTAL2
TGT_MOSI 88 87 GND
TGT_MISO 90 89 TOSC1
TGT_SCK 92 91 TOSC2
TDI 94 93 TGT_RESET
TDO 96 95 GND
TMS 98 97 Vext
TCK 100 99 Vcc
Table 2-3. STK600 J202 right, routing card connector J2 pin out
Signal name Pin number Signal name
VTG 2 1 GND
PJ1 4 3 PJ0
PJ3 6 5 PJ2
PJ5 8 7 PJ4
PJ7 10 9 PJ6
VTG 12 11 GND
PK1 14 13 PK0
PK3 16 15 PK2
PK5 18 17 PK4
PK7 20 19 PK6
VTG 22 21 GND
PL1 24 23 PL0
PL3 26 25 PL2
PL5 28 27 PL4
PL7 30 29 PL6
VTG 32 31 GND
PM1 34 33 PM0
PM3 36 35 PM2
PM5 38 37 PM4
PM7 40 39 PM6
VTG 42 41 GND
PN1 44 43 PN0
PN3 46 45 PN2
PN5 48 47 PN4
6
AVR600
8170A-AVR-08/08
Page 7

Signal name Pin number Signal name
PN7 50 49 PN6
VTG 52 51 GND
PP1 54 53 PP0
PP3 56 55 PP2
PP5 58 57 PP4
PP7 60 59 PP6
VTG 62 61 GND
PQ1 64 63 PQ0
PQ3 66 65 PQ2
PQ5 68 67 PQ4
PQ7 70 69 PQ6
VBUST 72 71 DP
UVCON 74 73 DN
Vcc 76 75 UID
Vext 78 77 GND
TGT_PDATA1 80 79 TGT_PDATA0
TGT_PDATA3 82 81 TGT_PDATA2
TGT_PDATA5 84 83 TGT_PDATA4
TGT_PDATA7 86 85 TGT_PDATA6
TGT_PCTRL1 88 87 TGT_PCTRL0
TGT_PCTRL3 90 89 TGT_PCTRL2
TGT_PCTRL5 92 91 TGT_PCTRL4
TGT_PCTRL7 94 93 TGT_PCTRL6
BOARD_ID1 96 95 BOARD_ID0
BOARD_ID3 98 97 BOARD_ID2
BOARD_ID5 100 99 BOARD_ID4
AVR600
2.3.1 Signal descriptions
8170A-AVR-08/08
Table 2-4. Socket ca
STK600 Signal name MCU Comment
PAx, PBx etc PAx, PBx etc 1-to-1 mcu pin mapping
VTG Vcc
GND GND
AREFx AREF
XTALx XTALx
rd connector pin description
Target supply rail controlled by
AVR Studio® / STK600
Analog reference voltage,
controlled by AVR Studio /
STK600
Clock pins connected to
oscillator on STK600.
7
Page 8
STK600 Signal name MCU Comment
TGT_SCK, TGT_MISO,
TGT_MOSI ISP pins ISP programming interface
TGT_TDI, TGT_TDO,
TGT_TMS, TGT_TCK JTAG pins JTAG programming interface
VBUST VBUS VBUS (sense) for USB
UID UID ID pin for USB OTG
USB VBUS generation control for
USB OTG. A low level on this
UVCON UVCON
DP, DN DP, DN USB differential pair
TGT_PDATAx (HV) data pins
TGT_CTRL0 (HV) Byte Select 2
TGT_CTRL1 (HV) Ready
TGT_CTRL2 (HV) Output Enable
TGT_CTRL3 (HV) Write Enable
TGT_CTRL4 (HV) Byte Select 1
TGT_CTRL5 (HV) XTAL0
TGT_CTRL6 (HV) XTAL1
TGT_CTRL7 (HV) PAGEL
BOARD_IDn none
Notes: 1. Not all AVR will have every pin (ex. two aref pins, tosc or usb)
2. A MCU pin will fan-out to both Pnx pin and to the programming interface(s)
located at that pin.
signal enables VBUS generation.
Data pins for high voltage
(PP/HVSP) programming.
Control signals for High voltage
Parallell Programming / Serial
Programming. Please refer to
AVR datasheet for further
information.
On AVRs with common BS1 /
PAGEL, BS1 is used.
ID system for router / socket /
expansion cards, see section 5 ID System
3 Socket cards
3.1 Power design issues
3.2 Connector MPN
8
AVR600
Socket cards route each pin from the IC socket to separate pins on the spring loaded
connectors on the bottom side, facing the routing card.
