Page 1

®
SP98-N
Mini NLX Motherboard
USER’S MANUAL
Page 2

USER’S NOTICE
No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it, may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language
in any form or by any means, except documentation kept by the purchaser for backup purposes, without the express written permission of ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (“ASUS”).
ASUS PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED
W ARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL ASUS, ITS DIRECTORS, OFFICERS,
EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF
PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF USE OR DAT A, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS AND THE LIKE), EVEN IF ASUS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGES ARISING FROM ANY DEFECT OR ERROR IN THIS MANUAL
OR PRODUCT.
Product warranty or service will not be extended if: (1) the product is repaired, modified or
altered, unless such repair, modification of alteration is authorized in writing by ASUS; or
(2) the serial number of the product is defaced or missing.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for identification or
explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
• Intel, LANDesk, and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
• IBM and OS/2 are registered trademarks of International Business Machines.
• Symbios is a registered trademark of Symbios Logic Corporation.
• Windows and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
• Sound Blaster AWE32 and SB16 are trademarks of Creative Technology Ltd.
• Adobe and Acrobat are registered trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
The product name and revision number are both printed on the product itself. Manual revi-
sions are released for each product design represented by the digit before and after the period
of the manual revision number. Manual updates are represented by the third digit in the
manual revision number.
For previous or updated manuals, BIOS, drivers, or product release information, contact ASUS
at http://www.asus.com.tw or through any of the means indicated on the following page.
SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL ARE FURNISHED FOR INFORMATIONAL USE ONLY, AND ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE AT
ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE, AND SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS A COMMITMENT BY ASUS. ASUS ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR
ANY ERRORS OR INACCURACIES THAT MA Y APPEAR IN THIS MANUAL, INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS AND SOFTWARE DESCRIBED IN IT.
Copyright © 1999 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved.
Product Name: ASUS SP98-N
Manual Revision: 1.03 E409
Release Date: August 1999
2
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 3

ASUS CONTACT INFORMATION
ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (Asia-Pacific)
Marketing
Address: 150 Li-Te Road, Peitou, Taipei, Taiwan 112
Telephone: +886-2-2890-3447
Fax: +886-2-2894-3449
Email: info@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
Telephone: +886-2-2890-7121
Fax: +886-2-2895-9254
Email: tsd@asus.com.tw
Newsgroup: news2.asus.com.tw
WWW: www.asus.com.tw
FTP: ftp.asus.com.tw/pub/ASUS
ASUS COMPUTER INTERNATIONAL (America)
Marketing
Address: 6737 Mowry Avenue, Mowry Business Center, Building 2
Newark, CA 94560, USA
Fax: +1-510-608-4555
Email: info-usa@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
Fax: +1-510-608-4555
BBS: +1-510-739-3774
Email: tsd@asus.com
WWW: www.asus.com
FTP: ftp.asus.com/Pub/ASUS
ASUS COMPUTER GmbH (Europe)
Marketing
Address: Harkortstr. 25, 40880 Ratingen, BRD, Germany
Fax: +49-2102-4420-66
Email: sales@asuscom.de
Technical Support
Hotline: +49-2102-9599-0
Online Support: www.asuscom.de/de/support
WWW: www.asuscom.de
FTP: ftp.asuscom.de/pub/ASUSCOM
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 3
Page 4

CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION ............................................................................. 7
1.1 How This Manual Is Organized .................................................. 7
1.2 Item Checklist ............................................................................. 7
1.2.1 Motherboard .................................................................... 7
1.2.2 Riser Card ........................................................................ 7
2. FEATURES ......................................................................................... 8
2.1 The ASUS SP98-N Motherboard................................................ 8
2.1.1 Specifications .................................................................. 8
2.2 Motherboard Parts....................................................................... 9
3. HARDWARE SETUP ..................................................................... 10
3.1 Motherboard Layout ................................................................. 10
3.2 Riser Card Layout ..................................................................... 12
3.2.1 NLX-R ........................................................................... 12
3.2.2 Yeong-Yang ................................................................... 12
3.3 Hardware Setup Procedure ....................................................... 15
3.4 Motherboard Settings................................................................ 15
3.5 System Memory (DIMM) ......................................................... 22
3.5.1 General DIMM Notes.................................................... 22
3.5.2 DIMM Memory Installation .......................................... 23
3.6 Central Processing Unit (CPU).................................................. 24
3.7. Expansion Cards ....................................................................... 25
3.7.1 Expansion Card Installation Procedure: ........................ 25
3.7.2 Assigning IRQs for Expansion Cards............................ 25
3.7.3 Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards...................... 26
3.7.4 ISA Cards and Hardware Monitor ................................. 26
3.8 External Connectors.................................................................. 27
3.8.1 Back Panel Connectors .................................................. 27
3.8.2 Midboard Connectors .................................................... 30
3.8.3 Riser Card Connectors................................................... 33
3.9 Power Connection Procedures .................................................. 39
4. BIOS SETUP.................................................................................... 40
4.1 Managing and Updating Your BIOS ......................................... 40
4.1.1 Upon First Use of the Computer System....................... 40
4.1.2 Updating BIOS Procedures (only when necessary) ...... 41
4.2 BIOS Setup ................................................................................ 43
4.2.1 Load Defaults ................................................................ 44
4.3 Standard CMOS Setup .............................................................. 44
4.3.1 Details of Standard CMOS Setup.................................. 44
4.4 BIOS Features Setup................................................................. 47
4.4.1 Details of BIOS Features Setup..................................... 47
4.5 Chipset Features Setup.............................................................. 50
4.5.1 Details of Chipset Features Setup.................................. 50
4
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 5

CONTENTS
4.6 Power Management Setup ........................................................ 53
4.6.1 Details of Power Management Setup ............................ 53
4.7 PNP and PCI Setup ................................................................... 55
4.7.1 Details of PNP and PCI Setup ....................................... 55
4.8 Load BIOS Defaults.................................................................. 57
4.9 Load Setup Defaults.................................................................. 57
4.10 Smart Alarm (LM78/LM75) Setup .......................................... 58
4.11 Supervisor and User Password ................................................ 59
4.11.1 Forgot the Password?..................................................... 59
4.12 IDE HDD Auto Detection ........................................................ 60
4.13 Save and Exit Setup ................................................................. 61
4.14 Exit Without Saving ................................................................. 61
5. SOFTWARE CONTENTS............................................................... 63
5.1 ASUS Support CD .................................................................... 63
6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE ............................................................ 65
6.1 Intel LANDesk Client Manager................................................ 65
6.2 ASUS PC Probe ........................................................................ 71
6.3 SVGAUTL.EXE ....................................................................... 75
6.4 Windows 3.1 ............................................................................. 82
6.5 Windows 95 .............................................................................. 86
6.6 Windows NT 3.5 & 3.51........................................................... 88
6.7 Windows NT 4.0 ....................................................................... 89
6.8 Autodesk ADI 4.2 -Protected Mode ......................................... 90
6.9 OS/2 V2.1 ................................................................................. 94
6.10 OS/2 V3.0 (Warp) ..................................................................... 95
6.11 Double Bytes OS/2 Warp .......................................................... 96
6.12 Desktop Management Interface (DMI)..................................... 97
7. APPENDIX...................................................................................... 101
7.1 PCI-L101 Fast Ethernet Card ................................................. 101
7.2 Network Controller ................................................................. 103
7.3 Glossary .................................................................................. 109
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 5
Page 6

FCC & DOC COMPLIANCE
Federal Communications Commission Statement
This device complies with FCC Rules Part 15. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference, and
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Re-orient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
W ARNING! Any changes or modifications to this product not expressly ap-
proved by the manufacturer could void any assurances of safety or performance
and could result in violation of Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Canadian Department of Communications Statement
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions
from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
6
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 7

1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 How This Manual Is Organized
This manual is divided into the following sections:
1) INTRODUCTION Manual information and checklist
2) FEATURES Product information and specifications
3) HARDWARE SETUP Instructions on setting up the motherboard
4) BIOS SETUP Instructions on setting up the BIOS software
5) SOFTWARE CONTENTS Information on included software
6) SOFTWARE REFERENCE Reference material for the included software
7) APPENDIX Optional items and general reference
1.2 Item Checklist
Check that your package is complete. If you discover damaged or missing items,
contact your retailer.
1.2.1 Motherboard
Manual / Checklist
I. INTRODUCTION
(1) ASUS Motherboard
(1) Support CD with drivers and utilities
(1) This Motherboard User’s Manual
(1) NLX form-factor system housing, riser card, and power supply
ASUS slim CD-ROM (optional)
LCD panel connector with bracket (for LCD model only)
ASUS IrDA-compliant infrared module (optional)
ASUS PCI-L101 Wake-On-LAN 10/100 Fast Ethernet Card (optional)
NOTE: This motherboard only works with ASUS riser cards. See your dealer
for more information.
1.2.2 Riser Card
(1) ASUS Riser Card
(1) Ribbon cable for master and slave UltraDMA/33 IDE drives
(1) Ribbon cable for (1) 3.5” floppy disk drive
(1) FDC slim CD-ROM cable (optional)
(1) Bag of spare jumper caps
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 7
Page 8

2. FEATURES
Features
2. FEATURES
2.1 The ASUS SP98-N Motherboard
The ASUS SP98-N motherboard is carefully designed for the demanding PC user
who wants many features in a small package:
2.1.1 Specifications
• Mini NLX: Features ASUS’ custom-designed mini-NLX form factor.
• SiS PCIset: SiS 5598 PCIset with built-in 64-bit PCI 2D graphics controller
and support for video-shared memory from 1MB to 4MB.
• Onboard Audio (optional): Features Yamaha’s ISA audio chip (OPL3-SA3®)
with 3D surround and positioning capability.
• Slim CD-ROM (optional): Supports a notebook-sized slim CD-ROM drive.
• Wake on LAN: Supports wake on LAN activity with built-in network support.
• Intel Network Interface: Equipped with the Intel 82558 Ethernet LAN Con-
troller (fully integrated 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX) with LED indicators for
monitoring network conditions.
• Multi-Processor/Multi-Speed Support: AMD® K6®-2/266 & faster, AMD® K6®/
166 & faster, AMD
®
/Cyrix® 6x86-PR166+ (Rev 2.7 or later), Intel® Pentium® 100–233MHz (P55C-
IBM
MMX
• Versatile Memory Support: Equipped with two DIMM sockets to support 8-
128MB 168-pin 3.3Volt SDRAM memory modules up to 256MB.
• Super Multi-I/O: Provides an onboard I/O processor for two high-speed UAR T -
compatible serial ports and one parallel port with EPP and ECP capabilities.
• Level 2 Cache: Comes with onboard 512K Pipelined Burst SRAM.
• Desktop Management Interface (DMI): Supports DMI through BIOS, which
allows hardware to communicate within a standard protocol creating a higher
level of compatibility. (Requires DMI-enabled components.) (See section V)
• PCI Bus Master IDE Controller: Onboard Ultra DMA/33 Bus Master IDE
controller with two connectors (one for CD-ROM only). Supports two IDE devices up to 8.4GB using one channel. Supports Bus Master UltraDMA/33 IDE,
PIO Modes 3 & 4, and Bus Master IDE DMA Mode 2. Includes integrated keyboard controller. Supports two of either 5.25-inch (360KB, 1.2KB) or 3.5-inch
disk drives (720KB, 1.44MB, 2.88MB). Supports Japanese “Floppy 3 mode”
(3.5-inch disk drive: 1.2MB) and LS-120 drives (3.5-inch disk drive: 120 MB,
1.44MB, 720K). BIOS supports IDE CD-ROM or SCSI device bootup.
• Symbios SCSI BIOS: Supports optional ASUS SCSI controller cards through
onboard firmware.
• Performance: Provides 528MB/s data transfer rate using SDRAM, 33MB/s
IDE transfer rate using Bus Master UltraDMA/33 IDE, concurrent PCI allows
multiple PCI transfers.
• Compliancy: ACPI ready for advanced power management features and PC97
compliancy for greater support.
• Easy Installation: Incorporates BIOS that supports autodetection of hard disk
drives, PS/2 mouse, and Plug and Play devices to make setup of hard disk drives,
expansion cards, and other devices virtually automatic.
• Riser Card: Provides NLX power, IDE, floppy disk drive, LAN wake-up con-
nectors, PCI/ISA slots, USB/infrared support.
™
, P54C/P54CS).
®
K5™/100–133, IBM®/Cyrix® 6x86MX™/M II™ (PR166 & faster),
8 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 9
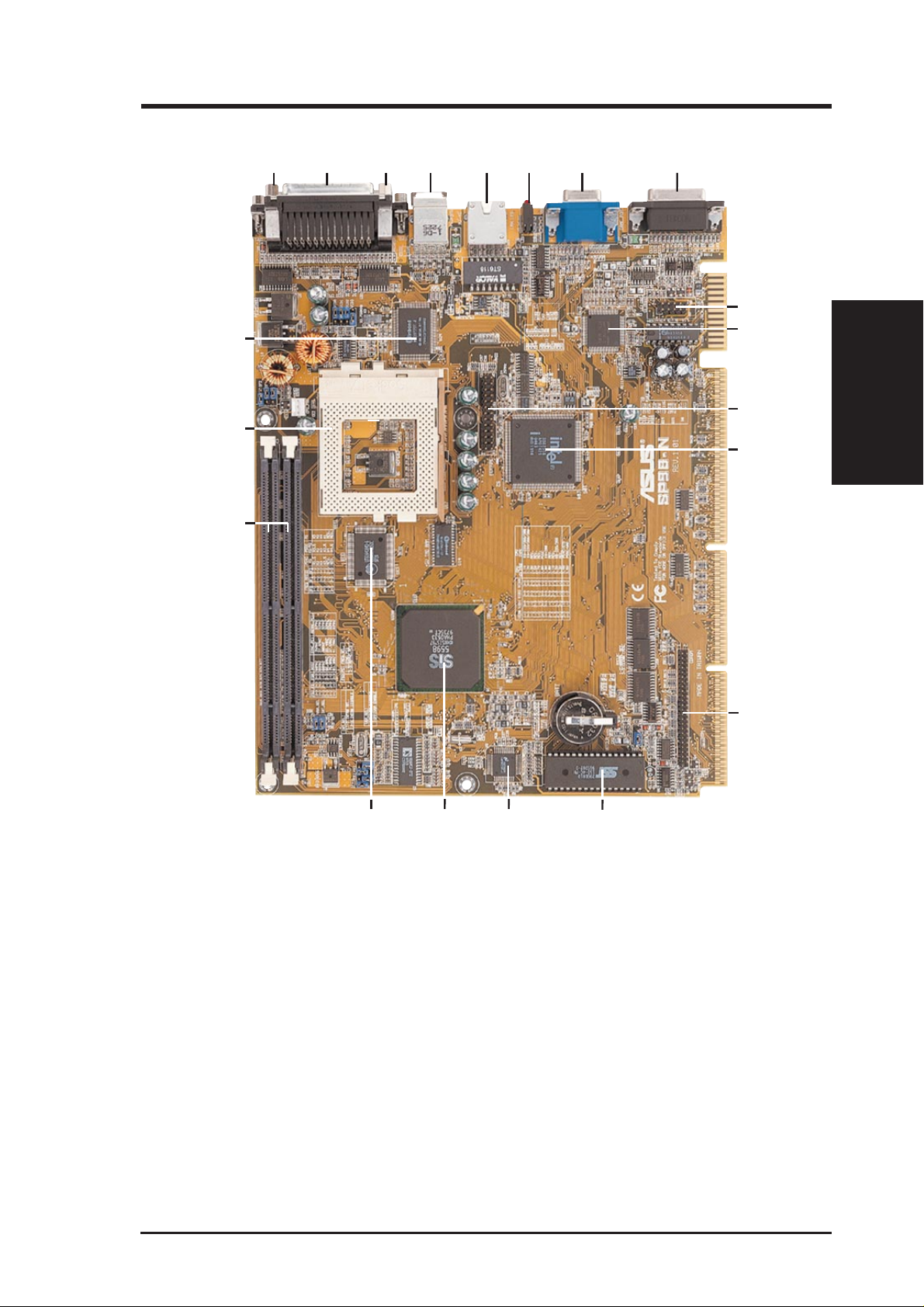
2. FEATURES
2.2 Motherboard Parts
20
19
18
321 456 7
8
9
10
11
12
2. FEATURES
Motherboard Parts
T: T op
B: Bottom
17 15 14
COM1 Connector (B)
1
Parallel Connector (
2
3
COM2 Connector (
PS/2 Mouse (
4
5
RJ-45 Connector
LAN LED
6
7
VGA Connector
Joystick/MIDI Connector
8
Back Panel Audio Connector (optional)
9
10
Audio CODEC (optional)
Video Feature Connector (optional)
11
T)/Keyboard (B) Connector
T)
B)
16
12
LAN Controller Chip (optional)
13
Slim CD-ROM Drive Connector
14
Programmable Flash EEPROM
15
Hardware Monitoring Chip
16
SiS Chipset with Integrated Video
Controller
17
512KB Pipelined Burst L2 Cache
18
DIMM Sockets
19
CPU ZIF Socket 7
20
Multi-I/O Chip
13
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 9
Page 10
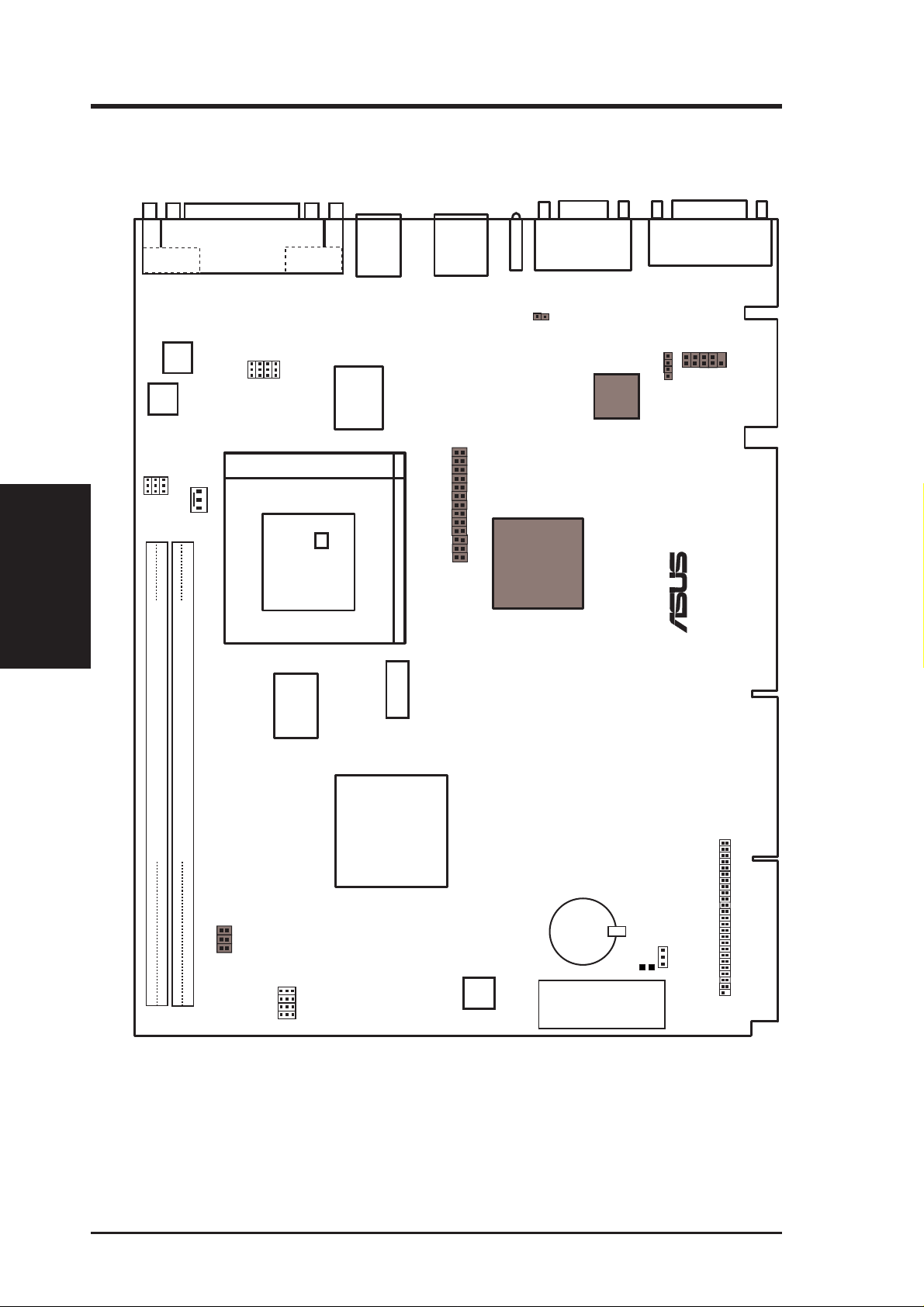
3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.1 Motherboard Layout
COM 1
BF2
BF1
BF0
Motherboard Layout
3. H/W SETUP
Freq. Ratio
Parallel Port
VID0
VID1
VID2
CPU Voltage
Switching Voltage Regulators
CPU ZIF Socket 7
CPU_FAN
CPU Thermal Sensor
(Hardware Monitor)
COM 2
VID3
LM75
PS/2
MOUSE (TOP PORT)
KEYBOARD (BOTTOM)
Multi
I/O Chip
RJ-45
VGA Setting 1
Feature Connector
Intel 82558
Ethernet LAN
Controller
VGA
Internal Speaker Connector
Audio
Chipset
Joystick/MIDI
Jack Connector
®
+5V TAG RAM
512KB Pipelined
Burst L2 Cache
SiS
5598
DIMM Socket 1 (64-bit, 168-pin module)
DIMM Socket 2 (64-bit, 168-pin module)
VGA Interrupt
VGA Setting
32
10
Row
PCI Freq. Sel.
FS0
FS1
FS2
BUS Freq.
FS3
Chipset
LM78
Hardware Monitoring
CMOS Power
(Programmable BIOS)
Grayed items are optional at the time of purchase.
CR2032
3 Volt Cell
CR2
Flash EEPROM
RTCLR
CDROM Connector
10 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 11