Since all routing is handled by the routing card, even power lines and power
decoupling is ignored at the socket card. This produces less than ideal power design
which may lead to unwanted noise, ground bounce and other effects. It should
therefore be expected that heavily loaded designs can not run at full speed on
STK600. Likewise, such power design is not recommended for custom design s.
Table 3-1. Socket card connector
Manufacturer and MPN Quantity Comment
SAMTEC, FSI-140-03-G-D-AD 2 Spring loaded 80-pin connector
8170A-AVR-08/08
Page 9

3.3 Physical dimensions and component placement
Figure 3-1. Socket card connector placement and dimensions
Error! Not a valid link.
The board thickness should be 1.6mm to be compatible with the clips.
4 Expansion cards
The STK600 features an expansion area where cards for custom peripherals like
memory expansion, LCD etc can be placed. STK600 routes all part pins and power to
the expansion card connectors.
4.1 Connector MPN
Table 4-1. Expansion card connector
Manufacturer and MPN Quantity Comment
FCI, 61082-101402LF 2
4.2 Physical dimensions and component placement
AVR600
Figure 4-1. Expansion card connector placement and dimensions
8170A-AVR-08/08
There is no requirement to board thickness.
9
Page 10
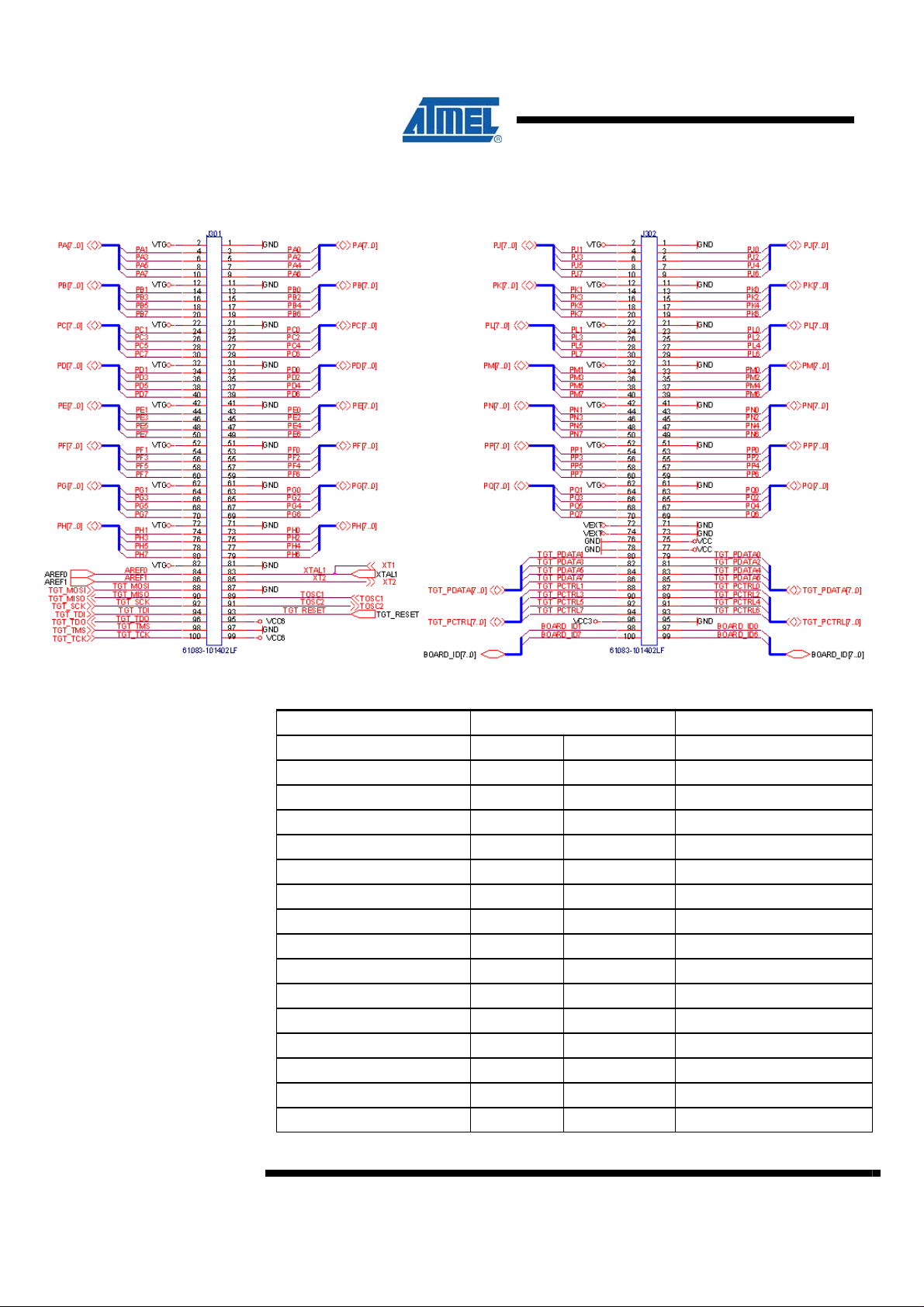
4.3 STK600 Expansion connectors pin out
Figure 4-2. Pinout for expansion connectors
Table 4-2. STK600 J301 “expand0” connector pin out
Signal name Pin number Signal name
VTG 2 1 GND
PA1 4 3 PA0
PA3 6 5 PA2
PA5 8 7 PA4
PA7 10 9 PA6
VTG 12 11 GND
PB1 14 13 PB0
PB3 16 15 PB2
PB5 18 17 PB4
PB7 20 19 PB6
VTG 22 21 GND
PC1 24 23 PC0
PC3 26 25 PC2
PC5 28 27 PC4
PC7 30 29 PC6
VTG 32 31 GND
10
AVR600
8170A-AVR-08/08
Page 11

Signal name Pin number Signal name
PD1 34 33 PD0
PD3 36 35 PD2