3. HARDWARE SETUP
Motherboard Settings
1) VGA_SEL,VGA_SEL1 p.16 VGA Setting
2) INT_SEL p.16 VGA Interrupt Setting
3) BF0, BF1, BF2 p.18 CPU:BUS Frequency Ratio
4) FS0, FS1, FS2 p.18 CPU External Frequency Setting
5) VID0, VID1, VID2, VID3 p.20 CPU Voltage Regulator Output Setting
6) RTCLR p.59 CMOS RTC RAM Setting
Sockets
1) DIMM1, DIMM2 p.22 168-Pin DIMM Memory Support
2) CPU ZIF Socket 7 p.24 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Socket
Back Panel Connectors
1) PARALLEL p.27 Parallel Port Connector (25-pin female)
2) COM1/COM2 p.27 Serial Port Connector (Two 9-pin male)
3) PS2KBMS p.28 PS/2 Mouse Port Connector (6-pin female)
4) PS2KBMS p.28 PS/2 Keyboard Port Connector (6-pin female)
5) RJ-45 p.28 Fast-Ethernet Port Connector (8-pin female) (optional)
6) LAN_LED p.28 LAN Diagnostic LEDs (3-diode Indicator)
7) VGA p.29 Monitor (VGA) Output Connector (15-pin female)
8) GAME p.29 Joystick/MIDI Connector (15-pin female) (optional)
Midboard Connectors
1) CPU_FAN p.30 CPU Fan Connectors (3 pins)
2) CDROM p.30 CD-ROM Drive Connector (50-1 pins)
3) INT_SPKR p.31 Internal Speaker Connector (4 pins)
4) JACK_CONN p.31 Back Panel Audio Connectors (10-1 pins)
5) FEATURE p.32 Video Feature Connector (26 pins)
3. H/W SETUP
Motherboard Contents
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 11
Page 12
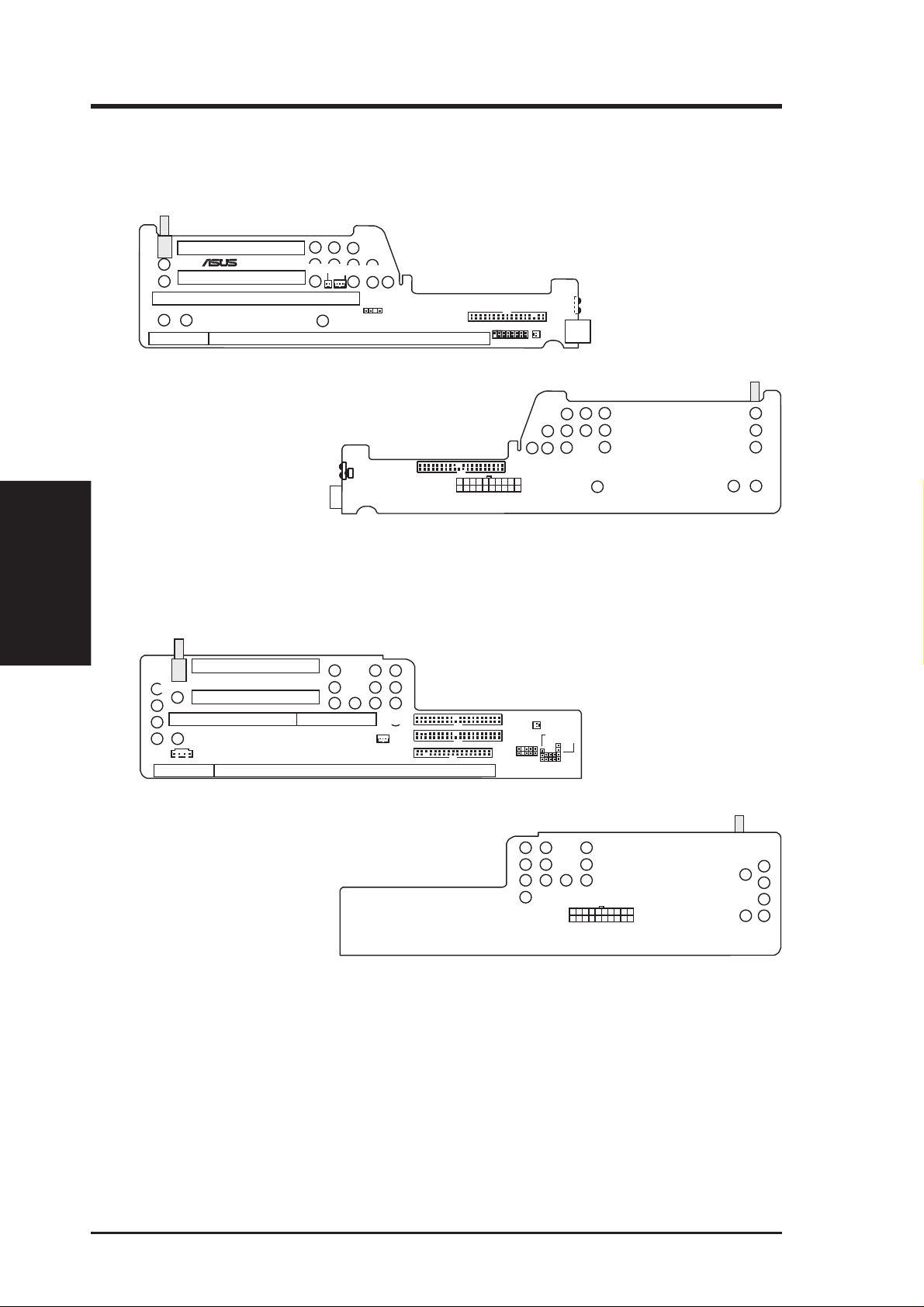
3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.2 Riser Card Layout
3.2.1 NLX-R
PCI2
®
CHASS_DET
NLX_EXT
NLX-R
PCI1
ISA
NLX-R Riser Card Front
LAN LED
WOL_CON
HEAD_SPK
NLX_SLOT
FLOPPY
FCON
MIC-CON
USB
Riser Card Parts & Layout
3. H/W SETUP
3.2.2 Yeong-Yang
SWITCH
YEONG-YANG
CDIN
NLX_EXT
Yeong-Yang Riser Card Front
SLOT1
PCI1
PCI2
IR
CIR
NLX-R Riser Card Back
SLOT1A
WOL_CON
RISER
IDE2
IDE1
FLOPPY
POWER
IDE1
MIC
USB
IR
Panel
PWRLED
HDD_LED
RESET
PWRSW
SPKR
Yeong-Yang Riser Card Back
12 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Power
Page 13

3. HARDWARE SETUP
Expansion Slots
1) ISA (NLX-R) p.25 16-bit ISA Bus Expansion Slot
SLOT1/1A (Yeong-Yang) 16-bit ISA Bus Expansion Slot
2) PCI1, PCI2 (NLX-R) p.25 32-bit PCI Bus Expansion Slots
PCI1, PCI2 (Yeong-Yang) 32-bit PCI Bus Expansion Slots
Connectors
1) LAN_LED (NLX-R) p.33 LAN Activity Connector (2 pins)
WOL_CON (NLX-R) LAN Activity Connector (3 pins)
WOL_CON (Yeong-Yang) LAN Activity Connector (3 pins)
2) MIC-CON (NLX-R) p.33 Front Panel Microphone Connector (2 pins)
MIC (Yeong-Yang) Front Panel Microphone Connector (2 pins)
3) POWER (NLX-R) p.34 NLX Power Supply Connector (20 pins)
Power (Yeong-Yang) NLX Power Supply Connector (20 pins)
4) IDE1 (NLX-R) p.34 IDE Connector (40-1 pins)
IDE1, IDE2 (Yeong-Yang) IDE Connectors (40-1 pins)
5) FLOPPY (NLX-R) p.35 3.5” Floppy Disk Drive Connnector (34-1 pins)
FLOPPY (Yeong-Yang) 3.5” Floppy Disk Drive Connnector (34-1 pins)
6) USB (NLX-R) p.35 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Ports (T wo 4-pin sockets)
USB (Yeong-Yang) USB Module Connector (5-1 pins)
7) IR, CIR (NLX-R) p.36 IrDA-Compliant Infrared Module (Lenses)
IR (Yeong-Yang) Infrared Module Connector (5-1 pins)
8) CDIN (Yeong-Yang) p.37 Stereo Audio In Connector (4 pins)
9) FCON/HEAD_SPK (NLX-R) p.37 Front Panel Connector (16-1 pins)
Panel (Yeong-Yang) Front Panel Connectors (13 pins)
3. H/W SETUP
Riser Card Contents
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 13
Page 14

(This page was intentionally left blank.)
14 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 15

3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.3 Hardware Setup Procedure
NOTE: The following procedure assumes that you have already installed the
motherboards in an appropriate housing or case.
Before using your computer, you must complete the following steps:
1. Check Motherboard Settings
2. Install Memory Modules
3. Install the Central Processing Unit (CPU)
4. Install Expansion Cards
5. Connect Ribbon Cables, Panel Wires, and Power Supply
3.4 Motherboard Settings
This section explains in detail how to change your motherboard’s function settings
through the use of switches and/or jumpers.
W ARNING! Computer motherboards and expansion cards contain very delicate
Integrated Circuit (IC) chips. To protect them against damage from static electricity, you should follow some precautions whenever you work on your computer.
1. Unplug your computer when working on the inside.
2. Use a grounded wrist strap before handling computer components. If you do
not have one, touch both of your hands to a safely grounded object or to a metal
object, such as the power supply case.
3. Hold components by the edges and try not to touch the IC chips, leads or connectors, or other components.
4. Place components on a grounded antistatic pad or on the bag that came with the
component whenever the components are separated from the system.
3. H/W SETUP
Motherboard Settings
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 15
Page 16
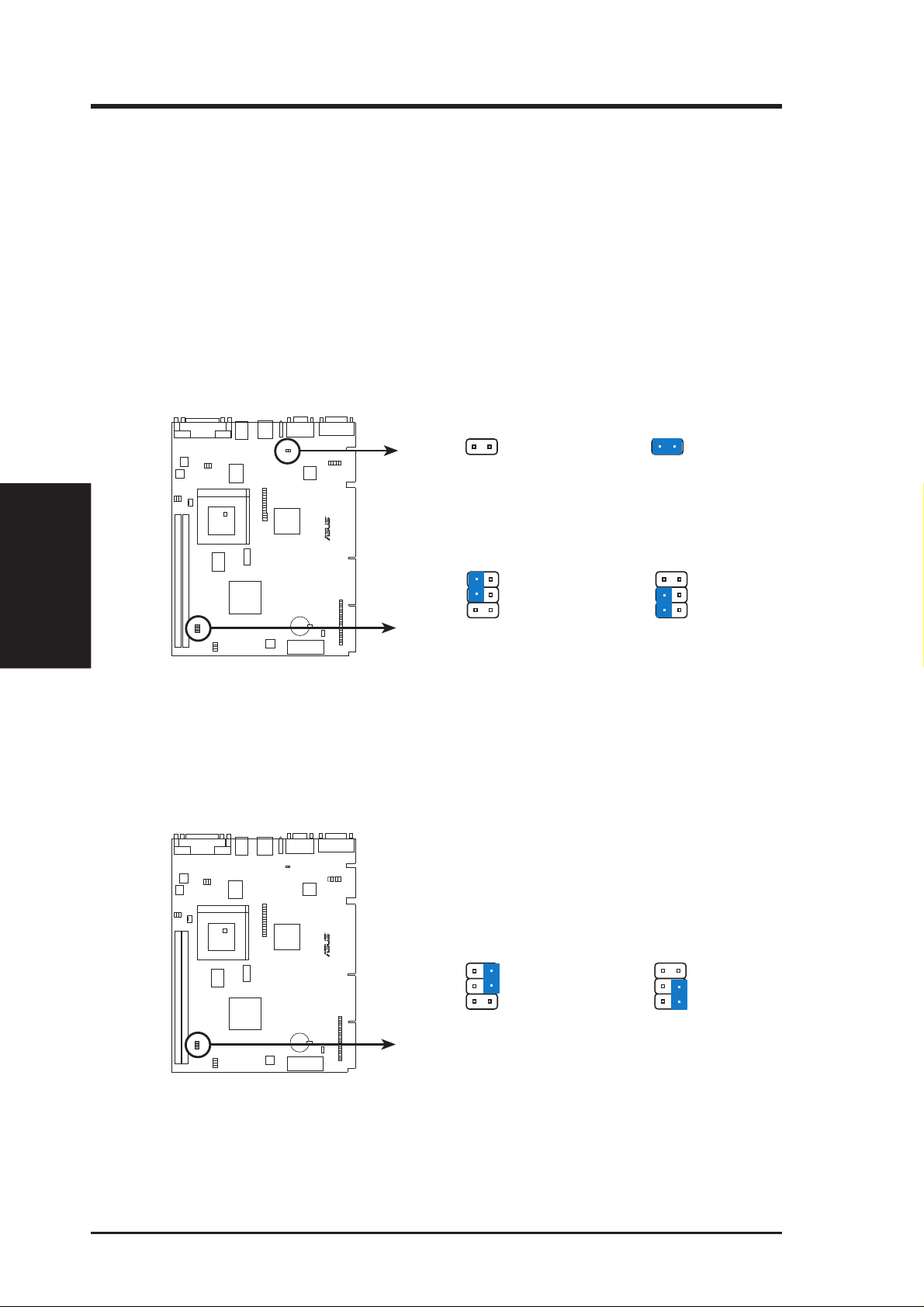
Using Your Own VGA Card on the PCI Expansion Slot
The motherboard’ s BIOS will autodetect whether a VGA card is installed on the PCI
expansion slot and disable or enable the onboard VGA but most operating systems
bypasses the BIOS and installs the onboard VGA through Plug and Play. The following VGA Selection jumpers are not required under standard configurations but if
you experience any conflicts, follow the jumper settings below.
1. VGA Selection (VGA_SEL, VGA_SEL1)
These jumpers allow you to turn the onboard VGA on or off. BIOS has automatic
Enable/Disable onboard VGA. You need to disable the onboard VGA only if
you have conflicts within your operating system.
Motherboard Settings
3. H/W SETUP
3. HARDWARE SETUP
VGA_SEL1 VGA_SEL1
R
VGA_SEL
INT_SEL
SP98-N Onboard VGA
VGA_SEL
INT_SEL
Enable VGA
(Default)
Disable VGA
2. VGA Interrupt Selection (INT_SEL)
These jumpers allow you to set the VGA interrupt method. The default disables
the chipset’s internal interrupt routing. Some video capture cards may require
that the interrupt be assigned by the onboard chipset.
R
VGA_SEL
VGA_SEL
INT_SEL
INT_SEL
Interrupt Disabled
(Default)
SP98-N Onboard VGA Interrupt
16 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Interrupt by Chipset
(Video Capture Cards)
Page 17

3. HARDWARE SETUP
(This page was intentionally left blank.)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 17
Page 18
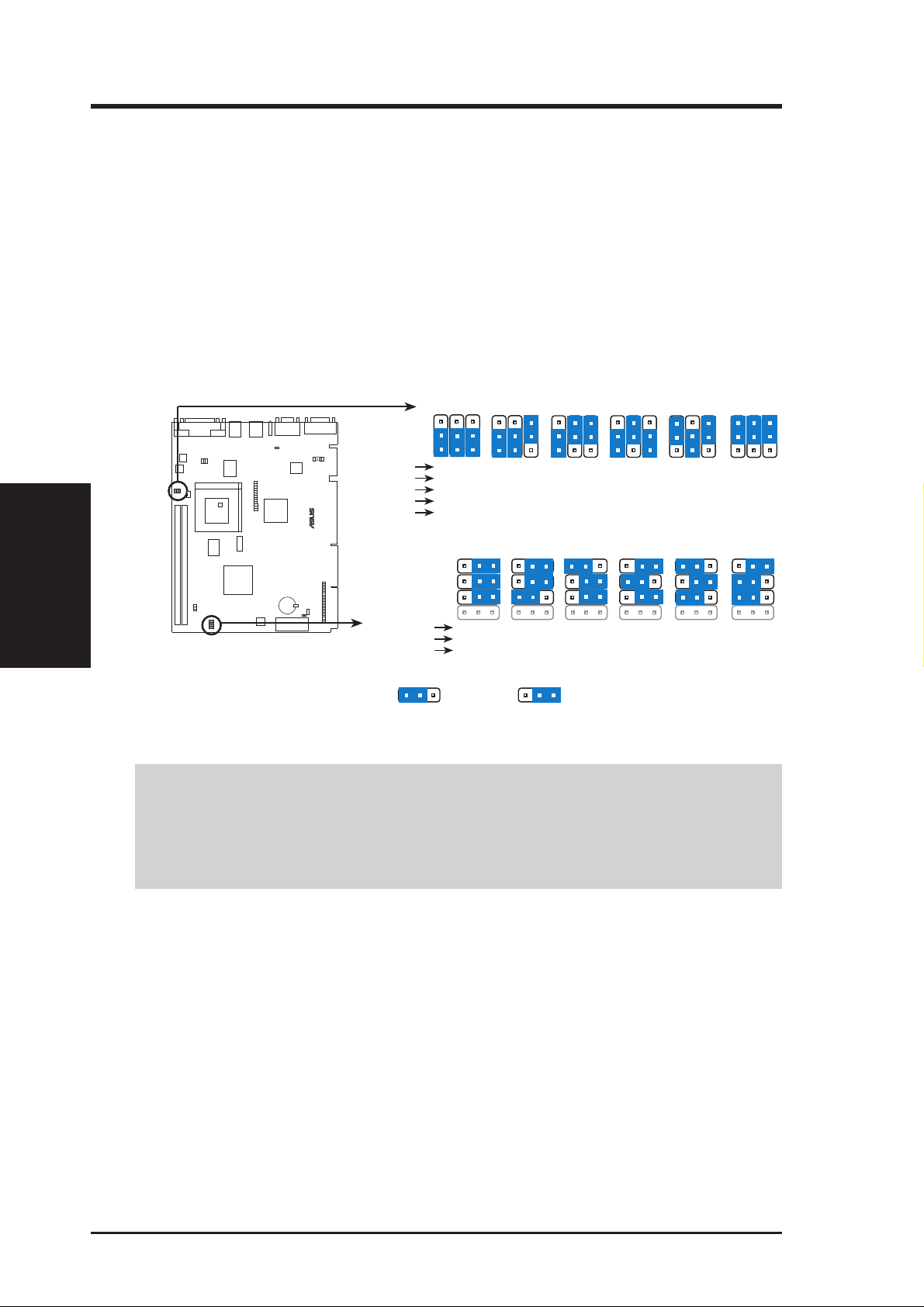
3. CPU to BUS Frequency Ratio (BF0, BF1, BF2)
These jumpers set the frequency ratio between the Internal frequency of the CPU
and the External frequency (called the BUS Clock) within the CPU. These must
be set together with the above jumpers CPU External (BUS) Frequency Selection.
4. CPU External Clock (BUS) (FS0, FS1, FS2) and PCI Fr equency Selection (FS3)
These jumpers tell the clock generator what frequency to send to the CPU. These
allow the selection of the CPU’ s External frequency (or BUS Clock). The BUS Clock
multiplied by the BUS Ratio equals the CPU’s Internal frequency (the advertised
CPU speed).
Motherboard Settings
3. IH/W SETUP
SP98-N
3. HARDWARE SETUP
®
Match the Mult. (Multiple) column
of the table on the opposite
page with these CPU types:
CPU A:AMD-K6-2, AMD-K6
CPU B:Intel Pentium P54C, AMD-K5
CPU C:Intel Pentium P55C, IBM/Cyrix
6x86MX, IBM/Cyrix M II
CPU D:IBM/Cyrix 6x86, IBM/Cyrix 6x86L
CPU E: IBM/Cyrix 6x86L
BF2
BF0
BF0
3
2
1
BF1
2.5x(5/2)
2.5x(5/2)
2.5x(5/2)
1.0x(1/1)
2.0x(2/1)
123
60MHz
30MHz
32MHz
3
2
1
3.0x(3/1)
3.0x(3/1)
3.0x(3/1)
66.8MHz
33.4MHz
BF2
BF2
BF2
BF1
CPU A
CPU B
CPU C
CPU D
CPU E
CPU : BUS Frquency Multiple
Host
Sync PCI
Async PCI
CPU External Clock (BUS) Frequency Selection
FS3
Synchronous PCI
PCI Frequency Selection
123
3.5x(7/2)
1.5x(3/2)
3.5x(3/1)
3.0x(3/1)
—
FS0
FS1
FS2
FS3
50MHz
25MHz
32MHz
123
BF1
BF0
3
2
1
2.0x(2/1)
2.0x(2/1)
2.0x(2/1)
2.0x(2/1)
2.0x(2/1)
123
55MHz
27.5MHz
32MHz
123
FS3
Asynchronous PCI
BF1
—
—
123
32MHz
BF0
3
2
1
BF2
BF1
4.0x(4/1)
—
—
—
1.5x(3/2)
123
75.9MHz
37.5MHz
32MHz
BF0
3
2
1
BF2
BF1
4.5x(9/2)
—
—
—
1.5x(3/2)
123
83.3MHz
41.7MHz
32MHz
BF0
WARNING! Do not overclock your processor. Overclocking can cause undue
stress on the CPU and motherboard. It may result in a slower speed or other
unpredictable outcomes. The table on the following page shows the approved
CPUs and their settings.
18 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 19

3. HARDWARE SETUP
Set the jumpers according to the internal speed of your processor as follows:
(BUS Freq.) (Freq. Ratio)
CPU Model Freq. Mult. BUS F. FS0 FS1 FS2 FS3 BF2 BF1 BF0
AMD-K6-2/266 266MHz A-4.0x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [2-3] [1-2] [2-3]
AMD-K6/300 300MHz A-4.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [2-3] [2-3] [2-3]
AMD-K6/266 266MHz A-4.0x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [2-3] [1-2] [2-3-]
AMD-K6/233 233MHz A-3.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K6/200 200MHz A-3.0x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [1-2]
AMD-K6/166 166MHz A-2.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [2-3]
AMD-K5/133 100MHz B-1.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K5/120 90MHz B-1.5x 60MHz [1-2] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K5/100 100MHz B-1.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K5/90 90MHz B-1.5x 60MHz [1-2] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K5/75 75MHz B-1.5x 50MHz [2-3] [2-3][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel Pentium P54C 166MHz B-2.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [2-3]
Intel Pentium P54C 150MHz B-2.5x 60MHz [1-2-] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [2-3]
Intel Pentium P54C 133MHz B-2.0x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3]
Intel Pentium P54C 120MHz B-2.0x 60MHz [1-2] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3]
Intel Pentium P54C 100MHz B-1.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel Pentium P54C 90MHz B-1.5x 60MHz [1-2] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel Pentium P54C 75MHz B-1.5x 50MHz [2-3] [2-3][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel Pentium P55C 233MHz C-3.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel Pentium P55C 200MHz C-3.0x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [1-2]
Intel Pentium P55C 166MHz C-2.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [2-3]
Jumpers
3. H/W SETUP
IBM/Cyrix M II-PR333 333MHz C-3.0x 83MHz [2-3] [1-2][1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [1-2]
IBM/Cyrix M II-PR300 300MHz C-3.0x 75MHz [1-2] [2-3][1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [1-2]
IBM/Cyrix M II-PR300 300MHz C-3.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86MX-PR233 200MHz C-3.0x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [1-2]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86MX-PR200 166MHz C-2.5x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [2-3]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86MX-PR166 150MHz C-2.5x 60MHz [1-2] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3] [2-3]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86-PR166+* 133MHz D-2.0x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86L-PR166+* 133MHz D-2.0x 66MHz [2-3] [1-2][2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86L-PR200+ 150MHz E-2.0x 75MHz [1-2] [2-3][1-2] [2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [2-3]
*Compatible Cyrix CPU Identification
The only IBM/Cyrix 6x86(L)-PR166+ (M1) CPU that is supported on this motherboard is revision 2.7 or later. Look at
the underside of the CPU for the serial number . The number
should read G8DC6620A or later.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 19
Page 20

3. HARDWARE SETUP
5. Voltage Regulator Output Selection (VID0, VID1, VID2, VID3)
These jumpers set the voltage supplied to the CPU.
WARNING! Because CPU designs change rapidly, the table below is only in-
tended as a simple guideline and thus may not be true for your CPU. Always
refer to the CPU documentation for your CPU’s voltage and then set the appropriate VID jumpers according to the illustration below.
Manufacturer CPU Type Single Plane Dual Plane VID0 VID1 VID2 VID3
AMD (.25micron) K6-2/266,300,333, ---- 2.2V(Dual) [2-3] [1-2] [2-3] [2-3]
350,366,380,400
K6/233,266,300
AMD K5 3.5V(VRE) ---- [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86 3.5V(VRE) ---- [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel P54C/P54CS 3.5V(VRE) ---- [1-2] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
3. H/W SETUP
Jumpers
AMD K5 3.4V(STD) ---- [2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel P54C/P54CS 3.4V(STD) --- [2-3] [1-2] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD (.35micron) K6/233 ---- 3.2V(Dual) [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD (.35micron) K6/166,200 ---- 2.9V(Dual) [1-2] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86MX ---- 2.9V(Dual) [1-2] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2]
AMD (.35micron) K6/166,200 ---- 2.9V(Dual) [1-2] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2]
Intel P55C-MMX ---- 2.8V(Dual) [2-3] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2]
VID2
VID1
VID0
3
2
1
R
SP98-N Voltage Regulator Output Selection
2.1 Volts
3
2
1
2.8 Volts 2.9 Volts 3.0 Volts 3.1 Volts
3
2
1
3.3 Volts 3.4 Volts 3.5 Volts
VID3
VID2
VID1
VID0
2.2 Volts
VID3
VID2
VID1
VID0
2.3 Volts
VID3
VID2
VID1
VID0
2.5 Volts
VID3
VID2
VID1
VID0
2.7 Volts
3.2 Volts
VID3
20 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 21

3. HARDWARE SETUP
(This page was intentionally left blank.)
Jumpers
3. H/W SETUP
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 21
Page 22
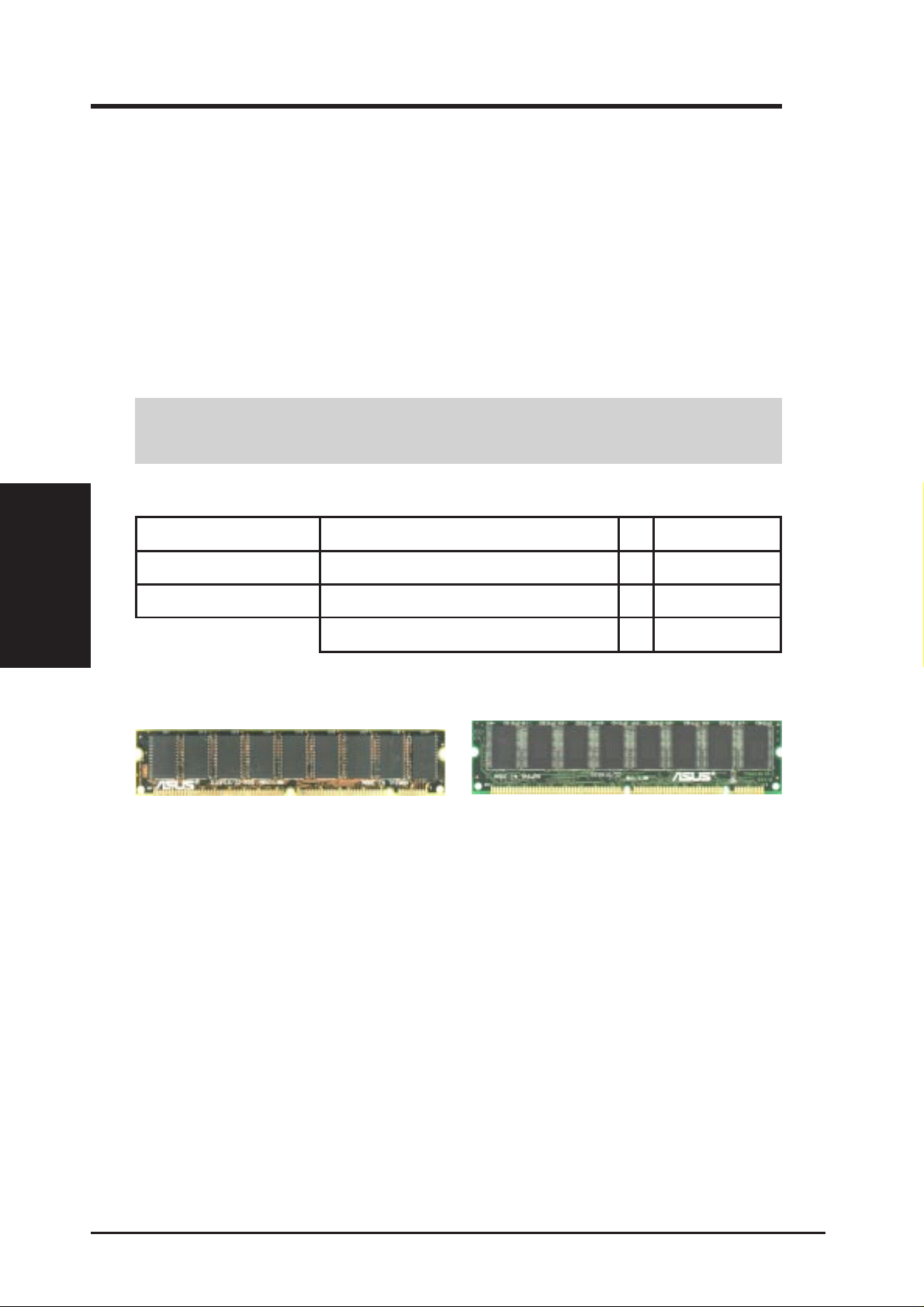
3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.5 System Memory (DIMM)
This motherboard uses only Dual Inline Memory Modules (DIMMs). S ockets are
available for 3.3Volt (power level) unbuffered Synchronous Dynamic Random Ac-
cess Memory (SDRAM) or EDO DRAM of either 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128MB to form a
memory size between 8MB to 256MB. One side (with memory chips) of the DIMM
takes up one row on the motherboard.
The SiS chipset does not support ECC. However, ECC memory modules may still
be used, but the ECC function will not be available.
IMPORTANT: Memory speed setup is required through “Auto Configuration”
in BIOS Chipset Features Setup.
System Memory
3. H/W SETUP
Install memory in any combination as follows:
DIMM Location 168-pin DIMM Memory Modules Total Memory
Socket 1 (Rows 0&1) SDRAM/EDO 8, 16, 32, 64, 128MB x1
Socket 2 (Rows 2&3) SDRAM/EDO 8, 16, 32, 64, 128MB x1
ASUS DIMM Module Examples
Parity EDO DIMM (9 chips)
3.5.1 General DIMM Notes
Total System Memory (Max 256MB) =
Non-Parity SDRAM DIMM (8 chips)
NOTE: These notes may not apply for all memory modules.
• Four possible memory chips are supported: EDO or SDRAM with and without parity .
• SDRAM chips are generally thinner with higher pin density than EDO chips.
• BIOS shows EDO or SDRAM memory on bootup screen.
• 8 chip/side modules do not support parity, only 9 chip/side modules support parity.
• Single sided modules are usually 16 or 64 MB, double sided are usually 8, 32, or 128MB.
22 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 23
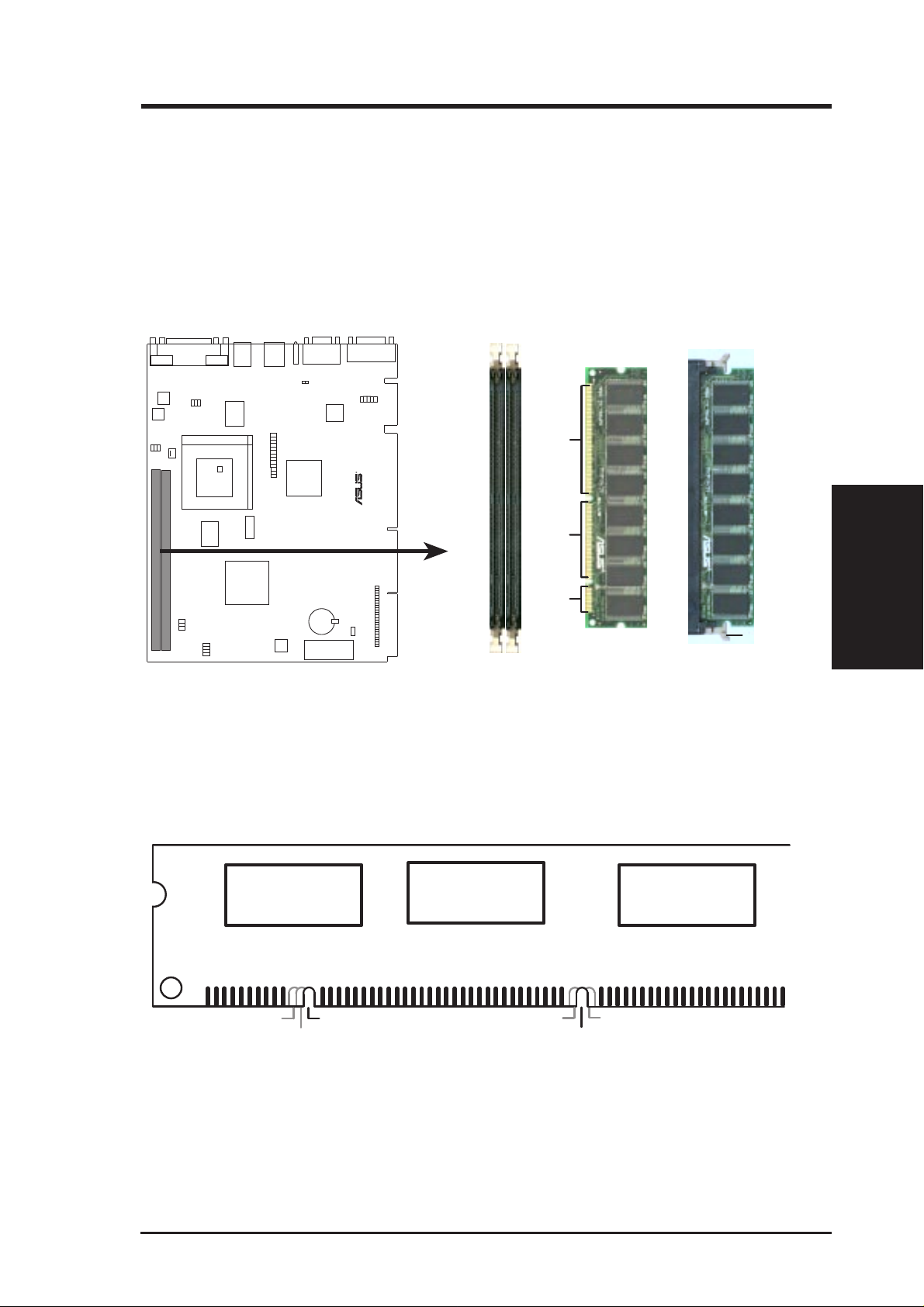
3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.5.2 DIMM Memory Installation
Insert the module(s) as shown. Because the number of pins are different on either
side of the breaks, the module will only fit in the orientation as shown. DIMM
modules are longer and have different pin contact on each side and therefore have a
higher pin density. SIMM modules have the same pin contact on both sides.
R
20 Pins88 Pins 60 Pins
Lock
SP98-N 168-Pin DIMM Memory Sockets
The DIMMs must be 3.3V Unbuffered for this motherboard. To determine the DIMM
type, check the notches on the DIMMs (see figure below).
168-Pin DIMM Notch Key Definitions (3.3V)
DRAM Key Position
RFU
Buffered
Unbuffered
Voltage Key Position
5.0V
Reserved
3.3V
3. H/W SETUP
System Memory
The notches on the DIMM module will shift between left, center, or right to identify
the type and also to prevent the wrong type from being inserted into the DIMM slot
on the motherboard. You must ask your retailer the correct DIMM type before purchasing. This motherboard supports four clock signals.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 23
Page 24

3. H/W SETUP
CPU
3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.6 Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The motherboard provides a 321-pin ZIF Socket 7 that is backwards compatible
with ZIF Socket 5 processors. The CPU that came with the motherboard should
have a fan attached to it to prevent overheating. If this is not the case then purchase
a fan before you turn on your system.
WARNING! Without a fan circulating air on the CPU, the CPU can overheat
and cause damage to both the CPU and the motherboard.
To install a CPU, first turn off your system and remove its cover. Locate the ZIF
socket and open it by first pulling the lever sideways away from the socket then
upward to a 90-degree right angle. Insert the CPU with the correct orientation as
shown. Use the notched corner of the CPU with the white dot as your guide. The
white dot should point towards the end the of the lever . Notice that there is a blank
area where one hole is missing from that corner of the square array of pin holes and
a “1” printed on the motherboard next to that corner . Because the CPU has a corner
pin for three of the four corners, the CPU will only fit in the one orientation as
shown. The picture is for reference only; you should have a CPU fan that will cover
the face of the CPU. With the added weight of the CPU fan, no force is required to
insert the CPU. Once completely inserted, hold down on the fan and close the socket’ s
lever.
IMPORT ANT: You must set jumpers for “CPU to BUS Frequency Ratio” and
jumpers for “BUS Frequency Selection” depending on the CPU that you install.
CAUTION! Be careful not to scrape the motherboard when mounting a clamp-
style processor fan or else damage may occur to the motherboard.
R
BlankLever Lock
1
SP98-N ZIF Socket 7 with Pentium MMX Processor
Notch
1
24 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 25

3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.7. Expansion Cards
WARNING! Make sure that you unplug your power supply when adding or
removing expansion cards or other system components. Failure to do so may
cause severe damage to both your motherboard and expansion cards.
First read your expansion card documentation on any hardware and software settings that may be required to setup your specific card.
3.7.1 Expansion Card Installation Procedure:
1. Read the documentation for your expansion card.
2. Set any necessary jumpers on your expansion card.
3. Remove your computer system’s cover.
4. Remove the bracket on the slot you intend to use. Keep the bracket for possible future use.
5. Carefully align the card’s connectors and press firmly.
6. Secure the card on the slot with the screw you removed in step 4.
7. Replace the computer system’s cover.
8. Setup the BIOS if necessary
(such as “IRQ xx Used By ISA: Yes” in PNP AND PCI SETUP)
9. Install the necessary software drivers for your expansion card.
3.7.2 Assigning IRQs for Expansion Cards
Some expansion cards need to use an IRQ to operate. Generally an IRQ must be
exclusively assigned to one use. In a standard design there are 16 IRQs available
but most of them are already in use by parts of the system which leaves 6 free for
expansion cards.
Both ISA and PCI expansion cards may need to use IRQs. System IRQs are available to cards installed in the ISA expansion bus first, and any remaining IRQs are
then used by PCI cards. Currently, there are two types of ISA cards.
3. H/W SETUP
Expansion Cards
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 25
Page 26

3. HARDWARE SETUP
The original ISA expansion card design, now referred to as “legacy” ISA cards,
requires that you configure the card’s jumpers manually and then install it in any
available slot on the ISA bus. You may use Microsoft’s Diagnostic (MSD.EXE)
utility included in the Windows directory to see a map of your used and free IRQs.
For Windows 95 users, the “Control Panel” icon in “My Computer,” contains a
“System” icon which gives you a “Device Manager” tab. Double clicking on a
specific device give you “Resources” tab which shows the Interrupt number and
address. Make sure that no two devices use the same IRQs or your computer will
experience problems when those two devices are in use at the same time.
T o simplify this process this motherboard has complied with the Plug and Play (PNP)
specification, which was developed to allow automatic system configuration whenever a PNP-compliant card is added to the system. For PNP cards, IRQs are assigned automatically from those available.
Expansion Cards
3. H/W SETUP
If the system has both legacy and PNP ISA cards installed, IRQs are
assigned to PNP cards from those not used by legacy cards. The PCI and PNP
configuration of the BIOS setup utility can be used to indicate which IRQs are being
used by legacy cards. For older legacy cards that does not work with the BIOS, you
can contact your vendor for an ISA Configuration Utility.
An IRQ number is automatically assigned to PCI expansion cards after those used
by legacy and PNP ISA cards. In the PCI bus design, the BIOS automatically assigns an IRQ to a PCI slot that has a card in it that requires an IRQ. To install a PCI
card, you need to set something called the INT (interrupt) assignment. Since all the
PCI slots on this motherboard use an INTA #, be sure that the jumpers on your PCI
cards are set to INT A.
3.7.3 Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards
Some ISA cards, both legacy and PnP, may also need to use a DMA (Direct Memory
Access) channel. DMA assignments for this motherboard are handled the same way
as the IRQ assignment process described earlier. You can select a DMA channel in
the PCI and PnP configuration section of the BIOS Setup utility.
IMPORTANT: To avoid conflicts, reserve the necessary IRQs and DMAs for legacy
ISA cards (under PNP AND PCI SETUP of the BIOS SOFTWARE, choose Yes in IRQ
xx Used By ISA and DMA x Used By ISA for those IRQs and DMAs you want to reserve).
3.7.4 ISA Cards and Hardware Monitor
The onboard hardware monitor uses the address 290H-297H so legacy ISA cards
must not use this address or else conflicts will occur.
26 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 27