PD5 38 37 PD4
PD7 40 39 PD6
VTG 42 41 GND
PE1 44 43 PE0
PE3 46 45 PE2
PE5 48 47 PE4
PE7 50 49 PE6
VTG 52 51 GND
PF1 54 53 PF0
PF3 56 55 PF2
PF5 58 57 PF4
PF7 60 59 PF6
VTG 62 61 GND
PG1 64 63 PG0
PG3 66 65 PG2
PG5 68 67 PG4
PG7 70 69 PG6
VTG 72 71 GND
PH1 74 73 PH0
PH3 76 75 PH2
PH5 78 77 PH4
PH7 80 79 PH6
VTG 82 81 GND
AREF0 84 83 XTAL1
AREF1 86 85 XTAL2
TGT_MOSI 88 87 GND
TGT_MISO 90 89 TOSC1
TGT_SCK 92 91 TOSC2
TDI 94 93 TGT_RESET
TDO 96 95 Vcc6
TMS 98 97 GND
TCK 100 99 Vcc6
AVR600
8170A-AVR-08/08
Table 4-2. STK600 J302 “expand1” connector pinout
Signal name Pin number Signal name
VTG 2 1 GND
PJ1 4 3 PJ0
11
Page 12

Signal name Pin number Signal name
PJ3 6 5 PJ2
PJ5 8 7 PJ4
PJ7 10 9 PJ6
VTG 12 11 GND
PK1 14 13 PK0
PK3 16 15 PK2
PK5 18 17 PK4
PK7 20 19 PK6
VTG 22 21 GND
PL1 24 23 PL0
PL3 26 25 PL2
PL5 28 27 PL4
PL7 30 29 PL6
VTG 32 31 GND
PM1 34 33 PM0
PM3 36 35 PM2
PM5 38 37 PM4
PM7 40 39 PM6
VTG 42 41 GND
PN1 44 43 PN0
PN3 46 45 PN2
PN5 48 47 PN4
PN7 50 49 PN6
VTG 52 51 GND
PP1 54 53 PP0
PP3 56 55 PP2
PP5 58 57 PP4
PP7 60 59 PP6
VTG 62 61 GND
PQ1 64 63 PQ0
PQ3 66 65 PQ2
PQ5 68 67 PQ4
PQ7 70 69 PQ6
Vext 72 71 GND
Vext 74 73 GND
GND 76 75 Vcc
GND 78 77 Vcc
TGT_PDATA1 80 79 TGT_PDATA0
TGT_PDATA3 82 81 TGT_PDATA2
12
AVR600
8170A-AVR-08/08
Page 13

5 ID System
Signal name Pin number Signal name
TGT_PDATA5 84 83 TGT_PDATA4
TGT_PDATA7 86 85 TGT_PDATA6
TGT_PCTRL1 88 87 TGT_PCTRL0
TGT_PCTRL3 90 89 TGT_PCTRL2
TGT_PCTRL5 92 91 TGT_PCTRL4
TGT_PCTRL7 94 93 TGT_PCTRL6
Vcc3 96 95 GND
BOARD_ID1 98 97 BOARD_ID0
BOARD_ID7 100 99 BOARD_ID6
AVR600
The STK600 features an id system to identify which routing, socket and expansion
card is attached. The STK600 can impose voltage limitations based on the IDs, and
AVR Studio will notify the user if the combination is incorrect.