3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.8 External Connectors
WARNING! Some pins are used for connectors or power sources. These are
clearly distinguished from jumpers in 3.1 Motherboard Layout. Placing jumper
caps over these connector pins will cause damage to your motherboard.
IMPORTANT: Ribbon cables should always be connected with the red stripe to
Pin 1 on the connectors. Pin 1 is usually on the side closest to the power connector on hard drives and CD-ROM drives, but may be on the opposite side on
floppy disk drives. Check the connectors before installation because there may
be exceptions. IDE ribbon cables must be less than 46 cm (18 in.), with the
second drive connector no more than 15 cm (6 in.) from the first connector.
3.8.1 Back Panel Connectors
1) Parallel Connector (25-pin PRINTER)
You can enable the parallel port and choose the IRQ through Onboard Parallel
Port (see 4.4.2 I/O Device Configuration). NOTE: Serial printers must be
connected to the serial port.
Parallel Port (25-pin female)
2) Serial Port Connectors (Two 9-pin COM1 and COM2)
The two serial ports can be used for pointing devices or other serial devices. See
Onboard Serial Port 1 and Onboard Serial Port 2 in 4.2.2 I/O Device Con-
figuration for settings.
Connectors
3. H/W SETUP
COM 2 COM 1
Serial Ports (9-pin male)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 27
Page 28
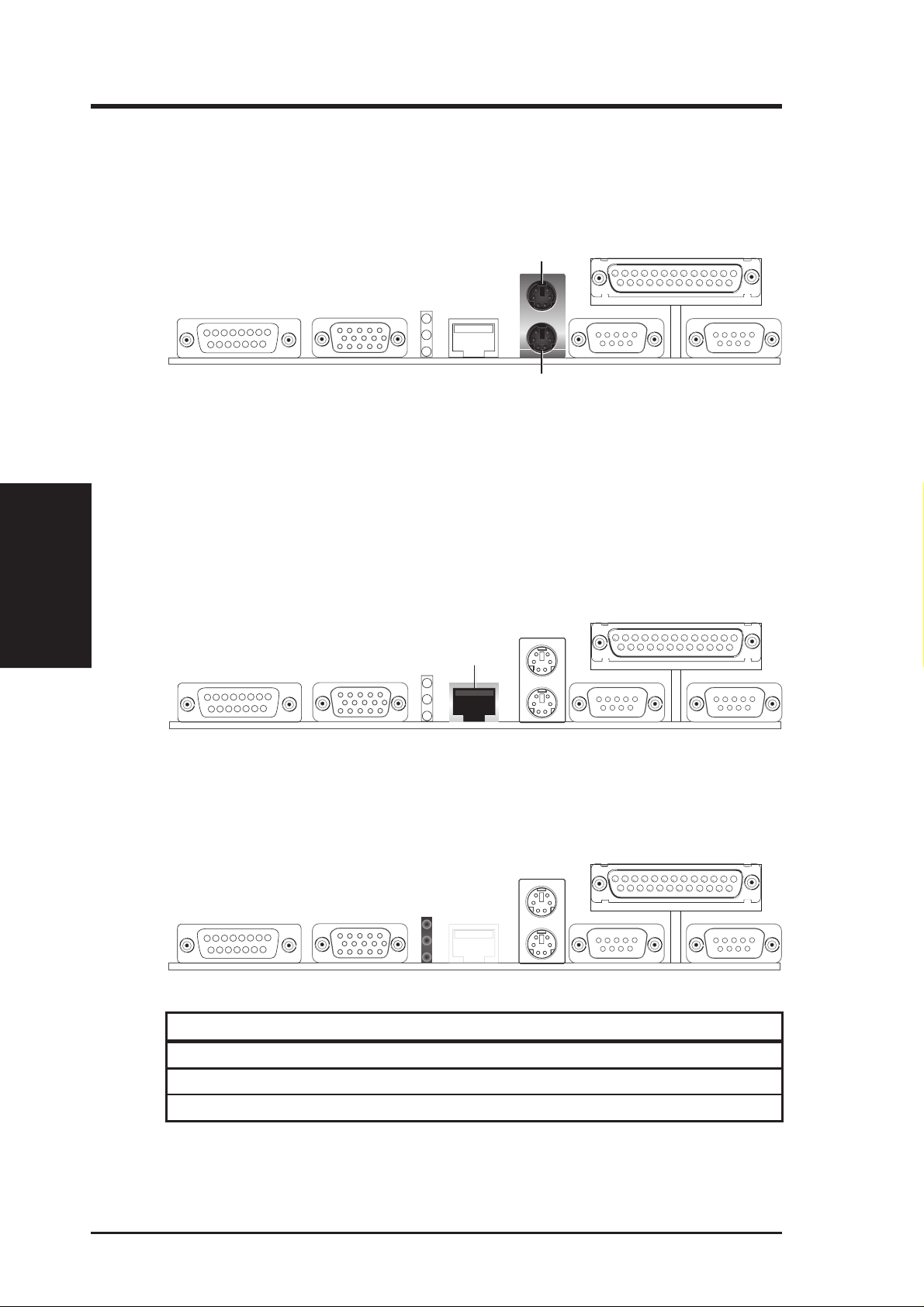
3. H/W SETUP
Connectors
3. HARDWARE SETUP
3) PS/2 Mouse Connector
The system will direct IRQ12 to the PS/2 mouse if one is detected. If not detected, expansion cards can use IRQ12. See PS/2 Mouse Function Control in
4.4 Advanced Menu.
PS/2 Mouse (6-pin female)
PS/2 Keyboard (6-pin female)
4) PS/2 Keyboard Connector (6-pin PS2KBMS)
This connector is for a standard keyboard using a PS/2 plug (mini DIN). This
connector will not allow standard AT size (large DIN) keyboard plugs. You
may use a DIN to mini DIN adapter on standard AT keyboards.
5) Fast-Ethernet Port Connector (RJ-45)
The RJ-45 connector is optional at the time of purchase. This connector allows the
motherboard to connect to a Local Area Network (LAN) through a network hub.
RJ-45
6) LAN Diagnostic LEDs (LAN_LED)
These diagnostic LEDs help indicate if there is a problem with the network
connector, cable, or hub.
1
Green
2
Yellow
3
Green
LED OFF LED ON
1 Speed 10Mbps 100Mbps
2 Activity No data Data transfer
3 Link Bad connection Good connection
28 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 29
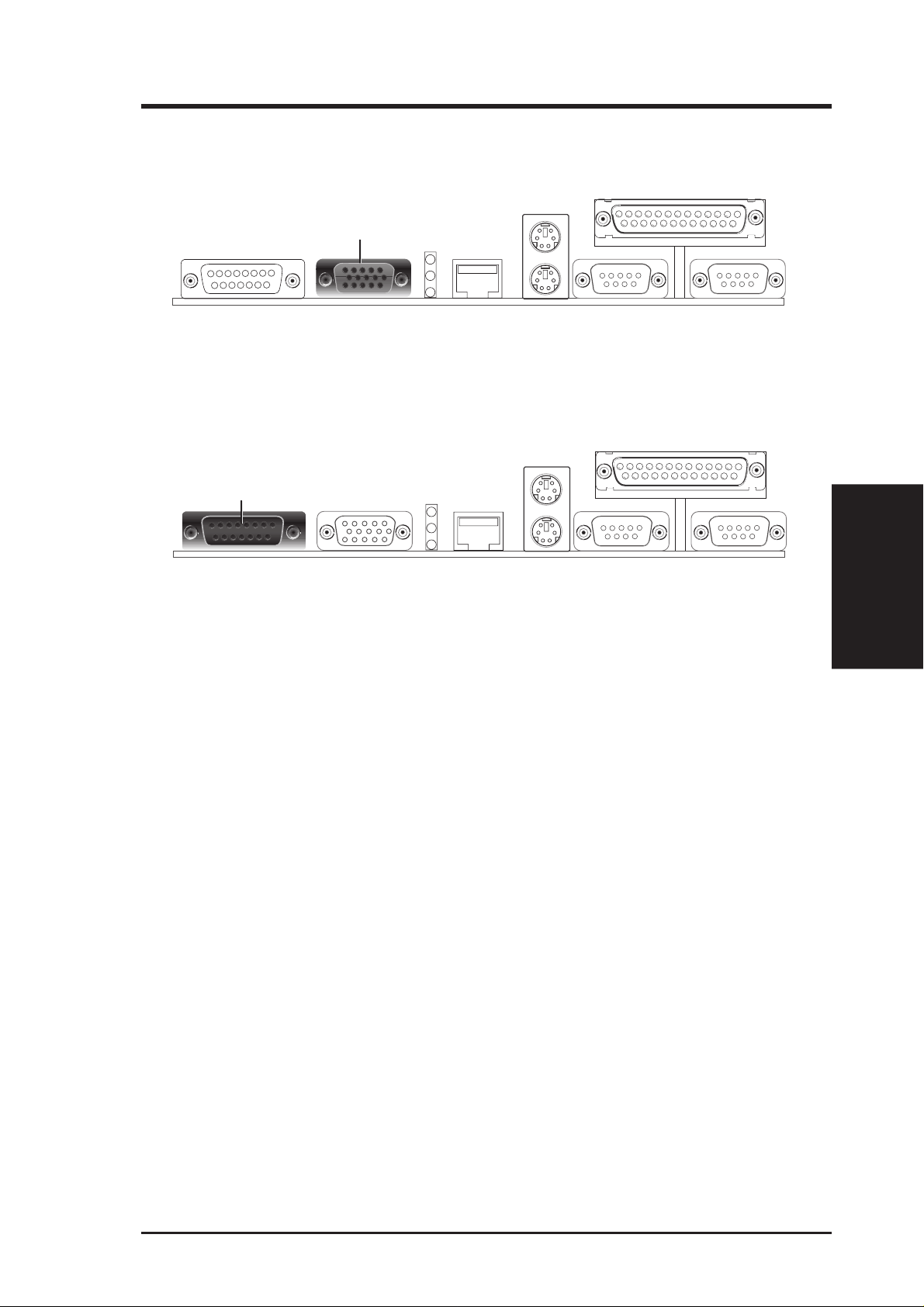
3. HARDWARE SETUP
7) Monitor Connector (15-pin VGA)
This connector is for output to a VGA-compatible device.
VGA Monitor (15-pin female)
8) Joystick/MIDI Connector (15-pin GAME)
You may connect game joysticks or game pades to this connector for playing
games. Connect MIDI devices for playing or editing professional audio.
Joystick/Midi (15-pin female)
Connectors
3. H/W SETUP
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 29
Page 30

3. H/W SETUP
Connectors
3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.8.2 Midboard Connectors
1) Chassis & CPU Fan Connectors (3-pin CHASIS_, CPU_FAN)
These connectors support cooling fans of 500mA (6 Watts) or less. Orientate the
fans so that the heat sink fins allow airflow to go across the onboard heat sink(s)
instead of the expansion slots. Depending on the fan manufacturer, the wiring
and plug may be different. The red wire should be positive, while the black
should be ground. Connect the fan’ s plug to the board taking into consideration
the polarity of the connector . NOTE: The “Rotation” signal is to be used only
by a specially designed fan with rotation signal.
WARNING! The CPU and/or motherboard will overheat if there is no airflow
across the CPU and onboard heatsinks. Damage may occur to the motherboard
and/or the CPU fan if these pins are incorrectly used. These are not jumpers,
do not place jumper caps over these pins.
CPU Fan Power
FANSTP#
+12 Volt
R
FSCPU#
SP98-N 12Volt Cooling Fan Power
2) CD-ROM Connector (50-1 pin CDROM)
This is a proprietary CD-ROM connector which requires a converter in order to
attach to a slim CD-ROM. Only a slim CD-ROM will fit into the NLX system
housing.
2
1
R
49
50
SP98-N CD-ROM Drive Connector
30 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 31

3. HARDWARE SETUP
3) Internal Speaker Connector (4-pin)
This connector is used to connect to an internal speaker.
1
AGND-A
AGND-A
PCSPKR-LFT
PCSPKR-RT
R
SP98-N Internal Speaker Connector
4) Audio Jack Connector (10-1 pin JACK_CON)
This header is provided for audio input and output signals.
Motherboard Audio Conn. Back Panel Audio Conn.
R
SP98-N Audio Jack Connector
2
1
A ribbon cable connects the Motherboard
Audio Conn. to the Back Panel Audio Conn.
10
9
Back Panel Audio Jacks
Speaker Out
Line Out
Connectors
3. H/W SETUP
Line In
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 31
Page 32

3. H/W SETUP
Connectors
3. HARDWARE SETUP
5) Video Feature Connector (26-pin FEATURE)
This connector is used for third party video accessories, such as video capture
cards or television tuners.
13
26
R
1
14
SP98-N Video Feature Connector
32 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 33

3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.8.3 Riser Card Connectors
1) LAN Activity Connectors
These connectors support Local Area Network (LAN) cards such as the ASUS
PCI-L101 (see 7.1 ASUS PCI-L101 Fast Ethernet Card) with output signals
for data transfer activity. The LAN_LED connector allows the front panel LED
to flash during transfer activity between the network and the computer. The
WOL_CON connector allows the system to power up when there is a wakeup
package (signal) received from the network.
IMPORTANT: This feature requires that W ake On LAN is set to Enabled (see
4.5.1 Power Up Control) and that your system has an NLX power supply with at
least 720mA +5V standby power.
®
YEONG-YANG
NLX-R
NLX-R (Front)
LAN_LED
(NLX-R only)
Yeong-Yang (Front)
+5 Volt Standby
Ground
+
NLX-R & Yeong-Yang Risers
PME
WOL_CON
LAN Activity Connectors
2) Front Panel Microphone Connector
This connector is used to connect the front panel microphone jack to the motherboard through a ribbon cable.
®
NLX-R
NLX-R (Front)
The front panel’s 1/8” microphone
jack connects to the riser card
through a ribbon cable
Connectors
3. H/W SETUP
Yeong-Yang (Front)
YEONG-YANG
Front Panel Microphone Jack
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 33
Page 34

3. H/W SETUP
Connectors
3. HARDWARE SETUP
3) NLX Power Supply Connector
This connector connects to an NLX power supply. The plug from the power supply will only insert in one orientation because of the different size holes. Find the
proper orientation and push down firmly making sure that the pins are aligned.
IMPORTANT: Make sure that the NLX power supply can deliver at least 720mA
on the 5volt standby lead (+5VSB). You may experience difficulty in powering
on your system if your power supply cannot support the load. For Wake-On-LAN
support, your NLX power supply must supply at least 720mA +5VSB.
NLX-R (Back)
+5.0 Volts
Yeong-Yang (Back)
NLX Power Connector
+5.0 Volts
-5.0 Volts
+12.0 Volts
Power Good
+5V Standby
Ground
Ground
Ground
+5.0 Volts
Ground
Ground
+3.3 Volts
Ground
-12.0 Volts
Power Supply On
Ground
+3.3 Volts
+3.3 Volts
+5.0 Volts
NLX Power Supply Connector
4) IDE Connectors
This connector supports the provided IDE hard disk drive ribbon cable. After
connecting one end to the riser card, connect the other end to a hard disk drive.
The primary IDE channel supports both a master and a slave IDE device but the
system housing size only permits a standard IDE hard drive to be installed.
NLX-R (Back)
Pin 1
Yeong-Yang (Front)
YEONG-YANG
IDE Connectors
Orient the red stripe on the
IDE ribbon cable to Pin 1
IMPORTANT: Ultra DMA/66 devices require a 40-pin 80-conductor cable to
be enabled and/or for Ultra DMA Mode 4.
34 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 35

3. HARDWARE SETUP
5) 3.5” Floppy Disk Drive Connector
This connector supports the provided floppy drive ribbon cable. After connecting the single end to the riser card, connect the other end to a 3.5” floppy disk
drive. (Pin 5 is r emoved to pr event inserting in the wr ong orientation when
using ribbon cables with pin 5 plugged).
®
YEONG-YANG
NLX-R
NLX-R (Front)
Yeong-Yang (Front)
NLX-R Riser
Orient the red stripe on the
floppy ribbon cable to Pin 1
Yeong-Yang Risers
Pin 1
Pin 1
Floppy Disk Drive Connector
6) Universal Serial Bus (USB) Ports / USB Module Connector
If you have the NLX-R or B9-N risers, two Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports
are available for connecting USB devices. If you have the Yeong-Y ang riser , a 5pin block is available for connecting an external connector set. This connector
set can be mounted to an open slot on your computer’s chassis. USB Function
must be set to Enabled and USB IRQ to Auto in 4.4.3 PCI Configuration to
use USB features.
Connectors
3. H/W SETUP
NLX-R Riser
NLX-R (Back)
Yeong-Yang (Front)
YEONG-YANG
Port 1 Port 2
The USB ports show
through the front
panel
Yeong-Yang Riser
15
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Ports / USB Module Connector
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 35
1: USB +5 Volt
2: (no connection)
3: USB Port 0+
4: USB Port 05: USB +5Volt
Page 36

3. HARDWARE SETUP
7) IrDA-Compliant Infrared Module / Infrared Module Connectors
The NLX-R riser includes an onboard infrared module for wireless transmitting
and receiving of data through the front panel infrared lense. 0The B9-N and
Yeong-Yang risers include an infrared module connector that supports an optional wireless transmitting and receiving infrared module. This module mounts
to a small opening on system cases that support this feature. You must also configure the setting through UART2 Use Infrar ed (see 4.4.2 I/O Device Configu-
ration) to select whether UART2 is directed for use with COM2 or IrDA. Use
the five pins as shown in Back View and connect an appropriate ribbon cable
from the module to the motherboard’ s IR connector according to the pin definitions. An optional consumer infrared (CIR) set connects to the CIR and IR connectors simultaneously for both wireless transmitting and remote control functions through one external infrared module.
3. H/W SETUP
Connectors
NLX-R (Back)
Yeong-Yang (Front)
YEONG-YANG
The infrared module sends
data through the front panel’s
infrared window
+5VNCIRRX
1
Infrared Module / Infrared Module Connector
GND
IRTX
Standard Infrared (SIR)
Front View
5
Back View
IRTX
GND
IRRX
+5V
(NC)
36 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 37

3. HARDWARE SETUP
8) Stereo Audio In Connector
This connector lets you receive stereo audio input from an internal CD-ROM
drive or other sound sources, such as a TV tuner or MPEG card.
CD_IN
Yeong-Yang (Front)
YEONG-YANG
Yeong-Yang Riser
Left Audio Channel
Ground
Ground
Right Audio Channel
Stereo Audio In Connector
9) Front Panel Connector
This connector is used to connect the front panel display LEDs and buttons to
the motherboard through a ribbon cable.
The front panel display &
®
YEONG-YANG
NLX-R
NLX-R (Front)
FCON
Yeong-Yang (Front)
buttons connect to the
riser card through a ribbon
cable.
Pin 1
Power LED
+
1
HDD LED
---
+++
-
Reset Switch
Power Switch
+
1
Speaker Connector
Connectors
3. H/W SETUP
Front Panel Display and Button Connector
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 37
Page 38

(This page was intentionally left blank.)
38 ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual
Page 39

3. HARDWARE SETUP
3.9 Power Connection Procedures
1. After all connections are made, close the system case cover.
2. Be sure that all switches are off (in some systems, marked with
3. Connect the power supply cord to the power supply located on the back of
your system case according to your system user’s manual.
4. Connect the power cord to a power outlet that is equipped with a surge protector.
5. You may then turn on your devices in the following order:
a. Your monitor
b. External SCSI devices (starting with the last device on the chain)
c. Your system power
For ATX power supplies, you need to switch ON the power supply if a
switch is provided as well as press the ATX power switch on the front of
the case.
6. The power LED on the front panel of the system case will light. For ATX
power supplies, the system LED will light when the ATX power switch is
pressed. The LED on the monitor may light up or switch between orange and
green after the system’s if it complies with “green” standards or if it has a
power standby feature. The system will then run power-on tests. While the
tests are running, additional messages will appear on the screen. If you do not
see anything within 30 seconds from the time you turn on the power, the system may have failed a power-on test. Check your jumper settings and connections again or call your retailer for assistance.
).
3. H/W SETUP
Power Connections
7. During power-on, hold down <Delete> to enter BIOS setup. Follow the instructions in 4. BIOS SETUP.
* Powering Off your computer: You must first exit or shut down your operat-
ing system before switching off the power switch. For ATX power supplies,
you can press the ATX power switch after exiting or shutting down your operating system. If you use Windows 95/98, click the Start button, click Shut
Down, and then click Shut down the computer?. The power supply should
turn off after Windows shuts down.
NOTE: The message “You can now safely turn off your computer” will not appear
when shutting down with ATX power supplies.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 39
Page 40

4. BIOS SETUP
4.1 Managing and Updating Your BIOS
4.1.1 Upon First Use of the Computer System
It is recommended that you save a copy of the original motherboard BIOS along
with a Flash Memory Writer utility (AFLASH.EXE) to a bootable floppy disk in
case you need to reinstall the BIOS later . AFLASH.EXE is a Flash Memory Writer
utility that updates the BIOS by uploading a new BIOS file to the programmable
flash ROM on the motherboard. This file works only in DOS mode. To determine
the BIOS version of your motherboard, check the last four numbers of the code
displayed on the upper left-hand corner of your screen during bootup. Larger numbers represent a newer BIOS file.
1. Type FORMAT A:/S at the DOS prompt to create a bootable system floppy
disk. DO NOT copy AUTOEXEC.BAT & CONFIG.SYS to the disk.
2. Type COPY D:\AFLASH\AFLASH.EXE A:\ (assuming D is your CD-ROM
drive) to copy AFLASH.EXE to the just created boot disk.
3. Reboot your computer from the floppy disk. NOTE: BIOS setup must specify
Flash Memory Writer
4. BIOS SETUP
4. In DOS mode, type A:\AFLASH <Enter> to run AFLASH.
NOTE: AFLASH works only in DOS mode. It will not work with DOS prompt
in Windows and will not work with certain memory drivers that may be loaded
when you boot from your hard drive. It it recommended that you reboot using a
floppy .
“Floppy” as the first item in the boot sequence.
IMPORTANT: If “unknown” is displayed after Flash Memory:, the memory chip is
either not programmable or is not supported by the ACPI BIOS and therefore, cannot be
programmed by the Flash Memory Writer utility.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual40
Page 41