The ID system consists of two common output and two board unique input signals.
Each input is one of sixteen possible values based in the input signals – giving a total
id space of 256.
5.1 Signal usage
Three IDs are reserved for custom use and can be implemented without use of ICs.
Table 5-1. IDs reserved for custom use
Type ID
Board limited to 1.8 V 0xCA
Board limited to 3.3 V 0xCC
No limit on voltage 0xCF
The id 0xff indicates no board present.
Table 5-2. ID system signal usage
name Direction Function
BOARD_ID0 Output (a) Common output to functions
BOARD_ID1 Output (b) Common output to functions
BOARD_ID2 Input Input from routing card
BOARD_ID3 Input Input from routing card
BOARD_ID4 Input Input from socket card
BOARD_ID5 Input Input from socket card
BOARD_ID6 Input Input from expansion card
BOARD_ID7 Input Input from expansion card
8170A-AVR-08/08
13
Page 14
5.2 ID functions
B
+
B
B
B
A
A
⊕
A
ABB
+
B
BAB
⋅
+
B
+
The functions and their output according to input A and B
B A 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Functions as logic expressions
Function Expression ID
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
A
A
AB
AB
A
0
1
BA
BA ⊕
0x0
0x1
0x2
0x3
0x4
0x5
0x6
0x7
0x8
0x9
0xA
0xB
0xC
0xD
0xE
0xF
5.3 Examples
14
For a socket card to report the ID 0xCA:
Route BOARD_ID0 to BOARD_ID4 and BOARD_ID1 to BOARD_ID5
Figure 5-1. Socket card id example
For an expansion card to report the ID 0xCF:
AVR600
8170A-AVR-08/08
Page 15

Route BOARD_ID0 to BOARD_ID6 and VCC to BOARD_ID7
Figure 5-2. Expansion card id example
For a router card to report the ID 0xCC:
Route BOARD_ID0 to both BOARD_ID3 and BOARD_ID4.
Figure 5-3. Routing card id example
AVR600
6 Design example
To support a new package type one would typically start with designing the socket
card. The pinout between the socket card and routing card is not defined and left to
the designer. An example is given in figure 6-1
Next is the design of the routing card (figure 6-3). The routing cards role is to connect
each pin from the socket card to the corresponding pin on STK600. In addition to
decoupling etc, the routing card should also fan-out the correct signals to
programming headers.
Each card in the stack has its own board_id pins, the routing card is responsible for
passing on the signal to the socket card.
8170A-AVR-08/08
15
Page 16
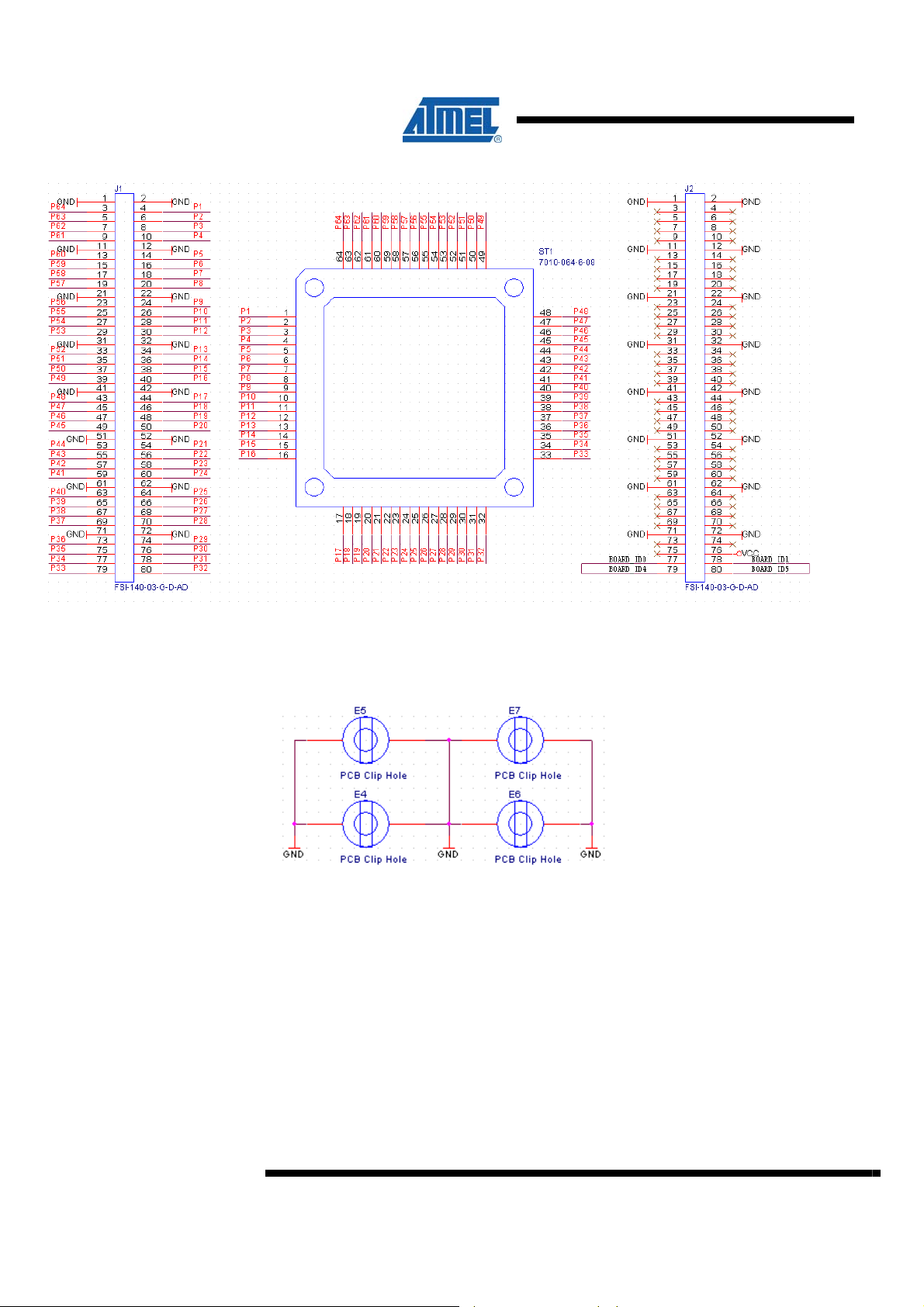
Figure 6-1. Schema capture of socket card
Both the socket and routing card must also include the clip holes:
Figure 6-2. Clip holes included in schematic.
16
AVR600
8170A-AVR-08/08
Page 17