4. BIOS SETUP
5. Select 1. Save Current BIOS to File from the Main menu and press <Enter>.
The Save Current BIOS To File screen appears.
6. Type a filename and the path, for example, A:\XXX-XX.XXX and then press
<Enter>.
4.1.2 Updating BIOS Procedures (only when necessary)
1. Download an updated ASUS BIOS file from the Internet (WWW or FTP) (see
ASUS CONTACT INFORMATION on page 3 for details) and save to the disk
you created earlier.
2. Boot from the disk you created earlier.
3. At the “A:\” prompt, type AFLASH and then press <Enter>.
4. At the Main Menu, type 2 and then press <Enter>. The Update BIOS Includ-
ing Boot Block and ESCD screen appears.
5. Type the filename of your new BIOS and the path, for example, A:\XXX-
XX.XXX, and then press <Enter>.
NOTE: To cancel this operation, press <Enter>.
4. BIOS SETUP
Flash Memory Writer
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 41
Page 42

4. BIOS SETUP
6. When prompted to confirm the BIOS update, press Y to start the update.
7. The utility starts to program the new BIOS information into the flash ROM. The
boot block will be updated automatically only when necessary. This will minimize the chance of a failed updating. When the programming is finished, Flashed
Successfully will be displayed.
4. BIOS SETUP
Updating BIOS
8. Follow the onscreen instructions to continue.
WARNING! If you encounter problems while updating the new BIOS, DO NOT
turn off your system since this might prevent your system from booting up. Just
repeat the process, and if the problem still persists, update the original BIOS file
you saved to disk above. If the Flash Memory Writer utility was not able to
successfully update a complete BIOS file, your system may not be able to boot
up. If this happens, your system will need servicing.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual42
Page 43

4. BIOS SETUP
4.2 BIOS Setup
The motherboard supports two programmable Flash ROM chips: 5 volts and 12
volts. Either of these memory chips can be updated when BIOS upgrades are released. Use the Flash Memory W riter utility to download the new BIOS file into the
ROM chip as described in detail in this section.
All computer motherboards provide a Setup utility program for specifying the system configuration and settings. If your motherboard came in a computer system, the
proper configuration entries may have already been made. If so, run the Setup utility, as described later, and take note of the configuration settings for future reference, in particular, the hard disk specifications.
If you are installing the motherboard, reconfiguring your system or you receive a
Run Setup message, you will need to enter new setup information. This section
describes how to configure your system using this utility.
The BIOS ROM of the system stores the Setup utility. When you turn on the computer, the system provides you with the opportunity to run this program. This appears during the Power-On Self Test (POST). Press <Delete> to call up the Setup
utility. If you are a little bit late pressing <Delete>, POST will continue with its test
routines, thus preventing you from calling up Setup. If you still need to call Setup,
reset the system by pressing <Ctrl> + <Alt> + <Delete>, or by pressing the Reset
button on the system case. You can also restart by turning the system off and then
back on again. Do this only, however, if the first two methods fail.
When you run Setup, the CMOS SETUP UTILITY main program screen will appear with the following options:
NOTE: Because the BIOS software is constantly being updated, the BIOS screens
and descriptions are for reference purposes only and may not exactly reflect
your BIOS screens.
BIOS Setup
4. BIOS SETUP
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 43
Page 44

4. BIOS SETUP
4.2.1 Load Defaults
Load BIOS Defaults loads the minimum settings for troubleshooting. Load Setup
Defaults, on the other hand, is for loading optimized defaults for regular use. Choos-
ing defaults at this level, will modify all applicable settings.
A section at the bottom of the above screen displays the control keys for this screen.
Take note of these keys and their respective uses. Another section just below the
control keys section displays information on the currently highlighted item in the list.
4.3 Standard CMOS Setup
Standard CMOS Setup allows you to record some basic system hardware configuration and set the system clock and error handling. If the motherboard is already
installed in a working system, you will not need to select this option anymore. However, if the configuration stored in the CMOS memory on the board gets lost or
damaged, or if you change your system hardware configuration, you will need to
respecify the configuration values. The configuration values usually get lost or
corrupted when the power of the onboard CMOS battery weakens.
4. BIOS SETUP
Standard CMOS
The preceding screen provides you with a list of options. At the bottom of this screen
are the control keys for this screen. Take note of these keys and their respective uses.
User-configurable fields appear in a different color. If you need information on the
selected field, press <F1>. The help menu will then appear to provide you with the
information you need. The memory display at the lower right-hand side of the screen
is read-only and automatically adjusts accordingly.
4.3.1 Details of Standard CMOS Setup
Date
T o set the date, highlight the “Date” field and then press either <Page Up>/<Page Down>
or <+>/<–> to set the current date. Follow the month, day and year format. Valid values
for month, day and year are: Month: (1 to 12), Day: (1 to 31), Year: (up to 2079)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual44
Page 45

4. BIOS SETUP
Time
T o set the time, highlight the “Time” field and then press either <Page Up>/<Page Down>
or <+>/<–> to set the current time. Follow the hour, minute and second format. Valid
values for hour, minute and second are: (Hour: (00 to 23), Minute: (00 to 59), Second:
(00 to 59).
NOTE: You can bypass the date and time prompts by creating an AUTOEXEC.BAT
file. For information on how to create this file, please refer to the MS-DOS manual.
Hard Disks
This field records the specifications for all non-SCSI hard disk drives installed in
your system. The onboard PCI IDE connectors provide Primary and Secondary channels for connecting up to four IDE hard disks or other IDE devices. Each channel
can support up to two hard disks; the first of which is the “master” and the second is
the “slave”.
Specifications for SCSI hard disks need not to be entered here since they operate
using device drivers and are not supported by the BIOS. If you install other SCSI
controller cards, refer to their respective documentations on how to install the required SCSI drivers.
For IDE hard disk drive setup, you can:
• Use the Auto setting for detection during bootup.
• Use the IDE HDD AUTO DETECTION in the main menu to automatically
enter the drive specifications.
• Enter the specifications yourself manually by using the “User” option.
The entries for specifying the hard disk type include CYLS (number of cylinders),
HEAD (number of read/write heads), PRECOMP (write precompensation), LANDZ
(landing zone), SECTOR (number of sectors) and MODE. The SIZE field automatically adjusts according to the configuration you specify. The documentation
that comes with your hard disk should provide you with the information regarding
the drive specifications.
The MODE entry is for IDE hard disks only , and can be ignored for MFM and ESDI
drives. This entry provides three options: Normal, Large, LBA, or Auto (see be-
low). Set MODE to the Normal for IDE hard disk drives smaller than 528MB; set
it to LBA for drives over 528MB that support Logical Block Addressing (LBA) to
allow larger IDE hard disks; set it to Large for drives over 528MB that do not sup-
port LBA. Large type of drive can only be used with MS-DOS and is very uncommon. Most IDE drives over 528MB support the LBA mode.
Standard CMOS
4. BIOS SETUP
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 45
Page 46

4. BIOS SETUP
Auto detection of hard disks on bootup
For each field: Primary Master, Primary Slave, Secondary Master, and Secondary
Slave, you can select Auto under the TYPE and MODE fields. This will enable auto
detection of your IDE hard disk during bootup. This will allow you to change your
hard disks (with the power off) and then power on without having to reconfigure
your hard disk type. If you use older hard disks that do not support this feature, then
you must configure the hard disk in the standard method as described earlier by the
“User” option.
NOTE: After the IDE hard disk drive information has been entered into BIOS, new
IDE hard disk drives must be partitioned (such as with FDISK) and then formatted
before data can be read from and write on. Primary IDE hard disk drives must have
its partition set to active (also possible with FDISK).
NOTE: SETUP Defaults are noted in parenthesis next to each function heading.
Drive A / Drive B (None)
These fields record the types of floppy disk drives installed in your system. The
available options for drives A and B are: 360K, 5.25 in.; 1.2M, 5.25 in.; 720K, 3.5
in.; 1.44M, 3.5 in.; 2.88M, 3.5 in.; None
4. BIOS SETUP
Standard CMOS
To enter the configuration value for a particular drive, highlight its corresponding
field and then select the drive type using the <page up>/<page down> or <+>/<->
keys.
Floppy 3 Mode Support (Disabled)
This is the Japanese standard floppy drive. The standard stores 1.2MB in a 3.5inch
diskette. This is normally disabled but you may choose from either: Drive A, Drive
B, Both, and Disabled
Video (EGA/VGA)
Set this field to the type of video display card installed in your system. The options
are EGA/VGA, CGA 40, CGA 80, and MONO (for Hercules or MDA).
If you are using a VGA or any higher resolution card, choose EGA/VGA.
Halt On (All Errors)
This field determines which types of errors will cause the system to halt. Choose from
All Errors; No Errors; All,But Keyboard, All,But Diskette; and All,But Disk/Key.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual46
Page 47

4. BIOS SETUP
4.4 BIOS Features Setup
BIOS Features Setup consists of configuration entries that allow you to improve
your system performance, or let you set up some system features according to your
preference. Some entries are required by the motherboard’ s design to remain in their
default settings.
NOTE: SETUP Defaults are noted in parenthesis next to each function heading.
4.4.1 Details of BIOS Features Setup
Boot Virus Detection (Enabled)
This field allows you to set boot virus detection, ensuring a virus-free boot sector.
This new antivirus solution is unlike native BIOS tools, which offer limited virus
protection typically by write-protecting the partition table. With this new solution,
your computer is protected against boot virus threats earlier in the boot cycle, that is,
before they have a chance to load into your system. This ensures your computer
boots to a clean operating system. The system halts and displays a warning message
when it detects a virus. If this occurs, you can either allow the operation to continue
or use a virus-free bootable floppy disk to restart and investigate your system. Because of conflicts with new operating systems, for example, during installation of
new software, you may have to set this to Disabled to prevent write errors.
CPU Internal Cache (Enabled)
Choose Disable to turn off the CPU’s built-in level 1 cache.
External Cache (Enabled)
Choose Disable to turn off the CPU’s external level 2 cache.
BIOS Features
4. BIOS SETUP
Quick Power On Self Test (Enabled)
This field speeds up the Power-On Self Test (POST) routine by skipping retesting a
second, third, and fourth time. A complete test of the system is done on each test.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 47
Page 48

4. BIOS SETUP
HDD Sequence SCSI/IDE First (IDE)
When using both SCSI and IDE hard disk drives, IDE is always the boot disk using
drive letter C (default setting of IDE). This field allows a SCSI hard disk drive to be
the boot disk when set to SCSI. This allows multiple operating systems to be used on
both IDE and SCSI drives or the primary operating system to boot using a SCSI drive
Boot Sequence (A,C)
This field determines where the system looks first for an operating system. Options
are A,C; C,A; A,CDROM,C; CDROM,C,A; D,A; E,A; F,A; C only; LS/ZIP, C; LAN,A,C;
and LAN,C,A. The setup default setting, A, C, is to check first the floppy disk and then
the hard disk drive.
Boot Up Floppy Seek (Disabled)
When enabled, the BIOS will seek drive A one time.
Floppy Disk Access Control (R/W)
This allows protection of files from the computer system to be copied to floppy disk
drives by allowing the setting of Read Only to only allow reads from the floppy disk
drive but not writes. The setup default R/W allows both reads and writes.
IDE HDD Block Mode Sectors (HDD MAX)
This field enhances hard disk performance by making multi-sector transfers instead
of one sector per transfer. Most IDE drives, except older versions, can utilize this
feature. Selections are HDD MAX, Disabled, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32.
HDD S.M.A.R.T. capability (Disabled)
4. BIOS SETUP
BIOS Features
This allows the enabling or disabling of the S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis
and Reporting Technology) system which utilizes internal hard disk drive monitoring technology. This feature is normally disabled because system resources used in
this feature may decrease system performance.
PS/2 Mouse Function Control (Auto)
Auto allows the BIOS to detect the PS/2 mouse on bootup. If detected, IRQ12 will
be used for the PS/2 Mouse. If not detected, IRQ12 will be reserved for expansion
cards. Enabled will always reserve IRQ12 for devices on the PS/2 mouse port.
OS/2 Onboard Memory > 64M (Disabled)
When using OS/2 operating systems with installed DRAM of greater than 64MB,
you need to Enable this option otherwise leave this on the setup default of Disabled.
......................................................................................................................................
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop (Disabled)
Some display cards that are nonstandard VGA such as graphics accelerators or MPEG
V ideo Cards may not show colors properly. The setting Enabled should correct this
problem. Otherwise leave this on the setup default setting of Disabled.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual48
Page 49

4. BIOS SETUP
Video ROM BIOS Shadow (Enabled)
This field allows you to change the video BIOS location from ROM to RAM. Relocating to RAM enhances system performance, as information access is faster than the ROM.
C8000-CBFFF to DC000-DFFFF (Disabled)
These fields are used for shadowing other expansion card ROMs. If you install other
expansion cards with ROMs on them, you will need to know which addresses the
ROMs use to shadow them specifically. Shadowing a ROM reduces the memory
available between 640KB and 1024KB by the amount used for this purpose.
Boot Up NumLock Status (On)
This field enables users to activate the Number Lock function upon system boot.
Typematic Rate Setting (Disabled)
When enabled, you can set the two typematic controls listed next.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) (6)
This field controls the speed at which the system registers repeated keystrokes. Options range from 6 to 30 characters per second. Setup default setting is 6; other
settings are 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 24, and 30.
Typematic Delay (Msec) (250)
This field sets the time interval for displaying the first and second characters. Four
delay rate options are available: 250, 500, 750, and 1000.
Security Option (System)
This field determines when the system prompts for the password. The default setting is System, where the system prompts for the User Password every time you boot
up. The other option is Setup, where the system always boots up, and prompts for
the Supervisor Password only when the Setup utility is called up. You can specify a
password by using the Supervisor Password or User Passwor d option from the main
screen as explained later in this section..
BIOS Features
4. BIOS SETUP
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 49
Page 50

4. BIOS SETUP
4.5 Chipset Features Setup
Chipset Features Setup controls the configuration of the board’s chipset. Control
keys for this screen are the same as for the previous screen.
NOTE: SETUP Defaults are noted in parenthesis next to each function heading.
4.5.1 Details of Chipset Features Setup
EDO/FPM Configuration (60ns DRAM)
The default setting of 60ns DRAM automatically sets the optimal timings for items 2–
Chipset Features
4. BIOS SETUP
7 for 60ns DRAM modules. If you are using 70ns DRAM modules, change this item
to 70ns DRAM. See 3.5 System Memory (DIMM) for memory installation informa-
tion. Disabled allows you to configure RAS Precharge Time, RAS to CAS Delay,
CAS Precharge Time, CAS Pulse Width (Read and Write), and Refresh RAS Assertion. For DRAM Read Leadoff Time, leave this item on its default setting of 5T.
SDRAM Configuration (12ns SDRAM): Leave on default setting.
SDRAM Read Leadoff Time (Normal): Leave on default setting.
CPU to PCI Posted Write (Enabled)
This is a mechanism that, when Enabled, improves the performance of CPU to PCI
memory write and CPU to Idle data port write.
ROM Cycle Wait States (1-Wait): T iming for 16-bit ISA cards. Leave on default.
16-bit I/O Recovery Time (5 BUSCLK): Timing for 16-bit ISA cards. Leave on default.
8-bit I/O Recovery Time (8 BUSCLK): T iming for 8-bit ISA cards. Leave on default.
ISA Bus Clock (PCICLK/4): Timing for the ISA bus clock. Leave on default.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual50
Page 51

4. BIOS SETUP
Memory Hole at Address (None)
This feature reserves memory address space, 15M-16M, 14M-16M, or 12M-16M, to
ISA expansion cards that specifically require this setting. This, however, makes the
memory from the specified and up unavailable to the system because expansion
cards can only access memory up to 16MB.
Refresh Cycle Time (187.2 us)
This function sets the DRAM refresh rate. A slow refresh cycle time increases the
bandwidth available for data transfers. NOTE: Some DRAMs are known to lose
data without frequent refreshing so the default is set at 187.2 us.
Delayed Transaction (Enabled)
The default setting of Enabled frees the PCI Bus during CPU accessing of 8-bit ISA
cards, which normally consume about 50–60 PCI clocks without PCI delayed transaction. For PCI bus masters that cannot use the PCI Bus and some ISA cards that are
not PCI 2.1 compliant, set this to Disabled.
Onboard VGA Memory Size (1MB)
This function allows the user to allocate either 1MB, 2MB or 4MB memory for the
onboard video controler . Larger memory allows more colors and a higher resoultion
to be selected within each operating system.
Onboard VGA Memory Clock (Leave on default setting of Fast)
This function allows the selection of the video speed. Normal uses 50MHz, Fast
uses 60MHz, and Fastest uses 66MHz. If your monitor displays unrecognizable information, you must decrease the speed to match your monitor’s frequency rate.
....................................................................................................................................
Onboard FDC Controller (Enabled)
When enabled, this field allows you to connect your floppy disk drives to the onboard floppy drive connector instead of a separate controller card. If you want to use
a different controller card, set this field to Disabled.
Onboard FDC Swap A & B (No Swap)
This field allows you to reverse the hardware drive letter assignments of your floppy
disk drives. T wo options are available: No Swap and Swap AB . If you want to switch
drive letter assignments through the onboard chipset, set this field to Swap AB.
Onboard Serial Port 1 (3F8H/IRQ4)
Settings are 3F8H/IRQ4, 2F8H/IRQ3, 3E8H/IRQ4, 2E8H/IRQ10, and Disabled for
the onboard serial connector.
Onboard Serial Port 2 (2F8H/IRQ3)
Settings are 3F8H/IRQ4, 2F8H/IRQ3, 3E8H/IRQ4, 2E8H/IRQ10, and Disabled for
the onboard serial connector.
4. BIOS SETUP
Chipset Features
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 51
Page 52

4. BIOS SETUP
Onboard Parallel Port (378H/IRQ7)
This field sets the address of the onboard parallel port connector . You can select either
3BCH / IRQ 7, 378H / IRQ 7, 278H / IRQ 5, or Disabled. If you install an I/O card with
a parallel port, ensure that there is no conflict in the address assignments. The PC can
support up to three parallel ports as long as there are no conflicts for each port.
Parallel Port Mode (ECP+EPP)
This field allows you to set the operation mode of the parallel port. The setting
Normal, allows normal-speed operation but in one direction only; EPP allows bidi-
rectional parallel port operation at maximum speed; ECP allows the parallel port to
operate in bidirectional mode and at a speed faster than the maximum data transfer
rate; ECP+EPP allows normal speed operation in a two-way mode.
ECP DMA Select (3)
This selection is available only if you select ECP or ECP+EPP in the
Parallel Port Mode. Select either DMA Channel 1, 3, or Disabled.
4. BIOS SETUP
Chipset Features
Chipset Features
4. BIOS SETUP
UART2 Use Infrared (Disabled)
When Enabled, this field activates the onboard infrared feature and sets the second
serial UART to support the infrared module connector on the motherboard using the
IrDA standard. Select ASKIR to enable the Japanese infrared standard. If your system
already has a second serial port connected to the onboard COM2 connector, it will no
longer work if you enable the infrared feature. By default, this field is set to Disabled,
which leaves the second serial port UAR T to support the COM2 serial port connector .
Onboard PCI IDE Enable (Both)
Y ou can select to enable the Primary IDE channel, Secondary IDE channel, Both, or
Disable both channels (for systems with only SCSI drives).
IDE Ultra DMA Mode (Auto)
This sets the IDE UltraDMA to be active when using UltraDMA-capable IDE devices. The BIOS will automatically adjust or disable this setting for slower IDE
devices so that Auto or high settings will not cause problems for older IDE devices.
Choose Disable if you do not want this feature for all devices.
IDE 0 Master/Slave PIO/DMA Mode, IDE 1 Master/Slave PIO/DMA Mode (Auto)
Each channel (0 & 1) has both a master and a slave making four IDE devices possible.
Because each IDE device may have a different Mode timing (0, 1, 2, 3, 4), it is necessary for these to be independent. PIO and DMA timings can be independently set. The
default setting of Auto will allow autodetection to ensure optimal performance.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual52
Page 53

4. BIOS SETUP
4.6 Power Management Setup
Power Management Setup allows you to reduce power consumption. This feature
turns off the video display and shuts down the hard disk after a period of inactivity.
NOTE: SETUP Defaults are noted in parenthesis next to each function heading.
4.6.1 Details of Power Management Setup
Power Management (User Define)
This field acts as the master control for the power management modes. User Define
allows you to set power saving options according to your preference; Disable disables the power saving features; Min Saving puts the system into power saving mode
after 40 min of system inactivity; Max Saving puts the system into power saving
mode after 30 sec of system inactivity.
IMPORTANT: Advanced Power Management (APM) should be installed to keep
the system time updated when the computer enters suspend mode activated by the
BIOS Power Management. For DOS environments, you need to add the statement,
DEVICE=C:\DOS\POWER.EXE, in your CONFIG.SYS. For Windows 3.x and
Windows 95, you need to install Windows with the APM feature. A battery and
power cord icon labeled “Power Management” will appear in the “Control Panel.”
Choose “Advanced” in the Power Management Field.
Video Off Option (Susp,Stby -> Off )
This field determines when to activate the video off feature for monitor power
management. The settings are All Modes -> Off; Always On; Suspend -> Off; and
Susp,Stby -> Off .
4. BIOS SETUP
Power Management
Video Off Method (DPMS OFF)
This field defines the video off features. The following options are available: DPMS
OFF, DPMS Reduce ON , Blank Screen, V/H SYNC+Blank, DPMS Standby, and
DPMS Suspend. The DPMS (Display Power Management System) features allow
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 53
Page 54

4. BIOS SETUP
the BIOS to control the video display card if it supports the DPMS feature. Blank
Screen only blanks the screen (use this for monitors without power management or
“green” features. If set up in your system, your screen saver will not display with
Blank Screen selected). V/H SYNC+Blank blanks the screen and turns off vertical
and horizontal scanning.
......................................................................................................................................
PM Timers
This section controls the time-out settings. The fields included in this section are
HDD Power Down, which places the hard disk into its lowest power consumption
mode, and the Doze, Standby and Suspend system inactivation modes. The system
automatically “wakes up” from any power saving mode when there is system activity, such as when a key is pressed from the keyboard, or when there is activity
detected from the enabled IRQ channels.
HDD Power Down (Disable)
This shuts down any IDE hard disk drives in the system after a period of inactivity , configurable
to 1 Min-10 Min, 20 Min or Disable. This feature does not affect SCSI hard disks.
Doze Mode, Standby Mode, Suspend Mode (Disable)
These fields set the period of time after which each of these modes activate: 20 Sec,
1 Min, 5 Min, 10 Min, 15 Min, 20 Min, 30 Min, 40 Min, and Disable.
.......................................................................................................................................
Power Up Control
This section determines the ways the system can be controlled when modem activity is detected, or when power to the computer is interrupted and reapplied.
Power Management
4. BIOS SETUP
Ring Power Up Act (Enable)
Allows either settings of Enable or Disable for powering up the computer (turns the
ATX power supply on) when the modem begins receiving or transmitting data while
the computer is off.
Wake On LAN (Disabled)
This allows you to remotely power up your system through your network by sending a wake-up frame or signal. W ith this feature, you can remotely upload/download
data to/from systems during off-peak hours. Enabled sets this feature.
IMPORTANT: This feature requires the optional network interface (see 7. Network
Interface) and an ATX power supply with at least 720mA +5V standby power.
Automatic Power Up (Disable)
This field allows you to have an unattended or automatic power up of your system.
You may configure your system to power up at a certain time of the day by selecting
Enable, which will allow you to set the days (SUN–SAT) and time (hh:mm:ss) when
you want this function to activate.
.....................................................................................................................................
IRQ3 (device)-IRQ15 (device)
You can individually Enable or Disable each IRQ to include in the sleep function.
IRQ8 (RTC Alarm) is usually set to Disable so that any software alarm clock or
event calendar can wake up the system.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual54
Page 55

4. BIOS SETUP
4.7 PNP and PCI Setup
PNP and PCI Setup configures the PCI bus slots. All PCI bus slots on the system
use INTA#, thus all installed PCI cards must be set to this value.
NOTE: SETUP Defaults are noted in parenthesis next to each function heading.
4.7.1 Details of PNP and PCI Setup
PNP OS Installed (No)
When Plug and Play operating systems (OS) are installed, interrupts may be reassigned by the OS when Yes is selected. When a non-Plug and Play OS is installed or
to prevent reassigning of interrupt settings, select No.
Slot 1 IRQ/Slot 2 IRQ/Slot 3 IRQ/Slot 4 IRQ (Auto)
These fields set how IRQ use is determined for each PCI slot on the riser card. The
default setting for each field is Auto, which uses autorouting to determine IRQ use.
The other options are the manual settings of NA, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, or 15 for
each slot.
PCI Latency Timer (32 PCI Clock)
The default setting enables maximum PCI performance for this motherboard.
IRQ xx Used By ISA (No/ICU)
These fields indicate whether or not the displayed IRQ for each field is being used by
a legacy (non-PnP) ISA card. Two options are available: No/ICU and Yes. No/ICU
indicates either that the displayed IRQ is not used or an ISA Configuration Utility
(ICU) is being used to determine if an ISA card is using that IRQ. If you install a
legacy (non-PnP) ISA card that requires a unique IRQ, and you are not using an ICU,
set the field for that IRQ to Yes.
......................................................................................................................................
Power Management
PnP and PCI
4. BIOS SETUP
DMA x Used By ISA (No/ICU)
These fields indicate whether or not the displayed DMA channel for each field is
being used by a legacy ISA card. Available options include: No/ICU and Yes. No/
ICU indicates either that the displayed DMA channel is not used or an ICU is being
used to determine if an ISA card is using that channel. If you install a legacy ISA
card that requires a unique DMA channel, and you are not using an ICU, you must
set the field for that channel to Yes.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 55
Page 56

4. BIOS SETUP
ISA MEM Block BASE (No/ICU)
This field allows you to set the base address and block size of a legacy ISA card that
uses any memory segment within the C800, CC00, D000, D400, D800, and DC00
address range. If you have such a card, and you are not using an ICU to specify its
address range, select a base address from the six available options; the ISA MEM
Block SIZE field will then appear for selecting the block size. If you have more than
one legacy ISA card in your system that requires to use this address range, you can
increase the block size to either 8K, 16K, 32K, or 64K. If you are using an ICU to
accomplish this task, leave ISA MEM Block BASE to its default setting of No/ICU.
SYMBIOS SCSI BIOS (Auto)
The default uses Auto settings for the onboard SCSI BIOS. If you do not want to use
the onboard SCSI BIOS, choose Disabled.
USB Function (Disabled)
The motherboard supports Universal Serial Bus (USB) devices but current operating
systems do not. The default is set to Disabled. If you have the necessary support disks
and USB devices, set this function to Enabled to use the onboard USB connector .
USB IRQ (Auto)
When USB devices are connected to the onboard USB connector, the resource settings or IRQs for these devices are, by default, automatically assigned by the BIOS.
You may manually select the settings: 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, and 15. If you are not
using any USB devices, you may set this field to N/A.
4. BIOS SETUP
PnP and PCI
ONB VGA BIOS First (No)
This allows you to select whether you want to use the onboard VGA BIOS as the
primary VGA BIOS. No allows external VGA cards to take precedent when detected. Yes always uses the onboard VGA BIOS, even when an external VGA card is
installed.
Onboard Audio Chip (Enabled)
This allows you to select whether you want to use the onboard audio or not. Disabled allows you to use an external audio card.
Onboard NIC BIOS (Enabled)
The default setting enables the onboard NIC BIOS so that your computer, with the
appropriate interface and configuration, can be connected to a network. If you do
not want to use the onboard NIC BIOS, choose Disabled.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual56
Page 57

4. BIOS SETUP
4.8 Load BIOS Defaults
Load BIOS Defaults option allows you to load the troubleshooting default values
permanently stored in the BIOS ROM. These default settings are non-optimal and
disable all high performance features. This feature does not affect the fields on the
Standard CMOS Setup screen.
4.9 Load Setup Defaults
Load Setup Defaults option allows you to load the default values to the system
configuration fields. These default values are the optimized configuration settings
for the system. This feature does not affect the fields on the Standard CMOS Setup
screen.
Load Defaults
4. BIOS SETUP
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 57
Page 58

4. BIOS SETUP
4.10 Smart Alarm (LM78/LM75) Setup
Smart Alarm (LM78/LM75) Setup allows you to set up your hardware monitoring
options. This feature monitors the fan, CPU and motherboard temperature, and voltage.
Fan Monitor (xxxxRPM)
The onboard hardware monitor is able to detect the CPU Fan Speed in Rotations Per
Minute (RPM). These values refresh upon any key entries in the BIOS setup screen.
Set to Ignore if one of these are not used so that error messages will not be given.
Thermal Monitor (xxxC/xxxF)
The onboard hardware monitor is able to detect the CPU and MB (motherboard) temperatures. These values refresh upon key entries. Set to Ignor e only if necessary.
Voltage Monitor (xx.xV)
The onboard hardware monitor is able to detect the voltages put out by the voltage
regulators. These values refresh upon key entries. Set to Ignore only if necessary.
NOTE: If any of the monitored items are out of range, you will be prompted by this
message: “Hardware Monitor found an error, enter POWER MANAGEMENT
SETUP for details” The bottom of the screen will instruct you to: “Press F1 to
continue, DEL to enter SETUP”.
4. BIOS SETUP
Smart Alarm
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual58
Page 59

4. BIOS SETUP
4.11 Supervisor and User Password
These two options set the system passwords. Supervisor Password sets a password
that will be used to protect the system and the Setup utility; User Password sets a
password that will be used exclusively on the system. By default, the system comes
without any passwords. To specify a password, highlight the type you want and then
press <Enter>. A password prompt appears on the screen. T aking note that the password
is case sensitive, and can be up to 8 alphanumeric characters long, type in your password
and then press <Enter>. The system confirms your password by asking you to type it
again. After setting a password, the screen automatically reverts to the main screen.
T o implement the password protection, specify in the “Security Option” field of 4.4
BIOS Features Setup when the system will prompt for the password. If you want to
disable either passwords, press <Enter> instead of entering a new password when
the “Enter Password” prompt appears. A message confirms the password has been
disabled.
4.11.1 Forgot the Password?
If you forgot the password, you can clear the password by erasing the CMOS Real
Time Clock (RTC) RAM. The RAM data containing the password information is
powered by the onboard button cell battery. To erase the RTC RAM: (1) Unplug
your computer, (2) Short the solder points, (3) Turn ON your computer, (4) Hold
down <Delete> during bootup and enter BIOS setup to re-enter user preferences.
WARNING! Move the jumper to the “Clear CMOS”
setting only when clearing RTC data. Otherwise, BIOS
R
setup information
RTCLR
3
2
1
Normal Setting (Default)
may
be cleared.
Battery test
RTCLR
3
2
1
Clear CMOS
Passwords
4. BIOS SETUP
SP98-N Real Time Clock (RTC) RAM
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 59
Page 60

4. BIOS SETUP
4.12 IDE HDD Auto Detection
This “IDE HDD Auto Detection” option detects the parameters of an IDE hard disk
drive, and automatically enters them into the “Standard CMOS Setup” screen.
Up to four IDE drives can be detected, with parameters for each listed inside the
box. To accept the optimal entries, press <Y>, otherwise select from the numbers
displayed under the OPTIONS field (2, 1, 3 in this case); to skip to the next drive,
press <N>. If you accept the values, the parameters will appear listed beside the
drive letter on the screen. The process then proceeds to the next drive letter . Pressing
4. BIOS SETUP
Hard Disk Detect
<N> to skip rather than to accept a set of parameters causes the program to enter
zeros after that drive letter.
If you are using another IDE controller that does not feature Enhanced IDE support
for four devices, you can only install two IDE hard disk drives. Your IDE controller
must support the Enhanced IDE features to use Drive E and Drive F. The onboard
PCI IDE controller supports Enhanced IDE, with two connectors for connecting up
to four IDE devices. If you want to use another controller that supports four drives,
you must disable the onboard IDE controller in the Chipset Features Setup screen.
When autodetection is completed, the program automatically enters all entries you
accepted on the field for that drive in the “Standard CMOS Setup” screen. Skipped
entries are ignored and are not entered in the screen.
If you are autodetecting a hard disk that supports the LBA mode, three lines will
appear in the parameter box. Choose the line that lists LBA for an LBA drive. Do not
select Large or Normal.
The autodetection feature can only detect one set of parameters for a particular IDE
hard disk. Some IDE drives can use more than one set. This is not a problem if the
drive is new and there is nothing on it.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual60
Page 61

4. BIOS SETUP
IMPORTANT: If your hard disk was already formatted on an older previous system,
incorrect parameters may be detected. You will need to enter the correct parameters
manually or use low-level format if you do not need the data stored on the hard disk.
If the parameters listed differ from the ones used when the drive was formatted, the
drive will not be readable. If the autodetected parameters do not match the ones that
should be used for your drive, do not accept them. Press <N> to reject the presented
settings and enter the correct ones manually from the “Standard CMOS Setup” screen.
4.13 Save and Exit Setup
Select this option to save into the CMOS memory all modifications you specify
during the current session. To save the configuration changes, highlight “Save &
Exit Setup” on the main screen, type “Y”, and then press <Enter>.
4.14 Exit Without Saving
Select this option to exit the Setup utility without saving the modifications you specify
during the current session. To exit without saving, highlight “Exit Without Saving”
on the main screen, type “Y”, and then press <Enter>.
4. BIOS SETUP
Load Setup Defaults
Save & Exit
4. BIOS SETUP
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 61
Page 62

(This page was intentionally left blank.)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual62
Page 63

5. SOFTWARE CONTENTS
5.1 ASUS Support CD
Insert the support CD or double-click your CD drive icon in “My Computer” to bring
up the autorun menu or run Setup.exe in the root directory of the Support CD.
NOTE: The support CD contents are subject to change at any time without notice.
5.1.1 Support CD Main Menu
• LDCM Local
Setup: Installs soft-
ware to monitor the
local system. The
LANDesk Client
Manager must be
installed to use the
hardware manager
features.
• LDCM Administrator Setup: In-
stalls software to
monitor PC systems
on the network
within the same
bridge address with the Local software installed. The administrator should install
both Local and Administrator Software.
• LDCM Introduce (MPEG VCD): Plays an overview of LDCM in MPEG format.
• Install ASUS PC Probe: Installs a simple utility to monitor your computer’s fan,
temperature, and voltages. (NOTE: This utility will not run with LDCM installed.)
A user’s manual in Adobe Acrobat PDF format is available under the ASUSLM
folder created on your system during setup.
• Install ADOBE Acrobat Reader: Installs the Adobe Acrobat Reader software necessary to view the LDCM manual in the LDCM directory.
• Install Y AMAHA Audio Driver: Installs the necessary audio drivers and utilities to
access the features of the built-in PCI audio chipset.
• Install IDE Driver: Installs the BusMaster IDE driver for improved performance.
(Available only for Windows NT)
• Install Display Driver: Installs the video driver and utilities for the integrated VGA
controller .
• Install LAN Driver: Installs the driver needed to access the onboard LAN controller.
• Browse this CD: Allows you to see the contents of the ASUS support CD.
• Read Me: View additional notes with Notepad.
• Exit: Exit the selection menu.
ASUS Support CD
5. S/W CONTENTS
Additonal CD Contents: DMI Configuration Utility in the DMI directory , Flash BIOS
writer in the AFLASH directory, and XingMPEG Player in the XING directory.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 63
Page 64

(This page was intentionally left blank.)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual64
Page 65

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.1 Intel LANDesk Client Manager
With the growth of the computer industry, computer systems have become more
complex and difficult to manage. Intel LANDesk Client Manager is a computer
management application that simplifies many aspects of managing a computer and
assists in troubleshooting common computer problems.
Intel LDCM
Use Client Manager to:
• Review system inventory
• View DMI-compliant component information
• Backup and restore system files
• Troubleshoot
• Monitor your computer’s health
• Receive notifications for system events
Client Manager has been implemented in two different ways:
The client version enables you to view information and manage alerts for a local
computer. This version does not permit you to select remote computers, transfer
files, or reboot other computers.
The first time you run Client Manager, it searches your network for other computers
running Client Manager . Client Manager creates a list of the computers it finds and
saves the list to the Windows registry. From this point on, when you run Client
Manager or open the Select Computer dialog box, Client Manager checks to see if
these computers (listed in the registry) are available and healthy.
6. S/W REFERENCE
6.1.1 Main Client Manager Window
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 65
Page 66

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
Intel LDCM
6.1.2 Using the Taskbar icons
Toolbar Descriptions
Opens the Select Computer dialog box
Opens the Export dialog box to export the
inventory to a file
Exports the inventory to the clipboard
Opens the notification log
Opens the global notification log
Opens the remote access log
Opens the Configure Notifications dialog
box
File | Select Computer
File | Export
File | Export to clipboard
View | Notification Log
V iew | Global Notification Log
View | Remote Access Log
T ools | Configure Notifications
Opens the Configure Global Notifications
dialog box
Opens the File Transfer dialog box
Reboots the computer
Opens the DMI Explorer
Opens the Set Access Rights dialog box
Tools | Configure Global
Tools | Transfer Files
Tools | Reboot
Tools | DMI Explorer
Tools | Set Access Rights
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual66
Page 67
6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.1.3 Using the Select Computer Dialog Box
Discovers new computers on the network
Intel LDCM
6. S/W REFERENCE
Refreshes the health of known computers
Removes a computer from the list of discovered computers
Wakes up a sleeping computer
Shows all discovered computers
Shows only available computers
Shows only unhealthy computers
Shows a simple list view
Shows a detailed list view
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 67
Page 68

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
Intel LDCM
To select a computer
1. From the main Client Manager window, click File | Select Computer.
2. In the Select Computer dialog box, click the computer you want to view.
3. Click the Select button.
To discover new computers
• In the Select Computer dialog box, click the Discover button on the toolbar or
press <Shift>+<F5>.
TIP: Use the Discover button each time you add a computer to the network,
change a computer’s network adapter , or upgrade a computer to a newer version
Client Manager.
To refresh PC health
• In the Select Computer dialog box, click the Refresh Known Computers but-
ton on the toolbar or press <F5>.
TIP: PC health does not automatically update as changes occur . For example, if
a computer’s health changes while you are displaying the Select Computer dialog box, you need to refresh the list in order to view the correct PC health.
To remove a computer from the list
1. In the Select Computer dialog box, click the computer name you want to remove.
2. Click the Remove Computer button on the toolbar or press Delete.
3. At the prompt, click the Yes button.
TIP: Perform this task each time you remove a computer from the network, since the
name of that computer is not automatically removed from this list.
To wake up a computer
1. In the Select Computer dialog box, click the computer name you want to wake
up. You can also <Shift>+click to select a continuous group of computers or
<Ctrl>+click to select individual computers in the list.
TIP: You can only attempt to wake up computers that have a status of Unavailable or Wakeable. If the Select Computer dialog box does not display any computers with a status of Unavailable or Wakeable and you suspect it should, the
list view may be filtered to display only unhealthy or available computers. You
may need to change your list view to display all computers.
2. Click the Wake Up Computer button on the toolbar to wake up the selected
computer(s) or press <Alt>+<W>.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual68
Page 69

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
After you attempt to wake up a computer, the status of that computer changes in the
list view to a Wake Pending status. If the attempt to wake up a computer is successful, the Wake Pending status changes to a status reflecting the computer’s health
(such as Normal, Warning, or Critical). If the computer does not wake up after five
minutes, a message box appears stating possible reasons why the computer did not
respond. (For example, the computer may be disabled or may not support Wake-OnLAN.) After clicking OK, the Wake Pending status reverts to its original status of
Unavailable or Wakeable.
NOTE: You computer must have a Wake-On-LAN network adapter to support this
feature. Some computers that support the Wake-On-LAN technology may have remote wakeup disabled in the BIOS by default. Before Client Manager can wake up
a remote computer, you will need to enable this option in the BIOS configuration of
each remote computer.
6.1.4 Displaying the Properties of a Client Computer
6. S/W REFERENCE
Intel LDCM
You can display the properties of any discovered client computer even if you cannot
otherwise access the computer because of access limitations or Unavailable status.
If you display the properties of an unavailable computer, the properties are read
from a database in the Windows registry on your computer. Since the Operating
System information is not stored in this same database, that information is not available for a computer with a status of Unavailable. Remember that some items may
not be current if the properties have changed while the computer was off the network.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 69
Page 70

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
Intel LDCM
6.1.5 Understanding the Computer Status Icons
When you open the Select Computer dialog box, each computer in the list displays
an icon indicating the current status of that computer . The table below describes the
seven states a computer may be in.
Unavailable The computer is currently in a powered-down state.
Wakeable The computer is currently in a powered-down state but
Wake Pending A temporary status (not to exceed five minutes) while
Normal The computer is operating within normal tolerances.
supports Remote Wakeup technology.
Client Manager attempts to wake up a computer . (A computer that is in the process of booting without having
received a wakeup instruction is listed as Unavailable,
not Wake Pending.)
Warning A computer that has exceeded a warning tolerance level.
For example, the PC Health indicator can be configured
to display a warning icon if a hard disk is running low
on space.
Critical A computer that has exceeded a critical tolerance level.
For example, if the hard disk is running critically low
on available space, the PC Health indicator displays a
critical icon.
Unknown A computer that is powered on, but the health status (Nor -
mal, Warning, or Critical) is not known.
Normal (Mobile) A computer that includes support for mobile PC fea-
tures, such as mobile battery . Mobile computers display
the same array of health icons (above) used for nonmobile computers.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual70
Page 71