Figure 6-3. Schema capture of routing card
AVR600
8170A-AVR-08/08
Copyright © 2008, Atmel Corporation
17
Page 18

Disclaimer
Headquarters International
Atmel Corporation
2325 Orchard Parkway
San Jose, CA 95131
USA
Tel: 1(408) 441-0311
Fax: 1(408) 487-2600
Atmel Asia
Room 1219
Chinachem Golden Plaza
77 Mody Road Tsimshatsui
East Kowloon
Hong Kong
Tel: (852) 2721-9778
Fax: (852) 2722-1369
Atmel Europe
Le Krebs
8, Rue Jean-Pierre Timbaud
BP 309
78054 Saint-Quentin-enYvelines Cedex
France
Tel: (33) 1-30-60-70-00
Fax: (33) 1-30-60-71-11
Atmel Japan
9F, Tonetsu Shinkawa Bldg.
1-24-8 Shinkawa
Chuo-ku, Tokyo 104-0033
Japan
Tel: (81) 3-3523-3551
Fax: (81) 3-3523-7581
Product Contact
Web Site
www.atmel.com
Disclaimer: The information in this document is provided in connection with Atmel products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any
intellectual property right is granted by this document or in connection with the sale of Atmel products. EXCEPT AS SET FORTH IN ATMEL’S TERMS AND
CONDITIONS OF SALE LOCATED ON ATMEL’S WEB SITE, ATMEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER AND DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS, IMPLIED
OR STATUTORY WARRANTY RELATING TO ITS PRODUCTS INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL ATMEL BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE, SPECIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS,
BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, OR LOSS OF INFORMATION) ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS DOCU MENT, EVEN IF ATMEL HAS
BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. Atmel makes no representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the
contents of this document and reserves the right to make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time without notice. Atmel does not make any
commitment to update the information contained herein. Unless specifically provided otherwise, Atmel products are not suitable for, and shall not be used in,
automotive applications. Atmel’s products are not intended, authorized, or warranted for use as components in applications intended to support or sustain life.
© 2008 Atmel Corporation. All rights reserved. Atmel®, logo and combinations thereof, AVR®, AVR Studio®, STK® and others, are the
registered trademarks or trademarks of Atmel Corporation or its subsidiaries. Other terms and product names may be trademarks of others.
Literature Request
www.atmel.com/literature
Technical Support
avr@atmel.com
Sales Contact
www.atmel.com/contacts
8170A-AVR-08/08
 Loading...
Loading...