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.2 ASUS PC Probe
ASUS PC Probe is a convenient utility to monitor the computer system’s
vital components: fan rotations, voltages, and temperatures.
6.2.1 Starting ASUS PC Probe
When ASUS PC Probe starts, a splash screen appears allowing you to “Show
Monitor” or “Hide”. You can select whether you want the splash screen to
show the next time it opens.
ASUS PC Probe
6. S/W REFERENCE
Click ASUS PC Probe from the Start button to run the utility if you exit the
utility or did not set it to “Run when Windows Starts.”
The PC Probe icon
that ASUS PC Probe is running. Left-clicking the icon will allow you to see
your PC status.
will appear on the taskbar’s system tray indicating
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 71
Page 72

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
ASUS PC Probe
6.2.2 Using the ASUS PC Probe
Fan Rotation Status
PC Temperature Status
temperature warning threshold
Analog view of
PC’s fan rotation
Digital view of
PC’s fan rotation
PC’s Fan warning
threshold adjustment
T emperature Warning
threshold adjustment
Analog view of
PC’s temperature
Digital view of
PC’s temperature
Digital view of PC’s
PC Voltage Status
Upper warning threshold adjustment
Analog view of PC’s voltages
Lower warning threshold adjustment
Digital view of PC’s voltages
Digital view of PC’s voltage
warning thresholds
PC Status Summary
PC’s Fan Rotations per minute
PC’s Temperature ˚C/˚F
PC’s Voltages
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual72
Page 73

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
PC Probe System Info.
Get information on your mainboard
and BIOS from this screen.
PC Probe Settings
Change PC Probe refresh times here
ASUS PC Probe
6. S/W REFERENCE
Click here to start PC Probe each
time you enter W indows.
Click the items you wish to reset to its
default values and click this button.
PC Probe Task Bar Icon
Right clicking the PC Probe icon will bring
up a menu to turn on, off, or exit ASUS PC
Probe.
The icon appears dimmed when off or unavailable.
When there is a problem, the icon’s head
mirror flashes red, the PC speaker beeps, and
the ASUS PC Probe monitor is displayed.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 73
Page 74

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
(This page was intentionally left blank.)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual74
Page 75

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.3 SVGAUTL.EXE
6.3.1 General Description
SVGAUTL.EXE is one of the utilities of SiS 5597/5598. It supports three functions:
(1) Video Mode Setting
SiS 5597/5598 supports many enhanced Text and Graphic Modes.
SVGAUTL.EXE can be used to select the desired video mode.
(2) Frame Rate Setting
For 640x480, 800x600, 1024x768, and 1280x1024 resolutions, SiS 5597/5598
supports multiple frame rates. If your monitor supports these frame rates,
SVGAUTL.EXE can be used to select a desired rate.
(3) Power Saving Setting
SiS 5597/5598 supports VESA DPMS Power Saving Modes. SVGAUTL.EXE
can be used to set any of the supported modes.
6.3.2 General Usage
To use SVGAUTL.EXE:
1. Type “SVGAUTL” in the directory where it resides and then press <Enter>.
For example: C:\> SVGAUTL <Enter> (assuming SVGAUTL.EXE is in C:\)
2. The Main Menu appears and directs you to configure SiS 5597/5598.
SVGAUTL.EXE
6. S/W REFERENCE
3. When you have completed the configuration, you may save your preferences to
AUTOEXEC.BAT and use it as your power-on (or hardware reset)
default environment. (See 6.1.3 Commandline Options)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 75
Page 76

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
6.3.3 Commandline Options
Video Modes
Syntax:
>SVGAUTL [/D:mode_no] [/F0:n0] [/F1:n1] [/F2:n2] [/F3:n3] [/PA:ta] [/PB:tb]
where
/D: Set the Video Mode to be mode_no which is a hex number.
For example: Set 1024x768 256 color graphic mode.
>SVGAUTL /D:38 <Enter>
/F0: For 640x480, set frame rate to be n0 Hz.
Three availabe frame rates are 60, 72, and 75 Hz.
For example : Set 640x480 graphic mode with 60Hz frame rate
>SVGAUTL /F0:60 <Enter>
/F1: For 800x600, set frame rate to be n1 Hz.
Four availabe frame rates are 56, 60, 72, and 75 Hz.
For example : Set 800x600 graphic mode with 72Hz frame rate.
>SVGAUTL /F1:72 <Enter>
/F2: For 1024x768, set frame rate to be n2 Hz.
Four availabe frame rates are 87 (Interlace), 60, 70, and 75 Hz.
For example : Set 1024x768 graphic mode with 60Hz frame rate.
>SVGAUTL /F2:60 <Enter>
/F3: For 1280x1024, set frame rate to be n3 Hz.
Two availabe frame rates are 87 (Interlace) and 60 Hz.
For example : Set 1280x1024 graphic mode with 60Hz frame rate.
>SVGAUTL /F3:60 <Enter>
/PA: Set Standby Timer to be ta minutes. (0 < ta < 15 min.)
For example : Set Standby Timer be 5 minutes.
>SVGAUTL /PA:5 <Enter>
/PB: Set Suspend Timer to be tb minutes. (0 < tb < 15 min.)
For example : Set Suspend Timer be 5 minutes.
>SVGAUTL /PB:5 <Enter>
NOTE:1. Suspend Time would be “ta + tb”. (i.e. standby time + suspend time)
2. The timers will not be very accurate and would just be around the time.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual76
Page 77

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.3.A1. Video Modes
6.3.A1.1 Standard VGA Modes
MODE TYPE DISPLAY COLORS ALPHA BUFFER BOX MAX
SIZE SHADES FORMAT START SIZE PAGES
Video Modes
0 A/N 320x200 16 40x25 B800 8x8 8
0* A/N 320x350 16 40x25 B800 8x14 8
0+ A/N 360x400 16 40x25 B800 9x16 8
1 A/N 320x200 16 40x25 B800 8x8 8
1* A/N 320x350 16 40x25 B800 8x14 8
1+ A/N 360x400 16 40x25 B800 9x16 8
2 A/N 640x200 16 80x25 B800 8x8 8
2* A/N 640x350 16 80x25 B800 8x14 8
2+ A/N 720x400 16 80x25 B800 9x16 8
3 A/N 640x200 16 80x25 B800 8x8 8
3* A/N 640x350 16 80x25 B800 8x14 8
3+ A/N 720x400 16 80x25 B800 9x16 8
4 APA 320x200 4 40x25 B800 8x8 1
5 APA 320x200 4 40x25 B800 8x8 1
6 APA 640x200 2 80x25 B800 8x8 1
7 A/N 720x350 4 80x25 B000 9x14 8
7+ A/N 720x400 4 80x25 B000 9x16 8
0D APA 320x200 16 40x25 A000 8x8 8
0E APA 640x200 16 80x25 A000 8x8 4
0F APA 640x350 2 80x25 B000 8x14 2
10 APA 640x350 16 80x25 A000 8x14 2
11 APA 640x480 2 80x30 A000 8x16 1
12 APA 640x480 16 80x30 A000 8x16 1
13 APA 320x200 256 40x25 A000 8x8 1
6. S/W REFERENCE
NOTE: 1. A/N: Alpha/Numeric
2. APA: All Point Addressable (Graphics)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 77
Page 78

6. S/W REFERENCE
MODE DISPLAY COLORS FRAME H-SYNC. VIDEO
Video Modes
0 320x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
0* 320x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
0+ 360x400 16 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
1 320x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
1* 320x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
1+ 360x400 16 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
2 640x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
2* 640x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
2+ 720x400 16 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
3 640x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
3* 640x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
3+ 720x400 16 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
4 320x200 4 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
5 320x200 4 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
6 640x200 2 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
7* 720x350 4 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
7+ 720x400 4 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
0D 320x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
0E 640x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
0F 640x350 2 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
10 640x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
11 640x480 2 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
12 640x480 16 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
13 320x200 256 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
SIZE SHADES RATE. FREQ.
NOTE: i - interlaced mode
n - noninterlaced mode
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual78
Page 79

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.3.A1.2 Enhanced Video Modes
MODE TYPE DISPLAY COLORS ALPHA BUFFER BOX MAX.
SIZE SHADES FORMAT START SIZE PAGES
22 A/N 1056x352 16 132x44 B800 8x8 2
23 A/N 1056x350 16 132x25 B800 8x14 4
24 A/N 1056x364 16 132x28 B800 8x13 4
25 APA 640x480 16 80x60 A000 8x8 1
26 A/N 720x480 16 80x60 B800 9x8 3
29 APA 800x600 16 100x37 A000 8x16 1
2A A/N 800x600 16 100x40 B800 8x15 4
2D APA 640x350 256 80x25 A000 8x14 1
2E APA 640x480 256 80x30 A000 8x16 1
2F APA 640x400 256 80x25 A000 8x16 1
30 APA 800x600 256 100x37 A000 8x16 1
37 APA 1024x768 16 128x48 A000 8x16 1
38 APA 1024x768 256 128x48 A000 8x16 1
39 APA 1280x1024 16 160x64 A000 8x16 1
3A APA 1280x1024 256 160x64 A000 8x16 1
40 APA 320x200 32K 40x25 A000 8x8 1
41 APA 320x200 64K 40x25 A000 8x8 1
42 APA 320x200 16.8M 40x25 A000 8x8 1
43 APA 640x480 32K 80x30 A000 8x16 1
44 APA 640x480 64K 80x30 A000 8x16 1
45 APA 640x480 16.8M 80x30 A000 8x16 1
46 APA 800x600 32K 100x37 A000 8x16 1
47 APA 800x600 64K 100x37 A000 8x16 1
48 APA 800x600 16.8M 100x37 A000 8x16 1
49 APA 1024x768 32K 128x48 A000 8x16 1
4A APA 1024x768 64K 128x48 A000 8x16 1
4B APA 1024x768 16.8M 128x48 A000 8x16 1
4C APA 1280x1024 32K 160x64 A000 8x16 1
4D APA 1280x1024 64K 160x64 A000 8x16 1
Video Modes
6. S/W REFERENCE
NOTE: 1. A/N: Alpha/Numeric
2. APA: All Point Addressable (Graphics)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 79
Page 80

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
MODE DISPLAY COLORS FRAME H-SYNC. VIDEO
Video Modes
22 1056x352 16 70 30.5 K 40.0 M
23 1056x350 16 70 30.5 K 40.0 M
24 1056x364 16 70 30.5 K 40.0 M
25 640x480 16 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
26 720x480 16 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
29 800x600 16 56 35.1 K 30.0 M
29* 800x600 16 60 37.9 K 40.0 M
29+ 800x600 16 72 48.0 K 50.0 M
29# 800x600 16 75 46.8 K 50.0 M
29## 800x600 16 85 53.7 K 56.3 M
2A 800x600 16 56 35.1 K 36.0 M
2D 640x350 256 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
2E 640x480 256 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
2E* 640x480 256 72 37.9 K 31.5 M
2E+ 640x480 256 75 37.5 K 31.5 M
2E++ 640x480 256 85 43.4 K 36.0 M
2F 640x400 256 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
30 800x600 256 56 35.1 K 36.0 M
30* 800x600 256 60 37.9 K 40.0 M
30+ 800x600 256 72 48.0 K 50.0 M
30# 800x600 256 75 46.8 K 50.0 M
30## 800x600 256 85 53.7 K 56.3 M
37i 1024x768 16 87 35.5 K 44.9 M
37n 1024x768 16 60 48.4 K 65.0 M
37n+ 1024x768 16 70 56.5 K 75.0 M
37n# 1024x768 16 75 60.2 K 80.0 M
37n## 1024x768 16 85 68.7 K 94.5 M
38i 1024x768 256 87 35.5 K 44.9 M
38n 1024x768 256 60 48.4 K 65.0 M
38n+ 1024x768 256 70 56.5 K 75.0 M
38n# 1024x768 256 75 60.2 K 80.0 M
38n## 1024x768 256 85 68.7 K 94.5 M
39i 1280x1024 16 87 48.8 K 80.0 M
39n 1280x1024 16 60 65.0 K 110.0 M
39n+ 1280x1024 16 75 80.0 K 135.0 M
3Ai 1280x1024 256 87 48.8 K 80.0 M
3An 1280x1024 256 60 65.0 K 110.0 M
3An+ 1280x1024 256 75 80.0 K 135.0 M
40 320x200 32K 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
41 320x200 64K 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
42 320x200 16.8M 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
43 640x480 32K 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
43* 640x480 32K 72 37.9 K 31.5 M
43+ 640x480 32K 75 37.5 K 31.5 M
43++ 640x480 32K 85 43.4 K 36.0 M
44 640x480 64K 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
44* 640x480 64K 72 37.9 K 31.5 M
44+ 640x480 64K 75 37.5 K 31.5 M
SIZE SHADES RATE. FREQ.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual80
Page 81

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
MODE DISPLAY COLORS FRAME H-SYNC. VIDEO
SIZE SHADES RATE. FREQ.
44++ 640x480 64K 85 43.4 K 36.0 M
45 640x480 16.8M 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
45* 640x480 16.8M 72 37.9 K 31.5 M
45+ 640x480 16.8M 75 37.5 K 31.5 M
45++ 640x480 16.8M 85 43.4 K 36.0 M
46 800x600 32K 56 35.1 K 36.0 M
46* 800x600 32K 60 37.9 K 40.0 M
46+ 800x600 32K 72 48.0 K 50.0 M
46# 800x600 32K 75 46.8 K 50.0 M
46## 800x600 32K 85 53.7 K 56.3 M
47 800x600 64K 56 35.1 K 36.0 M
47* 800x600 64K 60 37.9 K 40.0 M
47+ 800x600 64K 72 48.0 K 50.0 M
47# 800x600 64K 75 46.8 K 50.0 M
47## 800x600 64K 85 53.7 K 56.3 M
48 800x600 16.8M 56 35.1 K 36.0 M
48* 800x600 16.8M 60 37.9 K 40.0 M
48+ 800x600 16.8M 72 48.0 K 50.0 M
48# 800x600 16.8M 75 46.8 K 50.0 M
48## 800x600 16.8M 85 53.7 K 56.3 M
49i 1024x768 32K 87 35.5 K 44.9 M
49n 1024x768 32K 60 48.4 K 65.0 M
49n+ 1024x768 32K 70 56.5 K 75.0 M
49n# 1024x768 32K 75 60.2 K 80.0 M
49n## 1024x768 32K 85 68.7 K 94.5 M
4Ai 1024x768 64K 87 35.5 K 44.9 M
4An 1024x768 64K 60 48.4 K 65.0 M
4An+ 1024x768 64K 70 56.5 K 75.0 M
4An# 1024x768 64K 75 60.2 K 80.0 M
4An## 1024x768 64K 85 68.7 K 94.5 M
4Bi 1024x768 16.8M 87 35.5 K 44.9 M
4Bn 1024x768 16.8M 60 48.4 K 65.0 M
4Bn+ 1024x768 16.8M 70 56.5 K 75.0 M
4Bn# 1024x768 16.8M 75 60.2 K 80.0 M
4Bn## 1024x768 16.8M 85 68.7 K 94.5 M
4Ci 1280x1024 32K 89 48.8 K 80.0 M
4Di 1280x1024 64K 89 48.8 K 80.0 M
Video Modes
6. S/W REFERENCE
NOTE: i - interlaced mode
n - noninterlaced mode
*Due to the memory bandwidth limitation in a 1MB DRAM configuration, the
following video modes is not supported in 1MB configuration: modes 45*,
45+, 46+, 46#, 47+, and 47#.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 81
Page 82

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
Windows 3.1
To make use of the advance features of SiS 5597/5598, extended graphic and text
modes are supported by software application drivers developed by SiS. The following applications are currently supported:
• Microsoft Windows 3.1
• Microsoft Windows 95
• Microsoft Windows NT Ver. 3.1, 3.5, 3.51, 4.0
• AutoCAD/386 Release 11, 12
• Auto Shade/386 Ver. 2.0
• 3D Studio Ver. 3.0
• OS/2 Presentation Manager 2.1 & 3.0
6.4 Windows 3.1
6.4.1 Version Notes
The following descriptions apply to SiS 5597/5598 Driver Release V1.03 and later.
The descriptions, however, are subject to change at anytime without notice.
6.4.2 Driver Files
1. The enclosed SiS 5597/5598 W indows 3.1 driver contains SETUP .EXE and other
installation-related files.
6.4.3 Installation
6.4.3.1 Unpack & Copy
T o unpack and copy drivers to where they should reside, do the following procedures:
1. Boot up Windows using standard VGA mode.
2. In Windows Program Manager Screen, choose “File” item.
3. In “File Item List”, choose “Run” item.
4. In “Run” Screen, select your driver source, e.g., D:\MM\WIN31\SETUP.EXE.
5. Follow the directions that appear on the screen to complete the unpacking and
copying procedures.
6. After unpacking and copying is completed, an “SiS Multimedia Vx.xx” program group is created and shown onscreen.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual82
Page 83

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
7. In the “SiS Multimedia Vx.xx” program group, five icons are created:
(1) SiS Multimedia Manager: Creates a shortcut bar on your desktop for single-
click access to the display utilities.
(2) SVGA Setup: Accesses the SiS VGA graphics configuration system.
(3) SiS MMPlayer: Creates an “SiS MMPlayer” VCP-like icon on the screen.
(4) Center Screen: Lets you adjust the position of the display on the screen.
(5) Uninstall utility: Uninstalls all the installed driver files and utilities.
6.4.3.2 Graphics Setup
1. In the SiS Multimedia Vx.xx program group, double-click the SVGA Setup
icon. The SiS VGA Configuration System dialog box will appear with several
options to configure your VGA system.
2. In the SiS VGA Configuration System box, configure the options you would
like to use. Click OK after completing your selections.
NOTE: Any changes that you made will only take effect when you restart W indows.
Click Restart Windows to restart Windows using your new settings or click Con-
tinue to continue your current Windows session (your new settings will, however,
will not be shown — it will only take effect when you restart Windows).
6.4.3.3 Power Saving Setup in Windows
1. In the SiS VGA Configuration System box, click the Power Saver button to
open the Power Saver dialog box.
Windows 3.1
6. S/W REFERENCE
2. In the Power Saver box, configure the options you would like to enable or
change. Click OK after completing your selections. The power saver options
you selected will take effect as configured.
NOTE: The Power Saver’s timer settings are still in effect even when
you quit Windows to use DOS.
6.4.3.4 Zoom_Key Setup
In the SiS VGA Configuration System box, click the Zooming button to define the
hot keys to zoom-in or zoom-out your screen, that is, you can change the resolution
on-the-fly, without activating SVGA Setup.
The operating principles of this feature are:
(1) Zoom-in sequence:
1024x768 800x600 640x480
(2) Zoom-out sequence:
640x480 800x600 1024x768
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 83
Page 84

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
Windows 3.1
(3) You must first zoom-in before you can zoom-out, that is, you cannot zoom out
to a resolution larger than what you initially set or defined.
To use this feature, do the following:
1. In the SiS VGA Configuration System box, click the Zooming button to open
the Zooming Hotkey dialog box.
2. In the Zooming Hotkey box, click the hot key/s you would like to use for ZoomIn
and ZoomOut. Click OK after completing your selections.
3. After completing setup, you may use the hot key/s you defined to zoom-in or
zoom-out.
6.4.4 Video Operations
6.4.4.1 DCI Function
SiS 5597/5598 supports the Display Contro Interface (DCI) software interface standard for software MPEG playback and other media player programs that can take
advantage of DCI.
The SiS 5597/5598 DCI driver is automatically loaded during the driver installation
and therefore, should be transparent to the end-user.
6.4.4.2 SiS MMPlay (SW MPEG)
T o make SW MPEG playback more user-friendly than the original SW MPEG player
supplier provided, SiS provides an MMPlayer application program with a VCP-like
(Video Cassette Player) interface.
T o take advantage of the SiS MMPlayer , you must first install “SW MPEG Player”.
All the SiS provided is just an interface but not a SW MPEG Player at present. If the
SW MPEG Player does not exist, the SiS MMPlayer will not work. (Xing or
Mediamatics SW MPEG Player supported)
To use the SiS MMPlayer, do the following procedures:
1. In the SiS Multimedia Vx.xx program group, double-click the Sis MMPlayer
icon. The SiS MMPlayer VCP-like icon appears.
2. The SW MPEG playback is now ready for your use.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual84
Page 85

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.4.4.3 MMPLAY.EXE Button Description
Power On/Off
Open File & Type Control
Minimize This Application
Eject CD Title (Not implemented yet.)
Fast Backward
Fast Forward
Mark in
Mark out
Pause
Windows 3.1
6. S/W REFERENCE
Play
Stop
End
Begin
Volume increase (Not implemented yet.)
Volume decrease (Not implemented yet.)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 85
Page 86

6. S/W REFERENCE
6.5 Windows 95
Windows 95
6.5.1 Version Note
The following descriptions apply to SiS 5597/5598 Driver Release V1.03 and later.
The descriptions, however, are subject to change at anytime without notice.
6.5.2 Driver Files
1. The SiS 5597/5598 Windows 95 drivers files include
SETUP.EXE SIS597.DRV SIS597.INF
SISMINI.VXD Other Files
2. All the 16-color, 256-color, 32K/64K-color, and 16M-color drivers are available.
6.5.3 Installation
1. Start Windows 95.
2. In Windows 95, double-click the My Computer icon.
6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
3. In My Computer, double-click the Control Panel icon.
4. Click the Display icon in the Control Panel.
5. In the Display Properties dialog box, click the Settings tab and then click the
Change Display Type button.
6. In the Change Display Type box, click Adapter Type and then the Change
button.
7. In the Select Device box, click the Have Disk... button.
8. In the Install From Disk box, select your driver source, e.g., A:\WIN95.
9. In the Select Device box, SiS 5597/5598 appears. Click OK to begin installation.
10. When setup finishes copying the necessary files, the Change Display Type box
appears. Click Close.
11. The Display Properties box appears. Click either Close or Apply.
12. In the System Settings Change box, click Yes to restart your computer.
13. After restarting, Windows 95 will run on 640x480x256 color, 60NI (non-interlaced).
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual86
Page 87

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.5.4 Using “Display Modes”
1. When you open the Display Properties box after the driver installation, Display Modes will have been added.
2. Click Display Modes and select the desired resolution by dragging the Desktop
area slider to the desired resolution, desired color by changing the Color pal-
ette value, desired font size by changing Font size, and desired refresh rate by
changing Refresh rate.
3. After completing your selections, click OK or Apply to complete the installation.
4. In the SiS 5597/5598 Settings box, click OK.
5. Two cases may happen:
a) You did not change “color” and/or “font size”.
1. SiS 5597/5598 Settings box appears again,
2. Click Yes. You may begin working on your selected mode now.
b) You changed “color” and/or “font size”.
Windows 95
6. S/W REFERENCE
1. System will restart.
2. You may begin working on your selected mode now.
6.5.5 Utilities
6.5.5.1 Installation
1. Click Start and then point to Run.
2. In the Run box, type the source execution file.
For example, D:\MM\WIN95\SETUP.EXE
3. In the SiS Multimedia Setup Ver x.xx box, click OK.
4. A SiS Multimedia Vx.xx program group will be created and shown on screen.
Click Restart Now.
5. Three icons will be created in the program group:
(1) SiS Multimedia Package: Creates a shortcut bar on your desktop for single-
click access to the display utilities.
(2) SiS MMPlayer: Creates an SiS MMPlayer VCP-like icon on the screen.
(3) Center Screen: Allows you to adjust the position of display on the screen.
6. SiS Multimedia V x.xx program group will be created, click Restart Now.
6.5.5.2 Operation
1. For Video Operations (SiS MMPlay), refer to section 6.4.4.2.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 87
Page 88

6. S/W REFERENCE
6.6 Windows NT 3.5 & 3.51
Windows NT
6.6.1 Version Note
The following descriptions apply to SiS 5597/5598 Driver Release V1.03. The descriptions, however, are subject to change at anytime without notice.
6.6.2 Driver Files
(1) The enclosed SiS 5597/5598 Windows NT 3.5 & 3.51 drivers are SISTAG,
SISV.SYS, SISV256.DLL, SISV.DLL, OEMSETUP.INF.
(2) All the 16-color, 256-color, 32K/64K-color , and 16M-color drivers are available.
6.6.3 Installation
1. Double-click the Display icon under Control Panel.
2. Click Change Display Type from the Display Settings box.
3. Click Change from the Display Type box.
4. Click Other from the Select Device box.
5. Insert the SiS 5597/5598 CD disk into your CD-ROM Drive.
6. When the Install from Disk dialog box appears, type the location of the drivers
(D:\MM\WINNT\WINNT35, assumingyour CD-ROM drive is D:) and click OK.
7. Click Install and click Yes when the Installing Driver dialog box appears.
8. Click New when the Windows NT Setup dialog box appears.
9. Click Continue. A message appears stating that the drivers were successfully
installed. Click OK. You must now restart Windows NT 3.51.
6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.6.4 Selecting resolution and color depth
1. Double-click the Display icon under Control Panel.
2. Click Color Palette to change to either 16 colors, 256 colors, 32768 colors,
65536 colors, or 16777216 colors.
3. To select desktop resolution size, drag the slider in the Desktop area box to
change resolution to either 640x480, 800x600, 1024x768,or 1280x1024.
4. Click Test to test the resolution.
If the display test screen is acceptable, then click Yes when the Testing Mode
dialog box appears. If the display test screen is unacceptable, then click No.
Windows NT will give you an error message.
5. If the display test screen is acceptable and you clicked Yes, Windows
NT 3.51 will prompt you to restart Windows NT 3.51.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual88
Page 89

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.7 Windows NT 4.0
6.7.1 Version Note
The following descriptions apply to SiS 5597/5598 Driver Release V1.03. The
descriptions, however, are subject to change at anytime without notice.
6.7.2 Driver Files
(1) The enclosed SiS 5597/5598 Windows NT 4.0 drivers are SISV.SYS,
SISV256.DLL, SISV.DLL, SISV5597.INF.
(2) All the 16-color, 256-color, 32K/64K-color, and 16M-color drivers are available.
6.7.3 Installation
1. Click Start and then double-click the Display icon under Control Panel.
2. Click Settings in Display Properties.
3. Click Display Type.
4. Click Change from the Adapter T ype box.
5. Click Have Disk in the Change Display box.
6. Insert the SiS 5597/5598 CD disk into your CD-ROM Drive.
7. When the Install from Disk dialog box appears, type the location of the drivers
(D:\MM\WINNT\WINNT35, assumingyour CD-ROM drive is D:) and click OK.
8. When the Change Display dialog box appears, click OK.
9. When the Third-party Drivers dialog box appears, click Yes. A message appears stating that the drivers were successfully installed. Click OK. You must
now restart Windows 4.0.
Windows NT
6. S/W REFERENCE
6.7.4 Selecting resolution and color depth
1. Double-click the Display icon under Control Panel.
2. Click Color Palette to change to either 16 colors, 256 colors, 32768 colors,
65536 colors, or 16777216 colors.
3. To select desktop resolution size, drag the slider in the Desktop area box to
change resolution to either 640x480, 800x600, 1024x768,or 1280x1024.
4. Click Test to test the resolution.
If the display test screen is acceptable, then click Yes when the Testing Mode
dialog box appears. If the display test screen is unacceptable, then click No.
Windows NT will give you an error message.
6. Click OK. If the display test screen is acceptable and you clicked Yes, Windows
NT 4.0 will change the mode without restarting Windows NT 4.0.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 89
Page 90

6. S/W REFERENCE
Autodesk ADI 4.2
6.8 Autodesk ADI 4.2 -Protected Mode
6.8.1 General Description
6.8.1.1 Driver Files
1. The enclosed SiS 5597/5598 ADI driver contains the following file:
RCPSIS.EXP SiS ADI Driver (for all resolutions & colors)
Note: This version of ADI driver does not support 16-color operation.
2. This driver is compatible with some Autodesk Inc. products including:
(1) AutoCAD/386 R11
(2) AutoCAD/386 R12
(3) AutoShade/386 V2.0
(4) 3D Studio V3.0
3. The installation procedures are different from one program to the other. Only
the first step of the installation is the same for all these programs, that is, section
6.8.1.2 Unpack & Copy. Therefore, we will state this step below.
6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
4. As to the installation procedures for each program, see sections 6.8.2—6.8.5.
6.8.1.2 Unpack & Copy
To unpack and copy drivers to where they should reside, do the following:
1. Run “INSTDRV.EXE” where it resides.
2. In “SiS Super VGA Drivers Installation” menu, select “A. ADI 4.2” to unpack
and copy drivers. (To select, type “A”)
3. In “Unpack & Copy ADI 4.2 Drivers” screen, keyin the “drive:\directory”
where these drivers would reside (default C:\ADI42). Program would unpack
& copy all related driver files to where you assign.
4. After “unpack and copy” is completed, exit the INSTDRV.EXE program.
5. Refer to sections 6.8.2—6.8.5 for detailed installation procedures of each program.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual90
Page 91

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.8.2 AutoCAD R11 Setup
1. The following procedures assume that
(1) You have completed the “unpack & copy” procedure (section 6.8.1.2).
(2) Your ADI 4.2 drivers are located in C:\ADI42.
2. Add the following setting to your own batch file for AutoCAD R11 (e.g.,
ACADR11.BAT) or to your “AUTOEXEC.BAT” file:
SET DSPADI=\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP <Enter>
3. Delete the configure file ACAD.CFG in the \ACAD directory.
4. Type ACADR11 <Enter> to configure your AutoCAD R11 system.
5. In “Select Display Device:” item, choose “ADI P386 V4.0/4.1 display”
6. In “Select Display Resolution” screen, choose which display driver you want to use.
7. Go through the whole instrutions, and the system would start with the desired
display setting.
AutoCAD R11/R12
6. S/W REFERENCE
6.8.3 AutoCAD R12 Setup
1. The following procedures assume that
(1) You have completed the “unpack & copy” procedure (section 6.8.1.2).
(2) Your SiS ADI 4.2 drivers are located in C:\ADI42.
(3) Your AutoCAD R12 program is located in C:\ACADR12.
(4) Your AutoCAD R12 default drivers are located in C:\ACADR12\DRV.
(5) Your AutoCAD R12 configure file ACAD.CFG is located in C:\ACADR12.
2. Copy the following driver file to C:\ACADR12\DRV: RCPSIS.EXP.
You may complete this step by typing “COPY C:\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP
C:\ACADR12\DRV”.
3. Delete your original ACAD.CFG file. You may complete this step by typing
“DEL C:\ACADR12\ACAD.CFG”.
4. Restart your AutoCAD R12 program as usual.
5. AutoCAD R12 will ask you to complete the configuration procedures because it
cannot find the configure file ACAD.CFG.
6. Follow the instructions of AutoCAD R12 to proceed with the configuration.
7. In “Available V ideo Displays:” item, choose “SiS Super VGA ADI v4.2 Display
and Rendering driver”.
8. In “Select Display Resolution” screen, choose which display driver you want to use.
9. Go through the whole procedure. The system starts with the selected display
setting.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 91
Page 92

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
AutoShade/3D Studio
6.8.4 AutoShade R2.0 Setup
1. The following procedures assume that
(1) You have completed the “unpack & copy” procedure (section 6.8.1.2).
(2) Your ADI 4.2 drivers are located in C:\ADI42.
2. Add the following settings to your batch file for AutoShade R2.0 ( e.g.,
SHADE2.BAT) or to your “AUTOEXEC.BAT” file.
(a) For display driver setting, SET DSPADI=\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP.
(b) For rendering driver setting, SET RDPADI=\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP.
3. Delete the configure file SHADE.CFG.
4. Type SHADE2 <Enter> to re-configure the AutoShade.
5. When prompted to “Select display device:”, choose “P386 AutoDesk Device
Interface display driver.”
6. When prompted to “Select rendering display driver:”, choose “P386 AutoDesk
Device Interface rendering driver.”
7. Go through all the procedures. The system starts with the selecte display setting.
6.8.5 3D Studio Version 3.0 Setup
1. The following procedures assume that
(1) You have completed the “unpack & copy” procedure (section 6.8.1.2).
(2) Your ADI 4.2 drivers are located in C:\ADI42.
2. Create your own 3D Studio V3.0 batch file (e.g., 3DS3.BAT) and add the following settings to it, or add the following settings to your “AUTOEXEC.BAT” file.
(1) SET RCPADI=C:\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP
(2) SET RDPADI=C:\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP
3. Execute the new 3DS batch file or reboot the computer using the new
“AUTOEXEC.BAT” to make the new settings effective.
4. Change your current working directory to \3DS3 (where your 3D Studio V3.0
usually resides).
5. Delete the original configuration file “3DADI.CFG”.
6. Type 3DS VIBCGF <Enter> to configure your display environment.
7. After the “Company Register Screen” appears, press <Enter> to continue.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual92
Page 93

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
8. The “Video Environment Configuration Screen” will appear.
Do the following procedures to configure your video display environment.
(1) In Main-Display” item,
(a) Press <Enter> The selection menu will appear.
(b) In the selection menu, move cursor to “RCPADI”.
Press <Enter> to select.
(2) In “Material-Display” item,
(a) Press <Enter> The selection menu will appear.
(b) In the selection menu, move cursor to “RCPADI”.
Press <Enter> to select.
(3) In “Render-Display” item,
(a) Press <Enter> The selection menu will appear.
(b) In the selection menu, move cursor to “RCPADI” or “RDPADI”.
AutoShade/3D Studio
6. S/W REFERENCE
Press <Enter> to select.
(4) Complete the other selections and exit configuration.
9. After exiting configuration, 3DS will boot automatically using the environment
you have just selected.
10. If your previous configuration is OK, 3DS will ask you to make a detailed configuration for the SiS 5597/5598 drivers. If this does not occur, make sure that
you followed the previous procedures.
11. In the detailed configuration for the SiS 5597/5598 drivers, follow the instructions that appear on the screen and make your own choice.
12. After the detailed configuration, you will enter the 3DS main display screen.
You may begin your 3D Studio work in the environment that you previously
created.
13. Once the detailed configuration is finished, you may enter 3D Studio with the
same configuration by simply typing \3DS3\3DS <Enter> next time.
14. If you want to change your video configuration, just follow the procedures mentioned before to re-configure.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 93
Page 94

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
OS/2 V2.1
GENERAL NOTES FOR THE OS/2 DRIVERS:
• The descriptions apply to “SiS 5597/5598 Driver Release V1.03”. The descriptions, however, are subject to change at anytime without notice.
• All OS/2 Warp Versions up to SiS 5597/5598 driver Rev. 1.03 would be installed as described in “7. OS/2 V3.0 (Warp)” except for Double Bytes OS/2
Warp (e.g., Chinese, Japanese, and Korea).
•. For Double Bytes OS/2 Warp installation, refer to section 6.11 Double Bytes
OS/2 W arp.
6.9 OS/2 V2.1
6.9.1 Driver Files
1. The enclosed SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 2.1 driver contains the following files:
SISINST.CMD SiS driver install program
SVGA.EXE SiS PMI Generator
S768256.DL@ SiS IBMDEV32.DLL Display Driver
OTHERS other files required during installation
6.9.2 Installation
Before installing the SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 drivers, make sure to:
1. Install your OS/2 system using “VGA display” option (i.e., standard VGA).
2. Start your OS/2 system.
Install SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 2.1 drivers as follows:
1. Enter “OS/2 window” or “OS/2 full screen”.
2. Change to the directory where the SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 2.1 display drivers are
located and type SISINST <Enter>.
For example, A:\OS2\SBCS.21>SISINST
3. All the Driver Files will be copied to a subdirectory C:\SISDRV and the
“Select Screen parameters for SiS SVGA” menu appears and all the resolution
(and color) and frame rate supported would be shown on the screen.
4. Choose which one you would like to use and click OK.
5. The installation program would then complete all installation process and
create a “SiS Setup” for future change mode usage.
6. Shutdown and reboot OS/2 (your settings will only take effect when you reboot
OS/2).
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual94
Page 95

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.10 OS/2 V3.0 (Warp)
6.10.1 Driver Files
The enclosed SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 3.0 driver contains the following files:
SISINST.CMD SiS driver install program
SVGA.EXE SiS PMI Generator
S768256.DL@ SiS IBMDEV32.DLL Display Driver
OTHERS other files required during installation
6.10.2 Installation
Before install SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 drivers, make sure:
1. Install your OS/2 system using “VGA display” option (i.e. standard VGA).
2. Start your OS/2 system.
Install SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 Warp drivers as following procedures:
1. Enter “OS/2 window” or “OS/2 full screen”.
OS/2 V3.0 Warp
6. S/W REFERENCE
2. Change to the directory where the SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 3.0 display drivers are
located and type SISINST <Enter>.
For example, A:\OS2\SBCS.30>SISINST
3. All the Driver Files will be copied to a subdirectory C:\SISDRV and the
“Select Screen parameters for SiS SVGA” menu appears and all the resolution
(and color) and frame rate supported would be shown on the screen.
4. Choose which one you would like to use and click OK.
5. Then installation program would then complete all installation process and
create a “SiS Setup” for future change mode usage.
6. Shutdown and reboot OS/2 (your settings will only take effect when you reboot
OS/2).
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 95
Page 96

6. S/W REFERENCE
2 Byte OS/2 Warp
6.11 Double Bytes OS/2 Warp
6.11.1 Driver Files
The enclosed SiS 5597/5598 Double Byte OS/2 3.0 driver contains the following files:
SETUP .CMD SiS driver install program
SVGA.EXE SiS PMI Generator
S768256.DL@ SiS IBMDEV32.DLL Display Driver
OTHERS other files required during installation
6.11.2 Installation
Due to some limitations in Double Byte OS/2 W arp, the installation process is a
two-phased.
1st phase: copy files, modify “config.sys”, create “SiS Install” icon then shutdown
and re-boot OS/2.
2nd phase: double click the “SiS Install” icon to complete the installation
6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
Before install SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 drivers, make sure:
1. Install your OS/2 system using “VGA display” option (i.e., standard VGA).
2. Start your OS/2 system.
Install SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 Warp drivers as following procedures:
1st phase
1. Enter “OS/2 window” or “OS/2 full screen”.
2. Change to the directory where the SiS 5597/5598 OS/2 3.0 display drivers are
located and type SETUP <Enter>.
For example, A:\OS2\DBCS.30>SETUP
3. All the Driver Files will be copied to a subdirectory C:\SISDRV and an “SiS
Install” icon would be created.
4. After completing setup, shutdown and reboot OS/2.
2nd phase
5. After rebooting OS/2, double click the “SiS Install” icon. The “SiS Install”
icon would then be executed automatically and “Select Screen parameters for
SiS SVGA” screen would appear on the screen.
6. Select the desired resolution (and color) and frame rate from this screen, then
click OK to complete installation. An “SiS Setup” icon would be created for
future change modes and frame rate usage.
7. After completing installation, shutdown and reboot OS/2 (your settings will
only take effect when you reboot OS/2).
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual96
Page 97

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6.12 Desktop Management Interface (DMI)
6.12.1 Introducing the ASUS DMI Configuration Utility
This motherboard supports DMI within the BIOS level and provides a DMI Configuration Utility to maintain the Management Information Format Database (MIFD).
DMI is able to auto-detect and record information pertinent to a computer’s system
such as the CPU type, CPU speed, and internal/external frequencies, and memory
size. The onboard BIOS will detect as many system information as possible and
store those collected information in a 4KB block in the motherboard’ s Flash EPROM
and allow the DMI to retrieve data from this database. Unlike other BIOS software,
the BIOS on this motherboard uses the same technology implemented for Plug and
Play to allow dynamic real-time updating of DMI information versus creating a new
BIOS image file and requiring the user to update the whole BIOS. This DMI Configuration Utility also allows the system integrator or end user to add additional
information into the MIFD such as serial numbers, housing configurations, and vendor information. Those information not detected by the motherboard BIOS and has
to be manually entered through the DMI Configuration Utility and updated into the
MIFD. This DMI Configuration Utility provides the same reliability as PnP updating and will prevent the refreshing failures associated with updating the entire BIOS.
DMI
6. S/W REFERENCE
6.12.2 Starting the ASUS DMI Configuration Utility
The DMI Configuration Utility (DMICFG2.EXE) must be used in real mode in
order for the program to run, the base memory must be at least 180K. Memory
managers like HIMEM.SYS (required by windows) must not be installed. You can
boot up from a system diskette without AUT OEXEC.BAT and CONFIG.SYS files,
“REM” HIMEM.SYS in the CONFIG.SYS, or press <Shift>+<F5> during bootup
to bypass your AUTOEXEC.BAT and CONFIG.SYS files.
1. In Windows, copy DMICFG2.EXE to your hard disk drive.
2. Restart your computer and press <Shift>+<F5> during bootup to enter safe mode
command prompt.
3. Go to the directory containing DMICFG2.EXE.
4. Type
DMICFG2 and press <Enter> to run.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 97
Page 98

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
6. S/W REFERENCE
DMI
6.12.3 Using the ASUS DMI Configuration Utility
NOTE: The following screen displays are provided as examples only and may not
reflect the screen contents on your system.
Edit DMI (or delete)
Use the ←→ (left-right) cursors to move the top menu items and the ↑↓ (up-down)
cursor to move between the left hand menu items. The bottom of the screen will
show the available keys for each screen. Press enter at the menu item to enter the
right hand screen for editing. “Edit component” appears on top. The reversed color
field is the current cursor position and the blue text are available for editing. The
orange text shows auto-detected information and are not available for editing. The
blue text “Press [ENTER] for detail” contains a second pop-up menu is available,
use the + - (plus-minus) keys to change the settings. Enter to exit and save, ESC to
exit and not save.
If the user has made changes, ESC will prompt you to answer Y or N. Enter Y to go
back to the left-hand screen and save, enter N to go back to left-hand screen and not
save. If editing has not been made, ESC will send you back to the left hand menu
without any messages.
Notes
A heading,
the left side that has been auto detected by the system BIOS.
A heading,
have been modified by the user.
BIOS Auto Detect
***
User Modified
***
, appears on the right for each menu item on
***
, will appear on the right for menu items that
***
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual98
Page 99

6. SOFTWARE REFERENCE
Save MIFD
You can save the MIFD (normally only saved to flash ROM) to a file by entering the
drive and path here. If you want to cancel save, you may press ESC and a message
“Bad File Name” appears here to show it was not saved.
Load MIFD
DMI
6. S/W REFERENCE
You can load the disk file to memory by entering a drive and path and file name
here.
Load BIOS Defaults
You can load the BIOS defaults from a MIFD file and can clear all user modified
and added data. You must reboot your computer in order for the defaults to be saved
back into the Flash BIOS.
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual 99
Page 100

(This page was intentionally left blank.)
ASUS SP98-N User’s Manual100
 Loading...
Loading...